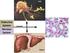
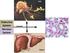
10.1: Introduction. Cell types in neural tissue: Neurons Neuroglial cells (also known as neuroglia, glia, and glial cells) Dendrites.
|
|
|
- Myles McCoy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 10.1: Introduction Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Cell types in neural tissue: Neurons Neuroglial cells (also known as neuroglia, glia, and glial cells) Dendrites Cell body Nuclei of neuroglia Axon Ed Reschke 1
2 10.2: General Functions of the Nervous System The three general functions of the nervous system: Receiving stimuli = sensory function Deciding about stimuli = integrative function Reacting to stimuli = motor function 2
3 Functions of Nervous System Sensory Function Sensory receptors gather information Information is carried to the CNS Integrative Function Sensory information used to create: Sensations Memory Thoughts Decisions Motor Function Decisions are acted upon Impulses are carried to effectors 3
4 Divisions of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain Spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Cranial nerves Spinal nerves 4
5 Divisions of Peripheral Nervous System Sensory Division Picks up sensory information and delivers it to the CNS Motor Division Carries information to muscles and glands Divisions of the Motor Division: Somatic carries information to skeletal muscle Autonomic carries information to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands 5
6 Divisions Nervous System Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Brain Cranial nerves Central Nervous System (brain and spinal cord) Peripheral Nervous System (cranial and spinal nerves) Spinal cord Spinal nerves Sensory division Sensory receptors Motor division Somatic Nervous System Skeletal muscle Autonomic Nervous System Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Glands (a) (b) 6
7 10.3: Description of Cells of the Nervous System Neurons vary in size and shape They may differ in length and size of their axons and dendrites Neurons share certain features: Dendrites A cell body An axon 7
8 Neuron Structure Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chromatophilic substance (Nissl bodies) Dendrites Nucleus Nucleolus Axonal hillock Cell body Neurofibrils Synaptic knob of axon terminal Nodes of Ranvier Myelin (cut) Impulse Axon Schwann cell Axon Nucleus of Schwann cell Portion of a collateral 8
9 Myelination of Axons White Matter Contains myelinated axons Considered fiber tracts Gray Matter Contains unmyelinated structures Cell bodies, dendrites (a) Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Dendrite Neuron cell body Neuron nucleus Unmyelinated region of axon Myelinated region of axon Node of Ranvier Axon Longitudinal groove (c) Enveloping Schwann cell Schwann cell nucleus Unmyelinated axon 9
10 Types of Neuroglial Cells in the PNS 1) Schwann Cells Produce myelin found on peripheral myelinated neurons Speed up neurotransmission 2) Satellite Cells Support clusters of neuron cell bodies (ganglia) 10
11 Types of Neuroglial Cells in the CNS 1) Microglia CNS Phagocytic cell 3) Oligodendrocytes CNS Myelinating cell 2) Astrocytes CNS Scar tissue Mop up excess ions, etc. Induce synapse formation Connect neurons to blood vessels Part of Blood Brain Barrier 4) Ependyma or ependymal CNS Ciliated Line central canal of spinal cord Line ventricles of brain Produce CSF 11
12 Types of Neuroglial Cells Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Fluid-filled cavity of the brain or spinal cord Ependymal cell Neuron Oligodendrocyte Astrocyte Microglial cell Capillary Axon Myelin sheath (cut) Node of Ranvier 12
13 10.4: Classification of Neurons Neurons vary in function and Neuroglia They can be sensory, motor, or integrative neurons Neurons vary in size and shape, and in the number of axons and dendrites that they may have Due to structural differences, neurons can be classified into three (3) major groups: Bipolar neurons Unipolar neurons Multipolar neurons 13
14 Classification of Neurons: Structural Differences Bipolar neurons dendrite, axon, cb in middle Eyes, ears, nose Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Dendrites Unipolar neurons Two ax process Ganglia of PNS Sensory Peripheral process Multipolar neurons 99% of neurons Many processes Most neurons of CNS Direction of impulse Axon (a) Multipolar Axon (b) Bipolar Central process Axon (c) Unipolar 14
15 Classification of Neurons: Sensory Neurons Afferent Carry impulse to CNS Most are unipolar Some are bipolar Interneurons Link neurons Aka association neurons or internuncial neurons Multipolar Located in CNS Functional Differences Motor Neurons Multipolar Carry impulses away from CNS Carry impulses to effectors Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Central nervous system Cell body Interneurons Axon Cell body Axon (central process) Axon Peripheral nervous system Sensory (afferent) neuron Motor (efferent) neuron Dendrites Sensory receptor Axon (peripheral process) Effector (muscle or gland) Axon terminal 15
16 Regeneration of A Nerve Axon Changes over time (a) Motor neuron cell body Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Axon Site of injury Schwann cells Distal portion of axon degenerates Skeletal muscle fiber (b) (c) (d) (e) Proximal end of injured axon regenerates into tube of sheath cells Schwann cells degenerate Schwann cells proliferate Former connection reestablished 16
17 10.5: The Synapse Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Nerve impulses pass from neuron to neuron at synapses, moving from a pre-synaptic neuron to a post-synaptic neuron. Synaptic cleft Dendrites Impulse Axon of presynaptic neuron Axon hillock of Postsynaptic neuron Axon of presynaptic neuron Impulse Cell body of postsynaptic neuron Impulse 17
18 Synaptic Transmission Neurotransmitters are released when impulse reaches synaptic knob Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Synaptic knob Direction of nerve impulse Axon Synaptic vesicles Ca 2 Ca 2 Presynaptic neuron Cell body or dendrite of postsynaptic neuron Mitochondrion Ca 2 Synaptic vesicle Vesicle releasing neurotransmitter Axon membrane Neurotransmitter Synaptic cleft (a) Polarized membrane Depolarized membrane 18
19 Animation: Chemical Synapse Please note that due to differing Please operating note systems, that due some to differing animations operating will not appear systems, until some the presentation animations is will viewed not in appear Presentation until the Mode presentation (Slide is viewed Show view). in Presentation You may see Mode blank (Slide slides Show in the Normal view). You or may Slide see Sorter blank slides views. in All the animations Normal will or Slide appear Sorter after viewing views. All in Presentation animations will Mode appear and playing after viewing each in animation. Presentation Most Mode animations and playing will require each animation. the latest version Most animations of the Flash will Player, require the which latest is available version of at the Flash Player, which is available at 19
20 10.6: Cell Membrane Potential A cell membrane is usually electrically charged, or polarized, so that the inside of the membrane is negatively charged with respect to the outside of the membrane (which is then positively charged). This is as a result of unequal distribution of ions on the inside and the outside of the membrane. 20
