Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells.
|
|
|
- William Carpenter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Figure 1 Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells. (a) Patterns of indicated transcription factor-binding at SEs and surrounding regions in T reg and T conv cells. Average normalized ChIPseq signals of global T reg -SEs, common-ses or T conv -SEs were plotted for merged SE regions ± 20 kb. Merged ends of SEs are marked as S (start) and E (end). (b) Frequency of sites co-occupied by Smc1a and Med1 within indicated regions in T reg and T conv cells. (c) H3K27ac, H3K4me1 and H3K27me3, ATAC-seq, and MBD-seq signals at global common-se and T conv -SE regions and H3K4me3 signal around transcription start sites (TSS) of common- or T conv -SE-associated genes in T reg and T conv cells. Average normalized ChIPseq density of common- or T conv -SEs is plotted for merged SE regions ± 20 kb or TSS ± 5 kb. Merged ends of SEs are marked as S (start) and E (end). (d) Heatmap showing the expression of genes associated with T reg -SE, common-se or T conv -SE in indicated immune cells. LT-HSC: long-term hematopoietic stem cell, ST-HSC: short-term hematopoietic stem cell, MPP: multipotent progenitor, CMP: common myeloid progenitor, MEP: megakaryocyte-erythrocyte progenitor, GMP: granulocyte-monocyte progenitor, and CLP: common lymphoid progenitor. (e) Expression of genes associated with common-ses (334 genes) or -TEs (3516 genes) (left) and with T conv -SEs (19 genes) or -TEs (146 genes) (right) in T reg and T conv cells. Average of two independent RNA-seq experiments are plotted in box-and-whisker plot (median and percentiles are shown). ns P > 0.05, * P 0.1, *** P 0.001, and **** P (Kruskal- Wallis test, followed by Dunn s multiple comparisons test). Data are from one experiment (transcription factor ChIP-seq, ATAC-seq, H3K4me1 and H3K27me3 ChIP-seq), representative of two independent experiments (H3K27ac ChIP-seq, H3K4me3 ChIP-seq and MBD-seq) (a-c), or are average of two independent experiments (RNA-seq) (d,e).
2 Supplementary Figure 2 Chromatin configuration changes at SE regions in developing tt reg cells. (a) Heatmaps showing various epigenetic modifications at individual T reg -SE regions in DP, immature CD4SP (imcd4sp), tt reg precursor (pre-tt reg ), thymic T reg (thyt reg ) and peripheral T reg cells. Individual T reg -SEs (row) are listed in the same order in all sections and normalized ChIP-seq signals are shown for T reg -SE regions with merged ends ± 20 kb. Overall status of T reg -SEs suggested by combination of histone marks is indicated (right). (b) H3K27ac signals at T reg -SE and T reg -TE regions and associated gene expression during T reg cell development. Average of normalized ChIP-seq signals per kb at 66 T reg -SEs or average FPKM of associated genes (± SEM) are plotted. (c) H3K27ac, H3K4me1 and H3K27me3, ATAC-seq, and MBD-seq signals at global common-se and T conv -SE regions and H3K4me3 signal around transcription start sites (TSS) of common- or T conv -SE-associated genes in indicated cells. Average normalized ChIP-seq density of common- or T conv -SEs is plotted for merged SE regions ± 20 kb or TSS ± 5 kb. Merged ends of SEs are marked as S (start) and E (end). Data in a c are from one experiment (ATAC-seq, H3K4me1 and H3K27me3 ChIP-seq), representative of two independent experiments (H3K27ac ChIP-seq, H3K4me3 ChIP-seq and MBD-seq), or average of two independent experiments (RNA-seq).
3 Supplementary Figure 3 Establishment of individual SEs in developing tt reg cells. (a-c) Changes in various epigenetic modifications, mrna transcription and transcription factor binding during T reg cell development around representative T reg -SE regions at the Ctla4, Il2ra and Ikzf2 loci (a), common-se region at the Ets1 locus (b) and T conv -SE region at the Tcf7 locus (c). H3K27ac, H3K4me1, H3K27me3, ATAC-seq, MBD-seq and RNA-seq signals in DP, immature CD4SP (imcd4sp), tt reg precursor (pre-tt reg ), thymic T reg (thyt reg ) and peripheral T reg cells, binding of various transcription factors in DP and T reg cells, and vertebrate conservation score are shown. Bars indicate 25 kb. Data are from one experiment (ATAC-seq, H3K4me1 and H3K27me3 ChIP-seq), representative of two independent experiments (H3K27ac ChIP-seq, H3K4me3 ChIP-seq and MBD-seq), or average of two independent experiments (RNA-seq).
4 Supplementary Figure 4 Satb1 binding to SEs and transcription factor binding motifs of Satb1-binding sites at the DP stage. (a) Percentage of common-ses and T conv -SEs occupied by Satb1 in indicated cell populations. (b) Enrichment of transcription factorbinding motifs in Satb1-binding sites at open chromatin (left) and at closed chromatin (right) within T reg -SEs at the DP stage. Data are from one experiment (a,b).
5 Supplementary Figure 5 Effects of T cell specific Satb1 deletion on characteristics of T reg cells and on thymic negative selection. (a) Suppressive function of peripheral CD4 + CD25 + GFP + cells from Satb1 fl/+ Cd4Cre + Foxp3 GFP and CD4 + CD25 + GFP + and CD4 + CD25 GFP + cells from Satb1 fl/fl Cd4Cre + Foxp3 GFP mice. Percentages of divided naive CD4 + T cells when cultured at indicated ratio with T reg cells are shown (mean ± SEM). (b) Scatter plot displaying global gene expression in CD4 + CD25 + GFP + cells from Satb1 fl/+ Cd4Cre + Foxp3 GFP and Satb1 fl/fl Cd4Cre + Foxp3 GFP mice. Average normalized fragments per kilobase of transcript per million reads mapped (FPKM) values from two independent RNA-seq experiments are plotted and T reg up and down signature genes are highlighted. (c) Flow cytometry of indicated cells after in vitro culture with TCR stimulation, with or without IL-2, for the expression of Foxp3. Numbers indicate percentages of Foxp3 + cells in live CD4 + T cells. (d) DNA methylation status of the T reg cell signature genes in thymic and peripheral CD4 + CD25 + Foxp3 + T cells from Satb1 fl/+ Cd4Cre + and Satb1 fl/fl Cd4Cre + mice, and peripheral CD4 + CD25 Foxp3 + T cells from Satb1 fl/fl Cd4Cre + mice. (e) Flow cytometry of CD25 + Foxp3 + T reg cells from 4-week-old Satb1 fl/+ Cd4Cre + and Satb1 fl/fl Cd4Cre + mice for the expression of Nrp1 and Helios, and summary graph showing the percentages of Nrp1 CD25 + Foxp3 + and Nrp1 + CD25 + Foxp3 + cells among CD4 + T cells (mean ± SEM, n = 4). ** P 0.01 and **** P (two-way ANOVA, followed by Holm-Sidak s multiple comparison test). (f) Flow cytometry of CD25 + Foxp3 + CD4SP cells found in the thymus of 4-week-old Satb1 fl/+ Cd4Cre + and Satb1 fl/fl Cd4Cre + mice, for the expression of T reg cell signature and activation-associated molecules. (g) Flow cytometry of Va2 + thymocytes from Satb1 fl/+ Cd4Cre + OTII, Satb1 fl/+ Cd4Cre + OTII-RIP-mOVA, Satb1 fl/fl Cd4Cre + OTII, and Satb1 fl/fl Cd4Cre + OTII-RIP-mOVA mice, for the examination of CD4SP thymocyte percentage. Data are representative or summary of three independent experiments with three or more mice (a,c-f), of two experiments with two mice (b), and of four experiments with four or more mice (g).
