Control of intestinal inflammation by regulatory T cells
|
|
|
- Gertrude Gaines
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Control of intestinal inflammation by regulatory T cells Fiona Powrie Sir William Dunn School of Pathology University of Oxford fiona.powrie@path.ox.ac.uk
2 Regulatory T cells prevent immune pathology in the intestine non-inflammatory DC Infection Inflammation T E activity DC inflammatory Foxp3 T R IL-10, TGF-β T R activity T Suppression X T E 1. Mechanisms of T R mediated suppression of colitis 2. Identification of the gut as a site of T R generation-role of specialised DC
3 Regulatory T Cells 1. Naturally occurring T R (CD4 + CD25 + Foxp3 + ) Foxp3 necessary for development and function Mutations in Foxp3 gene cause lethal multi-organ inflammatory condition Suppress response to self & foreign Ag: Autoimmunity Immunity to infection Allergy Tumour immunity IBD Transplant rejection 2. Adaptive/Induced T R IL-10, TGF-b, Foxp3 Thymus Periphery CD4 + CD25 + Foxp3 + CD4 + CD25 + Foxp3 + CD4 + Foxp3 - CD4 + Foxp3 - IL-10 Foxp3 TGF-b
4 T R cells prevent colitis CD4 + CD45RB hi X colitis CD4 + CD45RB low CD25 + Prevention of colitis involves IL-10, TGF-beta and CTLA4 T R cells prevent accumulation of activated DC Directly suppress the innate response via IL-10 production CD4 CD11c DAPI Powrie et al., JEM 1994, Read et al., JEM 2001, Maloy et al,. JEM 2003
5 T R cells cure colitis CD4 + CD45RB hi CD45.2 CD4 + CD25 + CD45.1 RAG -/- 4wk 2wk (early) 10wk (cured) T R cells cure established colitis. Proliferate in MLN and colon in close contact with T E and DC Dependent on IL-10 Uhlig et al, JI, 2006; Mottet et al., JI 2003
6 Regulatory T cells in the intestine produce IL-10 Spleen Colon IL-10 Foxp3 Uhlig et al, JI, 2006
7 Ag exposure in the gut induces tolerance Apoptotic IEL Luminal Ag IL-10 Constitutive Migration Gut Homing IL-10
8 Oral administration of ovalbumin induces Foxp3 + T cells from naïve precursors OVA BSA OVA BSA Foxp3 DO11.10 SCID 5d CD4 MLN, Spleen, Colon LP
9 CD103 a marker of gut DC αe integrin subunit Expressed by mucosal DC and T Cells DC Pairs with β7, binds to E-cadherin on epithelial cells E-cadherin alphae (CD103) beta7 Gated on CD11c high Annacker et al., JEM 2005, Lindbom et al., 2005
10 Functional properties of CD103 + DC CD103 + CD103 - Naïve T cell Proliferation IFN-gamma - + Inflammatory Cytokines (IL-6, IL-23) - + Imprint gut homing Receptors ++ - CD103 expression in RAG-/- required for T R activity Annacker et al., JEM 2005; Coombes et al., JEM 2007
11 Sorting DC for in vitro T cell differentiation assay MLN CD11c MACS CD103 + and CD103 - subsets sorted on MoFlo CD11c Balb/c CD103 CD103+ CFSE Naïve D011.10/SCID CD4 + T analysis analysis cytokines CD OVAp d4 IL-2 d7 αcd3 d8
12 CD103 + DC promote the expression of Foxp3 by naïve T cells CD103+ CD103- DC Foxp3 CD103 Proliferation Cytokines? T Regulatory Properties? Homing % Foxp3 + p Foxp CFSE CD4 CD103- CD103+ 1x10^5 0.5x10^5 0.25x10^5
13 TGF-β-mediated induction of Foxp3 is increased in the presence of CD103 + DC CD103+ CD103- % Foxp ng/ml 1ng/ml [TGF-β] Induction of Foxp3 by CD103 + DC is TGF-β dependent
14 CD103 + DCs express higher levels of retinal dehydrogenase than CD103 - DCs Cellular Retinoid Metabolism Retinol (Vitamin A) ADHs SDR Retinal ALDH1A1 ALDH1A2 ALDH1A3 Relative expression/hprt aldh1a2 CD103 + CD103 - Retinoic Acid Mucosal epithelial cells and CD11c + DCs in the dome areas of the small intestine express ALDH1A1, whilst MLN-DCs express ALDH1A2 (Iwata et al., Immunity, 2004)
15 Retinoic acid acts as a co-factor for Foxp3 induction + TGF-β + TGF-β/RA p<0.001 CD ns beta7 % Foxp p<0.001 CD103-0 CD103 + CD103 - CD RA CD RA Foxp3 Spontaneous induction of Foxp3 in the presence of CD103 + DC is inhibited by an RAR antagonist Foxp3+ cells suppress T cell proliferation in vitro (Yasmine Belkaid, Jason Hall) Coombes et al., 2007; Hall et al., 2007; Benson et al. 2007; Murcida et al 2007
16 Summary Natural T R cells respond to inflammation and cure established colitis Compartmentalisation of the T R response-key role of IL-10 in control of tissue inflammation Gut is a site that favours induction of Foxp3+T R cells GALT contains functionally specialised CD103 + DC CD103 + DC imprint gut homing receptors on T cells and induce FoxP3 expression by a TGF-β and RA dependent mechanism A mechanism to broaden the repertoire of T R cells responding to intestinal antigens In addition to natural T R cells, induced T R may play an important role in intestinal homeostasis
17 CD103+ DC: mucosal DC that support the development of Foxp3+ T R cells with a mucosal seeking phenotype Colon MLN Gut conditioning TGF-β, Vit A DC E-cadherin DC CD103? TGF-β RA CD103 T Foxp3 IFNγ CCR9
18 Complimentary therapies for intestinal inflammation? Dysregulated responses M N N N IL-17 TNF-α IL-6 IFN-γ DC IL-23 Th1 Th1 Th1 Tn IL-10 TGF-β Ab blockade Treg Treg Treg T R activity Treg Foxp3+
19 Acknowledgements SWDSP: Chris Mottet Holm Uhlig Oliver Annacker Ana Izcue Janine Coombes Sophie Hue Sophia Buonocore Karima Siddiqui Kevin Maloy NIH Yasmine Belkaid Jason Hall Wellcome Trust MRC EU
Supplemental Materials
