The Role of the Scaffolding Protein Tks4 in EGF Signaling. Gábor Bőgel. Semmelweis University Molceular Medicine PhD School
|
|
|
- Archibald Boone
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Role of the Scaffolding Protein Tks4 in EGF Signaling PhD Theses Gábor Bőgel Semmelweis University Molceular Medicine PhD School Supervisor: Dr. László Buday MD, D.Sc. Official reviewers: Dr. Beáta Lontay, Ph.D. Dr. László Csanády, Ph.D. Head of the final examination committee: Dr. László Tretter, D.Sc. Members of the final examination committee: Dr. Gabriella Sármay, D.Sc. Dr. Gábor Czirják, PhD Budapest 2013
2 1. Introduction 1.1. Structure of the Scaffolding Proteins Tks5 and Tks4 The Tks5 scaffolding protein was first identified in 1998 as a novel substrate of the non-receptor tyrosine kinase Src. It has an N-terminal PX (phox-homology) domain capable of binding membrane lipids and five SH3 domains which are well-known protein-protein interaction modules. The linker regions between the SH3 domains contain several proline rich regions which may also participate in the interaction of Tks5 with other proteins. This structure suggests that the protein may play the role of a scaffold in signaling pathways. Tks4 was recently identified as a homolog of Tks5 with a somewhat broader expression pattern. Its structure is very similar to that of Tks5 but it has only four SH3 domains The PX domain The PX domain was first identified in the p40 phox and p47 phox proteins as a lipid-binding conserved domain. Now, at least 49 PX domain-containing proteins are known in mammals. Most of these proteins are involved in the regulation of endocytic trafficking. According to structural and functional data the most important binding partners of PX domains seem to be phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PI3P), a product of PI3-kinases. PX domains have several conserved basic amino acid residues mostly arginines participated in 1
3 this interaction. Nevertheless, some PX domains were also shown to bind other phosphorylated inositol lipids and there are also data suggesting a role of PX domains in protein-protein interactions The SH3 domains SH3 domains are widespread protein-protein interaction modules among signaling proteins. Although in most of the cases they bind proteins with proline-rich sequences it has also been shown that some of them bind to partners lacking such an element. An interesting possibility is the regulation SH3 domain function by phosphorylation of binding partners or the domain itself. In most of the cases this leads to a decreased binding affinity. Biochemical data suggest that the first two SH3 domains of the Tks4 and Tks5 proteins may function together as a super-sh3 domain, that is they might be able to bind proteins with a common interface The Physiological and Pathological Roles of Tks5 and Tks Podosomes and invadopodia Both Tks5 and Tks4 are currently best known for their roles played in actin-rich ventral extensions called podosomes and invadopodia. These structures were first observed in Src-transformed cells as subcellular structures capable of binding and degrading the extracellular matrix. Now, it is known that they are not only present in transformed cells but also in some specialized cell types, such as macrophages or 2
4 osteoclasts. Although recent reviews on the subject suggest that that the name invadopodium should only be used for transformed or cancerous cells while the word podosome should refer to their physiological counterparts, the two designations are still often used interchangeably in the literature. Both Tks4 and Tks5 were shown to be localized to invadopodia and according to currently available data both of the proteins are also required for the formation of these invasive structures. Tks4 and Tks5 were also shown to bind several proteins present in invadopodia, such as members of the ADAM family of proteases, the cell adhesion molecule dystoglycan and the actin regulatory protein N-WASP. It has to be noted that although invadopodia are thought to play a role in tumor invasion it has been shown experimentally that knocking down Tks5 in Src transformed cells does not effectively inhibit their capability to form metastases. However, it does lead to a significant reduction in the size of the metastases due to reduced vascularization Regulation of NADPH oxidases As the closest relatives of Tks4 and Tks5 are proteins regulating the activity of the NADPH oxidase family of enzymes it has been investigated if these scaffolding proteins also play a role in this process. Although there are data in the literature supporting this possibility it is still not clear if these scaffolding proteins indeed contribute to the production of reactive oxygen species under physiological or pathological conditions. 3
5 Ontogenesis Investigation of animal models and a rare human genetic disease suggest a role for Tks4 and Tks5 in vertebrate ontogenesis. Mice lacking a functional Tks4 gene show a characteristic phenotype. Leading symptoms are reduced body size, cranial and other skeletal deformities, mineralization defects, glaucoma and infertility. Very similar symptoms were observed in patients with a rare genetic disease called the Frank ter Haar syndrome. Genetic analysis showed that 7 out of 13 families carrying the diseases had mutations in the gene coding for Tks4. Interestingly, while most of the mutations lead to the complete loss of a functional Tks4 protein, in one of the families Tks4 was only affected by a point mutation. This mutation causes the replacement of a conserved arginine in the PX domain of the protein to tryptophan. Although the mechanism underlying these symptoms is not clear it is very likely that podosome-dependent or - independent cell migration plays an important role in the pathomechanism. It is also interesting that Tks4 was shown to be required for in vitro adipocyte differentiation, a function obviously independent of podosomes. 4
6 2. Major Research Goals The cdna of Tks4 was first cloned and its sequence deposited to the EMBL databank by Miklós Geiszt and Árpád Lányi. During their investigations they showed that Tks4 is localized to actin-rich membrane ruffles in EGF-treated mammalian cells and knocking down the gene inhibits the formation of these structures. Since the major research area of our laboratory is the investigation of EGF signaling to the actin cytoskeleton, we continued to investigate the function of Tks4 in collaboration with Miklós Geiszt s and Árpád Lányi s laboratories. The major questions we asked were the following: 1. Does Tks4 become phosphorylated upon EGF treatment of cells? 2. If yes, which kinases can be responsible for this covalent modification and which side chains can be phosphorylated? 3. What is the role of the PX domain of Tks4? 4. Does Tks4 play a role in the regulation of the actin cytoskeleton? 5
