Research Article Th1 and Th2 Immune Response in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients during a Long-Term Treatment with Adefovir Dipivoxil
|
|
|
- Erika Hall
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mediators of Inflammation Volume 21, Article ID 14326, 1 pages doi:1.1155/21/14326 Research Article Th1 and Th2 Immune Response in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients during a Long-Term Treatment with Adefovir Dipivoxil Yanfang Jiang, 1 Zhenhua Ma, 1 Guijie Xin, 1 Hongqing Yan, 1 Wanyu Li, 1 Huining Xu, 1 Chunhai Hao, 2 Junqi Niu, 1 and Pingwei Zhao 1 1 Department of Hepatology, First Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun 1321, China 2 Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, Emory University, Atlanta, GA 3322, USA Correspondence should be addressed to Yanfang Jiang, yanfangjiang@hotmail.com and Junqi Niu, junqiniu@yeah.net Received 23 April 21; Revised 12 July 21; Accepted 7 September 21 Academic Editor: Dennis Daniel Taub Copyright 21 Yanfang Jiang et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Adefovir dipivoxil treatment has significantly improved the outcome of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. However, it remains largely unknown how immune system responds to the treatment. Chronic HBV patients were treated with adefovir dipivoxil and examined for serum HBV DNA loads, cytokines, and T helper (Th1) and 2 (Th2) cytokine producing T cells during 14 weeks of the treatment. Th1/Th2 cytokines producing T cells were significantly lower in chronic HBV patients as compared to normal individuals. Adefovir dipivoxil treatment led to the increase of Th1/Th2 cytokines producing T cells and serum cytokine levels in association with the dec of HVB DNA load. In contrast, Th1/Th2 cytokines producing T cells remained lower in one patient detected with adefovir dipivoxil resistant HBV A181T/V mutation. This study has established inverse correlation of the increase of Th1/Th2 immunity and the dec of HBV DNA load in chronic HBV patients during adefovir dipivoxil treatment. 1. Introduction Chronic HBV infection is one of the most common infectious diseases and contributes to a million death per year worldwide [1]. China is among the highly endemic countries with approximately 8% of the population being chronically infected with the virus [2]. In the last decade, clinical management of chronic HBV infection has significantly improved mainly due to the introduction of nucleoside and nucleotide analogs [3]. Lamivudine is the first approved nucleoside analog that has been clinically proved to be capable of inhibiting HBV replication, enhancing the seroconversion of hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) to antibody (HBeAb), and delaying the progression of the HBV-related complications [4 6]. However, prolonged treatment with lamivudine is limited by the emergence of HBV mutations and thereby drug resistance in up to 67% of patients [7]. Adefovir dipivoxil is a nucleotide analog of adenosine monophosphate [8, 9] that is converted intracellularly to the active metabolite, adefovir diphosphate, which can inhibit DNA polymerase of both wild-type HBV and lamivudine-resistant HBV mutant [1]. Randomized trials have proved the effectiveness of adefovir dipivoxil in treating HBeAg-positive [11 13] and HBeAg-negative chronic HBV patients [14, 15]. Adefovir dipivoxil resistance due to the mutations in the DNA polymerase of HBV [16]wasobserved only in 18% HBeAg-negative [17] and 2% HBeAg-positive chronic HBV patients treated up to four years [12]. In contrast, however, a multicenter randomized trial in Chinese patients has shown no drug resistance during the four years treatment [18]. T-cell immunity plays a critical role in determining the outcome of HBV infection [19]; however, it remains to be established how immune system responds to adefovir dipivoxil and thereby contributes to sustained viral control and improved liver function. In acute HBV infection, CD8 cytotoxic T and CD4 helper T-cells-mediated immunities are activated and involved in the clearance of HBV from the hepatocytes [2]. In chronic HBV infection, however, CD8 and CD4 T-cell immunity are hyporesponsive in association with persistent HBV serum load [21], which suggests that high HBV load may impair T-cell immunity and antiviral treatments can improve the immunity by reducing viral load [19]. In support of this, lamivudine therapy has been proven to reduce HBV serum load and restore CD4 T-cell immunity in chronic HBV patients [22, 23].
2 2 Mediators of Inflammation Recent studies have further shown that adefovir dipivoxil treatment leads to the seroclearance of HBV DNA and the recovery of CD4 [24, 25] but not CD8 T-cell immunity in chronic HBV patients [25]. Th1 cells are characterized by their capability of producing Th1 cytokines, interferon-γ (IFN-γ), interleukin-2 (IL-2), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) whereas Th2 cells are able to synthesize the Th2 cytokines IL-4 and IL-1 [26]. In this paper, we report that a long-term treatment with adefovir dipivoxil leads to the dec of HBV DNA load and the increase of Th1/Th2 immunity in chronic HBV patients in China. 2. Patients and Methods 2.1. Patients. A total of 22 CHB (17menand5women) patients who were presented to the Jilin University First Hospital and 2 healthy controls were included in the study. These patients were treated with adefovir dipivoxil (Gilead Science, Forster City, CA, USA) 1 mg orally once daily for 14 weeks. Th1 and Th2 cytokines including IL-2, IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-4, and IL-1 were measured before and at 12, 24, 36, 52, 65, 78, 92, and 14 weeks after treatment. Viral suppression was evaluated by measurement of HBV DNA along with biochemical markers, AST and ALT. During the followup, one and then three patients dropped out, respectively, at the 36th and 78th weeks of the treatment. The study was approved by the First Hospital Ethical Committee of Jilin University and carried out according to the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki. All patients provided written informed consent prior to study enrollment Flow Cytometric Analysis of Intracellular Cytokine Staining (ICS). Venous blood samples were collected from chronic HBV patients before ( week) and after the treatment with adefovir dipivoxil for 12, 24, 36, 52, 65, 78, 92, and 14 weeks. Blood cells were stimulated and cytokinesecreting cells were analyzed using flow cytometry according to previously reported protocol [27]. For the analysis of intracellular cytokines production, 1 μl blood was diluted with Iscove s modified Dulbecco s medium (1:1 volume). The diluted whole blood was stimulated with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA; Sigma Chemical Co.,St.Louis,MO)(5 ng/ml)plus 2 μg/ml of ionomycin for 6 hours. 1 μg/ml brefeldin A was added at 2 hours before the cells were collected and stained with antibodies. All antibodies were purchased from BD Biosciences (BD Bioscience, Heidelberg, Germany). After being stained with 1 μl antibodies to surface markers (anti-cd3-percp, anti- CD8-FITC, or anti-cd8-pe). The cells were permeabilized and fixed using fixing reagent (Caltag, US) and rupture of membrane and the dissolution of blood reagent (Caltag, US) according to the manufacturer s instructions. The anti-il-2-fitc, anti-tnf-α-fitc, anti-il-4-pe, anti-ifnγ-pe or isotope-matched control antibodies were added for 3 minute. All the samples were analyzed using a FACSCalibur instrument (FACSCalibur, Beckton Dickinson) and FlowJo software. At least 2, events per run were acquired Cytometric Bead Array of Serum Th1 and Th2 Cytokines. Serum cytokine levels were determined by cytometric bead array (CBA) [28], based on the manufacturer s protocol (CBA, BD Biosciences, San Joes, CA). The protocol was modified based on the earlier report to measure cytokines in 25 μl serum [29]. The amount of cytokines was quantified using the cytometric bead array kit on a FACSCalibur cytometry (BD Biosciences) equipped with CellQuestPro and CBA software (Becton Dickinson) Hepatitis Serology and HBV Mutation Analysis. Serum HBsAg, HBsAb, HBeAg, HBeAb, and hepatitis B core antigen antibody (HBcAb) were examined by commercial MURES Mikrotiterplatten enzyme immunoassays according to the manufacturer protocol (Abbott Laboratories, Abbott Park, US). HBsAg quantitation was performed by automated chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay [3], based on the manufacturer s protocol (Abbott Laboratories, Abbott Park, IL). Serum HBV DNA was measured by quantitative PCR assay using luciferase quantitation detection kit (Roche Amplicor, limit of quantification 3 copies/ml). Serum HBV DNA was examined for mutations using HBV Drug Resistant Mutations Assay (Gene Tech Company Limited, Shanghai, China) [31]. In brief, serum HBV DNA was amplified by PCR and pyrosequenced to detect the following mutations of HBV polymerase: I169T, V173L, L18M, A181V/T, T184G/S/A/C, A194T, S22G/I, M24V/I, N236T, and M25V Statistical Analysis. All clinical and flow cytometry data were compared using Wilcoxon rank sum test and Chisquare test. SAS version 8. software was used. Correlations were determined using Spearman s correlation test. Results are given in median (range), unless specified otherwise. For all tests, value of P <.5 was considered statistically significant. 3. Results 3.1. Demographic Background. Twenty-two Chinese patients (17 men and 5 women) were enrolled in the study after initiating screening of HBV serology and liver biochemistry (Table 1). The ages of these patients ranged from 3 to 61 years old (average age at 45.9 ± 8.1) with 1.3 ± 1.6 years of clinical history of chronic HBV infection. Initial screening of serum hepatitis virology detected HBsAg, HbeAb, and HBV DNA in all patients with an average HBV DNA load at 5.8 ±.2log 1 copies/ml. Biochemical analysis of serum revealed elevated ALT and AST, respectively, at the median of 27.6 ( ) and 26.8 ( ) units/l in all the patients. In contrast, twenty health volunteers were serologically negative for HbsAg, HbeAb, and HBV DNA and biochemically normal for ALT and AST Th1 and Th2 Cytokine Producing CD3+CD4+ T-Cells at Base in Chronic HBV Patients. The results revealed the base levels of Th1 and Th2 cells producing IL-2, IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-4, and IL-1, respectively, at the median of 12.16, 5.73, 15.75, 5.69, and 11.7 in the health volunteers (Table 2).
