Psychology 100 Exam 1 Spring. 98
|
|
|
- Barnaby Hardy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Psychology 100 Exam 1 Spring. 98 Name 1. Which is the first person to contended the mind is a blank slate? a. Pavlov b. Watson c. Plato d. Freud e. Aristotle 2. Which of the following individuals contend you should only study the function of a behavior and not the conscious mind? a. Pavlov b. Watson c. Wundt d. Freud e. James 3. Which school would define Psychology as the Science of Behavior? a. Structuralists b. Functionalists c. Gestaltists d. Behaviorists 4. As defined by lecture, Psychology is defined as a. The study of metaphysical processes only. b. The study of observable behavior. c. The scientific study of behavior and the mind. d. The scientific study of the conscious mind. 5. Psychologists receive which type of degree? a. M.D. b. Ph.D. c. MSW d. none of these 6. Which of the following psychologists would most likely study memory, reasoning, or problem solving. a. counseling, b. clinical c. cognitive d. personality 7. Which psychologist would most likely to use psychological tests? a. clinical b. personality c. developmental. d. both b and c 8. Which psychologist would most likely evaluate employee performance a. clinical b. industrial c. educational d. both a and c. 9. To examine the parenting behavior of panda's, two psychologists spent three years observing them in the mountains. Which method did the psychologists probably use? a. Survey b. Naturalistic Observation c. Case study. d. none of these 10. An extensive interview with a person would be an example of a. a case study. c. the survey method b. naturalistic observation. d. none of these 11. is a way of estimating the extent two variables are related to each other a. A case study c. both a and b are correct b. Naturalistic Observation d. Correlation 12. Which experimental method will only allow you to determine cause-effect relationships? a. A case study b. Naturalistic Observation c. Experimental d. a and b. 13. Of these correlation s, which indicates the weakest relationship a b c d e. +2
2 14. A group of 100 introductory psychology students takes an exam. The mean of the exam is 71 and the standard deviation is 8. Your score is 88. How many standard deviations away from the mean is your score? a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4 e Of these correlations, which indicates the greatest relationship? a b c d e An experiment was conducted where medical students were given various dosages of alcohol. Thirty minutes after consuming the alcohol, the students were asked to press a button as fast as they could for two minutes. Results indicated the more alcohol they consumed, the faster they pushed the button. In this example the is the independent variable while the is the dependent variable. a. alcohol, button press c. button press, alcohol b. button press, medical students d. none of these are correct 17. When you take three tests and each time get the same score, the test has high. a. Validity. b. Constancy. c. Reliability. d. Stability. 18. The medulla and pons are located in the a. hind brain b. mid brain c. brain stem d. both b and c e. both a and c 19. Mark blows into a new breathalyzer and gets a blood alcohol concentration of.10 (legal limit). He then proceeds to blow into the machine several more times. His blood alcohol concentrations are listed as follows. Time 1.10 Time 2.15 Time Time The breathalyzer has high, but low. a. reliability, validity c. validity, reliability b. stability, reliability d. stability, validity The range of these numbers is. (All totals are added correctly) a = 72 / 8 = 9 c = 14 / 2 = 7 b. b = 72 d = The mode of these numbers is a = 70 c. 6 b = 65 d Which neuron structure sends information toward the soma? a. The dendrite b. The axon c. The myelin d. none of these 23. The structure that decides if an action potential will begin is called a. The dendrite b. The axon cleft c. The myelin d. none of these 24. Mark has just been scared and ran up a tree. Once in the tree Mark begins to relax. Which of the following would be correct for Mark? a. Mark's digestive system would slow down b. Mark's blood pressure would go up. c. Mark's heart rate would increase d. Mark's pupils would get larger e. none of these are correct
3 25. Which brain structure begins voluntary movement. a. Pons b. Thalamus c. Frontal lobe d. Temporal lobe 26. Myelin is designed to a. Cause calcium to enter faster. c. Speed up the action potential. b. Cause the action potential to stop. d. None of these. 27. Neurons to communicate with other neurons by using. a. electric shocks b. neurotransmitters c. limbic substances d. all of these 28. The lobe of the brain responsible for hearing is called the a. Frontal lobe b. Parietal lobe c. Occipital lobe d. Temporal lobe. 29. Which brain structure is involved with breathing? a. Medulla b. Pons c. Thalamus d. Limbic system 30. Brain chemicals that are similar in effects to Morphine and other opiates are called a. tranquilizers b. colenergic enzymes c. MEOS d. endorphins 31. The somatic and autonomic systems are part of the nervous system. a. Central b. Peripheral c. Limbic d. endocrine 32. Which of the following can be used to examine brain functioning? a. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) c. Computerized Axial Tomography b. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) d. All can be used 33. The structure that connects the left and right hemisphere is called the a. Corpus Callosum c. limbic system b. Mammillary Body d. Hippocampus 34. Damage to the reticular activating system would disrupt a. speech comprehension c. thinking b. speech production d. none of these 35. Mark has a brain tumor which does not allow him to see. Mark has damaged the a. Frontal lobe b. Wernicke s area c. area 3 d. Occipital lobe e. area 22 The relay center of the brain is called a. Wernicke s area b. Broca s area c. Thymus d. Thalamus 37. The structure that assists with motor movement is called a. Arcuate Fasiculus b. Cerebellum c. Broca s area d. None of these 38. Which structure is involved with sleep. a. Cerebellum b. Parietal Lobe c. Temporal Lobe d. Pons
