T cell memory Friday, February 10, 17
|
|
|
- Cornelius Woods
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 T cell memory
2 expansion contraction memory recall EFFECTORS 10 6 pathogen load secondary challenge MEMORY 10 2 NAIVE >1 year days post-infection In mouse, ~100 naïve, CD8s become ~3x10 6 effectors in 7 days, then contract to ~10 5 by 14 days. Maybe 10x increase in TOTAL CD8 numbers! CD4 T cells response with ~same kinetics but ~10x lower numbers
3 Massive T cell response to acute viral or bacterial infection Clonal expansion of ag-specific T cells expansion contraction memory recall EFFECTORS 10 6 pathogen load secondary challenge MEMORY 10 2 NAIVE >1 year days post-infection In mouse, ~100 naïve, CD8s become ~3x10 6 effectors in 7 days, then contract to ~10 5 by 14 days. Maybe 10x increase in TOTAL CD8 numbers! CD4 T cells response with ~same kinetics but ~10x lower numbers N.B. EBV, infectious mononucleosis
4 Human CD8 T cell response to the yellow fever vaccine Tetramer HLA-A2+ peptide Blood
5 Dryvax (live Vaccinia) in Humans: antibody, CD4, CD8 CD8 antibody CD4
6 Human CD8 memory to smallpox vaccination CD8 memory Half-life = 8-15 yrs
7 Human CD4 memory to smallpox vaccination assessed by intracellular cytokine staining PBL stim with virus and ICCS SMALLPOX 1972 end vaccination 1978 eradicated CD4 memory Half-life 8-12 years Filled= >2 fold bg Open= <2 fold bg Slifka (2003) Nat Med 9, 1131
8 Serum antibody levels to smallpox vaccination Measured by ELISA and correlated with neutralization Not much boost with 2nd, 3rd vacc Correlation with neutralization
9 CD8 Effector cells are HETEROGENEOUS At the peak of response, a fraction of expanded CD8s express IL-7Rα (CD127) at high levels and these are enriched in memory precursors (MPEC). At the peak of response, most effectors are KLRG1 hi and these are destined to die by apoptosis, short-lived effectors (SLEC). How does effector cell heterogeneity come about?
10 Single OT-1 CD8 transfer and Listeria-Ova immunization ie naïve T cells are NOT pre-committed to dead-end Effector(SLEC) vs Memory(MTEC) Listeria-Ova OT-I cells are CD45.1 transferred into CD45.2 recip D.H. Busch, Immunity, vol 27, 2007
11 Single naïve OT-I CD8 transferred, Listeria-Ova infection makes heterogeneous effectors and makes memory cells % of spleen is about 10 4 cells Heterogeneous progeny. They also make memory ie at least 14 div
12 Do Memory cells arise from Effectors? Are memory precursors separate from effector precursors? Schoenberger, Science 323, 466 (2009)
13 Do Memory CD8s derive from cells that were once Effector CD8s? YES Sorted IFNγ producers make memory (Zink(CD8), Weaver(CD4)) CD8s which turn on Granzyme make memory (Fearon (2009) Science 323; ) gzmb promoter driving cre-er..(tamoxifen-inducible) cross to reporter mouse, ROSA-fl(stop)fl-YFP
14 Mice primed with flu and given tamoxifen on days 1-8. Assay response day 10 and 49 then boost with a 2nd flu and assay 7 days later. A fraction of effectors turn on cre (thus YFP+) They survive to memory They re-respond to 2nd hit ie they made memory cells.
15 Numbers of flu-specific (tetramer+) CD8+ T cells expressing granzyme reporter, same % become YFP+ in 2ndry as in 1ry Squares + = total CD8 ag-specific X = YFP+ CD8 ag-specific
16 Numbers of flu-specific (tetramer+) CD8+ T cells expressing granzyme reporter, same % become YFP+ in 2ndry as in 1ry Squares + = total CD8 ag-specific X = YFP+ CD8 ag-specific
17 Heterogeneity of CD8 Effectors and Memory Cells IL-7Rlo, KLRG1 hi, IL-2- SLEC N CD62L + CD44 - IL-7Rhi(CD127) KLRG1 lo MPEC IL-7Rhi,KLRG1 lo, IL-2+ CC62L lo,ccr7 lo,cd27 lo, kill, less turnover EM CM CD62L lo, CCR7 hi, IL-2+,higher turnover Longer-lived. Effectors Memory
18 Are SLECs really short-lived effectors? (Olson, Immunity, 2013)
19 Most protective population...
20 90-99% effectors die, while 1-10% live to memory. ie 90-99% will die by apoptosis, while 1-10% will survive contraction and become long-lived memory cells. What determines who dies?
21 How is the extent of contraction regulated? by competition between effector cells after the peak of the primary response versus contraction is programmed or cell-intrinsic not regulated by competition
22 bim-/- CD8s do not contract Bim a BH3-only member of Bcl2 family, required for contraction (Strasser) wt OT-I bim -/- OT-I Day 7 CD CD Spleen CD45.2 CD45.2 Day 14 CD CD CD45.2 CD45.2 Day 7 to day14. acute contraction: wt numbers decrease 10-fold bim-/- numbers decrease less than 2-fold
23 Is contraction regulated by competition for resources? Naïve T cells Effector T cells Memory T cell pool WT contraction Use bim-/- as non-dying competitors versus WT contraction?? bim -/- Competitors Martin Prlic
24 DAY 7 wt and bim -/- OT-I T cells expand equally Endog CD8s wt alone bim -/- alone 10 4 Mix 1:1 CD CD OT wt OT-1 MIX = 5,000 WT + 5,000 bim-/- Thy CD45.2 ko OT-1
25 Memory Contraction of wt cells is not influenced by bim -/- cells wt alone bim -/- alone Mix 1: CD CD Thy wt OT bim-/- OT-1 CD % of 5.2% = about 0.3% ie same decrease as wt alone
26 Factors influencing the differentiation of T cells after activation Asymmetric division? TCR affinity
27 Transcription factor Blimp-1 is involved in SLEC versus MPEC decision during the CD8 response
28 Mutual antagonism of Bcl-6 and Blimp-1, transcriptional repressors that regulate terminal effector versus memory differentiation in B cells and CD4s and CD8s 2 opposing players in differentiation Blimp-1 promotes Effector differentiation
29 CD8 T cell differentiation regulation by Blimp-1 and BCl-6 IL-2, IL-12
30 CD4 T cell differentiation
31
32 What determines upreg of Bcl6(Tfh) versus Blimp-1(Th1)?? Level of TCR-ag interaction? DC vs B cells as APC? Amount of IL-2 / CD25 signals (promote Blimp-1)?
