Chapter 2 (pages 22 33): Cells and Tissues of the Immune System. Prepared by Kristen Dazy, MD, Scripps Clinic Medical Group
|
|
|
- Lester Cole
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS; Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD; and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 2 (pages 22 33): Cells and Tissues of the Immune System Prepared by Kristen Dazy, MD, Scripps Clinic Medical Group 1. Which of the following surface proteins is highly expressed on effector T cells and indicative of recent activation? A. IL-2R (CD25) B. L-selectin (CD26L) C. IL-7R (CD127) D. CCR7 2. The epithelial component of the thymus is derived from invaginations of what germ cell layer? A. Endoderm B. Mesoderm C. Ectoderm D. Neural crest 3. The thoracic duct and right lymphatic duct drain return fluid to the blood stream via which major vessel? A. Aortic arch B. Superior vena cava C. Inferior vena cava D. Subclavian vein 4. Where does B-cell proliferation and generation of memory B cells take place within the lymph nodes? A. Germinal center B. Paracortex C. Subcapsular sinus D. Medulla 5. Chemokines promote naïve T cells to enter the T cell zones of the lymph node via which of the following? A. Afferent lymphatic vessels B. Medullary sinus lymphatic vessels C. High endothelial venules D. Marginal sinus 6. The chemokines CCL19 and CCL21 promote the migration of naïve T cells into the T cell zones of the lymph node by binding to which receptor located on the surface of naïve T cells?
2 A. CCR7 B. CXCR5 C. IL-7R D. IL-2R 7. Circulating naïve B cells enter lymph nodes and are attracted into the follicles by which chemokine? A. CCL19 B. IL-3 C. IL-7 D. CXCL13 8. During fetal life, which cell types are responsible for the development of lymph nodes as well as other secondary lymphoid organs? A. Fibroblastic reticular cells (FRCs) B. Lymphoid tissue-inducer cells C. Follicular dendritic cells (FDCs) D. Naïve T cells 9. Which of the following is not a true statement regarding the spleen? A. The spleen is responsible for removing aging and/or damaged blood cells from the circulation. B. Asplenic patients are susceptible to disseminated infections with encapsulated bacteri, including pneumococci and meningococci. C. Blood is carried out of the spleen through the splenic vein, which drains into the portal circulation. D. The spleen recognizes and removes un-opsonized microbes from the circulation. 10. The anatomic arrangement of antigen presenting cells, B cells, and T cells within the spleen helps to promote the interactions required for the efficient development of humoral immune responses. In which part of the spleen do these actions take place? A. Red pulp B. White pulp C. Hilum D. Vascular sinusoids E. Answers 1. A, pages 22 23, Table 2-3. Both CD4 and CD8 effector T cells usually express surface proteins indicative of recent activation, including CD25 (a component of the receptor for T cell growth factor IL-2), and altered patterns of adhesion molecules (selectins and integrins). Choices B, C, and D are all highly expressed on naïve T cells rather than effector T cells. 2. C, page 27. The epithelial component of the thymus is derived from invaginations of the ectoderm in the developing neck and chest of the embryo, forming structures called branchial pouches.
3 3. B, page 28. The efferent lymph vessel at the end of a lymph node chain joins other lymph vessels, eventually culminating in a large lymphatic vessel called the thoracic duct. Lymphatics from the right upper trunk, right arm, and right side of the head drains into the right lymphatic duct. The thoracic and right lymphatic ducts both empty into the superior vena cava, thus returning fluid to the blood stream. 4. A, pages Germinal centers develop in response to antigenic stimulation. They are sites of remarkable B cell proliferation, selection of B cells producing high-affinity antibodies, and generation of memory B cells and long-lived plasma cells. The T lymphocytes are located mainly beneath and more central to the follicles, in the paracortical cords, often called the paracortex. 5. C, page 30. T cell rich zones, called the paracortex, contains a network of fibroblastic reticular cells (FRCs), many of which form the outer layer of tube-like structures called FRC conduits. These conduits begin at the subcapsular sinus and extend to both medullary sinus lymphatic vessels and cortical blood vessels, call high endothelial venules (HEVs). Naïve T cells enter the T cell zones through the HEVs, specifically promoted by chemokines produced by stromal cells in the T cell zones of the lymph node. 6. A, page 30. Naïve T cells express a receptor called CCR7 that binds the chemokines CCL19 and CCL21 produced by stromal cells in the T cell zones of the lymph node. These chemokines promote naïve T cell movement from the blood, through the walls of the high endothelial venules (HEVs), and into the T cell zone. The chemokine CXCL13 and its receptor CXCR5 are responsible for B cell migration into the follicles. 7. D, page 30. Naïve B cells express high levels of the receptor CXCR5, which recognizes a chemokine, CXCL13, produced only in follicles by follicular dendritic cells (FDCs). Studies of CXCR5 knockout mice lack B cell-containing follicles in lymph nodes and spleen. 8. B, pages The development of lymph nodes, as well as peripheral lymphoid organs, depends on lymphoid tissue-inducer cells and the coordinated actions of several cytokines (e.g., lymphotoxin-α, lymphotoxin-β), chemokines, and transcription factors. These cells are a subset of innate lymphoid cells. Cytokines produced by these cells go on to activate stromal cells, such as FRCs and FDCs, to secrete additional cytokines, which help organize the structure of lymphoid organs. 9. D, page 31. The spleen is a highly vascularized organ whose major functions are to remove aging and damaged blood cells and particles (such as immune complexes and opsonized microbes) from the circulation and to initiate adaptive immune responses to blood-borne antigens. Macrophages within the red pulp of the spleen serve as an important filter for the blood and remove antibody-
4 coated (opsonized) cells and microbes. Individuals lacking a spleen are therefore susceptible to disseminated infections with encapsulated bacteria, such as pneumococci. Blood enters the spleen via the splenic artery and leaves via the splenic vein, which drains into the portal circulation. 10. B, pages The splenic parenchyma is anatomically and functionally divided into red pulp, which is composed mainly of blood-filled vascular sinusoids, and lymphocyte-rich white pulp. The white pulp is arranged into T cell (periarteriolar lymphoid sheath) and B cell (follicles) zones. This segregation is a highly regulated process and is dependent upon the production of different cytokines and chemokines in the stromal cells in these different areas, analogous to the case for lymph nodes. This arrangement is crucial to initiate the development of the adaptive humoral immune response to blood-borne antigens. Review Questions Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS, Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 3 (pages 38 45): Leukocyte Circulation and Migration into Tissues Prepared by Kara Wada, MD, Ohio State University/Nationwide Children s Hospital 1. Which molecule found on leukocytes promotes their adhesion to endothelial cells? A. Sialomucin B. P-selectin C. L-selectin D. E-selectin 2. Which best describes the properties of integrins? A. They mediate adhesion of cells to other cells or to the extracellular matrix through non-specific binding interactions with various ligands. B. They normally are present in a high-affinity state on the endothelial surface. C. They have the ability to respond to intracellular signals by decreasing their affinity for ligands. D. Chemokines induce membrane clustering of integrins. 3. The HIV virus uses which chemokine receptors as co-receptors? A. CCR5 and CXCR4 B. CCR5 and Mac-1 C. LFA-1 and CXCR4 D. Mac-1 and LFA-1 4. Chemokines are a large family of cytokines with diverse functions. Which best describes a property of chemokines?
