Principle of the FluoroSpot assay. Anti-tag mab-green. Streptavidin-Red. Detection mab-tag. Detection mab-biotin. Analyte. Analyte.
|
|
|
- Ethan Cannon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FluoroSpot 1
2 The principle objective of the FluoroSpot assay is the simultaneous measurement of dual cytokine secretion at the single cell level. This is accomplished by using a mixture of monoclonal antibodies (mabs) with different cytokine specificities in a sandwich assay. Unlike the related ELISpot method, the FluoroSpot assay employs fluorophore-labeled detection reagents, which enable analysis of several cytokines or other secreted analytes in the same well. The ELISpot assay has proven particularly useful when studying specific immune responses in infections, cancer, allergies and autoimmune diseases. Due to its simplicity and high sensitivity, it has become a standard tool in the development of new vaccines and monitoring of vaccine trials. However, due to the enzyme/substrate based detection, ELISpot is limited with regard to the number of different cytokines/analytes which can be analyzed in each well. Usually only one parameter per well is analyzed and IFN-γ has been the analyte of choice serving as an immunocorrelate for T-cell responses. To increase the versatility of the method and in response to the recent interest in antigenspecific polyfunctional T cells 1-8, Mabtech has developed FluoroSpot assays that differentiate between cells secreting one or both of two cytokines in the same well The FluoroSpot assay, which is as sensitive and simple to perform as the ELISpot, utilizes biotinylated detection mab for one analyte and tag-labeled detection mab for the other analyte (see Fig. 1). The detection step is amplified by secondary addition of Streptavidin conjugated to a red fluorophore and an anti-tag mab labeled with a green fluorophore. Spot analysis is performed with an automated fluorescence reader generating separate images for the two fluorophores. Two-colored spots, derived from cells secreting dual cytokines are identified by an analysis of co-positioned spots in a digital overlay of the single stain images (see Fig. 2). This procedure currently allows for analysis of two analytes in the same well, but can principally be extended to detect three or more analytes simultaneously Experimental systems for three-color FluoroSpot have been described 13 but the method needs further development before commercial reagents are made available. The FluoroSpot procedure (Example IFN-γ/IL-2) 1) A mixture of capture mabs specific for IFN-γ and IL-2 is added to an ethanol treated 96-well PVDF plate. 2) Cells are added in the presence or absence (control) of specific stimulus. 3) Activated cells start to produce and secrete cytokines that bind to the capture mabs. 4) Cells are removed and a mixture of tag-labeled anti-ifn-γ and biotinylated anti-il-2 detection mabs is added. 5) To amplify the detection, a mixture of antitag-green and Streptavidin-red is added. 6) Finally, a fluorescence enhancer solution is added. 7) The dried plate is preferably analyzed in an automated fluorescence plate reader fitted with separate filters for the two fluorophores. Anti-tag mab-green Streptavidin-Red Detection mab-tag Analyte Capture mab Detection mab-biotin Analyte Capture mab Figure 1. Principle of the FluoroSpot assay 2
3 Applications The FluoroSpot assay is well suited for individual tests as well as for large scale screening. The current method offers several advantages over ELISpot and can be applied to essentially any system where one would like to monitor dual protein secretion at the single cell level. The ability to analyze two analytes in the same well gives a more detailed characterization of T-cell populations and is particularly beneficial when the supply of cells is limited. Due to its higher sensitivity compared to flow cytometry, the FluoroSpot method is especially attractive in conditions where the producing cells represent only a small fraction of the cell population. IFN-γ T cells An interest in many vaccine development studies is to identify antigen-specific polyfunctional T cells. In several studies, cells co-expressing IFN-γ and IL-2 in particular, but also other cytokines like TNF-α and MIP-1β, have been suggested to represent cells more closely related to protective immunity than cells expressing only one of these cytokines 1-8. Figure 2 shows a FluoroSpot analysis of cells secreting IFN-γ and/or IL-2 in response to the CEF pool of MHC class-i restricted peptides derived from CMV, EBV and Flu 14. The CD8 + T-cell mediated response was dominated by IFN-γ-secreting cells of which a portion also secreted IL-2. The majority of IL-2-secreting cells also secreted IFN-γ. IL-2 Image overlay IFN-γ/IL-2 Figure 2. FluoroSpot analysis of human IFN-γ/ IL-2-secreting cells. PBMC (200,000 cells/well) were stimulated overnight with a pool of MHC class I-restricted peptides 14 derived from CMV, EBV and Flu (available from Mabtech as CEF peptide pool ) in the presence of anti-cd28 antibody. Cells secreting both cytokines (about 40% of responding cells) create yellow spots in an overlay of green and red images. The number of double colored spots in control wells with unstimulated cells were <1. Spot analysis was made with an ispot reader from AID (Autoimmun Diagnostika GmbH). Number of spots/well IFN -γ single IL-2 single IFN -γ/il-2-3
4 One recently published example of the value of the FluoroSpot method to delineate functional T-cell subsets is a study that distinguishes different clinical stages of human tuberculosis infection by using single and dual cytokine profiling 12. Other examples include the combined analysis of T-helper 1 (Th1) versus Th2 or Th1 versus Th17 responses as demonstrated in Figure 3. Other immune cells In addition to T cells, FluoroSpot may also be used to analyze other cells such as dendritic cells, monocytes and B cells. Figure 4 shows an analysis of cytokine secretion by monocytes where it may be useful for delineating distinct subpopulations based on their cytokine profile 15. Image overlay IL-6/GM-CSF Image overlay IFN-γ/IL-17A Number of spots/well Number of spots/well IFN -γ single IL-17A single IFN -γ/il -17A Figure 3. FluoroSpot analysis of human Th1 and Th17 cells in the same well. PBMC (500,000 cells/well) were stimulated overnight with an antigen extract from Candida albicans. 0 IL-6 single GM -CSF single IL-6/GM -CSF Figure 4. FluoroSpot analysis of cytokine secretion by human monocytes. Lipoteichoic acid (LTA) was used to induce Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) and IL-6 secretion by purified PBMC. Cells (4,000 cells/well) were incubated for 20 hours in the presence or absence of LTA. In the image overlay, yellow spots represent cells secreting both cytokines (about 30% of secreting cells). Wells with cells cultured in medium alone (no stimuli) are not shown but contained <5 spots. 4
5 The B-cell FluoroSpot can identify and enumerate both the total number of antibody-secreting cells in a sample and those secreting antibodies to a specific antigen. Detection based on fluorophores offers the possibility to analyze the secretion of different immunoglobulin isotypes or subclasses in the same well, thereby saving cell material. Major application areas are analysis of B-cell responses in various diseases and those elicited by vaccination. An example of a vaccine-induced response to swine flu (H1N1) is shown in Figure 5, where the number of antigen-specific IgA- and IgG-secreting cells was investigated before and after vaccination with Pandemrix (GlaxoSmithKline) 16. (A) Flu-specific IgA (green) and IgG (red) secreting B cells. Figure 5. (A) FluoroSpot analysis of swine flu specific IgA and IgG secretion by in vivo activated human B cells. PBMC were collected before and one week after vaccination with Pandemrix. Wells were coated with 0.75 μg of antigen per well. After overnight culturing of PBMC (200,000 cells/well), spots were detected by adding a mixture of anti-iga-green and anti-igg-red. There were no detectable spots before vaccination. (B) Analysis of B cells secreting IgA and IgG is shown as a reference. Wells were coated with a mixture of anti-igg and anti-iga capture mabs. After overnight culturing of PBMC (100,000 cells/well), spots were detected by adding a mixture of anti-iga-green and anti-igg-red. (B) Total IgA (green) and IgG (red) secreting B cells. FluoroSpot applications include: Analysis of polyfunctional T cells in infection, cancer, allergy and autoimmune disease. Monitoring and characterization of vaccine-induced T-cell responses. Analysis of T cells with distinct cytokine profiles (e.g. Th1 and Th17). Determination of Th1 versus Th2 responses in allergies and allergen immunotherapy. Enumeration of B cells secreting antigen-specific antibodies of different isotypes (e.g. IgG and IgA). 5