 Supplemental Materials Programmed death one homolog maintains the pool size of regulatory T cells by promoting their differentiation and stability Qi Wang 1, Jianwei He 1, Dallas B. Flies 2, Liqun Luo
Supplemental Materials Programmed death one homolog maintains the pool size of regulatory T cells by promoting their differentiation and stability Qi Wang 1, Jianwei He 1, Dallas B. Flies 2, Liqun Luo
Intestinal homeostasis and its breakdown in IBD. Fiona Powrie
 Intestinal homeostasis and its breakdown in IBD Fiona Powrie Translational Gastroenterology Unit Experimental Medicine Division Nuffield Dept of Clinical Medicine University of Oxford fiona.powrie@path.ox.ac.uk
Intestinal homeostasis and its breakdown in IBD Fiona Powrie Translational Gastroenterology Unit Experimental Medicine Division Nuffield Dept of Clinical Medicine University of Oxford fiona.powrie@path.ox.ac.uk
Determinants of Food Allergy Persistence and Severity
 Determinants of Persistence and Severity What determines sensitization? Bert Ruiter, Wayne Shreffler Immunology Institute and Jaffe Institute Mount Sinai School of Medicine Functional of a Unique Allergy-Immunology
Determinants of Persistence and Severity What determines sensitization? Bert Ruiter, Wayne Shreffler Immunology Institute and Jaffe Institute Mount Sinai School of Medicine Functional of a Unique Allergy-Immunology
Effector T Cells and
 1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
ALLERGY AND AUTOIMMUNITY
 ALLERGY AND AUTOIMMUNITY Allergies and Autoimmunity Allergies and autoimmunity can be prevented It all starts in the gut It is more than preventing leaky gut IgE allergies do not necessarily involve leaky
ALLERGY AND AUTOIMMUNITY Allergies and Autoimmunity Allergies and autoimmunity can be prevented It all starts in the gut It is more than preventing leaky gut IgE allergies do not necessarily involve leaky
Genetics. Environment. You Are Only 10% Human. Pathogenesis of IBD. Advances in the Pathogenesis of IBD: Genetics Leads to Function IBD
 Advances in the Pathogenesis of IBD: Genetics Leads to Function Pathogenesis of IBD Environmental Factors Microbes Scott Plevy, MD Associate Professor of Medicine, Microbiology & Immunology UNC School
Advances in the Pathogenesis of IBD: Genetics Leads to Function Pathogenesis of IBD Environmental Factors Microbes Scott Plevy, MD Associate Professor of Medicine, Microbiology & Immunology UNC School
Central tolerance. Mechanisms of Immune Tolerance. Regulation of the T cell response
 Immunoregulation: A balance between activation and suppression that achieves an efficient immune response without damaging the host. Mechanisms of Immune Tolerance ACTIVATION (immunity) SUPPRESSION (tolerance)
Immunoregulation: A balance between activation and suppression that achieves an efficient immune response without damaging the host. Mechanisms of Immune Tolerance ACTIVATION (immunity) SUPPRESSION (tolerance)
Mechanisms of Immune Tolerance
 Immunoregulation: A balance between activation and suppression that achieves an efficient immune response without damaging the host. ACTIVATION (immunity) SUPPRESSION (tolerance) Autoimmunity Immunodeficiency
Immunoregulation: A balance between activation and suppression that achieves an efficient immune response without damaging the host. ACTIVATION (immunity) SUPPRESSION (tolerance) Autoimmunity Immunodeficiency
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of basophils after reconstitution of SCID mice
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of after reconstitution of SCID mice with CD4 + CD62L + T cells. (A-C) SCID mice (n = 6 / group) were reconstituted with 2 x 1 6 CD4
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of after reconstitution of SCID mice with CD4 + CD62L + T cells. (A-C) SCID mice (n = 6 / group) were reconstituted with 2 x 1 6 CD4
Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells
 ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine
 Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured
 Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured under Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg conditions. mrna
Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured under Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg conditions. mrna
Immune Regulation and Tolerance
 Immune Regulation and Tolerance Immunoregulation: A balance between activation and suppression of effector cells to achieve an efficient immune response without damaging the host. Activation (immunity)
Immune Regulation and Tolerance Immunoregulation: A balance between activation and suppression of effector cells to achieve an efficient immune response without damaging the host. Activation (immunity)
Grup de fisiologia digestiva i adaptacions nutricionals Institut de Nutrició i Seguretat Alimentaria
 Grup de fisiologia digestiva i adaptacions nutricionals Institut de Nutrició i Seguretat Alimentaria 1 Outline Weaning and the consequences of stress Animal blood plasma Spray-drying SDP SDP in a model
Grup de fisiologia digestiva i adaptacions nutricionals Institut de Nutrició i Seguretat Alimentaria 1 Outline Weaning and the consequences of stress Animal blood plasma Spray-drying SDP SDP in a model
T cell maturation. T-cell Maturation. What allows T cell maturation?