5 A. Chemokines are large molecules with three or more external disulfide bonds. B. Chemokines are only produced by leukocytes. C. Chemokines are essential for the recruitment of leukocytes from blood vessels to extravascular sites. D. Chemokines are not involved in lymphoid organ development. 5. Selectins, integrins and chemokines work together to regulate migration of leukocytes into the tissues. What best describes this process? A. Selectin-mediated rolling on the endothelium, chemokine-mediated increased in integrin affinity, stable integrin-mediated adhesion of leukocytes to the endothelium and transmigration between endothelial cells. B. Selectin-mediated adhesion on the endothelium, chemokine-mediated increased in integrin affinity, stable integrin-mediated rolling of leukocytes to the endothelium and transmigration between endothelial cells. C. Selectin-mediated rolling on the endothelium, chemokine-mediated decreased in integrin affinity, stable integrin-mediated adhesion of leukocytes to the endothelium and transmigration between endothelial cells. D. Selectin-mediated rolling on the endothelium, chemokine-mediated increased in integrin affinity, stable integrin-mediated adhesion of leukocytes to the endothelium and transmigration through endothelial cells. 6. The interplay of selectins, integrins and chemokines in leukocyte migration is essential in normal host defense. What defect is responsible for leukocyte adhesion deficiency type 1 (LAD-1)? A. A deficiency in the subunit of LFA-1 and Mac-1 B. A lack in the golgi fucose transporter needed to express the carbohydrate ligands for E-selectin and P-selectin. C. A mutation in the signaling pathways linking chemokine receptors to integrin activation. D. A deficiency in the subunit of LFA-1 and Mac Migration of the inflammatory infiltrate generally follows the same pattern and is directed by chemokines and their receptors. Which pairing of cell types and chemokine receptor is correct? A. Monocytes & CCR7 B. Neutrophils & CXCR1 C. Monocytes & CCL2 D. Neutrophils & CXCL2 8. Migration of naïve T cells depends on efficient homing mechanisms. A. Naïve T cells are delivered through venous blood flow into the high endothelial venules (HEVs). B. Rolling of naïve T cells on the HEVs is mediated by P-selectin. C. Firm adhesion of naïve T cells is mediated by LFA-1. D. Chemokines that deactivate the naïve T cell integrins to a low-affinity state are CCL19 and CCL21.
6 9. How is S1P responsible for the exit of naïve T cells from the lymph nodes? A. S1P is in higher concentrations in the tissues attracting naïve T cells away from the lymph node. B. S1P binds to S1PR1 on T cells directing movement toward higher concentrations of S1P. C. S1P lyase degrades S1P and is responsible for the higher levels in the tissues. D. Naïve T cells are coated in S1PR1 receptors allowing for immediate interaction with the S1P. 10. Central memory T cells are characterized by what phenotype? A. CD45RO + with high expression of CCR7 & L-selectin B. CD45RO + with low expression of CCR7 & L-selectin C. CD45RO + with high expression of CXCR5 D. CD45RO + with low expression of CXCR5 Answers 1. C, page 38. L-selectin is expressed on leukocytes. Their ligands are sialomucins on endothelial cells, whose expression is increased by cytokine activation of the cells. E-selectin and P-selectin are also found on endothelial cells. 2. D, pages Integrins mediate adhesion through specific binding interactions. They are normally present in a low-affinity state. They will respond to intracellular signaling by increasing their affinity for ligands and chemokines will induce clustering on the membrane surface. 3. A, page 39. CCR5 and CXCR4 act as co-receptors for the HIV. Mac-1 and LFA-1 are integrins and not chemokine receptors. 4. C, pages Chemokines are 8-10-kD polypeptides that contain two internal disulfide bonds, which are produced by leukocytes, endothelial cells, epithelial cells and fibroblasts. They are essential for the recruitment of leukocytes from blood vessels to extravascular sites and are involved in the development of lymphoid organs. 5. A, pages Selectin-mediated interactions slow down the leukocyte, release of chemokines increase integrin affinity allowing the stronger integrin-mediated adhesion to occur. This allows the leukocyte to then migrate between the endothelial cells by transiently disrupting the adherens junction proteins. 6. D, page 42. Patients with LAD-2 lack the golgi fucose transporter thus are unable to express the carbohydrate ligands for E-selectin and P-selectin. LAD-3 is characterized by a mutation in the signaling
7 pathways. LAD-1 is characterized by an autosomal recessive deficiency in the b subunit of LFA- 1 and Mac B, page 42, Table 3.2 on page 40. In the nomenclature, all chemokine receptors contain the letter R whereas chemokines contain the letter L. CCR7 is responsible for T and dendritic cell migration in the lymph nodes. CXCR1 and CXCR2 are responsible for neutrophil migration. 8. C, page 44. Naïve T cells are delievered through arterial blood flow to the HEVs where rolling is mediated by L-selectin and firm adhesion is mediated by LFA-1. CCL19 and CCL21 are chemokines that activate the naïve T cell integrins to a high affinity state. 9. B, page 45. S1P is a lipid chemoattractant which binds to S1PR1 on T cells. S1P is found in higher concentrations in the blood and lymph. It is degraded by S1P lyase in the tissues. The binding of S1P to S1PR1 results in directed movement of T cells along the S1P concentration gradient and out of the lymph node parenchyma. Circulating T cells have very little S1PR1 due to high blood levels causing internalization of this receptor. It takes several hours for S1PR1 to be re-expressed thus allowing naïve T cells to interact with antigen presenting cells in the lymph node before exiting back into the circulation via the efferent lymphatic. 10. A. Central memory T cells are CD45RO+ with high expression of CCR7 & L-selectin. Effector memory T cells are defined as CD45RO+ with low expression of CCR7 & L-selectin. CXCR5 is a chemokine receptor found on B cells, which is found on mature naïve B cells.
