FLASH CARDS. Kalat s Book Chapter 4 Alphabetical
|
|
|
- Julie King
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FLASH CARDS Kalat s Book Chapter 4 Alphabetical
2 ablation
3 ablation Directly killing a single or few cells. Originally used to study what different parts of the brain do what (Flourens). Now used to fix heart arrhythmia, tremors or skin imperfections.
4 anterior commissure
5 anterior commissure One of several connections between brain hemispheres. Used for perception of smell and sharp pain. Connects the amygdalas.
6 basal ganglia
7 basal ganglia A series of nuclei that are part of the limbic system. Help control continuous movements by inhibition; use GABA as neurotransmitter.
8 Bell-Magendie law
9 Bell-Magendie law Anterior of spine holds motor neurons; posterior (dorsal) holds sensory neurons.
10 binding problem
11 binding problem How to get consciousness from neurons. Part of the mind-body problem.
12 brainstem
13 brainstem Where brain and spinal cord meet. Includes pons and medulla oblongata.
14 CAT scan
15 CAT scan Computerized axial tomography. Digital X- ray of brain, etc. Often used to find tumors.
16 central canal
17 central canal Fluid filled center of spinal cord.
18 CNS
19 CNS Central nervous system. Brain and spinal cord. Everything else is peripheral.
20 central sulcus
21 central sulcus Fissure that separates frontal lobe from parietal lobe.
22 cerebellum
23 cerebellum Little brain attached under cerebrum and behind the brain stem. Needed for motor skills, balance and coordination. More neurons than rest of brain combined but they are tiny; only 1/10th size of brain.
24 cerebral cortex
25 cerebral cortex Brain; composed of four lobes and two hemispheres. Six layers of neurons, folded and only about 3mm thick.
26 cerebrospinal fluid
27 cerebrospinal fluid Colorless fluid that cushions the brain & spinal cord to protect them from injury.
28 columns
29 columns Hypercolun or cortical module. A column of neurons; usually encode similar characteristics.
30 corpus callosum
31 corpus callosum Largest bungle of fibers connecting brain hemispheres. Looks like a wide, flat bridge.
32 cranial nerves
33 cranial nerves Come from brain, not spinal cord. Control face, tongue, eyes, etc.
34 delayed-response task
35 delayed-response task A delay between stimulus and response is imposed to study attention, memory and spatial reasoning.
36 dorsal
37 dorsal As in dorsal fin. For a human, toward the back.
38 dorsal root ganglia
39 dorsal root ganglia Sensory neurons taking information up the back of the spine to the brain.
40 EEG
41 EEG Electroencephalograph. Recording electrical signals on scalp. Used to measure brain waves, sleep patterns and diagnose epilepsy.
42 evoked potentials
43 evoked potentials Evoked responses. A recorded electrical potential after a stimulus is presented, often with a probe inside the brain. The stimulus evokes a response. Not the same as the spontaneous signals measured in an EEG.
44 fmri
45 fmri Functional magnetic resonance imaging. Measures blood flow in brain. Uses contrast that is dependent on the oxygen level in the blood. Compares oxygen-rich (arteries) and oxygen-poor (veins) regions.
46 forebrain
47 forebrain Develops into cerebrum, thalamus, hypothalamus and limbic system.
48 frontal lobe
49 frontal lobe Largest, most anterior, easiest to hurt lobe of the brain. Contains motor cortex, premotor cortex, orbitofrontal cortex, dorsolateral cortex and prefrontal cortex.
50 gray matter
51 gray matter Non-myelinated brain tissue. Capillaries & neurons look grey-brown.
52 hindbrain
53 hindbrain Includes medulla, cerebellum & pons.
54 hippocampus
55 hippocampus C-shaped, one in each hemisphere, lean toward each other. Pass through portions of temporal and frontal lobes. Needed to convert knowledge to long-term memory. Also involved in spatial reasoning and navigation.
