Chapter 07 Lecture Outline
|
|
|
- Ashlie Skinner
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 07 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1
2 The Lymphatic and Immune Systems 2
3 Points to ponder What are the parts of the lymphatic system and what are their functions? What are the first and second lines of defense in nonspecific immunity? What is cell-mediated and antibody-mediated immunity in the third line of defense? What are the different types of B cells in these processes? What is active and passive immunity? Be able to describe how they are different and examples of each. Understand allergic reactions, tissue rejection, and immune system disorders as problems that the immune system faces. 3
4 7.1 The Lymphatic System Functions of the lymphatic system Lymphatic capillaries absorb excess tissue fluid and return it to the bloodstream. Lymphatic capillaries (lacteals) in the small intestine absorb fats associated with proteins. The lymphatic system works in the production, maintenance, and distribution of lymphocytes in the body. It helps in defense against pathogens. 4
5 7.1 The Lymphatic System What are the components of the lymphatic system? Tonsil: patches of lymphatic tissue; help to prevent entrance of pathogens by way of the nose and mouth Right lymphatic duct: empties lymph into the right subclavian vein Red bone marrow: site for the origin of all types of blood cells Axillary lymph nodes: located in the underarm region Thymus: lymphatic tissue where T lymphocytes mature and learn to tell self from nonself Thoracic duct: empties lymph in to the left subclavian vein Spleen: cleanses the blood of cellular debris and bacteria, while resident lymphocytes respond to the presence of antigens tissue fluid lymphatic capillary Inguinal lymph nodes: located in the groin region; cleanse lymph and alert the immune system to pathogens tissue cell blood capillary Figure 7.1 Functions of the lymphatic system components. 5
6 7.1 The Lymphatic System Lymphatic vessels One-way valve system that carries fluid called lymph Made of capillaries, vessels, and ducts Function to return tissue fluid (which includes water, solutes, and cell products) to the bloodstream Larger vessels are similar in structure to veins and even have valves 6
7 7.1 The Lymphatic System Classifying lymphatic organs Primary Red bone marrow Thymus Figure 7.2 Tissue samples from primary lymphatic organs. 7
8 7.1 The Lymphatic System Classifying lymphatic organs Secondary Lymph nodes Spleen Figure 7.2 Tissue samples from secondary lymphatic organs. 8
9 7.1 The Lymphatic System Primary lymphatic organs Red bone marrow It is the site of blood cell production. More bones in children have red marrow and it decreases as we age. Some white blood cells mature here. Thymus It is a bilobed gland found in the thoracic cavity superior to the heart. It is largest in children and shrinks as we age. Immature T lymphocytes move from the marrow to the thymus where they mature and 95% will stay. 9
10 7.1 The Lymphatic System Secondary lymphatic organs Lymph nodes Small, oval-shaped structures found along the lymphatic vessels Filled with B cells, T cells, and macrophages Common in the neck, armpit, and groin regions Spleen In the upper left region of the abdominal cavity Filled with white pulp containing lymphocytes, and red pulp which is involved with filtering the blood 10
11 7.2 Innate Immune Defenses What do the nonspecific defenses include? First line of defense Barriers to entry: physical and chemical Second line of defense Phagocytic white blood cells Inflammatory response Protective proteins: complement and interferons 11
12 7.2 Innate Immune Defenses What are the innate immune defenses? Innate defenses Barriers to entry Protective proteins Phagocytes and natural killer cells Inflammatory response skin and mucous membranes dendritic cell antimicrobial molecules pathogens macrophage cytokines monocyte neutrophil natural killer ells complement proteins and interferons in plasma Figure 7.3 Overview of innate immune defenses. 12
13 7.2 Innate Immune Defenses The first line of defense Physical barriers The skin is an effective physical barrier. Tears, saliva, and urine physically flush out microbes. Mucous membranes line the respiratory, digestive, reproductive, and urinary tracts. Resident bacteria/normal flora that inhabit the body use available nutrients and space thus preventing pathogens from taking up residence. 13
14 7.2 Innate Immune Defenses The first line of defense Chemical barriers Secretions of the oil glands Lysozyme found in saliva, tears, and sweat Acidic ph of the stomach and vagina 14
15 7.2 Innate Immune Defenses The second line of defense: Phagocytic white blood cells Includes neutrophils and macrophages Both leave circulation and move into tissue Are important in the inflammatory response 15
16 7.2 Innate Immune Defenses The second line of defense: Inflammatory response Four hallmark symptoms are redness, heat, swelling, and pain. Histamine, released by mast cells, causes the capillaries to dilate and become more permeable to phagocytic white blood cells. Increased blood flow to an area increases warmth, inhibiting some pathogens. 16
17 7.2 Innate Immune Defenses The second line of defense: Inflammatory response Increased blood flow also brings more white blood cells to an injured area, with neutrophils being the first scouts to kill pathogens. This response can be short-lived, but if the neutrophils cannot control the damage, cytokines (chemicals) will call in more white blood cells including macrophages. 17
18 7.2 Innate Immune Defenses Summary of the inflammatory response Skin Tissue mast cell histamine 2. Macrophages phagocytize pathogens and release cytokines, which stimulate the inflammatory response. macrophage neutrophil monocyte injured tissue 1. Injured tissue cells and mast cells release histamine, which causes capillaries to dilate and increases blood flow. pathogen cytokines blood clot Capillary 4. Blood clotting walls off capillary and prevents blood loss. 3. Neutrophils and monocytes (become macrophages) squeeze through the capillary wall and phagocytize pathogens. Figure 7.4 Steps of the inflammatory response. 18
19 7.2 Innate Immune Defenses The second line of defense: Protective proteins Complement Group of blood plasma proteins Involved in the inflammatory response by binding to mast cells, causing them to release histamine Attract phagocytes to pathogens by binding them Form a membrane attack complex that makes holes in some bacteria and viruses, causing them to burst Interferons Proteins produced by virus-infected cells sent out to warn neighboring healthy cells 19
20 7.2 Innate Immune Defenses The second line of defense: Protective proteins complement proteins membrane attack complex fluids Figure 7.5 Action of the complement system. 20
21 7.3 Adaptive Immune Defenses What do the specific defenses Third line of defense include? Helps protect us against specific pathogens when nonspecific defenses fail Helps protect us against cancer Depends on the action of B and T cells (remember that these are lymphocytes) 21
22 7.3 Adaptive Immune Defenses What are the types of B and T cells? B cells produce plasma cells and memory cells. Plasma cells produce specific antibodies. Memory cells are ready to produce antibodies in the future. 22
23 7.3 Adaptive Immune Defenses What are the types of B and T cells? T cells regulate immune response; produce various types of T cells. Cytotoxic T (T c ) cells kill virus-infected and cancer cells. Helper T (T H ) cells regulate immunity. Memory T (T c and T H ) cells are ready to kill in the future. 23
24 7.3 Adaptive Immune Defenses What are the types of B and T cells? B cell memory B cell antibody Antibodymediated immunity BCR APC antigen TCR plasma cell memory T H cell Adaptive defenses T H cell activated T H cell Cellmediated immunity antigen activated T C cell memory T C cell virus-infected cell T C cell TCR Figure 7.6 Overview of adaptive immune defenses. 24
