Session ID: 1001 June 14, 2012
|
|
|
- Luke Arnold
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 It s Not Just Serotonin: Neurosignaling in Mental Illness Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC Professor of Nursing Linfield College Learning Outcomes Distinguish between metabotropic and ionotropic neuroreceptors Identify the major neuroreceptors and neurotransmitters involved in mental illnesses Describe neurosignaling in the brain in relation to mental illness Discuss new targets for psychiatric drug therapies Disclosure Statement I have no commercial financial conflicts of interest to disclose I may discuss some off label use of medications as examples of treatment options Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC 1
2 Agenda Synaptic Transmission Signal Transduction in the Brain Neurotransmitters Neuropharmacological Applications Synaptic Transmission Process of firing neurons to move a message between neurons and to different areas of the brain Neuron at rest is polarized by separating intracellular and extracellular ions High extracellular sodium, calcium and chloride High intracellular potassium Passive small amounts of ions flow without affecting the charge Maintains an equilibrium potential Action Potential Elements of the action potential Depolarization Repolarization Hyper polarization Voltage-gated sodium, calcium, and potassium channels generate the electrical signals through action potentials Sodium activates the signal Potassium ends the signal Calcium activates neurotransmitter release Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC 2
3 Animation of Action Potential /channel.html Neurotransmission Once depolarization occurs, calcium channels open and calcium activates the synaptic vesicle to move to the terminal button and fuse with the neuron membrane This fusion releases the neurotransmitters into the synaptic space to find and bind with a neuroreceptor on the post synaptic neuron Once this occurs the second neuron is activated Animation of Neurotransmission /chp44/4403s.swf Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC 3
4 Basic Receptor Types Ionotropic Receptors (ligand-gated ion channels) Five protein transmembrane subunits When ligand (neurotransmitter) binds with extracellular site, the subunits quickly open a pore through which ions pass Act quickly to depolarize neuron Metabotropic Receptors (G-protein-coupled) Metabotropic Receptors Seven protein transmembrane subunits without pore Ligand activates conformational change of the receptor causing the G-protein subunits to separate The G-protein replaced by GTP which activates the alpha subunit Alpha subunit undergoes conformation to then activate adenyl cyclase, which is converted to c-amp as a second messenger, which attaches to calcium ion channel to open Act to fire the neuron and then is inactivated by other proteins Animated MetabotropicReceptor fra&feature=related Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC 4
5 Neurotransmitters Neurotransmitters (NT) Excitatory: can inhibit hyperpolarization, thereby causing additive changes to the membrane potential Inhibitory: inside of the cell becomes more negative causing hyperpolarization, thereby delaying another action potential Neurons can have vesicles containing different NT but in different concentrations Common Neurotransmitters Acetylcholine Dopamine Norepinephrine Epinephrine Serotonin Histamine Glutamate GABA Neuroreceptors The binding units for neurotransmitters There can be multiple subtypes of neuroreceptors Ligands act on neuroreceptors Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC 5
6 Dopamine Receptors D-1 D-1 & D-2 receptors are synergistic D-2 Target of therapeutic & EPS effects of DA antagonists D-3 Unknown D-4 Target of Serotonin-Dopamine Antagonists D-5 Unknown Adrenergic Receptors α1a, B, D α2a, B, C β1 β2 β3 Antagonists antihypertensive Agonists sedative & antihypertensive Regulation of cardiac function Regulation of bronchial muscle contraction Regulation of adipose tissue function Histamine Receptors H-1 Antagonists produce sedation, weight gain H-2 Antagonists for peptic ulcer disease H-3 Antagonists produce arousal, appetite suppression Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC 6
7 Serotonin Receptors 5HT-1A 5HT-1B 5HT-1D 5HT-1F 5HT-2A 5HT-2B 5HT-2C Antidepressant action; partial agonist is anxiolytic Possible role in locomotor activity, aggression Target of antimigraine drugs Target of antimigraine drugs Target of hallucinogens, SDAs Regulation of stomach contraction Regulation of appetite, anxiety, seizures; target of hallucinogens Serotonin Receptors Con t 5HT-3 5HT-4 5HT-6 5HT-7 5HT- 1E, 5HT-5a & b Antagonists antiemetic, anxiolytic, cognitive enhancement Modulation of cognition, anxiety Target of hallucinogens, SDAs Possible regulation of circadian rhythms Unknown Glutamate Metabotropic Receptors S Group I Group II Group III Increase NMDA receptor activity, possible agonist for treatment of GAD Decrease NMDA receptor activity, possible agonist to treat schizophrenia Decrease NMDA receptor activity, possible agonist to treat schizophrenia Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC 7
8 Glutamate Ionotropic Receptors S AMPA NMDA Kainate Antagonists may treat epilepsy, agonists may treat neurodegenerative diseases Antagonists produce positive, negative & cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia Antagonists may have role in treatment of pain, migraine, epilepsy, stroke, & anxiety GABA-A Receptors GABA-A GABA-B Regulate neuronal excitability, responsible for rapid mood changes Mediate slow inhibitory potentials, effects memory and mood and pain response Neuropharmacological Applications Drugs are ligands, therefore they affect neurotransmission and neuroreception Expect to see more multi receptor drugs Drugs may have differential affects on receptor subtypes to produce different effects and adverse responses Newer drugs will target different neurotransmitters and receptors Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC 8
9 Neuropharmacologic Applications Drugs in the pipeline: Glutamate antagonists for dementia, schizophrenia & addictions GSK Phase II 5HT-6 antagonist for dementia Novartis Agomelatine Phase III 5HT-2 antagonist & agonist for melatonin 1 & 2 for treatment of depression Novartis Emapunil, Phase III selective agonist of BZD receptor site of GABA for treatment of anxiety & panic AstraZeneca Mecamylamine, Phase III neuronal nicotinic modulator to treat depression & anxiety Drugs in the Pipeline AstraZeneca Phase II NMDA channel blocker for treatment resistant depression AstraZeneca Phase II α4β2 nicotinic receptor modulator as adjunct to donepezil for Alzheimer s disease AstraZeneca Phase II histamine 3 antagonist for Alzheimer s disease Drugs in the Pipeline Lilly Pomaglumetad Methionil, Phase III agonist of metabotropic glutamate II/III for treatment of schizophrenia Lilly Edovoxetine, Phase III norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor for treatment of depression and ADD Lilly Solanezumab, Phase III binds to soluable amyloid β for treatment of Alzheimer s Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC 9