Chapter 3, Part A (Pages 37-45): Leukocyte Migration into Tissues
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 3, Part A (pages 37-45) of Cellular and Molecular Immunology (Seventh Edition), by Abul K. Abbas, Andrew H. Lichtman and Shiv Pillai. Chapter 3, Part A (Pages
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 3, Part A (pages 37-45) of Cellular and Molecular Immunology (Seventh Edition), by Abul K. Abbas, Andrew H. Lichtman and Shiv Pillai. Chapter 3, Part A (Pages
The recruitment of leukocytes and plasma proteins from the blood to sites of infection and tissue injury is called inflammation
 The migration of a particular type of leukocyte into a restricted type of tissue, or a tissue with an ongoing infection or injury, is often called leukocyte homing, and the general process of leukocyte
The migration of a particular type of leukocyte into a restricted type of tissue, or a tissue with an ongoing infection or injury, is often called leukocyte homing, and the general process of leukocyte
PBS Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs , 27-30
 PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
Allergy and Immunology Board Review Corner. Table of Contents
 Allergy and Immunology Board Review Corner 2015 Table of Contents Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition, by Abul K. Abbas, MBBS; Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD; and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD January
Allergy and Immunology Board Review Corner 2015 Table of Contents Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition, by Abul K. Abbas, MBBS; Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD; and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD January
The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues
 The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues : are the lymph nodes, spleen, Mucosal associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). All secondary lymphoid organs have one
The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues : are the lymph nodes, spleen, Mucosal associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). All secondary lymphoid organs have one
Immune - lymphatic system
 Immune system - organisation: Immune - lymphatic system - histology & embryology organised lymphoid structures cell components lymphocytes event. lymphatic follicles accessory cells monocytes-macrophages
Immune system - organisation: Immune - lymphatic system - histology & embryology organised lymphoid structures cell components lymphocytes event. lymphatic follicles accessory cells monocytes-macrophages
Chapter 10 (pages ): Differentiation and Functions of CD4+ Effector T Cells Prepared by Kristen Dazy, MD, Scripps Clinic Medical Group
 FIT Board Review Corner September 2015 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Andrew Nickels, MD, and Sarah Spriet, DO, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In-Training (FITs)
FIT Board Review Corner September 2015 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Andrew Nickels, MD, and Sarah Spriet, DO, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In-Training (FITs)
Lymphoid architecture & Leukocyte recirculation. Thursday Jan 26th, 2017
 Lymphoid architecture & Leukocyte recirculation Thursday Jan 26th, 2017 Topics The life of immune cells Where are they born? Where are they educated? Where do they function? How do they get there? The
Lymphoid architecture & Leukocyte recirculation Thursday Jan 26th, 2017 Topics The life of immune cells Where are they born? Where are they educated? Where do they function? How do they get there? The
Chapter10 Immune system
 Chapter10 Immune system Lyu Zhengmei Department of Histology and Embryology, Anhui Medical University Ⅰ.General Introduction Function ------ Defense The human body immune system has the ability to distinguish
Chapter10 Immune system Lyu Zhengmei Department of Histology and Embryology, Anhui Medical University Ⅰ.General Introduction Function ------ Defense The human body immune system has the ability to distinguish
Immunology 2017: Lecture 12 handout. Secondary lymphoid organs. Dr H Awad
 Immunology 2017: Lecture 12 handout Secondary lymphoid organs Dr H Awad INTRODUCTION So far we discussed the cells of the immune system and how they recognize their antigens and get stimulated. The number
Immunology 2017: Lecture 12 handout Secondary lymphoid organs Dr H Awad INTRODUCTION So far we discussed the cells of the immune system and how they recognize their antigens and get stimulated. The number
Lymphoid Organs and Lymphocyte Trafficking. Dr. Issa Abu-Dayyeh
 Lymphoid Organs and Lymphocyte Trafficking Dr. Issa Abu-Dayyeh Invader recognition Where does invader recognition take place?? Secondary lymphoid organs: Lymph nodes Spleen Mucosal-associated lymphoid
Lymphoid Organs and Lymphocyte Trafficking Dr. Issa Abu-Dayyeh Invader recognition Where does invader recognition take place?? Secondary lymphoid organs: Lymph nodes Spleen Mucosal-associated lymphoid
Lymphoid Organs. Dr. Sami Zaqout. Dr. Sami Zaqout IUG Faculty of Medicine
 Lymphoid Organs Dr. Sami Zaqout Cells of the Immune System Lymphocytes Plasma cells Mast cells Neutrophils Eosinophils Cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system Distribution of cells of the immune system
Lymphoid Organs Dr. Sami Zaqout Cells of the Immune System Lymphocytes Plasma cells Mast cells Neutrophils Eosinophils Cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system Distribution of cells of the immune system
LYMPHOID ORGANS. Dr. Iram Tassaduq
 LYMPHOID ORGANS Dr. Iram Tassaduq COMPONENTS OF IMMUNE SYSTEM Lymphocytes Diffuse Lymphatic Tissue Lymphatic Nodules Lymph node Spleen Bone marrow Thymus Functions of Immune System Has the ability to distinguish
LYMPHOID ORGANS Dr. Iram Tassaduq COMPONENTS OF IMMUNE SYSTEM Lymphocytes Diffuse Lymphatic Tissue Lymphatic Nodules Lymph node Spleen Bone marrow Thymus Functions of Immune System Has the ability to distinguish
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 20: Immunity and the Lymphatic System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 20: Immunity and the Lymphatic System Question No. 1 of 10 The lymphatic system is formed early during human development. Which of the following statements
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 20: Immunity and the Lymphatic System Question No. 1 of 10 The lymphatic system is formed early during human development. Which of the following statements
Lymphoid tissue. 1. Central Lymphoid tissue. - The central lymphoid tissue (also known as primary) is composed of bone morrow and thymus.
 1. Central Lymphoid tissue Lymphoid tissue - The central lymphoid tissue (also known as primary) is composed of bone morrow and thymus. Bone Morrow - The major site of hematopoiesis in humans. - Hematopoiesis
1. Central Lymphoid tissue Lymphoid tissue - The central lymphoid tissue (also known as primary) is composed of bone morrow and thymus. Bone Morrow - The major site of hematopoiesis in humans. - Hematopoiesis
ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY
 ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY The recognition of specific antigen by naïve T cell induces its own activation and effector phases. T helper cells recognize peptide antigens through
ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY The recognition of specific antigen by naïve T cell induces its own activation and effector phases. T helper cells recognize peptide antigens through
Lymphatic System and Immunity. Lymphatic System
 Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Lymphatic System High hydrostatic pressure in the arterioles and capillaries at the arterial part of the circulation leads to move plasma fluid from the capillaries
Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Lymphatic System High hydrostatic pressure in the arterioles and capillaries at the arterial part of the circulation leads to move plasma fluid from the capillaries
The Lymphoid System Pearson Education, Inc.
