Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) For the Courts and Correctional Systems
|
|
|
- Geraldine Miller
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) For the Courts and Correctional Systems Larry Burd, Ph.D
2 Collecting Data About Prenatal Alcohol Exposure (PAE). Some alcohol use occurs in about 40% of pregnancies. Prenatal alcohol exposure is a common cause of premature birth, low birth weight, birth defects, learning disabilities, heart defects, and life long problems with independent living. In this section you can use the tools provided to examine alcohol use during pregnancy. It will be helpful to note that illegal drug use increases risk for alcohol use. Prevalence of Substance Use/Abuse The prevalence of drinking during pregnancy is high. Does this woman fit into any of these categories? When taking a history remember that drug use does not exclude alcohol use. It increases risk. (Use by Income) Drinking During Pregnancy Total Exposure Throughout Pregnancy Drinking four beers results in about 17 hours of fetal exposure to alcohol. Outcomes from drinking 4 beers each Friday and Saturday during the 40 weeks of pregnancy. Prenatal Smoking Drug Use Late and Infrequent Prenatal Care Depression Inadequate Nutrition Miscarriage What PAE Forecasts Labor & Delivery Stillbirth Prematurity Birth Defects Hospitalizations Neglect Abuse Postnatal Birth Defects Poor Nutrition Smoking Parental Substance Abuse Violence Depression SIDS Prenatal alcohol exposure (PAE) is strongly associated with an increased risk for exposure to other environmental adversity and a wide-range of outcomes.
3 Screening for PAE Screening for alcohol use begins with one question. Charting PAE During Pregnancy On average, how many days per week did you drink during pregnancy? (a) On an average drinking day during pregnancy, how many drinks did you have? (b) How many days per month did you have 4 or more drinks during pregnancy? (c) What is the most you had to drink on any one day during pregnancy? (d) What is a drink? Alcohol % Drink vol If drinking is reported, you can provide important information on frequency and quantity of alcohol use. This will be important for other professionals who will need this information for diagnosis and treatment when they interact with the family. Complete as many of these items as you can. Estimating Exposure Risk Maternal Risk Score Age over 25 years Unmarried, divorced, widow, living with partner On TANF, WIC, Social Security or income < $16,000 per year Did not graduate from high school Poor diet Smokes more than 1/2 pack per day Check any one Add 5 Score If the mother or other reliable reporter is unavailable, you can provide information to estimate exposure risk for this fetus or baby and their siblings. Drinks, but less than 2 days/week & less than 2 drinks /drinking day Check here Add 20 Age first drunk less than 15 years In treatment over three times In treatment in last 12 months Previous child died Check any one Add 35 Previous child with FASD, or developmental disability Children out of home (foster care or adopted) Heavy drinker (drinks 3 or more drinks/day for 3 or more days per week, or more than 5 drinks/day on 6 or more occasions) Uses inhalants, sniffs or illegal drugs Score Risk Category 0 None 5 Low Moderate High Very High Check any one Add 45 Total Score Did this person have prenatal alcohol exposure? Yes. Alcohol use during pregnancy is confirmed. Uncertain No. We do not suspect PAE. Very important information.
4 Drinking During Pregnancy: A common cause of birth defects developmental disability and mental disorders. There is no safe level of alcohol use during pregnancy. It s never too late to stop drinking during pregnancy. Quitting now will protect future pregnancies. Fetal Breathing Placenta Fetal Swallowing Placenta Fetal Urine When alcohol enters the stomach it quickly passes into her blood. In minutes alcohol crosses the placenta into the baby. Alcohol passes from the baby into the amniotic fluid by fetal breathing movements and urination. When amniotic fluid is swallowed, alcohol passes back across the placenta into the mom where it is eliminated. Does this child need evaluation for FASD or followup as a child with high risk due to PAE? Use this section to determine if the person might have a fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD). Some findings are very important. If a sibling has been diagnosed with an FASD, or if a sibling or the mother is dead, the risk for FASD is high. Low nasal bridge Short palpebral fissures obscure the canthus (the inner corner of the eye) - a normal feature in some races Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Thin upper lip Small head circumference Epicanthic folds Short nose Flat midface Indistinct philtrum (an underdeveloped groove in the center of the upper lip between the nose and the lip edge) Fetal Alcohol Syndrome: The facial features of a child with fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS). Other Essential Signs Growth Impairment Height Weight Brain Damage/Dysfunction See chart on page 9. FASD is not Just FAS Most cases do NOT have - Dysmorphic features - Growth Impairment Majority 80+% - Developmental Delay - Cognitive Impairment - Mental Disorders - Substance Abuse Disorders It s important to remember that most people affected with a fetal alcohol spectrum disorder do not have the facial features of FAS.
5 FAS SCREEN FORM Larry Burd, Ph.D NAME/ID:_ DOB: / / AGE: SEX (circle one): F M RACE (circle one): Caucasian Hispanic Native American African American Other DATE OF EXAM: / / CIRCLE POINTS IF PRESENT: HEIGHT Inches If < 5th percentile: 10 WEIGHT Pounds If < 5th percentile: 10 HEAD CIRC. Centimeters If < 5th percentile: 10 HEAD AND FACE EARS STICK OUT (Protruding Auricles) 4 SKIN FOLDS NEAR INNER EYE (Epicanthal Folds) 5 DROOPING OF EYELIDS (Ptosis) 4 CROSS-EYES, ONE OR BOTH EYES (Strabismus) 3 FLAT MIDFACE/CHEEKS (Hypoplastic Maxilla) 7 FLAT/LOW NOSE BETWEEN EYES (Low Nasal Bridge) 2 UPTURNED NOSE 5 GROOVE BETWEEN LIP & NOSE ABSENT OR SHALLOW (Flat Philtrum) 5 THIN UPPER LIP 4 CLEFT LIP OR CLEFT OF ROOF OF MOUTH (Present or Repaired) 4 NECK AND BACK ARMS AND HANDS CHEST SKIN DEVELOPMENT SHORT, BROAD NECK 4 CURVATURE OF THE SPINE (Scoliosis) 1 SPINA BIFIDA (History of Neural Tube Defect) 4 LIMITED JOINT MOBILITY IN FINGERS & ELBOWS 4 PERMANENTLY CURVED, SMALL FINGERS, ESPECIALLY PINKIES (Clinomicrodactyly) 1 DEEP OR ACCENTUATED PALMAR CREASES 4 SMALL NAILS/NAIL BEDS (Hypoplastic Nails) 1 TREMULOUS, POOR FINGER AGILITY (Fine Motor Dysfunction) 1 SUNKEN CHEST (Pectus Excavatum) EXAM OPTIONAL 3 CHEST STICKS OUT (Pectus Carinatum) 1 HISTORY OF HEART MURMUR OR ANY HEART DEFECT 4 RAISED RED BIRTHMARKS (Capillary Hemangiomas) 4 GREATER THAN NORMAL BODY HAIR, HAIR ALSO ON FOREHEAD AND BACK (Hirsutism) 1 MILD TO MODERATE MENTAL RETARDATION (IQ < 70) 10 SPEECH AND LANGUAGE DELAYS 2 HEARING PROBLEMS 1 VISION PROBLEMS 1 ATTENTION CONCENTRATION PROBLEMS 2 HYPERACTIVITY 5 COMMENTS: For additional forms or information on FASD, contact: Larry Burd, Ph.D. 501 N. Columbia Road, Stop 9037 Grand Forks, ND larry.burd@med.und.edu Total Score: (Refer if score 20 or above)
6 THE ARND BEHAVIORAL CHECKLIST Larry Burd, Ph.D NAME/ID:_ DOB: / / AGE: SEX (circle one): F M RACE (circle one): Caucasian Hispanic Native American African American Other DATE OF EXAM: / / In order to complete this checklist: 1) Behaviors must be impaired for the age of the person being assessed. 2) Interviewer needs to have known the person being assessed for at least one month. Hyperactive Poor attention Impulsive Disorganized Seems unaware of consequences of actions No fear Would leave with a stranger Poor social skills Few friends Will talk or interact with anyone Easily manipulated and set up by others Socially inept (inappropriate speech or touching) Difficulty staying on topic during conversation Always talking Cocktail speech - little content Too loud Can t remember from one day to the next Below average IQ (<85) Poor school performance Suspended or expelled from school Poor sleeper Can t follow routine - needs reminders to get dressed, brush teeth, etc. Temper tantrums Extreme mood swings Requires constant supervision Been in trouble with the law Inpatient treatment for mental health or substance abuse, or in jail for a crime Inappropriate sexual behavior Poor motor skills Has or needs glasses Had foster care or was adopted Medication for behavior - ever Mother used alcohol during any pregnancy (OPTIONAL) Mother used alcohol in last five months of this pregnancy (OPTIONAL) Mother has been in treatment for alcohol use (OPTIONAL) BEHAVIOR CHECK ALL THAT APPLY FOR 3-6 THE YEARS APPROPRIATE 7 AGE YEARS RANGE: + For additional forms or information on ARND, contact: Larry Burd, Ph.D. 501 N. Columbia Road, Stop 9037 Grand Forks, ND larry.burd@med.und.edu TOTAL CHECKED: (Continue assessment if score is greater than or equal to above)