7 3. Materials and Methods 3.1. Plasmids and Constructs The vector encoding V5-Tks4 was a kind gift of Dr. Miklós Geiszt. pgex plasmids with the N (aa ) and C terminal (aa ) parts of cortactin were created using PCR based cloning. Point mutations were introduced using the QuickChange kit from Agilent Technologies Cell Lines and Transfection All cell lines used were cultured in Dulbecco s Modified Eagle s Medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum and antibiotics. This was replaced with serum free mediums one night before treating cells with EGF. Transient transfections were carried out using the Lipofectamine reagent from Invitrogen RNA Interference Tks4 specific sirna was introduced to the cells in 40 nm final concentration using the Lipofectamine RNAiMAX reagent. The control sirna contained four point mutations relative to the effective RNA used. Knockdown of Tks4 was controlled by Western blotting 48 hours after transfection. The sirna resistant version of Tks4 containing five silent point mutations in the sequence recognized by the sirna was also used. 6
8 3.4. Antibodies Most of the antibodies used were obtained from commercial sources. The Tks4 specific polyclonal antiserum were custom made for our laboratory by immunizing rabbits with a part of Tks4 expressed as a GST fusion protein Immunoprecipitation and Western Blotting Cells were harvested using a buffer containing Triton and protease inhibitors. Immunoprecipitations were done using anti-v5 Sepharose or Protein A Sepharose with the appropriate antibody. Cell lysates and immunoprecipitates were separated by SDS-PAGE and then blotted to nitrocellulose membranes. Western blot detection was carried out with HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies and an ECL detection kit Immunofluorescent Staining Cells were cultured in low density on glass coverslips. After transfection and appropriate treatment cells were fixed with paraformaldehyde and stained with unlabeled primary and fluorescently-labeled secondary antibodies. DAPI was used for staining cell nuclei. Images were taken with the confocal microscope Zeiss LSM GST Fusion Proteins GST fusion proteins were produced in E.coli and affinity purified with glutathione-agarose beads. The 7
9 beads were incubated with cell lysates in order to identify binding proteins. For the in vitro lipid binding assay, GST fusion proteins were eluted from the glutathione-agarose beads using a buffer containing reduced glutathione. The expression and purification of proteins were verified by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie staining In Vitro Lipid Binding The binding of purified GST-PX domains to membrane lipids was assayed using LipidStrips from Invitrogen. The membranes were blocked with fatty acid free BSA and then incubated with the appropriate protein. Bound proteins were detected by anti-gst antibodies Cell Migration Assay For our experiments we used the QCM 24-Well Colorimetric Cell Migation Assay kit from Millipore according to the manufacturer s instructions. 10% FBS or 200 ng/ml EGF were used as chemoattractants. Migrated cells were quantified by staining and photometry. 8
10 4. Results 4.1. Tks4 Becomes Phosphorylated and Associates with the EGF Receptor in EGF- Treated Cells In order to assess Tks4 tyrosine phosphorylation in response to EGF treatment V5-Tks4 transfected COS7 cells were serum-starved overnight and then treated with 100ng/mL EGF for 10 minutes. V5-Tks4 was immunoprecipitated and phosphorylation was assessed by anti-phosphotyrosine Western blotting. Interestingly, we could not only detect the phosphorylation of Tks4 but we also observed a phsophorylated protein with a molecular mass of approximately 170kDa. This band was identified as the EGF receptor using specific antibodies. The experiment was later repeated with endogenous Tks4 immunoprecipitated with specific antiserum and gave a similar result The Non-Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Src Phosphorylates Tks4 upon EGF Treatment Tks4 is a well-known substrate of the non-receptor tyrosine kinase Src. It is also known from the literature that Src is activated downstream of the EGF receptor. Therefore, Src was the most probable candidate for phosphorylating Tks4 in the investigated system. To test this hypothesis, PP1 a specific inhibitor of Src was used. 9
11 In our experiments we showed that pretreating cells with PP1 for one hour nearly completely prevents tyrosine phosphorylation of Tks4 upon EGF treatment. To further verify our hypothesis, we created a mutant V5-Tks4 construct by changing all three tyrosine residues known to be phosphorylated by Src to phenylalanine. We could not detect the phosphorylation of this protein after 10 minutes of EGF treatment, what further supports our presumption that Src phosphorylates Tks4 in this setting Src Associates with Tks4 in EGFstimulated Cells In many cases Src establishes a long-term contact with its substrates. To test this possibility V5-Tks4 was immunoprecipitated from serum-starved and EGF-treated cells. After resolving the samples by SDS-PAGE we performed a Western blot using monoclonal anti-src antibodies. Using this experimental procedure we could show that Src indeed associates with Tks4 in EGF treated but not in unstimulated cells Binding of the PX Domain to PI3K Lipid Products is Required for the Membrane Translocation and Phosphorylation of Tks4 According to the current literature the major binding partners of PX domains are lipid products of the PI 3- kinase. It was known from earlier experiments of Dr. Geiszt s laboratory that Tks4 is transolcated to membrane ruffles in EGF-treated cells and membrane translocation of the protein is also supported by our result concerning the association between Tks4 and the EGF receptor. 10
12 Since it is well known that PI 3-kinases are activated in EGF stimulated cells we tested if the PX domain of Tks4 contributes to its membrane translocation. First we showed that in cells pretreated with a specific inhibitor of PI3-kinases (LY294002) Tks4 is hardly present at the plasma membrane of EGF treated cells. This suggests a role of the PX domain in membrane translocation. As the phosphorylation of Tks4 most probably takes place close to the plasma membrane we also tested if Tks4 can be phosphorylated if PI 3-kinases are inhibited. Using immunoprecipitation and Western blotting we could show that the phosphorylation of Tks4 is inhibited by LY To further verify that an intact PX domain is required for the phosphorylation of Tks4 we showed that the mutation of two conservative arginine residues to leucine (R71,94L) prevents the phophorylation of Tks4 upon EGF treatment The R43W Mutant of Tks4 is not Able to Bind Membrane Lipids The R43W mutation of Tks4 was identified in one of the investigated Frank ter Haar syndrome families. As this point mutation lead to the presence of the same symptoms as the complete lack of the protein we decided to investigate the effects of this amino acid change. First we expressed the wild type and R43W mutant forms of the Tks4 PX domain as GST fusion proteins. Proteins were eluted from a glutathione-agarose beads using a buffer containing reduced glutathione. PIPStrip 11