25 7.3 Adaptive Immune Defenses What are the characteristics of B cells? Antibody-mediated immunity against pathogens Produced and mature in bone marrow Directly recognize antigen and then undergo clonal selection Clonal expansion produces antibody-secreting plasma cells as well as memory B cells 25
26 7.3 Adaptive Immune Defenses Third line of defense: Antibodymediated immunity by B cells Each B cell has a unique receptor called a BCR that binds a specific antigen. This binding and cytokines secreted by helper T cells result in clonal expansion in which this B cell makes copies of itself. Most of the cells produced are plasma cells that secrete antibodies. 26
27 7.3 Adaptive Immune Defenses Third line of defense: Antibodymediated immunity by B cells Other cells become memory cells which result in long-term immunity. After an infection has passed, plasma cells undergo apoptosis (programmed cell death) leaving memory cells. 27
28 7.3 Adaptive Immune Defenses Antibody-mediated immunity by B cells antigens B cell B-cell receptor (BCR) antigen cytokines from T cells Plasma cells Memory B cells a. Activation: When a B cell receptor binds to an antigen activation occurs. b. Clonal expansion During clonal expansion, cytokines secreted by helper T cells stimulate B cells to clone mostly into plasma cells or memory cells. Apoptosis c. Apoptosis Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, occurs to plasma cells left in the system after the infection has passed. Figure 7.7 B cell clonal selection. 28
29 7.3 Adaptive Immune Defenses Structure of antibodies The basic unit that composes antibody molecules is a Y-shaped protein. The trunk of the Y is a constant region that determines the class of the antibody. The ends of the arms (Y) are the variable regions where specific antigens bind. 29
30 7.3 Adaptive Immune Defenses Structure of antibodies antigen antigen-binding sites Antigen binds to binding site. Shape of antigen fits shape of binding site. C C heavy chain light chain a. C = constant V = variable Figure 7.8 The structure of an antibody. b. b: Courtesy Dr. Arthur J. Olson, Scripps Institute 30
31 7.3 Adaptive Immune Defenses What are the 5 classes of antibodies? 31
32 7.3 Adaptive Immune Defenses How do we make monoclonal antibodies? We make monoclonal antibodies (derived from plasma cells that originated from the same B cell) in glassware outside the body (in vitro). This is done through fusion of plasma cells with myeloma cells that allow them to divide indefinitely. This fusion results in a cell called a hybridoma. 32
33 7.3 Adaptive Immune Defenses How do we make monoclonal antibodies? antibody plasmacell antigen hybridomacell cancerous myelomacell monoclonal antibody Figure 7.9 The production of monoclonal antibodies. 33
34 7.3 Adaptive Immune Defenses What are the characteristics of T cells? Cell-mediated immunity against virus-infected cells and cancer cells Produced in bone marrow, mature in thymus Antigen must be presented in groove of an HLA (MHC) molecule Cytotoxic T cells destroy nonself antigenbearing cells Helper T cells secrete cytokines that control the immune response 34
35 7.3 Adaptive Immune Defenses Third line of defense: Cell-mediated immunity by T cells Each T cell has a unique receptor called a TCR that will recognize a piece of an antigen with the help of an antigen-presenting cell (APC). An APC engulfs an antigen, breaks it down, and presents it on its surface in association with a membrane protein called an MHC (called human leukocyte antigens in humans or HLA) then presents it to T cells in the lymph node or spleen. 35
36 7.3 Adaptive Immune Defenses Third line of defense: Cell-mediated immunity by T cells The T cell will specifically recognize the combination of the HLA protein and the piece of antigen. Clonal expansion will occur leading to mostly helper T cells, cytotoxic T cells, and a few memory T cells. After an infection has passed, helper and cytotoxic T cells undergo apoptosis, leaving memory cells. 36
37 7.3 Adaptive Immune Defenses Cell-mediated immunity by T cells T-cell receptor (TCR) T cell cytokines Activation self antigen (MHCI) bacterium Clonal expansion Macrophage Cytotoxic T cell Apoptosis Memory T cell Figure 7.10 The clonal selection model for T cells. 37
38 7.3 Adaptive Immune Defenses Helper and cytotoxic T cells Helper T cells secrete cytokines that help many immune cells function. Cytotoxic T cells have vacuoles containing granzymes and perforins. Perforins punch holes in target cells, followed by granzymes that cause the cell to undergo apoptosis. Cytotoxic T cell vesicle Perforin forms hole in target cell. Target cell a. perforin target cell Granzymes enter through the hole and cause target cell to undergo apoptosis. cytotoxic T cell target cell (virus-infected or cancer cell) granzyme cytotoxic T cell Figure 7.11 How cytotoxic T cells kill infected cells. b. Steve Gschmeissner/Science Source SEM 1,250 38
39 7.4 Acquired Immunity Immunity Immunity is the ability to combat diseases and cancer. It can be brought about naturally through an infection or artificially through medical intervention. There are 2 types of immunity, active and passive. 39
40 7.4 Acquired Immunity Active immunity The individual s body makes antibodies against a particular antigen. This can happen through natural infection or through immunization involving vaccines. Primary exposure is shorter-lived and slower to respond while a secondary exposure is a rapid, strong response. This type of immunity is usually long-lasting. It depends on memory B and T cells. 40
41 Plasma antibody concentration 7.4 Acquired Immunity Immunization: A type of active immunity high primary response secondary response second exposure to vaccine first exposure to vaccine low Time (days) Figure 7.12 How immunizations cause active immunity. 41
42 7.4 Acquired Immunity An individual is given antibodies against a particular antigen. This type of immunity is short-lived. Passive immunity This can happen naturally as antibodies are passed across the placenta or during breastfeeding, or artificially via an injection of antibodies. a. Antibodies (IgG) cross the placenta. b. Antibodies (IgG, IgA) are secreted into breast milk. Figure 7.13 Delivery mechanisms of passive immunity. c. Antibodies can be injected by a physician. 7.13a: John Lund/Drew Kelly/Blend Images/Corbis RF; 7.13b: Digital Vision/Getty RF; 7.13c: Photodisc Collection/Getty RF 42
43 7.5 Hypersensitivity Reactions How can the immune system harm the body? Allergies Tissue rejection Immune system disorders 43
44 7.5 Hypersensitivity Reactions Allergies Allergies are hypersensitivities to harmless substances such as pollen, food, or animal hair. An immediate allergic response is caused by the IgE antibodies that attach to mast cells and basophils. When allergens attach to these IgE molecules, histamine is released and we see allergy symptoms. An immediate allergic response that occurs when the allergen enters the bloodstream is anaphylactic shock, in which the blood pressure drops and is lifethreatening. Delayed allergic responses (such as the reaction to poison ivy) are initiated by memory T cells. 44
45 7.5 Hypersensitivity Reactions Tissue rejection Tissue rejection can occur when cytotoxic T cells respond to tissue that is not recognized as self. This can be controlled by giving patients immunosuppressive drugs and by transplanting organs that have the same MHC proteins in the donor and recipient. Currently, we are trying to grow organs in the lab that can be transplanted with less rejection. 45
46 7.6 Hypersensitivity Reactions Disorders of the immune system Autoimmune disease A disease in which cytotoxic T cells or antibodies attack the body s own cells as if they were foreign Examples: multiple sclerosis, lupus, myasthenia gravis, and rheumatoid arthritis Immunodeficiency disease A disease in which the immune system is compromised and thus unable to defend the body against disease Examples: AIDS and SCID 46
What are bacteria? Microbes are microscopic(bacteria, viruses, prions, & some fungi etc.) How do the sizes of our cells, bacteria and viruses compare?
