NKTR-255: Accessing The Immunotherapeutic Potential Of IL-15 for NK Cell Therapies
|
|
|
- Henry Wilkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NKTR-255: Accessing The Immunotherapeutic Potential Of IL-15 for NK Cell Therapies Saul Kivimäe Senior Scientist, Research Biology Nektar Therapeutics NK Cell-Based Cancer Immunotherapy, September 26-27, 2018 Boston, MA
2 The immunity cycle and multiple points of intervention for I-O therapies 4. Trafficking of immune cells to tumor 3. Priming and activation 5. Infiltration of cytotoxic cells into tumors 2. Cancer antigen presentation 6. Recognition of cancer cells by immune cells Source: Oncology Meets Immunology: The Cancer-Immunity Cycle Chen and Mellman Immunity, Volume 39, Issue 1, Release of cancer cell antigens 7. Killing of cancer cells 2
3 Nektar s immuno-oncology strategy to create therapies that cover the immunity cycle 4. Trafficking of T cells to tumor (CTLs) NKTR-214 (CD122 Agonist) Target as many steps as possible in the cycle with as few therapies as possible 3. Priming and activation (APCs & T cells) 2. Cancer antigen presentation (dendritic cells/apcs) Prime, Proliferate, Activate & Increase Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes (TILs), Increase PD-1 expression NKTR-262 (TLR Agonist) Activate Dendritic Cell Response 1. Release of cancer cell antigens (cancer cell death) 7. Killing of cancer cells (immune and cancer cells) 5. Infiltration of T cells into tumors (CTLs, endothelial cells) NKTR-255 (IL-15) 6. Recognition of cancer cells by t cells (CTLs, cancer cells) Stimulate NK Cells, Sustain Immune Response & Generate T Cell Memory Therapies need to be accessible as medicines 3
4 The potential of IL-15 in immuno-oncology Polymerconjugated IL-15 IL-15 is a pleiotropic cytokine with roles in innate and adaptive immunity Identified by NCI as one of the most promising immuno-oncology agents Key role in formation and maintenance of immunological memory Essential factor for NK development and homeostasis In vitro, IL-15 can reverse tumorinduced NK cell dysfunction 4
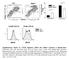
5 The challenge to therapeutic use of IL-15 IL-15 displays rapid clearance from plasma In vivo signaling activity is similarly short-lived Plasma concentration (ng/ml) %pstat5 STAT5 phosphorylation is an early and transient event in IL-15/IL-2 receptor signaling Time (hours) Mouse PK: IL mpk i.p., serum assayed by ELISA Mouse PD: IL mpk i.p., whole blood stained for leukocyte surface markers and pstat5, measured by flow cytometry Requires daily dosing or multi-day continuous infusion for optimal activity with high Cmax-related toxicity 5
6 NKTR-255 polymer conjugated IL-15 Design Goals: Improve PK and PD to sustain IL-15 activity and achieve large pharmacodynamic effect without need for daily dosing Retain binding to IL-15Rα to maintain full spectrum of IL-15 biology No mutagenesis or complex to soluble IL-15Rα As a result, NKTR-255: Stimulates NK cell activation and proliferation Supports CD8 T-cell survival and memory formation Shows efficacy in various syngeneic tumor models NKTR-255 is first potential medicine to access the IL-15 pathway by preserving receptor binding to IL-15R with antibody-like dosing 6
7 NKTR-255 achieves sustained plasma exposure in mice, rats and NHP after single dose IL-15 and NKTR-255 PK in Mice NKTR-255 PK in Rats µg/kg 300 µg/kg 100 µg/kg 30 µg/kg 10 µg/kg IL-15, 500 µg/kg ng/ml plasma conc. (mean SD) µg/kg 75 µg/kg 10 µg/kg ng/ml plasma conc. (mean SD) Hours post IV dose Hours post IV dose PEGylation Significantly Improved NKTR-255 PK Profiles: PEGylation significantly enhanced plasma exposure and reduced total clearance Extended plasma exposure across the species on single dose (Mice, Rat and NHP) NKTR-255 Half-life (t 1/2 ): Mouse: Rat: Monkey: ~14 hrs ~18 hrs ~30 hrs (100µg/kg) Note: Parent IL-15 was not dosed in the Rat PK study; No apparent gender differences are noted in the Cyno study 7
8 Binding to IL-15Rα is required to access the biological functions of IL-15 Three potential modes of interaction Trans-presentation: IL-15 binds to IL-15Rα on one cell (eg. DC) then signals through Rβγ on a second cell (eg. T-cell) Cis-presentation: soluble IL-15 binds to IL-15Rα and Rβγ on the same cell Binding of soluble complex: soluble IL-15:IL-15Rα heterodimer binds to Rβγ (Stonier and Schluns, 2010) Design NKTR-255 to maintain IL-15 biological context IL-15/IL-15Rα therapeutic fusion protein signals in an IL-15Rα independent manner, loses biological context 8
9 NKTR-255 retains affinity for IL-15R IL-15 NKTR-255 Conjugate k on (M -1 s -1 ) k off (s -1 ) K D (pm) IL x x NKTR x x Many conjugates were screened for ability to bind IL-15Rα Conjugation chemistry parameters were carefully optimized NKTR-255 affinity for IL-15Rα is ~10X weaker than IL-15 Affinity measured by BIAcore, using IL-15Rα:Fc captured by immobilized anti-fc NKTR-255 interaction with β and αβ were also ~8-10X weaker than IL-15 9
10 NKTR-255 signaling is mediated via IL-15Rα Wt IL-15Rα KO Whole blood + IL-15 NKTR-255 IL-15/IL-15Rα complex % of pstat5+ in CD45+ gate IL-15 NKTR-255 IL-15/IL-15Rα complex wt IL-15Rα IL-15Rα -/- NKTR255 NKTR255 wt NKTR255 IL-15Rα IL-15Rα NKTR255 -/- wt IL-15Rα IL-15Rα -/- Treatment IL-15 NKTR-255 IL-15/IL-15Rα complex WT KO WT KO WT KO pstat5 EC50 (ng/ml) EC50 ratio NKTR-255 signaling is dependent on IL-15Rα as with IL-15 10
11 NKTR-255 drives IL-15-like signaling across species Human Cyno-monkey Mouse CD4 T CD8 T + IL15/NKTR-255 % of pstat5+ population on sub-populations Whole Blood NK IL-15 EC50 (ng/ml) NK CD8 T CD4 T NKTR-255 EC50 (ng/ml) NK CD8 T CD4 T Human Cyno-monkey Mouse Human Cyno-monkey Mouse In human, NKTR-255 exhibits equal potency across three populations NKTR-255 potency to NK cells is preserved across species except for mouse NKTR-255 potency to T cells is different depending on species NKTR-255 species difference is similar to that for IL-15 Varying potency across species attributed to differences in IL-15 Rα expression level 11
12 Conclusions: NKTR-255 PK and target engagement NKTR-255 dramatically improves IL-15 receptor agonist exposure enabling low frequency administration NKTR-255 enables sustained IL-15 receptor pathway engagement in NK and T cells NKTR-255 retains IL-15Rα binding specificity maintaining IL-15 biological context 12
13 Functional characterization of NKTR-255 across immune cell subsets in rodents and nonhuman primates 13
14 NKTR-255 drives IL-15 receptor signaling and proliferation in CD8 T and NK cells in mice NK cell count in blood CD4 T cell count in blood Cell expansion mg/kg 0.03 mg/kg Vehicle Predose Hours post dose Hours post dose CD8 T cells %Ki Ki67+ %Ki67 (mean SD) %Ki67 (mean SD) %Ki67 (mean SD) Hours post dose 100 NK cells %pstat5+ pstat %pstat5 (mean SD) %pstat5 (mean SD) Hours post dose 14
15 NK cells are the most sensitive in NKTR-255 dose response compared to CD4 and CD8 T cells in vivo in NHPs NK cell expansion is detected at 0.01 mg/kg dose level NK cells Ki-67 and pstat5 induced at lowest dose level (0.001mg/kg). Cynomolgus monkeys NKTR-255 IV dose response PD: blood stained for leukocyte surface markers and pstat5 + Ki67, measured by flow cytometry 15
16 Increased NKTR-255 sensitivity in CD8 T cell memory populations compared to naïve CD8 T cells in vivo in NHPs Cynomolgus monkeys NKTR-255 IV dose response PD: blood stained memory markers (CD45RA, CD197, CD95) in CD8 T parent gate. 16