13 membranes were incubated with the proteins and than developed with anti-gst antibodies. While the wild type form was found to be associated with several phosphorylated inositol lipids the R43W mutant showed no specific binding to any of the investigated membrane components. This result suggests that the mutation of the conserved arginine 43 leads to the loss of lipid binding by the PX domain The R43W Mutant Aggregates in Cells In order to investigate the ability of the Tks4 R43W mutant to be translocated to the cell membrane where it can be phosphorylated we overexpressed the mutant protein in COS7 cells. By immunoprecipitation and Western blotting we could not detect the phosphorylation of Tks4. Interestingly, the expression of the mutant form was consequently and significantly lower than that of the wild type protein. Using immunofluorescent staining of the overexpressed proteins we could show that the R43W mutant aggregates in most of the cells and is often found sequestered in socalled aggresomes in the proximity of the nucleus. This might also be an explanation for the seemingly lower expression of the mutant protein on Western blots The SH3 Domain of Cortactin is Able to Bind Tks4 As early experiments of Dr. Gieszt s group showed that Tks4 and the actin regulatory protein cortactin colocalize in EGF-induced membrane ruffles we tested the possibility of a direct interaction between the two proteins. In order to asses this we expressed N- and C- 12
14 terminal parts of cortactin as GST fusion proteins and tested their ability to bind Tks4 in cell lysates. Using this method we could show that the C-terminal part of cortactin which posesses the SH3 domain of the protein could directly interact with Tks4. This interaction was abolished if a conserved tryptophan residue in the cortactin SH3 domain was mutated to lysine (W525K mutation) Silencing of Tks4 Inhibits Cell Spreading If cells in suspension are allowed to attach to a fibronectin-coated solid surface they begin to spread due to actin polymerization beneath the cell membrane, a process triggered by integrin engagement. Together with our collaborative partners we made use of this method in order to investigate the possible role of Tks4 in the regulation of the actin cytoskeleton. HeLa cell clones expressing a Tks4 specific shrna or ineffective scrambled shrna were seeded to fibronectincoated cover glasses and were allowed to spread for 30 minutes. Measuring average cell surface areas showed that clones with reduced Tks4 levels were less spread than the control cell lines Silencing of Tks4 Inhibits Cell Migration To further asses the role of Tks4 in regulating the actin cytoskeleton we tested the ability of Tks4-silenced cells to migrate in the direction of an EGF or serum gradient. Using a Boyden chamber based assay we showed that silencing of Tks4 by sirna causes a marked reduction of 13
15 cell motility in the direction of both chemoattractants used. To verify that this effect is indeed caused by reduced levels of Tks4 and not by off-target effects of the sirna used we re-expressed an sirna resistant form of Tks4 and showed that it nearly completely restored the ability of migration of the cells. 14
16 5. Conclusions From our research data we came to the following major conclusions: 1. Upon EGF treatement of COS7 cells the scaffolding protein Tks4 becomes phosphorylated on tyrosine residues and associates with the EGF receptor. 2. The abovementioned tyrosine phosphorylation is very likely to be mediated by the non-receptor tyrosine kinase Src which is also associated with Tks4 in EGF-treated cells. 3. We have shown that PI 3-kinase activity is required for the membrane translocation and tyrosine phosphorylation of Tks4. 4. We conclude furthermore that the point mutation R43W which was found in a Frank ter Haar syndrome family causes misfolding and aggregation of Tks4 in cells. 5. We have shown using RNA interference-based experiments that Tks4 is required for cell spreading and migration of HeLa cells in response to EGF and serum. 15
17 6. List of Publications 6.1. Publications Directly Concerning the Subject of the Dissertation 1. Lanyi A, Barath M, Peterfi Z, Bogel G, Orient A, Simon T, Petrovszki E, Kis-Toth K, Sirokmany G, Rajnavolgyi E, Terhorst C, Buday L, Geiszt M (2011) The homolog of the five SH3-domain protein (HOFI/SH3PXD2B) regulates lamellipodia formation and cell spreading. PLoS One 6: e Bogel G, Gujdar A, Geiszt M, Lanyi A, Fekete A, Sipeki S, Downward J, Buday L (2012) Frank-ter Haar syndrome protein Tks4 regulates epidermal growth factor-dependent cell migration. J Biol Chem 287: Other Publications 1. Illes A, Enyedi B, Tamas P, Balazs A, Bogel G, Buday L (2006) Inducible phosphorylation of cortactin is not necessary for cortactin-mediated actin polymerisation. Cell Signal 18: Illes A, Enyedi B, Tamas P, Balazs A, Bogel G, Melinda, Lukacs, Buday L (2006) Cortactin is required for integrin-mediated cell spreading. Immunol Lett 104:
18 3. Pesti S, Balazs A, Udupa R, Szabo B, Fekete A, Bogel G, Buday L (2012) Complex formation of EphB1/Nck/Caskin1 leads to tyrosine phosphorylation and structural changes of the Caskin1 SH3 domain. Cell Commun Signal 10:
The role of the scaffolding protein Tks5 in EGF signaling
 The role of the scaffolding protein Tks5 in EGF signaling PhD Thesis Anna Fekete Doctoral School in Biology Head of the School: Dr. Anna Erdei Structural Biochemistry Doctoral Program Head of the Program:
The role of the scaffolding protein Tks5 in EGF signaling PhD Thesis Anna Fekete Doctoral School in Biology Head of the School: Dr. Anna Erdei Structural Biochemistry Doctoral Program Head of the Program:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplements. Figure S1. B Phalloidin Alexa488
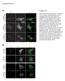 Supplements A, DMSO, PP2, PP3 Crk-myc Figure S1. (A) Src kinase activity is necessary for recruitment of Crk to Nephrin cytoplasmic domain. Human podocytes expressing /7-NephrinCD () were treated with
Supplements A, DMSO, PP2, PP3 Crk-myc Figure S1. (A) Src kinase activity is necessary for recruitment of Crk to Nephrin cytoplasmic domain. Human podocytes expressing /7-NephrinCD () were treated with
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature9814 a A SHARPIN FL B SHARPIN ΔNZF C SHARPIN T38L, F39V b His-SHARPIN FL -1xUb -2xUb -4xUb α-his c Linear 4xUb -SHARPIN FL -SHARPIN TF_LV -SHARPINΔNZF -SHARPIN
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature9814 a A SHARPIN FL B SHARPIN ΔNZF C SHARPIN T38L, F39V b His-SHARPIN FL -1xUb -2xUb -4xUb α-his c Linear 4xUb -SHARPIN FL -SHARPIN TF_LV -SHARPINΔNZF -SHARPIN
