Conditional and reversible disruption of essential herpesvirus protein functions
|
|
|
- Derick Gilbert
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 nature methods Conditional and reversible disruption of essential herpesvirus protein functions Mandy Glaß, Andreas Busche, Karen Wagner, Martin Messerle & Eva Maria Borst Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2 Supplementary Figure 3 Supplementary Figure 4 Supplementary Figure 5 Supplementary Table 1 Supplementary Note 1 Construction of genomes for CMV-FKBP mutants. Ligand-dependent expression of - fusion proteins following infection. -mediated disruption of PML nuclear bodies depending on shield-1. Analysis of brightly green fluorescent cells occasionally observed after infection with the HCMV-IE-FKBP mutant in the absence of shield-1. Validation of shield-1-dependent expression of CMV fusion proteins at the single cell level. Oligonucleotides used in this study. Analysis of genomes of HCMV-UL51-FKBP viruses that grew in the absence of shield-1. Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth.1346
2 Supplementary Figure 1. Construction of genomes for CMV-FKBP mutants a MIEP HCMV IE2 MCMV IE3 b /IE2 MIEP HCMV /IE2 /IE MIEP MIEP /IE3 MIEP HCMV-/IE2- MCMV MCMV-/IE3-5 ΔUL HCMV-ΔUL1-10 FRT kbp.. AseI HpaI P P P UL UL51 UL77 HCMV-UL51- ΔUL51 HCMV-UL77- ΔUL77 HCMV-UL77-C- ΔUL77 (a) Structure of the CMV major IE region. The CMV MIE gene loci consist of five exons, with the first exon being untranslated (open box). Exons encoding the and IE2 proteins are indicated as black rectangles at the top and IE transcripts are shown below. Exons 2, 3, and 4 encode the proteins, and exons 2, 3, and 5 give rise to the IE2 protein in HCMV and the IE3 homolog in MCMV. By fusing the DNA sequence in frame to the 5 -end of the respective second exons, both IE proteins became tagged in the MCMV as well as in the HCMV mutant. (b) Restriction analysis of the genomes of the CMV-FKBP mutants and of the parental CMVs. Relevant DNA fragments are marked with white dots, and size markers are indicated to the left. The lane numbers correspond to the schematic drawings of the genome structures shown to the right. The targeted genetic loci are shown enlarged and the sizes of DNA fragments (in kbp) characteristic of each virus genome are indicated. Deletions are marked as triangles (Δ). The grey boxes of the HCMV genomes represent the terminal and internal repeats and the numbers refer to nucleotide positions of the genomes. P: Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth and 500 base pairs of sequences upstream of the UL51 and UL77 start codon, respectively, served as promoter regions.
3 Supplementary Figure 2. Ligand-dependent expression of - fusion proteins following infection HCMV-/IE2- with shld-1 with shld-1 without shld-1 MCMV-/IE3- without shld-1 Cells infected with the mutants indicated (MOI 0.1) were kept with or without 1 µm shield-1, and stained 48 h (HCMV-/IE2-) or 24 h (MCMV-/IE3-) post infection with antibodies directed against the doi: HCMV or MCMV protein. Merge: overlay of images displaying non-infected Nature Methods: /nmeth.1346 cells (blue; DNA-staining) and infected cells (EGFP) with the images depicting the staining of the fusion proteins. Scale bars, 10 µm.
4 Supplementary Figure 3. -mediated disruption of promyelocytic leukemia protein-associated nuclear bodies depending on shield-1 SP100 with shld-1 Sp100 SP100 without shld-1 Sp100 egfp egfp egfp egfp Cells were infected with HCMV-/IE2- at an MOI of 0.1, kept in the presence Nature or absence Methods: of doi: shield-1, /nmeth.1346 and at 17 h p.i. were labelled with antibodies specific for the Sp100 protein or the protein. Nuclei of infected cells are marked with white arrows.
5 Supplementary Figure 4. Analysis of brightly green fluorescent cells occasionally observed after infection with the HCMV-/IE2- mutant in the absence of shield-1 a IE2 To-Pro3 To-Pro3 EGFP EGFP b HCMV-GFP d8 p.i. HCMV-/IE2- without shld-1 d8 p.i. (a) HFF were infected with HCMV-/IE2- and examined by immunofluorescence as described in Fig. 1. Shown are groups of infected cells with one cell displaying high-level EGFP expression (white arrows) among other cells with weak EGFP expression. IE2 and expression in these cells is depicted in the left and right panel, respectively. (b) HFF were infected with 500 PFU per Nature doi: /nmeth.1346 culture Methods: with HCMV-/IE2- or the parental HCMV. Cells were kept in the absence of shield-1 and analyzed on day 8 p.i. for plaque formation by fluorescence microscopy.
6 Supplementary Figure 5. Validation of shield-1-dependent expression of CMV fusion proteins at the single cell level pul51 HCMV- HCMV-IE2 pul77 MCMV-IE3 MCMV- Pictures of cells shown in Figure 1a and Supplementary Figure 2 were taken using epi-fluorescence and the intensity of the fluorescence signals in infected cells was quantified using the ImageJ 1.41 software 1,2. Approximately 100 cells were analyzed for each experimental setting. Representative pictures are shown below the diagrams. Please note that the strong fluorescence signals obtained from cells kept with shield-1 may have been underestimated Nature Methods: due doi: to saturation /nmeth.1346 of the signals, and cells which display low fluorescence in the presence of the ligand may be abortively infected. a. u., arbitrary units.