6 Supplementary Figure 6 Effects of mature CD4 + T cell specific and T reg -specific Satb1 deletion on T reg development, phenotype and T reg -type DNA hypomethylation. (a) Schematic diagram illustrating the timing of Satb1 deletion in Satb1 fl/fl Cd4Cre +, Satb1 fl/fl ThpokCre +, and Satb1 fl/fl Foxp3Cre + mice. Satb1 expression level is indicated by color code. (b) Flow cytometry of peripheral CD4 + CD25 + Foxp3 + T cells from Satb1 fl/+ ThpokCre + and Satb1 fl/fl ThpokCre + mice, and CD4 + CD25 Foxp3 + T cells from Satb1 fl/fl ThpokCre + mice, for the expression of T reg cell signature molecules. (c) Scatter plot displaying global gene expression in CD4 + CD25 cells from wild-type (WT) and Satb1 fl/fl ThpokCre + mice. Average normalized fragments per kilobase of transcript per million reads mapped (FPKM) values from two independent RNA-seq experiments are plotted and T reg up and down signature genes are highlighted. (d) DNA methylation status of the Foxp3 CNS2 region in peripheral CD4 + CD25 Foxp3, CD4 + CD25 + Foxp3 + Nrp1 + and CD4 + CD25 + Foxp3 + Nrp1 cells from Satb1 fl/+ ThpokCre + and Satb1 fl/fl ThpokCre + mice, and CD4 + CD25 Foxp3 + from Satb1 fl/fl ThpokCre + mice. Each block indicates CpG residues within amplicons. (e) H3K27ac modification in indicated cell types and Satb1 binding in WT T conv cells at the Foxp3 locus. Vertebrate conservation score and CNS0 region are shown. Bar indicates 5 kb. (f) Flow cytometry of peripheral CD25 + Foxp3 + T cells in Satb1 fl/+ ThpokCre + and Satb1 fl/fl ThpokCre + mice, for the expression of Nrp1 and Helios, and summary data showing the percentages of Nrp1 + tt reg and Nrp1 pt reg cells in peripheral CD4 + T cells (mean ± SEM, n = 6). ns P > 0.05 and **** P (two-way ANOVA, followed by Holm-Sidak s multiple comparison test). (g) Flow cytometry of CD and CD CD4 + T cells from Rag2 / mice, which received CD4 + CD25 CD45RB hi T cells from WT (CD ) and Satb1 fl/fl ThpokCre + (CD ) mice, for identification of T reg cells by CD25 and Foxp3 expression. Summary graph shows percentages of Foxp3 + cells among CD or CD T cells (n = 6, mean ± SEM). **** P (two-tailed t-test). (h) DNA methylation status of 6 CpG residues within the Foxp3 CNS2 in WT and Satb1-deficient CD4 + T cells isolated on day 17 in the experiment described in g. CpGs from 5 end are numbered as 1-6 (column) and amplicons are ordered from the most demethylated ones (row). Demethylated or methylated status is indicated by color code. 0-50% of fully methylated amplicons are omitted for presentation, as the wavy lines indicate (upper panel). Top 3.75% of total reads, when ordered from the most demethylated clones, are zoomed in (bottom). Summary data of two independent experiments, showing the percentage of fully demethylated amplicons, are also shown (right). (i) Flow cytometry of CD4SP thymocytes and CD4 + splenocytes from 4-day-old Satb1 fl/+ Foxp3Cre + and Satb1 fl/fl Foxp3Cre + mice, for identification of T reg cells by the expression of Foxp3 and CD25. (j) Percentages of
7 CD25 + Foxp3 + T reg cells among CD4SP thymocytes and CD4 + splenocytes in 4-day-old Satb1 fl/+ Foxp3Cre + (n = 5) and Satb1 fl/fl Foxp3Cre + mice (n = 8). Horizontal line indicates mean. ns P > 0.05 (two-tailed t-test). (k) Flow cytometry of peripheral CD4 + CD25 + Foxp3 + T reg cells from 4-week-old Satb1 fl/+ Foxp3Cre + and Satb1 fl/fl Foxp3Cre + mice, for T reg cell signature molecule expression. Data are representative or summary of three independent experiments with three or more mice (b,d,f,g,i-k), average of two independent RNA-seq experiments (c), representative of two independent experiments (e), or representative and summary of two independent experiments (h).
8 Supplementary Figure 7 Phenotypic and epigenetic characteristics of Satb1-deficient tt reg precursor cells. (a) Flow cytometry of ttreg precursor (pre-tt reg ) cells from Satb1 fl/+ Cd4Cre + and Satb1 fl/fl Cd4Cre + mice, for the expression of T reg cell signature molecules. (b) Percentages of CD25 Foxp3 + CD4SP thymocytes in 4-week-old Satb1 fl/+ Cd4Cre + and Satb1 fl/fl Cd4Cre + mice. ** P 0.01 (two-tailed t-test). (c) Percentages of Foxp3 + cells after TCR and IL-2 stimulation of cells in b. *** P (two-tailed t- test). (d) H3K4me1 signals at global T reg -SE regions in DP and immature CD4SP (imcd4sp) thymocytes from wild-type (WT) and Satb1 fl/fl Cd4Cre + mice. Average normalized ChIP-seq density of T reg -SEs is plotted for merged T reg -SE regions ± 20 kb. Merged ends of T reg -SEs are marked as S (start) and E (end). (e) Categorization of T reg -SEs by the chromatin state of initial Satb1 binding at the DP stage and effects of Satb1 deletion on their activation. T reg -SEs are divided into those with at least one Satb1-binding site at closed chromatin (left), with Satb1-binding sites at open chromatin only (middle), or with no Satb1 binding at the DP stage. Schematic diagram illustrating the categorization by Satb1 binding type (top panel), examples of T reg -SE loci (middle panel) and H3K27ac, H3K4me1 and gene transcription at representative T reg -SE during T reg cell development in WT and Satb1 fl/fl Cd4Cre + mice (bottom) are shown for each category. Bars indicate 10 kb. (f) Summary data showing the effects of Satb1 deletion on T reg -SEs categorized in e, shown as log2 foldchange (log2fc) of H3K27ac signal at T reg -SEs between pre-tt reg cells of WT and Satb1 fl/fl Cd4Cre + mice (mean ± SEM). Dots indicate individual T reg -SEs. (g) Heatmap showing relative H3K27ac signals at individual T reg -SE, common-se, and T conv -SE regions in indicated cell populations. Ratio to the maximum value among the listed cell populations is shown. (h) H3K27ac signals at global common-se and T conv -SE regions in DP, imcd4sp and pre-tt reg cells from WT and Satb1 fl/fl Cd4Cre + mice. Average normalized ChIP-seq density of common-ses or T conv -SEs is plotted for merged SE regions ± 20 kb. Merged ends of SEs are marked as S (start) and E (end). Data are representative of three independent experiments with three or more mice (a-c), from one experiment (d), or representative of two independent experiments (e-h).
9 Supplementary Figure 8 Effects of Satb1-dependent T reg -SE activation on associated gene expression. (a) Volcano plot showing the differential gene expression between wild-type (WT) and Satb1 fl/fl Cd4Cre + CD24 + CD25 + GITR + CD4SP thymocytes (mixture of immature thymic T reg (thyt reg ) and tt reg precursor (pre-tt reg ) cells). Genes associated with T reg -SEs, common- SEs and T conv -SEs are highlighted. (b) H3K27ac of individual T reg -SE regions at the pre-tt reg cell stage (top) and associated gene expression in CD24 + CD25 + GITR + CD4SP thymocytes (bottom) in WT and Satb1 fl/fl Cd4Cre + mice, shown as ratios to the average of two populations. T reg -SEs are grouped into three categories by the effects of Satb1 deletion, as shown in Fig. 8e. (c) Hypothetical model of super-enhancer establishment and subsequent transcriptional regulation during thymic T reg cell development. T reg -SE regions are poised at least from the DP stage and bound by Satb1. Upon receiving the signal to direct T reg cell differentiation, T reg -SE regions undergo Satb1-dependent activation, likely through the recruitment of epigenetic modifying enzymes, and become T reg lineagecommitted precursor cells. As T reg cell development proceeds, enhancer-promoter looping facilitates the expression of associated T reg cell signature genes, including Foxp3, as well as other epigenetic modifications such as T reg -specific DNA demethylation, histone modification of promoter regions and chromatin loosening of enhancer and promoter regions. Once T reg cell development is complete, Foxp3 amplifies pre-established molecular features 1 and Satb1 transcription is repressed by Foxp3 2 ; however, mediator, cohesin, and various transcription factors, including Foxp3, occupy the sites where Satb1 initially bound, maintaining the local chromatin structure. 1. Gavin, M.A. et al. Foxp3-dependent programme of regulatory T cell differentiation. Nature 445, (2007). 2. Beyer, M. et al. Repression of the genome organizer SATB1 in regulatory T cells is required for suppressive function and inhibition of effector differentiation. Nature immunology 12, (2011).