56 hypothalamus
57 hypothalamus About the size of a pearl or almond. Secretes hormones that regulate other hormones. Triggers adrenal glands to release adrenaline and cortisol. Also controls hunger and thirst.
58 inferior colliculus
59 inferior colliculus Two structure but both carry both left and right ear signals. Integrates sound source information.
60 Klüver-Bucy syndrome
61 Klüver-Bucy syndrome Characterized by bilateral lesions of amygdala. Symptoms vary but can include less response to fear, flat affect, overeating, difficulty recognizing faces, hypersexuality and hyper-alertness.
62 laminae
63 laminae A thin plate or layer. Can describe outside surface of cell, bone plates of the spinal, walls of the thyroid gland, flat part of a leaf or part of a horse s hoof.
64 lesion
65 lesion Trauma, damage or tissue abnormality. Includes tumors, ulcers, dental caries and discolored patches of skin.
66 limbic system
67 limbic system Includes thalamus, hypothalamus, hippocampus, amygdala, septum and a complex interactive network of nuclei. Involved in emotional response, emotional memory, encoding patterns & cognitive maps.
68 medulla
69 medulla Medulla oblongata. Bottom part of brainstem, just above spinal cord. Controls automatic nervous system processes such as heart rate, breathing, vomiting and coughing.
70 MEG
71 MEG Magnetoencephalograph. Measures magnetic fields naturally produced by brain. Records changes in ion currents as neurons depolarize. Like fmri, MEG measures activity over time but much more precisely. Used to study multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer s & schizophrenia.
72 meninges
73 meninges Tri-layer protection for brain and spinal cord. Composed of dura mater (tough and thick), anachnoid (thin, transparent web) and pia (thin, waterproof layer that conforms to surface of brain).
74 midbrain
75 midbrain Top of the brain stem, just above pons. Nuclei include the superior colliculi (vision), inferior colliculi (audition), the red nuclei (motor coordination), and substantia nigra (motor planning).
76 MRI
77 MRI Magnetic resonance imaging. Water molecule has 10 protons. MRI uses a electromagnetic field from a radio frequency generator to spin and align these protons. When generator is turned off, protons spin back & machine measures change. Used to study brain, muscle & detect tumors.
78 neuroanatomy
79 neuroanatomy The study of neuron structure, organization and function.
80 nucleus basalis
81 nucleus basalis In contrast to occipital lobe (what you actually see), tells the brain what it should expect to see. Best guess of what s important. Degrades in Parkinson s & Alzheimer s diseases.
82 occipital lobe
83 occipital lobe Located at the back of the head. Primary vision cortex. Processing visual input then sends summaries to the parietal (where) and temporal (what) lobes for further analysis.
84 parietal lobe
85 parietal lobe Named for location under parietal bone at topback of head. Integrates sensory information into 3-D view of perceived world. Help locate where things are (where stream) and how they are spatially related (how stream).
86 PET scan
87 PET scan Positron-emission tomography. After an injected radioactive isotope (usually a version of glucose) spreads thru body, scans for pair of gamma photons that move in opposite directions. Used to create 3-D view of scanned area to detect tumors and track their growth.
88 phrenology
89 phrenology Franz Gall s theory that skull topology reveals underlying mental function, faculties & personality characteristics. Popular in the 1800 s.
90 pituitary gland
91 pituitary gland Small gland on bottom of the hypothalamus. Secretes peptide hormones. Anterior pituitary secretes HGH, TSH, ACTH, beta-endorphin, LH, & prolactin. Posterior pituitary secretes oxytocin & vasopressin.
92 PNS
93 PNS Parasympathetic nervous system. Part of autonomic nervous system. It s the rest-and-digest system.
94 pons
95 pons Just above the medulla on the brain stem. Composed of two stalks or peduncles, it connects brain to cerebellum. Help regulate bladder control, posture, breathing in and out, sleep paralysis and dreams.
96 postcentral gyrus
97 postcentral gyrus Front part of parietal lobe. Contains primary somatosensory cortex for sensing touch.