 7.1 Microbes, pathogens and you Chp. 7 Lymphatic System & Immunity The interaction between microbes and humans? Microbes are very abundant in the environment and as well as in and on our bodies GOOD: We
7.1 Microbes, pathogens and you Chp. 7 Lymphatic System & Immunity The interaction between microbes and humans? Microbes are very abundant in the environment and as well as in and on our bodies GOOD: We
Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 The Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems 1 The Lymphatic Vessels Lymphoid Organs Three functions contribute to homeostasis 1. Return excess tissue fluid to the bloodstream 2. Help defend the body against
The Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems 1 The Lymphatic Vessels Lymphoid Organs Three functions contribute to homeostasis 1. Return excess tissue fluid to the bloodstream 2. Help defend the body against
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 13 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
LYMPHATIC AND IMMUNE SYSTEMS. Chapter 33
 LYMPHATIC AND IMMUNE SYSTEMS Chapter 33 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM The lymphatic system has three main functions Take up excess tissue fluid and return it to the bloodstream Receive fats called lipoproteins
LYMPHATIC AND IMMUNE SYSTEMS Chapter 33 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM The lymphatic system has three main functions Take up excess tissue fluid and return it to the bloodstream Receive fats called lipoproteins
- Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body. - Has disease-fighting functions - Helps maintain homeostasis
 Introduction Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
Introduction Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
2/28/18. Lymphatic System and Immunity. Introduction. Anatomy. Chapter 27. Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system
 Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 1 Introduction Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 1 Introduction Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
Immune System. Biology 105 Lecture 16 Chapter 13
 Immune System Biology 105 Lecture 16 Chapter 13 Outline: Immune System I. Functions of the immune system II. Barrier defenses III. Non-specific defenses A. Immune system cells B. Inflammatory response
Immune System Biology 105 Lecture 16 Chapter 13 Outline: Immune System I. Functions of the immune system II. Barrier defenses III. Non-specific defenses A. Immune system cells B. Inflammatory response
Immune System. Biol 105 Lecture 16 Chapter 13
 Immune System Biol 105 Lecture 16 Chapter 13 Outline Immune System I. Function of the Immune system II. Barrier Defenses III. Nonspecific Defenses A. Immune system cells B. Inflammatory response C. Complementary
Immune System Biol 105 Lecture 16 Chapter 13 Outline Immune System I. Function of the Immune system II. Barrier Defenses III. Nonspecific Defenses A. Immune system cells B. Inflammatory response C. Complementary
Immune System. Biol 105 Chapter 13
 Immune System Biol 105 Chapter 13 Outline Immune System I. Function of the Immune system II. Barrier Defenses III. Nonspecific Defenses A. Immune system cells B. Inflammatory response C. Complementary
Immune System Biol 105 Chapter 13 Outline Immune System I. Function of the Immune system II. Barrier Defenses III. Nonspecific Defenses A. Immune system cells B. Inflammatory response C. Complementary
Body Defense Mechanisms
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 13 Body Defense Mechanisms Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 13 Body Defense Mechanisms Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of
1. Lymphatic vessels recover about of the fluid filtered by capillaries. A. ~1% C. ~25% E. ~85% B. ~10% D. ~50%
 BIOL2030 Huaman A&P II -- Exam 3 -- XXXX -- Form A Name: 1. Lymphatic vessels recover about of the fluid filtered by capillaries. A. ~1% C. ~25% E. ~85% B. ~10% D. ~50% 2. Special lymphatic vessels called
BIOL2030 Huaman A&P II -- Exam 3 -- XXXX -- Form A Name: 1. Lymphatic vessels recover about of the fluid filtered by capillaries. A. ~1% C. ~25% E. ~85% B. ~10% D. ~50% 2. Special lymphatic vessels called
Chapter 17. The Lymphatic System and Immunity. Copyright 2010, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 17 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Immunity Innate Immunity Fast, non-specific and no memory Barriers, ph extremes, Phagocytes & NK cells, fever, inflammation, complement, interferon Adaptive
Chapter 17 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Immunity Innate Immunity Fast, non-specific and no memory Barriers, ph extremes, Phagocytes & NK cells, fever, inflammation, complement, interferon Adaptive
Chapter 16 Lymphatic System and Immunity. Lymphatic Pathways. Lymphatic Capillaries. network of vessels that assist in circulating fluids
 Chapter 16 Lymphatic System and Immunity network of vessels that assist in circulating fluids closely associated with the cardiovascular system transports excess fluid away from interstitial spaces transports
Chapter 16 Lymphatic System and Immunity network of vessels that assist in circulating fluids closely associated with the cardiovascular system transports excess fluid away from interstitial spaces transports
2. The normal of the gut, and vagina keep the growth of pathogens in check. 3. in the respiratory tract sweep out bacteria and particles.
 Chapter 39 Immunity I. Three Lines of Defense A. Surface Barriers to Invasion 1. is an important barrier. 2. The normal of the gut, and vagina keep the growth of pathogens in check. 3. in the respiratory
Chapter 39 Immunity I. Three Lines of Defense A. Surface Barriers to Invasion 1. is an important barrier. 2. The normal of the gut, and vagina keep the growth of pathogens in check. 3. in the respiratory
CHAPTER 16: LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY OBJECTIVES. Transport dietary fat. Transport excess tissue fluid back to blood stream
 CHAPTER 16: LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY OBJECTIVES 1. Name the organs that compose the lymphatic system and give three general functions performed by this system. Bone Marrow Control Disease Thymus Lymph
CHAPTER 16: LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY OBJECTIVES 1. Name the organs that compose the lymphatic system and give three general functions performed by this system. Bone Marrow Control Disease Thymus Lymph
Chapter 24 The Immune System
 Chapter 24 The Immune System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction: The Kissing Disease?!?
Chapter 24 The Immune System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction: The Kissing Disease?!?
Lymphatic System. Where s your immunity idol?
