Supplementary Information
|
|
|
- Adela Lawson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Information 5-hydroxymethylcytosine-mediated epigenetic dynamics during postnatal neurodevelopment and aging By Keith E. Szulwach 1,8, Xuekun Li 1,8, Yujing Li 1, Chun-Xiao Song 2, Hao Wu 3, Qing Dai 2, Hasan Irier 1, Anup K. Upadhyay 4, Marla Gearing 5, Allan I. Levey 5, Aparna Vasanthakumar 6, Lucy A. Godley 6, Qiang Chang 7, Xiaodong Cheng 4, Chuan He 2, Peng Jin 1* Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.2959
2 Supplementary Table 1. Summary of sequencing data. This table provides a summary of the number of biological replicates used per sample as well as the total number of aligned and monoclonal reads per sample. Sequence data is accessible though NCBI GEO Accession Biological Replicates Total reads Aligned Monoclonal Mouse Brain P7.Cb wk.Cb yr.Cb P7.Hipp wk.Hipp yr.Hipp Input Mecp2-/y tm1.1bird Cb Human Cerebellum Male Cb Male Input Female Cb Female Input Rat Brain 6-8wk brainstem Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn
3 Supplementary Table 2. qpcr primer sets. This table shows the list of qpcr primer sets used for validation of 5-hmC enriched regions and qpcr of MeDIP DNA. Tissue Specific qpcr En2-FW En2-RV Nr2e1-FW Nr2e1-RV MeDIP qpcr Exph5-FW Exph5-RV Pip5k1b-FW Pip5k1b-RV Grin2c-FW Grin2c-RV Mapk12-FW Mapk12-RV BC FW BC RV Dgkg-FW Dgkg-RV Il16-FW Il16-RV Gabrd-FW Gabrd-RV Tesc-FW Tesc-RV St8sia5-FW St8sia5-RV Psd3-FW Psd3-RV Syt1-FW Syt1-RV CCACTCTGGCAGCACGAA TTTAGCCCGGTGAGCTTGTC CCCCCACACAAGTGGCTTT TCCCATCCCCCAGCTTTC TCAACCTGGGTGCACTTAACC AACATAGTGCTGTGTACAGTGGACAA TGCTCACCCCGCTTGTG AGGCTGATAAGATAAACAGGTCATCA TGCCTTCCCTGGTCACATC GGGTGTAGGGCTGAGTTTGAAT CCAAGGCTCTGGGATGATAGAG AGACATACAGGATCCTAGGCATTCA CTCAGGGCCCAGAGTTCGT GAATTGGGTTCTCTAGGAGGTAACTG CGTTCCCTCTCATTCGTTACG CAAACTGAGAAGTTAGGAGATCAAGGA ATGCTAGGAAGCTGTGATATGTGAA TGTCTTTGGCCATTTAGATCCA CCAGAAGGCATGGGAAGGTA TTATCCGCCTACAGCCTGATG TGTGAGTTGAACCAACCTTTGC TGTCATTGCTACATCGTAACTGTAATTT TGGCATCGAGGATTTTGGA CACCGTACATGACAATCAGAAAGTT CGTCTTTCCACCTCAGTTGATTC CCACACATTTGCTGAGAGAAGCT GAAATAGATAGTAGCAGGGTGGAGAAC GGATGCCCTTTGGACATAGC Repeat 5-hmC qpcr validation IAPLTR1a_Mm- FW GTGCAGCATGGTGTAGTGTAGCT IAPLTR1a_Mm- RV CCTACACAAACAAGCAAACAAATGA B1_Mus2-FW GCCCCGTTGGTAGAGACATG Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn
4 B1_Mus2-RV B1_Mus1-FW B1_Mus1-RV RSINE1-FW RSINE1-RV B4A-FW B4A-RV PB1D9-FW PB1D9-RV RLTR4_MMint-FW RLTR4_MMint-RV MER3-FW MER3-RV GSAT_MM-FW GSAT_MM-RV TCCCCTGGCTCTCAATGG CCCACCACAGCCTGTTATACTTC GGGTGCCTTTTGCACTCTTG GAATTGAACCCAGTCAGTCTTGGT CAAAATCCAATTTACAGAAGCTGCTA TGGGCGTCCCGTCTCA TGGAGGAGCTTTGGGTCTGA AGCGGCAGTGTCGAGGAA AACAAGGGAGGACTTGCATCTTAA GGCTAAGGGACAATATTCCATCA CCCCTTGACGGCAGTAGGT GAGGCAGGACCAAGCCTTTT CAAGCTATGCAGAAAGGACATCA GACGACTTGAAAAATGACGAAATC CATATTCCAGGTCCTTCAGTGTGC Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn
5 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1. The expression and quantification of 5-hmC during neurodevelopment and aging. a. Photomontage images showing the expression of 5- hmc in cerebellum across three different ages: P7 (left), 6-week (middle), and 1-year (right). b. Photomontage images showing the expression of 5-hmC in hippocampus across three different ages: P7 (left), 6-week (middle), and 1-year (right). c. Neural stem/progenitor cells (Nestin+) display either weak 5-hmC or a complete lack of 5-hmC. Scale bar: 50 um. d. Dot blot quantification of 5-hmC in cerebellum at P7, 6-week, and 1- year. Images are derived from the same blot and are representative of multiple independent blots. e. Dot blot quantification of 5-hmC in hippocampus at P7, 6-week, and 1-year. Images are derived from the same blot and are representative of multiple independent blots. Supplementary Figure 2. The expression of 5-hmC in the rostral migratory stream and olfactory bulb during neurodevelopment. At P7, the anterior region of the subventricular zone (SVZa) is active neurogenic, and SVZa-derived neural stem cells migrate towards olfactory bulb (OB) along the rostral migratory stream (RMS). Neural stem cells become more fate-committed along migration. In the RMS-OB, the majority of cells are TuJ1 positive, but still NeuN negative. a. Low 5-hmC intensity is observed in SVZa at P7. Upper: DAPI, middle: 5-hmc; lower: NeuN. b. 5-hmC is enriched in the granular cell layer, where neuronal cells become postmitotic and become mature (NeuN+). Left: 5-hmC, right: NeuN. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn
6 Supplementary Figure 3. Heatmap representation of input normalized 5-hmC signals in genome-wide binned (10kb) data in cerebellum and hippocampus at each age. Input normalized 5-hmC values per 10kb were determined at each age for each brain regions and clustered using an uncentered correlation with pairwise complete linkage (Cluster3.0). 5-hmC values are equally scaled for all chromosomes, and chromosome number is indicated above the appropriate heatmap. Supplementary Figure 4. Metagene analysis of 5-hmC read distributions. a. Read densities around all RefSeq transcripts summed in 10-bp bins centered on either TSS or TTS at each age in cerebellum. b. Read densities around all RefSeq transcripts summed in 10-bp bins centered on either TSS or TTS at each age in hippocampus. Supplementary Figure 5. Gene expression dependent 5-hmC densities in P7 and 6wk cerebellum. a. 5-hmC densities ±5kb of TSS and TTS shown separately for P7 and 6wk Cb as a function of expression level. mrna expression levels were determined by Affymetrix microarray and ranked in descending order by RMA normalized signal intensity. 5-hmC read densities are determined as the number of reads in 100bp bins normalized to the total number of reads in millions and divided by bin size. Scale is indicated in bottom right-hand corner b. The change in 5-hmC (Δ5hmC) ±5kb of TSS and TTS as a function of the change in gene expression (ΔExp). All genes detected by microarray were ranked based on their change in RMA normalized signal intensity, determined as 6wk - P7, and ranked in descending order. Δ5hmC is determined as the difference in normalized 5-hmC read densities (6wk - P7) described above. Indicated to Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn
7 the left are the regions corresponding to activated, unchanged, or repressed genes in 6wk Cb relative to P7 Cb. c. Quantification of values presented in b., summarizing average Δ5hmC values ±5kb of TSS and TTS for activated, unchanged, or repressed genes, as determined by ANOVA, Benjamini-Hochberg adjusted p-value threshold of <0.05 (n=3). d. The cumulative fraction of genes at or below a given Δ5hmC value, considering only intragenic Δ5hmC at activated, unchanged, or repressed genes. Supplementary Figure 6. MeDIP analysis at developmentally activated genes with increased intragenic 5-hmC. a. qpcr quantification of the fold change in 5-mC at ten 5-hmC regulated regions within genes that exhibit increased gene expression and increased 5-hmC in 6wk Cb relative to P7 Cb. Below the average O/E CpG dinucleotide frequency for the ten regions assayed is indicated. Shown to the right are four control regions. Two regions are within genes that do not exhibit altered expression and contain similar levels of 5-hmC enrichment (determined by 5-hmC peak p-value). The two regions to the far right are regions that do not exhibit 5-hmC enrichment at either age. Data were determined in two independent samples per age and are calibrated to a single P7 Cb sample, with fold-change calculated as 2^-ΔCt. b. Summary of genes in a. showing the average fold-change in 5-mC determined by MeDIP for genes exhibiting increased gene expression and increased 5-hmC in 6wk Cb relative to P7 Cb. Supplementary Figure 7. Depletion of 5-hmC on chrx in rat brain and human male and female cerebellum. a. Summary of rat chromosome-wide read densities showing depletion of 5-hmC on chrx, relative to autosomes. Normalized chromosome-wide read Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn
8 densities were compared to those expected by chance assuming reads were randomly distributed amongst chromosomes. Dotted line represents a value of 1, or no enrichment. b. Summary of human chromosome-wide read densities showing depletion of 5-hmC on chrx in male and female human cerebellum. Shown is average 5-hmC enrichment on all autosomes compared to the enrichment observed on chrx. Dotted line represents a value of 1, or no enrichment. c. Genomic view of 5-hmC in male and female mouse cerebellum at two genes escaping X-inactivation, Xist and Utx. Shown is a heatmap representation of normalized read coverage in 25bp windows. Supplementary Figure 8. Sequence motifs, GC content, and CpG frequency associated with 5-hmC-regulated regions in mouse cerebellum and hippocampus. a. For the union of all detected mouse DhMRs, the fractional GC content and the observed-to-expected (O/E) CpG frequency was determined and then compared to that of either CpG islands or randomly chosen genomic locations. b. For all detected regions enriched for 5-hmC in human cerebellum, the fractional GC content and the observed-to-expected (O/E) CpG frequency was determined and then compared to that of either CpG islands or randomly chosen genomic locations. c. Sequence motif associated with the top 50 (based on MACS p-value) cerebellum-specific DhMRs identified by MEME (E-value = 5.8e-7). d. Sequence motif associated with the top 50 (based on MACS p-value) hippocampusspecific DhMRs identified by MEME (E-value = 6.3e-16). Supplementary Figure 9. Examples of Dynamic and stable DhMRs in mouse cerebellum and Hippocampus. a. Genomic view of a P7 Dynamic DhMR in cerebellum Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn
9 demonstrating the presence of 5-hmC in P7 and subsequent loss at 6wk which is maintained through 1yr. b. Genomic view of a P7 Dynamic DhMR in hippocampus demonstrating the presence of 5-hmC in P7 and subsequent loss at 6wk which is maintained through 1yr. c. Genomic view of a Adult stable DhMR in cerebellum demonstrating the absence of 5-hmC in P7, but acquisition at 6wk and maintenance through 1yr. d. Genomic view of a Adult stable DhMR in hippocampus demonstrating the absence of 5-hmC in P7, but acquisition at 6wk and maintenance through 1yr. e. Genomic view of an Adult Dynamic DhMR in cerebellum demonstrating acquisition of 5-hmC from P7 to 6wk, but subsequent loss at 1yr. f. Genomic view of an Adult Dynamic DhMR in hippocampus demonstrating acquisition of 5-hmC from P7 to 6wk, but subsequent loss at 1yr. g. Genomic view of an DhMR specific to 1yr cerebellum demonstrating acquisition of 5-hmC at 1yr relative to both P7 and 6wk. h. Genomic view of an DhMR specific to 1yr hippocampus demonstrating acquisition of 5-hmC at 1yr relative to both P7 and 6wk. For all views, identified DhMRs are indicated by solid colored bars below the Input track. Supplementary Figure 10. qpcr validation of 5-hmC enrichment and dynamic regulation at major repeat classes. a. qpcr quantification showing enrichment of 5-hmC at five subtypes of SINEs, an LTR, and depletion of 5-hmC in major Satellite DNA in P7, 6wk, and 1yr cerebellum. b. qpcr quantification showing enrichment of 5-hmC at two subtypes of LTRs, SINEs, and depletion of 5-hmC in major Satellite DNA in P7, 6wk, and 1yr Hippocampus. Values are determined as the average of two independent samples by 2^-ΔCt, with dct calculated as the change in Ct value relative to input DNA. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn
10 Supplementary Figure 11. In vitro 5-mC hydroxylation by Tet1-CD is blocked by MeCP2- MBD. To test the effect of MeCP2-MBD (aa97-167) on Tet1-CD (aa ) mediated hydroxylation of 5-mC, full 5-mC DNA (corresponding to 68 pmoles 5-mC) was held constant and MeCP2-MBD was varied to produce molecular ratios (MeCP2- MBD to 5mC) of 1:4, 1:2, 1:1, 2.5:1, 5:1, and no MeCP2-MBD), while also keeping the total amount of protein in the reaction constant by supplementing decreasing amounts of MeCP2-MBD with BSA. 5-hmC was quantified by 5-hmC specific immunoblot as described above, relative to the BSA only/no MeCP2-MBD control (mean ± SEM, n=3). Shown below the x-axis is an immunoblot representative of replicates. Supplementary Figure 12. Summary of Tet family mrna expression levels in P7 and 6wk cerebellum. Shown is the RMA normalized average signal intensity at P7 and 6wk Cb determined by Affymetrix microarray (n=3, mean ± SEM). Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn
11 Supplementary Datasets Supplementary Dataset 1. P7 and 6 week Cerebellum gene expression data. This dataset contains Affymetrix GeneChip Mouse Exon 1.0 ST array data from P7 and 6wk Cerebellum. Supplementary Dataset 2. P7 Cerebellum DhMRs. This dataset contains DhMRs identified as enriched for 5-hmC by pairwise comparisons to 6wk and 1yr cerebellum as well as P7, 6wk, and 1yr hippocampus. Supplementary Dataset 3. 6 week Cerebellum DhMRs. This dataset contains DhMRs identified as enriched for 5-hmC by pairwise comparisons to P7 and 1yr cerebellum as well as P7, 6wk, and 1yr hippocampus. Supplementary Dataset 4. 1 year Cerebellum DhMRs. This dataset contains DhMRs identified as enriched for 5-hmC by pairwise comparisons to P7 and 6wk cerebellum as well as P7, 6wk, and 1yr hippocampus. Supplementary Dataset 5. P7 Hippocampus Cerebellum DhMRs. This dataset contains DhMRs identified as enriched for 5-hmC by pairwise comparisons to 6wk and 1yr hippocampus as well as P7, 6wk, and 1yr cerebellum. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn
12 Supplementary Dataset 6. 6 week Hippocampus DhMRs. This dataset contains DhMRs identified as enriched for 5-hmC by pairwise comparisons to P7 and 1yr hippocampus as well as P7, 6wk, and 1yr cerebellum. Supplementary Dataset 7. 1 year Hippocampus Cerebellum DhMRs. This dataset contains DhMRs identified as enriched for 5-hmC by pairwise comparisons to P7 and 6wk hippocampus as well as P7, 6wk, and 1yr cerebellum. Supplementary Dataset 8. Tissue specific, Stable, and Dynamic. This dataset contains cerebellum and hippocampus specific DhMRs as well as the Stable and Dynamic DhMRs summarized in Fig. 3. Supplementary Dataset 9. Human 5-hmC enriched regions. This dataset contains regions identified as enriched for 5-hmC in both human samples tested. Supplementary Dataset 10. Gene Ontology Analyses. This dataset contains GO analyses for 1.) genes exhibiting activated gene expression in 6wk Cb relative to P7 Cb also with 5- hmc enriched in 6wk Cb relative to P7 Cb ( Adult_activated_5hmC_GO ) 2.) genes with overlapping Adult dynamic DhMRs in both cerebellum and hippocampus ( Adult_dynamic_DhMR_GO ) 3.) genes with overlapping Adult stable DhMRs in both cerebellum and hippocampus ( Adult_stable_DhMR_GO ) and 4.) genes with overlapping 1yr specific DhMRs in both cerebellum and hippocampus ( 1yr_specific_DhMR_GO ). Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn
13 Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.2959
14 Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.2959
15 Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.2959
16 Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.2959
17 Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.2959
18 Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.2959
19 Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.2959
20 Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.2959
21 Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.2959
22 Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.2959
23 Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.2959
24 Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.2959
Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types. (a) Pearson correlation heatmap among open chromatin profiles of different
Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types. (a) Pearson correlation heatmap among open chromatin profiles of different
Supplementary Figure S1. Gene expression analysis of epidermal marker genes and TP63.
 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure S1. Gene expression analysis of epidermal marker genes and TP63. A. Screenshot of the UCSC genome browser from normalized RNAPII and RNA-seq ChIP-seq data
Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure S1. Gene expression analysis of epidermal marker genes and TP63. A. Screenshot of the UCSC genome browser from normalized RNAPII and RNA-seq ChIP-seq data
7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans.
 Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10866 a b 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Match No Match 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Turcan et al. Supplementary Fig.1 Concepts mapping H3K27 targets in EF CBX8 targets in EF H3K27 targets in ES SUZ12 targets in ES
doi:10.1038/nature10866 a b 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Match No Match 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Turcan et al. Supplementary Fig.1 Concepts mapping H3K27 targets in EF CBX8 targets in EF H3K27 targets in ES SUZ12 targets in ES
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Heatmap of GO terms for differentially expressed genes. The terms were hierarchically clustered using the GO term enrichment beta. Darker red, higher positive
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Heatmap of GO terms for differentially expressed genes. The terms were hierarchically clustered using the GO term enrichment beta. Darker red, higher positive
Figure S1A. Blood glucose levels in mice after glucose injection
 ## Figure S1A. Blood glucose levels in mice after glucose injection Blood glucose (mm/l) 25 2 15 1 5 # 15 3 6 3+3 Time after glucose injection (min) # Figure S1B. α-kg levels in mouse livers after glucose
## Figure S1A. Blood glucose levels in mice after glucose injection Blood glucose (mm/l) 25 2 15 1 5 # 15 3 6 3+3 Time after glucose injection (min) # Figure S1B. α-kg levels in mouse livers after glucose
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Effect of HSP90 inhibition on expression of endogenous retroviruses. (a) Inducible shrna-mediated Hsp90 silencing in mouse ESCs. Immunoblots of total cell extract expressing the
Supplementary Figure 1 Effect of HSP90 inhibition on expression of endogenous retroviruses. (a) Inducible shrna-mediated Hsp90 silencing in mouse ESCs. Immunoblots of total cell extract expressing the
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
Computational Analysis of UHT Sequences Histone modifications, CAGE, RNA-Seq
 Computational Analysis of UHT Sequences Histone modifications, CAGE, RNA-Seq Philipp Bucher Wednesday January 21, 2009 SIB graduate school course EPFL, Lausanne ChIP-seq against histone variants: Biological
Computational Analysis of UHT Sequences Histone modifications, CAGE, RNA-Seq Philipp Bucher Wednesday January 21, 2009 SIB graduate school course EPFL, Lausanne ChIP-seq against histone variants: Biological
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Assessment of sample purity and quality.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Assessment of sample purity and quality. (a) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of formaldehyde-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections from a human testis biopsy collected concurrently with
Supplementary Figure 1 Assessment of sample purity and quality. (a) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of formaldehyde-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections from a human testis biopsy collected concurrently with
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES: Supplementary Figure 1
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES: Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Glioblastoma 5hmC quantified by paired BS and oxbs treated DNA hybridized to Infinium DNA methylation arrays. Workflow depicts analytic
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES: Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Glioblastoma 5hmC quantified by paired BS and oxbs treated DNA hybridized to Infinium DNA methylation arrays. Workflow depicts analytic
Tissue of origin determines cancer-associated CpG island promoter hypermethylation patterns