98 prefrontal cortex
99 prefrontal cortex Part of the frontal lobe of the brain. Composed of three regions: dorsolateral, orbitofrontal & ventral medial.
100 prefrontal lobotomy
101 prefrontal lobotomy Cutting the connections between either the two frontal lobes or between the prefrontal cortex of the frontal lobe and the rest of the brain. Developed in the 1930 s to treat depression, schizophrenia and epilepsy.
102 primates
103 primates Includes humans, apes, chimpanzees, gorillas, monkeys, lemurs, lorises, galagos (bushbabies), etc. Characteristics include domed cranium, forward-facing eyes, binocular vision & complex social relationships.
104 raphe system
105 raphe system Nuclei in brain stem that release serotonin.
106 reticular formation
107 reticular formation Coordinates 100+ neural circuits to regulate wake-sleep cycle.
108 somatic nervous system
109 somatic nervous system Part of peripheral nervous system. Controls voluntary movements and reflex arcs. Carries messages from skin and touch receptors to brain.
110 spinal cord
111 spinal cord A spinal column of 31 bony segments protects a long thin bundle of neurons that runs down the back. Damage can cause loss of sensation, movement or both.
112 stereotaxic instrument
113 stereotaxic instrument Uses 3-D coordinates to perform breast surgery, ablation and implantation.
114 substantia nigra
115 substantia nigra Parkinson s disease shows damage here. Involved in eye movement, learning, motor planning, addiction and rewards.
116 superior colliculus
117 superior colliculus Specialized nuclei for vision. Helps direct eye movements.
118 sympathetic nervous system
119 sympathetic nervous system The flight-flight aspect of the autonomic nervous system. Maintains homeostasis.
120 tectum
121 tectum Includes specialized nuclei, such as superior colliculi (vision) and inferior colliculi (audition).
122 tegmentum
123 tegmentum Floor of midbrain. Includes substania nigra and reticular formation.
124 temporal lobe
125 temporal lobe Lobe on side of brain. Involved in language, memory, vision and emotion. Identifies what we are looking at ( what stream ), supplies names for objectives and stores your dictionary-encyclopedia of knowledge.
126 thalamus
127 thalamus One in each hemisphere. Relays signals to and from cerebrum, including specialized centers for vision (LGN) and audition (MGN). Also important for sleep.
128 tract
129 tract Pathway. Can describe neural circuits or digestive functions.
130 transcranial magnetic stimulation
131 transcranial magnetic stimulation Used to treat depression. Magnetic fields stimulate neurons near scalp in hopes of improving mood.
132 ventral
133 ventral Toward stomach or anterior.
134 ventricle
135 ventricle Can describe heart chambers or regions in the brain that are filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
136 white matter
137 white matter Myelinated brain tissue. Axons are covered with a white fatty substance (myelin) to insulate signals.
138
biological psychology, p. 40 The study of the nervous system, especially the brain. neuroscience, p. 40
 biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
Chapter 3. Structure and Function of the Nervous System. Copyright (c) Allyn and Bacon 2004
 Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
The Nervous System. Biological School. Neuroanatomy. How does a Neuron fire? Acetylcholine (ACH) TYPES OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS
 Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Bio 105
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
3/15/17. Outline. Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Two Parts of the Nervous System
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
8.3 The Central Nervous System. SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau
 8.3 The Central Nervous System SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau The Central Nervous System the structural and functional centre for the entire nervous system the site of neural integration and processing The Central
8.3 The Central Nervous System SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau The Central Nervous System the structural and functional centre for the entire nervous system the site of neural integration and processing The Central
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16
 Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Chapter 6 Section 1. The Nervous System: The Basic Structure
 Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
Lesson 14. The Nervous System. Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1
 Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Somatic Nervous Systems. III. Autonomic Nervous System. Parasympathetic Nervous System. Sympathetic Nervous Systems
 7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
Nervous System and Brain Review. Bio 3201
 Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Biological Bases of Behavior. 3: Structure of the Nervous System
 Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
1. Processes nutrients and provides energy for the neuron to function; contains the cell's nucleus; also called the soma.