10 Drugs in the Pipeline Merck Suvorexant, Phase III orexin receptor antagonist for treatment of insomnia Roche, Phase II metabotropic glutamate II antagonist for treatment of depression Roche, bitopertin, Phase III glycine reuptake inhibitor to enhance NMDA activity to treat schizophrenia Roche, Phase II metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 modulator for treatment of depression and autism Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC 10
It s Not Just Serotonin: Neurosignaling in Mental Illness
 It s Not Just Serotonin: Neurosignaling in Mental Illness Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC Professor of Nursing Linfield College Learning Outcomes Distinguish between metabotropic and ionotropic neuroreceptors
It s Not Just Serotonin: Neurosignaling in Mental Illness Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC Professor of Nursing Linfield College Learning Outcomes Distinguish between metabotropic and ionotropic neuroreceptors
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY [THE SYNAPSE AND PHARMACOLOGY]
![QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY [THE SYNAPSE AND PHARMACOLOGY] QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY [THE SYNAPSE AND PHARMACOLOGY]](/thumbs/86/94924826.jpg) QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY [THE SYNAPSE AND PHARMACOLOGY] Learning Objectives: Explain how neurons communicate stimulus intensity Explain how action potentials are conducted along
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY [THE SYNAPSE AND PHARMACOLOGY] Learning Objectives: Explain how neurons communicate stimulus intensity Explain how action potentials are conducted along
Dania Ahmad. Tamer Barakat + Dania Ahmad. Faisal I. Mohammed
 16 Dania Ahmad Tamer Barakat + Dania Ahmad Faisal I. Mohammed Revision: What are the basic types of neurons? sensory (afferent), motor (efferent) and interneuron (equaled association neurons). We classified
16 Dania Ahmad Tamer Barakat + Dania Ahmad Faisal I. Mohammed Revision: What are the basic types of neurons? sensory (afferent), motor (efferent) and interneuron (equaled association neurons). We classified
Synaptic Communication. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Synaptic Communication Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News The first exam is next week on Friday! Be sure to checkout the sample exam on the course website. 2
Synaptic Communication Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News The first exam is next week on Friday! Be sure to checkout the sample exam on the course website. 2
Neurotransmitter Systems II Receptors. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems II Receptors Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important chemical
Neurotransmitter Systems II Receptors Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important chemical
Ion Channels (Part 2)
 Ion Channels (Part 2) Graphics are used with permission of : adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) -57- Quiz Question #2: Ion Channels This question asks
Ion Channels (Part 2) Graphics are used with permission of : adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) -57- Quiz Question #2: Ion Channels This question asks
Ion Channels Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com)
 Ion Channels Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction At synapses, ions move across cell membranes through
Ion Channels Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction At synapses, ions move across cell membranes through
Action Potentials and Synaptic Transmission. BIO 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Action Potentials and Synaptic Transmission BIO 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Review of action potentials Nodes of Ranvier Nucleus Dendrites Cell body In saltatory conduction, the nerve impulses
Action Potentials and Synaptic Transmission BIO 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Review of action potentials Nodes of Ranvier Nucleus Dendrites Cell body In saltatory conduction, the nerve impulses
Synapses and Neurotransmitters
 Synapses and Neurotransmitters Communication Between Neurons Synapse: A specialized site of contact, and transmission of information between a neuron and an effector cell Anterior Motor Neuron Figure 45-5
Synapses and Neurotransmitters Communication Between Neurons Synapse: A specialized site of contact, and transmission of information between a neuron and an effector cell Anterior Motor Neuron Figure 45-5
IONOTROPIC RECEPTORS
 BASICS OF NEUROBIOLOGY IONOTROPIC RECEPTORS ZSOLT LIPOSITS 1 NEURAL COMMUNICATION http://sciencecore.columbia.edu/s4.html 2 Post-synaptic mechanisms Receptors-signal transduction-messengers 3 TRANSMITTER
BASICS OF NEUROBIOLOGY IONOTROPIC RECEPTORS ZSOLT LIPOSITS 1 NEURAL COMMUNICATION http://sciencecore.columbia.edu/s4.html 2 Post-synaptic mechanisms Receptors-signal transduction-messengers 3 TRANSMITTER
Chapter 2: Cellular Mechanisms and Cognition
 Chapter 2: Cellular Mechanisms and Cognition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Two principles about neurons were defined by Ramón y Cajal. The principle of connectional specificity states that, whereas the principle
Chapter 2: Cellular Mechanisms and Cognition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Two principles about neurons were defined by Ramón y Cajal. The principle of connectional specificity states that, whereas the principle
Communication Between
 Communication Between Neurons Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The electrical changes taking place within a neuron, as described in the previous section, are similar to a light switch being turned on. A stimulus starts
Communication Between Neurons Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The electrical changes taking place within a neuron, as described in the previous section, are similar to a light switch being turned on. A stimulus starts
Portions from Chapter 6 CHAPTER 7. The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses. Chapter 7 Outline. and Supporting Cells
