J Sobajima, S Ozaki, H Uesugi, F Osakada, M Inoue, Y Fukuda, H Shirakawa, M Yoshida, A Rokuhara, H Imai, K Kiyosawa, K Nakao
|
|
|
- Raymond Nicholson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Gut 1999;44: Department of Medicine and Clinical Science, Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine, 54 Shogoin-Kawahara-cho, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto , Japan J Sobajima S Ozaki H Uesugi M Inoue Y Fukuda K Nakao Kaneka Corporation, 1-8, Miyamae-machi, Takasago-cho, Takasago-shi, Hyogo , Japan F Osakada Department of Biological Science and Technology, Science University of Tokyo, Yamazaki, Noda, Chiba , Japan H Shirakawa M Yoshida Second Department of Internal Medicine, Shinshu University School of Medicine, 3-1-1, Asahi, Matsumoto, Nagano , Japan A Rokuhara H Imai K Kiyosawa Correspondence to: Dr S Ozaki, Department of Medicine and Clinical Science, Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine, 54 Shogoin-Kawahara-cho, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto , Japan. Accepted for publication 5 January 1999 High mobility group (HMG) non-histone chromosomal proteins HMG1 and HMG2 are significant target antigens of perinuclear anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies in autoimmune hepatitis J Sobajima, S Ozaki, H Uesugi, F Osakada, M Inoue, Y Fukuda, H Shirakawa, M Yoshida, A Rokuhara, H Imai, K Kiyosawa, K Nakao Abstract Background High mobility group (HMG) non-histone chromosomal proteins HMG1 and HMG2 have been identified as novel antigens of perinuclear antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (p- ANCAs), and the existence of anti-hmg1 and anti-hmg2 antibodies in a population of patients with ulcerative colitis has been reported. Aims To investigate whether HMG1 and HMG2 are target antigens for p-ancas in autoimmune hepatitis (AIH). Patients Serum samples from 28 patients with AIH, 44 patients with primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC), 27 patients with chronic hepatitis C, and 23 patients with chronic hepatitis B were tested. Methods ANCAs were detected by routine indirect immunofluorescence (IIF). Anti-HMG1 and anti-hmg2 antibodies were assayed by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. Results p-ancas were detected in 89% (25/28) of patients with AIH, 36% (16/44) of patients with PBC, 11% (3/27) of patients with chronic hepatitis C, and 13% (3/23) of patients with chronic hepatitis B. Anti- HMG1 and/or anti-hmg2 antibodies were detected in 89% (25/28) of patients with AIH, 70% (31/44) with PBC, 26% (7/27) with chronic hepatitis C, and 9% (2/23) with chronic hepatitis B. In AIH, anti- HMG1 and/or anti-hmg2 antibodies were detected in 96% (24/25) of p-anca positive patients. The p-anca staining pattern detected by IIF using sera from patients with AIH disappeared or decreased in titre after preincubation with a mixture of HMG1/HMG2. The presence and titres of those antibodies in AIH correlated significantly with those of p-anca, but not with those of antinuclear antibody or anti-smooth muscle antibody. Conclusions HMG1 and HMG2 are significant target antigens of p-anca in AIH. (Gut 1999;44: ) Keywords: perinuclear anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies; chromosomal proteins; high mobility group 1 and 2; autoimmune; hepatitis Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCAs) are directed against the cytoplasmic components of neutrophils. They can be divided into two major subtypes by indirect immunofluorescence (IIF) using ethanol fixed neutrophils as substrates: those showing a cytoplasmic pattern (c-ancas) and those showing a perinuclear pattern (p-ancas). Most c-ancas are specific for proteinase 3, 1 3 and a substantial proportion of p-ancas are directed against myeloperoxidase. 4 The strong association of ANCAs with systemic vasculitis has been established: proteinase 3-ANCAs are more commonly found in patients with Wegener s granulomatosis 1 3 and myeloperoxidase ANCAs are more commonly found in patients with vasculitis limited to the kidney. 4 p-ancas have been associated not only with systemic vasculitis but also with nonvasculitic diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease 5 8 and chronic liver diseases In autoimmune liver diseases, particularly autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) and primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), p-ancas are commonly detected. These p-ancas do not react with myeloperoxidase, and it has been speculated that their target antigens are diverent from the granule proteins of neutrophils reported previously. Recent studies have reported that actin is one of the target antigens of ANCAs in AIH 14 and that catalase and α-enolase are those in PSC. 15 However, the main target antigens remain unclear. Recently, we identified high mobility group (HMG) non-histone chromosomal proteins HMG1 and HMG2 as novel antigens of p-ancas, and reported the existence of anti-hmg1/hmg2 antibodies in a population of patients with ulcerative colitis and systemic rheumatic diseases. 19 HMG1 and HMG2, which are distributed not only in the nuclei but also in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic Abbreviations used in this paper: ANCA, anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody; IIF, indirect immunofluorescence; c-anca, cytoplasmic anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody; p-anca, perinuclear anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody; AIH, autoimmune hepatitis; PSC, primary sclerosing cholangitis; HMG, high mobility group; ELISA, enzyme linked immunosorbent assay; PBC, primary biliary cirrhosis; ANA, anti-nuclear antibody; SMA, anti-smooth muscle antibody; AMA, anti-mitochondrial antibody.
2 868 Sobajima, Ozaki, Uesugi, et al cells, are known to act as transcriptional factors In spite of their ubiquitous distribution, we found that some monoclonal anti- HMG1/HMG2 antibodies showed a perinuclear staining pattern of ethanol fixed neutrophils on IIF, and that these antibodies did not stain lymphocytes or HEp-2 cells. 23 These results indicate that antibodies against HMG1 and HMG2 fulfil the criteria of p-ancas 4 Interestingly, in western blotting using neutrophils, these antibodies exhibited diverent bands from those using lymphocytes or HEp-2 cells (unpublished observation), suggesting that HMG1 and HMG2 in neutrophils may be distinct from those in lymphocytes or HEp-2 cells. The amino acid sequences of HMG1/ HMG2 are highly conserved among species for instance, there are only two amino acid differences between human and porcine HMG1/HMG Because of this high degree of conservation in primary sequences, anti-human HMG1/HMG2 sera cross reacted with porcine HMG1 and HMG2. 17 Therefore we established an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) system using porcine HMG1/HMG2 as antigens instead of human proteins. In this study, we studied the prevalence of anti-hmg1/hmg2 antibodies in chronic liver diseases that is, autoimmune hepatitis (AIH), primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC), and chronic hepatitis C and B, using the ELISA system and analysed the relations between anti-hmg1/ HMG2 antibodies and p-ancas in these diseases. Furthermore, we analysed the relations between anti-hmg1/hmg2 antibodies and antibodies to cathepsin G and lactoferrin, which are reported to be target antigens of p-ancas, and other autoantibodies such as anti-nuclear antibody (ANA), anti-smooth muscle antibody (SMA), and antimitochondrial antibody (AMA), which are useful seromarkers for AIH or PBC. Patients and methods PATIENTS Sera from 28 patients with AIH and 44 patients with PBC were studied (table 1). The diagnoses of AIH and PBC were made on the basis of clinical, serological, and histological criteria. 30 All 28 patients with AIH lacked other Table 1 Characteristics Patients and normal controls Diagnosis AIH causes of chronic liver disease such as metabolic, drug related, and viral including hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C virus. All patients had persistent elevation of serum aminotransferases, IgG (>2500 mg/dl), and non-organ-specific autoantibodies. In all cases, liver biopsy specimens showed moderate or severe piecemeal necrosis and inflammatory mononuclear cell infiltration into the portal tract. Seven patients had other immunological diseases: two had Sjögren s syndrome, one had Sjögren s syndrome and chronic thyroiditis, one had chronic thyroiditis, one had rheumatoid arthritis, one had rheumatoid arthritis and systemic sclerosis, and one had systemic sclerosis. The activity index was determined according to the definition of the international autoimmune hepatitis group. 31 Five patients had been treated with prednisolone (5 40 mg/day) at the time of blood sampling. All 44 patients with PBC had cholestatic liver disease. Thirty one patients showed chronic non-suppurative destructive cholangitis on liver biopsy specimens. The remaining 13 were positive for serum AMA and/or antipyruvate dehydrogenase antibody and showed liver histology compatible with PBC. Twelve patients had other immunological diseases: five had Sjögren s syndrome, one had Sjögren s syndrome and rheumatoid arthritis, two had Sjögren s syndrome and systemic sclerosis, one had systemic sclerosis, two had systemic sclerosis and chronic thyroiditis, and one had chronic thyroiditis. One patient had been treated with prednisolone (10 mg/day) at the time of blood sampling. As disease controls, we tested sera from patients with chronic viral hepatitis: 27 patients with chronic hepatitis C and 23 with chronic hepatitis B diagnosed by liver biopsy and serology (second generation assays). Twenty four age matched healthy blood donors served as normal controls. Informed consent was obtained from each subject. The sample sera were stored at 20 C. MATERIALS Porcine HMG1 and HMG2 were purified from pig thymus as described elsewhere. 32 Human cathepsin G (ICN Biomedicals, Cleveland, Ohio, USA) and human lactoferrin (Sigma, St Louis, Missouri, USA) were purchased. Their PBC Viral hepatitis C Viral hepatitis B Normal controls No of patients and controls Sex (M/F) 6/22 4/40 15/12 15/8 8/16 Median age (years)* 52 (24 80) 60 (36 71) 53 (30 62) 30 (20 56) 51 (34 77) Other immunological diseases 7 (25) 12 (27) 1 (4) 0 (0) 0 (0) (concomitant presence of UC ) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) Positive ANA (>1:40) 25 (89) 29 (66) 2 (7) 1 (4) 0 (0) Positive SMA (>1:40) 16 (57) 1 (2) 6 (22) 0 (0) 0 (0) Positive AMA (>1:40) 3 (11) 33 (75) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) Presence of cirrhosis 3 (11) 11 (25) 4 (15) 3 (13) 0 (0) Use of prednisolone at the time of sampling 5 (18) 1 (2) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) *Data in parentheses represent ranges. Data expressed as number of patients (percentage of whole). AIH, autoimmune hepatitis; PBC, primary biliary cirrhosis; UC, ulcerative colitis; ANA, anti-nuclear antibody; SMA, anti-smooth muscle antibody; AMA, anti-mitochondrial antibody.