17 NKTR-255 expands NK cell subpopulations NK cells at all stages of maturation are highly responsive to NKTR-255 Terminal Effector (CD11b+CD27+) Most mature Activation tightly regulation Higher activation threshold High Effector (CD11b+CD27+) High cytokine secretion Great effector function Lower activation threshold Terminal Effector NK High Effector NK pre-dose Vehicle 0.03 mg/kg mg/kg CD11b NK maturation Days Days cells/ul Immature (CD11b-CD27-) Potential to differentiate CD27 Early NK (CD11b-CD27+) High cytokine secretion 17
18 NKTR-255 increases expression of effector functions in NK cells in mice GzmB+ MFI untreated vehicle NKTR-255, 0.03 mg/kg NKTR-255, 0.3 mg/kg Days after single dose Days after single dose 18
19 NKTR-255 increases levels of cytotoxic enzymes in NK cells in NHPs GzmB MFI in NK cells Granzyme B MFI in NK cells GzmB MFI in NK cells GzmB MFI in NK cell Perforin MFI in NK Perforin cells Perforin MFI MFI in NK cellsperforin MFI in NK cells MFI (mean SD) MFI (mean SD) MFI (mean SD) peak levels 0 peak levels 0 peak levels 0 peak levels 0 peak levels 0 predose predose predose predose predose predose peak levels mg/kg 0.01 mg/kg 0.1 mg/kg mg/kg 0.01 mg/kg 0.1 mg/kg NKTR-255 increases protein levels of constitutively expressed cytolytic enzymes Granzyme B and Perforin in NK cells 19
20 NKTR-255 enhances murine splenic NK cytotoxicity NKTR-255 Spleens harvested at Day 1, 4, 6 Effector cells: NK cells isolated from spleens Target cells: YAC-1 cells labeled with PKH26 Co-culture at 12.5:1 (E:T ratio) for 4 hr Label cells with 7-AAD; Analyze lysis of target cells via flow cytometry % NK cells % lysis A single in vivo dose (0.3 mg/kg) of NKTR-255 sustains NK cell killing activity for at least 6 days ex vivo 20
21 In vivo comparison summary of NK vs T cell responses to NKTR-255 NK cells most sensitive to NKTR-255 stimulation in vivo in mice and NHPs - %pstat5 and %Ki67 increases measurable at lowest tested dose level (0.001 mg/kg) in NHP - Lowest dose level requirement for effective in vivo expansion in NK cells NKTR-255 increases intracellular levels of cytotoxic enzymes and prolongs cytotoxic activity of NK cells Higher sensitivity to NKTR-255 in CD8 memory T cells relative to naïve CD8 T cells - Graded sensitivity within memory subpopulations (T EM >T SCM >T CM >T Naive ) in proliferative response CD4 T cells are the less responsive T cell population to NKTR-255 stimulation in mice and NHPs 21
22 NKTR-255 in vivo anti-tumor efficacy 22
23 NKTR-255 has potential to enhance anti-cancer immunotherapy via both NK and CD8 cells NK cell biology Activation balance among human NK subtypes IL-15 is similarly potent to regulatory CD56 bright and cytotoxic CD56 dim/null NK sub-populations IL-15 pre-activated NK cells show sustained function CD8 cell biology Supporting memory CD8 T cell longevity and function IL-15 maintains Ag-specific effector CD8 T cells after the contraction phase by promoting their survival and proliferation IL-15 23
24 NKTR-255 enhances NK cell-dependent anti-tumor efficacy in disseminated CT26 lung metastasis model Female Balb/c mice (6-8 weeks) 10 5 cells CT26 i.v. Count lung nodules NKTR-255 D0 D1 D8 D 13 ( ) NKTR-255 efficacy in disseminated CT26 model is NK cell dependent NK cell proliferation in the lung NK cells NK cell proliferation % lung nodule inhibition (mean ± SEM) %NKp46 (CD3) (mean ± SEM ) Hrs post last dose %Ki-67 (NKp46) (mean ± SEM ) Hrs post last dose Vehicle NKTR mg/kg *=p<0.05 vs Vehicle, unpaired Student t test 24
25 A single dose of NKTR-255 provides sustained protection against lung colonization by circulating tumor cells 1x10 5 CT26 cells inoculated i.v Lung nodule count on Day 13 after inoculation Prophylactic NKTR-255: single dose treatment Day -9 Day -6 or Day -3 Day 0 or Vehicle NKTR mg/kg; IV days 6 days 9 days ****=p< vs respective Vehicle (One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test) # of days between NKTR-255 dose and CT26 inoculation 25
26 NKTR-255 inhibits establishment of spontaneous lung metastasis in 4T1 tumor model Mean tumor volumes of subcutaneous primary tumors Number of spontaneous metastatic colonies on Day 14 in lungs
27 Summary NKTR-255 may overcome many limitations of IL-15 as a therapeutic agent Improved PK to allow infrequent administration Provides sustained IL-15 PD activity from a single dose Achieves full breadth of signaling profile characteristic to IL-15 By design, NKTR-255 maintains binding affinity for IL-15Rα NKTR-255 promotes the proliferation of memory T cells and induces significant NK cell expansion and increased cytotoxic activity NKTR-255 enhances NK dependent anti-tumor immune responses in vivo NKTR-255 enables access to the immunotherapeutic potential of the IL-15 pathway by enhancing expansion and activation of both NK and CD8 T cells 27
NKTR-255: Accessing IL-15 Therapeutic Potential through Robust and Sustained Engagement of Innate and Adaptive Immunity
 NKTR-255: Accessing IL-15 Therapeutic Potential through Robust and Sustained Engagement of Innate and Adaptive Immunity Peiwen Kuo Scientist, Research Biology Nektar Therapeutics August 31 st, 2018 Emerging
NKTR-255: Accessing IL-15 Therapeutic Potential through Robust and Sustained Engagement of Innate and Adaptive Immunity Peiwen Kuo Scientist, Research Biology Nektar Therapeutics August 31 st, 2018 Emerging
NKTR-214 plus NKTR-262, a Scientifically-Guided Rational Combination Approach for Immune Oncology
 plus NKTR-262, a Scientifically-Guided Rational Combination Approach for Immune Oncology Jonathan Zalevsky SVP, Biology and Preclinical Development Nektar Therapeutics World Preclinical Congress, 2017
plus NKTR-262, a Scientifically-Guided Rational Combination Approach for Immune Oncology Jonathan Zalevsky SVP, Biology and Preclinical Development Nektar Therapeutics World Preclinical Congress, 2017
Enhanced Cancer Vaccine Effectiveness with NKTR-214, a CD122-Biased Cytokine
 Enhanced Cancer Vaccine Effectiveness with NKTR-214, a CD122-Biased Cytokine Jonathan Zalevsky SVP, Biology and Preclinical Development Nektar Therapeutics SMI Cancer Vaccines, September 2017 Nektar Therapeutics
Enhanced Cancer Vaccine Effectiveness with NKTR-214, a CD122-Biased Cytokine Jonathan Zalevsky SVP, Biology and Preclinical Development Nektar Therapeutics SMI Cancer Vaccines, September 2017 Nektar Therapeutics
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was
 Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was sorted by FACS. Surface markers for sorting were CD11c +
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was sorted by FACS. Surface markers for sorting were CD11c +
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS. Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT
 ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
Jefferies 2017 Global Healthcare Conference. Stephen Doberstein, Ph.D. Senior Vice President & Chief Scientific Officer
 Jefferies 2017 Global Healthcare Conference Stephen Doberstein, Ph.D. Senior Vice President & Chief Scientific Officer June 7, 2017 This presentation includes forward-looking statements regarding Nektar
Jefferies 2017 Global Healthcare Conference Stephen Doberstein, Ph.D. Senior Vice President & Chief Scientific Officer June 7, 2017 This presentation includes forward-looking statements regarding Nektar
John Langowski, Ph.D. Nektar Therapeutics San Francisco, CA USA
 NKTR-38: a selective, first-in-class IL-2 pathway agonist which increases number and suppressive function of regulatory T cells for the treatment of immune inflammatory disorders John Langowski, Ph.D.
