T Cell Receptor Optimized Peptide Skewing of the T-Cell Repertoire Can Enhance Antigen Targeting
|
|
|
- Melissa Summers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 T Cell Receptor Optimized Peptide Skewing of the T-Cell Repertoire Can Enhance Antigen Targeting Julia Ekeruche-Makinde 1*, Mathew Clement 1*, David K Cole 1*, Emily S J Edwards 1, Kristin Ladell 1, John J Miles 1,2, Katherine K Matthews 1, Anna Fuller 1, Katy A Lloyd 1, Florian Madura 1, Garry M Dolton 1, Johanne Pentier 1, Anna Lissina 1, Emma Gostick 1, Tiffany K Baxter 3, Brian M Baker 3, Pierre J Rizkallah 1, David A Price 1, Linda Wooldridge 1* and Andrew K Sewell 1* 1 Institute of Infection and Immunity, Cardiff University School of Medicine, Henry Wellcome Building, Heath Park, Cardiff CF14 4XN, Wales, UK. 2 Australian Centre for Vaccine Development, Human Immunity Laboratory, Queensland Institute of Medical Research, Brisbane 429, Australia. 3 Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Notre Dame, Notre Dame, Indiana 46556, USA. * These authors contributed equally to this work Running Head: TCR optimized peptide skewing of the T-cell repertoire To whom correspondence should be addressed: Andrew K Sewell. SewellAK@cardiff.ac.uk; Tel: (+) ; Fax: (+) Keywords: APL (altered peptide ligand), CTCL (cutaneous T-cell lymphoma), pmhc (peptide- MHC), pmhci (peptide-mhc class I), TCR (T-cell receptor), SPR (surface plasmon resonance), TOP (TCR optimized peptide), TOPSORT (TCR optimized peptide skewing of the repertoire of T- cells) Background: Current peptide vaccines may select sub-optimal antigen-specific T-cells from polyclonal populations Results: A combinatorial peptide library screen was used to generate an optimal ligand that could preferentially activate a known effective T-cell clonotype Conclusion: Rationally designed altered peptide ligands may enable the preferential selection of high quality, antigen-sensitive T-cell clonotypes Significance: This proof-of-principle study could facilitate the development of more effective peptide vaccination strategies
2 SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Supplementary Table S1. Data collection and refinement statistics (molecular replacement). Data set statistics HLA A*21-GIGIITV HLA A*21-FLTGIGIITV Space Group C C a=22.4, b=46.6, c=116.6 a=21.5, b=46.8, c=115.9 Unit Cell parameters (Å) α=9., β=121.5, γ=9. α=9., β=121.7, γ=9. Radiation Source DIAMOND I3 DIAMOND I3 Wavelength (Å) Resolution (Å) Unique reflections 26,5 (1,911) 36,5 (2,72) Completeness (%) 99.5 (99.6) 92.4 (94.2) Multiplicity 4 (4.1) 4 (3.6) I/Sigma(I) 1.4 (2.2) 8.8 (2.2) Rmerge (%) 9.4 (62.4) 9 (7.1) No reflections used 23,24 34,22 Rcryst (no cutoff) (%) Rfree (%) Bond lengths (Å) Bond Angles ( ) Mean B value (Å 2 ) Outliers Ramachandran plot (%) Overall ESU based on Maximum Likelihood (Å) One crystal was used for data collection. *Values in parentheses are for the highest-resolution shell.
3 Supplementary Table S2. Comparison of CD8+ T-cell frequencies primed by ELAGIGILTV and GIGIITV. Donor ID % EAA tetramer +ve cells % ELA tetramer +ve cells ELA primed primed ELA primed primed nm nm nm = not measured No statistically significant differences were detected between the ELAGIGILTV-primed and GIGIITV-primed CD8 + T-cell populations with respect to response frequencies.