21 Distribution of Ions Potassium (K ) ions are the major intracellular positive ions (cations). Sodium (Na ) ions are the major extracellular positive ions (cations). This distribution is largely created by the Sodium/Potassium Pump (Na /K pump). This pump actively transports 3 sodium ions out of the cell and 2 potassium ions into the cell. 21
22 Resting Potential Resting Membrane Potential (RMP): 70 mv difference from inside to outside of cell It is a polarized membrane Inside of cell is negative relative to the outside of the cell RMP = -70 mv Due to distribution of ions inside vs. outside Na /K pump restores (a) High Na Low Na Impermeant anions High K Low K Cell body High Na Na Low Na Pump K Low K High K Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 70 mv (b) Axon Axon terminal 70 mv (c) 22
23 Local Potential Changes Caused by various stimuli: Temperature changes Light Pressure Gate-like mechanism Protein Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Cell membrane (a) Channel closed Fatty acid tail Phosphate head (b) Channel open Environmental changes affect the membrane potential by opening a gated ion channel Channels are 1) chemically gated, 2) voltage gated, or 3) mechanically gated 23
24 Local Potential Changes If membrane potential becomes more negative, it has hyperpolarized If membrane potential becomes less negative, it has depolarized Graded (or proportional) to intensity of stimulation reaching threshold potential Reaching threshold potential results in a nerve impulse, starting an action potential 24
25 Local Potential Changes Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Na Na 62 mv Neurotransmitter Chemically-gated Na channel (a) Presynaptic neuron Voltage-gated Na channel Na Na Na Na Na Trigger zone (axon hillock) 55 mv (b) 25
26 Action Potentials At rest, the membrane is polarized (RMP = -70) Threshold stimulus reached (-55) K Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Na Na Na Na Na Na Na Na Na Na Na K K K K K K K K K K K K K K K Na Na Na Na Na Na Na Na Na Na Na (a) 0 70 Sodium channels open and membrane depolarizes (toward 0) Potassium leaves cytoplasm and membrane repolarizes (30) K Threshold stimulus K Region of depolarization (b) K Na Na Na K K K K Na Na Na K K K Na Na Na Na Na Na Na Na Na Na Na K K K K K K K K K K Na Na Na Na Na Na Na Na Na Na Na Na Na Na Na Na K K K K K Na channels open K channels closed K channels open Na channels closed Brief period of hyperpolarization (-90) K Na Na Na K K K Region of repolarization (c) K K K K K Na Na Na Na Na Na Na Na 70 26
27 Membrane potential (millivolts) Action Potentials Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Action potential Resting potential Resting potential reestablished 80 Hyperpolarization Milliseconds 27
28 Action Potentials Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Region of action potential (a) Direction of nerve impulse (b) (c) 28
29 Animation: Action Potential Propagation in Myelinated Neurons Please note that due to differing operating systems, some animations will not appear until the presentation is viewed in Presentation Mode (Slide Show view). You may see blank slides in the Normal or Slide Sorter views. All animations will appear after viewing in Presentation Mode and playing each animation. Most animations will require the latest version of the Flash Player, which is available at 29
30 Animation: Action Potential Propagation in Unmyelinated Neurons Please note that due to differing operating systems, some animations will not appear until the presentation is viewed in Presentation Mode (Slide Show view). You may see blank slides in the Normal or Slide Sorter views. All animations will appear after viewing in Presentation Mode and playing each animation. Most animations will require the latest version of the Flash Player, which is available at 30
31 All-or-None Response If a neuron axon responds at all, it responds completely with an action potential (nerve impulse) A nerve impulse is conducted whenever a stimulus of threshold intensity or above is applied to an axon All impulses carried on an axon are the same strength 31
32 Refractory Period Absolute Refractory Period Time when threshold stimulus does not start another action potential Relative Refractory Period Time when stronger threshold stimulus can start another action potential 32
33 Impulse Conduction 33
34 Animation: The Nerve Impulse Please note that due to differing Please operating note systems, that due some to differing animations operating will not appear systems, until some the presentation animations is will viewed not in appear Presentation until the Mode presentation (Slide is viewed Show view). in Presentation You may see Mode blank (Slide slides Show in the Normal view). You or may Slide see Sorter blank slides views. in All the animations Normal will or Slide appear Sorter after viewing views. All in Presentation animations will Mode appear and playing after viewing each in animation. Presentation Most Mode animations and playing will require each animation. the latest version Most animations of the Flash will Player, require the which latest is available version of at the Flash Player, which is available at 34
35 10.3 Clinical Application Factors Affecting Impulse Conduction 35
36 10.7: Synaptic Transmission This is where released neurotransmitters cross the synaptic cleft and react with specific molecules called receptors in the postsynaptic neuron membrane. Effects of neurotransmitters vary. Some neurotransmitters may open ion channels and others may close ion channels. 36
37 Synaptic Potentials EPSP Excitatory postsynaptic potential Graded Depolarizes membrane of postsynaptic neuron Action potential of postsynaptic neuron becomes more likely IPSP Inhibitory postsynaptic potential Graded Hyperpolarizes membrane of postsynaptic neuron Action potential of postsynaptic neuron becomes less likely 37
38 Summation of EPSPs and IPSPs EPSPs and IPSPs are added together in a process called summation More EPSPs lead to greater probability of an action potential Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Neuron cell body Nucleus Presynaptic knob Presynaptic axon 38
39 Neurotransmitters 39
40 Neurotransmitters 40
41 Neuropeptides Neurons in the brain or spinal cord synthesize neuropeptides. These neuropeptides act as neurotransmitters. Examples include: Enkephalins Beta endorphin Substance P 41
42 10.4 Clinical Application Opiates in the Human Body 42
43 10.8: Impulse Processing Way the nervous system processes nerve impulses and acts upon them Neuronal Pools Interneurons Work together to perform a common function May excite or inhibit Convergence Various sensory receptors Can allow for summation of impulses Divergence Branching axon Stimulation of many neurons ultimately 43
44 Neuronal Pools Groups of interneurons that make synaptic connections with each other Interneurons work together to perform a common function Each pool receives input from other neurons Each pool generates output to other neurons 44
45 Convergence Neuron receives input from several neurons Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Incoming impulses represent information from different types of sensory receptors 1 2 Allows nervous system to collect, process, and respond to information Makes it possible for a neuron to sum impulses from different sources 3 (a) 45
46 Divergence One neuron sends impulses to several neurons Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Can amplify an impulse Impulse from a single neuron in CNS may be amplified to activate enough motor units needed for muscle contraction (b) 46