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
The functional investigation of the interaction between TATA-associated factor 3 (TAF3) and p53 protein
 THESIS BOOK The functional investigation of the interaction between TATA-associated factor 3 (TAF3) and p53 protein Orsolya Buzás-Bereczki Supervisors: Dr. Éva Bálint Dr. Imre Miklós Boros University of
THESIS BOOK The functional investigation of the interaction between TATA-associated factor 3 (TAF3) and p53 protein Orsolya Buzás-Bereczki Supervisors: Dr. Éva Bálint Dr. Imre Miklós Boros University of
Supplemental information
 Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer
 Supplementary Information TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer Yabing Mu, Reshma Sundar, Noopur Thakur, Maria Ekman, Shyam Kumar Gudey, Mariya
Supplementary Information TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer Yabing Mu, Reshma Sundar, Noopur Thakur, Maria Ekman, Shyam Kumar Gudey, Mariya
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
The Src Substrate Tks5, Podosomes (Invadopodia), and Cancer Cell Invasion
 The Src Substrate Tks5, Podosomes (Invadopodia), and Cancer Cell Invasion S.A. COURTNEIDGE, * E.F. AZUCENA JR., * I. PASS, * D.F. SEALS, * AND L. TESFAY * * The Van Andel Research Institute, Grand Rapids,
The Src Substrate Tks5, Podosomes (Invadopodia), and Cancer Cell Invasion S.A. COURTNEIDGE, * E.F. AZUCENA JR., * I. PASS, * D.F. SEALS, * AND L. TESFAY * * The Van Andel Research Institute, Grand Rapids,
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.3866
 Nature Immunology: doi:10.1038/ni.3866 Supplementary Figure 1 The effect of TIPE2 on chemotaxis. a, The expression of TIPE2 in dhl-60c, dhl-60t, TIPE2-expressing and 15/16Q-expressing dhl-60t neutrophils
Nature Immunology: doi:10.1038/ni.3866 Supplementary Figure 1 The effect of TIPE2 on chemotaxis. a, The expression of TIPE2 in dhl-60c, dhl-60t, TIPE2-expressing and 15/16Q-expressing dhl-60t neutrophils
SUPPLEMENT. Materials and methods
 SUPPLEMENT Materials and methods Cell culture and reagents Cell media and reagents were from Invitrogen unless otherwise indicated. Antibiotics and Tet-certified serum were from Clontech. In experiments
SUPPLEMENT Materials and methods Cell culture and reagents Cell media and reagents were from Invitrogen unless otherwise indicated. Antibiotics and Tet-certified serum were from Clontech. In experiments
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES, LEGENDS AND METHODS
 A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures S1-S9. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit
 Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 0 3 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Ab-473) Antibody E021054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit Akt (Phospho-Ser473) Antibody
Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 0 3 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Ab-473) Antibody E021054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit Akt (Phospho-Ser473) Antibody
Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression. Quantitative real-time PCR of indicated mrnas in DCs stimulated with TLR2-Dectin-1 agonist zymosan
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression. Quantitative real-time PCR of indicated mrnas in DCs stimulated with TLR2-Dectin-1 agonist zymosan
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
William C. Comb, Jessica E. Hutti, Patricia Cogswell, Lewis C. Cantley, and Albert S. Baldwin
 Molecular Cell, Volume 45 Supplemental Information p85 SH2 Domain Phosphorylation by IKK Promotes Feedback Inhibition of PI3K and Akt in Response to Cellular Starvation William C. Comb, Jessica E. Hutti,
Molecular Cell, Volume 45 Supplemental Information p85 SH2 Domain Phosphorylation by IKK Promotes Feedback Inhibition of PI3K and Akt in Response to Cellular Starvation William C. Comb, Jessica E. Hutti,
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting. protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in. acute kidney injury
 Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1: Endogenous interaction between RNF2 and H2AX: Whole cell extracts from 293T were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-rnf2 or anti-γ-h2ax antibodies
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1: Endogenous interaction between RNF2 and H2AX: Whole cell extracts from 293T were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-rnf2 or anti-γ-h2ax antibodies
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet
 Website: thermofisher.com Customer Service (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 1 Technical Support (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 441 TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet Details
Website: thermofisher.com Customer Service (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 1 Technical Support (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 441 TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet Details
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the
 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the location of the transmembrane (TM), FRM binding (FB)
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the location of the transmembrane (TM), FRM binding (FB)
Characterization of the role of EGF-A of low density lipoprotein receptor in PCSK9 binding
 Characterization of the role of EGF-A of low density lipoprotein receptor in PCSK9 binding Hong-mei Gu, 1 Ayinuer Adijiang, 1 Matthew Mah, and Da-wei Zhang 2 Departments of Pediatrics and Biochemistry,
Characterization of the role of EGF-A of low density lipoprotein receptor in PCSK9 binding Hong-mei Gu, 1 Ayinuer Adijiang, 1 Matthew Mah, and Da-wei Zhang 2 Departments of Pediatrics and Biochemistry,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Table 1. Cell sphingolipids and S1P bound to endogenous TRAF2. Sphingolipid Cell pmol/mg TRAF2 immunoprecipitate pmol/mg Sphingomyelin 4200 ± 250 Not detected Monohexosylceramide 311 ± 18
Supplementary Table 1. Cell sphingolipids and S1P bound to endogenous TRAF2. Sphingolipid Cell pmol/mg TRAF2 immunoprecipitate pmol/mg Sphingomyelin 4200 ± 250 Not detected Monohexosylceramide 311 ± 18
Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were
 Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were isolated from wild type (PKC-θ- WT) or PKC-θ null (PKC-θ-KO)
Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were isolated from wild type (PKC-θ- WT) or PKC-θ null (PKC-θ-KO)
Procaspase-3. Cleaved caspase-3. actin. Cytochrome C (10 M) Z-VAD-fmk. Procaspase-3. Cleaved caspase-3. actin. Z-VAD-fmk
 A HeLa actin - + + - - + Cytochrome C (1 M) Z-VAD-fmk PMN - + + - - + actin Cytochrome C (1 M) Z-VAD-fmk Figure S1. (A) Pan-caspase inhibitor z-vad-fmk inhibits cytochrome c- mediated procaspase-3 cleavage.