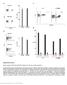
4 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1: Melan A-specific CD8 + T-cell clones exhibit differential recognition of natural tumor epitopes. (A) Relative stabilities of HLA A*21-AAGIGILTV (AAG9), HLA A*21- EAAGIGILTV (EAA1) and HLA A*21-ELAGIGILTV (ELA1) complexes. Thermal stability was monitored by circular dichroism (CD), which reports directly on peptide binding affinity for MHC. Thermal stability (T m ) values for the three complexes are shown on the plot and indicate an affinity ranking of AAGIGILTV < EAAGIGILTV << ELAGIGILTV. (B&C) 3x1 4 MEL5 (B) or MEL187.c5 (C) CD8 + T-cells were incubated overnight with 6x1 4 C1R A2 cells pre-pulsed with the indicated concentrations of the peptides shown in the key. Supernatants were harvested and assayed for MIP-1 by ELISA. (D&E) Binding of soluble MEL5 TCR (D) or MEL187.c5 TCR (E) to the HLA A*21-AAGIGILTV complex (A2-AAGIGILTV) measured by SPR.
5 A MEL187.c5 B MEL5 % CD17a +ve CD8+ T-cell IFN-γ [pg/ml] ELAGIGILTV vs FLTGIGIITV TNF-α [pg/ml] IL2 [pg/ml] C MEL187.c5 D MEL5 % CD17a +ve CD8+ T-cell IFN-γ [pg/ml] ELAGIGILTV vs GIGIITV TNF-α [pg/ml] Peptide concentration [M] IL2 [pg/ml] Figure S2: Recognition of the GIGIITV and FLTGIGIITV peptides by the MEL5 and MEL187.c5 CD8 + T-cell clones. C1R A2 cells were incubated with the indicated peptides for 1 hr at the concentrations shown and then used as targets for the MEL187.c5 and MEL5 CD8 + T-cell clones. (A&B) Recognition of the ELAGIGILTV and FLTGIGIITV peptides by the MEL187.c5 (A) and MEL5 (B) CD8 + T-cell clones. (C&D) Recognition of the ELAGIGILTV and GIGIITV peptides by the MEL187.c5 (C) and MEL5 (D) CD8 + T-cell clones.
6 A 4 3 Donor 2 MEL 526 ELA E 6 4 Donor 4 MEL 526 ELA I 4 Donor 6 MEL ELA B 6:1 12:1 6:1 3.1:1 3:1 Donor 2 MEL :1 6 ELA F 12:1 6:1 3.1:1.75:1 Donor 4 MEL ELA.75: J 15:1 7.5:1 3.7:1 1.8:1.9:1.4:1.2:1.1:1 Donor 6 MEL ELA C 6:1 12:1 6:1 3.1:1.75:1 3:1 Donor 3 MEL :1.375:1 4 ELA 3 G 12:1 6:1 3.1:1.75:1.75:1 Donor 5 MEL ELA 6 K 15:1 7.5:1 3.7:1 1.8:1.9:1.4:1.2:1.1:1 4 Donor 7 MEL :1 7.5:1 3.75: :1.9:1.46:1.23:1.12:1 6 ELA % specific lysis D 12:1 6:1 3.1:1.75:1.75:1 4 ELA :1 6:1 3.1:1.75:1 E:T ratio.75:1 Donor 3 MEL H :1 12:1 6:1 3.1: :1 6 ELA Donor 5 MEL :1 6:1 3.1:1.75:1 L 12:1 6:1 3.1:1.75:1.75:1.75:1 Donor 7 MEL ELA :1 6:1 3.1:1.75:1 Figure S3: The optimized analogue peptide GIGIITV can prime superior Melan A-specific CD8 + T-cells. 6x1 6 PBMCs from seven healthy HLA A*21 + donors were pulsed with 1 M peptide (ELAGIGILTV or GIGIITV) for 1 hr. Lines were grown out for 14 days and then tested for antigen specificity using pmhci tetramer staining. Specific lysis was measured for each primed CD8 + T-cell line after exposure to the melanoma cell lines Mel 526 and Mel624 at a range of effector:target (E:T) ratios (A-L). Error bars are standard deviation from three experiments.
7 Figure S4: GIGIITV-primed CD8 + T-cells are clonotypically distinct from those primed by the heteroclitic peptide ELAGIGILTV. 5x1 4 cells from HLA A*21-restricted Melan A-specific CD8 + T-cell lines were incubated with LIVE/DEAD Fixable Aqua amine-reactive fluorescent dye for 15 min at room temperature, washed once and stained with APC-conjugated HLA A*21- ELAGIGILTV tetramer. Cells were then stained with PerCP-conjugated anti-human CD8 and a panel of anti-human V antibodies for 3 min at 4 C. Corresponding data for HLA A*21-EAAGIGILTV tetramer + cells from the same CD8 + T-cell lines are shown in Figure 8.