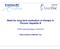
3 Mediators of Inflammation 3 Parameters Table 1: Demographic profiles of study participants. Chronic HBV patients Health volunteers No Age (years) Mean ± SD 45.9 ± ± 11.8 Median Range Sex N(%) Male 17 (77.3) 14 (7) Female 5 (22.7) 6 (3) Years from HBV diagnosis Mean ± SD 1.3 ± 1.6 NA HBV DNA (log1 copies/ml) Mean 5.8 NA SD.2 ALT (U/L) Median Range AST (U/L) Median Range HbsAg (log 1 IU/ml) Median NA Range Differences between treatment groups and health volunteers were statistically significant (P <.5). In contrast, however, both Th1 and Th2 cytokine-producing CD3+CD4+ T-cells were detected at very lower levels in the chronic HBV patients with the median of cytokineproducing cells at.6 (IL-2),.4 (IFN-γ),.7 (TNF-α),.4 (IL-4), and.6 (IL-1). This study further confirms that both Th1 and Th2 immunity are functionally impaired in chronic HBV patients Response of Th1/Th2 Cytokine-Producing T-Cells to Adefovir Dipivoxil Treatment. CD3+CD4+ T-cells were gated and examined by intracellular staining of Th1 (IL-2, IFN-γ, TNF-α) and Th2 cytokines (IL-4, IL-1) (Figure 1). Prior to adefovir dipivoxil treatment, Th1 (IL-2, IFN-γ, TNF-α) and Th2 cytokines (IL-4, IL-1) producing CD3+CD4+ T-cells were significantly lower in chronic HBV patients as compared to healthy individuals (Table 2). Four patients dropped out the study. Of the remaining eighteen patients in the study, sixteen showed no HBV mutations, whereas one had lamivudine resistant HBV M24V/I mutation and another showed adefovir dipivoxil resistant HBV A181T/V mutation. Adefovir dipivoxil treatment resulted in the increase of both Th1 and Th2 cytokines-producing CD3+CD4+ T- cells in all the patients without HBV mutations throughout the treatment (Table 3). Statistic analysis with SAS 8. software revealed a significant relationship (P <.5) Table 2: Comparison of intracellular Th1/Th2 cytokines in chronic HBV patients and healthy volunteers. Parameters Healthy volunteers Patients (no. 22) (% CD3+CD4+) (no. 2) P value IL-4.4 ( 6.) 5.69 ( ) <.1 IFN-γ.4 ( 9.4) 5.73 ( ) <.1 IL-2.6 ( 7.) ( ) <.1 IL-1.6 ( 3.8) 11.7 ( ) <.1 TNF-α.7 ( ) ( ) <.1 The data were expressed as median % and range. P value for all treatment were statistically different between patients and healthy volunteers (<.1). between the increase of Th1/Th2 cytokine-producing cells and the decrease of HBV DNA loads, ALT, AST during the treatment (Table 4). The levels of Th1 cytokines (IL-2, TNF-α) producing cells in the patients without HBV mutations reached the peaks at the 36th week of the treatment and started to drop and maintained the levels of normal healthy individuals at the 65th week of the treatment (Table 3). The peak of the number of Th2 cytokine, IL-4 producing cells was at the 65th week and started dropping to the normal individual levels approximately at the 78th week of the treatment (Table 3). The patient with the lamivudine resistant HBV M24V/I mutations showed a similar Th1/Th2 cytokine response with the nonmutation patients; however, the patient with adefovir dipivoxil resistant HBV A181T/V mutations presented with persistent lower levels of Th1/Th2 cytokines producing CD3+CD4+ T-cells Serum Th1 and Th2 Cytokine Response during Adefovir Dipivoxil Treatment. Our results have showed that the levels of intracellular cytokines were significantly lower in chronic HBV patients as compared to healthy individuals at base (Table 3), and increased during adefovir dipivoxil treatment (Table 4). In order to know the Th1/Th2 cytokines better, we further examined the same cytokines in the serum using cytometric bead array (CBA) and analyzed the data by Chi- Square Test. The results showed that there was a significant increase in the serum levels of Th1 (IL-2, IFN-γ,TNF-α) and Th2 cytokines (IL-4, IL-1) in the patients after the adefovir dipivoxil treatment as compared to the cytokine levels at the base. IFN-γ showed much more increase in the response to the adefovir dipivoxil treatment as compared to other four cytokines. The levels of Th1/Th2 cytokines producing cells reached the peaks at the 78th week of the treatment and maintained up to the 14th week of the treatment (Table 6). The levels and changes of serum cytokines were not associated with HBV DNA loads, ALT, and AST (P >.5) Biochemical and Virological Response to Adefovir Dipivoxil Treatment. Biochemical analysis of the patients showed that ALT and AST started to dec soon after the treatment became normalized between 12th to 36th weeks of the treatment and remained normal (Figure 2). Elevated serum
4 4 Mediators of Inflammation Counts IL-2 FITC IL-2 FITC (a) IL-2 FITC 12 Counts IFN-γ PE IFN-γ PE IFN-γ PE (b) 2 Counts TNF-α FITC TNF-α FITC TNF-α FITC (c) 1 Counts IL-4 PE IL-4 PE IL-4 PE (d) Figure 1: Analysis of intracellular cytokine staining of IL-2, IFN-γ,TNF-α, and IL-4 from gated CD3+CD4+, respectively. ALT and AST, however, remained in one of the patients through the 14 weeks of adefovir dipivoxil treatment. Serum HBsAg showed the tendency of dec. A basal serum HBV DNA load was high in all the patients, but decreased rapidly following the adefovir dipivoxil treatment. HBV DNA load dropped to the levels below the detection limit (<3 copies/ml), respectively, at 12 and 24 week treatment in 2 of 22 patients (Figure 2). Two remaining patients had detectable levels of HBV DNA throughout 14 weeks treatment. The serum samples of these two patients were examined for ten HBV mutations (I169T, V173L, L18M, A181V/T, T184G/S/A/C, A194T, S22G/I, M24V/I, N236T, M25V) that have been reported in the reverse transcriptase regions of HBV polymerase gene in association with the HBV resistance to the treatment of nucleoside and nucleotide analogs [17]. Of the two patients
5 Mediators of Inflammation 5 Table 3: Th1/Th2 cytokines producing CD3+CD4+ cells in patients. TW IL-2% CD3+CD4+ IFN-γ% CD3+CD4+ TNF-α% CD3+CD4+ IL-4% CD3+CD4+ IL-1% CD3+CD4+ TW.6 ( 7.).4 ( 9.4).7 ( ).4 ( 6.).6 ( 3.8) TW ( ) 3. ( ) 8.6 (.5 42.) 6.6 ( ) 6.5 ( ) TW (1.6 37) 22.5 (. 47.9) 24.7 ( ) 17.2 ( ) 21. ( ) TW ( ) 7.4 ( ) 22.9 ( ) 5.9 ( ) 19.7 ( ) TW ( ) 19.6 ( ) 15.5 (.6 47.) 34.4 ( ) 9.6 ( ) TW ( ) 12.5 ( ) 8.1 ( ) 32.9 ( ) 7.7 ( ) TW ( ) 9.8 ( ) 14.9 ( ) 13.6 ( ) 9.7 ( ) TW ( ) 11.9 ( ) 26.2 ( ) 21.1 ( ) 12. ( ) TW ( ) 14.2 ( ) 1.8 ( ) 1.6 ( ) 9.4 ( ) The data were expressed as median % and range. P value for all treatment were statistically different from TW <.5. Table 4: Correlation between intracellular Th1/Th2 cytokines and ALT, AST, HBV DNA load, and HBsAg. IL-2% CD3+CD4+ IFN-γ% CD3+CD4+ TNF-α% CD3+CD4+ IL-4% CD3+CD4+ IL-1% CD3+CD4+ ALT R P <.1 <.1 <.1 <.1 <.1 AST R P <.1 <.1 <.1 <.1 <.1 HBVDNA R P <.1 <.1.34 <.1.7 HBsAg R P Table 5: Comparison of serum cytokine in chronic HBV patients and healthy volunteers. Cytokine (pg/ml) Patients (no. 22) Healthy volunteers (no. 2) P value IL ( ) 3. ( ).16 IFN-γ 5.85 ( ) 4.4 ( ).9 IL ( ) 2.3 (.6 1.1).44 IL ( ) 1.6 ( ).499 TNF-α 2.9 ( ) 1.6 ( ).32 The data were expressed as median % and range. P value for all treatment were statistically different between patients and healthy volunteers (<.5). with consistently elevated HBV DNA load (Figure 3), one patient had HBV A181T/V mutations that are associated with adefovir dipivoxil resistance [11] and another patient had HBV M24V/I mutations of lamivudine resistance. Persistently elevated serum ALT and AST were detected in the patient with adefovir dipivoxil resistant HBV A181T/V mutations (Figure 3). All remaining patients without HBV mutations showed clear correlation between the dec of HBV DNA load and the normalization of ALT and AST through the 14 weeks of adefovir dipivoxil treatment (Figure 2). 4. Discussion The introduction of nucleoside and nucleotide analogs has dramatically improved clinical management of chronic HBV infection, a major health issue in China. Large clinical trials of adefovir dipivoxil, in HBeAg-positive chronic HBV patients in China have proven that adefovir dipivoxil can significantly improve HBV serology and liver biochemistry after 48 and 52 weeks of treatment [18, 32]. HBeAg purportedly acts via interference with Th1/Th2 cross-regulation, and prevention of severe liver injury during adult infections [33, 34]. However, in this study, we have examined adefovir dipivoxil treatment of HBeAb-positive chronic HBV patients in China and shown that after 14 weeks of the long term treatment, twenty of twenty-two patients (9%) showed the seroclearance of HBV DNA and normalization of ALT and AST. These results are consistent with the earlier reports [18, 32] and further indicate that adefovir dipivoxil is a safe and effective therapeutic agent in a long-term treatment of chronic HBV patients in China.
6 6 Mediators of Inflammation Table 6: Serum cytokine levels in the patients following adefovir dipivoxil treatment. IL-2 (pg/ml) IFN-γ (pg/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-4 (pg/ml) IL-1 (pg/ml) TW 5.5 ( ) 5.85 ( ) 2.9 ( ) 4.5 (2.2, 6.5) 5.7 ( ) TW ( ) 7.6 ( ) 3.4 ( ) 7.6 ( ) 7.4 ( ) TW ( ) 13.1 ( ) 3.3 ( ) 7.1 ( ) 7.4 ( ) TW ( ) 15.8 ( ) 4.6 ( ) 7.9 ( ) 7.55 ( ) TW ( ) 14.5 ( ) 3.9 (3. 6.1) 7.6 ( ) 7.6 ( ) The data were expressed as median % and range. P value for all treatment were statistically different from base < ALT U/L AST U/L Base Base (a) (b) HBV-DNA log1 copies (ml) HBSAG (IU/mL) Base Base (c) (d) Figure 2: Biochemical and virological responses after adefovir dipivoxil treatment. ALT (a), AST (b), HBV-DNA loading (c), and HBsAg levels (d) were examined in the serum samples from chronic HBV patients at adefovir dipivoxil treatment week of (base), 12, 24, 36, 52, 65, 78, 92, and 14 (P value for all treatment were statistically different from base <.5). In the investigation of HBV mutations in adefovir dipivoxil resistance, we have identified HBV A181T/V mutations in one and M24V/I mutations in another of two patients that showed HBV DNA persistence through 14 weeks of adefovir dipivoxil treatment. HBV A181V/T and N236T mutations known to adefovir dipivoxil resistance in adefovir dipivoxil resistant patients [16, 35 37]. HBV A181T and N236T mutations have been reported in adefovir dipivoxil resistant patients in Taiwan [38] and Singapore [11]. Although these mutations were not reported in an earlier study of patients in China [18], we have detected HBV A181T/I mutations in one of our patients in the Chinese
7 Mediators of Inflammation 7 IL-2 % CD3 + CD (A) IFN-γ % CD3 + CD (B) TFN-α % CD3 + CD (C) 2 Base Base Base IL-4 % CD3 + CD (D) IL-1 % CD3 + CD (E) 1 Base Base Mutation No Mutation Mutation No Mutation (a) A(IL-2), B(IFN-γ), C(TNF-α), D(IL-4), E(IL-1) showed the percentage of cytokines producd by CD3+CD4+ cells in mutation and nonmutation patients 5 (F) 4 (G) 4 3 ALT U/L AST U/L Base Base HBV-DNA log1 copies (ml) (H) HBSAG (I) 2 Base Mutation No mutation 1 Base Mutation No mutation (b) F(ALT), G(AST), H(HBV DNA), I(HBsAg) showed the biochemical and virological responses between mutation and no mutation Figure 3: Analysis of Th1/Th2 cytokine producing CD3+CD4+ cells at adefovir dipivoxil treatment week (TW) between mutation and no mutation.