 Lymphatic System Where s your immunity idol? Functions of the Lymphatic System Fluid Balance Drains excess fluid from tissues Lymph contains solutes from plasma Fat Absorption Lymphatic system absorbs
Lymphatic System Where s your immunity idol? Functions of the Lymphatic System Fluid Balance Drains excess fluid from tissues Lymph contains solutes from plasma Fat Absorption Lymphatic system absorbs
Section 9: Lymphatic system and immunity A. Definitions Bacteria Viruses Prions Lines of Defence: How we fight the invaders
 Section 9: Lymphatic system and immunity A. Definitions 1. Microbes = microscopic organisms such as bacteria Some microbes are useful to humans: contribute to production of yogurt, cheese, bread, beer,
Section 9: Lymphatic system and immunity A. Definitions 1. Microbes = microscopic organisms such as bacteria Some microbes are useful to humans: contribute to production of yogurt, cheese, bread, beer,
I. Lines of Defense Pathogen: Table 1: Types of Immune Mechanisms. Table 2: Innate Immunity: First Lines of Defense
 I. Lines of Defense Pathogen: Table 1: Types of Immune Mechanisms Table 2: Innate Immunity: First Lines of Defense Innate Immunity involves nonspecific physical & chemical barriers that are adapted for
I. Lines of Defense Pathogen: Table 1: Types of Immune Mechanisms Table 2: Innate Immunity: First Lines of Defense Innate Immunity involves nonspecific physical & chemical barriers that are adapted for
Immunity. Chapter 38
 Immunity Chapter 38 Impacts, Issues Frankie s Last Wish Infection with a common, sexually transmitted virus (HPV) causes most cervical cancers including the one that killed Frankie McCullogh 38.1 Integrated
Immunity Chapter 38 Impacts, Issues Frankie s Last Wish Infection with a common, sexually transmitted virus (HPV) causes most cervical cancers including the one that killed Frankie McCullogh 38.1 Integrated
General Biology. A summary of innate and acquired immunity. 11. The Immune System. Repetition. The Lymphatic System. Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.
 A summary of innate and acquired immunity General iology INNATE IMMUNITY Rapid responses to a broad range of microbes Course No: NG00 Credits:.00 External defenses Invading microbes (pathogens). The Immune
A summary of innate and acquired immunity General iology INNATE IMMUNITY Rapid responses to a broad range of microbes Course No: NG00 Credits:.00 External defenses Invading microbes (pathogens). The Immune
immunity produced by an encounter with an antigen; provides immunologic memory. active immunity clumping of (foreign) cells; induced by crosslinking
 active immunity agglutination allografts immunity produced by an encounter with an antigen; provides immunologic memory. clumping of (foreign) cells; induced by crosslinking of antigenantibody complexes.
active immunity agglutination allografts immunity produced by an encounter with an antigen; provides immunologic memory. clumping of (foreign) cells; induced by crosslinking of antigenantibody complexes.
Immune system. Aims. Immune system. Lymphatic organs. Inflammation. Natural immune system. Adaptive immune system
 Aims Immune system Lymphatic organs Inflammation Natural immune system Adaptive immune system Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) Disorders of the immune system 1 2 Immune system Lymphoid organs Immune
Aims Immune system Lymphatic organs Inflammation Natural immune system Adaptive immune system Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) Disorders of the immune system 1 2 Immune system Lymphoid organs Immune
4) What causes lymph to move? Skeletal muscle contraction; smooth muscle contraction, breathing (like blood moves through veins)
 NPHS Anatomy & Physiology UNIT 10 REVIEW GUIDE Lymphatic System 1) List the three functions of the lymphatic system. transports excess fluid to the bloodstream absorbs fats helps defend the body against
NPHS Anatomy & Physiology UNIT 10 REVIEW GUIDE Lymphatic System 1) List the three functions of the lymphatic system. transports excess fluid to the bloodstream absorbs fats helps defend the body against
Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System
 Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System Immune System Composed of many nonspecific and specific defenses Lymphatic System also plays an important role in establishing immunity Lymphatic System Major components
Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System Immune System Composed of many nonspecific and specific defenses Lymphatic System also plays an important role in establishing immunity Lymphatic System Major components
IMMUNITY AND DISEASE II
 IMMUNITY AND DISEASE II A. Evolution of the immune system. 1. Figure 1--57.25, p. 1167 from Raven and Johnson Biology 6 th ed. shows how the immune system evolved. Figure 1. How the immune system evolved.
IMMUNITY AND DISEASE II A. Evolution of the immune system. 1. Figure 1--57.25, p. 1167 from Raven and Johnson Biology 6 th ed. shows how the immune system evolved. Figure 1. How the immune system evolved.
Chapter 14. Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Chapter 14 Lymphatic System and Immunity 1 Introduction A. The lymphatic system is comprised of a network of vessels that transport body fluids, the cells and chemicals in those vessels and the organs
Chapter 14 Lymphatic System and Immunity 1 Introduction A. The lymphatic system is comprised of a network of vessels that transport body fluids, the cells and chemicals in those vessels and the organs
Internal Defense Notes
 Internal environment of animals provides attractive area for growth of bacteria, viruses, fungi Harm via: 1. destruction of cells 2. production of toxic chemicals To protect against foreign invaders, humans
Internal environment of animals provides attractive area for growth of bacteria, viruses, fungi Harm via: 1. destruction of cells 2. production of toxic chemicals To protect against foreign invaders, humans
The Immune System. These are classified as the Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses. Innate Immunity
 The Immune System Biological mechanisms that defend an organism must be 1. triggered by a stimulus upon injury or pathogen attack 2. able to counteract the injury or invasion 3. able to recognise foreign
The Immune System Biological mechanisms that defend an organism must be 1. triggered by a stimulus upon injury or pathogen attack 2. able to counteract the injury or invasion 3. able to recognise foreign
Immune System AP SBI4UP
 Immune System AP SBI4UP TYPES OF IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY ACQUIRED IMMUNITY EXTERNAL DEFENCES INTERNAL DEFENCES HUMORAL RESPONSE Skin Phagocytic Cells CELL- MEDIATED RESPONSE Mucus layer Antimicrobial
Immune System AP SBI4UP TYPES OF IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY ACQUIRED IMMUNITY EXTERNAL DEFENCES INTERNAL DEFENCES HUMORAL RESPONSE Skin Phagocytic Cells CELL- MEDIATED RESPONSE Mucus layer Antimicrobial
Blood and Immune system Acquired Immunity
 Blood and Immune system Acquired Immunity Immunity Acquired (Adaptive) Immunity Defensive mechanisms include : 1) Innate immunity (Natural or Non specific) 2) Acquired immunity (Adaptive or Specific) Cell-mediated
Blood and Immune system Acquired Immunity Immunity Acquired (Adaptive) Immunity Defensive mechanisms include : 1) Innate immunity (Natural or Non specific) 2) Acquired immunity (Adaptive or Specific) Cell-mediated
Chapter Pages Transmission
 Chapter 19.2 Pages 442-448 Transmission Immunity There are three lines of defense: 1 The skin and mucous membranes are a nonspecific barrier to infection. 2 Macrophages attack pathogens that enter the
Chapter 19.2 Pages 442-448 Transmission Immunity There are three lines of defense: 1 The skin and mucous membranes are a nonspecific barrier to infection. 2 Macrophages attack pathogens that enter the
Overview of the Lymphoid System
 Overview of the Lymphoid System The Lymphoid System Protects us against disease Lymphoid system cells respond to Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells, such as cancers Overview of the Lymphoid
Overview of the Lymphoid System The Lymphoid System Protects us against disease Lymphoid system cells respond to Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells, such as cancers Overview of the Lymphoid
The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses 12PART B Adaptive Defense System: Third Line of Defense Immune
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses 12PART B Adaptive Defense System: Third Line of Defense Immune
Immune System. Presented by Kazzandra Anton, Rhea Chung, Lea Sado, and Raymond Tanaka
 Immune System Presented by Kazzandra Anton, Rhea Chung, Lea Sado, and Raymond Tanaka Content Standards 35.1 In innate immunity, recognition and response rely on traits common to groups of pathogens 35.2
Immune System Presented by Kazzandra Anton, Rhea Chung, Lea Sado, and Raymond Tanaka Content Standards 35.1 In innate immunity, recognition and response rely on traits common to groups of pathogens 35.2
Overview. Barriers help animals defend against many dangerous pathogens they encounter.