Supplementary Table 1. Data collection and refinement statistics (molecular replacement).
 Supplementary Table 1. Data collection and refinement statistics (molecular replacement). Data set statistics HLA A*0201- ALWGPDPAAA PPI TCR PPI TCR/A2- ALWGPDPAAA PPI TCR/A2- ALWGPDPAAA Space Group P2
Supplementary Table 1. Data collection and refinement statistics (molecular replacement). Data set statistics HLA A*0201- ALWGPDPAAA PPI TCR PPI TCR/A2- ALWGPDPAAA PPI TCR/A2- ALWGPDPAAA Space Group P2
Low Avidity CMV + T Cells accumulate in Old Humans
 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1. CD45RA expressing CMVpp65-specific T cell populations accumulate within HLA-A*0201 and HLA-B*0701 individuals Pooled data showing the size of the NLV/HLA-A*0201-specific
Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1. CD45RA expressing CMVpp65-specific T cell populations accumulate within HLA-A*0201 and HLA-B*0701 individuals Pooled data showing the size of the NLV/HLA-A*0201-specific
BACKGROUND. Figure 1: Type 1 diabetes results from immune attack on insulin-producing beta-cells in the pancreas
 BACKGROUND Diabetes Diabetes is used to describe diseases where a person has high blood sugar. There are three main types of diabetes: Type 1 diabetes results from a failure to produce a hormone called
BACKGROUND Diabetes Diabetes is used to describe diseases where a person has high blood sugar. There are three main types of diabetes: Type 1 diabetes results from a failure to produce a hormone called
T cell recognition. Statistics & Dynamics of Functional Sensitivity
 T cell recognition Statistics & Dynamics of Functional Sensitivity C Molina-París LEEDS APPLIED MATHEMATICS G Lythe LEEDS APPLIED MATHEMATICS A K Sewell CARDIFF MEDICAL BIOCHEMISTRY & IMMUNOLOGY L Wooldridge
T cell recognition Statistics & Dynamics of Functional Sensitivity C Molina-París LEEDS APPLIED MATHEMATICS G Lythe LEEDS APPLIED MATHEMATICS A K Sewell CARDIFF MEDICAL BIOCHEMISTRY & IMMUNOLOGY L Wooldridge
Supplementary Table 1. Functional avidities of survivin-specific T-cell clones against LML-peptide
 Supplementary Table 1. Functional avidities of survivin-specific T-cell clones against LML-peptide pulsed T2 cells. clone avidity by 4-hour 51 Cr-release assay 50% lysis at E:T 10:1 [LML peptide, M] #24
Supplementary Table 1. Functional avidities of survivin-specific T-cell clones against LML-peptide pulsed T2 cells. clone avidity by 4-hour 51 Cr-release assay 50% lysis at E:T 10:1 [LML peptide, M] #24
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Binding capacity of DNA-barcoded MHC multimers and recovery of antigen specificity
 Supplementary Figure 1 Binding capacity of DNA-barcoded MHC multimers and recovery of antigen specificity (a, b) Fluorescent-based determination of the binding capacity of DNA-barcoded MHC multimers (+barcode)
Supplementary Figure 1 Binding capacity of DNA-barcoded MHC multimers and recovery of antigen specificity (a, b) Fluorescent-based determination of the binding capacity of DNA-barcoded MHC multimers (+barcode)
Supplementary Data 1. Alanine substitutions and position variants of APNCYGNIPL. Applied in
 Supplementary Data 1. Alanine substitutions and position variants of APNCYGNIPL. Applied in Supplementary Fig. 2 Substitution Sequence Position variant Sequence original APNCYGNIPL original APNCYGNIPL
Supplementary Data 1. Alanine substitutions and position variants of APNCYGNIPL. Applied in Supplementary Fig. 2 Substitution Sequence Position variant Sequence original APNCYGNIPL original APNCYGNIPL
Immune surveillance: The immune system can recognize and destroy nascent malignant cells
 Immune surveillance: The immune system can recognize and destroy nascent malignant cells Control Escape APC T C T H B NKT NK Innate Tumor T cells are believed to play a major role in controlling tumor
Immune surveillance: The immune system can recognize and destroy nascent malignant cells Control Escape APC T C T H B NKT NK Innate Tumor T cells are believed to play a major role in controlling tumor
Supplemental materials