 23 The Lymphoid System Introduction The lymphoid system consists of: Lymph Lymphatic vessels Lymphoid organs An Overview of the Lymphoid System Lymph consists of: Interstitial fluid Lymphocytes Macrophages
23 The Lymphoid System Introduction The lymphoid system consists of: Lymph Lymphatic vessels Lymphoid organs An Overview of the Lymphoid System Lymph consists of: Interstitial fluid Lymphocytes Macrophages
The Lymphatic System
 The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic Systems Overview General Functions Organization Components Lymphatic System General Functions Transportation Excess fluid from capillary exchange Fats & fat soluble vitamins
The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic Systems Overview General Functions Organization Components Lymphatic System General Functions Transportation Excess fluid from capillary exchange Fats & fat soluble vitamins
Sinusoids and venous sinuses
 LYMPHOID SYSTEM General aspects Consists of organs that are made of lymphoid tissue; Immune defense Breakdown of red blood cells. 1 Sinusoids In place of capillaries Endothelium; often fenestrated More
LYMPHOID SYSTEM General aspects Consists of organs that are made of lymphoid tissue; Immune defense Breakdown of red blood cells. 1 Sinusoids In place of capillaries Endothelium; often fenestrated More
Overview of the Lymphoid System
 Overview of the Lymphoid System The Lymphoid System Protects us against disease Lymphoid system cells respond to Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells, such as cancers Overview of the Lymphoid
Overview of the Lymphoid System The Lymphoid System Protects us against disease Lymphoid system cells respond to Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells, such as cancers Overview of the Lymphoid
Returns fluids that leaked from blood vessels back to blood Consists of three parts
 Lymphatic System Returns fluids that leaked from blood vessels back to blood Consists of three parts 1. Network of lymphatic vessels (lymphatics) 2. Lymph fluid in vessels 3. Lymph cleanse lymph 1 Lymphoid
Lymphatic System Returns fluids that leaked from blood vessels back to blood Consists of three parts 1. Network of lymphatic vessels (lymphatics) 2. Lymph fluid in vessels 3. Lymph cleanse lymph 1 Lymphoid
Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell?
 Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Effector T Cells and
 1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
The development of T cells in the thymus
 T cells rearrange their receptors in the thymus whereas B cells do so in the bone marrow. The development of T cells in the thymus The lobular/cellular organization of the thymus Immature cells are called
T cells rearrange their receptors in the thymus whereas B cells do so in the bone marrow. The development of T cells in the thymus The lobular/cellular organization of the thymus Immature cells are called
Flow Cytometry. Hanan Jafar (2017)
 1 Flow Cytometry Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology to analyze the characteristics of cells or particles. It is predominantly used to measure fluorescence intensity produced by fluorescent-labeled
1 Flow Cytometry Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology to analyze the characteristics of cells or particles. It is predominantly used to measure fluorescence intensity produced by fluorescent-labeled
Hematopoiesis. Hematopoiesis. Hematopoiesis
 Chapter. Cells and Organs of the Immune System Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis- formation and development of WBC and RBC bone marrow. Hematopoietic stem cell- give rise to any blood cells (constant number,
Chapter. Cells and Organs of the Immune System Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis- formation and development of WBC and RBC bone marrow. Hematopoietic stem cell- give rise to any blood cells (constant number,
LYMPHATIC ANATOMY LAB. BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D.
 LYMPHATIC ANATOMY LAB BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM ORGANS PRIMARY BONE MARROW THYMUS SECONDARY LYMPH NODES SPLEEN FUNCTIONS CONTROL DISEASE TRANSPORT
LYMPHATIC ANATOMY LAB BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM ORGANS PRIMARY BONE MARROW THYMUS SECONDARY LYMPH NODES SPLEEN FUNCTIONS CONTROL DISEASE TRANSPORT
LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE
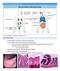 LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE - Small intestine in humans is around 3-4 metres long - Internal surface of the small intestines are lined by villi o Villi are composed of absorptive cells (epithelial/enterocytes)
LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE - Small intestine in humans is around 3-4 metres long - Internal surface of the small intestines are lined by villi o Villi are composed of absorptive cells (epithelial/enterocytes)
Test Bank for Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of the Immune System 4th Edition by Abbas
 Test Bank for Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of the Immune System 4th Edition by Abbas Chapter 04: Antigen Recognition in the Adaptive Immune System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Most T lymphocytes
Test Bank for Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of the Immune System 4th Edition by Abbas Chapter 04: Antigen Recognition in the Adaptive Immune System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Most T lymphocytes
2/19/2018. Lymphatic System and Lymphoid Organs and Tissues. What is Lymph?
 Lymphatic System and Lymphoid Organs and Tissues Lymphatic system a transport system for tissue fluids 1. elaborate network of one-way drainage vessels returning lymph to systemic circulation 2. Lymph:
Lymphatic System and Lymphoid Organs and Tissues Lymphatic system a transport system for tissue fluids 1. elaborate network of one-way drainage vessels returning lymph to systemic circulation 2. Lymph:
1. The scavenger receptor, CD36, functions as a coreceptor for which TLR? a. TLR ½ b. TLR 3 c. TLR 4 d. TLR 2/6
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS, Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 4 (pages 62-74): Innate Immunity
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS, Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 4 (pages 62-74): Innate Immunity
Lymph I: The Peripheral Lymph System
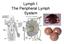 Lymph I: The Peripheral Lymph System Peripheral = Secondary Primary Immune Organs = bone marrow, thymus Site of maturation of cells of the immune system Secondary Immune Organs = Nodes, MALT, spleen Filter
Lymph I: The Peripheral Lymph System Peripheral = Secondary Primary Immune Organs = bone marrow, thymus Site of maturation of cells of the immune system Secondary Immune Organs = Nodes, MALT, spleen Filter
Immune response to infection
 Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
Chapter 21 The Lymphatic System Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 21 The Lymphatic System Overview of the Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System Protects us against disease Lymphatic system cells respond to: Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells,
Chapter 21 The Lymphatic System Overview of the Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System Protects us against disease Lymphatic system cells respond to: Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells,
Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity
 MICR2209 Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will discuss the T-cell mediated immune response, how it is activated,
MICR2209 Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will discuss the T-cell mediated immune response, how it is activated,
Immunobiology 7. The Humoral Immune Response
 Janeway Murphy Travers Walport Immunobiology 7 Chapter 9 The Humoral Immune Response Copyright Garland Science 2008 Tim Worbs Institute of Immunology Hannover Medical School 1 The course of a typical antibody
Janeway Murphy Travers Walport Immunobiology 7 Chapter 9 The Humoral Immune Response Copyright Garland Science 2008 Tim Worbs Institute of Immunology Hannover Medical School 1 The course of a typical antibody
8: Lymphatic vessels and lymphoid tissue. nur
 8: Lymphatic vessels and lymphoid tissue nur Lymphatic vascular system Functions return to the blood extracellular fluid (Lymph) from connective tissue spaces. ensures the return of water, electrolytes
8: Lymphatic vessels and lymphoid tissue nur Lymphatic vascular system Functions return to the blood extracellular fluid (Lymph) from connective tissue spaces. ensures the return of water, electrolytes
Follicular Lymphoma. ced3 APOPTOSIS. *In the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans 131 of the organism's 1031 cells die during development.