 Immunity Overview Barriers help animals defend against many dangerous pathogens they encounter. The immune system recognizes foreign bodies and responds with the production of immune cells and proteins.
Immunity Overview Barriers help animals defend against many dangerous pathogens they encounter. The immune system recognizes foreign bodies and responds with the production of immune cells and proteins.
(b) fluid returns to venous end of capillary due to hydrostatic pressure and osmotic pressure
 (Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Lymphatic System and Immunity (Body Defenses) I. (Slide 2) Introduction A) General 1) Lymphatic System performs 2 basic functions: 2) Organs of the Lymphatic System (a) lymphatic
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Lymphatic System and Immunity (Body Defenses) I. (Slide 2) Introduction A) General 1) Lymphatic System performs 2 basic functions: 2) Organs of the Lymphatic System (a) lymphatic
Lymphatic System. Chapter 14. Introduction. Main Channels of Lymphatics. Lymphatics. Lymph Tissue. Major Lymphatic Vessels of the Trunk
 Lymphatic System Chapter 14 Components Lymph is the fluid Vessels lymphatics Structures & organs Functions Return tissue fluid to the bloodstream Transport fats from the digestive tract to the bloodstream
Lymphatic System Chapter 14 Components Lymph is the fluid Vessels lymphatics Structures & organs Functions Return tissue fluid to the bloodstream Transport fats from the digestive tract to the bloodstream
Physiology Unit 3. ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY The Specific Immune Response
 Physiology Unit 3 ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY The Specific Immune Response In Physiology Today The Adaptive Arm of the Immune System Specific Immune Response Internal defense against a specific pathogen Acquired
Physiology Unit 3 ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY The Specific Immune Response In Physiology Today The Adaptive Arm of the Immune System Specific Immune Response Internal defense against a specific pathogen Acquired
Nonspecific External Barriers skin, mucous membranes
 Immune system Chapter 36 BI 103 Plant-Animal A&P Levels of Defense Against Disease Nonspecific External Barriers skin, mucous membranes Physical barriers? Brainstorm with a partner If these barriers are
Immune system Chapter 36 BI 103 Plant-Animal A&P Levels of Defense Against Disease Nonspecific External Barriers skin, mucous membranes Physical barriers? Brainstorm with a partner If these barriers are
All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 In innate immunity, recognition and
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 In innate immunity, recognition and
The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately
 The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 INNATE IMMUNITY (all animals) Recognition of traits shared
The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 INNATE IMMUNITY (all animals) Recognition of traits shared
4/28/2016. Host Defenses. Unit 8 Microorganisms & The Immune System. Types of Innate Defenses. Defensive Cells Leukocytes
 Host Defenses Unit 8 Microorganisms & The Immune System CH 16-18 Host defenses that produce resistance can be either innate or adaptive: Innate: those that protect against any type of invading agent Adaptive:
Host Defenses Unit 8 Microorganisms & The Immune System CH 16-18 Host defenses that produce resistance can be either innate or adaptive: Innate: those that protect against any type of invading agent Adaptive:
Diseases-causing agents, pathogens, can produce infections within the body.
 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II 1 CHAPTER 16 Lecture: Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. LYMPHATIC and IMMUNE Systems Body Defenses Against
BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II 1 CHAPTER 16 Lecture: Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. LYMPHATIC and IMMUNE Systems Body Defenses Against
Chapter 24 The Immune System
 Chapter 24 The Immune System The Immune System Layered defense system The skin and chemical barriers The innate and adaptive immune systems Immunity The body s ability to recognize and destroy specific
Chapter 24 The Immune System The Immune System Layered defense system The skin and chemical barriers The innate and adaptive immune systems Immunity The body s ability to recognize and destroy specific
AP Biology. Why an immune system? Chapter 43. Immune System. Lines of defense. 1st: External defense. 2nd: Internal, broad range patrol
 Chapter 43. Immune System lymphocytes attacking cancer cell lymph phagocytic leukocyte Why an immune system? Attack from outside lots of organisms want you for lunch! animals must defend themselves against
Chapter 43. Immune System lymphocytes attacking cancer cell lymph phagocytic leukocyte Why an immune system? Attack from outside lots of organisms want you for lunch! animals must defend themselves against
Outline. Animals: Immunity. Defenses Against Disease. Key Concepts:
 Animals: Immunity Defenses Against Disease Outline 1. Key concepts 2. Physical barriers: Skin, Mucus and HCL in stomach 3. Non-specific 4. Specific responses Immune System a. Components of Immune system
Animals: Immunity Defenses Against Disease Outline 1. Key concepts 2. Physical barriers: Skin, Mucus and HCL in stomach 3. Non-specific 4. Specific responses Immune System a. Components of Immune system
Chapter 43. Immune System. phagocytosis. lymphocytes. AP Biology
 Chapter 43. Immune System phagocytosis lymphocytes 1 Why an immune system? Attack from outside lots of organisms want you for lunch! animals must defend themselves against unwelcome invaders viruses protists
Chapter 43. Immune System phagocytosis lymphocytes 1 Why an immune system? Attack from outside lots of organisms want you for lunch! animals must defend themselves against unwelcome invaders viruses protists
Chapter 23 Immunity Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 23 Immunity Exam Study Questions 1. Define 1) Immunity 2) Neutrophils 3) Macrophage 4) Epitopes 5) Interferon 6) Complement system 7) Histamine 8) Mast cells 9) Antigen 10) Antigens receptors 11)
Chapter 23 Immunity Exam Study Questions 1. Define 1) Immunity 2) Neutrophils 3) Macrophage 4) Epitopes 5) Interferon 6) Complement system 7) Histamine 8) Mast cells 9) Antigen 10) Antigens receptors 11)
Immune System Notes Innate immunity Acquired immunity lymphocytes, humoral response Skin lysozyme, mucus membrane
 Immune System Notes I. The immune system consists of innate and acquired immunity. A. An animal must defend itself against unwelcome intruders the many potentially dangerous viruses, bacteria, and other
Immune System Notes I. The immune system consists of innate and acquired immunity. A. An animal must defend itself against unwelcome intruders the many potentially dangerous viruses, bacteria, and other
Chapter 12- The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
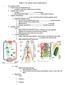 Chapter 12- The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses I. The Lymphatic System a. Consists of two semi-independent parts i. Lymphatic vessels and Lymphoid tissues and organs b. Lymphatic system functions i.