NKTR-38: a selective, first-in-class IL-2 pathway agonist which increases number and suppressive function of regulatory T cells for the treatment of immune inflammatory disorders John Langowski, Ph.D.
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. NKT ligand-loaded tumour antigen-presenting B cell- and monocyte-based vaccine induces NKT, NK and CD8 T cell responses. (A) The cytokine profiles of liver
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. NKT ligand-loaded tumour antigen-presenting B cell- and monocyte-based vaccine induces NKT, NK and CD8 T cell responses. (A) The cytokine profiles of liver
Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F10 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model.
 A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
Supplemental Materials for. Effects of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 phosphorylation in response to. FTY720 during neuroinflammation
 Supplemental Materials for Effects of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 phosphorylation in response to FTY7 during neuroinflammation This file includes: Supplemental Table 1. EAE clinical parameters of
Supplemental Materials for Effects of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 phosphorylation in response to FTY7 during neuroinflammation This file includes: Supplemental Table 1. EAE clinical parameters of
Therapeutic efficacy of MUC1- specific CTL and CD137 costimulation. mammary cancer model. Pinku Mukherjee & Sandra Gendler
 Therapeutic efficacy of MUC1- specific CTL and CD137 costimulation in a spontaneous mammary cancer model Pinku Mukherjee & Sandra Gendler Goal of Immunotherapy Boosting the low level anti-tumor immune
Therapeutic efficacy of MUC1- specific CTL and CD137 costimulation in a spontaneous mammary cancer model Pinku Mukherjee & Sandra Gendler Goal of Immunotherapy Boosting the low level anti-tumor immune
JP Morgan Healthcare Conference. Howard Robin President & CEO January 9, 2018
 JP Morgan Healthcare Conference Howard Robin President & CEO January 9, 2018 This presentation includes forward-looking statements regarding Nektar s proprietary drug candidates, the timing of the start
JP Morgan Healthcare Conference Howard Robin President & CEO January 9, 2018 This presentation includes forward-looking statements regarding Nektar s proprietary drug candidates, the timing of the start
Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured
 Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured under Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg conditions. mrna
Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured under Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg conditions. mrna
Supplementary Figure Legends. group) and analyzed for Siglec-G expression utilizing a monoclonal antibody to Siglec-G (clone SH2.1).
 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplemental Figure : Naïve T cells express Siglec-G. Splenocytes were isolated from WT B or Siglec-G -/- animals that have not been transplanted (n= per group) and analyzed
Supplementary Figure Legends Supplemental Figure : Naïve T cells express Siglec-G. Splenocytes were isolated from WT B or Siglec-G -/- animals that have not been transplanted (n= per group) and analyzed
DISCOVER MORE WITH LESS SAMPLE. nanostring.com/3d
 nanostring.com/3d DISCOVER MORE WITH LESS SAMPLE. WHY COMPROMISE? ncounter Vantage ASSAYS POWERED BY 3D BIOLOGY TECHNOLOGY Don t let sample volume limit your analytical aspirations. Quantify DNA, RNA,
nanostring.com/3d DISCOVER MORE WITH LESS SAMPLE. WHY COMPROMISE? ncounter Vantage ASSAYS POWERED BY 3D BIOLOGY TECHNOLOGY Don t let sample volume limit your analytical aspirations. Quantify DNA, RNA,
Cell-mediated Immunity
 Cellular & Molecular Immunology Cell-mediated Immunity Nicholas M. Ponzio, Ph.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine April 6, 2009 Today s Presentation: Overview Cellular Interactions In Humoral
Cellular & Molecular Immunology Cell-mediated Immunity Nicholas M. Ponzio, Ph.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine April 6, 2009 Today s Presentation: Overview Cellular Interactions In Humoral
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION
 Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 11 T-Cell Activation, Differentiation, and Memory Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 11 T-Cell Activation, Differentiation, and Memory Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and
Identification of novel immune regulators of tumor growth using highthroughput
 Identification of novel immune regulators of tumor growth using highthroughput screening in vivo Tom Brennan 1 Five Prime s Unique Platform Tests Nearly Every Extracellular Protein to Identify Protein
Identification of novel immune regulators of tumor growth using highthroughput screening in vivo Tom Brennan 1 Five Prime s Unique Platform Tests Nearly Every Extracellular Protein to Identify Protein
Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation. Abul K. Abbas UCSF. FOCiS
 1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
Jefferies 2016 Healthcare Conference. Howard Robin President & Chief Executive Officer
 Jefferies 2016 Healthcare Conference Howard Robin President & Chief Executive Officer June 8, 2016 This presentation includes forward-looking statements regarding Nektar s technology platform, drug candidates,
Jefferies 2016 Healthcare Conference Howard Robin President & Chief Executive Officer June 8, 2016 This presentation includes forward-looking statements regarding Nektar s technology platform, drug candidates,
Immunity and Cancer. Doriana Fruci. Lab di Immuno-Oncologia
 Immunity and Cancer Doriana Fruci Lab di Immuno-Oncologia Immune System is a network of cells, tissues and organs that work together to defend the body against attacks of foreign invaders (pathogens, cancer
Immunity and Cancer Doriana Fruci Lab di Immuno-Oncologia Immune System is a network of cells, tissues and organs that work together to defend the body against attacks of foreign invaders (pathogens, cancer
Piper Jaffray 29 th Annual Healthcare Conference
 Piper Jaffray 29 th Annual Healthcare Conference Jonathan Zalevsky, Ph.D. Senior Vice President, Research and Chief Scientific Officer November 28, 2017 This presentation includes forward-looking statements
Piper Jaffray 29 th Annual Healthcare Conference Jonathan Zalevsky, Ph.D. Senior Vice President, Research and Chief Scientific Officer November 28, 2017 This presentation includes forward-looking statements
Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD-
 Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation. Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre
 New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre No Disclosures
New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre No Disclosures
Enhanced cancer vaccine effectiveness with NKTR-214, a CD122 biased cytokine
 SMi Immuno-Oncology, London Loui Madakamutil, Ph. D Vice President, Head for Discovery Enhanced cancer vaccine effectiveness with NKTR-214, a CD122 biased cytokine Sept 26-27 2018 Nektar Therapeutics San
SMi Immuno-Oncology, London Loui Madakamutil, Ph. D Vice President, Head for Discovery Enhanced cancer vaccine effectiveness with NKTR-214, a CD122 biased cytokine Sept 26-27 2018 Nektar Therapeutics San
LAG-3: Validation Of Next Generation Checkpoint Pathways
 LAG-3: Validation Of Next Generation Checkpoint Pathways Frédéric Triebel, CO/CMO Immune Checkpoint Modulation & Combination Therapies April 13, 2016 London, UK. 1 AX:PRR; NADAQ:PBMD Notice: Forward Looking