6 Untreated Analysis of plates We recommend the use of an automated reader with filters for FITC and Cy3. The plate should be completely dry before analysis. Although the fluorescence in dry plates has been found to be stable (plates can be saved for months), it is recommended to analyze the plate within one week of development since the PVDF membrane may brighten over time. Although of low significance, false dual spots may occur, i.e. two adjacent cells secreting either of the two cytokines of interest may erroneously be counted as a dual spot. The number of such spots is primarily dependent on the number of spots of each cytokine in the well and the reader count settings (e.g. maximal distance between spot centers). One way to practically estimate the potential frequency of false dual spots in any given experiment is to analyze overlays of green and red images from different wells 13. All dual spots in such non-matched overlays will represent false positive spots. Ethanol-treated Figure 6. Impact of ethanol treatment of low fluorescent PVDF membrane plates prior to the coating step in human IL-2 FluoroSpot analysis. Technical aspects Several aspects of the FluoroSpot assay protocol are critical to achieve optimal detection of spots. The choice of highly specific mabs is the foundation for other aspects of optimization. To enable efficient binding of the capture mabs, we recommend using plates with low fluorescent PVDF membrane briefly pre-treated with ethanol (see Fig. 6). A high density of the capture mabs is important and will increase both quality and number of spots. This is especially critical when monitoring cell populations that secrete low amounts of cytokines. The final addition of a fluorescence enhancer solution will further increase the fluorescent spot signals. Stimulation of CD28 While antigen-specific T-cell stimulation is critically dependent on the interaction between the T-cell receptor and its cognate antigen, additional co-stimulatory signals from antigenpresenting cells and the surrounding cytokine environment are also required. These signals are not always optimally provided under in vitro cell culture conditions, which in turn may lead to suboptimal responses. Furthermore, in the FluoroSpot analysis, the possible biological effect of cytokine capture has to be taken into consideration 17. IL-2 is pivotal in T-cell activation and the presence of IL-2 capture mabs in a well will result in a reduced availability of free IL-2 in the culture, which in turn may result in reduced activation of IFN-γ- and IL-2-secreting T cells. To compensate for possible suboptimal conditions in the in vitro culture and to circumvent the attenuating effect of IL-2 capture, anti-cd28 mab can be added to the culture. An appropriate concentration of anti- CD28 mab will not increase the spontaneous secretion of cytokines in the absence of specific stimulus but will elevate the stimulator-specific 6
7 secretion of IL-2 and thus compensate for the effect of cytokine capture. Alternatively, cells can be pre-activated (about 6h) in vials, prior to their addition to the plate, in which case the capture effect will be negligible. Other anti-cytokine capture mabs may also cause capture effects and therefore stimulation of CD28 may be useful in many systems. Positive controls in FluoroSpot Relevant controls are crucial in FluoroSpot. The use of a polyclonal T-cell activator, e.g. certain antibodies to CD3, may serve as a positive control both for cell viability and assay functionality. A multitude of T-cell cytokines are elicited by this stimulation and this control can thus be used in a variety of FluoroSpot assays. Other commonly used positive controls include phytohemagglutinin (PHA) and concanavalin A (ConA). Both are potent T-cell activators and can be used in a similar way as anti-cd3 antibodies for activation of CD4 + and CD8 + T cells. A more specific positive control is the CEF peptide pool 14 mentioned earlier, which is based on viral antigens to which most people have specific T cells. It efficiently induces antigenspecific IFN-γ production by virus-specific CD8 + T cells in almost 90% of Caucasians. In addition to serving as a positive control, the CEF peptide pool is useful for standardization procedures. In summary Mabtech has worked extensively for more than 20 years to optimize the ELISpot protocol. Building on this experience, we have during the last years developed and optimized the FluoroSpot protocol by determining the best capture/detection mab pairs, fluorophores, concentration of reagents, choice and treatment of plates, etc. Our goal is to ensure delivery of analytical systems with the most accurate performance. If you have questions or wish to discuss applications or optimization strategies for the FluoroSpot assays, please contact us directly (see back cover for contact details). We continuously expand our range of FluoroSpot kits. For an updated list, please visit References 1. De Rosa SC, et al. Vaccination in humans generates broad T cell cytokine responses. J. Immunol. 173:5372, Harari A, et al. Skewed representation of functionally distinct populations of virus-specific CD4 T cells in HIV- 1-infected subjects with progressive disease: changes after antiretroviral theraphy. Blood 103:966, Betts MR, et al. HIV nonprogressors preferentially maintain highly functional HIV-specific CD8 + T cells. Blood 107:4781, Duvall MG, et al. Polyfunctional T cell responses are a hallmark of HIV-2 infection. Eur. J. Immunol. 38: 350, Ferre AL, et al. Mucosal immune responses to HIV-1 in elite controllers: A potential correlate of immune control. Blood 113:3978, Sun Y, et al. Magnitude and Quality of Vaccine-Elicited T-Cell Responses in the Control of Immunodeficiency Virus Replication in Rhesus Monkeys. J. Virol. 82:8812, Day CL, et al. Detection of polyfunctional Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific T cells and association with viral load in HIV-1-infected persons. J. Infect. Dis. 197:990, Darrah PA, et al. Multifunctional T H 1 cells define a correlate of vaccine-mediated protection against Leishmania major. Nat. Med. 7:843, Ahlborg N, et al. Dual- and triple-color fluorospot. Methods Mol. Biol. 792:77, Hallengärd D, et al. Comparison of plasmid vaccine immunization schedules using intradermal in vivo electroporation. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 18:1577, Gazagne A, et al. A Fluorospot assay to detect single T lymphocytes simultaneously producing multiple cytokines. J. Immunol. Methods 283: 91, Casey R, et al. Enumeration of functional T-cell subsets by Fluorescence-Immunospot defines signatures of pathogen burden in tuberculosis. PLoS One 5 (12): e15619, Rebhahn JA, et al. Automated analysis of two- and threecolor fluorescent Elispot (Fluorospot) assays for cytokine secretion. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 92:54, Currier JR, et al. A panel of MHC class I restricted viral peptides for use as a quality control for vaccine trial ELISPOT assays. J. Immunol. Methods 260:157, Smedman C, et al. FluoroSpot analysis of TLR-activated monocytes reveals several distinct cytokine-secreting subpopulations. Scand. J. Immunol. 75:249, Kesa G. Comparison of ELISpot and FluoroSpot in the analysis of swine flu-specific IgG and IgA secretion by in vivo activated human B cells. Cells 1:27, Quast S, et al. IL-2 absorption affect IFN-γ and IL-5, but not IL-4 producing memory T cells in double color cytokine ELISPOT assays. Cell. Immunol. 237:28,
8 Nacka 10/2013 SWEDEN (Head Office): Tel: mabtech@mabtech.com AUSTRALIA: Tel: mabtech.au@mabtech.com FRANCE: 2 Tel: +33 (0) mabtech.fr@mabtech.com GERMANY: Tel: mabtech.de@mabtech.com USA: mabtech.usa@mabtech.com Toll Free: 866 ELI-SPOT ( )
A Dual Color ELISPOT Assay
 A Dual Color ELISPOT Assay Nicole Bernard, Ph.D., Salix Boulet and Michel Lubaki Ndongala, Research Institute of the McGill University Health Center The ELISPOT assay is considered by many to be a gold
A Dual Color ELISPOT Assay Nicole Bernard, Ph.D., Salix Boulet and Michel Lubaki Ndongala, Research Institute of the McGill University Health Center The ELISPOT assay is considered by many to be a gold
Why are validated immunogenicity assays important for HIV vaccine development?