Chapter 12- The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses I. The Lymphatic System a. Consists of two semi-independent parts i. Lymphatic vessels and Lymphoid tissues and organs b. Lymphatic system functions i.
NOTES: CH 43, part 2 Immunity; Immune Disruptions ( )
 NOTES: CH 43, part 2 Immunity; Immune Disruptions (43.3-43.4) Activated B & T Lymphocytes produce: CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNE RESPONSE: involves specialized T cells destroying infected host cells HUMORAL IMMUNE
NOTES: CH 43, part 2 Immunity; Immune Disruptions (43.3-43.4) Activated B & T Lymphocytes produce: CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNE RESPONSE: involves specialized T cells destroying infected host cells HUMORAL IMMUNE
Warm-up. Parts of the Immune system. Disease transmission. Disease transmission. Why an immune system? Chapter 43 3/9/2012.
 Warm-up Objective: Explain how antigens react with specific lymphocytes to induce immune response and immunological memory. Warm-up: Which of the following would normally contain blood with the least amount
Warm-up Objective: Explain how antigens react with specific lymphocytes to induce immune response and immunological memory. Warm-up: Which of the following would normally contain blood with the least amount
3/17/2014. The Lymphatic System. Lymphatic System Overview Lymphatic Vessels and Flow of Lymph Lymphoid Cells, Tissues, and Organs
 The Lymphatic System Lymphatic System Overview Lymphatic Vessels and Flow of Lymph Lymphoid Cells, Tissues, and Organs Overview of the Lymphatic System Slide 2 Major Components of the Lymphatic System
The Lymphatic System Lymphatic System Overview Lymphatic Vessels and Flow of Lymph Lymphoid Cells, Tissues, and Organs Overview of the Lymphatic System Slide 2 Major Components of the Lymphatic System
NOTES: CH 43, part 1 The Immune System - Nonspecific & Specific Defenses ( )
 NOTES: CH 43, part 1 The Immune System - Nonspecific & Specific Defenses (43.1-43.2) The lymphatic system is closely associated with the cardiovascular system. LYMPHATIC PATHWAYS Lymphatic capillaries
NOTES: CH 43, part 1 The Immune System - Nonspecific & Specific Defenses (43.1-43.2) The lymphatic system is closely associated with the cardiovascular system. LYMPHATIC PATHWAYS Lymphatic capillaries
The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses Outline PART 1: INNATE DEFENSES 21.1 Surface barriers act as the first line of defense to keep
 The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses Outline PART 1: INNATE DEFENSES 21.1 Surface barriers act as the first line of defense to keep invaders out of the body (pp. 772 773; Fig. 21.1; Table
The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses Outline PART 1: INNATE DEFENSES 21.1 Surface barriers act as the first line of defense to keep invaders out of the body (pp. 772 773; Fig. 21.1; Table
I. Defense Mechanisms Chapter 15
 10/24/11 I. Defense Mechanisms Chapter 15 Immune System Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Defense Mechanisms Protect against
10/24/11 I. Defense Mechanisms Chapter 15 Immune System Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Defense Mechanisms Protect against
Immune System. Before You Read. Read to Learn
 Immune System 37 section 2 The Immune System Biology/Life Sciences 10.b Students know the role of antibodies in the body s response to infection. Also covers: Biology/Life Sciences 10.a, 10.e, 10.f Components
Immune System 37 section 2 The Immune System Biology/Life Sciences 10.b Students know the role of antibodies in the body s response to infection. Also covers: Biology/Life Sciences 10.a, 10.e, 10.f Components
Anatomy. Lymph: Tissue fluid that enters a lymphatic capillary (clear fluid that surrounds new piercings!)
 Lymphatic System Anatomy Lymphatic vessels: meet up in capillaries of of tissues to collect extra water, and have an end point of meeting up with lymphatic ducts that empty fluid into large veins in the
Lymphatic System Anatomy Lymphatic vessels: meet up in capillaries of of tissues to collect extra water, and have an end point of meeting up with lymphatic ducts that empty fluid into large veins in the
Unit 3 Dynamic Equilibrium Chapter Immune System
 Biology 2201 Unit 3 Dynamic Equilibrium Chapter 11.4 - Immune System Compiled by S. Whalen What is Immunity? Immunity Immunity The ability of the body to fight infection and/or foreign invaders by producing
Biology 2201 Unit 3 Dynamic Equilibrium Chapter 11.4 - Immune System Compiled by S. Whalen What is Immunity? Immunity Immunity The ability of the body to fight infection and/or foreign invaders by producing
Unit 12: The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
 Unit 12: The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses I. The Lymphatic System A. Consists of two semi-independent parts 1. Lymphatic vessels 2. Lymphoid tissues and organs B. Lymphatic system functions 1. Transports
Unit 12: The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses I. The Lymphatic System A. Consists of two semi-independent parts 1. Lymphatic vessels 2. Lymphoid tissues and organs B. Lymphatic system functions 1. Transports
Unit 12 - The Lymphatic System and 1
 Unit 12 - The Lymphatic System and 1 I. Unit 12: The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses A. The Lymphatic System 1. Consists of two semi-independent parts a) Lymphatic vessels b) Lymphoid tissues and organs
Unit 12 - The Lymphatic System and 1 I. Unit 12: The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses A. The Lymphatic System 1. Consists of two semi-independent parts a) Lymphatic vessels b) Lymphoid tissues and organs
Ch. 11: Immune Physiology. 1. Review Immune Organs & Cells. Immune system = The cells and organs involved in defense against pathogens and cancer.
