Dania Ahmad. Tamer Barakat + Dania Ahmad. Faisal I. Mohammed
|
|
|
- Hillary Williams
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 16 Dania Ahmad Tamer Barakat + Dania Ahmad Faisal I. Mohammed
2 Revision: What are the basic types of neurons? sensory (afferent), motor (efferent) and interneuron (equaled association neurons). We classified the neurotransmitters to two types; can you figure them out? What about their subtypes? 1)small molecules, (rapid reacting neurotransmitters) and it has many classes (subtypes): a) acetylcholine b) amines, which amino acid are they derived from? * c)amino acids: Glycine, aspartate, glutamine, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) which is an inhibitory neurotransmitter. d)gases: such as nitric oxide and carbon monoxide. What do you think is special about gases? # Notice that their vesicles are recycled because some of them are reuptaken (both the vesicles and NT are reabsorbed) plus that the enzymatic machinery for the formation of the small molecules neurotransmitters are found in the presynaptic terminals. 2)polypeptides (neuropeptides or neuromodulators because they modulate the act of peptides) and their characteristics are: 1-they are slowly reacting 2-each neuron has more than one type of them 3- they have a prolonged time of action 4- they are excreted in small quantities 5-they are not recycled 6- they are cosecreted with small molecules neurotransmitters 7- they are synthesized in the soma *note: any peptide in the nervous system can act as a neuromodulator. neuropeptides are synthesized in the soma and are secreted from the presynaptic terminals, how? They are transported by axonal transport which is very slow (2 millimeters per day). Also, their formation needs a lot of energy that's why they are secreted in smaller quantities compared to small molecule neurotransmitters. That s why vesicles of NP are not recycled, We don t have their enzymes in the terminals 1 P a g e *Tyrosine # lipid soluble and fast diffusion
3 HOW NEUROTRANSMITTERS ARE SECRETED? By The process of NEUROTRANSMISSION: 1- When the action potential reaches the presynaptic terminals it causes voltage gated calcium channels to open, Ca 2+ will move into the terminals according to the electrochemical gradient by diffusion. 2-The increase in the intracellular calcium causes movement of the vesicles (containing neurotransmitters) toward the membrane and fuse with it, after that, the vesicles release their content of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. 3-Neurotransmitters move to the postsynaptic membrane where they bind to their receptors. Binding of the neurotransmitters to the receptors changes the permeability of certain channels, accordingly, if the binding causes Na + channels to open, there will be a depolarization on the postsynaptic membrane, this state is called excitation (less negative=> closer to threshold). Since it occurs in the postsynaptic membrane we call it excitatory post synaptic potential (because it is on the postsynaptic membrane). Similarly, if the receptors are bound to K + channels or Cl - channels, what do you think will happen? K + => efflux => hyperpolarization => IPSP Cl - => influx => inhibition Why not hyperpolarization? Because the membrane potential is similar to Cl equilibrium potential, However, if we have Na + influx, Cl will inhibit any change in the potential. Finally, the NT will be inactivated by: 1)diffusion: the neurotransmitter might diffuse into the interstitial fluid (moving down their concentration gradient). 2)Enzymatic degradation: every neurotransmitter has enzymes that break it down, these enzymes are found on the postsynaptic membrane [they are peripheral membrane proteins], for example: the acetylcholine => acetylcholinesterase. Epinephrine and norepinephrine: catechol-o-methyl transferase(comt) and monoamine oxidase (MAO). 2 P a g e
4 3)Reuptake: by neurons terminals (to be reused in the vesicles) or glia cells (cells around the neurons). Examples: 1-after acetylcholine is broken down by acetylcholinesterase into choline and acetyl CoA, choline is reuptaken and then reused. 2-peptides are broken by peptidases Now you should be able to answer this, what would you do to prolong the effect of a neurotransmitter? You simply inhibit its enzyme by a drug (this is one of many ways). For example: 1-Prozac (a drug used for psychiatric patients) is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor. 2- Or you might use a drug that breaks down the neurotransmitter to stop the cycle, stopping the cycle is very important such as in Epilepsy Epilepsy =الصرع Note: in Epilepsy (which causes contraction of the muscles due to stimulations from the brain) if the cyclic AMP remain in the brain the muscles will stay contracted and that causes death. So, we must break down the cycle, HOW? acetylcholine is broken down by cholinesterase and the cycle is finished. (the doctor didn t mention them in section 1, so it's an additional information). you didn t understand anything? watch this=> 0:00-21:00 was a revision!! Basic Concepts of Neurotransmitters and Receptors Neuroreceptor: Proteins on the cell membrane or in the cytoplasm that could bind with specific neurotransmitters and alter the behavior of neurons of effector cells. Neurotransmitters: Endogenous signaling molecules that alter the behavior of neurons or effector cells. Endogenous: exist inside the body naturally. NOTE: there are no receptors for a substance that does not exist naturally inside the body, however, a substance from outside the body (not endogenous) can bind to the receptor only if this substance is similar to another endogenous substance in morphology (shape). 3 P a g e
5 Where does the receptor exist? It depends on the type of the neurotransmitter water soluble NT=> won't enter the cell => receptors are on the membrane. lipid soluble NT => enter the cell => receptors are inside the cell (in the cytoplasm or on the nucleus). Don t forget that receptors are specific Is acetyl choline neurotransmitter excitatory or inhibitory? The receptor determines whether the neurotransmitter is excitatory in that area or inhibitory NOT the neurotransmitter itself, for example: Acetylcholine receptors of the parasympathetic system in the heart is inhibitory because it lowers the heart rate [bradycardia]. In the gastrointestinal system (GI), it increases the GI movement (stomach, intestine) and it increases the secretion, so it is excitatory in the GI. Although it is the same neurotransmitter but its receptors in the heart are different to its receptors in the GI. Neurotransmitter (a classical definition): 1-The neurotransmitter should be synthesized in the presynaptic terminals and after that it must enter the vesicles (it is important to protect it) 2-Neurotransmitters have the same effect whether they are synthesized internally or administrated externally and that is important in drugs, for example: a- if someone suffers from colic (which result from increase movement in the GI) we give him a drug (Buscopan) which blocks acetylcholine receptors in the GI. b-if we want to increase the movement in the GI we give the patient a drug that contains acetylcholine. 3-neurotransmitters must be blocked by same drugs that block synaptic transmission. 4-they must be removed in specific ways (we mentioned them earlier) 5-they must be found in the presynaptic terminals. مغصe Colic= P a g 4
