Immunology Molecular regulation of the immune system
|
|
|
- Samantha Shaw
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Immunology Molecular regulation of the immune system - Introduction - Monika Raulf Lecture
2 Molecular medicine - Immunology Date Topic Lecturer Introduction Raulf Innate Immunity Peters Antigen presentation Peters T-cell biology Raulf B-cell biology & Antibodies Raulf Complement-System* Raulf Signal transduction in Immune cells Gnipp Pfingstferien/Whitsun holiday Immune cell traffic Gnipp Immune response to pathogens Nietsche Manipulation of the immune response* Peters Allergy & Autoimmunity* Peters Immunological methods* Peters Revision course Raulf *Workshop character Monika Raulf 2
3 For your credit, what is necessary? MSc: Regular participation Oral presentation of a workshop theme Exam (30 min) BSc: Regular participation Exam (30 min) Monika Raulf 3
4 What is immunology? Immunology is the science of the biological and biochemical essentials of the defence mechanisms, which protect the human body by contact with pathogens and toxins. Monika Raulf 4
5 Agenda I Introduction; Anatomy of the immune system Innate and acquired immunity Immunological methods Antigen presenting cells T-cells (development and TCR) Complement system Monika Raulf 5
6 Agenda II Antibodies/B-cells Allergy and autoimmunity Immunology of infection Tumor immunology and transplantation Monika Raulf 6
7 Tasks of the immune system Protection of the body against damaging influences Establishment of a powerful defense Monika Raulf 7
8 What is the immune system? Decentralized barrier immunis (lat.) = free, untouched The immune system is no single organ. It consists of specialized cells in blood and tissue, organs and a vascular system. primary lymph organs Bone marrow Thymus secondary lymph organs Lymph node Spleen Tonsils Appendix Nasal polyps Monika Raulf 8
9 Proceedings/milestones of immunology I 1796 Edward Jenner (brit. physician) Monika Raulf 9
10 1796 Edward Jenner (brit. physician) used the cowpox virus for an efficient smallpox vaccination. Monika Raulf 10
11 Proceedings/milestones of immunology II Louis Pasteur developed vaccines against chicken cholera, anthrax and hydrophobia/canine madness Robert Koch detected the pathogens of tuberculosis, cholera and anthrax (Nobel Prize 1905), Koch sche postulates Elie Metschnikow (rus.) detected phagocytic cells; Nobel Prize 1908 together with Paul Ehrlich; about their studies on Immunity Monika Raulf 11
12 Proceedings/milestones of the immunology III Emil von Behring and Shibasaburo Kitasato described antibodies in blood of immunized patients (Nobel Prize 1901) ( Circulating antitoxins against diphtheria and tetanus toxins ) Karl Landsteiner detected the A/B/0 blood group system (Nobel Prize 1930) C.P. von Pirquet created the term Hypersensitivity/Allergy Ludwig Hirszfeld and Emil von Dungern Genetic of the immune system/heredity of the blood groups Charles Richet Anaphylaxis (Nobel Prize). Monika Raulf 12
13 Proceedings/milestones of the immunology IV 1936 Peter Gorer Study to the transplant shedding (MHC-/H-2-antigens) Birth of the cellular immunology Frank Macfarlane Burnet described the clone selection theory as central principle of the adaptive immunity; immunological tolerance (Nobel Prize 1960 together with Peter B. Medawar) Detection of IgE; Kimishige and Teruko Ishizaka Research and detection of the lymphokine/cytokine (Stanley Cohen together with Rita Levi-Montalcini Nobel Prize 1986 for the detection of NGF and EGF; Cohen suggested 1974 the term Cytokine ). Monika Raulf 13
14 Proceedings/milestones of the immunology V 1974 Rolf Zinkernagel Description of the MHCrestriction for the T-cells antigen recognization (Nobel Prize 1996) Georges Köhler, César Milstein and Niels K. Jerne implementation of monoclonal antibodies (hybridoma formation) (Nobel Prize 1984). Sune Bergström, Bengt Ingemar Samuelsson, John Robert Vane Detection of prostagladines (Nobel Prize 1982) Tonegawa Susumu Identification of the immunoglobulin genes and antibody diversity (1987 Nobel Prize). Monika Raulf 14
15 Tasks of the immune system I Recognition and inactivation of the pathogens (viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoa and worms) penetrated in the organism or their toxins. Recognition and killing of virus infected somatic cells. Phagocytic cell Phagocytic cell engulfs the virus Demolition of the virus in the phagocytic cell Recognition and killing of cancer cells. Monika Raulf 15
16 Tasks of the immune system II Basic features to fulfil the tasks: Determination between self and foreign material Determination between harmless and potential harmful Monika Raulf 16
17 Development of the immune system The ability to distinguish self and foreign enables the integrity of the living body (education already very early in the evolution). Self-tolerance Monika Raulf 17
18 Advantage Protection against infections by: Bacteria Viruses Fungi Parasites Vaccination Disadvantage Mistakes of the immune defence: Innate or acquired immunodeficiency Tumour disease Autoimmune disease Allergies Transplantations Monika Raulf 18
19 Range of the infecting agents, which attack the immune system Worms Tapeworm Roundworm Schistosoma Filariae Protozoa Amoeba Leishmania Trypanosomes Malaria Fungi Aspergillus Candida Bacteria Mycobacteria Staphylococci Rickettsia Chlamydia Mycoplasma Viruses Pox Influenza Polio Monika Raulf 19
20 The defence line Innate immunity Mechanical/chemical and microbial barriers e.g. of skin, gut, lung, eyes, nose, oral cavity Symptoms like cough, sneezing, vomiting, diarrhoea Monika Raulf 20
21 Surface epithelia provide mechanical, chemical and microbiological barrier to infection Inner epithelia barriers against infections mechanical chemical microbiological by tight junctions connected epithelial cells Air- or fluid flow along the epithelia Mucus flow by cilia Fatty acids (skin) Enzymes: Lysozyme (saliva, sweat, tears), Pepsin (bowel/gut) low ph-value (stomach) antibacterial peptides; defensins (skin, gut), cryptidins (gut) The normal microorganism flora competes for nutrients and binding sites on epithelial cells and is able to synthesize antibacterial substances Monika Raulf 21
22 Immune response: defence reaction to exogenous substances Innate immunity Acquired/adaptive immunity Occurs without previous contact to the extrinsic substance, organism or tissue An initial first contact to the exogenous substance is necessary Learning impulse Monika Raulf 22
23 Possibility to get sick in the case of an infection yes or no? Infection Re-infection innate immunity unspecific immune system adaptive immune system specific immunological memory Disease Recovery No disease Monika Raulf 23
24 Innate Immunity Natural/mechanical barriers Skin, mucus movement via cilia (air- or fluid-flow along the epithelia; normal gut flora) Chemical barriers proteolytic enzymes in body fluids digestive enzymes, lysozyme in salivary fluid, in tear fluid low ph-value in the gut Two key player -celltypes monocytes/macrophages + granulocytes endocytosis Complement system Monika Raulf 24
25 Frontline Phagocytes 2. Line of defence Macrophages (in the tissue (mononuclear)) (Development) Monocytes (in blood) long lasting via activation cytokines* and other mediators are released, attraction of other cells, e.g. neutrophile granulocytes Neutrophile granulocytes = PMN=polymorphonuclear neutrophils (just in blood, not in tissue) short survival *important for local inflammatory reactions and mediation of the induced, not-adapted reaction Monika Raulf 25
26 Advantages of the innate immunity relative unspecific clear differentiation between self and foreign fast first frontline Monika Raulf 26