Supplementary Figure 1. Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. DNA-methylation machinery is essential for silencing of Cd4 in cytotoxic T cells.
 Supplementary Figure 1 DNA-methylation machinery is essential for silencing of Cd4 in cytotoxic T cells. (a) Scheme for the retroviral shrna screen. (b) Histogram showing CD4 expression (MFI) in WT cytotoxic
Supplementary Figure 1 DNA-methylation machinery is essential for silencing of Cd4 in cytotoxic T cells. (a) Scheme for the retroviral shrna screen. (b) Histogram showing CD4 expression (MFI) in WT cytotoxic
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Transcriptional program of the TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Transcriptional program of the TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets. (a) Comparison of gene expression of TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets by microarray. Genes that are 1.5-fold upregulated
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcriptional program of the TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets. (a) Comparison of gene expression of TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets by microarray. Genes that are 1.5-fold upregulated
Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types. (a) Pearson correlation heatmap among open chromatin profiles of different
Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types. (a) Pearson correlation heatmap among open chromatin profiles of different
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1! a! b! Nfatc1!! Nfatc1"! P1! P2! pa1! pa2! ex1! ex2! exons 3-9! ex1! ex11!!" #" Nfatc1A!!" Nfatc1B! #"!" Nfatc1C! #" DN1! DN2! DN1!!A! #A!!B! #B!!C! #C!!A!
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1! a! b! Nfatc1!! Nfatc1"! P1! P2! pa1! pa2! ex1! ex2! exons 3-9! ex1! ex11!!" #" Nfatc1A!!" Nfatc1B! #"!" Nfatc1C! #" DN1! DN2! DN1!!A! #A!!B! #B!!C! #C!!A!
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans.
 Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
Supplementary Figure 1 Cytokine receptors on developing thymocytes that can potentially signal Runx3d expression.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Cytokine receptors on developing thymocytes that can potentially signal Runx3d expression. (a) Characterization of c-independent SP8 cells. Stainings for maturation markers (top)
Supplementary Figure 1 Cytokine receptors on developing thymocytes that can potentially signal Runx3d expression. (a) Characterization of c-independent SP8 cells. Stainings for maturation markers (top)
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.3412
 Supplementary Figure 1 Gata1 expression in heamatopoietic stem and progenitor populations. (a) Unsupervised clustering according to 100 top variable genes across single pre-gm cells. The two main cell
Supplementary Figure 1 Gata1 expression in heamatopoietic stem and progenitor populations. (a) Unsupervised clustering according to 100 top variable genes across single pre-gm cells. The two main cell
Supplementary. presence of the. (c) mrna expression. Error. in naive or
 Figure 1. (a) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated in the presence of the indicated cytokines for 3 days. Enpp2 mrna expression was measured by qrt-pcrhr, infected with (b, c) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated
Figure 1. (a) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated in the presence of the indicated cytokines for 3 days. Enpp2 mrna expression was measured by qrt-pcrhr, infected with (b, c) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Broad H3K4me3 is associated with increased transcription elongation and enhancer activity at tumor suppressor genes
 Broad H3K4me3 is associated with increased transcription elongation and enhancer activity at tumor suppressor genes Kaifu Chen 1,2,3,4,5,10, Zhong Chen 6,10, Dayong Wu 6, Lili Zhang 7, Xueqiu Lin 1,2,8,
Broad H3K4me3 is associated with increased transcription elongation and enhancer activity at tumor suppressor genes Kaifu Chen 1,2,3,4,5,10, Zhong Chen 6,10, Dayong Wu 6, Lili Zhang 7, Xueqiu Lin 1,2,8,
Supplemental Figure S1. Tertiles of FKBP5 promoter methylation and internal regulatory region
 Supplemental Figure S1. Tertiles of FKBP5 promoter methylation and internal regulatory region methylation in relation to PSS and fetal coupling. A, PSS values for participants whose placentas showed low,
Supplemental Figure S1. Tertiles of FKBP5 promoter methylation and internal regulatory region methylation in relation to PSS and fetal coupling. A, PSS values for participants whose placentas showed low,
Supplementary Figure 1. Successful excision of genes from WBM lysates and
 Supplementary Information: Supplementary Figure 1. Successful excision of genes from WBM lysates and survival of mice with different genotypes. (a) The proper excision of Pten, p110α, p110α and p110δ was
Supplementary Information: Supplementary Figure 1. Successful excision of genes from WBM lysates and survival of mice with different genotypes. (a) The proper excision of Pten, p110α, p110α and p110δ was
Supplementary Figure 1 IL-27 IL
 Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Results. Abstract. Introduc4on. Conclusions. Methods. Funding
 . expression that plays a role in many cellular processes affecting a variety of traits. In this study DNA methylation was assessed in neuronal tissue from three pigs (frontal lobe) and one great tit (whole
. expression that plays a role in many cellular processes affecting a variety of traits. In this study DNA methylation was assessed in neuronal tissue from three pigs (frontal lobe) and one great tit (whole
Computational Analysis of UHT Sequences Histone modifications, CAGE, RNA-Seq
 Computational Analysis of UHT Sequences Histone modifications, CAGE, RNA-Seq Philipp Bucher Wednesday January 21, 2009 SIB graduate school course EPFL, Lausanne ChIP-seq against histone variants: Biological
Computational Analysis of UHT Sequences Histone modifications, CAGE, RNA-Seq Philipp Bucher Wednesday January 21, 2009 SIB graduate school course EPFL, Lausanne ChIP-seq against histone variants: Biological
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Assessment of sample purity and quality.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Assessment of sample purity and quality. (a) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of formaldehyde-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections from a human testis biopsy collected concurrently with
Supplementary Figure 1 Assessment of sample purity and quality. (a) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of formaldehyde-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections from a human testis biopsy collected concurrently with
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Effect of HSP90 inhibition on expression of endogenous retroviruses. (a) Inducible shrna-mediated Hsp90 silencing in mouse ESCs. Immunoblots of total cell extract expressing the
Supplementary Figure 1 Effect of HSP90 inhibition on expression of endogenous retroviruses. (a) Inducible shrna-mediated Hsp90 silencing in mouse ESCs. Immunoblots of total cell extract expressing the
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplemental Figure 1. Furin is efficiently deleted in CD4 + and CD8 + T cells. a, Western blot for furin and actin proteins in CD4cre-fur f/f and fur f/f Th1 cells. Wild-type and furin-deficient CD4 +
Supplemental Figure 1. Furin is efficiently deleted in CD4 + and CD8 + T cells. a, Western blot for furin and actin proteins in CD4cre-fur f/f and fur f/f Th1 cells. Wild-type and furin-deficient CD4 +
Supplementary Figure 1: Attenuation of association signals after conditioning for the lead SNP. a) attenuation of association signal at the 9p22.