3 Antibodies to HMG1 and HMG2 in autoimmune hepatitis 869 purity was confirmed by sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Neutrophils were isolated from peripheral blood obtained from normal human volunteers by Ficoll density gradient centrifugation. AYnity purified anti-hmg1/hmg2 antibody was obtained by applying the serum from a p-anca positive patient to an HMG1/HMG2 aynity column. IIF ASSAY ANCA activity was determined by IIF assay as described by Wiik. 33 Briefly, ethanol fixed cytospin preparations of human neutrophils were incubated with serum at room temperature for 20 minutes at an initial dilution of 1:10 or 1:125 in phosphate buvered saline and in twofold dilutions thereof. As the secondary antibody, fluorescein isothiocyanate conjugated F(ab ) 2 rabbit anti-human IgG (Serotec, Oxford, UK) was used. The slides were evaluated by fluorescence microscopy. ANCA titres were determined as the reciprocals of final dilutions to give positive staining. As controls, p-anca and c-anca positive sera were purchased from Binding Site (Birmingham, UK). Samples positive for perinuclear or nuclear staining were subjected to formalin fixation, instead of ethanol fixation, to distinguish ANCAs from antibodies to neutrophil nuclei. p-ancas were regarded as positive when they showed perinuclear or nuclear staining on ethanol fixed neutrophils and cytoplasmic or negative staining on formalin fixed neutrophils Competitive inhibition IIF using an HMG1/HMG2 mixture was performed to determine the specificity of reactivity to HMG1/HMG2. Double positive sera for p-anca and anti-hmg1/hmg2 antibodies were diluted at optimal dilutions that were 8- or 16-fold more concentrated than their final dilutions to give p-anca positive staining. These sera were preincubated with equal volumes of HMG1/HMG2 mixture (100 µg/ml) or phosphate buvered saline for 30 minutes at room temperature, and were used for subsequent IIF assays in parallel to determine the ANCA titres. ANA, SMA, and AMA were assayed by IIF using commercial kits: fluoro HEPANA test for ANA, and fluoro AID-1 test for SMA and AMA (MBL, Nagoya, Japan). Sera were considered positive for ANA, SMA, and AMA at a dilution of >1:40. Gut: first published as /gut on 1 June Downloaded from on 1 December 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright. Figure 1 Perinuclear anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody activities on indirect immunofluorescence. Sera from patients with autoimmune hepatitis (A, B) and primary biliary cirrhosis (C, D), and an aynity purified anti-hmg1/hmg2 antibody (E, F) showing perinuclear staining on ethanol fixed neutrophils (A, C, E) and cytoplasmic or negative staining on formalin fixed neutrophils (B, D, F).
4 870 Sobajima, Ozaki, Uesugi, et al Table 2 Frequencies of antibodies to HMG1, HMG2, cathepsin G, and lactoferrin Number of sera positive for antibodies to: Disease (n) p-anca (n) HMG1 HMG2 HMG1 or 2* HMG1 and 2 Cathepsin G Lactoferrin AIH (28) Positive (25) Negative (3) PBC (44) Positive (16) Negative (28) Chronic hepatitis C (27) Positive (3) Negative (24) Chronic hepatitis B (23) Positive (3) Negative (20) *Positive for antibodies to either HMG1 or HMG2. Positive for antibodies to both HMG1 and HMG2. p-anca, perinuclear anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies; AIH, autoimmune hepatitis; PBC, primary biliary cirrhosis. p = (Fisher s exact test). p = (Fisher s exact test). U/ml A p = p = AIH PBC Hepatitis C Hepatitis B Normal controls ELISA Antibodies to HMG1, HMG2, cathepsin G, and lactoferrin were assayed by ELISA as described elsewhere. 18 Briefly, 50 µl of 5 µg/ml HMG1 and HMG2 in phosphate buvered saline, ph 7.4, cathepsin G in 500 mm sodium acetate with 150 mm NaCl, ph 5.5, and lactoferrin in bicarbonate buver, ph 9.6, were respectively put on microtitre plates (Immunoplate maxisorp; Nunc, Roskilde, Denmark). Serum samples were diluted 1:40 in phosphate buvered saline containing 5% bovine serum albumin, and the secondary antibody used was alkaline phosphatase conjugated F(ab ) 2 goat anti-human IgG (Immunotech, Marseille, France). Antibody titres were expressed as U/ml by reference to the dilution curves for positive control sera, the titres of which were arbitrarily set at 100 U/ml. A level >3 SD above the mean for normal sera was regarded as positive. Competitive inhibition ELISA using HMG1, HMG2, cathepsin G, and lactoferrin was performed to determine the specificity of reactivity to the respective proteins. The corresponding antibody positive sera at optimal dilutions were preincubated with equal volumes of HMG1, HMG2, cathepsin G, and lactoferrin of various concentrations for 30 minutes at room temperature. Ovalbumin was used as a control. STATISTICAL ANALYSIS The results were analysed by the Mann- Whitney U test, Wilcoxon signed rank test, Fisher s exact test, and the Spearman rank correlation test. In these analyses, values of p<0.05 were considered statistically significant. Results DETECTION OF ANCAs BY IIF ANCAs were tested by IIF in serum from patients with chronic liver diseases. p-ancas were detected in 25 (89%) of 28 sera from patients with AIH, 16 (36%) of 44 from patients with PBC, three (11%) of 27 from patients with chronic hepatitis C, and three (13%) of 23 from patients with chronic hepatitis B. Among the sera with positive perinuclear Figure 2 Titres of antibodies to HMG1 (A) and HMG2 (B) determined by ELISA. AIH, autoimmune hepatitis; PBC, primary biliary cirrhosis. The solid lines represent median values of antibody titres. p values by Mann-Whitney U test. U/ml B p = p = AIH PBC Hepatitis C Hepatitis B Normal controls
5 Antibodies to HMG1 and HMG2 in autoimmune hepatitis 871 Optical density (405 nm) HMG1/HMG2 OVA Concentration of Ag (µg/ml) Figure 3 Competitive inhibition ELISA. Anti-HMG1/HMG2 antibody positive serum from a patient with autoimmune hepatitis was preincubated with a mixture of HMG1 and HMG2 or ovalbumin (OVA) at the concentrations indicated. In a subsequent HMG1/HMG2 ELISA, the reactivity decreased in a dose dependent manner when preincubated with HMG1/HMG2, but not with ovalbumin. Anti-HMG2 antibody (U/ml) p-anca titre (dilution 1 ) Figure 4 Correlation between the titres of anti-hmg2 antibody and perinuclear anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies in autoimmune hepatitis. A positive correlation was found between the two parameters (r = , p<0.0001, Spearman rank correlation test). Figure 5 Disappearance of perinuclear anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (p-anca) staining after preincubation with specific antigens. Serum from a patient with autoimmune hepatitis with a p-anca titre of 1280 was diluted at 1:160 and preincubated with an equal volume of 100 µg/ml of a mixture of HMG1 and HMG2 (B) or phosphate buvered saline (A). Subsequent IIF was performed by each solution, and photographs were taken at the same exposure. No fluorescence was visible in (B), where the only bright cell is an eosinophil with spontaneous fluorescence. staining on ethanol fixed neutrophils, cytoplasmic fluorescent patterns on formalin fixed neutrophils were detected in 24 (96%) of 25 sera from patients with AIH, 10 (62%) of 16 sera from patients with PBC, two (67%) of three sera from patients with chronic hepatitis C, and two (67%) of three sera from patients with chronic hepatitis B. The remaining sera showed negative staining. We considered these two patterns as positive for p-ancas as described elsewhere Median titres of the p-anca positive sera were 640 (range ) for AIH and 20 (range ) for PBC. Figure 1 shows some representative results. On the other hand, c-ancas were only detected in 9% of PBC sera. Neither p-ancas nor c-ancas were detected in normal control sera. ANTIBODIES TO HMG1, HMG2, CATHEPSIN G, AND LACTOFERRIN ASSAYED BY ELISA All sera from patients with AIH, PBC, chronic hepatitis C, and chronic hepatitis B were tested for reactivity to HMG1, HMG2, cathepsin G, and lactoferrin by ELISA. Table 2 summarises the frequencies of those antibodies. Antibodies to HMG1, HMG2, and cathepsin G were more commonly detected in patients with AIH and PBC than in patients with chronic hepatitis C and B. The titres of antibodies to HMG1 and HMG2 in AIH were significantly higher than in PBC, chronic hepatitis C and B (fig 2). The titres of antibodies to HMG1 and HMG2 in PBC were significantly higher than in chronic hepatitis C and B. These positive sera for antibodies to HMG1, HMG2, cathepsin G, and lactoferrin seemed to be specific, as the preincubation of the sera with the corresponding antigens abrogated reactivity in the subsequent ELISA. Figure 3 shows representative results. RELATIO BETWEEN p-ancas AND ANTI-HMG1 AND/OR ANTI-HMG2 ANTIBODIES In AIH, the presence of p-ancas correlated significantly with the presence of anti-hmg1 and/or anti-hmg2 antibodies, but not with the presence of anti-cathepsin G and antilactoferrin antibodies (table 2). The titres of p-ancas correlated significantly with the titres of anti-hmg2 antibody (fig 4) and weakly with the titres of anti-hmg1 antibody (Spearman rank correlation, r = , p = ). From p-anca and anti-hmg1/ HMG2 antibody positive sera of patients with AIH, we selected four specimens with negative or low titres of anti-cathepsin G or antilactoferrin antibodies for competitive inhibition IIF. The titres of p-ancas decreased after preincubation with a mixture of HMG1/ HMG2 (one serum from 5120 to <320, one serum from 1280 to <320, and two from 320 to 80). Figure 5 shows representative results. In PBC, the presence of p-ancas did not correlate with the presence of anti-hmg1 and/or anti-hmg2 antibodies (table 2), although titres of p-ancas correlated weakly with titres of anti-hmg2 antibody (Spearman rank correlation, p = 0.042).