 Supplemental materials 1 Supplemental Fig. 1 Immunogram This immunogram summarizes patient clinical data and immune parameters at corresponding time points for Patient IMF-32. The top panel illustrates
Supplemental materials 1 Supplemental Fig. 1 Immunogram This immunogram summarizes patient clinical data and immune parameters at corresponding time points for Patient IMF-32. The top panel illustrates
Immunocore Ltd isbtc Washington 30 th October 2009
 Ltd isbtc Washington 30 th October 2009 Bent Jakobsen Chief Scientific Officer Breaking immune tolerance to cancer The immune system has more cytotoxic potential and versatility than can be achieved with
Ltd isbtc Washington 30 th October 2009 Bent Jakobsen Chief Scientific Officer Breaking immune tolerance to cancer The immune system has more cytotoxic potential and versatility than can be achieved with
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Chapuis et al. 10.1073/pnas.1113748109 SI Methods Selection of Patients, Targets, Isolation, and Expansion of Melanoma- Specific CTL Clones. Patients were HLA-typed, and their tumors
Supporting Information Chapuis et al. 10.1073/pnas.1113748109 SI Methods Selection of Patients, Targets, Isolation, and Expansion of Melanoma- Specific CTL Clones. Patients were HLA-typed, and their tumors
Supplementary Figure 1. Using DNA barcode-labeled MHC multimers to generate TCR fingerprints
 Supplementary Figure 1 Using DNA barcode-labeled MHC multimers to generate TCR fingerprints (a) Schematic overview of the workflow behind a TCR fingerprint. Each peptide position of the original peptide
Supplementary Figure 1 Using DNA barcode-labeled MHC multimers to generate TCR fingerprints (a) Schematic overview of the workflow behind a TCR fingerprint. Each peptide position of the original peptide
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) analysis
 Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) analysis Soluble CD8αα and was manufactured as described previously. 1,2 The C12C heterodimeric TCR was produced using an engineered disulfide bridge between the constant
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) analysis Soluble CD8αα and was manufactured as described previously. 1,2 The C12C heterodimeric TCR was produced using an engineered disulfide bridge between the constant
Supplementary Figure 1. Example of gating strategy
 Supplementary Figure 1. Example of gating strategy Legend Supplementary Figure 1: First, gating is performed to include only single cells (singlets) (A) and CD3+ cells (B). After gating on the lymphocyte
Supplementary Figure 1. Example of gating strategy Legend Supplementary Figure 1: First, gating is performed to include only single cells (singlets) (A) and CD3+ cells (B). After gating on the lymphocyte
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information High throughput epitope discovery reveals frequent recognition of neo-antigens by CD4 + T-cells in human melanoma Carsten Linnemann, Marit M. van Buuren, Laura Bies, Els M.E.Verdegaal,
Supplementary Information High throughput epitope discovery reveals frequent recognition of neo-antigens by CD4 + T-cells in human melanoma Carsten Linnemann, Marit M. van Buuren, Laura Bies, Els M.E.Verdegaal,
<20 <20 <20 < <20 <20 <20 <20. Mock
 Cross-Lineage Neutralization PRNT 80 Titers Asian Asian West African Indian Ocean Group NHP Strain 181/25 Strain 99659 Strain 37997 Strain LR 142590 80 80 20 40 EILV/CHIKV 150844 640 640 160 320 Mock 150849
Cross-Lineage Neutralization PRNT 80 Titers Asian Asian West African Indian Ocean Group NHP Strain 181/25 Strain 99659 Strain 37997 Strain LR 142590 80 80 20 40 EILV/CHIKV 150844 640 640 160 320 Mock 150849
Cytotoxicity assays. Rory D. de Vries, PhD 1. Viroscience lab, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, the Netherlands
 Cytotoxicity assays Rory D. de Vries, PhD 1 1 Viroscience lab, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, the Netherlands Anti-influenza immunity Humoral / CD4+ / CD8+ / NK? Function of CTL Elimination of virus-infected cells?