7 Larry Burd, Ph.D Correction System Screening Protocol for FASD Adolescent (Anyone less than 19 years of age) NAME/ID:_ DOB: / / AGE: SEX (circle one): F M RACE (circle one): Caucasian Hispanic Native American African American Other DATE OF EXAM: / / Preferred Hand: Left/Right (circle one) Location Current Grade Step 1 Weight in lbs. Step 2 Height in inches Step 3 Review photographs Step 4 Physical findings Head Circumference cm Check if present Thin vermillion border upper lip Flat philtrum Decreased supination Angulated distal palmar crease Clinodactyly Midface hypoplasia Reading Spelling Math Reading Comprehension Adaptive Behavior NEUROBEHAVIORAL Standard Score Below average IQ Intellectual Deficiency Attention Deficit/ Hyperactivity disorder Impulsive Stubborn Seizures Check if Present Graduate from high school Yes No If no, what was the last grade completed? Ever take medication for hyperactivity as a child? Adaptive Behavior Scores Communication Socialization Daily Living Skills Gross/Fine Motor Composite For additional forms or information on ARND, contact: Larry Burd, Ph.D. North Dakota Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Center PO Box 9037, Grand Forks, ND (701) larry.burd@med.und.edu
8 Correction System Screening Protocol for FASD and Related Disorders Adult (Anyone 19 years of age or older) Larry Burd, Ph.D NAME/ID:_ DOB: / / AGE: SEX (circle one): F M RACE (circle one): Caucasian Hispanic Native American African American Other DATE OF EXAM: / / Location Step 1 Weight in lbs. Step 2 Height in inches Step 3 Review photographs Step 4 Physical findings Head Circumference cm Check if present Thin vermillion border upper lip Flat philtrum Decreased supination Angulated distal palmar crease Clinodactyly Midface hypoplasia 128 lbs for men 66 inches for men If less than Continue If less than 105 lbs for women 61 inches for men Neubehavioral Reading Spelling Math Reading Comprehension IQ Adaptive Behavior Standard Score Below average IQ Intellectual Deficiency Attention Deficit/ Hyperactivity disorder Impulsive Stubborn Seizures Check if Present Graduate from high school Yes No If no, what was the last grade completed? Ever take medication for Hyperactivity as a child? Adaptive Behavior Scores Communication Socialization Daily Living Skills Gross/Fine Motor Composite For additional forms or information on ARND, contact: Larry Burd, Ph.D. North Dakota Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Center PO Box 9037, Grand Forks, ND (701) larry.burd@med.und.edu
9 Age based impairments in FASD and Alcohol Related Neurodevelopmental Disorder Age Cognitive Motor Skills Socialization Behavior Infancy Developmental delay Learning games Attention Tremor Poor suckle Low tone Floppy Interactive activities and games Attachment Reading others expressions Sleep disturbance Regulation of behavior Irritable Temperament Impaired settling Cuddling Toddler Speech-language Understanding Toilet training Attention Impulsivity Memory Tremor Fine motor Gross motor Balance Late crawling or walking Frustration Threshold Separation problems Attachment Group participation Difficulty in group settings Tantrums Aggression Stubborn Child IQ Academic deficits (math, spelling, written language) Humor Memory Recall Speech-language comprehension Fine and gross motor Coordination Balance Handwriting Hand tremor Requires increased supervision Difficulty sustaining friendships Group activities Games activities with rules ADHD Increased frustration Lack of persistence Increased risk taking Impaired independence for age Impaired executive functioning Pre-Adolescence IQ Academic deficits (math, spelling, written language) Planning Memory and recall Comprehension Generalization of skills and behaviors Coordination Balance Handwriting Clumsy Independent functioning Needs increased supervision Exploitation by others Appropriate boundaries ADHD Impaired executive functioning Impulsive Repeats problem behavior Poor response to demands Risk taking Adolescence/ Adults Ability to work independently Self-care Money and time management Household routines Generalization of skills and behaviors Limited benefit from treatment programs without adaption Writing Fine motor Balance Coordination Independent functioning Peer exploitation Increased supervision Interpersonal boundaries Increased risk for substance abuse Depression Anxiety Repeats problem behavior Increased risk taking Impulse control Planning ahead Meeting deadlines Asking for help Organization Record keeping Peer exploitation
10 THE DADS Age 30.8 Education 10.9 Unmarried 63% Alcoholic 12+years Heavy Drinker + Treatment <3 Low SES + Previous Terminations Number of Prenatal Visits Number of Prenatal Complications Birth Weight The FASD Family h i h i THE CHILDREN Age Diagnosis 7.1 Years Older Sibs 2 Younger 2 Mean Birth Weight -701 grams Birth Defects 50% Cerebral Palsy 6% Mental Retardation 40% ADHD 75% Out of Home 85% Head Injury 15% If FAS Diagnosis 1 dead sibling (9%) 2 dead siblings (2%) 3 dead siblings (5%) Mortality Rate FASD = 5.4% FAS Sibling = 11.4% Sibling Controls = 2.0% RR = 530% Infection OR = 13.7 SIDS OR = 10.2 THE MOMS Age 27.4 Education 10.6 Unmarried 63% Smoker 82% Alcoholic 10+years Treatment >3 (45%) Low SES + Poor Diet + Parity 3 Prenatal Visits <5 (56%) 1st Prenatal >1st tri (56%) Mortality 4.9% Mortality FASD Mothers = 4.9% Controls = 0.11% OR = % Died age 50 < (41.5%) Cancer Alcohol Related 67% Accidents 31.3 YPLL per case Number of Prenatal Complications h Number of Prenatal Visits i Late Start Prenatal Care h Birth Weight i Number of Malformations h What risk factors are present for this family? Does this person have evidence of developmental delay, birth defects, sibling with FASD, sibling death or intellectual deficits? 1 Yes, consider referral for FASD evaluation. 2 No, but person does need monitoring as high risk for future problems. 3 No reason for concern Does this person/family need management for current alcohol related problems, substance abuse for prenatal alcohol exposure or as a person with FASD? Risk Factors Ahead The Road Ahead These are key areas for prevention efforts for people with an FASD. FASD Forecast The Future of FASD: Increasing Severity of Neurobehavioral Impairments The presentation of FASD varies by age and development. Severity and complexity almost always increase with age. Severity Birth Age in Years
11 1) Focus on Risk Reduction - Abuse - Neglect - Speech and Language - Foster Care - ADHD - School - Social Development - Self Care - Look Ahead - Adult Impairments 4 Keys to Success 2) FASD: The Keys to Intervention - Age & Development - Dependent Phenotype - Risk Reduction - Long-term Plan - Anticipatory Guidance - Appreciate Impairment The Developmental Triad 1) It is much easier to prevent or minimize problem outcomes. 2) Key components of a case management plan. It is crucial to remember that FASD changes over time and that intervention must include plans to prevent future problems. The child will require ongoing assessments to have the best outcome. 3) FASD: What we First See Behavior + A Better View Impairment 3) Most people with an FASD have fewer behaviors and more impairments than we first suspect. This results in day to day performance that is HIGHLY variable. Behavior + Impairment Inconsistant Performance Typical Day 4) FASD Management Keys - Yearly Follow-up - Few Live Independently - Remember the Familial and Generational Effects of FASD - Services MATTER 4) Begin a case management plan with the understanding that this is likely a lifelong disorder requiring lifelong management.
12 Parents or Adults with an FASD 1) Does either parent have an FASD? - Do they have Neurocognitive Impairment - Useful Measures - Intelligence Testing - Adaptive Behavior Testing - Selectively-More Detailed Neurocognitive Testing 2) Basic Cognitive Skills in Adolescents and Adults with FASD Characteristics Grade Level Reading 5.0 Reading comprehension 4.5 Oral Comprehension 5.0 Percent Affected Memory 80% Attention (ADHD) 75% Executive Function Impairments 80% Key issues: 1) Adults with FASD have significant learning deficits which impact their ability to learn and remember. 2) We can improve the success rate of treatment programs by building in these treatment keys. See #4 below. 3) Learning in FASD Decrease Factors which Impair Learning in FASD Comprehension Deficits Memory Burden Increase Use of These Modify Repeat Go Slow Go Low 3) Useful strategies: Modify content Repeat important content Modify pace with participants ability to learn and remember Short directions Learn reading and audio content 4) What should we change? Address one problem at a time allow participants to learn and apply solution before moving on to next topic Provide short directions an essential key for successful interventions Make it concrete picture guides are helpful for teaching key concepts Work in small groups allow more attention to topical material Minimize anxiety, which increases impairment especially important in treatment of substance abuse, sexual abuse or PTSD Understand impairments some problems cannot be treated and we need to learn how to adapt to them and minimize the effects Address mental health concerns need appropriate treatment Go slowly Treatment or interventions need to last longer Planning for aftercare is essential improves generalization of learned behaviors Think family history FASD is often familial Wishing and Anger Won t Help 5) Success rate of Substance Abuse Programs It is important to understand how well your intervention program works. Is the substance abuse program you use effective 5% or 40% of the time? The efficacy of the programs are important keys to participant success. 4) Essential factors for development of case management plans for adolescents and adults. 5) Most programs serving this population need to make more accommodations in response to their participants learning impairments. Otherwise the content of the programs is not easily available to the participants.