 T-cell Maturation What allows T cell maturation? Direct contact with thymic epithelial cells Influence of thymic hormones Growth factors (cytokines, CSF) T cell maturation T cell progenitor DN DP SP 2ry
T-cell Maturation What allows T cell maturation? Direct contact with thymic epithelial cells Influence of thymic hormones Growth factors (cytokines, CSF) T cell maturation T cell progenitor DN DP SP 2ry
Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails. Abul K. Abbas UCSF. FOCiS
 1 Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Regulatory T cells: functions and clinical relevance Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails
1 Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Regulatory T cells: functions and clinical relevance Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails
Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails. FOCiS. Lecture outline. Regulatory T cells. Regulatory T cells: functions and clinical relevance
 1 Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Regulatory T cells: functions and clinical relevance Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails
1 Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Regulatory T cells: functions and clinical relevance Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails
Immune Tolerance. Kyeong Cheon Jung. Department of Pathology Seoul National University College of Medicine
 Immune Tolerance Kyeong Cheon Jung Department of Pathology Seoul National University College of Medicine Immune tolerance Unresponsiveness to an antigen that is induced by previous exposure to that antigen
Immune Tolerance Kyeong Cheon Jung Department of Pathology Seoul National University College of Medicine Immune tolerance Unresponsiveness to an antigen that is induced by previous exposure to that antigen
Contrasting roles for all-trans retinoic acid in TGF- mediated induction of Foxp3 and Il10 genes in developing regulatory T cells
 Contrasting roles for all-trans retinoic acid in TGF- mediated induction of Foxp3 and Il10 genes in developing regulatory T cells Craig L. Maynard, 1 Robin D. Hatton, 1 Whitney S. Helms, 1 James R. Oliver,
Contrasting roles for all-trans retinoic acid in TGF- mediated induction of Foxp3 and Il10 genes in developing regulatory T cells Craig L. Maynard, 1 Robin D. Hatton, 1 Whitney S. Helms, 1 James R. Oliver,
CD4 + T-cell subsets in intestinal inflammation
 Matthew Shale Chris Schiering Fiona Powrie CD4 + T-cell subsets in intestinal inflammation Authors addresses Matthew Shale 1, Chris Schiering 1, Fiona Powrie 1,2 1 Sir William Dunn School of Pathology,
Matthew Shale Chris Schiering Fiona Powrie CD4 + T-cell subsets in intestinal inflammation Authors addresses Matthew Shale 1, Chris Schiering 1, Fiona Powrie 1,2 1 Sir William Dunn School of Pathology,
T Lymphocyte Activation and Costimulation. FOCiS. Lecture outline
 1 T Lymphocyte Activation and Costimulation Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family Inhibitory receptors of T cells Targeting costimulators for
1 T Lymphocyte Activation and Costimulation Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family Inhibitory receptors of T cells Targeting costimulators for
Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance. Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco
 Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco EIP Symposium Feb 2016 Why do some people respond to therapeutic proteins?
Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco EIP Symposium Feb 2016 Why do some people respond to therapeutic proteins?
of whole cell cultures in U-bottomed wells of a 96-well plate are shown. 2
 Supplementary online material Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1 Exposure to T reg cells causes loss of T resp cells in co-cultures. T resp cells were stimulated with CD3+CD28 alone or
Supplementary online material Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1 Exposure to T reg cells causes loss of T resp cells in co-cultures. T resp cells were stimulated with CD3+CD28 alone or
for six pairs of mice. (b) Representative FACS analysis of absolute number of T cells (CD4 + and
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure 1: Peripheral lymphoid organs of SMAR1 -/- mice have an effector memory phenotype. (a) Lymphocytes collected from MLNs and Peyer s patches (PPs) of WT and SMAR1
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure 1: Peripheral lymphoid organs of SMAR1 -/- mice have an effector memory phenotype. (a) Lymphocytes collected from MLNs and Peyer s patches (PPs) of WT and SMAR1
Lecture outline. Immunological tolerance and immune regulation. Central and peripheral tolerance. Inhibitory receptors of T cells. Regulatory T cells
 1 Immunological tolerance and immune regulation Abul K. Abbas UCSF 2 Lecture outline Central and peripheral tolerance Inhibitory receptors of T cells Regulatory T cells 1 The immunological equilibrium:
1 Immunological tolerance and immune regulation Abul K. Abbas UCSF 2 Lecture outline Central and peripheral tolerance Inhibitory receptors of T cells Regulatory T cells 1 The immunological equilibrium:
Challenges)facing)An./tumour) Immunotherapy)in)Myeloma)))
 Challenges)facing)An./tumour) Immunotherapy)in)Myeloma))) Immune Dysfunction Prof)Gordon)Cook) Leeds)Ins.tute)of)Cancer)&)Pathology) University)of)Leeds) Impaired)immunity)in)MM) )clinical) % of Infection-related
Challenges)facing)An./tumour) Immunotherapy)in)Myeloma))) Immune Dysfunction Prof)Gordon)Cook) Leeds)Ins.tute)of)Cancer)&)Pathology) University)of)Leeds) Impaired)immunity)in)MM) )clinical) % of Infection-related
Immunology, Faculty of Medicine University of Bari, Bari (Italy) Proprietà benefiche di latte, vino e olio extra vergine di oliva
 Immunology, Faculty of Medicine University of Bari, Bari (Italy) Proprietà benefiche di latte, vino e olio extra vergine di oliva Professor Emilio Jirillo basketball court (about 400 m 2 ) mucosa-associated
Immunology, Faculty of Medicine University of Bari, Bari (Italy) Proprietà benefiche di latte, vino e olio extra vergine di oliva Professor Emilio Jirillo basketball court (about 400 m 2 ) mucosa-associated
Review Questions: Janeway s Immunobiology 8th Edition by Kenneth Murphy
 Review Questions: Janeway s Immunobiology 8th Edition by Kenneth Murphy Chapter 11 (pages 429-460): Dynamics of Adaptive Immunity prepared by Kelly von Elten, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center,
Review Questions: Janeway s Immunobiology 8th Edition by Kenneth Murphy Chapter 11 (pages 429-460): Dynamics of Adaptive Immunity prepared by Kelly von Elten, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center,
The gastrointestinal tract represents a major gateway
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2011;140:2031 2043 Interleukin-12 Converts Foxp3 Regulatory T Cells to Interferon - Producing Foxp3 T Cells That Inhibit Colitis TING FENG,*,, ANTHONY T. CAO, CASEY T. WEAVER,*, CHARLES
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2011;140:2031 2043 Interleukin-12 Converts Foxp3 Regulatory T Cells to Interferon - Producing Foxp3 T Cells That Inhibit Colitis TING FENG,*,, ANTHONY T. CAO, CASEY T. WEAVER,*, CHARLES
Supplementary information. Characterization of c-maf + Foxp3 - Regulatory T Cells Induced by. Repeated Stimulation of Antigen-Presenting B Cells
 Chien 1 Supplementary information Manuscript: SREP-16-42480A Characterization of c-maf + Foxp3 - Regulatory T Cells Induced by Repeated Stimulation of Antigen-Presenting B Cells Chien-Hui Chien 1, Hui-Chieh
Chien 1 Supplementary information Manuscript: SREP-16-42480A Characterization of c-maf + Foxp3 - Regulatory T Cells Induced by Repeated Stimulation of Antigen-Presenting B Cells Chien-Hui Chien 1, Hui-Chieh
Mechanisms of allergen-specific immunotherapy
 2012 KAAACI/EAAS Spring Mechanisms of allergen-specific immunotherapy Woo-Jung Song, MD Division of Allergy and Clinical Immunology Department of Internal Medicine Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul,
2012 KAAACI/EAAS Spring Mechanisms of allergen-specific immunotherapy Woo-Jung Song, MD Division of Allergy and Clinical Immunology Department of Internal Medicine Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul,
Tolerance, autoimmunity and the pathogenesis of immunemediated inflammatory diseases. Abul K. Abbas UCSF
 Tolerance, autoimmunity and the pathogenesis of immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas UCSF Balancing lymphocyte activation and control Activation Effector T cells Tolerance Regulatory T cells
Tolerance, autoimmunity and the pathogenesis of immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas UCSF Balancing lymphocyte activation and control Activation Effector T cells Tolerance Regulatory T cells
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 19 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD.