 Supplementary Figure 1: Attenuation of association signals after conditioning for the lead SNP. a) attenuation of association signal at the 9p22.32 PCOS locus after conditioning for the lead SNP rs10993397;
Supplementary Figure 1: Attenuation of association signals after conditioning for the lead SNP. a) attenuation of association signal at the 9p22.32 PCOS locus after conditioning for the lead SNP rs10993397;
EPIGENOMICS PROFILING SERVICES
 EPIGENOMICS PROFILING SERVICES Chromatin analysis DNA methylation analysis RNA-seq analysis Diagenode helps you uncover the mysteries of epigenetics PAGE 3 Integrative epigenomics analysis DNA methylation
EPIGENOMICS PROFILING SERVICES Chromatin analysis DNA methylation analysis RNA-seq analysis Diagenode helps you uncover the mysteries of epigenetics PAGE 3 Integrative epigenomics analysis DNA methylation
Not IN Our Genes - A Different Kind of Inheritance.! Christopher Phiel, Ph.D. University of Colorado Denver Mini-STEM School February 4, 2014
 Not IN Our Genes - A Different Kind of Inheritance! Christopher Phiel, Ph.D. University of Colorado Denver Mini-STEM School February 4, 2014 Epigenetics in Mainstream Media Epigenetics *Current definition:
Not IN Our Genes - A Different Kind of Inheritance! Christopher Phiel, Ph.D. University of Colorado Denver Mini-STEM School February 4, 2014 Epigenetics in Mainstream Media Epigenetics *Current definition:
Accessing and Using ENCODE Data Dr. Peggy J. Farnham
 1 William M Keck Professor of Biochemistry Keck School of Medicine University of Southern California How many human genes are encoded in our 3x10 9 bp? C. elegans (worm) 959 cells and 1x10 8 bp 20,000
1 William M Keck Professor of Biochemistry Keck School of Medicine University of Southern California How many human genes are encoded in our 3x10 9 bp? C. elegans (worm) 959 cells and 1x10 8 bp 20,000
and follicular helper T cells is Egr2-dependent. (a) Diagrammatic representation of the
 Supplementary Figure 1. LAG3 + Treg-mediated regulation of germinal center B cells and follicular helper T cells is Egr2-dependent. (a) Diagrammatic representation of the experimental protocol for the
Supplementary Figure 1. LAG3 + Treg-mediated regulation of germinal center B cells and follicular helper T cells is Egr2-dependent. (a) Diagrammatic representation of the experimental protocol for the
sequences of a styx mutant reveals a T to A transversion in the donor splice site of intron 5
 sfigure 1 Styx mutant mice recapitulate the phenotype of SHIP -/- mice. (A) Analysis of the genomic sequences of a styx mutant reveals a T to A transversion in the donor splice site of intron 5 (GTAAC
sfigure 1 Styx mutant mice recapitulate the phenotype of SHIP -/- mice. (A) Analysis of the genomic sequences of a styx mutant reveals a T to A transversion in the donor splice site of intron 5 (GTAAC
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
Supplementary Figure S1. Gene expression analysis of epidermal marker genes and TP63.
 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure S1. Gene expression analysis of epidermal marker genes and TP63. A. Screenshot of the UCSC genome browser from normalized RNAPII and RNA-seq ChIP-seq data
Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure S1. Gene expression analysis of epidermal marker genes and TP63. A. Screenshot of the UCSC genome browser from normalized RNAPII and RNA-seq ChIP-seq data
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 A β-strand positions consistently places the residues at CDR3β P6 and P7 within human and mouse TCR-peptide-MHC interfaces. (a) E8 TCR containing V β 13*06 carrying with an 11mer
Supplementary Figure 1 A β-strand positions consistently places the residues at CDR3β P6 and P7 within human and mouse TCR-peptide-MHC interfaces. (a) E8 TCR containing V β 13*06 carrying with an 11mer
Supplemental Information. Genomic Characterization of Murine. Monocytes Reveals C/EBPb Transcription. Factor Dependence of Ly6C Cells
 Immunity, Volume 46 Supplemental Information Genomic Characterization of Murine Monocytes Reveals C/EBPb Transcription Factor Dependence of Ly6C Cells Alexander Mildner, Jörg Schönheit, Amir Giladi, Eyal
Immunity, Volume 46 Supplemental Information Genomic Characterization of Murine Monocytes Reveals C/EBPb Transcription Factor Dependence of Ly6C Cells Alexander Mildner, Jörg Schönheit, Amir Giladi, Eyal
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice. (a) Gene expression profile in the resting CD4 + T cells were analyzed by an Affymetrix microarray
Supplementary Figure 1 Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice. (a) Gene expression profile in the resting CD4 + T cells were analyzed by an Affymetrix microarray
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nature89 IFN- (ng ml ) 5 4 3 1 Splenocytes NS IFN- (ng ml ) 6 4 Lymph node cells NS Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / IL- (ng ml ) 3 1 Splenocytes IL- (ng ml ) 1 8 6 4 *** ** Lymph node cells
doi: 1.138/nature89 IFN- (ng ml ) 5 4 3 1 Splenocytes NS IFN- (ng ml ) 6 4 Lymph node cells NS Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / IL- (ng ml ) 3 1 Splenocytes IL- (ng ml ) 1 8 6 4 *** ** Lymph node cells
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.2419
 Supplementary Figure 1 Mapped sequence reads and nucleosome occupancies. (a) Distribution of sequencing reads on the mouse reference genome for chromosome 14 as an example. The number of reads in a 1 Mb
Supplementary Figure 1 Mapped sequence reads and nucleosome occupancies. (a) Distribution of sequencing reads on the mouse reference genome for chromosome 14 as an example. The number of reads in a 1 Mb
Hosoya et al. TRIM28 is essential for erythroblast differentiation in the mouse (supplemental information)
 TaqMan assay Gene TRIM28 GATA-1 Applied Biosystems TaqMan assay Mm00495594_m1 Mm01352636_m1 SYBR Green assay Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Reference adult α-globin CCCGGTGCCTTGTCTGCT GTGAAATCGGCAGGGTGG
TaqMan assay Gene TRIM28 GATA-1 Applied Biosystems TaqMan assay Mm00495594_m1 Mm01352636_m1 SYBR Green assay Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Reference adult α-globin CCCGGTGCCTTGTCTGCT GTGAAATCGGCAGGGTGG
Table S1. Total and mapped reads produced for each ChIP-seq sample
 Tale S1. Total and mapped reads produced for each ChIP-seq sample Sample Total Reads Mapped Reads Col- H3K27me3 rep1 125662 1334323 (85.76%) Col- H3K27me3 rep2 9176437 7986731 (87.4%) atmi1a//c H3K27m3
Tale S1. Total and mapped reads produced for each ChIP-seq sample Sample Total Reads Mapped Reads Col- H3K27me3 rep1 125662 1334323 (85.76%) Col- H3K27me3 rep2 9176437 7986731 (87.4%) atmi1a//c H3K27m3
Transcript-indexed ATAC-seq for immune profiling
 Transcript-indexed ATAC-seq for immune profiling Technical Journal Club 22 nd of May 2018 Christina Müller Nature Methods, Vol.10 No.12, 2013 Nature Biotechnology, Vol.32 No.7, 2014 Nature Medicine, Vol.24,
Transcript-indexed ATAC-seq for immune profiling Technical Journal Club 22 nd of May 2018 Christina Müller Nature Methods, Vol.10 No.12, 2013 Nature Biotechnology, Vol.32 No.7, 2014 Nature Medicine, Vol.24,