 RESEARCH Open Access Tissue of origin determines cancer-associated CpG island promoter hypermethylation patterns Duncan Sproul 1,2, Robert R Kitchen 1,3, Colm E Nestor 1,2, J Michael Dixon 1, Andrew H
RESEARCH Open Access Tissue of origin determines cancer-associated CpG island promoter hypermethylation patterns Duncan Sproul 1,2, Robert R Kitchen 1,3, Colm E Nestor 1,2, J Michael Dixon 1, Andrew H
Table S1. Total and mapped reads produced for each ChIP-seq sample
 Tale S1. Total and mapped reads produced for each ChIP-seq sample Sample Total Reads Mapped Reads Col- H3K27me3 rep1 125662 1334323 (85.76%) Col- H3K27me3 rep2 9176437 7986731 (87.4%) atmi1a//c H3K27m3
Tale S1. Total and mapped reads produced for each ChIP-seq sample Sample Total Reads Mapped Reads Col- H3K27me3 rep1 125662 1334323 (85.76%) Col- H3K27me3 rep2 9176437 7986731 (87.4%) atmi1a//c H3K27m3
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/375/ra41/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Actin cytoskeletal remodeling with protrusion formation is essential for heart regeneration in Hippo-deficient mice
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/375/ra41/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Actin cytoskeletal remodeling with protrusion formation is essential for heart regeneration in Hippo-deficient mice
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1: f-i
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1: Comparisons of the biological replicates of ChIP-seq, Input and Bisulfite-seq. (a) Density plot of MeCP2 ChIP-seq genome coverage (calculated using tiled 15 bp windows) shows high
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1: Comparisons of the biological replicates of ChIP-seq, Input and Bisulfite-seq. (a) Density plot of MeCP2 ChIP-seq genome coverage (calculated using tiled 15 bp windows) shows high
Results. Abstract. Introduc4on. Conclusions. Methods. Funding
 . expression that plays a role in many cellular processes affecting a variety of traits. In this study DNA methylation was assessed in neuronal tissue from three pigs (frontal lobe) and one great tit (whole
. expression that plays a role in many cellular processes affecting a variety of traits. In this study DNA methylation was assessed in neuronal tissue from three pigs (frontal lobe) and one great tit (whole
Broad Integration of Expression Maps and Co-Expression Networks Compassing Novel Gene Functions in the Brain
 Supplementary Information Broad Integration of Expression Maps and Co-Expression Networks Compassing Novel Gene Functions in the Brain Yuko Okamura-Oho a, b, *, Kazuro Shimokawa c, Masaomi Nishimura b,
Supplementary Information Broad Integration of Expression Maps and Co-Expression Networks Compassing Novel Gene Functions in the Brain Yuko Okamura-Oho a, b, *, Kazuro Shimokawa c, Masaomi Nishimura b,
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4547
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Supplementary Figure 1 IL-27 IL
 Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Supplementary Fig.S1. MeDIP RPKM distribution of 5kb windows. Relative expression of DNMT. Percentage of genome. (fold change)
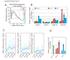 Supplementary Fig.S1 Percentage of genome 10% 8% 6% 4% 2% 0 MeDIP RPKM distribution of 5kb windows 0 0. 0.5 0.75 >1 MeDIP RPKM value EC Relative expression of DNMT (fold change) 12 6 4 3 2 1 EC DNMT1 DNMT2
Supplementary Fig.S1 Percentage of genome 10% 8% 6% 4% 2% 0 MeDIP RPKM distribution of 5kb windows 0 0. 0.5 0.75 >1 MeDIP RPKM value EC Relative expression of DNMT (fold change) 12 6 4 3 2 1 EC DNMT1 DNMT2
Supplementary Information. Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures.8 57 essential gene density 2 1.5 LTR insert frequency diversity DEL.5 DUP.5 INV.5 TRA 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 1 2 Supplementary Figure 1. Locations and minor
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures.8 57 essential gene density 2 1.5 LTR insert frequency diversity DEL.5 DUP.5 INV.5 TRA 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 1 2 Supplementary Figure 1. Locations and minor
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth.3115
 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of DNA methylation in a cancer cohort based on Infinium 450K data. RnBeads was used to rediscover a clinically distinct subgroup of glioblastoma patients characterized by
Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of DNA methylation in a cancer cohort based on Infinium 450K data. RnBeads was used to rediscover a clinically distinct subgroup of glioblastoma patients characterized by
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells. (a) Patterns of indicated transcription factor-binding at SEs and surrounding regions in T reg and T conv cells. Average normalized
Supplementary Figure 1 Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells. (a) Patterns of indicated transcription factor-binding at SEs and surrounding regions in T reg and T conv cells. Average normalized
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION GO term analysis of differentially methylated SUMIs. GO term analysis of the 458 SUMIs with the largest differential methylation between human and chimp shows that they are more
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION GO term analysis of differentially methylated SUMIs. GO term analysis of the 458 SUMIs with the largest differential methylation between human and chimp shows that they are more
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral training.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral training. a, Mazes used for behavioral training. Asterisks indicate reward location. Only some example mazes are shown (for example, right choice and not left choice maze
Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral training. a, Mazes used for behavioral training. Asterisks indicate reward location. Only some example mazes are shown (for example, right choice and not left choice maze
m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation and tumorigenicity of endometrial cancer
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation
 Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation indicated by the detection of -SMA and COL1 (log scale).
Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation indicated by the detection of -SMA and COL1 (log scale).
ErbB4 migrazione I parte. 3- ErbB4- NRG1
 ErbB4 migrazione I parte 3- ErbB4- NRG1 1 In rodent brains postnatal neuronal migration is evident in three main areas: the cerebellum (CB), the hippocampus (Hipp) and the rostral migratory stream (RMS).
ErbB4 migrazione I parte 3- ErbB4- NRG1 1 In rodent brains postnatal neuronal migration is evident in three main areas: the cerebellum (CB), the hippocampus (Hipp) and the rostral migratory stream (RMS).
