SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
|
|
|
- Gregory Scott
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Association of HLA-DRB1-restricted CD4 + T cell responses with HIV immune control Srinika Ranasinghe 1, Sam Cutler 1, Isaiah Davis 1, Richard Lu 2, Damien Z. Soghoian 1, Ying Qi 3, John Sidney 4, Gregory Kranias 2, Michael Flanders 1, Madelene Lindqvist 1, Bjorn Kuhl 1, Galit Alter 1, Steven G. Deeks 5, Bruce D. Walker 1, 6, Xiaojiang Gao 3, Alessandro Sette 4, Mary Carrington 1, 3 and Hendrik Streeck 2 1 Ragon Institute of MGH, MIT, and Harvard, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA. 2 new affiliation: U.S. Military HIV Research Program (MHRP), Henry M. Jackson Foundation, Walter Reed Army Institute of Research (WRAIR), Silver Spring, Maryland, USA. 3 Cancer and Inflammation Program, Laboratory of Experimental Immunology, SAIC-Frederick, NCI Frederick, Frederick, Maryland, USA. 4 La Jolla Institute for Allergy and Immunology, La Jolla, California, USA. 5 UCSF Department of Medicine at San Francisco General Hospital, San Francisco, California, USA. 6 Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Chevy Chase, Maryland, USA. * Corresponding author Hendrik Streeck, MD/PhD Mail: hstreeck@hivresearch.org Phone:
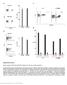
2 DRB1 *0 4:0 1 FQ 1 2 ( FYKTLR AEQASQ) or FS1 1 ( FYKTLR AEQAS) DRB1 *07 :0 1 RA1 1 ( RFYKT LRAE QA) or RQ 10 (RF YKT L RAE Q ) O LP-41 (YVDRFYKTLRAEQ ASQ EV) YVDRFYKTLRAEQ ASQ YVDRFYKTLRAEQ A YVDRFYKTLRAE YVDRFYKTLRA YVDRFYKTLR YVDRFYKTL YVDRFKT DRFYKTLRAEQ ASQ EV RFYKTLRAEQ ASQ EV FYKTLRAEQ ASQ EV KTLRAEQ ASQ EV LRAEQ ASQ EV RAEQ ASQ EV AEQ ASQ EV IFN y r es pons e ( % m ax im um ) O LP-41 (YVDRFYKTLRAEQ ASQ EV) YVDRFYKTLRAEQ ASQ YVDRFYKTLRAEQ A YVDRFYKTLRAE YVDRFYKTLRA YVDRFYKTLR YVDRFYKTL YVDRFKT DRFYKTLRAEQ ASQ EV RFYKTLRAEQ ASQ EV FYKTLRAEQ ASQ EV KTLRAEQ ASQ EV LRAEQ ASQ EV RAEQ ASQ EV AEQ ASQ EV IFN y r es pons e ( % m ax im um ) DRB1 *1 1:0 1 FA 10 (FY KTLR AEQ A) or FQ 9 (FY KTLR AEQ) DRB1 *13: 01 YE1 2 ( YVD RF YKT L RAE) o r VE1 1 ( VDRF YK TL RAE) O LP-41 (YVDRFYKTLRAEQ ASQ EV) YVDRFYKTLRAEQ ASQ YVDRFYKTLRAEQ A YVDRFYKTLRAE YVDRFYKTLRA YVDRFYKTLR YVDRFYKTL YVDRFKT DRFYKTLRAEQ ASQ EV RFYKTLRAEQ ASQ EV FYKTLRAEQ ASQ EV KTLRAEQ ASQ EV LRAEQ ASQ EV RAEQ ASQ EV AEQ ASQ EV IFN y r es pons e ( % m ax im um ) O LP-41 (YVDRFYKTLRAEQ ASQ EV) YVDRFYKTLRAEQ ASQ YVDRFYKTLRAEQ A YVDRFYKTLRAE YVDRFYKTLRA YVDRFYKTLR YVDRFYKTL YVDRFKT DRFYKTLRAEQ ASQ EV RFYKTLRAEQ ASQ EV FYKTLRAEQ ASQ EV KTLRAEQ ASQ EV LRAEQ ASQ EV RAEQ ASQ EV AEQ ASQ EV IFN y r espo nse ( % m axim um ) DRB1 *1 3: 02 YE1 2 ( YVD RF YKT L RAE) o r VE1 1 ( VDRF YK TL RAE) O LP-41 (YVDRFYKTLRAEQ ASQ EV) YVDRFYKTLRAEQ ASQ YVDRFYKTLRAEQ A YVDRFYKTLRAE YVDRFYKTLRA YVDRFYKTLR YVDRFYKTL YVDRFKT DRFYKTLRAEQ ASQ EV RFYKTLRAEQ ASQ EV FYKTLRAEQ ASQ EV KTLRAEQ ASQ EV LRAEQ ASQ EV RAEQ ASQ EV AEQ ASQ EV IFN y r es pons e ( % m ax im um ) Supplementary Figure S1: OLP-41 is promiscuously presented by multiple HLA-DRB1 alleles that share largely overlapping epitope-binding repertoires. The minimal stimulatory epitope(s) were delineated for each of the five HLA-DRB1 alleles. In fine-mapping analysis, each OLP-41 specific CD4 T cell line was tested in triplicate against 20 um of the original 18-mer OLP-41 (YVDRFYKTLRAEQASQEV) and 14 serial truncations from the N- and C-terminus presented by the restricting HLA-DRB1 expressing LCL. Bars denote standard error. The IFNγ SFU response to OLP-41 was normalized to 100%. Concordant with other CD4 T cell studies (15) the "minimal stimulatory epitope" was defined as the shortest peptide sequence triggering an IFNy response 50% of the original OLP-41 response.
3 % HLA-DRB1 Allele Expression MGH & SC OPE C ohort (n =1085) In dependent C ohort DRB1 alle le s Supplementary Figure S2: The MGH & SCOPE cohort (n=1085) and our independent cohort (n=42) of treatment naive chronically HIV-infected subjects demonstrated similar HLA-DRB1 allele expression frequencies.
4 a 6 P=0.25 b 1500 P=0.37 Lo g Vira l Load 4 2 CD4 T cell c ount Low OR High OR 0 Low OR High OR as sociated HL A-DR associated HL A-DR as sociated HL A-DR assoc iated HLA -DR Supplementary Figure S3: HIV-infected subjects expressing 1 DRB1 alleles associated with low OR vs. high OR demonstrated no significant differences in their mean viral load (log HIV RNA copies/ml) (a) or CD4 count (b) (P>0.05 Mann-Whitney). The 43 treatment-naive chronically HIV-infected subjects from MGH included 15 subjects expressing 1 DRB1 alleles linked with low OR and 28 subjects expressing 1 DRB1 alleles linked to higher OR, that were assayed for their plasma HIV viral load and CD4 T cell count at MGH, as previously described (8).
5 Gag Nef Env Pol Acc Total Number of peptides in each protein Number of peptides eliciting a CD4 T cell response* Number of peptides tested for HLA-DRB1 restriction Number of peptides with successfully defined HLA-DRB1 restriction % Peptides restricted by HLA-DRB1 after adjustment for CD4 T cell targeting Supplementary Table 1: A similar percentage of peptide restrictions were identified for each protein after adjustment for protein size and HIV-specific CD4 T cell targeting. The item highlighted with an asterisk (*) denotes data gathered from the solid black bars in Fig 1A, as previously described (8).