13 Policy Recommendations Judicial Bench Card Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders Adverse outcomes from alcohol use during pregnancy In the United States about 50% of pregnancies have some alcohol exposure. In most cases women find out they are pregnant and quit drinking. However, around 12% of women drink during pregnancy and 4-5% drink throughout pregnancy. Most of these women also smoke and many have other problematic life circumstances (other substance abuse, smoking, poor diet, late or no prenatal care). The United States has about 40,000 new cases of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASD) each year. For most affected people the primary problem from prenatal alcohol exposure is brain damage/dysfunction. This will usually result in lifelong impairments which will change in response to age and development. Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders Comprised of four diagnostic categories Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS) - Growth Impairments (height and weight <3d) - Abnormal Facial Features (2+) - Brain Damage/Dysfunction - Thought to result from prenatal alcohol exposure Alcohol Related Birth Defects (ARBD) - Birth defects though to be due to prenatal alcohol exposure - Not commonly diagnosed - Prevalence is as yet unknown Partial Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (pfas) - Missing one or two key findings - Prenatal Alcohol Exposure Alcohol Related Neurodevelopmental Disorder (ARND) - The primary features are brain damage/dysfunction developmental delays, mental illness or cognitive impairments) thought to result from prenatal alcohol exposure. - Most common FASD - Often undiagnosed - Changes across the lifespan Judicial officers often see people with prenatal alcohol exposure and FASD should be a frequent consideration. Judicial officers often see people with prenatal alcohol exposure and FASD should be a frequent consideration.
14 Mortality People with FASD have increased mortality rates. Mortality risk is also increased for siblings (even if they do not have a diagnosis of FASD). Miscarriage, stillbirth, sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), birth defects, infectious illness other causes. Mortality rates are also increased for mothers of cases and siblings. Prevalence of FASD - 1% live births - Highly recurrent in families - In some families FASD is generational - Most affected people are undiagnosed Cost of Care US lifetime cost is $2.5 million per person. Service systems most impacted are health care, foster care, education/special education, developmental disabilities, mental health systems, corrections systems, and substance abuse systems. Annual cost in US $3.4 billion Outcomes Manifestation of FASD changes over lifespan. A two year old is at low risk for a substance abuse disorder, but adolescents are at very high risk. Low rates of independent living In Canada a juvenile with FASD is 14 times more likely to be in Corrections system than an unaffected peer. Every day in the United States we have 120 new cases. FASD has a high recurrence rate and younger siblings tend to be the most severely affected. Diagnosis matters and appropriate services improve outcomes. Actions from the Bench System-Level Actions - Make prenatal alcohol exposure (PAE) screening * a regular component of child welfare cases. - Assess the community s diagnostic capacity. - Assess interventions and treatment facilties for facilties that have appropriate training on, and service for FASD. - Train systems of care personnel on FASD and work to expand the community s capacity to screen, diagnose and provide interventions for affected persons. Case-Level Actions - Screen all children for PAE. - Refer children with positive screens or sibling wtih an FASD for FASD assessments. - If positive, refer child for developmentally appropriate and proactive treatment. Follow up on service utilization in subse quent hearings. - When FASD is diagnosed. - Screen siblings and parents. - Pick placements carefully. Placements should be safe, stable and loving homes with caregivers willing to adopt if reunification fails. - Tailor affected parent s case plans to meet their developmental needs. * To learn more about prenatal alcohol exposure (PAE), please see the PAE Judicial Bench Card.
15 Policy Recommendations Judicial Bench Card Prenatal Alcohol Exposure Prevalence of Alcohol Use - Non-pregnant women during child bearing years: 54% - Month before pregnancy: 50% - Pregnant women: 12% (1 in 8) - Third trimester of pregnancy: 4.6% Rates of Prenatal Alcohol Exposure (PAE) - Children of women in substance abuse treatment: very high - Children of women in prison: 80% - Children in foster care: 70-80% - Increased in women with other drug use Drinking and Pregnancy In the majority of cases, drinking primarily occurs on weekends, but for women with alcohol use disorders drinking may occur on most days. Alcohol rapidly crosses from the mother to fetus. Increasing maternal blood alcohol can be detected in fetus in 1 minute. Maternal-fetal ethanol concentrations reach equilibrium in about two hours after women quit drinking. Alcohol elimination from the fetus and amniotic fluid relies on mother s alcohol metabolism. The alcohol elimination capacity of the fetus is 5% of the mother s capacity. Promptly after birth, alcohol elimination rates reach 83.5% of maternal elimination rate. Variation in Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC) BAC varies from person to person. For example, BAC varies by about 4 fold for women of the same weight consuming the same amount of ethanol. PAE is an important marker for increased risk of postnatal environmental adversity PAE is associated with increased rates of environmental adversity including other substance abuse, smoking, neglect, abuse, malnutrition, stressful life circumstances and mortality. These often persist throughout infancy and childhood. PAE should also be considered in risk stratification for alcohol exposure in both previous and future pregnancies.
16 Screening for PAE * What we might want to know about drinking during pregnancy When was your last drink? Before PREGNANCY Unexposed Pre-awareness Exposed Post-awareness Exposed & High Risk Assessment of exposure during pregnancy On average how many drinks per week did you drink during pregnancy? On an average drinking day during pregnancy how many drinks did you have? How many days per month did you have 4 or more drinks during pregnancy? What is the most you had to drink on any one day during pregnancy? (a) (b) (c) (d) Estimating cumulative exposure during pregnancy Pregnancy Drinking Days = (a x 40) = (e) Estimates number of drinking days during pregnancy Percent of Days Exposed During Pregnancy = e 280 = Estimates number of drinking days during pregnancy Number of Binge Days (4 or more drinks in one day = (c x 9) = Estimates number of binge days Number of Drinks During Pregnancy = (a x b x 40) = (f) Estimates number of drinks during pregnancy Ounces of absolute alcohol = (f / 2) = Estimates cumulative absolute alcohol exposure during pregnancy. Effective intervention NOW reduces risk for alcohol exposure in subsequent pregnancies Getting Services for Mothers - Ask when was your last drink? - Ask if she has been in treatment previously. Should she return to the same program or does she need a different treatment provider? - Determine if she may have an FASD. If yes, what modifications does she need to improve her response to treatment? - Ask what is the success rate of the treatment program for similar women? - Ask if planning to create a substance use free environment needs to start now. Who will participate and when will they report back to the court? * If the screening reveals a child was prenatally exposed to alcohol, see the Judicial Bench card on FASD for next steps.
UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON
 UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON THE FETAL ALCOHOL SYNDROME DIAGNOSTIC AND PREVENTION NETWORK (FAS DPN) Center for Human Development and Disability Dear Sir or Madam, Thank you very much for your request for an
UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON THE FETAL ALCOHOL SYNDROME DIAGNOSTIC AND PREVENTION NETWORK (FAS DPN) Center for Human Development and Disability Dear Sir or Madam, Thank you very much for your request for an
New Patient Information Form
 New Patient Information Form Patient Identification Prenatal Alcohol & Drug Exposure Clinic FASD CLINIC Patient s OHIP N. Female Male Race Patient s Name Birth Date Age First Middle Last Patient s Address
New Patient Information Form Patient Identification Prenatal Alcohol & Drug Exposure Clinic FASD CLINIC Patient s OHIP N. Female Male Race Patient s Name Birth Date Age First Middle Last Patient s Address
SAMHSA FASD Center for Excellence
 FASD FACTS: How You Can Help Prevent Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS The Basics Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) Umbrella term describing the range of effects that
FASD FACTS: How You Can Help Prevent Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS The Basics Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) Umbrella term describing the range of effects that
American Academy of Pediatrics 2014 Educational Webinar Series Monday, July 28, 3:00 3:30 pm ET
 American Academy of Pediatrics 2014 Educational Webinar Series Monday, July 28, 3:00 3:30 pm ET FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS (FASDS): DETECTION, DISCOVERY, AND DIAGNOSIS PRESENTED BY YASMIN SENTURIAS,
American Academy of Pediatrics 2014 Educational Webinar Series Monday, July 28, 3:00 3:30 pm ET FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS (FASDS): DETECTION, DISCOVERY, AND DIAGNOSIS PRESENTED BY YASMIN SENTURIAS,
The Mystery of Risk. Drugs, Alcohol, Pregnancy and the Vulnerable Child. Ira J. Chasnoff, MD
 The Mystery of Risk Drugs, Alcohol, Pregnancy and the Vulnerable Child Ira J. Chasnoff, MD irachasnoff@gmail.com Attachment: Basic Concepts n Attachment is the interconnectedness between human beings.
The Mystery of Risk Drugs, Alcohol, Pregnancy and the Vulnerable Child Ira J. Chasnoff, MD irachasnoff@gmail.com Attachment: Basic Concepts n Attachment is the interconnectedness between human beings.