A HeLa actin - + + - - + Cytochrome C (1 M) Z-VAD-fmk PMN - + + - - + actin Cytochrome C (1 M) Z-VAD-fmk Figure S1. (A) Pan-caspase inhibitor z-vad-fmk inhibits cytochrome c- mediated procaspase-3 cleavage.
Phosphoserine Detection Kit
 Kit 0701/PSER-KIT 02/080507 Background and Specificity extracellular signals to the nucleus. Phosphorylated epitopes may serve as docking sites for the assembley of protein complexes or may alter the 3-dimensional
Kit 0701/PSER-KIT 02/080507 Background and Specificity extracellular signals to the nucleus. Phosphorylated epitopes may serve as docking sites for the assembley of protein complexes or may alter the 3-dimensional
Nck Adapter Regulates Actin Polymerization in NIH 3T3 Fibroblasts in Response to Platelet-Derived Growth Factor bb
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, Nov. 2000, p. 7867 7880 Vol. 20, No. 21 0270-7306/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Nck Adapter Regulates Actin Polymerization
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, Nov. 2000, p. 7867 7880 Vol. 20, No. 21 0270-7306/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Nck Adapter Regulates Actin Polymerization
Effects of Second Messengers
 Effects of Second Messengers Inositol trisphosphate Diacylglycerol Opens Calcium Channels Binding to IP 3 -gated Channel Cooperative binding Activates Protein Kinase C is required Phosphorylation of many
Effects of Second Messengers Inositol trisphosphate Diacylglycerol Opens Calcium Channels Binding to IP 3 -gated Channel Cooperative binding Activates Protein Kinase C is required Phosphorylation of many
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11700 Figure 1: RIP3 as a potential Sirt2 interacting protein. Transfected Flag-tagged Sirt2 was immunoprecipitated from cells and eluted from the Sepharose beads using Flag peptide.
doi:10.1038/nature11700 Figure 1: RIP3 as a potential Sirt2 interacting protein. Transfected Flag-tagged Sirt2 was immunoprecipitated from cells and eluted from the Sepharose beads using Flag peptide.
Fang et al. NMuMG. PyVmT unstained Anti-CCR2-PE MDA-MB MCF MCF10A
 A NMuMG PyVmT 16.5+.5 47.+7.2 Fang et al. unstained Anti-CCR2-PE 4T1 Control 37.6+6.3 56.1+.65 MCF1A 16.1+3. MCF-7 3.1+5.4 MDA-M-231 42.1+5.5 unstained Secondary antibody only Anti-CCR2 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE
A NMuMG PyVmT 16.5+.5 47.+7.2 Fang et al. unstained Anti-CCR2-PE 4T1 Control 37.6+6.3 56.1+.65 MCF1A 16.1+3. MCF-7 3.1+5.4 MDA-M-231 42.1+5.5 unstained Secondary antibody only Anti-CCR2 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE
Dramatic increase in SHP2 binding activity of Helicobacter. pylori Western CagA by EPIYA-C duplication: its
 Supplementary Information Dramatic increase in SHP2 binding activity of Helicobacter pylori Western CagA by EPIYA-C duplication: its implications in gastric carcinogenesis Lisa Nagase, Takeru Hayashi,
Supplementary Information Dramatic increase in SHP2 binding activity of Helicobacter pylori Western CagA by EPIYA-C duplication: its implications in gastric carcinogenesis Lisa Nagase, Takeru Hayashi,
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/364/ra18/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The tyrosine phosphatase (Pez) inhibits metastasis by altering protein trafficking Leila Belle, Naveid Ali, Ana Lonic,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/364/ra18/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The tyrosine phosphatase (Pez) inhibits metastasis by altering protein trafficking Leila Belle, Naveid Ali, Ana Lonic,
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Gene Expression Analysis: Immunoblot analysis: Immunohistochemistry:
 General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
G-Protein Signaling. Introduction to intracellular signaling. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 G-Protein Signaling Introduction to intracellular signaling Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Cell signaling Cells communicate via extracellular signaling molecules (Hormones, growth factors and neurotransmitters
G-Protein Signaling Introduction to intracellular signaling Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Cell signaling Cells communicate via extracellular signaling molecules (Hormones, growth factors and neurotransmitters
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure S1: Fibroblast-induced elongation of cancer cells requires direct contact with living fibroblasts. A. Representative images of HT29-GFP cultured in the presence
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure S1: Fibroblast-induced elongation of cancer cells requires direct contact with living fibroblasts. A. Representative images of HT29-GFP cultured in the presence
NF-κB p65 (Phospho-Thr254)
 Assay Biotechnology Company www.assaybiotech.com Tel: 1-877-883-7988 Fax: 1-877-610-9758 NF-κB p65 (Phospho-Thr254) Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit Catalog #: OKAG02015 Please read the provided manual
Assay Biotechnology Company www.assaybiotech.com Tel: 1-877-883-7988 Fax: 1-877-610-9758 NF-κB p65 (Phospho-Thr254) Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit Catalog #: OKAG02015 Please read the provided manual
The Role of Sorting Nexins in Antigen Presentation
 The Role of Sorting Nexins in Antigen Presentation Chng X.R.J 1 and Wong S.H. 2 Department of Microbiology Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore Block MD4, 5 Science Drive 2,
The Role of Sorting Nexins in Antigen Presentation Chng X.R.J 1 and Wong S.H. 2 Department of Microbiology Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore Block MD4, 5 Science Drive 2,
Study of different types of ubiquitination
 Study of different types of ubiquitination Rudi Beyaert (rudi.beyaert@irc.vib-ugent.be) VIB UGent Center for Inflammation Research Ghent, Belgium VIB Training Novel Proteomics Tools: Identifying PTMs October
Study of different types of ubiquitination Rudi Beyaert (rudi.beyaert@irc.vib-ugent.be) VIB UGent Center for Inflammation Research Ghent, Belgium VIB Training Novel Proteomics Tools: Identifying PTMs October
Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis
 Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in ovarian cancer cells. (c) Western blot analysis
Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in ovarian cancer cells. (c) Western blot analysis
Anti-Lamin B1/LMNB1 Picoband Antibody
 Anti-Lamin B1/LMNB1 Picoband Antibody Catalog Number:PB9611 About LMNB1 Lamin-B1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LMNB1 gene. The nuclear lamina consists of a two-dimensional matrix of proteins
Anti-Lamin B1/LMNB1 Picoband Antibody Catalog Number:PB9611 About LMNB1 Lamin-B1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LMNB1 gene. The nuclear lamina consists of a two-dimensional matrix of proteins
Signal Transduction Cascades
 Signal Transduction Cascades Contents of this page: Kinases & phosphatases Protein Kinase A (camp-dependent protein kinase) G-protein signal cascade Structure of G-proteins Small GTP-binding proteins,
Signal Transduction Cascades Contents of this page: Kinases & phosphatases Protein Kinase A (camp-dependent protein kinase) G-protein signal cascade Structure of G-proteins Small GTP-binding proteins,
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates. Store Operated Calcium Entry
 TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 24, 2003
 7.06 Spring 2003 Exam 3 Name 1 of 8 7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 24, 2003 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books and notes. Please write your answers to the questions in the