 CHAPTER 7 The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Chapter 7 Outline Neurons and Supporting Cells Activity in Axons The Synapse Acetylcholine as a Neurotransmitter Monoamines as Neurotransmitters Other
CHAPTER 7 The Nervous System: Neurons and Synapses Chapter 7 Outline Neurons and Supporting Cells Activity in Axons The Synapse Acetylcholine as a Neurotransmitter Monoamines as Neurotransmitters Other
Synaptic transmission
 Outline Synaptic transmission Sompol Tapechum M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand. sisth@mahidol.ac.th 2 Structure of synapse Modes of synaptic
Outline Synaptic transmission Sompol Tapechum M.D., Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand. sisth@mahidol.ac.th 2 Structure of synapse Modes of synaptic
Section: Chapter 5: Multiple Choice. 1. The structure of synapses is best viewed with a(n):
 Section: Chapter 5: Multiple Choice 1. The structure of synapses is best viewed with a(n): p.155 electron microscope. light microscope. confocal microscope. nissle-stained microscopic procedure. 2. Electron
Section: Chapter 5: Multiple Choice 1. The structure of synapses is best viewed with a(n): p.155 electron microscope. light microscope. confocal microscope. nissle-stained microscopic procedure. 2. Electron
3.E.2 Continued. This is the essential knowledge statement from the curriculum framework. Detect---process--- response
 Nervous System: Part III What Happens at a Synapse? 3.E. Continued Animals have nervous systems that detect external and internal signals, transmit and integrate information, and produce responses. This
Nervous System: Part III What Happens at a Synapse? 3.E. Continued Animals have nervous systems that detect external and internal signals, transmit and integrate information, and produce responses. This
BIOL455 COMPARITIVE NEUROBIOLOGY LECTURE#7 DR. OLLIE HULME! FALL 2010! UBC
 BIOL455 COMPARITIVE NEUROBIOLOGY LECTURE#7 DR. OLLIE HULME! FALL 2010! UBC Days: MWF, 12-1, room 201! Same old details! Ollieʼs Office hours:! Fri 1.30-4.30pm (may change)! room 3308 Biosciences! Lindsayʼs
BIOL455 COMPARITIVE NEUROBIOLOGY LECTURE#7 DR. OLLIE HULME! FALL 2010! UBC Days: MWF, 12-1, room 201! Same old details! Ollieʼs Office hours:! Fri 1.30-4.30pm (may change)! room 3308 Biosciences! Lindsayʼs
NEUROCHEMISTRY Brief Review
 NEUROCHEMISTRY Brief Review UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL MBBS YEAR V SEMINAR VJ Temple 1 Membrane potential Membrane potential:
NEUROCHEMISTRY Brief Review UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL MBBS YEAR V SEMINAR VJ Temple 1 Membrane potential Membrane potential:
- Neurotransmitters Of The Brain -
 - Neurotransmitters Of The Brain - INTRODUCTION Synapsis: a specialized connection between two neurons that permits the transmission of signals in a one-way fashion (presynaptic postsynaptic). Types of
- Neurotransmitters Of The Brain - INTRODUCTION Synapsis: a specialized connection between two neurons that permits the transmission of signals in a one-way fashion (presynaptic postsynaptic). Types of
Ligand-Gated Ion Channels
 Ligand-Gated Ion Channels The Other Machines That Make It Possible... Topics I Introduction & Electrochemical Gradients Passive Membrane Properties Action Potentials Voltage-Gated Ion Channels Topics II
Ligand-Gated Ion Channels The Other Machines That Make It Possible... Topics I Introduction & Electrochemical Gradients Passive Membrane Properties Action Potentials Voltage-Gated Ion Channels Topics II
QUIZ YOURSELF COLOSSAL NEURON ACTIVITY
 QUIZ YOURSELF What are the factors that produce the resting potential? How is an action potential initiated and what is the subsequent flow of ions during the action potential? 1 COLOSSAL NEURON ACTIVITY
QUIZ YOURSELF What are the factors that produce the resting potential? How is an action potential initiated and what is the subsequent flow of ions during the action potential? 1 COLOSSAL NEURON ACTIVITY
Chapter 5 subtitles GABAergic synaptic transmission
 CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND Chapter 5 subtitles GABAergic synaptic transmission INTRODUCTION (2:57) In this fifth chapter, you will learn how the binding of the GABA neurotransmitter to
CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND Chapter 5 subtitles GABAergic synaptic transmission INTRODUCTION (2:57) In this fifth chapter, you will learn how the binding of the GABA neurotransmitter to
Ch. 45 Continues (Have You Read Ch. 45 yet?) u Central Nervous System Synapses - Synaptic functions of neurons - Information transmission via nerve
 Ch. 45 Continues (Have You Read Ch. 45 yet?) u Central Nervous System Synapses - Synaptic functions of neurons - Information transmission via nerve impulses - Impulse may be blocked in its transmission
Ch. 45 Continues (Have You Read Ch. 45 yet?) u Central Nervous System Synapses - Synaptic functions of neurons - Information transmission via nerve impulses - Impulse may be blocked in its transmission
Synaptic Transmission: Ionic and Metabotropic
 Synaptic Transmission: Ionic and Metabotropic D. Purves et al. Neuroscience (Sinauer Assoc.) Chapters 5, 6, 7. C. Koch. Biophysics of Computation (Oxford) Chapter 4. J.G. Nicholls et al. From Neuron to
Synaptic Transmission: Ionic and Metabotropic D. Purves et al. Neuroscience (Sinauer Assoc.) Chapters 5, 6, 7. C. Koch. Biophysics of Computation (Oxford) Chapter 4. J.G. Nicholls et al. From Neuron to
Psych 181: Dr. Anagnostaras
 Psych 181: Dr. Anagnostaras Lecture 5 Synaptic Transmission Introduction to synaptic transmission Synapses (Gk., to clasp or join) Site of action of most psychoactive drugs 6.5 1 Synapses Know basic terminology:
Psych 181: Dr. Anagnostaras Lecture 5 Synaptic Transmission Introduction to synaptic transmission Synapses (Gk., to clasp or join) Site of action of most psychoactive drugs 6.5 1 Synapses Know basic terminology:
Lojayn Salah. Razan Aburumman. Faisal Muhammad
 20 Lojayn Salah Razan Aburumman Faisal Muhammad Note: I tried to include everything that's important from the doctor's slides but you can refer back to them after studying this sheet.. After you read this
20 Lojayn Salah Razan Aburumman Faisal Muhammad Note: I tried to include everything that's important from the doctor's slides but you can refer back to them after studying this sheet.. After you read this
TA Review. Neuronal Synapses. Steve-Felix Belinga Neuronal synapse & Muscle
 TA Review Steve-Felix Belinga sbelinga@wustl.edu Neuronal synapse & Muscle Neuronal Synapses 1 Things you should know beyond the obvious stuff 1. Differences between ionotropic and metabotropic receptors.