Recommended Assessment Tools for Children and Adults with confirmed or suspected FASD
 Recommended Assessment Tools for Children and Adults with confirmed or suspected FASD 2001 Teresa Kellerman, revised October 2005 Thousands of children are born with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD),
Recommended Assessment Tools for Children and Adults with confirmed or suspected FASD 2001 Teresa Kellerman, revised October 2005 Thousands of children are born with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD),
Changing Behavior. Can t get up. Refuses to get up for school. I like school. Sad Poor sleep Angry Thoughts of self harm.
 Changing Behavior I like school Can t get up. Refuses to get up for school. Mostly happy Larry Burd, PhD North Dakota Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Center 501 North Columbia Road Grand Forks ND, 58203 larry.burd@med.und.edu
Changing Behavior I like school Can t get up. Refuses to get up for school. Mostly happy Larry Burd, PhD North Dakota Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Center 501 North Columbia Road Grand Forks ND, 58203 larry.burd@med.und.edu
Birth mother Foster carer Other
 PATIENT DETAILS NAME Sex Female Male Other Date of birth (DD/MM/YYYY) / / Age at assessment: Racial/ ethnic background Preferred language Hospital number (if applicable) Referral source, date, provider
PATIENT DETAILS NAME Sex Female Male Other Date of birth (DD/MM/YYYY) / / Age at assessment: Racial/ ethnic background Preferred language Hospital number (if applicable) Referral source, date, provider
Homework #1: CARING FOR A CHILD IMPACTED BY FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDER
 Homework #1: CARING FOR A CHILD IMPACTED BY FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDER A foster child has been placed in your home. You are told that she has been prenatally exposed to alcohol and has a Fetal Alcohol
Homework #1: CARING FOR A CHILD IMPACTED BY FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDER A foster child has been placed in your home. You are told that she has been prenatally exposed to alcohol and has a Fetal Alcohol
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD): How Judges Can Improve Outcomes for Affected Children and Parents
 Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD): How Judges Can Improve Outcomes for Affected Children and Parents Larry Burd, PhD, Professor, Department of Pediatrics, University of North Dakota School of Medicine
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD): How Judges Can Improve Outcomes for Affected Children and Parents Larry Burd, PhD, Professor, Department of Pediatrics, University of North Dakota School of Medicine
Fetal Alcohol Exposure
 Fetal Alcohol Exposure Fetal alcohol exposure occurs when a woman drinks while pregnant. Alcohol can disrupt fetal development at any stage during a pregnancy including at the earliest stages before a
Fetal Alcohol Exposure Fetal alcohol exposure occurs when a woman drinks while pregnant. Alcohol can disrupt fetal development at any stage during a pregnancy including at the earliest stages before a
FETAL ALCOHOL SYNDROME A SOUTH AFRICAN PERSPECTIVE
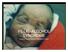 FETAL ALCOHOL SYNDROME A SOUTH AFRICAN PERSPECTIVE Fetal alcohol syndrome is the most common preventable cause of mental retardation in the world (Sampson PD et al.; Teratology (1997); 56:317-326) RISK
FETAL ALCOHOL SYNDROME A SOUTH AFRICAN PERSPECTIVE Fetal alcohol syndrome is the most common preventable cause of mental retardation in the world (Sampson PD et al.; Teratology (1997); 56:317-326) RISK
FASD Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder
 FAS pfas ARND Fetal Alcohol Syndrome partial Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Alcohol Related Neurodevelopment Disorder FASD Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder ARBD Alcohol Related Birth Defects #1 cause of birth defects
FAS pfas ARND Fetal Alcohol Syndrome partial Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Alcohol Related Neurodevelopment Disorder FASD Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder ARBD Alcohol Related Birth Defects #1 cause of birth defects
Understanding Prenatal Alcohol Exposure
 Understanding Prenatal Alcohol Exposure Prenatal Alcohol Exposure Causes Birth Defects Alcohol and pregnancy do not mix. Slide 2 The U.S. Surgeon General s Warning The dangers of consuming alcohol during
Understanding Prenatal Alcohol Exposure Prenatal Alcohol Exposure Causes Birth Defects Alcohol and pregnancy do not mix. Slide 2 The U.S. Surgeon General s Warning The dangers of consuming alcohol during
What is FASD? Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder
 FASD: Normalizing Insanity A Family Story Dennis Riddle, MA, LADAC Memphis, Tennessee 901-496-5762 dennisriddle60@aol.com Sometimes Life Gets This Way. With FASD, It Stays This Way!!!! What is FASD? Fetal
FASD: Normalizing Insanity A Family Story Dennis Riddle, MA, LADAC Memphis, Tennessee 901-496-5762 dennisriddle60@aol.com Sometimes Life Gets This Way. With FASD, It Stays This Way!!!! What is FASD? Fetal
Section F: Discussing the diagnosis and developing a management plan
 Section E: Formulating a diagnosis Information collected during the diagnostic assessment should be reviewed, ideally in a multi-disciplinary team context, to evaluate the strength of evidence to: Support
Section E: Formulating a diagnosis Information collected during the diagnostic assessment should be reviewed, ideally in a multi-disciplinary team context, to evaluate the strength of evidence to: Support
Safe Babies Foster Parent Training Program
 Safe Babies Foster Parent Training Program Module 1: Introduction to the Safe Babies Program 1 Begin the process of group participation Learning outcomes Understand the purpose and origins of the Safe
Safe Babies Foster Parent Training Program Module 1: Introduction to the Safe Babies Program 1 Begin the process of group participation Learning outcomes Understand the purpose and origins of the Safe
Alcohol and Pregnancy: What Have We Learned in 37 Years?
 Alcohol and Pregnancy: What Have We Learned in 37 Years? Kenneth Lyons Jones, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics University of California, San Diego School of Medicine La Jolla, CA Generalizations About Phenotype
Alcohol and Pregnancy: What Have We Learned in 37 Years? Kenneth Lyons Jones, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics University of California, San Diego School of Medicine La Jolla, CA Generalizations About Phenotype
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder (FASD)
 facts on For More Information Contact: 1319 Colony Street Saskatoon, SK S7N 2Z1 Bus. 306.655.2512 Fax. 306.655.2511 info@preventioninstitute.sk.ca www.preventioninstitute.sk.ca The Saskatchewan Prevention
facts on For More Information Contact: 1319 Colony Street Saskatoon, SK S7N 2Z1 Bus. 306.655.2512 Fax. 306.655.2511 info@preventioninstitute.sk.ca www.preventioninstitute.sk.ca The Saskatchewan Prevention
1/26/2018 PREVENTING THE RETRAUMITIZATION OF CHILDREN FROM ADDICTED FAMILIES THE PROBLEM RISK FACTORS FOR ENDANGERMENT
 PREVENTING THE RETRAUMITIZATION OF CHILDREN FROM ADDICTED FAMILIES Susan Kilman LCSW, AADC THE PROBLEM ABOUT 1 IN 8 (8.7 MILLION) AGED 17 OR YOUNGER LIVE IN HOUSEHOLDS WITH AT LEAST ONE PARENT WHO HAD
PREVENTING THE RETRAUMITIZATION OF CHILDREN FROM ADDICTED FAMILIES Susan Kilman LCSW, AADC THE PROBLEM ABOUT 1 IN 8 (8.7 MILLION) AGED 17 OR YOUNGER LIVE IN HOUSEHOLDS WITH AT LEAST ONE PARENT WHO HAD
DR. CESTNICK ADULT BACKGROUND QUESTIONNAIRE. Birth date: Age: Sex (circle one): Male Female. Home address: City: Zip Code:
 DR. CESTNICK ADULT BACKGROUND QUESTIONNAIRE Your name: Today s date: Birth date: Age: Sex (circle one): Male Female Home address: City: Zip Code: Phone: Home # Cell # Other # Email: School (if student):
DR. CESTNICK ADULT BACKGROUND QUESTIONNAIRE Your name: Today s date: Birth date: Age: Sex (circle one): Male Female Home address: City: Zip Code: Phone: Home # Cell # Other # Email: School (if student):
Overview of Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) IRETA February 1, 2012 Margo Singer, NYS OASAS Bureau of Prevention Services
 Overview of Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) IRETA February 1, 2012 Margo Singer, NYS OASAS Bureau of Prevention Services Course Objectives: Participants will learn to: Learn the causes of FASD
Overview of Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) IRETA February 1, 2012 Margo Singer, NYS OASAS Bureau of Prevention Services Course Objectives: Participants will learn to: Learn the causes of FASD
Part 2 Who Is at Risk? What Does FASD Look Like? FASD Diagnostic Guidelines. Common Challenges Across the Spectrum
 Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders Understanding Effects Improving Outcomes Part 2: Who Is at Risk? Presentation by Teresa Kellerman Director of the Fetal Alcohol Resource Center Arizona Division of Developmental
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders Understanding Effects Improving Outcomes Part 2: Who Is at Risk? Presentation by Teresa Kellerman Director of the Fetal Alcohol Resource Center Arizona Division of Developmental
Larry Burd, PhD Director, North Dakota Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Center
 Larry Burd, PhD Director, North Dakota Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Center larry.burd@med.und.edu 701-777-3683 Common Affects mother and children Increases mortality Index of addition severity Treatable Huge
