Case Report An adult case of systemic Epstein-Barr virus-positive T/natural killer-cell lymphoproliferative disorder with good outcome
|
|
|
- Carmel West
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6(11): /ISSN: /IJCEP Case Report An adult case of systemic Epstein-Barr virus-positive T/natural killer-cell lymphoproliferative disorder with good outcome Xiuming Zhang, Zhaoming Wang, Lijun Wang, Hongtian Yao Department of Pathology, The First Affiliated Hospital, College of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province, China Received August 18, 2013; Accepted September 15, 2013; Epub October 15, 2013; Published November 1, 2013 Abstract: Epstein-Barr virus-positive T/natural killer (NK)-cell lymphoproliferative disorder (EBV+T/NK LPD) encompasses a heterogeneous group of disorders that have a common feature with excessive lymphoid proliferation of mainly T cells and/or NK cells. This disease is rare, predominantly affects children and young adults, and associated with high mortality. Herein, we report a case of EBV+T/NK LPD that occurred in an old woman with good outcome. The patient presented with fever, splenomegaly, and pancytopenia. Computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen showed splenomegaly. The clinical impression was a malignant tumor of spleen, so splenectomy was performed. Microscopically, the architecture of the spleen was preserved. The white pulp Malpighian corpuscles were atrophied. The red pulp showed intact sinusoids and pulp cords with increased cellular infiltrate. The proliferating lymphoid cells were mostly small lymphoid cells with minimal or no nuclear atypia, mixed with rare medium-sized or large cells. Immunohistochemical study and in-situ hybridization showed that the EBER-positive lymphoid cells were positive for CD3 and CD56. They were also positive for cytotoxic molecules, such as T-cell restricted intracellular antigen (TIA1), granzyme B. The case exhibited polyclonal rearrangement of T-cell receptor gene (TCR) by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) studies. Without radiotherapy and chemotherapy, the patient is alive and well with no evidence of disease 25 months after surgery. Keywords: Epstein-Barr virus, T/natural killer-cell, lymphoproliferative disorder Introduction Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a ubiquitous virus that can cause both acute and chronic active infections. Most persons have a chronic asymptomatic infection with EBV, but the virus has been associated with a number of malignancies and can infect B cells, T cells, NK cells, and epithelial cells [1]. Rare persons infected with EBV develop a life-threatening condition termed chronic active EBV disease (CAEBV). This disease has been defined as a systemic EBVpositive lymphoproliferative disease (EBV+LPD) characterized by fever, lymphadenopathy, and splenomegaly developing after primary virus infection in patients without known immunodeficiency [2]. Affected patients have high levels of EBV DNA in the blood, histological evidence of organ disease, and elevated levels of EBV RNA or viral proteins in affected tissues. EBV+T/NK LPD encompass a heterogeneous group of disorders that have a common feature with excessive lymphoid proliferation of mainly T cells and/or NK cells. This disease is rare, predominantly affects children and young adults [1, 3-7], and associated with high mortality. Herein, we report an adult case of EBV+T/NK LPD with good outcome. Clinical history 74-year-old female was admitted with a persistent fever for more than 6 months. On admission, her temperature was 39.1 C and ranged from 37.2 C~39.3 C, leukocyte count was 1,500 units (segmented neutrophils 69.7%, lymphocytes 21.5%), hemoglobin was 114 g/l, and platelet count was 40,000/μL. Physical examination revealed marked splenomegaly, and no enlarged lymph nodes was found. Blood and urine cultures did not grow any bacteria or
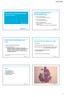
2 Figure 1. Histologic findings. The spleen shows depletion of white pulp and prominent sinusoidal small lymphoid infiltrate (A, hematoxylin and eosin, x200). B: The lymphocytes lack significant cytologic atypia (right, hematoxylin and eosin, x400). Figure 2. Immunophenotypic findings. The infiltrated lymphocytes of spleen are predominantly CD3+ (A, immunohistochemistry, x400) and some lymphocytes are also positive for CD56 (B, immunohistochemistry, x400). fungi. Computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen showed splenomegaly. Antibiotic treatment had no effect for two weeks. The clinical impression was a malignant tumor of spleen, so splenectomy was performed. After surgery, the serologic tests for EBV were investigated retrospectively and showed EBV viral capsid antigen (VCA)-IgG (+), EBV VCA-IgM ( ), EBV- early antigen (EA) (+). Seven days after surgery, her symptoms and signs had resolved without any other special therapies and she was discharged from the hospital. She was followed for 25 months and remained well clinically over the entire follow-up period. Pathological findings Grossly, the spleen was marked enlarged with measuring 18*15*10 cm and 435 g. There were no mass on cut surface. Microscopically, the architecture of the spleen was preserved. The white pulp Malpighian corpuscles were atrophied, whereas the red pulp showed intact sinusoids and pulp cords with prominent lymphoid infiltration (Figure 1A). The infiltrating lymphocytes were mostly small lymphoid cells with minimal or no nuclear atypia (Figure 1B), mixed with rare medium-sized or large lymphoid cells. Immunoblasts and plasma cells were not prominent. Bone marrow biopsy was available and showed no abnormality. Immunohistochemical (IHC) studies showed the infiltrated lymphocytes of spleen was composed predominantly of T-cell lineage, with CD3+ (Figure 2A) and CD20-. CD20 stained attenuated residual B-cell areas in the spleen Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6(11):
3 Figure 3. Some small lymphocytes are positive for EBER (A, in situ hybridization, x400). Double staining for CD3/ EBER and CD20/EBER shows that the CD3+ population harbors the EBV (B, stained in Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hong Kong, Courtesy of Dr. John K C Chan, x600). A few infiltrated cells was CD56+. Staining for CD4 and CD8 showed that the infiltrate was CD4- and CD8-. The infiltrated lymphocytes expressed cytotoxic molecules, such as TIA1, granzyme B (Figure 2B). The ratio of Ki-67- positive cells was estimated with lower than 30%. In situ hybridization(ish) for EBV using the EBVencoded RNA-1 (EBER1) probe (DAKO) showed up moderate number of positive cells (Figure 3A). These EBER+ cells were mostly small, and were scattered instead of forming clusters. Double-label ISH-IHC for EBER1 and CD20 or CD3 showed that most EBER+ cells were CD3+ (Figure 3B). Analysis of paraffin-embedded tissue from the spleen by PCR showed polyclonal rearrangements of the TCR-γ genes. Discussion In our case, the patient presented with fever, splenomegaly, and pancytopenia for more than 6 months with no evidence of previous immunological abnormalities or other recent infections. The serologic tests showed EBV VCA-IgG (+), EBV-EA (+). Histological examination revealed the infiltrated lymphocytes of spleen were composed predominantly of CD3+, CD56+T/ NK-cells and these cells were positive for EBER. Based on the clinical and histological findings, we consider this case as a rare adult EBV+T/NK LPD category A1. EBV+T/NK LPD was first incorporated into the 4th World Health Organization (WHO) classification of tumors of hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues, in which systemic EBV+ T-cell LPD of childhood and hydroa vacciniforme like lymphoma are proposed as distinct entities [8]. In 2008, an international meeting was organized at the National Institute of Health to better define the pathogenesis, classification, and treatment of EBV-associated LPDs in nonimmunocompromised hosts [1]. At that meeting, acute and chronic EBV syndromes of T cells and NK cells were clarified to have a broad spectrum, in which hydroa vacciniforme (HV), HV like lymphoma, severe mosquito bite allergy, and systemic EBV+T-LPD of childhood were listed as EBV+T/NK-LPDs under an umbrella term of CAEBV of T/NK-cell type. EBV+T/NK LPD include polyclonal, oligoclonal, and monoclonal proliferation of T and/or NK cells. Based on pathological evaluation and molecular data, K. Oshima proposed a categorization system of EBV+T/NK LPD in 2008 [9]. They divided these cases into four categories: A1 (polymorphic and polyclonal), A2 (polymorphic and generally monoclonal), A3 (monomorphic and monoclonal proliferation of T-cell or NK cell origin), and B (monomorphic and monoclonal T-cell LPD with fulminant clinical course). Categories A1, A2, and A3 possibly constitute a continuous spectrum and together are equivalent to CAEBV. Group B was defined as equivalent to fulminant EBV+LPD of childhood. Patients with CAEBV infections usually show 2622 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6(11):
