01.02 Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP) Occupational Post Exposure Prophylaxis
|
|
|
- Erik Lloyd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 01.02 Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP) Occupational Post Exposure Purpose Audience Establish protocol for management of occupational exposures to blood or potentially infectious materials. All employees of UTMB hospitals, clinics, outpatient surgical center, contract workers, volunteers, and students. Policy Definitions Contacts Exposures to bloodborne pathogens will be managed as described in sections to follow for any occupational exposure of healthcare workers or students. UTMB will assume responsibility for testing of a source patient in the care of a UTMB facility. Occupational exposures to blood and body fluids are defined as: Percutaneous injury (e.g. needlestick, laceration with a sharp object) Contact of mucous membranes or ocular membranes (permucosal exposure) Contact of non-intact skin (e.g. skin that is chapped, abraded) with Blood or other potentially infectious fluid (semen; vaginal secretions; and cerebrospinal, synovial, pleural, peritoneal, pericardial and amniotic fluids; bloody body fluids and unfixed tissue). Employee Health Clinic: emphlthc@utmb.edu Student Health: Fax: (409) Healthcare Epidemiology during office hours: Healthcare Epidemiology After hours pager: Page 1 of 11
2 Procedures A. Initial care of exposed area: exposed employee will cleanse site of percutaneous exposure or rinse exposed mucous membranes for permucosal exposure before reporting the exposure. B. Reporting an exposure: 1. Healthcare worker or student on main campus: report exposure to supervisor or supervising instructor/faculty. 2. First responder exposed to a UTMB patient during pre-hospital care: notify ED charge nurse and agency s infection control officer. 3. Employee: complete injury form: access on the Employee Health Clinic webpage ( Select BBP Process and Forms 4. Student: complete student injury form. 5. Correctional employee exposed to a UTMB patient: Report exposure TDCU triage nurse C. Testing source patient: 1. The priority for testing is to secure a specimen on the source patient, when known, and test the source patient for HIV. This determines the need for prophylaxis to prevent HIV, which should be provided within 4 hours. It is important that the source patient also be tested for hepatitis B and hepatitis C, but these are less time-sensitive tests. 2. Request charge nurse for patient s location (hospital/urgent care center/clinic) to obtain consent/blood sample. If patient is no longer in the care of UTMB, call the lab to determine if there is an adequate serum sample drawn for routine clinical care. Obtain consent for HIV testing when feasible. Use manual lab slips (available from Employee Health) to order labs. Obtain 1 serum separator tube and label with source patient s name and medical record number. 3. The source patient will be tested for the following: HIV, HBsAg, HCV antibody. a) Source patient testing at LCC or ADC: perform a rapid HIV test. Send remainder of sample to Sample Management on the main campus, CSW (core laboratory) via courier for confirmatory HIV test and for hepatitis B and C. b) Main campus: Sample should be sent to Sample Management, CSW for all testing. Page 2 of 11
3 4. Laboratory test results will be reported to student health for students and employee health for everyone else. If the exposed person does not belong to one of the following categories, results will be forwarded to Healthcare Epidemiology: UTMB employee, UTMB student, student from Galveston College (contract with UTMB student health), correctional officer. D. Exposure evaluation, counseling, and management 1. Location: a. Employee exposure: After arranging source patient testing, employee should report to Employee Health Clinic during office hours or to the nearest UTMB urgent care center or emergency department after hours. Employees at remote locations may use the LCC campus or a facility designated by Clinic management for remote locations. The exposure form can be faxed or scanned to the Employee Health Clinic for follow-up on the next business day. b. UTMB students: 1) Exposed on a UTMB campus: report to UTMB Student Health during office hours. After hours, report to the designated urgent care center or emergency department. 2) Student at off-site rotation at facility not operated by UTMB: report exposure per facility policy to assure source patient testing, then report exposure to UTMB student health. 3) School of Medicine students who are designated as Austinbased or Houston-based should follow the prearranged process with the appropriate facilities per the School of Medicine agreements. 4) Non-UTMB student-school has contract with UTMB (Galveston College): Follow UTMB student process by reporting to the Student Health Clinic. 5) Non-UTMB student-school does not have contract with UTMB Student Health: follow process outlined by school. The instructor or UTMB employee who is supervising the student s training should assist in procuring a blood specimen from the source patient and instruct the student in correct procedure: cleanse exposed area and report to the ED or Urgent Care for evaluation and treatment. Inform student that they should see their primary care provider for any additional follow-up and treatment indicated. 2. Laboratory tests for exposed individual a. On all employees/students: HIV-1/HIV-2 antibody, HCV antibody and total anti-hbc. b. In addition, HBV surface antibody should be ordered for employees/students who have a history of HBV immunization Page 3 of 11
4 prior to coming to UTMB. c. Additional laboratory tests required if Employee/Student is starting prophylaxis for HIV exposure/possible exposure CBC (use additional lavender top tube for CBC), ALT, AST, total bilirubin, GGT, creatinine, BUN, blood glucose and CPK. Females must have a urine or serum pregnancy test. 3. Evaluation for counseling, prophylaxis, and follow-up instructions a. UTMB employee: Employee Health clinicians will review the source patient and employee tests. They will provide counseling, prophylaxis, or vaccination as indicated, and instructions for any additional follow-up testing or assessment by a specialist (e.g. hepatologist, infectious disease physician, or obstetrician). b. Non-UTMB employee: 1) May register as a patient in an urgent care center or emergency department to start HIV prophylaxis 2) For counseling and additional evaluation, report to the employee s company/agency designated occupational health provider. 3) Source patient s results are reviewed by Healthcare Epidemiology and communicated after removing patient identifiers to company/agency designated infection control officer or occupational health provider 4) Any follow up care will be provided either by the agency s designated occupational health provider or the exposed person s personal physician. c. UTMB student or student from school with UTMB student health contract: 1) Main campus, during office hours for Student Health: report to Student Health clinic for initial evaluation 2) Off-site, during office hours for Student Health: notify Student Health Clinic for instructions, submit exposure report to Student Health. 3) School of Medicine students who are designated as Austinbased or Houston based should follow the prearranged process with the appropriate facilities per the School of Medicine Agreements. 4) Any location, after hours: report to a UTMB urgent care center or emergency department if one is in close proximity. The student should not delay treatment if they cannot report to and be evaluated within 2 hours. In that case, they should report to the nearest ED for evaluation. Page 4 of 11
5 5) Source patient results are reviewed by Student Health clinicians to determine need for additional prophylaxis, testing, vaccination, or treatment. 6) Any follow up care will be provided either by Student Health clinicians with appropriate referrals to specialists as needed. d. Non-UTMB student 1) May register as a patient in an urgent care center or emergency department for initial evaluation and/or to start HIV prophylaxis. 2) Any follow-up care will be through a healthcare provider designated by the school or the student s personal healthcare provider. Report to individual designated by school and follow school policy regarding evaluation and post-exposure testing/treatment. 3) Source patient s results without patient identifiers are communicated to designated school official by Healthcare Epidemiology. e. First responder: 1) May register as a patient in an urgent care center or emergency department for initial evaluation and/or to start HIV prophylaxis. Any follow up care will be provided by the agency s designated occupational health provider. 2) Any campus: report to the agency s designated infection control officer. 3) Source patient s results without patient identifiers are communicated to designated school official by Healthcare Epidemiology. f. Correctional care officer: 1) Register as a patient in the ED on the main campus for initial evaluation and prophylaxis as indicated. 2) Any follow-up care will be arranged through the TDCJ liaison. E. General guidelines for testing of exposed employee/student: Routine Occupational Exposure Follow-up Follow-up is determined by the results of the initial lab work drawn on the source of the occupational exposure. It proceeds as follows: Known HIV(+) source Obtain HIV exposure 6 weeks 3 months 6 months Known HBV (+) source Obtain Total exposure Obtain HBsAg and Total anti-hbc 6 months Page 5 of 11