 1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
Organization of the nervous system. The withdrawal reflex. The central nervous system. Structure of a neuron. Overview
 Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind
 Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
Basic Brain Structure
 The Human Brain Basic Brain Structure Composed of 100 billion cells Makes up 2% of bodies weight Contains 15% of bodies blood supply Uses 20% of bodies oxygen and glucose Brain Protection Surrounded by
The Human Brain Basic Brain Structure Composed of 100 billion cells Makes up 2% of bodies weight Contains 15% of bodies blood supply Uses 20% of bodies oxygen and glucose Brain Protection Surrounded by
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour
 Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
14 - Central Nervous System. The Brain Taft College Human Physiology
 14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy. Components of a Nervous System
 Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures
 III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures 1. Accidents (case study) In 1848, a railroad worker named Phineas Gage was involved in an accident that damaged the front part of his brain. Gage s doctor
III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures 1. Accidents (case study) In 1848, a railroad worker named Phineas Gage was involved in an accident that damaged the front part of his brain. Gage s doctor
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. The Brain & Spinal Cord
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
Neural Communication. Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System. Communication in the Nervous System. 4 Common Components of a Neuron
 Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Chapter 6. Body and Behavior
 Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
Forebrain Brain Structures Limbic System. Brain Stem Midbrain Basil Ganglia. Cerebellum Reticular Formation Medulla oblongata
 Brain structures (1) Cut out the following cards (2) Identify the three major divisions of the brain (as defined by your book). Initially, try this without any form of aid such as your textbook. (3) Organize
Brain structures (1) Cut out the following cards (2) Identify the three major divisions of the brain (as defined by your book). Initially, try this without any form of aid such as your textbook. (3) Organize
b. The groove between the two crests is called 2. The neural folds move toward each other & the fuse to create a
 Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Page 1. Neurons Transmit Signal via Action Potentials: neuron At rest, neurons maintain an electrical difference across
 Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES
 BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES Cranial Meninges Cranial meninges are continuous with spinal meninges Dura mater: inner layer (meningeal layer) outer layer (endosteal layer) fused to periosteum
BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES Cranial Meninges Cranial meninges are continuous with spinal meninges Dura mater: inner layer (meningeal layer) outer layer (endosteal layer) fused to periosteum
The Nervous System. Divisions of the Nervous System. Branches of the Autonomic Nervous System. Central versus Peripheral
 The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
PSY 215 Lecture #5 (01/26/2011) (Anatomy of the Brain) Dr. Achtman PSY 215. Lecture 5 Anatomy of the Brain Chapter 4, pages 86-96
 Corrections: none needed PSY 215 Lecture 5 Anatomy of the Brain Chapter 4, pages 86-96 Announcements: Reminder: The first midterm is in one week! Everyone is encouraged to start studying (recommend 30/night
Corrections: none needed PSY 215 Lecture 5 Anatomy of the Brain Chapter 4, pages 86-96 Announcements: Reminder: The first midterm is in one week! Everyone is encouraged to start studying (recommend 30/night
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2
 Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Chapter 3. Biological Processes
 Biological Processes Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Biological Solutions Communicating internally Initiating and coordinating behavior Regulating growth and other internal functions
Biological Processes Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Biological Solutions Communicating internally Initiating and coordinating behavior Regulating growth and other internal functions
Sincerely, Ms. Paoloni and Mrs. Whitney
 Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
Chapter 17. Nervous System Nervous systems receive sensory input, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands. !
 Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Sheep Brain Dissection
 Sheep Brain Dissection Mammalian brains have many features in common. Human brains may not be available, so sheep brains often are dissected as an aid to understanding the mammalian brain since he general
Sheep Brain Dissection Mammalian brains have many features in common. Human brains may not be available, so sheep brains often are dissected as an aid to understanding the mammalian brain since he general
Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology
 Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology NATURE or NURTURE What are the effects of biochemistry on behavior? VOCABULARY Central Nervous System (CNS): The central nervous system is the part of the nervous
Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology NATURE or NURTURE What are the effects of biochemistry on behavior? VOCABULARY Central Nervous System (CNS): The central nervous system is the part of the nervous
Nervous and Endocrine System Exam Review
 Directions: Read each question and complete the statement using the multiple choice responses I. Nervous System 1. The interpretation of olfactory receptor information would fall under which general function
Directions: Read each question and complete the statement using the multiple choice responses I. Nervous System 1. The interpretation of olfactory receptor information would fall under which general function
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374
 Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Acetylcholine (ACh) Action potential. Agonists. Drugs that enhance the actions of neurotransmitters.
 Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE BRAIN The central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, receives input from sensory neurons and directs
STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE BRAIN The central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, receives input from sensory neurons and directs
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II
 Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1
 Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter in Review 1. The human nervous system is a complex biological system designed for nearly instantaneous communication among billions of neurons throughout the body.
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter in Review 1. The human nervous system is a complex biological system designed for nearly instantaneous communication among billions of neurons throughout the body.
3/20/13. :: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 39 :: How Is the Nervous System Organized? Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System and Endocrine System
 :: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 39 :: How Is the Nervous System Organized? Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System and Endocrine System The nervous system is organized into several major branches, each
:: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 39 :: How Is the Nervous System Organized? Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System and Endocrine System The nervous system is organized into several major branches, each
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1
 Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer:
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer:
Modules 4 & 6. The Biology of Mind
 Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
PSY 302: CHAPTER 3 NOTES THE BRAIN (PART II) - 9/5/17. By: Joseline
 PSY 302: CHAPTER 3 NOTES THE BRAIN (PART II) - 9/5/17 By: Joseline Left 3 MAJOR FISSURES : 2HEMISPHERES Right Lateral Ventricle Central Fissure Third Ventricle Sulcus Lateral Fissure Gyros Fissure- Fissures
PSY 302: CHAPTER 3 NOTES THE BRAIN (PART II) - 9/5/17 By: Joseline Left 3 MAJOR FISSURES : 2HEMISPHERES Right Lateral Ventricle Central Fissure Third Ventricle Sulcus Lateral Fissure Gyros Fissure- Fissures
Gross Organization I The Brain. Reading: BCP Chapter 7
 Gross Organization I The Brain Reading: BCP Chapter 7 Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Located inside of bone Includes the brain (in the skull) and the spinal cord (in the backbone)
Gross Organization I The Brain Reading: BCP Chapter 7 Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Located inside of bone Includes the brain (in the skull) and the spinal cord (in the backbone)
TABLE OF CONTINENTS. PSYC1002 Notes. Neuroscience.2. Cognitive Processes Learning and Motivation. 37. Perception Mental Abilities..
 TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
The Human Brain. I Think Therefore I am
 The Human Brain I Think Therefore I am The Beginning The simplest creatures have very simple nervous systems made up of nothing but a bunch of nerve cells They have neural nets, individual neurons linked
The Human Brain I Think Therefore I am The Beginning The simplest creatures have very simple nervous systems made up of nothing but a bunch of nerve cells They have neural nets, individual neurons linked
Neurology study of the nervous system. nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis
 Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
fmri (functional MRI)
 Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Parts of the Brain. Hindbrain. Controls autonomic functions Breathing, Heartbeat, Blood pressure, Swallowing, Vomiting, etc. Upper part of hindbrain
 Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
Psychology study guide chapter 2
 Psychology study guide chapter 2 Phrenology Developed by Franz Gall in the early 1800 s Study of bumps on the skull and the relationship to mental abilities and character traits Yielded one big idea: different
Psychology study guide chapter 2 Phrenology Developed by Franz Gall in the early 1800 s Study of bumps on the skull and the relationship to mental abilities and character traits Yielded one big idea: different
10/15/2010. Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: Biology and Behavior. The Nervous System
 Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: 2-1 Biology and Behavior To survive, human beings must be able to perform three interrelated activities: sensing events, or stimuli; processing stimuli; and
Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: 2-1 Biology and Behavior To survive, human beings must be able to perform three interrelated activities: sensing events, or stimuli; processing stimuli; and
Myers Psychology for AP*
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM?