27 Acquired/adaptive immunity mammal and birds reached the highest development stage specific directed against the exogenous antigen humoral two systems Immunglobulins cellular T-cell mediated cytokines Monika Raulf 27
28 Key player of the adaptive immune response T-cells T-cells just recognize antigens, which are presented on the cell surfaces. Components thereby are: Proceedings that take place: APC with MHC-molecules T-cell receptor (TCR) Antigen processing, formation of peptide fragments, production of TCR-ligands Antigen presentation common with MHC Monika Raulf 28
29 Nonspecific and specific immune system Innate Immunity Adaptive or acquired immunity Repeated infection Soluble (humoral) factors Cell-mediated (cellular) defence The susceptibility does not decrease in the case of repeated infection Complement, lysozyme, cytokine of APC (interferon α and β, TNFα) Phagocytes (macrophages, neutrophile), NK-cells The susceptibility decreases in the case of repeated infection (immunological memory) Antibodies, cytokines of the lymphocytes (interleukin and interferon γ) Lymphocytes; (T- und B-cells) Monika Raulf 29
30 Cellular defence 1) Phagocytic cells: Neutrophile granulocytes (60-70%) Bacteria 2) NK-cells (natural killer cells) Polymorphic neutrophils Monocytes ( macrophages) (5%) Eosinophile granulocytes (1.5%) Parasites Monika Raulf 30
31 Phagocytosis, activation of anti bacterial mechanisms Mortification of (by antibodies marked) parasites Monika Raulf 31
32 Like mast cells, to find in blood Release of granule, which contain e.g. histamine and other active substances Monika Raulf 32
33 Phagocytosis and activation of anti bacterial mechanisms Antigen presentation Antigen admission in the periphery Antigen presentation in the lymph node Monika Raulf 33
34 NK-cells: natural killer cells Function Release of lytic granule, which can kill virusinfected cells and tumour cells ~ 10% of all lymphocytes in blood are NK-cells NK-cells: kill cells, which bear no, extrinsic, just a few or altered MHC I-molecules (inhibitory signals by intact MHC I) Activating signals based on e.g. carbohydrate-structures of cells ( Killer-receptors or C-type-lectin) NK-cells are activated by macrophage cytokines (IL-12, TNF-α) or interferon (α and β) γ Monika Raulf 34
35 Development of the blood cells Bone marrow pluripotent hematopoietic stem cell Bone marrow common lymphoid progenitor common myeloid progenitor granulocyte/ macrophage progenitor megakaryocytes/ erythrocyte progenitor megakaryocyte erythroblast All cells of the blood derive from one common precursor cell (haematopoietic stem cell), which can develop to a lymphoid precursor cell or to a myeloid precursor cell. Monika Raulf 35
36 Lymphatic Organs Lymphatic organs (structured tissue of lymphatic and non-lymphatic cells): Development of the lymphocytes Preface of the adaptive immune response Survival of the lymphocytes Lymphatic organs are separated into: central (primary) lymphatic organs as location of development of the lymphocytes. peripheral (secondary) lymphatic organs (Preface of the adaptive immune response). Monika Raulf 36
37 Primary lymphatic organs B-cells arise and mature in the marrow (bone-marrow). T-cells arise in the marrow but mature first in the thymus. Matured B- and T-cells move over the blood into the secondary lymphatic organs, where they encounter the antigens. Antigen = initially: antibodies generating now: Inducer of an adaptive immune response Monika Raulf 37
38 Specific disease adaptive immune response Antigen Exposure Infected cell humoral B-cell Antibodies Development and release Stimulation Antigen presenting cell (APC) T-helper cell Presentation Stimulation B- and T- memory cells Stimulation Presentation Cytotoxic T- cell cellular Lysis of infected cells and tumour cells Monika Raulf 38
39 Macroskopic site of the thymus Children Adults Trachea a Thyroid Thymus Lung Heart Diaphragm Liver Monika Raulf 39
40 Secondary lymphatic organs No matter where the pathogens penetrate, antigens and lymphocytes meet each other in the secondary lymphatic organs: Lymph node Spleen lymphatic tissue of the mucous membranes: Gut-associated lymphatic tissue (gut-associated: GALT): pharyngeal tonsils, palatal tonsils, appendix, Peyersche plaques (small intestine) Bronchia-associated lymphatic tissue BALT (Mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue MALT) in the respiration epithelia and other mucous membranes Monika Raulf 40
41 Construction of the spleen Red pulp: Degeneration of red blood cells (ca /day) White pulp: B- and T-cells Monika Raulf 41
42 Immunological processes at an infection Infection directly: 0-4 hrs Recognition by unspecific effectors Extraction of the pathogens Infection early: 4-96 hrs Attraction of effector cells Recognition, activation of effector cells Infection late: >96 hrs Transportation of antigens to the lymph organs Recognition by naive B- and T-cells Clonale expansion and differentiation to effector cells Renewed infection Recognition by existing antibodies and T-cells Renewed infection Recognition by B- memory cells and T- cells Quickly expansion and differentiation to effector cells Monika Raulf 42
Immunology Molecular regulation of the immune system
 Immunology Molecular regulation of the immune system - Introduction - Lecture 11.04.2018 Molecular medicine - Immunology Date Topic Lecturer 11.04.18 Introduction Raulf 18.04.18 Innate immunity Peters
Immunology Molecular regulation of the immune system - Introduction - Lecture 11.04.2018 Molecular medicine - Immunology Date Topic Lecturer 11.04.18 Introduction Raulf 18.04.18 Innate immunity Peters
Immune System. Biol 105 Lecture 16 Chapter 13
 Immune System Biol 105 Lecture 16 Chapter 13 Outline Immune System I. Function of the Immune system II. Barrier Defenses III. Nonspecific Defenses A. Immune system cells B. Inflammatory response C. Complementary
Immune System Biol 105 Lecture 16 Chapter 13 Outline Immune System I. Function of the Immune system II. Barrier Defenses III. Nonspecific Defenses A. Immune system cells B. Inflammatory response C. Complementary
Immunobiology. Readiness Exam. Immune Response (two phases)
 BIO401 Immunobiology BOOK Kuby 6 th Edition* EXAMS - 3 exams - 100 points - Final--> 100 points - Quizzes 50 points TOTAL: 450 points FINAL GRADE: Lab: 25% (300 points) Lecture: 75% (450 points) Immunobiology
BIO401 Immunobiology BOOK Kuby 6 th Edition* EXAMS - 3 exams - 100 points - Final--> 100 points - Quizzes 50 points TOTAL: 450 points FINAL GRADE: Lab: 25% (300 points) Lecture: 75% (450 points) Immunobiology
Immune System. Biology 105 Lecture 16 Chapter 13
 Immune System Biology 105 Lecture 16 Chapter 13 Outline: Immune System I. Functions of the immune system II. Barrier defenses III. Non-specific defenses A. Immune system cells B. Inflammatory response
Immune System Biology 105 Lecture 16 Chapter 13 Outline: Immune System I. Functions of the immune system II. Barrier defenses III. Non-specific defenses A. Immune system cells B. Inflammatory response
Immune System. Biol 105 Chapter 13
 Immune System Biol 105 Chapter 13 Outline Immune System I. Function of the Immune system II. Barrier Defenses III. Nonspecific Defenses A. Immune system cells B. Inflammatory response C. Complementary
Immune System Biol 105 Chapter 13 Outline Immune System I. Function of the Immune system II. Barrier Defenses III. Nonspecific Defenses A. Immune system cells B. Inflammatory response C. Complementary
General Biology. A summary of innate and acquired immunity. 11. The Immune System. Repetition. The Lymphatic System. Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.
