ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM.
|
|
|
- Imogen West
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 !!
2 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CONCEPT: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM: DIVISIONS AND STRUCTURE The Autonomic Nervous System and its Divisions: Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) controls all the involuntary, subconscious processes that keep you. Reflexes that maintain blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, digestive function, O2 and CO2 levels, etc. The ANS has two divisions that usually have effects: Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS)= Fight-or-Flight. Make you ready for activity/stress. - Heart Rate, Digestion, etc. Parasympathetic Nervous System (PSNS)= Rest-and-Digest. Housekeeping functions in times of low activity. - Heart Rate, Digestion, etc. SNS and PSNS activity ( tone ) are like a see-saw SNS happens with PSNS, and vice-versa. It s up or down, never on or off. EXAMPLE: Some organs innervated by one or both autonomic divisions and the effects on those organs. Page 2
3 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH ANS Patterns from the CNS: The ANS exerts its effects via the nervous system autonomic nerves leave the CNS and project into the periphery. The SNS and PSNS have nerves that leave the CNS in separate, specific, predictable places. SNS nerves leave the CNS from the middle of the spinal cord, specifically segments T1 through L2. PSNS nerves leave the CNS from the brainstem and the sacral spinal cord. - Cranial Nerve X the Vagus nerve is the most important PSNS nerve. EXAMPLE: Note where the sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves leave in that same figure. Page 3
4 General ANS Patterns in the Periphery: Both divisions work via a two-neuron pathway. One neuron leaves the CNS, the second neuron synapses onto the target. Ganglion= The cluster of cell bodies in the periphery where the two neurons synapse with each other. Preganglionic Neuron= The first neuron (with its cell body in the CNS that synapses onto the second neuron). Postganglionic Neuron= The second neuron (with its cell body in a ganglion that synapses onto target organ). EXAMPLE: A schematic of general ANS patterns. CNS Pre-Ganglionic Neuron Ganglion Post-Ganglionic Neuron Target Organ Location of Synapses in the Periphery: The two divisions differ in where the preganglionic and postganglionic neurons synapse. SNS: Synapse in the Sympathetic Chain Ganglion, a chain of cell bodies running parallel to the spinal cord. -Preganglionic neuron has a short axon, postganglionic has a longer axon. PSNS: Synapse is in a small, discrete ganglion, on or near target organ. -Preganglionic neuron has a long axon, postganglionic has a very short axon. EXAMPLE: A comparison of synapse/ganglion location between the SNS and PSNS: SYMPATHETIC: Spinal Cord Sympathetic Chain (T1-L2) Ganglion Pre-Ganglionic Neuron Post-Ganglionic Neuron Target Organ PARASYMPATHETIC: CNS (Brainstem or Sacral Spinal Cord) Pre-Ganglionic Neuron Ganglion Near Target Organ Post-Ganglionic Neuron Target Organ Page 4
5 Neurotransmitter and Receptor Patterns: Note how there are two synapses in these pathways: preganglionic postganglionic and postganglionic receptor. The SNS and PSNS have different patterns for the NT and post-synaptic receptor used at each. SNS Neurotransmitter and Receptor Patterns: For neurons in the SNS: Preganglionic NT=Acetylcholine Postganglionic NT= Norepinephrine Postganglionic Receptor= nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Target Organ Receptor= Adrenergic (possible subtypes: α1, β1, β2). EXAMPLE: A summary of the neurons, synapses, NTs, and receptors used by the sympathetic nervous system. Spinal Cord (T1-L2) Sympathetic Chain Ganglion Pre-Ganglionic Neuron Post-Ganglionic Neuron Target Organ NT= Acetylcholine Rec=Nicotinic AchR NT= Norepinephrine Rec=Adrenergic (α 1, β 1, β 2 ) PSNS Neurotransmitter and Receptor Patterns: For neurons in the PSNS: Preganglionic NT=Acetylcholine Postganglionic NT= Acetylcholine Postganglionic Receptor= nicotinic acetylcholine receptor Target Organ Receptor= muscarinic acetylcholine receptor EXAMPLE: A summary of the neurons, synapses, NTs, and receptors used by the parasympathetic nervous system. CNS (Brainstem or Sacral Spinal Cord) Pre-Ganglionic Neuron Ganglion Near Target Organ Post-Ganglionic Neuron Target Organ NT= Acetylcholine Rec=Nicotinic AchR NT=Acetylcholine Rec=Muscarininc AchR Page 5
6 PRACTICE 1: Oxybutynin is a drug used to relieve urinary incontinence. One of its major side effects is constipation. Based on that side effect, which branch of the autonomic nervous system is likely blocked by oxybutynin? a) Sympathetic NS. b) Parasympathetic NS. PRACTICE 2: Albuterol is a drug used to treat asthma. One of its major side effects is tachycardia (an increase in heart rate). Based on that side effect, which branch of the autonomic nervous is likely activated by albuterol? a) Sympathetic NS. b) Parasympathetic NS. PRACTICE 3: A cardiothoracic surgeon is implanting a pacemaker in a patient s heart. In the process she damages an autonomic ganglion located within the wall of the patient s heart. Which branch of the autonomic nervous system will be directly affected by damage to this ganglion? a) Sympathetic NS. b) Parasympathetic NS. PRACTICE 4: Rocuronium is a drug that blocks nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. On which of the following type(s) of cell(s) can rocuronium act? (Choose all that apply.) a) Pre-ganglionic sympathetic neurons. b) Pre-ganglionic parasympathetic neurons. c) Post-ganglionic sympathetic neurons. d) Post-ganglionic parasympathetic neurons. e) Targets of sympathetic innervation. f) Targets of parasympathetic innervation. Page 6