47 Important Points in Chapter 10: Outcomes to be Assessed 10.1: Introduction Describe the general functions of the nervous system. Identify the two types of cells that comprise nervous tissue. Identify the two major groups of nervous system organs. 10.2: General Functions of the Nervous System List the functions of sensory receptors. Describe how the nervous system responds to stimuli. 10.3: Description of Cells of the Nervous System Describe the three major parts of a neuron. Define neurofibrils and chromatophilic substance. 47
48 Important Points in Chapter 10: Outcomes to be Assessed Describe the relationship among myelin, the neurilemma, and the nodes of Ranvier. Distinguish between the sources of white matter and gray matter. 10.4: Classification of Neurons and Neuroglia Identify structural and functional differences among neurons. Identify the types of neuroglia in the central nervous system and their functions. Describe the Schwann cells of the peripheral nervous system. 10.5: The Synapse Define presynaptic and postsynaptic. Explain how information passes from a presynaptic to a postsynaptic neuron. 48
49 Important Points in Chapter 10: Outcomes to be Assessed 10.6: Cell Membrane Potential Explain how a cell membrane becomes polarized. Define resting potential, local potential, and action potential. Describe the events leading to the conduction of a nerve impulse. Compare nerve impulse conduction in myelinated and unmyelinated neurons. 10.7: Synaptic Transmission Identify the changes in membrane potential associated with excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters. 10.8: Impulse Processing Describe the basic ways in which the nervous system processes information. 49
50 Quiz 10 Complete Quiz 10 now! Read Chapter
Functions of Nervous System Neuron Structure
 Chapter 10 Nervous System I Divisions of the Nervous System Cell Types of Neural Tissue neurons neuroglial cells Central Nervous System brain spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System nerves cranial nerves
Chapter 10 Nervous System I Divisions of the Nervous System Cell Types of Neural Tissue neurons neuroglial cells Central Nervous System brain spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System nerves cranial nerves
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Chapter 10
 PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 10 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 10 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition. Chapter 10
 PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 10 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 10 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or
Unit Three. I. General Functions of the Nervous System. I. General Functions of the Nervous System
 10 Refer to the following URLs. It is a good idea to print them and bring them to class. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/ap.html
10 Refer to the following URLs. It is a good idea to print them and bring them to class. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/ap.html
Chapter 11: Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
 Chapter 11: Nervous System and Nervous Tissue I. Functions and divisions of the nervous system A. Sensory input: monitor changes in internal and external environment B. Integrations: make decisions about
Chapter 11: Nervous System and Nervous Tissue I. Functions and divisions of the nervous system A. Sensory input: monitor changes in internal and external environment B. Integrations: make decisions about
Outline. Neuron Structure. Week 4 - Nervous System. The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses
 Outline Week 4 - The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Neurons Neuron structures Types of neurons Electrical activity of neurons Depolarization, repolarization, hyperpolarization Synapses Release of
Outline Week 4 - The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Neurons Neuron structures Types of neurons Electrical activity of neurons Depolarization, repolarization, hyperpolarization Synapses Release of
The Nervous System. Nervous System Functions 1. gather sensory input 2. integration- process and interpret sensory input 3. cause motor output
 The Nervous System Nervous System Functions 1. gather sensory input 2. integration- process and interpret sensory input 3. cause motor output The Nervous System 2 Parts of the Nervous System 1. central
The Nervous System Nervous System Functions 1. gather sensory input 2. integration- process and interpret sensory input 3. cause motor output The Nervous System 2 Parts of the Nervous System 1. central
Major Structures of the Nervous System. Brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, spinal nerves, ganglia, enteric plexuses and sensory receptors
 Major Structures of the Nervous System Brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, spinal nerves, ganglia, enteric plexuses and sensory receptors Nervous System Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) consists
Major Structures of the Nervous System Brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, spinal nerves, ganglia, enteric plexuses and sensory receptors Nervous System Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) consists
The Nervous System 7PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART A Functions of the Nervous System Sensory input gathering information To monitor
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART A Functions of the Nervous System Sensory input gathering information To monitor
Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue
 Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue I. Functions of the Nervous System A. List and describe the five major nervous system functions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. II. Divisions of the Nervous System
Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue I. Functions of the Nervous System A. List and describe the five major nervous system functions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. II. Divisions of the Nervous System
Nervous System. Master controlling and communicating system of the body. Secrete chemicals called neurotransmitters
 Nervous System Master controlling and communicating system of the body Interacts with the endocrine system to control and coordinate the body s responses to changes in its environment, as well as growth,
Nervous System Master controlling and communicating system of the body Interacts with the endocrine system to control and coordinate the body s responses to changes in its environment, as well as growth,
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue. Nervous System. Basic Divisions of the Nervous System C H A P T E R 12.
 C H A P T E R 12 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Nervous System Sensory input Integration Motor output Figure 12.1 Basic Divisions of the Nervous System Brain CNS Spinal cord Nerves
C H A P T E R 12 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Nervous System Sensory input Integration Motor output Figure 12.1 Basic Divisions of the Nervous System Brain CNS Spinal cord Nerves
Endocrine System Nervous System
 Cells Endocrine System Nervous System Tissues Controls Organs Nervous System vs Endocrine System Electrical signals (graded potentials and action potentials) and chemical signals (neurotransmitters) Fast
Cells Endocrine System Nervous System Tissues Controls Organs Nervous System vs Endocrine System Electrical signals (graded potentials and action potentials) and chemical signals (neurotransmitters) Fast
The Nervous System: Neural Tissue Pearson Education, Inc.
