Sharon S. Evans, Ph.D. Dept. Immunology, RPCI Jan. 29 & Feb 3, 2015
|
|
|
- Rafe Blair
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Adhesion Molecules And Lymphocyte Homing Sharon S. Evans, Ph.D. Dept. Immunology, RPCI Jan. 29 & Feb 3, 2015
2 Outline General introduction to lymphocyte trafficking homeostatic recirculation vs active recruitment. Homeostatic trafficking of lymphocytes across specialized high endothelial venules (HEVs) Structure/function of adhesion molecules involved in initial tethering/rolling (L-selectin/PNAd) Structure/function of chemokine/chemokine receptors that mediate activation (CCR7/CCL21) Structure/function of adhesion molecules required for firm arrest/transendothelial migration (LFA-1/ICAM-1 & α4β7 integrin/madcam-1) Leukocyte recruitment in acute and chronic inflammation.
3 Lymphocyte Extravasation in LN HEV Initial Attachment Rolling Firm Adhesion Transmigration 1 L-Selectin/PNAd-1 3 LFA-1/ICAM-1/2 2 Chemokines (CCL21)
4 The CC Chemokine SLC/6CKine/CCL21 Mediates Tissue-Specific Homing L-selectin CCR7 LFA-1 PNAd ICAM 1 LN HEV CCL21 2 3&4
5 Chemokines C CC CXC CXXXC N C C N C CC +++ COOH +++ C N CXC COOH N C CXXXC C C C CCL (ligand) CCL21 (SLC) CXCL (ligand) CXCL12 (SDF-1) CCR (chemokine receptor) CCR7 CXCR (chemokine receptor) CXCR4
6 Structure of CC Chemokines C +++ COOH CCL21 NH 2 CC C Basic (positively charged) amino acids in C-terminus required for binding to glycosaminoglycans (heparin sulfate) that make up glycocalyx on endothelial cells 3-dimensional structure at N- terminus required for binding to chemokine receptor α-helixβ Anti-parallel β-pleated sheet
7 (CXCL12) (CXCL13) (CCL19, CCL21)
8 Chemokines Stimulate Chemotaxis and Migration Transwell Migration Assays 5 mm pore Chemokine (CCL21)
9 Chemokines Stimulate Chemotaxis and Migration Transwell Migration Assays 5 mm pore Chemokine (CCL21)
10 Evidence that CCL21 is a Tissue Specific Homing Chemokine Tissue specific localization of CCL21 in HEV Capsule L-selectin CCR7 LFA-1 B cell area (follicle) PNAd ICAM T cell area (paracortex) CCL21 HEV HEV CCL21 mrna Lymph Node
11 CCL21 (SLC) is Expressed by Lymph Node HEV In Situ Analysis (mrna) BCL/CXCL13 CCL21/SLC IHC Analysis (protein) PNAd CCL21 WT +/+ plt/plt Science 286:2098, 1999 J. Exp. Med. 191:61, 2000 BCL/CXCL13 binds CXCR5 (involved in B cell migration) SLC/CCL21 binds CCR7 (mediates B & T cell homing across HEV
12 In vivo Imaging of CCL21 Localization on PLN HEV by Intravital Microscopy (IVM) Femoral Artery Injection of FITC-labeled anti-ccl21 Ab) VCR PC Inguinal LN Adapted from von Andrian et al, Curr. Op. Immunol. 2004
13 CCL21 is Expressed by Lymph Node HEV in Wild Type But Not plt/plt Mice WT plt/plt J. Exp. Med. 191:61, 2000 Evidence that CCL21 and CCR7 receptor critical for T lymphocyte extravasation across HEV HEV express CCL21 [SLC] mrna and protein HEV of plt/plt mice lack CC21 [SLC] and CCL19 [ELC/MIP3b); can t support firm adhesion or homing Reconstitution of CCL21 in HEV of plt/plt mice restores firm adhesion T cells from CCR7 -/- suppressed in ability to enter LN, PP Chemokine desensitization of CCR7 (using high concentrations of CCL21) blocks arrest of rolling cells
14 Chemokine (CCL21) Chemokine (CCL21) Chemokine Receptor (CCR7) G ai GDP GTP G g G ai GTP G g G b G b PTX PI3K ERK Signaling Ca ++ Adhesion to HEV, EC, or ECM Migration Cytoskeletal Reorganization Gene Transcription Proliferation Differentiation
15 CCL21 Is Required for Lymphocyte Trafficking Across HEV Cells / Unit Area Short-Term Homing Assay (PLN) 80 *p < PTX CCR7 * * CCL21 mab 40 * HEV Chen et al., Nature Immunology, 2006 PTX : CCR7 Desens: CCL21 mab :
16 Outline General introduction to lymphocyte trafficking homeostatic recirculation vs active recruitment. Homeostatic trafficking of lymphocytes across specialized high endothelial venules (HEVs) Structure/function of adhesion molecules involved in initial tethering/rolling (L-selectin/PNAd) Structure/function of chemokine/chemokine receptors that mediate activation (CCR7/CCL21) Structure/function of adhesion molecules required for firm arrest/transendothelial migration (LFA-1/ICAM-1 & α4β7 integrin/madcam-1) Leukocyte recruitment in acute and chronic inflammation.