6 Agonist and Antagonist: Agonist: a substance that mimics a specific neurotransmitter, and it can attach to that to that neurotransmitter's receptor, and thereby produces the same action that the neurotransmitter usually produces. NOTE: drugs are often designed as receptor agonists to treat a variety of diseases and disorders when the original chemical substance is missing or depleted. Example: when we give a patient a drug to increase the GI movement, its action is similar to acetylcholine, so we call it parasympathomimetic or parasympathetic agonist [it has the same action as acetylcholine or the parasympathetic system] Antagonist: drugs that bind to but do not activate neuroreceptors, thereby blocking the actions of neurotransmitters or the neuroreceptor agonists. Example: when someone is suffering from hypertension (high blood pressure), we give him alpha antagonist [because alpha receptors causes vasoconstriction] so we block the action of alpha neurotransmitters. Note: the same neurotransmitter can bind to more than one receptor [In other words, a NT have more than one binding site for different receptors]. Accordingly, we might invent blockers (antagonists) for one of the receptors that bind to a specific binding site. In this case, we say that we have selectively inhibited that receptor. 5 P a g e
7 Example: beta receptors (ADRENOGENIC sympathetic system receptors): Beta-1 receptors are found in the heart, beta-2 are found in the lungs, we sometimes may need drugs that work on the lungs and not on the heart, so we have beta-2 agonist [ it is selective], however, we might use an antagonist that works on all beta receptor [in this case it is not selective]. This slide shows: 1- Nt that bind to both receptors A and B 2- We can synthesize a blocker for receptor A only or receptor B only, So we can control the effect on specific organs. Five Key Steps in Neurotransmission (what should NT have): 1-Synthesis: neurotransmitters are synthesized in cell body or terminals. 2-Storage: neurotransmitters are packaged into vesicles. 3-Release: neurotransmitters are released when the vesicles fuse. 4-Receptor binding: neurotransmitters bind to and activate post-synaptic receptors. 5-Inactivation: neurotransmitters diffuse away, are metabolized or transported back into terminals. Synaptic vesicles: *Vesicles of the small molecules neurotransmitters [small, clear-core] are different from the vesicles of neuropeptides neurotransmitters [large, dense-core]. *the importance of vesicles: they concentrate and protect neurotransmitters. *vesicles can be docked at active zone. 6 P a g e
8 Neurotransmitters Co-existence (Dale principle): Neurons in both the parasympathetic and sympathetic produce 1 classical neurotransmitter (ACh or a catecholamine) and 1 or more polypeptide neurotransmitters. *they are contained in different synaptic vesicles that can be distinguished using electron microscope (as previously shown). The neuron can thus release either the classical neurotransmitter or both the polypeptide and small molecule neurotransmitter under different conditions. For the thousands time any neuron contains only one type of classical neurotransmitters. BUT it might have one or more neuropeptide Neuropeptides are not secreted alone, they are co-secreted with the classical neurotransmitter. Hmmm, when do you think neuropeptides are secreted? It depends on the frequency of the stimulus and on the type of the stimulus, if the rate (frequency) of the stimulation is low (for example: if every 10 millisecond we have an action potential, the rate per second will equal 100 [1000/10]), then the neurotransmitter, which is secreted, is only the classical neurotransmitters BUT if the rate was 500, classical plus polypeptide neurotransmitters are secreted. Synapses are either excitatory or inhibitory that is determined by the receptors of the neurotransmitters (the type of channels) and there are two kinds of receptors: 1-Ionotropic receptors: receptors are connected directly to ion channels. They are fast. 7 P a g e
9 2-Metabotrobic receptors: receptors that are not coupled to ion channels directly, or are not coupled to ion channels at all, instead they work through G-protein system, they are slow. Receptor activation: Ionotropic: directly and it is fast, when a neurotransmitter binds to the receptor, the channels inverses its conformation (if it was open, it becomes closed and vice versa). So, the binding of the NT changes the permeability of the channel. Before binding (closed) After binding (opened) Metabotropic receptors: it uses G-protein system, G-protein uses a second messenger and it might be (c-amp, c-gmp, calcium, calmodulin, phospholipids.). What is the first messenger? It s the Neurotransmitter. Remember that: adenylyl cyclase converts ATP into c-amp/ Guanylate cyclase convert GTP into c-gmp. G-protein is a membrane protein and it consists or 3 subunits: alpha, beta, gamma. When there is no stimulation the three subunits are found together. However, when a neurotransmitter binds to a metabotropic receptor alpha subunit dissociates. Effects of metabotropic (mentioned in the slides) 1-control channel. 2-alter properties of receptors. 3-regulation of gene expression 8 P a g e
10 G-protein: direct control Binding of the neurotransmitter to the receptor activated the G-protein, that causes the channel to open [direct control] (relatively fast) G-protein: protein phosphorylation 1-Binding of the neurotransmitter to the receptor, causes dissociation of alpha subunit. 2- Alpha subunit activated enzyme adenylyl cyclase, the enzyme converted ATP to C-AMP 3- c-amp stimulates the protein kinase (c-amp dependent protein kinase) which is also called Protein kinase (A) which is a specific protein. When the protein kinase gets activated, it opens the channel. (slower than g-protein direct control) (the slide shows only alpha subunit) 9 P a g e
Omar Ismail. Dana Almanzalji. Faisal Mohammad
 11 Omar Ismail Dana Almanzalji Faisal Mohammad Neuronal classification: Neurons are responsible for transmitting the action potential to the brain. The speed at which the action potential is transmitted
11 Omar Ismail Dana Almanzalji Faisal Mohammad Neuronal classification: Neurons are responsible for transmitting the action potential to the brain. The speed at which the action potential is transmitted
Mohammad Tarek. Wahab Al-tekreeti Tamer Barakat. Faisal Mohammad