33 CD4 differentiation into Th1, Tfh or GC Tfh varies by clone (ie TCR repertoire) The whole mouse CD4 response Single ag-specific naïve CD4 T cells transferred, immunized with Listeria. 6 days later, ag-specific cells phenotyped for effector cell differentiation. Propose that TCR-MHC/pep dwell time, related to TCR affinity and ag dose, regulates CD25/Il-2 signals Jenkins (2013) Cell 153, 785 Single CD4 cells
34 CD4 Differentiation IL-2/IL-12à Blimp-1+ Tbet(Th1), vs Bcl6(Tfh) Based on (2011) Pepper et al Immunity 35, 553 (attenuated Listeria)
35 Models of CD4 effector and central memory Th1, Th2 or Th17 effectors can become EFFECTOR Mem, Treg, Tfh die/change Tfh or Tcm interact with B cells And become CENTRAL memory
36 Lineage committed Tfh and Th1 Memory cells following acute LCMV Infection Hale et al (2013) Immunity 38, 805
37 A third type of memory T cell Tcm.circulate like naïve T cells, LN homing, CCR7, great potential for expansion. Tem.circulate blood to non-lymphoid tissues to LN. Faster effector function, less expansion. Trm.non-recirculating, stay in tissues eg skin, ganglia, mucosa, brain
38 Tissue-Resident Memory Scheme showing Trm in dorsal root Sensory Ganglia which are latent for herpes simplex 1 (HSV-1) Transplant under kidney capsule Shave, abrade. HSV-1 flank skin day 0 HSV infects epithelia and sensory nerve Endings, then to ganglia Sensory DRG innervating site > day 20 Sensory neurons are latently infected HSV reactivate due to stress Assay + 5 days Carbone (2008) Science 319; Cold sores. Herpes zoster(shingles)
39 Local re-expansion of resident memory CD8+ T cells in DRG Put 2 DRG grafts under same kidney, one from mouse which has marked CD8s, one from a mouse that does not. Expansion occurs in the DRG, not in LN or spleen Science 319, (2008)
40 Tissue Resident T cell Memory Evidence for tissue-resident memory (Trm) CD8s in skin, DRG, IEL and LP in gut, brain. CD103+, CD69+, S1PR1lo, KLF2lo Non-Recirculating, separate from Tcm and Tem
41 Mechanisms promoting Trm residence in tissues. CD69 inhibits S1PR1; KLF2 regulates S1PR1 CD103 binds E-cadherin Immunity (2014) 41, 886
42 Issues studying Trm: Difficult to discern cells in vasculature (perfusion doesn t work) Difficult to study in humans Flow cytometry underestimates the true size of the population 42
43 Flow cytometry underestimates Trm 43
44 CD8 Trm in Mouse epidermis Female reproductive tract
45 Trm are the dominant memory population (Thome, Cell, 2014)
46 46
47 Prospect for HIV vaccine? Antibody sites are variable T cell response too slow? Need response at site of entry? A vaccine for SIV generates EFFECTOR CD4 and CD8 T cell memory Use of a Rhesus CMV vaccine vector.
48 Cytomegalovirus (CMV) targets multiple class I pathways and becomes latent
49 Recombinant Rhesus-CMV vectors for SIV vaccine Picker, L et al Nat Med (2009) 15, 293 and Nature (2011) 473, 523
50 Recombinant Rhesus-CMV vectors for SIV vaccine Vaccine subcutaneous, SIV challenge multiple low dose rectal 13/24 protected
51 T em phenotype of CMV-SIV vector vaccinated Rhesus monkeys T em provide faster response to mucosal infection than T cm
52 Different types of memory cells respond differently...
53 53
IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY. CD4 T Follicular Helper Cells. Memory CD8 T Cell Differentiation
 IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY CD4 T Follicular Helper Cells Memory CD8 T Cell Differentiation CD4 T Cell Differentiation Bcl-6 T-bet GATA-3 ROR t Foxp3 CD4 T follicular helper (Tfh) cells FUNCTION Provide essential
IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY CD4 T Follicular Helper Cells Memory CD8 T Cell Differentiation CD4 T Cell Differentiation Bcl-6 T-bet GATA-3 ROR t Foxp3 CD4 T follicular helper (Tfh) cells FUNCTION Provide essential
Micro 204. Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTL) Lewis Lanier
 Micro 204 Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTL) Lewis Lanier Lewis.Lanier@ucsf.edu Lymphocyte-mediated Cytotoxicity CD8 + αβ-tcr + T cells CD4 + αβ-tcr + T cells γδ-tcr + T cells Natural Killer cells CD8 + αβ-tcr
Micro 204 Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTL) Lewis Lanier Lewis.Lanier@ucsf.edu Lymphocyte-mediated Cytotoxicity CD8 + αβ-tcr + T cells CD4 + αβ-tcr + T cells γδ-tcr + T cells Natural Killer cells CD8 + αβ-tcr
CD4 T-Cell Memory Generation and Maintenance
 Critical Reviews in Immunology, 34(2):121 146 (2014) CD4 T-Cell Memory Generation and Maintenance David J. Gasper, 1,2 Melba Marie Tejera, 1 & M. Suresh 1,2, * 1 Department of Pathobiological Sciences;
Critical Reviews in Immunology, 34(2):121 146 (2014) CD4 T-Cell Memory Generation and Maintenance David J. Gasper, 1,2 Melba Marie Tejera, 1 & M. Suresh 1,2, * 1 Department of Pathobiological Sciences;
B and T cell Memory. Bengt Lindbom Adap6ve Immunity BMC D14
 B and T cell Memory Bengt Lindbom Adap6ve Immunity BMC D14 Immunity: a historical perspec6ve 430 B.C. Thucydides describes the ongoing plague of Athens:.the same man was never attacked twice 15th century:
B and T cell Memory Bengt Lindbom Adap6ve Immunity BMC D14 Immunity: a historical perspec6ve 430 B.C. Thucydides describes the ongoing plague of Athens:.the same man was never attacked twice 15th century:
IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY. May 28, 2017
 IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY May 28, 2017 Francesca Di Rosa Institute of Molecular Biology and Pathology National Research Council francesca.dirosa@uniroma1.it Pathogen infection and adaptive immune response Primary
IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY May 28, 2017 Francesca Di Rosa Institute of Molecular Biology and Pathology National Research Council francesca.dirosa@uniroma1.it Pathogen infection and adaptive immune response Primary
Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells
 ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Complete but curtailed T-cell response to very-low-affinity antigen Dietmar Zehn, Sarah Y. Lee & Michael J. Bevan Supp. Fig. 1: TCR chain usage among endogenous K b /Ova reactive T cells. C57BL/6 mice
Complete but curtailed T-cell response to very-low-affinity antigen Dietmar Zehn, Sarah Y. Lee & Michael J. Bevan Supp. Fig. 1: TCR chain usage among endogenous K b /Ova reactive T cells. C57BL/6 mice
General Overview of Immunology. Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center
 General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
Naive and memory CD8 T cell responses after antigen stimulation in vivo
 University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Summer 2011 Naive and memory CD8 T cell responses after antigen stimulation in vivo Matthew David Martin University of Iowa Copyright 2011
University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Summer 2011 Naive and memory CD8 T cell responses after antigen stimulation in vivo Matthew David Martin University of Iowa Copyright 2011
Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation. Abul K. Abbas UCSF. FOCiS
 1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
Carmen Gerlach 1, Jeroen W.J van Heijst 1 and Ton N.M. Schumacher 1
 3 The descent of memory T cells Carmen Gerlach 1, Jeroen W.J van Heijst 1 and Ton N.M. Schumacher 1 1 Division of Immunology, The Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam, the Netherlands Ann N Y Acad Sci.