Larry Burd, PhD Director, North Dakota Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Center larry.burd@med.und.edu 701-777-3683 Common Affects mother and children Increases mortality Index of addition severity Treatable Huge
Department of Psychiatry\Behavioral Health 200 Mercy Drive, Suite 201 Dubuque, IA or
 Department of Psychiatry\Behavioral Health 200 Mercy Drive, Suite 201 Dubuque, IA 52001 563 584 3500 or 800 648 6868 C H I L D H I S T O R Y F O R M Today s Date: Child s Name: Date of Birth: Age: Grade:
Department of Psychiatry\Behavioral Health 200 Mercy Drive, Suite 201 Dubuque, IA 52001 563 584 3500 or 800 648 6868 C H I L D H I S T O R Y F O R M Today s Date: Child s Name: Date of Birth: Age: Grade:
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder
 Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder Liz Kacew, MScN, NP-PHC & Terry Broda, NP-PHC January 28, 2015 Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder "" is an umbrella term describing the range of effects that can occur with
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder Liz Kacew, MScN, NP-PHC & Terry Broda, NP-PHC January 28, 2015 Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder "" is an umbrella term describing the range of effects that can occur with
PedsCases Podcast Scripts
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Approach to Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Approach to Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key
Indian Country Site Visit Executive Summary
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY As part of its outreach efforts in Indian Country, the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) Center for Excellence
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY As part of its outreach efforts in Indian Country, the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) Center for Excellence
Neurodevelopmental Disorders
 Neurodevelopmental Disorders Intellectual Disability Disorder Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADD/ADHD) Motor Disorders/Tourette s Disorder Intellectual Disability
Neurodevelopmental Disorders Intellectual Disability Disorder Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADD/ADHD) Motor Disorders/Tourette s Disorder Intellectual Disability
Understanding Prenatal Drug Exposure
 Understanding Prenatal Drug Exposure Prenatal Drug Exposure A mother s drug use hurts her unborn baby. Slide 2 Drug Categories Part 1 Prescription drugs: Prescribed by a doctor and used under a health
Understanding Prenatal Drug Exposure Prenatal Drug Exposure A mother s drug use hurts her unborn baby. Slide 2 Drug Categories Part 1 Prescription drugs: Prescribed by a doctor and used under a health
The Basics of FASD Awareness and Prevention Cheryl A. Wissick, Ph.D. Trainer, SC FASD Collaborative
 The Basics of FASD Awareness and Prevention Cheryl A. Wissick, Ph.D. Trainer, SC FASD Collaborative Presentation adapted from information from Dan Dubovsky, FASD Specialist, FASD CFE, SAMHSA Roger Zoorob,
The Basics of FASD Awareness and Prevention Cheryl A. Wissick, Ph.D. Trainer, SC FASD Collaborative Presentation adapted from information from Dan Dubovsky, FASD Specialist, FASD CFE, SAMHSA Roger Zoorob,
Child/ Adolescent Questionnaire
 Oconee Center for Behavioral Health 1360 Caduceus Way Building 400, Suite 102 Tel 706-286-8442 Fax 706-310-6907 Child/ Adolescent Questionnaire Patient s Name: Date of Birth: / / Patient s Birthplace:
Oconee Center for Behavioral Health 1360 Caduceus Way Building 400, Suite 102 Tel 706-286-8442 Fax 706-310-6907 Child/ Adolescent Questionnaire Patient s Name: Date of Birth: / / Patient s Birthplace:
By Dr. Pamela Gillen. Dr. Pamela Gillen
 By Dr. Pamela Gillen Dr. Pamela Gillen Working with every woman to prevent FASDs: Dr. Pamela Gillen Participants will be able to do the following: Discuss the risks of an alcohol-exposed pregnancy (AEP)
By Dr. Pamela Gillen Dr. Pamela Gillen Working with every woman to prevent FASDs: Dr. Pamela Gillen Participants will be able to do the following: Discuss the risks of an alcohol-exposed pregnancy (AEP)
Remote Alcohol & Other Drugs Workforce Northern Territory. Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder (FASD) Footprints across the Territory 1
 Remote Alcohol & Other Drugs Workforce Northern Territory Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder (FASD) 1 The aim of this presentation To understand what can happen to babies in the womb if the mother drinks
Remote Alcohol & Other Drugs Workforce Northern Territory Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder (FASD) 1 The aim of this presentation To understand what can happen to babies in the womb if the mother drinks
ADHD SCREENING & DEVELOPMENTAL QUESTIONNAIRE: FOR PARENT TO COMPLETE
 *PAPERWORK MAY BE MAILED, FAXED OR DROPPED-OFF (If faxing, send to: FAX: 585-244-9995 - Attention: Holly) ADHD SCREENING & DEVELOPMENTAL QUESTIONNAIRE: FOR PARENT TO COMPLETE Child s Name: DOB: Grade in
*PAPERWORK MAY BE MAILED, FAXED OR DROPPED-OFF (If faxing, send to: FAX: 585-244-9995 - Attention: Holly) ADHD SCREENING & DEVELOPMENTAL QUESTIONNAIRE: FOR PARENT TO COMPLETE Child s Name: DOB: Grade in
Developmental-Behavioral Pediatrics Questionnaire for New Patients
 Developmental-Behavioral Pediatrics Questionnaire for New Patients Date: Name of person completing questionnaire: Relationship to child: Email: IDENTIFYING INFORMATION: Information Child Name Child Birthdate
Developmental-Behavioral Pediatrics Questionnaire for New Patients Date: Name of person completing questionnaire: Relationship to child: Email: IDENTIFYING INFORMATION: Information Child Name Child Birthdate
Center For Autism and Neurodevelopmental Disabilities 3525 E Louise Dr Suite 250 Meridian, Idaho Phone: (208) Fax: (208)
 Center For Autism and Neurodevelopmental Disabilities 3525 E Louise Dr Suite 250 Meridian, Idaho 83642 Phone: (208) 381-7312 Fax: (208) 381-7313 ABOUT YOUR CHILD: Today's Date Child's Name Name child goes
Center For Autism and Neurodevelopmental Disabilities 3525 E Louise Dr Suite 250 Meridian, Idaho 83642 Phone: (208) 381-7312 Fax: (208) 381-7313 ABOUT YOUR CHILD: Today's Date Child's Name Name child goes
BACKGROUND HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE
 BACKGROUND HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE Name: Sex M F Address: Home Number: Work Number: Cell Number: Email: SSN: Name and Address of Employer: Date of Birth: Age: Ethnicity: Referred By: Referral Question or
BACKGROUND HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE Name: Sex M F Address: Home Number: Work Number: Cell Number: Email: SSN: Name and Address of Employer: Date of Birth: Age: Ethnicity: Referred By: Referral Question or
Disclosure Statement
 Disclosure Statement I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturer(s) of any commercial product(s) and/or provider of commercial services discussed in this CME activity. I do not intend
Disclosure Statement I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturer(s) of any commercial product(s) and/or provider of commercial services discussed in this CME activity. I do not intend
UNDERSTANDING FETAL ALCOHOL SYNDROME AND FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS (3 CE HOURS)
 UNDERSTANDING FETAL ALCOHOL SYNDROME AND FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS (3 CE HOURS) Learning objectives Define fetal alcohol syndrome and fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. List the prevalence of fetal
UNDERSTANDING FETAL ALCOHOL SYNDROME AND FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS (3 CE HOURS) Learning objectives Define fetal alcohol syndrome and fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. List the prevalence of fetal
9TH ANNUAL MENTAL HEALTH RECOVERY CONFERENCE 2015
 National Recovery Month is a national observance that educates Americans on the fact that addiction treatment and mental health services can enable those with a mental and/or substance use disorder to
National Recovery Month is a national observance that educates Americans on the fact that addiction treatment and mental health services can enable those with a mental and/or substance use disorder to
 FASD Foetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder The simple fact - there is no known safe level of alcohol consumption during pregnancy! Babies born with Foetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder (FASD) don t sleep well,
FASD Foetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder The simple fact - there is no known safe level of alcohol consumption during pregnancy! Babies born with Foetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder (FASD) don t sleep well,
THE IMPACT OF FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS ON DRUG & ALCOHOL ADDICTION AND TREATMENT
 THE IMPACT OF FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS ON DRUG & ALCOHOL ADDICTION AND TREATMENT FASd Estimated Incidence Rate: 9.1/1,000 live births (Sampson et al, Teratology 56:317-326, 1997) Incidence rates
THE IMPACT OF FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS ON DRUG & ALCOHOL ADDICTION AND TREATMENT FASd Estimated Incidence Rate: 9.1/1,000 live births (Sampson et al, Teratology 56:317-326, 1997) Incidence rates
THE HOSPITAL FOR SICK CHILDREN DEPARTMENT OF PSYCHIATRY PARENT INTERVIEW FOR CHILD SYMPTOMS (P. I. C. S.