Cytotoxicity assays Rory D. de Vries, PhD 1 1 Viroscience lab, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, the Netherlands Anti-influenza immunity Humoral / CD4+ / CD8+ / NK? Function of CTL Elimination of virus-infected cells?
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Identification of IFN-γ-producing CD8 + and CD4 + T cells with naive phenotype by alternative gating and sample-processing strategies. a. Contour 5% probability plots show definition
Supplementary Figure 1 Identification of IFN-γ-producing CD8 + and CD4 + T cells with naive phenotype by alternative gating and sample-processing strategies. a. Contour 5% probability plots show definition
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Complete but curtailed T-cell response to very-low-affinity antigen Dietmar Zehn, Sarah Y. Lee & Michael J. Bevan Supp. Fig. 1: TCR chain usage among endogenous K b /Ova reactive T cells. C57BL/6 mice
Complete but curtailed T-cell response to very-low-affinity antigen Dietmar Zehn, Sarah Y. Lee & Michael J. Bevan Supp. Fig. 1: TCR chain usage among endogenous K b /Ova reactive T cells. C57BL/6 mice
Tricks with tetramers: how to get the most from multimeric peptide MHC
 IMMUNOLOGY REVIEW ARTICLE Tricks with tetramers: how to get the most from multimeric peptide MHC Ó 2009 Blackwell Publishing Ltd, Immunology, 126, 147 164 147 L. Wooldridge et al. Linda Wooldridge, 1,
IMMUNOLOGY REVIEW ARTICLE Tricks with tetramers: how to get the most from multimeric peptide MHC Ó 2009 Blackwell Publishing Ltd, Immunology, 126, 147 164 147 L. Wooldridge et al. Linda Wooldridge, 1,
Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD-
 Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
Online supplement. Phenotypic, functional and plasticity features of classical and alternatively activated
 Online supplement Phenotypic, functional and plasticity features of classical and alternatively activated human macrophages Abdullah Al Tarique*, Jayden Logan *, Emma Thomas *, Patrick G Holt *, Peter
Online supplement Phenotypic, functional and plasticity features of classical and alternatively activated human macrophages Abdullah Al Tarique*, Jayden Logan *, Emma Thomas *, Patrick G Holt *, Peter
The Good, the Bad and the Ugly: Clinical trials which assess vaccine characteristics. ISBT Meeting, San Francisco, CA November 4-8, 2004
 The Good, the Bad and the Ugly: Clinical trials which assess vaccine characteristics ISBT Meeting, San Francisco, CA November 4-8, 2004 Ideal cancer vaccine trial 1. An informative immune assay 2. Ability
The Good, the Bad and the Ugly: Clinical trials which assess vaccine characteristics ISBT Meeting, San Francisco, CA November 4-8, 2004 Ideal cancer vaccine trial 1. An informative immune assay 2. Ability
Journal of Immunological Methods
 Journal of Immunological Methods 340 (2009) 11 24 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Immunological Methods journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jim Research paper Protein kinase
Journal of Immunological Methods 340 (2009) 11 24 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Immunological Methods journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jim Research paper Protein kinase
L-selectin Is Essential for Delivery of Activated CD8 + T Cells to Virus-Infected Organs for Protective Immunity
 Cell Reports Supplemental Information L-selectin Is Essential for Delivery of Activated CD8 + T Cells to Virus-Infected Organs for Protective Immunity Rebar N. Mohammed, H. Angharad Watson, Miriam Vigar,
Cell Reports Supplemental Information L-selectin Is Essential for Delivery of Activated CD8 + T Cells to Virus-Infected Organs for Protective Immunity Rebar N. Mohammed, H. Angharad Watson, Miriam Vigar,
MHC Tetramers and Monomers for Immuno-Oncology and Autoimmunity Drug Discovery
 MHC Tetramers and Monomers for Immuno-Oncology and Autoimmunity Drug Discovery Your Partner in Drug Discovery and Research MHC Tetramer Background T-Cell Receptors recognize and bind to complexes composed
MHC Tetramers and Monomers for Immuno-Oncology and Autoimmunity Drug Discovery Your Partner in Drug Discovery and Research MHC Tetramer Background T-Cell Receptors recognize and bind to complexes composed
Crystallization-grade After D After V3 cocktail. Time (s) Time (s) Time (s) Time (s) Time (s) Time (s)
 Ligand Type Name 6 Crystallization-grade After 447-52D After V3 cocktail Receptor CD4 Resonance Units 5 1 5 1 5 1 Broadly neutralizing antibodies 2G12 VRC26.9 Resonance Units Resonance Units 3 1 15 1 5
Ligand Type Name 6 Crystallization-grade After 447-52D After V3 cocktail Receptor CD4 Resonance Units 5 1 5 1 5 1 Broadly neutralizing antibodies 2G12 VRC26.9 Resonance Units Resonance Units 3 1 15 1 5
Use of BONSAI decision trees for the identification of potential MHC Class I peptide epitope motifs.
