Adjuvant Guidance of T cell Responses
|
|
|
- Albert Hensley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Adjuvant Guidance of T cell Responses Cellular Technology Limited Presented by Magdalena Tary-Lehmann, M.D., Ph.D. September 2014
2 Introduction to Cellular Technology Limited (CTL): Shaker Heights, Ohio, USA CTL-Laboratories (CRO) R&D-Laboratory (Research and Development) CLIA certified, GLP-Laboratory (ELISPOT, ELISA, multiplex cytokine bead arrays, FACS, ) assay development, qualification and validation, and testing Whole blood shipping kits and logistical support Serve as Central Laboratory for whole blood processing and cryopreservation of PBMC CTL-Consumables Cryopreserved, uncharacterized, HLA-typed and immune characterized PBMC Standardized solutions (Serum free Media, etc.) Antigens: Peptides CTL- Analyzers ISO certified: Data Acquisition Systems: ImmunoSpot Analyzer, UVinstrumentations, BioSpot Analyzer etc. Supporting Software Applications, etc..
3 Current challenges facing broad implementation of Cell Mediated Immune (CMI) monitoring Functional, correlative biomarker assays require living sample/cell material Sufficient quantity and quality of cell material needs to be collected by diverse clinical sites (and usually can not be tested directly on site) Need to establish Effective Monitoring Test Systems, Validation Procedures and Standardization Reagents for primary cellbased assays (not cell-line based systems)
4 Required characteristics of assays to monitor CMI in regulated environments Measures a physiological and clinically relevant response Has a adequate, relevant sensitivity that is able to detect low frequency responses Lends itself to validation (ability to determining Accuracy, Precision, Specificity, Linearity and Limits of Detection) and is a reproducible assay for testing serial samples Objectivity through data analysis equipment that can be integrated in 21 CFR Part 11 compliant laboratory settings (i.e., system validation, computer generated audit trails)
5 Desirable features of assays for monitoring CMI in regulated environments Performs identical with fresh and previously frozen samples Works with out bred, genetically diverse populations Uses the least amount of cells and clinical sample material Scalable to accommodate large-volume testing with hundreds of samples in later stage clinical trials Can be standardized; to enable, for example, inter-study comparisons to make data more robust for multicenter or large international clinical trials
6 Commonly available assay technologies to evaluate cytokine production CMI Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) Supernatant based Luminex & Cytometric Bead Array (CBA) Enzyme-Linked Immunospot Assay (ELISPOT) Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorter (FACS) Intracytoplasmatic Cytokine Staining (ICS) Tetramer staining Pentamer staining Surface marker staining Establishes binding or phenotype of cells (Not True Functional Assays) Cell based
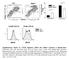
7 ELISPOT assay s unique qualification for immune monitoring Sensitivity: Routine detection limits of 1 in 500,000, or better. That is several ten to hundred folds more sensitive than ELISA, CBA, ICS, etc. Direct ex vivo cell frequencies: Measures the physiologic magnitude of T-cell immunity, with no need for in vitro expansion (not provided by ELISA, CBA, *ICS low, etc.) OD405 % IFN-γ positive cells FACS ELISA No need for HLA typing of subjects: Matching autologous APC are presented within the assay Samples not pharmacologically treated: No use of secretion inhibitors or cell permeability reagents as with ICS and FACS # of IFN-γ Spots/Well ELISPOT Number of Cells *(only applies to low frequency T cell responses)
8 ELISPOT assay s unique qualification for immune monitoring as fresh vs. cryopreserved cells perform equally Robustness: Cryopreservation allows collection of samples for trials, and testing in high throughput mode at a later time point. IFN-γ IL-2 Validation Capabilities: Assays can be validated under GLP with multiple cytokines and test systems (e.g., CTL Laboratories has validated for its clients human, mouse, NHP - non human primates, and pig test systems, among others) Linear Performance. IL-4 IL-5 Kreher et al. J. Immunol. Methods, 2003, 278 :79 93 Single cell resolution.
9 Principles of ELISPOT A Ab Membr ane B Antige n-st imulated cell Cytokine Un-stimulated cells C Plate bound cytokine D En zyme + dete ction ab ( e.g., anti-cytokine 2 ) Spot Chr omoge n E
10 Post-thymic T-cell differentiation
11 How Adjuvants guide T cell Responses Adjuvants are substances which enhance immune responses towards a co-administered antigen e.g. induce enhancement of antibody production, CD4 + T cell cytokine secretion, CD8 + T cell cytolytic activity Some mechanisms of action of adjuvants include: creating an antigen depot effect enhancing antigen delivery and uptake creating the appropriate cytokine milieu (immunomodulation) Is the influence the of the adjuvants on CD4 or CD8 T cells responses the same? (c) 2009 Cellular Technology Limited
12 Proliferation responses induced by all adjuvants used Yip et. Al,. J. Immunology, 162:
13 Influence of adjuvants on B-cell responses Different Ab isotypes with comparable magnitude were induced CFA (IgG1 and IgG2a) IFA (IgG1) Alum (IgG1) Yip et. Al,. J. Immunology, 162:
14 Detection of T cell response modulation requires parallel monitoring of multiple cytokines Yip et. Al,. J. Immunology, 162:
15 Yip et. Al,. J. Immunology, 162:
16 Forsthuber T, Yip HC, Lehmann PV Science 271: (c) 2009 Cellular Technology Limited - CONFIDENTIAL -
17 Detection of CD4 response modulation requires parallel monitoring of multiple cytokines Influence of adjuvants on CD4 T-cells: The choice of adjuvant during vaccination (i.e. IFA versus CFA) can switch peptide specific CD4 recall responses from Th1 (IFN-γ) to Th2 (IL-5) Yip et. Al,. J. Immunology, 162:
18 Induction of protective immunity against tumors continues to be a major challenge Tumor cells are immunologically similar to cells with normal growth characteristics. Tolerogenic mechanisms that normally prevent induction of autoimmunity may function to prevent protective immune response against the tumor. Mechanisms whereby tumors can escape immune recognition. Decreased expression of MHC molecules. Lack of costimulatory molecules. - can lead to deletion of specific T cells. - make the T cells unresponsive. Tumors can produce immunosuppressive molecules such as TGF-β
19 Tumor monitoring: Tumors are immunogenic in syngeneic mice RMA cell-induced IL-4, IL-6, IL-12 and TNF-α/β response in spleen cells of RAG-1 KO and naive C57BL/6 mice Bartholomae W.C. et.al J. Immunol. 173: J. Immunol. 168:
20 Tumors induced T cell immunity Bartholomae W.C. et.al J. Immunol., 173:
21 Cellular treatment with non tumorogenic tumor cells leads to protection to tumor challenge Bartholomae W.C. et.al J. Immunol. 2004, 173:
22 Immunity induced by vaccination with LS tumor is protective against LR tumor and induces a high frequency tumor specific type1 CD8 cell response α CD4 α CD8
23 Summary I : Tumors are immunogenic. Tumors induce a low frequency CD4 T cell response. Apoptotic and necrotic tumor cells do not change the cytokine signature, frequency, or CD4 / CD8 class of the T cell response and do not induce protective immunity. Immunity induced by vaccination with (non-tumorigenic) LS tumor is protective against (the syngeneic, but tumorigenic) LR tumor and induces a high frequency tumor specific type 1 CD4/CD8 cell response.