 A summary of innate and acquired immunity General iology INNATE IMMUNITY Rapid responses to a broad range of microbes Course No: NG00 Credits:.00 External defenses Invading microbes (pathogens). The Immune
A summary of innate and acquired immunity General iology INNATE IMMUNITY Rapid responses to a broad range of microbes Course No: NG00 Credits:.00 External defenses Invading microbes (pathogens). The Immune
Chapter 24 The Immune System
 Chapter 24 The Immune System The Immune System Layered defense system The skin and chemical barriers The innate and adaptive immune systems Immunity The body s ability to recognize and destroy specific
Chapter 24 The Immune System The Immune System Layered defense system The skin and chemical barriers The innate and adaptive immune systems Immunity The body s ability to recognize and destroy specific
Internal Defense Notes
 Internal environment of animals provides attractive area for growth of bacteria, viruses, fungi Harm via: 1. destruction of cells 2. production of toxic chemicals To protect against foreign invaders, humans
Internal environment of animals provides attractive area for growth of bacteria, viruses, fungi Harm via: 1. destruction of cells 2. production of toxic chemicals To protect against foreign invaders, humans
Immunology Lecture- 1
 Immunology Lecture- 1 Immunology and Immune System Immunology: Study of the components and function of the immune system Immune System a network collected from cells, tissues organs and soluble factors
Immunology Lecture- 1 Immunology and Immune System Immunology: Study of the components and function of the immune system Immune System a network collected from cells, tissues organs and soluble factors
Outline. Animals: Immunity. Defenses Against Disease. Key Concepts:
 Animals: Immunity Defenses Against Disease Outline 1. Key concepts 2. Physical barriers: Skin, Mucus and HCL in stomach 3. Non-specific 4. Specific responses Immune System a. Components of Immune system
Animals: Immunity Defenses Against Disease Outline 1. Key concepts 2. Physical barriers: Skin, Mucus and HCL in stomach 3. Non-specific 4. Specific responses Immune System a. Components of Immune system
Introduction to Immune System
 Introduction to Immune System Learning outcome You will be able to understand, at a fundamental level, the STRUCTURES and FUNCTIONS of cell surface and soluble molecules involved in recognition of foreign
Introduction to Immune System Learning outcome You will be able to understand, at a fundamental level, the STRUCTURES and FUNCTIONS of cell surface and soluble molecules involved in recognition of foreign
Immune system. Aims. Immune system. Lymphatic organs. Inflammation. Natural immune system. Adaptive immune system
 Aims Immune system Lymphatic organs Inflammation Natural immune system Adaptive immune system Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) Disorders of the immune system 1 2 Immune system Lymphoid organs Immune
Aims Immune system Lymphatic organs Inflammation Natural immune system Adaptive immune system Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) Disorders of the immune system 1 2 Immune system Lymphoid organs Immune
What is the immune system? Types of Immunity. Pasteur and rabies vaccine. Historical Role of smallpox. Recognition Response
 Recognition Response Effector memory What is the immune system? Types of Immunity Innate Adaptive Anergy: : no response Harmful response: Autoimmunity Historical Role of smallpox Pasteur and rabies vaccine
Recognition Response Effector memory What is the immune system? Types of Immunity Innate Adaptive Anergy: : no response Harmful response: Autoimmunity Historical Role of smallpox Pasteur and rabies vaccine
Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 The Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems 1 The Lymphatic Vessels Lymphoid Organs Three functions contribute to homeostasis 1. Return excess tissue fluid to the bloodstream 2. Help defend the body against
The Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems 1 The Lymphatic Vessels Lymphoid Organs Three functions contribute to homeostasis 1. Return excess tissue fluid to the bloodstream 2. Help defend the body against
Chapter 22: The Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Bio40C schedule Lecture Immune system Lab Quiz 2 this week; bring a scantron! Study guide on my website (see lab assignments) Extra credit Critical thinking questions at end of chapters 5 pts/chapter Due
Bio40C schedule Lecture Immune system Lab Quiz 2 this week; bring a scantron! Study guide on my website (see lab assignments) Extra credit Critical thinking questions at end of chapters 5 pts/chapter Due
The Immune System. These are classified as the Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses. Innate Immunity
 The Immune System Biological mechanisms that defend an organism must be 1. triggered by a stimulus upon injury or pathogen attack 2. able to counteract the injury or invasion 3. able to recognise foreign
The Immune System Biological mechanisms that defend an organism must be 1. triggered by a stimulus upon injury or pathogen attack 2. able to counteract the injury or invasion 3. able to recognise foreign
NOTES: CH 43, part 1 The Immune System - Nonspecific & Specific Defenses ( )
 NOTES: CH 43, part 1 The Immune System - Nonspecific & Specific Defenses (43.1-43.2) The lymphatic system is closely associated with the cardiovascular system. LYMPHATIC PATHWAYS Lymphatic capillaries
NOTES: CH 43, part 1 The Immune System - Nonspecific & Specific Defenses (43.1-43.2) The lymphatic system is closely associated with the cardiovascular system. LYMPHATIC PATHWAYS Lymphatic capillaries
immunity defenses invertebrates vertebrates chapter 48 Animal defenses --
 defenses Animal defenses -- immunity chapter 48 invertebrates coelomocytes, amoebocytes, hemocytes sponges, cnidarians, etc. annelids basophilic amoebocytes, acidophilic granulocytes arthropod immune systems
defenses Animal defenses -- immunity chapter 48 invertebrates coelomocytes, amoebocytes, hemocytes sponges, cnidarians, etc. annelids basophilic amoebocytes, acidophilic granulocytes arthropod immune systems
1. Lymphatic vessels recover about of the fluid filtered by capillaries. A. ~1% C. ~25% E. ~85% B. ~10% D. ~50%
 BIOL2030 Huaman A&P II -- Exam 3 -- XXXX -- Form A Name: 1. Lymphatic vessels recover about of the fluid filtered by capillaries. A. ~1% C. ~25% E. ~85% B. ~10% D. ~50% 2. Special lymphatic vessels called
BIOL2030 Huaman A&P II -- Exam 3 -- XXXX -- Form A Name: 1. Lymphatic vessels recover about of the fluid filtered by capillaries. A. ~1% C. ~25% E. ~85% B. ~10% D. ~50% 2. Special lymphatic vessels called
JPEMS Nantes, Basic Immunology Introduction to the immune system Definitions Structure and General Organization
 JPEMS Nantes, 2014- Basic Immunology Introduction to the immune system Definitions Structure and General Organization Teacher: Pr. Régis Josien, Laboratoire Immunologie and INSERM U1064, CHU Nantes Regis.Josien@univ-nantes.fr
JPEMS Nantes, 2014- Basic Immunology Introduction to the immune system Definitions Structure and General Organization Teacher: Pr. Régis Josien, Laboratoire Immunologie and INSERM U1064, CHU Nantes Regis.Josien@univ-nantes.fr
Physiology Unit 3. ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY The Specific Immune Response