17 Dynamic Regulation of Leukocyte-Endothelial Adhesion HEV Adapted from Immunol. Rev Tethering/Rolling L-selectin/PNAd α4β7/madcam-1 Activation CCL21/CCR7 Sticking LFA-1/ICAM-1/2 Transmigration HOMING
18 LAD Leukocyte Adhesion Deficiency TIME MAGAZINE 1992 LAD patient leukocytes do not express LFA-1 (leukocyte-function associated antigen-1) cannot make b2 integrin chain
19 Integrin Family alb2 a4b1 a4b7 Nature VOL August 1990
20 LFA-1 is Localized on Planar Membranes of Lymphocytes TK1 cells (low mag) LFA-1 Butcher and von Andrian Cell 1995
21 Ig Superfamily Nature VOL August 1990
22 LFA-1 is Required for Lymphocyte Homing Across HEV of Lymphoid Organs Cells / Unit Area Treat + LFA-1 blocking Ab TRITClabeled cells Isotype Control LFA-1 Blocking Ab 1 h Quantify redlabeled cells in organs 50 * * * PLN MLN PP SPL Pancreas Chen et al., Nature Immunol. 2006
23 LFA-1 Binds to Domain 1 (D1) of ICAM-1 Dimers D1 LFA-1 D1 D1-D1 dimer D2 D3 ICAM-1 D2 D4 D5 D3 D4 D5 ICAM-1 D4-D4 dimer D4-D4 dimer Y Yang, Molecular Cell 14: , April 23, 2004
24 CCL21 and ICAM-1 Engagement are both Required for Maximal LFA-1 Affinity Lymphocyte Inside-out Signaling LFA-1 CCR7 Microclusters formed Actin Folded (<5 nm) Low affinity CCL21 Extended (25 nm) Intermediate affinity Extended High affinity ICAM-1 Outside-in Signaling Alon et al., Nature Immunol Endothelium Actin
25 Dynamic Regulation of Leukocyte-Endothelial Adhesion HEV Adapted from Immunol. Rev Tethering/Rolling L-selectin/PNAd a4b7/madcam-1 Activation CCL21/CCR7 Sticking LFA-1/ICAM-1/2 Transmigration LFA-1/ICAM-1/2 HOMING
26 ICAM-1-Enriched Microvilli-Like Projections Form Cup- Like Structure that Guides Transendothelial Migration LFA-1 ICAM-1 Adherent Leukocyte Cup-like Structure (forms in min.) LFA-1 ICAM-1 Endothelial Cell Carman and Springer, J. Cell Biol Shaw et al., J. Exp. Med Yang et al., Blood 2005
27 Lymphocyte-Endothelial Adhesion in Peyer s Patches L-selectin a4b7 integrin CCR7 a4b7 integrin LFA-1 MAdCAM-1 HEV 1 CCL21 2 3&4 ICAM-1/2 MAdCAM-1
28 Mucosal Addressin Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 (MAdCAM-1) MAdCAM-1 staining of PP HEV with MECA-367 mab MAdCAM-1 structure Briskin, Butcher et al. Nature 363:461, 1993
29 MAdCAM-1 GLDTSL Ig Domain 1 Ig Domain 2 DE antenna Function blocking mab DATK32, HP1/2 I domain MIDAS Mg ++ b 7 XXXX b propeller a 4 Mucin Domain Ca ++ Lectin L-selectin Ig Domain 3 Glycocalyx 10 nm HEV Function blocking mab MEL-14, DREG-56 Lymphocyte Microvillous Membrane
30 Lymphocyte-Endothelial Adhesion in Lymph Nodes L-selectin CCR7 LFA-1 PNAd ICAM-1/2 1 CCL21 2 3&4 HEV
31 Homing Receptors Direct Lymphocyte Trafficking Naïve Central Memory L-selectin hi a4b7 + LFA-1 + CCR7 + Lymphoid Tissues (LN, PP) Inflamed Tissues (Autoimmune pathology) Effector Effector Memory L-selectin neg a4b7 hi LFA-1 hi CCR7 neg CLA + CCR5/CXCR3 + Extralymphoid Sites Infection, Inflammation Tumor Tissues
32 Current View of Lymphocyte Trafficking in PLN HEVs Girard JP et al., Nat Rev Immunol. 12:762-73, 2012
33 DCs Maintain Homeostatic Trafficking in HEVs Girard JP et al., Nat Rev Immunol. 12:762, 2012 Moussion C and Girard JP, Nature 13;479, 2011
34 Outline General introduction to lymphocyte trafficking homeostatic recirculation vs active recruitment. Homeostatic trafficking of lymphocytes across specialized high endothelial venules (HEVs) Structure/function of adhesion molecules involved in initial tethering/rolling (L-selectin/PNAd) Structure/function of chemokine/chemokine receptors that mediate activation (CCR7/CCL21) Structure/function of adhesion molecules required for firm arrest/transendothelial migration (LFA-1/ICAM-1 & α4β7 integrin/madcam-1) Leukocyte recruitment in acute and chronic inflammation.
35 Lymphocyte Recirculation and Recruitment Recruitment Trafficking to extralymphoid sites (HEV-like): Low basal level Active recruitment induced by infection, injury, acute & chronic inflammation Recirculation Efficient trafficking to lymphoid organs: PLN (HEV) Spleen (no HEV) Peyer s Patches (HEV)
36 Dynamic Regulation of Endothelial Adhesion at Sites of Infection/ Injury/ Inflammation ICAM-1 Role of cell adhesion receptors in inflammation. An inflammatory response to foregin antigens of bacteria begins with the attraction of leukocytes that release biologically active mediators (A). These cytokines or bacterial products stimulate the expression of adhesion molecules such as ICAM-1, E-selectin, P-selectin, and VCAM-1 on the surface of cuboidal endothelial cells (B). White blood cells then adhere to the activated endothelial cells, migrate through the endothelium and enter areas of infection or tissue damage (D). ( ) Up-regulated adhesion receptors on the surfaces of cells; Endo, endothelium. Control Inflammation Chen, et al. Nature Immunol. 2006
37 Local Cytokines Increase Lymphocyte Recruitment at Inflammatory Sites TNF-a LTab IL-1b IL-6 IFN-g Sites of Infection, Local Tissue Damage Transcription/ Expression of Chemokines & Vascular Adhesion Molecules ICAM-1 VCAM-1 E/P-selectin CXCL9/10 CCL5
38 mrna Expression in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVEC) Following TNF-a Treatment Hrs: VCAM-1 Terminal Ig domains VCAM Lectin, EGF Repeat E-selectin E-selectin
39 TNF-α TNFR Endothelium TRADD TRAF2 RIP MEKK3 P Cytoplasm IKK P IκB P IκB NF-κB Nuclear Translocation Nucleus κbbe VCAM-1 ICAM-1 E-selectin
40 Taming the Flames Within FEBRUARY 17, 2004
41 Venules Lined by High Endothelium in Synovium of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients RA Jalkanen, Butcher et al. Science Vol. 233:556, 1986
42 Chronic Inflammatory Diseases Associated With HEV-Like Vasculature Disease Affected organ Plump CAMs endothelium on endothelium Crohn s disease Gut + MAdCAM-1/PNAd/ICAM-1 Ulcerative colitis Gut + MAdCAM-1/PNAd/ICAM-1 Diabetes mellitus Pancreas + MAdCAM-1/PNAd/ICAM-1 Grave s disease Thyroid + PNAd/ICAM-1 Hashimoto s thyroiditis Thyroid + PNAd/ICAM-1 Rheumatoid arthritis Synovium + PNAd/ICAM-1 Cutaneous lesions Skin + PNAd/ICAM-1 Sjogren's syndrome Lacrimal/salivary glands + PNAd/MAdCAM-1/ICAM-1 Adapted from J.P. Girard and T.A. Springer, Immunol. Today 16: ; S.D. Rosen, Annual Rev. Immunol. 22:129, 2004.
43 Mechanisms of Neutrophil Recruitment to Inflamed Tissues PMN Mucin-like CAM E/P-Selectin CXCR2 LFA-1 ICAM-1 1 IL-8/MIP2 KC 2 3&4 Endothelium
44 Intravital Microscopy
45 Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Control: Ischemia: Reperfusion: Cells move through venules at high velocity (~2400 mm/sec); few adherent cells. Reduced blood flow; distinct cells visible. Increased number of rolling (~40 mm/sec) and adherent cells; adhesion is L-selectin and P- selectin dependent.
46 Process of Metastasis of Malignant Cells Involves Similar Adhesive Mechanisms As Lymphocyte Trafficking R. Hynes, Cell 68: , 1992
47 Outline General introduction to lymphocyte trafficking homeostatic recirculation vs active recruitment. Homeostatic trafficking of lymphocytes across specialized high endothelial venules (HEVs) Structure/function of adhesion molecules involved in initial tethering/rolling (L-selectin/PNAd) Structure/function of chemokine/chemokine receptors that mediate activation (CCR7/CCL21) Structure/function of adhesion molecules required for firm arrest/transendothelial migration (LFA-1/ICAM-1 & α4β7 integrin/madcam-1) Leukocyte recruitment in acute and chronic inflammation.