24 Can infectious non self signals help to trigger immune responses against tumor?
25 (c) 2009 Cellular Technology Limited - CONFIDENTIAL - CpG a type 1 adjuvant Chu RS J. Exp. Med. 186:
26 Can vaccination with purified tumor antigens or tumor peptides induce effective anti-tumor immunity? - peptide antigens are not immunogenic unless injected with adjuvant. - different adjuvants can guide T cell differentiation. - Alum: type 2 response - IFA : type 2 response - CFA :type 1 response - CpG : type 1 of T cell response
27 Adjuvant-guided CD4 cell response to H11.1 Stern B.V., Boehm B.B. and Tary-Lehmann M. J. Immunol. 168:
28 CpG: H11.1 injection induces specific protection against RMA tumor challenge Stern B.V., Boehm B.B. and Tary-Lehmann M. J. Immunol., 168:
29 CpG induces the highest frequency of H11.1- specific type 1 CD4 cells Stern B.V., Boehm B.B. and Tary-Lehmann M. J. Immunol.,168:
30 Intra-tumor injection of CpG ODN leads to tumor remission in immunocompetent B6 mice 30 CpG ncpg PBS * Tumor diameter (mm) I I 120 CpG Days after RMA challenge Lonsdorf A.S., et.al. J. Immunol. 171:
31 Intra-tumor CpG-injection induces tumorspecific CD4 and CD8 T cells in B6 mice Lonsdorf A.S., et.al. J. Immunol. 171:
32 CPG as treatment T cells adoptively transferred provide anti-tumor protection Lonsdorf A.S., et.al. J. Immunol. 171:
33 Summary II: (RMA-model) H11.1 peptide immunization in CFA and CpG both induced type 1 CD4 cell responses albeit of different magnitudes. Unlike the other adjuvants, H11.1: CpG induced protective immunity against RMA tumor. CpG-induced protection was IFN-γ-dependent Protection induced by the CD4 cells seems to be an indirect mechanism because the RMA tumor is class II negative. Intra-tumor CpG causes tumor rejection in immune competent, but not in T cell-deficient mice. Intra-tumor CpG induces anti-tumor T cell response (CD4 and CD8 cells that produce IFN-γ and are cytotoxic). These T cells adoptively transfer tumor specific protection.
34 Detection of CD4 response modulation requires parallel monitoring of multiple cytokines (cont.) Influence of adjuvants on CD4 T-cells (cont.): adjuvant induces similar numbers of IFN-γ and IL-2 producing CD4 cells, but IL-17 producing CD4 cells are induced by CFA only Tigno et al., J. Immunother, 32:
35 Immunizations using CFA but not CpG 1826/IFA result in DTH reactions (c) 2009 Cellular Technology Limited - CONFIDENTIAL -
36 (c) 2009 Cellular Technology Limited - CONFIDENTIAL - Immunizations with PLP: peptide in CFA induces EAE while immunization with CpG does not induce EAE Tigno et al., J. Immunother, 32:
37 (c) 2009 Cellular Technology Limited - CONFIDENTIAL - IL-17 neutralization reduces severity of clinical disease induced by CFA immunizations Tigno et al., J. Immunother, 32:
38 Differential induction of IFN-γ vs. IL-17 producing by CD4 cells, and of EAE by CFA and CpG immunizations In mice, injection of class II-restricted PLP peptide in different type 1 adjuvants induces: IFN-γ IL-2 IL-4 IL-5 IL-17 EAE DTH CFA CpG Tigno et al., J. Immunother, 32: (c) 2009 Cellular Technology Limited - CONFIDENTIAL -
39 Detection of CD8 response modulation requires parallel monitoring of multiple cytokines Use of Adjuvants with CD8 T-cells: A p < 0.01 IFN - g CFA CpG p < p < Immunization with Uty or SIINFEKL peptides plus CFA as adjuvant induce higher numbers of IFN-γ, IL-2 and IL-17 producing CD8 cells than immunizations with CpG SFU / 1 x 10 splenocytes B IL - 2 C IL - 17 p < 0.01 p < 0.01 p < 0.05 p < SFU / 2 x 10 CD8 T cells 50 p < Tigno et al., J. Immunother, 32: immunization PBS Uty challenge Uty bulk splenocytes PBS Uty PBS SIINFEKL Uty SIINFEKL purified CD8 T cells
40 Use of adjuvants with CD8 T-cells (cont.): Immunization with Uty or SIINFEKL peptides and CpG as adjuvant induces stronger in vivo killing than immunization with In vivo cytotoxicity CFA CpG PBS Uty 20 CFA 0 % specific lysis * p < * Uty 120 SIINFEKL % specific lysis * p = * 0 SIINFEKL Tigno et al., J. Immunother, 32:
41 Detection of CD8 response modulation requires parallel monitoring of multiple Cytokines (Summary) Use of Adjuvants with CD8 cells (cont.): The choice of adjuvant during vaccination (i.e. CFA versus CPG) can switch peptide specific CD8 recall responses between mainly DTH mediating or mainly cytotoxic responses IFN-γ IL-2 IL-17 Cytotoxicity DTH CFA CPG Tigno et al., J. Immunother, 32:
42 ELISPOT applications: Detection of vaccinia-specific CD8 + cells producing IFN-γ and GzB (cytolytic response) post vaccinia immunization A IFN-γ GzB 1 2 day day day 105 B IFN-γ spots/400,000 cells B IFN-γ day 0 day 14 day 105 C GzB spots/400,000 cells GzB day 0 day 14 day 105 Nowacki T.M. et al. Cell. Immunol May; 247 (1):36-48.
43 Other ELISPOT applications: B-cell monitoring: antigen-specific antibody production from PBMC Example of antigen-specific secretion of IgG (red) and IgA (blue) from PBMC Example of antigen-specific secretion of IgA, IgG2b, IgG3, IgG2a
44 B Cell ELISPOT vs. Serum Antibodies # 1 Spontaneous antibody secreting cells (ASC) identify active B cell response Saletti, et al.: Nature Protocols; Vol. 8, No. 6; 2013;
45 4-color B Cell ELISPOT
46 4-color Well
47 Dissecting the Ig classes: three-color detection of the HCMV specific antibody classes produced by polyclonally stimulated B cells: all three classes were produced yellow: IgG green: IgM blue: IgA PBMC were polyclonally stimulated for 4 days, then plated at 1 million cells per well in HCMV coated plate, followed by three color detection of Ig classes bound by HCMV. - CONFIDENTIAL - 47
48 - CONFIDENTIAL - Other ELISPOT platform applications: Example of in vitro Killing Assay Target CFSC-labeled cells (human PBMC) were mixed at different ratio with the effector cells (activated with peptide for 5 days) plus peptide.