3 The descent of memory T cells Carmen Gerlach 1, Jeroen W.J van Heijst 1 and Ton N.M. Schumacher 1 1 Division of Immunology, The Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam, the Netherlands Ann N Y Acad Sci.
days days and gbt-i.cd Recipient 20
 gbt-i. GFP+ Resident memory cells: gbt-i.gfp+ Recruited memory cells: gbt-i.cd45.1+ 1 2-3 gbt-i. flu.gb sc. CD45.1+ Graft with gbt-i.gfp+ 1 Recipient 1 re- 3 36 Graft with gbt-i.gfp+ and gbt-i.cd45.1+
gbt-i. GFP+ Resident memory cells: gbt-i.gfp+ Recruited memory cells: gbt-i.cd45.1+ 1 2-3 gbt-i. flu.gb sc. CD45.1+ Graft with gbt-i.gfp+ 1 Recipient 1 re- 3 36 Graft with gbt-i.gfp+ and gbt-i.cd45.1+
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice. (a) Gene expression profile in the resting CD4 + T cells were analyzed by an Affymetrix microarray
Supplementary Figure 1 Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice. (a) Gene expression profile in the resting CD4 + T cells were analyzed by an Affymetrix microarray
Tracking total polyclonal CD8 T cell responses in inbred and outbred hosts after infection
 University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations 2010 Tracking total polyclonal CD8 T cell responses in inbred and outbred hosts after infection Deepa Kumari Rai University of Iowa Copyright
University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations 2010 Tracking total polyclonal CD8 T cell responses in inbred and outbred hosts after infection Deepa Kumari Rai University of Iowa Copyright
Acquired Immunity 2. - Vaccines & Immunological Memory - Wataru Ise. WPI Immunology Frontier Research Center (IFReC) Osaka University.
 Acquired Immunity 2 - Vaccines & Immunological Memory - Wataru Ise WPI Immunology Frontier Research Center (IFReC) Osaka University Outline 1. What is vaccine (vaccination)? 2. What is immunological memory?
Acquired Immunity 2 - Vaccines & Immunological Memory - Wataru Ise WPI Immunology Frontier Research Center (IFReC) Osaka University Outline 1. What is vaccine (vaccination)? 2. What is immunological memory?
T Cell Activation, Costimulation and Regulation
 1 T Cell Activation, Costimulation and Regulation Abul K. Abbas, MD University of California San Francisco 2 Lecture outline T cell antigen recognition and activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
1 T Cell Activation, Costimulation and Regulation Abul K. Abbas, MD University of California San Francisco 2 Lecture outline T cell antigen recognition and activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance. Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco
 Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco EIP Symposium Feb 2016 Why do some people respond to therapeutic proteins?
Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco EIP Symposium Feb 2016 Why do some people respond to therapeutic proteins?
NKTR-255: Accessing IL-15 Therapeutic Potential through Robust and Sustained Engagement of Innate and Adaptive Immunity
 NKTR-255: Accessing IL-15 Therapeutic Potential through Robust and Sustained Engagement of Innate and Adaptive Immunity Peiwen Kuo Scientist, Research Biology Nektar Therapeutics August 31 st, 2018 Emerging
NKTR-255: Accessing IL-15 Therapeutic Potential through Robust and Sustained Engagement of Innate and Adaptive Immunity Peiwen Kuo Scientist, Research Biology Nektar Therapeutics August 31 st, 2018 Emerging
Biology of Immune Aging
 Biology of Immune Aging Jorg J. Goronzy Stanford University Immune deficiency Increase morbidity and mortality from infections Poor vaccine responses Cancer Immune Aging Chronic inflammation Coronary artery
Biology of Immune Aging Jorg J. Goronzy Stanford University Immune deficiency Increase morbidity and mortality from infections Poor vaccine responses Cancer Immune Aging Chronic inflammation Coronary artery
5/1/13. The proportion of thymus that produces T cells decreases with age. The cellular organization of the thymus
 T cell precursors migrate from the bone marrow via the blood to the thymus to mature 1 2 The cellular organization of the thymus The proportion of thymus that produces T cells decreases with age 3 4 1
T cell precursors migrate from the bone marrow via the blood to the thymus to mature 1 2 The cellular organization of the thymus The proportion of thymus that produces T cells decreases with age 3 4 1
Immunological memory.
 Chapter 11: Dynamics of Adaptive Immunity the answers will lie in the cytokines produced by the environment and by the T cells themselves, and in the affinity of the T-cell receptors for their antigens.
Chapter 11: Dynamics of Adaptive Immunity the answers will lie in the cytokines produced by the environment and by the T cells themselves, and in the affinity of the T-cell receptors for their antigens.