Supplemental Information For: The genetics of splicing in neuroblastoma
 Supplemental Information For: The genetics of splicing in neuroblastoma Justin Chen, Christopher S. Hackett, Shile Zhang, Young K. Song, Robert J.A. Bell, Annette M. Molinaro, David A. Quigley, Allan Balmain,
Supplemental Information For: The genetics of splicing in neuroblastoma Justin Chen, Christopher S. Hackett, Shile Zhang, Young K. Song, Robert J.A. Bell, Annette M. Molinaro, David A. Quigley, Allan Balmain,
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Transcriptional program of the TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Transcriptional program of the TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets. (a) Comparison of gene expression of TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets by microarray. Genes that are 1.5-fold upregulated
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcriptional program of the TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets. (a) Comparison of gene expression of TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets by microarray. Genes that are 1.5-fold upregulated
DNA methylation & demethylation
 DNA methylation & demethylation Lars Schomacher (Group Christof Niehrs) What is Epigenetics? Epigenetics is the study of heritable changes in gene expression (active versus inactive genes) that do not
DNA methylation & demethylation Lars Schomacher (Group Christof Niehrs) What is Epigenetics? Epigenetics is the study of heritable changes in gene expression (active versus inactive genes) that do not
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. SEER data for male and female cancer incidence from
 Supplementary Figure 1 SEER data for male and female cancer incidence from 1975 2013. (a,b) Incidence rates of oral cavity and pharynx cancer (a) and leukemia (b) are plotted, grouped by males (blue),
Supplementary Figure 1 SEER data for male and female cancer incidence from 1975 2013. (a,b) Incidence rates of oral cavity and pharynx cancer (a) and leukemia (b) are plotted, grouped by males (blue),
Supplementary. properties of. network types. randomly sampled. subsets (75%
 Supplementary Information Gene co-expression network analysis reveals common system-level prognostic genes across cancer types properties of Supplementary Figure 1 The robustness and overlap of prognostic
Supplementary Information Gene co-expression network analysis reveals common system-level prognostic genes across cancer types properties of Supplementary Figure 1 The robustness and overlap of prognostic
Supplementary Figure 1. Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Large conserved domains of low DNA methylation maintained by Dnmt3a
 Supplementary information Large conserved domains of low DNA methylation maintained by Dnmt3a Mira Jeong# 1, Deqiang Sun # 2, Min Luo# 1, Yun Huang 3, Grant A. Challen %1, Benjamin Rodriguez 2, Xiaotian
Supplementary information Large conserved domains of low DNA methylation maintained by Dnmt3a Mira Jeong# 1, Deqiang Sun # 2, Min Luo# 1, Yun Huang 3, Grant A. Challen %1, Benjamin Rodriguez 2, Xiaotian
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Clinical significance of ZNF322A overexpression in Caucasian lung cancer patients. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry images of ZNF322A protein expression in tissue
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Clinical significance of ZNF322A overexpression in Caucasian lung cancer patients. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry images of ZNF322A protein expression in tissue
MIR retrotransposon sequences provide insulators to the human genome
 Supplementary Information: MIR retrotransposon sequences provide insulators to the human genome Jianrong Wang, Cristina Vicente-García, Davide Seruggia, Eduardo Moltó, Ana Fernandez- Miñán, Ana Neto, Elbert
Supplementary Information: MIR retrotransposon sequences provide insulators to the human genome Jianrong Wang, Cristina Vicente-García, Davide Seruggia, Eduardo Moltó, Ana Fernandez- Miñán, Ana Neto, Elbert
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information High fat diet-induced changes of mouse hepatic transcription and enhancer activity can be reversed by subsequent weight loss Majken Siersbæk, Lyuba Varticovski, Shutong Yang,
Supplementary information High fat diet-induced changes of mouse hepatic transcription and enhancer activity can be reversed by subsequent weight loss Majken Siersbæk, Lyuba Varticovski, Shutong Yang,
Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain. - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function
 Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function Alexandre Jourdon 1,2, Aurélie Gresset 1, Nathalie Spassky 1, Patrick Charnay
Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function Alexandre Jourdon 1,2, Aurélie Gresset 1, Nathalie Spassky 1, Patrick Charnay
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.2419
 Supplementary Figure 1 Mapped sequence reads and nucleosome occupancies. (a) Distribution of sequencing reads on the mouse reference genome for chromosome 14 as an example. The number of reads in a 1 Mb
Supplementary Figure 1 Mapped sequence reads and nucleosome occupancies. (a) Distribution of sequencing reads on the mouse reference genome for chromosome 14 as an example. The number of reads in a 1 Mb
Processing, integrating and analysing chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (ChIP-seq) data
 Processing, integrating and analysing chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (ChIP-seq) data Bioinformatics methods, models and applications to disease Alex Essebier ChIP-seq experiment To
Processing, integrating and analysing chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (ChIP-seq) data Bioinformatics methods, models and applications to disease Alex Essebier ChIP-seq experiment To
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. DNA-methylation machinery is essential for silencing of Cd4 in cytotoxic T cells.
 Supplementary Figure 1 DNA-methylation machinery is essential for silencing of Cd4 in cytotoxic T cells. (a) Scheme for the retroviral shrna screen. (b) Histogram showing CD4 expression (MFI) in WT cytotoxic
Supplementary Figure 1 DNA-methylation machinery is essential for silencing of Cd4 in cytotoxic T cells. (a) Scheme for the retroviral shrna screen. (b) Histogram showing CD4 expression (MFI) in WT cytotoxic
Epigenetics. Jenny van Dongen Vrije Universiteit (VU) Amsterdam Boulder, Friday march 10, 2017
 Epigenetics Jenny van Dongen Vrije Universiteit (VU) Amsterdam j.van.dongen@vu.nl Boulder, Friday march 10, 2017 Epigenetics Epigenetics= The study of molecular mechanisms that influence the activity of
Epigenetics Jenny van Dongen Vrije Universiteit (VU) Amsterdam j.van.dongen@vu.nl Boulder, Friday march 10, 2017 Epigenetics Epigenetics= The study of molecular mechanisms that influence the activity of
Integrated analysis of sequencing data
 Integrated analysis of sequencing data How to combine *-seq data M. Defrance, M. Thomas-Chollier, C. Herrmann, D. Puthier, J. van Helden *ChIP-seq, RNA-seq, MeDIP-seq, Transcription factor binding ChIP-seq
Integrated analysis of sequencing data How to combine *-seq data M. Defrance, M. Thomas-Chollier, C. Herrmann, D. Puthier, J. van Helden *ChIP-seq, RNA-seq, MeDIP-seq, Transcription factor binding ChIP-seq
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1. Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus.
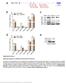 Supplementary Figure 1 Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus. (a) The mir-17-92a expression unit in the third intron of the host mir-17hg transcript. (b,c) Impact of knockdown
Supplementary Figure 1 Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus. (a) The mir-17-92a expression unit in the third intron of the host mir-17hg transcript. (b,c) Impact of knockdown
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 U1 inhibition causes a shift of RNA-seq reads from exons to introns. (a) Evidence for the high purity of 4-shU-labeled RNAs used for RNA-seq. HeLa cells transfected with control
Supplementary Figure 1 U1 inhibition causes a shift of RNA-seq reads from exons to introns. (a) Evidence for the high purity of 4-shU-labeled RNAs used for RNA-seq. HeLa cells transfected with control
RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice Paul N Valdmanis, Shuo Gu, Kirk Chu, Lan Jin, Feijie Zhang,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice Paul N Valdmanis, Shuo Gu, Kirk Chu, Lan Jin, Feijie Zhang,
Expanded View Figures
 Solip Park & Ben Lehner Epistasis is cancer type specific Molecular Systems Biology Expanded View Figures A B G C D E F H Figure EV1. Epistatic interactions detected in a pan-cancer analysis and saturation
Solip Park & Ben Lehner Epistasis is cancer type specific Molecular Systems Biology Expanded View Figures A B G C D E F H Figure EV1. Epistatic interactions detected in a pan-cancer analysis and saturation
SUPPLEMENTARY APPENDIX
 SUPPLEMENTARY APPENDIX 1) Supplemental Figure 1. Histopathologic Characteristics of the Tumors in the Discovery Cohort 2) Supplemental Figure 2. Incorporation of Normal Epidermal Melanocytic Signature
SUPPLEMENTARY APPENDIX 1) Supplemental Figure 1. Histopathologic Characteristics of the Tumors in the Discovery Cohort 2) Supplemental Figure 2. Incorporation of Normal Epidermal Melanocytic Signature
p = formed with HCI-001 p = Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-002 Control Bevacizumab + 17AAG Bevacizumab 17AAG
 A.. Relative # of ECs associated with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 ol b p < 0.001 Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 l b p = 0.002 Control IHC:
A.. Relative # of ECs associated with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 ol b p < 0.001 Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 l b p = 0.002 Control IHC:
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression deviation of the genes mapped to gene-wise recurrent mutations in the TCGA breast cancer cohort (top) and the TCGA lung cancer cohort (bottom). For each gene (each pair
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression deviation of the genes mapped to gene-wise recurrent mutations in the TCGA breast cancer cohort (top) and the TCGA lung cancer cohort (bottom). For each gene (each pair
Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2+ cells in different brain regions.