6 Known HCV(+) source Obtain HCV exposure Obtain HCV Qual RNA (PCR) 6 weeks 3 months 6 months Unknown source Obtain HIV & HCV exposure 3 months 6 months Obtain Total exposure and HBsAg and Total anti-hbc 6 months Special Precautions after an HIV(+) or High Risk Exposure Do not share a toothbrush. Gums can bleed easily, getting blood on the toothbrush. Do not share razors as blood may go undetected on the blade. Avoid pregnancy until HIV infection is ruled out (i.e. generally 6 months following exposure, but up to one year). Use safe sex practices-male/female latex condoms for barrier protection or abstain from sex during the follow-up period until HIV infection has been ruled out. Do not donate blood, plasma, organs, tissue or semen during the followup period. Seek medical evaluation for any acute illness that occurs during the follow-up period. F. HIV exposure prophylaxis specifics 1. Post-exposure prophylaxis and testing for HIV exposure a. Risk of HIV Infection The average risk of HIV infection due to all types of reported percutaneous exposures to HIV-infected blood is 0.3%. A percutaneous exposure is defined as a needlestick or laceration/puncture with a sharp object. The risk appears to be greater than 0.3% for exposure to HIV (+) patients involving deep injury, visible blood on the device causing the injury or a device previously placed in the source patient s vein or artery. b. Prescriptions 1) Initial dose: Pharmacy has stocked several locations, including EDs, urgent cares and some clinics with initial 24 hr dose if source pt results are not available yet, if source patient is HIV positive, or if the source patient is unknown. 2) When continued prophylaxis is required, the prescription Page 6 of 11
7 will be faxed to the Pharmacy. The Pharmacy will arrange to deliver medication to employees who do not work on the main campus via courier. c. Regimens for Exposure to HIV (Revised September, 2013) is being offered to employees and students who have a percutaneous injury or contamination of mucous membranes or nonintact skin exposure to HIV during the performance of their duties. in these circumstances is voluntary. The CDC says, Because most occupational exposures to HIV do not result in infection transmission, potential toxicity must be carefully considered when prescribing post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) Medication Schedule will be treatment for four weeks with: Dolutegravir 50 mg tablet (Tivicay) One tablet by mouth with or without food once daily for 4 weeks. AND Emtricitabine/Tenofovir 200mg/300mg tablet (Truvada) One tablet by mouth with or without food once daily for 4 weeks. Side effects associated with dolutegravir (Tivicay) include nausea, diarrhea, headache, dizziness, abnormal dreams and difficulty sleeping. Side effects associated with emtricitabine/tenofovir (Truvada) include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, dizziness, gas, loss of appetite, headache, rash, skin discoloration, joint pain and muscle pain. Rarely, this medication may cause jaundice with dark urine and yellowing of the skin or eyes. Page 7 of 11
8 Situations for which Infectious Diseases Consultation for Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) postexposure prophylaxis (PEP) is recommended. Provision of PEP should not be delayed while awaiting expert consultation. Delayed (ie, later than 72 hours) exposure report. Interval after which benefits from PEP are undefined. Breastfeeding in the exposed person If source person s virus is known or suspected to be resistant to one or more of the drugs considered for PEP, selection of drugs to which the source person s virus is unlikely to be resistant is recommended. Toxicity of the initial PEP regimen Symptoms (eg, gastrointestinal symptoms and others) are often manageable without changing the PEP regimen by prescribing antimotility or antiemetic agents. Serious medical illness in the exposed person who is already taking multiple medications may increase the risk of drug toxicity and drugdrug interactions. G. Post-exposure for Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C 1. Risk of Hepatitis B or Hepatitis C Infection The average risk of Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection in susceptible persons after percutaneous exposure to HBVinfected blood is 6 30%. The risk of Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection after percutaneous exposure to HCV-infected blood is 7.4% (95% CI 3.9%-12.5%). 2. Testing and vaccination regimens for Hepatitis B: a. For vaccinated HCW (who have written documentation of a complete, 3-dose of Hepatitis B vaccine series) with subsequent 10 miu/ml, testing the source patient for HBsAg is unnecessary. b. Exposed HCW/Student has never received Hepatitis B vaccine 1) Offer HBV vaccine if source is known to be positive for hepatitis B or is high risk for hepatitis B or source is unknown, (e.g., needle puncture through a trash bag) and employee/student has not been vaccinated against hepatitis B. 2) Offer Hepatitis B Immune Globulin 0.06 ml/kg IM if source is known to be positive for hepatitis B, or is high risk for hepatitis B or source is unknown, (e.g. needle puncture through a trash bag) and employee/student has not been vaccinated against hepatitis B.Exposed HCW/Student has received 3 doses of Hepatitis B vaccine twice and anti-hbs < 10 miu/ml 3) For vaccinated HCW/Student (who have written documentation of Hepatitis B vaccination) with anti-hbs < 10 miu/ml after two complete 3-dose Hepatitis B Page 8 of 11
9 vaccine series, the source patient should be tested for HbsAg as soon as possible after the exposure. If the source patient is HbsAg-positive or has unknown HbsAg status, HCW/Student should receive 2 doses of HBIG. The first dose should be administered as soon as possible after exposure and the second dose should be administered 1 month later. If the source patient is HbsAg-negative neither HBIG nor Hepatitis B vaccine is necessary. 4) Exposed HCW/Student has received 3 doses of Hepatitis B vaccine but has not been tested for anti- HBs: For vaccinated HCW/Student (who have written documentation of a complete, 3-dose Hepatitis B vaccine series) without previous anti-hbs testing, the HCW/Student should be tested for anti-hbs and the source patient (if known) should be tested for HbsAg as soon as possible after the exposure. Testing the source patient and the HCW/Student should occur simultaneously; testing the source patient should not be delayed while waiting for the HCW/Student anti-hbs test results, and likewise, testing the HCW/Student should not be delayed while waiting for the source patient HbsAg results. 5) Exposed HCW/Student has < 10 miu/ml anti-hbs and source patient positive or has unknown HbsAg status. If the HCW/Student has anti-hbs < 10 miu/ml and the source patient is HbsAg- positive or has unknown HbsAg status, the HCW/Student should receive 1 dose of HBIG and be revaccinated as soon as possible after the exposure. The HCW/Student should then receive the second 2 doses to complete the second Hepatitis B vaccine series (6 doses total when accounting for the original 3-dose series) according to the vaccination schedule. To document the HCW s/student s vaccine response status for future exposures, anti-hbs testing should be performed 1-2 months after the last dose of vaccine. 6) Exposed HCW/Student has anti-hbs < 10 miu/ml and the source patient is HbsAg negative. If the HCW/Student has anti-hbs < 10 miu/ml and the source patient is HbsAg-negative, the HCW/Student should receive an additional Hepatitis B vaccine dose, followed by repeat anti-hbs testing 1-2 months later. HCWs/Students whose anti-hbs remains < 10 miu/ml should undergo revaccination with 2 more doses (6 doses total when accounting for the original 3-dose series). To document the HCW s/student s vaccine response status for future exposures, anti-hbs testing Page 9 of 11
10 should be performed 1-2 months after the last dose of vaccine. 7) Exposed HCW/Student has anti-hbs 10 miu/ml at time of exposure. If the HCW/Student has anti-hbs 10 miu/ml at the time of exposure, no postexposure HBV management is necessary, regardless of the source patient s HbsAg status. 8) Exposed HCW/Student unvaccinated or incompletely vaccinated (including those who refused vaccination). For unvaccinated or incompletely vaccinated HCW/Student (including those who refused vaccination), the source patient should be tested for HbsAg as soon as possible after the exposure. Testing unvaccinated or incompletely vaccinated HCW/Student for anti-hbs is not necessary and is potentially misleading, because anti-hbs 10 miu/ml as a correlate of vaccine-induced protection has only been determined for persons who have completed an approved vaccination series. If the source patient is HbsAg-positive or has unknown HbsAg status, the HCW/Student should receive one dose of HBIG and one dose of Hepatitis B vaccine administered as soon as possible after the exposure. The HCW/Student should complete the Hepatitis B vaccine series according to the vaccination schedule. To document the HCW s/student s vaccine response status for future exposures, anti-hbs testing should be performed approximately 1-2 months after the last dose of vaccine. Because anti-hbs testing of HCW/Student who received HBIG should be performed after anti-hbs from HBIG is no longer detectable (6 months after administration), it will likely be necessary to defer anti-hbs testing for a period longer than 1-2 months after the last vaccine dose. 3. Testing and follow-up recommendations for Hepatitis C. Employees/Students testing positive for Hepatitis C Qualitative RNA (PCR) at 6 weeks, 3 months or 6 months, will be referred immediately to a hepatologist for treatment. Page 10 of 11
11 References: 1. Kuhar DT, Henderson DK, Struble KA, Heneine W, et al. Updated US Public Health Service Guidelines for the Management of Occupational Exposures to Human Immunodeficiency Virus and Recommendations for Postexposure. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2013;34: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. CDC Guidance for Evaluating Health-Care Personnel for Hepatitis B Virus Protection and for Administering Postexposure Management, 2013;62(No. RR-10): Jaeckel E, Cornberg M, Wedemeyer H, et al. Treatment of acute hepatitis C with interferon alfa-2b. N Engl J Med 2001; 345: Tivicay package insert. Research Triangle Park, NC: GlaxoSmithKline; 2013 Aug. 5. Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in HIV-1-infected adults and adolescents. Department of Health and Human Services. Available at: Accessed January 29, Page 11 of 11
01.02 Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP) Occupational Post Exposure Management
 01.02 Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP) Occupational Post Exposure Purpose Audience Policy Definitions Establish protocol for management of occupational exposures to blood or potentially infectious materials.