LAG-3: Validation Of Next Generation Checkpoint Pathways Frédéric Triebel, CO/CMO Immune Checkpoint Modulation & Combination Therapies April 13, 2016 London, UK. 1 AX:PRR; NADAQ:PBMD Notice: Forward Looking
Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells
 Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells Andrew H. Lichtman, M.D. Ph.D. Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard
Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells Andrew H. Lichtman, M.D. Ph.D. Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard
General Overview of Immunology. Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center
 General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
NK cell flow cytometric assay In vivo DC viability and migration assay
 NK cell flow cytometric assay 6 NK cells were purified, by negative selection with the NK Cell Isolation Kit (Miltenyi iotec), from spleen and lymph nodes of 6 RAG1KO mice, injected the day before with
NK cell flow cytometric assay 6 NK cells were purified, by negative selection with the NK Cell Isolation Kit (Miltenyi iotec), from spleen and lymph nodes of 6 RAG1KO mice, injected the day before with
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10134 Supplementary Figure 1. Anti-inflammatory activity of sfc. a, Autoantibody immune complexes crosslink activating Fc receptors, promoting activation of macrophages, and WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
doi:10.1038/nature10134 Supplementary Figure 1. Anti-inflammatory activity of sfc. a, Autoantibody immune complexes crosslink activating Fc receptors, promoting activation of macrophages, and WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
Novel RCC Targets from Immuno-Oncology and Antibody-Drug Conjugates
 Novel RCC Targets from Immuno-Oncology and Antibody-Drug Conjugates Christopher Turner, MD Vice President, Clinical Science 04 November 2016 Uveal Melanoma Celldex Pipeline CANDIDATE INDICATION Preclinical
Novel RCC Targets from Immuno-Oncology and Antibody-Drug Conjugates Christopher Turner, MD Vice President, Clinical Science 04 November 2016 Uveal Melanoma Celldex Pipeline CANDIDATE INDICATION Preclinical
Long-term consumption of Carnosine contributes to improving effector functions of NK cells
 International Journal of Science Vol.5 No.7 218 ISSN: 1813-489 Long-term consumption of arnosine contributes to improving effector functions of NK cells bstract Guangao Liu ollege of Life Science and Technology,
International Journal of Science Vol.5 No.7 218 ISSN: 1813-489 Long-term consumption of arnosine contributes to improving effector functions of NK cells bstract Guangao Liu ollege of Life Science and Technology,
37th Annual J.P. Morgan Healthcare Conference. Howard Robin President & CEO January 8, 2019
 37th Annual J.P. Morgan Healthcare Conference Howard Robin President & CEO January 8, 2019 This presentation includes forward-looking statements regarding Nektar s proprietary drug candidates, the timing
37th Annual J.P. Morgan Healthcare Conference Howard Robin President & CEO January 8, 2019 This presentation includes forward-looking statements regarding Nektar s proprietary drug candidates, the timing
Micro 204. Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTL) Lewis Lanier
 Micro 204 Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTL) Lewis Lanier Lewis.Lanier@ucsf.edu Lymphocyte-mediated Cytotoxicity CD8 + αβ-tcr + T cells CD4 + αβ-tcr + T cells γδ-tcr + T cells Natural Killer cells CD8 + αβ-tcr
Micro 204 Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTL) Lewis Lanier Lewis.Lanier@ucsf.edu Lymphocyte-mediated Cytotoxicity CD8 + αβ-tcr + T cells CD4 + αβ-tcr + T cells γδ-tcr + T cells Natural Killer cells CD8 + αβ-tcr
Jefferies 2018 Healthcare Conference. June 6, 2018
 Jefferies 2018 Healthcare Conference z June 6, 2018 This presentation includes forward-looking statements regarding Nektar s proprietary drug candidates, the timing of the start and conclusion of ongoing
Jefferies 2018 Healthcare Conference z June 6, 2018 This presentation includes forward-looking statements regarding Nektar s proprietary drug candidates, the timing of the start and conclusion of ongoing
Immune Checkpoints. PD Dr med. Alessandra Curioni-Fontecedro Department of Hematology and Oncology Cancer Center Zurich University Hospital Zurich
 Immune Checkpoints PD Dr med. Alessandra Curioni-Fontecedro Department of Hematology and Oncology Cancer Center Zurich University Hospital Zurich Activation of T cells requires co-stimulation Science 3
Immune Checkpoints PD Dr med. Alessandra Curioni-Fontecedro Department of Hematology and Oncology Cancer Center Zurich University Hospital Zurich Activation of T cells requires co-stimulation Science 3
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of basophils after reconstitution of SCID mice
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of after reconstitution of SCID mice with CD4 + CD62L + T cells. (A-C) SCID mice (n = 6 / group) were reconstituted with 2 x 1 6 CD4
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of after reconstitution of SCID mice with CD4 + CD62L + T cells. (A-C) SCID mice (n = 6 / group) were reconstituted with 2 x 1 6 CD4
Shiv Pillai Ragon Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School
 CTLs, Natural Killers and NKTs 1 Shiv Pillai Ragon Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School CTL inducing tumor apoptosis 3 Lecture outline CD8 + Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) Activation/differentiation
CTLs, Natural Killers and NKTs 1 Shiv Pillai Ragon Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School CTL inducing tumor apoptosis 3 Lecture outline CD8 + Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) Activation/differentiation
Supplementary Figure 1. ETBF activate Stat3 in B6 and Min mice colons
 Supplementary Figure 1 ETBF activate Stat3 in B6 and Min mice colons a pstat3 controls Pos Neg ETBF 1 2 3 4 b pstat1 pstat2 pstat3 pstat4 pstat5 pstat6 Actin Figure Legend: (a) ETBF induce predominantly
Supplementary Figure 1 ETBF activate Stat3 in B6 and Min mice colons a pstat3 controls Pos Neg ETBF 1 2 3 4 b pstat1 pstat2 pstat3 pstat4 pstat5 pstat6 Actin Figure Legend: (a) ETBF induce predominantly
Evaluation of an Agonist Anti-CD27 Human Antibody (Varlilumab) and its Potential for Combination With Checkpoint Inhibitors
 Evaluation of an Agonist Anti-CD27 Human Antibody (Varlilumab) and its Potential for Combination With Checkpoint Inhibitors Tibor Keler, PhD Chief Scientific Officer Enhancing immunity with immune modulating
Evaluation of an Agonist Anti-CD27 Human Antibody (Varlilumab) and its Potential for Combination With Checkpoint Inhibitors Tibor Keler, PhD Chief Scientific Officer Enhancing immunity with immune modulating
Naive, memory and regulatory T lymphocytes populations analysis
 Naive, memory and regulatory T lymphocytes populations analysis Jaen Olivier, PhD ojaen@beckmancoulter.com Cellular Analysis application specialist Beckman Coulter France Introduction Flow cytometric analysis
Naive, memory and regulatory T lymphocytes populations analysis Jaen Olivier, PhD ojaen@beckmancoulter.com Cellular Analysis application specialist Beckman Coulter France Introduction Flow cytometric analysis
2019 ASCO-SITC. Nektar Therapeutics Investor & Analyst Call. March 1, 2019
 Nektar Therapeutics Investor & Analyst Call March 1, 2019 This presentation includes forward-looking statements regarding Nektar s proprietary drug candidates, the timing of the start and conclusion of