4 39. Receptors are located on the a. Axon b. Dendrite c. Axon Hillock d. None of these e. all of these b. 40. The structure that is involved with attention and arousal is called the a. Reticular Activating System b. Medulla c. Pons. d. Frontal lobe 41. When an axon is at rest, the outside is a. Positive b. Negative c. Negative and Positive 42. When an axon potential is occurring, which ion is at high concentrations on the inside of the axon. a. Chloride b. Potassium c. Helium d. Sodium. 43. Sacks that contain neurotransmitters are called a. Boles sacks b. Synaptic Vesicles c. Teleodendria d. none of these 44. Structure 1 is called the and is involved with a. Frontal lobe, vision c. Occipital lobe, audition b. Parietal lobe, vision d. Occipital lobe, vision 45. Referring to the figure in the previous question: Structure 2 is called the and is involved with. a. Frontal lobe, vision c. Parietal Lobe, Sensation b. Parietal lobe, vision d. Occipital lobe, vision 46. Referring to the figure in the previous question: Structure 3 is called the and is involved with. a. Insular lobe, hearing c. Wernicke s area, vision e. Cerebellum, balance b Broca's area, speech, d. Wernicke's area, thinking, 47. Structure 1 is called. a. Teleodendria b. Presynaptic element c. axon hillock d. dendrite 48. Referring to the figure in question 47, Structure 2 is called a. Teleodendria b. Presynaptic element c. axon hillock d. dendrite 49. Referring to the figure in question 47, structure 3 is called a. synaptic cleft b. axon hillock c. dendrite d. post synaptic element 50. This is a free question. Answer A on your scantron sheet.
5
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind
 Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
The Nervous System. Biological School. Neuroanatomy. How does a Neuron fire? Acetylcholine (ACH) TYPES OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS
 Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Chapter 3. Biological Processes
 Biological Processes Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Biological Solutions Communicating internally Initiating and coordinating behavior Regulating growth and other internal functions
Biological Processes Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Biological Solutions Communicating internally Initiating and coordinating behavior Regulating growth and other internal functions
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1
 Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer:
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer:
PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1
 PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1 1 What is a neuron? 2 Name and describe the functions of the three main parts of the neuron. 3 What do glial cells do? 4 Describe the three basic
PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1 1 What is a neuron? 2 Name and describe the functions of the three main parts of the neuron. 3 What do glial cells do? 4 Describe the three basic
Sincerely, Ms. Paoloni and Mrs. Whitney
 Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2
 Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
Modules 4 & 6. The Biology of Mind
 Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour
 Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Chapter 6 Section 1. The Nervous System: The Basic Structure
 Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
Psychology 101 Exam 1 Fall 2000 Name
 Psychology 101 Exam 1 Fall 2000 Name 1. Psychology is defined as: a. the scientific investigation of thought processes b. the understanding of abnormal behavior c. the scientific study of behavior and
Psychology 101 Exam 1 Fall 2000 Name 1. Psychology is defined as: a. the scientific investigation of thought processes b. the understanding of abnormal behavior c. the scientific study of behavior and
biological psychology, p. 40 The study of the nervous system, especially the brain. neuroscience, p. 40
 biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
Primary Functions. Monitor changes. Integrate input. Initiate a response. External / internal. Process, interpret, make decisions, store information
 NERVOUS SYSTEM Monitor changes External / internal Integrate input Primary Functions Process, interpret, make decisions, store information Initiate a response E.g., movement, hormone release, stimulate/inhibit
NERVOUS SYSTEM Monitor changes External / internal Integrate input Primary Functions Process, interpret, make decisions, store information Initiate a response E.g., movement, hormone release, stimulate/inhibit
psychology. experience. mind when Answer the questions, then look up the correct answers in the te xt, course web pages, etc.