6 872 Sobajima, Ozaki, Uesugi, et al Table 3 Relations between antibodies to HMG1/HMG2 and ANA, SMA and AMA Disease (n) Autoantibodies (n) Number of sera positive for antibodies to HMG1 or HMG2 Positive Negative AIH (28) ANA+ (25) 23 2 ANA (3) 2 1 SMA+ (16) 15 1 SMA (12) 10 2 PBC (44) ANA+ (29) 24* 5 ANA (15) 7 8 AMA+ (33) 25 8 AMA (11) 6 5 AIH, autoimmune hepatitis; PBC, primary biliary cirrhosis; ANA, anti-nuclear antibody; SMA, anti-smooth muscle antibody; AMA, anti-mitochondrial antibody. *p = (Fisher s exact test). RELATIO BETWEEN ANTI-HMG1 AND/OR ANTI-HMG2 ANTIBODIES AND ANA, SMA, AND AMA Of 28 patients with AIH, ANA and SMA were detected in 25 (89%) and 16 (57%) respectively (table 1). Of 44 patients with PBC, ANA and AMA were detected in 29 (66%) and 33 (75%) respectively. The frequencies of SMA and AMA in our study were lower than in previous studies, presumably because we considered ANA, SMA, and AMA as positive at a dilution of >1:40, instead of >1:20. In AIH, the presence of anti-hmg1 and/or anti- HMG2 antibodies did not correlate with the presence or absence of ANA or SMA (table 3). In PBC, however, anti-hmg1 and/or anti- HMG2 antibodies significantly correlated with the presence of ANA, but did not correlate with the presence of AMA. ASSOCIATION OF ANTI-HMG1 OR ANTI-HMG2 ANTIBODIES AND CLINICAL FEATURES We investigated the association between anti- HMG1 or anti-hmg2 antibodies with clinical features in patients with AIH and PBC. The Table 4 Association of anti-hmg1 or anti-hmg2 antibodies and clinical features in patients with autoimmune hepatitis Anti-HMG1 Positive (median values) n=22 Negative n=6 Anti-HMG2 Positive (median values) n=24 Negative n=4 AST (IU/l) ALT (IU/l) IgG (mg/dl) IgM (mg/dl) p=0.025 Anti-HMG1 antibodies (median values) Sex Men (n=6) 14.2 J p=0.029 Anti-HMG2 antibodies (median values) 17.5 J p=0.012 Women (n=22) Other immunological diseases + (n=7) J J (n=21) Liver cirrhosis + (n=3) 28.2 J 60.8 (n=25) J Use of prednisolone at time of sampling + (n=5) 31.9 J 84.3 (n=23) J p values by Mann-Whitney U test. AST, serum aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, serum alanine aminotransferase. clinical parameters selected were age, sex, serum aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, IgG, IgM, histology, treatment, clinical course, presence of liver cirrhosis and complications of any other immunological diseases. In AIH, as shown in table 4, anti-hmg1 and anti-hmg2 antibody titres were significantly higher in women than in men. Patients with AIH with positive anti- HMG1 antibody showed lower IgM. In eleven of the 12 patients with AIH, who had high titres of anti-hmg1 or anti-hmg2 antibody before corticosteroid treatment (prednisolone, between 20 and 60 mg/day), the antibody titre returned to normal or decreased after 5 10 months of treatment (data not shown). In PBC, however, no significant relation was observed between the presence of anti-hmg1 and/or anti-hmg2 antibodies and clinical status (data not shown). Discussion We found that antibodies to either HMG1 or HMG2 were detected more often in patients with AIH and PBC than in those with chronic hepatitis C and B. In AIH, the titres of antibodies to either HMG1 or HMG2 were significantly higher than in PBC and chronic hepatitis C and B. Interestingly, the presence and titres of these antibodies in AIH correlated significantly with those of p-ancas. Preincubation of sera from patients with AIH with an excess mixture of HMG1 and HMG2 resulted in a decrease in the p-anca titre. These results strongly suggest that HMG1 and HMG2 are significant target antigens of p-ancas in AIH. However, p-ancas in AIH may recognise several candidate antigens other than HMG1 and HMG2. For example, cathepsin G and actin are reported to be antigens of ANCAs in AIH. Indeed, anti-cathepsin G antibodies were detected more often here than in a previous study. 34 ANA and SMA are useful seromarkers for AIH. In our study, the presence of anti-hmg1 and/or anti-hmg2 antibodies was independent of the presence of ANA and SMA. Interestingly, anti-hmg1 and/or anti-hmg2 antibodies disappeared or significantly decreased in titre after corticosteroid therapy in AIH. If the titres of anti-hmg1 and/or anti-hmg2 antibodies reflect disease activity, these antibodies can serve as useful clinical markers in AIH, because the detection systems for these antibodies are simpler and more quantitative than those for ANA and SMA. The relations between the titre of anti-hmg1 and/or anti-hmg2 antibodies and the activity index of AIH are at present being analysed in a prospective follow up study. In PBC, anti-hmg1 and/or anti-hmg2 antibodies were detected in both p-anca positive patients and p-anca negative patients, although these antibodies were hardly detected in p-anca negative patients with AIH. Moreover, some monoclonal anti-hmg1 and/or anti-hmg2 antibodies showed a p-anca staining pattern, whereas others did not (unpublished observation). These observations suggest that anti-hmg1 and/or anti-
7 Antibodies to HMG1 and HMG2 in autoimmune hepatitis 873 HMG2 antibodies can be divided into two subtypes by IIF using ethanol fixed neutrophils: a p-anca staining subtype and a negative staining one. Clarifying the epitopes of these antibodies would facilitate our understanding of the pathological diverence between AIH and PBC. p-ancas are also commonly detected in PSC In our preliminary study, p-ancas were detected in eight of 11 patients with PSC. Among p-anca positive patients, however, anti-hmg1 and/or anti-hmg2 antibodies were positive in only two patients (unpublished observation). It is unlikely that HMG1 and HMG2 are major p-anca antigens in PSC. It has been considered that the main autoimmune targets in AIH are hepatocytes, whereas those in PBC and PSC are intrahepatic bile capillary epithelia and bile duct epithelia respectively. Therefore the presence of anti-hmg1 and anti-hmg2 antibodies may reflect hepatocellular damage rather than bile duct epithelial damage. The way in which HMG1 and HMG2 are involved in the pathogenesis of autoimmune liver disease is unknown. Besides its cytoplasmic and intranuclear localisation, HMG1 exists on the membrane of nerve cells and plays a role in enhancing neurite outgrowth. It has also been reported that HMG1 is secreted by a murine erythroleukaemia cell line 37 Thus, if HMG1 exists on the surface of cells or in extracellular environments at inflammatory sites, the anti-hmg1 antibody may bind to HMG1, resulting in modification of the inflammatory process in autoimmune liver diseases. It therefore seems important to determine the distribution and expression of HMG1 and HMG2 molecules in liver cells to clarify the pathological role of anti-hmg1 and anti-hmg2 antibodies. This work was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture of Japan, by research grants from the Ministry of Health and Welfare of Japan, and by grants from the Japan Rheumatism Association. 1 Lüdemann J, Utecht B, Gross WL. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibodies in Wegener s granulomatosis recognize an elastinolytic enzyme. J Exp Med 1990;171: Cohen Tervaert JW, van der Woude FJ, Fauci AS, et al. Association between active Wegener s granulomatosis and anticytoplasmic antibodies. Arch Intern Med 1989;149: Nölle B, Specks U, Lüdemann J, et al. Anticytoplasmic autoantibodies: their immunodiagnostic value in Wegener s granulomatosis. Ann Intern Med 1989;111: Falk RJ, Jennette JC. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies with specificity for myeloperoxidase in patients with systemic vasculitis and idiopathic necrotizing and crescentic glomerulonephritis. N Engl J Med 1988;318: Saxon A, Shanahan F, Landers C, et al. A distinct subset of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies is associated with inflammatory bowel disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1990;86: Duerr RH, Targan SR, Landers CJ, et al. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies in ulcerative colitis: comparison with other colitides/diarrheal illnesses. Gastroenterology 1991;100: Seibold F, Weber P, Klein R, et al. Clinical significance of antibodies against neutrophils in patients with inflammatory bowel disease and primary sclerosing cholangitis. Gut 1992;33: Cambridge G, Rampton DS, Stevens TRJ, et al. Antineutrophil antibodies in inflammatory bowel disease: prevalence and diagnostic role. Gut 1992;33: Klein R, Eisenburg J, Weber P, et al. Significance and specificity of antibodies to neutrophils detected by Western blotting for the serological diagnosis of primary sclerosing cholangitis. Hepatology 1991;14: Mulder AHL, Horst G, Haagsma EB, et al. Prevalence and characterization of neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies in autoimmune liver diseases. Hepatology 1993;17: Vidrich A, Lee J, James E, et al. Segregation of panca antigenic recognition by DNase treatment of neutrophils: ulcerative colitis, type 1 autoimmune hepatitis, and primary sclerosing cholangitis. J Clin Immunol 1995;15: Hardarson S, Labrecque DR, Mitros FA, et al. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody in inflammatory bowel and hepatobiliary diseases: high prevalence in ulcerative colitis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, and autoimmune hepatitis. Clin Microbiol Immunol 1993;99: Targan SR, Landers C, Vidrich A, et al. High-titre antineutrophil cytoplasmic anibodies in type-1 autoimmune hepatitis. Gastroenterology 1995;108: Orth T, Gerken G, Kellner R, et al. Actin is a target antigen of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA) in autoimmune hepatitis type-1. J Hepatol 1997;26: Orth T, Keller R, Diekmann SO, et al. Identification and characterization of new ANCA antigens in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis: catalase and alpha-enolase. Clin Exp Immunol 1998;112(suppl 1): Sobajima J, Ozaki S, Okazaki T, et al. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA) in ulcerative colitis: anticathepsin G and a novel antibody correlate with a refractory type. Clin Exp Immunol 1996;105: Sobajima J, Ozaki S, Osakada F, et al. Novel autoantigens of perinuclear anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (p- ANCA) in ulcerative colitis: non-histone chromosomal proteins, HMG1 and HMG2. Clin Exp Immunol 1997;107: Sobajima J, Ozaki S, Uesugi H, et al. Prevalence and characterization of p-anca directed against HMG1 and HMG2 in ulcerative colitis. Clin Exp Immunol 1998;111: Uesugi H, Ozaki S, Sobajima J, et al. Prevalence and characterization of novel p-anca, antibodies to the high mobility group non-histone chromosomal proteins HMG1 and HMG2, in systemic rheumatic diseases. J Rheumatol 1998; 25: Bustin M, Lehn DA, Landsman D. Structural features of the HMG chromosomal proteins and their genes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1990;1049: Einck L, Bustin M. The intracellular distribution and function of the high mobility group chromosomal proteins. Exp Cell Res 1985;156: Bustin M, Neihart NK. Antibodies against chromosomal HMG proteins stain the cytoplasm of mammalian cells. Cell 1979;16: Uesugi H, Ozaki S, Sobajima J, et al. High mobility group non-histone chromosomal proteins HMG1 and HMG2: Are they p-anca target antigens? Clin Exp Immunol 1998; 112(suppl 1): Majumdar A, Brown D, Kerby S, et al. Sequence of human HMG2 cdna. Nucleic Acids Res 1991;19: Wen L, Huang JK, Johnson BH, et al. A human placental cdna clone that encodes nonhistone chromosomal protein HMG-1. Nucleic Acids Res 1989;17: Shirakawa H, Yoshida M. Structure of a gene coding for human HMG2 protein. J Biol Chem 1992;267: Shirakawa H, Tsuda K, Yoshida M. Primary structure of non-histone chromosomal protein HMG2 revealed by the nucleotide sequence. Biochemistry 1990;29: Halbwachs-Mecarelli L, Nusbaum P, Noël LH, et al. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA) directed against cathepsin G in ulcerative colitis, Crohn s disease and primary sclerosing cholangitis. Clin Exp Immunol 1992;90: Peen E, Almer S, Bodemar G, et al. Anti-lactoferrin antibodies and other types of ANCA in ulcerative colitis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, and Crohn s disease. Gut 1993;34: Ohta Y. Report of the research subgroup of autoimmune hepatitis/primary biliary cirrhosis. Gastroenterol Jpn 1993; 28(suppl 4): Johnson PJ, Macfarlane IG. Meeting report: international autoimmune hepatitis group. Hepatology 1993;18: Yoshida M, Shimura K. Unwinding of DNA by nonhistone chromosomal protein HMG(1+2) from pig thymus as determined with endonuclease. J Biochem (Tokyo) 1984;95: Wiik A. Delineation of a standard procedure for indirect immunofluorescence detection of ANCA. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand 1989;97: Lesavre P, Nusbaum P, Halbwachs-Mecarelli. Methods of detection of anticathepsin G autoantibodies in human. In: Gross WL, ed. ANCA-associated vasculitides: immunological and clinical aspects. New York: Plenum Press, 1993: Merenmies J, Pihlaskari R, Laitinen J, et al. 30-kDa heparinbinding protein of brain (amphoterin) involved in neurite outgrowth: amino acid sequence and localization in the filopodia of the advancing plasma membrane. J Biol Chem 1991;266: Parkkinen J, Raulo E, Merenmies J, et al. Amphoterin, the 30-kDa protein in a family of HMG1-type polypeptides: enhanced expression in transformed cells, leading edge localization, and interactions with plasminogen activation. J Biol Chem 1993;268: Melloni E, Sparatore B, Patrone M, et al. Extracellular release of the diverentiation enhancing factor, a HMG1 protein type, is an early step in murine erythroleukemia cell diverentiation. FEBS Lett 1995;368:
A Dual-Fixed Neutrophil Substrate Improves Interpretation of Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies by Indirect Immunofluorescence
 AJCP / Original Article A Dual-Fixed Neutrophil Substrate Improves Interpretation of Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies by Indirect Immunofluorescence Ming-Wei Lin, MBBS, 1,2 Roger A. Silvestrini, 1
AJCP / Original Article A Dual-Fixed Neutrophil Substrate Improves Interpretation of Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies by Indirect Immunofluorescence Ming-Wei Lin, MBBS, 1,2 Roger A. Silvestrini, 1
IgA class antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies in primary sclerosing cholangitis and autoimmune hepatitis
 Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKCEIClinical and Experimental Immunology0009-9104Blackwell Publishing Ltd, 2003 133 283289 Original Article Clin Exp Immunol 2003; 133:283 289 IgA class ANCA in PSC and AIHC.
Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKCEIClinical and Experimental Immunology0009-9104Blackwell Publishing Ltd, 2003 133 283289 Original Article Clin Exp Immunol 2003; 133:283 289 IgA class ANCA in PSC and AIHC.
Abstract. Immunopathology / ADDENDUM TO CONSENSUS STATEMENT ON TESTING AND REPORTING OF ANCA
 Immunopathology / ADDENDUM TO CONSENSUS STATEMENT ON TESTING AND REPORTING OF ANCA Addendum to the International Consensus Statement on Testing and Reporting of Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies Quality
Immunopathology / ADDENDUM TO CONSENSUS STATEMENT ON TESTING AND REPORTING OF ANCA Addendum to the International Consensus Statement on Testing and Reporting of Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies Quality
Autoimmune Hepatobiliary Diseases PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP
 Autoimmune Hepatobiliary Diseases PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP Autoimmune hepatobiliary diseases The liver is an important target for immunemediated injury. Three disease phenotypes are recognized:
Autoimmune Hepatobiliary Diseases PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP Autoimmune hepatobiliary diseases The liver is an important target for immunemediated injury. Three disease phenotypes are recognized:
Comparative Study of ELISA and Indirect Immunofluorescence for the Detection of Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies
 IMMUNOPATHOLOGY Comparative Study of ELISA and Indirect Immunofluorescence for the Detection of Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies Evaluation of the SCIMEDX/EURO Diagnostica ELISA Assay in a Clinical
IMMUNOPATHOLOGY Comparative Study of ELISA and Indirect Immunofluorescence for the Detection of Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies Evaluation of the SCIMEDX/EURO Diagnostica ELISA Assay in a Clinical
NOVA Lite ANCA (Ethanol) Kit with DAPI For In Vitro Diagnostic Use CLIA Complexity: High
 Format to CLSI Standards GP2-A5 (Formerly NCCLS) Vol. 26 No. 12 Issue Date: 09/11/13 NOVA Lite ANCA (Ethanol) 708301 Kit with DAPI For In Vitro Diagnostic Use CLIA Complexity: High Principles of the Procedure
Format to CLSI Standards GP2-A5 (Formerly NCCLS) Vol. 26 No. 12 Issue Date: 09/11/13 NOVA Lite ANCA (Ethanol) 708301 Kit with DAPI For In Vitro Diagnostic Use CLIA Complexity: High Principles of the Procedure
Evaluation of the revised versus the simplified scoring system in patients with autoimmune hepatitis
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 7: 131-136, 2014 Evaluation of the revised versus the simplified scoring system in patients with autoimmune hepatitis YI LI, MILIN PENG and GUOZHONG GONG Institute
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 7: 131-136, 2014 Evaluation of the revised versus the simplified scoring system in patients with autoimmune hepatitis YI LI, MILIN PENG and GUOZHONG GONG Institute
VASCULITIS PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
 VASCULITIS PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS AESKU.DIAGNOSTICS offers a comprehensive and complete diagnostic portfolio in the field of vasculitis diagnostics. Not only are screening and profiling s available but also
VASCULITIS PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS AESKU.DIAGNOSTICS offers a comprehensive and complete diagnostic portfolio in the field of vasculitis diagnostics. Not only are screening and profiling s available but also
Medical Policy Title: Serum Antibodies for ARBenefits Approval: 10/12/11
 Medical Policy Title: Serum Antibodies for ARBenefits Approval: 10/12/11 Diagnosis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Document: ARB0314 Revision Date: Code(s): 83516 Immunoassay for
Medical Policy Title: Serum Antibodies for ARBenefits Approval: 10/12/11 Diagnosis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Document: ARB0314 Revision Date: Code(s): 83516 Immunoassay for
Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy
 Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy Goals Share an interesting case Important because it highlights a common problem that we re likely to
Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy Goals Share an interesting case Important because it highlights a common problem that we re likely to
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases. Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants
 Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants I have nothing to disclose Educational Objectives What is PSC? Understand the cholestatic
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants I have nothing to disclose Educational Objectives What is PSC? Understand the cholestatic
EDITORIAL. Issue Seventeen, October Editorial Team. Issue Seventeen. Info link
 EDITORIAL, October 2004 Welcome to the Spring 2004 Edition of InfoLink. The feature article in this edition has been written by Dr Rodger Laurent, Head of Department, PaLMS Rheumatology Laboratory. The
EDITORIAL, October 2004 Welcome to the Spring 2004 Edition of InfoLink. The feature article in this edition has been written by Dr Rodger Laurent, Head of Department, PaLMS Rheumatology Laboratory. The
ACCME/Disclosures. The Overlap Syndromes: Do They Exist? Key Points and Questions 4/6/2016. Hans Popper Hepatopathology Society
 ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
A Case of Autoimmune Hepatitis with Antimitochondrial Antibody and No Detectable Antinuclear Antibody
 FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF St. Marianna Med. J. Case Report Vol. 32, pp. 33 38, 2004 FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF A Case
FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF St. Marianna Med. J. Case Report Vol. 32, pp. 33 38, 2004 FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF A Case
HEPETIC SYSTEMS BIOCHEMICAL HEPATOCYTIC SYSTEM HEPATOBILIARY SYSTEM RETICULOENDOTHELIAL SYSTEM
 EVALUATION OF LIVER FUNCTION R. Mohammadi Biochemist (Ph.D.) Faculty member of Medical Faculty HEPETIC SYSTEMS BIOCHEMICAL HEPATOCYTIC SYSTEM HEPATOBILIARY SYSTEM RETICULOENDOTHELIAL SYSTEM METABOLIC FUNCTION
EVALUATION OF LIVER FUNCTION R. Mohammadi Biochemist (Ph.D.) Faculty member of Medical Faculty HEPETIC SYSTEMS BIOCHEMICAL HEPATOCYTIC SYSTEM HEPATOBILIARY SYSTEM RETICULOENDOTHELIAL SYSTEM METABOLIC FUNCTION
Clinical Laboratory. 14:41:00 Complement Component 3 50 mg/dl Oct-18
 Clinical Laboratory Procedure Result Units Ref Interval Accession Collected Received Thyroid Peroxidase (TPO) Antibody 5.0 IU/mL [0.0-9.0] 18-289-900139 16-Oct-18 Complement Component 3 50 mg/dl 18-289-900139
Clinical Laboratory Procedure Result Units Ref Interval Accession Collected Received Thyroid Peroxidase (TPO) Antibody 5.0 IU/mL [0.0-9.0] 18-289-900139 16-Oct-18 Complement Component 3 50 mg/dl 18-289-900139
CASE 1 Plasma Cell Infiltrates: Significance in post liver transplantation and in chronic liver disease
 CASE 1 Plasma Cell Infiltrates: Significance in post liver transplantation and in chronic liver disease Maria Isabel Fiel, M.D. The Mount Sinai Medical Center New York, New York Case A 57 yo man, 7 months
CASE 1 Plasma Cell Infiltrates: Significance in post liver transplantation and in chronic liver disease Maria Isabel Fiel, M.D. The Mount Sinai Medical Center New York, New York Case A 57 yo man, 7 months
Anti-PR3 and Anti-MPO IgG ANCA in Autistic Children With Chronic GI Disease
 Anti-PR3 and Anti-MPO IgG ANCA in Autistic Children With Chronic GI Disease A.J. Russo 1, A Krigsman 2, B Jepson 2 and Andrew Wakefield 2 ORIGINAL RESEARCH 1 Science Department, Mount Saint Mary s University,
Anti-PR3 and Anti-MPO IgG ANCA in Autistic Children With Chronic GI Disease A.J. Russo 1, A Krigsman 2, B Jepson 2 and Andrew Wakefield 2 ORIGINAL RESEARCH 1 Science Department, Mount Saint Mary s University,
LIVER TRANSPLANTATION FOR OVERLAP SYNDROMES OF AUTOIMMUNE LIVER DISEASES
 LIVER TRANSPLANTATION FOR OVERLAP SYNDROMES OF AUTOIMMUNE LIVER DISEASES No conflict of interest Objectives Introduction Methods Results Conclusions Objectives Introduction Methods Results Conclusions
LIVER TRANSPLANTATION FOR OVERLAP SYNDROMES OF AUTOIMMUNE LIVER DISEASES No conflict of interest Objectives Introduction Methods Results Conclusions Objectives Introduction Methods Results Conclusions
Revised 2017 international consensus on testing of ANCAs in granulomatosis with polyangiitis and microscopic polyangiitis.