 A Child s Name or ID: Date: 2013 THE HOSPITAL FOR SICK CHILDREN DEPARTMENT OF PSYCHIATRY PARENT INTERVIEW FOR CHILD SYMPTOMS (P. I. C. S. - 6) Revised for DSM-III - R (1989) and DSM-IV (1995, 2008) GENERAL
A Child s Name or ID: Date: 2013 THE HOSPITAL FOR SICK CHILDREN DEPARTMENT OF PSYCHIATRY PARENT INTERVIEW FOR CHILD SYMPTOMS (P. I. C. S. - 6) Revised for DSM-III - R (1989) and DSM-IV (1995, 2008) GENERAL
CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, SACRAMENTO
 COLLEGE OF EDUCATION DEPARTMENT OF SPECIAL EDUCATION, REHABILITATION AND SCHOOL PSYCHOLOGY CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, SACRAMENTO School Psychology Diagnostic Clinic 6000 J Street Sacramento, California
COLLEGE OF EDUCATION DEPARTMENT OF SPECIAL EDUCATION, REHABILITATION AND SCHOOL PSYCHOLOGY CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, SACRAMENTO School Psychology Diagnostic Clinic 6000 J Street Sacramento, California
Beacon Assessment Center Developmental Questionnaire Please complete prior to your first appointment
 Beacon Assessment Center Developmental Questionnaire Please complete prior to your first appointment If you would prefer to complete the electronic version of this questionnaire on the Beacon Assessment
Beacon Assessment Center Developmental Questionnaire Please complete prior to your first appointment If you would prefer to complete the electronic version of this questionnaire on the Beacon Assessment
Beacon Assessment Center
 Beacon Assessment Center Developmental Questionnaire Please complete prior to your first appointment Contact Information: Client Name: DOB: Dates of Evaluation: Age: Grade: Gender: Language(s) spoken in
Beacon Assessment Center Developmental Questionnaire Please complete prior to your first appointment Contact Information: Client Name: DOB: Dates of Evaluation: Age: Grade: Gender: Language(s) spoken in
Teresa s Background. Close Family. Sources. The Faces of FASD. Today We Will Learn About
 Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders Understanding Effects Improving Outcomes Part 1: The Faces of FASD Presentation by Teresa Kellerman Director of the Fetal Alcohol Resource Center Arizona Division of Developmental
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders Understanding Effects Improving Outcomes Part 1: The Faces of FASD Presentation by Teresa Kellerman Director of the Fetal Alcohol Resource Center Arizona Division of Developmental
SUBSTANCE EXPOSED INFANTS PRESENTED BY ECOLE J. BARROW-BROOKS M.ED & DARLENE D. OWENS MBA, LBSW, CADC, ADS
 SUBSTANCE EXPOSED INFANTS PRESENTED BY ECOLE J. BARROW-BROOKS M.ED & DARLENE D. OWENS MBA, LBSW, CADC, ADS 1 SUBSTANCE-EXPOSED INFANTS Refers to infants exposed to alcohol and or other substances ingested
SUBSTANCE EXPOSED INFANTS PRESENTED BY ECOLE J. BARROW-BROOKS M.ED & DARLENE D. OWENS MBA, LBSW, CADC, ADS 1 SUBSTANCE-EXPOSED INFANTS Refers to infants exposed to alcohol and or other substances ingested
Understanding Fetal Alcohol Syndrome and Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders
 Understanding Fetal Alcohol Syndrome and Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders 2 CE Hours By: Marvin C. Chaffi n, II, M.S., LMHC Learning objectives This workshop is designed to help you: Discuss fetal alcohol
Understanding Fetal Alcohol Syndrome and Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders 2 CE Hours By: Marvin C. Chaffi n, II, M.S., LMHC Learning objectives This workshop is designed to help you: Discuss fetal alcohol
Chapter 10 Section 1 Notes
 Chapter 10 Section 1 Notes Alcohol Is a Drug Alcohol is the drug found in beer, wine, and liquor that causes intoxication. Intoxication includes all the physical and mental changes produced by drinking
Chapter 10 Section 1 Notes Alcohol Is a Drug Alcohol is the drug found in beer, wine, and liquor that causes intoxication. Intoxication includes all the physical and mental changes produced by drinking
The Essential Role of Growth Deficiency in the Diagnosis of FASD
 The Essential Role of Growth Deficiency in the Diagnosis of FASD Susan Astley PhD Julia Bledsoe MD Julian Davies MD Members of the FAS DPN FASD Diagnostic Team University of Washington Seattle WA Published
The Essential Role of Growth Deficiency in the Diagnosis of FASD Susan Astley PhD Julia Bledsoe MD Julian Davies MD Members of the FAS DPN FASD Diagnostic Team University of Washington Seattle WA Published
The Intersection of FASD and Infant Mental Health: Applying a Trauma-Informed Lens for Children in the Child Welfare System
 The Intersection of FASD and Infant Mental Health: Applying a Trauma-Informed Lens for Children in the Child Welfare System Mary Motz, Ph.D., C.Psych. Clinical Psychologist Mothercraft/Breaking the Cycle
The Intersection of FASD and Infant Mental Health: Applying a Trauma-Informed Lens for Children in the Child Welfare System Mary Motz, Ph.D., C.Psych. Clinical Psychologist Mothercraft/Breaking the Cycle
Emergent Issues Affecting Early Intervention/ Early Childhood. Workforce Development for Inclusion in Early Childhood November 4, 2017 Washington, DC
 Emergent Issues Affecting Early Intervention/ Early Childhood Workforce Development for Inclusion in Early Childhood November 4, 2017 Washington, DC Conversation Points Changing Demographics Emergent Trends
Emergent Issues Affecting Early Intervention/ Early Childhood Workforce Development for Inclusion in Early Childhood November 4, 2017 Washington, DC Conversation Points Changing Demographics Emergent Trends
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders update
 Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders 2017 update Objectives recognize the wide range of physical and behavioral effects of alcohol exposure understand why the effects of alcohol exposure can vary widely be
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders 2017 update Objectives recognize the wide range of physical and behavioral effects of alcohol exposure understand why the effects of alcohol exposure can vary widely be
FASD: A Social Work Perspective. Liam Curran Principal Social Worker Disability Voluntary Services
 FASD: A Social Work Perspective Liam Curran Principal Social Worker Disability Voluntary Services What is Social Work? The definition of Social work is centred on the social context of people s s lives
FASD: A Social Work Perspective Liam Curran Principal Social Worker Disability Voluntary Services What is Social Work? The definition of Social work is centred on the social context of people s s lives
FETAL ALCOHOL SYNDROME
 FETAL ALCOHOL SYNDROME Written by: Damita Lachman Sherwani THINK TWICE! ARE YOU SURE THAT DRINK IS WORTH IT? http://www.recovery.org/topics/fetal-alcohol-syndrome/ The Fitzroy Valley of Western Australia
FETAL ALCOHOL SYNDROME Written by: Damita Lachman Sherwani THINK TWICE! ARE YOU SURE THAT DRINK IS WORTH IT? http://www.recovery.org/topics/fetal-alcohol-syndrome/ The Fitzroy Valley of Western Australia
FASD: What is it? When and How to Start the Conversation. Kathy Hotelling, Ph.D., ABPP
 FASD: What is it? When and How to Start the Conversation Kathy Hotelling, Ph.D., ABPP www.kathyhotelling.com www.facebook.com/navigatinglifewithfasd Disclosure Declarations Name Kathy Hotelling (Instructor)
FASD: What is it? When and How to Start the Conversation Kathy Hotelling, Ph.D., ABPP www.kathyhotelling.com www.facebook.com/navigatinglifewithfasd Disclosure Declarations Name Kathy Hotelling (Instructor)
CHILD/ADOLESCENT INTAKE INFORMATION
 CHILD/ADOLESCENT INTAKE INFORMATION Personal Data Today s Date: Client s Name: DOB: Age: Sex: M or F (circle one) Home Address: (street address, city, state, zip code) Home Phone: Work Phone Cell Phone
CHILD/ADOLESCENT INTAKE INFORMATION Personal Data Today s Date: Client s Name: DOB: Age: Sex: M or F (circle one) Home Address: (street address, city, state, zip code) Home Phone: Work Phone Cell Phone
FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS (FASDs)
 FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS (FASDs) An Ounce of Prevention NC Child Fatality Task Force February 10 th, 2016 Amy Hendricks, Coordinator NC Fetal Alcohol Prevention Program FASDinNC.org Mission s Fullerton
FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS (FASDs) An Ounce of Prevention NC Child Fatality Task Force February 10 th, 2016 Amy Hendricks, Coordinator NC Fetal Alcohol Prevention Program FASDinNC.org Mission s Fullerton
Child s Information (Please print) Name Birth Date Age Home Address City State Zip Code
 The following questions are asked so that we can best understand your child. Please fill out this questionnaire before the child is evaluated. Please read the questions carefully and answer them as fully
The following questions are asked so that we can best understand your child. Please fill out this questionnaire before the child is evaluated. Please read the questions carefully and answer them as fully
ADULT INTAKE/PSYCHOSOCIAL ASSESSMENT. Name: Date: Referred by:
 ADULT INTAKE/PSYCHOSOCIAL ASSESSMENT Name: Date: Referred by: Date of Birth: SSN: Identifying Information (age, marital status, ethnicity, and sex) 1. Reason for Referral: (Why are you here? Describe problems,
ADULT INTAKE/PSYCHOSOCIAL ASSESSMENT Name: Date: Referred by: Date of Birth: SSN: Identifying Information (age, marital status, ethnicity, and sex) 1. Reason for Referral: (Why are you here? Describe problems,
Dysmorphology. Sue White. Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase. Victorian Clinical Genetics Services
 Dysmorphology Sue White www.rch.unimelb.edu.au/nets/handbook Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase Dysmorphology Assessment Algorithm no Are the features familial? yes Recognised syndrome yes no AD/XL syndrome