 Hip SVZ OB Cere Hypo Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2 + cells in different brain regions. Three weeks after the last tamoxifen injection, TBR2 immunostaining images reveal a large reduction of TBR2 + cells in
Hip SVZ OB Cere Hypo Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2 + cells in different brain regions. Three weeks after the last tamoxifen injection, TBR2 immunostaining images reveal a large reduction of TBR2 + cells in
Supplemental Information. A Highly Sensitive and Robust Method. for Genome-wide 5hmC Profiling. of Rare Cell Populations
 Molecular ell, Volume 63 Supplemental Information Highly Sensitive and Robust Method for enome-wide hm Profiling of Rare ell Populations Dali Han, Xingyu Lu, lan H. Shih, Ji Nie, Qiancheng You, Meng Michelle
Molecular ell, Volume 63 Supplemental Information Highly Sensitive and Robust Method for enome-wide hm Profiling of Rare ell Populations Dali Han, Xingyu Lu, lan H. Shih, Ji Nie, Qiancheng You, Meng Michelle
Variation in 5-hydroxymethylcytosine across human cortex and cerebellum
 Cover art produced by Helen Spiers (www.helenspiers.com) Variation in 5-hydroxymethylcytosine across human cortex and cerebellum Lunnon et al. Lunnon et al. Genome Biology (2016) 17:27 DOI 10.1186/s13059-016-0871-x
Cover art produced by Helen Spiers (www.helenspiers.com) Variation in 5-hydroxymethylcytosine across human cortex and cerebellum Lunnon et al. Lunnon et al. Genome Biology (2016) 17:27 DOI 10.1186/s13059-016-0871-x
fl/+ KRas;Atg5 fl/+ KRas;Atg5 fl/fl KRas;Atg5 fl/fl KRas;Atg5 Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) (b)
 KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At a b Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) GO gene sets (MSigDB v3. c5) enriched in KRas;Atg5 fl/+ as compared to KRas;Atg5 fl/fl tumors using gene set
KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At a b Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) GO gene sets (MSigDB v3. c5) enriched in KRas;Atg5 fl/+ as compared to KRas;Atg5 fl/fl tumors using gene set
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Astrocytes regulate adult hippocampal neurogenesis through ephrin-b signaling Randolph S. Ashton, Anthony Conway, Chinmay Pangarkar, Jamie Bergen, Kwang-Il Lim, Priya Shah, Mina
Supplementary Information Astrocytes regulate adult hippocampal neurogenesis through ephrin-b signaling Randolph S. Ashton, Anthony Conway, Chinmay Pangarkar, Jamie Bergen, Kwang-Il Lim, Priya Shah, Mina
Discovery of Novel Human Gene Regulatory Modules from Gene Co-expression and
 Discovery of Novel Human Gene Regulatory Modules from Gene Co-expression and Promoter Motif Analysis Shisong Ma 1,2*, Michael Snyder 3, and Savithramma P Dinesh-Kumar 2* 1 School of Life Sciences, University
Discovery of Novel Human Gene Regulatory Modules from Gene Co-expression and Promoter Motif Analysis Shisong Ma 1,2*, Michael Snyder 3, and Savithramma P Dinesh-Kumar 2* 1 School of Life Sciences, University
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Gene and Genome Parameters of Mammalian Liver Circadian Genes (LCGs)
 Gene and Genome Parameters of Mammalian Liver Circadian Genes (LCGs) The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters Citation
Gene and Genome Parameters of Mammalian Liver Circadian Genes (LCGs) The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters Citation
Measuring DNA Methylation with the MinION. Winston Timp Department of Biomedical Engineering Johns Hopkins University 12/1/16
 Measuring DNA Methylation with the MinION Winston Timp Department of Biomedical Engineering Johns Hopkins University 12/1/16 Epigenetics: Modern Modern Definition of epigenetics involves heritable changes
Measuring DNA Methylation with the MinION Winston Timp Department of Biomedical Engineering Johns Hopkins University 12/1/16 Epigenetics: Modern Modern Definition of epigenetics involves heritable changes
Supplemental Information. Menin Deficiency Leads to Depressive-like. Behaviors in Mice by Modulating. Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation
 Neuron, Volume 100 Supplemental Information Menin Deficiency Leads to Depressive-like Behaviors in Mice by Modulating Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation Lige Leng, Kai Zhuang, Zeyue Liu, Changquan Huang,
Neuron, Volume 100 Supplemental Information Menin Deficiency Leads to Depressive-like Behaviors in Mice by Modulating Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation Lige Leng, Kai Zhuang, Zeyue Liu, Changquan Huang,
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Immunofluorescence (IF) confirms absence of H3K9me in met-2 set-25 worms.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Immunofluorescence (IF) confirms absence of H3K9me in met-2 set-25 worms. IF images of wild-type (wt) and met-2 set-25 worms showing the loss of H3K9me2/me3 at the indicated developmental
Supplementary Figure 1 Immunofluorescence (IF) confirms absence of H3K9me in met-2 set-25 worms. IF images of wild-type (wt) and met-2 set-25 worms showing the loss of H3K9me2/me3 at the indicated developmental
Epigenetics DNA methylation. Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 13. DNA Methylation
 Epigenetics DNA methylation Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 13 DNA Methylation Most methylated cytosines are found in the dinucleotide sequence CG, denoted mcpg. The restriction enzyme HpaII
Epigenetics DNA methylation Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 13 DNA Methylation Most methylated cytosines are found in the dinucleotide sequence CG, denoted mcpg. The restriction enzyme HpaII
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. MADM labeling of thalamic clones.
 Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary text Collectively, we were able to detect ~14,000 expressed genes with RPKM (reads per kilobase per million) > 1 or ~16,000 with RPKM > 0.1 in at least one cell type from oocyte to the morula
Supplementary text Collectively, we were able to detect ~14,000 expressed genes with RPKM (reads per kilobase per million) > 1 or ~16,000 with RPKM > 0.1 in at least one cell type from oocyte to the morula
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine
 Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
An Unexpected Function of the Prader-Willi Syndrome Imprinting Center in Maternal Imprinting in Mice
 An Unexpected Function of the Prader-Willi Syndrome Imprinting Center in Maternal Imprinting in Mice Mei-Yi Wu 1 *, Ming Jiang 1, Xiaodong Zhai 2, Arthur L. Beaudet 2, Ray-Chang Wu 1 * 1 Department of
An Unexpected Function of the Prader-Willi Syndrome Imprinting Center in Maternal Imprinting in Mice Mei-Yi Wu 1 *, Ming Jiang 1, Xiaodong Zhai 2, Arthur L. Beaudet 2, Ray-Chang Wu 1 * 1 Department of
Assignment 5: Integrative epigenomics analysis
 Assignment 5: Integrative epigenomics analysis Due date: Friday, 2/24 10am. Note: no late assignments will be accepted. Introduction CpG islands (CGIs) are important regulatory regions in the genome. What
Assignment 5: Integrative epigenomics analysis Due date: Friday, 2/24 10am. Note: no late assignments will be accepted. Introduction CpG islands (CGIs) are important regulatory regions in the genome. What
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Illustration of the working of network-based SVM to confidently predict a new (and now confirmed) ASD gene. Gene CTNND2 s brain network neighborhood that enabled its prediction by
Supplementary Figure 1 Illustration of the working of network-based SVM to confidently predict a new (and now confirmed) ASD gene. Gene CTNND2 s brain network neighborhood that enabled its prediction by
Supplemental Information. Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate. Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation. through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway
 Neuron, Volume 73 Supplemental Information Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway Thomas M. Coate, Steven Raft, Xiumei Zhao, Aimee K.
Neuron, Volume 73 Supplemental Information Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway Thomas M. Coate, Steven Raft, Xiumei Zhao, Aimee K.
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
TEB. Id4 p63 DAPI Merge. Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge
 a Duct TEB b Id4 p63 DAPI Merge Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge c d e Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of Id4-positive MECs and characterization of the Comma-D model. (a) IHC analysis of ID4 expression in the
a Duct TEB b Id4 p63 DAPI Merge Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge c d e Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of Id4-positive MECs and characterization of the Comma-D model. (a) IHC analysis of ID4 expression in the
Mnemonic representations of transient stimuli and temporal sequences in the rodent hippocampus in vitro
 Supplementary Material Mnemonic representations of transient stimuli and temporal sequences in the rodent hippocampus in vitro Robert. Hyde and en W. Strowbridge Mossy ell 1 Mossy ell Mossy ell 3 Stimulus
Supplementary Material Mnemonic representations of transient stimuli and temporal sequences in the rodent hippocampus in vitro Robert. Hyde and en W. Strowbridge Mossy ell 1 Mossy ell Mossy ell 3 Stimulus
Gene Ontology and Functional Enrichment. Genome 559: Introduction to Statistical and Computational Genomics Elhanan Borenstein
 Gene Ontology and Functional Enrichment Genome 559: Introduction to Statistical and Computational Genomics Elhanan Borenstein The parsimony principle: A quick review Find the tree that requires the fewest
Gene Ontology and Functional Enrichment Genome 559: Introduction to Statistical and Computational Genomics Elhanan Borenstein The parsimony principle: A quick review Find the tree that requires the fewest
ONLINE. Online supplementary information S1 (Box) Method. Supplementary data. Online links
 ONLINE Online supplementary information S1 (Box) Method The of the human or mouse genomes were downloaded from the UCSC Genome Browser using the Tables feature. The d component of each genome was comprehensively
ONLINE Online supplementary information S1 (Box) Method The of the human or mouse genomes were downloaded from the UCSC Genome Browser using the Tables feature. The d component of each genome was comprehensively
oocytes were pooled for RT-PCR analysis. The number of PCR cycles was 35. Two
 Supplementary Fig. 1 a Kdm3a Kdm4b β-actin Oocyte Testis Oocyte Testis Oocyte Testis b 1.8 Relative expression.6.4.2 Kdm3a Kdm4b RT-PCR analysis of Kdm3a and Kdm4b expression in oocytes and testes. Twenty
Supplementary Fig. 1 a Kdm3a Kdm4b β-actin Oocyte Testis Oocyte Testis Oocyte Testis b 1.8 Relative expression.6.4.2 Kdm3a Kdm4b RT-PCR analysis of Kdm3a and Kdm4b expression in oocytes and testes. Twenty
EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH
 EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH Supplementary Figure 1. Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of KP and KPH2 autochthonous UPS tumors. a) Genotyping of KPH2
EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH Supplementary Figure 1. Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of KP and KPH2 autochthonous UPS tumors. a) Genotyping of KPH2
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Pan-cancer analysis of global and local DNA methylation variation a) Variations in global DNA methylation are shown as measured by averaging the genome-wide
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Pan-cancer analysis of global and local DNA methylation variation a) Variations in global DNA methylation are shown as measured by averaging the genome-wide
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice. (a) Gene expression profile in the resting CD4 + T cells were analyzed by an Affymetrix microarray
Supplementary Figure 1 Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice. (a) Gene expression profile in the resting CD4 + T cells were analyzed by an Affymetrix microarray
Social deficits in Shank3-deficient mouse models of autism are rescued by histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibition
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0110-8 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Social deficits in Shank3-deficient mouse models of autism are rescued by
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0110-8 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Social deficits in Shank3-deficient mouse models of autism are rescued by
Stem Cell Epigenetics
 Stem Cell Epigenetics Philippe Collas University of Oslo Institute of Basic Medical Sciences Norwegian Center for Stem Cell Research www.collaslab.com Source of stem cells in the body Somatic ( adult )
Stem Cell Epigenetics Philippe Collas University of Oslo Institute of Basic Medical Sciences Norwegian Center for Stem Cell Research www.collaslab.com Source of stem cells in the body Somatic ( adult )
Gene expression analysis. Roadmap. Microarray technology: how it work Applications: what can we do with it Preprocessing: Classification Clustering
 Gene expression analysis Roadmap Microarray technology: how it work Applications: what can we do with it Preprocessing: Image processing Data normalization Classification Clustering Biclustering 1 Gene
Gene expression analysis Roadmap Microarray technology: how it work Applications: what can we do with it Preprocessing: Image processing Data normalization Classification Clustering Biclustering 1 Gene
Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells.