8 8 Mediators of Inflammation population. In addition, we have shown the persistent elevations of HBV DNA load and ALT and AST in this patient during adefovir dipivoxil long-term treatment. The HBV L18M and M24V/I mutations are associated with lamivudine resistance [17] and the concept that these mutations can be responsible for adefovir dipivoxil resistance is intriguing and remains to be confirmed in a sizable group of adefovir dipivoxil resistant patients. A recent study based in Hong Kong has indeed suggested that M24V/I mutation is associated with the resistance of HBeAg-positive chronic HBV patients to lamivudine and adefovir dipivoxil combination treatment [39]. It is generally believed that Chronic HBV infection is caused by the persistence of HBV covalently closed circular DNA (cccdna) in hepatocytes [4], in which HBV cccdna accumulates in the nuclei, persists as a stable episome, and serves as a template for the HBV mrna transcription [41]. T-cell immunity is required for the clearance of cccdna from hepatocytes through two immune mechanisms as established in acute HBV infection models: CD8+ cytotoxic T-cells clear HBV from hepatocytes through cytolysis of infected hepatocytes and regeneration of new hepatocytes [42] and Th1 and Th2 CD4+ T-cells-mediated humoral and cellular immunity is able to neutralize HBV by antibodies and inhibit HBV replication through cytokines [43]. In contrast, however, both CD8+ and CD4+ T immunities are functionally impaired in chronic HBV infection [21]. Here, we report that Th1 and Th2 T-cells-mediated immunity, as determined by the percentage of Th1 and Th2 cytokine producing cells in peripheral blood cells, are much weaker from chronic HBV patients than in those from health volunteers. The impaired Th1 and Th2 immunity are associated with the persistence of HBV load and the elevation of ALT and AST of blood samples from chronic HBV patients. In the study, we have further demonstrated the inverse correlation of the increase of Th1/Th2 cytokine producing T-cells and the dec of HBV DNA load in blood samples from chronic HBV patients during the long-term treatment with adefovir dipivoxil. It is well known that both CD8+ and CD4+ T-cell immunity are hyporesponsive in association with persistent HBV load in serum [21], which leads to the suggestion that high HBV load may impair T- cell immunity and antiviral treatments can improve T-cell immunity by reducing viral load [19]. Recent studies have shown indeed that adefovir dipivoxil treatment leads to the seroclearance of HBV [44] and the recovery of CD4 T-cell immunity [24, 25]. These studies suggest the possibility that adefovir dipivoxil, once converted intracellularly to adefovir diphosphate, inhibits HBV DNA polymerase, thus reduces HBV DNA load and thereby contributes to the recovery of T-cell-mediated cellular immunity. 5. Conclusion This study has clearly shown that the long-term treatment with adefovir dipivoxil leads to the seroclearance of HBV DNA, normalization of ALT and AST, response of Th1 and Th2 cell immunity, and increase of serum Th1 and Th2 cytokines in chronic HBV patients and therefore suggested that adefovir dipivoxil treatment contributes to the reduction of HBV DNA load and the recovery of T-cell-mediated immunity in chronic HBV patients. Acknowledgments This study was supported by Grants from the Eleventh Five-year Plan for AIDS and viral hepatitis, prevention and treatment of infectious diseases and other major science and technology (no. 28ZX12-4), Ministry of Health Clinical Branches (no ), National Natural Science Foundation of China (no and ), and Jilin Province Science and Technology Agency (no ). References [1] D. Lavanchy, Hepatitis B virus epidemiology, disease burden, treatment, arid current and emerging prevention and control measures, Journal of Viral Hepatitis, vol. 11, no. 2, pp , 24. [2] W. C. Maddrey, Hepatitis B: an important public health issue, Journal of Medical Virology, vol. 61, no. 3, pp , 2. [3] G. V. Papatheodoridis, S. Manolakopoulos, G. Dusheiko, and A. J. Archimandritis, Therapeutic strategies in the management of patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection, The Lancet Infectious Diseases, vol. 8, no. 3, pp , 28. [4] C.-L. Lai, R.-N. Chien, N. W. Y. Leung et al., A one-year trial of lamivudine for chronic hepatitis B, The New England Journal of Medicine, vol. 339, no. 2, pp , [5] J. L. Dienstag, E. R. Schiff, T. L. Wright et al., Lamivudine as initial treatment for chronic hepatitis B in the United States, The New England Journal of Medicine, vol. 341, no. 17, pp , [6] Y.-F. Liaw, J. J. Y. Sung, W. C. Chow et al., Lamivudine for patients with chronic hepatitis B and advanced liver disease, The New England Journal of Medicine, vol. 351, no. 15, pp , 24. [7] A. S. F. Lok, C.-L. Lai, N. Leung et al., Long-term safety of lamivudine treatment in patients with chronic hepatitis B, Gastroenterology, vol. 125, no. 6, pp , 23. [8] R. Perrillo, E. Schiff, E. Yoshida et al., Adefovir dipivoxil for the treatment of lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B mutants, Hepatology, vol. 32, no. 1, pp , 2. [9] Y. Benhamou, M. Bochet, V. Thibault et al., Safety and efficacy of adefovir dipivoxil in patients co-infected with HIV- 1 and lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B virus: an open-label pilot study, The Lancet, vol. 358, no. 9283, pp , 21. [1] X. Xiong, C. Flores, H. Yang, J. J. Toole, and C. S. Gibbs, Mutations in hepatitis B DNA polymerase associated with resistance to lamivudine do not confer resistance to adefovir in vitro, Hepatology, vol. 28, no. 6, pp , [11] S. J. Hadziyannis, N. C. Tassopoulos, E. J. Heathcote et al., Adefovir dipivoxil for the treatment of hepatitis B e antigennegative chronic hepatitis B, The New England Journal of Medicine, vol. 348, no. 9, pp. 8 87, 23. [12] P. Marcellin, T.-T. Chang, S. G. L. Lim et al., Long-term efficacy and safety of adefovir dipivoxil for the treatment of hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B, Hepatology, vol. 48, no. 3, pp , 28.
9 Mediators of Inflammation 9 [13] N. Leung, C.-Y. Peng, H.-W. Hann et al., Early hepatitis B virus DNA reduction in hepatitis B e antigen-positive patients with chronic hepatitis B: a randomized international study of entecavir versus adefovir, Hepatology, vol. 49, no. 1, pp , 29. [14] S. J. Hadziyannis, N. C. Tassopoulos, E. J. Heathcote et al., Adefovir dipivoxil for the treatment of hepatitis B e antigennegative chronic hepatitis B, The New England Journal of Medicine, vol. 348, no. 9, pp. 8 87, 23. [15] S. J. Hadziyannis, N. C. Tassopoulos, E. J. Heathcote et al., Long-term therapy with adefovir dipivoxil for HBeAgnegative chronic hepatitis B for up to 5 years, Gastroenterology, vol. 131, no. 6, pp , 26. [16] P. Angus, R. Vaughan, S. Xiong et al., Resistance to adefovir dipivoxil therapy associated with the selection of a novel mutation in the HBV polymerase, Gastroenterology, vol. 125, no. 2, pp , 23. [17] S. Locarnini and W. S. Mason, Cellular and virological mechanisms of HBV drug resistance, Journal of Hepatology, vol. 44, no. 2, pp , 26. [18] M. Zeng, Y. Mao, G. Yao et al., A double-blind randomized trial of adefovir dipivoxil in Chinese subjects with HBeAgpositive chronic hepatitis B, Hepatology, vol.44,no.1,pp , 26. [19] B. Rehermann and M. Nascimbeni, Immunology of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infection, Nature Reviews Immunology, vol. 5, no. 3, pp , 25. [2] R. Thimme, S. Wieland, C. Steiger et al., CD8 + T cells mediate viral clearance and disease pathogenesis during acute hepatitis B virus infection, Journal of Virology, vol. 77, no. 1, pp , 23. [21] C. Boni, P. Fisicaro, C. Valdatta et al., Characterization of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-specific T-cell dysfunction in chronic HBV infection, Journal of Virology, vol. 81, no. 8, pp , 27. [22] C. Boni, A. Bertoletti, A. Penna et al., Lamivudine treatment can restore T cell responsiveness in chronic hepatitis B, Journal of Clinical Investigation, vol. 12, no. 5, pp , [23] C. Boni, A. Penna, A. Bertoletti et al., Transient restoration of anti-viral T cell responses induced by lamivudine therapy in chronic hepatitis B, Journal of Hepatology, vol. 39, no. 4, pp , 23. [24] G. K. K. Lau, H. Cooksley, R. M. Ribeiro et al., Impact of early viral kinetics on T-cell reactivity during antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis B, Antiviral Therapy, vol.12,no.5,pp , 27. [25] H. Cooksley, S. Chokshi, Y. Maayan et al., Hepatitis B virus e antigen loss during adefovir dipivoxil therapy is associated with enhanced virus-specific CD4 + T-cell reactivity, Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, vol. 52, no. 1, pp , 28. [26] T. R. Mosmann and S. Sad, The expanding universe of T-cell subsets: Th1, Th2 and more, Immunology Today, vol. 17, no. 3, pp , [27] P. Duramad, C. W. McMahon, A. Hubbard, B. Eskenazi, and N. T. Holland, Flow cytometric detection of intracellular Th1/Th2 cytokines using whole blood: validation of immunologic biomarker for use in epidemiologic studies, Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers and Prevention, vol.13,no.9,pp , 24. [28] E. Morgan, R. Varro, H. Sepulveda et al., Cytometric bead array: a multiplexed assay platform with applications in various areas of biology, Clinical Immunology, vol. 11, no. 3, pp , 24. [29] A. Tárnok, J. Hambsch, R. Chen, and R. Varro, Cytometric bead array to measure six cytokines in twenty-five microliters of serum, Clinical Chemistry, vol. 49, no. 6, pp. 1 12, 23. [3] M. R. Brunetto, F. Moriconi, F. Bonino et al., Hepatitis B virus surface antigen levels: a guide to sustained response to peginterferon alfa-2a in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B, Hepatology, vol. 49, no. 4, pp , 29. [31] A. Lindström, J. Odeberg, and J. Albert, Pyrosequencing for detection of lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B virus, Journal of Clinical Microbiology, vol. 42, no. 1, pp , 24. [32] A.-Z. Zeng, H. Deng, C. Yang et al., Hepatitis B virus genotype-associated variability in antiviral response to adefovir dipivoxil therapy in Chinese han population, Tohoku Journal of Experimental Medicine, vol. 216, no. 3, pp , 28. [33] M.Chen,M.Sällberg, J. Hughes et al., Immune tolerance split between hepatitis B virus precore and core proteins, Journal of Virology, vol. 79, no. 5, pp , 25. [34] M. T. Chen, J.-N. Billaud, M. Sällberg et al., A function of the hepatitis B virus precore protein is to regulate the immune response to the core antigen, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, vol. 11, no. 41, pp , 24. [35] J.-P. Villeneuve, D. Durantel, S. Durantel et al., Selection of a hepatitis B virus strain resistant to adefovir in a liver transplantation patient, JournalofHepatology, vol. 39, no. 6, pp , 23. [36] Y.-S. Lee, D. J. Suh, Y.-S. Lim et al., Increased risk of adefovir resistance in patients with lamivudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B after 48 weeks of adefovir dipivoxil monotherapy, Hepatology, vol. 43, no. 6, pp , 26. [37] J. Tan, B. Degertekin, S. N. Wong, M. Husain, K. Oberhelman, and A. S. F. Lok, Tenofovir monotherapy is effective in hepatitis B patients with antiviral treatment failure to adefovir in the absence of adefovir-resistant mutations, Journal of Hepatology, vol. 48, no. 3, pp , 28. [38] C.-H. Chen, J.-H. Wang, C.-M. Lee et al., Virological response and incidence of adefovir resistance in lamivudineresistant patients treated with adefovir dipivoxil, Antiviral Therapy, vol. 11, no. 6, pp , 26. [39] J. J. Y. Sung, J.-Y. Lai, S. Zeuzem et al., Lamivudine compared with lamivudine and adefovir dipivoxil for the treatment of HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B, JournalofHepatology, vol. 48, no. 5, pp , 28. [4] J. S. Tuttleman, C. Pourcel, and J. Summers, Formation of the pool of covalently closed circular viral DNA in hepadnavirusinfected cells, Cell, vol. 47, no. 3, pp , [41] C. Seeger and W. S. Mason, Hepatitis B virus biology, Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, vol. 64, no. 1, pp , 2. [42] I. Fourel, J. M. Cullen, J. Saputelli et al., Evidence that hepatocyte turnover is required for rapid clearance of duck hepatitis B virus during antiviral therapy of chronically infected ducks, Journal of Virology, vol. 68, no. 12, pp , [43] L. G. Guidotti, R. Rochford, J. Chung, M. Shapiro, R. Purcell, and F. V. Chisari, Viral clearance without destruction of infected cells during acute HBV infection, Science, vol. 284, no. 5415, pp , 1999.