01.02 Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP) Occupational Post Exposure Purpose Audience Policy Definitions Establish protocol for management of occupational exposures to blood or potentially infectious materials.
Bloodbourne Pathogens (BBP) Occupational Post-Exposure Chemophrophylaxis
 Bloodbourne Pathogens (BBP) Audience: All personnel in the. Purpose: The purpose of this document is to establish UTMB policy for the initiation of prophylaxis after occupational exposure to the human
Bloodbourne Pathogens (BBP) Audience: All personnel in the. Purpose: The purpose of this document is to establish UTMB policy for the initiation of prophylaxis after occupational exposure to the human
Blood-borne Pathogens Exposure Policy
 Blood-borne Pathogens Exposure Policy Contents Blood Borne Pathogen(s) Exposure (BBPE) -Post-Exposure Prophylaxis... 1 STUDENT CHECKLIST... 3 PROGRAM CHECKLIST... 4 PROVIDER CHECKLIST... 5 POST-EXPOSURE
Blood-borne Pathogens Exposure Policy Contents Blood Borne Pathogen(s) Exposure (BBPE) -Post-Exposure Prophylaxis... 1 STUDENT CHECKLIST... 3 PROGRAM CHECKLIST... 4 PROVIDER CHECKLIST... 5 POST-EXPOSURE
To provide the guidelines for the management of healthcare workers who have had an occupational exposure to blood and/or body fluids.
 TITLE/DESCRIPTION: MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE TO HBV, HCV, and HIV INDEX NUMBER: EFFECTIVE DATE: APPLIES TO: ISSUING AUTHORITY: 01/01/2009 01/01/2013 All GCC Countries GULF COOPERATION COUNCIL
TITLE/DESCRIPTION: MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE TO HBV, HCV, and HIV INDEX NUMBER: EFFECTIVE DATE: APPLIES TO: ISSUING AUTHORITY: 01/01/2009 01/01/2013 All GCC Countries GULF COOPERATION COUNCIL
EXPOSURE (HIV/HEPATITIS) BLOOD & BODY FLUIDS
 Page(s): 1 of 11 PURPOSE To set a standardized procedure to ensure that employees are evaluated in a consistent and timely manner.. POLICY A. The treatment of Team Member exposure to bloodborne pathogens
Page(s): 1 of 11 PURPOSE To set a standardized procedure to ensure that employees are evaluated in a consistent and timely manner.. POLICY A. The treatment of Team Member exposure to bloodborne pathogens
Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Procedure
 Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Procedure Background: Bloodborne pathogens are infectious microorganisms present in blood that can cause disease in humans. These pathogens include, but are not limited to,
Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Procedure Background: Bloodborne pathogens are infectious microorganisms present in blood that can cause disease in humans. These pathogens include, but are not limited to,
INITIAL EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT FOLLOWING EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR BODY FLUIDS
 Page 1 of 11 Original Date of Issue: June 1991 Reviewed 2/96 5/97 11/98 11/99 5/01 5/02 12/05 Revised 9/95 5/97 5/00 7/02 3/06 6/08 6/10 The following are the procedures to be followed when a person sustains
Page 1 of 11 Original Date of Issue: June 1991 Reviewed 2/96 5/97 11/98 11/99 5/01 5/02 12/05 Revised 9/95 5/97 5/00 7/02 3/06 6/08 6/10 The following are the procedures to be followed when a person sustains
Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure STUDENT. Blood Borne Pathogen Exposure. Student. Rev:
 Blood Borne Pathogen Exposure Student INSTRUCTIONS 1. Student: Get name, DOB and, if available, health record number of source patient Obtain form and assist your supervisor with providing information
Blood Borne Pathogen Exposure Student INSTRUCTIONS 1. Student: Get name, DOB and, if available, health record number of source patient Obtain form and assist your supervisor with providing information
Blood/Body Fluid Exposure Option
 Introduction: Transmission of bloodborne pathogens [e.g., Hepatitis B virus (HBV), Hepatitis C virus (HBC), Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)] from patients to healthcare workers (HCW) is an important
Introduction: Transmission of bloodborne pathogens [e.g., Hepatitis B virus (HBV), Hepatitis C virus (HBC), Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)] from patients to healthcare workers (HCW) is an important
Needlestick and Splash Exposure Flow Chart Page 1 Clinical Practice Guidelines
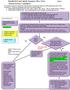 Needlestick and Splash Exposure Flow Chart Page 1 If ANY student experiences a needlestick or splash exposure ANY time of day/night, they need to page #11709 which will be forwarded to: (**in the event
Needlestick and Splash Exposure Flow Chart Page 1 If ANY student experiences a needlestick or splash exposure ANY time of day/night, they need to page #11709 which will be forwarded to: (**in the event
MUSC Occupational Bloodborne Pathogen Protocol Off Campus Procedure Packet. Instructions for Employees/Students:
 MUSC Occupational Bloodborne Pathogen Protocol Off Campus Procedure Packet MUSC has established these protocols in accordance with the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogen Standard and Center for Disease Control recommendations
MUSC Occupational Bloodborne Pathogen Protocol Off Campus Procedure Packet MUSC has established these protocols in accordance with the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogen Standard and Center for Disease Control recommendations
Exposures at Non-MUSC Clinical Sites
 BLOOD BORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE CHECKLIST Exposures at Non-MUSC Clinical Sites (Students on clinical rotations at Roper Hospital, Trident Hospital, Affiliated Local Clinical Sites, Out of Town Clinical Sites,
BLOOD BORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE CHECKLIST Exposures at Non-MUSC Clinical Sites (Students on clinical rotations at Roper Hospital, Trident Hospital, Affiliated Local Clinical Sites, Out of Town Clinical Sites,
Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens
 Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens 11/22/2017 Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens BY SOLYMOLE KURUVILLA, PHD, RN, ACNP-BC DIRECTOR, OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH SERVICES
Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens 11/22/2017 Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens BY SOLYMOLE KURUVILLA, PHD, RN, ACNP-BC DIRECTOR, OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH SERVICES
Bloodborne Pathogens Across the Continuum of Care Sue Sebazco, Arlington, Texas A Webber Training Teleclass
 Bloodborne Pathogens Across the Continuum of Care Objectives Sue Sebazco, RN, BS, CIC Infection Control/Employee Health Director Arlington, TX Pittsburg Mercy Health System skrystofiak@mercy.pmhs.org Define
Bloodborne Pathogens Across the Continuum of Care Objectives Sue Sebazco, RN, BS, CIC Infection Control/Employee Health Director Arlington, TX Pittsburg Mercy Health System skrystofiak@mercy.pmhs.org Define
Blood Borne Pathogen Exposure Employee
 Blood Borne Pathogen Exposure Employee INSTRUCTIONS 1. Employee: Get name, DOB and, if available, health record number of source patient Obtain form and assist your supervisor with providing information