 The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System
 The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
Nervous Systems. Brain Development
 Nervous Systems Brain Development 2007-2008 Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal cord Sensory pathways Motor pathways Sympathetic arousal & energy production fight
Nervous Systems Brain Development 2007-2008 Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal cord Sensory pathways Motor pathways Sympathetic arousal & energy production fight
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2
 Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
Organization of the nervous system. [See Fig. 48.1]
![Organization of the nervous system. [See Fig. 48.1] Organization of the nervous system. [See Fig. 48.1]](/thumbs/90/103926552.jpg) Nervous System [Note: This is the text version of this lecture file. To make the lecture notes downloadable over a slow connection (e.g. modem) the figures have been replaced with figure numbers as found
Nervous System [Note: This is the text version of this lecture file. To make the lecture notes downloadable over a slow connection (e.g. modem) the figures have been replaced with figure numbers as found
Ways we Study the Brain. Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI
 The Brain Ways we Study the Brain Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI Accidents Phineas Gage Story Personality changed after the accident. What this this tell us? That different part
The Brain Ways we Study the Brain Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI Accidents Phineas Gage Story Personality changed after the accident. What this this tell us? That different part
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES
 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
The Central Nervous System I. Chapter 12
 The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System
 Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Human Nervous System
 Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System. Anatomy of the CNS
 CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System Anatomy of the CNS in human consists of brain and spinal cord as stated earlier neurons have little support from their extracellular matrix and depend on glial
CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System Anatomy of the CNS in human consists of brain and spinal cord as stated earlier neurons have little support from their extracellular matrix and depend on glial
Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord. Major Divisions of the nervous system:
 Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord Major Divisions of the nervous system: Afferent (sensory input) -> cell bodies outside of the central nervous system (CNS), carry info into the CNS
Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord Major Divisions of the nervous system: Afferent (sensory input) -> cell bodies outside of the central nervous system (CNS), carry info into the CNS
CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts
 CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts The Brain: A Quick Tour Frontal Lobe Control of skeletal muscles Personality Concentration
CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts The Brain: A Quick Tour Frontal Lobe Control of skeletal muscles Personality Concentration
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7)
 Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
Unit Three. The brain includes: cerebrum, diencephalon, brain stem, & cerebellum. The brain lies within the cranial cavity of the skull.
 Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
The Nervous System PART B
 7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
Course Booklet. We have felt the pain that Neuroscience is giving you.
 Exams Stressing You Out? Take Action! Course Booklet NEUR 1202 Carleton University* *TranscendFinals is not affiliated with the university We have felt the pain that Neuroscience is giving you. Our mission
Exams Stressing You Out? Take Action! Course Booklet NEUR 1202 Carleton University* *TranscendFinals is not affiliated with the university We have felt the pain that Neuroscience is giving you. Our mission
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the brain is organized, protected, and supplied
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the brain is organized, protected, and supplied
Functional Organization of the Central Nervous System
 Functional Organization of the Central Nervous System Hierarchical orgnization CNS consists of the brain and the spinal cord The brain analyzes and interprets the information Response messages are
Functional Organization of the Central Nervous System Hierarchical orgnization CNS consists of the brain and the spinal cord The brain analyzes and interprets the information Response messages are
To understand AD, it is important to
 To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized?