7.06 Spring 2003 Exam 3 Name 1 of 8 7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 24, 2003 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books and notes. Please write your answers to the questions in the
B cell activation from actin rearrangements to cell survival
 B cell activation from actin rearrangements to cell survival Ph.D. thesis Maus Máté Supervisor: Prof. Sármay Gabriella D.Sc. Biology Doctoral School Immunology Programme Programme leader: Prof. Anna Erdei
B cell activation from actin rearrangements to cell survival Ph.D. thesis Maus Máté Supervisor: Prof. Sármay Gabriella D.Sc. Biology Doctoral School Immunology Programme Programme leader: Prof. Anna Erdei
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate. immune responses by maintaining Btk activation
 Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Signaling. Dr. Sujata Persad Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research
 Signaling Dr. Sujata Persad 3-020 Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research E-mail:sujata.persad@ualberta.ca 1 Growth Factor Receptors and Other Signaling Pathways What we will cover today: How
Signaling Dr. Sujata Persad 3-020 Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research E-mail:sujata.persad@ualberta.ca 1 Growth Factor Receptors and Other Signaling Pathways What we will cover today: How
hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
BIO360 Quiz #1. September 14, Name five of the six Hallmarks of Cancer (not emerging hallmarks or enabling characteristics ): (5 points)
 Name: BIO360 Quiz #1 September 14, 2012 1. Name five of the six Hallmarks of Cancer (not emerging hallmarks or enabling characteristics ): (5 points) 2. The controversial hypothesis that only a small subset
Name: BIO360 Quiz #1 September 14, 2012 1. Name five of the six Hallmarks of Cancer (not emerging hallmarks or enabling characteristics ): (5 points) 2. The controversial hypothesis that only a small subset
CA Tel.: ; Fax: ; ucsd.edu.
 THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY VOL. 283, NO. 10, pp. 6300 6311, March 7, 2008 2008 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in the U.S.A. The Phosphatase PHLPP
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY VOL. 283, NO. 10, pp. 6300 6311, March 7, 2008 2008 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in the U.S.A. The Phosphatase PHLPP
Supplementary information. MARCH8 inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins
 Supplementary information inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins Takuya Tada, Yanzhao Zhang, Takayoshi Koyama, Minoru Tobiume, Yasuko Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Shoji
Supplementary information inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins Takuya Tada, Yanzhao Zhang, Takayoshi Koyama, Minoru Tobiume, Yasuko Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Shoji
ab SREBP-2 Translocation Assay Kit (Cell-Based)
 ab133114 SREBP-2 Translocation Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For analysis of translocation of SREBP-2 into nuclei. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab133114 SREBP-2 Translocation Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For analysis of translocation of SREBP-2 into nuclei. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
Invadopodia are matrix-degrading membrane protrusions
 Published Online: 24 August, 2009 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200812176 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on July 14, 2018 JCB: ARTICLE Cortactin regulates cofilin and N-WASp activities to control
Published Online: 24 August, 2009 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200812176 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on July 14, 2018 JCB: ARTICLE Cortactin regulates cofilin and N-WASp activities to control
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system
 Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
UIM domain-dependent recruitment of the endocytic adaptor protein Eps15 to ubiquitin-enriched endosomes
 UIM domain-dependent recruitment of the endocytic adaptor protein Eps15 to ubiquitin-enriched endosomes Gucwa and Brown Gucwa and Brown BMC Cell Biology 2014, 15:34 Gucwa and Brown BMC Cell Biology 2014,
UIM domain-dependent recruitment of the endocytic adaptor protein Eps15 to ubiquitin-enriched endosomes Gucwa and Brown Gucwa and Brown BMC Cell Biology 2014, 15:34 Gucwa and Brown BMC Cell Biology 2014,
FGL2 A new biomarker for cancer in a simple blood test
 FGL2 A new biomarker for cancer in a simple blood test WHO IS FGL2 Human gene (chromosome 7) is 7 kb long, 2 exons, monomer protein 70 KD, tetramer in solution. Fibrinogen-like protein 2 (Fgl2), a member
FGL2 A new biomarker for cancer in a simple blood test WHO IS FGL2 Human gene (chromosome 7) is 7 kb long, 2 exons, monomer protein 70 KD, tetramer in solution. Fibrinogen-like protein 2 (Fgl2), a member
Development of a Human Cell-Free Expression System to Generate Stable-Isotope-Labeled Protein Standards for Quantitative Mass Spectrometry
 Development of a Human Cell-Free Expression System to Generate Stable-Isotope-Labeled Protein Standards for Quantitative Mass Spectrometry Ryan D. omgarden 1, Derek aerenwald 2, Eric Hommema 1, Scott Peterman
Development of a Human Cell-Free Expression System to Generate Stable-Isotope-Labeled Protein Standards for Quantitative Mass Spectrometry Ryan D. omgarden 1, Derek aerenwald 2, Eric Hommema 1, Scott Peterman
Many G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) 2 are rapidly endocytosed after agonist binding, but the pathway of postendocytic
 THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY VOL. 282, NO. 40, pp. 29646 29657, October 5, 2007 2007 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in the U.S.A. Hepatocyte Growth
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY VOL. 282, NO. 40, pp. 29646 29657, October 5, 2007 2007 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in the U.S.A. Hepatocyte Growth
p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO
 Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS)
 Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Invasive cancer cells form dynamic adhesive structures
 Published Online: 10 March, 2008 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200708048 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on November 7, 2018 JCB: ARTICLE Calpain 2 and PTP1B function in a novel pathway with Src
Published Online: 10 March, 2008 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200708048 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on November 7, 2018 JCB: ARTICLE Calpain 2 and PTP1B function in a novel pathway with Src
Nature Structural and Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Mutational analysis of the SA2-Scc1 interaction in vitro and in human cells. (a) Autoradiograph (top) and Coomassie stained gel (bottom) of 35 S-labeled Myc-SA2 proteins (input)
Supplementary Figure 1 Mutational analysis of the SA2-Scc1 interaction in vitro and in human cells. (a) Autoradiograph (top) and Coomassie stained gel (bottom) of 35 S-labeled Myc-SA2 proteins (input)
Tel: ; Fax: ;
 Tel.: +98 216 696 9291; Fax: +98 216 696 9291; E-mail: mrasadeghi@pasteur.ac.ir Tel: +98 916 113 7679; Fax: +98 613 333 6380; E-mail: abakhshi_e@ajums.ac.ir A Soluble Chromatin-bound MOI 0 1 5 0 1 5 HDAC2
Tel.: +98 216 696 9291; Fax: +98 216 696 9291; E-mail: mrasadeghi@pasteur.ac.ir Tel: +98 916 113 7679; Fax: +98 613 333 6380; E-mail: abakhshi_e@ajums.ac.ir A Soluble Chromatin-bound MOI 0 1 5 0 1 5 HDAC2