Blood Borne Pathogen Exposure Employee INSTRUCTIONS 1. Employee: Get name, DOB and, if available, health record number of source patient Obtain form and assist your supervisor with providing information
Bloodborne Pathogens and Exposure Control
 Bloodborne Pathogens and Exposure Control 2016 Information in the Exposure Control Plan The Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure Control Plan was developed to communicate information to you about: - Your risk
Bloodborne Pathogens and Exposure Control 2016 Information in the Exposure Control Plan The Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure Control Plan was developed to communicate information to you about: - Your risk
Exposure. What Healthcare Personnel Need to Know
 Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
CONTINUING CARE ADMINISTRATIVE MANUAL POLICY
 CONTINUING CARE ADMINISTRATIVE MANUAL POLICY NUMBER III-10 DATE Draft June 8, 2010 PAGE 1 OF 3 APPROVED BY: SITE: CATEGORY TITLE: Vice President & Senior Operating Officer, Rehab & Continuing Care Edmonton
CONTINUING CARE ADMINISTRATIVE MANUAL POLICY NUMBER III-10 DATE Draft June 8, 2010 PAGE 1 OF 3 APPROVED BY: SITE: CATEGORY TITLE: Vice President & Senior Operating Officer, Rehab & Continuing Care Edmonton
Effective Date: 6/10/2013 Review Date: 6/10/2016
 Policy Title: Sterilization and Disinfection of Patient-Care Items Policy Number: 11 6.2.2. Examples of useful items to maintain in the office sterilization log are as following: o Date and time of cycle
Policy Title: Sterilization and Disinfection of Patient-Care Items Policy Number: 11 6.2.2. Examples of useful items to maintain in the office sterilization log are as following: o Date and time of cycle
El Paso - Ambulatory Clinic Policy and Procedure
 Regulation Reference: Title: NEEDLESTICK INJURIES/EXPOSURES TO BODY FLUIDS, CARE & FOLLOW UP Policy Number: EP 7.3 Effective Date: 6/2010 Policy Statement: A system is established and maintained to assure
Regulation Reference: Title: NEEDLESTICK INJURIES/EXPOSURES TO BODY FLUIDS, CARE & FOLLOW UP Policy Number: EP 7.3 Effective Date: 6/2010 Policy Statement: A system is established and maintained to assure
Clinical Education Initiative OCCUPATIONAL POST- EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS. Antonio E. Urbina, MD
 Clinical Education Initiative Support@ceitraining.org OCCUPATIONAL POST- EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS Antonio E. Urbina, MD 5/22/2013 Occupational Post-Exposure Prophylaxis [Video Transcript] 00:00:15 - [Tony]
Clinical Education Initiative Support@ceitraining.org OCCUPATIONAL POST- EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS Antonio E. Urbina, MD 5/22/2013 Occupational Post-Exposure Prophylaxis [Video Transcript] 00:00:15 - [Tony]
One of your office personnel
 Doug Campos-Outcalt, MD, MPA Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of Arizona College of Medicine, Phoenix HIV postexposure prophylaxis: Who should get it? CORRESPONDENCE Doug Campos-Outcalt,
Doug Campos-Outcalt, MD, MPA Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of Arizona College of Medicine, Phoenix HIV postexposure prophylaxis: Who should get it? CORRESPONDENCE Doug Campos-Outcalt,
Safety Regulations and Procedures Occupational Health Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan S80.10, updated, May Contains information for:
 APPENDIX A Safety Regulations and Procedures Occupational Health Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan S80.10, updated, May 2018 BLOODBORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE INCIDENT PACKET Contains information for:
APPENDIX A Safety Regulations and Procedures Occupational Health Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan S80.10, updated, May 2018 BLOODBORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE INCIDENT PACKET Contains information for:
You will now begin the Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training.
 You will now begin the Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training. The following program will review your occupational risks and the steps that you and your Client must take to reduce your risks of exposure.
You will now begin the Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training. The following program will review your occupational risks and the steps that you and your Client must take to reduce your risks of exposure.
Bloodborne Pathogens Training
 Bloodborne Pathogens Training OSHA S Bloodborne Pathogen Standard 29CFR 1910.1030 Employers must: Develop an Exposure Control Plan (ECP) that details their Bloodborne Pathogens (BBP) Program Provide employees
Bloodborne Pathogens Training OSHA S Bloodborne Pathogen Standard 29CFR 1910.1030 Employers must: Develop an Exposure Control Plan (ECP) that details their Bloodborne Pathogens (BBP) Program Provide employees
Revised April WGH ER #5 Hospital Rd. Whitehorse Phone: (867) Outside of Whitehorse: Local Community Health Centre/Clinic/ER
 Where to access care Who to consult and when Please consult whenever questions arise on how to proceed with postexposure management and when exposure is beyond the scope of guidelines. Blood and Body Fluid
Where to access care Who to consult and when Please consult whenever questions arise on how to proceed with postexposure management and when exposure is beyond the scope of guidelines. Blood and Body Fluid
Bloodborne Pathogens. Exposure Control Plan
 Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan Maryland Institute College of Art Revision Date(s): January 2007/January 2008 Maryland Institute College of Art (MICA) Subject: Occupational/Non-occupational
Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan Maryland Institute College of Art Revision Date(s): January 2007/January 2008 Maryland Institute College of Art (MICA) Subject: Occupational/Non-occupational
Infection Control Standard Precautions. CDC Recommendations: Application of Standard Precautions for All Patients
 Infection Control Standard Precautions Standard Precautions Hand Hygiene CDC Recommendations: Application of Standard Precautions for All Patients Component Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Gloves Mask,
Infection Control Standard Precautions Standard Precautions Hand Hygiene CDC Recommendations: Application of Standard Precautions for All Patients Component Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Gloves Mask,
An International Antiviral Society-USA
 Doug Campos-Outcalt, MD, MPA University of Arizona, Phoenix dougco@email.arizona. edu A look at new guidelines for HIV treatment and prevention Start antiretroviral therapy as soon as possible after HIV
Doug Campos-Outcalt, MD, MPA University of Arizona, Phoenix dougco@email.arizona. edu A look at new guidelines for HIV treatment and prevention Start antiretroviral therapy as soon as possible after HIV
HIV and PEP. LTC Rose Ressner WRNMMC ID staff Oct 2014 UNCLASSIFIED
 HIV and PEP LTC Rose Ressner WRNMMC ID staff Oct 2014 UNCLASSIFIED Disclaimer The views expressed in this presentation are those of the speaker and do not reflect the official policy of the Department