10 1 Mediators of Inflammation [44] H. Ataseven, I. H. Bahcecioglu, N. Kuzu et al., The levels of ghrelin, leptin, TNF-α, and IL-6 in liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma due to HBV and HDV infection, Mediators of Inflammation, vol. 26, Article ID 7838, 6 pages, 26.
11 MEDIATORS of INFLAMMATION The Scientific World Journal Gastroenterology Research and Practice Journal of Diabetes Research International Journal of Journal of Endocrinology Immunology Research Disease Markers Submit your manuscripts at BioMed Research International PPAR Research Journal of Obesity Journal of Ophthalmology Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Stem Cells International Journal of Oncology Parkinson s Disease Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine AIDS Behavioural Neurology Research and Treatment Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity
on T-helper 1 Cell and T-helper 2 Cell Cytokine Synthesis in Patients with Hepatitis B Virus e Antigenpositive Chronic Hepatitis B
 The Journal of International Medical Research 21; 38: 253 262 Effect of Thymosin-α 1 on T-helper 1 Cell and T-helper 2 Cell Cytokine Synthesis in Patients with Hepatitis B Virus e Antigenpositive Chronic
The Journal of International Medical Research 21; 38: 253 262 Effect of Thymosin-α 1 on T-helper 1 Cell and T-helper 2 Cell Cytokine Synthesis in Patients with Hepatitis B Virus e Antigenpositive Chronic
Prediction of HBsAg Loss by Quantitative HBsAg Kinetics during Long-Term 2015
 THAI J 16 GASTROENTEROL Treatment with Nucleos(t)ide Original Analogues Article Prediction of HBsAg Loss by Quantitative HBsAg Kinetics during Long-Term Treatment with Nucleos(t)ide Analogues Sombutsook
THAI J 16 GASTROENTEROL Treatment with Nucleos(t)ide Original Analogues Article Prediction of HBsAg Loss by Quantitative HBsAg Kinetics during Long-Term Treatment with Nucleos(t)ide Analogues Sombutsook
Sustained HBs seroconversion during lamivudine and adefovir dipivoxil combination therapy for lamivudine failure
 Sustained HBs seroconversion during lamivudine and adefovir dipivoxil combination therapy for lamivudine failure Marianne Maynard, Parviz Parvaz, Sandra Durantel, Michèle Chevallier, Philippe Chevallier,
Sustained HBs seroconversion during lamivudine and adefovir dipivoxil combination therapy for lamivudine failure Marianne Maynard, Parviz Parvaz, Sandra Durantel, Michèle Chevallier, Philippe Chevallier,
Cornerstones of Hepatitis B: Past, Present and Future
 Cornerstones of Hepatitis B: Past, Present and Future Professor Man-Fung Yuen Queen Mary Hospital The University of Hong Kong Hong Kong 1 Outline Past Natural history studies Development of HBV-related
Cornerstones of Hepatitis B: Past, Present and Future Professor Man-Fung Yuen Queen Mary Hospital The University of Hong Kong Hong Kong 1 Outline Past Natural history studies Development of HBV-related
Chronic hepatitis B - New goals, new treatment. New England Journal Of Medicine, 2008, v. 359 n. 23, p
 Title Chronic hepatitis B - New goals, new treatment Author(s) Lai, CL; Yuen, MF Citation New England Journal Of Medicine, 2008, v. 359 n. 23, p. 2488-2491 Issued Date 2008 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/59270
Title Chronic hepatitis B - New goals, new treatment Author(s) Lai, CL; Yuen, MF Citation New England Journal Of Medicine, 2008, v. 359 n. 23, p. 2488-2491 Issued Date 2008 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/59270
Acute Hepatitis B Virus Infection with Recovery
 Hepatitis B: Clear as Mud Melissa Osborn, MD, MSCR Assistant Professor Emory University School of Medicine Atlanta, GA 1 Objectives 1. Distinguish the various stages in the natural history of chronic hepatitis
Hepatitis B: Clear as Mud Melissa Osborn, MD, MSCR Assistant Professor Emory University School of Medicine Atlanta, GA 1 Objectives 1. Distinguish the various stages in the natural history of chronic hepatitis
Clinical Study High Dose of Lamivudine and Resistance in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B
 Hepatitis Research and Treatment, Article ID 615621, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/615621 Clinical Study High Dose of Lamivudine and Resistance in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Hamid Ullah
Hepatitis Research and Treatment, Article ID 615621, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/615621 Clinical Study High Dose of Lamivudine and Resistance in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Hamid Ullah
Dynamics of HBV DNA Levels, HBV Mutations and Biochemical Parameters during Antiviral Therapy in a Patient with HBeAg-Negative Chronic Hepatitis B
 ASIAN PACIFIC JOURNAL OF ALLERGY AND IMMUNOLOGY (2007) 25: 183-188 CASE REPORT Dynamics of HBV DNA Levels, HBV Mutations and Biochemical Parameters during Antiviral Therapy in a Patient with HBeAg-Negative
ASIAN PACIFIC JOURNAL OF ALLERGY AND IMMUNOLOGY (2007) 25: 183-188 CASE REPORT Dynamics of HBV DNA Levels, HBV Mutations and Biochemical Parameters during Antiviral Therapy in a Patient with HBeAg-Negative
Who to Treat? Consider biopsy Treat. > 2 ULN Treat Treat Treat Treat CIRRHOTIC PATIENTS Compensated Treat HBV DNA detectable treat
 Who to Treat? Parameter AASLD US Algorithm EASL APASL HBV DNA CRITERIA HBeAg+ >, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL >, IU/mL HBeAg- > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL ALT CRITERIA PNALT 1-2 ULN Monitor
Who to Treat? Parameter AASLD US Algorithm EASL APASL HBV DNA CRITERIA HBeAg+ >, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL >, IU/mL HBeAg- > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL > 2, IU/mL ALT CRITERIA PNALT 1-2 ULN Monitor
MedInform. HBsAg-guided extension of Peg-IFN therapy in HBeAg-negative responders. Original Article
 HBsAg-guided extension of Peg-IFN therapy in HBeAg-negative responders Nina Nikolova, Deian Jelev, Krassimir Antonov, Lyudmila Mateva, Zahariy Krastev. University Hospital St. Ivan Rilski Sofia, Clinic
HBsAg-guided extension of Peg-IFN therapy in HBeAg-negative responders Nina Nikolova, Deian Jelev, Krassimir Antonov, Lyudmila Mateva, Zahariy Krastev. University Hospital St. Ivan Rilski Sofia, Clinic
Viral Hepatitis The Preventive Potential of Antiviral Therapy. Thomas Berg
 Viral Hepatitis The Preventive Potential of Antiviral Therapy Thomas Berg Therapeutic and preventive strategies in patients with hepatitis virus infection Treatment of acute infection Treatment of chronic
Viral Hepatitis The Preventive Potential of Antiviral Therapy Thomas Berg Therapeutic and preventive strategies in patients with hepatitis virus infection Treatment of acute infection Treatment of chronic
Natural History of Chronic Hepatitis B
 Natural History of Chronic Hepatitis B Anna SF Lok, MD Alice Lohrman Andrews Professor in Hepatology Director of Clinical Hepatology Assistant Dean for Clinical Research University of Michigan Ann Arbor,
Natural History of Chronic Hepatitis B Anna SF Lok, MD Alice Lohrman Andrews Professor in Hepatology Director of Clinical Hepatology Assistant Dean for Clinical Research University of Michigan Ann Arbor,
Management of hepatitis B virus
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy Advance Access published May 14, 2008 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy doi:10.1093/jac/dkn188 Management of hepatitis B virus Nidhi A. Singh and Nancy Reau* Section
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy Advance Access published May 14, 2008 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy doi:10.1093/jac/dkn188 Management of hepatitis B virus Nidhi A. Singh and Nancy Reau* Section
How to use pegylated Interferon for Chronic Hepatitis B in 2015
 How to use pegylated Interferon for Chronic Hepatitis B in 215 Teerha Piratvisuth NKC Institute of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Prince of Songkla University, Thailand ASIAN-PACIFIC CLINICAL PRACTICE
How to use pegylated Interferon for Chronic Hepatitis B in 215 Teerha Piratvisuth NKC Institute of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Prince of Songkla University, Thailand ASIAN-PACIFIC CLINICAL PRACTICE
Hepatitis B surface antigen levels: association with 5-year response to peginterferon alfa-2a in hepatitis B e-antigen-negative patients
 Hepatol Int (2013) 7:88 97 DOI 10.1007/s12072-012-9343-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hepatitis B surface antigen levels: association with 5-year response to peginterferon alfa-2a in hepatitis B e-antigen-negative
Hepatol Int (2013) 7:88 97 DOI 10.1007/s12072-012-9343-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hepatitis B surface antigen levels: association with 5-year response to peginterferon alfa-2a in hepatitis B e-antigen-negative
Diagnostic Methods of HBV and HDV infections
 Diagnostic Methods of HBV and HDV infections Zohreh Sharifi,ph.D Blood Transfusion Research Center, High Institute for Research and Education in Transfusion Medicine Hepatitis B-laboratory diagnosis Detection
Diagnostic Methods of HBV and HDV infections Zohreh Sharifi,ph.D Blood Transfusion Research Center, High Institute for Research and Education in Transfusion Medicine Hepatitis B-laboratory diagnosis Detection
Is there a need for combination treatment? Yes!