6 Peptide (OLP) Protein Peptide Sequence Number of restrictions HLA-DR defined restrictions 41 Gag YVDRFYKTLRAEQASQEV 12 DRB1*0401, *0701, *0801, *1001, *1101, *1301, *1302, *1303, *1501, *1502, DRB4*0101, DRB5* Gag GKKKYKLKHIVWASREL 10 DRB1*0101, *0701, *0801, *1101, *1302, *1303, DRB3*0101, DRB3*0301, DRB4*0101, DRB5* Gag KHIVWASRELERFAV 6 DRB1*0301, *1301, *1302, *1303, DRB3*0101, DRB5* Gag SGGELDRWEKIRLRPGGK 5 DRB1*0701, *1101, *1301, *1302, DRB3* Gag WIILGLNKIVRMYSPTSI 5 DRB1*0302, *1101, *1301, *1501, * Nef LWVYHTQGYFPDWQNY 5 DRB1*0701, *1301, *1401, DRB3*0101, DRB4* Gag ERFAVNPGLLETSEGCR 4 DRB1*1302, *1303, *1501, DRB3* Gag AFSPEVIPMFSALSEGA 4 DRB1*0401, *0701, *1501, DRB4* Gag STLQEQIGWMTNNPPIPV 4 DRB1*0101, *1303, *DRB3*0101, DRB3* Nef KFDSRLAFHHMARELH 4 DRB1*0302, *1302, *1303, DRB3* Tat TKGLGISYGRKKRRQRRR 4 DRB1*1302, *1303, DRB3*0101, DRB3* Gag ASRELERFAVNPGLL 3 DRB1*1301, *1302, DRB4* Gag RQANFLGKIWPSHKGR 3 DRB1*1301, *1501, DRB5* Gag GKIWPSHKGRPGNFLQSR 3 DRB1*0701, *1301, * Nef KFDSRLAFHHMARELH 3 DRB1*1302, *1303, DRB3* Env NVTENFNMWKNNMVEQMH 3 DRB1*1101, *1501, * Env YALFYKLDVVPIDNDNTSY 3 DRB1*0101, *0701, * Env KVSFEPIPIHYCAPAGFA 3 DRB1*0101, *1101, DRB3* Gag TGSEELRSLYNTVATLY 2 DRB1*0405, * Gag SLYNTVATLYCVHQRIEV 2 DRB1*0701, * Gag PRTLNAWVKVVEEKAF 2 DRB1*1301, * Gag SDIAGTTSTLQEQIGWM 2 DRB1*0404, DRB1* Gag WMTNNPPIPVGEIYKRWI 2 DRB3*0101, DRB3* Gag CFNCGKEGHIAKNCRAPR 2 DRB1*0901, *1301, 55 Gag HIAKNCRAPRKKGCWK 2 DRB1*0701, * Nef YKAAVDLSHFLKEKGGL 2 DRB1*0701, * Rev PSPEGTRQARRNRRRRW 2 DRB1*1301, DRB3* Pol VIWGKTPKFKLPIQKETW 2 DRB1*1301, DRB3* Env AAEQLWVTVYYGVPVWK 2 DRB1*1101, * Gag IVQNLQGQMVHQAISPR 1 DRB1* Gag WVKVVEEKAFSPEVIPMF 1 DRB1* Gag AAEWDRLHPVHAGPIA 1 DRB1* Gag LHPVHAGPIAPGQMREPR 1 DRB1*1101
7 40 Gag GPKEPFRDYVDRFYKTLR 1 DRB1* Gag EVKNWMTETLLVQNA 1 DRB1* Gag AATLEEMMTACQGVGGPGH 1 DRB1* Gag TNSATIMMQRGNFRNQRK 1 DRB1* Gag RAPRKKGCWKCGKEGHQM 1 DRB1* Gag FLQSRPEPTAPPEESFRF 1 DRB1* Gag QKQEPIDKELYPLASLR 1 DRB1* Gag KELYPLASLRSLFGNDPSSQ 1 DRB1* Nef RSVVGWPAVRERMRRA 1 DRB1* Nef PAVRERMRRAEPAADGV 1 DRB1* Nef GLEGLIYSQKRQDILDLW 1 DRB1* Nef QKRQDILDLWVYHTQGYF 1 DRB1* Nef FGWCFKLVPVEPEKVEEA 1 DRB1* Vpu IVFIEYRKILRQKIDRL 1 DRB1* Pol EEKIKALVEICTEMEK 1 DRB1* Pol QKTELQAIHLALQDSGL 1 DRB1* Pol TIHTDNGSNFTSTTVKAA 1 DRB1* Pol PYNPQSQGVVESMNKELK 1 DRB1* Pol LKTAVQMAVFIHNFKRK 1 DRB1* Vpr ILQQLFIHFRIGCQHSR 1 DRB1* Env LGMLMICSAAEQLWVTVY 1 DRB1* Env TVYYGVPVWKEATTTLF 1 DRB1* Env LFCASDACAYDTEVHNVW 1 DRB3* Env NPQEVVLENVTENFNMWK 1 DRB1* Env CSFNITTSIRDKVQKEYA 1 DRB1* Env IRDKVQKEYALFYKLDVV 1 DRB1* Env NCTRPNNNTRKSIHI 1 DRB1* Env SFNCGGEFFYCNTTQLF 1 DRB1* Env ELYKYKVVKIEPLGVA 1 DRB1* Env LWNWFDITNWLWYIKIFI 1 DRB1* Env IFIMIVGGLVGLRIVFAV 1 DRB1* Env RLVDGFLALIWVDLRSL 1 DRB1* Vif HIPLGDARLVITTYWGL 1 DRB1* Vif IRNAILGHIVSPRCEYQA 1 DRB1*1501 Supplementary Table 2: Peptide-DRB restrictions were identified across the HIV proteome in our IFNγ ELISpot HLA-DR restriction assay. HIV-specific CD4 T cell peptides are here defined as 'promiscuous' if a peptide is recognized in the context of two or more DRB alleles expressed by different individuals. Yet, please note that the list of potential HLA-DRB restrictions is most likely far greater than determined here.
8 Supplementary Table 3: Five immunodominant HIV-specific CD4 T cell peptides demonstrated high levels of promiscuity in a well-characterized radioactively labeled competition assay to determine the peptide-drb1 binding capacity. Each peptide was tested against a standardized panel of 13 HLA-DRB1 alleles, as previously described (13). IC 50 nm values were generated for each peptide-drb1 interaction, with IC 50 values less than the threshold value of 1000 nm denoting 'binders', while non-binders (>1000 nm ) are highlighted in grey with bold font.
9 HLA-DRB1 Allele Expressed (n=1085) % Allele Frequency (n=1085) DRB1*01: DRB1*01: DRB1*01: DRB1*03: DRB1*03: DRB1*04: DRB1*04: DRB1*04: DRB1*04: DRB1*07: DRB1*08: DRB1*08: DRB1*08: DRB1*09: DRB1*10: DRB1*11: DRB1*11: DRB1*11: DRB1*12: DRB1*13: DRB1*13: DRB1*13: DRB1*13: DRB1*14: DRB1*15: DRB1*15: DRB1*15: DRB1*16: DRB1*16: Supplementary Table 4: HLA-DRB1 allele expression frequencies in our MGH & SCOPE cohort of HIVinfected treatment naive individuals (n=1085).
10 HLA-DRB1 P-value OR 95% CI 15: : : : : : : Supplementary Table 5: The P-values, odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) are shown for DRB1 alleles trending to lower OR (DRB1*15:02, *10:01, *13:03, *13:02) and DRB1 alleles trending to higher OR (DRB1 *15:01, *01:01 *03:01) at 10% significance prior to multiple comparisons. The statistical differences observed in our functional analysis remained significant when HLA-DRB1 alleles were more stringently selected based on 10% significance prior to multiple comparisons (Fig. 3a P= Fishers exact test, Fig. 3b P= Mann-Whitney Test).