 13 The Nervous System: Neural Tissue Introduction Nervous System Characteristics Controls and adjust the activity of the body Provides swift but brief responses The nervous system includes: Central Nervous
13 The Nervous System: Neural Tissue Introduction Nervous System Characteristics Controls and adjust the activity of the body Provides swift but brief responses The nervous system includes: Central Nervous
Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline
 Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline Module 11.1 Overview of the Nervous System (Figures 11.1-11.3) A. The nervous system controls our perception and experience
Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline Module 11.1 Overview of the Nervous System (Figures 11.1-11.3) A. The nervous system controls our perception and experience
Endocrine System Nervous System
 Cells Endocrine System Nervous System Tissues Controls Organs Nervous System vs Endocrine System Electrical signals (graded potentials and action potentials) and chemical signals (neurotransmitters) Fast
Cells Endocrine System Nervous System Tissues Controls Organs Nervous System vs Endocrine System Electrical signals (graded potentials and action potentials) and chemical signals (neurotransmitters) Fast
A. Subdivisions of the Nervous System: 1. The two major subdivisions of the nervous system:
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Ch 10 A Ch 10 B CHAPTER 10 NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 BASIC STRUCTURE and FUNCTION Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Ch 10 A Ch 10 B CHAPTER 10 NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 BASIC STRUCTURE and FUNCTION Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
DO NOW: ANSWER ON PG 73
 DO NOW: ANSWER ON PG 73 1. Name 1 neurotransmitter that we have learned about. 2. Draw a basic graph of a neuron action potential. Label resting potential, threshold, depolarization, and repolarization
DO NOW: ANSWER ON PG 73 1. Name 1 neurotransmitter that we have learned about. 2. Draw a basic graph of a neuron action potential. Label resting potential, threshold, depolarization, and repolarization
BIOL241 - Lecture 12a
 Cranial Nerves, source: training.seer.cancer.gov Nervous System Overview BIOL241 - Lecture 12a 1 Topics Divisions of the NS: CNS and PNS Structure and types of neurons Synapses Structure and function of
Cranial Nerves, source: training.seer.cancer.gov Nervous System Overview BIOL241 - Lecture 12a 1 Topics Divisions of the NS: CNS and PNS Structure and types of neurons Synapses Structure and function of
Neurophysiology scripts. Slide 2
 Neurophysiology scripts Slide 2 Nervous system and Endocrine system both maintain homeostasis in the body. Nervous system by nerve impulse and Endocrine system by hormones. Since the nerve impulse is an
Neurophysiology scripts Slide 2 Nervous system and Endocrine system both maintain homeostasis in the body. Nervous system by nerve impulse and Endocrine system by hormones. Since the nerve impulse is an
Neurophysiology. Corresponding textbook pages: ,
 Neurophysiology Corresponding textbook pages: 436-440, 442-455 Organization Helps maintain homeostasis in the body Nervous system and endocrine system Nervous system is faster due to nerve impulses 1 Fig.
Neurophysiology Corresponding textbook pages: 436-440, 442-455 Organization Helps maintain homeostasis in the body Nervous system and endocrine system Nervous system is faster due to nerve impulses 1 Fig.
NERVOUS SYSTEM CELLS. a. afferent division CHAPTER 12 ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. Student Name
 Student Name CHAPTER 12 NERVOUS SYSTEM CELLS T he nervous system organizes and coordinates the millions of impulses received each day to make communication with and enjoyment of our environment possible.
Student Name CHAPTER 12 NERVOUS SYSTEM CELLS T he nervous system organizes and coordinates the millions of impulses received each day to make communication with and enjoyment of our environment possible.
The Nervous System & Nervous tissue. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Nervous System & Nervous tissue Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of the Nervous System 1. Nervous system and endocrine system are the chief control centers in maintaining body homeostasis. 2. Nervous
The Nervous System & Nervous tissue Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of the Nervous System 1. Nervous system and endocrine system are the chief control centers in maintaining body homeostasis. 2. Nervous
Collin County Community College BIOL Week 5. Nervous System. Nervous System
 Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 Week 5 Nervous System 1 Nervous System The process of homeostasis makes sure that the activities that occur in the body are maintained within normal physiological
Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 Week 5 Nervous System 1 Nervous System The process of homeostasis makes sure that the activities that occur in the body are maintained within normal physiological
Chapter 7. The Nervous System
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System General overview of the nervous system functions Sensory input (info travels in along afferent pathways) Integration (information is processed) Sensory neurons Spinal cord
Chapter 7 The Nervous System General overview of the nervous system functions Sensory input (info travels in along afferent pathways) Integration (information is processed) Sensory neurons Spinal cord
Chapter 9. Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Nervous tissue, charachteristics, neurons, glial cells
 Nervous tissue, charachteristics, neurons, glial cells Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue The Nervous System Components Brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory receptors Responsible for Sensory perceptions,
Nervous tissue, charachteristics, neurons, glial cells Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue The Nervous System Components Brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory receptors Responsible for Sensory perceptions,
Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue. Nervous tissue, charachteristics, neurons, glial cells. The Nervous System. The Nervous System 21/12/2010
 Nervous tissue, charachteristics, neurons, glial cells Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue The Nervous System Components Brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory receptors Responsible for Sensory perceptions,
Nervous tissue, charachteristics, neurons, glial cells Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue The Nervous System Components Brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory receptors Responsible for Sensory perceptions,
NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 CHAPTER 10 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Ch 10 A This set Ch 10 B CHAPTER 10 NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 BASIC STRUCTURE and FUNCTION Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Ch 10 A This set Ch 10 B CHAPTER 10 NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 BASIC STRUCTURE and FUNCTION Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
Overview of the Nervous System A. Subdivisions of the Nervous System: 1. The two major subdivisions of the nervous system:
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Ch 10 A This set Ch 10 B CHAPTER 10 NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 BASIC STRUCTURE and FUNCTION Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Ch 10 A This set Ch 10 B CHAPTER 10 NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 BASIC STRUCTURE and FUNCTION Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
2/27/2019. Functions of the Nervous System. Nervous Tissue and Neuron Function. Fundamentals Of The Nervous System And Nervous Tissue
 Nervous Tissue and Neuron Function Fundamentals Of The Nervous System And Nervous Tissue Learn and Understand 1. Like muscle cells, neurons use membrane polarity upset (AP) as a signal therefore keeping
Nervous Tissue and Neuron Function Fundamentals Of The Nervous System And Nervous Tissue Learn and Understand 1. Like muscle cells, neurons use membrane polarity upset (AP) as a signal therefore keeping
Warm-Up. Label the parts of the neuron below.