49 Other ELISPOT platform applications: FluoroSpot TM virus Neutralization Assay - CONFIDENTIAL - 49
50 Standardization strategies for CMI monitoring and ELISPOT Harmonize sample collection at clinical sites Training and qualification of all clinical sites in proper sample handling, PBMC processing, cryopreservation and shipping standard operating procedures (SOPs) Harmonize methods across all participating laboratories Implementation of detailed SOPs for cell thawing, cell counting, assay procedures and the analysis of assay results Standardize all assay materials, including plates (CTL-kit), antibodies (CTL-kit), media (CTL) and enzymes Utilize cell-based reference sample PBMC (epbmc) to optimize assays and compare performance between laboratories
51 Inter-Lab standardization of ELISPOT: NEUCAPS Effort S. McArdle, R. Rees (UK, Nottingham) N. Haicheur, E. Tartour (France, Paris) A. Abdelsalam, A. DeLeo (USA, Pittsburgh) K. Johannesen, E.M. Inderberg-Suso, G. Gaudernack (Norway) Virginie Vignard, N. Labarriere, F. Jotereau (France, Nantes) P. Dudzik, K. Garula, Piotr Laidler (Poland) K. Georgakopoulou, S. Perez, C. Baxevanis (Greece) A. Mihaylova, E. Naumova (Bulgaria) K. Silina, A. Line (Latvia) N. Aptsiauri, F. Garrido (Spain) V. Adams (ONYVAX, UK) CTL reference laboratory (USA) Zhang W, et.al. J Immunotoxicol. Dec;6(4):
52 All laboratories were provided with THE SAME: Cryopreserved PBMC of three donors (provided by CTL) Serum free thawing, washing and testing reagents (by CTL) In addition, each lab also used its favorite tested serum HLA Class I restricted peptide (CMV pp65 NLVPMVATV frozen and ready to use concentration provided by CTL) Human IFN-γ ELISPOT Kit (provided by BD) Protocol (provided by CTL) All individuals performing the assay were ELISPOT inexperienced (except CTL reference laboratory) Zhang W, et.al. J Immunotoxicol Dec;6(4):
53 Inter-laboratory reproducibility of data for Reference Sample 1. IFNγ spots/400,000 PBMC IFN-γ spots/400,000 PBMC A Reference Results from laboratories 100% of labs detected the response Mean of the 9 labs results is within 3 standard deviation of the reference value
54 Inter-laboratory reproducibility of data for Reference Sample 2. IFNγ spots/400,000 PBMC B Reference Results from laboratories 100% of labs detected the response Mean of the 9 labs results are within 3 standard deviation of the reference value
55 Inter-laboratory reproducibility of data for Reference Sample 3 IFNγ spots/400,000 PBMC C Reference Results from laboratories 100% of labs detected the response Mean of the 9 labs results is within 3 standard deviation of the reference value
56 Assay performance in CTL media (serum free) versus serum containing media.
57 Conclusion Immunological assays are pivotal for the clinical development and monitoring phase. Immunology assays are scientifically sound and precise. ELISPOT is an ideal assay system for immune monitoring Works with frozen cells identical as with fresh samples Uses physiological stimuli (e.g. antigens, peptides, proteins) Very sensitive Robust High throughput capable (CTL can test up to 450 samples per week) Can be standardized Reproducible Appropriate readout system are essential to evaluate your drug/biologic or vaccine. Using inappropriate readout systems to asses the potential advocacy and effectiveness of drugs, biologics, vaccines etc. may render them undetected and for this reason, may have been rejected.
58 Acknowledgements W. Bartholomae T. Helms P. V. Lehmann A. S. Lonsdorf T. M. Nowacki B. V. Stern O. Targoni J. Tigno W. Zang H. Yip Magdalena Tary-Lehmann
The Adaptive Immune Responses
 The Adaptive Immune Responses The two arms of the immune responses are; 1) the cell mediated, and 2) the humoral responses. In this chapter we will discuss the two responses in detail and we will start
The Adaptive Immune Responses The two arms of the immune responses are; 1) the cell mediated, and 2) the humoral responses. In this chapter we will discuss the two responses in detail and we will start
Bead Based Assays for Cytokine Detection
 Bead Based Assays for Cytokine Detection September 27, 2014 6 th EFIS-EJI South East European Immunology School SEEIS 2014 Timisoara, Romania The Cells of the Immune System The Immune Reaction (Th2) (Th1)
Bead Based Assays for Cytokine Detection September 27, 2014 6 th EFIS-EJI South East European Immunology School SEEIS 2014 Timisoara, Romania The Cells of the Immune System The Immune Reaction (Th2) (Th1)
Challenges in Development and Validation of an Intracellular Cytokine Staining assay
 Challenges in Development and Validation of an Intracellular Cytokine Staining assay Jenny Hendriks, Crucell Hatching @ EBF, Brussels, June 202 www.crucell.com Vaccines vs Protein therapeutics Protein
Challenges in Development and Validation of an Intracellular Cytokine Staining assay Jenny Hendriks, Crucell Hatching @ EBF, Brussels, June 202 www.crucell.com Vaccines vs Protein therapeutics Protein
TITLE: Development of Antigen Presenting Cells for adoptive immunotherapy in prostate cancer
 AD Award Number: W8XWH-5-- TITLE: Development of Antigen Presenting Cells for adoptive immunotherapy in prostate cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Mathias Oelke Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Johns Hopkins
AD Award Number: W8XWH-5-- TITLE: Development of Antigen Presenting Cells for adoptive immunotherapy in prostate cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Mathias Oelke Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Johns Hopkins
TITLE: Development of Antigen Presenting Cells for adoptive immunotherapy in prostate cancer
 AD Award Number: W8-XWH-5-- TITLE: Development of Antigen Presenting Cells for adoptive immunotherapy in prostate cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Mathias Oelke,. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Johns Hopkins
AD Award Number: W8-XWH-5-- TITLE: Development of Antigen Presenting Cells for adoptive immunotherapy in prostate cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Mathias Oelke,. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Johns Hopkins
TITLE: Development of Antigen Presenting Cells for adoptive immunotherapy in prostate cancer
 AD Award Number: W8-XWH-5-- TITLE: Development of Antigen Presenting Cells for adoptive immunotherapy in prostate cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Mathias Oelke, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Johns Hopkins
AD Award Number: W8-XWH-5-- TITLE: Development of Antigen Presenting Cells for adoptive immunotherapy in prostate cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Mathias Oelke, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Johns Hopkins
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION
 Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Effector Responses: Cell- and Antibody-Mediated Immunity Copyright 2013 by W. H.
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Effector Responses: Cell- and Antibody-Mediated Immunity Copyright 2013 by W. H.
staining and flow cytometry
 Detection of influenza virus-specific T cell responses by intracellular by cytokine intracellular staining cytokine staining and flow cytometry Detection of influenza virus-specific T cell responses and
Detection of influenza virus-specific T cell responses by intracellular by cytokine intracellular staining cytokine staining and flow cytometry Detection of influenza virus-specific T cell responses and
Cellular Immune response. Jianzhong Chen, Ph.D Institute of immunology, ZJU
 Cellular Immune response Jianzhong Chen, Ph.D Institute of immunology, ZJU Concept of adaptive immune response T cell-mediated adaptive immune response I. Concept of immune response A collective and coordinated
Cellular Immune response Jianzhong Chen, Ph.D Institute of immunology, ZJU Concept of adaptive immune response T cell-mediated adaptive immune response I. Concept of immune response A collective and coordinated
HTRF MEASUREMENT OF CYTOKINE RELEASE FROM FRESH BLOOD SAMPLES
 HTRF MEASUREMENT OF CYTOKINE RELEASE FROM FRESH BLOOD SAMPLES APPLICATION NOTE ABSTRACT Cisbio offers a comprehensive line of HTRF cytokine assays to investigate the functional response of immune cells.
HTRF MEASUREMENT OF CYTOKINE RELEASE FROM FRESH BLOOD SAMPLES APPLICATION NOTE ABSTRACT Cisbio offers a comprehensive line of HTRF cytokine assays to investigate the functional response of immune cells.