 Why are validated immunogenicity assays important for HIV vaccine development? There is a need to compare immunogenicity of products in the pipeline, when similar or different in class when developed by
Why are validated immunogenicity assays important for HIV vaccine development? There is a need to compare immunogenicity of products in the pipeline, when similar or different in class when developed by
Evaluation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis specific T cell response to ESAT-6 and PPD antigen with ELISPOT assay
 In the name of God Evaluation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis specific T cell response to ESAT-6 and PPD antigen with ELISPOT assay presented by: M. Taheri Symptoms of TB Cough for more than two week Bloody
In the name of God Evaluation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis specific T cell response to ESAT-6 and PPD antigen with ELISPOT assay presented by: M. Taheri Symptoms of TB Cough for more than two week Bloody
Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells Inhibit Cytomegalovirus Inflammation through Interleukin-27 and B7-H4
 Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells Inhibit Cytomegalovirus Inflammation through Interleukin-27 and B7-H4 Ankita Garg, Rodney Trout and Stephen A. Spector,,* Department
Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells Inhibit Cytomegalovirus Inflammation through Interleukin-27 and B7-H4 Ankita Garg, Rodney Trout and Stephen A. Spector,,* Department
Vaccine Delivery and TLR Ligands Influence the Quality of T cell Responses in NHP. Robert A. Seder, M.D. Vaccine Research Center NIAID, NIH
 Vaccine Delivery and TLR Ligands Influence the Quality of T cell Responses in NHP Robert A. Seder, M.D. Vaccine Research Center NIAID, NIH Vaccines Against HIV, Malaria and Tuberculosis Will Require Neutralizing
Vaccine Delivery and TLR Ligands Influence the Quality of T cell Responses in NHP Robert A. Seder, M.D. Vaccine Research Center NIAID, NIH Vaccines Against HIV, Malaria and Tuberculosis Will Require Neutralizing
staining and flow cytometry
 Detection of influenza virus-specific T cell responses by intracellular by cytokine intracellular staining cytokine staining and flow cytometry Detection of influenza virus-specific T cell responses and
Detection of influenza virus-specific T cell responses by intracellular by cytokine intracellular staining cytokine staining and flow cytometry Detection of influenza virus-specific T cell responses and
Bead Based Assays for Cytokine Detection
 Bead Based Assays for Cytokine Detection September 27, 2014 6 th EFIS-EJI South East European Immunology School SEEIS 2014 Timisoara, Romania The Cells of the Immune System The Immune Reaction (Th2) (Th1)
Bead Based Assays for Cytokine Detection September 27, 2014 6 th EFIS-EJI South East European Immunology School SEEIS 2014 Timisoara, Romania The Cells of the Immune System The Immune Reaction (Th2) (Th1)
Chapter 35 Active Reading Guide The Immune System
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 35 Active Reading Guide The Immune System Section 1 Phagocytosis plays an important role in the immune systems of both invertebrates and vertebrates. Review the process
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 35 Active Reading Guide The Immune System Section 1 Phagocytosis plays an important role in the immune systems of both invertebrates and vertebrates. Review the process
Cellular Immunity in Aging and HIV: Correlates of Protection. Immune Senescence
 Cellular Immunity in Aging and HIV: Correlates of Protection Janet E. McElhaney, MD Professor of Medicine Allan M. McGavin Chair in Research Geriatrics University of British Columbia Vancouver, BC and
Cellular Immunity in Aging and HIV: Correlates of Protection Janet E. McElhaney, MD Professor of Medicine Allan M. McGavin Chair in Research Geriatrics University of British Columbia Vancouver, BC and
Challenges in Development and Validation of an Intracellular Cytokine Staining assay
 Challenges in Development and Validation of an Intracellular Cytokine Staining assay Jenny Hendriks, Crucell Hatching @ EBF, Brussels, June 202 www.crucell.com Vaccines vs Protein therapeutics Protein
Challenges in Development and Validation of an Intracellular Cytokine Staining assay Jenny Hendriks, Crucell Hatching @ EBF, Brussels, June 202 www.crucell.com Vaccines vs Protein therapeutics Protein
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry:
 Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry: Simultaneous Detection of Cytokines and Transcription Factors An encore presentation by Jurg Rohrer, PhD, BD Biosciences 10.26.10 Outline Introduction Cytokines
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry: Simultaneous Detection of Cytokines and Transcription Factors An encore presentation by Jurg Rohrer, PhD, BD Biosciences 10.26.10 Outline Introduction Cytokines
Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154 + CD4 + T cells Rapid antigen-reactive T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE)
 Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154 + CD4 + T cells Rapid antigen-reactive T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central
Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154 + CD4 + T cells Rapid antigen-reactive T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central
The Adaptive Immune Responses
 The Adaptive Immune Responses The two arms of the immune responses are; 1) the cell mediated, and 2) the humoral responses. In this chapter we will discuss the two responses in detail and we will start
The Adaptive Immune Responses The two arms of the immune responses are; 1) the cell mediated, and 2) the humoral responses. In this chapter we will discuss the two responses in detail and we will start
Third line of Defense
 Chapter 15 Specific Immunity and Immunization Topics -3 rd of Defense - B cells - T cells - Specific Immunities Third line of Defense Specific immunity is a complex interaction of immune cells (leukocytes)
Chapter 15 Specific Immunity and Immunization Topics -3 rd of Defense - B cells - T cells - Specific Immunities Third line of Defense Specific immunity is a complex interaction of immune cells (leukocytes)
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry:
 Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry: Simultaneous Detection of Cytokines and Transcription Factors Presented by Jurg Rohrer, PhD, BD Biosciences 23-10780-00 Outline Introduction Cytokines Transcription
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry: Simultaneous Detection of Cytokines and Transcription Factors Presented by Jurg Rohrer, PhD, BD Biosciences 23-10780-00 Outline Introduction Cytokines Transcription
Rapid antigen-specific T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE)
 Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154+CD4+ T cell Rapid antigen-specific T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central role
Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154+CD4+ T cell Rapid antigen-specific T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central role
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS. Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT
 ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
Commercially available HLA Class II tetramers (Beckman Coulter) conjugated to
 Class II tetramer staining Commercially available HLA Class II tetramers (Beckman Coulter) conjugated to PE were combined with dominant HIV epitopes (DRB1*0101-DRFYKTLRAEQASQEV, DRB1*0301- PEKEVLVWKFDSRLAFHH,
Class II tetramer staining Commercially available HLA Class II tetramers (Beckman Coulter) conjugated to PE were combined with dominant HIV epitopes (DRB1*0101-DRFYKTLRAEQASQEV, DRB1*0301- PEKEVLVWKFDSRLAFHH,
Immunology. T-Lymphocytes. 16. Oktober 2014, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Karin Peters,
 Immunology T-Lymphocytes 16. Oktober 2014, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Karin Peters, karin.peters@rub.de The role of T-effector cells in the immune response against microbes cellular immunity humoral immunity
Immunology T-Lymphocytes 16. Oktober 2014, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Karin Peters, karin.peters@rub.de The role of T-effector cells in the immune response against microbes cellular immunity humoral immunity
Treatment with IL-7 Prevents the Decline of Circulating CD4 + T Cells during the Acute Phase of SIV Infection in Rhesus Macaques