HIV and PEP LTC Rose Ressner WRNMMC ID staff Oct 2014 UNCLASSIFIED Disclaimer The views expressed in this presentation are those of the speaker and do not reflect the official policy of the Department
Healthcare Professionals
 EMPLOYEE HEALTH Employee Health: Screening and immunization programs Counseling, follow up work restrictions Analysis and trending of occupational exposure incidents Assess risk for occupational exposure
EMPLOYEE HEALTH Employee Health: Screening and immunization programs Counseling, follow up work restrictions Analysis and trending of occupational exposure incidents Assess risk for occupational exposure
STUDENT EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR OTHER POTENTIALLY INFECTIOUS MATERIALS
 STUDENT EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR OTHER POTENTIALLY INFECTIOUS MATERIALS (See Bloodborne Pathogen Worksheet and Post Exposure Prophylaxis consent immediately following this policy ) 1. Student must report immediately
STUDENT EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR OTHER POTENTIALLY INFECTIOUS MATERIALS (See Bloodborne Pathogen Worksheet and Post Exposure Prophylaxis consent immediately following this policy ) 1. Student must report immediately
POLICY ON BLOOD AND BODY FLUID EXPOSURE (NEEDLE STICK)
 POLICY ON BLOOD AND BODY FLUID EXPOSURE (NEEDLE STICK) Dated: January 1, 2018 Supersedes: Blood and Body Fluid Exposure (Needle stick) dated July 1, 2015 I. POLICY It is the policy of New York Medical
POLICY ON BLOOD AND BODY FLUID EXPOSURE (NEEDLE STICK) Dated: January 1, 2018 Supersedes: Blood and Body Fluid Exposure (Needle stick) dated July 1, 2015 I. POLICY It is the policy of New York Medical
Definitions. Appendix A
 Definitions Appendix A 1. Blood means human blood, human blood components, and products made from human blood. 2. Bloodborne Pathogens means pathogenic microorganisms that are present in human blood and
Definitions Appendix A 1. Blood means human blood, human blood components, and products made from human blood. 2. Bloodborne Pathogens means pathogenic microorganisms that are present in human blood and
B. Tasks and Procedures where employees, students or contractors can be exposed to bloodborne pathogens:
 Page 1 of 6 BLOODBORNE PATHOGEN PROGRAM INTRODUCTION The intended purpose of this document is to comply with OSHA s Occupational Exposures to Bloodborne Pathogens in Title 29 Code of Federal Regulations
Page 1 of 6 BLOODBORNE PATHOGEN PROGRAM INTRODUCTION The intended purpose of this document is to comply with OSHA s Occupational Exposures to Bloodborne Pathogens in Title 29 Code of Federal Regulations
Emergency Department Blood/Body Fluid Exposure Instructions
 Emergency Department Blood/Body Fluid Exposure Instructions For employees sent to the Emergency Department after hours to be evaluated for needle stick / body fluid exposure 1. Floor or unit Charge RN
Emergency Department Blood/Body Fluid Exposure Instructions For employees sent to the Emergency Department after hours to be evaluated for needle stick / body fluid exposure 1. Floor or unit Charge RN
SIV/SHIV Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison
 SIV/SHIV SIV/SHIV Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison 1.0 Instructions: Information in this guidance is meant to inform both laboratory staff and health professionals
SIV/SHIV SIV/SHIV Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison 1.0 Instructions: Information in this guidance is meant to inform both laboratory staff and health professionals
Central Franciscan Health Rensselaer Blood and Body Fluid Exposures Procedure COPY
 Current Status: Active PolicyStat ID: 2625043 Original: 7/18/2011 Last Reviewed: 8/19/2016 Last Revised: 8/19/2016 Next Review: 8/19/2019 Responsible Party: Kristin Deno: Manager Policy Area: References:
Current Status: Active PolicyStat ID: 2625043 Original: 7/18/2011 Last Reviewed: 8/19/2016 Last Revised: 8/19/2016 Next Review: 8/19/2019 Responsible Party: Kristin Deno: Manager Policy Area: References:
Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP)
 Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP) Healthcare facilities are high-risk areas for exposure to bloodborne pathogens, so protect yourself and remind others to do the same. There are three bloodborne pathogens of
Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP) Healthcare facilities are high-risk areas for exposure to bloodborne pathogens, so protect yourself and remind others to do the same. There are three bloodborne pathogens of
Environmental Health and Safety Offices BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS
 Environmental Health and Safety Offices BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Purpose! Reduce / eliminate exposure potential Comply with Ohio s Public Employment Risk Reduction Act (reference OSHA) 2! Exposure Determination!
Environmental Health and Safety Offices BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Purpose! Reduce / eliminate exposure potential Comply with Ohio s Public Employment Risk Reduction Act (reference OSHA) 2! Exposure Determination!
Exposure. Blood. Department of Health & Human Services
 Exposure to Blood What Health-Care Workers Need to Know Department of Health & Human Services OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOOD Introduction Health-care workers are at risk for occupational exposure to bloodborne
Exposure to Blood What Health-Care Workers Need to Know Department of Health & Human Services OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOOD Introduction Health-care workers are at risk for occupational exposure to bloodborne
Policy S- 15 FLORIDA STATE UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF NURSING BLOODBORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN FOR NURSING STUDENTS
 TITLE: Policy S- 15 FLORIDA STATE UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF NURSING BLOODBORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN FOR NURSING STUDENTS Page 1 of 2 POLICY: The College of Nursing shall maintain a bloodborne pathogen
TITLE: Policy S- 15 FLORIDA STATE UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF NURSING BLOODBORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN FOR NURSING STUDENTS Page 1 of 2 POLICY: The College of Nursing shall maintain a bloodborne pathogen
Contamination Incidents Frequently Asked Questions
 Contamination Incidents Frequently Asked Questions WWR- 004 Index 1. What is a contamination injury? 2. What should I do immediately if I have sustained a contamination injury? 3. What should I do immediately
Contamination Incidents Frequently Asked Questions WWR- 004 Index 1. What is a contamination injury? 2. What should I do immediately if I have sustained a contamination injury? 3. What should I do immediately
EMPLOYEE HEALTH TABLE OF CONTENTS
 EMPLOYEE HEALTH TABLE OF CONTENTS PHYSICAL ASSESSMENT.2 REPORTING EMPLOYEE INFECTIONS...3 SUMMARY OF IMPORTANT RECOMMENDATIONS AND WORK RESTRICTIONS FOR PERSONNEL WITH INFECTIOUS DISEASES.4 HEPATITIS B
EMPLOYEE HEALTH TABLE OF CONTENTS PHYSICAL ASSESSMENT.2 REPORTING EMPLOYEE INFECTIONS...3 SUMMARY OF IMPORTANT RECOMMENDATIONS AND WORK RESTRICTIONS FOR PERSONNEL WITH INFECTIOUS DISEASES.4 HEPATITIS B
Needles and Sharps Exposure: How do We Proceed?