NK cell flow cytometric assay In vivo DC viability and migration assay
 NK cell flow cytometric assay 6 NK cells were purified, by negative selection with the NK Cell Isolation Kit (Miltenyi iotec), from spleen and lymph nodes of 6 RAG1KO mice, injected the day before with
NK cell flow cytometric assay 6 NK cells were purified, by negative selection with the NK Cell Isolation Kit (Miltenyi iotec), from spleen and lymph nodes of 6 RAG1KO mice, injected the day before with
Immune Regulation and Tolerance
 Immune Regulation and Tolerance Immunoregulation: A balance between activation and suppression of effector cells to achieve an efficient immune response without damaging the host. Activation (immunity)
Immune Regulation and Tolerance Immunoregulation: A balance between activation and suppression of effector cells to achieve an efficient immune response without damaging the host. Activation (immunity)
Cellular Immunity in Aging and HIV: Correlates of Protection. Immune Senescence
 Cellular Immunity in Aging and HIV: Correlates of Protection Janet E. McElhaney, MD Professor of Medicine Allan M. McGavin Chair in Research Geriatrics University of British Columbia Vancouver, BC and
Cellular Immunity in Aging and HIV: Correlates of Protection Janet E. McElhaney, MD Professor of Medicine Allan M. McGavin Chair in Research Geriatrics University of British Columbia Vancouver, BC and
Engineering an in vitro human immune system for rapid vaccine evaluation
 Engineering an in vitro human immune system for rapid vaccine evaluation William Warren, Ph.D. VaxDesign Corporation Orlando, FL 32826 wwarren@vaxdesign.com www.vaxdesign.com 1 MIMIC Technology Overview
Engineering an in vitro human immune system for rapid vaccine evaluation William Warren, Ph.D. VaxDesign Corporation Orlando, FL 32826 wwarren@vaxdesign.com www.vaxdesign.com 1 MIMIC Technology Overview
Bioassays for Quality Control of Cell & Gene Therapy Products
 Bioassays for Quality Control of Cell & Gene Therapy Products Erik Rutjens, Cell & Gene Therapy, Novartis Pharma AG CASSS Bioassays, Silver Spring, March2015 CTL019 Introduction CARTs = Chimeric Antigen
Bioassays for Quality Control of Cell & Gene Therapy Products Erik Rutjens, Cell & Gene Therapy, Novartis Pharma AG CASSS Bioassays, Silver Spring, March2015 CTL019 Introduction CARTs = Chimeric Antigen
Cationic Liposome-DNA Complexes as Immunomodulators and Vaccine Adjuvants
 Cationic Liposome-DNA Complexes as Immunomodulators and Vaccine Adjuvants September 29, 28 Platform Technology Proprietary Cationic Lipid-DNA Complexes Cationic/Neutral Lipid + DNA = JVRS-1 JVRS-1 + Antigen
Cationic Liposome-DNA Complexes as Immunomodulators and Vaccine Adjuvants September 29, 28 Platform Technology Proprietary Cationic Lipid-DNA Complexes Cationic/Neutral Lipid + DNA = JVRS-1 JVRS-1 + Antigen
Human and mouse T cell regulation mediated by soluble CD52 interaction with Siglec-10. Esther Bandala-Sanchez, Yuxia Zhang, Simone Reinwald,
 Human and mouse T cell regulation mediated by soluble CD52 interaction with Siglec-1 Esther Bandala-Sanchez, Yuxia Zhang, Simone Reinwald, James A. Dromey, Bo Han Lee, Junyan Qian, Ralph M Böhmer and Leonard
Human and mouse T cell regulation mediated by soluble CD52 interaction with Siglec-1 Esther Bandala-Sanchez, Yuxia Zhang, Simone Reinwald, James A. Dromey, Bo Han Lee, Junyan Qian, Ralph M Böhmer and Leonard
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Complete but curtailed T-cell response to very-low-affinity antigen Dietmar Zehn, Sarah Y. Lee & Michael J. Bevan Supp. Fig. 1: TCR chain usage among endogenous K b /Ova reactive T cells. C57BL/6 mice
Complete but curtailed T-cell response to very-low-affinity antigen Dietmar Zehn, Sarah Y. Lee & Michael J. Bevan Supp. Fig. 1: TCR chain usage among endogenous K b /Ova reactive T cells. C57BL/6 mice
Cell-mediated Immunity
 Cellular & Molecular Immunology Cell-mediated Immunity Nicholas M. Ponzio, Ph.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine April 6, 2009 Today s Presentation: Overview Cellular Interactions In Humoral
Cellular & Molecular Immunology Cell-mediated Immunity Nicholas M. Ponzio, Ph.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine April 6, 2009 Today s Presentation: Overview Cellular Interactions In Humoral
Using Multiplex Assays and Assay Development to Enhance your Research Program James A. Lederer, PhD
 Using Multiplex Assays and Assay Development to Enhance your Research Program James A. Lederer, PhD Department of Surgery Brigham and Women s Hospital (BWH), BWH Biomedical Research Institute (BWH-BRI)
Using Multiplex Assays and Assay Development to Enhance your Research Program James A. Lederer, PhD Department of Surgery Brigham and Women s Hospital (BWH), BWH Biomedical Research Institute (BWH-BRI)
ELISPOTs Produced by CD8 and CD4 Cells Follow Log Normal Size Distribution Permitting Objective Counting
 Cells 2015, 4, 56-70; doi:10.3390/cells4010056 OPEN ACCESS cells ISSN 2073-4409 www.mdpi.com/journal/cells Article ELISPOTs Produced by CD8 and CD4 Cells Follow Log Normal Size Distribution Permitting
Cells 2015, 4, 56-70; doi:10.3390/cells4010056 OPEN ACCESS cells ISSN 2073-4409 www.mdpi.com/journal/cells Article ELISPOTs Produced by CD8 and CD4 Cells Follow Log Normal Size Distribution Permitting
Rapid antigen-specific T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE)
 Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154+CD4+ T cell Rapid antigen-specific T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central role
Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154+CD4+ T cell Rapid antigen-specific T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central role
TITLE: MODULATION OF T CELL TOLERANCE IN A MURINE MODEL FOR IMMUNOTHERAPY OF PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA
 AD Award Number: DAMD17-01-1-0085 TITLE: MODULATION OF T CELL TOLERANCE IN A MURINE MODEL FOR IMMUNOTHERAPY OF PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: ARTHUR A HURWITZ, Ph.d. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AD Award Number: DAMD17-01-1-0085 TITLE: MODULATION OF T CELL TOLERANCE IN A MURINE MODEL FOR IMMUNOTHERAPY OF PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: ARTHUR A HURWITZ, Ph.d. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance. Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco
 Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco EIP Symposium Feb 2016 Why do some people respond to therapeutic proteins?
Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco EIP Symposium Feb 2016 Why do some people respond to therapeutic proteins?
Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD-
 Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY. CD4 T Follicular Helper Cells. Memory CD8 T Cell Differentiation
 IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY CD4 T Follicular Helper Cells Memory CD8 T Cell Differentiation CD4 T Cell Differentiation Bcl-6 T-bet GATA-3 ROR t Foxp3 CD4 T follicular helper (Tfh) cells FUNCTION Provide essential
IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY CD4 T Follicular Helper Cells Memory CD8 T Cell Differentiation CD4 T Cell Differentiation Bcl-6 T-bet GATA-3 ROR t Foxp3 CD4 T follicular helper (Tfh) cells FUNCTION Provide essential
Principle of the FluoroSpot assay. Anti-tag mab-green. Streptavidin-Red. Detection mab-tag. Detection mab-biotin. Analyte. Analyte.