Nektar Therapeutics Investor & Analyst Call March 1, 2019 This presentation includes forward-looking statements regarding Nektar s proprietary drug candidates, the timing of the start and conclusion of
Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity
 MICR2209 Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will discuss the T-cell mediated immune response, how it is activated,
MICR2209 Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will discuss the T-cell mediated immune response, how it is activated,
Combining ADCs with Immuno-Oncology Agents
 Combining ADCs with Immuno-Oncology Agents Chad May, PhD Senior Director Targeted Immunotherapy Oncology Research Unit, Pfizer 7 th Annual World ADC October 10, 2016 Cancer-Immunity Cycle Innate Immunity
Combining ADCs with Immuno-Oncology Agents Chad May, PhD Senior Director Targeted Immunotherapy Oncology Research Unit, Pfizer 7 th Annual World ADC October 10, 2016 Cancer-Immunity Cycle Innate Immunity
Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance. Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco
 Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco EIP Symposium Feb 2016 Why do some people respond to therapeutic proteins?
Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco EIP Symposium Feb 2016 Why do some people respond to therapeutic proteins?
LESSON 2: THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY
 Introduction to immunology. LESSON 2: THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY Today we will get to know: The adaptive immunity T- and B-cells Antigens and their recognition How T-cells work 1 The adaptive immunity Unlike
Introduction to immunology. LESSON 2: THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY Today we will get to know: The adaptive immunity T- and B-cells Antigens and their recognition How T-cells work 1 The adaptive immunity Unlike
Immune response to infection
 Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
Defensive mechanisms include :
 Acquired Immunity Defensive mechanisms include : 1) Innate immunity (Natural or Non specific) 2) Acquired immunity (Adaptive or Specific) Cell-mediated immunity Humoral immunity Two mechanisms 1) Humoral
Acquired Immunity Defensive mechanisms include : 1) Innate immunity (Natural or Non specific) 2) Acquired immunity (Adaptive or Specific) Cell-mediated immunity Humoral immunity Two mechanisms 1) Humoral
Effective activity of cytokine-induced killer cells against autologous metastatic melanoma including cells with stemness features
 Effective activity of cytokine-induced killer cells against autologous metastatic melanoma including cells with stemness features Loretta Gammaitoni, Lidia Giraudo, Valeria Leuci, et al. Clin Cancer Res
Effective activity of cytokine-induced killer cells against autologous metastatic melanoma including cells with stemness features Loretta Gammaitoni, Lidia Giraudo, Valeria Leuci, et al. Clin Cancer Res
TCR, MHC and coreceptors
 Cooperation In Immune Responses Antigen processing how peptides get into MHC Antigen processing involves the intracellular proteolytic generation of MHC binding proteins Protein antigens may be processed
Cooperation In Immune Responses Antigen processing how peptides get into MHC Antigen processing involves the intracellular proteolytic generation of MHC binding proteins Protein antigens may be processed
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION. for both infectious diseases and malignancies. Immunity is known as the innate
 CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION 1.1. Background of Study The immune system s function is to provide defense of the human body for both infectious diseases and malignancies. Immunity is known as the innate immunity
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION 1.1. Background of Study The immune system s function is to provide defense of the human body for both infectious diseases and malignancies. Immunity is known as the innate immunity
T Cell Activation, Costimulation and Regulation
 1 T Cell Activation, Costimulation and Regulation Abul K. Abbas, MD University of California San Francisco 2 Lecture outline T cell antigen recognition and activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
1 T Cell Activation, Costimulation and Regulation Abul K. Abbas, MD University of California San Francisco 2 Lecture outline T cell antigen recognition and activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
W/T Itgam -/- F4/80 CD115. F4/80 hi CD115 + F4/80 + CD115 +
 F4/8 % in the peritoneal lavage 6 4 2 p=.15 n.s p=.76 CD115 F4/8 hi CD115 + F4/8 + CD115 + F4/8 hi CD115 + F4/8 + CD115 + MHCII MHCII Supplementary Figure S1. CD11b deficiency affects the cellular responses
F4/8 % in the peritoneal lavage 6 4 2 p=.15 n.s p=.76 CD115 F4/8 hi CD115 + F4/8 + CD115 + F4/8 hi CD115 + F4/8 + CD115 + MHCII MHCII Supplementary Figure S1. CD11b deficiency affects the cellular responses
Lecture 4. T lymphocytes
 Lecture 4 T lymphocytes Objectives Mention the types of T cells List the Types of T helper cell (CD4+) Discuss the Activation of T cells Define Interleukins Distinguish the Super Ag from ordinary Ag Show
Lecture 4 T lymphocytes Objectives Mention the types of T cells List the Types of T helper cell (CD4+) Discuss the Activation of T cells Define Interleukins Distinguish the Super Ag from ordinary Ag Show
Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells
 ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
Cellular Immune response. Jianzhong Chen, Ph.D Institute of immunology, ZJU
 Cellular Immune response Jianzhong Chen, Ph.D Institute of immunology, ZJU Concept of adaptive immune response T cell-mediated adaptive immune response I. Concept of immune response A collective and coordinated
Cellular Immune response Jianzhong Chen, Ph.D Institute of immunology, ZJU Concept of adaptive immune response T cell-mediated adaptive immune response I. Concept of immune response A collective and coordinated
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Advances in Cancer Immunotherapy
 Advances in Cancer Immunotherapy Immunology 101 for the Non-Immunologist Arnold H. Zea, PhD azea@lsuhsc.edu Disclosures No relevant financial relationships to disclose This presentation does not contain
Advances in Cancer Immunotherapy Immunology 101 for the Non-Immunologist Arnold H. Zea, PhD azea@lsuhsc.edu Disclosures No relevant financial relationships to disclose This presentation does not contain
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Complete but curtailed T-cell response to very-low-affinity antigen Dietmar Zehn, Sarah Y. Lee & Michael J. Bevan Supp. Fig. 1: TCR chain usage among endogenous K b /Ova reactive T cells. C57BL/6 mice
Complete but curtailed T-cell response to very-low-affinity antigen Dietmar Zehn, Sarah Y. Lee & Michael J. Bevan Supp. Fig. 1: TCR chain usage among endogenous K b /Ova reactive T cells. C57BL/6 mice
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/8/352/352ra110/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Spatially selective depletion of tumor-associated regulatory T cells with near-infrared photoimmunotherapy
www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/8/352/352ra110/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Spatially selective depletion of tumor-associated regulatory T cells with near-infrared photoimmunotherapy
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION
 Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Effector Responses: Cell- and Antibody-Mediated Immunity Copyright 2013 by W. H.