 Warm-Up Label the parts of the neuron below. A B C D E F G Warm-Up 1. One neuron transmits a nerve impulse at 40 m/s. Another conducts at the rate of 1 m/s. Which neuron has a myelinated axon? 2. List
Warm-Up Label the parts of the neuron below. A B C D E F G Warm-Up 1. One neuron transmits a nerve impulse at 40 m/s. Another conducts at the rate of 1 m/s. Which neuron has a myelinated axon? 2. List
Chapter 4 Neuronal Physiology
 Chapter 4 Neuronal Physiology V edit. Pg. 99-131 VI edit. Pg. 85-113 VII edit. Pg. 87-113 Input Zone Dendrites and Cell body Nucleus Trigger Zone Axon hillock Conducting Zone Axon (may be from 1mm to more
Chapter 4 Neuronal Physiology V edit. Pg. 99-131 VI edit. Pg. 85-113 VII edit. Pg. 87-113 Input Zone Dendrites and Cell body Nucleus Trigger Zone Axon hillock Conducting Zone Axon (may be from 1mm to more
You can follow the path of the neural signal. The sensory neurons detect a stimulus in your finger and send that information to the CNS.
 1 Nervous system maintains coordination through the use of electrical and chemical processes. There are three aspects: sensory, motor, and integrative, which we will discuss throughout the system. The
1 Nervous system maintains coordination through the use of electrical and chemical processes. There are three aspects: sensory, motor, and integrative, which we will discuss throughout the system. The
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
BIOLOGY 2050 LECTURE NOTES ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I (A. IMHOLTZ) FUNDAMENTALS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM AND NERVOUS TISSUE P1 OF 5
 P1 OF 5 The nervous system controls/coordinates the activities of cells, tissues, & organs. The endocrine system also plays a role in control/coordination. The nervous system is more dominant. Its mechanisms
P1 OF 5 The nervous system controls/coordinates the activities of cells, tissues, & organs. The endocrine system also plays a role in control/coordination. The nervous system is more dominant. Its mechanisms
sensory input receptors integration Human Anatomy motor output Ch. 7 effectors Structural classification
 Human Anatomy Ch. 7 I. The Nervous System A. General characteristics 1. body s control & communication center a. 3 overlapping functions 1) sensory input: receptors monitor stimuli 2) integration: processes,
Human Anatomy Ch. 7 I. The Nervous System A. General characteristics 1. body s control & communication center a. 3 overlapping functions 1) sensory input: receptors monitor stimuli 2) integration: processes,
BI 232: Human Anatomy & Physiology
 BI 232: Human Anatomy & Physiology Roster Business Course Introduction and Syllabus Notecard Name E-mail Why you are taking the course Something interesting you did over break Lecture Tips Use the Study
BI 232: Human Anatomy & Physiology Roster Business Course Introduction and Syllabus Notecard Name E-mail Why you are taking the course Something interesting you did over break Lecture Tips Use the Study
Nervous System. 2. Receives information from the environment from CNS to organs and glands. 1. Relays messages, processes info, analyzes data
 Nervous System 1. Relays messages, processes info, analyzes data 2. Receives information from the environment from CNS to organs and glands 3. Transmits impulses from CNS to muscles and glands 4. Transmits
Nervous System 1. Relays messages, processes info, analyzes data 2. Receives information from the environment from CNS to organs and glands 3. Transmits impulses from CNS to muscles and glands 4. Transmits
Nervous Tissue and Neurophysiology
 Nervous Tissue and Neurophysiology Objectives Describe the two major divisions of the nervous system and their characteristics. Identify the structures/functions of a typical neuron. Describe the location
Nervous Tissue and Neurophysiology Objectives Describe the two major divisions of the nervous system and their characteristics. Identify the structures/functions of a typical neuron. Describe the location
Meyers' A&P February 15, Unit 7. The Nervous System. I. Functions of the Nervous System. Monitors body's internal and external enviornments
 Unit 7 The Nervous System I. Functions of the Nervous System Monitors body's internal and external enviornments Integrates sensory information Coordinates voluntary & involuntary responses of many other
Unit 7 The Nervous System I. Functions of the Nervous System Monitors body's internal and external enviornments Integrates sensory information Coordinates voluntary & involuntary responses of many other
The Nervous System PART A
 7 The Nervous System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Structural Classification
7 The Nervous System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Structural Classification
Nervous System. Electrical Signals.III Signal Transmission at Synapses Neurotransmitters.V Neural Circuits.VI
 Nervous System Overview.I Histology.II Electrical Signals.III Signal Transmission at Synapses Neurotransmitters.V Neural Circuits.VI Repairs.VII Pathology.VIII.IV 1 Controls and integrates all body activities
Nervous System Overview.I Histology.II Electrical Signals.III Signal Transmission at Synapses Neurotransmitters.V Neural Circuits.VI Repairs.VII Pathology.VIII.IV 1 Controls and integrates all body activities
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 11: Neural Tissue & The Nervous System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 11: Neural Tissue & The Nervous System Question No. 1 of 10 The human body contains different types of tissue. The tissue is formed into organs and organ systems.
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 11: Neural Tissue & The Nervous System Question No. 1 of 10 The human body contains different types of tissue. The tissue is formed into organs and organ systems.