Temporal effect of HLA-B*57 on viral control during primary HIV-1 infection
 Vaidya et al. Retrovirology 2013, 10:139 SHORT REPORT Temporal effect of HLA-B*57 on viral control during primary HIV-1 infection Open Access Sagar A Vaidya 1,2, Hendrik Streeck 1,3,4, Noor Beckwith 1,
Vaidya et al. Retrovirology 2013, 10:139 SHORT REPORT Temporal effect of HLA-B*57 on viral control during primary HIV-1 infection Open Access Sagar A Vaidya 1,2, Hendrik Streeck 1,3,4, Noor Beckwith 1,
How HIV Causes Disease Prof. Bruce D. Walker
 How HIV Causes Disease Howard Hughes Medical Institute Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School 1 The global AIDS crisis 60 million infections 20 million deaths 2 3 The screen versions of
How HIV Causes Disease Howard Hughes Medical Institute Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School 1 The global AIDS crisis 60 million infections 20 million deaths 2 3 The screen versions of
Epitope Specific CD8 + T Cell Responses Predict Spontaneous Control of HIV Replication
 Epitope Specific CD8 + T Cell Responses Predict Spontaneous Control of HIV Replication Florencia Pereyra, MD Partners AIDS Research Center Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Background HIV -1 elicits HLA
Epitope Specific CD8 + T Cell Responses Predict Spontaneous Control of HIV Replication Florencia Pereyra, MD Partners AIDS Research Center Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Background HIV -1 elicits HLA
Inconsistent HIV reservoir dynamics and immune responses following anti-pd-1 therapy
 Letter to Editor (Annals of Oncology): Inconsistent HIV reservoir dynamics and immune responses following anti-pd-1 therapy in cancer patients with HIV infection E. P. Scully 1,2,3, R. L. Rutishauser 4,
Letter to Editor (Annals of Oncology): Inconsistent HIV reservoir dynamics and immune responses following anti-pd-1 therapy in cancer patients with HIV infection E. P. Scully 1,2,3, R. L. Rutishauser 4,
Alessandra Franco MD PhD UCSD School of Medicine Department of Pediatrics Division of Allergy Immunology and Rheumatology
 Immunodominant peptides derived from the heavy constant region of IgG1 stimulate natural regulatory T cells: identification of pan- HLA binders for clinical translation Alessandra Franco MD PhD UCSD School
Immunodominant peptides derived from the heavy constant region of IgG1 stimulate natural regulatory T cells: identification of pan- HLA binders for clinical translation Alessandra Franco MD PhD UCSD School
NK mediated Antibody Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity in HIV infections
 NK mediated Antibody Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity in HIV infections Amy Chung Dr. Ivan Stratov Prof. Stephen Kent ADCC process consists of Target cell QuickTime and a TIFF (Uncompressed) FcγR decompressor
NK mediated Antibody Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity in HIV infections Amy Chung Dr. Ivan Stratov Prof. Stephen Kent ADCC process consists of Target cell QuickTime and a TIFF (Uncompressed) FcγR decompressor
Induction of Gag-Specific CD4 T Cell Responses during Acute HIV Infection Is Associated with Improved Viral Control
 Induction of Gag-Specific CD4 T Cell Responses during Acute HIV Infection Is Associated with Improved Viral Control Miriam Schieffer, a,f Heiko K. Jessen, a Alexander F. Oster, b,c Franco Pissani, b,c
Induction of Gag-Specific CD4 T Cell Responses during Acute HIV Infection Is Associated with Improved Viral Control Miriam Schieffer, a,f Heiko K. Jessen, a Alexander F. Oster, b,c Franco Pissani, b,c
HIV-1 Dual Infection and Neurocognitive Impairment
 HIV-1 Dual Infection and Neurocognitive Impairment Gabriel Wagner, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Infectious Diseases & Global Public Health UC San Diego HIV-Associated End Organ Damage Antiretroviral
HIV-1 Dual Infection and Neurocognitive Impairment Gabriel Wagner, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Infectious Diseases & Global Public Health UC San Diego HIV-Associated End Organ Damage Antiretroviral
Rapid perforin upregulation directly ex vivo by CD8 + T cells is a defining characteristic of HIV elite controllers
 Rapid perforin upregulation directly ex vivo by CD8 + T cells is a defining characteristic of HIV elite controllers Adam R. Hersperger Department of Microbiology University of Pennsylvania Evidence for
Rapid perforin upregulation directly ex vivo by CD8 + T cells is a defining characteristic of HIV elite controllers Adam R. Hersperger Department of Microbiology University of Pennsylvania Evidence for
Superior Control of HIV-1 Replication by CD8+ T Cells Targeting Conserved Epitopes: Implications for HIV Vaccine Design
 Superior Control of HIV-1 Replication by CD8+ T Cells Targeting Conserved Epitopes: Implications for HIV Vaccine Design Pratima Kunwar 1,7, Natalie Hawkins 2, Warren L. Dinges 1,3, Yi Liu 5, Erin E. Gabriel
Superior Control of HIV-1 Replication by CD8+ T Cells Targeting Conserved Epitopes: Implications for HIV Vaccine Design Pratima Kunwar 1,7, Natalie Hawkins 2, Warren L. Dinges 1,3, Yi Liu 5, Erin E. Gabriel
Potential cross reactions between HIV 1 specific T cells and the microbiome. Andrew McMichael Suzanne Campion
 Potential cross reactions between HIV 1 specific T cells and the microbiome Andrew McMichael Suzanne Campion Role of the Microbiome? T cell (and B cell) immune responses to HIV and Vaccines are influenced
Potential cross reactions between HIV 1 specific T cells and the microbiome Andrew McMichael Suzanne Campion Role of the Microbiome? T cell (and B cell) immune responses to HIV and Vaccines are influenced
HIV acute infections and elite controllers- what can we learn?
 HIV acute infections and elite controllers- what can we learn? Thumbi Ndung u, BVM, PhD KwaZulu-Natal Research Institute for Tuberculosis and HIV (K-RITH) and HIV Pathogenesis Programme (HPP), Doris Duke
HIV acute infections and elite controllers- what can we learn? Thumbi Ndung u, BVM, PhD KwaZulu-Natal Research Institute for Tuberculosis and HIV (K-RITH) and HIV Pathogenesis Programme (HPP), Doris Duke
DEBATE ON HIV ENVELOPE AS A T CELL IMMUNOGEN HAS BEEN GAG-GED
 DEBATE ON HIV ENVELOPE AS A T CELL IMMUNOGEN HAS BEEN GAG-GED Viv Peut Kent Laboratory, University of Melbourne, Australia WHY ENVELOPE? Env subject to both humoral and cellular immune responses Perhaps
DEBATE ON HIV ENVELOPE AS A T CELL IMMUNOGEN HAS BEEN GAG-GED Viv Peut Kent Laboratory, University of Melbourne, Australia WHY ENVELOPE? Env subject to both humoral and cellular immune responses Perhaps
HIV Antibody Characterization for Reservoir and Eradication Studies. Michael Busch, Sheila Keating, Chris Pilcher, Steve Deeks
 HIV Antibody Characterization for Reservoir and Eradication Studies Michael Busch, Sheila Keating, Chris Pilcher, Steve Deeks Blood Systems Research Institute University of California San Francisco, CA
HIV Antibody Characterization for Reservoir and Eradication Studies Michael Busch, Sheila Keating, Chris Pilcher, Steve Deeks Blood Systems Research Institute University of California San Francisco, CA
Higher priming doses enhance HIV-specific humoral but not cellular. responses in a randomized, double-blind phase Ib clinical trial of
 Higher priming doses enhance HIV-specific humoral but not cellular responses in a randomized, double-blind phase Ib clinical trial of preventive HIV-1 vaccines Pierre-Alexandre Bart a,b, Yunda Huang c,
Higher priming doses enhance HIV-specific humoral but not cellular responses in a randomized, double-blind phase Ib clinical trial of preventive HIV-1 vaccines Pierre-Alexandre Bart a,b, Yunda Huang c,
Defining kinetic properties of HIV-specific CD8 + T-cell responses in acute infection
 Defining kinetic properties of HIV-specific CD8 + T-cell responses in acute infection Yiding Yang 1 and Vitaly V. Ganusov 1,2,3 1 Department of Microbiology, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN 37996,
Defining kinetic properties of HIV-specific CD8 + T-cell responses in acute infection Yiding Yang 1 and Vitaly V. Ganusov 1,2,3 1 Department of Microbiology, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN 37996,
Panther has new prey
 Raising the Bar for Performance Testing Panther has new prey The Aptima HIV-1 Quant Dx assay leads the hunt for HIV-1 diagnosis and viral load monitoring. Freedom to work the way you choose Run what assays
Raising the Bar for Performance Testing Panther has new prey The Aptima HIV-1 Quant Dx assay leads the hunt for HIV-1 diagnosis and viral load monitoring. Freedom to work the way you choose Run what assays
Human Leukocyte Antigen Genotype and Risk of HIV Disease Progression before and after Initiation of Antiretroviral Therapy
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Public Health Resources Public Health Resources 2011 Human Leukocyte Antigen Genotype and Risk of HIV Disease Progression
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Public Health Resources Public Health Resources 2011 Human Leukocyte Antigen Genotype and Risk of HIV Disease Progression
Development of a Universal T Cell Vaccine. Tomáš Hanke Weatherall Institute of Molecular Medicine University of Oxford United Kingdom