 Revised 2017 international consensus on testing of ANCAs in granulomatosis with polyangiitis and microscopic polyangiitis. Bossuyt X, Cohen Tervaert JW, Arimura Y, Blockmans D, Flores-Suárez LF, Guillevin
Revised 2017 international consensus on testing of ANCAs in granulomatosis with polyangiitis and microscopic polyangiitis. Bossuyt X, Cohen Tervaert JW, Arimura Y, Blockmans D, Flores-Suárez LF, Guillevin
Anti-neutrophil antibodies in inflammatory bowel
 668 Department of Renal Medicine, Institute of Urology, University College and Middlesex School of Medicine, London, WI G Cambridge B Leaker Department of Gastroenterology, The Royal London Hospital, London
668 Department of Renal Medicine, Institute of Urology, University College and Middlesex School of Medicine, London, WI G Cambridge B Leaker Department of Gastroenterology, The Royal London Hospital, London
News. Laboratory. CHANGES IN CARDIAC TROPONIN I REPORTING Gene Shaw, MD, Annu Khajuria, PhD. Inside This Issue
 Laboratory News Inside This Issue CHANGES IN CARDIAC TROPONIN I REPORTING...1 FOUR NEW SEROLOGY TESTS FOR AUTOIMMUNE LIVER DISEASES...3 INSULIN LIKE GROWTH FACTOR-1 (IGF-1) METHOD CHANGES...6 CHANGES IN
Laboratory News Inside This Issue CHANGES IN CARDIAC TROPONIN I REPORTING...1 FOUR NEW SEROLOGY TESTS FOR AUTOIMMUNE LIVER DISEASES...3 INSULIN LIKE GROWTH FACTOR-1 (IGF-1) METHOD CHANGES...6 CHANGES IN
Autoimmune Liver Diseases
 2nd Pannonia Congress of pathology Hepato-biliary pathology Autoimmune Liver Diseases Vera Ferlan Marolt Institute of pathology, Medical faculty, University of Ljubljana Slovenia Siofok, Hungary, May 2012
2nd Pannonia Congress of pathology Hepato-biliary pathology Autoimmune Liver Diseases Vera Ferlan Marolt Institute of pathology, Medical faculty, University of Ljubljana Slovenia Siofok, Hungary, May 2012
Diagnostic value of classical and atypical antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) immunofluorescence patterns
 124 Immunopathology Department, ICPMR, Westmead Hospital, NSW 2145, Australia RCWWong R A Silvestrini D A Fulcher E M Benson University Department of Medicine, Austin and Repatriation Medical Centre, Heidelberg,
124 Immunopathology Department, ICPMR, Westmead Hospital, NSW 2145, Australia RCWWong R A Silvestrini D A Fulcher E M Benson University Department of Medicine, Austin and Repatriation Medical Centre, Heidelberg,
4. KIDNEYS AND AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE
 How to Cite this article: Kidneys and Autoimmune Disease - ejifcc 20/01 2009 http://www.ifcc.org 4. KIDNEYS AND AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE Maksimiljan Gorenjak 4.1 Autoimmune diseases The human immune system limits
How to Cite this article: Kidneys and Autoimmune Disease - ejifcc 20/01 2009 http://www.ifcc.org 4. KIDNEYS AND AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE Maksimiljan Gorenjak 4.1 Autoimmune diseases The human immune system limits
International Consensus Statement on Testing and
 I m m u n o p a t h o l o g y / TESTING FOR A N C A S International Consensus Statement on Testing and Reporting of Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies (ANCA) Key Words: ANCA; Autoantibodies; Glomerulonephritis;
I m m u n o p a t h o l o g y / TESTING FOR A N C A S International Consensus Statement on Testing and Reporting of Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies (ANCA) Key Words: ANCA; Autoantibodies; Glomerulonephritis;
International Consensus Statement on Testing and
 I m m u n o p a t h o l o g y / TESTING FOR A N C A S International Consensus Statement on Testing and Reporting of Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies (ANCA) Judy Savige, MB, PhD, David Gillis, MB,
I m m u n o p a t h o l o g y / TESTING FOR A N C A S International Consensus Statement on Testing and Reporting of Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies (ANCA) Judy Savige, MB, PhD, David Gillis, MB,
Value of Autoantibody Analysis in the Differential Diagnosis of Chronic Cholestatic Liver Disease
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:1355 1360 Value of Autoantibody Analysis in the Differential Diagnosis of Chronic Cholestatic Liver Disease PIOTR MILKIEWICZ,*, HAYMAN BUWANESWARAN,* CATALINA
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:1355 1360 Value of Autoantibody Analysis in the Differential Diagnosis of Chronic Cholestatic Liver Disease PIOTR MILKIEWICZ,*, HAYMAN BUWANESWARAN,* CATALINA
A review of immunofluorescent patterns associated with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA) and their diverentiation from other antibodies
 568 J Clin Pathol 1998;51:568 575 Papers University Medicine, Austin and Repatriation Medical Centre, Heidelberg, Victoria, Australia J A Savige Biochemistry, St Vincent s Hospital, Fitzroy, Victoria,
568 J Clin Pathol 1998;51:568 575 Papers University Medicine, Austin and Repatriation Medical Centre, Heidelberg, Victoria, Australia J A Savige Biochemistry, St Vincent s Hospital, Fitzroy, Victoria,
Hépatopathies auto-immunes
 16 ème Journée d'automne Lausanne, le 19 octobre 2017 Hépatopathies auto-immunes Nurullah Aslan et Darius Moradpour Service de Gastroentérologie et d'hépatologie Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois
16 ème Journée d'automne Lausanne, le 19 octobre 2017 Hépatopathies auto-immunes Nurullah Aslan et Darius Moradpour Service de Gastroentérologie et d'hépatologie Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois
HBV Core and Core-Related Antigen Quantitation in Chinese Patients with. Chronic Hepatitis B Genotype B and C Virus Infection
 Title page HBV Core and Core-Related Antigen Quantitation in Chinese Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Genotype B and C Virus Infection Short Title: Quantitation of HBc and HBcrAg in Chinese patients Akinori
Title page HBV Core and Core-Related Antigen Quantitation in Chinese Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Genotype B and C Virus Infection Short Title: Quantitation of HBc and HBcrAg in Chinese patients Akinori
AUTOANTIBODIES PRECEDING AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES
 AUTOANTIBODIES PRECEDING AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES STUDY GROUP - AUTOANTIBODY STANDARDIZING COMMITTEE Washington, November 12th 2012 Luis Eduardo Coelho Andrade, M.D, Ph.D. Associate Professor Rheumatology Division
AUTOANTIBODIES PRECEDING AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES STUDY GROUP - AUTOANTIBODY STANDARDIZING COMMITTEE Washington, November 12th 2012 Luis Eduardo Coelho Andrade, M.D, Ph.D. Associate Professor Rheumatology Division
Two types of myeloperoxidase-antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies with a high affinity and a low affinity in small vessel vasculitis
 Two types of myeloperoxidase-antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies with a high affinity and a low affinity in small vessel vasculitis M. Yoshida, M. Sasaki, I. Nakabayashi, M. Akashi, T. Tomiyasu,
Two types of myeloperoxidase-antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies with a high affinity and a low affinity in small vessel vasculitis M. Yoshida, M. Sasaki, I. Nakabayashi, M. Akashi, T. Tomiyasu,
A Review of Liver Function Tests. James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver
 A Review of Liver Function Tests James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
A Review of Liver Function Tests James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
Overview of PSC Making the Diagnosis
 Overview of PSC Making the Diagnosis Tamar Taddei, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Yale University School of Medicine Overview Definition Epidemiology Diagnosis Modes of presentation Associated diseases
Overview of PSC Making the Diagnosis Tamar Taddei, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Yale University School of Medicine Overview Definition Epidemiology Diagnosis Modes of presentation Associated diseases
Autoimmune hepatitis
 Autoimmune hepatitis: Autoimmune hepatitis a spectrum within a spectrum Alastair Burt Professor of Pathology and Dean of Clinical Medicine Newcastle University Spectrum of autoimmune liver disease Autoimmune
Autoimmune hepatitis: Autoimmune hepatitis a spectrum within a spectrum Alastair Burt Professor of Pathology and Dean of Clinical Medicine Newcastle University Spectrum of autoimmune liver disease Autoimmune
Supplementary Figure Legends
 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1. Comparison of RNP IC-mediated NET formation. Quantification of DNA release induced by ICs consisting of SmRNP combined with SLE IgG 961 (n = 10), 1032
Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1. Comparison of RNP IC-mediated NET formation. Quantification of DNA release induced by ICs consisting of SmRNP combined with SLE IgG 961 (n = 10), 1032
PBC/AIH variant/ overlap syndrome vs PBC with hepatitic features?