7 PRACTICE 5: Propranolol is a drug that blocks β adrenergic receptors. On which of the following type(s) of cell(s) can propranolol act? (Choose all that apply.) a) Pre-ganglionic sympathetic neurons. b) Pre-ganglionic parasympathetic neurons. c) Post-ganglionic sympathetic neurons. d) Post-ganglionic parasympathetic neurons. e) Targets of sympathetic innervation. f) Targets of parasympathetic innervation. PRACTICE 6: Physostigmine is a drug that blocks acetylcholinesterase, thereby raising the amount of acetylcholine present in the synaptic cleft at all synapses that use Ach as an NT. Which of the following type(s) of cell(s) will be affected by the actions of physostigmine? (Choose all that apply.) a) Pre-ganglionic sympathetic neurons. b) Pre-ganglionic parasympathetic neurons. c) Post-ganglionic sympathetic neurons. d) Post-ganglionic parasympathetic neurons. e) Targets of sympathetic innervation. f) Targets of parasympathetic innervation. PRACTICE 7: Atropine is a drug that blocks muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. On which of the following type(s) of cell(s) can atropine act? (Choose all that apply.) a) Pre-ganglionic sympathetic neurons. b) Pre-ganglionic parasympathetic neurons. c) Post-ganglionic sympathetic neurons. d) Post-ganglionic parasympathetic neurons. e) Targets of sympathetic innervation. f) Targets of parasympathetic innervation. Page 7
8 CONCEPT: PARASYMPATHETIC DIVISION The parasympathetic division maintains homeostasis at rest There are two main components: the cranial and sacral The cranial components of the parasympathetic division include several cranial nerves - Oculomotor nerve (CN III): extends to ciliary ganglion to cause pupil and lens contraction - Facial (CN VII): extends to pterygopalatine ganglion and submandibular ganglion - Causes gland secretion (lacrimal, salivary) - Glossopharyngeal (CN IX): extends to otic ganglion to cause parotid gland secretion - Vagus (CN X): travels to various viscera The sacral components include the pelvic splanchnic nerves in S2-S4 spinal cord segments - Organs innervated here include the intestine, rectum, bladder, ureter, and reproductive organs Page 8
9 EXAMPLE: Page 9
10 CONCEPT: SYMPATHETIC DIVISION ORGANIZATION The sympathetic division is more complex than the parasympathetic division The lateral horn of T1-L2 spinal cord regions hold the pre-ganglionic cell bodies - They then exit the spinal cord through the ventral horn and the anterior roots of T1-L2 spinal nerves Sympathetic trunk ganglia sit lateral to the vertebral column and anterior to the spinal nerves - Looks like a pearl necklace, where the trunks are the strings and the pearls are the ganglions - One sympathetic trunk ganglion is associated with each spinal nerve Exception: there are 3 cervical ganglia; superior, middle, inferior (not 8 for C1-C8) EXAMPLE: Page 10
11 Rami communicantes connect the spinal nerves to the sympathetic trunk - White rami communicantes is the area where preganglionic axons enter the sympathetic trunk - Gray rami communicantes is the area where postganglionic axons leave the trunk to the spinal nerve EXAMPLE: Page 11
12 Sympathetic splanchnic nerves are preganglionic axons that don t synapse with the sympathetic trunk ganglion - Terminate in prevertebral ganglia located in the cavity - Celiac ganglia synapse with the greater thoracic splanchnic nerves (T5-T9) - Innervate: stomach, spleen, gallbladder, liver, small intestine, pancreas - Superior mesenteric ganglia synapse with preganglionic neurons from T10-T12 - Innervate: small intestine, large intestine, pancreas, kidneys, ureters - Inferior mesenteric ganglia synapse with preganglionic axons from L1-L2 - Innervate: large intestine, rectum, urinary bladder, ureters, reproductive organs Page 12
13 EXAMPLE: Page 13
14 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CONCEPT: SYMPATHETIC PATHWAYS There are 4 pathways sympathetic preganglionic neurons synapse with the 1. Spinal nerve pathway - Spinal cord à white rami communicansà sympathetic trunk ganglion à gray rami communicans à spinal nerve à skin gland, vessels, and muscles 2. Postganglionic sympathetic nerve pathway - Spinal cord à white rami communicans à sympathetic trunk ganglion à internal organs, skin and eye Page 14
15 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH 3. Splanchnic nerve pathway - Spinal cord à white rami communicans à through the sympathetic trunk ganglion (does not synapse here) à prevertebral ganglia à abdominal and pelvic organs 4. Adrenal medulla pathway - Spinal cord à white rami communicans à sympathetic trunk (does not synapse here) à preverebral ganglion (does not synapse here) à synapse on adrenal medulla (part of adrenal gland) EXAMPLE: Page 15
16 CONCEPT: AUTONOMIC PLEXUSES Autonomic plexuses are groups collections of various types of axons These axons include: - Sympathetic postganglionic axons - Parasympathetic preganglionic axons - Visceral sensory axons The collections of axons do not synapse with each other, just similar organs EXAMPLE: Page 16
17 There are 5 main autonomic plexuses The cardiac plexus is found in the mediastinum, controls heart rate and blood pressure - Sympathetic: Postganglionic axons from the cervical and thoracic sympathetic trunk ganglia - Works to increase heart rate and blood pressure - Parasympathetic Preganglionic axons from the nerve - Works to decrease heart rate Page 17
18 The pulmonary plexus controls bronchodilation and - Sympathetic: Postganglionic axons from the cervical and thoracic sympathetic trunk ganglia - Works to cause bronchodilation (increase bronchi diameter) - Parasympathetic Preganglionic axons from the vagus nerve - Works to cause bronchoconstrction (decrease bronchi diameter) EXAMPLE Page 18
19 The esophogeal plexus controls of the esophagus - Sympathetic: Postganglionic axons from the cervical sympathetic trunk ganglia - Works to inhibits muscle movement - Parasympathetic Preganglionic axons from the vagus nerve - Works to control swallowing reflex EXAMPLE: Page 19
20 The abdominal aortic plexus controls abdominal and pelvic organs - Sympathetic: Postganglionic axons from the prevertebral ganglia - Parasympathetic Preganglionic axons from the vagus nerve and pelvic splanchnic nerves - Composed of sub-plexuses: - Celiac plexus, superior mesenteric plexus, and inferior mesenteric plexus EXAMPLE: Page 20
21 The hypogastric plexus controls pelvic - Sympathetic: Postganglionic axons from the aortic plexus and lumbar region of sympathetic trunk - Parasympathetic Preganglionic axons from pelvic splanchnic nerves EXAMPLE: Page 21
Human Anatomy. Autonomic Nervous System
 Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
Chp. 16: AUTONOMIC N.S. (In Review: Peripheral N. S.)