The Immune Response in Time and Space
 The Immune Response in Time and Space Chapters 14 & 4 Sharon S. Evans, Ph.D. Department of Immunology 845-3421 sharon.evans@roswellpark.org September 18 & 23, 2014 Inflammation Inflammation Complex response
The Immune Response in Time and Space Chapters 14 & 4 Sharon S. Evans, Ph.D. Department of Immunology 845-3421 sharon.evans@roswellpark.org September 18 & 23, 2014 Inflammation Inflammation Complex response
Innate immune cells---- one time migration preprogrammed homing properties
 Innate immune cells---- one time migration preprogrammed homing properties neutrophils---acute inflammation monocytes---subacute/chronic inflammation eosinophils---parasitic or allergic inflammation natural
Innate immune cells---- one time migration preprogrammed homing properties neutrophils---acute inflammation monocytes---subacute/chronic inflammation eosinophils---parasitic or allergic inflammation natural
Chapter 3, Part A (Pages 37-45): Leukocyte Migration into Tissues
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 3, Part A (pages 37-45) of Cellular and Molecular Immunology (Seventh Edition), by Abul K. Abbas, Andrew H. Lichtman and Shiv Pillai. Chapter 3, Part A (Pages
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 3, Part A (pages 37-45) of Cellular and Molecular Immunology (Seventh Edition), by Abul K. Abbas, Andrew H. Lichtman and Shiv Pillai. Chapter 3, Part A (Pages
The recruitment of leukocytes and plasma proteins from the blood to sites of infection and tissue injury is called inflammation
 The migration of a particular type of leukocyte into a restricted type of tissue, or a tissue with an ongoing infection or injury, is often called leukocyte homing, and the general process of leukocyte
The migration of a particular type of leukocyte into a restricted type of tissue, or a tissue with an ongoing infection or injury, is often called leukocyte homing, and the general process of leukocyte
Homing and Inflammation!
 Homing and Inflammation! Micro 204. Molecular and Cellular Immunology! Lecturer: Jason Cyster! jason.cyster@ucsf.edu! How do cells migrate from blood into tissue?! the four step model! role of selectins,
Homing and Inflammation! Micro 204. Molecular and Cellular Immunology! Lecturer: Jason Cyster! jason.cyster@ucsf.edu! How do cells migrate from blood into tissue?! the four step model! role of selectins,
Homing and Inflammation!
 Homing and Inflammation! Micro 204. Molecular and Cellular Immunology! Lecturer: Jason Cyster! jason.cyster@ucsf.edu! How do cells migrate from blood into tissue?! the four step model! role of selectins,
Homing and Inflammation! Micro 204. Molecular and Cellular Immunology! Lecturer: Jason Cyster! jason.cyster@ucsf.edu! How do cells migrate from blood into tissue?! the four step model! role of selectins,
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System
 Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Review Questions: Janeway s Immunobiology 8th Edition by Kenneth Murphy
 Review Questions: Janeway s Immunobiology 8th Edition by Kenneth Murphy Chapter 11 (pages 429-460): Dynamics of Adaptive Immunity prepared by Kelly von Elten, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center,
Review Questions: Janeway s Immunobiology 8th Edition by Kenneth Murphy Chapter 11 (pages 429-460): Dynamics of Adaptive Immunity prepared by Kelly von Elten, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center,
Monocytes must also leave the circulation in response to inflammatory signals, and neutrophils and other granulocytes must be able to do so as well.
 Immunology Dr. John J. Haddad Chapter 15 Leukocyte Migration and inflammation Lymphocytes must recirculate in the body in search of antigens. Since antigens are brought to lymph nodes and the spleen, the
Immunology Dr. John J. Haddad Chapter 15 Leukocyte Migration and inflammation Lymphocytes must recirculate in the body in search of antigens. Since antigens are brought to lymph nodes and the spleen, the
Chapter 2 (pages 22 33): Cells and Tissues of the Immune System. Prepared by Kristen Dazy, MD, Scripps Clinic Medical Group
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS; Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD; and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 2 (pages 22 33): Cells and
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS; Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD; and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 2 (pages 22 33): Cells and
Lymphoid architecture & Leukocyte recirculation. Thursday Jan 26th, 2017
 Lymphoid architecture & Leukocyte recirculation Thursday Jan 26th, 2017 Topics The life of immune cells Where are they born? Where are they educated? Where do they function? How do they get there? The
Lymphoid architecture & Leukocyte recirculation Thursday Jan 26th, 2017 Topics The life of immune cells Where are they born? Where are they educated? Where do they function? How do they get there? The
Date of preparation: 06/ IBD/
 Mechanisms Mechanisms of of Disease Disease: The The Science of of IBD IBD 64002 Date of preparation: 06/11 2013 IBD/2013-11-01 Table of Contents IBD Background and Disease Management Etiology and Pathophysiology
Mechanisms Mechanisms of of Disease Disease: The The Science of of IBD IBD 64002 Date of preparation: 06/11 2013 IBD/2013-11-01 Table of Contents IBD Background and Disease Management Etiology and Pathophysiology
LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE
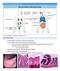 LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE - Small intestine in humans is around 3-4 metres long - Internal surface of the small intestines are lined by villi o Villi are composed of absorptive cells (epithelial/enterocytes)
LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE - Small intestine in humans is around 3-4 metres long - Internal surface of the small intestines are lined by villi o Villi are composed of absorptive cells (epithelial/enterocytes)
Immune response to infection
 Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
Lymphocyte homing to the gut: attraction, adhesion, and commitment
 Marko Salmi Sirpa Jalkanen Lymphocyte homing to the gut: attraction, adhesion, and commitment Authors address Marko Salmi, Sirpa Jalkanen National Public Health Institute Turku, MediCity Research Laboratory,
Marko Salmi Sirpa Jalkanen Lymphocyte homing to the gut: attraction, adhesion, and commitment Authors address Marko Salmi, Sirpa Jalkanen National Public Health Institute Turku, MediCity Research Laboratory,
Follicular Lymphoma. ced3 APOPTOSIS. *In the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans 131 of the organism's 1031 cells die during development.