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION FOR: Treatment with IL-7 Prevents the Decline of Circulating CD4 + T Cells during the Acute Phase of SIV Infection in Rhesus Macaques Lia Vassena, 1,2 Huiyi Miao, 1 Raffaello Cimbro,
SUPPORTING INFORMATION FOR: Treatment with IL-7 Prevents the Decline of Circulating CD4 + T Cells during the Acute Phase of SIV Infection in Rhesus Macaques Lia Vassena, 1,2 Huiyi Miao, 1 Raffaello Cimbro,
Supplementary Data Table of Contents:
 Supplementary Data Table of Contents: - Supplementary Methods - Supplementary Figures S1(A-B) - Supplementary Figures S2 (A-B) - Supplementary Figures S3 - Supplementary Figures S4(A-B) - Supplementary
Supplementary Data Table of Contents: - Supplementary Methods - Supplementary Figures S1(A-B) - Supplementary Figures S2 (A-B) - Supplementary Figures S3 - Supplementary Figures S4(A-B) - Supplementary
CD4 + T-cell-inducing HIV vaccines may have an impact on viral control
 CD4 + T-cell-inducing HIV vaccines may have an impact on viral control Clues from cytokines produced by CD4 + T-cells from HIVinfected patients and vaccinated seronegative volunteers Eva Van Braeckel 1,
CD4 + T-cell-inducing HIV vaccines may have an impact on viral control Clues from cytokines produced by CD4 + T-cells from HIVinfected patients and vaccinated seronegative volunteers Eva Van Braeckel 1,
Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under normal and pathologic conditions Interleukins,
 Cytokines http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter22/animation the_immune_response.html Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under
Cytokines http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter22/animation the_immune_response.html Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under
Heterosubtypic immunity. Professor Ajit Lalvani FMedSci Chair of Infectious Diseases 14/07/2014
 Protective cellular immune correlates against pandemic influenza: implications for universal vaccines 2 nd WHO Meeting on development and clinical trials of broadly protective influenza vaccines 5th 7th
Protective cellular immune correlates against pandemic influenza: implications for universal vaccines 2 nd WHO Meeting on development and clinical trials of broadly protective influenza vaccines 5th 7th
Generation of monocytederived Dendritic Cells (modcs)
 monocytederived Dendritic (modcs) Application Note Background Dendritic (DCs) are so called because of their characteristic cell surface projections that resemble the dendrites of neurons (see Fig 1 and
monocytederived Dendritic (modcs) Application Note Background Dendritic (DCs) are so called because of their characteristic cell surface projections that resemble the dendrites of neurons (see Fig 1 and
Using Multiplex Assays and Assay Development to Enhance your Research Program James A. Lederer, PhD
 Using Multiplex Assays and Assay Development to Enhance your Research Program James A. Lederer, PhD Department of Surgery Brigham and Women s Hospital (BWH), BWH Biomedical Research Institute (BWH-BRI)
Using Multiplex Assays and Assay Development to Enhance your Research Program James A. Lederer, PhD Department of Surgery Brigham and Women s Hospital (BWH), BWH Biomedical Research Institute (BWH-BRI)
Innate and Cellular Immunology Control of Infection by Cell-mediated Immunity
 Innate & adaptive Immunity Innate and Cellular Immunology Control of Infection by Cell-mediated Immunity Helen Horton PhD Seattle Biomedical Research Institute Depts of Global Health & Medicine, UW Cellular
Innate & adaptive Immunity Innate and Cellular Immunology Control of Infection by Cell-mediated Immunity Helen Horton PhD Seattle Biomedical Research Institute Depts of Global Health & Medicine, UW Cellular
Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation. Abul K. Abbas UCSF. FOCiS
 1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
Engineering an in vitro human immune system for rapid vaccine evaluation
 Engineering an in vitro human immune system for rapid vaccine evaluation William Warren, Ph.D. VaxDesign Corporation Orlando, FL 32826 wwarren@vaxdesign.com www.vaxdesign.com 1 MIMIC Technology Overview
Engineering an in vitro human immune system for rapid vaccine evaluation William Warren, Ph.D. VaxDesign Corporation Orlando, FL 32826 wwarren@vaxdesign.com www.vaxdesign.com 1 MIMIC Technology Overview
Part III Innate and Adaptive Immune Cells: General Introduction
 Innate and Adaptive Immune Cells: General Introduction Iván López-Expósito As an organ specialized in food digestion and nutrient absorption, the intestinal mucosa presents a huge surface area (almost
Innate and Adaptive Immune Cells: General Introduction Iván López-Expósito As an organ specialized in food digestion and nutrient absorption, the intestinal mucosa presents a huge surface area (almost
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Valkenburg et al. 10.1073/pnas.1403684111 SI Materials and Methods ELISA and Microneutralization. Sera were treated with Receptor Destroying Enzyme II (RDE II, Accurate) before ELISA
Supporting Information Valkenburg et al. 10.1073/pnas.1403684111 SI Materials and Methods ELISA and Microneutralization. Sera were treated with Receptor Destroying Enzyme II (RDE II, Accurate) before ELISA
Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells
 ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Sui et al..7/pnas.997 Pre-CLP CM9 LA9 SL Tat# Pol Vif % Tetramer + CD + CD + Vac+IL- +IL- Vac Fig. S. Frequencies of six different CD + CD + Mamu-A*-tetramer + cells were measured
Supporting Information Sui et al..7/pnas.997 Pre-CLP CM9 LA9 SL Tat# Pol Vif % Tetramer + CD + CD + Vac+IL- +IL- Vac Fig. S. Frequencies of six different CD + CD + Mamu-A*-tetramer + cells were measured
MHC Tetramers and Monomers for Immuno-Oncology and Autoimmunity Drug Discovery
 MHC Tetramers and Monomers for Immuno-Oncology and Autoimmunity Drug Discovery Your Partner in Drug Discovery and Research MHC Tetramer Background T-Cell Receptors recognize and bind to complexes composed
MHC Tetramers and Monomers for Immuno-Oncology and Autoimmunity Drug Discovery Your Partner in Drug Discovery and Research MHC Tetramer Background T-Cell Receptors recognize and bind to complexes composed
CD25-PE (BD Biosciences) and labeled with anti-pe-microbeads (Miltenyi Biotec) for depletion of CD25 +
 Supplements Supplemental Materials and Methods Depletion of CD25 + T-cells from PBMC. Fresh or HD precultured PBMC were stained with the conjugate CD25-PE (BD Biosciences) and labeled with anti-pe-microbeads
Supplements Supplemental Materials and Methods Depletion of CD25 + T-cells from PBMC. Fresh or HD precultured PBMC were stained with the conjugate CD25-PE (BD Biosciences) and labeled with anti-pe-microbeads
Adaptive Immunity. Jeffrey K. Actor, Ph.D. MSB 2.214,
 Adaptive Immunity Jeffrey K. Actor, Ph.D. MSB 2.214, 500-5344 Lecture Objectives: Understand role of various molecules including cytokines, chemokines, costimulatory and adhesion molecules in the development
Adaptive Immunity Jeffrey K. Actor, Ph.D. MSB 2.214, 500-5344 Lecture Objectives: Understand role of various molecules including cytokines, chemokines, costimulatory and adhesion molecules in the development
Mouse Serum Anti-HDM IgE Antibody Assay Kit
 Mouse Serum Anti-HDM IgE Antibody Assay Kit Catalog # 3037 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Asthma is a common chronic inflammatory disease that affects 300 million people
Mouse Serum Anti-HDM IgE Antibody Assay Kit Catalog # 3037 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Asthma is a common chronic inflammatory disease that affects 300 million people
System Biology analysis of innate and adaptive immune responses during HIV infection
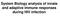 System Biology analysis of innate and adaptive immune responses during HIV infection Model of T cell memory persistence and exhaustion Naive Ag+APC Effector TEM (Pfp, Gr.B, FasL, TNF) Ag stim. IL-2, IL-7,
System Biology analysis of innate and adaptive immune responses during HIV infection Model of T cell memory persistence and exhaustion Naive Ag+APC Effector TEM (Pfp, Gr.B, FasL, TNF) Ag stim. IL-2, IL-7,
Immunity. Acquired immunity differs from innate immunity in specificity & memory from 1 st exposure
 Immunity (1) Non specific (innate) immunity (2) Specific (acquired) immunity Characters: (1) Non specific: does not need special recognition of the foreign cell. (2) Innate: does not need previous exposure.