 Chp. 16: AUTONOMIC N.S. (In Review: Peripheral N. S.) Peripheral nerves contain both motor and sensory neurons Among the motor neurons, some of these are somatic and innervate skeletal muscles while some
Chp. 16: AUTONOMIC N.S. (In Review: Peripheral N. S.) Peripheral nerves contain both motor and sensory neurons Among the motor neurons, some of these are somatic and innervate skeletal muscles while some
Chapter 16. APR Enhanced Lecture Slides
 Chapter 16 APR Enhanced Lecture Slides See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
Chapter 16 APR Enhanced Lecture Slides See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems Anatomy of Autonomic Motor Pathways Preganglionic neuron
Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems Anatomy of Autonomic Motor Pathways Preganglionic neuron
The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Pearson Education, Inc.
 17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Introduction The autonomic nervous system: Functions outside of our conscious awareness Makes routine adjustments in our body s systems The autonomic nervous
17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Introduction The autonomic nervous system: Functions outside of our conscious awareness Makes routine adjustments in our body s systems The autonomic nervous
I. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) A. Dual Innervation B. Autonomic Motor Pathway 1. Preganglionic Neuron a. Preganglionic Fibers (Axons) (1)
 I. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) A. Dual Innervation B. Autonomic Motor Pathway 1. Preganglionic Neuron a. Preganglionic Fibers (Axons) (1) Acetylcholine - ACh 2. Ganglion (Ganglia) 3. Ganglionic Neuron
I. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) A. Dual Innervation B. Autonomic Motor Pathway 1. Preganglionic Neuron a. Preganglionic Fibers (Axons) (1) Acetylcholine - ACh 2. Ganglion (Ganglia) 3. Ganglionic Neuron
The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System
 17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The autonomic nervous system functions
17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The autonomic nervous system functions
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PART I: SPINAL CORD
 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PART I: SPINAL CORD How is the organization of the autonomic nervous system different from that of the somatic nervous system? Peripheral Nervous System Divisions Somatic Nervous
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PART I: SPINAL CORD How is the organization of the autonomic nervous system different from that of the somatic nervous system? Peripheral Nervous System Divisions Somatic Nervous
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 14 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 14 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
Fig Glossopharyngeal nerve transmits signals to medulla oblongata. Integrating center. Receptor. Baroreceptors sense increased blood pressure
 Fig. 5. Integrating center Glossopharyngeal nerve transmits signals to medulla oblongata Receptor 3 Vagus nerve transmits inhibitory signals to cardiac pacemaker Baroreceptors sense increased blood pressure
Fig. 5. Integrating center Glossopharyngeal nerve transmits signals to medulla oblongata Receptor 3 Vagus nerve transmits inhibitory signals to cardiac pacemaker Baroreceptors sense increased blood pressure
I. Neural Control of Involuntary Effectors. Chapter 9. Autonomic Motor Nerves. Autonomic Neurons. Autonomic Ganglia. Autonomic Neurons 9/19/11
 Chapter 9 I. Neural Control of Involuntary Effectors The Autonomic Nervous System Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Autonomic
Chapter 9 I. Neural Control of Involuntary Effectors The Autonomic Nervous System Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Autonomic
Divisions of ANS. Divisions of ANS 2 Divisions dualing innervate most organs. Autonomic Nervous System (Chapter 9)
 Autonomic Nervous System (Chapter 9) Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) general properties anatomy Autonomic Effects on Target Organs Subs of Nervous System Central nervous system Brain Spinal cord Peripheral
Autonomic Nervous System (Chapter 9) Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) general properties anatomy Autonomic Effects on Target Organs Subs of Nervous System Central nervous system Brain Spinal cord Peripheral
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 20 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 632) 1. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. 2.
Chapter 20 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 632) 1. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. 2.