 Development of a Universal T Cell Vaccine Tomáš Hanke Weatherall Institute of Molecular Medicine University of Oxford United Kingdom Development of HIV-1 vaccines Induction of cell-mediated responses Immunogens
Development of a Universal T Cell Vaccine Tomáš Hanke Weatherall Institute of Molecular Medicine University of Oxford United Kingdom Development of HIV-1 vaccines Induction of cell-mediated responses Immunogens
LETTERS. Effects of thymic selection of the T-cell repertoire on HLA class I-associated control of HIV infection
 Vol 465 20 May 2010 doi:10.1038/nature08997 LETTERS Effects of thymic selection of the T-cell repertoire on HLA class I-associated control of HIV infection Andrej Košmrlj 1,2 *, Elizabeth L. Read 1,3,4
Vol 465 20 May 2010 doi:10.1038/nature08997 LETTERS Effects of thymic selection of the T-cell repertoire on HLA class I-associated control of HIV infection Andrej Košmrlj 1,2 *, Elizabeth L. Read 1,3,4
Epitope discovery and Rational vaccine design Morten Nielsen
 Epitope discovery and Rational vaccine design Morten Nielsen mniel@cbs.dtu.dk Bioinformatics in a nutshell List of peptides that have a given biological feature Mathematical model (neural network, hidden
Epitope discovery and Rational vaccine design Morten Nielsen mniel@cbs.dtu.dk Bioinformatics in a nutshell List of peptides that have a given biological feature Mathematical model (neural network, hidden
Supplementary Figure 1. Enhanced detection of CTLA-4 on the surface of HIV-specific
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGEND Supplementary Figure 1. Enhanced detection of CTLA-4 on the surface of HIV-specific CD4 + T cells correlates with intracellular CTLA-4 levels. (a) Comparative CTLA-4 levels
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGEND Supplementary Figure 1. Enhanced detection of CTLA-4 on the surface of HIV-specific CD4 + T cells correlates with intracellular CTLA-4 levels. (a) Comparative CTLA-4 levels
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Honegger et al. /pnas.0 HCV proteins Core E E P NS NS NSA NSB NSA NSB HCV peptide pools 9 Fig. S. HCV proteins represented in the nine peptide pool arrays used for the IFN-γ ELISpot
Supporting Information Honegger et al. /pnas.0 HCV proteins Core E E P NS NS NSA NSB NSA NSB HCV peptide pools 9 Fig. S. HCV proteins represented in the nine peptide pool arrays used for the IFN-γ ELISpot
ALVAC -HIV and AIDSVAX B/E Prime-Boost HIV-1 Preventive Vaccine Regimen. Results of the Thai HIV Vaccine Trial, RV144
 ALVAC -HIV and AIDSVAX B/E Prime-Boost HIV-1 Preventive Vaccine Regimen Results of the Thai HIV Vaccine Trial, RV144 SupachaiRerks-Ngarm, PunneePittisutthithum, SorachaiNitayaphan, JaranitKaewkungwal,
ALVAC -HIV and AIDSVAX B/E Prime-Boost HIV-1 Preventive Vaccine Regimen Results of the Thai HIV Vaccine Trial, RV144 SupachaiRerks-Ngarm, PunneePittisutthithum, SorachaiNitayaphan, JaranitKaewkungwal,
Why are validated immunogenicity assays important for HIV vaccine development?
 Why are validated immunogenicity assays important for HIV vaccine development? There is a need to compare immunogenicity of products in the pipeline, when similar or different in class when developed by
Why are validated immunogenicity assays important for HIV vaccine development? There is a need to compare immunogenicity of products in the pipeline, when similar or different in class when developed by
In Vitro Priming Recapitulates In Vivo HIV-1 Specific T Cell Responses, Revealing Rapid Loss of Virus Reactive CD4+ T Cells in Acute HIV-1 Infection
 In Vitro Priming Recapitulates In Vivo HIV-1 Specific T Cell Responses, Revealing Rapid Loss of Virus Reactive CD4+ T Cells in Acute HIV-1 Infection The Harvard community has made this article openly available.
In Vitro Priming Recapitulates In Vivo HIV-1 Specific T Cell Responses, Revealing Rapid Loss of Virus Reactive CD4+ T Cells in Acute HIV-1 Infection The Harvard community has made this article openly available.
CD4 + T-cell-inducing HIV vaccines may have an impact on viral control
 CD4 + T-cell-inducing HIV vaccines may have an impact on viral control Clues from cytokines produced by CD4 + T-cells from HIVinfected patients and vaccinated seronegative volunteers Eva Van Braeckel 1,
CD4 + T-cell-inducing HIV vaccines may have an impact on viral control Clues from cytokines produced by CD4 + T-cells from HIVinfected patients and vaccinated seronegative volunteers Eva Van Braeckel 1,
Safety and viral load changes in HIV-1 infected subjects treated with autologous dendritic cell immune therapy following ART discontinuation
 Safety and viral load changes in HIV-1 infected subjects treated with autologous dendritic cell immune therapy following ART discontinuation (CTN #239) Jean-Pierre Routy M.D. McGill University Paris 21
Safety and viral load changes in HIV-1 infected subjects treated with autologous dendritic cell immune therapy following ART discontinuation (CTN #239) Jean-Pierre Routy M.D. McGill University Paris 21
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Notes 1: accuracy of prediction algorithms for peptide binding affinities to HLA and Mamu alleles For each HLA and Mamu allele we have analyzed the accuracy of four predictive algorithms
Supplementary Notes 1: accuracy of prediction algorithms for peptide binding affinities to HLA and Mamu alleles For each HLA and Mamu allele we have analyzed the accuracy of four predictive algorithms
On an individual level. Time since infection. NEJM, April HIV-1 evolution in response to immune selection pressures
 HIV-1 evolution in response to immune selection pressures BISC 441 guest lecture Zabrina Brumme, Ph.D. Assistant Professor, Faculty of Health Sciences Simon Fraser University http://www3.niaid.nih.gov/topics/hivaids/understanding/biology/structure.htm
HIV-1 evolution in response to immune selection pressures BISC 441 guest lecture Zabrina Brumme, Ph.D. Assistant Professor, Faculty of Health Sciences Simon Fraser University http://www3.niaid.nih.gov/topics/hivaids/understanding/biology/structure.htm
Vertical T cell immunodominance and epitope entropy determine HIV-1 escape
 Vertical T cell immunodominance and epitope entropy determine HIV-1 escape Michael K.P. Liu,, Andrew McMichael, Nilu Goonetilleke J Clin Invest. 2013;123(1):380-393. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci65330. Research
Vertical T cell immunodominance and epitope entropy determine HIV-1 escape Michael K.P. Liu,, Andrew McMichael, Nilu Goonetilleke J Clin Invest. 2013;123(1):380-393. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci65330. Research
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Sui et al..7/pnas.997 Pre-CLP CM9 LA9 SL Tat# Pol Vif % Tetramer + CD + CD + Vac+IL- +IL- Vac Fig. S. Frequencies of six different CD + CD + Mamu-A*-tetramer + cells were measured
Supporting Information Sui et al..7/pnas.997 Pre-CLP CM9 LA9 SL Tat# Pol Vif % Tetramer + CD + CD + Vac+IL- +IL- Vac Fig. S. Frequencies of six different CD + CD + Mamu-A*-tetramer + cells were measured
Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells Inhibit Cytomegalovirus Inflammation through Interleukin-27 and B7-H4
 Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells Inhibit Cytomegalovirus Inflammation through Interleukin-27 and B7-H4 Ankita Garg, Rodney Trout and Stephen A. Spector,,* Department
Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells Inhibit Cytomegalovirus Inflammation through Interleukin-27 and B7-H4 Ankita Garg, Rodney Trout and Stephen A. Spector,,* Department
Trial Objectives immunogenicity safety
 Optimal priming of poxvirus vector (NYVAC)-based HIV vaccine regimens requires 3 DNA injections. Long term Results of the EV03/ANRS Vac20 Phase I/II Trial. Yves Levy, Kim Ellefsen, Wolfgang Stöehr, Pierre-Alexandre
Optimal priming of poxvirus vector (NYVAC)-based HIV vaccine regimens requires 3 DNA injections. Long term Results of the EV03/ANRS Vac20 Phase I/II Trial. Yves Levy, Kim Ellefsen, Wolfgang Stöehr, Pierre-Alexandre
Whole Genome Deep Sequencing of HIV-1 Reveals the Impact of Early Minor Variants Upon Immune Recognition During Acute Infection
 Whole Genome Deep Sequencing of HIV-1 Reveals the Impact of Early Minor Variants Upon Immune Recognition During Acute Infection The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share
Whole Genome Deep Sequencing of HIV-1 Reveals the Impact of Early Minor Variants Upon Immune Recognition During Acute Infection The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share
RAISON D ETRE OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM:
 RAISON D ETRE OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM: To Distinguish Self from Non-Self Thereby Protecting Us From Our Hostile Environment. Innate Immunity Acquired Immunity Innate immunity: (Antigen nonspecific) defense
RAISON D ETRE OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM: To Distinguish Self from Non-Self Thereby Protecting Us From Our Hostile Environment. Innate Immunity Acquired Immunity Innate immunity: (Antigen nonspecific) defense
Supplementary material Anti-citrullinated fibronectin antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis are associated with HLA-DRB1 shared epitope alleles.