7 Supplementary Table 1: Oligonucleotides used in this study primer name HIEf HIEr MIEf MIEr UL51kof UL51kor UL51f UL51Pror FKBP-DDf FKBP-DDr UL77kof UL77-kor UL77-f UL77-r sequence 5 -CTTTCCATGGGTCTTTTCTGCAGTCACCGTCCTTGACACGCAGGAACACTTAACGGCTGA 3 5 -CAGGATTATCAGGGTCCATCTTTCTCTTGGCAGAGGACTCCAATTGGCGCGCGGATCCTT-3 5 -GACATCTGTTGATGATAAAAAATTATATTTTTTTAGAGAGCAGGAACACTTAACGGCTGA 3 5 -CGGCGATCATGATCATGTTGCAACTGGGTGCGGCGGGCTCCAATTGGCGCGCGGATCCTT-3 5 -CGCGCGTCCAGAGAGGGCAGCAACAGATCGTAGACGCGCGGAAAAGTGCCACCTGCAGAT-3 5 -GACGGACACGCGCTACCCGATCTTGACGACGATCTGCTATAGCAGGAACACTTAACGGCTGA-3 5 -CGCGGATCCCGCACCGACGCCACCGCCGAT-3 5 -GGCGATATCGCCATAGCAGCTCAGTTGTCAA-3 5 -CGCGGATCCGCCACCATGGGAGTGCAGGT-3 5 -CGCGGATCCTTCCGGTTTTAGAAGCTCCA-3 5 -ACGATGCCATCACGGGACCCGCCGCCGCCCCGTCTGACGTGGAAAAGTGCCACCTGCAGAT-3 5 -CCGAGGACGTTCGCCCTTTATGCAGCGAGCGACACGTGGTGCAGGAACACTTAACGGCTGA-3 5 -CGCGGTACCGCCTCACGTGCGTAAGCGGAT-3 5 -CCCGTTAACTTAAGCGTAGTCTGGGACGTCGTATGGGTACAACACCGCCACGCTCGGAAG-3 Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth.1346
8 Supplementary Note 1. Analysis of genomes of HCMV-UL51- viruses that grew in the absence of shield-1 HCMV-UL51- P FKBP-DD UL51 UL51 (21 nt) BAC GFP HCMV-UL51- rep P FKBP-DD UL51 UL51 repaired BAC GFP ( % of viruses) Circular replicative intermediates were isolated from infected cells and amplified in E. coli. The BAC genomes were then re-isolated from the bacteria and examined by restriction analysis and sequencing. The ectopic -UL51 sequences turned out to be unaltered, while the subtle 21 nt deletion introduced into the original UL51 ORF was repaired, probably by recombination between the original and the ectopic UL51 sequences during viral genome replication. We have generated several similar CMV mutants before, containing a deletion in an ORF at the authentic genomic locus, followed by re-insertion of the respective ORF at an ectopic position and never observed any revertants before 3,4. By titrating the virus preparation in the presence and absence of shield-1, we determined the portion of revertants to be %. Repair of the UL51 ORF is presumably due to the very small deletion introduced, and the presence Nature of Methods: large homologous doi: /nmeth.1346 regions between the authentic and ectopic sequences. Consequently, repair by recombination can be prevented by designing the deletion in the original ORF as large as possible, and/or changing the codon usage of the ORF inserted at the ectopic position.
9 References 1. Abramoff, M.D., Magelhaes, P.J. & Ram, S.J. Image Processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics International 11, (2004). 2. Rasband,W.S. ImageJ. (2008). 3. Borst, E.M. & Messerle, M. Analysis of human cytomegalovirus orilyt sequence requirements in the context of the viral genome. J. Virol. 79, (2005). 4. Borst, E.M. et al. The essential human cytomegalovirus gene UL52 is required for cleavage-packaging of the viral genome. J. Virol. 82, (2008). Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth.1346
33VASTVNGATSANNHGEPPS51PADARPR58
 Pro-rich region Trans-membrane region 214 246 359 381 UL50 1 397 211SSRTAS216PPPPPR222 NLS CR1 CR2 CR3 CR4 UL53 1 376 11RERRS15ALRS19LLRKRRR25 33VASTVNGATSANNHGEPPS51PADARPR58 FIG S1. UL97 phosphorylation
Pro-rich region Trans-membrane region 214 246 359 381 UL50 1 397 211SSRTAS216PPPPPR222 NLS CR1 CR2 CR3 CR4 UL53 1 376 11RERRS15ALRS19LLRKRRR25 33VASTVNGATSANNHGEPPS51PADARPR58 FIG S1. UL97 phosphorylation
Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid.
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4322
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Predicted RNA structure of 3 UTR and sequence alignment of deleted nucleotides. (a) Predicted RNA secondary structure of ZIKV 3 UTR. The stem-loop structure
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Predicted RNA structure of 3 UTR and sequence alignment of deleted nucleotides. (a) Predicted RNA secondary structure of ZIKV 3 UTR. The stem-loop structure
Supplementary Information. Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional assay of the hcas9-2a-mcherry construct (a) Gene correction of a mutant EGFP reporter cell line mediated by hcas9 or
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional assay of the hcas9-2a-mcherry construct (a) Gene correction of a mutant EGFP reporter cell line mediated by hcas9 or
Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
 open reading frame 1565 (segment 5) 47 (-) 3 5 (+) 76 101 125 149 173 197 221 246 287 open reading frame 890 (segment 8) 60 (-) 3 5 (+) 172 Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
open reading frame 1565 (segment 5) 47 (-) 3 5 (+) 76 101 125 149 173 197 221 246 287 open reading frame 890 (segment 8) 60 (-) 3 5 (+) 172 Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
Antiviral restriction factor transgenesis in the domestic cat
 Nature Methods Antiviral restriction factor transgenesis in the domestic cat Pimprapar Wongsrikeao, Dyana Saenz, Tommy Rinkoski, Takeshige Otoi & Eric Poeschla Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure
Nature Methods Antiviral restriction factor transgenesis in the domestic cat Pimprapar Wongsrikeao, Dyana Saenz, Tommy Rinkoski, Takeshige Otoi & Eric Poeschla Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure
Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV) Immediate early proteins, gene expression and signaling
 Viruses, Cells and Disease November 13, 2008 Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV) Immediate early proteins, gene expression and signaling Dr. Hua Zhu ICPH E350D UMDNJ - New Jersey Medical School 973-972-4483 X
Viruses, Cells and Disease November 13, 2008 Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV) Immediate early proteins, gene expression and signaling Dr. Hua Zhu ICPH E350D UMDNJ - New Jersey Medical School 973-972-4483 X
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein
 Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Exon 3 of the Human Cytomegalovirus Major Immediate-Early Region Is Required for Efficient Viral Gene Expression and for Cellular Cyclin Modulation
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, June 2005, p. 7438 7452 Vol. 79, No. 12 0022-538X/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.79.12.7438 7452.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Exon 3 of
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, June 2005, p. 7438 7452 Vol. 79, No. 12 0022-538X/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.79.12.7438 7452.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Exon 3 of
Analysis of Human Cytomegalovirus orilyt Sequence Requirements in the Context of the Viral Genome
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Mar. 2005, p. 3615 3626 Vol. 79, No. 6 0022-538X/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.79.6.3615 3626.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Analysis of
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Mar. 2005, p. 3615 3626 Vol. 79, No. 6 0022-538X/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.79.6.3615 3626.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Analysis of
Supplementary material Legends to Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Figure S2. Figure S3.