 Physiology Unit 3 ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY The Specific Immune Response In Physiology Today The Adaptive Arm of the Immune System Specific Immune Response Internal defense against a specific pathogen Acquired
Physiology Unit 3 ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY The Specific Immune Response In Physiology Today The Adaptive Arm of the Immune System Specific Immune Response Internal defense against a specific pathogen Acquired
Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 24 The Immune System Multiple-Choice Questions
 Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 24 The Immune System 24.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The body's innate defenses against infection include A) several nonspecific
Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 24 The Immune System 24.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The body's innate defenses against infection include A) several nonspecific
Body Defense Mechanisms
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 13 Body Defense Mechanisms Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 13 Body Defense Mechanisms Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of
Chapter 43. Immune System. phagocytosis. lymphocytes. AP Biology
 Chapter 43. Immune System phagocytosis lymphocytes 1 Why an immune system? Attack from outside lots of organisms want you for lunch! animals must defend themselves against unwelcome invaders viruses protists
Chapter 43. Immune System phagocytosis lymphocytes 1 Why an immune system? Attack from outside lots of organisms want you for lunch! animals must defend themselves against unwelcome invaders viruses protists
The Lymphatic System and Immunity. Chapters 20 & 21
 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapters 20 & 21 Objectives 1. SC.912.L.14.52 - Explain the basic functions of the human immune system, including specific and nonspecific immune response, vaccines, and
The Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapters 20 & 21 Objectives 1. SC.912.L.14.52 - Explain the basic functions of the human immune system, including specific and nonspecific immune response, vaccines, and
Immunity. Chapter 38
 Immunity Chapter 38 Impacts, Issues Frankie s Last Wish Infection with a common, sexually transmitted virus (HPV) causes most cervical cancers including the one that killed Frankie McCullogh 38.1 Integrated
Immunity Chapter 38 Impacts, Issues Frankie s Last Wish Infection with a common, sexually transmitted virus (HPV) causes most cervical cancers including the one that killed Frankie McCullogh 38.1 Integrated
Chapter 1. Chapter 1 Concepts. MCMP422 Immunology and Biologics Immunology is important personally and professionally!
 MCMP422 Immunology and Biologics Immunology is important personally and professionally! Learn the language - use the glossary and index RNR - Reading, Note taking, Reviewing All materials in Chapters 1-3
MCMP422 Immunology and Biologics Immunology is important personally and professionally! Learn the language - use the glossary and index RNR - Reading, Note taking, Reviewing All materials in Chapters 1-3
Chapter 23 Immunity Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 23 Immunity Exam Study Questions 1. Define 1) Immunity 2) Neutrophils 3) Macrophage 4) Epitopes 5) Interferon 6) Complement system 7) Histamine 8) Mast cells 9) Antigen 10) Antigens receptors 11)
Chapter 23 Immunity Exam Study Questions 1. Define 1) Immunity 2) Neutrophils 3) Macrophage 4) Epitopes 5) Interferon 6) Complement system 7) Histamine 8) Mast cells 9) Antigen 10) Antigens receptors 11)
Warm-up. Parts of the Immune system. Disease transmission. Disease transmission. Why an immune system? Chapter 43 3/9/2012.
 Warm-up Objective: Explain how antigens react with specific lymphocytes to induce immune response and immunological memory. Warm-up: Which of the following would normally contain blood with the least amount
Warm-up Objective: Explain how antigens react with specific lymphocytes to induce immune response and immunological memory. Warm-up: Which of the following would normally contain blood with the least amount
Immune system - introduction. Radek Spisek Institute of Immunology, 2nd Medical School, Charles University
 Immune system - introduction Radek Spisek Institute of Immunology, 2nd Medical School, Charles University Edward JENNER 1749-1823 Eradication of variola (smallpox) Know The Enemy The immune system exists
Immune system - introduction Radek Spisek Institute of Immunology, 2nd Medical School, Charles University Edward JENNER 1749-1823 Eradication of variola (smallpox) Know The Enemy The immune system exists
Defense mechanism against pathogens
 Defense mechanism against pathogens Immune System What is immune system? Cells and organs within an animal s body that contribute to immune defenses against pathogens ( ) Bacteria -Major entry points ;open
Defense mechanism against pathogens Immune System What is immune system? Cells and organs within an animal s body that contribute to immune defenses against pathogens ( ) Bacteria -Major entry points ;open
Chapter 17. The Lymphatic System and Immunity. Copyright 2010, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 17 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Immunity Innate Immunity Fast, non-specific and no memory Barriers, ph extremes, Phagocytes & NK cells, fever, inflammation, complement, interferon Adaptive
Chapter 17 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Immunity Innate Immunity Fast, non-specific and no memory Barriers, ph extremes, Phagocytes & NK cells, fever, inflammation, complement, interferon Adaptive
AP Biology. Why an immune system? Chapter 43. Immune System. Lines of defense. 1st: External defense. 2nd: Internal, broad range patrol
 Chapter 43. Immune System lymphocytes attacking cancer cell lymph phagocytic leukocyte Why an immune system? Attack from outside lots of organisms want you for lunch! animals must defend themselves against
Chapter 43. Immune System lymphocytes attacking cancer cell lymph phagocytic leukocyte Why an immune system? Attack from outside lots of organisms want you for lunch! animals must defend themselves against
General Overview of Immunology. Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center
 General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
Prof. Ibtesam Kamel Afifi Professor of Medical Microbiology & Immunology
 By Prof. Ibtesam Kamel Afifi Professor of Medical Microbiology & Immunology Lecture objectives: At the end of the lecture you should be able to: Enumerate features that characterize acquired immune response
By Prof. Ibtesam Kamel Afifi Professor of Medical Microbiology & Immunology Lecture objectives: At the end of the lecture you should be able to: Enumerate features that characterize acquired immune response
Immune System AP SBI4UP
 Immune System AP SBI4UP TYPES OF IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY ACQUIRED IMMUNITY EXTERNAL DEFENCES INTERNAL DEFENCES HUMORAL RESPONSE Skin Phagocytic Cells CELL- MEDIATED RESPONSE Mucus layer Antimicrobial
Immune System AP SBI4UP TYPES OF IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY ACQUIRED IMMUNITY EXTERNAL DEFENCES INTERNAL DEFENCES HUMORAL RESPONSE Skin Phagocytic Cells CELL- MEDIATED RESPONSE Mucus layer Antimicrobial
1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity
 Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 13 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Lymphatic System. Where s your immunity idol?