 15 Mohammad Tarek Wahab Al-tekreeti Tamer Barakat Faisal Mohammad Things to remember Types of synapse: Neuron types and neurotransmitters When it happens between an axon and dendrites it is called axodendritic
15 Mohammad Tarek Wahab Al-tekreeti Tamer Barakat Faisal Mohammad Things to remember Types of synapse: Neuron types and neurotransmitters When it happens between an axon and dendrites it is called axodendritic
Lojayn Salah. Razan Aburumman. Faisal Muhammad
 20 Lojayn Salah Razan Aburumman Faisal Muhammad Note: I tried to include everything that's important from the doctor's slides but you can refer back to them after studying this sheet.. After you read this
20 Lojayn Salah Razan Aburumman Faisal Muhammad Note: I tried to include everything that's important from the doctor's slides but you can refer back to them after studying this sheet.. After you read this
Neuron types and Neurotransmitters
 Neuron types and Neurotransmitters Faisal I. Mohammed. PhD, MD University of Jordan 1 Transmission of Receptor Information to the Brain the larger the nerve fiber diameter the faster the rate of transmission
Neuron types and Neurotransmitters Faisal I. Mohammed. PhD, MD University of Jordan 1 Transmission of Receptor Information to the Brain the larger the nerve fiber diameter the faster the rate of transmission
Section: Chapter 5: Multiple Choice. 1. The structure of synapses is best viewed with a(n):
 Section: Chapter 5: Multiple Choice 1. The structure of synapses is best viewed with a(n): p.155 electron microscope. light microscope. confocal microscope. nissle-stained microscopic procedure. 2. Electron
Section: Chapter 5: Multiple Choice 1. The structure of synapses is best viewed with a(n): p.155 electron microscope. light microscope. confocal microscope. nissle-stained microscopic procedure. 2. Electron
Synaptic transmission
 Outline Synaptic transmission Sompol Tapechum M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand. sisth@mahidol.ac.th 2 Structure of synapse Modes of synaptic
Outline Synaptic transmission Sompol Tapechum M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand. sisth@mahidol.ac.th 2 Structure of synapse Modes of synaptic
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part C
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part C Warm Up What is a neurotransmitter? What is the
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part C Warm Up What is a neurotransmitter? What is the
What are the 6 types of neuroglia and their functions?!
 Warm Up! Take out your 11C Notes What are the 6 types of neuroglia and their functions?! Astrocytes Microglia Ependymal Cells Satellite Cells Schwann Cells Oligodendrocytes Support, brace, & nutrient transfer
Warm Up! Take out your 11C Notes What are the 6 types of neuroglia and their functions?! Astrocytes Microglia Ependymal Cells Satellite Cells Schwann Cells Oligodendrocytes Support, brace, & nutrient transfer
Autonomic Nervous System. Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry
 Autonomic Nervous System Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Peripheral Nervous System A. Sensory Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous System 1. Sympathetic Nervous
Autonomic Nervous System Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Peripheral Nervous System A. Sensory Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous System 1. Sympathetic Nervous
G-Proteins Receptors and 2nd Messenger Mechanism
 G-Proteins Receptors and 2nd Messenger Mechanism (A lot of information in this sheet is repeated over and over. In my opinion, this is the easiest lecture, enjoy ) Recap: Receptors are specific protein
G-Proteins Receptors and 2nd Messenger Mechanism (A lot of information in this sheet is repeated over and over. In my opinion, this is the easiest lecture, enjoy ) Recap: Receptors are specific protein
Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important
Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important
NEURONS COMMUNICATE WITH OTHER CELLS AT SYNAPSES 34.3
 NEURONS COMMUNICATE WITH OTHER CELLS AT SYNAPSES 34.3 NEURONS COMMUNICATE WITH OTHER CELLS AT SYNAPSES Neurons communicate with other neurons or target cells at synapses. Chemical synapse: a very narrow
NEURONS COMMUNICATE WITH OTHER CELLS AT SYNAPSES 34.3 NEURONS COMMUNICATE WITH OTHER CELLS AT SYNAPSES Neurons communicate with other neurons or target cells at synapses. Chemical synapse: a very narrow
Lujain Hamdan. Tamer Barakat. Faisal Mohammad
 17 Lujain Hamdan Tamer Barakat Faisal Mohammad Review : Summary of synaptic transmission: 1) Action potential arrives to presynaptic terminals of a nerve and causes depolarization by opening Ca 2+ voltage-gated
17 Lujain Hamdan Tamer Barakat Faisal Mohammad Review : Summary of synaptic transmission: 1) Action potential arrives to presynaptic terminals of a nerve and causes depolarization by opening Ca 2+ voltage-gated
Neurochemistry 2. Loewi s experiment
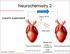 Neurochemistry 2 Loewi s experiment Cengage Learning 2016 AP reaches the axon terminal and activates voltage-gated Ca++ channels (3 major classes). Ca++ influx results in exocytosis of neurotransmitters
Neurochemistry 2 Loewi s experiment Cengage Learning 2016 AP reaches the axon terminal and activates voltage-gated Ca++ channels (3 major classes). Ca++ influx results in exocytosis of neurotransmitters
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology 1 Lecture 3. Synaptic Transmission p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology 1 Lecture 3. Synaptic Transmission p. 1 Terms you should know: synapse, neuromuscular junction (NMJ), pre-synaptic, post-synaptic, synaptic cleft, acetylcholine (ACh), acetylcholine
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology 1 Lecture 3. Synaptic Transmission p. 1 Terms you should know: synapse, neuromuscular junction (NMJ), pre-synaptic, post-synaptic, synaptic cleft, acetylcholine (ACh), acetylcholine
Psych 181: Dr. Anagnostaras
 Psych 181: Dr. Anagnostaras Lecture 5 Synaptic Transmission Introduction to synaptic transmission Synapses (Gk., to clasp or join) Site of action of most psychoactive drugs 6.5 1 Synapses Know basic terminology:
Psych 181: Dr. Anagnostaras Lecture 5 Synaptic Transmission Introduction to synaptic transmission Synapses (Gk., to clasp or join) Site of action of most psychoactive drugs 6.5 1 Synapses Know basic terminology:
Notes are online at The Neuron
 Notes are online at http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/~clovett/neuronotescogs17.pdf A. What is a neuron? The Neuron 1. A neuron is a type of cell that receives and transmits information in the Central Nervous System
Notes are online at http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/~clovett/neuronotescogs17.pdf A. What is a neuron? The Neuron 1. A neuron is a type of cell that receives and transmits information in the Central Nervous System
What effect would an AChE inhibitor have at the neuromuscular junction?