 FluoroSpot 1 The principle objective of the FluoroSpot assay is the simultaneous measurement of dual cytokine secretion at the single cell level. This is accomplished by using a mixture of monoclonal antibodies
FluoroSpot 1 The principle objective of the FluoroSpot assay is the simultaneous measurement of dual cytokine secretion at the single cell level. This is accomplished by using a mixture of monoclonal antibodies
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS. Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT
 ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154 + CD4 + T cells Rapid antigen-reactive T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE)
 Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154 + CD4 + T cells Rapid antigen-reactive T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central
Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154 + CD4 + T cells Rapid antigen-reactive T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central
Innate and Cellular Immunology Control of Infection by Cell-mediated Immunity
 Innate & adaptive Immunity Innate and Cellular Immunology Control of Infection by Cell-mediated Immunity Helen Horton PhD Seattle Biomedical Research Institute Depts of Global Health & Medicine, UW Cellular
Innate & adaptive Immunity Innate and Cellular Immunology Control of Infection by Cell-mediated Immunity Helen Horton PhD Seattle Biomedical Research Institute Depts of Global Health & Medicine, UW Cellular
BD CBA on the BD Accuri C6: Bringing Multiplexed Cytokine Detection to the Benchtop
 BD CBA on the BD Accuri C6: Bringing Multiplexed Cytokine Detection to the Benchtop Maria Dinkelmann, PhD Senior Marketing Applications Specialist BD Biosciences, Ann Arbor, MI 23-14380-00 Cellular Communication
BD CBA on the BD Accuri C6: Bringing Multiplexed Cytokine Detection to the Benchtop Maria Dinkelmann, PhD Senior Marketing Applications Specialist BD Biosciences, Ann Arbor, MI 23-14380-00 Cellular Communication
Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured
 Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured under Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg conditions. mrna
Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured under Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg conditions. mrna
General Overview of Immunology. Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center
 General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
Significance of the MHC
 CHAPTER 7 Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) What is is MHC? HLA H-2 Minor histocompatibility antigens Peter Gorer & George Sneell (1940) Significance of the MHC role in immune response role in organ
CHAPTER 7 Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) What is is MHC? HLA H-2 Minor histocompatibility antigens Peter Gorer & George Sneell (1940) Significance of the MHC role in immune response role in organ
Mouse Anti-OVA IgM Antibody Assay Kit
 Mouse Anti-OVA IgM Antibody Assay Kit Catalog # 3017 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Ovalbumin (OVA) is a widely used antigen for inducing allergic reactions in experimental
Mouse Anti-OVA IgM Antibody Assay Kit Catalog # 3017 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Ovalbumin (OVA) is a widely used antigen for inducing allergic reactions in experimental
Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity
 MICR2209 Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will discuss the T-cell mediated immune response, how it is activated,
MICR2209 Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will discuss the T-cell mediated immune response, how it is activated,
Supplementary Fig. 1: Ex vivo tetramer enrichment with anti-c-myc beads
 Supplementary Fig. 1: Ex vivo tetramer enrichment with anti-c-myc beads Representative example of comparative ex vivo tetramer enrichment performed in three independent experiments with either conventional
Supplementary Fig. 1: Ex vivo tetramer enrichment with anti-c-myc beads Representative example of comparative ex vivo tetramer enrichment performed in three independent experiments with either conventional
Why are validated immunogenicity assays important for HIV vaccine development?
 Why are validated immunogenicity assays important for HIV vaccine development? There is a need to compare immunogenicity of products in the pipeline, when similar or different in class when developed by
Why are validated immunogenicity assays important for HIV vaccine development? There is a need to compare immunogenicity of products in the pipeline, when similar or different in class when developed by
Cancer Biometrics: Results of the 2003 isbtc Workshop. Theresa L. Whiteside, Ph.D., ABMLI University of Pittsburgh Cancer Institute
 Cancer Biometrics: Results of the 2003 isbtc Workshop Theresa L. Whiteside, Ph.D., ABMLI University of Pittsburgh Cancer Institute The workshop objective The objective was to consider state-of-theart approaches
Cancer Biometrics: Results of the 2003 isbtc Workshop Theresa L. Whiteside, Ph.D., ABMLI University of Pittsburgh Cancer Institute The workshop objective The objective was to consider state-of-theart approaches
Micro 204. Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTL) Lewis Lanier
 Micro 204 Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTL) Lewis Lanier Lewis.Lanier@ucsf.edu Lymphocyte-mediated Cytotoxicity CD8 + αβ-tcr + T cells CD4 + αβ-tcr + T cells γδ-tcr + T cells Natural Killer cells CD8 + αβ-tcr
Micro 204 Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTL) Lewis Lanier Lewis.Lanier@ucsf.edu Lymphocyte-mediated Cytotoxicity CD8 + αβ-tcr + T cells CD4 + αβ-tcr + T cells γδ-tcr + T cells Natural Killer cells CD8 + αβ-tcr
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature1554 a TNF-α + in CD4 + cells [%] 1 GF SPF 6 b IL-1 + in CD4 + cells [%] 5 4 3 2 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of microbiota on cytokine profiles of T cells in GALT. Frequencies of TNF-α
doi:1.138/nature1554 a TNF-α + in CD4 + cells [%] 1 GF SPF 6 b IL-1 + in CD4 + cells [%] 5 4 3 2 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of microbiota on cytokine profiles of T cells in GALT. Frequencies of TNF-α
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of basophils after reconstitution of SCID mice
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of after reconstitution of SCID mice with CD4 + CD62L + T cells. (A-C) SCID mice (n = 6 / group) were reconstituted with 2 x 1 6 CD4
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of after reconstitution of SCID mice with CD4 + CD62L + T cells. (A-C) SCID mice (n = 6 / group) were reconstituted with 2 x 1 6 CD4
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Identification of IFN-γ-producing CD8 + and CD4 + T cells with naive phenotype by alternative gating and sample-processing strategies. a. Contour 5% probability plots show definition
Supplementary Figure 1 Identification of IFN-γ-producing CD8 + and CD4 + T cells with naive phenotype by alternative gating and sample-processing strategies. a. Contour 5% probability plots show definition
Tolerance, autoimmunity and the pathogenesis of immunemediated inflammatory diseases. Abul K. Abbas UCSF
 Tolerance, autoimmunity and the pathogenesis of immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas UCSF Balancing lymphocyte activation and control Activation Effector T cells Tolerance Regulatory T cells
Tolerance, autoimmunity and the pathogenesis of immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas UCSF Balancing lymphocyte activation and control Activation Effector T cells Tolerance Regulatory T cells
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry:
 Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry: Simultaneous Detection of Cytokines and Transcription Factors An encore presentation by Jurg Rohrer, PhD, BD Biosciences 10.26.10 Outline Introduction Cytokines
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry: Simultaneous Detection of Cytokines and Transcription Factors An encore presentation by Jurg Rohrer, PhD, BD Biosciences 10.26.10 Outline Introduction Cytokines
The Adaptive Immune Response. B-cells
 The Adaptive Immune Response B-cells The innate immune system provides immediate protection. The adaptive response takes time to develop and is antigen specific. Activation of B and T lymphocytes Naive
The Adaptive Immune Response B-cells The innate immune system provides immediate protection. The adaptive response takes time to develop and is antigen specific. Activation of B and T lymphocytes Naive
MHC Tetramers and Monomers for Immuno-Oncology and Autoimmunity Drug Discovery
 MHC Tetramers and Monomers for Immuno-Oncology and Autoimmunity Drug Discovery Your Partner in Drug Discovery and Research MHC Tetramer Background T-Cell Receptors recognize and bind to complexes composed
MHC Tetramers and Monomers for Immuno-Oncology and Autoimmunity Drug Discovery Your Partner in Drug Discovery and Research MHC Tetramer Background T-Cell Receptors recognize and bind to complexes composed