 Lymphatic System Where s your immunity idol? Functions of the Lymphatic System Fluid Balance Drains excess fluid from tissues Lymph contains solutes from plasma Fat Absorption Lymphatic system absorbs
Lymphatic System Where s your immunity idol? Functions of the Lymphatic System Fluid Balance Drains excess fluid from tissues Lymph contains solutes from plasma Fat Absorption Lymphatic system absorbs
Chapter 38- Immune System
 Chapter 38- Immune System First Line of Defense: Barriers Nonspecific defenses, such as the skin and mucous membranes, are barriers to potential pathogens. In addition to being a physical barrier to pathogens,
Chapter 38- Immune System First Line of Defense: Barriers Nonspecific defenses, such as the skin and mucous membranes, are barriers to potential pathogens. In addition to being a physical barrier to pathogens,
Nonspecific External Barriers skin, mucous membranes
 Immune system Chapter 36 BI 103 Plant-Animal A&P Levels of Defense Against Disease Nonspecific External Barriers skin, mucous membranes Physical barriers? Brainstorm with a partner If these barriers are
Immune system Chapter 36 BI 103 Plant-Animal A&P Levels of Defense Against Disease Nonspecific External Barriers skin, mucous membranes Physical barriers? Brainstorm with a partner If these barriers are
ANATOMY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
 Immunity Learning objectives Explain what triggers an immune response and where in the body the immune response occurs. Understand how the immune system handles exogenous and endogenous antigen differently.
Immunity Learning objectives Explain what triggers an immune response and where in the body the immune response occurs. Understand how the immune system handles exogenous and endogenous antigen differently.
Blood and Immune system Acquired Immunity
 Blood and Immune system Acquired Immunity Immunity Acquired (Adaptive) Immunity Defensive mechanisms include : 1) Innate immunity (Natural or Non specific) 2) Acquired immunity (Adaptive or Specific) Cell-mediated
Blood and Immune system Acquired Immunity Immunity Acquired (Adaptive) Immunity Defensive mechanisms include : 1) Innate immunity (Natural or Non specific) 2) Acquired immunity (Adaptive or Specific) Cell-mediated
The Immune System. A macrophage. ! Functions of the Immune System. ! Types of Immune Responses. ! Organization of the Immune System
 The Immune System! Functions of the Immune System! Types of Immune Responses! Organization of the Immune System! Innate Defense Mechanisms! Acquired Defense Mechanisms! Applied Immunology A macrophage
The Immune System! Functions of the Immune System! Types of Immune Responses! Organization of the Immune System! Innate Defense Mechanisms! Acquired Defense Mechanisms! Applied Immunology A macrophage
Chapter Pages Transmission
 Chapter 19.2 Pages 442-448 Transmission Immunity There are three lines of defense: 1 The skin and mucous membranes are a nonspecific barrier to infection. 2 Macrophages attack pathogens that enter the
Chapter 19.2 Pages 442-448 Transmission Immunity There are three lines of defense: 1 The skin and mucous membranes are a nonspecific barrier to infection. 2 Macrophages attack pathogens that enter the
Lymphatic System. Chapter 14. Introduction. Main Channels of Lymphatics. Lymphatics. Lymph Tissue. Major Lymphatic Vessels of the Trunk
 Lymphatic System Chapter 14 Components Lymph is the fluid Vessels lymphatics Structures & organs Functions Return tissue fluid to the bloodstream Transport fats from the digestive tract to the bloodstream
Lymphatic System Chapter 14 Components Lymph is the fluid Vessels lymphatics Structures & organs Functions Return tissue fluid to the bloodstream Transport fats from the digestive tract to the bloodstream
11/25/2017. THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS BARRIER DEFENSES INNATE IMMUNITY OF VERTEBRATES
 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS Exoskeleton made of chitin forms the first barrier to pathogens Digestive system is protected by a chitin-based barrier and lysozyme,
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS Exoskeleton made of chitin forms the first barrier to pathogens Digestive system is protected by a chitin-based barrier and lysozyme,
VMC-221: Veterinary Immunology and Serology (1+1) Question Bank
 VMC-221: Veterinary Immunology and Serology (1+1) Objective type Questions Question Bank Q. No. 1 - Fill up the blanks with correct words 1. The British physician, who developed the first vaccine against
VMC-221: Veterinary Immunology and Serology (1+1) Objective type Questions Question Bank Q. No. 1 - Fill up the blanks with correct words 1. The British physician, who developed the first vaccine against
Adaptive Immunity: Specific Defenses of the Host
 17 Adaptive Immunity: Specific Defenses of the Host SLOs Differentiate between innate and adaptive immunity, and humoral and cellular immunity. Define antigen, epitope, and hapten. Explain the function
17 Adaptive Immunity: Specific Defenses of the Host SLOs Differentiate between innate and adaptive immunity, and humoral and cellular immunity. Define antigen, epitope, and hapten. Explain the function
The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses Outline PART 1: INNATE DEFENSES 21.1 Surface barriers act as the first line of defense to keep
 The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses Outline PART 1: INNATE DEFENSES 21.1 Surface barriers act as the first line of defense to keep invaders out of the body (pp. 772 773; Fig. 21.1; Table
The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses Outline PART 1: INNATE DEFENSES 21.1 Surface barriers act as the first line of defense to keep invaders out of the body (pp. 772 773; Fig. 21.1; Table
There are 2 major lines of defense: Non-specific (Innate Immunity) and. Specific. (Adaptive Immunity) Photo of macrophage cell
 There are 2 major lines of defense: Non-specific (Innate Immunity) and Specific (Adaptive Immunity) Photo of macrophage cell Development of the Immune System ery pl neu mφ nk CD8 + CTL CD4 + thy TH1 mye
There are 2 major lines of defense: Non-specific (Innate Immunity) and Specific (Adaptive Immunity) Photo of macrophage cell Development of the Immune System ery pl neu mφ nk CD8 + CTL CD4 + thy TH1 mye
Immune System. Before You Read. Read to Learn
 Immune System 37 section 2 The Immune System Biology/Life Sciences 10.b Students know the role of antibodies in the body s response to infection. Also covers: Biology/Life Sciences 10.a, 10.e, 10.f Components
Immune System 37 section 2 The Immune System Biology/Life Sciences 10.b Students know the role of antibodies in the body s response to infection. Also covers: Biology/Life Sciences 10.a, 10.e, 10.f Components
Ch. 11: Immune Physiology. 1. Review Immune Organs & Cells. Immune system = The cells and organs involved in defense against pathogens and cancer.