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv Pillai Follicular Lymphoma 1. Characterized by t(14:18) translocation 2. Ig heavy
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv Pillai Follicular Lymphoma 1. Characterized by t(14:18) translocation 2. Ig heavy
Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the
 Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the targeted allele in ES cells, and the mutant allele in
Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the targeted allele in ES cells, and the mutant allele in
Lecture 9: T-cell Mediated Immunity
 Lecture 9: T-cell Mediated Immunity Questions to Consider How do T cells know where to go? Questions to Consider How do T cells know where to go? How does antigen get targeted to a T cell expressing the
Lecture 9: T-cell Mediated Immunity Questions to Consider How do T cells know where to go? Questions to Consider How do T cells know where to go? How does antigen get targeted to a T cell expressing the
Naive T cells are programmed to recirculate through secondary
 Naive T Cell Recruitment to Nonlymphoid Tissues: A Role for Endothelium-Expressed CC Chemokine Ligand 21 in Autoimmune Disease and Lymphoid Neogenesis 1 Wolfgang Weninger, 2 * Hege S. Carlsen, Mahmoud
Naive T Cell Recruitment to Nonlymphoid Tissues: A Role for Endothelium-Expressed CC Chemokine Ligand 21 in Autoimmune Disease and Lymphoid Neogenesis 1 Wolfgang Weninger, 2 * Hege S. Carlsen, Mahmoud
Molecular and Cellular Basis of Immune Protection of Mucosal Surfaces
 Molecular and Cellular Basis of Immune Protection of Mucosal Surfaces Department of Biologic & Materials Sciences School of Dentistry University of Michigan Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109-1078 1 Image quality
Molecular and Cellular Basis of Immune Protection of Mucosal Surfaces Department of Biologic & Materials Sciences School of Dentistry University of Michigan Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109-1078 1 Image quality
T Lymphocyte Activation and Costimulation. FOCiS. Lecture outline
 1 T Lymphocyte Activation and Costimulation Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family Inhibitory receptors of T cells Targeting costimulators for
1 T Lymphocyte Activation and Costimulation Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family Inhibitory receptors of T cells Targeting costimulators for
Loss of HS1 inhibits neutrophil extravasation during. inflammation via disturbed PKA signaling. IV. Immunology Summit, Houston,
 Loss of HS1 inhibits neutrophil extravasation during inflammation via disturbed PKA signaling IV. Immunology Summit, Houston, 29.09.2015 Michael Schnoor, PhD Center for Research and Advanced Studies, (Cinvestav-IPN),
Loss of HS1 inhibits neutrophil extravasation during inflammation via disturbed PKA signaling IV. Immunology Summit, Houston, 29.09.2015 Michael Schnoor, PhD Center for Research and Advanced Studies, (Cinvestav-IPN),
T Cell Activation, Costimulation and Regulation
 1 T Cell Activation, Costimulation and Regulation Abul K. Abbas, MD University of California San Francisco 2 Lecture outline T cell antigen recognition and activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
1 T Cell Activation, Costimulation and Regulation Abul K. Abbas, MD University of California San Francisco 2 Lecture outline T cell antigen recognition and activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
Lymphoid Organs and Lymphocyte Trafficking. Dr. Issa Abu-Dayyeh
 Lymphoid Organs and Lymphocyte Trafficking Dr. Issa Abu-Dayyeh Invader recognition Where does invader recognition take place?? Secondary lymphoid organs: Lymph nodes Spleen Mucosal-associated lymphoid
Lymphoid Organs and Lymphocyte Trafficking Dr. Issa Abu-Dayyeh Invader recognition Where does invader recognition take place?? Secondary lymphoid organs: Lymph nodes Spleen Mucosal-associated lymphoid
Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation. Abul K. Abbas UCSF. FOCiS
 1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
Endogenous TNFα orchestrates the trafficking of neutrophils into and within lymphatic vessels during acute inflammation
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Endogenous TNFα orchestrates the trafficking of neutrophils into and within lymphatic vessels during acute inflammation Samantha Arokiasamy 1,2, Christian Zakian 1, Jessica Dilliway
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Endogenous TNFα orchestrates the trafficking of neutrophils into and within lymphatic vessels during acute inflammation Samantha Arokiasamy 1,2, Christian Zakian 1, Jessica Dilliway
Fisher et al. Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 A TNF IL-1 IL-6 CCL2 CCL5 CXCL10 pg/mg total protein 50 30 10 4,000 3,000 2,000 1,000 n.d. 1 1 14,000 12,000 10,000 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 6,000,000 CT26 5,000 16,000 B16 4,000 12,000
Supplemental Figure 1 A TNF IL-1 IL-6 CCL2 CCL5 CXCL10 pg/mg total protein 50 30 10 4,000 3,000 2,000 1,000 n.d. 1 1 14,000 12,000 10,000 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 6,000,000 CT26 5,000 16,000 B16 4,000 12,000
Basic immunology. Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration. Péter Engelmann
 Basic immunology Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of innate immunity Initiation of local and systemic
Basic immunology Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of innate immunity Initiation of local and systemic
Genetics. Environment. You Are Only 10% Human. Pathogenesis of IBD. Advances in the Pathogenesis of IBD: Genetics Leads to Function IBD
 Advances in the Pathogenesis of IBD: Genetics Leads to Function Pathogenesis of IBD Environmental Factors Microbes Scott Plevy, MD Associate Professor of Medicine, Microbiology & Immunology UNC School
Advances in the Pathogenesis of IBD: Genetics Leads to Function Pathogenesis of IBD Environmental Factors Microbes Scott Plevy, MD Associate Professor of Medicine, Microbiology & Immunology UNC School
Leukocyte Rolling Velocities and Migration Are Optimized by Cooperative L-Selectin and Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 Functions
 This information is current as of November 24, 2018. Leukocyte Rolling Velocities and Migration Are Optimized by Cooperative L-Selectin and Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 Functions Takafumi Kadono,
This information is current as of November 24, 2018. Leukocyte Rolling Velocities and Migration Are Optimized by Cooperative L-Selectin and Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 Functions Takafumi Kadono,
Abstract. Introduction
 The CC Chemokine Thymus-derived Chemotactic Agent 4 (TCA-4, Secondary Lymphoid Tissue Chemokine, 6Ckine, Exodus-2) Triggers Lymphocyte Function associated Antigen 1 mediated Arrest of Rolling T Lymphocytes
The CC Chemokine Thymus-derived Chemotactic Agent 4 (TCA-4, Secondary Lymphoid Tissue Chemokine, 6Ckine, Exodus-2) Triggers Lymphocyte Function associated Antigen 1 mediated Arrest of Rolling T Lymphocytes
ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY
 ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY The recognition of specific antigen by naïve T cell induces its own activation and effector phases. T helper cells recognize peptide antigens through
ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY The recognition of specific antigen by naïve T cell induces its own activation and effector phases. T helper cells recognize peptide antigens through
Immunology 2017: Lecture 12 handout. Secondary lymphoid organs. Dr H Awad
 Immunology 2017: Lecture 12 handout Secondary lymphoid organs Dr H Awad INTRODUCTION So far we discussed the cells of the immune system and how they recognize their antigens and get stimulated. The number
Immunology 2017: Lecture 12 handout Secondary lymphoid organs Dr H Awad INTRODUCTION So far we discussed the cells of the immune system and how they recognize their antigens and get stimulated. The number
CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
 CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION What is Cytokine? Secreted popypeptide (protein) involved in cell-to-cell signaling. Acts in paracrine or autocrine fashion through specific cellular receptors.
CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION What is Cytokine? Secreted popypeptide (protein) involved in cell-to-cell signaling. Acts in paracrine or autocrine fashion through specific cellular receptors.