 Supplementary material Anti-citrullinated fibronectin antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis are associated with HLA-DRB1 shared epitope alleles. Joyce J.B.C. van Beers, Annemiek Willemze, Judith Stammen-Vogelzangs,
Supplementary material Anti-citrullinated fibronectin antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis are associated with HLA-DRB1 shared epitope alleles. Joyce J.B.C. van Beers, Annemiek Willemze, Judith Stammen-Vogelzangs,
DNA and Protein Vaccination Confers Protection Upon Mucosal Challenge with Heterologous SIVsmE660 (OA 10.04)
 DNA and Protein Vaccination Confers Protection Upon Mucosal Challenge with Heterologous SIVsmE660 (OA 10.04) Rashmi Jalah Human Retrovirus Pathogenesis Section, Vaccine Branch, CCR, National Cancer Institute
DNA and Protein Vaccination Confers Protection Upon Mucosal Challenge with Heterologous SIVsmE660 (OA 10.04) Rashmi Jalah Human Retrovirus Pathogenesis Section, Vaccine Branch, CCR, National Cancer Institute
Received 19 September 2007/Accepted 21 November 2007
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Feb. 2008, p. 1723 1738 Vol. 82, No. 4 0022-538X/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.02084-07 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Patterns of CD8 Immunodominance
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Feb. 2008, p. 1723 1738 Vol. 82, No. 4 0022-538X/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.02084-07 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Patterns of CD8 Immunodominance
Variable HIV peptide stability in human cytosol is critical to epitope presentation and immune escape
 Research article Variable HIV peptide stability in human cytosol is critical to epitope presentation and immune escape Estibaliz Lazaro, 1 Carl Kadie, 2 Pamela Stamegna, 1 Shao Chong Zhang, 1 Pauline Gourdain,
Research article Variable HIV peptide stability in human cytosol is critical to epitope presentation and immune escape Estibaliz Lazaro, 1 Carl Kadie, 2 Pamela Stamegna, 1 Shao Chong Zhang, 1 Pauline Gourdain,
Under the Radar Screen: How Bugs Trick Our Immune Defenses
 Under the Radar Screen: How Bugs Trick Our Immune Defenses Session 7: Cytokines Marie-Eve Paquet and Gijsbert Grotenbreg Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research HHV-8 Discovered in the 1980 s at the
Under the Radar Screen: How Bugs Trick Our Immune Defenses Session 7: Cytokines Marie-Eve Paquet and Gijsbert Grotenbreg Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research HHV-8 Discovered in the 1980 s at the
Laboratory diagnostics CH/HIV/0052/17/10/2017
 Laboratory diagnostics CH/HIV/0052/17/10/2017 This slide set was created by ViiV Healthcare GmbH with great care in order to provide balanced information about ViiV products and / or application areas.
Laboratory diagnostics CH/HIV/0052/17/10/2017 This slide set was created by ViiV Healthcare GmbH with great care in order to provide balanced information about ViiV products and / or application areas.
T Memory Stem Cells: A Long-term Reservoir for HIV-1
 Towards an HIV Cure Pre-Conference Symposium 20 & 21 July 2012 T Memory Stem Cells: A Long-term Reservoir for HIV-1 Maria J Buzon, PhD Ragon Institute of MGH, MIT and Harvard, Massachussetts General Hospital,
Towards an HIV Cure Pre-Conference Symposium 20 & 21 July 2012 T Memory Stem Cells: A Long-term Reservoir for HIV-1 Maria J Buzon, PhD Ragon Institute of MGH, MIT and Harvard, Massachussetts General Hospital,
Genetic and Immunologic Heterogeneity among Persons Who Control HIV Infection in the Absence of Therapy
 MAJOR ARTICLE Genetic and Immunologic Heterogeneity among Persons Who Control HIV Infection in the Absence of Therapy Florencia Pereyra, 1,2 Marylyn M. Addo, 1 Daniel E. Kaufmann, 1 Yang Liu, 5 Toshiyuki
MAJOR ARTICLE Genetic and Immunologic Heterogeneity among Persons Who Control HIV Infection in the Absence of Therapy Florencia Pereyra, 1,2 Marylyn M. Addo, 1 Daniel E. Kaufmann, 1 Yang Liu, 5 Toshiyuki
Innate and Cellular Immunology Control of Infection by Cell-mediated Immunity
 Innate & adaptive Immunity Innate and Cellular Immunology Control of Infection by Cell-mediated Immunity Helen Horton PhD Seattle Biomedical Research Institute Depts of Global Health & Medicine, UW Cellular
Innate & adaptive Immunity Innate and Cellular Immunology Control of Infection by Cell-mediated Immunity Helen Horton PhD Seattle Biomedical Research Institute Depts of Global Health & Medicine, UW Cellular
Selection on the Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Proteome following Primary Infection
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Oct. 2006, p. 9519 9529 Vol. 80, No. 19 0022-538X/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.00575-06 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Selection on the Human
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Oct. 2006, p. 9519 9529 Vol. 80, No. 19 0022-538X/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.00575-06 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Selection on the Human
Fostering Clinical Development for HIV-1 Vaccine
 W Fostering Clinical Development for HIV-1 Vaccine Ravimiarenduse alane seminar 9. oktoobril Tallinnas Mart Ustav, PhD CSO, SVP 1 FIT Biotech Founded in 1995 Operations in Tampere, Finland and Tartu, Estonia
W Fostering Clinical Development for HIV-1 Vaccine Ravimiarenduse alane seminar 9. oktoobril Tallinnas Mart Ustav, PhD CSO, SVP 1 FIT Biotech Founded in 1995 Operations in Tampere, Finland and Tartu, Estonia
Evidence of HIV-1 Adaptation to HLA- Restricted Immune Responses at a Population Level. Corey Benjamin Moore
 Evidence of HIV-1 Adaptation to HLA- Restricted Immune Responses at a Population Level Corey Benjamin Moore This thesis is presented for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy of Murdoch University, 2002 I
Evidence of HIV-1 Adaptation to HLA- Restricted Immune Responses at a Population Level Corey Benjamin Moore This thesis is presented for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy of Murdoch University, 2002 I
Supplementary information. MARCH8 inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins
 Supplementary information inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins Takuya Tada, Yanzhao Zhang, Takayoshi Koyama, Minoru Tobiume, Yasuko Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Shoji
Supplementary information inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins Takuya Tada, Yanzhao Zhang, Takayoshi Koyama, Minoru Tobiume, Yasuko Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Shoji
The Immune Epitope Database Analysis Resource: MHC class I peptide binding predictions. Edita Karosiene, Ph.D.
 The Immune Epitope Database Analysis Resource: MHC class I peptide binding predictions Edita Karosiene, Ph.D. edita@liai.org IEDB Workshop October 29, 2015 Outline Introduction MHC-I peptide binding prediction
The Immune Epitope Database Analysis Resource: MHC class I peptide binding predictions Edita Karosiene, Ph.D. edita@liai.org IEDB Workshop October 29, 2015 Outline Introduction MHC-I peptide binding prediction
The first T cell response to transmitted/ founder virus contributes to the control of acute viremia in HIV-1 infection
 Published Online: 1 June, 2009 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20090365 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on December 10, 2018 ARTICLE The first T cell response to transmitted/ founder virus contributes
Published Online: 1 June, 2009 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20090365 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on December 10, 2018 ARTICLE The first T cell response to transmitted/ founder virus contributes
Citation for published version (APA): Von Eije, K. J. (2009). RNAi based gene therapy for HIV-1, from bench to bedside
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) RNAi based gene therapy for HIV-1, from bench to bedside Von Eije, K.J. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Von Eije, K. J. (2009). RNAi based
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) RNAi based gene therapy for HIV-1, from bench to bedside Von Eije, K.J. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Von Eije, K. J. (2009). RNAi based
HHS Public Access Author manuscript Nat Med. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2016 November 16.