Effect of Cytomegalovirus Infection on Immune Responsiveness. Rene van Lier Sanquin Blood Supply Foundation
 Effect of Cytomegalovirus Infection on Immune Responsiveness Rene van Lier Sanquin Blood Supply Foundation OUTLINE CMV infection and vaccination responses Effects of CMV infection on CD8 + T cell numbers
Effect of Cytomegalovirus Infection on Immune Responsiveness Rene van Lier Sanquin Blood Supply Foundation OUTLINE CMV infection and vaccination responses Effects of CMV infection on CD8 + T cell numbers
Lecture 11. Immunology and disease: parasite antigenic diversity
 Lecture 11 Immunology and disease: parasite antigenic diversity RNAi interference video and tutorial (you are responsible for this material, so check it out.) http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/sciencenow/3210/02.html
Lecture 11 Immunology and disease: parasite antigenic diversity RNAi interference video and tutorial (you are responsible for this material, so check it out.) http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/sciencenow/3210/02.html
NK1.1 þ CD8 þ T cells escape TGF-b control and contribute to early microbial pathogen response
 Received 24 Apr 214 Accepted 5 Sep 214 Published 6 Oct 214 DOI: 1.138/ncomms615 NK1.1 þ CD8 þ T cells escape TGF-b control and contribute to early microbial pathogen response Anne L. Ruiz 1,2,3,4, Saidi
Received 24 Apr 214 Accepted 5 Sep 214 Published 6 Oct 214 DOI: 1.138/ncomms615 NK1.1 þ CD8 þ T cells escape TGF-b control and contribute to early microbial pathogen response Anne L. Ruiz 1,2,3,4, Saidi
Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells Inhibit Cytomegalovirus Inflammation through Interleukin-27 and B7-H4
 Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells Inhibit Cytomegalovirus Inflammation through Interleukin-27 and B7-H4 Ankita Garg, Rodney Trout and Stephen A. Spector,,* Department
Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells Inhibit Cytomegalovirus Inflammation through Interleukin-27 and B7-H4 Ankita Garg, Rodney Trout and Stephen A. Spector,,* Department
Memory NK cells during mousepox infection. Min Fang, Ph.D, Professor Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Science
 Memory NK cells during mousepox infection Min Fang, Ph.D, Professor Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Science Infectious Diseases are a Major Cause of Death Worldwide May 14 th 1796 Prevalence
Memory NK cells during mousepox infection Min Fang, Ph.D, Professor Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Science Infectious Diseases are a Major Cause of Death Worldwide May 14 th 1796 Prevalence
Persistent Infections
 Persistent Infections Lecture 17 Biology 3310/4310 Virology Spring 2017 Paralyze resistance with persistence WOODY HAYES Acute vs persistent infections Acute infection - rapid and self-limiting Persistent
Persistent Infections Lecture 17 Biology 3310/4310 Virology Spring 2017 Paralyze resistance with persistence WOODY HAYES Acute vs persistent infections Acute infection - rapid and self-limiting Persistent
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Signal 3 requirement for memory CD8 1 T-cell activation is determined by the infectious pathogen
 3176 DOI 1.12/eji.21141537 Eur. J. Immunol. 211. 41: 3176 3186 Signal 3 requirement for memory CD8 1 T-cell activation is determined by the infectious pathogen Selina J. Keppler 1,2 and Peter Aichele 1
3176 DOI 1.12/eji.21141537 Eur. J. Immunol. 211. 41: 3176 3186 Signal 3 requirement for memory CD8 1 T-cell activation is determined by the infectious pathogen Selina J. Keppler 1,2 and Peter Aichele 1
FOCiS. Lecture outline. The immunological equilibrium: balancing lymphocyte activation and control. Immunological tolerance and immune regulation -- 1
 1 Immunological tolerance and immune regulation -- 1 Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Principles of immune regulation Self-tolerance; mechanisms of central and peripheral tolerance Inhibitory
1 Immunological tolerance and immune regulation -- 1 Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Principles of immune regulation Self-tolerance; mechanisms of central and peripheral tolerance Inhibitory
The Adaptive Immune Response. B-cells
 The Adaptive Immune Response B-cells The innate immune system provides immediate protection. The adaptive response takes time to develop and is antigen specific. Activation of B and T lymphocytes Naive
The Adaptive Immune Response B-cells The innate immune system provides immediate protection. The adaptive response takes time to develop and is antigen specific. Activation of B and T lymphocytes Naive
Out-of-sequence signal 3 as a mechanism for virusinduced immune suppression of CD8 T cell responses
 University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms Open Access Articles Open Access Publications by UMMS Authors 9-25-2014 Out-of-sequence signal 3 as a mechanism for virusinduced immune suppression
University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms Open Access Articles Open Access Publications by UMMS Authors 9-25-2014 Out-of-sequence signal 3 as a mechanism for virusinduced immune suppression
Properties & Overview of IRs Dr. Nasser M. Kaplan JUST, Jordan. 10-Jul-16 NM Kaplan 1
 Properties & Overview of IRs Dr. Nasser M. Kaplan JUST, Jordan 10-Jul-16 NM Kaplan 1 Major components of IS & their properties Definitions IS = cells & molecules responsible for: 1- Physiologic; protective
Properties & Overview of IRs Dr. Nasser M. Kaplan JUST, Jordan 10-Jul-16 NM Kaplan 1 Major components of IS & their properties Definitions IS = cells & molecules responsible for: 1- Physiologic; protective
Presented by Lucas Nemec. Nat. Med. 21, (2015)
 Presented by Lucas Nemec Nat. Med. 21, 647 53 (2015) 1 Introduction Sylvia S. Mader, Inquiry into Life, 8th Edition, 1997 2 Introduction Sylvia S. Mader, Inquiry into Life, 8th Edition, 1997 3 Introduction
Presented by Lucas Nemec Nat. Med. 21, 647 53 (2015) 1 Introduction Sylvia S. Mader, Inquiry into Life, 8th Edition, 1997 2 Introduction Sylvia S. Mader, Inquiry into Life, 8th Edition, 1997 3 Introduction
T cells III: Cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer cells
 T cells III: Cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer cells Margrit Wiesendanger Division of Rheumatology, CUMC September 17, 2008 Killer cells: CD8 + T cells (adaptive) vs. natural killer (innate) Shared
T cells III: Cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer cells Margrit Wiesendanger Division of Rheumatology, CUMC September 17, 2008 Killer cells: CD8 + T cells (adaptive) vs. natural killer (innate) Shared
Immune response. This overview figure summarizes simply how our body responds to foreign molecules that enter to it.
 Immune response This overview figure summarizes simply how our body responds to foreign molecules that enter to it. It s highly recommended to watch Dr Najeeb s lecture that s titled T Helper cells and
Immune response This overview figure summarizes simply how our body responds to foreign molecules that enter to it. It s highly recommended to watch Dr Najeeb s lecture that s titled T Helper cells and
B cell activation and antibody production. Abul K. Abbas UCSF
 1 B cell activation and antibody production Abul K. Abbas UCSF 2 Lecture outline B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production Therapeutic targeting of B cells 3 Principles of humoral
1 B cell activation and antibody production Abul K. Abbas UCSF 2 Lecture outline B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production Therapeutic targeting of B cells 3 Principles of humoral
Institute t of Experimental Immunology University of Bonn, Germany