 Needles and Sharps Exposure: How do We Proceed? UMAYYA MUSHARRAFIEH,MD AMERICAN UNIVERSITY OF BEIRUT MEDICAL CENTER JUNE 14, 2013 Health care workers who use or may be exposed to needles are at increased
Needles and Sharps Exposure: How do We Proceed? UMAYYA MUSHARRAFIEH,MD AMERICAN UNIVERSITY OF BEIRUT MEDICAL CENTER JUNE 14, 2013 Health care workers who use or may be exposed to needles are at increased
PEDIATRIC EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT CLINICAL GUIDELINE: NON- OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE TO BLOOD-BORNE PATHOGENS (HIV, Hepatitis B, AND Hepatitis C)
 General Definition: Blood-borne pathogens are infectious agents that can be transmitted through contact with blood or certain other body fluids. The primary pathogens are HIV, Hepatitis B, and C. Before
General Definition: Blood-borne pathogens are infectious agents that can be transmitted through contact with blood or certain other body fluids. The primary pathogens are HIV, Hepatitis B, and C. Before
Goldenrod Hills Community Action. Bloodborne Pathogen (BBP) Training according to OSHA Standard 29 CFR
 Goldenrod Hills Community Action Bloodborne Pathogen (BBP) Training according to OSHA Standard 29 CFR 1910.1030 Welcome to GHCA s Bloodborne Pathogen Training based upon the Occupational Safety and Health
Goldenrod Hills Community Action Bloodborne Pathogen (BBP) Training according to OSHA Standard 29 CFR 1910.1030 Welcome to GHCA s Bloodborne Pathogen Training based upon the Occupational Safety and Health
Colgate University. Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan
 Colgate University Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan COLGATE UNIVERSITY BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN I. STATEMENT OF POLICY It is the policy of Colgate University (CU) to limit or
Colgate University Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan COLGATE UNIVERSITY BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN I. STATEMENT OF POLICY It is the policy of Colgate University (CU) to limit or
Bloodborne Pathogens Training (OHS_BIO500) Course Material
 Introduction (OHS_BIO500) Course Material Welcome to the Bloodborne Pathogens (BBP) Training Course (OHS_BIO500). UAB Campus Employees whose job duties put them at increased risk for exposure to bloodborne
Introduction (OHS_BIO500) Course Material Welcome to the Bloodborne Pathogens (BBP) Training Course (OHS_BIO500). UAB Campus Employees whose job duties put them at increased risk for exposure to bloodborne
Commonly Asked Questions About Chronic Hepatitis C
 Commonly Asked Questions About Chronic Hepatitis C From the American College of Gastroenterology 1. How common is the hepatitis C virus? The hepatitis C virus is the most common cause of chronic viral
Commonly Asked Questions About Chronic Hepatitis C From the American College of Gastroenterology 1. How common is the hepatitis C virus? The hepatitis C virus is the most common cause of chronic viral
Guidelines for Post- Exposure Prophylaxis for HAV, HBV, HCV & HIV
 Guidelines for Post- Exposure Prophylaxis for HAV, HBV, HCV & HIV By Dr. Sinan Butrus F.I.C.M.S Clinical Standards & Guidelines Kurdistan Board For Medical Specialties An exposure that might place health
Guidelines for Post- Exposure Prophylaxis for HAV, HBV, HCV & HIV By Dr. Sinan Butrus F.I.C.M.S Clinical Standards & Guidelines Kurdistan Board For Medical Specialties An exposure that might place health
Bloodborne Pathogens. Montclair Kimberley Academy 1
 Bloodborne Pathogens Montclair Kimberley Academy 1 Introduction! Approximately 5.6 million workers in health care and other facilities are at risk of exposure to bloodborne pathogens such as human immunodeficiency
Bloodborne Pathogens Montclair Kimberley Academy 1 Introduction! Approximately 5.6 million workers in health care and other facilities are at risk of exposure to bloodborne pathogens such as human immunodeficiency
2017 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS
 2017 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS OSHA TERMS UPDATES HEPATITIS B HEPATITIS C HIV REPORTING AN EXPOSURE To have a basic understanding of bloodborne pathogens and the role of Greenwood School District 50 and OSHA.
2017 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS OSHA TERMS UPDATES HEPATITIS B HEPATITIS C HIV REPORTING AN EXPOSURE To have a basic understanding of bloodborne pathogens and the role of Greenwood School District 50 and OSHA.
PROCEDURE TITLE: BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN PROCEDURE NO.: 5.21:1
 PROCEDURE TITLE: BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN PROCEDURE NO.: 5.21:1 RELATED POLICY: 5.21REV PAGE NO.: 1 OF 9 RESPONSIBLE ADMINISTRATOR(S): VPF&A/EHS EFECTIVE DATE: 07/11/14 NEXT REVIEW DATE:
PROCEDURE TITLE: BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN PROCEDURE NO.: 5.21:1 RELATED POLICY: 5.21REV PAGE NO.: 1 OF 9 RESPONSIBLE ADMINISTRATOR(S): VPF&A/EHS EFECTIVE DATE: 07/11/14 NEXT REVIEW DATE:
Training for Employees of Taylor Special Care Services, Inc.
 Training for Employees of Taylor Special Care Services, Inc. TSCS Taylor Special Care Services housing staffing counseling on-going support Simon Pop, MBA Chief Operating Officer 2015 2016 Guidelines:
Training for Employees of Taylor Special Care Services, Inc. TSCS Taylor Special Care Services housing staffing counseling on-going support Simon Pop, MBA Chief Operating Officer 2015 2016 Guidelines:
Bloodborne Pathogen Module. Chelmsford Public Schools September, 2016
 Bloodborne Pathogen Module Chelmsford Public Schools September, 2016 Why is this important? v OSHA BB Pathogen Standard anyone whose job requires exposure to BB pathogens is required to complete training
Bloodborne Pathogen Module Chelmsford Public Schools September, 2016 Why is this important? v OSHA BB Pathogen Standard anyone whose job requires exposure to BB pathogens is required to complete training
Hepatitis B and C Overview, Outbreaks, and Recommendations. Viral Hepatitis Language. Types of Viral Hepatitis 7/1/2013
 Hepatitis B and C Overview, Outbreaks, and Recommendations Elizabeth Lawlor, MS Healthy Kansans living in safe and sustainable environments. Viral Hepatitis Language Acute infection is when the infection
Hepatitis B and C Overview, Outbreaks, and Recommendations Elizabeth Lawlor, MS Healthy Kansans living in safe and sustainable environments. Viral Hepatitis Language Acute infection is when the infection
Bloodborne Pathogens: Recognition and Treatment 2011
 Bloodborne Pathogens: Recognition and Treatment 2011 Occupational Health Services at The Summit Rita M. Lopez, APRN-BC, MSN 751-4189 rlopez@krmc.org OBJECTIVES DEFINE Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure WHO must
Bloodborne Pathogens: Recognition and Treatment 2011 Occupational Health Services at The Summit Rita M. Lopez, APRN-BC, MSN 751-4189 rlopez@krmc.org OBJECTIVES DEFINE Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure WHO must
43. Guidelines on Needle stick Injury
 43. Guidelines on Needle stick Injury The following information is abstracted from the South African Department of Health guidelines entitled: Management of Occupational Exposure to the Human Immunodeficiency
43. Guidelines on Needle stick Injury The following information is abstracted from the South African Department of Health guidelines entitled: Management of Occupational Exposure to the Human Immunodeficiency
BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS FOR HEALTH CARE WORKERS CURRICULUM
 Page 1 of 13 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS FOR HEALTH CARE WORKERS CURRICULUM INTRODUCTION The attached materials will assist in teaching the information about bloodborne pathogens for health care workers as required
Page 1 of 13 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS FOR HEALTH CARE WORKERS CURRICULUM INTRODUCTION The attached materials will assist in teaching the information about bloodborne pathogens for health care workers as required
BAY-ARENAC BEHAVIORAL HEALTH AUTHORITY POLICIES AND PROCEDURES MANUAL
 Page: 1 of 8 Policy Bay-Arenac Behavioral Health Authority (BABHA) is committed to high standards of employee and consumer safety practices. This standard will include the prevention, surveillance, identification
Page: 1 of 8 Policy Bay-Arenac Behavioral Health Authority (BABHA) is committed to high standards of employee and consumer safety practices. This standard will include the prevention, surveillance, identification
Needlestick Policy and Actions to be taken after Exposure to Blood and Body Fluids (including HIV Post- Exposure Prophylaxis).
 LTHT Infection Control Policies Needlestick Policy and Actions to be taken after Exposure to Blood and Body Fluids (including HIV Post- Exposure Prophylaxis). This policy covers the immediate actions to
LTHT Infection Control Policies Needlestick Policy and Actions to be taken after Exposure to Blood and Body Fluids (including HIV Post- Exposure Prophylaxis). This policy covers the immediate actions to
3/23/2016. Managing Bloodborne Pathogen Exposures. Managing Bloodborne Pathogen Exposures
 This webinar begins at 11 a.m., Eastern. You will not hear anything over your telephone line until the program starts. If the system did not prompt you to enter your phone number and receive a call back,
This webinar begins at 11 a.m., Eastern. You will not hear anything over your telephone line until the program starts. If the system did not prompt you to enter your phone number and receive a call back,
Greenwood School District 50 OSHA UPDATE BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS
 Greenwood School District 50 OSHA UPDATE 2012 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS TOPICS OSHA TERMS UPDATES HEPATITIS B HEPATITIS C HIV REPORTING AN EXPOSURE OBJECTIVES To have a basic understanding of bloodborne pathogens
Greenwood School District 50 OSHA UPDATE 2012 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS TOPICS OSHA TERMS UPDATES HEPATITIS B HEPATITIS C HIV REPORTING AN EXPOSURE OBJECTIVES To have a basic understanding of bloodborne pathogens
TRANSMISSION OF BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS: HIV,HBV,HCV. Dr Daniel Kimani HIV Prevention Medical Transmission CDC, Kenya.