Outline. Animals: Nervous system. Neuron and connection of neurons. Key Concepts:
 Animals: Nervous system Neuron and connection of neurons Outline 1. Key concepts 2. An Overview and Evolution 3. Human Nervous System 4. The Neurons 5. The Electrical Signals 6. Communication between Neurons
Animals: Nervous system Neuron and connection of neurons Outline 1. Key concepts 2. An Overview and Evolution 3. Human Nervous System 4. The Neurons 5. The Electrical Signals 6. Communication between Neurons
The Nervous System -The master controlling and communicating system of the body
 The Nervous System -The master controlling and communicating system of the body Functions: -Sensory input -Integration -Motor output Organization of the Nervous System Central nervous system (CNS) -Brain
The Nervous System -The master controlling and communicating system of the body Functions: -Sensory input -Integration -Motor output Organization of the Nervous System Central nervous system (CNS) -Brain
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 5 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology Introduction Neural Tissue TextBook Readings Pages 388 through 397. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand words! Work
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 5 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology Introduction Neural Tissue TextBook Readings Pages 388 through 397. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand words! Work
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling The Neuron is the functional unit of the nervous system. Neurons are composed of a cell body, which contains the nucleus and organelles; Dendrites which are extensions
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling The Neuron is the functional unit of the nervous system. Neurons are composed of a cell body, which contains the nucleus and organelles; Dendrites which are extensions
Nervous System. Chapter 9 Pages
 Nervous System Chapter 9 Pages 211-257 Chapter 9 Wordbytes 1. af- = toward 11. -ferrent = carried 2. arachn- = spider 12. gangli- = swelling 3. astro- = star 13. -glia = glue 4. auto- = self 14. mening-
Nervous System Chapter 9 Pages 211-257 Chapter 9 Wordbytes 1. af- = toward 11. -ferrent = carried 2. arachn- = spider 12. gangli- = swelling 3. astro- = star 13. -glia = glue 4. auto- = self 14. mening-
Nerve Cell Flashcards
 1. What does the word innervates mean? Refers to a nerve supplying a muscle or organ. For example, The phrenic nerve innervates the diaphragm muscle. 2. 3 parts of the Nervous System 1. Central Nervous
1. What does the word innervates mean? Refers to a nerve supplying a muscle or organ. For example, The phrenic nerve innervates the diaphragm muscle. 2. 3 parts of the Nervous System 1. Central Nervous
Chapter 12: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
 Chapter 12: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Overview of the NS PNS (Peripheral Nervous System) CNS (Central Nervous System) Neurons Neuroglia Synapse Some nomenclature Developed by
Chapter 12: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Overview of the NS PNS (Peripheral Nervous System) CNS (Central Nervous System) Neurons Neuroglia Synapse Some nomenclature Developed by
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 17 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of the Nervous System (p. 537) 1. The nervous system and the endocrine system are the body s major control and integrating centers.
Chapter 17 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of the Nervous System (p. 537) 1. The nervous system and the endocrine system are the body s major control and integrating centers.
The 7 th lecture. Anatomy and Physiology For the. 1 st Class. By Dr. Ala a Hassan Mirza
 The 7 th lecture In Anatomy and Physiology For the 1 st Class By Dr. Ala a Hassan Mirza Nervous System (part I) The Nerve Tissue and the Nervous System The Tissues of the Body There are 4 types of tissues
The 7 th lecture In Anatomy and Physiology For the 1 st Class By Dr. Ala a Hassan Mirza Nervous System (part I) The Nerve Tissue and the Nervous System The Tissues of the Body There are 4 types of tissues
Chapter 11. Lecture Outline. See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations.
 Chapter 11 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE BMP-218 November 4, 2014 DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary divisions: 1. CNS - Central Nervous System (Brain + Spinal Cord)
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE BMP-218 November 4, 2014 DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary divisions: 1. CNS - Central Nervous System (Brain + Spinal Cord)
Chapter 17 Nervous System
 Chapter 17 Nervous System 1 The Nervous System Two Anatomical Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Two Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses
Chapter 17 Nervous System 1 The Nervous System Two Anatomical Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Two Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses
Learning expectations for BIOL 131. Chapters 11, Nervous System Overview Read Chapter 11. You should be able to:
 NOTE The quiz will have question ONLY from the material we get through on Tuesday. The first midterm will cover all material from day one until the lecture before the second midterm. Learning expectations
NOTE The quiz will have question ONLY from the material we get through on Tuesday. The first midterm will cover all material from day one until the lecture before the second midterm. Learning expectations
Functions of the Nervous System. Fundamentals of the Nervous System & Nervous Tissue
 Fundamentals of the Nervous System & Nervous Tissue Overview Structure cell types & structures Neurophysiology membrane potential Synapse, neurotransmitters & receptors Functions of the Nervous System
Fundamentals of the Nervous System & Nervous Tissue Overview Structure cell types & structures Neurophysiology membrane potential Synapse, neurotransmitters & receptors Functions of the Nervous System
D) around, bypassing B) toward
 Nervous System Practice Questions 1. Which of the following are the parts of neurons? A) brain, spinal cord, and vertebral column B) dendrite, axon, and cell body C) sensory and motor D) cortex, medulla
Nervous System Practice Questions 1. Which of the following are the parts of neurons? A) brain, spinal cord, and vertebral column B) dendrite, axon, and cell body C) sensory and motor D) cortex, medulla
Chapter 7 Nerve Cells and Electrical Signaling
 Chapter 7 Nerve Cells and Electrical Signaling 7.1. Overview of the Nervous System (Figure 7.1) 7.2. Cells of the Nervous System o Neurons are excitable cells which can generate action potentials o 90%
Chapter 7 Nerve Cells and Electrical Signaling 7.1. Overview of the Nervous System (Figure 7.1) 7.2. Cells of the Nervous System o Neurons are excitable cells which can generate action potentials o 90%
! BIOL 2401! Week 5. Nervous System. Nervous System
 Collin County Community College! BIOL 2401! Week 5 Nervous System 1 Nervous System The process of homeostasis makes sure that the activities that occur in the body are maintained within normal physiological
Collin County Community College! BIOL 2401! Week 5 Nervous System 1 Nervous System The process of homeostasis makes sure that the activities that occur in the body are maintained within normal physiological
STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURE AND MAINTENANCE OF NEURONS (a) (b) Dendrites Cell body Initial segment collateral terminals (a) Diagrammatic representation of a neuron. The break in
STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURE AND MAINTENANCE OF NEURONS (a) (b) Dendrites Cell body Initial segment collateral terminals (a) Diagrammatic representation of a neuron. The break in
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A This is Your Brain on Music Assignment 1 With your
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A This is Your Brain on Music Assignment 1 With your
Functions of the Nervous System
 Chapter 11 Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue 11-1 Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input. Monitor internal and external stimuli 2. Integration. Brain and spinal cord process sensory input
Chapter 11 Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue 11-1 Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input. Monitor internal and external stimuli 2. Integration. Brain and spinal cord process sensory input