 How T cells recognize antigen Christian Kurts Institute t of Experimental Immunology University of Bonn, Germany When do T cells recognize antigen? Antigen uptake Activation phase 1st recognition Effector
How T cells recognize antigen Christian Kurts Institute t of Experimental Immunology University of Bonn, Germany When do T cells recognize antigen? Antigen uptake Activation phase 1st recognition Effector
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was
 Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was sorted by FACS. Surface markers for sorting were CD11c +
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was sorted by FACS. Surface markers for sorting were CD11c +
Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells
 Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells Andrew H. Lichtman, M.D. Ph.D. Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard
Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells Andrew H. Lichtman, M.D. Ph.D. Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard
Lineage relationship and protective immunity of memory CD8 T cell subsets
 23 Nature Publishing Group http://www.nature.com/natureimmunology Lineage relationship and protective immunity of memory CD8 T cell subsets E. John Wherry 1 *,Volker Teichgräber 1 *,Todd C. Becker 1,David
23 Nature Publishing Group http://www.nature.com/natureimmunology Lineage relationship and protective immunity of memory CD8 T cell subsets E. John Wherry 1 *,Volker Teichgräber 1 *,Todd C. Becker 1,David
NKTR-255: Accessing The Immunotherapeutic Potential Of IL-15 for NK Cell Therapies
 NKTR-255: Accessing The Immunotherapeutic Potential Of IL-15 for NK Cell Therapies Saul Kivimäe Senior Scientist, Research Biology Nektar Therapeutics NK Cell-Based Cancer Immunotherapy, September 26-27,
NKTR-255: Accessing The Immunotherapeutic Potential Of IL-15 for NK Cell Therapies Saul Kivimäe Senior Scientist, Research Biology Nektar Therapeutics NK Cell-Based Cancer Immunotherapy, September 26-27,
The development of T cells in the thymus
 T cells rearrange their receptors in the thymus whereas B cells do so in the bone marrow. The development of T cells in the thymus The lobular/cellular organization of the thymus Immature cells are called
T cells rearrange their receptors in the thymus whereas B cells do so in the bone marrow. The development of T cells in the thymus The lobular/cellular organization of the thymus Immature cells are called
CD8 T cells leave the thymus 4 5 days after undergoing positive
 Exploring regulatory mechanisms of T cell contraction Martin Prlic and Michael J. Bevan 1 Department of Immunology and Howard Hughes Medical Institute, University of Washington, Seattle, WA 98195 Contributed
Exploring regulatory mechanisms of T cell contraction Martin Prlic and Michael J. Bevan 1 Department of Immunology and Howard Hughes Medical Institute, University of Washington, Seattle, WA 98195 Contributed
Supplementary Figure S1. PTPN2 levels are not altered in proliferating CD8+ T cells. Lymph node (LN) CD8+ T cells from C57BL/6 mice were stained with
 Supplementary Figure S1. PTPN2 levels are not altered in proliferating CD8+ T cells. Lymph node (LN) CD8+ T cells from C57BL/6 mice were stained with CFSE and stimulated with plate-bound α-cd3ε (10µg/ml)
Supplementary Figure S1. PTPN2 levels are not altered in proliferating CD8+ T cells. Lymph node (LN) CD8+ T cells from C57BL/6 mice were stained with CFSE and stimulated with plate-bound α-cd3ε (10µg/ml)
CD40-Activated B Cells Can Efficiently Prime Antigen- Specific Naïve CD8 + T Cells to Generate Effector but Not Memory T cells
 CD40-Activated B Cells Can Efficiently Prime Antigen- Specific Naïve CD8 + T Cells to Generate Effector but Not Memory T cells Mélissa Mathieu 1,2, Natacha Cotta-Grand 1,2, Jean-François Daudelin 1, Salix
CD40-Activated B Cells Can Efficiently Prime Antigen- Specific Naïve CD8 + T Cells to Generate Effector but Not Memory T cells Mélissa Mathieu 1,2, Natacha Cotta-Grand 1,2, Jean-François Daudelin 1, Salix
Origin of CD8 + Effector and Memory T Cell Subsets
 Cellular & Molecular Immunology 399 Review Origin of CD8 + Effector and Memory T Cell Subsets Christian Stemberger 1, Michael Neuenhahn 1, Veit R. Buchholz 1 1, 2, 3 and Dirk H. Busch It is well accepted
Cellular & Molecular Immunology 399 Review Origin of CD8 + Effector and Memory T Cell Subsets Christian Stemberger 1, Michael Neuenhahn 1, Veit R. Buchholz 1 1, 2, 3 and Dirk H. Busch It is well accepted
Human Effector and Memory CD8 + T Cell Responses to Smallpox and Yellow Fever Vaccines
 Article Human Effector and Memory CD8 + T Cell Responses to Smallpox and Yellow Fever Vaccines Joseph D. Miller, 1,2 Robbert G. van der Most, 1,2 Rama S. Akondy, 1 John T. Glidewell, 1 Sophia Albott, 1
Article Human Effector and Memory CD8 + T Cell Responses to Smallpox and Yellow Fever Vaccines Joseph D. Miller, 1,2 Robbert G. van der Most, 1,2 Rama S. Akondy, 1 John T. Glidewell, 1 Sophia Albott, 1
ROLES OF TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR T-BET IN MEMORY CD4 + T CELL GENERATION, FUNCTION, HOMEOSTASIS AND TISSUE TARGETING. Jun-Kui Chen
 ROLES OF TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR T-BET IN MEMORY CD4 + T CELL GENERATION, FUNCTION, HOMEOSTASIS AND TISSUE TARGETING Jun-Kui Chen Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor
ROLES OF TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR T-BET IN MEMORY CD4 + T CELL GENERATION, FUNCTION, HOMEOSTASIS AND TISSUE TARGETING Jun-Kui Chen Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor
T Lymphocyte Activation and Costimulation. FOCiS. Lecture outline
 1 T Lymphocyte Activation and Costimulation Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family Inhibitory receptors of T cells Targeting costimulators for
1 T Lymphocyte Activation and Costimulation Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family Inhibitory receptors of T cells Targeting costimulators for
ABSTRACT. Title of Document: GENERATING FUNCTIONAL CYTOTOXIC T LYMPHOCYTES THROUGH REPETITIVE PEPTIDE BOOSTING.
 ABSTRACT Title of Document: GENERATING FUNCTIONAL CYTOTOXIC T LYMPHOCYTES THROUGH REPETITIVE PEPTIDE BOOSTING. Kendra Nicole Smyth, Master of Science, 2012 Directed By: Assistant Professor Zhengguo Xiao,
ABSTRACT Title of Document: GENERATING FUNCTIONAL CYTOTOXIC T LYMPHOCYTES THROUGH REPETITIVE PEPTIDE BOOSTING. Kendra Nicole Smyth, Master of Science, 2012 Directed By: Assistant Professor Zhengguo Xiao,
T Cell Activation. Patricia Fitzgerald-Bocarsly March 18, 2009
 T Cell Activation Patricia Fitzgerald-Bocarsly March 18, 2009 Phases of Adaptive Immune Responses Phases of T cell responses IL-2 acts as an autocrine growth factor Fig. 11-11 Clonal Expansion of T cells
T Cell Activation Patricia Fitzgerald-Bocarsly March 18, 2009 Phases of Adaptive Immune Responses Phases of T cell responses IL-2 acts as an autocrine growth factor Fig. 11-11 Clonal Expansion of T cells
Effector T Cells and
 1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
Tbk1-TKO! DN cells (%)! 15! 10!
 a! T Cells! TKO! B Cells! TKO! b! CD4! 8.9 85.2 3.4 2.88 CD8! Tbk1-TKO! 1.1 84.8 2.51 2.54 c! DN cells (%)! 4 3 2 1 DP cells (%)! 9 8 7 6 CD4 + SP cells (%)! 5 4 3 2 1 5 TKO! TKO! TKO! TKO! 15 1 5 CD8
a! T Cells! TKO! B Cells! TKO! b! CD4! 8.9 85.2 3.4 2.88 CD8! Tbk1-TKO! 1.1 84.8 2.51 2.54 c! DN cells (%)! 4 3 2 1 DP cells (%)! 9 8 7 6 CD4 + SP cells (%)! 5 4 3 2 1 5 TKO! TKO! TKO! TKO! 15 1 5 CD8
Medical Virology Immunology. Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University
 Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
General Biology. A summary of innate and acquired immunity. 11. The Immune System. Repetition. The Lymphatic System. Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.