TA Review Steve-Felix Belinga sbelinga@wustl.edu Neuronal synapse & Muscle Neuronal Synapses 1 Things you should know beyond the obvious stuff 1. Differences between ionotropic and metabotropic receptors.
Basics of Pharmacology
 Basics of Pharmacology Pekka Rauhala Transmed 2013 What is pharmacology? Pharmacology may be defined as the study of the effects of drugs on the function of living systems Pharmacodynamics The mechanism(s)
Basics of Pharmacology Pekka Rauhala Transmed 2013 What is pharmacology? Pharmacology may be defined as the study of the effects of drugs on the function of living systems Pharmacodynamics The mechanism(s)
Neurons: Structure and communication
 Neurons: Structure and communication http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/gall1.html Common Components of a Neuron Dendrites Input, receives neurotransmitters Soma Processing, decision Axon Transmits
Neurons: Structure and communication http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/gall1.html Common Components of a Neuron Dendrites Input, receives neurotransmitters Soma Processing, decision Axon Transmits
BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES
 BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES CHAPTER 3 1 LEARNING GOALS Discuss how the nervous system communicates internally. Describe the structure and function of neurons Describe how the neuron transmits information Describe
BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES CHAPTER 3 1 LEARNING GOALS Discuss how the nervous system communicates internally. Describe the structure and function of neurons Describe how the neuron transmits information Describe
1. What are the two basic types of cells in the nervous system? Neurons and Glial Cells
 Biological Psychology Basic Structure of a Neuron 1. What are the two basic types of cells in the nervous system? Neurons and Glial Cells a. Cells that process incoming signals and respond by sending out
Biological Psychology Basic Structure of a Neuron 1. What are the two basic types of cells in the nervous system? Neurons and Glial Cells a. Cells that process incoming signals and respond by sending out
Neuropharmacology NOTES
 Neuropharmacology NOTES Contents Topic Page # Lecture 1- Intro to Neurochemical Transmission & Neuromodulation 2 Lecture 2- Serotonin & Noradrenaline 7 Lecture 3- Acetylcholine & Dopamine 14 Lecture 4-
Neuropharmacology NOTES Contents Topic Page # Lecture 1- Intro to Neurochemical Transmission & Neuromodulation 2 Lecture 2- Serotonin & Noradrenaline 7 Lecture 3- Acetylcholine & Dopamine 14 Lecture 4-
NEURONS COMMUNICATE WITH OTHER CELLS AT SYNAPSES 34.3
 NEURONS COMMUNICATE WITH OTHER CELLS AT SYNAPSES 34.3 NEURONS COMMUNICATE WITH OTHER CELLS AT SYNAPSES Neurons communicate with other neurons or target cells at synapses. Chemical synapse: a very narrow
NEURONS COMMUNICATE WITH OTHER CELLS AT SYNAPSES 34.3 NEURONS COMMUNICATE WITH OTHER CELLS AT SYNAPSES Neurons communicate with other neurons or target cells at synapses. Chemical synapse: a very narrow
Receptors and Drug Action. Dr. Subasini Pharmacology Department Ishik University, Erbil
 Receptors and Drug Action Dr. Subasini Pharmacology Department Ishik University, Erbil Receptors and Drug Action Receptor Receptor is defined as a macromolecule or binding site located on the surface or
Receptors and Drug Action Dr. Subasini Pharmacology Department Ishik University, Erbil Receptors and Drug Action Receptor Receptor is defined as a macromolecule or binding site located on the surface or
Nervous System. Nervous system cells. Transmission of a signal 2/27/2015. Neuron
 Nervous System 2007-2008 signal direction Neuron a nerve cell Nervous system cells dendrites axon cell body Structure fits function many entry points for signal one path out transmits signal signal direction
Nervous System 2007-2008 signal direction Neuron a nerve cell Nervous system cells dendrites axon cell body Structure fits function many entry points for signal one path out transmits signal signal direction
NEURAL TISSUE (NEUROPHYSIOLOGY) PART I (A): NEURONS & NEUROGLIA
 PART I (A): NEURONS & NEUROGLIA Neural Tissue Contains 2 kinds of cells: neurons: cells that send and receive signals neuroglia (glial cells): cells that support and protect neurons Neuron Types Sensory
PART I (A): NEURONS & NEUROGLIA Neural Tissue Contains 2 kinds of cells: neurons: cells that send and receive signals neuroglia (glial cells): cells that support and protect neurons Neuron Types Sensory
Lec 2b Structure and Function of Cells. Cogs17 Cognitive Neuroscience UCSD
 Lec 2b Structure and Function of Cells Cogs17 Cognitive Neuroscience UCSD THE SYNAPSE Communication between cells VESICLE Double lipid membrane NTs Exocytosis VESICLE Exocytosis Double lipid membrane
Lec 2b Structure and Function of Cells Cogs17 Cognitive Neuroscience UCSD THE SYNAPSE Communication between cells VESICLE Double lipid membrane NTs Exocytosis VESICLE Exocytosis Double lipid membrane
BIPN140 Lecture 8: Synaptic Transmission II
 BIPN140 Lecture 8: Synaptic Transmission II 1. Postsynaptic Receptors: Metabotropic & Ionotropic 2. Postsynaptic Responses (Postsynaptic Potentials, PSPs) 3. Neurotransmitters Su (FA16) Chemical Synapse:
BIPN140 Lecture 8: Synaptic Transmission II 1. Postsynaptic Receptors: Metabotropic & Ionotropic 2. Postsynaptic Responses (Postsynaptic Potentials, PSPs) 3. Neurotransmitters Su (FA16) Chemical Synapse:
Division Ave. High School AP Biology. cell body. signal direction
 signal direction Nervous system cells Neuron a nerve cell dendrites myelin sheath axon cell body dendrite cell body axon Structure fits function many entry points for signal one path out transmits signal
signal direction Nervous system cells Neuron a nerve cell dendrites myelin sheath axon cell body dendrite cell body axon Structure fits function many entry points for signal one path out transmits signal