 Ch. 11: Immune Physiology Objectives: 1. Review immune organs & cells. 2. Two types of immunity. 3. Understand functions of immune cells (T-cells and B-cells) 4. Understand autoimmunity disorders. 1. Review
Ch. 11: Immune Physiology Objectives: 1. Review immune organs & cells. 2. Two types of immunity. 3. Understand functions of immune cells (T-cells and B-cells) 4. Understand autoimmunity disorders. 1. Review
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e (Marieb) Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses Multiple Choice Part I Questions
 Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e (Marieb) Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses 12.1 Multiple Choice Part I Questions Using Figure 12.1, identify the following: 1) A lymph capillary
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e (Marieb) Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses 12.1 Multiple Choice Part I Questions Using Figure 12.1, identify the following: 1) A lymph capillary
CH. 24. The Immune System
 CH. 24 The Immune System The immune systems consists of organs, cells, and molecules that fight infections and protect us from invaders. Pathogens: Bacteria, Viruses, Parasites, Fungi 1. Innate (nonspecific)
CH. 24 The Immune System The immune systems consists of organs, cells, and molecules that fight infections and protect us from invaders. Pathogens: Bacteria, Viruses, Parasites, Fungi 1. Innate (nonspecific)
Chapter 21: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses
 Chapter 21: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses I. 2 main types of body defenses A. Innate (nonspecific) defense: not to a specific microorganism or substance B. Adaptive (specific) defense: immunity to
Chapter 21: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses I. 2 main types of body defenses A. Innate (nonspecific) defense: not to a specific microorganism or substance B. Adaptive (specific) defense: immunity to
Chapter 33: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 Chapter 33: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems AP Curriculum Alignment The immune system is one of the human systems that is detailed in Big Idea 2and Chapter 33 provides these details. Programmed cell death
Chapter 33: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems AP Curriculum Alignment The immune system is one of the human systems that is detailed in Big Idea 2and Chapter 33 provides these details. Programmed cell death
Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 24 The Immune System Multiple-Choice Questions
 Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 24 The Immune System 24.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The body's innate defenses against infection include A) several nonspecific
Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 24 The Immune System 24.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The body's innate defenses against infection include A) several nonspecific
Return tissue fluid to the bloodstream (fluid balance) Immunity. Transport fats from the digestive tract to the bloodstream
 Lymphatic System L Y M P H A T I C C O M P O N E N T S What is a Lymphatic System? The lymphatic system is a complex system of fluid drainage and transport, immune response, and disease resistance. Fluid
Lymphatic System L Y M P H A T I C C O M P O N E N T S What is a Lymphatic System? The lymphatic system is a complex system of fluid drainage and transport, immune response, and disease resistance. Fluid
11/25/2017. THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS BARRIER DEFENSES INNATE IMMUNITY OF VERTEBRATES
 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS Exoskeleton made of chitin forms the first barrier to pathogens Digestive system is protected by a chitin-based barrier and lysozyme,
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS Exoskeleton made of chitin forms the first barrier to pathogens Digestive system is protected by a chitin-based barrier and lysozyme,
Chapter 35 Active Reading Guide The Immune System
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 35 Active Reading Guide The Immune System Section 1 Phagocytosis plays an important role in the immune systems of both invertebrates and vertebrates. Review the process
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 35 Active Reading Guide The Immune System Section 1 Phagocytosis plays an important role in the immune systems of both invertebrates and vertebrates. Review the process
Chapter 38- Immune System
 Chapter 38- Immune System First Line of Defense: Barriers Nonspecific defenses, such as the skin and mucous membranes, are barriers to potential pathogens. In addition to being a physical barrier to pathogens,
Chapter 38- Immune System First Line of Defense: Barriers Nonspecific defenses, such as the skin and mucous membranes, are barriers to potential pathogens. In addition to being a physical barrier to pathogens,
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses. Short Answer. Figure 12.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses Short Answer Figure 12.1 Using Figure 12.1, identify the following: 1) A lymph capillary is indicated
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses Short Answer Figure 12.1 Using Figure 12.1, identify the following: 1) A lymph capillary is indicated
BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Spring 2011 Section A. Steve Thompson:
 BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Spring 2011 Section A Steve Thompson: stthompson@valdosta.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net 1 Keeping the bad guys at bay immunology The vertebrate immune
BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Spring 2011 Section A Steve Thompson: stthompson@valdosta.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net 1 Keeping the bad guys at bay immunology The vertebrate immune
2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Exposure to pathogens naturally activates the immune system. Takes days to be effective Pearson Education, Inc.
 The innate immune interact with the adaptive immune system 1. Damage to skin causes bleeding = bradykinin activated, resulting in inflammation 2. Dendritic phagocytose pathogens Adaptive immunity 4. Dendritic
The innate immune interact with the adaptive immune system 1. Damage to skin causes bleeding = bradykinin activated, resulting in inflammation 2. Dendritic phagocytose pathogens Adaptive immunity 4. Dendritic
phagocytic leukocyte Immune System lymphocytes attacking cancer cell lymph system
 phagocytic leukocyte Immune System lymphocytes attacking cancer cell lymph system 2006-2007 1) recognizing the presence of an infection; 2) containing the infection and working to eliminate it; 3) regulating
phagocytic leukocyte Immune System lymphocytes attacking cancer cell lymph system 2006-2007 1) recognizing the presence of an infection; 2) containing the infection and working to eliminate it; 3) regulating
The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses Slides 12.1 12.22 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Lymphatic
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses Slides 12.1 12.22 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Lymphatic
Topics in Parasitology BLY Vertebrate Immune System
 Topics in Parasitology BLY 533-2008 Vertebrate Immune System V. Vertebrate Immune System A. Non-specific defenses against pathogens 1. Skin - physical barrier a. Tough armor protein KERATIN b. Surface
Topics in Parasitology BLY 533-2008 Vertebrate Immune System V. Vertebrate Immune System A. Non-specific defenses against pathogens 1. Skin - physical barrier a. Tough armor protein KERATIN b. Surface
Chapter 37 Section 1: Protecting Against Disease. Key Vocabulary Terms 9
 Chapter 37 Section 1: Protecting Against Disease Key Vocabulary Terms 9 Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Pathogen A microorganism, another organism, a virus, or a protein that causes disease; an infectious
Chapter 37 Section 1: Protecting Against Disease Key Vocabulary Terms 9 Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Pathogen A microorganism, another organism, a virus, or a protein that causes disease; an infectious
Prof. Ibtesam Kamel Afifi Professor of Medical Microbiology & Immunology
 By Prof. Ibtesam Kamel Afifi Professor of Medical Microbiology & Immunology Lecture objectives: At the end of the lecture you should be able to: Enumerate features that characterize acquired immune response
By Prof. Ibtesam Kamel Afifi Professor of Medical Microbiology & Immunology Lecture objectives: At the end of the lecture you should be able to: Enumerate features that characterize acquired immune response
Defense mechanism against pathogens
 Defense mechanism against pathogens Immune System What is immune system? Cells and organs within an animal s body that contribute to immune defenses against pathogens ( ) Bacteria -Major entry points ;open
Defense mechanism against pathogens Immune System What is immune system? Cells and organs within an animal s body that contribute to immune defenses against pathogens ( ) Bacteria -Major entry points ;open
The Lymphatic System and Immunity. Chapters 20 & 21
 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapters 20 & 21 Objectives 1. SC.912.L.14.52 - Explain the basic functions of the human immune system, including specific and nonspecific immune response, vaccines, and
The Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapters 20 & 21 Objectives 1. SC.912.L.14.52 - Explain the basic functions of the human immune system, including specific and nonspecific immune response, vaccines, and
INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response. Physiology Unit 3
 INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response Physiology Unit 3 Protection Against Infection The body has several defenses to protect itself from getting an infection Skin Mucus membranes Serous membranes
INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response Physiology Unit 3 Protection Against Infection The body has several defenses to protect itself from getting an infection Skin Mucus membranes Serous membranes
Lymphatic System. The targets of the immune defenses are infectious organisms such as,, parasites, fungi, and some protists.