VISTA, a novel immune checkpoint protein ligand that suppresses anti-tumor tumor T cell responses. Li Wang. Dartmouth Medical School
 VISTA, a novel immune checkpoint protein ligand that suppresses anti-tumor tumor T cell responses Li Wang Dartmouth Medical School The B7 Immunoglobulin Super-Family immune regulators APC T cell Co-stimulatory:
VISTA, a novel immune checkpoint protein ligand that suppresses anti-tumor tumor T cell responses Li Wang Dartmouth Medical School The B7 Immunoglobulin Super-Family immune regulators APC T cell Co-stimulatory:
T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH
 T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH Ned Braunstein, MD The Major T Cell Subsets p56 lck + T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ p56 lck CD8+ T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 CD8 Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 MHC II peptide
T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH Ned Braunstein, MD The Major T Cell Subsets p56 lck + T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ p56 lck CD8+ T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 CD8 Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 MHC II peptide
Relevant Disclosures
 6/18/215 Therapeutic developments for autoimmune demyelinating diseases: Musings from a MD (Mouse Doctor) Michael K. Racke, M.D. May 28, 215 Relevant Disclosures Editorial Boards for Journal of Neuroimmunology,
6/18/215 Therapeutic developments for autoimmune demyelinating diseases: Musings from a MD (Mouse Doctor) Michael K. Racke, M.D. May 28, 215 Relevant Disclosures Editorial Boards for Journal of Neuroimmunology,
Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells Inhibit Cytomegalovirus Inflammation through Interleukin-27 and B7-H4
 Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells Inhibit Cytomegalovirus Inflammation through Interleukin-27 and B7-H4 Ankita Garg, Rodney Trout and Stephen A. Spector,,* Department
Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells Inhibit Cytomegalovirus Inflammation through Interleukin-27 and B7-H4 Ankita Garg, Rodney Trout and Stephen A. Spector,,* Department
TCR, MHC and coreceptors
 Cooperation In Immune Responses Antigen processing how peptides get into MHC Antigen processing involves the intracellular proteolytic generation of MHC binding proteins Protein antigens may be processed
Cooperation In Immune Responses Antigen processing how peptides get into MHC Antigen processing involves the intracellular proteolytic generation of MHC binding proteins Protein antigens may be processed
Objectives. Abbas Chapter 11: Immunological Tolerance. Question 1. Question 2. Question 3. Definitions
 Objectives Abbas Chapter 11: Immunological Tolerance Christina Ciaccio, MD Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics February 1, 2010 To introduce the concept of immunologic tolerance To understand what factors
Objectives Abbas Chapter 11: Immunological Tolerance Christina Ciaccio, MD Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics February 1, 2010 To introduce the concept of immunologic tolerance To understand what factors
The Good, the Bad and the Ugly: Clinical trials which assess vaccine characteristics. ISBT Meeting, San Francisco, CA November 4-8, 2004
 The Good, the Bad and the Ugly: Clinical trials which assess vaccine characteristics ISBT Meeting, San Francisco, CA November 4-8, 2004 Ideal cancer vaccine trial 1. An informative immune assay 2. Ability
The Good, the Bad and the Ugly: Clinical trials which assess vaccine characteristics ISBT Meeting, San Francisco, CA November 4-8, 2004 Ideal cancer vaccine trial 1. An informative immune assay 2. Ability
Defensive mechanisms include :
 Acquired Immunity Defensive mechanisms include : 1) Innate immunity (Natural or Non specific) 2) Acquired immunity (Adaptive or Specific) Cell-mediated immunity Humoral immunity Two mechanisms 1) Humoral
Acquired Immunity Defensive mechanisms include : 1) Innate immunity (Natural or Non specific) 2) Acquired immunity (Adaptive or Specific) Cell-mediated immunity Humoral immunity Two mechanisms 1) Humoral
Page 4: Antigens: Self-Antigens The body has a vast number of its own antigens called self-antigens. These normally do not trigger immune responses.
 Common Characteristics of B and T Lymphocytes Graphics are used with permission of Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com). Page 1: Introduction While B and T lymphocytes
Common Characteristics of B and T Lymphocytes Graphics are used with permission of Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com). Page 1: Introduction While B and T lymphocytes
Immune response to infection
 Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY
 ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY The recognition of specific antigen by naïve T cell induces its own activation and effector phases. T helper cells recognize peptide antigens through
ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY The recognition of specific antigen by naïve T cell induces its own activation and effector phases. T helper cells recognize peptide antigens through
B6/COLODR/SPL/11C/83/LAP/#2.006 B6/COLODR/SPL/11C/86/LAP/#2.016 CD11C B6/COLODR/SPL/11C/80/LAP/#2.011 CD11C
 CD3-specific antibody-induced immune tolerance and suppression of autoimmune encephalomyelitis involves TGF-β production through phagocytes digesting apoptotic T cells Sylvain Perruche 1,3, Pin Zhang 1,
CD3-specific antibody-induced immune tolerance and suppression of autoimmune encephalomyelitis involves TGF-β production through phagocytes digesting apoptotic T cells Sylvain Perruche 1,3, Pin Zhang 1,
Estimating primate effector T cell responses to DNA vaccination
 Estimating primate effector T cell responses to DNA vaccination Oct 22 nd, 21 Devon J. Shedlock, PhD th Vaccine Renaissance Conference Estimating vaccineinduced effector T cell responses Vaccineinduced
Estimating primate effector T cell responses to DNA vaccination Oct 22 nd, 21 Devon J. Shedlock, PhD th Vaccine Renaissance Conference Estimating vaccineinduced effector T cell responses Vaccineinduced
Dendritic cells in cancer immunotherapy Aimin Jiang
 Dendritic cells in cancer immunotherapy Aimin Jiang Feb. 11, 2014 Dendritic cells at the interface of innate and adaptive immune responses Dendritic cells: initiators of adaptive immune responses Dendritic
Dendritic cells in cancer immunotherapy Aimin Jiang Feb. 11, 2014 Dendritic cells at the interface of innate and adaptive immune responses Dendritic cells: initiators of adaptive immune responses Dendritic
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nature775 4 O.D. (595-655) 3 1 -ζ no antibody isotype ctrl Plated Soluble 1F6 397 7H11 Supplementary Figure 1 Soluble and plated anti- Abs induce -! signalling. B3Z cells stably expressing!
doi: 1.138/nature775 4 O.D. (595-655) 3 1 -ζ no antibody isotype ctrl Plated Soluble 1F6 397 7H11 Supplementary Figure 1 Soluble and plated anti- Abs induce -! signalling. B3Z cells stably expressing!
Principles of Adaptive Immunity
 Principles of Adaptive Immunity Chapter 3 Parham Hans de Haard 17 th of May 2010 Agenda Recognition molecules of adaptive immune system Features adaptive immune system Immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors
Principles of Adaptive Immunity Chapter 3 Parham Hans de Haard 17 th of May 2010 Agenda Recognition molecules of adaptive immune system Features adaptive immune system Immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors
Immune Tolerance. Kyeong Cheon Jung. Department of Pathology Seoul National University College of Medicine
 Immune Tolerance Kyeong Cheon Jung Department of Pathology Seoul National University College of Medicine Immune tolerance Unresponsiveness to an antigen that is induced by previous exposure to that antigen
Immune Tolerance Kyeong Cheon Jung Department of Pathology Seoul National University College of Medicine Immune tolerance Unresponsiveness to an antigen that is induced by previous exposure to that antigen
CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR REQUIREMENTS FOR REJECTION OF B16 MELANOMA IN THE SETTING OF REGULATORY T CELL DEPLETION AND HOMEOSTATIC PROLIFERATION
 CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR REQUIREMENTS FOR REJECTION OF B16 MELANOMA IN THE SETTING OF REGULATORY T CELL DEPLETION AND HOMEOSTATIC PROLIFERATION Justin Kline 1, Long Zhang 1, and Thomas F. Gajewski 1,2 Departments
CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR REQUIREMENTS FOR REJECTION OF B16 MELANOMA IN THE SETTING OF REGULATORY T CELL DEPLETION AND HOMEOSTATIC PROLIFERATION Justin Kline 1, Long Zhang 1, and Thomas F. Gajewski 1,2 Departments
Therapeutic PD L1 and LAG 3 blockade rapidly clears established blood stage Plasmodium infection
 Supplementary Information Therapeutic PD L1 and LAG 3 blockade rapidly clears established blood stage Plasmodium infection Noah S. Butler, Jacqueline Moebius, Lecia L. Pewe, Boubacar Traore, Ogobara K.
Supplementary Information Therapeutic PD L1 and LAG 3 blockade rapidly clears established blood stage Plasmodium infection Noah S. Butler, Jacqueline Moebius, Lecia L. Pewe, Boubacar Traore, Ogobara K.