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology 1 Lecture 3. Synaptic Transmission p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology 1 Lecture 3. Synaptic Transmission p. 1 Terms you should know: synapse, neuromuscular junction (NMJ), pre-synaptic, post-synaptic, synaptic cleft, acetylcholine (ACh), acetylcholine
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology 1 Lecture 3. Synaptic Transmission p. 1 Terms you should know: synapse, neuromuscular junction (NMJ), pre-synaptic, post-synaptic, synaptic cleft, acetylcholine (ACh), acetylcholine
Targets of Psychopharmacological Drug Action
 Targets of Psychopharmacological Drug Action (page 33 in syllabus) Stephen M. Stahl, MD, PhD Adjunct Professor, Department of Psychiatry University of California, San Diego School of Medicine Honorary
Targets of Psychopharmacological Drug Action (page 33 in syllabus) Stephen M. Stahl, MD, PhD Adjunct Professor, Department of Psychiatry University of California, San Diego School of Medicine Honorary
Neuron types and Neurotransmitters
 Neuron types and Neurotransmitters Faisal I. Mohammed. PhD, MD University of Jordan 1 Transmission of Receptor Information to the Brain the larger the nerve fiber diameter the faster the rate of transmission
Neuron types and Neurotransmitters Faisal I. Mohammed. PhD, MD University of Jordan 1 Transmission of Receptor Information to the Brain the larger the nerve fiber diameter the faster the rate of transmission
11/8/16. Cell Signaling Mechanisms. Dr. Abercrombie 11/8/2016. Principal Parts of Neurons A Signal Processing Computer
 Cell Signaling Mechanisms Dr. Abercrombie 11/8/2016 Principal Parts of Neurons A Signal Processing Computer A Multitude of Synapses and Synaptic Actions Summation/Synaptic Integration 1 The Synapse Signal
Cell Signaling Mechanisms Dr. Abercrombie 11/8/2016 Principal Parts of Neurons A Signal Processing Computer A Multitude of Synapses and Synaptic Actions Summation/Synaptic Integration 1 The Synapse Signal
Notes are online at The Neuron
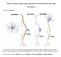 Notes are online at http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/~clovett/neuronotescogs17.pdf A. What is a neuron? The Neuron 1. A neuron is a type of cell that receives and transmits information in the Central Nervous System
Notes are online at http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/~clovett/neuronotescogs17.pdf A. What is a neuron? The Neuron 1. A neuron is a type of cell that receives and transmits information in the Central Nervous System
CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY
 CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND 4. SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION II: GLUTAMATERGIC TRANSMISSION Video 4-1: Observations and glutamate receptor channels Synaptic transmission II 1 Constance Hammond Observation
CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND 4. SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION II: GLUTAMATERGIC TRANSMISSION Video 4-1: Observations and glutamate receptor channels Synaptic transmission II 1 Constance Hammond Observation
Lecture 14. Insect nerve system (II)
 Lecture 14. Insect nerve system (II) Structures (Anatomy) Cells Anatomy How NS functions Signal transduction Signal transmission Overview More on neurons: ions, ion channel, ligand receptor Signal transduction:
Lecture 14. Insect nerve system (II) Structures (Anatomy) Cells Anatomy How NS functions Signal transduction Signal transmission Overview More on neurons: ions, ion channel, ligand receptor Signal transduction:
NEUROTRANSMITTERS, POSSIBLE SITES OF ACTIONS, AND DRUG INFLUENCES. Prof. K. Chilaka Prof. P.c. Unekwe Dr. Eyibe Michael I.
 NEUROTRANSMITTERS, POSSIBLE SITES OF ACTIONS, AND DRUG INFLUENCES Prof. K. Chilaka Prof. P.c. Unekwe Dr. Eyibe Michael I. Abstract Neurotransmitter, also known as chemical messengeris enodegenons chemical
NEUROTRANSMITTERS, POSSIBLE SITES OF ACTIONS, AND DRUG INFLUENCES Prof. K. Chilaka Prof. P.c. Unekwe Dr. Eyibe Michael I. Abstract Neurotransmitter, also known as chemical messengeris enodegenons chemical
LESSON 3.2 WORKBOOK How do our neurons communicate with each other?
 LESSON 3.2 WORKBOOK How do our neurons communicate with each other? This lesson introduces you to how one neuron communicates with another neuron during the process of synaptic transmission. In this lesson
LESSON 3.2 WORKBOOK How do our neurons communicate with each other? This lesson introduces you to how one neuron communicates with another neuron during the process of synaptic transmission. In this lesson
Synapses and Neurotransmitters
 Synapses and Neurotransmitters Action Potentials We have been talking about action potentials and how they allow an electrical impulse to travel from the dendrites to the end plates of a neuron. These
Synapses and Neurotransmitters Action Potentials We have been talking about action potentials and how they allow an electrical impulse to travel from the dendrites to the end plates of a neuron. These
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling The Neuron is the functional unit of the nervous system. Neurons are composed of a cell body, which contains the nucleus and organelles; Dendrites which are extensions
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling The Neuron is the functional unit of the nervous system. Neurons are composed of a cell body, which contains the nucleus and organelles; Dendrites which are extensions
Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important
Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important
Synaptic Transmission
 Synaptic Transmission Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction Synaptic transmission involves the release
Synaptic Transmission Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction Synaptic transmission involves the release
Synapse. 1. Presynaptic Terminal Button 2. Postsynaptic Membrane 3. Vesicles 4. Synaptic Cleft 5. Neurotransmitters 6.