 HHS Public Access Author manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nat Med. 2016 June ; 22(6): 606 613. doi:10.1038/nm.4100. Impact of Pre-adapted HIV Transmission Jonathan M. Carlson 1, Victor Y.
HHS Public Access Author manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nat Med. 2016 June ; 22(6): 606 613. doi:10.1038/nm.4100. Impact of Pre-adapted HIV Transmission Jonathan M. Carlson 1, Victor Y.
Mina John Institute for Immunology and Infectious Diseases Royal Perth Hospital & Murdoch University Perth, Australia
 Mina John Institute for Immunology and Infectious Diseases Royal Perth Hospital & Murdoch University Perth, Australia AIDSvaccine conference, 14 th September 2011 IMGT HLA database July 2011 >5000 class
Mina John Institute for Immunology and Infectious Diseases Royal Perth Hospital & Murdoch University Perth, Australia AIDSvaccine conference, 14 th September 2011 IMGT HLA database July 2011 >5000 class
UNIVERSITY OF KWAZULU-NATAL
 UNIVERSITY OF KWAZULU-NATAL Mapping immunodominant patterns and HLA class II restriction characteristics of HIV-specific CD4+ T cell responses in acute and chronic HIV-1 subtype C infection By Faatima
UNIVERSITY OF KWAZULU-NATAL Mapping immunodominant patterns and HLA class II restriction characteristics of HIV-specific CD4+ T cell responses in acute and chronic HIV-1 subtype C infection By Faatima
HIV Immunopathogenesis. Modeling the Immune System May 2, 2007
 HIV Immunopathogenesis Modeling the Immune System May 2, 2007 Question 1 : Explain how HIV infects the host Zafer Iscan Yuanjian Wang Zufferey Abhishek Garg How does HIV infect the host? HIV infection
HIV Immunopathogenesis Modeling the Immune System May 2, 2007 Question 1 : Explain how HIV infects the host Zafer Iscan Yuanjian Wang Zufferey Abhishek Garg How does HIV infect the host? HIV infection
RAISON D ETRE OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM:
 RAISON D ETRE OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM: To Distinguish Self from Non-Self Thereby Protecting Us From Our Hostile Environment. Innate Immunity Adaptive Immunity Innate immunity: (Antigen - nonspecific) defense
RAISON D ETRE OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM: To Distinguish Self from Non-Self Thereby Protecting Us From Our Hostile Environment. Innate Immunity Adaptive Immunity Innate immunity: (Antigen - nonspecific) defense
Received 25 April 2002/Accepted 21 May 2002
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Sept. 2002, p. 8757 8768 Vol. 76, No. 17 0022-538X/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.76.17.8757 8768.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Clustering
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Sept. 2002, p. 8757 8768 Vol. 76, No. 17 0022-538X/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.76.17.8757 8768.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Clustering
Mitochondrial DNA variation associated with gait speed decline among older HIVinfected non-hispanic white males
 Mitochondrial DNA variation associated with gait speed decline among older HIVinfected non-hispanic white males October 2 nd, 2017 Jing Sun, Todd T. Brown, David C. Samuels, Todd Hulgan, Gypsyamber D Souza,
Mitochondrial DNA variation associated with gait speed decline among older HIVinfected non-hispanic white males October 2 nd, 2017 Jing Sun, Todd T. Brown, David C. Samuels, Todd Hulgan, Gypsyamber D Souza,
Treatment with IL-7 Prevents the Decline of Circulating CD4 + T Cells during the Acute Phase of SIV Infection in Rhesus Macaques
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION FOR: Treatment with IL-7 Prevents the Decline of Circulating CD4 + T Cells during the Acute Phase of SIV Infection in Rhesus Macaques Lia Vassena, 1,2 Huiyi Miao, 1 Raffaello Cimbro,
SUPPORTING INFORMATION FOR: Treatment with IL-7 Prevents the Decline of Circulating CD4 + T Cells during the Acute Phase of SIV Infection in Rhesus Macaques Lia Vassena, 1,2 Huiyi Miao, 1 Raffaello Cimbro,
Press conference abstracts Vaccine and Antibody Research Monday, 22 October 2018
 Press conference abstracts Vaccine and Antibody Research Monday, 22 October 2018 OA02.05LB Vaccine-induced Gene Signature Correlates with Protection against Acquisition in Three Independent Vaccine Efficacy
Press conference abstracts Vaccine and Antibody Research Monday, 22 October 2018 OA02.05LB Vaccine-induced Gene Signature Correlates with Protection against Acquisition in Three Independent Vaccine Efficacy
Transmitted Virus Fitness and Host T Cell Responses Collectively Define Divergent Infection Outcomes in Two HIV-1 Recipients
 Transmitted Virus Fitness and Host T Cell Responses Collectively Define Divergent Infection Outcomes in Two HIV-1 Recipients Ling Yue, Emory University Katja J. Pfafferott, University of Oxford Joshua
Transmitted Virus Fitness and Host T Cell Responses Collectively Define Divergent Infection Outcomes in Two HIV-1 Recipients Ling Yue, Emory University Katja J. Pfafferott, University of Oxford Joshua
Establishment and Targeting of the Viral Reservoir in Rhesus Monkeys
 Establishment and Targeting of the Viral Reservoir in Rhesus Monkeys Dan H. Barouch, M.D., Ph.D. Center for Virology and Vaccine Research Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Ragon Institute of MGH, MIT,
Establishment and Targeting of the Viral Reservoir in Rhesus Monkeys Dan H. Barouch, M.D., Ph.D. Center for Virology and Vaccine Research Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Ragon Institute of MGH, MIT,
The major obstacle in the development of new treatment
 Broadly Immunogenic HLA Class I Supertype-Restricted Elite CTL Epitopes Recognized in a Diverse Population Infected with Different HIV-1 Subtypes 1 Carina L. Pérez,* Mette V. Larsen, Rasmus Gustafsson,*
Broadly Immunogenic HLA Class I Supertype-Restricted Elite CTL Epitopes Recognized in a Diverse Population Infected with Different HIV-1 Subtypes 1 Carina L. Pérez,* Mette V. Larsen, Rasmus Gustafsson,*
Conserved epitopes on HIV-1, FIV and SIV p24 proteins are recognized by HIV-1 infected subjects
 Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics ISSN: 2164-5515 (Print) 2164-554X (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/khvi20 Conserved epitopes on HIV-1, FIV and SIV p24 proteins are recognized
Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics ISSN: 2164-5515 (Print) 2164-554X (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/khvi20 Conserved epitopes on HIV-1, FIV and SIV p24 proteins are recognized
Antiviral CD8 + T Cells Restricted by Human Leukocyte Antigen Class II Exist during Natural HIV Infection and Exhibit Clonal Expansion
 Article Antiviral CD8 + T Cells Restricted by Human Leukocyte Antigen Class II Exist during Natural HIV Infection and Exhibit Clonal Expansion Highlights d CD8 + T cells restricted by HLA-DRB1 exist in
Article Antiviral CD8 + T Cells Restricted by Human Leukocyte Antigen Class II Exist during Natural HIV Infection and Exhibit Clonal Expansion Highlights d CD8 + T cells restricted by HLA-DRB1 exist in
Relative rate and location of intra-host HIV evolution to evade cellular immunity are predictable
 Received 2 Nov 2015 Accepted 18 Apr 2016 Published 23 May 2016 DOI: 10.1038/ncomms11660 Relative rate and location of intra-host HIV evolution to evade cellular immunity are predictable John P. Barton
Received 2 Nov 2015 Accepted 18 Apr 2016 Published 23 May 2016 DOI: 10.1038/ncomms11660 Relative rate and location of intra-host HIV evolution to evade cellular immunity are predictable John P. Barton
Destruction of the Residual Active HIV-1 Reservoir by Env-specific Immunotoxin
 Destruction of the Residual Active HIV-1 Reservoir by Env-specific Immunotoxin J. Victor Garcia-Martinez, Ph.D. University of North Carolina, at Chapel Hill IAS 2013 Towards an HIV Cure Symposium Delivering
Destruction of the Residual Active HIV-1 Reservoir by Env-specific Immunotoxin J. Victor Garcia-Martinez, Ph.D. University of North Carolina, at Chapel Hill IAS 2013 Towards an HIV Cure Symposium Delivering
levels of genes were separated by their expression levels; 2,000 high, medium, and low
 Figure S1. Histone modification profiles near transcription start sites. The overall histone modification around transcription start sites (TSSs) was calculated. Histone modification levels of genes were
Figure S1. Histone modification profiles near transcription start sites. The overall histone modification around transcription start sites (TSSs) was calculated. Histone modification levels of genes were
HIV/AIDS in Practice. An Expert Commentary with Nelson Michael, MD, PhD. A Clinical Context Report
 HIV/AIDS in Practice An Expert Commentary with Nelson Michael, MD, PhD A Clinical Context Report Clinical Context: HIV/AIDS in Practice Expert Commentary Jointly Sponsored by: and Clinical Context: HIV/AIDS
HIV/AIDS in Practice An Expert Commentary with Nelson Michael, MD, PhD A Clinical Context Report Clinical Context: HIV/AIDS in Practice Expert Commentary Jointly Sponsored by: and Clinical Context: HIV/AIDS
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Binding capacity of DNA-barcoded MHC multimers and recovery of antigen specificity
 Supplementary Figure 1 Binding capacity of DNA-barcoded MHC multimers and recovery of antigen specificity (a, b) Fluorescent-based determination of the binding capacity of DNA-barcoded MHC multimers (+barcode)
Supplementary Figure 1 Binding capacity of DNA-barcoded MHC multimers and recovery of antigen specificity (a, b) Fluorescent-based determination of the binding capacity of DNA-barcoded MHC multimers (+barcode)
Novel Heterologous Prime-Boost Vaccine Strategies for HIV. Dan Barouch April 18, 2012
 Novel Heterologous Prime-Boost Vaccine Strategies for HIV Dan Barouch April 18, 2012 Desired Features of a Next Generation HIV-1 Vaccine Candidate The RV1 study suggests that an HIV-1 vaccine is possible
Novel Heterologous Prime-Boost Vaccine Strategies for HIV Dan Barouch April 18, 2012 Desired Features of a Next Generation HIV-1 Vaccine Candidate The RV1 study suggests that an HIV-1 vaccine is possible
What s New in Acute HIV Infection?