4 clonal proliferation, although non-clonal cases do exist [1, 4]. In a national survey conducted in Japan, clonality of EBV-infected cells was analyzed in 54 patients, of whom 41 (76%) had monoclonal, seven (13%) had oligoclonal, and six (11%) had polyclonal [4]. In our case, the patient showed polyclonal proliferation of T lymphocytes. According to the above categorization criteria of EBV+T/NK LPD, our case should be diagnosed as CAEBV category A1. Recently Kimura et al. also found that most systemic EBV+T/NK LPDs are monoclonal [10]. In their study, most of the 108 patients with EBV+T/NK-LPDs had clonality of EBV-infected cells and eventually developed overt leukemia and lymphoma. They postulated that there should be a prodromal phase of expansion of EBV+T/NK-cells with variable clonality that may or may not progress to EBV+T/NK LPD. Most cases of previously reported EBV+T/NK LPD were Asians or Native Americans [4, 5, 11-13], and were mainly children or young adults. Elderly patients were seldom reported in the literature. The phenotypes of proliferating cells vary from case to case and include CD4+T cells, CD8+T cells, γδ T-cell, NK cells, and a mixture of these types [4, 14-17]. Notably, in addition to the phenotypic diversity, all cases examined were positive for cytotoxic molecules, such as TIA1, granzyme B, and perforin, indicating their derivation from cytotoxic T cells [11, 15]. Kimura et al. demonstrated that patients with CD4+ T-cell infection had shorter survival rates than those with NK infection [10]. But it is not clear whether the EBV-infected populations in CAEBV are correlated with survival rates at present, which need to be further study on the basis of more cases. Although with characteristic clinical features and pathological findings, differential diagnosis with extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type is requisite before making a definite EBV+T/NK LPD. They have some common characteristics, such as prevalent in Asians or Native Americans, EBV presence, cytotoxic phenotype, and aggressive behavior. NK/T-cell lymphoma is characterized by expression of CD2+, cytoplasmic CD3ε+, cytotoxic molecules, EBER, and CD56 may be positive or negative. These immunophenotypic features are similar with our case. Nevertheless, geographical necrosis and vasculitis characterized by NK/Tcell lymphoma were absent, and the architecture of the spleen was preserved with intact sinusoids and pulp cords in our case. Thus, we considered that overall clinicopathologic features of this elderly patient were fully consistent with those of EBV+T/NK LPD. In conclusion, EBV+T/NK LPD encompasses a continuous spectrum of diseases from benign to malignant that is always associated with poor clinical outcome and can be life-threatening. A recent report demonstrated that adult patients with CAEBV had progressive and more aggressive courses than those of childhood [18]. The patients often die of malignant lymphoma/leukemia of T or NK-cell type, hemophagocytic syndrome and multiple organ failure. Though our patient has a relatively good outcome to date, the behavior of this disorder requires long-term follow up. Acknowledgements The authors are deeply grateful to Dr John K. C. Chan of the Department of Pathology, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hong Kong for consultation of this case. Disclosure of conflict of interest The authors have disclosed that they have no significant relationships with any commercial companies pertaining to this article. Address correspondence to: Dr. Zhaoming Wang, Department of Pathology, The First Affiliated Hospital, College of Medicine, Zhejiang University, No.79 Qingchun Road, Hangzhou, Zhejiang , PR China. Tel: ; Fax: ; wangzhaoming1963@163.com References [1] Cohen JI, Kimura H, Nakamura S, Ko YH, Jaffe ES. Epstein-Barr virus-associated lymphoproliferative disease in non-immunocompromised hosts: a status report and summary of an international meeting, 8-9 September Ann Oncol 2009; 20: [2] Straus SE. The chronic mononucleosis syndrome. J Infect Dis 1988; 157: [3] Kimura H, Hoshino Y, Kanegane H, Tsuge I, Okamura T, Kawa K, Morishima T. Clinical and virologic characteristics of chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection. Blood 2001; 98: [4] Kimura H, Morishima T, Kanegane H, Ohga S, Hoshino Y, Maeda A, Imai S, Okano M, Morio T, 2623 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6(11):
5 Yokota S, Tsuchiya S, Yachie A, Imashuku S, Kawa K, Wakiguchi H; Japanese Association for Research on Epstein-Barr Virus and Related Diseases. Progostic factors for chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection. J Infec Dis 2003; 187: [5] Quintanilla-Martinez L, Kumar S, Fend F, Reyes E, Teruya-Feldstein J, Kingma DW, Sorbara L, Raffeld M, Straus SE, Jaffe ES. Fulminant EBV(+) T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder following acute/chronic EBV infection: a distinct clinicopathologic syndrome. Blood 2000; 96: [6] Kimura H, Hoshino Y, Hara S, Sugaya N, Kawada J, Shibata Y, Kojima S, Nagasaka T, Kuzushima K, Morishima T. Differences between T cell-type and natural killer cell-type chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection. J Infect Dis 2005; 191: [7] Okano M, Kawa K, Kimura H, Yachie A, Wakiguchi H, Maeda A, Imai S, Ohga S, Kanegane H, Tsuchiya S, Morio T, Mori M, Yokota S, Imashuku S. Proposed guidelines for diagnosing chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection. Am J Hematol 2005; 80: [8] Quintanilla-Martinez L, Kimura H, Jaffe ES. EBV+ T-cell lymphoma of childhood. In: Swerdlow S, Campo E, Harris NL, eds. International Agency for Research on Cancer. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissue. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization 2008; pp: [9] Ohshima K, Kimura H, Yoshino T, Kim CW, Ko YH, Lee SS, Peh SC, Chan JK; CAEBV Study Group. Proposed categorization of pathological states of EBV-associated T/natural killercell lymphoproliferative disorder (LPD) in children and young adults: overlap with chronic active EBV infection and infantile fulminant EBV T-LPD. Pathol Int 2008; 58: [10] Kimura H, Ito Y, Kawabe S, Gotoh K, Takahashi Y, Kojima S, Naoe T, Esaki S, Kikuta A, Sawada A, Kawa K, Ohshima K, Nakamura S. EBV-associated T/NK-cell lymphoproliferative diseases in nonimmunocompromised hosts: prospective analysis of 108 cases. Blood 2012; 119: [11] Park S, Kim K, Kim WS, Yoo KH, Koo HH, Ko YH. Systemic EBV+ T-cell lymphoma in elderly patients: comparison with children and young adult patients. Virchows Arch 2008; 453: [12] Joo EJ, Ha YE, Jung DS, Cheong HS, Wi YM, Song JH, Peck KR. An adult case of chronic active Epstein-Barr Virus infection with interstitial pneumonitis. Korean J Intern Med 2011; 26: [13] Hashimoto T, Sakata Y, Fukushima K, Maeda T, Arita Y, Shioyama W, Nakaoka Y, Hori Y, Morii E, Aozasa K, Kanakura Y, Yamauchi-Takihara K, Komuro I. Pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection. Intern Med 2011; 50: [14] Suzuki K, Ohshima K, Karube K, Suzumiya J, Ohga S, Ishihara S, Tamura K, Kikuchi M. Clinicopathological states of Epstein-Barr virus-associated T/NK-cell lymphoproliferative disorders (severe chronic active EBV infection) of children and young adults. Int J Oncol 2004; 24: [15] Kanegane H, Bhatia K, Gutierrez M, Kaneda H, Wada T, Yachie A, Seki H, Arai T, Kagimoto S, Okazaki M, Oh-ishi T, Moghaddam A, Wang F, Tosato G. A syndrome of peripheral blood T-cell infection with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) followed by EBV-positive T-cell lymphoma. Blood 1998; 91: [16] Kawa K, Okamura T, Yagi K, Takeuchi M, Nakayama M, Inoue M. Mosquito allergy and Epstein-Barr virus-associated T/natural killer-cell lymphoproliferative disease. Blood 2001; 98: [17] Kasahara Y, Yachie A, Takei K, Kanegane C, Okada K, Ohta K, Seki H, Igarashi N, Maruhashi K, Katayama K, Katoh E, Terao G, Sakiyama Y, Koizumi S. Differential cellular targets of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection between acute EBV associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and chronic active EBV infection. Blood 2001; 98: [18] Arai A, Imadome K, Watanabe Y, Yoshimori M, Koyama T, Kawaguchi T, Nakaseko C, Fujiwara S, Miura O. Clinical features of adult-onset chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection: a retrospective analysis. Int J Hematol 2011; 93: Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6(11):
Original Article EBV-positive T/NK lymphoproliferative diseases: analysis of prognostic factors for patients in China
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11(3):1281-1288 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0071322 Original Article EBV-positive T/NK lymphoproliferative diseases: analysis of prognostic factors for patients in China
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11(3):1281-1288 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0071322 Original Article EBV-positive T/NK lymphoproliferative diseases: analysis of prognostic factors for patients in China
A Unique Case of Nasal NK/T Cell Lymphoma with Frequent Remission and Relapse Showing Different Histological Features During 12 Years of Follow Up
 J Clin Exp Hematopathol Vol. 50, No. 1, May 2010 Case Study A Unique Case of Nasal NK/T Cell Lymphoma with Frequent Remission and Relapse Showing Different Histological Features During 12 Years of Follow
J Clin Exp Hematopathol Vol. 50, No. 1, May 2010 Case Study A Unique Case of Nasal NK/T Cell Lymphoma with Frequent Remission and Relapse Showing Different Histological Features During 12 Years of Follow