 TRANSMISSION OF BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS: HIV,HBV,HCV Dr Daniel Kimani HIV Prevention Medical Transmission CDC, Kenya. Nevada Hepatitis C Outbreak Tied to Las Vegas Clinic. Thousands Now At Risk for Hepatitis,
TRANSMISSION OF BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS: HIV,HBV,HCV Dr Daniel Kimani HIV Prevention Medical Transmission CDC, Kenya. Nevada Hepatitis C Outbreak Tied to Las Vegas Clinic. Thousands Now At Risk for Hepatitis,
Bloodborne Pathogens Training. IEA, Inc.
 Bloodborne Pathogens Training IEA, Inc. Review the potential hazard of exposure to blood and other potentially infectious materials (OPIMs). Review safe work practices to prevent occupational exposure
Bloodborne Pathogens Training IEA, Inc. Review the potential hazard of exposure to blood and other potentially infectious materials (OPIMs). Review safe work practices to prevent occupational exposure
NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS
 NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and HIV may be contracted through exposure to any body fluid, particularly blood. IMMEDIATE ACTION
NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and HIV may be contracted through exposure to any body fluid, particularly blood. IMMEDIATE ACTION
C 肝職業暴露後之處置 衛福部疾病管制署 中區傳染病防治醫療網 王任賢指揮官
 C 肝職業暴露後之處置 衛福部疾病管制署 中區傳染病防治醫療網 王任賢指揮官 HCV:Structure and Classification Unclassified virus, Member of the flavivirus family (other members yellow fever and dengue) Enveloped single stranded RNA virus Humans
C 肝職業暴露後之處置 衛福部疾病管制署 中區傳染病防治醫療網 王任賢指揮官 HCV:Structure and Classification Unclassified virus, Member of the flavivirus family (other members yellow fever and dengue) Enveloped single stranded RNA virus Humans
Hepatitis B Control. Table of Contents
 Control Table of Contents 1.0 INTRODUCTION... 1 2.0 GOALS... 1 3.0 DEFINITIONS... 1 4.0 CASE MANAGEMENT... 3 5.0 HEPATITIS B POST- EXPOSURE MANAGEMENT... 4 TABLE 1: HEPATITIS B POST EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS...
Control Table of Contents 1.0 INTRODUCTION... 1 2.0 GOALS... 1 3.0 DEFINITIONS... 1 4.0 CASE MANAGEMENT... 3 5.0 HEPATITIS B POST- EXPOSURE MANAGEMENT... 4 TABLE 1: HEPATITIS B POST EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS...
Hepatitis C Virus (HCV)
 Clinical Practice Guidelines Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) OBJECTIVE The purpose is to guide the appropriate diagnosis and management of Hepatitis C Virus (HCV). GUIDELINE These are only guidelines, and are
Clinical Practice Guidelines Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) OBJECTIVE The purpose is to guide the appropriate diagnosis and management of Hepatitis C Virus (HCV). GUIDELINE These are only guidelines, and are
OVERVIEW OF PRESENTATION
 OVERVIEW OF PRESENTATION This training is required by the Texas Department of Health Ch. 96, Bloodborne Pathogen Control. Every employee of the district will be required to have some training on bloodborne
OVERVIEW OF PRESENTATION This training is required by the Texas Department of Health Ch. 96, Bloodborne Pathogen Control. Every employee of the district will be required to have some training on bloodborne
Blood-Borne Pathogens and Post-Exposure Prophylaxis
 Blood-Borne Pathogens and Post-Exposure Prophylaxis Christopher Behrens MD Northwest Association of Occupational and Environmental Medicine October 2017 with thanks to Shireesha Dhanireddy MD Disclosures
Blood-Borne Pathogens and Post-Exposure Prophylaxis Christopher Behrens MD Northwest Association of Occupational and Environmental Medicine October 2017 with thanks to Shireesha Dhanireddy MD Disclosures
SUBJECT: Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Counseling/Education, Testing, Referral, and Partner Notification
 SUBJECT: Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Counseling/Education, Testing, Referral, and Partner Notification Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is the most common chronic bloodborne infection in the United States.
SUBJECT: Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Counseling/Education, Testing, Referral, and Partner Notification Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is the most common chronic bloodborne infection in the United States.
Bloodborne Pathogens and Regulated Medical Waste
 Bloodborne Pathogens and Regulated Medical Waste OSHA Ensure employees can safely perform their normal duties without undue health risks Bloodborne Pathogen (BBP) Standard developed to protect employees
Bloodborne Pathogens and Regulated Medical Waste OSHA Ensure employees can safely perform their normal duties without undue health risks Bloodborne Pathogen (BBP) Standard developed to protect employees
Blood borne Pathogen
 Blood borne Pathogen Training For Certified Nursing Assistants Meets the Blood borne Pathogens & Infection Control Update (Formerly HIV/AIDS) 1 0 In-service Hour Meets the Blood borne Pathogens & Infection
Blood borne Pathogen Training For Certified Nursing Assistants Meets the Blood borne Pathogens & Infection Control Update (Formerly HIV/AIDS) 1 0 In-service Hour Meets the Blood borne Pathogens & Infection
Occupational Exposures to Bloodborne Pathogen (BBP) Training
 Occupational Exposures to Bloodborne Pathogen (BBP) Training OSHA 29 CFR 1910.1030 Protects workers exposed to blood or other potentially infectious diseases Who are at Risk? Workers in many different
Occupational Exposures to Bloodborne Pathogen (BBP) Training OSHA 29 CFR 1910.1030 Protects workers exposed to blood or other potentially infectious diseases Who are at Risk? Workers in many different
Gwynedd Mercy University Bloodborne Pathogen Safety and Awareness Training
 Gwynedd Mercy University Bloodborne Pathogen Safety and Awareness Training Education is the KEY Here are Gwynedd Mercy University, we recognize the importance of providing a safe working environment for
Gwynedd Mercy University Bloodborne Pathogen Safety and Awareness Training Education is the KEY Here are Gwynedd Mercy University, we recognize the importance of providing a safe working environment for
NEOMED ACADEMIC POLICY
 (A) PURPOSE The purpose of this Policy is to delineate the management of incidents of exposure to blood-borne pathogens that occur to students while they are in the educational setting. (B) SCOPE This
(A) PURPOSE The purpose of this Policy is to delineate the management of incidents of exposure to blood-borne pathogens that occur to students while they are in the educational setting. (B) SCOPE This
Post Blood & Body Fluid Exposure Checklist
 Post Blood & Body Fluid Exposure Checklist Employee Name: : First Aid completed (If exposure was to eye, irrigate for 20 minutes at the nearest eye wash station. If exposure was to skin, wash affected
Post Blood & Body Fluid Exposure Checklist Employee Name: : First Aid completed (If exposure was to eye, irrigate for 20 minutes at the nearest eye wash station. If exposure was to skin, wash affected
Chapter 2 Hepatitis B Overview
 Chapter 2 Hepatitis B Overview 23 24 This page intentionally left blank. HEPATITIS B OVERVIEW Hepatitis B Virus The hepatitis B virus (HBV) belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family and is known to cause both
Chapter 2 Hepatitis B Overview 23 24 This page intentionally left blank. HEPATITIS B OVERVIEW Hepatitis B Virus The hepatitis B virus (HBV) belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family and is known to cause both
MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL AND NON-OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOODBORNE VIRUSES INCLUDING NEEDLESTICK INJURIES & SEXUAL EXPOSURES
 NHS GREATER GLASGOW CONTROL OF INFECTION COMMITTEE GUIDELINE MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL AND NON-OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOODBORNE VIRUSES INCLUDING NEEDLESTICK INJURIES & SEXUAL EXPOSURES Effective
NHS GREATER GLASGOW CONTROL OF INFECTION COMMITTEE GUIDELINE MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL AND NON-OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOODBORNE VIRUSES INCLUDING NEEDLESTICK INJURIES & SEXUAL EXPOSURES Effective