T-LYMPHOCYTE INTERACTIONS WITH ENDOTHELIUM AND EXTRACELLULAR MATRIX
 T-LYMPHOCYTE INTERACTIONS WITH ENDOTHELIUM AND EXTRACELLULAR MATRIX Stephen W. Hunt III Division of Immunopathology, Warner-Lambert/Parke-Davis Pharmaceutical Research Division, Ann Arbor, Ml 48105 Estelle
T-LYMPHOCYTE INTERACTIONS WITH ENDOTHELIUM AND EXTRACELLULAR MATRIX Stephen W. Hunt III Division of Immunopathology, Warner-Lambert/Parke-Davis Pharmaceutical Research Division, Ann Arbor, Ml 48105 Estelle
1. Introduction Cell adhesion: the basis of multicellular life Cell adhesion in the immune system
 INTRODUCTION 1 1. Introduction 1.1. Cell adhesion: the basis of multicellular life The capability of cells to adhere to each other and to the secreted macromolecules that constitute the extracellular matrix
INTRODUCTION 1 1. Introduction 1.1. Cell adhesion: the basis of multicellular life The capability of cells to adhere to each other and to the secreted macromolecules that constitute the extracellular matrix
Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under normal and pathologic conditions Interleukins,
 Cytokines http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter22/animation the_immune_response.html Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under
Cytokines http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter22/animation the_immune_response.html Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under
Shining a light on intestinal traffic. McCafferty, Donna-Marie. Article (peer-reviewed)
 Title Author(s) Editor(s) Shining a light on intestinal traffic Murphy, Carola T.; Nally, Kenneth; Shanahan, Fergus; Melgar, Silvia McCafferty, Donna-Marie Publication date 2012-01 Original citation Type
Title Author(s) Editor(s) Shining a light on intestinal traffic Murphy, Carola T.; Nally, Kenneth; Shanahan, Fergus; Melgar, Silvia McCafferty, Donna-Marie Publication date 2012-01 Original citation Type
Cell Adhesion and Migration IV. Lymphocyte trafficking in the intestine and liver *
 themes Cell Adhesion and Migration IV. Lymphocyte trafficking in the intestine and liver * M. SALMI, 1 D. ADAMS, 2 AND S. JALKANEN 1 1 MediCity Research Laboratories, University of Turku and National Public
themes Cell Adhesion and Migration IV. Lymphocyte trafficking in the intestine and liver * M. SALMI, 1 D. ADAMS, 2 AND S. JALKANEN 1 1 MediCity Research Laboratories, University of Turku and National Public
Effector T Cells and
 1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
The Journal of Experimental Medicine
 CXCL12 Mediates CCR7-independent Homing of Central Memory Cells, But Not Naive T Cells, in Peripheral Lymph Nodes M. Lucila Scimone, Thomas W. Felbinger, Irina B. Mazo, Jens V. Stein, Ulrich H. von Andrian,
CXCL12 Mediates CCR7-independent Homing of Central Memory Cells, But Not Naive T Cells, in Peripheral Lymph Nodes M. Lucila Scimone, Thomas W. Felbinger, Irina B. Mazo, Jens V. Stein, Ulrich H. von Andrian,
Putting it Together. Stephen Canfield Secondary Lymphoid System. Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s
 Putting it Together Stephen Canfield smc12@columbia.edu Secondary Lymphoid System Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s Axillary LN s Mediastinal/Retroperitoneal LN s Thoracic Duct Appendix Spleen Inguinal LN
Putting it Together Stephen Canfield smc12@columbia.edu Secondary Lymphoid System Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s Axillary LN s Mediastinal/Retroperitoneal LN s Thoracic Duct Appendix Spleen Inguinal LN
T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH
 T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH Ned Braunstein, MD The Major T Cell Subsets p56 lck + T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ p56 lck CD8+ T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 CD8 Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 MHC II peptide
T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH Ned Braunstein, MD The Major T Cell Subsets p56 lck + T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ p56 lck CD8+ T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 CD8 Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 MHC II peptide
Primary immune surveillance: some like it hot
 J Mol Med (2007) 85:1361 1367 DOI 10.1007/s00109-007-0245-7 REVIEW ARTICLE Primary immune surveillance: some like it hot Joseph J. Skitzki & Qing Chen & W. C. Wang & Sharon S. Evans Received: 17 April
J Mol Med (2007) 85:1361 1367 DOI 10.1007/s00109-007-0245-7 REVIEW ARTICLE Primary immune surveillance: some like it hot Joseph J. Skitzki & Qing Chen & W. C. Wang & Sharon S. Evans Received: 17 April
MOLECULAR IMMUNOLOGY Manipulation of immune response Autoimmune diseases & the pathogenic mechanism
 MOLECULAR IMMUNOLOGY Manipulation of immune response Autoimmune diseases & the pathogenic mechanism SCHMAIEL SHIRDEL CONTENT 2 Introduction Autoimmune diseases Classification Involved components Autoimmune
MOLECULAR IMMUNOLOGY Manipulation of immune response Autoimmune diseases & the pathogenic mechanism SCHMAIEL SHIRDEL CONTENT 2 Introduction Autoimmune diseases Classification Involved components Autoimmune
Thomas HAIDER Journal Club
 Thomas HAIDER Journal Club 20.10.2014 Background Immunology of the CNS - History Ehrlich, 1885 & 1904 dye did not stain brain -> BBB Shirai, Y. (1921) On the transplantation of the rat sarcoma in adult
Thomas HAIDER Journal Club 20.10.2014 Background Immunology of the CNS - History Ehrlich, 1885 & 1904 dye did not stain brain -> BBB Shirai, Y. (1921) On the transplantation of the rat sarcoma in adult
CHAPTER 9 BIOLOGY OF THE T LYMPHOCYTE
 CHAPTER 9 BIOLOGY OF THE T LYMPHOCYTE Coico, R., Sunshine, G., (2009) Immunology : a short course, 6 th Ed., Wiley-Blackwell 1 CHAPTER 9 : Biology of The T Lymphocytes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Introduction
CHAPTER 9 BIOLOGY OF THE T LYMPHOCYTE Coico, R., Sunshine, G., (2009) Immunology : a short course, 6 th Ed., Wiley-Blackwell 1 CHAPTER 9 : Biology of The T Lymphocytes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Introduction
Test Bank for Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of the Immune System 4th Edition by Abbas
 Test Bank for Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of the Immune System 4th Edition by Abbas Chapter 04: Antigen Recognition in the Adaptive Immune System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Most T lymphocytes
Test Bank for Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of the Immune System 4th Edition by Abbas Chapter 04: Antigen Recognition in the Adaptive Immune System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Most T lymphocytes
Effector Mechanisms of Cell-Mediated Immunity
 Effector Mechanisms of Cell-Mediated Immunity Dr. Julia Rempel Section of Hepatology 789-3825 jdrempel@cc.umanitoba.ca 804D JBRC Topics: I. Types of Cell-Mediated Immunity II. Migration of Effector T Lymphocytes
Effector Mechanisms of Cell-Mediated Immunity Dr. Julia Rempel Section of Hepatology 789-3825 jdrempel@cc.umanitoba.ca 804D JBRC Topics: I. Types of Cell-Mediated Immunity II. Migration of Effector T Lymphocytes
Hidenobu Kanda, Rebecca Newton, Russell Klein, Yuka Morita, Michael D. Gunn & Steven D. Rosen
 Autotaxin, a lysophosphatidic acid-producing ectoenzyme, promotes lymphocyte entry into secondary lymphoid organs Hidenou Kanda, Reecca Newton, Russell Klein, Yuka Morita, Michael D. Gunn & Steven D. Rosen
Autotaxin, a lysophosphatidic acid-producing ectoenzyme, promotes lymphocyte entry into secondary lymphoid organs Hidenou Kanda, Reecca Newton, Russell Klein, Yuka Morita, Michael D. Gunn & Steven D. Rosen
Recruitment of regulatory and conventional T cells to colon adenocarcinomas. Veronica Langenes
 Recruitment of regulatory and conventional T cells to colon adenocarcinomas Veronica Langenes Department of Microbiology and Immunology Institute of Biomedicine The Sahlgrenska academy, University of Gothenburg
Recruitment of regulatory and conventional T cells to colon adenocarcinomas Veronica Langenes Department of Microbiology and Immunology Institute of Biomedicine The Sahlgrenska academy, University of Gothenburg
Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell?
 Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Inhibition of E-Selectin or E-selectin together with CXCR4 Re-sensitizes Multiple Myeloma to Treatment
 Inhibition of E-Selectin or E-selectin together with CXCR4 Re-sensitizes Multiple Myeloma to Treatment 1, Ph.D. Henna Bazai 1, Anita Sekula 1, William Fogler 2, Ted Smith 2, John Magnani 2 and Abdel Kareem
Inhibition of E-Selectin or E-selectin together with CXCR4 Re-sensitizes Multiple Myeloma to Treatment 1, Ph.D. Henna Bazai 1, Anita Sekula 1, William Fogler 2, Ted Smith 2, John Magnani 2 and Abdel Kareem
Generation of post-germinal centre myeloma plasma B cell.