fl/+ KRas;Atg5 fl/+ KRas;Atg5 fl/fl KRas;Atg5 fl/fl KRas;Atg5 Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) (b)
 KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At a b Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) GO gene sets (MSigDB v3. c5) enriched in KRas;Atg5 fl/+ as compared to KRas;Atg5 fl/fl tumors using gene set
KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At a b Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) GO gene sets (MSigDB v3. c5) enriched in KRas;Atg5 fl/+ as compared to KRas;Atg5 fl/fl tumors using gene set
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Cellularity of leukocytes and their progenitors in naive wild-type and Spp1 / mice.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Cellularity of leukocytes and their progenitors in naive wild-type and Spp1 / mice. (a, b) Gating strategies for differentiated cells including PMN (CD11b + Ly6G hi and CD11b + Ly6G
Supplementary Figure 1 Cellularity of leukocytes and their progenitors in naive wild-type and Spp1 / mice. (a, b) Gating strategies for differentiated cells including PMN (CD11b + Ly6G hi and CD11b + Ly6G
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/3/114/ra23/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Regulation of Zap70 Expression During Thymocyte Development Enables Temporal Separation of CD4 and CD8 Repertoire Selection
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/3/114/ra23/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Regulation of Zap70 Expression During Thymocyte Development Enables Temporal Separation of CD4 and CD8 Repertoire Selection
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12215 Supplementary Figure 1. The effects of full and dissociated GR agonists in supporting BFU-E self-renewal divisions. BFU-Es were cultured in self-renewal medium with indicated GR
doi:10.1038/nature12215 Supplementary Figure 1. The effects of full and dissociated GR agonists in supporting BFU-E self-renewal divisions. BFU-Es were cultured in self-renewal medium with indicated GR
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.3812
 Nature Genetics: doi:10.1038/ng.3812 Supplementary Figure 1 Smarcd2-knockout mice die perinatally with impaired energy homeostasis. (a) Generation of the Smarcd2 conditional knockout allele. Deletion of
Nature Genetics: doi:10.1038/ng.3812 Supplementary Figure 1 Smarcd2-knockout mice die perinatally with impaired energy homeostasis. (a) Generation of the Smarcd2 conditional knockout allele. Deletion of
Session 6: Integration of epigenetic data. Peter J Park Department of Biomedical Informatics Harvard Medical School July 18-19, 2016
 Session 6: Integration of epigenetic data Peter J Park Department of Biomedical Informatics Harvard Medical School July 18-19, 2016 Utilizing complimentary datasets Frequent mutations in chromatin regulators
Session 6: Integration of epigenetic data Peter J Park Department of Biomedical Informatics Harvard Medical School July 18-19, 2016 Utilizing complimentary datasets Frequent mutations in chromatin regulators
Dynamic Changes in Chromatin Accessibility Occur in CD8 + T Cells Responding to Viral Infection
 Resource Dynamic Changes in Chromatin Accessibility Occur in CD8 + T Cells Responding to Viral Infection Highlights d Examined chromatin accessibility in endogenous CD8 + T cells during viral infection
Resource Dynamic Changes in Chromatin Accessibility Occur in CD8 + T Cells Responding to Viral Infection Highlights d Examined chromatin accessibility in endogenous CD8 + T cells during viral infection
Supplemental Information. Checkpoint Blockade Immunotherapy. Induces Dynamic Changes. in PD-1 CD8 + Tumor-Infiltrating T Cells
 Immunity, Volume 50 Supplemental Information Checkpoint Blockade Immunotherapy Induces Dynamic Changes in PD-1 CD8 + Tumor-Infiltrating T Cells Sema Kurtulus, Asaf Madi, Giulia Escobar, Max Klapholz, Jackson
Immunity, Volume 50 Supplemental Information Checkpoint Blockade Immunotherapy Induces Dynamic Changes in PD-1 CD8 + Tumor-Infiltrating T Cells Sema Kurtulus, Asaf Madi, Giulia Escobar, Max Klapholz, Jackson
Supplemental Information. A Highly Sensitive and Robust Method. for Genome-wide 5hmC Profiling. of Rare Cell Populations
 Molecular ell, Volume 63 Supplemental Information Highly Sensitive and Robust Method for enome-wide hm Profiling of Rare ell Populations Dali Han, Xingyu Lu, lan H. Shih, Ji Nie, Qiancheng You, Meng Michelle
Molecular ell, Volume 63 Supplemental Information Highly Sensitive and Robust Method for enome-wide hm Profiling of Rare ell Populations Dali Han, Xingyu Lu, lan H. Shih, Ji Nie, Qiancheng You, Meng Michelle
Akt and mtor pathways differentially regulate the development of natural and inducible. T H 17 cells
 Akt and mtor pathways differentially regulate the development of natural and inducible T H 17 cells Jiyeon S Kim, Tammarah Sklarz, Lauren Banks, Mercy Gohil, Adam T Waickman, Nicolas Skuli, Bryan L Krock,
Akt and mtor pathways differentially regulate the development of natural and inducible T H 17 cells Jiyeon S Kim, Tammarah Sklarz, Lauren Banks, Mercy Gohil, Adam T Waickman, Nicolas Skuli, Bryan L Krock,
Large conserved domains of low DNA methylation maintained by Dnmt3a
 Supplementary information Large conserved domains of low DNA methylation maintained by Dnmt3a Mira Jeong# 1, Deqiang Sun # 2, Min Luo# 1, Yun Huang 3, Grant A. Challen %1, Benjamin Rodriguez 2, Xiaotian
Supplementary information Large conserved domains of low DNA methylation maintained by Dnmt3a Mira Jeong# 1, Deqiang Sun # 2, Min Luo# 1, Yun Huang 3, Grant A. Challen %1, Benjamin Rodriguez 2, Xiaotian
Epigenetics DNA methylation. Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 13. DNA Methylation
 Epigenetics DNA methylation Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 13 DNA Methylation Most methylated cytosines are found in the dinucleotide sequence CG, denoted mcpg. The restriction enzyme HpaII
Epigenetics DNA methylation Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 13 DNA Methylation Most methylated cytosines are found in the dinucleotide sequence CG, denoted mcpg. The restriction enzyme HpaII
Supporting Information Table of Contents
 Supporting Information Table of Contents Supporting Information Figure 1 Page 2 Supporting Information Figure 2 Page 4 Supporting Information Figure 3 Page 5 Supporting Information Figure 4 Page 6 Supporting
Supporting Information Table of Contents Supporting Information Figure 1 Page 2 Supporting Information Figure 2 Page 4 Supporting Information Figure 3 Page 5 Supporting Information Figure 4 Page 6 Supporting
Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells.
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
Nature Structural and Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Mutational analysis of the SA2-Scc1 interaction in vitro and in human cells. (a) Autoradiograph (top) and Coomassie stained gel (bottom) of 35 S-labeled Myc-SA2 proteins (input)
Supplementary Figure 1 Mutational analysis of the SA2-Scc1 interaction in vitro and in human cells. (a) Autoradiograph (top) and Coomassie stained gel (bottom) of 35 S-labeled Myc-SA2 proteins (input)
Supplemental Table I.