 Lymphatic System I. Non-specific Defenses The immune system is a body wide network of cells and organs that have evolved to defend the body against attacks by invaders. The targets of the immune defenses
Lymphatic System I. Non-specific Defenses The immune system is a body wide network of cells and organs that have evolved to defend the body against attacks by invaders. The targets of the immune defenses
Lymphatic System and Immune System. Blood capillaries. Lymphatic vessels/ lymph nodes. Then, identify by labeling these specific structures in part B.
 Name: Date: Period: Lymphatic System and Immune System 1. Figure 21.1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. In part A the relationship between lymphatic vessels and the blood vessels of the cardiovascular
Name: Date: Period: Lymphatic System and Immune System 1. Figure 21.1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. In part A the relationship between lymphatic vessels and the blood vessels of the cardiovascular
Innate Immunity. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Innate Immunity Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The vertebrate, including human, immune system is a complex multilayered system for defending against external and internal threats to the integrity of the body. The
Innate Immunity Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The vertebrate, including human, immune system is a complex multilayered system for defending against external and internal threats to the integrity of the body. The
BIO 116 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 3 - The Lymphatic, Immune and Digestive Systems This is not a required assignment
 BIO 116 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 3 - The Lymphatic, Immune and Digestive Systems This is not a required assignment 1. Which are components of the lymphatic system? a: Thyroid gland b:
BIO 116 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 3 - The Lymphatic, Immune and Digestive Systems This is not a required assignment 1. Which are components of the lymphatic system? a: Thyroid gland b:
The Immune System. Specific Immunity
 The Immune System Specific Immunity What You Should Know Immune surveillance A range of white blood cells constantly circulate monitoring the tissues. If tissues become damaged or invaded, cells release
The Immune System Specific Immunity What You Should Know Immune surveillance A range of white blood cells constantly circulate monitoring the tissues. If tissues become damaged or invaded, cells release
White Blood Cells (WBCs)
 YOUR ACTIVE IMMUNE DEFENSES 1 ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE 2! Innate Immunity - invariant (generalized) - early, limited specificity - the first line of defense 1. Barriers - skin, tears 2. Phagocytes - neutrophils,
YOUR ACTIVE IMMUNE DEFENSES 1 ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE 2! Innate Immunity - invariant (generalized) - early, limited specificity - the first line of defense 1. Barriers - skin, tears 2. Phagocytes - neutrophils,
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 28 The Immune System Lesson 1: The Immune System Lesson Objectives Upon completion of this lesson,
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 28 The Immune System Lesson 1: The Immune System Lesson Objectives Upon completion of this lesson,
Fluid movement in capillaries. Not all fluid is reclaimed at the venous end of the capillaries; that is the job of the lymphatic system
 Capillary exchange Fluid movement in capillaries Not all fluid is reclaimed at the venous end of the capillaries; that is the job of the lymphatic system Lymphatic vessels Lymphatic capillaries permeate
Capillary exchange Fluid movement in capillaries Not all fluid is reclaimed at the venous end of the capillaries; that is the job of the lymphatic system Lymphatic vessels Lymphatic capillaries permeate
Adaptive Immunity. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 16 Adaptive Immunity The Body s Third Line of Defense Adaptive Immunity Adaptive immunity
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 16 Adaptive Immunity The Body s Third Line of Defense Adaptive Immunity Adaptive immunity
BIOLOGY. CONCEPTS & CONNECTIONS Fourth Edition. Neil A. Campbell Jane B. Reece Lawrence G. Mitchell Martha R. Taylor. CHAPTER 24 The Immune System
 BIOLOGY CONCEPTS & CONNECTIONS Fourth Edition Neil A. Campbell Jane B. Reece Lawrence G. Mitchell Martha R. Taylor CHAPTER 24 The Immune System Modules 24.1 24.2 From PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts
BIOLOGY CONCEPTS & CONNECTIONS Fourth Edition Neil A. Campbell Jane B. Reece Lawrence G. Mitchell Martha R. Taylor CHAPTER 24 The Immune System Modules 24.1 24.2 From PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts
Adaptive Immunity. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R
 CSLO7. Describe functions of host defenses and the immune system in combating infectious diseases and explain how immunizations protect against specific diseases. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared
CSLO7. Describe functions of host defenses and the immune system in combating infectious diseases and explain how immunizations protect against specific diseases. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared
Unit 23: Immunity from Disease
 Unit 5 The Human Body Unit 23 Immunity from Disease- Unit 23: Immunity from Disease Name: Period: Page 1 of 51 Unit 5 The Human Body Unit 23 Immunity from Disease- Chapter 23 assignments Pages/Sections
Unit 5 The Human Body Unit 23 Immunity from Disease- Unit 23: Immunity from Disease Name: Period: Page 1 of 51 Unit 5 The Human Body Unit 23 Immunity from Disease- Chapter 23 assignments Pages/Sections
The Immune System. Chapter 43. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 43 The Immune System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 43 The Immune System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Guided Reading Activities
 Name Period Chapter 24: The Immune System Guided Reading Activities Big idea: Innate immunity Answer the following questions as you read modules 24.1 24.2: 1. Bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms
Name Period Chapter 24: The Immune System Guided Reading Activities Big idea: Innate immunity Answer the following questions as you read modules 24.1 24.2: 1. Bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms
The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
 12 PART A The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
12 PART A The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
Immunity. Innate & Adaptive
 Immunity Innate & Adaptive Immunity Innate: response to attack is always the same Mechanical mechanisms Chemical mediators Cellular response Inflammatory response Adaptive: response to attack improves
Immunity Innate & Adaptive Immunity Innate: response to attack is always the same Mechanical mechanisms Chemical mediators Cellular response Inflammatory response Adaptive: response to attack improves
Instructor s Guide. Films for the. Humanities & Sciences i A Wealth of Information. A World of Ideas. The Human Body: How It Works THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
 i A Wealth of Information. A World of Ideas. Instructor s Guide The Human Body: How It Works Introduction This program is part of the nine-part series The Human Body: How It Works. The series uses physiologic
i A Wealth of Information. A World of Ideas. Instructor s Guide The Human Body: How It Works Introduction This program is part of the nine-part series The Human Body: How It Works. The series uses physiologic