Introduction to Neurobiology
 Biology 240 General Zoology Introduction to Neurobiology Nervous System functions: communication of information via nerve signals integration and processing of information control of physiological and
Biology 240 General Zoology Introduction to Neurobiology Nervous System functions: communication of information via nerve signals integration and processing of information control of physiological and
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF NEURONS. AP Biology Chapter 48
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF NEURONS AP Biology Chapter 48 Objectives Describe the different types of neurons Describe the structure and function of dendrites, axons, a synapse, types of ion channels, and
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF NEURONS AP Biology Chapter 48 Objectives Describe the different types of neurons Describe the structure and function of dendrites, axons, a synapse, types of ion channels, and
1. Name the two major divisions of the nervous system and list the organs within each. Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System
 CHAPTER 10: NERVOUS SYSTEM I OBJECTIVES 1. Name the two major divisions of the nervous system and list the organs within each. Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Cranial
CHAPTER 10: NERVOUS SYSTEM I OBJECTIVES 1. Name the two major divisions of the nervous system and list the organs within each. Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Cranial
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. Neurons & Impulses
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Neurons & Impulses Organization of the Nervous System: Two Major Portions: The central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). CNS = Brain/Spinal Cord PNS = Nerves-provide
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Neurons & Impulses Organization of the Nervous System: Two Major Portions: The central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). CNS = Brain/Spinal Cord PNS = Nerves-provide
Neurons Chapter 7 2/19/2016. Learning Objectives. Cells of the Nervous System. Cells of the Nervous System. Cells of the Nervous System
 Learning Objectives Neurons Chapter 7 Identify and describe the functions of the two main divisions of the nervous system. Differentiate between a neuron and neuroglial cells in terms of structure and
Learning Objectives Neurons Chapter 7 Identify and describe the functions of the two main divisions of the nervous system. Differentiate between a neuron and neuroglial cells in terms of structure and
Chapter Six Review Sections 1 and 2
 NAME PER DATE Chapter Six Review Sections 1 and 2 Matching: 1. afferent nerves 2. autonomic nervous system 3. cell body 4. central nervous system (CNS) 5. dendrites 6. efferent nerves 7. myelin sheath
NAME PER DATE Chapter Six Review Sections 1 and 2 Matching: 1. afferent nerves 2. autonomic nervous system 3. cell body 4. central nervous system (CNS) 5. dendrites 6. efferent nerves 7. myelin sheath
ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS
 Lab 14 Introduction to Nervous System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. orbicularis oculi b. sternocleidomastoid c. deltoid d. pectoralis major e. biceps brachii f. rectus
Lab 14 Introduction to Nervous System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. orbicularis oculi b. sternocleidomastoid c. deltoid d. pectoralis major e. biceps brachii f. rectus
The Nervous System 12/11/2015
 The Nervous System Biology 12 Unit 3: Homeostasis December 11, 2015 The nervous system is an elaborate communication system that contains more than 100 billion nerve cells in the brain alone There are
The Nervous System Biology 12 Unit 3: Homeostasis December 11, 2015 The nervous system is an elaborate communication system that contains more than 100 billion nerve cells in the brain alone There are
Chapter 7. The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7. Objectives
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue. Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Overview of the Nervous System The nervous system, along with the endocrine system, helps to keep controlled conditions within limits
Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Overview of the Nervous System The nervous system, along with the endocrine system, helps to keep controlled conditions within limits
FLASH CARDS. Kalat s Book Chapter 2 Alphabetical
 FLASH CARDS www.biologicalpsych.com Kalat s Book Chapter 2 Alphabetical absolute refractory period absolute refractory period Time when neuron will not re-fire no matter how much stimulus it gets. action
FLASH CARDS www.biologicalpsych.com Kalat s Book Chapter 2 Alphabetical absolute refractory period absolute refractory period Time when neuron will not re-fire no matter how much stimulus it gets. action
THE HISTORY OF NEUROSCIENCE
 THE HISTORY OF NEUROSCIENCE BIOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF BEHAVIOR: THE NEURON & NEURAL COMMUNICATION NERVOUS SYSTEM Combined activity of the brain, spinal cord & other nerve fibers Acts as an information processing
THE HISTORY OF NEUROSCIENCE BIOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF BEHAVIOR: THE NEURON & NEURAL COMMUNICATION NERVOUS SYSTEM Combined activity of the brain, spinal cord & other nerve fibers Acts as an information processing
Chapter Nervous Systems
 The Nervous System Chapter Nervous Systems Which animals have nervous systems? (Which do not) What are the basic components of a NS? What kind of fish performs brain operations? What differentiates one
The Nervous System Chapter Nervous Systems Which animals have nervous systems? (Which do not) What are the basic components of a NS? What kind of fish performs brain operations? What differentiates one
Neurobiology. Cells of the nervous system
 Neurobiology Cells of the nervous system Anthony Heape 2010 1 The nervous system Central nervous system (CNS) Peripheral nervous system (PNS) 2 Enteric nervous system (digestive tract, gall bladder and
Neurobiology Cells of the nervous system Anthony Heape 2010 1 The nervous system Central nervous system (CNS) Peripheral nervous system (PNS) 2 Enteric nervous system (digestive tract, gall bladder and
Chapter 11: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
 Chapter 11: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Objectives: 1. List the basic functions of the nervous system. 2. Explain the structural and functional divisions of the nervous system.
Chapter 11: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Objectives: 1. List the basic functions of the nervous system. 2. Explain the structural and functional divisions of the nervous system.
Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue. Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Terms to Know CNS PNS Afferent division Efferent division Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system Sympathetic nervous system Parasympathetic
Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Terms to Know CNS PNS Afferent division Efferent division Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system Sympathetic nervous system Parasympathetic
Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Nervous system The nervous system is responsible for communication between different regions of the body, it is divided
 Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Nervous system The nervous system is responsible for communication between different regions of the body, it is divided into: CNS (central nervous system) = brain + spinal cord
Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Nervous system The nervous system is responsible for communication between different regions of the body, it is divided into: CNS (central nervous system) = brain + spinal cord
Nervous system Overview ( The master communication system)
 Nervous system Overview ( The master communication system) Neuron process Cell body nucleus Neuroglia Nerve Tissue COMPOSITION OF NERVE TISSUE Two principal types of cells, neurons and supporting cells
Nervous system Overview ( The master communication system) Neuron process Cell body nucleus Neuroglia Nerve Tissue COMPOSITION OF NERVE TISSUE Two principal types of cells, neurons and supporting cells
Introduction to Nervous Tissue
 Introduction to Nervous Tissue Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
Introduction to Nervous Tissue Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
What is Anatomy and Physiology?