 Use of BONSAI decision trees for the identification of potential MHC Class I peptide epitope motifs. C.J. SAVOIE, N. KAMIKAWAJI, T. SASAZUKI Dept. of Genetics, Medical Institute of Bioregulation, Kyushu
Use of BONSAI decision trees for the identification of potential MHC Class I peptide epitope motifs. C.J. SAVOIE, N. KAMIKAWAJI, T. SASAZUKI Dept. of Genetics, Medical Institute of Bioregulation, Kyushu
ILC1 and ILC3 isolation and culture Following cell sorting, we confirmed that the recovered cells belonged to the ILC1, ILC2 and
 Supplementary Methods and isolation and culture Following cell sorting, we confirmed that the recovered cells belonged to the, ILC2 and subsets. For this purpose we performed intracellular flow cytometry
Supplementary Methods and isolation and culture Following cell sorting, we confirmed that the recovered cells belonged to the, ILC2 and subsets. For this purpose we performed intracellular flow cytometry
CD40L TCR IL-12 TLR-L
 CD40L B cells plasmacells Neutrophils TCR inkt cells IL-12 Ab production Can inkt cells modulate the cytokine profile of neutrophils? TLR-L CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses 1. The invariant TCR expressed
CD40L B cells plasmacells Neutrophils TCR inkt cells IL-12 Ab production Can inkt cells modulate the cytokine profile of neutrophils? TLR-L CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses 1. The invariant TCR expressed
Figure S1. HP1α localizes to centromeres in mitosis and interacts with INCENP. (A&B) HeLa
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. HP1α localizes to centromeres in mitosis and interacts with INCENP. (A&B) HeLa tet-on cells that stably express HP1α-CFP, HP1β-CFP, or HP1γ-CFP were monitored with livecell
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. HP1α localizes to centromeres in mitosis and interacts with INCENP. (A&B) HeLa tet-on cells that stably express HP1α-CFP, HP1β-CFP, or HP1γ-CFP were monitored with livecell
Defective STAT1 activation associated with impaired IFN-g production in NK and T lymphocytes from metastatic melanoma patients treated with IL-2
 Defective STAT1 activation associated with impaired IFN-g production in NK and T lymphocytes from metastatic melanoma patients treated with IL-2 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES Supplementary Figure S1:
Defective STAT1 activation associated with impaired IFN-g production in NK and T lymphocytes from metastatic melanoma patients treated with IL-2 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES Supplementary Figure S1:
Antigen capture and presentation to T lymphocytes
 Antigen capture and presentation to T lymphocytes What T lymphocytes see Innate Immunity Immediately available or Very broad specificity rapidly recruited Adaptive Immunity Rare and naïve cells require
Antigen capture and presentation to T lymphocytes What T lymphocytes see Innate Immunity Immediately available or Very broad specificity rapidly recruited Adaptive Immunity Rare and naïve cells require
Supplementary Figure 1. Enhanced detection of CTLA-4 on the surface of HIV-specific
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGEND Supplementary Figure 1. Enhanced detection of CTLA-4 on the surface of HIV-specific CD4 + T cells correlates with intracellular CTLA-4 levels. (a) Comparative CTLA-4 levels
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGEND Supplementary Figure 1. Enhanced detection of CTLA-4 on the surface of HIV-specific CD4 + T cells correlates with intracellular CTLA-4 levels. (a) Comparative CTLA-4 levels
Atypical Natural Killer T-cell receptor recognition of CD1d-lipid antigens supplementary Information.