Dysmorphology Sue White www.rch.unimelb.edu.au/nets/handbook Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase Dysmorphology Assessment Algorithm no Are the features familial? yes Recognised syndrome yes no AD/XL syndrome
The child-parent relationship is core to a child s development
 M. C O N N I E A L M E I D A, P H D The child-parent relationship is core to a child s development ATTACHMENT The central theme of attachment theory is that mothers / fathers who are available and responsive
M. C O N N I E A L M E I D A, P H D The child-parent relationship is core to a child s development ATTACHMENT The central theme of attachment theory is that mothers / fathers who are available and responsive
2/23/ Transition Conference Harrisburg PA February 23, 2017
 2017 Transition Conference Harrisburg PA February 23, 2017 1 ddubovksy@verizon.net 215-694-8450 2 is a spectrum of disorders There is a wide range of intellectual capabilities in individuals with an There
2017 Transition Conference Harrisburg PA February 23, 2017 1 ddubovksy@verizon.net 215-694-8450 2 is a spectrum of disorders There is a wide range of intellectual capabilities in individuals with an There
Biographical History Form Child/Adolescent
 Biographical History Form Child/Adolescent First Name: Middle Name: Last Name: Address: Child s Age: Child s DOB: / / Male Female Today s Date: / / Mother/Guardian: Cell #: Home#: Father/Guardian: Cell
Biographical History Form Child/Adolescent First Name: Middle Name: Last Name: Address: Child s Age: Child s DOB: / / Male Female Today s Date: / / Mother/Guardian: Cell #: Home#: Father/Guardian: Cell
Today we will. Understanding Dysmaturity. Common Challenges Across the Spectrum. Yellowknife. Teach Not Learn
 Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders Understanding Effects Improving Outcomes Part 5: Screening and Referral Presentation by Teresa Kellerman Director of the Fetal Alcohol Resource Center Arizona Division
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders Understanding Effects Improving Outcomes Part 5: Screening and Referral Presentation by Teresa Kellerman Director of the Fetal Alcohol Resource Center Arizona Division
Chapter 10. Alcohol Is a Drug
 Section 1 Alcohol Affects the Body Alcohol Is a Drug Alcohol is the drug found in beer, wine, and liquor that causes intoxication. Intoxication includes all the physical and mental changes produced by
Section 1 Alcohol Affects the Body Alcohol Is a Drug Alcohol is the drug found in beer, wine, and liquor that causes intoxication. Intoxication includes all the physical and mental changes produced by
THE FASD PATHWAY. Dr Patricia D. Jackson SACCH MEETING March 2016
 THE FASD PATHWAY Dr Patricia D. Jackson SACCH MEETING March 2016 Why do we need an FASD Pathway? Other countries recognise this as one of the commonest causes of learning disability In Scotland over the
THE FASD PATHWAY Dr Patricia D. Jackson SACCH MEETING March 2016 Why do we need an FASD Pathway? Other countries recognise this as one of the commonest causes of learning disability In Scotland over the
Assessment Intake/History Form
 Assessment Intake/History Form PATIENT INFORMATION Patient Name: Date of Birth: Age: Parent/Guardian Name(s): Who has legal custody of this child? Please circle one of the following: Address: City, State,
Assessment Intake/History Form PATIENT INFORMATION Patient Name: Date of Birth: Age: Parent/Guardian Name(s): Who has legal custody of this child? Please circle one of the following: Address: City, State,
PRINCIPLES OF CAREGIVING DEVELOPMENTAL DISABILITIES MODULE
 PRINCIPLES OF CAREGIVING DEVELOPMENTAL DISABILITIES MODULE CHAPTER 1: KNOWLEDGE OF DEVELOPMENTAL DISABILITIES CONTENT: A. Developmental Disabilities B. Introduction to Human Development C. The Four Developmental
PRINCIPLES OF CAREGIVING DEVELOPMENTAL DISABILITIES MODULE CHAPTER 1: KNOWLEDGE OF DEVELOPMENTAL DISABILITIES CONTENT: A. Developmental Disabilities B. Introduction to Human Development C. The Four Developmental
Brain Development and the Impact of Trauma
 1 Brain Development and the Impact of Trauma Sarah Lusardi, MSW and Alison Morrisey, LCSW July 17, 2013 2 Objectives: Understand the critical importance of early brain development and architecture. Understand
1 Brain Development and the Impact of Trauma Sarah Lusardi, MSW and Alison Morrisey, LCSW July 17, 2013 2 Objectives: Understand the critical importance of early brain development and architecture. Understand
Fetal Alcohol Exposure and Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
 Fetal Alcohol Exposure and Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Dana E. Johnson, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Pediatrics Divisions of Neonatology and Global Pediatrics University of Minnesota This presentation is made possible,
Fetal Alcohol Exposure and Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Dana E. Johnson, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Pediatrics Divisions of Neonatology and Global Pediatrics University of Minnesota This presentation is made possible,
Addiction Across the Lifespan
 Addiction Across the Lifespan David Galbis-Reig, M.D., DFASAM Medical Director of Addiction Services Ascension Wisconsin All Saints OBJECTIVES Be able to explain how addiction interacts with psychosocial
Addiction Across the Lifespan David Galbis-Reig, M.D., DFASAM Medical Director of Addiction Services Ascension Wisconsin All Saints OBJECTIVES Be able to explain how addiction interacts with psychosocial
Child and Youth Background Information
 Child and Youth Background Information CHILD S NAME: SUBSTANCE USE HISTORY (for ages 12 and older or if applicable) Substance Type Current Use (last 6 months) Past Use: Please check and complete all that
Child and Youth Background Information CHILD S NAME: SUBSTANCE USE HISTORY (for ages 12 and older or if applicable) Substance Type Current Use (last 6 months) Past Use: Please check and complete all that
Therapy Intake Form Today's Date: General Information: Full name of child: Male/Female: Parents/Guardians Name #1: Parents/Guardians Name #2: Address:
 Inspiring Talkers 10184 E. I25 Frontage Rd. Firestone, CO 80504 720-378-6670 Therapy Intake Form Today's Date: General Information: Full name of child: DOB: Male/Female: Parents/Guardians Name #1: Parents/Guardians
Inspiring Talkers 10184 E. I25 Frontage Rd. Firestone, CO 80504 720-378-6670 Therapy Intake Form Today's Date: General Information: Full name of child: DOB: Male/Female: Parents/Guardians Name #1: Parents/Guardians
Understanding Fetal Alcohol Syndrome and Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders
 Understanding Fetal Alcohol Syndrome and Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders 3 CE Hours By: Marvin C. Chaffin, II, M.S., LMHC Revised and Edited by: Wade T. Lijewski, Ph.D. Learning objectives Define fetal
Understanding Fetal Alcohol Syndrome and Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders 3 CE Hours By: Marvin C. Chaffin, II, M.S., LMHC Revised and Edited by: Wade T. Lijewski, Ph.D. Learning objectives Define fetal
Health Care Information for Families of Children with Down Syndrome
 American Academy of Pediatrics Introduction Down syndrome is a common condition caused by having extra copies of genes on the 21st chromosome. Those extra genes change development during pregnancy, and
American Academy of Pediatrics Introduction Down syndrome is a common condition caused by having extra copies of genes on the 21st chromosome. Those extra genes change development during pregnancy, and
ARE MOTHERS WHO DRINK HEAVILY IN PREGNANCY VICTIMS OF FAS? Maud Rouleau,BSc, Zina Levichek, MD, Gideon Koren, MD, FRCPC
 ARE MOTHERS WHO DRINK HEAVILY IN PREGNANCY VICTIMS OF FAS? Maud Rouleau,BSc, Zina Levichek, MD, Gideon Koren, MD, FRCPC ABSTRACT Background Consumption of large amounts of alcohol in pregnancy adversely
ARE MOTHERS WHO DRINK HEAVILY IN PREGNANCY VICTIMS OF FAS? Maud Rouleau,BSc, Zina Levichek, MD, Gideon Koren, MD, FRCPC ABSTRACT Background Consumption of large amounts of alcohol in pregnancy adversely
Dr Vinesh Gupta
 Dr Vinesh Gupta vinesh.gupta@albertahealthservices.ca The FASD Learning Series is part of the Alberta government s commitment to programs and services for people affected by FASD and those who support
Dr Vinesh Gupta vinesh.gupta@albertahealthservices.ca The FASD Learning Series is part of the Alberta government s commitment to programs and services for people affected by FASD and those who support
PAGE 1 NEURO-OPHTHALMIC QUESTIONNAIRE NAME: AGE: DATE OF EXAM: CHART #: (Office Use Only)
 PAGE 1 NEURO-OPHTHALMIC QUESTIONNAIRE NAME: AGE: DATE OF EXAM: CHART #: (Office Use Only) 1. What is the main problem that you are having? (If additional space is required, please use the back of this
PAGE 1 NEURO-OPHTHALMIC QUESTIONNAIRE NAME: AGE: DATE OF EXAM: CHART #: (Office Use Only) 1. What is the main problem that you are having? (If additional space is required, please use the back of this
Cardiovascular Genetics Clinic Vascular Questionnaire
 Name: Address: Home Phone: Cell Phone: Email Address: Date of Birth: Primary Care Physician: Why have you been referred for a Cardiovascular Genetics Appointment? Have you had a genetics evaluation? If
Name: Address: Home Phone: Cell Phone: Email Address: Date of Birth: Primary Care Physician: Why have you been referred for a Cardiovascular Genetics Appointment? Have you had a genetics evaluation? If
CHANGING PUBLIC POLICY WITH THE JUVENILE COURTS: WHAT WORKS WITH KIDS WITH FAS?