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 19 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD. Chapter 19: Tolerance, Autoimmunity, and Autoinflammation Prepared
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 19 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD. Chapter 19: Tolerance, Autoimmunity, and Autoinflammation Prepared
Basic Immunology. Immunological tolerance. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of the immunological tolerance. Lecture 23 rd
 Basic Immunology Lecture 23 rd Immunological tolerance Cellular and molecular mechanisms of the immunological tolerance Tolerated skin grafts on MHC (H2) identical mice TOLERANCE & AUTOIMMUNITY Upon encountering
Basic Immunology Lecture 23 rd Immunological tolerance Cellular and molecular mechanisms of the immunological tolerance Tolerated skin grafts on MHC (H2) identical mice TOLERANCE & AUTOIMMUNITY Upon encountering
High and Low Vitamin A Therapies Induce Distinct FoxP3 T-Cell Subsets and Effectively Control Intestinal Inflammation
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2009;137:1391 1402 High and Low Vitamin A Therapies Induce Distinct FoxP3 T-Cell Subsets and Effectively Control Intestinal Inflammation SEUNG G. KANG,* CHUANWU WANG,* SATOSHI MATSUMOTO,
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2009;137:1391 1402 High and Low Vitamin A Therapies Induce Distinct FoxP3 T-Cell Subsets and Effectively Control Intestinal Inflammation SEUNG G. KANG,* CHUANWU WANG,* SATOSHI MATSUMOTO,
Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD-
 Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Mechanisms by which Vitamin A and D may Contribute to (Oral) Tolerance Induction
 Mechanisms by which Vitamin A and D may Contribute to (Oral) Tolerance Induction Possible relevance for inflammatory bowel disease, food allergy and asthma Therese Klamer 3647951 March/ April 2014 Examiner:
Mechanisms by which Vitamin A and D may Contribute to (Oral) Tolerance Induction Possible relevance for inflammatory bowel disease, food allergy and asthma Therese Klamer 3647951 March/ April 2014 Examiner:
Gender Differences in Autoimmune Diseases
 //9 Impact of Gender on the Pathogenesis of Crohn s Disease Theresa T. Pizarro Department of Pathology, CWRU Gender Differences in Autoimmune Diseases n Autoimmune diseases affect ~.7-. million people
//9 Impact of Gender on the Pathogenesis of Crohn s Disease Theresa T. Pizarro Department of Pathology, CWRU Gender Differences in Autoimmune Diseases n Autoimmune diseases affect ~.7-. million people
Innate immune cells---- one time migration preprogrammed homing properties
 Innate immune cells---- one time migration preprogrammed homing properties neutrophils---acute inflammation monocytes---subacute/chronic inflammation eosinophils---parasitic or allergic inflammation natural
Innate immune cells---- one time migration preprogrammed homing properties neutrophils---acute inflammation monocytes---subacute/chronic inflammation eosinophils---parasitic or allergic inflammation natural
SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER
 Judy Owen Jenni Punt Sharon Stranford Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 16 Tolerance, Autoimmunity, and Transplantation Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and Company Immune tolerance: history * Some
Judy Owen Jenni Punt Sharon Stranford Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 16 Tolerance, Autoimmunity, and Transplantation Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and Company Immune tolerance: history * Some
Intestinal Microflora and Immunoregulation
 Intestinal Microflora and Immunoregulation Monica Boirivant Istituto Superiore di Sanità Roma Microflora-immune cells interactions Ethanol AT 12 T Effect of ir Ethanol 5% administration 115 weight (% of
Intestinal Microflora and Immunoregulation Monica Boirivant Istituto Superiore di Sanità Roma Microflora-immune cells interactions Ethanol AT 12 T Effect of ir Ethanol 5% administration 115 weight (% of
T Regulatory Cell and Body Tolerance
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2017, 9 [5]:23-28 [http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html] ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2017, 9 [5]:23-28 [http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html] ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Dendritic cells in cancer immunotherapy Aimin Jiang
 Dendritic cells in cancer immunotherapy Aimin Jiang Feb. 11, 2014 Dendritic cells at the interface of innate and adaptive immune responses Dendritic cells: initiators of adaptive immune responses Dendritic
Dendritic cells in cancer immunotherapy Aimin Jiang Feb. 11, 2014 Dendritic cells at the interface of innate and adaptive immune responses Dendritic cells: initiators of adaptive immune responses Dendritic
SUPPLEMENT Supplementary Figure 1: (A) (B)
 SUPPLEMENT Supplementary Figure 1: CD4 + naïve effector T cells (CD4 effector) were labeled with CFSE, stimulated with α-cd2/cd3/cd28 coated beads (at 2 beads/cell) and cultured alone or cocultured with
SUPPLEMENT Supplementary Figure 1: CD4 + naïve effector T cells (CD4 effector) were labeled with CFSE, stimulated with α-cd2/cd3/cd28 coated beads (at 2 beads/cell) and cultured alone or cocultured with
RORγt and IL-17 Responses`
 Falk Workshop Mechanisms of Intestinal Inflammation October 10, 2007 and IL-17 Responses` Dan Littman HHMI, Skirball Institute New York University School of Medicine New paradigm for T Helper Cell Differentiation
Falk Workshop Mechanisms of Intestinal Inflammation October 10, 2007 and IL-17 Responses` Dan Littman HHMI, Skirball Institute New York University School of Medicine New paradigm for T Helper Cell Differentiation
T Cell Activation, Costimulation and Regulation
 1 T Cell Activation, Costimulation and Regulation Abul K. Abbas, MD University of California San Francisco 2 Lecture outline T cell antigen recognition and activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
1 T Cell Activation, Costimulation and Regulation Abul K. Abbas, MD University of California San Francisco 2 Lecture outline T cell antigen recognition and activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