 CASE 4 A 32-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician s office with difficulty chewing food. She states that when she eats certain foods that require a significant amount of chewing (meat),
CASE 4 A 32-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician s office with difficulty chewing food. She states that when she eats certain foods that require a significant amount of chewing (meat),
Neurotransmitters. Chemical transmission of a nerve signal by neurotransmitters at a synapse
 Neurotransmitters A chemical released by one neuron that affects another neuron or an effector organ (e.g., muscle, gland, blood vessel). Neurotransmitters are small molecules that serve as messengers
Neurotransmitters A chemical released by one neuron that affects another neuron or an effector organ (e.g., muscle, gland, blood vessel). Neurotransmitters are small molecules that serve as messengers
Review of Neurochemistry What are neurotransmitters?
 Review of Neurochemistry What are neurotransmitters? In molecular terms, neurotransmitters are molecules that ( ) and of neurons by, for example, increasing or decreasing enzymatic activity or altering
Review of Neurochemistry What are neurotransmitters? In molecular terms, neurotransmitters are molecules that ( ) and of neurons by, for example, increasing or decreasing enzymatic activity or altering
BIPN140 Lecture 8: Synaptic Transmission II
 BIPN140 Lecture 8: Synaptic Transmission II 1. Postsynaptic Receptors: Metabotropic & Ionotropic 2. Postsynaptic Responses (Postsynaptic Potentials, PSPs) 3. Neurotransmitters Su (FA16) Chemical Synapse:
BIPN140 Lecture 8: Synaptic Transmission II 1. Postsynaptic Receptors: Metabotropic & Ionotropic 2. Postsynaptic Responses (Postsynaptic Potentials, PSPs) 3. Neurotransmitters Su (FA16) Chemical Synapse:
The Nervous System Mark Stanford, Ph.D.
 The Nervous System Functional Neuroanatomy and How Neurons Communicate Mark Stanford, Ph.D. Santa Clara Valley Health & Hospital System Addiction Medicine and Therapy Services The Nervous System In response
The Nervous System Functional Neuroanatomy and How Neurons Communicate Mark Stanford, Ph.D. Santa Clara Valley Health & Hospital System Addiction Medicine and Therapy Services The Nervous System In response
NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 CHAPTER 10 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Ch 10 A Ch 10 B This set CHAPTER 10 NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 BASIC STRUCTURE and FUNCTION Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Ch 10 A Ch 10 B This set CHAPTER 10 NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 BASIC STRUCTURE and FUNCTION Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
Leen Osama, Lujain Hamdan, Osama Mohd, Razi Kittaneh... Faisal Mohammad
 23 Leen Osama, Lujain Hamdan, Osama Mohd, Razi Kittaneh... Faisal Mohammad Revision of previous lectures G-proteins coupled receptors mechanism: When a hormone binds to G-protein coupled receptor, GTP
23 Leen Osama, Lujain Hamdan, Osama Mohd, Razi Kittaneh... Faisal Mohammad Revision of previous lectures G-proteins coupled receptors mechanism: When a hormone binds to G-protein coupled receptor, GTP
Synaptic Communication. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Synaptic Communication Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News The first exam is next week on Friday! Be sure to checkout the sample exam on the course website. 2
Synaptic Communication Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News The first exam is next week on Friday! Be sure to checkout the sample exam on the course website. 2
Biol 219 Lec 12 Fall 2016
 Cell-to-Cell: Neurons Communicate at Synapses Electrical synapses pass electrical signals through gap junctions Signal can be bi-directional Synchronizes the activity of a network of cells Primarily in
Cell-to-Cell: Neurons Communicate at Synapses Electrical synapses pass electrical signals through gap junctions Signal can be bi-directional Synchronizes the activity of a network of cells Primarily in
Chapter 45: Synapses Transmission of Nerve Impulses Between Neurons. Chad Smurthwaite & Jordan Shellmire
 Chapter 45: Synapses Transmission of Nerve Impulses Between Neurons Chad Smurthwaite & Jordan Shellmire The Chemical Synapse The most common type of synapse used for signal transmission in the central
Chapter 45: Synapses Transmission of Nerve Impulses Between Neurons Chad Smurthwaite & Jordan Shellmire The Chemical Synapse The most common type of synapse used for signal transmission in the central
Ion Channels Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com)
 Ion Channels Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction At synapses, ions move across cell membranes through
Ion Channels Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction At synapses, ions move across cell membranes through
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY [THE SYNAPSE AND PHARMACOLOGY]
![QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY [THE SYNAPSE AND PHARMACOLOGY] QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY [THE SYNAPSE AND PHARMACOLOGY]](/thumbs/86/94924826.jpg) QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY [THE SYNAPSE AND PHARMACOLOGY] Learning Objectives: Explain how neurons communicate stimulus intensity Explain how action potentials are conducted along
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY [THE SYNAPSE AND PHARMACOLOGY] Learning Objectives: Explain how neurons communicate stimulus intensity Explain how action potentials are conducted along
Portions from Chapter 6 CHAPTER 7. The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses. Chapter 7 Outline. and Supporting Cells
 CHAPTER 7 The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Chapter 7 Outline Neurons and Supporting Cells Activity in Axons The Synapse Acetylcholine as a Neurotransmitter Monoamines as Neurotransmitters Other
CHAPTER 7 The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Chapter 7 Outline Neurons and Supporting Cells Activity in Axons The Synapse Acetylcholine as a Neurotransmitter Monoamines as Neurotransmitters Other
By the name of Allah
 By the name of Allah Receptors function and signal transduction ( Hormones and receptors Types) We were talking about receptors of the neurotransmitters; we have 2 types of receptors: 1- Ionotropic receptors
By the name of Allah Receptors function and signal transduction ( Hormones and receptors Types) We were talking about receptors of the neurotransmitters; we have 2 types of receptors: 1- Ionotropic receptors
Ion Channels (Part 2)
 Ion Channels (Part 2) Graphics are used with permission of : adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) -57- Quiz Question #2: Ion Channels This question asks
Ion Channels (Part 2) Graphics are used with permission of : adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) -57- Quiz Question #2: Ion Channels This question asks
Synaptic Transmission
 Synaptic Transmission Postsynaptic Mechanisms Synapses electrical and chemical Part I Neurotransmitters categories and life cycle Neurotransmitters examples and postsynaptic effects Pathology Part II Neurotransmitter
Synaptic Transmission Postsynaptic Mechanisms Synapses electrical and chemical Part I Neurotransmitters categories and life cycle Neurotransmitters examples and postsynaptic effects Pathology Part II Neurotransmitter
Communication Between
 Communication Between Neurons Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The electrical changes taking place within a neuron, as described in the previous section, are similar to a light switch being turned on. A stimulus starts
Communication Between Neurons Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The electrical changes taking place within a neuron, as described in the previous section, are similar to a light switch being turned on. A stimulus starts