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Effector Responses: Cell- and Antibody-Mediated Immunity Copyright 2013 by W. H.
Dual Targeting Nanoparticle Stimulates the Immune
 Dual Targeting Nanoparticle Stimulates the Immune System to Inhibit Tumor Growth Alyssa K. Kosmides, John-William Sidhom, Andrew Fraser, Catherine A. Bessell, Jonathan P. Schneck * Supplemental Figure
Dual Targeting Nanoparticle Stimulates the Immune System to Inhibit Tumor Growth Alyssa K. Kosmides, John-William Sidhom, Andrew Fraser, Catherine A. Bessell, Jonathan P. Schneck * Supplemental Figure
Glioblastoma and CNS tumors
 Glioblastoma and CNS tumors PRECEPTORSHIP PROGRAMME IMMUNO-ONCOLOGY Amsterdam, 27 May 2017 Patrick Roth Department of Neurology and Brain Tumor Center University Hospital Zurich Challenges in immunooncology
Glioblastoma and CNS tumors PRECEPTORSHIP PROGRAMME IMMUNO-ONCOLOGY Amsterdam, 27 May 2017 Patrick Roth Department of Neurology and Brain Tumor Center University Hospital Zurich Challenges in immunooncology
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information lpek et al. 1.173/pnas.1121217 SI Materials and Methods Mice. cell knockout, inos / (Taconic arms), Rag1 /, INγR /, and IL-12p4 / mice (The Jackson Laboratory) were maintained and/or
Supporting Information lpek et al. 1.173/pnas.1121217 SI Materials and Methods Mice. cell knockout, inos / (Taconic arms), Rag1 /, INγR /, and IL-12p4 / mice (The Jackson Laboratory) were maintained and/or
Radiation Therapy as an Immunomodulator
 Radiation Therapy as an Immunomodulator Yvonne Mowery, MD, PhD February 20, 2017 Tumor/Immune System Balance Kalbasi, JCI 2013 UNC-Duke-NC State-Wake Forest Spring 2017 2 RT Can Shift Balance Toward Elimination
Radiation Therapy as an Immunomodulator Yvonne Mowery, MD, PhD February 20, 2017 Tumor/Immune System Balance Kalbasi, JCI 2013 UNC-Duke-NC State-Wake Forest Spring 2017 2 RT Can Shift Balance Toward Elimination
Supplementary Figure S1. PTPN2 levels are not altered in proliferating CD8+ T cells. Lymph node (LN) CD8+ T cells from C57BL/6 mice were stained with
 Supplementary Figure S1. PTPN2 levels are not altered in proliferating CD8+ T cells. Lymph node (LN) CD8+ T cells from C57BL/6 mice were stained with CFSE and stimulated with plate-bound α-cd3ε (10µg/ml)
Supplementary Figure S1. PTPN2 levels are not altered in proliferating CD8+ T cells. Lymph node (LN) CD8+ T cells from C57BL/6 mice were stained with CFSE and stimulated with plate-bound α-cd3ε (10µg/ml)
Third line of Defense
 Chapter 15 Specific Immunity and Immunization Topics -3 rd of Defense - B cells - T cells - Specific Immunities Third line of Defense Specific immunity is a complex interaction of immune cells (leukocytes)
Chapter 15 Specific Immunity and Immunization Topics -3 rd of Defense - B cells - T cells - Specific Immunities Third line of Defense Specific immunity is a complex interaction of immune cells (leukocytes)
T cell-mediated immunity
 T cell-mediated immunity Overview For microbes within phagosomes in phagocytes.cd4+ T lymphocytes (TH1) Activate phagocyte by cytokines studies on Listeria monocytogenes For microbes infecting and replicating
T cell-mediated immunity Overview For microbes within phagosomes in phagocytes.cd4+ T lymphocytes (TH1) Activate phagocyte by cytokines studies on Listeria monocytogenes For microbes infecting and replicating
Therapeutic effect of baicalin on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. is mediated by SOCS3 regulatory pathway
 Therapeutic effect of baicalin on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis is mediated by SOCS3 regulatory pathway Yuan Zhang 1,2, Xing Li 1,2, Bogoljub Ciric 1, Cun-gen Ma 3, Bruno Gran 4, Abdolmohamad
Therapeutic effect of baicalin on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis is mediated by SOCS3 regulatory pathway Yuan Zhang 1,2, Xing Li 1,2, Bogoljub Ciric 1, Cun-gen Ma 3, Bruno Gran 4, Abdolmohamad
% of live splenocytes. STAT5 deletion. (open shapes) % ROSA + % floxed
 Supp. Figure 1. a 14 1 1 8 6 spleen cells (x1 6 ) 16 % of live splenocytes 5 4 3 1 % of live splenocytes 8 6 4 b 1 1 c % of CD11c + splenocytes (closed shapes) 8 6 4 8 6 4 % ROSA + (open shapes) % floxed
Supp. Figure 1. a 14 1 1 8 6 spleen cells (x1 6 ) 16 % of live splenocytes 5 4 3 1 % of live splenocytes 8 6 4 b 1 1 c % of CD11c + splenocytes (closed shapes) 8 6 4 8 6 4 % ROSA + (open shapes) % floxed
Adaptive (acquired) immunity. Professor Peter Delves University College London
 Adaptive (acquired) immunity Professor Peter Delves University College London p.delves@ucl.ac.uk Haematopoiesis Haematopoiesis Lymphocytes = adaptive response Recognition of pathogens by adaptive cells,
Adaptive (acquired) immunity Professor Peter Delves University College London p.delves@ucl.ac.uk Haematopoiesis Haematopoiesis Lymphocytes = adaptive response Recognition of pathogens by adaptive cells,
Natural Killer Cells: Development, Diversity, and Applications to Human Disease Dr. Michael A. Caligiuri
 Natural Killer Cells: Development, Diversity, November 26, 2008 The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center The James Cancer Hospital and Solove Research Institute Columbus, Ohio, USA 1 Human
Natural Killer Cells: Development, Diversity, November 26, 2008 The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center The James Cancer Hospital and Solove Research Institute Columbus, Ohio, USA 1 Human
ImmunoTools special Award 2014