 Supplementary material Legends to Supplementary Figures. Figure S1. Expression of BICD-N-MTS fusion does not affect the distribution of the Golgi and endosomes. HeLa cells were transfected with GFP-BICD-N-MTS
Supplementary material Legends to Supplementary Figures. Figure S1. Expression of BICD-N-MTS fusion does not affect the distribution of the Golgi and endosomes. HeLa cells were transfected with GFP-BICD-N-MTS
Elizabeth A. White, Charles L. Clark, Veronica Sanchez, and Deborah H. Spector*
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Feb. 2004, p. 1817 1830 Vol. 78, No. 4 0022-538X/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.4.1817 1830.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Small Internal
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Feb. 2004, p. 1817 1830 Vol. 78, No. 4 0022-538X/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.4.1817 1830.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Small Internal
Genome-editing via Oviductal Nucleic Acids Delivery (GONAD) system: a novel microinjection-independent genome engineering method in mice
 Supplementary Information Genome-editing via Oviductal Nucleic Acids Delivery (GONAD) system: a novel microinjection-independent genome engineering method in mice Gou Takahashi, Channabasavaiah B Gurumurthy,
Supplementary Information Genome-editing via Oviductal Nucleic Acids Delivery (GONAD) system: a novel microinjection-independent genome engineering method in mice Gou Takahashi, Channabasavaiah B Gurumurthy,
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
Structural vs. nonstructural proteins
 Why would you want to study proteins associated with viruses or virus infection? Receptors Mechanism of uncoating How is gene expression carried out, exclusively by viral enzymes? Gene expression phases?
Why would you want to study proteins associated with viruses or virus infection? Receptors Mechanism of uncoating How is gene expression carried out, exclusively by viral enzymes? Gene expression phases?
Murine Cytomegalovirus with a Transposon Insertional Mutation at Open Reading Frame M35 Is Defective in Growth In Vivo
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, July 2003, p. 7746 7755 Vol. 77, No. 14 0022-538X/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.77.14.7746 7755.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Murine Cytomegalovirus
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, July 2003, p. 7746 7755 Vol. 77, No. 14 0022-538X/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.77.14.7746 7755.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Murine Cytomegalovirus
Supporting Information
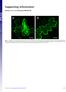 Supporting Information Harries et al. 1.173/pnas.9923916 A Fig. S1. Disruption of microfilaments within epidermal cells after treatment with 5 M Lat. Images of N. benthamiana cells are from plants expressing
Supporting Information Harries et al. 1.173/pnas.9923916 A Fig. S1. Disruption of microfilaments within epidermal cells after treatment with 5 M Lat. Images of N. benthamiana cells are from plants expressing
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1! a! b! Nfatc1!! Nfatc1"! P1! P2! pa1! pa2! ex1! ex2! exons 3-9! ex1! ex11!!" #" Nfatc1A!!" Nfatc1B! #"!" Nfatc1C! #" DN1! DN2! DN1!!A! #A!!B! #B!!C! #C!!A!
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1! a! b! Nfatc1!! Nfatc1"! P1! P2! pa1! pa2! ex1! ex2! exons 3-9! ex1! ex11!!" #" Nfatc1A!!" Nfatc1B! #"!" Nfatc1C! #" DN1! DN2! DN1!!A! #A!!B! #B!!C! #C!!A!