Immunity (1) Non specific (innate) immunity (2) Specific (acquired) immunity Characters: (1) Non specific: does not need special recognition of the foreign cell. (2) Innate: does not need previous exposure.
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adaptive immune response biologic response modifiers and, 735 737 S-Adenosylmethionine (SAMe) for hepatitis, 825 826 Albinterferon for hepatitis,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adaptive immune response biologic response modifiers and, 735 737 S-Adenosylmethionine (SAMe) for hepatitis, 825 826 Albinterferon for hepatitis,
Microbiology 204: Cellular and Molecular Immunology
 Microbiology 204: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Class meets MWF 1:00-2:30PM (*exceptions: no class Fri Sept 23, Fri Oct 14, Nov 11, or Wed Nov 23) Lectures are open to auditors and will be live-streamed
Microbiology 204: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Class meets MWF 1:00-2:30PM (*exceptions: no class Fri Sept 23, Fri Oct 14, Nov 11, or Wed Nov 23) Lectures are open to auditors and will be live-streamed
TNF-alpha ELISA. For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
 TNF-alpha ELISA For the quantitative determination of TNF-alpha in serum, plasma, buffered solution or cell culture medium. For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog Number:
TNF-alpha ELISA For the quantitative determination of TNF-alpha in serum, plasma, buffered solution or cell culture medium. For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog Number:
Mouse Anti-OVA IgM Antibody Assay Kit
 Mouse Anti-OVA IgM Antibody Assay Kit Catalog # 3017 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Ovalbumin (OVA) is a widely used antigen for inducing allergic reactions in experimental
Mouse Anti-OVA IgM Antibody Assay Kit Catalog # 3017 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Ovalbumin (OVA) is a widely used antigen for inducing allergic reactions in experimental
M.Sc. III Semester Biotechnology End Semester Examination, 2013 Model Answer LBTM: 302 Advanced Immunology
 Code : AS-2246 M.Sc. III Semester Biotechnology End Semester Examination, 2013 Model Answer LBTM: 302 Advanced Immunology A. Select one correct option for each of the following questions:- 2X10=10 1. (b)
Code : AS-2246 M.Sc. III Semester Biotechnology End Semester Examination, 2013 Model Answer LBTM: 302 Advanced Immunology A. Select one correct option for each of the following questions:- 2X10=10 1. (b)
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material accompanying the manuscript Interleukin 37 is a fundamental inhibitor of innate immunity Marcel F Nold, Claudia A Nold-Petry, Jarod A Zepp, Brent E Palmer, Philip Bufler & Charles
Supplementary Material accompanying the manuscript Interleukin 37 is a fundamental inhibitor of innate immunity Marcel F Nold, Claudia A Nold-Petry, Jarod A Zepp, Brent E Palmer, Philip Bufler & Charles
Supplementary Figures
 Inhibition of Pulmonary Anti Bacterial Defense by IFN γ During Recovery from Influenza Infection By Keer Sun and Dennis W. Metzger Supplementary Figures d a Ly6G Percentage survival f 1 75 5 1 25 1 5 1
Inhibition of Pulmonary Anti Bacterial Defense by IFN γ During Recovery from Influenza Infection By Keer Sun and Dennis W. Metzger Supplementary Figures d a Ly6G Percentage survival f 1 75 5 1 25 1 5 1
Measuring Dendritic Cells
 Measuring Dendritic Cells A.D. Donnenberg, V.S. Donnenberg UNIVERSITY of PITTSBURGH CANCER INSTITUTE CCS Longbeach 10_04 Measuring DC Rare event detection The basics of DC measurement Applications Cancer
Measuring Dendritic Cells A.D. Donnenberg, V.S. Donnenberg UNIVERSITY of PITTSBURGH CANCER INSTITUTE CCS Longbeach 10_04 Measuring DC Rare event detection The basics of DC measurement Applications Cancer
MHC MULTIMER PROFICIENCY PANEL 2017
 MHC MULTIMER PROFICIENCY PANEL 2017 August 2017 CONTACT Charlotte Halgreen ProficiencyPanel@immudex.com FOR MORE INFORMATION www.proficiencypanel.com MHC MULTIMER PROFICIENCY PANEL 2017 This report summarizes
MHC MULTIMER PROFICIENCY PANEL 2017 August 2017 CONTACT Charlotte Halgreen ProficiencyPanel@immudex.com FOR MORE INFORMATION www.proficiencypanel.com MHC MULTIMER PROFICIENCY PANEL 2017 This report summarizes
1. The scavenger receptor, CD36, functions as a coreceptor for which TLR? a. TLR ½ b. TLR 3 c. TLR 4 d. TLR 2/6
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS, Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 4 (pages 62-74): Innate Immunity
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS, Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 4 (pages 62-74): Innate Immunity
BD CBA on the BD Accuri C6: Bringing Multiplexed Cytokine Detection to the Benchtop
 BD CBA on the BD Accuri C6: Bringing Multiplexed Cytokine Detection to the Benchtop Maria Dinkelmann, PhD Senior Marketing Applications Specialist BD Biosciences, Ann Arbor, MI 23-14380-00 Cellular Communication
BD CBA on the BD Accuri C6: Bringing Multiplexed Cytokine Detection to the Benchtop Maria Dinkelmann, PhD Senior Marketing Applications Specialist BD Biosciences, Ann Arbor, MI 23-14380-00 Cellular Communication
Human Cytomegalovirus Latency-Associated Proteins Elicit Immune-Suppressive IL-10 Producing CD4 + T Cells
 Human Cytomegalovirus Latency-Associated Proteins Elicit Immune-Suppressive IL-10 Producing CD4 + T Cells Gavin M. Mason, Sarah Jackson, Georgina Okecha, Emma Poole, J. G. Patrick Sissons, John Sinclair,
Human Cytomegalovirus Latency-Associated Proteins Elicit Immune-Suppressive IL-10 Producing CD4 + T Cells Gavin M. Mason, Sarah Jackson, Georgina Okecha, Emma Poole, J. G. Patrick Sissons, John Sinclair,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Chapuis et al. 10.1073/pnas.1113748109 SI Methods Selection of Patients, Targets, Isolation, and Expansion of Melanoma- Specific CTL Clones. Patients were HLA-typed, and their tumors
Supporting Information Chapuis et al. 10.1073/pnas.1113748109 SI Methods Selection of Patients, Targets, Isolation, and Expansion of Melanoma- Specific CTL Clones. Patients were HLA-typed, and their tumors
Immune System. Presented by Kazzandra Anton, Rhea Chung, Lea Sado, and Raymond Tanaka
 Immune System Presented by Kazzandra Anton, Rhea Chung, Lea Sado, and Raymond Tanaka Content Standards 35.1 In innate immunity, recognition and response rely on traits common to groups of pathogens 35.2
Immune System Presented by Kazzandra Anton, Rhea Chung, Lea Sado, and Raymond Tanaka Content Standards 35.1 In innate immunity, recognition and response rely on traits common to groups of pathogens 35.2
Understanding basic immunology. Dr Mary Nowlan
 Understanding basic immunology Dr Mary Nowlan 1 Immunology Immunology the study of how the body fights disease and infection Immunity State of being able to resist a particular infection or toxin 2 Overview
Understanding basic immunology Dr Mary Nowlan 1 Immunology Immunology the study of how the body fights disease and infection Immunity State of being able to resist a particular infection or toxin 2 Overview
Towards an HIV Cure Pre-Conference Symposium 20 & 21 July 2012
 Towards an HIV Cure Pre-Conference Symposium 20 & 21 July 2012 Your logo Natural control of HIV infection is associated with an isotype switched IgG antibody response to HIV Gag antigens in patients with
Towards an HIV Cure Pre-Conference Symposium 20 & 21 July 2012 Your logo Natural control of HIV infection is associated with an isotype switched IgG antibody response to HIV Gag antigens in patients with
Cellular Immune response. Jianzhong Chen, Ph.D Institute of immunology, ZJU
 Cellular Immune response Jianzhong Chen, Ph.D Institute of immunology, ZJU Concept of adaptive immune response T cell-mediated adaptive immune response I. Concept of immune response A collective and coordinated
Cellular Immune response Jianzhong Chen, Ph.D Institute of immunology, ZJU Concept of adaptive immune response T cell-mediated adaptive immune response I. Concept of immune response A collective and coordinated
General Overview of Immunology. Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center
 General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance. Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco
 Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco EIP Symposium Feb 2016 Why do some people respond to therapeutic proteins?
Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco EIP Symposium Feb 2016 Why do some people respond to therapeutic proteins?
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry
 Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry Detection of Cytokines, Transcription Factors, and Phosphoprotein by Flow Cytometry Presented by Erika O Donnell, PhD, BD Biosciences 23-14876-00 Outline Basic principles
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry Detection of Cytokines, Transcription Factors, and Phosphoprotein by Flow Cytometry Presented by Erika O Donnell, PhD, BD Biosciences 23-14876-00 Outline Basic principles
The CAPRI-T was one of two (along with the CAPRI-NK, see reference. [29]) basic immunological studies nested within the CAMELIA trial.
![The CAPRI-T was one of two (along with the CAPRI-NK, see reference. [29]) basic immunological studies nested within the CAMELIA trial. The CAPRI-T was one of two (along with the CAPRI-NK, see reference. [29]) basic immunological studies nested within the CAMELIA trial.](/thumbs/88/117921481.jpg) 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Patient description and recruitment The CAPRI-T was one of two (along with the CAPRI-NK, see reference [29]) basic immunological studies nested within the CAMELIA trial. Patients
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Patient description and recruitment The CAPRI-T was one of two (along with the CAPRI-NK, see reference [29]) basic immunological studies nested within the CAMELIA trial. Patients
Development of a VP6 subunit rotavirus vaccine A dual role of VP6 as a vaccine antigen and an adjuvant
 30 August 2018, Minsk 13TH INTERNATIONAL ROTAVIRUS SYMPOSIUM Development of a VP6 subunit rotavirus vaccine A dual role of VP6 as a vaccine antigen and an adjuvant Dr. Vesna Blazevic Head of Laboratory
30 August 2018, Minsk 13TH INTERNATIONAL ROTAVIRUS SYMPOSIUM Development of a VP6 subunit rotavirus vaccine A dual role of VP6 as a vaccine antigen and an adjuvant Dr. Vesna Blazevic Head of Laboratory
Overview: The immune responses of animals can be divided into innate immunity and acquired immunity.
 GUIDED READING - Ch. 43 - THE IMMUNE SYSTEM NAME: Please print out these pages and HANDWRITE the answers directly on the printouts. Typed work or answers on separate sheets of paper will not be accepted.
GUIDED READING - Ch. 43 - THE IMMUNE SYSTEM NAME: Please print out these pages and HANDWRITE the answers directly on the printouts. Typed work or answers on separate sheets of paper will not be accepted.
PBMC from each patient were suspended in AIM V medium (Invitrogen) with 5% human
 Anti-CD19-CAR transduced T-cell preparation PBMC from each patient were suspended in AIM V medium (Invitrogen) with 5% human AB serum (Gemini) and 300 international units/ml IL-2 (Novartis). T cell proliferation
Anti-CD19-CAR transduced T-cell preparation PBMC from each patient were suspended in AIM V medium (Invitrogen) with 5% human AB serum (Gemini) and 300 international units/ml IL-2 (Novartis). T cell proliferation
A Multicistronic DNA Vaccine Induces Significant Protection against Tuberculosis in Mice and Offers Flexibility in the Expressed Antigen Repertoire.
 Company LOGO A Multicistronic DNA Vaccine Induces Significant Protection against Tuberculosis in Mice and Offers Flexibility in the Expressed Antigen Repertoire. Fayaz Ahmad Mir, Stefan H. E. Kaufmann,
Company LOGO A Multicistronic DNA Vaccine Induces Significant Protection against Tuberculosis in Mice and Offers Flexibility in the Expressed Antigen Repertoire. Fayaz Ahmad Mir, Stefan H. E. Kaufmann,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Bellora et al. 10.1073/pnas.1007654108 SI Materials and Methods Cells. NK cells purified from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) of healthy donors (Human NK Cell Isolation
Supporting Information Bellora et al. 10.1073/pnas.1007654108 SI Materials and Methods Cells. NK cells purified from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) of healthy donors (Human NK Cell Isolation
Cell Mediated Immunity (I) Dr. Aws Alshamsan Department of Pharmaceu5cs Office: AA87 Tel:
 Cell Mediated Immunity (I) Dr. Aws Alshamsan Department of Pharmaceu5cs Office: AA87 Tel: 4677363 aalshamsan@ksu.edu.sa Learning Objectives By the end of this lecture you will be able to: 1 Understand
Cell Mediated Immunity (I) Dr. Aws Alshamsan Department of Pharmaceu5cs Office: AA87 Tel: 4677363 aalshamsan@ksu.edu.sa Learning Objectives By the end of this lecture you will be able to: 1 Understand
IMMUNE CELL SURFACE RECEPTORS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS
 LECTURE: 07 Title: IMMUNE CELL SURFACE RECEPTORS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: The chemical nature of the cellular surface receptors. Define the location of the
LECTURE: 07 Title: IMMUNE CELL SURFACE RECEPTORS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: The chemical nature of the cellular surface receptors. Define the location of the
CHAPTER 3 LABORATORY PROCEDURES
 CHAPTER 3 LABORATORY PROCEDURES CHAPTER 3 LABORATORY PROCEDURES 3.1 HLA TYPING Molecular HLA typing will be performed for all donor cord blood units and patients in the three reference laboratories identified
CHAPTER 3 LABORATORY PROCEDURES CHAPTER 3 LABORATORY PROCEDURES 3.1 HLA TYPING Molecular HLA typing will be performed for all donor cord blood units and patients in the three reference laboratories identified
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION
 Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 11 T-Cell Activation, Differentiation, and Memory Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 11 T-Cell Activation, Differentiation, and Memory Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and
Chapter 23 Immunity Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 23 Immunity Exam Study Questions 1. Define 1) Immunity 2) Neutrophils 3) Macrophage 4) Epitopes 5) Interferon 6) Complement system 7) Histamine 8) Mast cells 9) Antigen 10) Antigens receptors 11)
Chapter 23 Immunity Exam Study Questions 1. Define 1) Immunity 2) Neutrophils 3) Macrophage 4) Epitopes 5) Interferon 6) Complement system 7) Histamine 8) Mast cells 9) Antigen 10) Antigens receptors 11)
Grass pollen immunotherapy induces Foxp3 expressing CD4 + CD25 + cells. in the nasal mucosa. Suzana Radulovic MD, Mikila R Jacobson PhD,
 Radulovic 1 1 2 3 Grass pollen immunotherapy induces Foxp3 expressing CD4 + CD25 + cells in the nasal mucosa 4 5 6 7 Suzana Radulovic MD, Mikila R Jacobson PhD, Stephen R Durham MD, Kayhan T Nouri-Aria
Radulovic 1 1 2 3 Grass pollen immunotherapy induces Foxp3 expressing CD4 + CD25 + cells in the nasal mucosa 4 5 6 7 Suzana Radulovic MD, Mikila R Jacobson PhD, Stephen R Durham MD, Kayhan T Nouri-Aria
Chapter 24 The Immune System
 Chapter 24 The Immune System The Immune System Layered defense system The skin and chemical barriers The innate and adaptive immune systems Immunity The body s ability to recognize and destroy specific