 1 Practice Questions for Unit 1 Answer the questions, then look up the correct answers in the te xt, course web pages, etc. 2 The concept of the reflex arc was developed by a. Rene Descartes b. John Locke
1 Practice Questions for Unit 1 Answer the questions, then look up the correct answers in the te xt, course web pages, etc. 2 The concept of the reflex arc was developed by a. Rene Descartes b. John Locke
The Nervous System. Divisions of the Nervous System. Branches of the Autonomic Nervous System. Central versus Peripheral
 The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7)
 Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
1. Processes nutrients and provides energy for the neuron to function; contains the cell's nucleus; also called the soma.
 1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
Overview of Neurons. Psychology 470. Introduction to Chemical Additions. Neurons2. Axons and Related Structures. Structures
 Soma Collateral Overview of Neurons Psychology 470 Axon Hillock Teleodendria Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Node of Ranvier Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides
Soma Collateral Overview of Neurons Psychology 470 Axon Hillock Teleodendria Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Node of Ranvier Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides
Overview of Brain Structures
 First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
Organization of the nervous system. The withdrawal reflex. The central nervous system. Structure of a neuron. Overview
 Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Chapter 6. Body and Behavior
 Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
synapse neurotransmitters Extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons, muscles, or glands
 neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
Nervous System Review
 Nervous System Review Name: Block: 1. Which processes are involved in the movement of molecule Y from point X to point Z? A. exocytosis and diffusion B. endocytosis and diffusion C. exocytosis and facilitated
Nervous System Review Name: Block: 1. Which processes are involved in the movement of molecule Y from point X to point Z? A. exocytosis and diffusion B. endocytosis and diffusion C. exocytosis and facilitated
Acetylcholine (ACh) Action potential. Agonists. Drugs that enhance the actions of neurotransmitters.
 Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Human Nervous System
 Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
10/15/2010. Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: Biology and Behavior. The Nervous System
 Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: 2-1 Biology and Behavior To survive, human beings must be able to perform three interrelated activities: sensing events, or stimuli; processing stimuli; and
Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: 2-1 Biology and Behavior To survive, human beings must be able to perform three interrelated activities: sensing events, or stimuli; processing stimuli; and
Neural Basis of Motor Control
 Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
fmri (functional MRI)
 Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Cognitive domain: Knowledge Answer location: Introduction: Knowledge from Cognitive Deficits Question type: MS Ans: C
 1 McBride and Cutting, Cognitive Psychology: Theory, Process, and Methodology Instructor Resources Chapter 2: Cognitive Neuroscience Multiple Choice 1. Neuroscientists have learned a great deal about which
1 McBride and Cutting, Cognitive Psychology: Theory, Process, and Methodology Instructor Resources Chapter 2: Cognitive Neuroscience Multiple Choice 1. Neuroscientists have learned a great deal about which
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. The Brain & Spinal Cord
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1
 Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter in Review 1. The human nervous system is a complex biological system designed for nearly instantaneous communication among billions of neurons throughout the body.
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter in Review 1. The human nervous system is a complex biological system designed for nearly instantaneous communication among billions of neurons throughout the body.