 A summary of innate and acquired immunity General iology INNATE IMMUNITY Rapid responses to a broad range of microbes Course No: NG00 Credits:.00 External defenses Invading microbes (pathogens). The Immune
A summary of innate and acquired immunity General iology INNATE IMMUNITY Rapid responses to a broad range of microbes Course No: NG00 Credits:.00 External defenses Invading microbes (pathogens). The Immune
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Id2 and Id3 define polyclonal T H 1 and T FH cell subsets.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Id2 and Id3 define polyclonal T H 1 and T FH cell subsets. Id2 YFP/+ (a) or Id3 GFP/+ (b) mice were analyzed 7 days after LCMV infection. T H 1 (SLAM + CXCR5 or CXCR5 PD-1 ), T FH
Supplementary Figure 1 Id2 and Id3 define polyclonal T H 1 and T FH cell subsets. Id2 YFP/+ (a) or Id3 GFP/+ (b) mice were analyzed 7 days after LCMV infection. T H 1 (SLAM + CXCR5 or CXCR5 PD-1 ), T FH
Supplementary Figure 1. Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation. Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre
 New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre No Disclosures
New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre New insights into CD8+ T cell function and regulation Pam Ohashi Princess Margaret Cancer Centre No Disclosures
Darwinian selection and Newtonian physics wrapped up in systems biology
 Darwinian selection and Newtonian physics wrapped up in systems biology Concept published in 1957* by Macfarland Burnet (1960 Nobel Laureate for the theory of induced immune tolerance, leading to solid
Darwinian selection and Newtonian physics wrapped up in systems biology Concept published in 1957* by Macfarland Burnet (1960 Nobel Laureate for the theory of induced immune tolerance, leading to solid
ECM1 controls T H 2 cell egress from lymph nodes through re-expression of S1P 1
 ZH, Li et al, page 1 ECM1 controls T H 2 cell egress from lymph nodes through re-expression of S1P 1 Zhenhu Li 1,4,Yuan Zhang 1,4, Zhiduo Liu 1, Xiaodong Wu 1, Yuhan Zheng 1, Zhiyun Tao 1, Kairui Mao 1,
ZH, Li et al, page 1 ECM1 controls T H 2 cell egress from lymph nodes through re-expression of S1P 1 Zhenhu Li 1,4,Yuan Zhang 1,4, Zhiduo Liu 1, Xiaodong Wu 1, Yuhan Zheng 1, Zhiyun Tao 1, Kairui Mao 1,
What to Measure, How to Measure It
 Dale and Betty Bumpers Vaccine Research Center National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases National Institutes of Health Monitoring Memory T-cells: What to Measure, How to Measure It Pratip K.
Dale and Betty Bumpers Vaccine Research Center National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases National Institutes of Health Monitoring Memory T-cells: What to Measure, How to Measure It Pratip K.
Supplemental Figure 1. Activated splenocytes upregulate Serpina3g and Serpina3f expression.
 Relative Serpin expression 25 2 15 1 5 Serpina3f 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 6 4 2 Serpina3g 1 2 3 4 5 6 C57BL/6 DBA/2 Supplemental Figure 1. Activated splenocytes upregulate Serpina3g and Serpina3f expression. Splenocytes
Relative Serpin expression 25 2 15 1 5 Serpina3f 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 6 4 2 Serpina3g 1 2 3 4 5 6 C57BL/6 DBA/2 Supplemental Figure 1. Activated splenocytes upregulate Serpina3g and Serpina3f expression. Splenocytes
Antigen Presentation to T lymphocytes
 Antigen Presentation to T lymphocytes Immunology 441 Lectures 6 & 7 Chapter 6 October 10 & 12, 2016 Jessica Hamerman jhamerman@benaroyaresearch.org Office hours by arrangement Antibodies and T cell receptors
Antigen Presentation to T lymphocytes Immunology 441 Lectures 6 & 7 Chapter 6 October 10 & 12, 2016 Jessica Hamerman jhamerman@benaroyaresearch.org Office hours by arrangement Antibodies and T cell receptors
EBV Infection and Immunity. Andrew Hislop Institute for Cancer Studies University of Birmingham
 EBV Infection and Immunity Andrew Hislop Institute for Cancer Studies University of Birmingham EBV Introduction Large ds DNA virus Spread by saliva contact Lifelong infection Predominantly B-lymphotropic
EBV Infection and Immunity Andrew Hislop Institute for Cancer Studies University of Birmingham EBV Introduction Large ds DNA virus Spread by saliva contact Lifelong infection Predominantly B-lymphotropic
Herpesviruses. Virion. Genome. Genes and proteins. Viruses and hosts. Diseases. Distinctive characteristics
 Herpesviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Enveloped icosahedral capsid (T=16), diameter 125 nm Diameter of enveloped virion 200 nm Capsid
Herpesviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Enveloped icosahedral capsid (T=16), diameter 125 nm Diameter of enveloped virion 200 nm Capsid
Cellular Immunity in Aging and HIV: Correlates of Protection. Immune Senescence
 Cellular Immunity in Aging and HIV: Correlates of Protection Janet E. McElhaney, MD Professor of Medicine Allan M. McGavin Chair in Research Geriatrics University of British Columbia Vancouver, BC and
Cellular Immunity in Aging and HIV: Correlates of Protection Janet E. McElhaney, MD Professor of Medicine Allan M. McGavin Chair in Research Geriatrics University of British Columbia Vancouver, BC and
Peer review correspondence
 OX40 controls effector CD4 + T-cell expansion, not follicular T helper cell generation in acute Listeria infection Clare L. Marriott, Emma C. Mackley, Cristina Ferreira, Marc Veldhoen, Hideo Yagita and
OX40 controls effector CD4 + T-cell expansion, not follicular T helper cell generation in acute Listeria infection Clare L. Marriott, Emma C. Mackley, Cristina Ferreira, Marc Veldhoen, Hideo Yagita and
Gp96-Ig-SIV VACCINES INDUCE PREDOMINANT IMMUNE RESPONSES AT MUCOSAL SITES
 Gp96-Ig-SIV VACCINES INDUCE PREDOMINANT IMMUNE RESPONSES AT MUCOSAL SITES Natasa Strbo M.D. Ph.D. Paris, AIDS Vaccine 29 October 19 22 Why is cell secreted gp96 Ig vaccine approach innovative and unconventional?
Gp96-Ig-SIV VACCINES INDUCE PREDOMINANT IMMUNE RESPONSES AT MUCOSAL SITES Natasa Strbo M.D. Ph.D. Paris, AIDS Vaccine 29 October 19 22 Why is cell secreted gp96 Ig vaccine approach innovative and unconventional?