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline
 Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. B. Operation of the ANS to maintain homeostasis,
CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. B. Operation of the ANS to maintain homeostasis,
Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor of the Chair of Human Anatomy, Candidate of Medicine
 Theoretical background to the study of the autonomic nervous system. Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system. Features of the structure, function Composed by Natalia Leonidovna
Theoretical background to the study of the autonomic nervous system. Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system. Features of the structure, function Composed by Natalia Leonidovna
4/8/2015. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Learn and Understand: Divisions of the ANS. Sympathetic division Parasympathetic division Dual innervation
 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Learn and Understand: Divisions of the ANS Sympathetic division Parasympathetic division Dual innervation ~ All visceral organs served by both divisions, usually cause opposite
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Learn and Understand: Divisions of the ANS Sympathetic division Parasympathetic division Dual innervation ~ All visceral organs served by both divisions, usually cause opposite
4/9/2019. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Learn and Understand: What appears to be two separate systems actually work together to maintain homeostasis under varying conditions. Receptors on the membranes of ANS effectors
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Learn and Understand: What appears to be two separate systems actually work together to maintain homeostasis under varying conditions. Receptors on the membranes of ANS effectors
Part 1. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Stimulatory
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 15 Part 1 The Autonomic Nervous System and Visceral Sensory Neurons The ANS and Visceral Sensory Neurons
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 15 Part 1 The Autonomic Nervous System and Visceral Sensory Neurons The ANS and Visceral Sensory Neurons
Autonomic Nervous System DR JAMILA EL MEDANY
 Autonomic Nervous System DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the autonomic nervous system. Describe the structure of autonomic nervous system Trace
Autonomic Nervous System DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the autonomic nervous system. Describe the structure of autonomic nervous system Trace
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 15 The Autonomic Nervous System Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems The somatic nervous system includes both sensory and motor
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 15 The Autonomic Nervous System Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems The somatic nervous system includes both sensory and motor
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 15: The Autonomic Nervous System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements is correct about the component of the autonomic nervous system identified
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements is correct about the component of the autonomic nervous system identified
Sympathetic Nervous System
 Sympathetic Nervous System Lecture Objectives Review the subdivisions of the nervous system. Review the general arrangement and compare the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts. Describe the following
Sympathetic Nervous System Lecture Objectives Review the subdivisions of the nervous system. Review the general arrangement and compare the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts. Describe the following
Chapter 15 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 15 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
Chapter 15 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
ParasymPathetic Nervous system. Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem
 ParasymPathetic Nervous system Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem In this lecture we are going to discuss Parasympathetic, in the last lecture we took sympathetic and one of the objectives of last lecture was
ParasymPathetic Nervous system Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem In this lecture we are going to discuss Parasympathetic, in the last lecture we took sympathetic and one of the objectives of last lecture was
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic nervous system organization Sympathetic Nervous System division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic nervous system organization Sympathetic Nervous System division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
Chapter 16. Autonomic nervous system. AP2 Chapter 16: ANS
 Chapter 16 Autonomic nervous system AP2 Chapter 16: ANS 1 Quick Review Nervous System Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Sensory Division Motor Division Somatic Nervous System Autonomic Nervous
Chapter 16 Autonomic nervous system AP2 Chapter 16: ANS 1 Quick Review Nervous System Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Sensory Division Motor Division Somatic Nervous System Autonomic Nervous
Systems Neuroscience November 21, 2017 The autonomic nervous system
 Systems Neuroscience November 21, 2017 The autonomic nervous system Daniel C. Kiper kiper@ini.phys.ethz.ch http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html How is the organization of the autonomic nervous
Systems Neuroscience November 21, 2017 The autonomic nervous system Daniel C. Kiper kiper@ini.phys.ethz.ch http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html How is the organization of the autonomic nervous
Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System Keri Muma Bio 6 Organization of the Nervous System Efferent Division Somatic Nervous System Voluntary control Effector = skeletal muscles Muscles must be excited by a motor neuron
Autonomic Nervous System Keri Muma Bio 6 Organization of the Nervous System Efferent Division Somatic Nervous System Voluntary control Effector = skeletal muscles Muscles must be excited by a motor neuron
Organisation of the nervous system
 Chapter1 Organisation of the nervous system 1. Subdivisions of the nervous system The nervous system is divided: i) Structurally The central nervous system (CNS) composed of the brain and spinal cord.
Chapter1 Organisation of the nervous system 1. Subdivisions of the nervous system The nervous system is divided: i) Structurally The central nervous system (CNS) composed of the brain and spinal cord.
Introduction to The Autonomic Nervous System. Sympathetic VS Parasympathetic Divisions. Adrenergic and Cholinergic Fibers. ANS Neurotransmitters
 Chapter 15 Introduction to The Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic VS Parasympathetic Divisions Adrenergic and Cholinergic Fibers ANS Neurotransmitters Autonomic Nervous System Portion of the nervous
Chapter 15 Introduction to The Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic VS Parasympathetic Divisions Adrenergic and Cholinergic Fibers ANS Neurotransmitters Autonomic Nervous System Portion of the nervous
The Autonomic Nervous
 Autonomic Nervous System The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq System Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University LECTUR (1) Functional Anatomy & Physiology of Autonomic