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv Pillai Follicular Lymphoma 1. Characterized by t(14:18) translocation 2. Ig heavy
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv Pillai Follicular Lymphoma 1. Characterized by t(14:18) translocation 2. Ig heavy
Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells
 ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
MACROPHAGE "MONOCYTES" SURFACE RECEPTORS
 LECTURE: 13 Title: MACROPHAGE "MONOCYTES" SURFACE RECEPTORS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Describe the blood monocytes (size, and shape of nucleus). Enumerate some of the monocytes
LECTURE: 13 Title: MACROPHAGE "MONOCYTES" SURFACE RECEPTORS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Describe the blood monocytes (size, and shape of nucleus). Enumerate some of the monocytes
Putting it Together. Stephen Canfield Secondary Lymphoid System. Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s
 Putting it Together Stephen Canfield smc12@columbia.edu Secondary Lymphoid System Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s Axillary LN s Mediastinal/Retroperitoneal LN s Thoracic Duct Appendix Spleen Inguinal LN
Putting it Together Stephen Canfield smc12@columbia.edu Secondary Lymphoid System Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s Axillary LN s Mediastinal/Retroperitoneal LN s Thoracic Duct Appendix Spleen Inguinal LN
Lymphatic System. Where s your immunity idol?
 Lymphatic System Where s your immunity idol? Functions of the Lymphatic System Fluid Balance Drains excess fluid from tissues Lymph contains solutes from plasma Fat Absorption Lymphatic system absorbs
Lymphatic System Where s your immunity idol? Functions of the Lymphatic System Fluid Balance Drains excess fluid from tissues Lymph contains solutes from plasma Fat Absorption Lymphatic system absorbs
Homing and Inflammation!
 Homing and Inflammation! Micro 204. Molecular and Cellular Immunology! Lecturer: Jason Cyster! jason.cyster@ucsf.edu! How do cells migrate from blood into tissue?! the four step model! role of selectins,
Homing and Inflammation! Micro 204. Molecular and Cellular Immunology! Lecturer: Jason Cyster! jason.cyster@ucsf.edu! How do cells migrate from blood into tissue?! the four step model! role of selectins,
5/1/13. The proportion of thymus that produces T cells decreases with age. The cellular organization of the thymus
 T cell precursors migrate from the bone marrow via the blood to the thymus to mature 1 2 The cellular organization of the thymus The proportion of thymus that produces T cells decreases with age 3 4 1
T cell precursors migrate from the bone marrow via the blood to the thymus to mature 1 2 The cellular organization of the thymus The proportion of thymus that produces T cells decreases with age 3 4 1
Chapter 16 Lymphatic System and Immunity. Lymphatic Pathways. Lymphatic Capillaries. network of vessels that assist in circulating fluids
 Chapter 16 Lymphatic System and Immunity network of vessels that assist in circulating fluids closely associated with the cardiovascular system transports excess fluid away from interstitial spaces transports
Chapter 16 Lymphatic System and Immunity network of vessels that assist in circulating fluids closely associated with the cardiovascular system transports excess fluid away from interstitial spaces transports
The Immune Response in Time and Space
 The Immune Response in Time and Space Chapters 14 & 4 Sharon S. Evans, Ph.D. Department of Immunology 845-3421 sharon.evans@roswellpark.org September 18 & 23, 2014 Inflammation Inflammation Complex response
The Immune Response in Time and Space Chapters 14 & 4 Sharon S. Evans, Ph.D. Department of Immunology 845-3421 sharon.evans@roswellpark.org September 18 & 23, 2014 Inflammation Inflammation Complex response
Review Questions: Janeway s Immunobiology 8th Edition by Kenneth Murphy
 Review Questions: Janeway s Immunobiology 8th Edition by Kenneth Murphy Chapter 11 (pages 429-460): Dynamics of Adaptive Immunity prepared by Kelly von Elten, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center,
Review Questions: Janeway s Immunobiology 8th Edition by Kenneth Murphy Chapter 11 (pages 429-460): Dynamics of Adaptive Immunity prepared by Kelly von Elten, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center,
Introduction to Immunology Lectures 1-3 by Bellur S. Prabhakar. March 13-14, 2007
 Introduction to Immunology Lectures 1-3 by Bellur S. Prabhakar. March 13-14, 2007 TheComponents Of The Immune System and Innate Immunity: Ref: Immunobiology-5 th edition. Janeway et al. Chapters-1 & 2.
Introduction to Immunology Lectures 1-3 by Bellur S. Prabhakar. March 13-14, 2007 TheComponents Of The Immune System and Innate Immunity: Ref: Immunobiology-5 th edition. Janeway et al. Chapters-1 & 2.