Intestinal dendritic cells in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease
 Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327office wjg@wjgnet.com doi:10.3748/wjg.v17.i33.3761 World J Gastroenterol 2011 September 7; 17(33): 3761-3775 ISSN 1007-9327 (print) ISSN 2219-2840 (online)
Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327office wjg@wjgnet.com doi:10.3748/wjg.v17.i33.3761 World J Gastroenterol 2011 September 7; 17(33): 3761-3775 ISSN 1007-9327 (print) ISSN 2219-2840 (online)
Accepted Manuscript. Innate immune cells regulate oncoimmunity and cancer development. Ai-Ping Bai, Yuan Guo
 Accepted Manuscript Innate immune cells regulate oncoimmunity and cancer development Ai-Ping Bai, Yuan Guo PII: S0016-5085(18)34974-6 DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.08.057 Reference: YGAST 62119 To appear
Accepted Manuscript Innate immune cells regulate oncoimmunity and cancer development Ai-Ping Bai, Yuan Guo PII: S0016-5085(18)34974-6 DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.08.057 Reference: YGAST 62119 To appear
Molecular mechanisms of the T cellinflamed tumor microenvironment: Implications for cancer immunotherapy
 Molecular mechanisms of the T cellinflamed tumor microenvironment: Implications for cancer immunotherapy Thomas F. Gajewski, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, Departments of Pathology and Medicine Program Leader,
Molecular mechanisms of the T cellinflamed tumor microenvironment: Implications for cancer immunotherapy Thomas F. Gajewski, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, Departments of Pathology and Medicine Program Leader,
D CD8 T cell number (x10 6 )
 IFNγ Supplemental Figure 1. CD T cell number (x1 6 ) 18 15 1 9 6 3 CD CD T cells CD6L C CD5 CD T cells CD6L D CD8 T cell number (x1 6 ) 1 8 6 E CD CD8 T cells CD6L F Log(1)CFU/g Feces 1 8 6 p
IFNγ Supplemental Figure 1. CD T cell number (x1 6 ) 18 15 1 9 6 3 CD CD T cells CD6L C CD5 CD T cells CD6L D CD8 T cell number (x1 6 ) 1 8 6 E CD CD8 T cells CD6L F Log(1)CFU/g Feces 1 8 6 p
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is characterized by a
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2012;142:335 345 CCL17 Promotes Intestinal Inflammation in Mice and Counteracts Regulatory T Cell Mediated Protection From Colitis ALEXANDER F. HEISEKE,* ANTONIA C. FAUL,* HANS ANTON LEHR,
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2012;142:335 345 CCL17 Promotes Intestinal Inflammation in Mice and Counteracts Regulatory T Cell Mediated Protection From Colitis ALEXANDER F. HEISEKE,* ANTONIA C. FAUL,* HANS ANTON LEHR,
Dendritic cell subsets and CD4 T cell immunity in Melanoma. Ben Wylie 1 st year PhD Candidate
 Dendritic cell subsets and CD4 T cell immunity in Melanoma Ben Wylie 1 st year PhD Candidate Melanoma Melanoma is the 4 th most common cancer in Australia. Current treatment options are ineffective resulting
Dendritic cell subsets and CD4 T cell immunity in Melanoma Ben Wylie 1 st year PhD Candidate Melanoma Melanoma is the 4 th most common cancer in Australia. Current treatment options are ineffective resulting
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry:
 Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry: Simultaneous Detection of Cytokines and Transcription Factors Presented by Jurg Rohrer, PhD, BD Biosciences 23-10780-00 Outline Introduction Cytokines Transcription
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry: Simultaneous Detection of Cytokines and Transcription Factors Presented by Jurg Rohrer, PhD, BD Biosciences 23-10780-00 Outline Introduction Cytokines Transcription
Immunological Tolerance
 Immunological Tolerance Introduction Definition: Unresponsiveness to an antigen that is induced by exposure to that antigen Tolerogen = tolerogenic antigen = antigen that induces tolerance Important for
Immunological Tolerance Introduction Definition: Unresponsiveness to an antigen that is induced by exposure to that antigen Tolerogen = tolerogenic antigen = antigen that induces tolerance Important for
Immune response to infection
 Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
Supplementary Figure 1. IL-12 serum levels and frequency of subsets in FL patients. (A) IL-12
 1 Supplementary Data Figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. IL-12 serum levels and frequency of subsets in FL patients. (A) IL-12 serum levels measured by multiplex ELISA (Luminex) in FL patients before
1 Supplementary Data Figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. IL-12 serum levels and frequency of subsets in FL patients. (A) IL-12 serum levels measured by multiplex ELISA (Luminex) in FL patients before
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry:
 Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry: Simultaneous Detection of Cytokines and Transcription Factors An encore presentation by Jurg Rohrer, PhD, BD Biosciences 10.26.10 Outline Introduction Cytokines
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry: Simultaneous Detection of Cytokines and Transcription Factors An encore presentation by Jurg Rohrer, PhD, BD Biosciences 10.26.10 Outline Introduction Cytokines
IL-12 family members in experimental colitis. Markus F. Neurath I. Medical Clinic Johannes Gutenberg-University Mainz, Germany
 IL-12 family members in experimental colitis Markus F. Neurath I. Medical Clinic Johannes Gutenberg-University Mainz, Germany IBD - Pathogenesis Genetic Predisposition Bacterial Antigens Activation of
IL-12 family members in experimental colitis Markus F. Neurath I. Medical Clinic Johannes Gutenberg-University Mainz, Germany IBD - Pathogenesis Genetic Predisposition Bacterial Antigens Activation of
A crucial role for HVEM and BTLA in preventing intestinal inflammation
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2008 A crucial role for HVEM and BTLA in preventing intestinal inflammation Marcos W. Steinberg La Jolla Institute
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2008 A crucial role for HVEM and BTLA in preventing intestinal inflammation Marcos W. Steinberg La Jolla Institute
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.3922