 18.0.2012 C Hep Meeting Berlin Is there a need for combination treatment? Yes! Florian van Bömmel University Hospital Leipzig Hepatology Section Germany Most patients respond to monotherapy with entecavir
18.0.2012 C Hep Meeting Berlin Is there a need for combination treatment? Yes! Florian van Bömmel University Hospital Leipzig Hepatology Section Germany Most patients respond to monotherapy with entecavir
29th Viral Hepatitis Prevention Board Meeting
 29th Viral Hepatitis Prevention Board Meeting Madrid, November 2006 Treatment of chronic hepatitis B José M. Sánchez-Tapias Liver Unit Hospital Clínic University of Barcelona Spain CHRONIC HBV INFECTION
29th Viral Hepatitis Prevention Board Meeting Madrid, November 2006 Treatment of chronic hepatitis B José M. Sánchez-Tapias Liver Unit Hospital Clínic University of Barcelona Spain CHRONIC HBV INFECTION
NATURAL HISTORY OF HEPATITIS B
 NATURAL HISTORY OF HEPATITIS B AND DIAGNOSTIC: STATE OF THE ART O. BAHRI LABORATORY OF MEDICAL BIOLOGY AZIZA OTHMANA HOSPITAL TUNIS, TUNISIA The 2 nd Congress of The Federation of Arab Societies of Clinical
NATURAL HISTORY OF HEPATITIS B AND DIAGNOSTIC: STATE OF THE ART O. BAHRI LABORATORY OF MEDICAL BIOLOGY AZIZA OTHMANA HOSPITAL TUNIS, TUNISIA The 2 nd Congress of The Federation of Arab Societies of Clinical
Research Article HBV Genotype B/C and Response to Lamivudine Therapy: A Systematic Review
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation BioMed Research International Volume 2013, Article ID 672614, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/672614 Research Article HBV Genotype B/C and Response to Lamivudine Therapy:
Hindawi Publishing Corporation BioMed Research International Volume 2013, Article ID 672614, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/672614 Research Article HBV Genotype B/C and Response to Lamivudine Therapy:
Identification of hepatitis B virus DNA reverse transcriptase variants associated with partial response to entecavir
 Title Identification of hepatitis B virus DNA reverse transcriptase variants associated with partial response to entecavir Author(s) Wong, DKH; Fung, JYY; Lai, CL; Yuen, RMF Citation Hong Kong Medical
Title Identification of hepatitis B virus DNA reverse transcriptase variants associated with partial response to entecavir Author(s) Wong, DKH; Fung, JYY; Lai, CL; Yuen, RMF Citation Hong Kong Medical
Basics of hepatitis B diagnostics. Dr Emma Page MRCP MD(Res) Locum Consultant Sexual Health & Virology
 Basics of hepatitis B diagnostics Dr Emma Page MRCP MD(Res) Locum Consultant Sexual Health & Virology Basics of hepatitis B diagnostics Background Epidemiology Morphology Life-cycle Diagnostic markers
Basics of hepatitis B diagnostics Dr Emma Page MRCP MD(Res) Locum Consultant Sexual Health & Virology Basics of hepatitis B diagnostics Background Epidemiology Morphology Life-cycle Diagnostic markers
Long-term lamivudine therapy reduces the risk of long-term complications of chronic hepatitis B infection even in patients without advanced disease
 Antiviral Therapy 12:1295 133 Long-term lamivudine therapy reduces the risk of long-term complications of chronic hepatitis B infection even in patients without advanced disease Man-Fung Yuen, Wai-Kay
Antiviral Therapy 12:1295 133 Long-term lamivudine therapy reduces the risk of long-term complications of chronic hepatitis B infection even in patients without advanced disease Man-Fung Yuen, Wai-Kay
The Impact of HBV Therapy on Fibrosis and Cirrhosis
 The Impact of HBV Therapy on Fibrosis and Cirrhosis Jordan J. Feld, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine University of Toronto Hepatologist Toronto Centre for Liver Disease Sandra Rotman Centre for
The Impact of HBV Therapy on Fibrosis and Cirrhosis Jordan J. Feld, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine University of Toronto Hepatologist Toronto Centre for Liver Disease Sandra Rotman Centre for
Management of Chronic Hepatitis B in Asian Americans
 Management of Chronic Hepatitis B in Asian Americans Myron J Tong; UCLA, CA Calvin Q. Pan; Mount Sinai, NY Hie-Won Hann; Thomas Jefferson, PA Kris V. Kowdley; Virginia Mason, WA Steven Huy B Han; UCLA,
Management of Chronic Hepatitis B in Asian Americans Myron J Tong; UCLA, CA Calvin Q. Pan; Mount Sinai, NY Hie-Won Hann; Thomas Jefferson, PA Kris V. Kowdley; Virginia Mason, WA Steven Huy B Han; UCLA,
CURRENT TREATMENT. Mitchell L Shiffman, MD Director Liver Institute of Virginia Bon Secours Health System Richmond and Newport News, Virginia
 CURRENT TREATMENT OF HBV Mitchell L Shiffman, MD Director Liver Institute of Virginia Bon Secours Health System Richmond and Newport News, Virginia CHRONIC HBV INFECTION DEMOGRAPHICS IN THE USA Estimated
CURRENT TREATMENT OF HBV Mitchell L Shiffman, MD Director Liver Institute of Virginia Bon Secours Health System Richmond and Newport News, Virginia CHRONIC HBV INFECTION DEMOGRAPHICS IN THE USA Estimated
Antiviral Therapy 14:
 Antiviral Therapy 14:679 685 Original article Combination of baseline parameters and on-treatment hepatitis B virus DNA levels to start and continue patients with lamivudine therapy Man-Fung Yuen 1 *,
Antiviral Therapy 14:679 685 Original article Combination of baseline parameters and on-treatment hepatitis B virus DNA levels to start and continue patients with lamivudine therapy Man-Fung Yuen 1 *,
Investigation into withdrawal of entecavir after 20 months in an HBsAb-positive patient who received HBsAg allogeneic stem cell transplantation
 Investigation into withdrawal of entecavir after 20 months in an HBsAb-positive patient who received HBsAg allogeneic stem cell transplantation J. Peng, W.F. Luo, B. Zhou and W.Q. Wen Department of Infectious
Investigation into withdrawal of entecavir after 20 months in an HBsAb-positive patient who received HBsAg allogeneic stem cell transplantation J. Peng, W.F. Luo, B. Zhou and W.Q. Wen Department of Infectious
Response-guided antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis B: nucleot(s)ide analogues vs. pegylated interferon
 Response-guided antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis B: Sang Hoon Ahn, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Institute of Gastroenterology, Liver Cirrhosis
Response-guided antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis B: Sang Hoon Ahn, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Institute of Gastroenterology, Liver Cirrhosis
Pros and Cons of Peginterferon Versus Nucleos(t)ide Analogues for Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B
 Curr Hepatitis Rep (2010) 9:91 98 DOI 10.1007/s11901-010-0041-7 Pros and Cons of Peginterferon Versus Nucleos(t)ide Analogues for Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B Milan J. Sonneveld & Harry L. A. Janssen
Curr Hepatitis Rep (2010) 9:91 98 DOI 10.1007/s11901-010-0041-7 Pros and Cons of Peginterferon Versus Nucleos(t)ide Analogues for Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B Milan J. Sonneveld & Harry L. A. Janssen
Hepatitis B Diagnosis and Management. Marion Peters University of California San Francisco
 Hepatitis B Diagnosis and Management Marion Peters University of California San Francisco COI Spouse works for Hoffmann-La Roche HBV is a life long, dynamic disease Changes over time Risk of end stage
Hepatitis B Diagnosis and Management Marion Peters University of California San Francisco COI Spouse works for Hoffmann-La Roche HBV is a life long, dynamic disease Changes over time Risk of end stage
Clinical impact of the early alanine amininotransferase flare during tenofovir monotherapy in treatment-naïve patients with chronic hepatitis B
 pissn 2287-2728 eissn 2287-285X Original Article Clinical and Molecular Hepatology 217;23:154-159 Clinical impact of the early alanine amininotransferase flare during tenofovir monotherapy in treatment-naïve
pissn 2287-2728 eissn 2287-285X Original Article Clinical and Molecular Hepatology 217;23:154-159 Clinical impact of the early alanine amininotransferase flare during tenofovir monotherapy in treatment-naïve
Spontaneous resolution of de novo hepatitis B after living donor liver transplantation with hepatitis B core antibody positive graft: a case report
 Hara et al. Surgical Case Reports (2016) 2:118 DOI 10.1186/s40792-016-0246-2 CASE REPORT Open Access Spontaneous resolution of de novo hepatitis B after living donor liver transplantation with hepatitis
Hara et al. Surgical Case Reports (2016) 2:118 DOI 10.1186/s40792-016-0246-2 CASE REPORT Open Access Spontaneous resolution of de novo hepatitis B after living donor liver transplantation with hepatitis
MedInform. HBV DNA loss in Bulgarian patients on NUC therapy. Speed related factors. (NUC related speed of HBV DNA loss in Bulgaria) Original Article
 DOI: 10.18044/Medinform.201852.897 ISSUE 3, 2018 HBV DNA loss in Bulgarian patients on NUC therapy. Speed related factors. (NUC related speed of HBV DNA loss in Bulgaria) Donika Krasteva, Radosveta Tomova,
DOI: 10.18044/Medinform.201852.897 ISSUE 3, 2018 HBV DNA loss in Bulgarian patients on NUC therapy. Speed related factors. (NUC related speed of HBV DNA loss in Bulgaria) Donika Krasteva, Radosveta Tomova,
Natural History of HBV Infection
 Natural History of HBV Infection Joseph JY Sung MD PhD Institute of Digestive Disease Department of Medicine & Therapeutics Prince of Wales Hospital The Chinese University of Hong Kong HBV Infection 2
Natural History of HBV Infection Joseph JY Sung MD PhD Institute of Digestive Disease Department of Medicine & Therapeutics Prince of Wales Hospital The Chinese University of Hong Kong HBV Infection 2
Consensus AASLD-EASL HBV Treatment Endpoint and HBV Cure Definition
 Consensus AASLD-EASL HBV Treatment Endpoint and HBV Cure Definition Anna S. Lok, MD, DSc Alice Lohrman Andrews Professor in Hepatology Director of Clinical Hepatology Assistant Dean for Clinical Research
Consensus AASLD-EASL HBV Treatment Endpoint and HBV Cure Definition Anna S. Lok, MD, DSc Alice Lohrman Andrews Professor in Hepatology Director of Clinical Hepatology Assistant Dean for Clinical Research
ARTICLE IN PRESS. A Treatment Algorithm for the Management of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection in the United States: An Update
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2006;4:xxx REVIEW A Treatment Algorithm for the Management of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection in the United States: An Update EMMET B. KEEFFE,* DOUGLAS T. DIETERICH,
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2006;4:xxx REVIEW A Treatment Algorithm for the Management of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection in the United States: An Update EMMET B. KEEFFE,* DOUGLAS T. DIETERICH,
Dual Therapy for Chronic Hepatitis B Virus
 Dual Therapy for Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Hussien Elsiesy, MD, and Douglas Dieterich, MD Corresponding author Douglas Dieterich, MD Division of Liver Diseases, Mount Sinai School of Medicine, One Gustave