Neurons. Biological Basis of Behavior. Three Types of Neurons. Three Types of Neurons. The Withdrawal Reflex. Transmission of message 10/2/2017
 Neurons Basic units of the nervous system Receive, integrate, and transmit information Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 The adult human brain has ~180 BILLION cells ~ 80 billion neurons Three Types
Neurons Basic units of the nervous system Receive, integrate, and transmit information Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 The adult human brain has ~180 BILLION cells ~ 80 billion neurons Three Types
Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology
 Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology NATURE or NURTURE What are the effects of biochemistry on behavior? VOCABULARY Central Nervous System (CNS): The central nervous system is the part of the nervous
Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology NATURE or NURTURE What are the effects of biochemistry on behavior? VOCABULARY Central Nervous System (CNS): The central nervous system is the part of the nervous
Ways we Study the Brain. Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI
 The Brain Ways we Study the Brain Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI Accidents Phineas Gage Story Personality changed after the accident. What this this tell us? That different part
The Brain Ways we Study the Brain Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI Accidents Phineas Gage Story Personality changed after the accident. What this this tell us? That different part
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Biological Basis of Behavior. Chapter 2
 Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 Neurons Basic units of the nervous system Receive, integrate, and transmit information The adult human brain has ~180 BILLION cells ~ 80 billion neurons Three Types
Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 Neurons Basic units of the nervous system Receive, integrate, and transmit information The adult human brain has ~180 BILLION cells ~ 80 billion neurons Three Types
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES
 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
Lesson 14. The Nervous System. Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1
 Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Page 1. Neurons Transmit Signal via Action Potentials: neuron At rest, neurons maintain an electrical difference across
 Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
Chapter 3 Biological Psychology
 Chapter 3 Biological Psychology Introduction Reductionism? Scientists in many fields use a strategy called reductionism; they attempt to explain complex phenomena by reducing them to combinations of simpler
Chapter 3 Biological Psychology Introduction Reductionism? Scientists in many fields use a strategy called reductionism; they attempt to explain complex phenomena by reducing them to combinations of simpler
The Biological Basis of Behavior
 The Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 Chapter Overview I. Introduction II. Neurons III. The Human Nervous System IV. The Brain I. Introduction A. Announcement: The Brain Game B. Phrenology I. Introduction
The Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 Chapter Overview I. Introduction II. Neurons III. The Human Nervous System IV. The Brain I. Introduction A. Announcement: The Brain Game B. Phrenology I. Introduction
Copyright 2017 Pearson Education. All rights reserved. 1
 1 Learning Objectives LO 2.13 Name the parts of the cortex that are responsible for higher forms of thought, such as language. LO 2.14 Explain how some brain functions differ between the left and right
1 Learning Objectives LO 2.13 Name the parts of the cortex that are responsible for higher forms of thought, such as language. LO 2.14 Explain how some brain functions differ between the left and right
Chapter 12 Nervous System Written Assignment KEY
 Chapter 12 Nervous System Written Assignment KEY 1. Describe, in correct order, the events that occur during the transmission of a nerve impulse (action potential) as it travels from point X to point Y.
Chapter 12 Nervous System Written Assignment KEY 1. Describe, in correct order, the events that occur during the transmission of a nerve impulse (action potential) as it travels from point X to point Y.
18. The visual cortex is located in the: A) occipital lobe. B) temporal lobe. C) frontal lobe. D) parietal lobe.
 Name: Date: 1. A biological psychologist would be more likely to study: A) how you learn to express emotions. B) how to help people overcome emotional disorders. C) life-span changes in the expression
Name: Date: 1. A biological psychologist would be more likely to study: A) how you learn to express emotions. B) how to help people overcome emotional disorders. C) life-span changes in the expression
Chapter 2 Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior. Neural Communication. Neural Communication. Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed)
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 2 Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Neural Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links
Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 2 Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Neural Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links
The Nervous System II Neurons
 The Nervous System II Neurons Review Nervous System What is it? The system that receives, processes, stores and transmits information that comes from various parts of the body and the external world. Composed
The Nervous System II Neurons Review Nervous System What is it? The system that receives, processes, stores and transmits information that comes from various parts of the body and the external world. Composed
General Psychology Biology & Behavior: The Brain
 General Psychology Biology & Behavior: The Brain These are general notes designed to assist students who are regularly attending class and reading assigned material: they are supplemental rather than exhaustive
General Psychology Biology & Behavior: The Brain These are general notes designed to assist students who are regularly attending class and reading assigned material: they are supplemental rather than exhaustive
2) All of our thoughts, feelings, and behaviour can be traced to the activity of the a. neurons. b. ganglia. c. genes. d. nerve fibres.