Autonomic Nervous System The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq System Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University LECTUR (1) Functional Anatomy & Physiology of Autonomic
Autonomic Division of NS
 Autonomic Division of NS Compare and contrast the structures of the sympathetic and the parasympathetic divisions, including functions and neurotransmitters. Show the levels of integration in the ANS,
Autonomic Division of NS Compare and contrast the structures of the sympathetic and the parasympathetic divisions, including functions and neurotransmitters. Show the levels of integration in the ANS,
Chapter 14 Autonomic Nervous System
 Chapter 14 Autonomic Nervous System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Why This Matters Understanding the autonomic
Chapter 14 Autonomic Nervous System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Why This Matters Understanding the autonomic
Chapter 15 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 15 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
Chapter 15 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
Autonomic Nervous System. Ms. DS Pillay Room 2P24
 Autonomic Nervous System Ms. DS Pillay Room 2P24 OVERVIEW OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM NERVOUS SYSTEM CNS PNS BRAIN SPINAL CORD SOMATIC ANS SYMPATHEIC PARASYMPATHEIC LOCATION OF GANGLIA IN THE ANS Short post-ganglionic
Autonomic Nervous System Ms. DS Pillay Room 2P24 OVERVIEW OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM NERVOUS SYSTEM CNS PNS BRAIN SPINAL CORD SOMATIC ANS SYMPATHEIC PARASYMPATHEIC LOCATION OF GANGLIA IN THE ANS Short post-ganglionic
Derived copy of Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m56161 1 Derived copy of Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System * Stephanie Fretham Based on Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX
OpenStax-CNX module: m56161 1 Derived copy of Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System * Stephanie Fretham Based on Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX
Introduction. Autonomic means self-governed ; the autonomic nervous system (ANS) is independent of our will
 Introduction Autonomic means self-governed ; the autonomic nervous system (ANS) is independent of our will It regulates fundamental states and life processes such as heart rate, BP, and body temperature
Introduction Autonomic means self-governed ; the autonomic nervous system (ANS) is independent of our will It regulates fundamental states and life processes such as heart rate, BP, and body temperature
Tymaa Al-zaben & Amin Al-ajalouni
 Done by: Tymaa Al-zaben & Amin Al-ajalouni ** Hello SERTONIN! SLIDE 3 note:: the slide included within the sheet but make sure back to slide for pictures The Autonomic Nervous System Function : Regulate
Done by: Tymaa Al-zaben & Amin Al-ajalouni ** Hello SERTONIN! SLIDE 3 note:: the slide included within the sheet but make sure back to slide for pictures The Autonomic Nervous System Function : Regulate
Neural Integration II: The Autonomic Nervous System and Higher-Order Functions
 16 Neural Integration II: The Autonomic Nervous System and Higher-Order Functions PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris Figure 16-1 An Overview of Neural
16 Neural Integration II: The Autonomic Nervous System and Higher-Order Functions PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris Figure 16-1 An Overview of Neural
Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System Objectives 1. Describe the CNS components of the ANS 2. Understand the peripheral pathways that connect the ANS with targets in the body. 3. Understand the classes of disorders
Autonomic Nervous System Objectives 1. Describe the CNS components of the ANS 2. Understand the peripheral pathways that connect the ANS with targets in the body. 3. Understand the classes of disorders
The Nervous System. Autonomic Division. C h a p t e r. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas
 C h a p t e r 17 The Nervous System Autonomic Division PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson
C h a p t e r 17 The Nervous System Autonomic Division PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson
The Autonomic Nervous System
 The Autonomic Nervous System Responsible for control of visceral effectors and visceral reflexes: smooth muscle, glands, the heart. e.g. blood pressure, cardiac output, plasma glucose The autonomic system
The Autonomic Nervous System Responsible for control of visceral effectors and visceral reflexes: smooth muscle, glands, the heart. e.g. blood pressure, cardiac output, plasma glucose The autonomic system
Ahmad Rabei & Hamad Mrayat. Ahmad Rabei & Hamad Mrayat. Mohd.Khatatbeh
 10 Ahmad Rabei & Hamad Mrayat Ahmad Rabei & Hamad Mrayat Mohd.Khatatbeh Before you start: Important terminology: 1 Ganglion: Nerve cell cluster, where neurons are typically linked by synapses. Also, it`s
10 Ahmad Rabei & Hamad Mrayat Ahmad Rabei & Hamad Mrayat Mohd.Khatatbeh Before you start: Important terminology: 1 Ganglion: Nerve cell cluster, where neurons are typically linked by synapses. Also, it`s
The Autonomic Nervous System
 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Note to the Instructor: For the third edition of Visual Anatomy & Physiology, we have updated our PowerPoints to fully integrate text
14 The Autonomic Nervous System Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Note to the Instructor: For the third edition of Visual Anatomy & Physiology, we have updated our PowerPoints to fully integrate text
Neuropsychiatry Block
 Neuropsychiatry Block Physiology of the Autonomic Nervous System By Laiche Djouhri, PhD Dept. of Physiology Email: ldjouhri@ksu.edu.sa Ext:71044 References The Autonomic Nervous System and the Adrenal
Neuropsychiatry Block Physiology of the Autonomic Nervous System By Laiche Djouhri, PhD Dept. of Physiology Email: ldjouhri@ksu.edu.sa Ext:71044 References The Autonomic Nervous System and the Adrenal
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system o Integumentary system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system o Integumentary system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system o Integumentary system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
Ch 9. The Autonomic Nervous System
 Ch 9 The Autonomic Nervous System SLOs Review the organization of the ANS Describe how neural regulation of smooth and cardiac muscles differs from that of skeletal muscles Describe the structure and innervation
Ch 9 The Autonomic Nervous System SLOs Review the organization of the ANS Describe how neural regulation of smooth and cardiac muscles differs from that of skeletal muscles Describe the structure and innervation
Autonomic Nervous System. Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry
 Autonomic Nervous System Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Peripheral Nervous System A. Sensory Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous System 1. Sympathetic Nervous
Autonomic Nervous System Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Peripheral Nervous System A. Sensory Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous System 1. Sympathetic Nervous
number Done by Corrected by Doctor
 number 13 Done by Tamara Wahbeh Corrected by Doctor Omar Shaheen In this sheet the following concepts will be covered: 1. Divisions of the nervous system 2. Anatomy of the ANS. 3. ANS innervations. 4.
number 13 Done by Tamara Wahbeh Corrected by Doctor Omar Shaheen In this sheet the following concepts will be covered: 1. Divisions of the nervous system 2. Anatomy of the ANS. 3. ANS innervations. 4.
Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous System(ANS)
 Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous System(ANS) ANS Pharmacology Lecture 1 Dr. Hiwa K. Saaed College of Pharmacy, University of Sulaimani 2018-2019 AUTOMATIC NERVOUS SYSTEM (ANS) The ANS is the major
Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous System(ANS) ANS Pharmacology Lecture 1 Dr. Hiwa K. Saaed College of Pharmacy, University of Sulaimani 2018-2019 AUTOMATIC NERVOUS SYSTEM (ANS) The ANS is the major
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
Autonomic nervous system
 Autonomic nervous system 1. Autonomic nervous system (ANS) nomenclature 2. Topographic organization and structural features of ANS 3. Main subdivisions of the ANS: sympathetic nervous system parasympathetic
Autonomic nervous system 1. Autonomic nervous system (ANS) nomenclature 2. Topographic organization and structural features of ANS 3. Main subdivisions of the ANS: sympathetic nervous system parasympathetic
Organization of Nervous System: Comparison of Somatic vs. Autonomic: Nervous system. Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS)
 NS Parasympathetic Somatic NS Organization of Nervous System: Nervous system Comparison of Somatic vs. : Cell body location NTs organs Marieb & Hoehn Figure 14.2 Ganglion: A group of cell bodies located
NS Parasympathetic Somatic NS Organization of Nervous System: Nervous system Comparison of Somatic vs. : Cell body location NTs organs Marieb & Hoehn Figure 14.2 Ganglion: A group of cell bodies located
The Autonomic Nervous System
 The Autonomic Nervous System Objectives Describe the structure and general functions of the sympathetic nervous system. Describe the structure and general functions of the parasympathetic nervous system.
The Autonomic Nervous System Objectives Describe the structure and general functions of the sympathetic nervous system. Describe the structure and general functions of the parasympathetic nervous system.
Autonomic nervous system
 Autonomic nervous system Key notes Autonomic: an independent system that runs on its own The ANS is a visceral and involuntary sensory and motor system The visceral motor fibers in the autonomic nerves
Autonomic nervous system Key notes Autonomic: an independent system that runs on its own The ANS is a visceral and involuntary sensory and motor system The visceral motor fibers in the autonomic nerves
Autonomic Nervous System. Autonomic (Visceral) Nervous System. Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition. Martini & Ober
 Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 14 Autonomic Nervous System Lecture 21 1 Autonomic (Visceral) Nervous System CNS PNS 2 Autonomic Nervous System functions without conscious
Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 14 Autonomic Nervous System Lecture 21 1 Autonomic (Visceral) Nervous System CNS PNS 2 Autonomic Nervous System functions without conscious
The Autonomic Nervous System Outline of class lecture for Physiology
 The Autonomic Nervous System Outline of class lecture for Physiology 1 After studying the endocrine system you should be able to: 1. Describe the organization of the nervous system. 2. Compare and contrast
The Autonomic Nervous System Outline of class lecture for Physiology 1 After studying the endocrine system you should be able to: 1. Describe the organization of the nervous system. 2. Compare and contrast
[ANATOMY #12] April 28, 2013
![[ANATOMY #12] April 28, 2013 [ANATOMY #12] April 28, 2013](/thumbs/86/93473883.jpg) Sympathetic chain : Sympathetic chain is each of the pair of ganglionated longitudinal cords of the sympathetic nervous system; extend from level of atlas (base of skull) till coccyx. It is paravertebral
Sympathetic chain : Sympathetic chain is each of the pair of ganglionated longitudinal cords of the sympathetic nervous system; extend from level of atlas (base of skull) till coccyx. It is paravertebral
Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy
 Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM (ANS):
 University of Jordan Faculty of Medicine Department of Physiology & Biochemistry Medical 1 st year students, 2017/2018. ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ Textbook of Medical Physiology,
University of Jordan Faculty of Medicine Department of Physiology & Biochemistry Medical 1 st year students, 2017/2018. ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ Textbook of Medical Physiology,
Neural Integration II: The Autonomic Nervous System and Higher-Order Functions
 16 Neural Integration II: The Autonomic Nervous System and Higher-Order Functions PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the ANS and
16 Neural Integration II: The Autonomic Nervous System and Higher-Order Functions PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the ANS and
NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY
 INTRODUCTION to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science
INTRODUCTION to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science
Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization
 Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization Diversity of Neural Signaling The diversity of neuron structure and function allows neurons to play many roles. 3 basic function of all neurons: Receive
Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization Diversity of Neural Signaling The diversity of neuron structure and function allows neurons to play many roles. 3 basic function of all neurons: Receive
Introduction to Autonomic
 Part 2 Autonomic Pharmacology 3 Introduction to Autonomic Pharmacology FUNCTIONS OF THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM The autonomic nervous system (Figure 3 1) is composed of the sympathetic and parasympathetic
Part 2 Autonomic Pharmacology 3 Introduction to Autonomic Pharmacology FUNCTIONS OF THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM The autonomic nervous system (Figure 3 1) is composed of the sympathetic and parasympathetic
cardiac plexus is continuous with the coronary and no named branches pain from the heart and lungs
 Nerves of the Thoracic Region Nerve Source Branches Motor Sensory Notes cardiac plexus cardiac brs. of the vagus n. and cervical ; thoracic l nn. the heart and lungs cardiac, cervical cardiac, vagal vagus
Nerves of the Thoracic Region Nerve Source Branches Motor Sensory Notes cardiac plexus cardiac brs. of the vagus n. and cervical ; thoracic l nn. the heart and lungs cardiac, cervical cardiac, vagal vagus
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS):
 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): ANS is the major involuntary, unconscious, automatic portion of the nervous system. involuntary voluntary The motor (efferent)portion of the ANS is the major pathway for
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): ANS is the major involuntary, unconscious, automatic portion of the nervous system. involuntary voluntary The motor (efferent)portion of the ANS is the major pathway for
General organization of central and peripheral components of the nervous system
 General organization of central and peripheral components of the nervous system Today we are focusing on the ANS Part of ANS?? Life depends on the innervation of the viscera... all the rest is biological
General organization of central and peripheral components of the nervous system Today we are focusing on the ANS Part of ANS?? Life depends on the innervation of the viscera... all the rest is biological
Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System Touqeer Ahmed PhD 3 rd March, 2017 Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Nervous System Divisions The peripheral nervous system
Autonomic Nervous System Touqeer Ahmed PhD 3 rd March, 2017 Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Nervous System Divisions The peripheral nervous system
Lujain Hamdan. Ayman Musleh & Yahya Salem. Mohammed khatatbeh
 12 Lujain Hamdan Ayman Musleh & Yahya Salem Mohammed khatatbeh the last lecture, we have studied the differences between the two divisions of the ANS: sympathetic and parasympathetic pathways which work
12 Lujain Hamdan Ayman Musleh & Yahya Salem Mohammed khatatbeh the last lecture, we have studied the differences between the two divisions of the ANS: sympathetic and parasympathetic pathways which work
The Nervous System PART D. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART D PNS: Spinal Nerves There is a pair of spinal nerves at the level of each
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART D PNS: Spinal Nerves There is a pair of spinal nerves at the level of each
Do Now pg What is the fight or flight response? 2. Give an example of when this response would kick in.