 Title: Glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor-related protein co-stimulation facilitates tumor regression by inducing IL-9-producing helper T cells Authors: Il-Kyu Kim, Byung-Seok Kim, Choong-Hyun
Title: Glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor-related protein co-stimulation facilitates tumor regression by inducing IL-9-producing helper T cells Authors: Il-Kyu Kim, Byung-Seok Kim, Choong-Hyun
Autoimmunity. Autoimmunity arises because of defects in central or peripheral tolerance of lymphocytes to selfantigens
 Autoimmunity Autoimmunity arises because of defects in central or peripheral tolerance of lymphocytes to selfantigens Autoimmune disease can be caused to primary defects in B cells, T cells and possibly
Autoimmunity Autoimmunity arises because of defects in central or peripheral tolerance of lymphocytes to selfantigens Autoimmune disease can be caused to primary defects in B cells, T cells and possibly
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature1554 a TNF-α + in CD4 + cells [%] 1 GF SPF 6 b IL-1 + in CD4 + cells [%] 5 4 3 2 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of microbiota on cytokine profiles of T cells in GALT. Frequencies of TNF-α
doi:1.138/nature1554 a TNF-α + in CD4 + cells [%] 1 GF SPF 6 b IL-1 + in CD4 + cells [%] 5 4 3 2 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of microbiota on cytokine profiles of T cells in GALT. Frequencies of TNF-α
Objectives. Abbas Chapter 11: Immunological Tolerance. Question 1. Question 2. Question 3. Definitions
 Objectives Abbas Chapter 11: Immunological Tolerance Christina Ciaccio, MD Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics February 1, 2010 To introduce the concept of immunologic tolerance To understand what factors
Objectives Abbas Chapter 11: Immunological Tolerance Christina Ciaccio, MD Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics February 1, 2010 To introduce the concept of immunologic tolerance To understand what factors
General Overview of Immunology. Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center
 General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
Intestinal Microbiota in Health and Disease
 Intestinal Microbiota in Health and Disease February 27, 2015 Master s Course in Gastroenterology Prof. Kathy McCoy 1 Overview Overview of Gut Microbiota Microbiota in Health Microbiota in Disease 2 Gut
Intestinal Microbiota in Health and Disease February 27, 2015 Master s Course in Gastroenterology Prof. Kathy McCoy 1 Overview Overview of Gut Microbiota Microbiota in Health Microbiota in Disease 2 Gut
Immune response. This overview figure summarizes simply how our body responds to foreign molecules that enter to it.
 Immune response This overview figure summarizes simply how our body responds to foreign molecules that enter to it. It s highly recommended to watch Dr Najeeb s lecture that s titled T Helper cells and
Immune response This overview figure summarizes simply how our body responds to foreign molecules that enter to it. It s highly recommended to watch Dr Najeeb s lecture that s titled T Helper cells and
Part III Innate and Adaptive Immune Cells: General Introduction
 Innate and Adaptive Immune Cells: General Introduction Iván López-Expósito As an organ specialized in food digestion and nutrient absorption, the intestinal mucosa presents a huge surface area (almost
Innate and Adaptive Immune Cells: General Introduction Iván López-Expósito As an organ specialized in food digestion and nutrient absorption, the intestinal mucosa presents a huge surface area (almost
Dendritic cells in intestinal homeostasis and disease
 Dendritic cells in intestinal homeostasis and disease Maria Rescigno, Antonio Di Sabatino J Clin Invest. 2009;119(9):2441-2450. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci39134. Science in Medicine DCs are specialized
Dendritic cells in intestinal homeostasis and disease Maria Rescigno, Antonio Di Sabatino J Clin Invest. 2009;119(9):2441-2450. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci39134. Science in Medicine DCs are specialized
Diverting T helper cell trafficking through increased plasticity attenuates autoimmune encephalomyelitis
 Research article Diverting T helper cell trafficking through increased plasticity attenuates autoimmune encephalomyelitis Danielle Califano, 1,2 Keith J. Sweeney, 1 Hung Le, 1,2 Jeffrey VanValkenburgh,
Research article Diverting T helper cell trafficking through increased plasticity attenuates autoimmune encephalomyelitis Danielle Califano, 1,2 Keith J. Sweeney, 1 Hung Le, 1,2 Jeffrey VanValkenburgh,
CHAPTER 9 BIOLOGY OF THE T LYMPHOCYTE
 CHAPTER 9 BIOLOGY OF THE T LYMPHOCYTE Coico, R., Sunshine, G., (2009) Immunology : a short course, 6 th Ed., Wiley-Blackwell 1 CHAPTER 9 : Biology of The T Lymphocytes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Introduction
CHAPTER 9 BIOLOGY OF THE T LYMPHOCYTE Coico, R., Sunshine, G., (2009) Immunology : a short course, 6 th Ed., Wiley-Blackwell 1 CHAPTER 9 : Biology of The T Lymphocytes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Introduction
Cell-mediated Immunity
 Cellular & Molecular Immunology Cell-mediated Immunity Nicholas M. Ponzio, Ph.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine April 6, 2009 Today s Presentation: Overview Cellular Interactions In Humoral
Cellular & Molecular Immunology Cell-mediated Immunity Nicholas M. Ponzio, Ph.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine April 6, 2009 Today s Presentation: Overview Cellular Interactions In Humoral
CD90 + Human Dermal Stromal Cells Are Potent Inducers of FoxP3 + Regulatory T Cells
 CD90 + Human Dermal Stromal Cells Are Potent Inducers of FoxP3 + Regulatory T Cells Karin Pfisterer, Karoline M Lipnik, Erhard Hofer and Adelheid Elbe-Bürger Journal of Investigative Dermatology (2015)
CD90 + Human Dermal Stromal Cells Are Potent Inducers of FoxP3 + Regulatory T Cells Karin Pfisterer, Karoline M Lipnik, Erhard Hofer and Adelheid Elbe-Bürger Journal of Investigative Dermatology (2015)
Harnessing tolerance mechanisms with monoclonal antibodies Prof. Herman Waldmann
 Harnessing tolerance mechanisms Herman Waldmann Sir William Dunn School of Pathology, Oxford University, UK 1 1. Transplantation 2 Lymphocyte depletion strategies to minimise drug immunosuppression in