W. L. William Chang* and Peter A. Barry
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, May 2003, p. 5073 5083 Vol. 77, No. 9 0022-538X/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.77.9.5073 5083.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Cloning of
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, May 2003, p. 5073 5083 Vol. 77, No. 9 0022-538X/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.77.9.5073 5083.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Cloning of
Montse Gustems, 1 Eva Borst, 2,3 Chris A. Benedict, 4 Carmen Pérez, 1 Martin Messerle, 2 Peter Ghazal, 5 and Ana Angulo 1 *
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Oct. 2006, p. 9899 9904 Vol. 80, No. 19 0022-538X/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.00640-06 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Regulation of the Transcription
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Oct. 2006, p. 9899 9904 Vol. 80, No. 19 0022-538X/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.00640-06 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Regulation of the Transcription
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
Supplementary Information. Novel lentiviral vectors with mutated reverse transcriptase for mrna delivery of TALE nucleases
 Supplementary Information Novel lentiviral vectors with mutated reverse transcriptase for mrna delivery of TALE nucleases Ulrike Mock 1, Kristoffer Riecken 1, Belinda Berdien 1, Waseem Qasim 2, Emma Chan
Supplementary Information Novel lentiviral vectors with mutated reverse transcriptase for mrna delivery of TALE nucleases Ulrike Mock 1, Kristoffer Riecken 1, Belinda Berdien 1, Waseem Qasim 2, Emma Chan
Molecular investigation of the 7.2 kb RNA of murine cytomegalovirus
 Schwarz et al. Virology Journal 203, :38 RESEARCH Open Access Molecular investigation of the 7.2 kb RNA of murine cytomegalovirus Toni M Schwarz, Lysa-Anne M Volpe, Christopher G Abraham and Caroline A
Schwarz et al. Virology Journal 203, :38 RESEARCH Open Access Molecular investigation of the 7.2 kb RNA of murine cytomegalovirus Toni M Schwarz, Lysa-Anne M Volpe, Christopher G Abraham and Caroline A
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nature8645 Physical coverage (x haploid genomes) 11 6.4 4.9 6.9 6.7 4.4 5.9 9.1 7.6 125 Neither end mapped One end mapped Chimaeras Correct Reads (million ns) 1 75 5 25 HCC1187 HCC1395 HCC1599
doi: 1.138/nature8645 Physical coverage (x haploid genomes) 11 6.4 4.9 6.9 6.7 4.4 5.9 9.1 7.6 125 Neither end mapped One end mapped Chimaeras Correct Reads (million ns) 1 75 5 25 HCC1187 HCC1395 HCC1599
Determination of the temporal pattern and importance of BALF1 expression in Epstein-Barr viral infection
 Determination of the temporal pattern and importance of BALF1 expression in Epstein-Barr viral infection Melissa Mihelidakis May 6, 2004 7.340 Research Proposal Introduction Apoptosis, or programmed cell
Determination of the temporal pattern and importance of BALF1 expression in Epstein-Barr viral infection Melissa Mihelidakis May 6, 2004 7.340 Research Proposal Introduction Apoptosis, or programmed cell
Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids and viruses Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR Generation of molecular standard for quantitative PCR
 Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids and viruses To generate pseudotyped viruses, the previously described recombinant plasmids pnl4-3-δnef-gfp or pnl4-3-δ6-drgfp and a vector expressing HIV-1 X4
Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids and viruses To generate pseudotyped viruses, the previously described recombinant plasmids pnl4-3-δnef-gfp or pnl4-3-δ6-drgfp and a vector expressing HIV-1 X4
Human Cytomegalovirus with IE-2 (UL122) Deleted Fails To Express Early Lytic Genes
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Feb. 2001, p. 1870 1878 Vol. 75, No. 4 0022-538X/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.4.1870 1878.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Human Cytomegalovirus
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Feb. 2001, p. 1870 1878 Vol. 75, No. 4 0022-538X/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.4.1870 1878.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Human Cytomegalovirus
Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Lack of cadherins Celsr2 and Celsr3 impairs ependymal ciliogenesis, leading to fatal
 Lack of cadherins Celsr2 and Celsr3 impairs ependymal ciliogenesis, leading to fatal hydrocephalus Fadel TISSIR, Yibo QU, Mireille MONTCOUQUIOL, Libing ZHOU, Kouji KOMATSU, Dongbo SHI, Toshihiko FUJIMORI,
Lack of cadherins Celsr2 and Celsr3 impairs ependymal ciliogenesis, leading to fatal hydrocephalus Fadel TISSIR, Yibo QU, Mireille MONTCOUQUIOL, Libing ZHOU, Kouji KOMATSU, Dongbo SHI, Toshihiko FUJIMORI,
Institut für Hygiene und Medizinische Mikrobiologie, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität. D Munich, Germany
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Oct. 1999, p. 8320 8329 Vol. 73, No. 10 0022-538X/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Cloning of the Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV) Genome
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Oct. 1999, p. 8320 8329 Vol. 73, No. 10 0022-538X/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Cloning of the Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV) Genome
LESSON 3.2 WORKBOOK. How do normal cells become cancer cells? Workbook Lesson 3.2
 For a complete list of defined terms, see the Glossary. Transformation the process by which a cell acquires characteristics of a tumor cell. LESSON 3.2 WORKBOOK How do normal cells become cancer cells?
For a complete list of defined terms, see the Glossary. Transformation the process by which a cell acquires characteristics of a tumor cell. LESSON 3.2 WORKBOOK How do normal cells become cancer cells?
Supplementary materials
 Supplementary materials Chemical library from ChemBridge 50,240 structurally diverse small molecule compounds dissolved in DMSO Hits Controls: No virus added μ Primary screening at 20 g/ml of compounds
Supplementary materials Chemical library from ChemBridge 50,240 structurally diverse small molecule compounds dissolved in DMSO Hits Controls: No virus added μ Primary screening at 20 g/ml of compounds
Cytomegalovirus UL91 Is Essential for Transcription of Viral True Late (?2) Genes
 Cytomegalovirus UL91 Is Essential for Transcription of Viral True Late (?) Genes Shinya Omoto, Emory University Edward S Mocarski, Emory University Journal Title: Journal of Virology Volume: Volume 87,
Cytomegalovirus UL91 Is Essential for Transcription of Viral True Late (?) Genes Shinya Omoto, Emory University Edward S Mocarski, Emory University Journal Title: Journal of Virology Volume: Volume 87,
Tyrosine phosphorylation and protein degradation control the transcriptional activity of WRKY involved in benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis
 Supplementary information Tyrosine phosphorylation and protein degradation control the transcriptional activity of WRKY involved in benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis Yasuyuki Yamada, Fumihiko Sato
Supplementary information Tyrosine phosphorylation and protein degradation control the transcriptional activity of WRKY involved in benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis Yasuyuki Yamada, Fumihiko Sato
Life Sciences 1A Midterm Exam 2. November 13, 2006
 Name: TF: Section Time Life Sciences 1A Midterm Exam 2 November 13, 2006 Please write legibly in the space provided below each question. You may not use calculators on this exam. We prefer that you use
Name: TF: Section Time Life Sciences 1A Midterm Exam 2 November 13, 2006 Please write legibly in the space provided below each question. You may not use calculators on this exam. We prefer that you use
nature methods Organelle-specific, rapid induction of molecular activities and membrane tethering
 nature methods Organelle-specific, rapid induction of molecular activities and membrane tethering Toru Komatsu, Igor Kukelyansky, J Michael McCaffery, Tasuku Ueno, Lidenys C Varela & Takanari Inoue Supplementary
nature methods Organelle-specific, rapid induction of molecular activities and membrane tethering Toru Komatsu, Igor Kukelyansky, J Michael McCaffery, Tasuku Ueno, Lidenys C Varela & Takanari Inoue Supplementary
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by
 The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by regulating F-actin dynamics Xing-Jiang Yu 1,2, Zhaohong Yi 1, Zheng Gao 1,2, Dan-dan Qin 1,2, Yanhua Zhai 1, Xue Chen 1,
The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by regulating F-actin dynamics Xing-Jiang Yu 1,2, Zhaohong Yi 1, Zheng Gao 1,2, Dan-dan Qin 1,2, Yanhua Zhai 1, Xue Chen 1,
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated
 Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated from 7 day-old seedlings treated with or without
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated from 7 day-old seedlings treated with or without
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1. Generation and validation of mtef4-knockout mice.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Generation and validation of mtef4-knockout mice. (a) Alignment of EF4 (E. coli) with mouse, yeast and human EF4. (b) Domain structures of mouse mtef4 compared to those of EF4 (E.