 Do Now pg 81 1. What is the fight or flight response? 2. Give an example of when this response would kick in. Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the PNS that functions independently (autonomously)
Do Now pg 81 1. What is the fight or flight response? 2. Give an example of when this response would kick in. Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the PNS that functions independently (autonomously)
Drugs Affecting the Autonomic Nervous System-1. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Drugs Affecting the Autonomic Nervous System-1 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia The autonomic nervous system, along with the endocrine system,
Drugs Affecting the Autonomic Nervous System-1 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia The autonomic nervous system, along with the endocrine system,
Autonomic Nervous System (the visceral motor system) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Autonomic Nervous System (the visceral motor system) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Monday, Nov 6, 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium
Autonomic Nervous System (the visceral motor system) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Monday, Nov 6, 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium
When motor nervous severed (cut, damaged), SK. Ms enter state of paralysis & atrophy
 11/25/2012 1 Somatic NS have their cell bodies within CNS Conduct impulses along single axon from spinal cord to neuromuscular junction Send axon to SK.M Muscles consciously induced to contract or relax
11/25/2012 1 Somatic NS have their cell bodies within CNS Conduct impulses along single axon from spinal cord to neuromuscular junction Send axon to SK.M Muscles consciously induced to contract or relax
NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY
 NTRODUCTON to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science Engineering
NTRODUCTON to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science Engineering
THE GOOFY ANATOMIST QUIZZES
 THE GOOFY ANATOMIST QUIZZES 5. NERVES Q1. Which of the following classifications of the nervous systems is correct? A. The autonomic nervous system is composed of the brain, cranial nerves and spinal nerves.
THE GOOFY ANATOMIST QUIZZES 5. NERVES Q1. Which of the following classifications of the nervous systems is correct? A. The autonomic nervous system is composed of the brain, cranial nerves and spinal nerves.
Peripheral Nervous System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
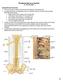 Peripheral Nervous System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Spinal Nerves Overview Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves are connected to the spinal cord No special names; numbered by level of vertebral column at which they
Peripheral Nervous System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Spinal Nerves Overview Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves are connected to the spinal cord No special names; numbered by level of vertebral column at which they
Constriction and dilatation of blood vessels. Contraction and relaxation of smooth muscle in various organs. Visual accommodation, pupillary size.
 The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Dr. L. Al tmimi Academic year 2011-2012 This text is focused mostly on the anatomy and physiology of the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS), more specifically, about the
The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Dr. L. Al tmimi Academic year 2011-2012 This text is focused mostly on the anatomy and physiology of the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS), more specifically, about the
Autonomic Nervous System, Visceral Sensation and Visceral Reflexes Jeff Dupree, Ph.D.
 Autonomic Nervous System, Visceral Sensation and Visceral Reflexes Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should know the: 1. basic divisions of the autonomic
Autonomic Nervous System, Visceral Sensation and Visceral Reflexes Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should know the: 1. basic divisions of the autonomic
Nerves on the Posterior Abdominal Wall
 Nerves on the Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar Plexus The lumbar plexus, which is one of the main nervous pathways supplying the lower limb, is formed in the psoasmuscle from the anterior ramiof the upper
Nerves on the Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar Plexus The lumbar plexus, which is one of the main nervous pathways supplying the lower limb, is formed in the psoasmuscle from the anterior ramiof the upper
Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System 6 th March, 2015 & 19 th March, 2015 Touqeer Ahmed Ph.D. Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Autonomic Nervous System Role
Autonomic Nervous System 6 th March, 2015 & 19 th March, 2015 Touqeer Ahmed Ph.D. Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Autonomic Nervous System Role
The Autonomic Nervous System & Higher Order Functions. An overview of the ANS. Divisions of the ANS. The Sympathetic Division (16-3) 2/19/2015
 The Autonomic Nervous System & Higher Order Functions Chapter 16 An overview of the ANS The autonomic nervous system coordinates cardiovascular, respiratory, digestive, urinary and reproductive functions
The Autonomic Nervous System & Higher Order Functions Chapter 16 An overview of the ANS The autonomic nervous system coordinates cardiovascular, respiratory, digestive, urinary and reproductive functions
THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
 1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the portion of the nervous system which innervates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & glands, & controls the visceral functions of the
1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the portion of the nervous system which innervates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle & glands, & controls the visceral functions of the
Brain and spinal nerve. By: shirin Kashfi
 Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
Group of students. - Rawan almujabili د. محمد المحتسب - 1 P a g e
 - 14 - Group of students - Rawan almujabili د. محمد المحتسب - 1 P a g e Nerves of the posterior abdominal wall The spinal cord gives off spinal nerves between the vertebrae. In the abdomen, through the
- 14 - Group of students - Rawan almujabili د. محمد المحتسب - 1 P a g e Nerves of the posterior abdominal wall The spinal cord gives off spinal nerves between the vertebrae. In the abdomen, through the
Brain Stem. Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14
 Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
Autonomic Targets. Review (again) Efferent Peripheral NS: The Autonomic & Somatic Motor Divisions
 Review (again) Efferent Peripheral NS: The Autonomic & Somatic Motor Divisions Running Problem: Smoking Homeostasis and the Autonomic Division BP, HR, Resp., H 2 O balance, Temp... Mostly dual reciprocal
Review (again) Efferent Peripheral NS: The Autonomic & Somatic Motor Divisions Running Problem: Smoking Homeostasis and the Autonomic Division BP, HR, Resp., H 2 O balance, Temp... Mostly dual reciprocal
Sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. Autonomic innervation and reflexes of pelvic organs. János Hanics M.D.
 Sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. Autonomic innervation and reflexes of pelvic organs János Hanics M.D. Vegetative (autonomic) nervous system General function: to keep the homeostasis of
Sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. Autonomic innervation and reflexes of pelvic organs János Hanics M.D. Vegetative (autonomic) nervous system General function: to keep the homeostasis of
Autonomic nervous system
 Autonomic nervous system Sompol Tapechum, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Objectives เม อจบบทเร ยน น กศ กษาสามารถ 1. บอกความแตกต างระหว าง Autonomic และ Somatic
Autonomic nervous system Sompol Tapechum, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Objectives เม อจบบทเร ยน น กศ กษาสามารถ 1. บอกความแตกต างระหว าง Autonomic และ Somatic
Cerebral hemisphere. Parietal Frontal Occipital Temporal
 Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
ACTIVITY2.15 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter48 DATE HOUR NERVOUS SYSTEMS NEURON
 AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.15 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter48 NAME DATE HOUR NERVOUS SYSTEMS NEURON SIMPLE REFLEX RESTING POTENTIAL ACTION POTENTIAL ACTION POTENTIAL GRAPH TRANSMISSION ACROSS A SYNAPSE QUESTIONS:
AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.15 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter48 NAME DATE HOUR NERVOUS SYSTEMS NEURON SIMPLE REFLEX RESTING POTENTIAL ACTION POTENTIAL ACTION POTENTIAL GRAPH TRANSMISSION ACROSS A SYNAPSE QUESTIONS:
NEURONS ARE ORGANIZED INTO NERVOUS SYSTEMS 34.5
 NEURONS ARE ORGANIZED INTO NERVOUS SYSTEMS 34.5 INTRODUCTION The cnidarians have nerve nets, the most simple type of nervous system. The sea anemone has a nerve net that serves simple behaviours such as
NEURONS ARE ORGANIZED INTO NERVOUS SYSTEMS 34.5 INTRODUCTION The cnidarians have nerve nets, the most simple type of nervous system. The sea anemone has a nerve net that serves simple behaviours such as
Laboratory Manual for Comparative Anatomy and Physiology Figure 15.1 Transparency Master 114
 Neuron Capillary Astrocyte Microglial cell Neuron Fluid-filled cavity Process of oligodendrocyte Ependymal cells Brain or spinal cord tissue Myelin sheath Nerve fibers Figure 15.1 Transparency Master 114
Neuron Capillary Astrocyte Microglial cell Neuron Fluid-filled cavity Process of oligodendrocyte Ependymal cells Brain or spinal cord tissue Myelin sheath Nerve fibers Figure 15.1 Transparency Master 114
Cranial Nerves. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
Autonomic Nervous System and Hypothalamus
 Lu Chen LSA room 201 Phone: (510) 643-8163 Email: luchen@berkeley.edu Office hours: M,W,F, 10-11 am 1 Autonomic Nervous System and Hypothalamus Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley 2 Hypothalamus Brain stem
Lu Chen LSA room 201 Phone: (510) 643-8163 Email: luchen@berkeley.edu Office hours: M,W,F, 10-11 am 1 Autonomic Nervous System and Hypothalamus Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley 2 Hypothalamus Brain stem
Overview of the autonomic (vegetative) nervous system
 Overview of the autonomic (vegetative) nervous system 1 The nervous system for topographic indication is divided into two divisions: the central nervous system (CNS) i peripheral nervous system (PNS).
Overview of the autonomic (vegetative) nervous system 1 The nervous system for topographic indication is divided into two divisions: the central nervous system (CNS) i peripheral nervous system (PNS).
NERVOUS SYSTEM. Academic Resource Center. Forskellen mellem oscillator og krystal
 NERVOUS SYSTEM Academic Resource Center Forskellen mellem oscillator og krystal Overview of the Nervous System Peripheral nervous system-pns cranial nerves spinal nerves ganglia peripheral nerves enteric
NERVOUS SYSTEM Academic Resource Center Forskellen mellem oscillator og krystal Overview of the Nervous System Peripheral nervous system-pns cranial nerves spinal nerves ganglia peripheral nerves enteric
Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System Ref: Textbook of Medical Physiology, Guyton, 12th ed: 729-738, 11th ed. P748-760, and 10th ed. p697-708. Fig.17.02 General functions Control and Adaptation
Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System Ref: Textbook of Medical Physiology, Guyton, 12th ed: 729-738, 11th ed. P748-760, and 10th ed. p697-708. Fig.17.02 General functions Control and Adaptation