 Ch. 11: Immune Physiology Objectives: 1. Review immune organs & cells. 2. Two types of immunity. 3. Understand functions of immune cells (T-cells and B-cells) 4. Understand autoimmunity disorders. 1. Review
Ch. 11: Immune Physiology Objectives: 1. Review immune organs & cells. 2. Two types of immunity. 3. Understand functions of immune cells (T-cells and B-cells) 4. Understand autoimmunity disorders. 1. Review
Introduction to the immune system Innate humoral immunity
 Introduction to the immune system Innate humoral immunity Bartosz Wojciuk Immunology course for the 2nd year Medical Faculty students Pomeranian Medical University Academic year 2017/2018, winter semester
Introduction to the immune system Innate humoral immunity Bartosz Wojciuk Immunology course for the 2nd year Medical Faculty students Pomeranian Medical University Academic year 2017/2018, winter semester
Introduction to Immunology Lectures 1-3 by Bellur S. Prabhakar. March 13-14, 2007
 Introduction to Immunology Lectures 1-3 by Bellur S. Prabhakar. March 13-14, 2007 TheComponents Of The Immune System and Innate Immunity: Ref: Immunobiology-5 th edition. Janeway et al. Chapters-1 & 2.
Introduction to Immunology Lectures 1-3 by Bellur S. Prabhakar. March 13-14, 2007 TheComponents Of The Immune System and Innate Immunity: Ref: Immunobiology-5 th edition. Janeway et al. Chapters-1 & 2.
What are bacteria? Microbes are microscopic(bacteria, viruses, prions, & some fungi etc.) How do the sizes of our cells, bacteria and viruses compare?
 7.1 Microbes, pathogens and you Chp. 7 Lymphatic System & Immunity The interaction between microbes and humans? Microbes are very abundant in the environment and as well as in and on our bodies GOOD: We
7.1 Microbes, pathogens and you Chp. 7 Lymphatic System & Immunity The interaction between microbes and humans? Microbes are very abundant in the environment and as well as in and on our bodies GOOD: We
WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT?
 CHAPTER 16 THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? The adaptive immune system protects us from many infections The adaptive immune system has memory so we are not infected by the same pathogen
CHAPTER 16 THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? The adaptive immune system protects us from many infections The adaptive immune system has memory so we are not infected by the same pathogen
CH. 24. The Immune System
 CH. 24 The Immune System The immune systems consists of organs, cells, and molecules that fight infections and protect us from invaders. Pathogens: Bacteria, Viruses, Parasites, Fungi 1. Innate (nonspecific)
CH. 24 The Immune System The immune systems consists of organs, cells, and molecules that fight infections and protect us from invaders. Pathogens: Bacteria, Viruses, Parasites, Fungi 1. Innate (nonspecific)
(b) fluid returns to venous end of capillary due to hydrostatic pressure and osmotic pressure
 (Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Lymphatic System and Immunity (Body Defenses) I. (Slide 2) Introduction A) General 1) Lymphatic System performs 2 basic functions: 2) Organs of the Lymphatic System (a) lymphatic
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Lymphatic System and Immunity (Body Defenses) I. (Slide 2) Introduction A) General 1) Lymphatic System performs 2 basic functions: 2) Organs of the Lymphatic System (a) lymphatic
Overview. Barriers help animals defend against many dangerous pathogens they encounter.
 Immunity Overview Barriers help animals defend against many dangerous pathogens they encounter. The immune system recognizes foreign bodies and responds with the production of immune cells and proteins.
Immunity Overview Barriers help animals defend against many dangerous pathogens they encounter. The immune system recognizes foreign bodies and responds with the production of immune cells and proteins.
All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 In innate immunity, recognition and
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 In innate immunity, recognition and
Resisting infection. Cellular Defenses: Leukocytes. Chapter 16: Innate host defenses Phagocytosis Lymph Inflammation Complement
 Resisting infection Chapter 16: Innate host defenses Lymph Inflammation Complement Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Innate defenses (ch. 16) Physical & chemical barriers; cellular defenses; inflammation, fever;
Resisting infection Chapter 16: Innate host defenses Lymph Inflammation Complement Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Innate defenses (ch. 16) Physical & chemical barriers; cellular defenses; inflammation, fever;
2/28/18. Lymphatic System and Immunity. Introduction. Anatomy. Chapter 27. Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system
 Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 1 Introduction Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 1 Introduction Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
Fluid movement in capillaries. Not all fluid is reclaimed at the venous end of the capillaries; that is the job of the lymphatic system
 Capillary exchange Fluid movement in capillaries Not all fluid is reclaimed at the venous end of the capillaries; that is the job of the lymphatic system Lymphatic vessels Lymphatic capillaries permeate
Capillary exchange Fluid movement in capillaries Not all fluid is reclaimed at the venous end of the capillaries; that is the job of the lymphatic system Lymphatic vessels Lymphatic capillaries permeate
Diseases-causing agents, pathogens, can produce infections within the body.
 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II 1 CHAPTER 16 Lecture: Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. LYMPHATIC and IMMUNE Systems Body Defenses Against
BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II 1 CHAPTER 16 Lecture: Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. LYMPHATIC and IMMUNE Systems Body Defenses Against
Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity
 MICR2209 Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will discuss the T-cell mediated immune response, how it is activated,
MICR2209 Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will discuss the T-cell mediated immune response, how it is activated,
- Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body. - Has disease-fighting functions - Helps maintain homeostasis
 Introduction Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
Introduction Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
Anatomy. Lymph: Tissue fluid that enters a lymphatic capillary (clear fluid that surrounds new piercings!)