 Honors Biology Guided Notes Chapter 28 Nervous System Name 28.10 28.19 The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized? ANIMAL NERVOUS SYSTEMS Define Cephalization and Centralization. What type of
Honors Biology Guided Notes Chapter 28 Nervous System Name 28.10 28.19 The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized? ANIMAL NERVOUS SYSTEMS Define Cephalization and Centralization. What type of
Biology. Slide 1 of 37. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 37 35-3 Divisions of the Nervous 2 of 37 The Nervous The human nervous system has two major divisions: central nervous system peripheral nervous system 3 of 37 The Central Nervous The Central
Biology 1 of 37 35-3 Divisions of the Nervous 2 of 37 The Nervous The human nervous system has two major divisions: central nervous system peripheral nervous system 3 of 37 The Central Nervous The Central
Visualizing Psychology
 Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
Nervous System. 1. What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? 3. What kind of neuroglia myelinates axons in the PNS?
 . What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? Nervous System SRS Review %. Central nervous system %. Peripheral nervous system %. Afferent division %. Somatic division %. Autonomic division %. Sympathetic
. What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? Nervous System SRS Review %. Central nervous system %. Peripheral nervous system %. Afferent division %. Somatic division %. Autonomic division %. Sympathetic
Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves. Origin of the Brain
 Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves BIO 218 Fall 2015 Origin of the Brain The brain originates from a structure called the neural tube, which arises during a developmental stage called neurulation.
Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves BIO 218 Fall 2015 Origin of the Brain The brain originates from a structure called the neural tube, which arises during a developmental stage called neurulation.
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONCEPT 2: THE VERTEBRATE BRAIN IS REGIONALLY SPECIALIZED
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONCEPT 2: THE VERTEBRATE BRAIN IS REGIONALLY SPECIALIZED Images of the human brain in popular culture almost always focus on the cerebrum, the part of the brain whose surface lies just
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONCEPT 2: THE VERTEBRATE BRAIN IS REGIONALLY SPECIALIZED Images of the human brain in popular culture almost always focus on the cerebrum, the part of the brain whose surface lies just
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS
 CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
Nervous system, integration: Overview, and peripheral nervous system:
 Nervous system, integration: Overview, and peripheral nervous system: Some review & misc. parts [Fig. 28.11B, p. 573]: - white matter --> looks white due to the myelinated sheaths, which are quite fatty.
Nervous system, integration: Overview, and peripheral nervous system: Some review & misc. parts [Fig. 28.11B, p. 573]: - white matter --> looks white due to the myelinated sheaths, which are quite fatty.
The Nervous System. Lab Exercise 29. Objectives. Introduction
 Lab Exercise The Nervous System Objectives -You should be able to recognize a neuron and identify its components. - Be able to identify the principal components of the brain and be able to name at least
Lab Exercise The Nervous System Objectives -You should be able to recognize a neuron and identify its components. - Be able to identify the principal components of the brain and be able to name at least
Overview of Brain Structures
 First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
Chapter 9. Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater arachnoid mater pia mater membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system
 membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater middle layer of the meninges, contains no blood vessels arachnoid mater Innermost
membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater middle layer of the meninges, contains no blood vessels arachnoid mater Innermost
Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture. caudal = toward the spinal cord)
 Insight: Some cranial nerve disorders Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture I. Overview (Directional terms: rostral = toward the forehead caudal = toward the spinal cord) A. 3 Major parts
Insight: Some cranial nerve disorders Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture I. Overview (Directional terms: rostral = toward the forehead caudal = toward the spinal cord) A. 3 Major parts
Brain Architecture and Function Parts Size and Cognition
 Brain Architecture and Function Parts Size and Cognition Q: In what way has paedomorphosis been important in human evolution? Brain Architecture F F F F H H 3 Q. How d we get to this point? Evolutionary
Brain Architecture and Function Parts Size and Cognition Q: In what way has paedomorphosis been important in human evolution? Brain Architecture F F F F H H 3 Q. How d we get to this point? Evolutionary
II. Nervous System (NS) Organization: can be organized by location/ structure or by function A. Structural Organization 1. Central N.S.
 Nervous System I. Nervous system Functions A. Detect Changes in the environment (stimuli) B. Interpret/evaluate those stimuli C. Initiate responses (trigger muscle contractions or glandular response) II.