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation and validation of mtef4-knockout mice. (a) Alignment of EF4 (E. coli) with mouse, yeast and human EF4. (b) Domain structures of mouse mtef4 compared to those of EF4 (E.
Supplemental Information. Figures. Figure S1
 Supplemental Information Figures Figure S1 Identification of JAGGER T-DNA insertions. A. Positions of T-DNA and Ds insertions in JAGGER are indicated by inverted triangles, the grey box represents the
Supplemental Information Figures Figure S1 Identification of JAGGER T-DNA insertions. A. Positions of T-DNA and Ds insertions in JAGGER are indicated by inverted triangles, the grey box represents the
Partial Functional Complementation between Human and Mouse Cytomegalovirus Chemokine Receptor Homologues
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, June 2011, p. 6091 6095 Vol. 85, No. 12 0022-538X/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jvi.02113-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Partial Functional Complementation
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, June 2011, p. 6091 6095 Vol. 85, No. 12 0022-538X/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jvi.02113-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Partial Functional Complementation
Introduction retroposon
 17.1 - Introduction A retrovirus is an RNA virus able to convert its sequence into DNA by reverse transcription A retroposon (retrotransposon) is a transposon that mobilizes via an RNA form; the DNA element
17.1 - Introduction A retrovirus is an RNA virus able to convert its sequence into DNA by reverse transcription A retroposon (retrotransposon) is a transposon that mobilizes via an RNA form; the DNA element
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Supplementary Figure 1: Components of Arabidopsis tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. Schematic summary of the TCA cycle and the enzymes related to the reactions. The large text and
Supplementary information Supplementary Figure 1: Components of Arabidopsis tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. Schematic summary of the TCA cycle and the enzymes related to the reactions. The large text and
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Dec. 1999, p Vol. 73, No. 12. Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Dec. 1999, p. 10458 10471 Vol. 73, No. 12 0022-538X/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. The Human Cytomegalovirus IE2 and UL112-113
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Dec. 1999, p. 10458 10471 Vol. 73, No. 12 0022-538X/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. The Human Cytomegalovirus IE2 and UL112-113
Cytomegalovirus m154 Hinders CD48 Cell-Surface Expression and Promotes Viral Escape from Host Natural Killer Cell Control
 Cytomegalovirus m154 Hinders CD48 Cell-Surface Expression and Promotes Viral Escape from Host Natural Killer Cell Control Angela Zarama 1., Natàlia Pérez-Carmona 1., Domènec Farré 1, Adriana Tomic 2, Eva
Cytomegalovirus m154 Hinders CD48 Cell-Surface Expression and Promotes Viral Escape from Host Natural Killer Cell Control Angela Zarama 1., Natàlia Pérez-Carmona 1., Domènec Farré 1, Adriana Tomic 2, Eva
Alpha thalassemia mental retardation X-linked. Acquired alpha-thalassemia myelodysplastic syndrome
 Alpha thalassemia mental retardation X-linked Acquired alpha-thalassemia myelodysplastic syndrome (Alpha thalassemia mental retardation X-linked) Acquired alpha-thalassemia myelodysplastic syndrome Schematic
Alpha thalassemia mental retardation X-linked Acquired alpha-thalassemia myelodysplastic syndrome (Alpha thalassemia mental retardation X-linked) Acquired alpha-thalassemia myelodysplastic syndrome Schematic
Edited by Elliott D. Kieff, Harvard University, Boston, MA, and approved September 29, 2003 (received for review June 30, 2003)
 Functional profiling of a human cytomegalovirus genome Walter Dunn*, Cassie Chou*, Hong Li*, Rong Hai*, David Patterson*, Viktor Stolc, Hua Zhu, and Fenyong Liu* *Division of Infectious Diseases, School
Functional profiling of a human cytomegalovirus genome Walter Dunn*, Cassie Chou*, Hong Li*, Rong Hai*, David Patterson*, Viktor Stolc, Hua Zhu, and Fenyong Liu* *Division of Infectious Diseases, School
Problem Set 5 KEY
 2006 7.012 Problem Set 5 KEY ** Due before 5 PM on THURSDAY, November 9, 2006. ** Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. You are studying the development
2006 7.012 Problem Set 5 KEY ** Due before 5 PM on THURSDAY, November 9, 2006. ** Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. You are studying the development
CDC website:
 Hepatitis B virus CDC website: http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/diseases/hepatitis/slideset/hep_b/slide_1.htm Relevance Key Features es of Hepatitis t B Virus 250 million people infected worldwide. In areas of
Hepatitis B virus CDC website: http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/diseases/hepatitis/slideset/hep_b/slide_1.htm Relevance Key Features es of Hepatitis t B Virus 250 million people infected worldwide. In areas of
Supplementary Figure 1. Quantile-quantile (Q-Q) plots. (Panel A) Q-Q plot graphical
 Supplementary Figure 1. Quantile-quantile (Q-Q) plots. (Panel A) Q-Q plot graphical representation using all SNPs (n= 13,515,798) including the region on chromosome 1 including SORT1 which was previously
Supplementary Figure 1. Quantile-quantile (Q-Q) plots. (Panel A) Q-Q plot graphical representation using all SNPs (n= 13,515,798) including the region on chromosome 1 including SORT1 which was previously
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni eee Supplementary Figure 1
 eee Supplementary Figure 1 Hyphae induce NET release, but yeast do not. (a) NET release by human peripheral neutrophils stimulated with a hgc1 yeast-locked C. albicans mutant (yeast) or pre-formed WT C.