Laboratory Exposure Control Plan WAC
 A. Introduction Because laboratories and classrooms working directly with blood or other potentially infectious materials have different bloodborne pathogen exposure concerns than the general university,
A. Introduction Because laboratories and classrooms working directly with blood or other potentially infectious materials have different bloodborne pathogen exposure concerns than the general university,
Management of Exposure to Needlestick Injuries & Body Fluids
 Management of Exposure to Needlestick Injuries & Body Fluids Clinical S.O.P. No.:28 Compiled by: Approved by: Review date: November 2016 DOCUMENT HISTORY Version Detail of purpose / change Author / edited
Management of Exposure to Needlestick Injuries & Body Fluids Clinical S.O.P. No.:28 Compiled by: Approved by: Review date: November 2016 DOCUMENT HISTORY Version Detail of purpose / change Author / edited
The Bloodborne Pathogen Standard. An Overview
 The Bloodborne Pathogen Standard An Overview The Standard l In 1990, OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration), developed the Bloodborne Pathogen Standard to protect workers by limiting occupational
The Bloodborne Pathogen Standard An Overview The Standard l In 1990, OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration), developed the Bloodborne Pathogen Standard to protect workers by limiting occupational
Bloodborne Pathogens. Penn State University Environmental Health & Safety
 Bloodborne Pathogens Penn State University Environmental Health & Safety Diseases of Concern Hepatitis B (Serum Hepatitis) Hepatitis C (non-a non-b Hepatitis) HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus aka the
Bloodborne Pathogens Penn State University Environmental Health & Safety Diseases of Concern Hepatitis B (Serum Hepatitis) Hepatitis C (non-a non-b Hepatitis) HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus aka the
2014 OSHA Blood-borne Pathogens (BBP) Update JHS Annual Mandatory Education
 2014 OSHA Blood-borne Pathogens (BBP) Update 2014 JHS Annual Mandatory Education Objectives Discuss the epidemiology of Bloodborne Pathogens. List the statistics of HIV/AIDS cases Identify the correlation
2014 OSHA Blood-borne Pathogens (BBP) Update 2014 JHS Annual Mandatory Education Objectives Discuss the epidemiology of Bloodborne Pathogens. List the statistics of HIV/AIDS cases Identify the correlation
Guidance for management of exposure events where there is a risk of transmission of blood borne viruses
 Guidance for management of exposure events where there is a risk of transmission of blood borne viruses (HIV, Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C) in the community SUMMARY Where a child is thought to have had
Guidance for management of exposure events where there is a risk of transmission of blood borne viruses (HIV, Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C) in the community SUMMARY Where a child is thought to have had
Blood and Body Fluid Exposure
 Blood and Body Fluid Exposure Infection Prevention and Control Contents Policy... 1 Purpose... 1 Scope/Audience... 1 Definitions... 2 Associated documents... 2 1.1 Indications for BBFE reporting... 2 1.2
Blood and Body Fluid Exposure Infection Prevention and Control Contents Policy... 1 Purpose... 1 Scope/Audience... 1 Definitions... 2 Associated documents... 2 1.1 Indications for BBFE reporting... 2 1.2
Bloodborne Pathogens For School Employees
 Bloodborne Pathogens For School Employees Waynesboro Public Schools Bloodborne Pathogens Training and Annual Review Created on May 5, 2010 Reviewed/Revised April 6, 2017 Introduction In an educational
Bloodborne Pathogens For School Employees Waynesboro Public Schools Bloodborne Pathogens Training and Annual Review Created on May 5, 2010 Reviewed/Revised April 6, 2017 Introduction In an educational
Infectious Disease and Bloodborne Pathogens Training St. Michael-Albertville Public Schools
 Infectious Disease and Bloodborne Pathogens Training St. Michael-Albertville Public Schools Questions? Any time throughout the slide show or throughout the school year: Contact Jake Baxter at IEA Phone:
Infectious Disease and Bloodborne Pathogens Training St. Michael-Albertville Public Schools Questions? Any time throughout the slide show or throughout the school year: Contact Jake Baxter at IEA Phone:
Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training
 Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training This program will review your occupational risks and the steps that you and the County must take to reduce your risks of exposure. Employees must report any occupational
Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training This program will review your occupational risks and the steps that you and the County must take to reduce your risks of exposure. Employees must report any occupational
Bloodborne Pathogens. By Deborah Massarella RN, MSN
 Bloodborne Pathogens By Deborah Massarella RN, MSN 2010, 2014 Objectives At conclusion of in-service learners will: 1. Identify two types of personal protective equipment. 2. Identify two prevention measures
Bloodborne Pathogens By Deborah Massarella RN, MSN 2010, 2014 Objectives At conclusion of in-service learners will: 1. Identify two types of personal protective equipment. 2. Identify two prevention measures
Hepatitis C January 26, 2018
 Hepatitis C January 26, 2018 Case Investigation Guidelines Contents A. Purpose...2 B. Case Definitions...2 a. Acute Hepatitis C (2016...2 b. Chronic Hepatitis C (2016)...3 c. Perinatal Hepatitis C (2017
Hepatitis C January 26, 2018 Case Investigation Guidelines Contents A. Purpose...2 B. Case Definitions...2 a. Acute Hepatitis C (2016...2 b. Chronic Hepatitis C (2016)...3 c. Perinatal Hepatitis C (2017
Self-Instructional Packet (SIP)
 Self-Instructional Packet (SIP) Advanced Infection Prevention and Control Training Module 1 Intro to Infection Prevention Control February 11, 2013 Page 1 Learning Objectives Module One Introduction to
Self-Instructional Packet (SIP) Advanced Infection Prevention and Control Training Module 1 Intro to Infection Prevention Control February 11, 2013 Page 1 Learning Objectives Module One Introduction to
A. Background for Trainer: B. What OSHA Requires: Bloodborne Pathogens. Lesson Plan 6080a
 Lesson Plan 6080a This training session outline is designed to follow the accompanying booklet, OSHA s Bloodborne Pathogens Standard. The booklet reviews what employees who are potentially exposed to the
Lesson Plan 6080a This training session outline is designed to follow the accompanying booklet, OSHA s Bloodborne Pathogens Standard. The booklet reviews what employees who are potentially exposed to the
Bloodborne Pathogens 29 CFR
 Bloodborne Pathogens 29 CFR 1910.1030 Revised OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Compliance Directive (CPL2-2.44D) Could You Contract a Disease at Work? Administering first aid? Cleaning the restrooms? Using a
Bloodborne Pathogens 29 CFR 1910.1030 Revised OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Compliance Directive (CPL2-2.44D) Could You Contract a Disease at Work? Administering first aid? Cleaning the restrooms? Using a
Oley Valley School District Bloodborne Pathogen Policy. Exposure Control Plan
 Oley Valley School District Bloodborne Pathogen Policy Exposure Control Plan Commonwealth of Pennsylvania Resources: A copy of the PA State Guidelines on Bloodborne Pathogens for the Public Sector can
Oley Valley School District Bloodborne Pathogen Policy Exposure Control Plan Commonwealth of Pennsylvania Resources: A copy of the PA State Guidelines on Bloodborne Pathogens for the Public Sector can
Bloodborne Pathogens. Kathleen Stefek, RN, MSN
 Bloodborne Pathogens Kathleen Stefek, RN, MSN What are Bloodborne Pathogens? Infectious agents carried in the blood and other body fluids that are capable of infecting a host (people like you and me) with
Bloodborne Pathogens Kathleen Stefek, RN, MSN What are Bloodborne Pathogens? Infectious agents carried in the blood and other body fluids that are capable of infecting a host (people like you and me) with