MATERIALS AND METHODS. Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
The Enemy Within: Human Cytomegalovirus. Juliet V. Spencer University of San Francisco
 The Enemy Within: Human Cytomegalovirus Juliet V. Spencer University of San Francisco NCASM Spring Meeting March 8, 2014 Herpes is all around us Human Herpesviruses Clinical Presentation Herpes simplex
The Enemy Within: Human Cytomegalovirus Juliet V. Spencer University of San Francisco NCASM Spring Meeting March 8, 2014 Herpes is all around us Human Herpesviruses Clinical Presentation Herpes simplex
LESSON 2: THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY
 Introduction to immunology. LESSON 2: THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY Today we will get to know: The adaptive immunity T- and B-cells Antigens and their recognition How T-cells work 1 The adaptive immunity Unlike
Introduction to immunology. LESSON 2: THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY Today we will get to know: The adaptive immunity T- and B-cells Antigens and their recognition How T-cells work 1 The adaptive immunity Unlike
Immune Regulation and Tolerance
 Immune Regulation and Tolerance Immunoregulation: A balance between activation and suppression of effector cells to achieve an efficient immune response without damaging the host. Activation (immunity)
Immune Regulation and Tolerance Immunoregulation: A balance between activation and suppression of effector cells to achieve an efficient immune response without damaging the host. Activation (immunity)
Adaptive Immunity: Humoral Immune Responses
 MICR2209 Adaptive Immunity: Humoral Immune Responses Dr Allison Imrie 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will review the different mechanisms which constitute the humoral immune response, and examine the antibody
MICR2209 Adaptive Immunity: Humoral Immune Responses Dr Allison Imrie 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will review the different mechanisms which constitute the humoral immune response, and examine the antibody
How plasma cells develop. Deutsches Rheuma Forschungs Zentrum, Berlin Institut der Leibniz Gemeinschaft
 How plasma cells develop Deutsches Rheuma Forschungs Zentrum, Berlin Institut der Leibniz Gemeinschaft 1 Plasma cells develop from activated B cells Toll Like Receptor B Cell Receptor B cell B cell microbia
How plasma cells develop Deutsches Rheuma Forschungs Zentrum, Berlin Institut der Leibniz Gemeinschaft 1 Plasma cells develop from activated B cells Toll Like Receptor B Cell Receptor B cell B cell microbia
T Cell Development II: Positive and Negative Selection
 T Cell Development II: Positive and Negative Selection 8 88 The two phases of thymic development: - production of T cell receptors for antigen, by rearrangement of the TCR genes CD4 - selection of T cells
T Cell Development II: Positive and Negative Selection 8 88 The two phases of thymic development: - production of T cell receptors for antigen, by rearrangement of the TCR genes CD4 - selection of T cells
Phenotypical and Functional Analysis of Peripheral T Cells in Foxn1 Transgenic Mice: Effects of Aging
 Loyola University Chicago Loyola ecommons Master's Theses Theses and Dissertations 2010 Phenotypical and Functional Analysis of Peripheral T Cells in Foxn1 Transgenic Mice: Effects of Aging Paulette Krishack
Loyola University Chicago Loyola ecommons Master's Theses Theses and Dissertations 2010 Phenotypical and Functional Analysis of Peripheral T Cells in Foxn1 Transgenic Mice: Effects of Aging Paulette Krishack
TGF-β receptor maintains CD4 T helper cell identity during chronic viral infections
 TGF-β receptor maintains CD4 T helper cell identity during chronic viral infections Gavin M. Lewis, 1 Ellen J. Wehrens, 1 Lara Labarta-Bajo, 1 Hendrik Streeck, 2 and Elina I. Zuniga 1 1 Division of Biological
TGF-β receptor maintains CD4 T helper cell identity during chronic viral infections Gavin M. Lewis, 1 Ellen J. Wehrens, 1 Lara Labarta-Bajo, 1 Hendrik Streeck, 2 and Elina I. Zuniga 1 1 Division of Biological
Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity
 MICR2209 Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will discuss the T-cell mediated immune response, how it is activated,
MICR2209 Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will discuss the T-cell mediated immune response, how it is activated,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Text Results In vitro activation experiments established that treatment with anti-cd3 plus anti- CD28 was sufficient to promote EBI2 transcript on CD4 T cells (Extended Data Fig. 1d, e).
Supplementary Text Results In vitro activation experiments established that treatment with anti-cd3 plus anti- CD28 was sufficient to promote EBI2 transcript on CD4 T cells (Extended Data Fig. 1d, e).
Lecture outline. Immunological tolerance and immune regulation. Central and peripheral tolerance. Inhibitory receptors of T cells. Regulatory T cells
 1 Immunological tolerance and immune regulation Abul K. Abbas UCSF 2 Lecture outline Central and peripheral tolerance Inhibitory receptors of T cells Regulatory T cells 1 The immunological equilibrium:
1 Immunological tolerance and immune regulation Abul K. Abbas UCSF 2 Lecture outline Central and peripheral tolerance Inhibitory receptors of T cells Regulatory T cells 1 The immunological equilibrium:
HD1 (FLU) HD2 (EBV) HD2 (FLU)
 ramer staining + anti-pe beads ramer staining a HD1 (FLU) HD2 (EBV) HD2 (FLU).73.11.56.46.24 1.12 b CD127 + c CD127 + d CD127 - e CD127 - PD1 - PD1 + PD1 + PD1-1 1 1 1 %CD127 + PD1-8 6 4 2 + anti-pe %CD127
ramer staining + anti-pe beads ramer staining a HD1 (FLU) HD2 (EBV) HD2 (FLU).73.11.56.46.24 1.12 b CD127 + c CD127 + d CD127 - e CD127 - PD1 - PD1 + PD1 + PD1-1 1 1 1 %CD127 + PD1-8 6 4 2 + anti-pe %CD127
Self-antigen specific CD8 + T cell precursor frequency determines the quality of the antitumor immune response
 ARTICLE Self-antigen specific CD8 + T cell precursor frequency determines the quality of the antitumor immune response Gabrielle A. Rizzuto, 1,3 Taha Merghoub, 1 Daniel Hirschhorn-Cymerman, 1 Cailian Liu,
ARTICLE Self-antigen specific CD8 + T cell precursor frequency determines the quality of the antitumor immune response Gabrielle A. Rizzuto, 1,3 Taha Merghoub, 1 Daniel Hirschhorn-Cymerman, 1 Cailian Liu,
TCR, MHC and coreceptors
 Cooperation In Immune Responses Antigen processing how peptides get into MHC Antigen processing involves the intracellular proteolytic generation of MHC binding proteins Protein antigens may be processed
Cooperation In Immune Responses Antigen processing how peptides get into MHC Antigen processing involves the intracellular proteolytic generation of MHC binding proteins Protein antigens may be processed
Active STAT5 promotes long lived cytotoxic CD8 T cells that induce regression of autochthonous mouse melanoma.