 3 4 Disclosure I have received research grants awarded to my institution from Gilead Sciences, Inc. ntiretroviral medications have been provided by Gilead Sciences, Inc. Susan Little, M.D. Professor of
3 4 Disclosure I have received research grants awarded to my institution from Gilead Sciences, Inc. ntiretroviral medications have been provided by Gilead Sciences, Inc. Susan Little, M.D. Professor of
Impact of TLR7/8 Triggering on HIV Pathogenesis
 University Hospital Zurich u Division of Infectious Diseases and Hospital Epidemiology Impact of TLR7/8 Triggering on HIV Pathogenesis Roberto F. Speck, MD Hallmark of HIV-Infection is the Progressive
University Hospital Zurich u Division of Infectious Diseases and Hospital Epidemiology Impact of TLR7/8 Triggering on HIV Pathogenesis Roberto F. Speck, MD Hallmark of HIV-Infection is the Progressive
Replicating measles-shiv vaccine induces long term preservation of central memory CD4 cells in the gut of macaques challenged with SHIV89.
 Replicating measles-shiv vaccine induces long term preservation of central memory CD4 cells in the gut of macaques challenged with SHIV89.6P Frédéric Tangy Viral Genomics and Vaccination Laboratory Measles
Replicating measles-shiv vaccine induces long term preservation of central memory CD4 cells in the gut of macaques challenged with SHIV89.6P Frédéric Tangy Viral Genomics and Vaccination Laboratory Measles
Activation of NK Cells by ADCC Antibodies and HIV Disease Progression
 RAPID COMMUNICATION Activation of NK Cells by ADCC Antibodies and HIV Disease Progression Amy W. Chung, BSc, PhD,* Marjon Navis, PhD,* Gamze Isitman, BSc,* Leia Wren, BSc,* Julie Silvers, RN, Janaki Amin,
RAPID COMMUNICATION Activation of NK Cells by ADCC Antibodies and HIV Disease Progression Amy W. Chung, BSc, PhD,* Marjon Navis, PhD,* Gamze Isitman, BSc,* Leia Wren, BSc,* Julie Silvers, RN, Janaki Amin,
Immunologic Failure and Chronic Inflammation. Steven G. Deeks Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco
 Immunologic Failure and Chronic Inflammation Steven G. Deeks Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco Plasma HIV RNA (log) 6 5 4 3 2 52 year old HIV+/HCV+ man presents with symptomatic
Immunologic Failure and Chronic Inflammation Steven G. Deeks Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco Plasma HIV RNA (log) 6 5 4 3 2 52 year old HIV+/HCV+ man presents with symptomatic
Fayth K. Yoshimura, Ph.D. September 7, of 7 HIV - BASIC PROPERTIES
 1 of 7 I. Viral Origin. A. Retrovirus - animal lentiviruses. HIV - BASIC PROPERTIES 1. HIV is a member of the Retrovirus family and more specifically it is a member of the Lentivirus genus of this family.
1 of 7 I. Viral Origin. A. Retrovirus - animal lentiviruses. HIV - BASIC PROPERTIES 1. HIV is a member of the Retrovirus family and more specifically it is a member of the Lentivirus genus of this family.
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Nat Med. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2010 September 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nat Med. 2010 March ; 16(3): 319 323. doi:10.1038/nm.2089. Mosaic HIV-1 Vaccines Expand the Breadth and Depth of Cellular Immune Responses
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nat Med. 2010 March ; 16(3): 319 323. doi:10.1038/nm.2089. Mosaic HIV-1 Vaccines Expand the Breadth and Depth of Cellular Immune Responses
Human T Cell Lymphotropic Virus (HTLV) Type 1 Specific CD8 + T Cells: Frequency and Immunodominance Hierarchy
 MAJOR ARTICLE Human T Cell Lymphotropic Virus (HTLV) Type 1 Specific CD8 + T Cells: Frequency and Immunodominance Hierarchy Peter K. C. Goon, 1,a Alix Biancardi, 1,a Noam Fast, 1 Tadahiko Igakura, 1,b
MAJOR ARTICLE Human T Cell Lymphotropic Virus (HTLV) Type 1 Specific CD8 + T Cells: Frequency and Immunodominance Hierarchy Peter K. C. Goon, 1,a Alix Biancardi, 1,a Noam Fast, 1 Tadahiko Igakura, 1,b
Supplementary Figure 1. ALVAC-protein vaccines and macaque immunization. (A) Maximum likelihood
 Supplementary Figure 1. ALVAC-protein vaccines and macaque immunization. (A) Maximum likelihood tree illustrating CRF01_AE gp120 protein sequence relationships between 107 Envs sampled in the RV144 trial
Supplementary Figure 1. ALVAC-protein vaccines and macaque immunization. (A) Maximum likelihood tree illustrating CRF01_AE gp120 protein sequence relationships between 107 Envs sampled in the RV144 trial
Potential Elucidation of a Novel CTL Epitope in HIV-1 Protease by the Protease Inhibitor Resistance Mutation L90M
 Potential Elucidation of a Novel CTL Epitope in HIV-1 Protease by the Protease Inhibitor Resistance Mutation L90M Werner Smidt* Bioinformatics and Computational Biology Unit, Department of Biochemistry,
Potential Elucidation of a Novel CTL Epitope in HIV-1 Protease by the Protease Inhibitor Resistance Mutation L90M Werner Smidt* Bioinformatics and Computational Biology Unit, Department of Biochemistry,
Frequency and Dynamics of Transmitted Polymorphisms and their Impact on Early Pathogenesis in Heterosexual Couples in Zambia
 Frequency and Dynamics of Transmitted Polymorphisms and their Impact on Early Pathogenesis in Heterosexual Couples in Zambia 8 th International Workshop on HIV Transmission Principles of Intervention Barcelona,
Frequency and Dynamics of Transmitted Polymorphisms and their Impact on Early Pathogenesis in Heterosexual Couples in Zambia 8 th International Workshop on HIV Transmission Principles of Intervention Barcelona,
Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance. Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco
 Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco EIP Symposium Feb 2016 Why do some people respond to therapeutic proteins?
Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco EIP Symposium Feb 2016 Why do some people respond to therapeutic proteins?
With over 20 drugs and several viable regimens, the mo6vated pa6ent with life- long access to therapy can control HIV indefinitely, elimina6ng the
 Towards an HIV Cure Steven G. Deeks, MD Professor of Medicine in Residence HIV/AIDS Division University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) WorldMedSchool; July 22, 2013 1 With over 20 drugs and several
Towards an HIV Cure Steven G. Deeks, MD Professor of Medicine in Residence HIV/AIDS Division University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) WorldMedSchool; July 22, 2013 1 With over 20 drugs and several
Supplementary information. Early development of broad neutralizing antibodies in HIV-1 infected infants
 Supplementary information Early development of broad neutralizing antibodies in HIV-1 infected infants Leslie Goo, Vrasha Chohan, Ruth Nduati, Julie Overbaugh Supplementary Figure 1. Neutralization profile
Supplementary information Early development of broad neutralizing antibodies in HIV-1 infected infants Leslie Goo, Vrasha Chohan, Ruth Nduati, Julie Overbaugh Supplementary Figure 1. Neutralization profile
Immunization with single-cycle SIV significantly reduces viral loads after an intravenous challenge with SIV(mac)239
 University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms Preventive and Behavioral Medicine Publications and Presentations Preventive and Behavioral Medicine 1-23-2009 Immunization with single-cycle
University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms Preventive and Behavioral Medicine Publications and Presentations Preventive and Behavioral Medicine 1-23-2009 Immunization with single-cycle
Efficacy Results from the Step Study
 Efficacy Results from the Step Study (Merck V520 Protocol 023/HVTN 502) A Phase II Test-of-Concept Trial of the MRKAd5 HIV-1 Gag/Pol/Nef Trivalent Vaccine CROI February 5, 2008 Boston, MA Rationale for
Efficacy Results from the Step Study (Merck V520 Protocol 023/HVTN 502) A Phase II Test-of-Concept Trial of the MRKAd5 HIV-1 Gag/Pol/Nef Trivalent Vaccine CROI February 5, 2008 Boston, MA Rationale for
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SPPLEMENTY INFOMTION 2 =.75 SHPE + 1 (eplicate 2) 2 1 1 2 SHPE + 1 (eplicate 1) Figure S1. eproducibility of SHPE measurements between biological replicates. eactivities corresponding to extension reactions
SPPLEMENTY INFOMTION 2 =.75 SHPE + 1 (eplicate 2) 2 1 1 2 SHPE + 1 (eplicate 1) Figure S1. eproducibility of SHPE measurements between biological replicates. eactivities corresponding to extension reactions
Richard S. Kornbluth, M.D., Ph.D.
 Treatment of established tumors with peritumoral injections of CD40 ligand (CD40L), CpG, poly(i:c), and extracellular ATP in murine models Richard S. Kornbluth, M.D., Ph.D. Disclosure: Richard Kornbluth
Treatment of established tumors with peritumoral injections of CD40 ligand (CD40L), CpG, poly(i:c), and extracellular ATP in murine models Richard S. Kornbluth, M.D., Ph.D. Disclosure: Richard Kornbluth
Supplementary Fig. 1: Ex vivo tetramer enrichment with anti-c-myc beads
 Supplementary Fig. 1: Ex vivo tetramer enrichment with anti-c-myc beads Representative example of comparative ex vivo tetramer enrichment performed in three independent experiments with either conventional
Supplementary Fig. 1: Ex vivo tetramer enrichment with anti-c-myc beads Representative example of comparative ex vivo tetramer enrichment performed in three independent experiments with either conventional
Perforin Expression Directly Ex Vivo by HIV-Specific CD8+ T-Cells Is. Is a Correlate of HIV Elite Control
 Perforin Expression Directly Ex Vivo by HIV-Specific CD8+ T-Cells Is a Correlate of HIV Elite Control The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
Perforin Expression Directly Ex Vivo by HIV-Specific CD8+ T-Cells Is a Correlate of HIV Elite Control The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
IAS 2015 Towards an HIV Cure symposium Vancouver Immune recognition following latency reversal
 IAS 2015 Towards an HIV Cure symposium Vancouver Immune recognition following latency reversal Marcus Altfeld Professor of Medicine Outline Immune recognition of HIV-1-infected cells Kinetics of antigen
IAS 2015 Towards an HIV Cure symposium Vancouver Immune recognition following latency reversal Marcus Altfeld Professor of Medicine Outline Immune recognition of HIV-1-infected cells Kinetics of antigen
Developing Understanding of CMI. Dr Tom Wilkinson Associate Professor of Respiratory Medicine Faculty of Medicine University of Southampton UK
 Pre-existing influenza-specific CD4+ T cells correlate with homologous and heterotypic response and disease protection against influenza challenge in humans Do At Risk Groups Rely more on CMI to Viruses?
Pre-existing influenza-specific CD4+ T cells correlate with homologous and heterotypic response and disease protection against influenza challenge in humans Do At Risk Groups Rely more on CMI to Viruses?
HLA-B*57 micropolymorphism shapes HLA allele-specific epitope. immunogenicity, selection pressure and HIV immune control
 JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 16 November 2011 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.06150-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 16 November 2011 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.06150-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
A HLA-DRB supertype chart with potential overlapping peptide binding function
 A HLA-DRB supertype chart with potential overlapping peptide binding function Arumugam Mohanapriya 1,2, Satish Nandagond 1, Paul Shapshak 3, Uma Kangueane 1, Pandjassarame Kangueane 1, 2 * 1 Biomedical
A HLA-DRB supertype chart with potential overlapping peptide binding function Arumugam Mohanapriya 1,2, Satish Nandagond 1, Paul Shapshak 3, Uma Kangueane 1, Pandjassarame Kangueane 1, 2 * 1 Biomedical
Supplementary Figure 1. Using DNA barcode-labeled MHC multimers to generate TCR fingerprints
 Supplementary Figure 1 Using DNA barcode-labeled MHC multimers to generate TCR fingerprints (a) Schematic overview of the workflow behind a TCR fingerprint. Each peptide position of the original peptide
Supplementary Figure 1 Using DNA barcode-labeled MHC multimers to generate TCR fingerprints (a) Schematic overview of the workflow behind a TCR fingerprint. Each peptide position of the original peptide
Toinform rational design of prophylactic vaccines and
 Kinetics of Expansion of Epitope-Specific T Cell Responses during Primary HIV-1 Infection 1 Emma L. Turnbull, 2 * MaiLee Wong,* Shuyi Wang, Xiping Wei, Nicola A. Jones,* Karen E. Conrod,* Diana Aldam,
Kinetics of Expansion of Epitope-Specific T Cell Responses during Primary HIV-1 Infection 1 Emma L. Turnbull, 2 * MaiLee Wong,* Shuyi Wang, Xiping Wei, Nicola A. Jones,* Karen E. Conrod,* Diana Aldam,
Heterologous Tier 1 R5 SHIV-C Challenges: Correlates of Protection
 Heterologous Tier 1 R5 SHIV-C Challenges: Correlates of Protection Enterprise Meeting: The Appropriate Use of Tiered Virus Panels when Assessing HIV-1 Vaccine-elicited Neutralizing Antibodies" July 7 th,
Heterologous Tier 1 R5 SHIV-C Challenges: Correlates of Protection Enterprise Meeting: The Appropriate Use of Tiered Virus Panels when Assessing HIV-1 Vaccine-elicited Neutralizing Antibodies" July 7 th,
L I F E S C I E N C E S
 1a L I F E S C I E N C E S 5 -UUA AUA UUC GAA AGC UGC AUC GAA AAC UGU GAA UCA-3 5 -TTA ATA TTC GAA AGC TGC ATC GAA AAC TGT GAA TCA-3 3 -AAT TAT AAG CTT TCG ACG TAG CTT TTG ACA CTT AGT-5 OCTOBER 31, 2006
1a L I F E S C I E N C E S 5 -UUA AUA UUC GAA AGC UGC AUC GAA AAC UGU GAA UCA-3 5 -TTA ATA TTC GAA AGC TGC ATC GAA AAC TGT GAA TCA-3 3 -AAT TAT AAG CTT TCG ACG TAG CTT TTG ACA CTT AGT-5 OCTOBER 31, 2006