5-Nervous system II: Physiology of Neurons
 5-Nervous system II: Physiology of Neurons AXON ION GRADIENTS ACTION POTENTIAL (axon conduction) GRADED POTENTIAL (cell-cell communication at synapse) SYNAPSE STRUCTURE & FUNCTION NEURAL INTEGRATION CNS
5-Nervous system II: Physiology of Neurons AXON ION GRADIENTS ACTION POTENTIAL (axon conduction) GRADED POTENTIAL (cell-cell communication at synapse) SYNAPSE STRUCTURE & FUNCTION NEURAL INTEGRATION CNS
Ch. 45 Continues (Have You Read Ch. 45 yet?) u Central Nervous System Synapses - Synaptic functions of neurons - Information transmission via nerve
 Ch. 45 Continues (Have You Read Ch. 45 yet?) u Central Nervous System Synapses - Synaptic functions of neurons - Information transmission via nerve impulses - Impulse may be blocked in its transmission
Ch. 45 Continues (Have You Read Ch. 45 yet?) u Central Nervous System Synapses - Synaptic functions of neurons - Information transmission via nerve impulses - Impulse may be blocked in its transmission
Synaptic Transmission
 Synaptic Transmission Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction Synaptic transmission involves the release
Synaptic Transmission Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction Synaptic transmission involves the release
NEUROCHEMISTRY Brief Review
 NEUROCHEMISTRY Brief Review UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL MBBS YEAR V SEMINAR VJ Temple 1 Membrane potential Membrane potential:
NEUROCHEMISTRY Brief Review UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL MBBS YEAR V SEMINAR VJ Temple 1 Membrane potential Membrane potential:
QUIZ YOURSELF COLOSSAL NEURON ACTIVITY
 QUIZ YOURSELF What are the factors that produce the resting potential? How is an action potential initiated and what is the subsequent flow of ions during the action potential? 1 COLOSSAL NEURON ACTIVITY
QUIZ YOURSELF What are the factors that produce the resting potential? How is an action potential initiated and what is the subsequent flow of ions during the action potential? 1 COLOSSAL NEURON ACTIVITY
Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed.,
 Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Laith Khreisat. Ahmad Ali Massad. Faisal Muhammad
 21 Laith Khreisat Ahmad Ali Massad Faisal Muhammad * Note: I tried my best to include everything mentioned in the slides, but feel free to refer back to them in case I missed anything. * Last time we talked
21 Laith Khreisat Ahmad Ali Massad Faisal Muhammad * Note: I tried my best to include everything mentioned in the slides, but feel free to refer back to them in case I missed anything. * Last time we talked
Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline
 Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline Module 11.1 Overview of the Nervous System (Figures 11.1-11.3) A. The nervous system controls our perception and experience
Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline Module 11.1 Overview of the Nervous System (Figures 11.1-11.3) A. The nervous system controls our perception and experience
Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Nervous system development Part of the ectoderm
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Nervous system development Part of the ectoderm
3) Most of the organelles in a neuron are located in the A) dendritic region. B) axon hillock. C) axon. D) cell body. E) axon terminals.
 Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Multiple-Choice Questions 1) A simple nervous system A) must include chemical senses, mechanoreception, and vision. B) includes a minimum of 12 ganglia. C) has
Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Multiple-Choice Questions 1) A simple nervous system A) must include chemical senses, mechanoreception, and vision. B) includes a minimum of 12 ganglia. C) has
Sarah Jaar Marah Al-Darawsheh
 22 Sarah Jaar Marah Al-Darawsheh Faisal Mohammad Receptors can be membrane proteins (for water-soluble hormones/ligands) or intracellular (found in the cytosol or nucleus and bind to DNA, for lipid-soluble
22 Sarah Jaar Marah Al-Darawsheh Faisal Mohammad Receptors can be membrane proteins (for water-soluble hormones/ligands) or intracellular (found in the cytosol or nucleus and bind to DNA, for lipid-soluble
Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue. Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Terms to Know CNS PNS Afferent division Efferent division Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system Sympathetic nervous system Parasympathetic
Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Terms to Know CNS PNS Afferent division Efferent division Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system Sympathetic nervous system Parasympathetic
Biopsychology 2012 sec 003 (Dr. Campeau)
 Biopsychology 2012 sec 003 (Dr. Campeau) Study Guide for First Midterm What are some fun facts about the human brain? - there are approximately 100 billion neurons in the brain; - each neuron makes between
Biopsychology 2012 sec 003 (Dr. Campeau) Study Guide for First Midterm What are some fun facts about the human brain? - there are approximately 100 billion neurons in the brain; - each neuron makes between
Chapter 2: Cellular Mechanisms and Cognition
 Chapter 2: Cellular Mechanisms and Cognition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Two principles about neurons were defined by Ramón y Cajal. The principle of connectional specificity states that, whereas the principle
Chapter 2: Cellular Mechanisms and Cognition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Two principles about neurons were defined by Ramón y Cajal. The principle of connectional specificity states that, whereas the principle
NEURAL TISSUE (NEUROPHYSIOLOGY) PART I (A): NEURONS & NEUROGLIA
 PART I (A): NEURONS & NEUROGLIA Neural Tissue Contains 2 kinds of cells: neurons: cells that send and receive signals neuroglia (glial cells): cells that support and protect neurons Neuron Types Sensory
PART I (A): NEURONS & NEUROGLIA Neural Tissue Contains 2 kinds of cells: neurons: cells that send and receive signals neuroglia (glial cells): cells that support and protect neurons Neuron Types Sensory
Introduction to Neurobiology
 Biology 240 General Zoology Introduction to Neurobiology Nervous System functions: communication of information via nerve signals integration and processing of information control of physiological and
Biology 240 General Zoology Introduction to Neurobiology Nervous System functions: communication of information via nerve signals integration and processing of information control of physiological and
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling The Neuron is the functional unit of the nervous system. Neurons are composed of a cell body, which contains the nucleus and organelles; Dendrites which are extensions
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling The Neuron is the functional unit of the nervous system. Neurons are composed of a cell body, which contains the nucleus and organelles; Dendrites which are extensions
3.E.2 Continued. This is the essential knowledge statement from the curriculum framework. Detect---process--- response
 Nervous System: Part III What Happens at a Synapse? 3.E. Continued Animals have nervous systems that detect external and internal signals, transmit and integrate information, and produce responses. This
Nervous System: Part III What Happens at a Synapse? 3.E. Continued Animals have nervous systems that detect external and internal signals, transmit and integrate information, and produce responses. This
NEUROTRANSMITTERS, POSSIBLE SITES OF ACTIONS, AND DRUG INFLUENCES. Prof. K. Chilaka Prof. P.c. Unekwe Dr. Eyibe Michael I.