 Active STAT5 promotes long lived cytotoxic CD8 T cells that induce regression of autochthonous mouse melanoma. SITC 211 Grégory Verdeil No relationships to disclose T cell adoptive transfer for cancer
Active STAT5 promotes long lived cytotoxic CD8 T cells that induce regression of autochthonous mouse melanoma. SITC 211 Grégory Verdeil No relationships to disclose T cell adoptive transfer for cancer
Prepared by Cyrus H. Nozad, MD, University of Tennessee and John Seyerle, MD, Ohio State University
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 21 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, Seventh Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 21: Antigen-Presenting Dendritic Cells (Pages
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 21 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, Seventh Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 21: Antigen-Presenting Dendritic Cells (Pages
Page 4: Antigens: Self-Antigens The body has a vast number of its own antigens called self-antigens. These normally do not trigger immune responses.
 Common Characteristics of B and T Lymphocytes Graphics are used with permission of Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com). Page 1: Introduction While B and T lymphocytes
Common Characteristics of B and T Lymphocytes Graphics are used with permission of Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com). Page 1: Introduction While B and T lymphocytes
The two faces of heterologous immunity: protection or immunopathology
 Review The two faces of heterologous immunity: protection or immunopathology Shalini Sharma and Paul G. Thomas 1 Department of Immunology, St. Jude Children s Research Hospital, Memphis Tennessee, USA
Review The two faces of heterologous immunity: protection or immunopathology Shalini Sharma and Paul G. Thomas 1 Department of Immunology, St. Jude Children s Research Hospital, Memphis Tennessee, USA
Immunology Lecture 4. Clinical Relevance of the Immune System
 Immunology Lecture 4 The Well Patient: How innate and adaptive immune responses maintain health - 13, pg 169-181, 191-195. Immune Deficiency - 15 Autoimmunity - 16 Transplantation - 17, pg 260-270 Tumor
Immunology Lecture 4 The Well Patient: How innate and adaptive immune responses maintain health - 13, pg 169-181, 191-195. Immune Deficiency - 15 Autoimmunity - 16 Transplantation - 17, pg 260-270 Tumor
System Biology analysis of innate and adaptive immune responses during HIV infection
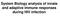 System Biology analysis of innate and adaptive immune responses during HIV infection Model of T cell memory persistence and exhaustion Naive Ag+APC Effector TEM (Pfp, Gr.B, FasL, TNF) Ag stim. IL-2, IL-7,
System Biology analysis of innate and adaptive immune responses during HIV infection Model of T cell memory persistence and exhaustion Naive Ag+APC Effector TEM (Pfp, Gr.B, FasL, TNF) Ag stim. IL-2, IL-7,
Putting it Together. Stephen Canfield Secondary Lymphoid System. Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s
 Putting it Together Stephen Canfield smc12@columbia.edu Secondary Lymphoid System Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s Axillary LN s Mediastinal/Retroperitoneal LN s Thoracic Duct Appendix Spleen Inguinal LN
Putting it Together Stephen Canfield smc12@columbia.edu Secondary Lymphoid System Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s Axillary LN s Mediastinal/Retroperitoneal LN s Thoracic Duct Appendix Spleen Inguinal LN
Test Bank for Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of the Immune System 4th Edition by Abbas
 Test Bank for Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of the Immune System 4th Edition by Abbas Chapter 04: Antigen Recognition in the Adaptive Immune System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Most T lymphocytes
Test Bank for Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of the Immune System 4th Edition by Abbas Chapter 04: Antigen Recognition in the Adaptive Immune System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Most T lymphocytes
Third line of Defense. Topic 8 Specific Immunity (adaptive) (18) 3 rd Line = Prophylaxis via Immunization!
 Topic 8 Specific Immunity (adaptive) (18) Topics - 3 rd Line of Defense - B cells - T cells - Specific Immunities 1 3 rd Line = Prophylaxis via Immunization! (a) A painting of Edward Jenner depicts a cow
Topic 8 Specific Immunity (adaptive) (18) Topics - 3 rd Line of Defense - B cells - T cells - Specific Immunities 1 3 rd Line = Prophylaxis via Immunization! (a) A painting of Edward Jenner depicts a cow
Hepatitis virus immunity. Mar 9, 2005 Rehermann and Nascimbeni review Crispe review
 Hepatitis virus immunity Mar 9, 2005 Rehermann and Nascimbeni review Crispe review HBV & HCV infection outcomes Both viruses cause immune-mediated active and chronic hepatitis HBV Vertical transmission
Hepatitis virus immunity Mar 9, 2005 Rehermann and Nascimbeni review Crispe review HBV & HCV infection outcomes Both viruses cause immune-mediated active and chronic hepatitis HBV Vertical transmission
BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES: Immunology and Inflammation. Anne Rogel, Jane E. Willoughby, Sarah L. Buchan, Henry J. Leonard, Stephen M.
 BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES: Immunology and Inflammation Akt signaling is critical for memory CD8 + T cell development and tumor immune surveillance Anne Rogel, Jane E. Willoughby, Sarah L. Buchan, Henry J. Leonard,
BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES: Immunology and Inflammation Akt signaling is critical for memory CD8 + T cell development and tumor immune surveillance Anne Rogel, Jane E. Willoughby, Sarah L. Buchan, Henry J. Leonard,
The antigen-specific CD8 + T cell repertoire in unimmunized mice includes memory phenotype cells bearing markers of homeostatic expansion
 ARTICLE The antigen-specific CD8 + T cell repertoire in unimmunized mice includes memory phenotype cells bearing markers of homeostatic expansion Catherine Haluszczak, 1 Adovi D. Akue, 2 Sara E. Hamilton,
ARTICLE The antigen-specific CD8 + T cell repertoire in unimmunized mice includes memory phenotype cells bearing markers of homeostatic expansion Catherine Haluszczak, 1 Adovi D. Akue, 2 Sara E. Hamilton,
Supplementary Fig. 1: Ex vivo tetramer enrichment with anti-c-myc beads
 Supplementary Fig. 1: Ex vivo tetramer enrichment with anti-c-myc beads Representative example of comparative ex vivo tetramer enrichment performed in three independent experiments with either conventional
Supplementary Fig. 1: Ex vivo tetramer enrichment with anti-c-myc beads Representative example of comparative ex vivo tetramer enrichment performed in three independent experiments with either conventional
Examples of questions for Cellular Immunology/Cellular Biology and Immunology
 Examples of questions for Cellular Immunology/Cellular Biology and Immunology Each student gets a set of 6 questions, so that each set contains different types of questions and that the set of questions
Examples of questions for Cellular Immunology/Cellular Biology and Immunology Each student gets a set of 6 questions, so that each set contains different types of questions and that the set of questions
VZV, EBV, and HHV-6-8
 VZV, EBV, and HHV-6-8 Anne Gershon Common Features of Herpesviruses Morphology Basic mode of replication Primary infection followed by latency Ubiquitous Ability to cause recurrent infections (reactivation
VZV, EBV, and HHV-6-8 Anne Gershon Common Features of Herpesviruses Morphology Basic mode of replication Primary infection followed by latency Ubiquitous Ability to cause recurrent infections (reactivation