Nervous System I. Nervous system Functions A. Detect Changes in the environment (stimuli) B. Interpret/evaluate those stimuli C. Initiate responses (trigger muscle contractions or glandular response) II.
Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet
 1. What are the two parts of the CNS? 2. What are the four functions of the CNS Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet 3. What are the four functions of the meninges? (p430) 4. Starting
1. What are the two parts of the CNS? 2. What are the four functions of the CNS Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet 3. What are the four functions of the meninges? (p430) 4. Starting
Primary Functions. Monitor changes. Integrate input. Initiate a response. External / internal. Process, interpret, make decisions, store information
 NERVOUS SYSTEM Monitor changes External / internal Integrate input Primary Functions Process, interpret, make decisions, store information Initiate a response E.g., movement, hormone release, stimulate/inhibit
NERVOUS SYSTEM Monitor changes External / internal Integrate input Primary Functions Process, interpret, make decisions, store information Initiate a response E.g., movement, hormone release, stimulate/inhibit
Nervous System. Oct 15 10:00 AM
 Nervous System Oct 15 10:00 AM 1 Nerve net = series of interconnected nerve cells Nerve = axons of many nerve cells Oct 15 10:10 AM 2 bilateral organisms exhibit cephalization (evolutionary trend towards
Nervous System Oct 15 10:00 AM 1 Nerve net = series of interconnected nerve cells Nerve = axons of many nerve cells Oct 15 10:10 AM 2 bilateral organisms exhibit cephalization (evolutionary trend towards
Composed of gray matter and arranged in raised ridges (gyri), grooves (sulci), depressions (fissures).
 PSYC1020 Neuro and Pysc Notes Structure Description Major Functions Brainstem Stemlike portion of the brain, continuous with diencephalon above and spinal cord below. Composed of midbrain, pons, medulla
PSYC1020 Neuro and Pysc Notes Structure Description Major Functions Brainstem Stemlike portion of the brain, continuous with diencephalon above and spinal cord below. Composed of midbrain, pons, medulla
Central vs. Peripheral Nervous System
 Nervous System 2 C 1 2 : A N A L Y Z E T H E F U N C T I O N A L I N T E R R E L A T I O N S H I P S O F T H E D I V I S I O N S O F T H E N E R V O U S S Y S T E M Central vs. Peripheral Nervous System
Nervous System 2 C 1 2 : A N A L Y Z E T H E F U N C T I O N A L I N T E R R E L A T I O N S H I P S O F T H E D I V I S I O N S O F T H E N E R V O U S S Y S T E M Central vs. Peripheral Nervous System
Nervous Systems. Chapter 49. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 49 Nervous Systems PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Concept
Chapter 49 Nervous Systems PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Concept
IV. The Divisions of the Brain. Slide # 1
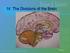 IV. The Divisions of the Brain Slide # 1 The Hindbrain Hindbrain, located at the rear base of the skull, controlling automatic functions Contains: Cerebellum (balance & coordination) Medulla (heartbeat,
IV. The Divisions of the Brain Slide # 1 The Hindbrain Hindbrain, located at the rear base of the skull, controlling automatic functions Contains: Cerebellum (balance & coordination) Medulla (heartbeat,
LESSON 1.2 WORKBOOK How does brain structure impact its function?
 DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Central nervous system (CNS) contains the brain and spinal cord. Peripheral nervous system (PNS) includes all the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. For a complete list of defined
DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Central nervous system (CNS) contains the brain and spinal cord. Peripheral nervous system (PNS) includes all the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. For a complete list of defined
2/22/2012. Cerebrum CNS
 Chapter 8 outline CNS: Consists of???? Structural organization of the brain Cerebrum Diencephalon Midbrain and hindbrain Spinal cord tracts Cranial and spinal nerves Receives input from???? neurons Directs
Chapter 8 outline CNS: Consists of???? Structural organization of the brain Cerebrum Diencephalon Midbrain and hindbrain Spinal cord tracts Cranial and spinal nerves Receives input from???? neurons Directs