Case Report Epstein-Barr virus associated T-cell lymphoproliferative disease misdiagnosed as ulcerative colitis: a case report
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(7):8598-8602 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009564 Case Report Epstein-Barr virus associated T-cell lymphoproliferative disease misdiagnosed as ulcerative colitis: a case
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(7):8598-8602 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009564 Case Report Epstein-Barr virus associated T-cell lymphoproliferative disease misdiagnosed as ulcerative colitis: a case
Original Article Spectrum of Epstein-Barr virus-associated T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder in adolescents and young adults in Taiwan
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(5):2430-2437 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP000096 Original Article Spectrum of Epstein-Barr virus-associated T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder in adolescents and young
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(5):2430-2437 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP000096 Original Article Spectrum of Epstein-Barr virus-associated T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder in adolescents and young
CASE REPORT. Abstract. Introduction. Methods
 CASE REPORT Recurrence of Chronic Active Epstein-Barr Virus Infection from Donor Cells after Achieving Complete Response Through Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplantation Ayako Arai 1, Ken-Ichi Imadome 2,
CASE REPORT Recurrence of Chronic Active Epstein-Barr Virus Infection from Donor Cells after Achieving Complete Response Through Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplantation Ayako Arai 1, Ken-Ichi Imadome 2,
Quantification of Epstein-Barr Virus DNA Is Helpful for Evaluation of Chronic Active Epstein-Barr Virus Infection
 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2012, 227, 307-311 Quantification of EBV DNA in Chronic Active EBV Infection 307 Quantification of Epstein-Barr Virus DNA Is Helpful for Evaluation of Chronic Active Epstein-Barr Virus
Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2012, 227, 307-311 Quantification of EBV DNA in Chronic Active EBV Infection 307 Quantification of Epstein-Barr Virus DNA Is Helpful for Evaluation of Chronic Active Epstein-Barr Virus
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(1): /ISSN: /IJCEP
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(1):411-417 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP1310057 Case Report A probable identical Epstein-Barr virus clone-positive composite lymphoma with aggressive natural killer-cell
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(1):411-417 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP1310057 Case Report A probable identical Epstein-Barr virus clone-positive composite lymphoma with aggressive natural killer-cell
Detection of EBV in reactive and neoplastic lymphoproliferations in adults when and how?
 J Hematopathol (2014) 7:165 170 DOI 10.1007/s12308-014-0209-0 REVIEW ARTICLE Detection of EBV in reactive and neoplastic lymphoproliferations in adults when and how? Christiane Stuhlmann-Laeisz Ilske Oschlies
J Hematopathol (2014) 7:165 170 DOI 10.1007/s12308-014-0209-0 REVIEW ARTICLE Detection of EBV in reactive and neoplastic lymphoproliferations in adults when and how? Christiane Stuhlmann-Laeisz Ilske Oschlies
Case Report A case of EBV positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the adolescent
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(1):307-311 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM1311029 Case Report A case of EBV positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the adolescent Qilin Ao 2, Ying Wang 1, Sanpeng Xu 2,
Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(1):307-311 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM1311029 Case Report A case of EBV positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the adolescent Qilin Ao 2, Ying Wang 1, Sanpeng Xu 2,
Systematic Epstein-Barr virus-positive T-cell lymphoproliferative disease presenting as a persistent fever and cough: a case report
 Ameli et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2014, 8:288 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Systematic Epstein-Barr virus-positive T-cell lymphoproliferative disease presenting as
Ameli et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2014, 8:288 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Systematic Epstein-Barr virus-positive T-cell lymphoproliferative disease presenting as
Hepatic Lymphoma Diagnosis An Algorithmic Approach
 Hepatic Lymphoma Diagnosis An Algorithmic Approach Ryan M. Gill, M.D., Ph.D. University of California, San Francisco PLEASE TURN OFF YOUR CELL PHONES Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP
Hepatic Lymphoma Diagnosis An Algorithmic Approach Ryan M. Gill, M.D., Ph.D. University of California, San Francisco PLEASE TURN OFF YOUR CELL PHONES Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP
Extranodal natural killer/t-cell lymphoma with long-term survival and repeated relapses: does it indicate the presence of indolent subtype?
 VOLUME 47 ㆍ NUMBER 3 ㆍ September 2012 THE KOREAN JOURNAL OF HEMATOLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE Extranodal natural killer/t-cell lymphoma with long-term survival and repeated relapses: does it indicate the presence
VOLUME 47 ㆍ NUMBER 3 ㆍ September 2012 THE KOREAN JOURNAL OF HEMATOLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE Extranodal natural killer/t-cell lymphoma with long-term survival and repeated relapses: does it indicate the presence
CASE REPORT. Mineui Hong Young Hyeh Ko 1
 Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2015; 49: 525-530 CASE STUDY CD30-Positive T-Cell Lymphoproliferative Disease of the Oral Mucosa in Children: A Manifestation of Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2015; 49: 525-530 CASE STUDY CD30-Positive T-Cell Lymphoproliferative Disease of the Oral Mucosa in Children: A Manifestation of Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated
Case Report Infectious mononucleosis mimicking malignant T-cell lymphoma in the nasopharynx: a case report and review of the literature
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6(1):105-109 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP1208012 Case Report Infectious mononucleosis mimicking malignant T-cell lymphoma in the nasopharynx: a case report and review
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6(1):105-109 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP1208012 Case Report Infectious mononucleosis mimicking malignant T-cell lymphoma in the nasopharynx: a case report and review
What s new on the horizon in T-cell lymphoma Elaine S Jaffe National Cancer Institute, Bethesda MD
 What s new on the horizon in T-cell lymphoma Elaine S Jaffe National Cancer Institute, Bethesda MD WHO classification: where are we today? Of 12 monographs planned for 4 th Edition Bluebook series, only
What s new on the horizon in T-cell lymphoma Elaine S Jaffe National Cancer Institute, Bethesda MD WHO classification: where are we today? Of 12 monographs planned for 4 th Edition Bluebook series, only
Natural Killer Cell-Type Body Cavity Lymphoma Following Chronic Active Epstein-Barr Virus Infection
 American Journal of Hematology 73:126 130 (2003) Natural Killer Cell-Type Body Cavity Lymphoma Following Chronic Active Epstein-Barr Virus Infection Masao Ogata, 1 * Tomoyuki Imamura, 1 Syunji Mizunoe,
American Journal of Hematology 73:126 130 (2003) Natural Killer Cell-Type Body Cavity Lymphoma Following Chronic Active Epstein-Barr Virus Infection Masao Ogata, 1 * Tomoyuki Imamura, 1 Syunji Mizunoe,
News Release. Identification of the cause of chronic active Epstein Barr virus (EBV) infection and the mechanism by which EBV causes cancer
 News Release Title Identification of the cause of chronic active Epstein Barr virus (EBV) infection and the mechanism by which EBV causes cancer Key Points A research group in Japan, led by Dr. Hiroshi
News Release Title Identification of the cause of chronic active Epstein Barr virus (EBV) infection and the mechanism by which EBV causes cancer Key Points A research group in Japan, led by Dr. Hiroshi
ACCME/Disclosures 4/13/2016. Clinical History
 ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
JMSCR Vol. 03 Issue 06 Page June 2015
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x An Indolent Natural Killer Cell Leukemia Presenting with Bilateral Ankle Arthritis and Low Grade Fever Abstract Author Subhash Chandra
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x An Indolent Natural Killer Cell Leukemia Presenting with Bilateral Ankle Arthritis and Low Grade Fever Abstract Author Subhash Chandra
Clinical Aspect and Application of Laboratory Test in Herpes Virus Infection. Masoud Mardani M.D,FIDSA
 Clinical Aspect and Application of Laboratory Test in Herpes Virus Infection Masoud Mardani M.D,FIDSA Shahidhid Bh BeheshtiMdi Medical lui Universityit Cytomegalovirus (CMV), Epstein Barr Virus(EBV), Herpes