 Lymphatic System Anatomy Lymphatic vessels: meet up in capillaries of of tissues to collect extra water, and have an end point of meeting up with lymphatic ducts that empty fluid into large veins in the
Lymphatic System Anatomy Lymphatic vessels: meet up in capillaries of of tissues to collect extra water, and have an end point of meeting up with lymphatic ducts that empty fluid into large veins in the
phagocytic leukocyte Immune System lymphocytes attacking cancer cell lymph system
 phagocytic leukocyte Immune System lymphocytes attacking cancer cell lymph system 2006-2007 1) recognizing the presence of an infection; 2) containing the infection and working to eliminate it; 3) regulating
phagocytic leukocyte Immune System lymphocytes attacking cancer cell lymph system 2006-2007 1) recognizing the presence of an infection; 2) containing the infection and working to eliminate it; 3) regulating
A short History of Immunology
 A short History of Immunology Note: I would like to point out that the doctor explained some theories that are not mentioned in the slides. - The first documented evidence regarding the concept of immunity
A short History of Immunology Note: I would like to point out that the doctor explained some theories that are not mentioned in the slides. - The first documented evidence regarding the concept of immunity
LYMPHATIC AND IMMUNE SYSTEMS. Chapter 33
 LYMPHATIC AND IMMUNE SYSTEMS Chapter 33 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM The lymphatic system has three main functions Take up excess tissue fluid and return it to the bloodstream Receive fats called lipoproteins
LYMPHATIC AND IMMUNE SYSTEMS Chapter 33 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM The lymphatic system has three main functions Take up excess tissue fluid and return it to the bloodstream Receive fats called lipoproteins
Aging of the skin results in a loss of elasticity and the appearance of wrinkles
 Aging of the skin results in a loss of elasticity and the appearance of wrinkles University of Baghdad College of Nursing Department of Basic Medical Sciences Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second
Aging of the skin results in a loss of elasticity and the appearance of wrinkles University of Baghdad College of Nursing Department of Basic Medical Sciences Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second
4) What causes lymph to move? Skeletal muscle contraction; smooth muscle contraction, breathing (like blood moves through veins)
 NPHS Anatomy & Physiology UNIT 10 REVIEW GUIDE Lymphatic System 1) List the three functions of the lymphatic system. transports excess fluid to the bloodstream absorbs fats helps defend the body against
NPHS Anatomy & Physiology UNIT 10 REVIEW GUIDE Lymphatic System 1) List the three functions of the lymphatic system. transports excess fluid to the bloodstream absorbs fats helps defend the body against
Chapter 07 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 07 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 07 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
The immune system is made up of a complex and vital network of cells and organs that protect the body from infection.
 IMMUNE SYSTEM Viruses, bacteria and other germs are all around us. Most of the time, a healthy immune system keeps us well. The purpose of the immune system is to keep infectious micro-organisms, such
IMMUNE SYSTEM Viruses, bacteria and other germs are all around us. Most of the time, a healthy immune system keeps us well. The purpose of the immune system is to keep infectious micro-organisms, such
The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately
 The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 INNATE IMMUNITY (all animals) Recognition of traits shared
The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 INNATE IMMUNITY (all animals) Recognition of traits shared
I. Lines of Defense Pathogen: Table 1: Types of Immune Mechanisms. Table 2: Innate Immunity: First Lines of Defense
 I. Lines of Defense Pathogen: Table 1: Types of Immune Mechanisms Table 2: Innate Immunity: First Lines of Defense Innate Immunity involves nonspecific physical & chemical barriers that are adapted for
I. Lines of Defense Pathogen: Table 1: Types of Immune Mechanisms Table 2: Innate Immunity: First Lines of Defense Innate Immunity involves nonspecific physical & chemical barriers that are adapted for
CHAPTER-VII IMMUNOLOGY R.KAVITHA, M.PHARM, LECTURER, DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACEUTICS, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY, SRM UNIVERSITY, KATTANKULATHUR.
 CHAPTER-VII IMMUNOLOGY R.KAVITHA, M.PHARM, LECTURER, DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACEUTICS, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY, SRM UNIVERSITY, KATTANKULATHUR. The Immune Response Immunity: Free from burden. Ability of an
CHAPTER-VII IMMUNOLOGY R.KAVITHA, M.PHARM, LECTURER, DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACEUTICS, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY, SRM UNIVERSITY, KATTANKULATHUR. The Immune Response Immunity: Free from burden. Ability of an
Overview of the immune system
 Overview of the immune system Immune system Innate (nonspecific) 1 st line of defense Adaptive (specific) 2 nd line of defense Cellular components Humoral components Cellular components Humoral components
Overview of the immune system Immune system Innate (nonspecific) 1 st line of defense Adaptive (specific) 2 nd line of defense Cellular components Humoral components Cellular components Humoral components
Topics in Parasitology BLY Vertebrate Immune System
 Topics in Parasitology BLY 533-2008 Vertebrate Immune System V. Vertebrate Immune System A. Non-specific defenses against pathogens 1. Skin - physical barrier a. Tough armor protein KERATIN b. Surface
Topics in Parasitology BLY 533-2008 Vertebrate Immune System V. Vertebrate Immune System A. Non-specific defenses against pathogens 1. Skin - physical barrier a. Tough armor protein KERATIN b. Surface
PATHOGENS AND DEFENCE AGAINST INFECTIOUS DISEASE. By: Stephanie, Emily, Cem, and Julie
 PATHOGENS AND DEFENCE AGAINST INFECTIOUS DISEASE By: Stephanie, Emily, Cem, and Julie Pathogen Pathogen: an organism or virus that causes a disease. Examples: bacteria, fungi, protozoa, virus Disease Cause
PATHOGENS AND DEFENCE AGAINST INFECTIOUS DISEASE By: Stephanie, Emily, Cem, and Julie Pathogen Pathogen: an organism or virus that causes a disease. Examples: bacteria, fungi, protozoa, virus Disease Cause
chapter 17: specific/adaptable defenses of the host: the immune response
 chapter 17: specific/adaptable defenses of the host: the immune response defense against infection & illness body defenses innate/ non-specific adaptable/ specific epithelium, fever, inflammation, complement,
chapter 17: specific/adaptable defenses of the host: the immune response defense against infection & illness body defenses innate/ non-specific adaptable/ specific epithelium, fever, inflammation, complement,
Immunology. Lecture ( 7 ) Dr, Baha,Hamdi,AL-Amedi Ph. D.Microbiology HOST DEFENSE
 Immunology Lecture ( 7 ) Dr, Baha,Hamdi,AL-Amedi Ph. D.Microbiology HOST DEFENSE The Origin of Immune Concept-I The term Immunity-1 Latin word Immunitas :Protection from legal prosecution Biological definition:
Immunology Lecture ( 7 ) Dr, Baha,Hamdi,AL-Amedi Ph. D.Microbiology HOST DEFENSE The Origin of Immune Concept-I The term Immunity-1 Latin word Immunitas :Protection from legal prosecution Biological definition:
Comparative Physiology. Bio 2 Unit 3a
 Comparative Physiology Bio 2 Unit 3a Life Cell (Plasma) Membrane Homeostasis Thermoregulation Conduction Convection Radiation Evaporative Cooling Ectotherm Endotherm Respiration O 2 Cellular Level Diffusion
Comparative Physiology Bio 2 Unit 3a Life Cell (Plasma) Membrane Homeostasis Thermoregulation Conduction Convection Radiation Evaporative Cooling Ectotherm Endotherm Respiration O 2 Cellular Level Diffusion
immunity produced by an encounter with an antigen; provides immunologic memory. active immunity clumping of (foreign) cells; induced by crosslinking
 active immunity agglutination allografts immunity produced by an encounter with an antigen; provides immunologic memory. clumping of (foreign) cells; induced by crosslinking of antigenantibody complexes.