 Synapse 1. Presynaptic Terminal Button 2. Postsynaptic Membrane 3. Vesicles 4. Synaptic Cleft 5. Neurotransmitters 6. Receptor Sites For communication between neurons to occur, an electrical impulse must
Synapse 1. Presynaptic Terminal Button 2. Postsynaptic Membrane 3. Vesicles 4. Synaptic Cleft 5. Neurotransmitters 6. Receptor Sites For communication between neurons to occur, an electrical impulse must
IBRO CIHR & UNESCO ADVANCED BEHVIOURAL NEUROSCEINCE SCHOOL KENYA 2008
 IBRO CIHR & UNESCO ADVANCED BEHVIOURAL NEUROSCEINCE SCHOOL KENYA 2008 SYNAPTIC FUNCTION & DRUG ACTION Associate Professor Laurie Kellaway Faculty of Health Sciences University of Cape Town WHAT DOES A
IBRO CIHR & UNESCO ADVANCED BEHVIOURAL NEUROSCEINCE SCHOOL KENYA 2008 SYNAPTIC FUNCTION & DRUG ACTION Associate Professor Laurie Kellaway Faculty of Health Sciences University of Cape Town WHAT DOES A
Cogs 107b Systems Neuroscience lec9_ neuromodulators and drugs of abuse principle of the week: functional anatomy
 Cogs 107b Systems Neuroscience www.dnitz.com lec9_02042010 neuromodulators and drugs of abuse principle of the week: functional anatomy Professor Nitz circa 1986 neurotransmitters: mediating information
Cogs 107b Systems Neuroscience www.dnitz.com lec9_02042010 neuromodulators and drugs of abuse principle of the week: functional anatomy Professor Nitz circa 1986 neurotransmitters: mediating information
Neurons have cell membranes that separate them from the environment outside the neuron.
 Neural Communication Lecture 11 A. Resting Potential In this section, we will consider the basic unit of the nervous system the neuron and how neurons communicate with each other. The story of neural communication
Neural Communication Lecture 11 A. Resting Potential In this section, we will consider the basic unit of the nervous system the neuron and how neurons communicate with each other. The story of neural communication
Omar Ismail. Dana Almanzalji. Faisal Mohammad
 11 Omar Ismail Dana Almanzalji Faisal Mohammad Neuronal classification: Neurons are responsible for transmitting the action potential to the brain. The speed at which the action potential is transmitted
11 Omar Ismail Dana Almanzalji Faisal Mohammad Neuronal classification: Neurons are responsible for transmitting the action potential to the brain. The speed at which the action potential is transmitted
Communication Between Neurons *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46503 1 Communication Between Neurons * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m46503 1 Communication Between Neurons * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed.,
 Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Neurochemistry 2. Loewi s experiment
 Neurochemistry 2 Loewi s experiment Cengage Learning 2016 AP reaches the axon terminal and activates voltage-gated Ca++ channels (3 major classes). Ca++ influx results in exocytosis of neurotransmitters
Neurochemistry 2 Loewi s experiment Cengage Learning 2016 AP reaches the axon terminal and activates voltage-gated Ca++ channels (3 major classes). Ca++ influx results in exocytosis of neurotransmitters
The Nervous System. Chapter 4. Neuron 3/9/ Components of the Nervous System
 Chapter 4 The Nervous System 1. Components of the Nervous System a. Nerve cells (neurons) Analyze and transmit information Over 100 billion neurons in system Four defined regions Cell body Dendrites Axon
Chapter 4 The Nervous System 1. Components of the Nervous System a. Nerve cells (neurons) Analyze and transmit information Over 100 billion neurons in system Four defined regions Cell body Dendrites Axon
Notes: Synapse. Overview. PSYC Summer Professor Claffey PDF. Conversion from an signal to a signal - electrical signal is the
 PSYC 170 - Summer 2013 - Professor Claffey Notes: Synapse PDF Overview Conversion from an signal to a signal - electrical signal is the - chemical signal is the Presynaptic - refers to that sends/receives
PSYC 170 - Summer 2013 - Professor Claffey Notes: Synapse PDF Overview Conversion from an signal to a signal - electrical signal is the - chemical signal is the Presynaptic - refers to that sends/receives
What effect would an AChE inhibitor have at the neuromuscular junction?
 CASE 4 A 32-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician s office with difficulty chewing food. She states that when she eats certain foods that require a significant amount of chewing (meat),
CASE 4 A 32-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician s office with difficulty chewing food. She states that when she eats certain foods that require a significant amount of chewing (meat),
Action potential. Definition: an all-or-none change in voltage that propagates itself down the axon
 Action potential Definition: an all-or-none change in voltage that propagates itself down the axon Action potential Definition: an all-or-none change in voltage that propagates itself down the axon Naturally
Action potential Definition: an all-or-none change in voltage that propagates itself down the axon Action potential Definition: an all-or-none change in voltage that propagates itself down the axon Naturally
Synaptic Transmission
 Synaptic Transmission Postsynaptic Mechanisms Synapses electrical and chemical Part I Neurotransmitters categories and life cycle Neurotransmitters examples and postsynaptic effects Pathology Part II Neurotransmitter
Synaptic Transmission Postsynaptic Mechanisms Synapses electrical and chemical Part I Neurotransmitters categories and life cycle Neurotransmitters examples and postsynaptic effects Pathology Part II Neurotransmitter
Receptors Families. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Receptors Families Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Receptor Families 1. Ligand-gated ion channels 2. G protein coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-linked
Receptors Families Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Receptor Families 1. Ligand-gated ion channels 2. G protein coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-linked
Cell communication. Gated ion channels. Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open
 increase decrease Cell communication Gated ion channels Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open Triggered by: potential change, chemical binding, temperature change, stretching 1 Voltage-Gated
increase decrease Cell communication Gated ion channels Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open Triggered by: potential change, chemical binding, temperature change, stretching 1 Voltage-Gated
Cell communication. Gated ion channels. Voltage-Gated Na + Channel. Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open
 increase decrease Cell communication Gated ion channels Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open Voltage-Gated Na + Channel Activation gate ECF Triggered by: change, chemical binding, temperature
increase decrease Cell communication Gated ion channels Allow specific ions to pass only when gates are open Voltage-Gated Na + Channel Activation gate ECF Triggered by: change, chemical binding, temperature
Chapter 24 Chemical Communications Neurotransmitters & Hormones
 Chapter 24 Chemical Communications Neurotransmitters & Hormones 1 Chemical Communication Terms and definitions: Neuron: A nerve cell. Neurotransmitter: A chemical messenger between a neuron and another
Chapter 24 Chemical Communications Neurotransmitters & Hormones 1 Chemical Communication Terms and definitions: Neuron: A nerve cell. Neurotransmitter: A chemical messenger between a neuron and another
CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY
 CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND 5. SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION II: GABAERGIC TRANSMISSION Video 5-1: GABA A receptor-mediated current and potential changes GABAergic synaptic transmission 1 Constance
CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND 5. SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION II: GABAERGIC TRANSMISSION Video 5-1: GABA A receptor-mediated current and potential changes GABAergic synaptic transmission 1 Constance
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE BMP-218 November 4, 2014 DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary divisions: 1. CNS - Central Nervous System (Brain + Spinal Cord)
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE BMP-218 November 4, 2014 DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary divisions: 1. CNS - Central Nervous System (Brain + Spinal Cord)
Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Nervous system development Part of the ectoderm
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Nervous system development Part of the ectoderm
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. Homeostasis Strand
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Homeostasis Strand Introduction In general, a nervous system has three overlapping functions : 1. Sensory input conduction of signals from sensory receptors to integration centres 2.