 Supplemental Table I Male / Mean ± SEM n Mean ± SEM n Body weight, g 29.2±0.4 17 29.7±0.5 17 Total cholesterol, mg/dl 534.0±30.8 17 561.6±26.1 17 HDL-cholesterol, mg/dl 9.6±0.8 17 10.1±0.7 17 Triglycerides,
Supplemental Table I Male / Mean ± SEM n Mean ± SEM n Body weight, g 29.2±0.4 17 29.7±0.5 17 Total cholesterol, mg/dl 534.0±30.8 17 561.6±26.1 17 HDL-cholesterol, mg/dl 9.6±0.8 17 10.1±0.7 17 Triglycerides,
Mst1 regulates integrin-dependent thymocyte trafficking and antigen recognition in the thymus
 Mst1 regulates integrin-dependent thymocyte trafficking and antigen recognition in the thymus Yoshihiro Ueda, Koko Katagiri, Takashi Tomiyama, Kaneki Yasuda, Katsuyoshi Habiro, Tomoya Katakai, Susumu Ikehara,
Mst1 regulates integrin-dependent thymocyte trafficking and antigen recognition in the thymus Yoshihiro Ueda, Koko Katagiri, Takashi Tomiyama, Kaneki Yasuda, Katsuyoshi Habiro, Tomoya Katakai, Susumu Ikehara,
An epigenetic approach to understanding (and predicting?) environmental effects on gene expression
 www.collaslab.com An epigenetic approach to understanding (and predicting?) environmental effects on gene expression Philippe Collas University of Oslo Institute of Basic Medical Sciences Stem Cell Epigenetics
www.collaslab.com An epigenetic approach to understanding (and predicting?) environmental effects on gene expression Philippe Collas University of Oslo Institute of Basic Medical Sciences Stem Cell Epigenetics
The epigenetic landscape of T cell subsets in SLE identifies known and potential novel drivers of the autoimmune response
 Abstract # 319030 Poster # F.9 The epigenetic landscape of T cell subsets in SLE identifies known and potential novel drivers of the autoimmune response Jozsef Karman, Brian Johnston, Sofija Miljovska,
Abstract # 319030 Poster # F.9 The epigenetic landscape of T cell subsets in SLE identifies known and potential novel drivers of the autoimmune response Jozsef Karman, Brian Johnston, Sofija Miljovska,
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Heatmap of GO terms for differentially expressed genes. The terms were hierarchically clustered using the GO term enrichment beta. Darker red, higher positive
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Heatmap of GO terms for differentially expressed genes. The terms were hierarchically clustered using the GO term enrichment beta. Darker red, higher positive
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1 33,312. Aire rep 1. Aire rep 2 # 44,325 # 44,055. Aire rep 1. Aire rep 2.
 a 33,312 b rep 1 rep 1 # 44,325 rep 2 # 44,055 [0-84] rep 2 [0-84] 1810043G02Rik Pfkl Dnmt3l Icosl rep 1 [0-165] rep 2 [0-165] Rps14 Cd74 Mir5107 Tcof1 rep 1 [0-69] rep 2 [0-68] Id3 E2f2 Asap3 rep 1 [0-141]
a 33,312 b rep 1 rep 1 # 44,325 rep 2 # 44,055 [0-84] rep 2 [0-84] 1810043G02Rik Pfkl Dnmt3l Icosl rep 1 [0-165] rep 2 [0-165] Rps14 Cd74 Mir5107 Tcof1 rep 1 [0-69] rep 2 [0-68] Id3 E2f2 Asap3 rep 1 [0-141]
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. RNA-Seq analysis of CD8 + TILs and N-TILs.
 Supplementary Figure 1 RNA-Seq analysis of CD8 + TILs and N-TILs. (a) Schematic representation of the tumor and cell types used for the study. HNSCC, head and neck squamous cell cancer; NSCLC, non-small
Supplementary Figure 1 RNA-Seq analysis of CD8 + TILs and N-TILs. (a) Schematic representation of the tumor and cell types used for the study. HNSCC, head and neck squamous cell cancer; NSCLC, non-small
T cell maturation. T-cell Maturation. What allows T cell maturation?
 T-cell Maturation What allows T cell maturation? Direct contact with thymic epithelial cells Influence of thymic hormones Growth factors (cytokines, CSF) T cell maturation T cell progenitor DN DP SP 2ry
T-cell Maturation What allows T cell maturation? Direct contact with thymic epithelial cells Influence of thymic hormones Growth factors (cytokines, CSF) T cell maturation T cell progenitor DN DP SP 2ry
Sirt1 Hmg20b Gm (0.17) 24 (17.3) 877 (857)
 3 (0.17) 24 (17.3) Sirt1 Hmg20 Gm4763 877 (857) c d Suppl. Figure 1. Screen validation for top candidate antagonists of Dot1L (a) Numer of genes with one (gray), two (cyan) or three (red) shrna scored
3 (0.17) 24 (17.3) Sirt1 Hmg20 Gm4763 877 (857) c d Suppl. Figure 1. Screen validation for top candidate antagonists of Dot1L (a) Numer of genes with one (gray), two (cyan) or three (red) shrna scored
Control shrna#9 shrna#12. shrna#12 CD14-PE CD14-PE
 a Control shrna#9 shrna#12 c Control shrna#9 shrna#12 e Control shrna#9 shrna#12 h 14 12 CFU-E BFU-E GEMM GM b Colony number 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 6 pm A pa pc CFU-E BFU-E GEMM GM pu pgm A p pg B d f CD11b-APC
a Control shrna#9 shrna#12 c Control shrna#9 shrna#12 e Control shrna#9 shrna#12 h 14 12 CFU-E BFU-E GEMM GM b Colony number 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 6 pm A pa pc CFU-E BFU-E GEMM GM pu pgm A p pg B d f CD11b-APC
Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice
 Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
DNA Methylation Dynamics of Human Hematopoietic Stem Cell Differentiation
 Resource DNA Methylation Dynamics of Human Hematopoietic Stem Cell Differentiation Graphical Abstract Authors Matthias Farlik, Florian Halbritter, Fabian M uller,..., Thomas Lengauer, Mattia Frontini,
Resource DNA Methylation Dynamics of Human Hematopoietic Stem Cell Differentiation Graphical Abstract Authors Matthias Farlik, Florian Halbritter, Fabian M uller,..., Thomas Lengauer, Mattia Frontini,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10866 a b 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Match No Match 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Turcan et al. Supplementary Fig.1 Concepts mapping H3K27 targets in EF CBX8 targets in EF H3K27 targets in ES SUZ12 targets in ES
doi:10.1038/nature10866 a b 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Match No Match 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Turcan et al. Supplementary Fig.1 Concepts mapping H3K27 targets in EF CBX8 targets in EF H3K27 targets in ES SUZ12 targets in ES
Heintzman, ND, Stuart, RK, Hon, G, Fu, Y, Ching, CW, Hawkins, RD, Barrera, LO, Van Calcar, S, Qu, C, Ching, KA, Wang, W, Weng, Z, Green, RD,
 Heintzman, ND, Stuart, RK, Hon, G, Fu, Y, Ching, CW, Hawkins, RD, Barrera, LO, Van Calcar, S, Qu, C, Ching, KA, Wang, W, Weng, Z, Green, RD, Crawford, GE, Ren, B (2007) Distinct and predictive chromatin
Heintzman, ND, Stuart, RK, Hon, G, Fu, Y, Ching, CW, Hawkins, RD, Barrera, LO, Van Calcar, S, Qu, C, Ching, KA, Wang, W, Weng, Z, Green, RD, Crawford, GE, Ren, B (2007) Distinct and predictive chromatin
cis-regulatory enrichment analysis in human, mouse and fly
 cis-regulatory enrichment analysis in human, mouse and fly Zeynep Kalender Atak, PhD Laboratory of Computational Biology VIB-KU Leuven Center for Brain & Disease Research Laboratory of Computational Biology
cis-regulatory enrichment analysis in human, mouse and fly Zeynep Kalender Atak, PhD Laboratory of Computational Biology VIB-KU Leuven Center for Brain & Disease Research Laboratory of Computational Biology
Cluster Dendrogram. dist(cor(na.omit(tss.exprs.chip[, c(1:10, 24, 27, 30, 48:50, dist(cor(na.omit(tss.exprs.chip[, c(1:99, 103, 104, 109, 110,
 A Transcriptome (RNA-seq) Transcriptome (RNA-seq) 3. 2.5 2..5..5...5..5 2. 2.5 3. 2.5 2..5..5...5..5 2. 2.5 Cluster Dendrogram RS_ES3.2 RS_ES3. RS_SHS5.2 RS_SHS5. PS_SHS5.2 PS_SHS5. RS_LJ3 PS_LJ3..4 _SHS5.2