eee Supplementary Figure 1 Hyphae induce NET release, but yeast do not. (a) NET release by human peripheral neutrophils stimulated with a hgc1 yeast-locked C. albicans mutant (yeast) or pre-formed WT C.
Probe. Hind III Q,!?R'!! /0!!!!D1"?R'! vector. Homologous recombination
 Supple-Zhang Page 1 Wild-type locus Targeting construct Targeted allele Exon Exon3 Exon Probe P1 P P3 FRT FRT loxp loxp neo vector amh I Homologous recombination neo P1 P P3 FLPe recombination Q,!?R'!!
Supple-Zhang Page 1 Wild-type locus Targeting construct Targeted allele Exon Exon3 Exon Probe P1 P P3 FRT FRT loxp loxp neo vector amh I Homologous recombination neo P1 P P3 FLPe recombination Q,!?R'!!
s u p p l e m e n ta ry i n f o r m at i o n
 Figure S1 Characterization of tet-off inducible cell lines expressing GFPprogerin and GFP-wt lamin A. a, Western blot analysis of GFP-progerin- or GFP-wt lamin A- expressing cells before induction (0d)
Figure S1 Characterization of tet-off inducible cell lines expressing GFPprogerin and GFP-wt lamin A. a, Western blot analysis of GFP-progerin- or GFP-wt lamin A- expressing cells before induction (0d)
Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells.
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
100 mm Sucrose. +Berberine +Quinine
 8 mm Sucrose Probability (%) 7 6 5 4 3 Wild-type Gr32a / 2 +Caffeine +Berberine +Quinine +Denatonium Supplementary Figure 1: Detection of sucrose and bitter compounds is not affected in Gr32a / flies.
8 mm Sucrose Probability (%) 7 6 5 4 3 Wild-type Gr32a / 2 +Caffeine +Berberine +Quinine +Denatonium Supplementary Figure 1: Detection of sucrose and bitter compounds is not affected in Gr32a / flies.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system
 Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Choi YL, Soda M, Yamashita Y, et al. EML4-ALK mutations in
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Choi YL, Soda M, Yamashita Y, et al. EML4-ALK mutations in
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/8/e1500296/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Transcriptional regulation of APOBEC3 antiviral immunity through the CBF- /RUNX axis This PDF file includes: Brett
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/8/e1500296/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Transcriptional regulation of APOBEC3 antiviral immunity through the CBF- /RUNX axis This PDF file includes: Brett
Supplementary Figure 1. Properties of various IZUMO1 monoclonal antibodies and behavior of SPACA6. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) .
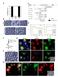 Supplementary Figure 1. Properties of various IZUMO1 monoclonal antibodies and behavior of SPACA6. (a) The inhibitory effects of new antibodies (Mab17 and Mab18). They were investigated in in vitro fertilization
Supplementary Figure 1. Properties of various IZUMO1 monoclonal antibodies and behavior of SPACA6. (a) The inhibitory effects of new antibodies (Mab17 and Mab18). They were investigated in in vitro fertilization
Cellular and Viral Control over the Initial Events of Human Cytomegalovirus Experimental Latency in CD34 Cells
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, June 2010, p. 5594 5604 Vol. 84, No. 11 0022-538X/10/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jvi.00348-10 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Cellular and Viral Control
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, June 2010, p. 5594 5604 Vol. 84, No. 11 0022-538X/10/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jvi.00348-10 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Cellular and Viral Control
Viral Genetics. BIT 220 Chapter 16
 Viral Genetics BIT 220 Chapter 16 Details of the Virus Classified According to a. DNA or RNA b. Enveloped or Non-Enveloped c. Single-stranded or double-stranded Viruses contain only a few genes Reverse
Viral Genetics BIT 220 Chapter 16 Details of the Virus Classified According to a. DNA or RNA b. Enveloped or Non-Enveloped c. Single-stranded or double-stranded Viruses contain only a few genes Reverse
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Fig. 1: Quality assessment of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE)-derived DNA and nuclei. (a) Multiplex PCR analysis of unrepaired and repaired bulk FFPE gdna from
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Fig. 1: Quality assessment of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE)-derived DNA and nuclei. (a) Multiplex PCR analysis of unrepaired and repaired bulk FFPE gdna from
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at
 Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/375/ra41/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Actin cytoskeletal remodeling with protrusion formation is essential for heart regeneration in Hippo-deficient mice
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/375/ra41/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Actin cytoskeletal remodeling with protrusion formation is essential for heart regeneration in Hippo-deficient mice
Supplemental Figures:
 Supplemental Figures: Figure 1: Intracellular distribution of VWF by electron microscopy in human endothelial cells. a) Immunogold labeling of LC3 demonstrating an LC3-positive autophagosome (white arrow)
Supplemental Figures: Figure 1: Intracellular distribution of VWF by electron microscopy in human endothelial cells. a) Immunogold labeling of LC3 demonstrating an LC3-positive autophagosome (white arrow)
Stability determinants of Murine Cytomegalovirus long non-coding RNA7.2
 JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 23 July 2014 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.01695-14 Copyright 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 Stability determinants of Murine
JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 23 July 2014 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.01695-14 Copyright 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 Stability determinants of Murine
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
Transcription of the German Cockroach Densovirus BgDNV Genome: Alternative Processing of Viral RNAs
 ISSN 1607-6729, Doklady Biochemistry and Biophysics, 2008, Vol. 421, pp. 176 180. Pleiades Publishing, Ltd., 2008. Original Russian Text T.V. Kapelinskaya, E.U. Martynova, A.L. Korolev, C. Schal, D.V.