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Homeostasis Strand Introduction In general, a nervous system has three overlapping functions : 1. Sensory input conduction of signals from sensory receptors to integration centres 2.
Summarized by B.-W. Ku, E. S. Lee, and B.-T. Zhang Biointelligence Laboratory, Seoul National University.
 Chapter 2. The Cellular l and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 3 rd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2008. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Chapter 2. The Cellular l and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 3 rd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2008. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Na + K + pump. The beauty of the Na + K + pump. Cotransport. The setup Cotransport the result. Found along the plasma membrane of all cells.
 The beauty of the Na + K + pump Na + K + pump Found along the plasma membrane of all cells. Establishes gradients, controls osmotic effects, allows for cotransport Nerve cells have a Na + K + pump and
The beauty of the Na + K + pump Na + K + pump Found along the plasma membrane of all cells. Establishes gradients, controls osmotic effects, allows for cotransport Nerve cells have a Na + K + pump and
The Nervous System Mark Stanford, Ph.D.
 The Nervous System Functional Neuroanatomy and How Neurons Communicate Mark Stanford, Ph.D. Santa Clara Valley Health & Hospital System Addiction Medicine and Therapy Services The Nervous System In response
The Nervous System Functional Neuroanatomy and How Neurons Communicate Mark Stanford, Ph.D. Santa Clara Valley Health & Hospital System Addiction Medicine and Therapy Services The Nervous System In response
Introduction to CNS 1
 Introduction to CNS 1 Types of ion channels 1- voltage-gated 2-legends-gated Voltage-gated channel A voltage Sensor component of the protein controls the gating (broken arrow) of the channel. Voltage-gated
Introduction to CNS 1 Types of ion channels 1- voltage-gated 2-legends-gated Voltage-gated channel A voltage Sensor component of the protein controls the gating (broken arrow) of the channel. Voltage-gated
9/28/2016. Neuron. Multipolar Neuron. Astrocytes Exchange Materials With Neurons. Glia or Glial Cells ( supporting cells of the nervous system)
 Neuron Multipolar Neuron https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lw-psbnu5xago to :38 Glia or Glial Cells ( supporting cells of the nervous system) 10X more numerous than neurons but one-tenth the size make up
Neuron Multipolar Neuron https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lw-psbnu5xago to :38 Glia or Glial Cells ( supporting cells of the nervous system) 10X more numerous than neurons but one-tenth the size make up
Function of the Nervous System
 Nervous System Function of the Nervous System Receive sensory information, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands to form a response Composed of neurons (functional unit of the nervous system)
Nervous System Function of the Nervous System Receive sensory information, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands to form a response Composed of neurons (functional unit of the nervous system)
11/10/16. Neurotransmitters and their Receptors. Professor Abercrombie, Chapter 6, Neuroscience, 4 th ed, D. Purves et el.
 Chapter 6, Neuroscience, 4 th ed, D. Purves et el. Neurotransmitters and their Receptors Professor Abercrombie, 2016 Events from neurotransmitter release to postsynaptic excitation or inhibition Sequence
Chapter 6, Neuroscience, 4 th ed, D. Purves et el. Neurotransmitters and their Receptors Professor Abercrombie, 2016 Events from neurotransmitter release to postsynaptic excitation or inhibition Sequence
Chapter 45: Synapses Transmission of Nerve Impulses Between Neurons. Chad Smurthwaite & Jordan Shellmire
 Chapter 45: Synapses Transmission of Nerve Impulses Between Neurons Chad Smurthwaite & Jordan Shellmire The Chemical Synapse The most common type of synapse used for signal transmission in the central
Chapter 45: Synapses Transmission of Nerve Impulses Between Neurons Chad Smurthwaite & Jordan Shellmire The Chemical Synapse The most common type of synapse used for signal transmission in the central
Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition
 Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga,, R. B. Ivry,, and G. R. Mangun,, Norton, 2002. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
Chapter 2. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga,, R. B. Ivry,, and G. R. Mangun,, Norton, 2002. Summarized by B.-W. Ku,
At a Glance. Background Information. Lesson 3 Drugs Change the Way Neurons Communicate
 Lesson 3 Drugs Change the Way Neurons Communicate Overview Students build upon their understanding of neurotransmission by learning how different drugs of abuse disrupt communication between neurons. Students
Lesson 3 Drugs Change the Way Neurons Communicate Overview Students build upon their understanding of neurotransmission by learning how different drugs of abuse disrupt communication between neurons. Students
Anatomy of a Neuron. Copyright 2000 by BSCS and Videodiscovery, Inc. Permission granted for classroom use. Master 2.1
 Anatomy of a Neuron Master 2.1 Neurons Interact With Other Neurons Through Synapses Master 2.2 How Do Neurons Communicate? 1 2 3 4 5 6 Master 2.3 Neurons Communicate by Neurotransmission Neurons communicate
Anatomy of a Neuron Master 2.1 Neurons Interact With Other Neurons Through Synapses Master 2.2 How Do Neurons Communicate? 1 2 3 4 5 6 Master 2.3 Neurons Communicate by Neurotransmission Neurons communicate
Synaptic Integration
 Synaptic Integration 3 rd January, 2017 Touqeer Ahmed PhD Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Excitatory Synaptic Actions Excitatory Synaptic Action
Synaptic Integration 3 rd January, 2017 Touqeer Ahmed PhD Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Excitatory Synaptic Actions Excitatory Synaptic Action
Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3e. Chapter 4: The action potential
 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3e Chapter 4: The action potential Introduction Action Potential in the Nervous System Conveys information over long distances Action potential Initiated in the axon
Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3e Chapter 4: The action potential Introduction Action Potential in the Nervous System Conveys information over long distances Action potential Initiated in the axon