 Generation of post-germinal centre myeloma. DNA DAMAGE CXCR4 Homing to Lytic lesion activation CD38 CD138 CD56 Phenotypic markers Naive Secondary lymphoid organ Multiple myeloma is a malignancy of s caused
Generation of post-germinal centre myeloma. DNA DAMAGE CXCR4 Homing to Lytic lesion activation CD38 CD138 CD56 Phenotypic markers Naive Secondary lymphoid organ Multiple myeloma is a malignancy of s caused
IMMUNE CELL SURFACE RECEPTORS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS
 LECTURE: 07 Title: IMMUNE CELL SURFACE RECEPTORS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: The chemical nature of the cellular surface receptors. Define the location of the
LECTURE: 07 Title: IMMUNE CELL SURFACE RECEPTORS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: The chemical nature of the cellular surface receptors. Define the location of the
Brain barriers control immune cell trafficking to the CNS. Britta Engelhardt Theodor Kocher Institute University of Bern - Switzerland
 Brain barriers control immune cell trafficking to the CNS Britta Engelhardt Theodor Kocher Institute University of Bern - Switzerland The brain barriers 2 The BBB establishes a physical and metabolic barrier
Brain barriers control immune cell trafficking to the CNS Britta Engelhardt Theodor Kocher Institute University of Bern - Switzerland The brain barriers 2 The BBB establishes a physical and metabolic barrier
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Neuronal guidance protein semaphorin 7A influences neutrophil arrest and aggravates inflammatory lung injury. Dr. Tiago Granja
 Neuronal guidance protein semaphorin 7A influences neutrophil arrest and aggravates inflammatory lung injury Dr. Tiago Granja Neuronal guidance proteins (NGPs) force cells to move NPGs give axons and dendrites
Neuronal guidance protein semaphorin 7A influences neutrophil arrest and aggravates inflammatory lung injury Dr. Tiago Granja Neuronal guidance proteins (NGPs) force cells to move NPGs give axons and dendrites
B cell activation and antibody production. Abul K. Abbas UCSF
 1 B cell activation and antibody production Abul K. Abbas UCSF 2 Lecture outline B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production Therapeutic targeting of B cells 3 Principles of humoral
1 B cell activation and antibody production Abul K. Abbas UCSF 2 Lecture outline B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production Therapeutic targeting of B cells 3 Principles of humoral
Integrin 4 7 Antagonists: Activities, Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Prospects
 118 Current Immunology Reviews, 2012, 8, 118-134 Integrin 4 7 Antagonists: Activities, Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Prospects Dulce Soler-Ferran *,1 and Michael J. Briskin 2 1 Former Affiliation:
118 Current Immunology Reviews, 2012, 8, 118-134 Integrin 4 7 Antagonists: Activities, Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Prospects Dulce Soler-Ferran *,1 and Michael J. Briskin 2 1 Former Affiliation:
An overview of lymphocytes activation
 An overview of lymphocytes activation lymphocytes activation denotes an ordered series of events through which a resting lymphocyte is stimulated to divide and produce progeny,some of which become effectors
An overview of lymphocytes activation lymphocytes activation denotes an ordered series of events through which a resting lymphocyte is stimulated to divide and produce progeny,some of which become effectors
Emerging g therapies for IBD: A practical approach to positioning. Sequential Therapies for IBD
 Emerging g therapies for IBD: A practical approach to positioning Stephen B. Hanauer, MD Sequential Therapies for IBD Disease Severity at Presentation Severe Anti-TNF +/IS Cyclosporine (UC) Colectomy (UC)
Emerging g therapies for IBD: A practical approach to positioning Stephen B. Hanauer, MD Sequential Therapies for IBD Disease Severity at Presentation Severe Anti-TNF +/IS Cyclosporine (UC) Colectomy (UC)
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine
 Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Specific Compartmentalization of IgA ASCs in Mouse Salivary Glands via Differential Expression of Chemokines and Chemokine Receptors
 Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2008-11-21 Specific Compartmentalization of IgA ASCs in Mouse Salivary Glands via Differential Expression of Chemokines and Chemokine
Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2008-11-21 Specific Compartmentalization of IgA ASCs in Mouse Salivary Glands via Differential Expression of Chemokines and Chemokine
Homing properties of mesenchymal stromal cells
 Homing properties of mesenchymal stromal cells Karlien Kallmeyer and Michael S. Pepper Corresponding Author Prof. Michael S. Pepper Department of Immunology Faculty of Health Sciences University of Pretoria
Homing properties of mesenchymal stromal cells Karlien Kallmeyer and Michael S. Pepper Corresponding Author Prof. Michael S. Pepper Department of Immunology Faculty of Health Sciences University of Pretoria
?Who binds to it. ? Who binds these inflammatory proteins RAGE SUGAR-FREE GLYCOBIOLOGY INFLAMMATION. BASIC SCIENCE?sugar chain structure
 SUGAR-FREE GLYCOBIOLOGY BASIC SCIENCE?sugar chain structure Unusual Sugar Chain It -- is a carboxylate Make lots of It Make an It antibody Inflammatory proteins?who binds to it? Who binds these inflammatory
SUGAR-FREE GLYCOBIOLOGY BASIC SCIENCE?sugar chain structure Unusual Sugar Chain It -- is a carboxylate Make lots of It Make an It antibody Inflammatory proteins?who binds to it? Who binds these inflammatory
Review. Endothelial-Dependent Mechanisms of Leukocyte Recruitment to the Vascular Wall
 Review This Review is part of a thematic series on Migration of Vascular Cells, which includes the following articles: Mechanisms of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Migration Endothelial Cell Migration During
Review This Review is part of a thematic series on Migration of Vascular Cells, which includes the following articles: Mechanisms of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Migration Endothelial Cell Migration During
Cellular Immune response. Jianzhong Chen, Ph.D Institute of immunology, ZJU
 Cellular Immune response Jianzhong Chen, Ph.D Institute of immunology, ZJU Concept of adaptive immune response T cell-mediated adaptive immune response I. Concept of immune response A collective and coordinated