 Introduction BI 212 BI 213 BI 211 Ecosystems Organs / organ systems Cells Organelles Communities Tissues Molecules Populations Organisms Campbell et al. Figure 1.4 Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology?
Introduction BI 212 BI 213 BI 211 Ecosystems Organs / organ systems Cells Organelles Communities Tissues Molecules Populations Organisms Campbell et al. Figure 1.4 Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology?
Neurons. Pyramidal neurons in mouse cerebral cortex expressing green fluorescent protein. The red staining indicates GABAergic interneurons.
 Neurons Pyramidal neurons in mouse cerebral cortex expressing green fluorescent protein. The red staining indicates GABAergic interneurons. MBL, Woods Hole R Cheung MSc Bioelectronics: PGEE11106 1 Neuron
Neurons Pyramidal neurons in mouse cerebral cortex expressing green fluorescent protein. The red staining indicates GABAergic interneurons. MBL, Woods Hole R Cheung MSc Bioelectronics: PGEE11106 1 Neuron
NEURAL TISSUE (NEUROPHYSIOLOGY) PART I (A): NEURONS & NEUROGLIA
 PART I (A): NEURONS & NEUROGLIA Neural Tissue Contains 2 kinds of cells: neurons: cells that send and receive signals neuroglia (glial cells): cells that support and protect neurons Neuron Types Sensory
PART I (A): NEURONS & NEUROGLIA Neural Tissue Contains 2 kinds of cells: neurons: cells that send and receive signals neuroglia (glial cells): cells that support and protect neurons Neuron Types Sensory
Nervous System Dr. Naim Kittana Department of Biomedical Sciences Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University
 Nervous System Department of Biomedical Sciences Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly adopted from the
Nervous System Department of Biomedical Sciences Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly adopted from the
Nervous Tissue and Histology of CNS
 Nervous Tissue and Histology of CNS Functions of Nervous System Like the CPU of a computer, the nervous system is the master controlling system of the body. It is designed to constantly and rapidly adjust
Nervous Tissue and Histology of CNS Functions of Nervous System Like the CPU of a computer, the nervous system is the master controlling system of the body. It is designed to constantly and rapidly adjust
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 12 Nervous Tissue Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the nervous system helps to keep controlled conditions within
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 12 Nervous Tissue Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the nervous system helps to keep controlled conditions within
LECTURE STRUCTURE ASC171 NERVOUS SYSTEM PART 1: BACKGROUND 26/07/2015. Module 5
 LECTURE STRUCTURE PART 1: Background / Introduction PART 2: Structure of the NS, how it operates PART 3: CNS PART 4: PNS Why did the action potential cross the synaptic junction? To get to the other side
LECTURE STRUCTURE PART 1: Background / Introduction PART 2: Structure of the NS, how it operates PART 3: CNS PART 4: PNS Why did the action potential cross the synaptic junction? To get to the other side
Neural Tissue. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris Pearson Education, Inc.
 12 Neural Tissue PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Nervous System Organs of the Nervous System Brain and spinal cord Sensory
12 Neural Tissue PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Nervous System Organs of the Nervous System Brain and spinal cord Sensory
Ameen Alsaras. Ameen Alsaras. Mohd.Khatatbeh
 9 Ameen Alsaras Ameen Alsaras Mohd.Khatatbeh Nerve Cells (Neurons) *Remember: The neural cell consists of: 1-Cell body 2-Dendrites 3-Axon which ends as axon terminals. The conduction of impulse through
9 Ameen Alsaras Ameen Alsaras Mohd.Khatatbeh Nerve Cells (Neurons) *Remember: The neural cell consists of: 1-Cell body 2-Dendrites 3-Axon which ends as axon terminals. The conduction of impulse through
6.5 Nerves, Hormones and Homeostasis
 6.5 Nerves, Hormones and Homeostasis IB Biology SL Part 1 - Nerves Outcomes Part 1 6.5.1State that the nervous system consists of the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nerves, and is composed
6.5 Nerves, Hormones and Homeostasis IB Biology SL Part 1 - Nerves Outcomes Part 1 6.5.1State that the nervous system consists of the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nerves, and is composed
Human Histology The Nervous System. Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed
 Human Histology The Nervous System Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed The organization of the nervous system Anatomically, the nervous system is divided into:- Neurohistology Structurally, nerve tissue consists of
Human Histology The Nervous System Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed The organization of the nervous system Anatomically, the nervous system is divided into:- Neurohistology Structurally, nerve tissue consists of
Man and his environment
 Man and his environment Dr. Elriah M. Makie 0122858517 Nervous Tissue BSc.M.Sc.MBBS Introduction The nervous system is divided into two main parts: The central nervous system (CNS) comprising the brain
Man and his environment Dr. Elriah M. Makie 0122858517 Nervous Tissue BSc.M.Sc.MBBS Introduction The nervous system is divided into two main parts: The central nervous system (CNS) comprising the brain
Nervous System. Control center & communication network of the body
 Nervous System Control center & communication network of the body Nervous System Doctor: Neurologist Fxn: Communication through an electrochemical impulse/nerve impulse that works fast to maintain short-term
Nervous System Control center & communication network of the body Nervous System Doctor: Neurologist Fxn: Communication through an electrochemical impulse/nerve impulse that works fast to maintain short-term
Nervous System. Nervous System. Organization of the Nervous System. Histology of Nerve Tissue. Motor Division: Two Main Parts
 Nervous System The master controlling and communicating system of the body Functions: Sensory input monitoring stimuli occurring inside and outs1ide the body Nervous System Integration interpretation of
Nervous System The master controlling and communicating system of the body Functions: Sensory input monitoring stimuli occurring inside and outs1ide the body Nervous System Integration interpretation of