Clinical Aspect and Application of Laboratory Test in Herpes Virus Infection Masoud Mardani M.D,FIDSA Shahidhid Bh BeheshtiMdi Medical lui Universityit Cytomegalovirus (CMV), Epstein Barr Virus(EBV), Herpes
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR
 Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
Case Reports. De Novo CD3 Negative Hepatosplenic T-cell Lymphoma. Diagnostic Challenges and Pitfalls
 Case Reports De Novo CD3 Negative Hepatosplenic T-cell Lymphoma Diagnostic Challenges and Pitfalls Lucy Harn Kapur, MD; Yasser Khaled, MD; Melhem Solh, MD; David Ward, DO; Chung-Che Chang, MD Hepatosplenic
Case Reports De Novo CD3 Negative Hepatosplenic T-cell Lymphoma Diagnostic Challenges and Pitfalls Lucy Harn Kapur, MD; Yasser Khaled, MD; Melhem Solh, MD; David Ward, DO; Chung-Che Chang, MD Hepatosplenic
Differential diagnosis of hematolymphoid tumors composed of medium-sized cells. Brian Skinnider B.C. Cancer Agency, Vancouver General Hospital
 Differential diagnosis of hematolymphoid tumors composed of medium-sized cells Brian Skinnider B.C. Cancer Agency, Vancouver General Hospital Lymphoma classification Lymphoma diagnosis starts with morphologic
Differential diagnosis of hematolymphoid tumors composed of medium-sized cells Brian Skinnider B.C. Cancer Agency, Vancouver General Hospital Lymphoma classification Lymphoma diagnosis starts with morphologic
Fulminant EBV T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder following acute/chronic EBV infection: a distinct clinicopathologic syndrome
 CLINICAL OBSERVATIONS, INTERVENTIONS, AND THERAPEUTIC TRIALS Fulminant EBV T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder following acute/chronic EBV infection: a distinct clinicopathologic syndrome Leticia Quintanilla-Martinez,
CLINICAL OBSERVATIONS, INTERVENTIONS, AND THERAPEUTIC TRIALS Fulminant EBV T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder following acute/chronic EBV infection: a distinct clinicopathologic syndrome Leticia Quintanilla-Martinez,
Molecular Pathology of Lymphoma (Part 1) Rex K.H. Au-Yeung Department of Pathology, HKU
 Molecular Pathology of Lymphoma (Part 1) Rex K.H. Au-Yeung Department of Pathology, HKU Lecture outline Time 10:00 11:00 11:15 12:10 12:20 13:15 Content Introduction to lymphoma Review of lymphocyte biology
Molecular Pathology of Lymphoma (Part 1) Rex K.H. Au-Yeung Department of Pathology, HKU Lecture outline Time 10:00 11:00 11:15 12:10 12:20 13:15 Content Introduction to lymphoma Review of lymphocyte biology
Blastic NK-Cell Leukemia / Lymphoma
 * * Blastic NK-Cell Leukemia / Lymphoma A Case Report Chun-Ming Lin Shu-Hui Wang Tseng-tong Kuo* Ching-Chi Chi Hsin-Chun Ho Hong-Shang Hong Blastic natural killer (NK) cell lymphoma / leukemia is a rare
* * Blastic NK-Cell Leukemia / Lymphoma A Case Report Chun-Ming Lin Shu-Hui Wang Tseng-tong Kuo* Ching-Chi Chi Hsin-Chun Ho Hong-Shang Hong Blastic natural killer (NK) cell lymphoma / leukemia is a rare
Case Report Epstein-Barr Virus Infection in an Elderly Nonimmunocompromised Adult Successfully Treated with Rituximab
 Case Reports in Hematology, Article ID 641483, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/641483 Case Report Epstein-Barr Virus Infection in an Elderly Nonimmunocompromised Adult Successfully Treated with
Case Reports in Hematology, Article ID 641483, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/641483 Case Report Epstein-Barr Virus Infection in an Elderly Nonimmunocompromised Adult Successfully Treated with
Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Secondary to T cell/histiocyte-rich Large B-cell Lymphoma
 Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Secondary to T cell/histiocyte-rich Large B-cell Lymphoma Katherine Devitt, M.D., Benjamin Chen, M.D., Ph.D., Hongbo Yu, M.D., Ph.D., Bruce Woda, M.D. 1 1 Department
Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Secondary to T cell/histiocyte-rich Large B-cell Lymphoma Katherine Devitt, M.D., Benjamin Chen, M.D., Ph.D., Hongbo Yu, M.D., Ph.D., Bruce Woda, M.D. 1 1 Department
Instructions for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Post-HSCT Data (Form 2113)
 Instructions for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Post-HSCT Data (Form 2113) This section of the CIBMTR Forms Instruction Manual is intended to be a resource for completing the CLL Post-HSCT Data Form. E-mail
Instructions for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Post-HSCT Data (Form 2113) This section of the CIBMTR Forms Instruction Manual is intended to be a resource for completing the CLL Post-HSCT Data Form. E-mail
Epstein-Barr Virus-associated Enteropathy as a Complication of Infectious Mononucleosis Mimicking Peripheral T-cell Lymphoma
 CASE REPORT Epstein-Barr Virus-associated Enteropathy as a Complication of Infectious Mononucleosis Mimicking Peripheral T-cell Lymphoma Shinobu Tamura 1, Dai Maruyama 1, Akiko Miyagi Maeshima 2, Hirokazu
CASE REPORT Epstein-Barr Virus-associated Enteropathy as a Complication of Infectious Mononucleosis Mimicking Peripheral T-cell Lymphoma Shinobu Tamura 1, Dai Maruyama 1, Akiko Miyagi Maeshima 2, Hirokazu
Original Article EBV-positive lymphoproliferative disease: a case report
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11(2):922-928 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0065307 Original Article EBV-positive lymphoproliferative disease: a case report Haojie Du 1, Hongtan Chen 1, Panpan Ma 2, Juan
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11(2):922-928 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0065307 Original Article EBV-positive lymphoproliferative disease: a case report Haojie Du 1, Hongtan Chen 1, Panpan Ma 2, Juan
Case Report Traumatic Haemorrhagic Cervical Lymphadenopathy with Underlying Infectious Mononucleosis
 Hindawi Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2017, Article ID 3097414, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3097414 Case Report Traumatic Haemorrhagic Cervical Lymphadenopathy with Underlying Infectious Mononucleosis
Hindawi Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2017, Article ID 3097414, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3097414 Case Report Traumatic Haemorrhagic Cervical Lymphadenopathy with Underlying Infectious Mononucleosis
CASE REPORT. Abstract. Case Report. Introduction
 CASE REPORT Polymyositis as a Paraneoplastic Syndrome in Cytotoxic Molecule-positive and Epstein-Barr Virus-associated Peripheral T-cell Lymphoma, Not Otherwise Specified Hiroko Tsunemine 1, Hayato Maruoka
CASE REPORT Polymyositis as a Paraneoplastic Syndrome in Cytotoxic Molecule-positive and Epstein-Barr Virus-associated Peripheral T-cell Lymphoma, Not Otherwise Specified Hiroko Tsunemine 1, Hayato Maruoka
Results. Clinical reports of transplant recipients
 Cloning of EBV genes as fusion proteins with Renilla luciferase for Luciferase Immunoprecipitation System (LIPS) analysis A panel of 13 different EBV proteins was generated as Renilla luciferase (Ruc)
Cloning of EBV genes as fusion proteins with Renilla luciferase for Luciferase Immunoprecipitation System (LIPS) analysis A panel of 13 different EBV proteins was generated as Renilla luciferase (Ruc)
Lymphoma/CLL 101: Know your Subtype. Dr. David Macdonald Hematologist, The Ottawa Hospital
 Lymphoma/CLL 101: Know your Subtype Dr. David Macdonald Hematologist, The Ottawa Hospital Function of the Lymph System Lymph Node Lymphocytes B-cells develop in the bone marrow and influence the immune
Lymphoma/CLL 101: Know your Subtype Dr. David Macdonald Hematologist, The Ottawa Hospital Function of the Lymph System Lymph Node Lymphocytes B-cells develop in the bone marrow and influence the immune
Hydroa Vacciniforme Is Associated with Increased Numbers of Epstein Barr Virus Infected cdt Cells
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hydroa Vacciniforme Is Associated with Increased Numbers of Epstein Barr Virus Infected cdt Cells Yoji Hirai 1, Takenobu Yamamoto 1,2, Hiroshi Kimura 3, Yoshinori Ito 4, Kazuhide Tsuji
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hydroa Vacciniforme Is Associated with Increased Numbers of Epstein Barr Virus Infected cdt Cells Yoji Hirai 1, Takenobu Yamamoto 1,2, Hiroshi Kimura 3, Yoshinori Ito 4, Kazuhide Tsuji
Epstein-Barr Virus Infection Associated With Bone Marrow Fibrin-Ring Granuloma
 Hematopathology / EBV-Associated BM Fibrin-Ring Granuloma Epstein-Barr Virus Infection Associated With Bone Marrow Fibrin-Ring Granuloma Hee-Jung Chung, MD, Hyun-Sook Chi, MD, Seongsoo Jang, MD, and Chan-Jeoung
Hematopathology / EBV-Associated BM Fibrin-Ring Granuloma Epstein-Barr Virus Infection Associated With Bone Marrow Fibrin-Ring Granuloma Hee-Jung Chung, MD, Hyun-Sook Chi, MD, Seongsoo Jang, MD, and Chan-Jeoung
Methods used to diagnose lymphomas
 Institut für Pathologie Institut für Pathologie Methods used to diagnose lymphomas Prof. Dr.Med. Leticia Quintanilla-Fend Molecular techniques NGS histology Cytology AS-PCR Sanger seq. MYC Immunohistochemistry
Institut für Pathologie Institut für Pathologie Methods used to diagnose lymphomas Prof. Dr.Med. Leticia Quintanilla-Fend Molecular techniques NGS histology Cytology AS-PCR Sanger seq. MYC Immunohistochemistry
Mimics of Lymphoma in Routine Biopsies. I have nothing to disclose regarding the information to be reported in this talk.