Harnessing tolerance mechanisms Herman Waldmann Sir William Dunn School of Pathology, Oxford University, UK 1 1. Transplantation 2 Lymphocyte depletion strategies to minimise drug immunosuppression in
Inflammatory Bowel Disease A model for translational medicine. D P Jewell Professor Emeritus of Gastroenterology University of Oxford
 Inflammatory Bowel Disease A model for translational medicine D P Jewell Professor Emeritus of Gastroenterology University of Oxford Samuel Wilks 1859, Pathological Treatises of Guy s Hospital The London
Inflammatory Bowel Disease A model for translational medicine D P Jewell Professor Emeritus of Gastroenterology University of Oxford Samuel Wilks 1859, Pathological Treatises of Guy s Hospital The London
Supplementary Table 1 Clinicopathological characteristics of 35 patients with CRCs
 Supplementary Table Clinicopathological characteristics of 35 patients with CRCs Characteristics Type-A CRC Type-B CRC P value Sex Male / Female 9 / / 8.5 Age (years) Median (range) 6. (9 86) 6.5 (9 76).95
Supplementary Table Clinicopathological characteristics of 35 patients with CRCs Characteristics Type-A CRC Type-B CRC P value Sex Male / Female 9 / / 8.5 Age (years) Median (range) 6. (9 86) 6.5 (9 76).95
T cell-mediated immunity
 T cell-mediated immunity Overview For microbes within phagosomes in phagocytes.cd4+ T lymphocytes (TH1) Activate phagocyte by cytokines studies on Listeria monocytogenes For microbes infecting and replicating
T cell-mediated immunity Overview For microbes within phagosomes in phagocytes.cd4+ T lymphocytes (TH1) Activate phagocyte by cytokines studies on Listeria monocytogenes For microbes infecting and replicating
Topic (Final-02): Immunologic Tolerance
 Topic (Final-02): Immunologic Tolerance Immunologic tolerance is defined as unresponsiveness to an antigen that is induced by previous exposure to that antigen. The term arose from the experimental observation
Topic (Final-02): Immunologic Tolerance Immunologic tolerance is defined as unresponsiveness to an antigen that is induced by previous exposure to that antigen. The term arose from the experimental observation
Lecture 9: T-cell Mediated Immunity
 Lecture 9: T-cell Mediated Immunity Questions to Consider How do T cells know where to go? Questions to Consider How do T cells know where to go? How does antigen get targeted to a T cell expressing the
Lecture 9: T-cell Mediated Immunity Questions to Consider How do T cells know where to go? Questions to Consider How do T cells know where to go? How does antigen get targeted to a T cell expressing the
VISTA, a novel immune checkpoint protein ligand that suppresses anti-tumor tumor T cell responses. Li Wang. Dartmouth Medical School
 VISTA, a novel immune checkpoint protein ligand that suppresses anti-tumor tumor T cell responses Li Wang Dartmouth Medical School The B7 Immunoglobulin Super-Family immune regulators APC T cell Co-stimulatory:
VISTA, a novel immune checkpoint protein ligand that suppresses anti-tumor tumor T cell responses Li Wang Dartmouth Medical School The B7 Immunoglobulin Super-Family immune regulators APC T cell Co-stimulatory:
T Cell Development II: Positive and Negative Selection
 T Cell Development II: Positive and Negative Selection 8 88 The two phases of thymic development: - production of T cell receptors for antigen, by rearrangement of the TCR genes CD4 - selection of T cells
T Cell Development II: Positive and Negative Selection 8 88 The two phases of thymic development: - production of T cell receptors for antigen, by rearrangement of the TCR genes CD4 - selection of T cells
B6/COLODR/SPL/11C/83/LAP/#2.006 B6/COLODR/SPL/11C/86/LAP/#2.016 CD11C B6/COLODR/SPL/11C/80/LAP/#2.011 CD11C
 CD3-specific antibody-induced immune tolerance and suppression of autoimmune encephalomyelitis involves TGF-β production through phagocytes digesting apoptotic T cells Sylvain Perruche 1,3, Pin Zhang 1,
CD3-specific antibody-induced immune tolerance and suppression of autoimmune encephalomyelitis involves TGF-β production through phagocytes digesting apoptotic T cells Sylvain Perruche 1,3, Pin Zhang 1,
DNA vaccine, peripheral T-cell tolerance modulation 185
 Subject Index Airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) animal models 41 43 asthma inhibition 45 overview 41 mast cell modulation of T-cells 62 64 respiratory tolerance 40, 41 Tregs inhibition role 44 respiratory
Subject Index Airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) animal models 41 43 asthma inhibition 45 overview 41 mast cell modulation of T-cells 62 64 respiratory tolerance 40, 41 Tregs inhibition role 44 respiratory
Gut-Tropic T Cells That Express Integrin 4 7 and CCR9 Are Required for Induction of Oral Immune Tolerance in Mice
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2011;141:2109 2118 Gut-Tropic T Cells That Express Integrin 4 7 and CCR9 Are Required for Induction of Oral Immune Tolerance in Mice BARBARA CASSANI,* EDUARDO J. VILLABLANCA,* FRANCISCO
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2011;141:2109 2118 Gut-Tropic T Cells That Express Integrin 4 7 and CCR9 Are Required for Induction of Oral Immune Tolerance in Mice BARBARA CASSANI,* EDUARDO J. VILLABLANCA,* FRANCISCO
LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE
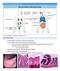 LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE - Small intestine in humans is around 3-4 metres long - Internal surface of the small intestines are lined by villi o Villi are composed of absorptive cells (epithelial/enterocytes)
LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE - Small intestine in humans is around 3-4 metres long - Internal surface of the small intestines are lined by villi o Villi are composed of absorptive cells (epithelial/enterocytes)
5/1/13. The proportion of thymus that produces T cells decreases with age. The cellular organization of the thymus
 T cell precursors migrate from the bone marrow via the blood to the thymus to mature 1 2 The cellular organization of the thymus The proportion of thymus that produces T cells decreases with age 3 4 1