 Chapter 2 Biology and Behaviour 1) The specialized cell that transmits signals throughout the nervous system is called the a. neuron. b. glial cell. c. myelin. d. neurotransmitter. Correct: The neuron
Chapter 2 Biology and Behaviour 1) The specialized cell that transmits signals throughout the nervous system is called the a. neuron. b. glial cell. c. myelin. d. neurotransmitter. Correct: The neuron
Practice test 1 spring 2011 copy
 Practice test 1 spring 2011 copy Student: 1. The fundamental units of the nervous system are nerve cells, called: A. axons B. glial cells C. neurons D. neurotransmitters 2. Which of the following is NOT
Practice test 1 spring 2011 copy Student: 1. The fundamental units of the nervous system are nerve cells, called: A. axons B. glial cells C. neurons D. neurotransmitters 2. Which of the following is NOT
Nervous System, Neuroanatomy, Neurotransmitters
 Nervous System, Neuroanatomy, Neurotransmitters Neurons Structure of neurons Soma Dendrites Spines Axon Myelin Nodes of Ranvier Neurons Structure of neurons Axon collaterals 1 Neurons Structure of neurons
Nervous System, Neuroanatomy, Neurotransmitters Neurons Structure of neurons Soma Dendrites Spines Axon Myelin Nodes of Ranvier Neurons Structure of neurons Axon collaterals 1 Neurons Structure of neurons
Neural Communication. Neural Communication. Myers PSYCHOLOGY - Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior. Definitions
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY - Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior 1. Neural communication - Neurons - How Neurons Communicate - How Neurotransmitters Influence Us 2. The nervous system 3. The endocrine system 4.
Myers PSYCHOLOGY - Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior 1. Neural communication - Neurons - How Neurons Communicate - How Neurotransmitters Influence Us 2. The nervous system 3. The endocrine system 4.
UNIT 5 REVIEW GUIDE - NERVOUS SYSTEM 1) State the 3 functions of the nervous system. 1) 2) 3)
 UNIT 5 REVIEW GUIDE - NERVOUS SYSTEM State the 3 functions of the nervous system. Briefly describe the general function(s) of each of the following neuron types: a) SENSORY NEURONS: b) INTERNEURONS: c)
UNIT 5 REVIEW GUIDE - NERVOUS SYSTEM State the 3 functions of the nervous system. Briefly describe the general function(s) of each of the following neuron types: a) SENSORY NEURONS: b) INTERNEURONS: c)
Body control systems. Let s start at the top: the human brain. The Cerebrum. The human brain. What parts of your brain are you using right now?
 What parts of your brain are you using right now? Body control systems Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Movement and conscious thought; Frontal speech
What parts of your brain are you using right now? Body control systems Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Movement and conscious thought; Frontal speech
Nervous system, integration: Overview, and peripheral nervous system:
 Nervous system, integration: Overview, and peripheral nervous system: Some review & misc. parts [Fig. 28.11B, p. 573]: - white matter --> looks white due to the myelinated sheaths, which are quite fatty.
Nervous system, integration: Overview, and peripheral nervous system: Some review & misc. parts [Fig. 28.11B, p. 573]: - white matter --> looks white due to the myelinated sheaths, which are quite fatty.
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II
 Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy. Components of a Nervous System
 Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
Module 5 : Anatomy The nervous system
 Module 5 : Anatomy The nervous system In this module you will learn: The main parts of the nervous system The different sections of the brain and how it functions The structure and function of the spinal
Module 5 : Anatomy The nervous system In this module you will learn: The main parts of the nervous system The different sections of the brain and how it functions The structure and function of the spinal
Neural Communication. Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System. Communication in the Nervous System. 4 Common Components of a Neuron
 Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Unit 3 REVIEW. Name: Date:
 Name: Date: 1. A person whose hand had been amputated actually felt sensations on his nonexistent fingers when his face was stroked. This best illustrates the consequences of A) lateralization. B) hemispherectomy.
Name: Date: 1. A person whose hand had been amputated actually felt sensations on his nonexistent fingers when his face was stroked. This best illustrates the consequences of A) lateralization. B) hemispherectomy.
Myers Psychology for AP*
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior
 Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Name: Period: Due Key Terms for CR 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Key Term Definition Application Acetylcholine (Ach) Action potential Adrenal glands
Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Name: Period: Due Key Terms for CR 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Key Term Definition Application Acetylcholine (Ach) Action potential Adrenal glands
Visualizing Psychology
 Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
PSYC 221 Introduction to General Psychology
 PSYC 221 Introduction to General Psychology Session 2 Biological foundations of behaviour Lecturer: Dr. Joana Salifu Yendork, Psychology Department Contact Information: jyendork@ug.edu.gh College of Education
PSYC 221 Introduction to General Psychology Session 2 Biological foundations of behaviour Lecturer: Dr. Joana Salifu Yendork, Psychology Department Contact Information: jyendork@ug.edu.gh College of Education
The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized?