Ex vivo Human Antigen-specific T Cell Proliferation and Degranulation Willemijn Hobo 1, Wieger Norde 1 and Harry Dolstra 2*
 Ex vivo Human Antigen-specific T Cell Proliferation and Degranulation Willemijn Hobo 1, Wieger Norde 1 and Harry Dolstra 2* 1 Department of Laboratory Medicine - Laboratory of Hematology, Radboud University
Ex vivo Human Antigen-specific T Cell Proliferation and Degranulation Willemijn Hobo 1, Wieger Norde 1 and Harry Dolstra 2* 1 Department of Laboratory Medicine - Laboratory of Hematology, Radboud University
Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails. FOCiS. Lecture outline. Regulatory T cells. Regulatory T cells: functions and clinical relevance
 1 Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Regulatory T cells: functions and clinical relevance Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails
1 Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Regulatory T cells: functions and clinical relevance Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails
W/T Itgam -/- F4/80 CD115. F4/80 hi CD115 + F4/80 + CD115 +
 F4/8 % in the peritoneal lavage 6 4 2 p=.15 n.s p=.76 CD115 F4/8 hi CD115 + F4/8 + CD115 + F4/8 hi CD115 + F4/8 + CD115 + MHCII MHCII Supplementary Figure S1. CD11b deficiency affects the cellular responses
F4/8 % in the peritoneal lavage 6 4 2 p=.15 n.s p=.76 CD115 F4/8 hi CD115 + F4/8 + CD115 + F4/8 hi CD115 + F4/8 + CD115 + MHCII MHCII Supplementary Figure S1. CD11b deficiency affects the cellular responses
Supplementary Data Table of Contents:
 Supplementary Data Table of Contents: - Supplementary Methods - Supplementary Figures S1(A-B) - Supplementary Figures S2 (A-B) - Supplementary Figures S3 - Supplementary Figures S4(A-B) - Supplementary
Supplementary Data Table of Contents: - Supplementary Methods - Supplementary Figures S1(A-B) - Supplementary Figures S2 (A-B) - Supplementary Figures S3 - Supplementary Figures S4(A-B) - Supplementary
Medical Virology Immunology. Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University
 Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Supplementary Information:
 Supplementary Information: Follicular regulatory T cells with Bcl6 expression suppress germinal center reactions by Yeonseok Chung, Shinya Tanaka, Fuliang Chu, Roza Nurieva, Gustavo J. Martinez, Seema
Supplementary Information: Follicular regulatory T cells with Bcl6 expression suppress germinal center reactions by Yeonseok Chung, Shinya Tanaka, Fuliang Chu, Roza Nurieva, Gustavo J. Martinez, Seema
Examples of questions for Cellular Immunology/Cellular Biology and Immunology
 Examples of questions for Cellular Immunology/Cellular Biology and Immunology Each student gets a set of 6 questions, so that each set contains different types of questions and that the set of questions
Examples of questions for Cellular Immunology/Cellular Biology and Immunology Each student gets a set of 6 questions, so that each set contains different types of questions and that the set of questions
Supplementary Table 1. Functional avidities of survivin-specific T-cell clones against LML-peptide
 Supplementary Table 1. Functional avidities of survivin-specific T-cell clones against LML-peptide pulsed T2 cells. clone avidity by 4-hour 51 Cr-release assay 50% lysis at E:T 10:1 [LML peptide, M] #24
Supplementary Table 1. Functional avidities of survivin-specific T-cell clones against LML-peptide pulsed T2 cells. clone avidity by 4-hour 51 Cr-release assay 50% lysis at E:T 10:1 [LML peptide, M] #24
Masashi Takahara,* Manami Miyai,* Mai Tomiyama,* Masato Mutou,* Andrew J. Nicol, and Mie Nieda*,1
 Copulsing tumor antigen-pulsed dendritic cells with zoledronate efficiently enhance the expansion of tumor antigen-specific CD8 T cells via V 9 T cell activation Masashi Takahara,* Manami Miyai,* Mai Tomiyama,*
Copulsing tumor antigen-pulsed dendritic cells with zoledronate efficiently enhance the expansion of tumor antigen-specific CD8 T cells via V 9 T cell activation Masashi Takahara,* Manami Miyai,* Mai Tomiyama,*
Mucosal Immune System
 Exam Format 100 points - 60 pts mandatory; 40 points where 4, 10 point questions will be chosen Some open-ended questions, some short answer. Kuby question Cytokines Terminology How do cytokines achieve
Exam Format 100 points - 60 pts mandatory; 40 points where 4, 10 point questions will be chosen Some open-ended questions, some short answer. Kuby question Cytokines Terminology How do cytokines achieve
# Required If available Optional MIATA Sub-Modules
 # Required If available Optional MIATA Sub-Modules. Module - Sample Module A - Donor O Essential donor info Captured in patient demographics, Table Module B Source. O Source of cell material Study subjects:
# Required If available Optional MIATA Sub-Modules. Module - Sample Module A - Donor O Essential donor info Captured in patient demographics, Table Module B Source. O Source of cell material Study subjects:
Cell Mediated Immunity CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY. Basic Elements of Cell Mediated Immunity (CMI) Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)
 Chapter 16 CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY Cell Mediated Immunity Also known as Cellular Immunity or CMI The effector phase T cells Specificity for immune recognition reactions TH provide cytokines CTLs do the
Chapter 16 CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY Cell Mediated Immunity Also known as Cellular Immunity or CMI The effector phase T cells Specificity for immune recognition reactions TH provide cytokines CTLs do the
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION
 Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 11 T-Cell Activation, Differentiation, and Memory Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 11 T-Cell Activation, Differentiation, and Memory Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and