BIO 116 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 3 - The Lymphatic, Immune and Digestive Systems This is not a required assignment
 BIO 116 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 3 - The Lymphatic, Immune and Digestive Systems This is not a required assignment 1. Which are components of the lymphatic system? a: Thyroid gland b:
BIO 116 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 3 - The Lymphatic, Immune and Digestive Systems This is not a required assignment 1. Which are components of the lymphatic system? a: Thyroid gland b:
The Adaptive Immune Response. B-cells
 The Adaptive Immune Response B-cells The innate immune system provides immediate protection. The adaptive response takes time to develop and is antigen specific. Activation of B and T lymphocytes Naive
The Adaptive Immune Response B-cells The innate immune system provides immediate protection. The adaptive response takes time to develop and is antigen specific. Activation of B and T lymphocytes Naive
Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System
 Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System Immune System Composed of many nonspecific and specific defenses Lymphatic System also plays an important role in establishing immunity Lymphatic System Major components
Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System Immune System Composed of many nonspecific and specific defenses Lymphatic System also plays an important role in establishing immunity Lymphatic System Major components
Basic immunology. Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration. Péter Engelmann
 Basic immunology Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of innate immunity Initiation of local and systemic
Basic immunology Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of innate immunity Initiation of local and systemic
TCR, MHC and coreceptors
 Cooperation In Immune Responses Antigen processing how peptides get into MHC Antigen processing involves the intracellular proteolytic generation of MHC binding proteins Protein antigens may be processed
Cooperation In Immune Responses Antigen processing how peptides get into MHC Antigen processing involves the intracellular proteolytic generation of MHC binding proteins Protein antigens may be processed
The Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 21 Part 1 The Lymphatic and Immune Systems The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Lymphatic system Main function
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 21 Part 1 The Lymphatic and Immune Systems The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Lymphatic system Main function
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II THE BODY SYSTEMS Anatomy & Physiology II The Body Systems Michelle Cochrane 2014 All rights reserved. This material is subject to copyright and may not be reprinted or reproduced
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II THE BODY SYSTEMS Anatomy & Physiology II The Body Systems Michelle Cochrane 2014 All rights reserved. This material is subject to copyright and may not be reprinted or reproduced
Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation. Abul K. Abbas UCSF. FOCiS
 1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
LYMPH GLAND. By : Group 1
 LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 Lymphatic and Immune www.vastaccess.com 2 Specialized component of circulatory system Lymphatic system functions: Maintenance of internal fluid balance Immunity Lymph derived from blood and tissue fluid
Lymphatic and Immune www.vastaccess.com 2 Specialized component of circulatory system Lymphatic system functions: Maintenance of internal fluid balance Immunity Lymph derived from blood and tissue fluid
Adaptive Immunity: Humoral Immune Responses
 MICR2209 Adaptive Immunity: Humoral Immune Responses Dr Allison Imrie 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will review the different mechanisms which constitute the humoral immune response, and examine the antibody
MICR2209 Adaptive Immunity: Humoral Immune Responses Dr Allison Imrie 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will review the different mechanisms which constitute the humoral immune response, and examine the antibody
Lymphatic System. Chapter 14. Introduction. Main Channels of Lymphatics. Lymphatics. Lymph Tissue. Major Lymphatic Vessels of the Trunk
 Lymphatic System Chapter 14 Components Lymph is the fluid Vessels lymphatics Structures & organs Functions Return tissue fluid to the bloodstream Transport fats from the digestive tract to the bloodstream
Lymphatic System Chapter 14 Components Lymph is the fluid Vessels lymphatics Structures & organs Functions Return tissue fluid to the bloodstream Transport fats from the digestive tract to the bloodstream
CELLS, ORGANS, AND MOLECULES: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM THE CELLS OF THE BLOOD FROM AN IMMUNOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVE.
 CELLS, ORGANS, AND MOLECULES: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM THE CELLS OF THE BLOOD FROM AN IMMUNOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVE. Erythrocytes: Red blood cells (~5 x 10 6 / L) (~5 x 10 12 /L) of blood.
CELLS, ORGANS, AND MOLECULES: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM THE CELLS OF THE BLOOD FROM AN IMMUNOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVE. Erythrocytes: Red blood cells (~5 x 10 6 / L) (~5 x 10 12 /L) of blood.
The Development of Lymphocytes: B Cell Development in the Bone Marrow & Peripheral Lymphoid Tissue Deborah A. Lebman, Ph.D.
 The Development of Lymphocytes: B Cell Development in the Bone Marrow & Peripheral Lymphoid Tissue Deborah A. Lebman, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To understand how ordered Ig gene rearrangements lead to the development
The Development of Lymphocytes: B Cell Development in the Bone Marrow & Peripheral Lymphoid Tissue Deborah A. Lebman, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To understand how ordered Ig gene rearrangements lead to the development
Introduction. Introduction. Lymphocyte development (maturation)
 Introduction Abbas Chapter 8: Lymphocyte Development and the Rearrangement and Expression of Antigen Receptor Genes Christina Ciaccio, MD Children s Mercy Hospital January 5, 2009 Lymphocyte development
Introduction Abbas Chapter 8: Lymphocyte Development and the Rearrangement and Expression of Antigen Receptor Genes Christina Ciaccio, MD Children s Mercy Hospital January 5, 2009 Lymphocyte development
T Lymphocyte Activation and Costimulation. FOCiS. Lecture outline
 1 T Lymphocyte Activation and Costimulation Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family Inhibitory receptors of T cells Targeting costimulators for
1 T Lymphocyte Activation and Costimulation Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family Inhibitory receptors of T cells Targeting costimulators for
Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems
 Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems Note: Not all of the lymphatic system will be on the actual exam next Monday so disregard any questions that deal with something that wasn t covered
Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems Note: Not all of the lymphatic system will be on the actual exam next Monday so disregard any questions that deal with something that wasn t covered
IDENTIFYING THE MECHANISMS OF LYMPH NODE HYPERTROPHY IN ATHEROSCLEROTIC MICE. LEONG YEW FAI IVAN B.Sc (Hons.), NUS
 IDENTIFYING THE MECHANISMS OF LYMPH NODE HYPERTROPHY IN ATHEROSCLEROTIC MICE LEONG YEW FAI IVAN B.Sc (Hons.), NUS A THESIS SUBMITTED FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF MICROBIOLOGY NATIONAL
IDENTIFYING THE MECHANISMS OF LYMPH NODE HYPERTROPHY IN ATHEROSCLEROTIC MICE LEONG YEW FAI IVAN B.Sc (Hons.), NUS A THESIS SUBMITTED FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF MICROBIOLOGY NATIONAL
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 11 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 11 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY Functions of the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system has three primary functions. First of all, it returns excess interstitial
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 11 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY Functions of the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system has three primary functions. First of all, it returns excess interstitial
Immune system. Lecture(8 ) Dr.Baha,Hamdi.AL-Amiedi Ph.D.Microbiology
 Immune system Lecture(8 ) Dr.Baha,Hamdi.AL-Amiedi Ph.D.Microbiology Immune system :The Immune system comprise a network cells with each other cooperates directly to reach the effectors mechanism. and defense
Immune system Lecture(8 ) Dr.Baha,Hamdi.AL-Amiedi Ph.D.Microbiology Immune system :The Immune system comprise a network cells with each other cooperates directly to reach the effectors mechanism. and defense
Homing and Inflammation!