 22 November 2018 BD-IAP UK-LPG Liver Update PBC/AIH variant/ overlap syndrome vs PBC with hepatitic features? in a UDCA non-responder Dina G. Tiniakos Institute of Cellular Medicine, Faculty of Medical
22 November 2018 BD-IAP UK-LPG Liver Update PBC/AIH variant/ overlap syndrome vs PBC with hepatitic features? in a UDCA non-responder Dina G. Tiniakos Institute of Cellular Medicine, Faculty of Medical
Autoimmune Hepatitis in Clinical Practice
 1 Autoimmune Hepatitis in Clinical Practice Atif Zaman, MD MPH Professor of Medicine Senior Associate Dean for Clinical and Faculty Affairs School of Medicine Oregon Health & Science University Disclosure
1 Autoimmune Hepatitis in Clinical Practice Atif Zaman, MD MPH Professor of Medicine Senior Associate Dean for Clinical and Faculty Affairs School of Medicine Oregon Health & Science University Disclosure
High-Titer Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies in Type-1 Autoimmune Hepatitis
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 1995;108:1159-1166 High-Titer Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies in Type-1 Autoimmune Hepatitis STEPHAN R. TARGAN,* CAROL LANDERS,* ALDA VIDRICH,* and ALBERT J. CZAJA t *Cedars-Sinai
GASTROENTEROLOGY 1995;108:1159-1166 High-Titer Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies in Type-1 Autoimmune Hepatitis STEPHAN R. TARGAN,* CAROL LANDERS,* ALDA VIDRICH,* and ALBERT J. CZAJA t *Cedars-Sinai
ANTINEUTROPHIL CYTOPLASMIC ANTIBODIES IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS PATIENTS
 British Journal of Rheumatology 1996;35:38-43 ANTINEUTROPHIL CYTOPLASMIC ANTIBODIES IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS PATIENTS M. DE BANDT, O. MEYER, T. HAIM ind M.-F. KAHN Laboratory of Immuno-Rheumatology, Bichat
British Journal of Rheumatology 1996;35:38-43 ANTINEUTROPHIL CYTOPLASMIC ANTIBODIES IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS PATIENTS M. DE BANDT, O. MEYER, T. HAIM ind M.-F. KAHN Laboratory of Immuno-Rheumatology, Bichat
ORIGINAL ARTICLES LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:98 103 ORIGINAL ARTICLES LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT Serologic Markers Do Not Predict Histologic Severity or Response to Treatment in Patients With
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:98 103 ORIGINAL ARTICLES LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT Serologic Markers Do Not Predict Histologic Severity or Response to Treatment in Patients With
Slide 7 demonstrates acute pericholangitisis with neutrophils around proliferating bile ducts.
 Many of the histologic images and the tables are from MacSween s Pathology of the Liver (5 th Edition). Other images were used from an online source called PathPedia.com. A few images from other sources
Many of the histologic images and the tables are from MacSween s Pathology of the Liver (5 th Edition). Other images were used from an online source called PathPedia.com. A few images from other sources
Autoimmune diagnostics. A comprehensive product line for the detection of autoantibodies
 Autoimmune diagnostics A comprehensive product line for the detection of autoantibodies Autoimmune diagnostics Autoimmune diseases are chronic inflammatory processes with an indeterminate etiology. They
Autoimmune diagnostics A comprehensive product line for the detection of autoantibodies Autoimmune diagnostics Autoimmune diseases are chronic inflammatory processes with an indeterminate etiology. They
Primary Biliary Cholangitis
 Primary Biliary Cholangitis PBC Foundation (UK) Ltd 6 Hill Street Edinburgh EH2 3JZ Tel: +44 (0) 131 556 6811 info@pbcfoundation.org.uk www.pbcfoundation.org.uk PBC for Healthcare Practitioners Introduction
Primary Biliary Cholangitis PBC Foundation (UK) Ltd 6 Hill Street Edinburgh EH2 3JZ Tel: +44 (0) 131 556 6811 info@pbcfoundation.org.uk www.pbcfoundation.org.uk PBC for Healthcare Practitioners Introduction
Biliary tract diseases of the liver
 Biliary tract diseases of the liver Digestive Diseases Course Bucharest 2016 Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk How important are biliary tract diseases? Hepatology 2011 53(5):1608-17 Approximately 16%
Biliary tract diseases of the liver Digestive Diseases Course Bucharest 2016 Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk How important are biliary tract diseases? Hepatology 2011 53(5):1608-17 Approximately 16%
Secondary fluorescent staining of virus antigens by rheumatoid factor and fluorescein-conjugated anti-lgm
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1973), 32, 53 Secondary fluorescent staining of virus antigens by rheumatoid factor and fluorescein-conjugated anti-lgm P. V. SHIRODARIA, K. B. FRASER, AND F. STANFORD From the Department
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1973), 32, 53 Secondary fluorescent staining of virus antigens by rheumatoid factor and fluorescein-conjugated anti-lgm P. V. SHIRODARIA, K. B. FRASER, AND F. STANFORD From the Department
Current Concepts in the Management and Treatment of PBC & PSC
 Current Concepts in the Management and Treatment of PBC & PSC Michael A Heneghan, MD, MMedSc, FRCPI. Institute of Liver Studies, King s College Hospital, London A family affair? Central vein Hepatocytes
Current Concepts in the Management and Treatment of PBC & PSC Michael A Heneghan, MD, MMedSc, FRCPI. Institute of Liver Studies, King s College Hospital, London A family affair? Central vein Hepatocytes
Clinical Laboratory. [None
 Clinical Laboratory Procedure Result Units Ref Interval Accession Collected Received Double-Stranded DNA (dsdna) Ab IgG ELISA Detected * [None 18-289-900151 Detected] Double-Stranded DNA (dsdna) Ab IgG
Clinical Laboratory Procedure Result Units Ref Interval Accession Collected Received Double-Stranded DNA (dsdna) Ab IgG ELISA Detected * [None 18-289-900151 Detected] Double-Stranded DNA (dsdna) Ab IgG
In 1993, the International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:417 421 Validation and Modification of Simplified Diagnostic Criteria for Autoimmune Hepatitis in Children ELIZABETH MILETI,* PHILIP ROSENTHAL,*, and MARION
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:417 421 Validation and Modification of Simplified Diagnostic Criteria for Autoimmune Hepatitis in Children ELIZABETH MILETI,* PHILIP ROSENTHAL,*, and MARION
Key Points: Autoimmune Liver Disease: Update for Pathologists from the Hepatologist s Perspective. Jenny Heathcote, MD. University of Toronto
 Autoimmune Liver Disease: Update for Pathologists from the Hepatologist s Perspective Jenny Heathcote, MD University of Toronto Key Points: AILD comprise autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis
Autoimmune Liver Disease: Update for Pathologists from the Hepatologist s Perspective Jenny Heathcote, MD University of Toronto Key Points: AILD comprise autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis
Screening of Auto Antibodies using Indirect Immunofluorescence in Auto Immune Disease Patients
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 02 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.702.386
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 02 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.702.386
TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet
 Website: thermofisher.com Customer Service (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 1 Technical Support (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 441 TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet Details
Website: thermofisher.com Customer Service (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 1 Technical Support (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 441 TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet Details
Mikako Nakajima 1, Hidetake Shimizu 1, Akihisa Miyazaki, Sumio Watanabe 1, Noriyuki Kitami 2, and Nobuhiro Sato 1
 J Gastroenterol 1999; 34:607 612 Detection of IgA, IgM, and IgG subclasses of anti-m2 antibody by immunoblotting in autoimmune cholangitis: Is autoimmune cholangitis an early stage of primary biliary cirrhosis?
J Gastroenterol 1999; 34:607 612 Detection of IgA, IgM, and IgG subclasses of anti-m2 antibody by immunoblotting in autoimmune cholangitis: Is autoimmune cholangitis an early stage of primary biliary cirrhosis?
Two Cases of Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Overlapping with Autoimmune Hepatitis in Adults
 CASE REPORT Two Cases of Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Overlapping with Autoimmune Hepatitis in Adults Go Igarashi 1, Tetsu Endo 1, Kenichiro Mikami 1, Naoya Sawada 1,RyuSatake 1, Rie Ohta 1, Juichi Sakamoto
CASE REPORT Two Cases of Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Overlapping with Autoimmune Hepatitis in Adults Go Igarashi 1, Tetsu Endo 1, Kenichiro Mikami 1, Naoya Sawada 1,RyuSatake 1, Rie Ohta 1, Juichi Sakamoto
Hangzhou, 15 March Ulrich Beuers Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Academic Medical Center University of Amsterdam
 Clinical Aspects of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Hangzhou, 15 March 2008 Ulrich Beuers Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Academic Medical Center University of Amsterdam Epidemiology of Primary
Clinical Aspects of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Hangzhou, 15 March 2008 Ulrich Beuers Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Academic Medical Center University of Amsterdam Epidemiology of Primary
doi: /s
 doi: 10.1007/s10620-013-2734-6 Harada - 1 - Clinicopathological significance of serum fractalkine in primary biliary cirrhosis Kenichi Harada 1), Yuko Kakuda 1), Minoru Nakamura 2), Shinji Shimoda 3),
doi: 10.1007/s10620-013-2734-6 Harada - 1 - Clinicopathological significance of serum fractalkine in primary biliary cirrhosis Kenichi Harada 1), Yuko Kakuda 1), Minoru Nakamura 2), Shinji Shimoda 3),
AN OVERVIEW OF ANCA-ASSOCIATED VASCULITIS
 GRANULOMATOSIS WITH POLYANGIITIS (GPA), MICROSCOPIC POLYANGIITIS (MPA), and EOSINOPHILIC GRANULOMATOSIS WITH POLYANGIITIS (EGPA) AN OVERVIEW OF ANCA-ASSOCIATED VASCULITIS What is ANCA-associated Vasculitis?
GRANULOMATOSIS WITH POLYANGIITIS (GPA), MICROSCOPIC POLYANGIITIS (MPA), and EOSINOPHILIC GRANULOMATOSIS WITH POLYANGIITIS (EGPA) AN OVERVIEW OF ANCA-ASSOCIATED VASCULITIS What is ANCA-associated Vasculitis?