Learning Objectives. How do drugs work? Mechanisms of Drug Action. Liam Anderson Dept Pharmacology & Clinical Pharmacology
 How do drugs work? Mechanisms of Drug Action Liam Anderson Dept Pharmacology & Clinical Pharmacology Learning Objectives Describe the potential drug targets within a human body. Describe the role of receptors,
How do drugs work? Mechanisms of Drug Action Liam Anderson Dept Pharmacology & Clinical Pharmacology Learning Objectives Describe the potential drug targets within a human body. Describe the role of receptors,
Biol 219 Lec 12 Fall 2016
 Cell-to-Cell: Neurons Communicate at Synapses Electrical synapses pass electrical signals through gap junctions Signal can be bi-directional Synchronizes the activity of a network of cells Primarily in
Cell-to-Cell: Neurons Communicate at Synapses Electrical synapses pass electrical signals through gap junctions Signal can be bi-directional Synchronizes the activity of a network of cells Primarily in
Autonomic Nervous System. Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry
 Autonomic Nervous System Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Peripheral Nervous System A. Sensory Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous System 1. Sympathetic Nervous
Autonomic Nervous System Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Peripheral Nervous System A. Sensory Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous System 1. Sympathetic Nervous
Communication within a Neuron
 Neuronal Communication, Ph.D. Communication within a Neuron Measuring Electrical Potentials of Axons The Membrane Potential The Action Potential Conduction of the Action Potential 1 The withdrawal reflex
Neuronal Communication, Ph.D. Communication within a Neuron Measuring Electrical Potentials of Axons The Membrane Potential The Action Potential Conduction of the Action Potential 1 The withdrawal reflex
1. (1 pt) At the equilibrium potential of an ion, what two things are equal? Electrical potential (voltage) and chemical potential (concentration)
 MIDERM REVIEW QUESIONS: IO 3411 (hese are questions from 3 of the previous years midterms) 1. (1 pt) t the equilibrium potential of an ion, what two things are equal? Electrical potential (voltage) and
MIDERM REVIEW QUESIONS: IO 3411 (hese are questions from 3 of the previous years midterms) 1. (1 pt) t the equilibrium potential of an ion, what two things are equal? Electrical potential (voltage) and
Synapses and Neurotransmitters.
 Synapses and Neurotransmitters Loai.physiology@yahoo.com Communication Between Neurons Synapse: A specialized site of contact, and transmission of information between a neuron and an effector cell Anterior
Synapses and Neurotransmitters Loai.physiology@yahoo.com Communication Between Neurons Synapse: A specialized site of contact, and transmission of information between a neuron and an effector cell Anterior
Thinking Outside the Box: Prescribing by Synthesis & Integration
 Thinking Outside the Box: Prescribing by Synthesis & Integration Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC Linfield College School of Nursing Portland DBT Program AGENDA Neuroanatomy and neurophysiology review
Thinking Outside the Box: Prescribing by Synthesis & Integration Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC Linfield College School of Nursing Portland DBT Program AGENDA Neuroanatomy and neurophysiology review
Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer
 Name Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Period Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer 1. What is
Name Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Period Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer 1. What is
Neurotransmitters. Chemical transmission of a nerve signal by neurotransmitters at a synapse
 Neurotransmitters A chemical released by one neuron that affects another neuron or an effector organ (e.g., muscle, gland, blood vessel). Neurotransmitters are small molecules that serve as messengers
Neurotransmitters A chemical released by one neuron that affects another neuron or an effector organ (e.g., muscle, gland, blood vessel). Neurotransmitters are small molecules that serve as messengers
Sarah Jaar Marah Al-Darawsheh
 22 Sarah Jaar Marah Al-Darawsheh Faisal Mohammad Receptors can be membrane proteins (for water-soluble hormones/ligands) or intracellular (found in the cytosol or nucleus and bind to DNA, for lipid-soluble
22 Sarah Jaar Marah Al-Darawsheh Faisal Mohammad Receptors can be membrane proteins (for water-soluble hormones/ligands) or intracellular (found in the cytosol or nucleus and bind to DNA, for lipid-soluble
3) Most of the organelles in a neuron are located in the A) dendritic region. B) axon hillock. C) axon. D) cell body. E) axon terminals.
 Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Multiple-Choice Questions 1) A simple nervous system A) must include chemical senses, mechanoreception, and vision. B) includes a minimum of 12 ganglia. C) has
Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Multiple-Choice Questions 1) A simple nervous system A) must include chemical senses, mechanoreception, and vision. B) includes a minimum of 12 ganglia. C) has
Introduction to Neurobiology
 Biology 240 General Zoology Introduction to Neurobiology Nervous System functions: communication of information via nerve signals integration and processing of information control of physiological and
Biology 240 General Zoology Introduction to Neurobiology Nervous System functions: communication of information via nerve signals integration and processing of information control of physiological and
Brain Neurotransmitters
 Brain Neurotransmitters Brain neurotransmitters Chemical substances released by electrical impulses into the synaptic cleft from synaptic vesicles of presynaptic membrane Diffuses to the postsynaptic membrane
Brain Neurotransmitters Brain neurotransmitters Chemical substances released by electrical impulses into the synaptic cleft from synaptic vesicles of presynaptic membrane Diffuses to the postsynaptic membrane
1. Name the two major divisions of the nervous system and list the organs within each. Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System
 CHAPTER 10: NERVOUS SYSTEM I OBJECTIVES 1. Name the two major divisions of the nervous system and list the organs within each. Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Cranial
CHAPTER 10: NERVOUS SYSTEM I OBJECTIVES 1. Name the two major divisions of the nervous system and list the organs within each. Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Cranial