 CHANGING PUBLIC POLICY WITH THE JUVENILE COURTS: WHAT WORKS WITH KIDS WITH FAS? William J. Edwards Deputy Public Defender County of Los Angeles 1. ASSESSMENT A. Early Diagnosis- Many families that enter
CHANGING PUBLIC POLICY WITH THE JUVENILE COURTS: WHAT WORKS WITH KIDS WITH FAS? William J. Edwards Deputy Public Defender County of Los Angeles 1. ASSESSMENT A. Early Diagnosis- Many families that enter
Francine Grevin, Psy.D. Licensed Clinical Psychologist PSY South Main Plaza, Suite 225 Telephone (925) CHILD HISTORY FORM
 Email: Dr.Grevin@eastbaypsychotherapyservices.com www.therapywalnutcreek.com CHILD HISTORY FORM Date Child s name Last First Child s birth date Gender Home address(es) Parent(s) names(s): Home phone (s)
Email: Dr.Grevin@eastbaypsychotherapyservices.com www.therapywalnutcreek.com CHILD HISTORY FORM Date Child s name Last First Child s birth date Gender Home address(es) Parent(s) names(s): Home phone (s)
A court team model for young children in foster care: The role of prenatal alcohol exposure and Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders
 Journal of Psychiatry & Law 39/Spring 2011 179 A court team model for young children in foster care: The role of prenatal alcohol exposure and Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders BY LARRY BURD, PH.D., HON.
Journal of Psychiatry & Law 39/Spring 2011 179 A court team model for young children in foster care: The role of prenatal alcohol exposure and Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders BY LARRY BURD, PH.D., HON.
History Form for Adult Client
 History Form for Adult Client Referral Date: Who referred you to our office (please circle one)? Self Other, please specify: Reason for Referral: Require a Diagnostic Evaluation for Autism Spectrum Disorder
History Form for Adult Client Referral Date: Who referred you to our office (please circle one)? Self Other, please specify: Reason for Referral: Require a Diagnostic Evaluation for Autism Spectrum Disorder
NEW PATIENT INFORMATION FORM - CHILD
 NEW PATIENT INFORMATION FORM - CHILD (Please fill out and return at or prior to first appointment) Patient Legal Name DEMOGRAPHIC INFORMATION Preferred Name Date Date of Birth Age Sex Male Female Address
NEW PATIENT INFORMATION FORM - CHILD (Please fill out and return at or prior to first appointment) Patient Legal Name DEMOGRAPHIC INFORMATION Preferred Name Date Date of Birth Age Sex Male Female Address
Safe, Healthy, Happy Children
 September 20, 2012 Safe, Healthy, Happy Children Parental Substance Abuse Negative Impact on Children Chaotic & Unpredictable Environments Drug Endangered Children Children are drug endangered when their
September 20, 2012 Safe, Healthy, Happy Children Parental Substance Abuse Negative Impact on Children Chaotic & Unpredictable Environments Drug Endangered Children Children are drug endangered when their
ADOLESCENT FLUENCY CASE HISTORY
 COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCES Department of Communication Sciences and Disorders Speech-Language-Hearing Clinic 3750 Lindell Blvd., Suite 32 St. Louis, MO 63108 Ph 314-977-3365 F 314-977-1615 ADOLESCENT FLUENCY
COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCES Department of Communication Sciences and Disorders Speech-Language-Hearing Clinic 3750 Lindell Blvd., Suite 32 St. Louis, MO 63108 Ph 314-977-3365 F 314-977-1615 ADOLESCENT FLUENCY
Lisa Karabelnik, MD 68 South Main Street; Suite 200 West Hartford, CT P (860) F (860) Patient Name (Last, First, Middle)
 Lisa Karabelnik, MD 68 South Main Street; Suite 200 West Hartford, CT 06107 P (860)521-3380 F (860)561-6184 Patient Name (Last, First, Middle) Date of Birth Significant Childhood History Pregnancy and
Lisa Karabelnik, MD 68 South Main Street; Suite 200 West Hartford, CT 06107 P (860)521-3380 F (860)561-6184 Patient Name (Last, First, Middle) Date of Birth Significant Childhood History Pregnancy and
Techniques for Optimizing Success in Identifying and Working with American Indian/Alaska Native Children
 Techniques for Optimizing Success in Identifying and Working with American Indian/Alaska Native Children 6 th International Meeting on Indigenous Child Health - Resilience: Our Ancestors legacy, our children
Techniques for Optimizing Success in Identifying and Working with American Indian/Alaska Native Children 6 th International Meeting on Indigenous Child Health - Resilience: Our Ancestors legacy, our children
Alcohol affects your brain. Alcohol affects your body.
 Alcohol Alcohol affects your brain. Drinking alcohol leads to a loss of coordination, poor judgment, slowed reflexes, distorted vision, memory lapses, and even blackouts. Alcohol affects your body. Alcohol
Alcohol Alcohol affects your brain. Drinking alcohol leads to a loss of coordination, poor judgment, slowed reflexes, distorted vision, memory lapses, and even blackouts. Alcohol affects your body. Alcohol
ESP 755A SUMMER Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Autosomal recessive disorders
 ESP 755A SUMMER 2017 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Autosomal recessive disorders a. affect only males c. are caused when the abnormal
ESP 755A SUMMER 2017 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Autosomal recessive disorders a. affect only males c. are caused when the abnormal
WHO International Collaborative Research Project on Child Development and Prenatal Risk Factors with a Focus on FASD. Dr V. Poznyak and Mr Dag Rekve
 WHO International Collaborative Research Project on Child Development and Prenatal Risk Factors with a Focus on FASD Dr V. Poznyak and Mr Dag Rekve 1 Guiding principles of the Global strategy to reduce
WHO International Collaborative Research Project on Child Development and Prenatal Risk Factors with a Focus on FASD Dr V. Poznyak and Mr Dag Rekve 1 Guiding principles of the Global strategy to reduce
FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS
 FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS Implications for Juvenile and Family Court Judges 1 FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS Implications for Juvenile and Family Court Judges 03 Table of Contents Acknowledgements
FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS Implications for Juvenile and Family Court Judges 1 FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS Implications for Juvenile and Family Court Judges 03 Table of Contents Acknowledgements
Taking Control of Alcohol Use
 Taking Control of Alcohol Use Session 1: About Alcohol Use. This workbook accompanies the e-course Taking Control of Alcohol Use and is for the exclusive use of clients and customers of Homewood Human
Taking Control of Alcohol Use Session 1: About Alcohol Use. This workbook accompanies the e-course Taking Control of Alcohol Use and is for the exclusive use of clients and customers of Homewood Human
Pediatric Primary Care Mental Health Specialist Certification Exam. Detailed Content Outline
 Pediatric Primary Care Mental Health Specialist Certification Exam Detailed Content Outline Description of the Specialty The Pediatric Primary Care Mental Health Specialist (PMHS) builds upon the Advanced
Pediatric Primary Care Mental Health Specialist Certification Exam Detailed Content Outline Description of the Specialty The Pediatric Primary Care Mental Health Specialist (PMHS) builds upon the Advanced
Population approaches to the primary prevention of birth defects. Carol Bower RACP Conference Adelaide 2016
 Population approaches to the primary prevention of birth defects Carol Bower RACP Conference Adelaide 2016 Acknowledgements Research collaborators Consumer and community advisors and representatives Stakeholders
Population approaches to the primary prevention of birth defects Carol Bower RACP Conference Adelaide 2016 Acknowledgements Research collaborators Consumer and community advisors and representatives Stakeholders
Two Decades of Research on FAS and FASD in the Western Cape
 Two Decades of Research on FAS and FASD in the Western Cape Philip A. May, Ph.D. Research Professor Nutrition Research Institute Gillings School of Global Public Health University of North Carolina at
Two Decades of Research on FAS and FASD in the Western Cape Philip A. May, Ph.D. Research Professor Nutrition Research Institute Gillings School of Global Public Health University of North Carolina at