Patologia sistematica V Gastroenterologia Prof. Stefano Fiorucci Autoimmune liver diseases
 Patologia sistematica V Gastroenterologia Prof. Stefano Fiorucci Autoimmune liver diseases Harrison s Principles of Internal Medicine 18-19 Ed. 2012 e seguenti Chronic hepatitis classification by cause
Patologia sistematica V Gastroenterologia Prof. Stefano Fiorucci Autoimmune liver diseases Harrison s Principles of Internal Medicine 18-19 Ed. 2012 e seguenti Chronic hepatitis classification by cause
Improvement of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Autoimmune Hepatitis in a Patient Treated with the Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitor, Etanercept
 CASE REPORT Improvement of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Autoimmune Hepatitis in a Patient Treated with the Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitor, Etanercept Kunihiko Umekita 1, Shunichi Miyauchi 1, Shiro Ueno 1,
CASE REPORT Improvement of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Autoimmune Hepatitis in a Patient Treated with the Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitor, Etanercept Kunihiko Umekita 1, Shunichi Miyauchi 1, Shiro Ueno 1,
I have no disclosures relevant to this presentation LIVER TESTS: WHAT IS INCLUDED? LIVER TESTS: HOW TO UTILIZE THEM OBJECTIVES
 LIVER TESTS: HOW TO UTILIZE THEM I have no disclosures relevant to this presentation José Franco, MD Professor of Medicine, Surgery and Pediatrics Medical College of Wisconsin OBJECTIVES Differentiate
LIVER TESTS: HOW TO UTILIZE THEM I have no disclosures relevant to this presentation José Franco, MD Professor of Medicine, Surgery and Pediatrics Medical College of Wisconsin OBJECTIVES Differentiate
Investigation of Ornithine Carbamoyltransferase as a Biomarker of Liver Cirrhosis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Investigation of Ornithine Carbamoyltransferase as a Biomarker of Liver Cirrhosis Noriko Matsushita 1,2, Etsuko Hashimoto 1, Katsutoshi Tokushige 1, Kazuhisa Kodama 1, Maki Tobari 1, Tomomi
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Investigation of Ornithine Carbamoyltransferase as a Biomarker of Liver Cirrhosis Noriko Matsushita 1,2, Etsuko Hashimoto 1, Katsutoshi Tokushige 1, Kazuhisa Kodama 1, Maki Tobari 1, Tomomi
Noncalculous Biliary Disease Dean Abramson, M.D. Gastroenterologists, P.C. Cedar Rapids. Cholestasis
 Noncalculous Biliary Disease Dean Abramson, M.D. Gastroenterologists, P.C. Cedar Rapids Cholestasis Biochemical hallmark Impaired bile flow from liver to small intestine Alkaline phosphatase is primary
Noncalculous Biliary Disease Dean Abramson, M.D. Gastroenterologists, P.C. Cedar Rapids Cholestasis Biochemical hallmark Impaired bile flow from liver to small intestine Alkaline phosphatase is primary
Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Auto Antibodies (ANCA) in Pakistani Patients with Systemic Vasculitides
 Abstract Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Auto Antibodies (ANCA) in Pakistani Patients with Systemic Vasculitides Pages with reference to book, From 272 To 275 Tahir A. Ahmed, Iftikhar A. Malik ( Armed Forces
Abstract Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Auto Antibodies (ANCA) in Pakistani Patients with Systemic Vasculitides Pages with reference to book, From 272 To 275 Tahir A. Ahmed, Iftikhar A. Malik ( Armed Forces
Diagnosing Autoimmune Hepatitis in Children: Is the International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group Scoring System Useful?
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2004;2:935 940 Diagnosing Autoimmune Hepatitis in Children: Is the International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group Scoring System Useful? REGAN L. EBBESON* and RICHARD
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2004;2:935 940 Diagnosing Autoimmune Hepatitis in Children: Is the International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group Scoring System Useful? REGAN L. EBBESON* and RICHARD
Diagnostic Value of Distinguishing and Reporting Different Perinuclear ANCA (P-ANCA) Immunofluorescence Patterns A Prospective Study
 Diagnostic Value of Distinguishing and Reporting Different Perinuclear ANCA (P-ANCA) Immunofluorescence Patterns A Prospective Study CME/SAM Susan B. Perel, MBBS, FRACP, FRCPA, 1,2 Kerri M. Prain, 1 Robert
Diagnostic Value of Distinguishing and Reporting Different Perinuclear ANCA (P-ANCA) Immunofluorescence Patterns A Prospective Study CME/SAM Susan B. Perel, MBBS, FRACP, FRCPA, 1,2 Kerri M. Prain, 1 Robert
Prototypes of autoimmune hepatitis and sclerosing cholangitis in childhood
 RIUNIONE MONOTEMATICA AISF 2013 Personalizzazione della Cura in Epatologia 17-19 ottobre 2013, PISA Prototypes of autoimmune hepatitis and sclerosing cholangitis in childhood La sottoscritta dichiara di
RIUNIONE MONOTEMATICA AISF 2013 Personalizzazione della Cura in Epatologia 17-19 ottobre 2013, PISA Prototypes of autoimmune hepatitis and sclerosing cholangitis in childhood La sottoscritta dichiara di
Inflammatory bowel disease with cytoplasmic-staining. antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody and extensive colitis.
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Inflammatory bowel disease with cytoplasmic-staining antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody and extensive colitis Hugh James Freeman MD HJ Freeman. Inflammatory bowel disease with cytoplasmicstaining
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Inflammatory bowel disease with cytoplasmic-staining antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody and extensive colitis Hugh James Freeman MD HJ Freeman. Inflammatory bowel disease with cytoplasmicstaining
Presentation and mortality of primary biliary cirrhosis in older patients
 Age and Ageing 2000; 29: 305 309 Presentation and mortality of primary biliary cirrhosis in older patients JULIA L. NEWTON 1,DAVID E. JONES 2,JANE V. METCALF 2,JAY B. PARK 2,ALISTAIR D. BURT 2, MARGARET
Age and Ageing 2000; 29: 305 309 Presentation and mortality of primary biliary cirrhosis in older patients JULIA L. NEWTON 1,DAVID E. JONES 2,JANE V. METCALF 2,JAY B. PARK 2,ALISTAIR D. BURT 2, MARGARET
Chronic Cholestatic Liver Diseases
 Chronic Cholestatic Liver Diseases - EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines - Rome, 8 October 2010 Ulrich Beuers Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Tytgat Institute of Liver and Intestinal Research
Chronic Cholestatic Liver Diseases - EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines - Rome, 8 October 2010 Ulrich Beuers Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Tytgat Institute of Liver and Intestinal Research
Management of autoimmune hepatitis. Pierre-Emmanuel RAUTOU Inserm U970, Paris Service d hépatologie, Hôpital Beaujon, Clichy, France
 Management of autoimmune hepatitis Pierre-Emmanuel RAUTOU Inserm U970, PARCC@HEGP, Paris Service d hépatologie, Hôpital Beaujon, Clichy, France Case 1 52 year-old woman, referred for liver blood tests
Management of autoimmune hepatitis Pierre-Emmanuel RAUTOU Inserm U970, PARCC@HEGP, Paris Service d hépatologie, Hôpital Beaujon, Clichy, France Case 1 52 year-old woman, referred for liver blood tests
Methodological update How and why should we detect ANCA?
 Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 2000; 18: 000-000. Methodological update How and why should we detect ANCA? CASE REPORT M. Segelmark, K. Westman, J. Wieslander 1 Department of Nephrology, University
Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 2000; 18: 000-000. Methodological update How and why should we detect ANCA? CASE REPORT M. Segelmark, K. Westman, J. Wieslander 1 Department of Nephrology, University
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need?
 Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Fatty liver disease Is there fatty
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Fatty liver disease Is there fatty
Antineutrophil Antibodies in Familial Inflammatory Bowel Disease
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 1995;108:428-433 Antineutrophil Antibodies in Familial Inflammatory Bowel Disease JOHN C. W. LEE,* JOHN E. LENNARD-JONES,* and GERALDINE CAMBRIDGE* *St. Mark's Hospital, and *Department
GASTROENTEROLOGY 1995;108:428-433 Antineutrophil Antibodies in Familial Inflammatory Bowel Disease JOHN C. W. LEE,* JOHN E. LENNARD-JONES,* and GERALDINE CAMBRIDGE* *St. Mark's Hospital, and *Department
Is it Autoimmune or NOT! Presented to AONP! October 2015!
 Is it Autoimmune or NOT! Presented to AONP! October 2015! Four main jobs of immune system Detects Contains and eliminates Self regulates Protects Innate Immune System! Epithelial cells, phagocytic cells
Is it Autoimmune or NOT! Presented to AONP! October 2015! Four main jobs of immune system Detects Contains and eliminates Self regulates Protects Innate Immune System! Epithelial cells, phagocytic cells
CLINICAL ADVANCES IN LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2011;140:1472 1480 Comparability of Probable and Definite Autoimmune Hepatitis by International Diagnostic Scoring Criteria ALBERT J. CZAJA Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology,
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2011;140:1472 1480 Comparability of Probable and Definite Autoimmune Hepatitis by International Diagnostic Scoring Criteria ALBERT J. CZAJA Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology,
Serologic Markers CONVENTIONAL ANTIBODIES ANTIBODIES UNCONVENTIONAL. AIH Type I
 Autoimmune Hepatitis By Thomas Frazier Objective What we need to know about AIH Diagnosis Treatment Difficulties in both Liver transplantation concerns AASLD Guidelines: Hepatology. 2010 Jun;51(6):2193-213.
Autoimmune Hepatitis By Thomas Frazier Objective What we need to know about AIH Diagnosis Treatment Difficulties in both Liver transplantation concerns AASLD Guidelines: Hepatology. 2010 Jun;51(6):2193-213.
Assays. New. New. Combinations. Possibilities. Patents: EP , AU
 Assays Patents: EP 2362222, AU 2011217190 New Combinations New Possibilities Technology Classical Handling of Autoimmune Diagnostics 2-Step Diagnostics 1 st Screening 2 nd Confirmation Cell based IFA ELISA
Assays Patents: EP 2362222, AU 2011217190 New Combinations New Possibilities Technology Classical Handling of Autoimmune Diagnostics 2-Step Diagnostics 1 st Screening 2 nd Confirmation Cell based IFA ELISA
A historical essay on detection of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2015) 30: i8 i13 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfv070 NDT Perspectives A historical essay on detection of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies Niels Rasmussen 1, Allan Wiik 1 and David R.
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2015) 30: i8 i13 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfv070 NDT Perspectives A historical essay on detection of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies Niels Rasmussen 1, Allan Wiik 1 and David R.