Cellular Immune response Jianzhong Chen, Ph.D Institute of immunology, ZJU Concept of adaptive immune response T cell-mediated adaptive immune response I. Concept of immune response A collective and coordinated
Lecture 11: Mucosal Immunity (based on lecture by Dr. Betsy Herold, Einstein)
 Lecture 11: Mucosal Immunity (based on lecture by Dr. Betsy Herold, Einstein) Questions to Consider How is the mucusal immune system different from the systemic immune system? How does the immune system
Lecture 11: Mucosal Immunity (based on lecture by Dr. Betsy Herold, Einstein) Questions to Consider How is the mucusal immune system different from the systemic immune system? How does the immune system
MECHANISMS OF CELLULAR REJECTION IN ORGAN TRANSPLANTATION AN OVERVIEW
 MECHANISMS OF CELLULAR REJECTION IN ORGAN TRANSPLANTATION AN OVERVIEW YVON LEBRANCHU Service Néphrologie et Immunologie Clinique CHU TOURS ANTIGEN PRESENTING CELL CD4 + T CELL CYTOKINE PRODUCTION CLONAL
MECHANISMS OF CELLULAR REJECTION IN ORGAN TRANSPLANTATION AN OVERVIEW YVON LEBRANCHU Service Néphrologie et Immunologie Clinique CHU TOURS ANTIGEN PRESENTING CELL CD4 + T CELL CYTOKINE PRODUCTION CLONAL
IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY. CD4 T Follicular Helper Cells. Memory CD8 T Cell Differentiation
 IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY CD4 T Follicular Helper Cells Memory CD8 T Cell Differentiation CD4 T Cell Differentiation Bcl-6 T-bet GATA-3 ROR t Foxp3 CD4 T follicular helper (Tfh) cells FUNCTION Provide essential
IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY CD4 T Follicular Helper Cells Memory CD8 T Cell Differentiation CD4 T Cell Differentiation Bcl-6 T-bet GATA-3 ROR t Foxp3 CD4 T follicular helper (Tfh) cells FUNCTION Provide essential
Nutrition & Gut Immunity
 Nutrition & Gut Immunity Kenneth A. Kudsk, MD FACS Professor of Surgery University of Wisconsin - Madison Madison, Wisconsin No conflicts of interest to disclose % Survival Survival vs. Malnutrition (after
Nutrition & Gut Immunity Kenneth A. Kudsk, MD FACS Professor of Surgery University of Wisconsin - Madison Madison, Wisconsin No conflicts of interest to disclose % Survival Survival vs. Malnutrition (after
An Investigation into the Effects of the Addition of Synthetic Receptor on Chemokine Induced Jurkat T-Cell Migration
 An Investigation into the Effects of the Addition of Synthetic Receptor on Chemokine Induced Jurkat T-Cell Migration Jessica Jurado, Jianfang Hu, Avery August, PhD PSU Undergraduate Animal Bioscience July
An Investigation into the Effects of the Addition of Synthetic Receptor on Chemokine Induced Jurkat T-Cell Migration Jessica Jurado, Jianfang Hu, Avery August, PhD PSU Undergraduate Animal Bioscience July
Cytokines, adhesion molecules and apoptosis markers. A comprehensive product line for human and veterinary ELISAs
 Cytokines, adhesion molecules and apoptosis markers A comprehensive product line for human and veterinary ELISAs IBL International s cytokine product line... is extremely comprehensive. The assays are
Cytokines, adhesion molecules and apoptosis markers A comprehensive product line for human and veterinary ELISAs IBL International s cytokine product line... is extremely comprehensive. The assays are
ROLE OF INFLAMMATION IN HYPERTENSION. Dr Barasa FA Physician Cardiologist Eldoret
 ROLE OF INFLAMMATION IN HYPERTENSION Dr Barasa FA Physician Cardiologist Eldoret Outline Inflammation in CVDs the evidence Basic Science in Cardiovascular inflammation: The Main players Inflammation as
ROLE OF INFLAMMATION IN HYPERTENSION Dr Barasa FA Physician Cardiologist Eldoret Outline Inflammation in CVDs the evidence Basic Science in Cardiovascular inflammation: The Main players Inflammation as
7/6/2009. The study of the immune system and of diseases that occur as a result of inappropriate or inadequate actions of the immune system.
 Diseases of Immunity 2009 CL Davis General Pathology Paul W. Snyder, DVM, PhD Purdue University Acknowledgements Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease, 4 th Ed Veterinary Immunology, An Introduction 8
Diseases of Immunity 2009 CL Davis General Pathology Paul W. Snyder, DVM, PhD Purdue University Acknowledgements Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease, 4 th Ed Veterinary Immunology, An Introduction 8
Biochemistry. Immunology. Principal Investigator. Dr. Sunil Kumar Khare,Professor Dept. of Chemistry, I.I.T. Delhi
 Paper : 16 Module : 19 Principal Investigator Paper Coordinator and Content Writer Dr. Sunil Kumar Khare,Professor Dept. of Chemistry, I.I.T. Delhi Dr. M.N.Gupta, Emeritus Professor Dept. of Biochemical
Paper : 16 Module : 19 Principal Investigator Paper Coordinator and Content Writer Dr. Sunil Kumar Khare,Professor Dept. of Chemistry, I.I.T. Delhi Dr. M.N.Gupta, Emeritus Professor Dept. of Biochemical
PBS Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs , 27-30
 PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
Supplementary Information
 Nature Immunology doi:1.138/ni.2477 Supplementary Information Capillary and arteriolar pericytes attract innate leukocytes exiting through venules and instruct them with pattern recognition and motility
Nature Immunology doi:1.138/ni.2477 Supplementary Information Capillary and arteriolar pericytes attract innate leukocytes exiting through venules and instruct them with pattern recognition and motility
TCR, MHC and coreceptors
 Cooperation In Immune Responses Antigen processing how peptides get into MHC Antigen processing involves the intracellular proteolytic generation of MHC binding proteins Protein antigens may be processed
Cooperation In Immune Responses Antigen processing how peptides get into MHC Antigen processing involves the intracellular proteolytic generation of MHC binding proteins Protein antigens may be processed
VWF other roles than hemostasis. Summary 1: VWF & hemostasis synthesis 11/4/16. Structure/function relationship & functions kDa.
 VWF other roles than hemostasis Len$ng PJ, Casari C et al JTH 2012 Summary 1: VWF & hemostasis synthesis Structure/function relationship & functions (HMWM) 20.000kDa multimerization propeptide FVIII GPIb
VWF other roles than hemostasis Len$ng PJ, Casari C et al JTH 2012 Summary 1: VWF & hemostasis synthesis Structure/function relationship & functions (HMWM) 20.000kDa multimerization propeptide FVIII GPIb
a 4 Integrins as Therapeutic Targets in Autoimmune Disease Ulrich H. von Andrian, M.D., Ph.D., and Britta Engelhardt, Ph.D.