 Mimics of Lymphoma in Routine Biopsies Patrick Treseler, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology University of California San Francisco I have nothing to disclose regarding the information to be reported in this
Mimics of Lymphoma in Routine Biopsies Patrick Treseler, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology University of California San Francisco I have nothing to disclose regarding the information to be reported in this
Lymphoma: What You Need to Know. Richard van der Jagt MD, FRCPC
 Lymphoma: What You Need to Know Richard van der Jagt MD, FRCPC Overview Concepts, classification, biology Epidemiology Clinical presentation Diagnosis Staging Three important types of lymphoma Conceptualizing
Lymphoma: What You Need to Know Richard van der Jagt MD, FRCPC Overview Concepts, classification, biology Epidemiology Clinical presentation Diagnosis Staging Three important types of lymphoma Conceptualizing
Virally associated lymphoid proliferations
 1 Virally associated lymphoid proliferations Stefania Pittaluga, M.D., Ph.D. National Cancer Institute, Laboratory of Pathology Hematopathology Section Bethesda MD The focus of this presentation is on
1 Virally associated lymphoid proliferations Stefania Pittaluga, M.D., Ph.D. National Cancer Institute, Laboratory of Pathology Hematopathology Section Bethesda MD The focus of this presentation is on
Contents. vii. Preface... Acknowledgments... v xiii
 Contents Preface... Acknowledgments... v xiii SECTION I 1. Introduction... 3 Knowledge-Based Diagnosis... 4 Systematic Examination of the Lymph Node... 7 Cell Type Identification... 9 Cell Size and Cellularity...
Contents Preface... Acknowledgments... v xiii SECTION I 1. Introduction... 3 Knowledge-Based Diagnosis... 4 Systematic Examination of the Lymph Node... 7 Cell Type Identification... 9 Cell Size and Cellularity...
Leukaemia Section Short Communication
 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology OPEN ACCESS JOURNAL INIST-CNRS Leukaemia Section Short Communication Ding-Bao Chen Department of Pathology, Peking University People's Hospital,
Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology OPEN ACCESS JOURNAL INIST-CNRS Leukaemia Section Short Communication Ding-Bao Chen Department of Pathology, Peking University People's Hospital,
88-year-old Female with Lymphadenopathy. Faizi Ali, MD
 88-year-old Female with Lymphadenopathy Faizi Ali, MD Clinical History A 88-year-old caucasian female presented to our hospital with the complaints of nausea, vomiting,diarrhea, shortness of breath and
88-year-old Female with Lymphadenopathy Faizi Ali, MD Clinical History A 88-year-old caucasian female presented to our hospital with the complaints of nausea, vomiting,diarrhea, shortness of breath and
Primary Cutaneous CD30-Positive T-cell Lymphoproliferative Disorders
 Primary Cutaneous CD30-Positive T-cell Lymphoproliferative Disorders Definition A spectrum of related conditions originating from transformed or activated CD30-positive T-lymphocytes May coexist in individual
Primary Cutaneous CD30-Positive T-cell Lymphoproliferative Disorders Definition A spectrum of related conditions originating from transformed or activated CD30-positive T-lymphocytes May coexist in individual
EBV in HSCT 2015 update of ECIL guidelines
 ECIL-6 EBV in HSCT 2015 update of ECIL guidelines Jan Styczynski (Poland, chair), Walter van der Velden (Netherlands), Christopher Fox (United Kingdom), Dan Engelhard (Israel), Rafael de la Camara (Spain),
ECIL-6 EBV in HSCT 2015 update of ECIL guidelines Jan Styczynski (Poland, chair), Walter van der Velden (Netherlands), Christopher Fox (United Kingdom), Dan Engelhard (Israel), Rafael de la Camara (Spain),
3/27/2017. Pulmonary Pathology Specialty Conference. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. Clinical History:
 Pulmonary Pathology Specialty Conference Saul Suster, M.D. Medical College of Wisconsin Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position
Pulmonary Pathology Specialty Conference Saul Suster, M.D. Medical College of Wisconsin Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position
CASE REPORT. Abstract. Introduction. Materials and Methods
 CASE REPORT T-γ δlarge Granular Lymphocyte Leukemia Preceded by Pure Red Cell Aplasia and Complicated with Hemophagocytic Syndrome Caused by Epstein-Barr Virus Infection Yoshinori Tanaka 1,KumikoMatsui
CASE REPORT T-γ δlarge Granular Lymphocyte Leukemia Preceded by Pure Red Cell Aplasia and Complicated with Hemophagocytic Syndrome Caused by Epstein-Barr Virus Infection Yoshinori Tanaka 1,KumikoMatsui
EXTRANODAL NATURAL KILLER
 OBSERVATION A Unique Presentation of an Epstein-Barr Virus Associated Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoproliferative Disorder in a White Male Adolescent Erika Summers, MD; George Samadashwily, MD, PhD; Scott
OBSERVATION A Unique Presentation of an Epstein-Barr Virus Associated Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoproliferative Disorder in a White Male Adolescent Erika Summers, MD; George Samadashwily, MD, PhD; Scott
Classification of Hematologic Malignancies. Patricia Aoun MD MPH
 Classification of Hematologic Malignancies Patricia Aoun MD MPH Objectives Know the basic principles of the current classification system for hematopoietic and lymphoid malignancies Understand the differences
Classification of Hematologic Malignancies Patricia Aoun MD MPH Objectives Know the basic principles of the current classification system for hematopoietic and lymphoid malignancies Understand the differences
Disclosures. Diagnostic Issues. Sinusoidal Infiltrates in the Liver. Ryan M. Gill, M.D., Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Pathology.
 Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Sinusoidal Infiltrates in the Liver Ryan M. Gill, M.D., Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Pathology Diagnostic Issues Reactive infiltrates are common and may
Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Sinusoidal Infiltrates in the Liver Ryan M. Gill, M.D., Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Pathology Diagnostic Issues Reactive infiltrates are common and may
Novel Mouse Xenograft Models Reveal a Critical Role of CD4 + T Cells in the Proliferation of EBV-Infected T and NK Cells
 Novel Mouse Xenograft Models Reveal a Critical Role of CD4 + T Cells in the Proliferation of EBV-Infected T and NK Cells Ken-Ichi Imadome 1. *, Misako Yajima 1., Ayako Arai 2, Atsuko Nakazawa 3, Fuyuko
Novel Mouse Xenograft Models Reveal a Critical Role of CD4 + T Cells in the Proliferation of EBV-Infected T and NK Cells Ken-Ichi Imadome 1. *, Misako Yajima 1., Ayako Arai 2, Atsuko Nakazawa 3, Fuyuko
Lymphoma co existing with Tuberculosis granulomatous
 Available online at www.worldscientificnews.com WSN 90 (2017) 265-270 EISSN 2392-2192 SHORT COMMUNICATION Lymphoma co existing with Tuberculosis granulomatous Madeeha Subhan 1, *, Waleed Sadiq 2 1 Ayub
Available online at www.worldscientificnews.com WSN 90 (2017) 265-270 EISSN 2392-2192 SHORT COMMUNICATION Lymphoma co existing with Tuberculosis granulomatous Madeeha Subhan 1, *, Waleed Sadiq 2 1 Ayub
Epstein Barr. hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis HLH FHL X EBV AHS EBV HLH NK HLH EBV HLH HLH FHL 2 HLH HLH EBV HLH
 2010 Vol. 22No. 159 41 1 EpsteinBarr hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosishlh EB HLH 3 1 HLHFHL HLH EBV 2 X XLPSAP 3 EBVHLH EB CAEBV 2 T NK EBV HLH 1 HLH HLHFHL 2 HLH EB EB HLH EBVHLH FHLX EBVAHS EBVHLHNK
2010 Vol. 22No. 159 41 1 EpsteinBarr hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosishlh EB HLH 3 1 HLHFHL HLH EBV 2 X XLPSAP 3 EBVHLH EB CAEBV 2 T NK EBV HLH 1 HLH HLHFHL 2 HLH EB EB HLH EBVHLH FHLX EBVAHS EBVHLHNK
Mimics of Lymphoma in Routine Biopsies. Mixed follicular and paracortical hyperplasia. Types of Lymphoid Hyperplasia
 Mimics of Lymphoma in Routine Biopsies Patrick Treseler, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology University of California San Francisco Types of Lymphoid Hyperplasia Follicular hyperplasia (B-cells) Paracortical
Mimics of Lymphoma in Routine Biopsies Patrick Treseler, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology University of California San Francisco Types of Lymphoid Hyperplasia Follicular hyperplasia (B-cells) Paracortical
Acta Medica Okayama AUGUST A spectrum of clinical manifestations caused by host immune responses against Epstein-Barr virus infections.
 Acta Medica Okayama Volume 58, Issue 4 2004 Article 1 AUGUST 2004 A spectrum of clinical manifestations caused by host immune responses against Epstein-Barr virus infections. Keiji Iwatsuki Takenobu Yamamoto
Acta Medica Okayama Volume 58, Issue 4 2004 Article 1 AUGUST 2004 A spectrum of clinical manifestations caused by host immune responses against Epstein-Barr virus infections. Keiji Iwatsuki Takenobu Yamamoto
Case Report Precursor B Lymphoblastic Lymphoma Involving the Stomach
 Volume 2013, Article ID 930918, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/930918 Case Report Precursor B Lymphoblastic Lymphoma Involving the Stomach Masaya Iwamuro, 1,2 Yoshinari Kawai, 1 Yasuhide Yamawaki,
Volume 2013, Article ID 930918, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/930918 Case Report Precursor B Lymphoblastic Lymphoma Involving the Stomach Masaya Iwamuro, 1,2 Yoshinari Kawai, 1 Yasuhide Yamawaki,
T cell lymphoma diagnostics and differential diagnosis to Hodgkin lymphoma
 T cell lymphoma diagnostics and differential diagnosis to Hodgkin lymphoma Sylvia Hartmann Dr. Senckenberg Institute of Pathology Goethe University Frankfurt Overview Borderline ALCL classical HL Borderline
T cell lymphoma diagnostics and differential diagnosis to Hodgkin lymphoma Sylvia Hartmann Dr. Senckenberg Institute of Pathology Goethe University Frankfurt Overview Borderline ALCL classical HL Borderline
Recent diagnostic and therapeutic innovations of T-cell-lymphoma. Prof. Nossrat Firusian, Recklinghausen, Germany
 Recent diagnostic and therapeutic innovations of T-cell-lymphoma Prof. Nossrat Firusian, Recklinghausen, Germany NODAL Angioimmunoblastic T-cell Lymphoma Peripheral T-cell-Lymphoma Anaplastic Large-cell-Lymphoma
Recent diagnostic and therapeutic innovations of T-cell-lymphoma Prof. Nossrat Firusian, Recklinghausen, Germany NODAL Angioimmunoblastic T-cell Lymphoma Peripheral T-cell-Lymphoma Anaplastic Large-cell-Lymphoma
Case Report Intravascular NK/T-cell lymphoma in the testis: a novel case report and review of the literature
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(9):9793-9797 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0031597 Case Report Intravascular NK/T-cell lymphoma in the testis: a novel case report and review of the literature Hong Yu
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(9):9793-9797 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0031597 Case Report Intravascular NK/T-cell lymphoma in the testis: a novel case report and review of the literature Hong Yu
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), a member of the herpesvirus
 Epstein-Barr Virus Hepatitis A Review of Clinicopathologic Features and Differential Diagnosis Shula Schechter, MD; Laura Lamps, MD Context. The liver is frequently affected by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)
Epstein-Barr Virus Hepatitis A Review of Clinicopathologic Features and Differential Diagnosis Shula Schechter, MD; Laura Lamps, MD Context. The liver is frequently affected by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)
Commentary on the 2008 WHO classification of mature T- and NK-cell neoplasms
 J Hematopathol (2009) 2:65 73 DOI 10.1007/s12308-009-0034-z COMMENT Commentary on the 2008 WHO classification of mature T- and NK-cell neoplasms Megan S. Lim & Laurence de Leval & Leticia Quintanilla-Martinez
J Hematopathol (2009) 2:65 73 DOI 10.1007/s12308-009-0034-z COMMENT Commentary on the 2008 WHO classification of mature T- and NK-cell neoplasms Megan S. Lim & Laurence de Leval & Leticia Quintanilla-Martinez
Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (of T cell lineage)
 Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (of T cell lineage) Definition T-cell lymphoma comprised of large cells with abundant cytoplasm and pleomorphic, often horseshoe-shaped nuclei CD30+ Most express cytotoxic
Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (of T cell lineage) Definition T-cell lymphoma comprised of large cells with abundant cytoplasm and pleomorphic, often horseshoe-shaped nuclei CD30+ Most express cytotoxic
11/2/2017. Immunodeficiencies. Joo Y. Song, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pathology. I have no financial disclosures.
 I have no financial disclosures Joo Y. Song, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pathology City of Hope National Medical Center Immunodeficiencies Transplant Autoimmunity Drugs T-cell dysfunction (Age,
I have no financial disclosures Joo Y. Song, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pathology City of Hope National Medical Center Immunodeficiencies Transplant Autoimmunity Drugs T-cell dysfunction (Age,
10/31/2017. Immunodeficiencies. Outline. Discuss EBV. Non-destructive Polymorphic Monomorphic Therapies Challenges
 I have no financial disclosures Joo Y. Song, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pathology City of Hope National Medical Center Immunodeficiencies Outline Transplant Congenital Autoimmunity T-cell/immune
I have no financial disclosures Joo Y. Song, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pathology City of Hope National Medical Center Immunodeficiencies Outline Transplant Congenital Autoimmunity T-cell/immune
7 Omar Abu Reesh. Dr. Ahmad Mansour Dr. Ahmad Mansour
 7 Omar Abu Reesh Dr. Ahmad Mansour Dr. Ahmad Mansour -Leukemia: neoplastic leukocytes circulating in the peripheral bloodstream. -Lymphoma: a neoplastic process in the lymph nodes, spleen or other lymphatic
7 Omar Abu Reesh Dr. Ahmad Mansour Dr. Ahmad Mansour -Leukemia: neoplastic leukocytes circulating in the peripheral bloodstream. -Lymphoma: a neoplastic process in the lymph nodes, spleen or other lymphatic
Case Report Pitfalls in the Diagnosis of Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma with a Small Cell Pattern
 Case Reports in Hematology Volume 23, Article ID 84253, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/23/84253 Case Report Pitfalls in the Diagnosis of Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma with a Small Cell Pattern Rowan L.