Immunoglobulins in chronic liver disease
 Gut, 1968, 9, 193-198 Immunoglobulins in chronic liver disease TEN FEIZI From the Department of Medicine, Royal Free Hospital, London The association of high gamma globulin levels with hepatic cirrhosis
Gut, 1968, 9, 193-198 Immunoglobulins in chronic liver disease TEN FEIZI From the Department of Medicine, Royal Free Hospital, London The association of high gamma globulin levels with hepatic cirrhosis
Resident, PGY1 David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA. Los Angeles Society of Pathology Resident and Fellow Symposium 2013
 Resident, PGY1 David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Los Angeles Society of Pathology Resident and Fellow Symposium 2013 85 year old female with past medical history including paroxysmal atrial fibrillation,
Resident, PGY1 David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Los Angeles Society of Pathology Resident and Fellow Symposium 2013 85 year old female with past medical history including paroxysmal atrial fibrillation,
Kappa/lambda Ratios of IgG, IgA and IgM in the Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients
 Original Article Kappa/lambda Ratios of IgG, IgA and IgM in the Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients with Syndrome Shigeru ARAGA, Hiroshi KAGIMOTO, Akiko ADACHI, Koji FUNAMOTO,Kazuhiko INOUE and Kazuro TAKAHASHI
Original Article Kappa/lambda Ratios of IgG, IgA and IgM in the Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients with Syndrome Shigeru ARAGA, Hiroshi KAGIMOTO, Akiko ADACHI, Koji FUNAMOTO,Kazuhiko INOUE and Kazuro TAKAHASHI
Clinical audit. An audit of ANCA in routine clinical practice. JDM Edgar, SA McMillan, IN Bruce, SK Conlan. biochemical, radiological, and
 Postgrad Med J 1995; 71: 605-612 C The Fellowship of Postgraduate Medicine, 1995 Clinical audit Department of Immunology, Queen's Medical Centre, Nottingham, NG7 2UH, UK JDM Edgar Regional Immunology Laboratory,
Postgrad Med J 1995; 71: 605-612 C The Fellowship of Postgraduate Medicine, 1995 Clinical audit Department of Immunology, Queen's Medical Centre, Nottingham, NG7 2UH, UK JDM Edgar Regional Immunology Laboratory,
Key words: Collagen synthesis - N-Terminal peptide of type III procollagen - Tumor marker - Liver cancer - Liver cirrhosis
 [Gann, 75, 130-135; February, 1984] HIGH CONCENTRATIONS OF N-TERMINAL PEPTIDE OF TYPE III PROCOLLAGEN IN THE SERA OF PATIENTS WITH VARIOUS CANCERS, WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO LIVER CANCER Terumasa HATAHARA,
[Gann, 75, 130-135; February, 1984] HIGH CONCENTRATIONS OF N-TERMINAL PEPTIDE OF TYPE III PROCOLLAGEN IN THE SERA OF PATIENTS WITH VARIOUS CANCERS, WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO LIVER CANCER Terumasa HATAHARA,
Association of Immunofluorescence pattern of Antinuclear Antibody with Specific Autoantibodies in the Bangladeshi Population
 Bangladesh Med Res Counc Bull 2014; 40: 74-78 Association of Immunofluorescence pattern of Antinuclear Antibody with Specific Autoantibodies in the Bangladeshi Population Sharmin S 1, Ahmed S 2, Abu Saleh
Bangladesh Med Res Counc Bull 2014; 40: 74-78 Association of Immunofluorescence pattern of Antinuclear Antibody with Specific Autoantibodies in the Bangladeshi Population Sharmin S 1, Ahmed S 2, Abu Saleh
Simultaneous comprehensive multiplex autoantibody analysis by CytoBead technology for Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis.
 Simultaneous comprehensive multiplex autoantibody analysis by CytoBead technology for Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis l Assays Indirect Immunofluorescence Goldstandard for Diagnosis of Autoimmune
Simultaneous comprehensive multiplex autoantibody analysis by CytoBead technology for Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis l Assays Indirect Immunofluorescence Goldstandard for Diagnosis of Autoimmune
Presenting Features in Pakistani Patients Suffering from the Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody - Classical Subtype (c- ANCA) Associated Vasculitis
 Presenting Features in Pakistani Patients Suffering from the Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody - Classical Subtype (c- ANCA) Associated Vasculitis Tahir Aziz Ahmed,Abdul Halim,Tassawar Hussain,Nadeem
Presenting Features in Pakistani Patients Suffering from the Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody - Classical Subtype (c- ANCA) Associated Vasculitis Tahir Aziz Ahmed,Abdul Halim,Tassawar Hussain,Nadeem
Introduction. Kaoru Omori 1 Masahiro Kan 1. Kanako Yoshida
 Clin J Gastroenterol (2016) 9:312 318 DOI 10.1007/s28-016-0676-1 CASE REPORT Familial occurrence of autoimmune liver disease with overlapping features of primary biliary cholangitis and autoimmune hepatitis
Clin J Gastroenterol (2016) 9:312 318 DOI 10.1007/s28-016-0676-1 CASE REPORT Familial occurrence of autoimmune liver disease with overlapping features of primary biliary cholangitis and autoimmune hepatitis
Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction. Ductal Diseases: Stones Tumors. Acute Injury: Viral Hepatitis Toxin (APAP/Etoh) Reye s Shock.
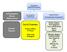 Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction Stones Tumors Ductal Diseases: Ductal Diseases: Primary Biliary Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Cirrhosis Sclerosing Cholangitis Sclerosing Cholangitis Acute Injury: Viral Hepatitis
Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction Stones Tumors Ductal Diseases: Ductal Diseases: Primary Biliary Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Cirrhosis Sclerosing Cholangitis Sclerosing Cholangitis Acute Injury: Viral Hepatitis
Hepatocytes produce. Proteins Clotting factors Hormones. Bile Flow
 R.J.Bailey MD Hepatocytes produce Proteins Clotting factors Hormones Bile Flow Trouble.. for the liver! Trouble for the Liver Liver Gall Bladder Common Alcohol Hep C Fatty Liver Cancer Drugs Viruses Uncommon
R.J.Bailey MD Hepatocytes produce Proteins Clotting factors Hormones Bile Flow Trouble.. for the liver! Trouble for the Liver Liver Gall Bladder Common Alcohol Hep C Fatty Liver Cancer Drugs Viruses Uncommon
Clinical Laboratory. 14:42:00 SSA-52 (Ro52) (ENA) Antibody, IgG 1 AU/mL [0-40] Oct-18
![Clinical Laboratory. 14:42:00 SSA-52 (Ro52) (ENA) Antibody, IgG 1 AU/mL [0-40] Oct-18 Clinical Laboratory. 14:42:00 SSA-52 (Ro52) (ENA) Antibody, IgG 1 AU/mL [0-40] Oct-18](/thumbs/95/125595183.jpg) Clinical Laboratory Procedure Result Units Ref Interval Accession Collected Received Rheumatoid Factor
Clinical Laboratory Procedure Result Units Ref Interval Accession Collected Received Rheumatoid Factor
Test Name Results Units Bio. Ref. Interval
 135091662 Age 45 Years Gender Male 29/8/2017 120000AM 29/8/2017 100215AM 29/8/2017 110825AM Ref By Final RHEUMATOID AUTOIMMUNE COMREHENSIVE ANEL ANTI NUCLEAR ANTIBODY / FACTOR (ANA/ANF), SERUM ----- 20-60
135091662 Age 45 Years Gender Male 29/8/2017 120000AM 29/8/2017 100215AM 29/8/2017 110825AM Ref By Final RHEUMATOID AUTOIMMUNE COMREHENSIVE ANEL ANTI NUCLEAR ANTIBODY / FACTOR (ANA/ANF), SERUM ----- 20-60
IgG4-Negative Autoimmune Pancreatitis with Sclerosing Cholangitis and Colitis: Possible Association with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis?
 CASE REPORT IgG4-Negative Autoimmune Pancreatitis with Sclerosing Cholangitis and Colitis: Possible Association with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis? Keita Saeki 1, Shigenari Hozawa 1, Naoteru Miyata 1,
CASE REPORT IgG4-Negative Autoimmune Pancreatitis with Sclerosing Cholangitis and Colitis: Possible Association with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis? Keita Saeki 1, Shigenari Hozawa 1, Naoteru Miyata 1,
Diagnostic Criteria for Autoimmune Hepatitis : Historical Review and Present Problems
 Jikeikai Med J 2011 ; 58 : 89-93 Review Diagnostic Criteria for Autoimmune Hepatitis : Historical Review and Present Problems Mikio Zeniya and Hiroki Takahashi Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology,
Jikeikai Med J 2011 ; 58 : 89-93 Review Diagnostic Criteria for Autoimmune Hepatitis : Historical Review and Present Problems Mikio Zeniya and Hiroki Takahashi Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology,
Update on Autoimmune Liver Disease. Role of Liver Biopsy in Autoimmune Hepatitis, PBC and PSC
 Update on Autoimmune Liver Disease Role of Liver Biopsy in Autoimmune Hepatitis, PBC and PSC Stefan Hübscher, School of Cancer Sciences, University of Birmingham Dept of Cellular Pathology, Queen Elizabeth
Update on Autoimmune Liver Disease Role of Liver Biopsy in Autoimmune Hepatitis, PBC and PSC Stefan Hübscher, School of Cancer Sciences, University of Birmingham Dept of Cellular Pathology, Queen Elizabeth
Anti-Nuclear Antibodies (ANA). (Incorporating Anti-double stranded DNA (dsdna) and Anti-Extractable Nuclear Antigen (ENA) Antibodies)
 Autoimmune Antibody Testing Points of Note: The interpretation of all autoantibody tests is highly dependent on the likelihood of disease in the patient. The results should always be interpreted with the
Autoimmune Antibody Testing Points of Note: The interpretation of all autoantibody tests is highly dependent on the likelihood of disease in the patient. The results should always be interpreted with the
Chronic Biliary Disease. Dr Susan Davies & Dr Bill Griffiths
 Chronic Biliary Disease Dr Susan Davies & Dr Bill Griffiths Chronic Biliary Disease Terminology is confusing with pathologists and hepatologists using the same language BUT with different meanings. Chronic
Chronic Biliary Disease Dr Susan Davies & Dr Bill Griffiths Chronic Biliary Disease Terminology is confusing with pathologists and hepatologists using the same language BUT with different meanings. Chronic
Idiopathic adulthood ductopenia manifesting as jaundice in a young male
 Idiopathic adulthood ductopenia manifesting as jaundice in a young male Deepak Jain*,1, H. K. Aggarwal 1, Avinash Rao 1, Shaveta Dahiya 1, Promil Jain 2 1 Department of Medicine, Pt. B.D. Sharma University
Idiopathic adulthood ductopenia manifesting as jaundice in a young male Deepak Jain*,1, H. K. Aggarwal 1, Avinash Rao 1, Shaveta Dahiya 1, Promil Jain 2 1 Department of Medicine, Pt. B.D. Sharma University
Laboratory diagnosis of congenital infections
 Laboratory diagnosis of congenital infections Laboratory diagnosis of HSV Direct staining Tzanck test Immunostaining HSV isolation Serology PCR Tzanck test Cell scrape from base of the lesion smear on
Laboratory diagnosis of congenital infections Laboratory diagnosis of HSV Direct staining Tzanck test Immunostaining HSV isolation Serology PCR Tzanck test Cell scrape from base of the lesion smear on
Autoantibodies in the Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies
 Autoantibodies in the Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies Steven R. Ytterberg, M.D. Division of Rheumatology Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN The Myositis Association Annual Conference St. Louis, MO Sept. 25,
Autoantibodies in the Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies Steven R. Ytterberg, M.D. Division of Rheumatology Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN The Myositis Association Annual Conference St. Louis, MO Sept. 25,