 artery catheter and there were several disease processes that warranted study. 10,14 Concern was voiced, however, that it could be difficult to convince physicians to participate in the trials. 12 This
artery catheter and there were several disease processes that warranted study. 10,14 Concern was voiced, however, that it could be difficult to convince physicians to participate in the trials. 12 This
INFLAMMATION: Cellular Functions
 INFLAMMATION: Cellular Functions Sequence of Vascular Events 1. Vasodilation (increased blood flow) CALOR & RUBOR 2. Increased microvascular permeability: fluids into tissues TUMOR 3. Blood flow slows
INFLAMMATION: Cellular Functions Sequence of Vascular Events 1. Vasodilation (increased blood flow) CALOR & RUBOR 2. Increased microvascular permeability: fluids into tissues TUMOR 3. Blood flow slows
Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system. Answer Sheet
 Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system Answer Sheet Q1 Which areas of the lymph node have most CD3 staining? A1 Most CD3 staining is present in the paracortex (T cell areas). This is towards the outside
Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system Answer Sheet Q1 Which areas of the lymph node have most CD3 staining? A1 Most CD3 staining is present in the paracortex (T cell areas). This is towards the outside
Mucosal Immunology Sophomore Dental and Optometry Microbiology Section I: Immunology. Robin Lorenz
 Mucosal Immunology Sophomore Dental and Optometry Microbiology Section I: Immunology Robin Lorenz rlorenz@uab.edu Why do we Need to Understand How the Mucosal Immune System Works? The mucosa is the major
Mucosal Immunology Sophomore Dental and Optometry Microbiology Section I: Immunology Robin Lorenz rlorenz@uab.edu Why do we Need to Understand How the Mucosal Immune System Works? The mucosa is the major
Selectins and mechanisms of signal transduction
 Selectins and mechanisms of signal transduction Elahe Crockett-Torabi Department of Surgery, Michigan State University-College of Human Medicine, East Lansing Abstract: Leukocyte emigration is essential
Selectins and mechanisms of signal transduction Elahe Crockett-Torabi Department of Surgery, Michigan State University-College of Human Medicine, East Lansing Abstract: Leukocyte emigration is essential
NEUTROPHIL, BASOPHIL, EOSINOPHIL, AND PLATELETS SURFACE RECEPTORS
 LECTURE: 15 Title NEUTROPHIL, BASOPHIL, EOSINOPHIL, AND PLATELETS SURFACE RECEPTORS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Determine the relative percentages in blood for the various types
LECTURE: 15 Title NEUTROPHIL, BASOPHIL, EOSINOPHIL, AND PLATELETS SURFACE RECEPTORS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Determine the relative percentages in blood for the various types
Immunology 2011 Lecture 17 Lymphoid Tissue Architecture 13 October
 Immunology 2011 Lecture 17 Lymphoid Tissue Architecture 13 October TODAY Lymphoid Tissue Architecture, Chap. 16 APC Antigen processing (dendritic cells, MΦ et al.) Antigen "presentation" Ag/Ab complexes
Immunology 2011 Lecture 17 Lymphoid Tissue Architecture 13 October TODAY Lymphoid Tissue Architecture, Chap. 16 APC Antigen processing (dendritic cells, MΦ et al.) Antigen "presentation" Ag/Ab complexes
IL-17 in health and disease. March 2014 PSO13-C051n
 IL-17 in health and disease March 2014 PSO13-C051n Originally Researchers Suggested That IL-12 and IL-4 drove Th Cell Differentiation Naïve CD4 + T cell Question: Which of these cell types is responsible
IL-17 in health and disease March 2014 PSO13-C051n Originally Researchers Suggested That IL-12 and IL-4 drove Th Cell Differentiation Naïve CD4 + T cell Question: Which of these cell types is responsible
Lymphoid tissue. 1. Central Lymphoid tissue. - The central lymphoid tissue (also known as primary) is composed of bone morrow and thymus.
 1. Central Lymphoid tissue Lymphoid tissue - The central lymphoid tissue (also known as primary) is composed of bone morrow and thymus. Bone Morrow - The major site of hematopoiesis in humans. - Hematopoiesis
1. Central Lymphoid tissue Lymphoid tissue - The central lymphoid tissue (also known as primary) is composed of bone morrow and thymus. Bone Morrow - The major site of hematopoiesis in humans. - Hematopoiesis
Andrea s SI Session PCB Practice Test Test 3
 Practice Test Test 3 READ BEFORE STARTING PRACTICE TEST: Remember to please use this practice test as a tool to measure your knowledge, and DO NOT use it as your only tool to study for the test, since
Practice Test Test 3 READ BEFORE STARTING PRACTICE TEST: Remember to please use this practice test as a tool to measure your knowledge, and DO NOT use it as your only tool to study for the test, since
Molecules controlling lymphocyte migration to the gut
 148 Gut 1999;45:148 153 Review Molecules controlling lymphocyte migration to the gut Preface Continuous lymphocyte migration to normal gut is a prerequisite for immune homoeostasis in humans. In this review
148 Gut 1999;45:148 153 Review Molecules controlling lymphocyte migration to the gut Preface Continuous lymphocyte migration to normal gut is a prerequisite for immune homoeostasis in humans. In this review
Rémy T. Boscacci, Friederike Pfeiffer, Kathrin Gollmer, Ana Isabel Checa Sevilla, Ana Maria Martin, Silvia ,5 2
 Blood. 2010 August 12; 116(6): 915 925. Prepublished online 2010 April 15. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-11-254334 Immunobiology PMCID: PMC3324225 Comprehensive analysis of lymph node stroma-expressed Ig superfamily
Blood. 2010 August 12; 116(6): 915 925. Prepublished online 2010 April 15. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-11-254334 Immunobiology PMCID: PMC3324225 Comprehensive analysis of lymph node stroma-expressed Ig superfamily
Naive, memory and regulatory T lymphocytes populations analysis
 Naive, memory and regulatory T lymphocytes populations analysis Jaen Olivier, PhD ojaen@beckmancoulter.com Cellular Analysis application specialist Beckman Coulter France Introduction Flow cytometric analysis
Naive, memory and regulatory T lymphocytes populations analysis Jaen Olivier, PhD ojaen@beckmancoulter.com Cellular Analysis application specialist Beckman Coulter France Introduction Flow cytometric analysis
Helper-T-cell regulated B-cell differentiation. Phase I begins at the site of infection with acute inflammation that leads to the activation and
 1 2 Helper-T-cell regulated B-cell differentiation. Phase I begins at the site of infection with acute inflammation that leads to the activation and emigration of DCs to the T- cell zones of the lymph
1 2 Helper-T-cell regulated B-cell differentiation. Phase I begins at the site of infection with acute inflammation that leads to the activation and emigration of DCs to the T- cell zones of the lymph
manner to enable rapid recruitment of cells into the tissue. The mucosal vascular addressin (MAdCAM- 1 ) ' and the
 Vascular Addressins Are Induced on Islet Vessels during Insulitis in Nonobese Diabetic Mice and Are Involved in Lymphoid Cell Binding to Islet Endothelium Arno Hanninen,** Cariel Taylor,' Philip R. Streeter,11
Vascular Addressins Are Induced on Islet Vessels during Insulitis in Nonobese Diabetic Mice and Are Involved in Lymphoid Cell Binding to Islet Endothelium Arno Hanninen,** Cariel Taylor,' Philip R. Streeter,11
Time course of immune response
 Time course of immune response Route of entry Route of entry (cont.) Steps in infection Barriers to infection Mf receptors Facilitate engulfment Glucan, mannose Scavenger CD11b/CD18 Allows immediate response
Time course of immune response Route of entry Route of entry (cont.) Steps in infection Barriers to infection Mf receptors Facilitate engulfment Glucan, mannose Scavenger CD11b/CD18 Allows immediate response
invited review Chemokines and chemokine receptors in leukocyte trafficking
 Am J Physiol Regulatory Integrative Comp Physiol 283: R7 R28, 2002; 10.1152/ajpregu.00738.2001. Chemokines and chemokine receptors in leukocyte trafficking invited review TIMOTHY S. OLSON AND KLAUS LEY
Am J Physiol Regulatory Integrative Comp Physiol 283: R7 R28, 2002; 10.1152/ajpregu.00738.2001. Chemokines and chemokine receptors in leukocyte trafficking invited review TIMOTHY S. OLSON AND KLAUS LEY
T cell maturation. T-cell Maturation. What allows T cell maturation?
 T-cell Maturation What allows T cell maturation? Direct contact with thymic epithelial cells Influence of thymic hormones Growth factors (cytokines, CSF) T cell maturation T cell progenitor DN DP SP 2ry
T-cell Maturation What allows T cell maturation? Direct contact with thymic epithelial cells Influence of thymic hormones Growth factors (cytokines, CSF) T cell maturation T cell progenitor DN DP SP 2ry