ISSN 1607-6729, Doklady Biochemistry and Biophysics, 2008, Vol. 421, pp. 176 180. Pleiades Publishing, Ltd., 2008. Original Russian Text T.V. Kapelinskaya, E.U. Martynova, A.L. Korolev, C. Schal, D.V.
Trim29 gene-targeting strategy. (a) Genotyping of wildtype mice (+/+), Trim29 heterozygous mice (+/ ) and homozygous mice ( / ).
 Supplementary Figure 1 Trim29 gene-targeting strategy. (a) Genotyping of wildtype mice (+/+), Trim29 heterozygous mice (+/ ) and homozygous mice ( / ). (b) Immunoblot analysis of TRIM29 in lung primary
Supplementary Figure 1 Trim29 gene-targeting strategy. (a) Genotyping of wildtype mice (+/+), Trim29 heterozygous mice (+/ ) and homozygous mice ( / ). (b) Immunoblot analysis of TRIM29 in lung primary
Supplementary Figure 1 Induction of cellular senescence and isolation of exosome. a to c, Pre-senescent primary normal human diploid fibroblasts
 Supplementary Figure 1 Induction of cellular senescence and isolation of exosome. a to c, Pre-senescent primary normal human diploid fibroblasts (TIG-3 cells) were rendered senescent by either serial passage
Supplementary Figure 1 Induction of cellular senescence and isolation of exosome. a to c, Pre-senescent primary normal human diploid fibroblasts (TIG-3 cells) were rendered senescent by either serial passage
Received 13 August 2010/Accepted 10 November 2010
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Feb. 2011, p. 1732 1746 Vol. 85, No. 4 0022-538X/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jvi.01713-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. The Activator Protein 1
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Feb. 2011, p. 1732 1746 Vol. 85, No. 4 0022-538X/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jvi.01713-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. The Activator Protein 1
Nuclear export of VP19C is not essential for replication of herpes simplex virus type 1
 Li et al. Cell & Bioscience 2014, 4:55 Cell & Bioscience SHORT REPORT Nuclear export of VP19C is not essential for replication of herpes simplex virus type 1 Open Access You Li 1,3, Dongwei Mao 2, Guoda
Li et al. Cell & Bioscience 2014, 4:55 Cell & Bioscience SHORT REPORT Nuclear export of VP19C is not essential for replication of herpes simplex virus type 1 Open Access You Li 1,3, Dongwei Mao 2, Guoda
Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.
 Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.129-Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(cre/ert2)tyj /J mice. To induce deletion of the Pten locus,
Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.129-Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(cre/ert2)tyj /J mice. To induce deletion of the Pten locus,
Herpes Simplex Virus 1 pul34 Plays a Critical Role in Cell-to-Cell Spread of Virus in Addition to Its Role in Virus Replication
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, July 2011, p. 7203 7215 Vol. 85, No. 14 0022-538X/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jvi.00262-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Herpes Simplex Virus 1
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, July 2011, p. 7203 7215 Vol. 85, No. 14 0022-538X/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jvi.00262-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Herpes Simplex Virus 1
Evaluation of the Lytic Origins of Replication of Kaposi s Sarcoma-Associated Virus/Human Herpesvirus 8 in the Context of the Viral Genome
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Oct. 2006, p. 9905 9909 Vol. 80, No. 19 0022-538X/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.01004-06 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Evaluation of the Lytic
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Oct. 2006, p. 9905 9909 Vol. 80, No. 19 0022-538X/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.01004-06 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Evaluation of the Lytic
Polyomaviridae. Spring
 Polyomaviridae Spring 2002 331 Antibody Prevalence for BK & JC Viruses Spring 2002 332 Polyoma Viruses General characteristics Papovaviridae: PA - papilloma; PO - polyoma; VA - vacuolating agent a. 45nm
Polyomaviridae Spring 2002 331 Antibody Prevalence for BK & JC Viruses Spring 2002 332 Polyoma Viruses General characteristics Papovaviridae: PA - papilloma; PO - polyoma; VA - vacuolating agent a. 45nm
Innate Immunity & Inflammation
 Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
Identification of Mutation(s) in. Associated with Neutralization Resistance. Miah Blomquist
 Identification of Mutation(s) in the HIV 1 gp41 Subunit Associated with Neutralization Resistance Miah Blomquist What is HIV 1? HIV-1 is an epidemic that affects over 34 million people worldwide. HIV-1
Identification of Mutation(s) in the HIV 1 gp41 Subunit Associated with Neutralization Resistance Miah Blomquist What is HIV 1? HIV-1 is an epidemic that affects over 34 million people worldwide. HIV-1
Oxford Expression Technologies Ltd
 Oxford Expression Technologies Ltd Founded in 2007 as a spin out from Oxford Brookes University and Natural Environment Research Council Technology based on the insect baculovirus expression vectors (BEVs)
Oxford Expression Technologies Ltd Founded in 2007 as a spin out from Oxford Brookes University and Natural Environment Research Council Technology based on the insect baculovirus expression vectors (BEVs)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
Supplemental Information. Myocardial Polyploidization Creates a Barrier. to Heart Regeneration in Zebrafish
 Developmental Cell, Volume 44 Supplemental Information Myocardial Polyploidization Creates a Barrier to Heart Regeneration in Zebrafish Juan Manuel González-Rosa, Michka Sharpe, Dorothy Field, Mark H.