 Honors Biology Guided Notes Chapter 28 Nervous System Name 28.10 28.19 The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized? ANIMAL NERVOUS SYSTEMS Define Cephalization and Centralization. What type of
Honors Biology Guided Notes Chapter 28 Nervous System Name 28.10 28.19 The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized? ANIMAL NERVOUS SYSTEMS Define Cephalization and Centralization. What type of
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System
 The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
Bio11: The Nervous System. Body control systems. The human brain. The human brain. The Cerebrum. What parts of your brain are you using right now?
 Bio11: The Nervous System Body control systems Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Can target several organs
Bio11: The Nervous System Body control systems Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Can target several organs
14 - Central Nervous System. The Brain Taft College Human Physiology
 14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
Axon Nerve impulse. Axoplasm Receptor. Axomembrane Stimuli. Schwann cell Effector. Myelin Cell body
 Nervous System Review 1. Explain a reflex arc. 2. Know the structure, function and location of a sensory neuron, interneuron, and motor neuron 3. What is (a) Neuron Axon Nerve impulse Axoplasm Receptor
Nervous System Review 1. Explain a reflex arc. 2. Know the structure, function and location of a sensory neuron, interneuron, and motor neuron 3. What is (a) Neuron Axon Nerve impulse Axoplasm Receptor
BIOLOGY 12 NERVOUS SYSTEM PRACTICE
 1 Name: BIOLOGY 12 NERVOUS SYSTEM PRACTICE Date: 1) Identify structures X, Y and Z and give one function of each. 2) Which processes are involved in the movement of molecule Y from point X to point Z?
1 Name: BIOLOGY 12 NERVOUS SYSTEM PRACTICE Date: 1) Identify structures X, Y and Z and give one function of each. 2) Which processes are involved in the movement of molecule Y from point X to point Z?
Homeostasis Practice Quiz 20 Questions SBI 4UI
 Homeostasis Practice Quiz 20 Questions SBI 4UI Question 1 Which system reverses a change in a variable, bringing it back to within a normal range? a. negative feedback system b. positive feedback system
Homeostasis Practice Quiz 20 Questions SBI 4UI Question 1 Which system reverses a change in a variable, bringing it back to within a normal range? a. negative feedback system b. positive feedback system
Neuroscience. Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior 1/11/2010. The Brain and Behavior
 Neuroscience The Brain and Behavior Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior I. How is the Nervous System Organized? II. Methods of Studying the Brain III. How Does the Brain Function? IV. What Effects Do
Neuroscience The Brain and Behavior Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior I. How is the Nervous System Organized? II. Methods of Studying the Brain III. How Does the Brain Function? IV. What Effects Do
Neuroscience. Biological psychology: a branch of psych concerned with the links between biology and behavior.
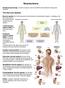 Biological psychology: a branch of psych concerned with the links between biology and behavior. The Nervous System: Nervous system: the body s speedy electrochemical communication network, consisting of
Biological psychology: a branch of psych concerned with the links between biology and behavior. The Nervous System: Nervous system: the body s speedy electrochemical communication network, consisting of
6. When the release of ACh is blocked, the result is A) depression. B) muscular paralysis. C) aggression. D) schizophrenia. E) euphoria.