 NEUROTRANSMITTERS, POSSIBLE SITES OF ACTIONS, AND DRUG INFLUENCES Prof. K. Chilaka Prof. P.c. Unekwe Dr. Eyibe Michael I. Abstract Neurotransmitter, also known as chemical messengeris enodegenons chemical
NEUROTRANSMITTERS, POSSIBLE SITES OF ACTIONS, AND DRUG INFLUENCES Prof. K. Chilaka Prof. P.c. Unekwe Dr. Eyibe Michael I. Abstract Neurotransmitter, also known as chemical messengeris enodegenons chemical
Synaptic Transmission: Ionic and Metabotropic
 Synaptic Transmission: Ionic and Metabotropic D. Purves et al. Neuroscience (Sinauer Assoc.) Chapters 5, 6, 7. C. Koch. Biophysics of Computation (Oxford) Chapter 4. J.G. Nicholls et al. From Neuron to
Synaptic Transmission: Ionic and Metabotropic D. Purves et al. Neuroscience (Sinauer Assoc.) Chapters 5, 6, 7. C. Koch. Biophysics of Computation (Oxford) Chapter 4. J.G. Nicholls et al. From Neuron to
Communication within a Neuron
 Neuronal Communication, Ph.D. Communication within a Neuron Measuring Electrical Potentials of Axons The Membrane Potential The Action Potential Conduction of the Action Potential 1 The withdrawal reflex
Neuronal Communication, Ph.D. Communication within a Neuron Measuring Electrical Potentials of Axons The Membrane Potential The Action Potential Conduction of the Action Potential 1 The withdrawal reflex
Na + K + pump. The beauty of the Na + K + pump. Cotransport. The setup Cotransport the result. Found along the plasma membrane of all cells.
 The beauty of the Na + K + pump Na + K + pump Found along the plasma membrane of all cells. Establishes gradients, controls osmotic effects, allows for cotransport Nerve cells have a Na + K + pump and
The beauty of the Na + K + pump Na + K + pump Found along the plasma membrane of all cells. Establishes gradients, controls osmotic effects, allows for cotransport Nerve cells have a Na + K + pump and
Synapses and Neurotransmitters
 Synapses and Neurotransmitters Action Potentials We have been talking about action potentials and how they allow an electrical impulse to travel from the dendrites to the end plates of a neuron. These
Synapses and Neurotransmitters Action Potentials We have been talking about action potentials and how they allow an electrical impulse to travel from the dendrites to the end plates of a neuron. These
Summarized by B.-W. Ku, E. S. Lee, and B.-T. Zhang Biointelligence Laboratory, Seoul National University.
 Chapter 2. The Cellular l and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 3 rd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2008. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Chapter 2. The Cellular l and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 3 rd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2008. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Outline. Neuron Structure. Week 4 - Nervous System. The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses
 Outline Week 4 - The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Neurons Neuron structures Types of neurons Electrical activity of neurons Depolarization, repolarization, hyperpolarization Synapses Release of
Outline Week 4 - The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Neurons Neuron structures Types of neurons Electrical activity of neurons Depolarization, repolarization, hyperpolarization Synapses Release of
It s Not Just Serotonin: Neurosignaling in Mental Illness
 It s Not Just Serotonin: Neurosignaling in Mental Illness Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC Professor of Nursing Linfield College Learning Outcomes Distinguish between metabotropic and ionotropic neuroreceptors
It s Not Just Serotonin: Neurosignaling in Mental Illness Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC Professor of Nursing Linfield College Learning Outcomes Distinguish between metabotropic and ionotropic neuroreceptors
Function of the Nervous System
 Nervous System Function of the Nervous System Receive sensory information, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands to form a response Composed of neurons (functional unit of the nervous system)
Nervous System Function of the Nervous System Receive sensory information, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands to form a response Composed of neurons (functional unit of the nervous system)
Session ID: 1001 June 14, 2012
 It s Not Just Serotonin: Neurosignaling in Mental Illness Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC Professor of Nursing Linfield College Learning Outcomes Distinguish between metabotropic and ionotropic neuroreceptors
It s Not Just Serotonin: Neurosignaling in Mental Illness Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC Professor of Nursing Linfield College Learning Outcomes Distinguish between metabotropic and ionotropic neuroreceptors
Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition
 Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga,, R. B. Ivry,, and G. R. Mangun,, Norton, 2002. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga,, R. B. Ivry,, and G. R. Mangun,, Norton, 2002. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Integrated Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology Third Edition
 Integrated Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology Third Edition Chapter 3 Pharmacology of the Autonomic Nervous System Multimedia Directory Slide 19 Slide 37 Slide 38 Slide 39 Slide 40 Slide 41 Slide 42 Slide 43
Integrated Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology Third Edition Chapter 3 Pharmacology of the Autonomic Nervous System Multimedia Directory Slide 19 Slide 37 Slide 38 Slide 39 Slide 40 Slide 41 Slide 42 Slide 43
Thursday, January 22, Nerve impulse
 Nerve impulse Transmembrane Potential caused by ions moving through cell membrane at different rates Two main ions of concern Na + - Sodium K + - potassium Cell membrane not freely permeable therefore
Nerve impulse Transmembrane Potential caused by ions moving through cell membrane at different rates Two main ions of concern Na + - Sodium K + - potassium Cell membrane not freely permeable therefore
Chapter 4 Neuronal Physiology
 Chapter 4 Neuronal Physiology V edit. Pg. 99-131 VI edit. Pg. 85-113 VII edit. Pg. 87-113 Input Zone Dendrites and Cell body Nucleus Trigger Zone Axon hillock Conducting Zone Axon (may be from 1mm to more
Chapter 4 Neuronal Physiology V edit. Pg. 99-131 VI edit. Pg. 85-113 VII edit. Pg. 87-113 Input Zone Dendrites and Cell body Nucleus Trigger Zone Axon hillock Conducting Zone Axon (may be from 1mm to more
Chapter 24 Chemical Communications Neurotransmitters & Hormones
 Chapter 24 Chemical Communications Neurotransmitters & Hormones 1 Chemical Communication Terms and definitions: Neuron: A nerve cell. Neurotransmitter: A chemical messenger between a neuron and another
Chapter 24 Chemical Communications Neurotransmitters & Hormones 1 Chemical Communication Terms and definitions: Neuron: A nerve cell. Neurotransmitter: A chemical messenger between a neuron and another
The Nervous System. Nervous System Functions 1. gather sensory input 2. integration- process and interpret sensory input 3. cause motor output
 The Nervous System Nervous System Functions 1. gather sensory input 2. integration- process and interpret sensory input 3. cause motor output The Nervous System 2 Parts of the Nervous System 1. central
The Nervous System Nervous System Functions 1. gather sensory input 2. integration- process and interpret sensory input 3. cause motor output The Nervous System 2 Parts of the Nervous System 1. central
Neurotransmitter Systems II Receptors. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems II Receptors Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important chemical
Neurotransmitter Systems II Receptors Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important chemical
Synaptic transmission
 Michael J. Fox Hollywood actor John Nash Nobel prize laureate 1994 Synaptic transmission Sompol Tapechum, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital sisth@mahidol.ac.th www.ps.si.mahidol.ac.th