active immunity agglutination allografts immunity produced by an encounter with an antigen; provides immunologic memory. clumping of (foreign) cells; induced by crosslinking of antigenantibody complexes.
Chapter 33: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 Chapter 33: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems AP Curriculum Alignment The immune system is one of the human systems that is detailed in Big Idea 2and Chapter 33 provides these details. Programmed cell death
Chapter 33: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems AP Curriculum Alignment The immune system is one of the human systems that is detailed in Big Idea 2and Chapter 33 provides these details. Programmed cell death
Overview of the Lymphoid System
 Overview of the Lymphoid System The Lymphoid System Protects us against disease Lymphoid system cells respond to Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells, such as cancers Overview of the Lymphoid
Overview of the Lymphoid System The Lymphoid System Protects us against disease Lymphoid system cells respond to Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells, such as cancers Overview of the Lymphoid
Chapter 21: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses
 Chapter 21: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses I. 2 main types of body defenses A. Innate (nonspecific) defense: not to a specific microorganism or substance B. Adaptive (specific) defense: immunity to
Chapter 21: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses I. 2 main types of body defenses A. Innate (nonspecific) defense: not to a specific microorganism or substance B. Adaptive (specific) defense: immunity to
The Immune System is the Third Line of Defense Against Infection. Components of Human Immune System
 Chapter 17: Specific Host Defenses: The Immune Response The Immune Response Immunity: Free from burden. Ability of an organism to recognize and defend itself against specific pathogens or antigens. Immune
Chapter 17: Specific Host Defenses: The Immune Response The Immune Response Immunity: Free from burden. Ability of an organism to recognize and defend itself against specific pathogens or antigens. Immune
1. Specificity: specific activity for each type of pathogens. Immunity is directed against a particular pathogen or foreign substance.
 L13: Acquired or adaptive (specific) immunity The resistance, which absent at the time of first exposure to a pathogen, but develops after being exposed to the pathogen is called acquired immunity. It
L13: Acquired or adaptive (specific) immunity The resistance, which absent at the time of first exposure to a pathogen, but develops after being exposed to the pathogen is called acquired immunity. It
Immunology. Recognition and Response
 Immunology Recognition and Response Immunology, before the germ theory of disease Disease was believed to have a spiritual cause, thus cures and treatments were also spiritual During the Plague of Athens,
Immunology Recognition and Response Immunology, before the germ theory of disease Disease was believed to have a spiritual cause, thus cures and treatments were also spiritual During the Plague of Athens,
all of the above the ability to impart long term memory adaptive immunity all of the above bone marrow none of the above
 1. (3 points) Immediately after a pathogen enters the body, it faces the cells and soluble proteins of the innate immune system. Which of the following are characteristics of innate immunity? a. inflammation
1. (3 points) Immediately after a pathogen enters the body, it faces the cells and soluble proteins of the innate immune system. Which of the following are characteristics of innate immunity? a. inflammation
Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au
 Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 8 Immune System 1 Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan
Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 8 Immune System 1 Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan
INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response. Physiology Unit 3
 INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response Physiology Unit 3 Protection Against Infection The body has several defenses to protect itself from getting an infection Skin Mucus membranes Serous membranes
INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response Physiology Unit 3 Protection Against Infection The body has several defenses to protect itself from getting an infection Skin Mucus membranes Serous membranes
primary : thymus, bone marrow lymphoid tissue secondary : lymph nodes, MALT, spleen spleen: there are 2 main types of tissues in the spleen :
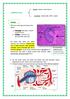 primary : thymus, bone marrow lymphoid tissue secondary : lymph nodes, MALT, spleen spleen: there are 2 main types of tissues in the spleen : 1. white pulp (gray area) : contains lymphoid tissue 2. red
primary : thymus, bone marrow lymphoid tissue secondary : lymph nodes, MALT, spleen spleen: there are 2 main types of tissues in the spleen : 1. white pulp (gray area) : contains lymphoid tissue 2. red
Chapter 35 Active Reading Guide The Immune System
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 35 Active Reading Guide The Immune System Section 1 Phagocytosis plays an important role in the immune systems of both invertebrates and vertebrates. Review the process
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 35 Active Reading Guide The Immune System Section 1 Phagocytosis plays an important role in the immune systems of both invertebrates and vertebrates. Review the process
Immune System Notes Innate immunity Acquired immunity lymphocytes, humoral response Skin lysozyme, mucus membrane
 Immune System Notes I. The immune system consists of innate and acquired immunity. A. An animal must defend itself against unwelcome intruders the many potentially dangerous viruses, bacteria, and other
Immune System Notes I. The immune system consists of innate and acquired immunity. A. An animal must defend itself against unwelcome intruders the many potentially dangerous viruses, bacteria, and other
3/28/2012. Immune System. Activation of Innate Immunity. Innate (non-specific) Immunity
 Chapter 5 Outline Defense Mechansims Functions of B Lymphocytes Functions of T Lymphocytes Active and Passive Immunity Tumor Immunology Diseases Caused By Immune System Immune System Anatomy - Lymphoid
Chapter 5 Outline Defense Mechansims Functions of B Lymphocytes Functions of T Lymphocytes Active and Passive Immunity Tumor Immunology Diseases Caused By Immune System Immune System Anatomy - Lymphoid
Instructor s Guide. Films for the. Humanities & Sciences i A Wealth of Information. A World of Ideas. The Human Body: How It Works THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
 i A Wealth of Information. A World of Ideas. Instructor s Guide The Human Body: How It Works Introduction This program is part of the nine-part series The Human Body: How It Works. The series uses physiologic
i A Wealth of Information. A World of Ideas. Instructor s Guide The Human Body: How It Works Introduction This program is part of the nine-part series The Human Body: How It Works. The series uses physiologic