Case Reports in Hematology Volume 23, Article ID 84253, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/23/84253 Case Report Pitfalls in the Diagnosis of Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma with a Small Cell Pattern Rowan L.
Learn more about diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), the most common aggressive form of B-cell non-hodgkin s lymphoma 1
 Learn more about diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), the most common aggressive form of B-cell non-hodgkin s lymphoma 1 Expression of B-cell surface antigens drives several non-hodgkin s lymphomas (NHLs)
Learn more about diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), the most common aggressive form of B-cell non-hodgkin s lymphoma 1 Expression of B-cell surface antigens drives several non-hodgkin s lymphomas (NHLs)
Case 3. Ann T. Moriarty,MD
 Case 3 Ann T. Moriarty,MD Case 3 59 year old male with asymptomatic cervical lymphadenopathy. These images are from a fine needle biopsy of a left cervical lymph node. Image 1 Papanicolaou Stained smear,100x.
Case 3 Ann T. Moriarty,MD Case 3 59 year old male with asymptomatic cervical lymphadenopathy. These images are from a fine needle biopsy of a left cervical lymph node. Image 1 Papanicolaou Stained smear,100x.
Case Report Anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive large B-cell lymphoma: a case report with emphasis on the cytological features of the pleural effusion
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6(11):2631-2635 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP1308070 Case Report Anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive large B-cell lymphoma: a case report with emphasis on the cytological
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6(11):2631-2635 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP1308070 Case Report Anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive large B-cell lymphoma: a case report with emphasis on the cytological
Epstein-Barr Virus Associated High-Grade B-Cell Lymphoma of Mucosal-Associated Lymphoid Tissue in a 9-Year-Old Boy
 Epstein-Barr Virus Associated High-Grade B-Cell Lymphoma of Mucosal-Associated Lymphoid Tissue in a 9-Year-Old Boy We report an unusual case of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)- associated mucosal-associated lymphoid
Epstein-Barr Virus Associated High-Grade B-Cell Lymphoma of Mucosal-Associated Lymphoid Tissue in a 9-Year-Old Boy We report an unusual case of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)- associated mucosal-associated lymphoid
Case conference. Welcome Dr. Lawrence Tierney
 Case conference Welcome Dr. Lawrence Tierney Case: 18 year-old male CC) hamatomesis, Fever and cough HPI) 1 st admission One month ago, he admitted to our hospital because of hematemesis. He had weight
Case conference Welcome Dr. Lawrence Tierney Case: 18 year-old male CC) hamatomesis, Fever and cough HPI) 1 st admission One month ago, he admitted to our hospital because of hematemesis. He had weight
CASE 35 CLINICAL HISTORY
 Female, 24 Painful ulcerated lesion Left buttock Developed over a few weeks?abscess Excision CASE 35 CLINICAL HISTORY Two months later developed a similar lesion on right buttock CD30 CD3 CD4
Female, 24 Painful ulcerated lesion Left buttock Developed over a few weeks?abscess Excision CASE 35 CLINICAL HISTORY Two months later developed a similar lesion on right buttock CD30 CD3 CD4
Case Workshop of Society for Hematopathology and European Association for Haematopathology
 Case 148 2007 Workshop of Society for Hematopathology and European Association for Haematopathology Robert P Hasserjian Department of Pathology Massachusetts General Hospital Boston, MA Clinical history
Case 148 2007 Workshop of Society for Hematopathology and European Association for Haematopathology Robert P Hasserjian Department of Pathology Massachusetts General Hospital Boston, MA Clinical history
hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis; refractory celiac disease; ebstein barr virus; cutaneous leukocytoclastic vasculitis; immunocompromised patient
 Open Journal of Clinical & Medical Case Reports Volume 3 (2017) Issue 23 ISSN 2379-1039 Hemophagocytic syndrome EBV-related associated with leukocytoclastic vasculitis in a type-2 refractory celiac patient
Open Journal of Clinical & Medical Case Reports Volume 3 (2017) Issue 23 ISSN 2379-1039 Hemophagocytic syndrome EBV-related associated with leukocytoclastic vasculitis in a type-2 refractory celiac patient
2017 CST-Astellas Canadian Transplant Fellows Symposium. EBV Post Transplantation Implications and Approach to Management
 2017 CST-Astellas Canadian Transplant Fellows Symposium EBV Post Transplantation Implications and Approach to Management Atul Humar, MD Atul Humar is a Professor in the Department of Medicine, University
2017 CST-Astellas Canadian Transplant Fellows Symposium EBV Post Transplantation Implications and Approach to Management Atul Humar, MD Atul Humar is a Professor in the Department of Medicine, University
Nasopharynx. 1. Introduction. 1.1 General Information and Aetiology
 Nasopharynx 1. Introduction 1.1 General Information and Aetiology The nasopharynx is the uppermost, nasal part of the pharynx. It extends from the base of the skull to the upper surface of the soft palate.
Nasopharynx 1. Introduction 1.1 General Information and Aetiology The nasopharynx is the uppermost, nasal part of the pharynx. It extends from the base of the skull to the upper surface of the soft palate.
Composite mantle cell and follicular lymphoma. A case report
 Human Pathology (2009) 40, 259 263 www.elsevier.com/locate/humpath Case study Composite mantle cell and follicular lymphoma. A case report Raquel B. Ilgenfritz MD a,, Agnès Le Tourneau MD a, Michel Arborio
Human Pathology (2009) 40, 259 263 www.elsevier.com/locate/humpath Case study Composite mantle cell and follicular lymphoma. A case report Raquel B. Ilgenfritz MD a,, Agnès Le Tourneau MD a, Michel Arborio
Lymphomatoid Granulomatosis: a Case Report with Unique Clinical and Histopathologic Features
 Annals of Clinical & Laboratory Science, vol. 43, no. 2, 2013 Available online at www.annclinlabsci.org Lymphomatoid Granulomatosis: a Case Report with Unique Clinical and Histopathologic Features Jamie
Annals of Clinical & Laboratory Science, vol. 43, no. 2, 2013 Available online at www.annclinlabsci.org Lymphomatoid Granulomatosis: a Case Report with Unique Clinical and Histopathologic Features Jamie
EBV and Infectious Mononucleosis. Infectious Disease Definitions. Infectious Diseases
 Infectious Disease Definitions Infection when a microorganism invades a host and multiplies enough to disrupt normal function by causing signs and symptoms Pathogencity ability of an organism to cause
Infectious Disease Definitions Infection when a microorganism invades a host and multiplies enough to disrupt normal function by causing signs and symptoms Pathogencity ability of an organism to cause
21/07/2017. Lymphoproliferations in immunodeficiency. IBD and EBV associated LPD in GIT Han van Krieken. Inflammatory bowel disease and cancer
 IBD and EBV associated LPD in GIT Han van Krieken Lymphoproliferations in immunodeficiency Primary immunodeficiencies Large variation in conditions and lesions Acquired immunodeficiencies HIV: changes
IBD and EBV associated LPD in GIT Han van Krieken Lymphoproliferations in immunodeficiency Primary immunodeficiencies Large variation in conditions and lesions Acquired immunodeficiencies HIV: changes
B-cell lymphoma showing typical features of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma
 B-cell lymphoma showing typical features of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma Masaki Mori, Yusuke Furukawa, Masaaki Takatoku, Tadashi Nagai, Kazuo Muroi, Keiya Ozawa Abstract We present a -year-old man
B-cell lymphoma showing typical features of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma Masaki Mori, Yusuke Furukawa, Masaaki Takatoku, Tadashi Nagai, Kazuo Muroi, Keiya Ozawa Abstract We present a -year-old man
Nephrology Grand Rounds
 Nephrology Grand Rounds PTLD in Kidney Transplantation Charles Le University of Colorado 6/15/12 Objectives Background Pathogenesis Epidemiology and Clinical Manifestation Incidence Risk Factors CNS Lymphoma
Nephrology Grand Rounds PTLD in Kidney Transplantation Charles Le University of Colorado 6/15/12 Objectives Background Pathogenesis Epidemiology and Clinical Manifestation Incidence Risk Factors CNS Lymphoma