Michael J. Fox Hollywood actor John Nash Nobel prize laureate 1994 Synaptic transmission Sompol Tapechum, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital sisth@mahidol.ac.th www.ps.si.mahidol.ac.th
The Nervous System -The master controlling and communicating system of the body
 The Nervous System -The master controlling and communicating system of the body Functions: -Sensory input -Integration -Motor output Organization of the Nervous System Central nervous system (CNS) -Brain
The Nervous System -The master controlling and communicating system of the body Functions: -Sensory input -Integration -Motor output Organization of the Nervous System Central nervous system (CNS) -Brain
Receptors Families. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Receptors Families Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Receptor Families 1. Ligand-gated ion channels 2. G protein coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-linked
Receptors Families Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Receptor Families 1. Ligand-gated ion channels 2. G protein coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-linked
Synapses. Objectives. Synaptic Relationships Between Neurons. Structure of a Chemical Synapse. Structure of a Chemical Synapse
 bjectives Synapses s Temporal & Spatial Summation EPSP & IPSP Coding Memory Synapses a nerve signal AP travels to the end of the axon triggers the release of a neurotransmitter stimulates a new wave of
bjectives Synapses s Temporal & Spatial Summation EPSP & IPSP Coding Memory Synapses a nerve signal AP travels to the end of the axon triggers the release of a neurotransmitter stimulates a new wave of
CHAPTER 44: Neurons and Nervous Systems
 CHAPTER 44: Neurons and Nervous Systems 1. What are the three different types of neurons and what are their functions? a. b. c. 2. Label and list the function of each part of the neuron. 3. How does the
CHAPTER 44: Neurons and Nervous Systems 1. What are the three different types of neurons and what are their functions? a. b. c. 2. Label and list the function of each part of the neuron. 3. How does the
Division Ave. High School AP Biology. cell body. signal direction
 signal direction Nervous system cells Neuron a nerve cell dendrites myelin sheath axon cell body dendrite cell body axon Structure fits function many entry points for signal one path out transmits signal
signal direction Nervous system cells Neuron a nerve cell dendrites myelin sheath axon cell body dendrite cell body axon Structure fits function many entry points for signal one path out transmits signal
Neural Tissue. Chapter 12 Part B
 Neural Tissue Chapter 12 Part B CNS Tumors - Neurons stop dividing at age 4 but glial cells retain the capacity to divide. - Primary CNS tumors in adults- division of abnormal neuroglia rather than from
Neural Tissue Chapter 12 Part B CNS Tumors - Neurons stop dividing at age 4 but glial cells retain the capacity to divide. - Primary CNS tumors in adults- division of abnormal neuroglia rather than from
9/28/2016. Neuron. Multipolar Neuron. Astrocytes Exchange Materials With Neurons. Glia or Glial Cells ( supporting cells of the nervous system)
 Neuron Multipolar Neuron https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lw-psbnu5xago to :38 Glia or Glial Cells ( supporting cells of the nervous system) 10X more numerous than neurons but one-tenth the size make up
Neuron Multipolar Neuron https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lw-psbnu5xago to :38 Glia or Glial Cells ( supporting cells of the nervous system) 10X more numerous than neurons but one-tenth the size make up
Basics of Pharmacology
 Basics of Pharmacology Pekka Rauhala Transmed 2013 What is pharmacology? Pharmacology may be defined as the study of the effects of drugs on the function of living systems Pharmacodynamics The mechanism(s)
Basics of Pharmacology Pekka Rauhala Transmed 2013 What is pharmacology? Pharmacology may be defined as the study of the effects of drugs on the function of living systems Pharmacodynamics The mechanism(s)
BIOL Week 6. Nervous System. Transmission at Synapses
 Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 Week 6 Nervous System 1 Transmission at Synapses Synapses are the site of communication between 2 or more neurons. It mediates the transfer of information and
Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 Week 6 Nervous System 1 Transmission at Synapses Synapses are the site of communication between 2 or more neurons. It mediates the transfer of information and
Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer
 Name Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Period Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer 1. What is
Name Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Period Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer 1. What is
- Neurotransmitters Of The Brain -
 - Neurotransmitters Of The Brain - INTRODUCTION Synapsis: a specialized connection between two neurons that permits the transmission of signals in a one-way fashion (presynaptic postsynaptic). Types of
- Neurotransmitters Of The Brain - INTRODUCTION Synapsis: a specialized connection between two neurons that permits the transmission of signals in a one-way fashion (presynaptic postsynaptic). Types of
Nervous System. Nervous system cells. Transmission of a signal 2/27/2015. Neuron
 Nervous System 2007-2008 signal direction Neuron a nerve cell Nervous system cells dendrites axon cell body Structure fits function many entry points for signal one path out transmits signal signal direction
Nervous System 2007-2008 signal direction Neuron a nerve cell Nervous system cells dendrites axon cell body Structure fits function many entry points for signal one path out transmits signal signal direction
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1
 GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1 1. The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete chemical signals, called hormones, into the blood. In addition, other organs and cells
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1 1. The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete chemical signals, called hormones, into the blood. In addition, other organs and cells
Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the
Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the
Homeostasis. Endocrine System Nervous System
 Homeostasis Endocrine System Nervous System 2004-2005 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation
Homeostasis Endocrine System Nervous System 2004-2005 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation
Chapter 7. The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Cell communication. Gated ion channels. Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open
 increase decrease Cell communication Gated ion channels Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open Triggered by: potential change, chemical binding, temperature change, stretching 1 Voltage-Gated
increase decrease Cell communication Gated ion channels Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open Triggered by: potential change, chemical binding, temperature change, stretching 1 Voltage-Gated
Cell communication. Gated ion channels. Voltage-Gated Na + Channel. Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open
 increase decrease Cell communication Gated ion channels Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open Voltage-Gated Na + Channel Activation gate ECF Triggered by: change, chemical binding, temperature
increase decrease Cell communication Gated ion channels Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open Voltage-Gated Na + Channel Activation gate ECF Triggered by: change, chemical binding, temperature
Goals and Challenges of Communication. Communication and Signal Transduction. How Do Cells Communicate?