Developmental Cell, Volume 44 Supplemental Information Myocardial Polyploidization Creates a Barrier to Heart Regeneration in Zebrafish Juan Manuel González-Rosa, Michka Sharpe, Dorothy Field, Mark H.
In Vitro and In Vivo Characterization of a Murine Cytomegalovirus with a Transposon Insertional Mutation at Open Reading Frame M43
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Oct. 2000, p. 9488 9497 Vol. 74, No. 20 0022-538X/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. In Vitro and In Vivo Characterization of a Murine
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Oct. 2000, p. 9488 9497 Vol. 74, No. 20 0022-538X/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. In Vitro and In Vivo Characterization of a Murine
Fine Mapping of a cis-acting Sequence Element in Yellow Fever Virus RNA That Is Required for RNA Replication and Cyclization
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Feb. 2003, p. 2265 2270 Vol. 77, No. 3 0022-538X/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.77.3.2265 2270.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Fine Mapping
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Feb. 2003, p. 2265 2270 Vol. 77, No. 3 0022-538X/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.77.3.2265 2270.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Fine Mapping
The R33 G Protein-Coupled Receptor Gene of Rat Cytomegalovirus Plays an Essential Role in the Pathogenesis of Viral Infection
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Mar. 1998, p. 2352 2363 Vol. 72, No. 3 0022-538X/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology The R33 G Protein-Coupled Receptor Gene of Rat Cytomegalovirus Plays
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Mar. 1998, p. 2352 2363 Vol. 72, No. 3 0022-538X/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology The R33 G Protein-Coupled Receptor Gene of Rat Cytomegalovirus Plays
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice. (a) Gene expression profile in the resting CD4 + T cells were analyzed by an Affymetrix microarray
Supplementary Figure 1 Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice. (a) Gene expression profile in the resting CD4 + T cells were analyzed by an Affymetrix microarray
Supplemental Data. Beck et al. (2010). Plant Cell /tpc
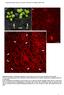 Supplemental Figure 1. Phenotypic comparison of the rosette leaves of four-week-old mpk4 and Col-0 plants. A mpk4 vs Col-0 plants grown in soil. Note the extreme dwarfism of the mpk4 plants (white arrows)
Supplemental Figure 1. Phenotypic comparison of the rosette leaves of four-week-old mpk4 and Col-0 plants. A mpk4 vs Col-0 plants grown in soil. Note the extreme dwarfism of the mpk4 plants (white arrows)
Last time we talked about the few steps in viral replication cycle and the un-coating stage:
 Zeina Al-Momani Last time we talked about the few steps in viral replication cycle and the un-coating stage: Un-coating: is a general term for the events which occur after penetration, we talked about
Zeina Al-Momani Last time we talked about the few steps in viral replication cycle and the un-coating stage: Un-coating: is a general term for the events which occur after penetration, we talked about
Variations in Chromosome Structure & Function. Ch. 8
 Variations in Chromosome Structure & Function Ch. 8 1 INTRODUCTION! Genetic variation refers to differences between members of the same species or those of different species Allelic variations are due
Variations in Chromosome Structure & Function Ch. 8 1 INTRODUCTION! Genetic variation refers to differences between members of the same species or those of different species Allelic variations are due
of TERT, MLL4, CCNE1, SENP5, and ROCK1 on tumor development were discussed.
 Supplementary Note The potential association and implications of HBV integration at known and putative cancer genes of TERT, MLL4, CCNE1, SENP5, and ROCK1 on tumor development were discussed. Human telomerase
Supplementary Note The potential association and implications of HBV integration at known and putative cancer genes of TERT, MLL4, CCNE1, SENP5, and ROCK1 on tumor development were discussed. Human telomerase
Identification of a Mouse Cytomegalovirus Gene Selectively Targeting CD86 Expression on Antigen-Presenting Cells
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Dec. 2004, p. 13062 13071 Vol. 78, No. 23 0022-538X/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.23.13062 13071.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Identification
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Dec. 2004, p. 13062 13071 Vol. 78, No. 23 0022-538X/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.23.13062 13071.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Identification
Supplemental information contains 7 movies and 4 supplemental Figures
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplemental information contains 7 movies and 4 supplemental Figures Movies: Movie 1. Single virus tracking of A4-mCherry-WR MV
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplemental information contains 7 movies and 4 supplemental Figures Movies: Movie 1. Single virus tracking of A4-mCherry-WR MV
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1171320/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Frazzled/DCC-Dependent Transcriptional Switch Regulates Midline Axon Guidance Long Yang, David S. Garbe, Greg J. Bashaw*
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1171320/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Frazzled/DCC-Dependent Transcriptional Switch Regulates Midline Axon Guidance Long Yang, David S. Garbe, Greg J. Bashaw*
Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS
 Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS nucleotide sequences (a, b) or amino acid sequences (c) from
Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS nucleotide sequences (a, b) or amino acid sequences (c) from
Supplementary Figure 1 The plasmids used for the GPCR-CRISPR ChaCha and the GPCR-CRISPR Tango systems. (a) The plasmids for the GPCR-CRISPR ChaCha
 Supplementary Figure 1 The plasmids used for the GPCR-CRISPR ChaCha and the GPCR-CRISPR Tango systems. (a) The plasmids for the GPCR-CRISPR ChaCha system. The dcas9-vpr effector is fused to the C-terminus
Supplementary Figure 1 The plasmids used for the GPCR-CRISPR ChaCha and the GPCR-CRISPR Tango systems. (a) The plasmids for the GPCR-CRISPR ChaCha system. The dcas9-vpr effector is fused to the C-terminus
Virology 426 (2012) Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect. Virology. journal homepage:
 Virology 426 (2012) 60 65 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Virology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/yviro Splicing of goose parvovirus pre-mrna influences cytoplasmic translation
Virology 426 (2012) 60 65 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Virology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/yviro Splicing of goose parvovirus pre-mrna influences cytoplasmic translation