Dual Therapy for Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Hussien Elsiesy, MD, and Douglas Dieterich, MD Corresponding author Douglas Dieterich, MD Division of Liver Diseases, Mount Sinai School of Medicine, One Gustave
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 06 Page June 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.02 An Open Label Prospective Study to Evaluate
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.02 An Open Label Prospective Study to Evaluate
Dynamic analysis of lymphocyte subsets of peripheral blood in patients with acute self-limited hepatitis B
 Vol.2, No.7, 736-741 (2010) doi:10.4236/health.2010.27112 Health Dynamic analysis of lymphocyte subsets of peripheral blood in patients with acute self-limited hepatitis B Bo Liu, Jun Li*, Yaping Han,
Vol.2, No.7, 736-741 (2010) doi:10.4236/health.2010.27112 Health Dynamic analysis of lymphocyte subsets of peripheral blood in patients with acute self-limited hepatitis B Bo Liu, Jun Li*, Yaping Han,
Hepatitis B Treatment Pearls. Agenda
 Hepatitis B Treatment Pearls Fredric D. Gordon, MD Vice Chair Dept. of Transplantation and Hepatobiliary Diseases Lahey Hospital & Medical Center Associate Professor of Medicine Tufts Medical School Boston,
Hepatitis B Treatment Pearls Fredric D. Gordon, MD Vice Chair Dept. of Transplantation and Hepatobiliary Diseases Lahey Hospital & Medical Center Associate Professor of Medicine Tufts Medical School Boston,
Treatment of chronic hepatitis B: Evolution over two decades_
 doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.2010.06545.x REVIEW Treatment of chronic hepatitis B: Evolution over two decades_6545 138..143 Man-Fung Yuen and Ching-Lung Lai Department of Medicine, the University of Hong Kong,
doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.2010.06545.x REVIEW Treatment of chronic hepatitis B: Evolution over two decades_6545 138..143 Man-Fung Yuen and Ching-Lung Lai Department of Medicine, the University of Hong Kong,
Chronic infection with the hepatitis B virus (HBV)
 Adding-on Versus Switching-to Adefovir Therapy in Lamivudine-Resistant HBeAg-Negative Chronic Hepatitis B Irene Rapti, 1 Evangelini Dimou, 1,2 Panayota Mitsoula, 2 and Stephanos J. Hadziyannis 1,2 We studied
Adding-on Versus Switching-to Adefovir Therapy in Lamivudine-Resistant HBeAg-Negative Chronic Hepatitis B Irene Rapti, 1 Evangelini Dimou, 1,2 Panayota Mitsoula, 2 and Stephanos J. Hadziyannis 1,2 We studied
A preliminary report on the influence of baseline cellular immunity to the therapeutic responses of peg-interferon
 146 2009 9 4 3 Journal of Microbes and Infection, September 2009, Vol. 4, No. 3 e 2a 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 1., 200025; 2., 200032 : ( CHB) ( IFN), IFN IFN, e ( HBeAg) CHB 19, 14, IFN- 2a 180 g, 1, 48,
146 2009 9 4 3 Journal of Microbes and Infection, September 2009, Vol. 4, No. 3 e 2a 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 1., 200025; 2., 200032 : ( CHB) ( IFN), IFN IFN, e ( HBeAg) CHB 19, 14, IFN- 2a 180 g, 1, 48,
New therapeutic perspectives in HBV: when to stop NAs
 Liver International ISSN 1478-3223 REVIEW ARTICLE New therapeutic perspectives in HBV: when to stop NAs Cristina Perez-Cameo, Monica Pons and Rafael Esteban Liver Unit, Department of Internal Medicine,
Liver International ISSN 1478-3223 REVIEW ARTICLE New therapeutic perspectives in HBV: when to stop NAs Cristina Perez-Cameo, Monica Pons and Rafael Esteban Liver Unit, Department of Internal Medicine,
Chronic Hepatitis B: management update.
 Chronic Hepatitis B: management update. E.O.Ogutu Department of clinical medicine & therapeutics, University of Nairobi. Physicians meeting,kisumu 2011. Background epidemiology Chronic hepatitis B (CHB)
Chronic Hepatitis B: management update. E.O.Ogutu Department of clinical medicine & therapeutics, University of Nairobi. Physicians meeting,kisumu 2011. Background epidemiology Chronic hepatitis B (CHB)
The role of entecavir in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B
 REVIEW The role of entecavir in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B Evangelini Dimou Vasilios Papadimitropoulos Stephanos J Hadziyannis Department of Medicine and Liver Unit, Henry Dunant Hospital, Athens,
REVIEW The role of entecavir in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B Evangelini Dimou Vasilios Papadimitropoulos Stephanos J Hadziyannis Department of Medicine and Liver Unit, Henry Dunant Hospital, Athens,
Hepatitis B. What's the impact on the risk? Dr Himanshu Bhatia, Asia Chief Medical Officer ALUCA, Brisbane, Sept 2013
 Hepatitis B What's the impact on the risk? Dr Himanshu Bhatia, Asia Chief Medical Officer ALUCA, Brisbane, Sept 2013 Some quick facts about Hepatitis B Worldwide: 350-400 Million are chronic infections
Hepatitis B What's the impact on the risk? Dr Himanshu Bhatia, Asia Chief Medical Officer ALUCA, Brisbane, Sept 2013 Some quick facts about Hepatitis B Worldwide: 350-400 Million are chronic infections
CLINICAL LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2008;134:405 415 BILIARY TRACT Virologic Monitoring of Hepatitis B Virus Therapy in Clinical Trials and Practice: Recommendations for a Standardized Approach JEAN MICHEL PAWLOTSKY,*, GEOFFREY
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2008;134:405 415 BILIARY TRACT Virologic Monitoring of Hepatitis B Virus Therapy in Clinical Trials and Practice: Recommendations for a Standardized Approach JEAN MICHEL PAWLOTSKY,*, GEOFFREY
Recent achievements in the treatment of hepatitis B by nucleosides and nucleotides. K. Zhdanov
 EASL endorsed conference White Nights of Hepatology 2012 Adverse events during antiviral therapy: how to predict, manage and monitor June 7-8 Saint-Petersburg Recent achievements in the treatment of hepatitis
EASL endorsed conference White Nights of Hepatology 2012 Adverse events during antiviral therapy: how to predict, manage and monitor June 7-8 Saint-Petersburg Recent achievements in the treatment of hepatitis
Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is an important. New and Emerging Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2007;5:285 294 New and Emerging Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B EMMET B. KEEFFE* and PATRICK MARCELLIN *Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Stanford University
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2007;5:285 294 New and Emerging Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B EMMET B. KEEFFE* and PATRICK MARCELLIN *Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Stanford University
Management of chronic hepatitis B : recent advance in the treatment of antiviral resistance
 anagement of chronic hepatitis B : recent advance in the treatment of antiviral resistance / 김강모 연수강좌 anagement of chronic hepatitis B : recent advance in the treatment of antiviral resistance 김강모 울산대학교의과대학서울아산병원소화기내과
anagement of chronic hepatitis B : recent advance in the treatment of antiviral resistance / 김강모 연수강좌 anagement of chronic hepatitis B : recent advance in the treatment of antiviral resistance 김강모 울산대학교의과대학서울아산병원소화기내과
Viral Hepatitis Diagnosis and Management
 Viral Hepatitis Diagnosis and Management CLINICAL BACKGROUND Viral hepatitis is a relatively common disease (25 per 100,000 individuals in the United States) caused by a diverse group of hepatotropic agents
Viral Hepatitis Diagnosis and Management CLINICAL BACKGROUND Viral hepatitis is a relatively common disease (25 per 100,000 individuals in the United States) caused by a diverse group of hepatotropic agents
New therapeutic strategies in HBV patients
 New therapeutic strategies in HBV patients Philippe HALFON MD, PhD Associate Professor of Medecine Internal Medecine and Infectious Diseases, Hopital Europeen, Marseille, France. NUC + PEG IFN, HBsAg Clearance
New therapeutic strategies in HBV patients Philippe HALFON MD, PhD Associate Professor of Medecine Internal Medecine and Infectious Diseases, Hopital Europeen, Marseille, France. NUC + PEG IFN, HBsAg Clearance
Dr David Rowbotham NHS. The Leeds Teaching Hospitals. NHS Trust
 Dr David Rowbotham The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust NHS Nurses Update June 2010 Chronic Hepatitis HBV / HCV David Rowbotham Clinical Director & Consultant Gastroenterologist Dept of Gastroenterology
Dr David Rowbotham The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust NHS Nurses Update June 2010 Chronic Hepatitis HBV / HCV David Rowbotham Clinical Director & Consultant Gastroenterologist Dept of Gastroenterology
Hepatitis B Virus therapy. Maria Buti Hospital Universitario Valle Hebron Barcelona Spain
 Hepatitis B Virus therapy Maria Buti Hospital Universitario Valle Hebron Barcelona Spain Disclosures Advisor: AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, Merck Sharp &
Hepatitis B Virus therapy Maria Buti Hospital Universitario Valle Hebron Barcelona Spain Disclosures Advisor: AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, Merck Sharp &
Hepatitis B Update. Jorge L. Herrera, M.D. University of South Alabama Mobile, AL. Gastroenterology
 Hepatitis B Update Jorge L. Herrera, M.D. University of South Alabama Mobile, AL Deciding Who to Treat Is hepatitis B a viral disease or a liver disease? Importance of HBV-DNA Levels in the Natural History
Hepatitis B Update Jorge L. Herrera, M.D. University of South Alabama Mobile, AL Deciding Who to Treat Is hepatitis B a viral disease or a liver disease? Importance of HBV-DNA Levels in the Natural History
Durability Of Lamivudine Associated HBe Antigen Seroconversion in Chinese-Canadian Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Gastroenterology Volume 4 Number 2 Durability Of Lamivudine Associated HBe Antigen Seroconversion in Chinese-Canadian Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Gastroenterology Volume 4 Number 2 Durability Of Lamivudine Associated HBe Antigen Seroconversion in Chinese-Canadian Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
Choice of Oral Drug for Hepatitis B: Status Asokananda Konar
 Choice of Oral Drug for Hepatitis B: Status 2011 Asokananda Konar Chronic hepatitis B (CHB) is a global public health challenge with an estimated 350 to 400 million people with chronic HBV infection, despite
Choice of Oral Drug for Hepatitis B: Status 2011 Asokananda Konar Chronic hepatitis B (CHB) is a global public health challenge with an estimated 350 to 400 million people with chronic HBV infection, despite
Final Clinical Study Report. to the Dossier SYNOPSIS. Final Clinical Study Report for Study AI463110
 BMS-475 AI463 Name of Sponsor/Company: Bristol-Myers Squibb Individual Study Table Referring to the Dossier For National Authority Use Only) Name of Finished Product: Baraclude Name of Active Ingredient:
BMS-475 AI463 Name of Sponsor/Company: Bristol-Myers Squibb Individual Study Table Referring to the Dossier For National Authority Use Only) Name of Finished Product: Baraclude Name of Active Ingredient:
Treatment of chronic hepatitis B 2013 update
 22 February 213 Treatment of chronic hepatitis B 213 update Pietro Lampertico 1st Gastroenterology Unit Fondazione IRCCS Cà Granda - Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico Università di Milano EASL 212 Clinical
22 February 213 Treatment of chronic hepatitis B 213 update Pietro Lampertico 1st Gastroenterology Unit Fondazione IRCCS Cà Granda - Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico Università di Milano EASL 212 Clinical
Y. Xiang*, P. Chen*, J.R Xia and L.P. Zhang
 A large-scale analysis study on the clinical and viral characteristics of hepatitis B infection with concurrence of hepatitis B surface or E antigens and their corresponding antibodies Y. Xiang*, P. Chen*,
A large-scale analysis study on the clinical and viral characteristics of hepatitis B infection with concurrence of hepatitis B surface or E antigens and their corresponding antibodies Y. Xiang*, P. Chen*,
Our better understanding of the natural
 TREATMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS B: MASTERING THE BASICS ON A COMPLEX TOPIC Ke-Qin Hu, MD* ABSTRACT The availability of newer antiviral agents, as well as comprehensive treatment recommendations, has equipped
TREATMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS B: MASTERING THE BASICS ON A COMPLEX TOPIC Ke-Qin Hu, MD* ABSTRACT The availability of newer antiviral agents, as well as comprehensive treatment recommendations, has equipped
J.C. WANG, L.L. HE, Q. CHEN 1. Introduction. Abstract. BACKGROUND: Either combination. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Comparison of re-treatment outcomes of lamivudine plus adefovir or entecavir in chronic hepatitis B patients with viral relapse after cessation
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Comparison of re-treatment outcomes of lamivudine plus adefovir or entecavir in chronic hepatitis B patients with viral relapse after cessation
Pegasys Hepatitis B. Pegasys (peginterferon alfa-2a) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.03.02 Subject: Pegasys Hepatitis B Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: September 18, 2015 Pegasys Hepatitis
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.03.02 Subject: Pegasys Hepatitis B Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: September 18, 2015 Pegasys Hepatitis
Hepatitis B Virus therapy. Maria Buti Hospital Universitario Valle Hebron Barcelona Spain
 Hepatitis B Virus therapy Maria Buti Hospital Universitario Valle Hebron Barcelona Spain Disclosures Advisor: AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, Merck Sharp &
Hepatitis B Virus therapy Maria Buti Hospital Universitario Valle Hebron Barcelona Spain Disclosures Advisor: AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, Merck Sharp &
STUDY IN BETWEEN SERUM HBsAg, HBV DNA & BLOOD IMMUNE CELLS IN VIRAL HEPATITIS-B INFECTION OF NORTH INDIANS
 STUDY IN BETWEEN SERUM HBsAg, HBV DNA & BLOOD IMMUNE CELLS IN VIRAL HEPATITIS-B INFECTION OF NORTH INDIANS *Javed B. Mulla Department of Medical Biochemistry, F H Medical College &Hospital, Firozabad *Author
STUDY IN BETWEEN SERUM HBsAg, HBV DNA & BLOOD IMMUNE CELLS IN VIRAL HEPATITIS-B INFECTION OF NORTH INDIANS *Javed B. Mulla Department of Medical Biochemistry, F H Medical College &Hospital, Firozabad *Author
An Update HBV Treatment
 An Update HBV Treatment Epidemiology Natural history Treatment Daryl T.-Y. Lau, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine Director of Translational Liver Research Division of Gastroenterology BIDMC, Harvard
An Update HBV Treatment Epidemiology Natural history Treatment Daryl T.-Y. Lau, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine Director of Translational Liver Research Division of Gastroenterology BIDMC, Harvard
Chronic HBV Management in 2013
 Chronic HBV Management in 2013 Mohammad Hossein Somi MD Professor of Gastroentrology and hepatology Liver and Gastrointestinal Disease Research Center Tabriz University of Medical Sciences 1 HBV in 2013
Chronic HBV Management in 2013 Mohammad Hossein Somi MD Professor of Gastroentrology and hepatology Liver and Gastrointestinal Disease Research Center Tabriz University of Medical Sciences 1 HBV in 2013
Management of Hepatitis B - Information for primary care providers
 Management of Hepatitis B - Information for primary care providers July 2018 Chronic hepatitis B (CHB) is often a lifelong condition. Not everyone infected needs anti-viral therapy. This document outlines
Management of Hepatitis B - Information for primary care providers July 2018 Chronic hepatitis B (CHB) is often a lifelong condition. Not everyone infected needs anti-viral therapy. This document outlines
Novedades en el tratamiento de la hepatitis B: noticias desde la EASL. Maria Buti Hospital Universitario Valle Hebrón Barcelona
 Novedades en el tratamiento de la hepatitis B: noticias desde la EASL Maria Buti Hospital Universitario Valle Hebrón Barcelona Milestones in CHB treatment Conventional IFN 1991 Lamivudine (LAM) 1998 Adefovir
Novedades en el tratamiento de la hepatitis B: noticias desde la EASL Maria Buti Hospital Universitario Valle Hebrón Barcelona Milestones in CHB treatment Conventional IFN 1991 Lamivudine (LAM) 1998 Adefovir
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy Advance Access published April 25, 2013
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy Advance Access published April 25, 213 J Antimicrob Chemother doi:1.193/jac/dkt147 Virological response to entecavir reduces the risk of liver disease progression
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy Advance Access published April 25, 213 J Antimicrob Chemother doi:1.193/jac/dkt147 Virological response to entecavir reduces the risk of liver disease progression
Chronic Hepatitis B - Antiviral Resistance in Korea -
 Chronic Hepatitis B - Antiviral Resistance in Korea - Young-Suk Lim University of Ulsan College of Medicine Asan Medical Center Seoul, Korea HBV Genome partially double-stranded DNA genome about 3200 nucleotides
Chronic Hepatitis B - Antiviral Resistance in Korea - Young-Suk Lim University of Ulsan College of Medicine Asan Medical Center Seoul, Korea HBV Genome partially double-stranded DNA genome about 3200 nucleotides
HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. with a nucleos(t)ide analogue?
 4 th PARIS HEPATITIS CONFERENCE HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B Why do I treat my chronic hepatitis B patients with a nucleos(t)ide analogue? George V. Papatheodoridis, MD 2nd Department of Internal
4 th PARIS HEPATITIS CONFERENCE HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B Why do I treat my chronic hepatitis B patients with a nucleos(t)ide analogue? George V. Papatheodoridis, MD 2nd Department of Internal
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Centre for Clinical Practice SCOPE Clinical guideline title: Hepatitis B (chronic): diagnosis and management of chronic hepatitis B in children, young
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Centre for Clinical Practice SCOPE Clinical guideline title: Hepatitis B (chronic): diagnosis and management of chronic hepatitis B in children, young
Treatment as a form of liver cancer prevention The clinical efficacy and cost effectiveness of treatment across Asia
 Treatment as a form of liver cancer prevention The clinical efficacy and cost effectiveness of treatment across Asia Prof. Henry LY Chan Head, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Director, Institute
Treatment as a form of liver cancer prevention The clinical efficacy and cost effectiveness of treatment across Asia Prof. Henry LY Chan Head, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Director, Institute
Need for long-term evaluation of therapy in Chronic Hepatitis B
 Need for long-term evaluation of therapy in Chronic Hepatitis B VHPB meeting Budapest 18/03/2010 Solko Schalm & Mehlika Toy Licensed Therapy Chronic hepatitis B Drug Date of Efficacy Disease Clinical Mortality
Need for long-term evaluation of therapy in Chronic Hepatitis B VHPB meeting Budapest 18/03/2010 Solko Schalm & Mehlika Toy Licensed Therapy Chronic hepatitis B Drug Date of Efficacy Disease Clinical Mortality
Scottish Medicines Consortium
 Scottish Medicines Consortium tenofovir disoproxil (as fumarate), 245 mg film-coated tablet (Viread ) No. (479/08) Gilead Sciences 06 June 2008 The Scottish Medicines Consortium has completed its assessment
Scottish Medicines Consortium tenofovir disoproxil (as fumarate), 245 mg film-coated tablet (Viread ) No. (479/08) Gilead Sciences 06 June 2008 The Scottish Medicines Consortium has completed its assessment
Antiviral Therapy 2012; 17: (doi: /IMP1945)
 Antiviral Therapy 2012; 17:387 394 (doi: 10.3851/IMP1945) Original article HBV DNA level at 24 weeks is the best predictor of virological response to adefovir add-on therapy in patients with lamivudine
Antiviral Therapy 2012; 17:387 394 (doi: 10.3851/IMP1945) Original article HBV DNA level at 24 weeks is the best predictor of virological response to adefovir add-on therapy in patients with lamivudine
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Centre for Clinical Practice SCOPE Clinical guideline title: Hepatitis B (chronic): diagnosis and management of chronic hepatitis B in children, young
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Centre for Clinical Practice SCOPE Clinical guideline title: Hepatitis B (chronic): diagnosis and management of chronic hepatitis B in children, young
Emerging Drug List ADEFOVIR DIPIVOXIL FOR HEPATITIS B VIRUS INFECTION NO. 48 SEPTEMBER Generic (Trade Name): Adefovir dipivoxil (Hepsera TM )
 Generic (Trade Name): Manufacturer: Adefovir dipivoxil (Hepsera TM ) Gilead Sciences, Inc. NO. 48 SEPTEMBER 2003 Indication: Current Regulatory Status: For the treatment of adults showing evidence of active
Generic (Trade Name): Manufacturer: Adefovir dipivoxil (Hepsera TM ) Gilead Sciences, Inc. NO. 48 SEPTEMBER 2003 Indication: Current Regulatory Status: For the treatment of adults showing evidence of active
Role of Hepatitis B Virus Genotypes in Chronic Hepatitis B Exacerbation
 BRIEF REPORT Role of Hepatitis B Virus Genotypes in Chronic Hepatitis B Exacerbation Man-Fung Yuen, 1 Erwin Sablon, 2 Danny Ka-Ho Wong, 1 He-Jun Yuan, 1 Benjamin Chun-Yu Wong, 1 Annie On-On Chan, 1 and
BRIEF REPORT Role of Hepatitis B Virus Genotypes in Chronic Hepatitis B Exacerbation Man-Fung Yuen, 1 Erwin Sablon, 2 Danny Ka-Ho Wong, 1 He-Jun Yuan, 1 Benjamin Chun-Yu Wong, 1 Annie On-On Chan, 1 and
Discontinuation of Nucleotide or Nucleoside Analogue therapy for Chronic Hepatitis B infection
 Discontinuation of Nucleotide or Nucleoside Analogue therapy for Chronic Hepatitis B infection Dr Abid Suddle Institute of Liver Studies King s College Hospital Why consider discontinuation of NA therapy?