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons
 Supplemental Material mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons Antoine de Chevigny, Nathalie Coré, Philipp Follert, Marion Gaudin, Pascal
Supplemental Material mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons Antoine de Chevigny, Nathalie Coré, Philipp Follert, Marion Gaudin, Pascal
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) 108 (b-c) (d) (e) (f) (g)
 Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 )
 770 771 Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 ) Human CXCL1 GCGCCCAAACCGAAGTCATA ATGGGGGATGCAGGATTGAG PF4 CCCCACTGCCCAACTGATAG TTCTTGTACAGCGGGGCTTG
770 771 Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 ) Human CXCL1 GCGCCCAAACCGAAGTCATA ATGGGGGATGCAGGATTGAG PF4 CCCCACTGCCCAACTGATAG TTCTTGTACAGCGGGGCTTG
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/8/e1500296/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Transcriptional regulation of APOBEC3 antiviral immunity through the CBF- /RUNX axis This PDF file includes: Brett
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/8/e1500296/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Transcriptional regulation of APOBEC3 antiviral immunity through the CBF- /RUNX axis This PDF file includes: Brett
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Rett Syndrome Mutation MeCP2 T158A Disrupts DNA Binding, Protein Stability and ERP Responses
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Rett Syndrome Mutation T158A Disrupts DNA Binding, Protein Stability and ERP Responses Darren Goffin, Megan Allen, Le Zhang, Maria Amorim, I-Ting Judy Wang, Arith-Ruth S. Reyes,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Rett Syndrome Mutation T158A Disrupts DNA Binding, Protein Stability and ERP Responses Darren Goffin, Megan Allen, Le Zhang, Maria Amorim, I-Ting Judy Wang, Arith-Ruth S. Reyes,
An epigenetic approach to understanding (and predicting?) environmental effects on gene expression
 www.collaslab.com An epigenetic approach to understanding (and predicting?) environmental effects on gene expression Philippe Collas University of Oslo Institute of Basic Medical Sciences Stem Cell Epigenetics
www.collaslab.com An epigenetic approach to understanding (and predicting?) environmental effects on gene expression Philippe Collas University of Oslo Institute of Basic Medical Sciences Stem Cell Epigenetics
Supplementary Figure 1. ALVAC-protein vaccines and macaque immunization. (A) Maximum likelihood
 Supplementary Figure 1. ALVAC-protein vaccines and macaque immunization. (A) Maximum likelihood tree illustrating CRF01_AE gp120 protein sequence relationships between 107 Envs sampled in the RV144 trial
Supplementary Figure 1. ALVAC-protein vaccines and macaque immunization. (A) Maximum likelihood tree illustrating CRF01_AE gp120 protein sequence relationships between 107 Envs sampled in the RV144 trial
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature19357 Figure 1a Chd8 +/+ Chd8 +/ΔSL Chd8 +/+ Chd8 +/ΔL E10.5_Whole brain E10.5_Whole brain E10.5_Whole brain E14.5_Whole brain E14.5_Whole brain E14.5_Whole
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature19357 Figure 1a Chd8 +/+ Chd8 +/ΔSL Chd8 +/+ Chd8 +/ΔL E10.5_Whole brain E10.5_Whole brain E10.5_Whole brain E14.5_Whole brain E14.5_Whole brain E14.5_Whole
Cluster Dendrogram. dist(cor(na.omit(tss.exprs.chip[, c(1:10, 24, 27, 30, 48:50, dist(cor(na.omit(tss.exprs.chip[, c(1:99, 103, 104, 109, 110,
 A Transcriptome (RNA-seq) Transcriptome (RNA-seq) 3. 2.5 2..5..5...5..5 2. 2.5 3. 2.5 2..5..5...5..5 2. 2.5 Cluster Dendrogram RS_ES3.2 RS_ES3. RS_SHS5.2 RS_SHS5. PS_SHS5.2 PS_SHS5. RS_LJ3 PS_LJ3..4 _SHS5.2
A Transcriptome (RNA-seq) Transcriptome (RNA-seq) 3. 2.5 2..5..5...5..5 2. 2.5 3. 2.5 2..5..5...5..5 2. 2.5 Cluster Dendrogram RS_ES3.2 RS_ES3. RS_SHS5.2 RS_SHS5. PS_SHS5.2 PS_SHS5. RS_LJ3 PS_LJ3..4 _SHS5.2
Mechanisms underlying epigene2c effects of endocrine disrup2ve chemicals. Joëlle Rüegg
 Mechanisms underlying epigene2c effects of endocrine disrup2ve chemicals Joëlle Rüegg 2 EDCs and human health Bisphenol A Epigenetic mechanisms Behavioural and psychiatric disorders Phthalates DNA methylation
Mechanisms underlying epigene2c effects of endocrine disrup2ve chemicals Joëlle Rüegg 2 EDCs and human health Bisphenol A Epigenetic mechanisms Behavioural and psychiatric disorders Phthalates DNA methylation
Supplemental Information. Derivation of Human Trophoblast Stem Cells
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Derivation of Human Trophoblast Stem Cells Hiroaki Okae, Hidehiro Toh, Tetsuya Sato, Hitoshi Hiura, Sota Takahashi, Kenjiro Shirane, Yuka Kabayama, Mikita
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Derivation of Human Trophoblast Stem Cells Hiroaki Okae, Hidehiro Toh, Tetsuya Sato, Hitoshi Hiura, Sota Takahashi, Kenjiro Shirane, Yuka Kabayama, Mikita
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Frequency of alternative-cassette-exon engagement with the ribosome is consistent across data from multiple human cell types and from mouse stem cells. Box plots showing AS frequency
Supplementary Figure 1 Frequency of alternative-cassette-exon engagement with the ribosome is consistent across data from multiple human cell types and from mouse stem cells. Box plots showing AS frequency
RNA-Seq Preparation Comparision Summary: Lexogen, Standard, NEB
 RNA-Seq Preparation Comparision Summary: Lexogen, Standard, NEB CSF-NGS January 22, 214 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Experimental Details 1 3 Results And Discussion 1 3.1 ERCC spike ins............................................
RNA-Seq Preparation Comparision Summary: Lexogen, Standard, NEB CSF-NGS January 22, 214 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Experimental Details 1 3 Results And Discussion 1 3.1 ERCC spike ins............................................
A novel and universal method for microrna RT-qPCR data normalization
 A novel and universal method for microrna RT-qPCR data normalization Jo Vandesompele professor, Ghent University co-founder and CEO, Biogazelle 4 th International qpcr Symposium Weihenstephan, March 1,
A novel and universal method for microrna RT-qPCR data normalization Jo Vandesompele professor, Ghent University co-founder and CEO, Biogazelle 4 th International qpcr Symposium Weihenstephan, March 1,
Computational aspects of ChIP-seq. John Marioni Research Group Leader European Bioinformatics Institute European Molecular Biology Laboratory
 Computational aspects of ChIP-seq John Marioni Research Group Leader European Bioinformatics Institute European Molecular Biology Laboratory ChIP-seq Using highthroughput sequencing to investigate DNA
Computational aspects of ChIP-seq John Marioni Research Group Leader European Bioinformatics Institute European Molecular Biology Laboratory ChIP-seq Using highthroughput sequencing to investigate DNA