 ImmunoTools special Award 2014 Davide Ferrari, PhD University of Ferrara, Department of Morphology, Surgery and Experimental Medicine. Section of Pathology, Oncology and Exper. Biology via L. Borsari 46,
ImmunoTools special Award 2014 Davide Ferrari, PhD University of Ferrara, Department of Morphology, Surgery and Experimental Medicine. Section of Pathology, Oncology and Exper. Biology via L. Borsari 46,
NATURAL KILLER T CELLS EBOOK
 08 April, 2018 NATURAL KILLER T CELLS EBOOK Document Filetype: PDF 90.41 KB 0 NATURAL KILLER T CELLS EBOOK Natural killer T cells (NK T cells) are a type of lymphocyte, or white blood cell. Natural killer
08 April, 2018 NATURAL KILLER T CELLS EBOOK Document Filetype: PDF 90.41 KB 0 NATURAL KILLER T CELLS EBOOK Natural killer T cells (NK T cells) are a type of lymphocyte, or white blood cell. Natural killer
MHC Tetramers and Monomers for Immuno-Oncology and Autoimmunity Drug Discovery
 MHC Tetramers and Monomers for Immuno-Oncology and Autoimmunity Drug Discovery Your Partner in Drug Discovery and Research MHC Tetramer Background T-Cell Receptors recognize and bind to complexes composed
MHC Tetramers and Monomers for Immuno-Oncology and Autoimmunity Drug Discovery Your Partner in Drug Discovery and Research MHC Tetramer Background T-Cell Receptors recognize and bind to complexes composed
Supplementary Table 1 Clinicopathological characteristics of 35 patients with CRCs
 Supplementary Table Clinicopathological characteristics of 35 patients with CRCs Characteristics Type-A CRC Type-B CRC P value Sex Male / Female 9 / / 8.5 Age (years) Median (range) 6. (9 86) 6.5 (9 76).95
Supplementary Table Clinicopathological characteristics of 35 patients with CRCs Characteristics Type-A CRC Type-B CRC P value Sex Male / Female 9 / / 8.5 Age (years) Median (range) 6. (9 86) 6.5 (9 76).95
IMMUNOTHERAPY FOR CANCER A NEW HORIZON. Ekaterini Boleti MD, PhD, FRCP Consultant in Medical Oncology Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust
 IMMUNOTHERAPY FOR CANCER A NEW HORIZON Ekaterini Boleti MD, PhD, FRCP Consultant in Medical Oncology Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust ASCO Names Advance of the Year: Cancer Immunotherapy No recent
IMMUNOTHERAPY FOR CANCER A NEW HORIZON Ekaterini Boleti MD, PhD, FRCP Consultant in Medical Oncology Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust ASCO Names Advance of the Year: Cancer Immunotherapy No recent
Chapter 10 (pages ): Differentiation and Functions of CD4+ Effector T Cells Prepared by Kristen Dazy, MD, Scripps Clinic Medical Group
 FIT Board Review Corner September 2015 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Andrew Nickels, MD, and Sarah Spriet, DO, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In-Training (FITs)
FIT Board Review Corner September 2015 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Andrew Nickels, MD, and Sarah Spriet, DO, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In-Training (FITs)
Immunology - Lecture 2 Adaptive Immune System 1
 Immunology - Lecture 2 Adaptive Immune System 1 Book chapters: Molecules of the Adaptive Immunity 6 Adaptive Cells and Organs 7 Generation of Immune Diversity Lymphocyte Antigen Receptors - 8 CD markers
Immunology - Lecture 2 Adaptive Immune System 1 Book chapters: Molecules of the Adaptive Immunity 6 Adaptive Cells and Organs 7 Generation of Immune Diversity Lymphocyte Antigen Receptors - 8 CD markers
Designing clinical trials with BiTE antibody constructs by leveraging from nonclinical data. Benno Rattel Biologics Congress Berlin, 2015
 Designing clinical trials with BiTE antibody constructs by leveraging from nonclinical data Benno Rattel Biologics Congress Berlin, 215 1 BiTE Antibody Contructs are Designed to Function as a Bridge between
Designing clinical trials with BiTE antibody constructs by leveraging from nonclinical data Benno Rattel Biologics Congress Berlin, 215 1 BiTE Antibody Contructs are Designed to Function as a Bridge between
Biology of Immune Aging
 Biology of Immune Aging Jorg J. Goronzy Stanford University Immune deficiency Increase morbidity and mortality from infections Poor vaccine responses Cancer Immune Aging Chronic inflammation Coronary artery
Biology of Immune Aging Jorg J. Goronzy Stanford University Immune deficiency Increase morbidity and mortality from infections Poor vaccine responses Cancer Immune Aging Chronic inflammation Coronary artery
Cell Mediated Immunity CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY. Basic Elements of Cell Mediated Immunity (CMI) Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)
 Chapter 16 CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY Cell Mediated Immunity Also known as Cellular Immunity or CMI The effector phase T cells Specificity for immune recognition reactions TH provide cytokines CTLs do the
Chapter 16 CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY Cell Mediated Immunity Also known as Cellular Immunity or CMI The effector phase T cells Specificity for immune recognition reactions TH provide cytokines CTLs do the
COURSE: Medical Microbiology, PAMB 650/720 - Fall 2008 Lecture 16
 COURSE: Medical Microbiology, PAMB 650/720 - Fall 2008 Lecture 16 Tumor Immunology M. Nagarkatti Teaching Objectives: Introduction to Cancer Immunology Know the antigens expressed by cancer cells Understand
COURSE: Medical Microbiology, PAMB 650/720 - Fall 2008 Lecture 16 Tumor Immunology M. Nagarkatti Teaching Objectives: Introduction to Cancer Immunology Know the antigens expressed by cancer cells Understand
Active STAT5 promotes long lived cytotoxic CD8 T cells that induce regression of autochthonous mouse melanoma.