C. Incorrect! MHC class I molecules are not involved in the process of bridging in ADCC.
 Immunology - Problem Drill 13: T- Cell Mediated Immunity Question No. 1 of 10 1. During Antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), the antibody acts like a bridge between the specific antigen
Immunology - Problem Drill 13: T- Cell Mediated Immunity Question No. 1 of 10 1. During Antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), the antibody acts like a bridge between the specific antigen
Cellular Pathology of immunological disorders
 Cellular Pathology of immunological disorders SCBM344 Cellular and Molecular Pathology Witchuda Payuhakrit, Ph.D (Pathobiology) witchuda.pay@mahidol.ac.th Objectives Describe the etiology of immunological
Cellular Pathology of immunological disorders SCBM344 Cellular and Molecular Pathology Witchuda Payuhakrit, Ph.D (Pathobiology) witchuda.pay@mahidol.ac.th Objectives Describe the etiology of immunological
How T cells recognize antigen: The T Cell Receptor (TCR) Identifying the TCR: Why was it so hard to do? Monoclonal antibody approach
 How T cells recognize antigen: The T Cell Receptor (TCR) Identifying the TCR: Why was it so hard to do By the early 1980s, much about T cell function was known, but the receptor genes had not been identified
How T cells recognize antigen: The T Cell Receptor (TCR) Identifying the TCR: Why was it so hard to do By the early 1980s, much about T cell function was known, but the receptor genes had not been identified
A second type of TCR TCR: An αβ heterodimer
 How s recognize antigen: The T Cell Receptor (TCR) Identifying the TCR: Why was it so hard to do By the early 1980s, much about function was known, but the receptor genes had not been identified Recall
How s recognize antigen: The T Cell Receptor (TCR) Identifying the TCR: Why was it so hard to do By the early 1980s, much about function was known, but the receptor genes had not been identified Recall
Third line of Defense
 Chapter 15 Specific Immunity and Immunization Topics -3 rd of Defense - B cells - T cells - Specific Immunities Third line of Defense Specific immunity is a complex interaction of immune cells (leukocytes)
Chapter 15 Specific Immunity and Immunization Topics -3 rd of Defense - B cells - T cells - Specific Immunities Third line of Defense Specific immunity is a complex interaction of immune cells (leukocytes)
UNISEC Universal Influenza Vaccines Secured
 UNISEC Universal Influenza Vaccines Secured Partners in the UNISEC Consortium UNISEC has been made possible by contributions from the European Commission DG-Research and the European member states Project
UNISEC Universal Influenza Vaccines Secured Partners in the UNISEC Consortium UNISEC has been made possible by contributions from the European Commission DG-Research and the European member states Project
Lecture outline. Immunological tolerance and immune regulation. Central and peripheral tolerance. Inhibitory receptors of T cells. Regulatory T cells
 1 Immunological tolerance and immune regulation Abul K. Abbas UCSF 2 Lecture outline Central and peripheral tolerance Inhibitory receptors of T cells Regulatory T cells 1 The immunological equilibrium:
1 Immunological tolerance and immune regulation Abul K. Abbas UCSF 2 Lecture outline Central and peripheral tolerance Inhibitory receptors of T cells Regulatory T cells 1 The immunological equilibrium:
SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER
 Judy Owen Jenni Punt Sharon Stranford Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 16 Tolerance, Autoimmunity, and Transplantation Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and Company Immune tolerance: history * Some
Judy Owen Jenni Punt Sharon Stranford Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 16 Tolerance, Autoimmunity, and Transplantation Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and Company Immune tolerance: history * Some
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice. (a) Gene expression profile in the resting CD4 + T cells were analyzed by an Affymetrix microarray
Supplementary Figure 1 Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice. (a) Gene expression profile in the resting CD4 + T cells were analyzed by an Affymetrix microarray
CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Baltimore, MD 21205
 AD Award Number: DAMD7---7 TITLE: Development of Artificial Antigen Presenting Cells for Prostate Cancer Immunotherapy PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Jonathan P. Schneck, M.D., Ph.D. Mathias Oelke, Ph.D. CONTRACTING
AD Award Number: DAMD7---7 TITLE: Development of Artificial Antigen Presenting Cells for Prostate Cancer Immunotherapy PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Jonathan P. Schneck, M.D., Ph.D. Mathias Oelke, Ph.D. CONTRACTING
Rationale for Combining Immunotherapy with Chemotherapy or Targeted Therapy
 Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) Rationale for Combining Immunotherapy with Chemotherapy or Targeted Therapy Qing Yi, MD, PhD Staff and Chair, Department of Cancer Biology Betsy B. DeWindt Endowed
Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) Rationale for Combining Immunotherapy with Chemotherapy or Targeted Therapy Qing Yi, MD, PhD Staff and Chair, Department of Cancer Biology Betsy B. DeWindt Endowed
M.Sc. III Semester Biotechnology End Semester Examination, 2013 Model Answer LBTM: 302 Advanced Immunology
 Code : AS-2246 M.Sc. III Semester Biotechnology End Semester Examination, 2013 Model Answer LBTM: 302 Advanced Immunology A. Select one correct option for each of the following questions:- 2X10=10 1. (b)
Code : AS-2246 M.Sc. III Semester Biotechnology End Semester Examination, 2013 Model Answer LBTM: 302 Advanced Immunology A. Select one correct option for each of the following questions:- 2X10=10 1. (b)
CD40L TCR IL-12 TLR-L
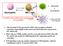 CD40L B cells plasmacells Neutrophils TCR inkt cells IL-12 Ab production Can inkt cells modulate the cytokine profile of neutrophils? TLR-L CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses 1. The invariant TCR expressed
CD40L B cells plasmacells Neutrophils TCR inkt cells IL-12 Ab production Can inkt cells modulate the cytokine profile of neutrophils? TLR-L CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses 1. The invariant TCR expressed
B cell activation and antibody production. Abul K. Abbas UCSF
 1 B cell activation and antibody production Abul K. Abbas UCSF 2 Lecture outline B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production Therapeutic targeting of B cells 3 Principles of humoral
1 B cell activation and antibody production Abul K. Abbas UCSF 2 Lecture outline B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production Therapeutic targeting of B cells 3 Principles of humoral
Supplemental Figure 1. Cell-bound Cetuximab reduces EGFR staining intensity. Blood
 Antibody-mediated depletion of CD19-CAR T cells Supplemental 1 Supplemental Materials Supplemental Figure 1. Supplemental Figure 1. Cell-bound Cetuximab reduces EGFR staining intensity. Blood cells were
Antibody-mediated depletion of CD19-CAR T cells Supplemental 1 Supplemental Materials Supplemental Figure 1. Supplemental Figure 1. Cell-bound Cetuximab reduces EGFR staining intensity. Blood cells were
Third line of Defense. Topic 8 Specific Immunity (adaptive) (18) 3 rd Line = Prophylaxis via Immunization!
 Topic 8 Specific Immunity (adaptive) (18) Topics - 3 rd Line of Defense - B cells - T cells - Specific Immunities 1 3 rd Line = Prophylaxis via Immunization! (a) A painting of Edward Jenner depicts a cow
Topic 8 Specific Immunity (adaptive) (18) Topics - 3 rd Line of Defense - B cells - T cells - Specific Immunities 1 3 rd Line = Prophylaxis via Immunization! (a) A painting of Edward Jenner depicts a cow
COURSE: Medical Microbiology, PAMB 650/720 - Fall 2008 Lecture 16
 COURSE: Medical Microbiology, PAMB 650/720 - Fall 2008 Lecture 16 Tumor Immunology M. Nagarkatti Teaching Objectives: Introduction to Cancer Immunology Know the antigens expressed by cancer cells Understand
COURSE: Medical Microbiology, PAMB 650/720 - Fall 2008 Lecture 16 Tumor Immunology M. Nagarkatti Teaching Objectives: Introduction to Cancer Immunology Know the antigens expressed by cancer cells Understand
Mouse Total IgA Antibody Detection Kit
 Mouse Total IgA Antibody Detection Kit Catalog # 3019 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION The total IgA levels in specimens are often determined in mouse disease models involving
Mouse Total IgA Antibody Detection Kit Catalog # 3019 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION The total IgA levels in specimens are often determined in mouse disease models involving
Practical Solution: presentation to cytotoxic T cells. How dendritic cells present antigen. How dendritic cells present antigen
 Christian Kurts Institutes of Molecular Medicine and Experimental Immunology University of Bonn, Germany - presentation and (CTL) activation - I presentation and CD4 + T cell (Th cell) activation Different
Christian Kurts Institutes of Molecular Medicine and Experimental Immunology University of Bonn, Germany - presentation and (CTL) activation - I presentation and CD4 + T cell (Th cell) activation Different
Chapter 10 (pages ): Differentiation and Functions of CD4+ Effector T Cells Prepared by Kristen Dazy, MD, Scripps Clinic Medical Group
 FIT Board Review Corner September 2015 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Andrew Nickels, MD, and Sarah Spriet, DO, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In-Training (FITs)
FIT Board Review Corner September 2015 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Andrew Nickels, MD, and Sarah Spriet, DO, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In-Training (FITs)
Adaptive Immunity. Jeffrey K. Actor, Ph.D. MSB 2.214,
 Adaptive Immunity Jeffrey K. Actor, Ph.D. MSB 2.214, 500-5344 Lecture Objectives: Understand role of various molecules including cytokines, chemokines, costimulatory and adhesion molecules in the development
Adaptive Immunity Jeffrey K. Actor, Ph.D. MSB 2.214, 500-5344 Lecture Objectives: Understand role of various molecules including cytokines, chemokines, costimulatory and adhesion molecules in the development