Age-related Epstein-Barr virus-positive cutaneous ulcer arising after a self-limited subcutaneous abscess: a case report
 Sadiku et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2012, 6:288 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Age-related Epstein-Barr virus-positive cutaneous ulcer arising after a self-limited subcutaneous
Sadiku et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2012, 6:288 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Age-related Epstein-Barr virus-positive cutaneous ulcer arising after a self-limited subcutaneous
Form 2033 R3.0: Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome Pre-HSCT Data
 Key Fields Sequence Number: Date Received: - - CIBMTR Center Number: CIBMTR Recipient ID: Has this patient's data been previously reported to USIDNET? USIDNET ID: Today's Date: - - Date of HSCT for which
Key Fields Sequence Number: Date Received: - - CIBMTR Center Number: CIBMTR Recipient ID: Has this patient's data been previously reported to USIDNET? USIDNET ID: Today's Date: - - Date of HSCT for which
Michi Shinohara MD Associate Professor University of Washington/Seattle Cancer Care Alliance Dermatology, Dermatopathology
 Michi Shinohara MD Associate Professor University of Washington/Seattle Cancer Care Alliance Dermatology, Dermatopathology Agenda Overview of cutaneous T and B- cell lymphomas Diagnosis, Staging, Prognosis
Michi Shinohara MD Associate Professor University of Washington/Seattle Cancer Care Alliance Dermatology, Dermatopathology Agenda Overview of cutaneous T and B- cell lymphomas Diagnosis, Staging, Prognosis
Immune system. Aims. Immune system. Lymphatic organs. Inflammation. Natural immune system. Adaptive immune system
 Aims Immune system Lymphatic organs Inflammation Natural immune system Adaptive immune system Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) Disorders of the immune system 1 2 Immune system Lymphoid organs Immune
Aims Immune system Lymphatic organs Inflammation Natural immune system Adaptive immune system Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) Disorders of the immune system 1 2 Immune system Lymphoid organs Immune
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(1): /ISSN: /IJCEP
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(1):438-442 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP1310053 Case Report Epstein-Barr virus-related post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder occurring after bone marrow transplantation
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(1):438-442 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP1310053 Case Report Epstein-Barr virus-related post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder occurring after bone marrow transplantation
NK/T cell lymphoma Recent advances. Y.L Kwong University Department of Medicine Queen Mary Hospital
 NK/T cell lymphoma Recent advances Y.L Kwong University Department of Medicine Queen Mary Hospital Natural killer cell lymphomas NK cell lymphomas are mainly extranodal lymphomas Clinical classification
NK/T cell lymphoma Recent advances Y.L Kwong University Department of Medicine Queen Mary Hospital Natural killer cell lymphomas NK cell lymphomas are mainly extranodal lymphomas Clinical classification
EBV Infection and Immunity. Andrew Hislop Institute for Cancer Studies University of Birmingham
 EBV Infection and Immunity Andrew Hislop Institute for Cancer Studies University of Birmingham EBV Introduction Large ds DNA virus Spread by saliva contact Lifelong infection Predominantly B-lymphotropic
EBV Infection and Immunity Andrew Hislop Institute for Cancer Studies University of Birmingham EBV Introduction Large ds DNA virus Spread by saliva contact Lifelong infection Predominantly B-lymphotropic
MAJOR ARTICLE. (See the editorial commentary by Gottschalk on pages )
 MAJOR ARTICLE Clinical and Virological Characteristics of 15 Patients with Chronic Active Epstein-Barr Virus Infection Treated with Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Kensei Gotoh, 1 Yoshinori Ito,
MAJOR ARTICLE Clinical and Virological Characteristics of 15 Patients with Chronic Active Epstein-Barr Virus Infection Treated with Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Kensei Gotoh, 1 Yoshinori Ito,
Medical Virology Immunology. Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University
 Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Gastritis Associated with Epstein-Barr Virus Infection
 CASE REPORT Gastritis Associated with Epstein-Barr Virus Infection Akari Hisamatsu 1, Takayuki Nagai 1, Hitoshi Okawara 1, Hiroshi Nakashima 1, Takako Tasaki 1, Yoshifumi Nakagawa 1, Masahiko Hashinaga
CASE REPORT Gastritis Associated with Epstein-Barr Virus Infection Akari Hisamatsu 1, Takayuki Nagai 1, Hitoshi Okawara 1, Hiroshi Nakashima 1, Takako Tasaki 1, Yoshifumi Nakagawa 1, Masahiko Hashinaga
The patient had a mild splenomegaly but no obvious lymph node enlargement. The consensus phenotype obtained from part one of the exercise was:
 Case History An 86 year old male was admitted to hospital with chest infection. Haematological examination subsequently revealed the following: Hb- 11.0 g/dl; WBC- 67.1 x 10^9/l; PLT- 99 x10^9/l; RBC-
Case History An 86 year old male was admitted to hospital with chest infection. Haematological examination subsequently revealed the following: Hb- 11.0 g/dl; WBC- 67.1 x 10^9/l; PLT- 99 x10^9/l; RBC-
Defined lymphoma entities in the current WHO classification
 Defined lymphoma entities in the current WHO classification Luca Mazzucchelli Istituto cantonale di patologia, Locarno Bellinzona, January 29-31, 2016 Evolution of lymphoma classification Rappaport Lukes
Defined lymphoma entities in the current WHO classification Luca Mazzucchelli Istituto cantonale di patologia, Locarno Bellinzona, January 29-31, 2016 Evolution of lymphoma classification Rappaport Lukes
Overview of Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis and Staging. Lauren C. Pinter-Brown MD, FACP Health Sciences Professor of Medicine and Dermatology
 Overview of Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis and Staging Lauren C. Pinter-Brown MD, FACP Health Sciences Professor of Medicine and Dermatology Definition of Lymphoma A cancer or malignancy that comes from
Overview of Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis and Staging Lauren C. Pinter-Brown MD, FACP Health Sciences Professor of Medicine and Dermatology Definition of Lymphoma A cancer or malignancy that comes from
Case Presentation. Maha Akkawi, MD, Fatima Obeidat, MD, Tariq Aladily, MD. Department of Pathology Jordan University Hospital Amman, Jordan
 Case Presentation Maha Akkawi, MD, Fatima Obeidat, MD, Tariq Aladily, MD Department of Pathology Jordan University Hospital Amman, Jordan The 25th Annual Congress of the ADIAP The 8/11/2013 1 5th International
Case Presentation Maha Akkawi, MD, Fatima Obeidat, MD, Tariq Aladily, MD Department of Pathology Jordan University Hospital Amman, Jordan The 25th Annual Congress of the ADIAP The 8/11/2013 1 5th International
FOLLICULARITY in LYMPHOMA
 FOLLICULARITY in LYMPHOMA Reactive Follicular Hyperplasia Follicular Hyperplasia irregular follicles Follicular Hyperplasia dark and light zones Light Zone Dark Zone Follicular hyperplasia MIB1 Follicular
FOLLICULARITY in LYMPHOMA Reactive Follicular Hyperplasia Follicular Hyperplasia irregular follicles Follicular Hyperplasia dark and light zones Light Zone Dark Zone Follicular hyperplasia MIB1 Follicular
NK/T-cell lymphoma of bilateral adrenal glands in a patient with pyothorax
 Tsukahara et al. Diagnostic Pathology 2012, 7:114 CASE REPORT Open Access NK/T-cell lymphoma of bilateral adrenal glands in a patient with pyothorax Tomohide Tsukahara 1*, Akira Takasawa 1, Masaki Murata
Tsukahara et al. Diagnostic Pathology 2012, 7:114 CASE REPORT Open Access NK/T-cell lymphoma of bilateral adrenal glands in a patient with pyothorax Tomohide Tsukahara 1*, Akira Takasawa 1, Masaki Murata
T-Cell Prolymphocytic Leukemia, Small Cell Variant, Possibly at the Stage of Intracytoplasmic Expression of CD3
 Case Study J Clin Exp Hematop Vol. 55, No. 1, June 2015 T-Cell Prolymphocytic Leukemia, Small Cell Variant, Possibly at the Stage of Intracytoplasmic Expression of CD3 in T-Cell Ontogenesis Yuriko Yoshioka,
Case Study J Clin Exp Hematop Vol. 55, No. 1, June 2015 T-Cell Prolymphocytic Leukemia, Small Cell Variant, Possibly at the Stage of Intracytoplasmic Expression of CD3 in T-Cell Ontogenesis Yuriko Yoshioka,