 Active STAT5 promotes long lived cytotoxic CD8 T cells that induce regression of autochthonous mouse melanoma. SITC 211 Grégory Verdeil No relationships to disclose T cell adoptive transfer for cancer
Active STAT5 promotes long lived cytotoxic CD8 T cells that induce regression of autochthonous mouse melanoma. SITC 211 Grégory Verdeil No relationships to disclose T cell adoptive transfer for cancer
Glioblastoma and CNS tumors
 Glioblastoma and CNS tumors PRECEPTORSHIP PROGRAMME IMMUNO-ONCOLOGY Amsterdam, 1 October 2016 Patrick Roth Department of Neurology and Brain Tumor Center University Hospital Zurich Immunology in the CNS
Glioblastoma and CNS tumors PRECEPTORSHIP PROGRAMME IMMUNO-ONCOLOGY Amsterdam, 1 October 2016 Patrick Roth Department of Neurology and Brain Tumor Center University Hospital Zurich Immunology in the CNS
Fluorochrome Panel 1 Panel 2 Panel 3 Panel 4 Panel 5 CTLA-4 CTLA-4 CD15 CD3 FITC. Bio) PD-1 (MIH4, BD) ICOS (C398.4A, Biolegend) PD-L1 (MIH1, BD)
 Additional file : Table S. Antibodies used for panel stain to identify peripheral immune cell subsets. Panel : PD- signaling; Panel : CD + T cells, CD + T cells, B cells; Panel : Tregs; Panel :, -T, cdc,
Additional file : Table S. Antibodies used for panel stain to identify peripheral immune cell subsets. Panel : PD- signaling; Panel : CD + T cells, CD + T cells, B cells; Panel : Tregs; Panel :, -T, cdc,
T Cell Activation. Patricia Fitzgerald-Bocarsly March 18, 2009
 T Cell Activation Patricia Fitzgerald-Bocarsly March 18, 2009 Phases of Adaptive Immune Responses Phases of T cell responses IL-2 acts as an autocrine growth factor Fig. 11-11 Clonal Expansion of T cells
T Cell Activation Patricia Fitzgerald-Bocarsly March 18, 2009 Phases of Adaptive Immune Responses Phases of T cell responses IL-2 acts as an autocrine growth factor Fig. 11-11 Clonal Expansion of T cells
How T cells recognize antigen: The T Cell Receptor (TCR) Identifying the TCR: Why was it so hard to do? Monoclonal antibody approach
 How T cells recognize antigen: The T Cell Receptor (TCR) Identifying the TCR: Why was it so hard to do By the early 1980s, much about T cell function was known, but the receptor genes had not been identified
How T cells recognize antigen: The T Cell Receptor (TCR) Identifying the TCR: Why was it so hard to do By the early 1980s, much about T cell function was known, but the receptor genes had not been identified
A second type of TCR TCR: An αβ heterodimer
 How s recognize antigen: The T Cell Receptor (TCR) Identifying the TCR: Why was it so hard to do By the early 1980s, much about function was known, but the receptor genes had not been identified Recall
How s recognize antigen: The T Cell Receptor (TCR) Identifying the TCR: Why was it so hard to do By the early 1980s, much about function was known, but the receptor genes had not been identified Recall
Clinical Pipeline Highlights
 Clinical Pipeline Highlights Geoffrey M. Nichol, M.D., M.B.A. Senior Vice President, Product Development Medarex, Inc. R&D Day December 9, 25 MDX-7: Anti-PSMA HuMAb for Prostate Cancer Biology PSMA expressed
Clinical Pipeline Highlights Geoffrey M. Nichol, M.D., M.B.A. Senior Vice President, Product Development Medarex, Inc. R&D Day December 9, 25 MDX-7: Anti-PSMA HuMAb for Prostate Cancer Biology PSMA expressed
Belatacept: An Opportunity to Personalize Immunosuppression? Andrew Adams MD/PhD Emory Transplant Center
 Belatacept: An Opportunity to Personalize Immunosuppression? Andrew Adams MD/PhD Emory Transplant Center Disclosure Research Funding from BMS. Learning Objectives -Define belatacept-resistant rejection
Belatacept: An Opportunity to Personalize Immunosuppression? Andrew Adams MD/PhD Emory Transplant Center Disclosure Research Funding from BMS. Learning Objectives -Define belatacept-resistant rejection
T Lymphocyte Activation and Costimulation. FOCiS. Lecture outline
 1 T Lymphocyte Activation and Costimulation Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family Inhibitory receptors of T cells Targeting costimulators for
1 T Lymphocyte Activation and Costimulation Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family Inhibitory receptors of T cells Targeting costimulators for
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature1554 a TNF-α + in CD4 + cells [%] 1 GF SPF 6 b IL-1 + in CD4 + cells [%] 5 4 3 2 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of microbiota on cytokine profiles of T cells in GALT. Frequencies of TNF-α
doi:1.138/nature1554 a TNF-α + in CD4 + cells [%] 1 GF SPF 6 b IL-1 + in CD4 + cells [%] 5 4 3 2 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of microbiota on cytokine profiles of T cells in GALT. Frequencies of TNF-α
Adaptive Immune System
 Short Course on Immunology Adaptive Immune System Bhargavi Duvvuri Ph.D IIIrd Year (Immunology) bhargavi@yorku.ca Supervisor Dr.Gillian E Wu Professor, School of Kinesiology and Health Sciences York University,
Short Course on Immunology Adaptive Immune System Bhargavi Duvvuri Ph.D IIIrd Year (Immunology) bhargavi@yorku.ca Supervisor Dr.Gillian E Wu Professor, School of Kinesiology and Health Sciences York University,
Tumor Microenvironment and Immune Suppression
 Tumor Microenvironment and Immune Suppression Hassane M. Zarour,, MD Department of Medicine, Division of Hematology-Oncology, University of Pittsburgh Cancer Institute Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation
Tumor Microenvironment and Immune Suppression Hassane M. Zarour,, MD Department of Medicine, Division of Hematology-Oncology, University of Pittsburgh Cancer Institute Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation
The Adaptive Immune Responses
 The Adaptive Immune Responses The two arms of the immune responses are; 1) the cell mediated, and 2) the humoral responses. In this chapter we will discuss the two responses in detail and we will start
The Adaptive Immune Responses The two arms of the immune responses are; 1) the cell mediated, and 2) the humoral responses. In this chapter we will discuss the two responses in detail and we will start
08/02/59. Tumor Immunotherapy. Development of Tumor Vaccines. Types of Tumor Vaccines. Immunotherapy w/ Cytokine Gene-Transfected Tumor Cells
 Tumor Immunotherapy Autologous virus Inactivation Inactivated virus Lymphopheresis Culture? Monocyte s Dendritic cells Immunization Autologous vaccine Development of Tumor Vaccines Types of Tumor Vaccines
Tumor Immunotherapy Autologous virus Inactivation Inactivated virus Lymphopheresis Culture? Monocyte s Dendritic cells Immunization Autologous vaccine Development of Tumor Vaccines Types of Tumor Vaccines
LTX-315 is an immunotherapy in Phase I/IIa
 Tromsø...improving nature s own defence mechanisms Norwegian nonlisted company Oslo Develops novel therapeutics within oncology LTX-315 is an immunotherapy in Phase I/IIa LTX-315 is an intratumoral cancer
Tromsø...improving nature s own defence mechanisms Norwegian nonlisted company Oslo Develops novel therapeutics within oncology LTX-315 is an immunotherapy in Phase I/IIa LTX-315 is an intratumoral cancer
Immunological alterations in mice irradiated with low doses
 Immunological alterations in mice irradiated with low doses "Frédéric Joliot-Curie" National Research Institute for Radiobiology and Radiohygiene, Budapest, Hungary The structure of the immune system INNATE
Immunological alterations in mice irradiated with low doses "Frédéric Joliot-Curie" National Research Institute for Radiobiology and Radiohygiene, Budapest, Hungary The structure of the immune system INNATE