Discontinuation of Nucleotide or Nucleoside Analogue therapy for Chronic Hepatitis B infection Dr Abid Suddle Institute of Liver Studies King s College Hospital Why consider discontinuation of NA therapy?
HBV NATURAL HISTORY. Mitchell L. Shiffman, MD Director Liver Institute of Virginia Bon Secours Health System Richmond and Newport News, Virginia
 HBV NATURAL HISTORY AND MANAGMENT Mitchell L. Shiffman, MD Director Liver Institute of Virginia Bon Secours Health System Richmond and Newport News, Virginia IVer Liver Institute of Virginia Education,
HBV NATURAL HISTORY AND MANAGMENT Mitchell L. Shiffman, MD Director Liver Institute of Virginia Bon Secours Health System Richmond and Newport News, Virginia IVer Liver Institute of Virginia Education,
Intron A Hepatitis B. Intron A (interferon alfa-2b) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.01.01 Subject: Intron A Hepatitis B Page: 1 of 7 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Intron A Hepatitis
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.01.01 Subject: Intron A Hepatitis B Page: 1 of 7 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Intron A Hepatitis
entecavir, 0.5mg and 1mg film-coated tablets and 0.05 mg/ml oral solution, Baraclude SMC No. (747/11) Bristol-Myers Squibb Pharmaceuticals Ltd
 entecavir, 0.5mg and 1mg film-coated tablets and 0.05 mg/ml oral solution, Baraclude SMC No. (747/11) Bristol-Myers Squibb Pharmaceuticals Ltd 09 December 2011 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has
entecavir, 0.5mg and 1mg film-coated tablets and 0.05 mg/ml oral solution, Baraclude SMC No. (747/11) Bristol-Myers Squibb Pharmaceuticals Ltd 09 December 2011 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has
A Treatment Algorithm for the Management of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection in the United States: 2015 Update
 Accepted Manuscript A Treatment Algorithm for the Management of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection in the United States: 2015 Update Paul Martin, MD, Daryl T.-Y. Lau, MD, MSc, MPH, Mindie H. Nguyen, MD,
Accepted Manuscript A Treatment Algorithm for the Management of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection in the United States: 2015 Update Paul Martin, MD, Daryl T.-Y. Lau, MD, MSc, MPH, Mindie H. Nguyen, MD,
Hepatitis B: Treatment Strategies for Currently Available Drugs
 Hepatitis B: Treatment Strategies for Currently Available Drugs Robert P. Perrillo, MD Address Section of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Ochsner Clinic, 1514 Jefferson Highway, New Orleans, LA 70124,
Hepatitis B: Treatment Strategies for Currently Available Drugs Robert P. Perrillo, MD Address Section of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Ochsner Clinic, 1514 Jefferson Highway, New Orleans, LA 70124,
Management of HBV in KidneyTransplanted Patients Dr.E.Nemati
 Management of HBV in KidneyTransplanted Patients Dr.E.Nemati Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection confers a significantly negative impact on the clinical outcomes of kidney
Management of HBV in KidneyTransplanted Patients Dr.E.Nemati Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection confers a significantly negative impact on the clinical outcomes of kidney
Is there a need for combination therapy? No. Maria Buti Hospital General Universitario Valle Hebron Barcelona. Spain
 Is there a need for combination therapy? No Maria Buti Hospital General Universitario Valle Hebron Barcelona. Spain No, No and No EASL Update HBV Guidelines 2012 The most potent drugs with the optimal
Is there a need for combination therapy? No Maria Buti Hospital General Universitario Valle Hebron Barcelona. Spain No, No and No EASL Update HBV Guidelines 2012 The most potent drugs with the optimal
Don t interfere My first choice is always nucs!
 Don t interfere My first choice is always nucs! Robert G Gish MD Professor Consultant Stanford University Medical Director, Hepatitis B Foundation Singapore Viral Hepatitis Meeting 2014 1 Disclosures Dr
Don t interfere My first choice is always nucs! Robert G Gish MD Professor Consultant Stanford University Medical Director, Hepatitis B Foundation Singapore Viral Hepatitis Meeting 2014 1 Disclosures Dr
Hepatitis B Cure: from discovery to regulatory endpoints in HBV clinical research A summary of the AASLD/EASL statement
 Hepatitis B Cure: from discovery to regulatory endpoints in HBV clinical research A summary of the AASLD/EASL statement Fabien Zoulim Service d hépatologie, Hospices Civils de Lyon INSERM U1052, Cancer
Hepatitis B Cure: from discovery to regulatory endpoints in HBV clinical research A summary of the AASLD/EASL statement Fabien Zoulim Service d hépatologie, Hospices Civils de Lyon INSERM U1052, Cancer
Hepatitis B and D Update on clinical aspects
 Hepatitis B and D Update on clinical aspects B. Müllhaupt Gastroenterology and Hepatology Swiss Transplant and HPB-Center University Hospital Zurich beat.muellhaupt@usz.ch B.M. 11.11.17 Hepatitis Strategy
Hepatitis B and D Update on clinical aspects B. Müllhaupt Gastroenterology and Hepatology Swiss Transplant and HPB-Center University Hospital Zurich beat.muellhaupt@usz.ch B.M. 11.11.17 Hepatitis Strategy
HBV in HIV Forgotten but not Gone
 Activity Code FA376 HBV in HIV Forgotten but not Gone Richard K. Sterling, MD, MSc VCU Hepatology Professor of Medicine Chief, Section of Hepatology Virginia Commonwealth University Learning Objectives
Activity Code FA376 HBV in HIV Forgotten but not Gone Richard K. Sterling, MD, MSc VCU Hepatology Professor of Medicine Chief, Section of Hepatology Virginia Commonwealth University Learning Objectives
Chronic hepatitis B (CHB) infection is a large
 AMERICAN ASSOCIATION FOR THE STUDY OFLIVERD I S E ASES HEPATOLOGY, VOL. 64, NO. 2, 2016 Serum Levels of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen and DNA Can Predict Inactive Carriers With Low Risk of Disease Progression
AMERICAN ASSOCIATION FOR THE STUDY OFLIVERD I S E ASES HEPATOLOGY, VOL. 64, NO. 2, 2016 Serum Levels of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen and DNA Can Predict Inactive Carriers With Low Risk of Disease Progression
Hepatitis B virus infection. Chow Wan Cheng Dept of Gastroenterology & Hepatology Singapore General Hospital
 Hepatitis B virus infection Chow Wan Cheng Dept of Gastroenterology & Hepatology Singapore General Hospital Chronic Hepatitis B - are we in the same situation as hepatitis C? Treatment of chronic hepatitis
Hepatitis B virus infection Chow Wan Cheng Dept of Gastroenterology & Hepatology Singapore General Hospital Chronic Hepatitis B - are we in the same situation as hepatitis C? Treatment of chronic hepatitis
Min Weng, Wei-Zheng Zeng *, Xiao-Ling Wu, Yong Zhang, Ming-De Jiang, Zhao Wang, De-Jiang Zhou and Xuan He
 Weng et al. Virology Journal 2013, 10:277 RESEARCH Open Access Quantification of serum hepatitis B surface antigen in predicting the response of pegylated interferon alfa-2a in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis
Weng et al. Virology Journal 2013, 10:277 RESEARCH Open Access Quantification of serum hepatitis B surface antigen in predicting the response of pegylated interferon alfa-2a in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis
NH2 N N N O N O O P O O O O O
 N N NH 2 N N O O P O O O O O O James Watson and Francis Crick Double Helix 1953 Baruch Blumberg, MD, PhD 1925-2011 Australia Antigen 1965 Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Hepadnaviridae member that primarily infects
N N NH 2 N N O O P O O O O O O James Watson and Francis Crick Double Helix 1953 Baruch Blumberg, MD, PhD 1925-2011 Australia Antigen 1965 Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Hepadnaviridae member that primarily infects
C hronic hepatitis B (CHB) virus infection affects more
 161 HEPATITIS Prognostic determinants for chronic hepatitis B in Asians: therapeutic implications MF Yuen, HJ Yuan, D KH Wong, J CH Yuen, WM Wong, A OO Chan, B CY Wong, KC Lai, CL Lai... See end of article
161 HEPATITIS Prognostic determinants for chronic hepatitis B in Asians: therapeutic implications MF Yuen, HJ Yuan, D KH Wong, J CH Yuen, WM Wong, A OO Chan, B CY Wong, KC Lai, CL Lai... See end of article
Scottish Medicines Consortium
 Scottish Medicines Consortium pegylated Interferon alfa 2a, 180 mcg for subcutaneous injection (Pegasys ) No. (186/05) Roche New indication (chronic hepatitis B) 10 June 2005 The Scottish Medicines Consortium
Scottish Medicines Consortium pegylated Interferon alfa 2a, 180 mcg for subcutaneous injection (Pegasys ) No. (186/05) Roche New indication (chronic hepatitis B) 10 June 2005 The Scottish Medicines Consortium