T cell precursors migrate from the bone marrow via the blood to the thymus to mature 1 2 The cellular organization of the thymus The proportion of thymus that produces T cells decreases with age 3 4 1
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Identification of IFN-γ-producing CD8 + and CD4 + T cells with naive phenotype by alternative gating and sample-processing strategies. a. Contour 5% probability plots show definition
Supplementary Figure 1 Identification of IFN-γ-producing CD8 + and CD4 + T cells with naive phenotype by alternative gating and sample-processing strategies. a. Contour 5% probability plots show definition
Characterization of Foxp3 IL-10-Secreting CD4 + + CD4
 This information is current as of June 20, 2018. Characterization of Foxp3 IL-10-Secreting CD4 + + CD4 CD25 + + CD25 + and T Cells during Cure of Colitis Holm H. Uhlig, Janine Coombes, Christian Mottet,
This information is current as of June 20, 2018. Characterization of Foxp3 IL-10-Secreting CD4 + + CD4 CD25 + + CD25 + and T Cells during Cure of Colitis Holm H. Uhlig, Janine Coombes, Christian Mottet,
New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation. Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre
 New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre No Disclosures
New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre No Disclosures
Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation. Abul K. Abbas UCSF. FOCiS
 1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
Modulation of immunogenicity by engineered antigen-specific regulatory T cells: Fighting fire with fireman or police CARs
 Modulation of immunogenicity by engineered antigen-specific regulatory T cells: Fighting fire with fireman or police CARs David W. Scott Department of Medicine Uniformed Services University of the Health
Modulation of immunogenicity by engineered antigen-specific regulatory T cells: Fighting fire with fireman or police CARs David W. Scott Department of Medicine Uniformed Services University of the Health
T Cell Receptor & T Cell Development
 T Cell Receptor & T Cell Development Questions for the next 2 lectures: How do you generate a diverse T cell population with functional TCR rearrangements? How do you generate a T cell population that
T Cell Receptor & T Cell Development Questions for the next 2 lectures: How do you generate a diverse T cell population with functional TCR rearrangements? How do you generate a T cell population that
Supplemental Figures: Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figures: Supplemental Figure 1 Suppl. Figure 1. BM-DC infection with H. pylori does not induce cytotoxicity and treatment of BM-DCs with H. pylori sonicate, but not heat-inactivated bacteria,
Supplemental Figures: Supplemental Figure 1 Suppl. Figure 1. BM-DC infection with H. pylori does not induce cytotoxicity and treatment of BM-DCs with H. pylori sonicate, but not heat-inactivated bacteria,
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author):
 Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): The manuscript by Sun et al., provide data showing that short-chain fatty acids produced by intestinal microbiota act through GPR43 to induced
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): The manuscript by Sun et al., provide data showing that short-chain fatty acids produced by intestinal microbiota act through GPR43 to induced
Necrotizing Enterocolitis: The Role of the Immune System
 Necrotizing Enterocolitis: The Role of the Immune System Patricia Denning, M.D. Associate Professor in Pediatrics Division of Neonatology Emory University School of Medicine What is NEC? What is NEC? Necrotizing
Necrotizing Enterocolitis: The Role of the Immune System Patricia Denning, M.D. Associate Professor in Pediatrics Division of Neonatology Emory University School of Medicine What is NEC? What is NEC? Necrotizing
The development of T cells in the thymus
 T cells rearrange their receptors in the thymus whereas B cells do so in the bone marrow. The development of T cells in the thymus The lobular/cellular organization of the thymus Immature cells are called
T cells rearrange their receptors in the thymus whereas B cells do so in the bone marrow. The development of T cells in the thymus The lobular/cellular organization of the thymus Immature cells are called
CD4 + T cells recovered in Rag2 / recipient ( 10 5 ) Heart Lung Pancreas
 a CD4 + T cells recovered in Rag2 / recipient ( 1 5 ) Heart Lung Pancreas.5 1 2 4 6 2 4 6 Ctla4 +/+ Ctla4 / Ctla4 / Lung Ctla4 / Pancreas b Heart Lung Pancreas Ctla4 +/+ Ctla4 / Ctla4 / Lung Ctla4 / Pancreas
a CD4 + T cells recovered in Rag2 / recipient ( 1 5 ) Heart Lung Pancreas.5 1 2 4 6 2 4 6 Ctla4 +/+ Ctla4 / Ctla4 / Lung Ctla4 / Pancreas b Heart Lung Pancreas Ctla4 +/+ Ctla4 / Ctla4 / Lung Ctla4 / Pancreas
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nature89 IFN- (ng ml ) 5 4 3 1 Splenocytes NS IFN- (ng ml ) 6 4 Lymph node cells NS Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / IL- (ng ml ) 3 1 Splenocytes IL- (ng ml ) 1 8 6 4 *** ** Lymph node cells
doi: 1.138/nature89 IFN- (ng ml ) 5 4 3 1 Splenocytes NS IFN- (ng ml ) 6 4 Lymph node cells NS Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / IL- (ng ml ) 3 1 Splenocytes IL- (ng ml ) 1 8 6 4 *** ** Lymph node cells
Recruitment of regulatory and conventional T cells to colon adenocarcinomas. Veronica Langenes
 Recruitment of regulatory and conventional T cells to colon adenocarcinomas Veronica Langenes Department of Microbiology and Immunology Institute of Biomedicine The Sahlgrenska academy, University of Gothenburg
Recruitment of regulatory and conventional T cells to colon adenocarcinomas Veronica Langenes Department of Microbiology and Immunology Institute of Biomedicine The Sahlgrenska academy, University of Gothenburg
Human Innate Lymphoid Cells: crosstalk with CD4 + regulatory T cells and role in Type 1 Diabetes
 Joint Lab Meeting 03/03/2015 Human Innate Lymphoid Cells: crosstalk with CD4 + regulatory T cells and role in Type 1 Diabetes Caroline Raffin Bluestone Lab ILCs: Definition - Common lymphoid progenitor
Joint Lab Meeting 03/03/2015 Human Innate Lymphoid Cells: crosstalk with CD4 + regulatory T cells and role in Type 1 Diabetes Caroline Raffin Bluestone Lab ILCs: Definition - Common lymphoid progenitor