 Goals and Challenges of Communication Reaching (only) the correct recipient(s) Imparting correct information Timeliness Causing the desired effect Effective termination Communication and Signal Transduction
Goals and Challenges of Communication Reaching (only) the correct recipient(s) Imparting correct information Timeliness Causing the desired effect Effective termination Communication and Signal Transduction
Chapter 7. Objectives
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Physiology of synapses and receptors
 Physiology of synapses and receptors Dr Syed Shahid Habib Professor & Consultant Clinical Neurophysiology Dept. of Physiology College of Medicine & KKUH King Saud University REMEMBER These handouts will
Physiology of synapses and receptors Dr Syed Shahid Habib Professor & Consultant Clinical Neurophysiology Dept. of Physiology College of Medicine & KKUH King Saud University REMEMBER These handouts will
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE BMP-218 November 4, 2014 DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary divisions: 1. CNS - Central Nervous System (Brain + Spinal Cord)
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE BMP-218 November 4, 2014 DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary divisions: 1. CNS - Central Nervous System (Brain + Spinal Cord)
Abdulrahman Nidal. Ameen Alsaras. Faisal I. Mohammed
 13 Abdulrahman Nidal Ameen Alsaras Faisal I. Mohammed Recall that Acetyl Choline is synthesized from the reaction between Acetyl Coenzyme A (Acetyl CoA) with Choline under the presence of Choline acetyltransferase
13 Abdulrahman Nidal Ameen Alsaras Faisal I. Mohammed Recall that Acetyl Choline is synthesized from the reaction between Acetyl Coenzyme A (Acetyl CoA) with Choline under the presence of Choline acetyltransferase
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Overview: Lines of Communication Chapter 8 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Fig. 8- The cone snail kills prey with venom that disables neurons Neurons are nerve s that transfer information within the body
Overview: Lines of Communication Chapter 8 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Fig. 8- The cone snail kills prey with venom that disables neurons Neurons are nerve s that transfer information within the body
Hormones, Receptors and Receptor-Hormone Interactions
 Classification of Hormones Hormones, Receptors and Receptor-Hormone Interactions Synthesis of Protein Hormones and Amine Hormones Hormone Activity Locations of Receptors Mechanisms of Hormone Action Types
Classification of Hormones Hormones, Receptors and Receptor-Hormone Interactions Synthesis of Protein Hormones and Amine Hormones Hormone Activity Locations of Receptors Mechanisms of Hormone Action Types
Lecture 14. Insect nerve system (II)
 Lecture 14. Insect nerve system (II) Structures (Anatomy) Cells Anatomy How NS functions Signal transduction Signal transmission Overview More on neurons: ions, ion channel, ligand receptor Signal transduction:
Lecture 14. Insect nerve system (II) Structures (Anatomy) Cells Anatomy How NS functions Signal transduction Signal transmission Overview More on neurons: ions, ion channel, ligand receptor Signal transduction:
Communication Between Neurons *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46503 1 Communication Between Neurons * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m46503 1 Communication Between Neurons * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
Synapses and Neurotransmitters
 Synapses and Neurotransmitters Communication Between Neurons Synapse: A specialized site of contact, and transmission of information between a neuron and an effector cell Anterior Motor Neuron Figure 45-5
Synapses and Neurotransmitters Communication Between Neurons Synapse: A specialized site of contact, and transmission of information between a neuron and an effector cell Anterior Motor Neuron Figure 45-5
1. At the venous end of a capillary, is the dominant force determining water movement. a. Pcap b. cap c. PIF d. IF e. [Na+]
![1. At the venous end of a capillary, is the dominant force determining water movement. a. Pcap b. cap c. PIF d. IF e. [Na+] 1. At the venous end of a capillary, is the dominant force determining water movement. a. Pcap b. cap c. PIF d. IF e. [Na+]](/thumbs/95/122587355.jpg) P531: Exam 1 Sample Question Set #3 The first 9 questions are the relevant questions from the beginning of lecture each day. The remaining 16 questions cover material from the last week of lectures. 1.
P531: Exam 1 Sample Question Set #3 The first 9 questions are the relevant questions from the beginning of lecture each day. The remaining 16 questions cover material from the last week of lectures. 1.
Neurons! John A. White Dept. of Bioengineering
 Neurons! John A. White Dept. of Bioengineering john.white@utah.edu What makes neurons different from cardiomyocytes? Morphological polarity Transport systems Shape and function of action potentials Neuronal
Neurons! John A. White Dept. of Bioengineering john.white@utah.edu What makes neurons different from cardiomyocytes? Morphological polarity Transport systems Shape and function of action potentials Neuronal