A Transcriptome (RNA-seq) Transcriptome (RNA-seq) 3. 2.5 2..5..5...5..5 2. 2.5 3. 2.5 2..5..5...5..5 2. 2.5 Cluster Dendrogram RS_ES3.2 RS_ES3. RS_SHS5.2 RS_SHS5. PS_SHS5.2 PS_SHS5. RS_LJ3 PS_LJ3..4 _SHS5.2
5/1/13. The proportion of thymus that produces T cells decreases with age. The cellular organization of the thymus
 T cell precursors migrate from the bone marrow via the blood to the thymus to mature 1 2 The cellular organization of the thymus The proportion of thymus that produces T cells decreases with age 3 4 1
T cell precursors migrate from the bone marrow via the blood to the thymus to mature 1 2 The cellular organization of the thymus The proportion of thymus that produces T cells decreases with age 3 4 1
Stem Cell Epigenetics
 Stem Cell Epigenetics Philippe Collas University of Oslo Institute of Basic Medical Sciences Norwegian Center for Stem Cell Research www.collaslab.com Source of stem cells in the body Somatic ( adult )
Stem Cell Epigenetics Philippe Collas University of Oslo Institute of Basic Medical Sciences Norwegian Center for Stem Cell Research www.collaslab.com Source of stem cells in the body Somatic ( adult )
Supplementary Figure 1
 d f a IL7 b IL GATA RORγt h HDM IL IL7 PBS Ilra R7 PBS HDM Ilra R7 HDM Foxp Foxp Ilra R7 HDM HDM Ilra R7 HDM. 9..79. CD + FOXP + T reg cell CD + FOXP T conv cell PBS Ilra R7 PBS HDM Ilra R7 HDM CD + FOXP
d f a IL7 b IL GATA RORγt h HDM IL IL7 PBS Ilra R7 PBS HDM Ilra R7 HDM Foxp Foxp Ilra R7 HDM HDM Ilra R7 HDM. 9..79. CD + FOXP + T reg cell CD + FOXP T conv cell PBS Ilra R7 PBS HDM Ilra R7 HDM CD + FOXP
Lung Met 1 Lung Met 2 Lung Met Lung Met H3K4me1. Lung Met H3K27ac Primary H3K4me1
 a Gained Met-VELs 1.5 1.5 -.5 Lung Met 1 Lung Met Lung Met 3 1. Lung Met H3K4me1 Lung Met H3K4me1 1 Lung Met H3K4me1 Lung Met H3K7ac 1.5 Lung Met H3K7ac Lung Met H3K7ac.8 Primary H3K4me1 Primary H3K7ac
a Gained Met-VELs 1.5 1.5 -.5 Lung Met 1 Lung Met Lung Met 3 1. Lung Met H3K4me1 Lung Met H3K4me1 1 Lung Met H3K4me1 Lung Met H3K7ac 1.5 Lung Met H3K7ac Lung Met H3K7ac.8 Primary H3K4me1 Primary H3K7ac
SUPPLEMENT Supplementary Figure 1: (A) (B)
 SUPPLEMENT Supplementary Figure 1: CD4 + naïve effector T cells (CD4 effector) were labeled with CFSE, stimulated with α-cd2/cd3/cd28 coated beads (at 2 beads/cell) and cultured alone or cocultured with
SUPPLEMENT Supplementary Figure 1: CD4 + naïve effector T cells (CD4 effector) were labeled with CFSE, stimulated with α-cd2/cd3/cd28 coated beads (at 2 beads/cell) and cultured alone or cocultured with
Supplemental Figure 1. Genes showing ectopic H3K9 dimethylation in this study are DNA hypermethylated in Lister et al. study.
 mc mc mc mc SUP mc mc Supplemental Figure. Genes showing ectopic HK9 dimethylation in this study are DNA hypermethylated in Lister et al. study. Representative views of genes that gain HK9m marks in their
mc mc mc mc SUP mc mc Supplemental Figure. Genes showing ectopic HK9 dimethylation in this study are DNA hypermethylated in Lister et al. study. Representative views of genes that gain HK9m marks in their
L1 on PyMT tumor cells but Py117 cells are more responsive to IFN-γ. (A) Flow
 A MHCI B PD-L1 Fold expression 8 6 4 2 Fold expression 3 2 1 No tx 1Gy 2Gy IFN Py117 Py117 Supplementary Figure 1. Radiation and IFN-γ enhance MHCI expression and PD- L1 on PyMT tumor cells but Py117 cells
A MHCI B PD-L1 Fold expression 8 6 4 2 Fold expression 3 2 1 No tx 1Gy 2Gy IFN Py117 Py117 Supplementary Figure 1. Radiation and IFN-γ enhance MHCI expression and PD- L1 on PyMT tumor cells but Py117 cells
Kerdiles et al - Figure S1
 Kerdiles et al - Figure S1 a b Homo sapiens T B ce ce l ls c l M ls ac r PM oph N ag es Mus musculus Foxo1 PLCγ Supplementary Figure 1 Foxo1 expression pattern is conserved between mouse and human. (a)
Kerdiles et al - Figure S1 a b Homo sapiens T B ce ce l ls c l M ls ac r PM oph N ag es Mus musculus Foxo1 PLCγ Supplementary Figure 1 Foxo1 expression pattern is conserved between mouse and human. (a)
T cell development October 28, Dan Stetson
 T cell development October 28, 2016 Dan Stetson stetson@uw.edu 441 Lecture #13 Slide 1 of 29 Three lectures on T cells (Chapters 8, 9) Part 1 (Today): T cell development in the thymus Chapter 8, pages
T cell development October 28, 2016 Dan Stetson stetson@uw.edu 441 Lecture #13 Slide 1 of 29 Three lectures on T cells (Chapters 8, 9) Part 1 (Today): T cell development in the thymus Chapter 8, pages
Lecture outline. Immunological tolerance and immune regulation. Central and peripheral tolerance. Inhibitory receptors of T cells. Regulatory T cells
 1 Immunological tolerance and immune regulation Abul K. Abbas UCSF 2 Lecture outline Central and peripheral tolerance Inhibitory receptors of T cells Regulatory T cells 1 The immunological equilibrium:
1 Immunological tolerance and immune regulation Abul K. Abbas UCSF 2 Lecture outline Central and peripheral tolerance Inhibitory receptors of T cells Regulatory T cells 1 The immunological equilibrium:
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Id2 and Id3 define polyclonal T H 1 and T FH cell subsets.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Id2 and Id3 define polyclonal T H 1 and T FH cell subsets. Id2 YFP/+ (a) or Id3 GFP/+ (b) mice were analyzed 7 days after LCMV infection. T H 1 (SLAM + CXCR5 or CXCR5 PD-1 ), T FH
Supplementary Figure 1 Id2 and Id3 define polyclonal T H 1 and T FH cell subsets. Id2 YFP/+ (a) or Id3 GFP/+ (b) mice were analyzed 7 days after LCMV infection. T H 1 (SLAM + CXCR5 or CXCR5 PD-1 ), T FH
Effects of UBL5 knockdown on cell cycle distribution and sister chromatid cohesion
 Supplementary Figure S1. Effects of UBL5 knockdown on cell cycle distribution and sister chromatid cohesion A. Representative examples of flow cytometry profiles of HeLa cells transfected with indicated
Supplementary Figure S1. Effects of UBL5 knockdown on cell cycle distribution and sister chromatid cohesion A. Representative examples of flow cytometry profiles of HeLa cells transfected with indicated
CRISPR-mediated Editing of Hematopoietic Stem Cells for the Treatment of β-hemoglobinopathies
 CRISPR-mediated Editing of Hematopoietic Stem Cells for the Treatment of β-hemoglobinopathies Jennifer Gori American Society of Gene & Cell Therapy May 11, 2017 editasmedicine.com 1 Highlights Developed
CRISPR-mediated Editing of Hematopoietic Stem Cells for the Treatment of β-hemoglobinopathies Jennifer Gori American Society of Gene & Cell Therapy May 11, 2017 editasmedicine.com 1 Highlights Developed
Supplementary Figure 1. Using DNA barcode-labeled MHC multimers to generate TCR fingerprints
 Supplementary Figure 1 Using DNA barcode-labeled MHC multimers to generate TCR fingerprints (a) Schematic overview of the workflow behind a TCR fingerprint. Each peptide position of the original peptide
Supplementary Figure 1 Using DNA barcode-labeled MHC multimers to generate TCR fingerprints (a) Schematic overview of the workflow behind a TCR fingerprint. Each peptide position of the original peptide
The Ufm1-activating enzyme Uba5 is indispensable for erythroid differentiation in mice
 Supplementary information The Ufm1-activating enzyme Uba5 is indispensable for erythroid differentiation in mice Kanako Tatsumi 1, 2, Harumi Yamamoto-Mukai 2, Ritsuko Shimizu 3, Satoshi Waguri 4, Yu-Shin
Supplementary information The Ufm1-activating enzyme Uba5 is indispensable for erythroid differentiation in mice Kanako Tatsumi 1, 2, Harumi Yamamoto-Mukai 2, Ritsuko Shimizu 3, Satoshi Waguri 4, Yu-Shin