 Homing and Inflammation! Micro 204. Molecular and Cellular Immunology! Lecturer: Jason Cyster! jason.cyster@ucsf.edu! How do cells migrate from blood into tissue?! the four step model! role of selectins,
Homing and Inflammation! Micro 204. Molecular and Cellular Immunology! Lecturer: Jason Cyster! jason.cyster@ucsf.edu! How do cells migrate from blood into tissue?! the four step model! role of selectins,
Examples of questions for Cellular Immunology/Cellular Biology and Immunology
 Examples of questions for Cellular Immunology/Cellular Biology and Immunology Each student gets a set of 6 questions, so that each set contains different types of questions and that the set of questions
Examples of questions for Cellular Immunology/Cellular Biology and Immunology Each student gets a set of 6 questions, so that each set contains different types of questions and that the set of questions
CHAPTER VI PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY. Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer.
 CHAPTER VI PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. Lymphatic System: Lymphatic System which consists of vessels and organs plays two vital roles in our lives: 1) The vessels
CHAPTER VI PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. Lymphatic System: Lymphatic System which consists of vessels and organs plays two vital roles in our lives: 1) The vessels
Reticuloendothelial System (RES) & Spleen Dr. Nervana Bayoumy
 Haematology Lectures Reticuloendothelial System (RES) & Spleen Dr. Nervana Bayoumy 1 Objectives 1. Define the term Reticuloendothelial system (RES). 2. Describe the cellular components of RES. 3. Describe
Haematology Lectures Reticuloendothelial System (RES) & Spleen Dr. Nervana Bayoumy 1 Objectives 1. Define the term Reticuloendothelial system (RES). 2. Describe the cellular components of RES. 3. Describe
Chapter 1. Chapter 1 Concepts. MCMP422 Immunology and Biologics Immunology is important personally and professionally!
 MCMP422 Immunology and Biologics Immunology is important personally and professionally! Learn the language - use the glossary and index RNR - Reading, Note taking, Reviewing All materials in Chapters 1-3
MCMP422 Immunology and Biologics Immunology is important personally and professionally! Learn the language - use the glossary and index RNR - Reading, Note taking, Reviewing All materials in Chapters 1-3
FIT Board Review Corner March 2016
 FIT Board Review Corner March 2016 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Sarah Spriet, DO, and Tammy Peng, MD, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In-Training (FITs) to the
FIT Board Review Corner March 2016 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Sarah Spriet, DO, and Tammy Peng, MD, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In-Training (FITs) to the
Generation of post-germinal centre myeloma plasma B cell.
 Generation of post-germinal centre myeloma. DNA DAMAGE CXCR4 Homing to Lytic lesion activation CD38 CD138 CD56 Phenotypic markers Naive Secondary lymphoid organ Multiple myeloma is a malignancy of s caused
Generation of post-germinal centre myeloma. DNA DAMAGE CXCR4 Homing to Lytic lesion activation CD38 CD138 CD56 Phenotypic markers Naive Secondary lymphoid organ Multiple myeloma is a malignancy of s caused
3/17/2014. The Lymphatic System. Lymphatic System Overview Lymphatic Vessels and Flow of Lymph Lymphoid Cells, Tissues, and Organs
 The Lymphatic System Lymphatic System Overview Lymphatic Vessels and Flow of Lymph Lymphoid Cells, Tissues, and Organs Overview of the Lymphatic System Slide 2 Major Components of the Lymphatic System
The Lymphatic System Lymphatic System Overview Lymphatic Vessels and Flow of Lymph Lymphoid Cells, Tissues, and Organs Overview of the Lymphatic System Slide 2 Major Components of the Lymphatic System
Medical Virology Immunology. Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University
 Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Unit 5 The Human Immune Response to Infection
 Unit 5 The Human Immune Response to Infection Unit 5-page 1 FOM Chapter 21 Resistance and the Immune System: Innate Immunity Preview: In Chapter 21, we will learn about the branch of the immune system
Unit 5 The Human Immune Response to Infection Unit 5-page 1 FOM Chapter 21 Resistance and the Immune System: Innate Immunity Preview: In Chapter 21, we will learn about the branch of the immune system
Chapter 14. Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Chapter 14 Lymphatic System and Immunity 1 Introduction A. The lymphatic system is comprised of a network of vessels that transport body fluids, the cells and chemicals in those vessels and the organs
Chapter 14 Lymphatic System and Immunity 1 Introduction A. The lymphatic system is comprised of a network of vessels that transport body fluids, the cells and chemicals in those vessels and the organs
The Lymphatic System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Lymphatic System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Lymphatic System Lymphatic capillaries reabsorb excessive tissue fluid and transport the fluid through the lymphatic pathway, and ultimately dispose
The Lymphatic System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Lymphatic System Lymphatic capillaries reabsorb excessive tissue fluid and transport the fluid through the lymphatic pathway, and ultimately dispose
Development of B and T lymphocytes
 Development of B and T lymphocytes What will we discuss today? B-cell development T-cell development B- cell development overview Stem cell In periphery Pro-B cell Pre-B cell Immature B cell Mature B cell
Development of B and T lymphocytes What will we discuss today? B-cell development T-cell development B- cell development overview Stem cell In periphery Pro-B cell Pre-B cell Immature B cell Mature B cell
CHAPTER 16: LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY OBJECTIVES. Transport dietary fat. Transport excess tissue fluid back to blood stream
 CHAPTER 16: LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY OBJECTIVES 1. Name the organs that compose the lymphatic system and give three general functions performed by this system. Bone Marrow Control Disease Thymus Lymph
CHAPTER 16: LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY OBJECTIVES 1. Name the organs that compose the lymphatic system and give three general functions performed by this system. Bone Marrow Control Disease Thymus Lymph
B cell activation and antibody production. Abul K. Abbas UCSF
 1 B cell activation and antibody production Abul K. Abbas UCSF 2 Lecture outline B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production Therapeutic targeting of B cells 3 Principles of humoral
1 B cell activation and antibody production Abul K. Abbas UCSF 2 Lecture outline B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production Therapeutic targeting of B cells 3 Principles of humoral
IMMUNE CELL SURFACE RECEPTORS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS
 LECTURE: 07 Title: IMMUNE CELL SURFACE RECEPTORS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: The chemical nature of the cellular surface receptors. Define the location of the