Chapter 24 The Immune System The Immune System Layered defense system The skin and chemical barriers The innate and adaptive immune systems Immunity The body s ability to recognize and destroy specific
Dendritic cells in cancer immunotherapy Aimin Jiang
 Dendritic cells in cancer immunotherapy Aimin Jiang Feb. 11, 2014 Dendritic cells at the interface of innate and adaptive immune responses Dendritic cells: initiators of adaptive immune responses Dendritic
Dendritic cells in cancer immunotherapy Aimin Jiang Feb. 11, 2014 Dendritic cells at the interface of innate and adaptive immune responses Dendritic cells: initiators of adaptive immune responses Dendritic
Naive, memory and regulatory T lymphocytes populations analysis
 Naive, memory and regulatory T lymphocytes populations analysis Jaen Olivier, PhD ojaen@beckmancoulter.com Cellular Analysis application specialist Beckman Coulter France Introduction Flow cytometric analysis
Naive, memory and regulatory T lymphocytes populations analysis Jaen Olivier, PhD ojaen@beckmancoulter.com Cellular Analysis application specialist Beckman Coulter France Introduction Flow cytometric analysis
Rapid perforin upregulation directly ex vivo by CD8 + T cells is a defining characteristic of HIV elite controllers
 Rapid perforin upregulation directly ex vivo by CD8 + T cells is a defining characteristic of HIV elite controllers Adam R. Hersperger Department of Microbiology University of Pennsylvania Evidence for
Rapid perforin upregulation directly ex vivo by CD8 + T cells is a defining characteristic of HIV elite controllers Adam R. Hersperger Department of Microbiology University of Pennsylvania Evidence for
CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Baltimore, MD 21205
 AD Award Number: DAMD7---7 TITLE: Development of Artificial Antigen Presenting Cells for Prostate Cancer Immunotherapy PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Jonathan P. Schneck, M.D., Ph.D. Mathias Oelke, Ph.D. CONTRACTING
AD Award Number: DAMD7---7 TITLE: Development of Artificial Antigen Presenting Cells for Prostate Cancer Immunotherapy PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Jonathan P. Schneck, M.D., Ph.D. Mathias Oelke, Ph.D. CONTRACTING
Principles of Adaptive Immunity
 Principles of Adaptive Immunity Chapter 3 Parham Hans de Haard 17 th of May 2010 Agenda Recognition molecules of adaptive immune system Features adaptive immune system Immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors
Principles of Adaptive Immunity Chapter 3 Parham Hans de Haard 17 th of May 2010 Agenda Recognition molecules of adaptive immune system Features adaptive immune system Immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors
Study Guide 23, 24 & 47
 Study Guide 23, 24 & 47 STUDY GUIDE SECTION 23-3 Bacteria and Humans Name Period Date 1. One bacterial disease that is transmitted by contaminated drinking water is a. Lyme disease b. gonorrhea c. tuberculosis
Study Guide 23, 24 & 47 STUDY GUIDE SECTION 23-3 Bacteria and Humans Name Period Date 1. One bacterial disease that is transmitted by contaminated drinking water is a. Lyme disease b. gonorrhea c. tuberculosis
Supplementary Information. A vital role for IL-2 trans-presentation in DC-mediated T cell activation in humans as revealed by daclizumab therapy
 Supplementary Information A vital role for IL-2 trans-presentation in DC-mediated T cell activation in humans as revealed by daclizumab therapy Simone C. Wuest 1, Jehad Edwan 1, Jayne F. Martin 1, Sungpil
Supplementary Information A vital role for IL-2 trans-presentation in DC-mediated T cell activation in humans as revealed by daclizumab therapy Simone C. Wuest 1, Jehad Edwan 1, Jayne F. Martin 1, Sungpil
Adaptive Immunity: Humoral Immune Responses
 MICR2209 Adaptive Immunity: Humoral Immune Responses Dr Allison Imrie 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will review the different mechanisms which constitute the humoral immune response, and examine the antibody
MICR2209 Adaptive Immunity: Humoral Immune Responses Dr Allison Imrie 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will review the different mechanisms which constitute the humoral immune response, and examine the antibody
Immune correlates of protection from congenital cytomegalovirus after primary infection in pregnancy
 Laboratori Sperimentali di Ricerca, Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo, Pavia, Italia Immune correlates of protection from congenital cytomegalovirus after primary infection in pregnancy Daniele Lilleri
Laboratori Sperimentali di Ricerca, Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo, Pavia, Italia Immune correlates of protection from congenital cytomegalovirus after primary infection in pregnancy Daniele Lilleri
Third line of Defense. Topic 8 Specific Immunity (adaptive) (18) 3 rd Line = Prophylaxis via Immunization!
 Topic 8 Specific Immunity (adaptive) (18) Topics - 3 rd Line of Defense - B cells - T cells - Specific Immunities 1 3 rd Line = Prophylaxis via Immunization! (a) A painting of Edward Jenner depicts a cow
Topic 8 Specific Immunity (adaptive) (18) Topics - 3 rd Line of Defense - B cells - T cells - Specific Immunities 1 3 rd Line = Prophylaxis via Immunization! (a) A painting of Edward Jenner depicts a cow
Allergic rhinitis (Hay fever) Asthma Anaphylaxis Urticaria Atopic dermatitis
 Hypersensitivity Disorders Hypersensitivity Disorders Immune Response IgE Disease Example Ragweed hay fever IgG Cytotoxic Immune complex T Cell Hemolytic anemia Serum sickness Poison ivy IgE-mediated Diseases
Hypersensitivity Disorders Hypersensitivity Disorders Immune Response IgE Disease Example Ragweed hay fever IgG Cytotoxic Immune complex T Cell Hemolytic anemia Serum sickness Poison ivy IgE-mediated Diseases
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/381/ra59/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Analysis of single-cell cytokine secretion reveals a role for paracrine signaling in coordinating macrophage responses
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/381/ra59/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Analysis of single-cell cytokine secretion reveals a role for paracrine signaling in coordinating macrophage responses
Supplementary Data 1. Alanine substitutions and position variants of APNCYGNIPL. Applied in
 Supplementary Data 1. Alanine substitutions and position variants of APNCYGNIPL. Applied in Supplementary Fig. 2 Substitution Sequence Position variant Sequence original APNCYGNIPL original APNCYGNIPL
Supplementary Data 1. Alanine substitutions and position variants of APNCYGNIPL. Applied in Supplementary Fig. 2 Substitution Sequence Position variant Sequence original APNCYGNIPL original APNCYGNIPL
CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
 CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION What is Cytokine? Secreted popypeptide (protein) involved in cell-to-cell signaling. Acts in paracrine or autocrine fashion through specific cellular receptors.
CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION What is Cytokine? Secreted popypeptide (protein) involved in cell-to-cell signaling. Acts in paracrine or autocrine fashion through specific cellular receptors.
ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY
 ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY The recognition of specific antigen by naïve T cell induces its own activation and effector phases. T helper cells recognize peptide antigens through
ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY The recognition of specific antigen by naïve T cell induces its own activation and effector phases. T helper cells recognize peptide antigens through
Helminth worm, Schistosomiasis Trypanosomes, sleeping sickness Pneumocystis carinii. Ringworm fungus HIV Influenza
 Helminth worm, Schistosomiasis Trypanosomes, sleeping sickness Pneumocystis carinii Ringworm fungus HIV Influenza Candida Staph aureus Mycobacterium tuberculosis Listeria Salmonella Streptococcus Levels
Helminth worm, Schistosomiasis Trypanosomes, sleeping sickness Pneumocystis carinii Ringworm fungus HIV Influenza Candida Staph aureus Mycobacterium tuberculosis Listeria Salmonella Streptococcus Levels
Monitoring tuberculosis progression using MRI and stereology
 Monitoring tuberculosis progression using MRI and stereology TB the problem Estimated number of new cases in 2007 2 million deaths; 9 million new cases p.a. TB kills someone every 15 secs, 9,153 cases
Monitoring tuberculosis progression using MRI and stereology TB the problem Estimated number of new cases in 2007 2 million deaths; 9 million new cases p.a. TB kills someone every 15 secs, 9,153 cases
Chapter 10 (pages ): Differentiation and Functions of CD4+ Effector T Cells Prepared by Kristen Dazy, MD, Scripps Clinic Medical Group
 FIT Board Review Corner September 2015 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Andrew Nickels, MD, and Sarah Spriet, DO, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In-Training (FITs)
FIT Board Review Corner September 2015 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Andrew Nickels, MD, and Sarah Spriet, DO, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In-Training (FITs)
Application of μmacs Streptavidin MicroBeads for the analysis of HIV-1 directly from patient plasma
 Excerpt from MACS&more Vol 8 1/2004 Application of μmacs Streptavidin MicroBeads for the analysis of HIV-1 directly from patient plasma L. Davis Lupo and Salvatore T. Butera HIV and Retrovirology Branch,
Excerpt from MACS&more Vol 8 1/2004 Application of μmacs Streptavidin MicroBeads for the analysis of HIV-1 directly from patient plasma L. Davis Lupo and Salvatore T. Butera HIV and Retrovirology Branch,
Assessing vaccine-induced correlates of protection: Antigen-specific readouts versus system vaccinology
 Assessing vaccine-induced correlates of protection: Antigen-specific readouts versus system vaccinology Professor Artur Summerfield Chair of Veterinary Immunology Vetsuisse Faculty, University of Bern
Assessing vaccine-induced correlates of protection: Antigen-specific readouts versus system vaccinology Professor Artur Summerfield Chair of Veterinary Immunology Vetsuisse Faculty, University of Bern
Dual Targeting Nanoparticle Stimulates the Immune
 Dual Targeting Nanoparticle Stimulates the Immune System to Inhibit Tumor Growth Alyssa K. Kosmides, John-William Sidhom, Andrew Fraser, Catherine A. Bessell, Jonathan P. Schneck * Supplemental Figure
Dual Targeting Nanoparticle Stimulates the Immune System to Inhibit Tumor Growth Alyssa K. Kosmides, John-William Sidhom, Andrew Fraser, Catherine A. Bessell, Jonathan P. Schneck * Supplemental Figure
Physiology Unit 3. ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY The Specific Immune Response
 Physiology Unit 3 ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY The Specific Immune Response In Physiology Today The Adaptive Arm of the Immune System Specific Immune Response Internal defense against a specific pathogen Acquired
Physiology Unit 3 ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY The Specific Immune Response In Physiology Today The Adaptive Arm of the Immune System Specific Immune Response Internal defense against a specific pathogen Acquired
The Immune System. A macrophage. ! Functions of the Immune System. ! Types of Immune Responses. ! Organization of the Immune System
 The Immune System! Functions of the Immune System! Types of Immune Responses! Organization of the Immune System! Innate Defense Mechanisms! Acquired Defense Mechanisms! Applied Immunology A macrophage
The Immune System! Functions of the Immune System! Types of Immune Responses! Organization of the Immune System! Innate Defense Mechanisms! Acquired Defense Mechanisms! Applied Immunology A macrophage
TITLE: Development of Antigen Presenting Cells for adoptive immunotherapy in prostate cancer
 AD Award Number: W8-XWH-5-- TITLE: Development of Antigen Presenting Cells for adoptive immunotherapy in prostate cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Mathias Oelke, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Johns Hopkins
AD Award Number: W8-XWH-5-- TITLE: Development of Antigen Presenting Cells for adoptive immunotherapy in prostate cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Mathias Oelke, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Johns Hopkins
- 1 - Cell types Monocytes THP-1 cells Macrophages. LPS Treatment time (Hour) IL-6 level (pg/ml)
 Supplementary Table ST1: The dynamic effect of LPS on IL-6 production in monocytes and THP-1 cells after GdA treatment. Monocytes, THP-1 cells and macrophages (5x10 5 ) were incubated with 10 μg/ml of
Supplementary Table ST1: The dynamic effect of LPS on IL-6 production in monocytes and THP-1 cells after GdA treatment. Monocytes, THP-1 cells and macrophages (5x10 5 ) were incubated with 10 μg/ml of
Mouse Total IgA Antibody Detection Kit
 Mouse Total IgA Antibody Detection Kit Catalog # 3019 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION The total IgA levels in specimens are often determined in mouse disease models involving
Mouse Total IgA Antibody Detection Kit Catalog # 3019 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION The total IgA levels in specimens are often determined in mouse disease models involving
IFN-γ Secretion Assay Detection Kit (PE) human
 Miltenyi Biotec GmbH Friedrich-Ebert-Straße 68 51429 Bergisch Gladbach, Germany Phone +49 2204 8306-0 Fax +49 2204 85197 macs@miltenyibiotec.de Miltenyi Biotec Inc. 12740 Earhart Avenue Auburn CA 95602,
Miltenyi Biotec GmbH Friedrich-Ebert-Straße 68 51429 Bergisch Gladbach, Germany Phone +49 2204 8306-0 Fax +49 2204 85197 macs@miltenyibiotec.de Miltenyi Biotec Inc. 12740 Earhart Avenue Auburn CA 95602,
PRIME-XV Dendritic Cell Maturation CDM
 PRIME-XV Dendritic Cell Maturation CDM Chemically defined, animal component-free medium for dendritic cell culture Optimized for differentiation of monocytes into immature dendritic cells (idcs) and subsequent
PRIME-XV Dendritic Cell Maturation CDM Chemically defined, animal component-free medium for dendritic cell culture Optimized for differentiation of monocytes into immature dendritic cells (idcs) and subsequent