Yue Wei 1, Rui Chen 2, Carlos E. Bueso-Ramos 3, Hui Yang 1, and Guillermo Garcia-Manero 1
 Genome-wide CHIP-Seq Analysis of Histone Methylation Reveals Modulators of NF- B Signaling And the Histone Demethylase JMJD3 Implicated in Myelodysplastic Syndrome Yue Wei 1, Rui Chen 2, Carlos E. Bueso-Ramos
Genome-wide CHIP-Seq Analysis of Histone Methylation Reveals Modulators of NF- B Signaling And the Histone Demethylase JMJD3 Implicated in Myelodysplastic Syndrome Yue Wei 1, Rui Chen 2, Carlos E. Bueso-Ramos
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Pan-cancer analysis of global and local DNA methylation variation a) Variations in global DNA methylation are shown as measured by averaging the genome-wide
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Pan-cancer analysis of global and local DNA methylation variation a) Variations in global DNA methylation are shown as measured by averaging the genome-wide
H3K4 demethylase KDM5B regulates global dynamics of transcription elongation and alternative splicing in embryonic stem cells
 Nucleic Acids Research, 2017 1 doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx251 H3K4 demethylase KDM5B regulates global dynamics of transcription elongation and alternative splicing in embryonic stem cells Runsheng He 1,2 and
Nucleic Acids Research, 2017 1 doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx251 H3K4 demethylase KDM5B regulates global dynamics of transcription elongation and alternative splicing in embryonic stem cells Runsheng He 1,2 and
Supplemental Information. Granulocyte-Monocyte Progenitors and. Monocyte-Dendritic Cell Progenitors Independently
 Immunity, Volume 47 Supplemental Information Granulocyte-Monocyte Progenitors and Monocyte-endritic ell Progenitors Independently Produce Functionally istinct Monocytes lberto Yáñez, Simon G. oetzee, ndre
Immunity, Volume 47 Supplemental Information Granulocyte-Monocyte Progenitors and Monocyte-endritic ell Progenitors Independently Produce Functionally istinct Monocytes lberto Yáñez, Simon G. oetzee, ndre
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1. Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus.
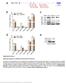 Supplementary Figure 1 Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus. (a) The mir-17-92a expression unit in the third intron of the host mir-17hg transcript. (b,c) Impact of knockdown
Supplementary Figure 1 Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus. (a) The mir-17-92a expression unit in the third intron of the host mir-17hg transcript. (b,c) Impact of knockdown
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Supplementary Information:
 Supplementary Information: Follicular regulatory T cells with Bcl6 expression suppress germinal center reactions by Yeonseok Chung, Shinya Tanaka, Fuliang Chu, Roza Nurieva, Gustavo J. Martinez, Seema
Supplementary Information: Follicular regulatory T cells with Bcl6 expression suppress germinal center reactions by Yeonseok Chung, Shinya Tanaka, Fuliang Chu, Roza Nurieva, Gustavo J. Martinez, Seema
GATA-3 Not Just for Th2 Cells Anymore
 Cellular & Molecular Immunology 15 Review GATA-3 Not Just for Th2 Cells Anymore I-Cheng Ho 1 and Sung-Yun Pai 2 GATA-3 was first cloned as a T cell specific transcription factor in 1991 and its importance
Cellular & Molecular Immunology 15 Review GATA-3 Not Just for Th2 Cells Anymore I-Cheng Ho 1 and Sung-Yun Pai 2 GATA-3 was first cloned as a T cell specific transcription factor in 1991 and its importance
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Taghon, Yui, and Rothenberg: Mast cell diversion of T-lineage precursor cells by the essential T-lineage transcription factor GATA Supplemental Table Supplemental Figures 1-6 Supplemental
Supplementary Material Taghon, Yui, and Rothenberg: Mast cell diversion of T-lineage precursor cells by the essential T-lineage transcription factor GATA Supplemental Table Supplemental Figures 1-6 Supplemental
The autoimmune disease-associated PTPN22 variant promotes calpain-mediated Lyp/Pep
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The autoimmune disease-associated PTPN22 variant promotes calpain-mediated Lyp/Pep degradation associated with lymphocyte and dendritic cell hyperresponsiveness Jinyi Zhang, Naima
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The autoimmune disease-associated PTPN22 variant promotes calpain-mediated Lyp/Pep degradation associated with lymphocyte and dendritic cell hyperresponsiveness Jinyi Zhang, Naima
T Cell Development. Xuefang Cao, MD, PhD. November 3, 2015
 T Cell Development Xuefang Cao, MD, PhD November 3, 2015 Thymocytes in the cortex of the thymus Early thymocytes development Positive and negative selection Lineage commitment Exit from the thymus and
T Cell Development Xuefang Cao, MD, PhD November 3, 2015 Thymocytes in the cortex of the thymus Early thymocytes development Positive and negative selection Lineage commitment Exit from the thymus and
Effector T Cells and
 1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation,
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Chronic variable stress activates hematopoietic stem cells
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Chronic variable stress activates hematopoietic stem cells Timo Heidt *, Hendrik B. Sager *, Gabriel Courties, Partha Dutta, Yoshiko Iwamoto, Alex Zaltsman, Constantin von zur
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Chronic variable stress activates hematopoietic stem cells Timo Heidt *, Hendrik B. Sager *, Gabriel Courties, Partha Dutta, Yoshiko Iwamoto, Alex Zaltsman, Constantin von zur
Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured
 Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured under Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg conditions. mrna
Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured under Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg conditions. mrna
Transcriptional control of CD4 and CD8 coreceptor expression during T cell development
 Cell. Mol. Life Sci. (2013) 70:4537 4553 DOI 10.1007/s00018-013-1393-2 Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences Review Transcriptional control of CD4 and CD8 coreceptor expression during T cell development
Cell. Mol. Life Sci. (2013) 70:4537 4553 DOI 10.1007/s00018-013-1393-2 Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences Review Transcriptional control of CD4 and CD8 coreceptor expression during T cell development
Polycomb Repressive Complex 2-Mediated Chromatin Repression Guides Effector CD8 + T Cell Terminal Differentiation and Loss of Multipotency
 Article Polycomb Repressive Complex 2-Mediated Chromatin Repression Guides Effector CD8 + T Cell Terminal Differentiation and Loss of Multipotency Graphical Abstract Authors Simon M. Gray, Robert A. Amezquita,
Article Polycomb Repressive Complex 2-Mediated Chromatin Repression Guides Effector CD8 + T Cell Terminal Differentiation and Loss of Multipotency Graphical Abstract Authors Simon M. Gray, Robert A. Amezquita,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of apoptosis-related genes in tumor T reg cells. (a) Identification of FOXP3 T reg cells by FACS. CD45 + cells were gated as enriched lymphoid cell populations with low-granularity.
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of apoptosis-related genes in tumor T reg cells. (a) Identification of FOXP3 T reg cells by FACS. CD45 + cells were gated as enriched lymphoid cell populations with low-granularity.