LECTURE: 07 Title: IMMUNE CELL SURFACE RECEPTORS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: The chemical nature of the cellular surface receptors. Define the location of the
Chapter 19: IgE-Dependent Immune Responses and Allergic Disease
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 19 of Cellular and Molecular Immunology (Seventh Edition), by Abul K. Abbas, Andrew H. Lichtman and Shiv Pillai. Chapter 19: IgE-Dependent Immune Responses
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 19 of Cellular and Molecular Immunology (Seventh Edition), by Abul K. Abbas, Andrew H. Lichtman and Shiv Pillai. Chapter 19: IgE-Dependent Immune Responses
KEY - Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems - KEY
 KEY - Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems - KEY Note: Not all of the lymphatic system will be on the actual exam next Monday so disregard any questions that deal with something that
KEY - Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems - KEY Note: Not all of the lymphatic system will be on the actual exam next Monday so disregard any questions that deal with something that
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells. Part II: Cells (aka the Sentinels)
 Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
T cell-mediated immunity
 T cell-mediated immunity Overview For microbes within phagosomes in phagocytes.cd4+ T lymphocytes (TH1) Activate phagocyte by cytokines studies on Listeria monocytogenes For microbes infecting and replicating
T cell-mediated immunity Overview For microbes within phagosomes in phagocytes.cd4+ T lymphocytes (TH1) Activate phagocyte by cytokines studies on Listeria monocytogenes For microbes infecting and replicating
Lymphatic System & Immunity
 Lymphatic System & Immunity Arteriole Venule Tissue Blood Lymph cells capilla capillaries ries Lymphatic System -closely related to cardiovascular system -conducting system that carries fluid from extracellular
Lymphatic System & Immunity Arteriole Venule Tissue Blood Lymph cells capilla capillaries ries Lymphatic System -closely related to cardiovascular system -conducting system that carries fluid from extracellular
The Adaptive Immune Responses
 The Adaptive Immune Responses The two arms of the immune responses are; 1) the cell mediated, and 2) the humoral responses. In this chapter we will discuss the two responses in detail and we will start
The Adaptive Immune Responses The two arms of the immune responses are; 1) the cell mediated, and 2) the humoral responses. In this chapter we will discuss the two responses in detail and we will start
Principles of Adaptive Immunity
 Principles of Adaptive Immunity Chapter 3 Parham Hans de Haard 17 th of May 2010 Agenda Recognition molecules of adaptive immune system Features adaptive immune system Immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors
Principles of Adaptive Immunity Chapter 3 Parham Hans de Haard 17 th of May 2010 Agenda Recognition molecules of adaptive immune system Features adaptive immune system Immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors
Andrea s SI Session PCB Practice Test Test 3
 Practice Test Test 3 READ BEFORE STARTING PRACTICE TEST: Remember to please use this practice test as a tool to measure your knowledge, and DO NOT use it as your only tool to study for the test, since
Practice Test Test 3 READ BEFORE STARTING PRACTICE TEST: Remember to please use this practice test as a tool to measure your knowledge, and DO NOT use it as your only tool to study for the test, since
Immune System AP SBI4UP
 Immune System AP SBI4UP TYPES OF IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY ACQUIRED IMMUNITY EXTERNAL DEFENCES INTERNAL DEFENCES HUMORAL RESPONSE Skin Phagocytic Cells CELL- MEDIATED RESPONSE Mucus layer Antimicrobial
Immune System AP SBI4UP TYPES OF IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY ACQUIRED IMMUNITY EXTERNAL DEFENCES INTERNAL DEFENCES HUMORAL RESPONSE Skin Phagocytic Cells CELL- MEDIATED RESPONSE Mucus layer Antimicrobial
Paper No.: 10: Immunology Module : 04: Phylogeny and Ontogeny of immune system: Organization and structure of immune system.
 Paper No.: 10: Module : 04: Phylogeny and Ontogeny of immune system: Organization and Development Team Principal Investigator: Co-Principal Investigator: Paper Coordinator: Content Writer: Content Reviewer:
Paper No.: 10: Module : 04: Phylogeny and Ontogeny of immune system: Organization and Development Team Principal Investigator: Co-Principal Investigator: Paper Coordinator: Content Writer: Content Reviewer:
General Biology. A summary of innate and acquired immunity. 11. The Immune System. Repetition. The Lymphatic System. Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.
 A summary of innate and acquired immunity General iology INNATE IMMUNITY Rapid responses to a broad range of microbes Course No: NG00 Credits:.00 External defenses Invading microbes (pathogens). The Immune
A summary of innate and acquired immunity General iology INNATE IMMUNITY Rapid responses to a broad range of microbes Course No: NG00 Credits:.00 External defenses Invading microbes (pathogens). The Immune
Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system. Answer Sheet
 Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system Answer Sheet Q1 Which areas of the lymph node have most CD3 staining? A1 Most CD3 staining is present in the paracortex (T cell areas). This is towards the outside
Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system Answer Sheet Q1 Which areas of the lymph node have most CD3 staining? A1 Most CD3 staining is present in the paracortex (T cell areas). This is towards the outside
CHAPTER 9 BIOLOGY OF THE T LYMPHOCYTE
 CHAPTER 9 BIOLOGY OF THE T LYMPHOCYTE Coico, R., Sunshine, G., (2009) Immunology : a short course, 6 th Ed., Wiley-Blackwell 1 CHAPTER 9 : Biology of The T Lymphocytes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Introduction
CHAPTER 9 BIOLOGY OF THE T LYMPHOCYTE Coico, R., Sunshine, G., (2009) Immunology : a short course, 6 th Ed., Wiley-Blackwell 1 CHAPTER 9 : Biology of The T Lymphocytes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Introduction
Introduction to Immunology Part 2 September 30, Dan Stetson
 Introduction to Immunology Part 2 September 30, 2016 Dan Stetson stetson@uw.edu 441 Lecture #2 Slide 1 of 26 CLASS ANNOUNCEMENT PLEASE NO TREE NUTS IN CLASS!!! (Peanuts, walnuts, almonds, cashews, etc)
Introduction to Immunology Part 2 September 30, 2016 Dan Stetson stetson@uw.edu 441 Lecture #2 Slide 1 of 26 CLASS ANNOUNCEMENT PLEASE NO TREE NUTS IN CLASS!!! (Peanuts, walnuts, almonds, cashews, etc)
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley
 Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam #2 Name: Instructions This exam consists of 50 questions. You may write on the exam itself, but be sure to answer all your questions on a Scantron
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam #2 Name: Instructions This exam consists of 50 questions. You may write on the exam itself, but be sure to answer all your questions on a Scantron