Lysosomes and endocytic pathways 9/27/2012 Phyllis Hanson
 Lysosomes and endocytic pathways 9/27/2012 Phyllis Hanson General principles Properties of lysosomes Delivery of enzymes to lysosomes Endocytic uptake clathrin, others Endocytic pathways recycling vs.
Lysosomes and endocytic pathways 9/27/2012 Phyllis Hanson General principles Properties of lysosomes Delivery of enzymes to lysosomes Endocytic uptake clathrin, others Endocytic pathways recycling vs.
Mapping the Ligand-binding Site on a GPCR Using Genetically-encoded Photocrosslinkers
 Mapping the Ligand-binding Site on a GPCR Using Genetically-encoded Photocrosslinkers Amy Grunbeck, Thomas Huber, Pallavi Sachdev, Thomas P. Sakmar Laboratory of Molecular Biology and Biochemistry, The
Mapping the Ligand-binding Site on a GPCR Using Genetically-encoded Photocrosslinkers Amy Grunbeck, Thomas Huber, Pallavi Sachdev, Thomas P. Sakmar Laboratory of Molecular Biology and Biochemistry, The
Enzyme-coupled Receptors. Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors
 Enzyme-coupled Receptors Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors Cell-surface receptors allow a flow of ions across the plasma
Enzyme-coupled Receptors Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors Cell-surface receptors allow a flow of ions across the plasma
CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Rush University Medical Center Chicago, IL 60612
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-1-0302 TITLE: Yin and Yang of Heparanase in breast Tumor Initiation PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Xiulong Xu, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Rush University Medical Center Chicago,
AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-1-0302 TITLE: Yin and Yang of Heparanase in breast Tumor Initiation PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Xiulong Xu, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Rush University Medical Center Chicago,
HOMEWORK RUBRICS MECHANOTRANSDUCTION UNIT: HOMEWORK #1 (20 pts towards your grade)
 HOMEWORK RUBRICS MECHANOTRANSDUCTION UNIT: HOMEWORK #1 (20 pts towards your grade) 1. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) cultured on extracellular matrices with different stiffness exhibit diverse lineage commitment
HOMEWORK RUBRICS MECHANOTRANSDUCTION UNIT: HOMEWORK #1 (20 pts towards your grade) 1. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) cultured on extracellular matrices with different stiffness exhibit diverse lineage commitment
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus
 Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Impact of hyper-o-glcnacylation on apoptosis and NF-κB activity SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS 3D culture and cell proliferation- MiaPaCa-2 cell culture in 3D was performed as described previously (1). Briefly, 8-well glass chamber slides were evenly coated with 50 µl/well
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS 3D culture and cell proliferation- MiaPaCa-2 cell culture in 3D was performed as described previously (1). Briefly, 8-well glass chamber slides were evenly coated with 50 µl/well
Supplemental Materials. STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle
 Supplemental Materials STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle Juanjuan Liu 1,2,3, Xingxing Yang 1,3, Binhua Li 1, Junjun Wang 1,2, Wenchao Wang 1, Jing Liu 1, Qingsong
Supplemental Materials STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle Juanjuan Liu 1,2,3, Xingxing Yang 1,3, Binhua Li 1, Junjun Wang 1,2, Wenchao Wang 1, Jing Liu 1, Qingsong
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival
 Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
Brd4 Coactivates Transcriptional Activation of NF- B via Specific Binding to Acetylated RelA
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, Mar. 2009, p. 1375 1387 Vol. 29, No. 5 0270-7306/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/mcb.01365-08 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Brd4 Coactivates
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, Mar. 2009, p. 1375 1387 Vol. 29, No. 5 0270-7306/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/mcb.01365-08 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Brd4 Coactivates
(A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939 (5 µm)
 Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Tankyrase inhibition suppresses cell proliferation in an axin/β-catenin independent manner. (A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939
Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Tankyrase inhibition suppresses cell proliferation in an axin/β-catenin independent manner. (A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939
SUPPORTING MATREALS. Methods and Materials
 SUPPORTING MATREALS Methods and Materials Cell Culture MC3T3-E1 (subclone 4) cells were maintained in -MEM with 10% FBS, 1% Pen/Strep at 37ºC in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. MC3T3 cell differentiation
SUPPORTING MATREALS Methods and Materials Cell Culture MC3T3-E1 (subclone 4) cells were maintained in -MEM with 10% FBS, 1% Pen/Strep at 37ºC in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. MC3T3 cell differentiation
Role of Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase in Activation of Ras and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase by Epidermal Growth Factor
 Role of Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase in Activation of Ras and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase by Epidermal Growth Factor Stefan Wennström and Julian Downward Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19(6):4279. REFERENCES
Role of Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase in Activation of Ras and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase by Epidermal Growth Factor Stefan Wennström and Julian Downward Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19(6):4279. REFERENCES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Discussion The cell cycle machinery and the DNA damage response network are highly interconnected and co-regulated in assuring faithful duplication and partition of genetic materials into
Supplementary Discussion The cell cycle machinery and the DNA damage response network are highly interconnected and co-regulated in assuring faithful duplication and partition of genetic materials into
Slit2N/Robo1 Inhibit HIV-gp120-Induced Migration and Podosome Formation in Immature Dendritic Cells by Sequestering LSP1 and WASp
 Slit2N/Robo1 Inhibit HIV-gp120-Induced Migration and Podosome Formation in Immature Dendritic Cells by Sequestering LSP1 and WASp The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share
Slit2N/Robo1 Inhibit HIV-gp120-Induced Migration and Podosome Formation in Immature Dendritic Cells by Sequestering LSP1 and WASp The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share
Lecture 36: Review of membrane function
 Chem*3560 Lecture 36: Review of membrane function Membrane: Lipid bilayer with embedded or associated proteins. Bilayers: 40-70% neutral phospholipid 10-20% negative phospholipid 10-30% cholesterol 10-30%
Chem*3560 Lecture 36: Review of membrane function Membrane: Lipid bilayer with embedded or associated proteins. Bilayers: 40-70% neutral phospholipid 10-20% negative phospholipid 10-30% cholesterol 10-30%
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein
 Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.
 Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.129-Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(cre/ert2)tyj /J mice. To induce deletion of the Pten locus,
Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.129-Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(cre/ert2)tyj /J mice. To induce deletion of the Pten locus,
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Chairoungdua et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201002049/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Expression of CD9 and CD82 inhibits Wnt/ -catenin
Supplemental material Chairoungdua et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201002049/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Expression of CD9 and CD82 inhibits Wnt/ -catenin
Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2)
 Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11095 Supplementary Table 1. Summary of the binding between Angptls and various Igdomain containing receptors as determined by flow cytometry analysis. The results were summarized from
doi:10.1038/nature11095 Supplementary Table 1. Summary of the binding between Angptls and various Igdomain containing receptors as determined by flow cytometry analysis. The results were summarized from
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
Growth and Differentiation Phosphorylation Sampler Kit
 Growth and Differentiation Phosphorylation Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 1 4 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Phospho-Ser473) E011054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit
Growth and Differentiation Phosphorylation Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 1 4 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Phospho-Ser473) E011054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit
Expanded View Figures
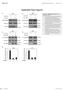 MO reports PR3 dephosphorylates TZ Xian-o Lv et al xpanded View igures igure V1. PR3 dephosphorylates and inactivates YP/TZ., Overexpression of tight junction proteins Pals1 () or LIN7 () has no effect
MO reports PR3 dephosphorylates TZ Xian-o Lv et al xpanded View igures igure V1. PR3 dephosphorylates and inactivates YP/TZ., Overexpression of tight junction proteins Pals1 () or LIN7 () has no effect
Nature Immunology doi: /ni.3268
 Supplementary Figure 1 Loss of Mst1 and Mst2 increases susceptibility to bacterial sepsis. (a) H&E staining of colon and kidney sections from wild type and Mst1 -/- Mst2 fl/fl Vav-Cre mice. Scale bar,
Supplementary Figure 1 Loss of Mst1 and Mst2 increases susceptibility to bacterial sepsis. (a) H&E staining of colon and kidney sections from wild type and Mst1 -/- Mst2 fl/fl Vav-Cre mice. Scale bar,
Cell Biology Lecture 9 Notes Basic Principles of cell signaling and GPCR system
 Cell Biology Lecture 9 Notes Basic Principles of cell signaling and GPCR system Basic Elements of cell signaling: Signal or signaling molecule (ligand, first messenger) o Small molecules (epinephrine,
Cell Biology Lecture 9 Notes Basic Principles of cell signaling and GPCR system Basic Elements of cell signaling: Signal or signaling molecule (ligand, first messenger) o Small molecules (epinephrine,
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Nuclear import of purified HIV-1 Integrase. Integrase remains associated to the RTC throughout the infection process until provirus integration occurs and is therefore one likely
Supplementary Material Nuclear import of purified HIV-1 Integrase. Integrase remains associated to the RTC throughout the infection process until provirus integration occurs and is therefore one likely
Supplemental information contains 7 movies and 4 supplemental Figures
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplemental information contains 7 movies and 4 supplemental Figures Movies: Movie 1. Single virus tracking of A4-mCherry-WR MV
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplemental information contains 7 movies and 4 supplemental Figures Movies: Movie 1. Single virus tracking of A4-mCherry-WR MV
S1a S1b S1c. S1d. S1f S1g S1h SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1. - si sc Il17rd Il17ra bp. rig/s IL-17RD (ng) -100 IL-17RD
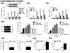 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 0 20 50 80 100 IL-17RD (ng) S1a S1b S1c IL-17RD β-actin kda S1d - si sc Il17rd Il17ra rig/s15-574 - 458-361 bp S1f S1g S1h S1i S1j Supplementary Figure 1. Knockdown of IL-17RD enhances
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 0 20 50 80 100 IL-17RD (ng) S1a S1b S1c IL-17RD β-actin kda S1d - si sc Il17rd Il17ra rig/s15-574 - 458-361 bp S1f S1g S1h S1i S1j Supplementary Figure 1. Knockdown of IL-17RD enhances
Integrin CD11b negatively regulates TLR-triggered inflammatory responses by. activating Syk and promoting MyD88 and TRIF degradation via cbl-b
 Integrin CD11b negatively regulates TLR-triggered inflammatory responses by activating Syk and promoting MyD88 and TRIF degradation via cbl-b Chaofeng Han, Jing Jin, Sheng Xu, Haibo Liu, Nan Li, and Xuetao
Integrin CD11b negatively regulates TLR-triggered inflammatory responses by activating Syk and promoting MyD88 and TRIF degradation via cbl-b Chaofeng Han, Jing Jin, Sheng Xu, Haibo Liu, Nan Li, and Xuetao