 Name: Date: 1. Research on left-handedness suggests that A) genes or prenatal factors play a role in handedness. B) a greater proportion of women than men are left-handed. C) left-handers generally demonstrate
Name: Date: 1. Research on left-handedness suggests that A) genes or prenatal factors play a role in handedness. B) a greater proportion of women than men are left-handed. C) left-handers generally demonstrate
Body control systems. Nervous system. Organization of Nervous Systems. The Nervous System. Two types of cells. Organization of Nervous System
 Body control systems Nervous system Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Slower acting Longer lasting response
Body control systems Nervous system Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Slower acting Longer lasting response
To understand AD, it is important to
 To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
Neural Basis of Motor Control. Chapter 4
 Neural Basis of Motor Control Chapter 4 Neurological Perspective A basic understanding of the physiology underlying the control of voluntary movement establishes a more comprehensive appreciation and awareness
Neural Basis of Motor Control Chapter 4 Neurological Perspective A basic understanding of the physiology underlying the control of voluntary movement establishes a more comprehensive appreciation and awareness
CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts
 CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts The Brain: A Quick Tour Frontal Lobe Control of skeletal muscles Personality Concentration
CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts The Brain: A Quick Tour Frontal Lobe Control of skeletal muscles Personality Concentration
Topic/Objective: Identify the structures and functions of
 Cornell Notes Textbook Diagrams Video notes Topic/Objective: Identify the structures and functions of the human nervous system. Name: Class/Period: Date: Essential Question: How does the nervous system
Cornell Notes Textbook Diagrams Video notes Topic/Objective: Identify the structures and functions of the human nervous system. Name: Class/Period: Date: Essential Question: How does the nervous system
The Nervous System PART B
 7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
Nervous System. Chapter Structure of the Nervous System. Neurons
 33.1 Structure of the Neurons Neurons are specialized nerve cells that help you gather information about your environment, interpret the information, and react to it. Neurons consist of three main regions:
33.1 Structure of the Neurons Neurons are specialized nerve cells that help you gather information about your environment, interpret the information, and react to it. Neurons consist of three main regions:
IV. The Divisions of the Brain. Slide # 1
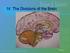 IV. The Divisions of the Brain Slide # 1 The Hindbrain Hindbrain, located at the rear base of the skull, controlling automatic functions Contains: Cerebellum (balance & coordination) Medulla (heartbeat,
IV. The Divisions of the Brain Slide # 1 The Hindbrain Hindbrain, located at the rear base of the skull, controlling automatic functions Contains: Cerebellum (balance & coordination) Medulla (heartbeat,
Forebrain Brain Structures Limbic System. Brain Stem Midbrain Basil Ganglia. Cerebellum Reticular Formation Medulla oblongata
 Brain structures (1) Cut out the following cards (2) Identify the three major divisions of the brain (as defined by your book). Initially, try this without any form of aid such as your textbook. (3) Organize
Brain structures (1) Cut out the following cards (2) Identify the three major divisions of the brain (as defined by your book). Initially, try this without any form of aid such as your textbook. (3) Organize
Parts of the Brain. Hindbrain. Controls autonomic functions Breathing, Heartbeat, Blood pressure, Swallowing, Vomiting, etc. Upper part of hindbrain
 Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
All questions below pertain to mandatory material: all slides, and mandatory homework (if any).
 ECOL 182 Spring 2008 Dr. Ferriere s lectures Lecture 6: Nervous system and brain Quiz Book reference: LIFE-The Science of Biology, 8 th Edition. http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire8e/ All questions below
ECOL 182 Spring 2008 Dr. Ferriere s lectures Lecture 6: Nervous system and brain Quiz Book reference: LIFE-The Science of Biology, 8 th Edition. http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire8e/ All questions below
TABLE OF CONTINENTS. PSYC1002 Notes. Neuroscience.2. Cognitive Processes Learning and Motivation. 37. Perception Mental Abilities..
 TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
DATE: NAME: CLASS: Chapter 11 Test
 Multiple Choice Questions Decide which of the choices best completes the statement or answers the question. Locate that question number on the separate answer sheet provided. Use the procedure described
Multiple Choice Questions Decide which of the choices best completes the statement or answers the question. Locate that question number on the separate answer sheet provided. Use the procedure described
Chapter 3. The Biological basis of Behavior 8 th Edition
 Chapter 3 The Biological basis of Behavior 8 th Edition Communication in the Nervous System Hardware: Glia structural support and insulation Neurons communication Soma cell body Dendrites receive Axon
Chapter 3 The Biological basis of Behavior 8 th Edition Communication in the Nervous System Hardware: Glia structural support and insulation Neurons communication Soma cell body Dendrites receive Axon
The nervous system regulates most body systems using direct connections called nerves. It enables you to sense and respond to stimuli
 The nervous system regulates most body systems using direct connections called nerves. It enables you to sense and respond to stimuli The basic function of nervous system are: Receive sensory input internal
The nervous system regulates most body systems using direct connections called nerves. It enables you to sense and respond to stimuli The basic function of nervous system are: Receive sensory input internal
:: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: :: Slide 3 :: :: Slide 4 :: :: Slide 5 :: :: Slide 6 ::
 :: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: Left blank Your nervous system is a complex communication network in which signals are constantly being received, integrated, and transmitted. The nervous system handles information,
:: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: Left blank Your nervous system is a complex communication network in which signals are constantly being received, integrated, and transmitted. The nervous system handles information,
Chapter 9. Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
AP Psychology Chapter 3 Test
 AP Psychology Chapter 3 Test Please make all marks on the Scan-Tron provided. Multiple Choice 1. In the opening vignette, what did the 5 million people who had fallen ill at the beginning of the 20 th
AP Psychology Chapter 3 Test Please make all marks on the Scan-Tron provided. Multiple Choice 1. In the opening vignette, what did the 5 million people who had fallen ill at the beginning of the 20 th
PSYCH 260 Exam 2. March 2, Answer the questions using the Scantron form. Name:
 PSYCH 260 Exam 2 March 2, 2017 Answer the questions using the Scantron form. Name: 1 1 Main Please put in their proper order the steps that lead to synaptic communication between neurons. Begin with the
PSYCH 260 Exam 2 March 2, 2017 Answer the questions using the Scantron form. Name: 1 1 Main Please put in their proper order the steps that lead to synaptic communication between neurons. Begin with the
Composed of gray matter and arranged in raised ridges (gyri), grooves (sulci), depressions (fissures).
 PSYC1020 Neuro and Pysc Notes Structure Description Major Functions Brainstem Stemlike portion of the brain, continuous with diencephalon above and spinal cord below. Composed of midbrain, pons, medulla
PSYC1020 Neuro and Pysc Notes Structure Description Major Functions Brainstem Stemlike portion of the brain, continuous with diencephalon above and spinal cord below. Composed of midbrain, pons, medulla
Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2.
Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2.
49a A&P: Nervous System -! Synaptic Transmission and Central Nervous System
 49a A&P: Nervous System -! Synaptic Transmission and Central Nervous System 49a A&P: Nervous System -! Synaptic Transmission and Central Nervous System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of
49a A&P: Nervous System -! Synaptic Transmission and Central Nervous System 49a A&P: Nervous System -! Synaptic Transmission and Central Nervous System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of
Chapter 3: Biology and Behavior
 Chapter 3: Case Study: The Brain of Phineas Gage Section 1: The Nervous System Section 2: The Brain: Our Control Center Section 3: The Endocrine System Section 4: Heredity: Our Genetic Background Lab:
Chapter 3: Case Study: The Brain of Phineas Gage Section 1: The Nervous System Section 2: The Brain: Our Control Center Section 3: The Endocrine System Section 4: Heredity: Our Genetic Background Lab:
Nervous Systems. Brain Development
 Nervous Systems Brain Development 2007-2008 Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal cord Sensory pathways Motor pathways Sympathetic arousal & energy production fight
Nervous Systems Brain Development 2007-2008 Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal cord Sensory pathways Motor pathways Sympathetic arousal & energy production fight
Bio11 schedule. Chapter 13 and 14. The Nervous System. The Nervous System. Organization of Nervous Systems. Nerves. Nervous and Sensory Systems
 Bio11 schedule Lecture Nervous system and senses Lab Current events reports (10 pts) Urinalysis Lecture exam 2 Thursday Feb 24 Same format as before Study guide will be posted Your total points so far
Bio11 schedule Lecture Nervous system and senses Lab Current events reports (10 pts) Urinalysis Lecture exam 2 Thursday Feb 24 Same format as before Study guide will be posted Your total points so far
CHAPTER 13 NERVOUS SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 13 NERVOUS SYSTEM LEARNING OUTCOMES 13.1 Overview of the Nervous System 1. Distinguish between the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system with regard to location and function. 2.
CHAPTER 13 NERVOUS SYSTEM LEARNING OUTCOMES 13.1 Overview of the Nervous System 1. Distinguish between the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system with regard to location and function. 2.
Psychology AP Mid-Term Review Packet
 Psychology AP Mid-Term Review Packet How you choose to complete this packet is up to you. I would suggest including more than just a basic definition. Chapter One Psychology Trained Introspection Functionalism
Psychology AP Mid-Term Review Packet How you choose to complete this packet is up to you. I would suggest including more than just a basic definition. Chapter One Psychology Trained Introspection Functionalism