 Atypical Natural Killer T-cell receptor recognition of CD1d-lipid antigens supplementary Information. Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotypic analysis of TRBV25-1 + and TRBV25-1 - CD1d-α-GalCerreactive cells.
Atypical Natural Killer T-cell receptor recognition of CD1d-lipid antigens supplementary Information. Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotypic analysis of TRBV25-1 + and TRBV25-1 - CD1d-α-GalCerreactive cells.
TITLE: Development of Antigen Presenting Cells for adoptive immunotherapy in prostate cancer
 AD Award Number: W8-XWH-5-- TITLE: Development of Antigen Presenting Cells for adoptive immunotherapy in prostate cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Mathias Oelke, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Johns Hopkins
AD Award Number: W8-XWH-5-- TITLE: Development of Antigen Presenting Cells for adoptive immunotherapy in prostate cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Mathias Oelke, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Johns Hopkins
Summary. Introduction. Clinical and Experimental Immunology ORIGINAL ARTICLE doi: /cei.12828
 Clinical and Experimental Immunology ORIGINAL ARTICLE doi:10.1111/cei.12828 Human leucocyte antigen class I-redirected anti-tumour CD4 1 T cells require a higher T cell receptor binding affinity for optimal
Clinical and Experimental Immunology ORIGINAL ARTICLE doi:10.1111/cei.12828 Human leucocyte antigen class I-redirected anti-tumour CD4 1 T cells require a higher T cell receptor binding affinity for optimal
Supplementary Data Table of Contents:
 Supplementary Data Table of Contents: - Supplementary Methods - Supplementary Figures S1(A-B) - Supplementary Figures S2 (A-B) - Supplementary Figures S3 - Supplementary Figures S4(A-B) - Supplementary
Supplementary Data Table of Contents: - Supplementary Methods - Supplementary Figures S1(A-B) - Supplementary Figures S2 (A-B) - Supplementary Figures S3 - Supplementary Figures S4(A-B) - Supplementary
MHC MULTIMER PROFICIENCY PANEL 2017
 MHC MULTIMER PROFICIENCY PANEL 2017 August 2017 CONTACT Charlotte Halgreen ProficiencyPanel@immudex.com FOR MORE INFORMATION www.proficiencypanel.com MHC MULTIMER PROFICIENCY PANEL 2017 This report summarizes
MHC MULTIMER PROFICIENCY PANEL 2017 August 2017 CONTACT Charlotte Halgreen ProficiencyPanel@immudex.com FOR MORE INFORMATION www.proficiencypanel.com MHC MULTIMER PROFICIENCY PANEL 2017 This report summarizes
Four main classes of human tumor antigens recognized by T cells: 1- "Cancer-testis" antigens: non-mutated genes reactivated in neoplastic cells, but
 Tumor antigens Andrea Anichini Human Tumors Immunobiology Unit, Dept. of Experimental Oncology and Molecular Medicine Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori, Milan Timeline of the discovery of
Tumor antigens Andrea Anichini Human Tumors Immunobiology Unit, Dept. of Experimental Oncology and Molecular Medicine Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori, Milan Timeline of the discovery of
Dissecting therapy-induced T-cell responses in melanoma
 Dissecting therapy-induced T-cell responses in melanoma Tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) therapy of melanoma TIL are grown from melanoma tumors Rapid Expansion Infusion of TIL + IL-2 Patient pretreated
Dissecting therapy-induced T-cell responses in melanoma Tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) therapy of melanoma TIL are grown from melanoma tumors Rapid Expansion Infusion of TIL + IL-2 Patient pretreated
Adoptive T Cell Therapy:
 Adoptive T Cell Therapy: A Paradigm for Combination Strategies Cassian Yee MD Professor Melanoma Medical Oncology Immunology Director Solid Tumor Cell Therapy cyee@mdanderson.org skype name: tcelltherapy
Adoptive T Cell Therapy: A Paradigm for Combination Strategies Cassian Yee MD Professor Melanoma Medical Oncology Immunology Director Solid Tumor Cell Therapy cyee@mdanderson.org skype name: tcelltherapy
TITLE: Development of Antigen Presenting Cells for adoptive immunotherapy in prostate cancer
 AD Award Number: W8-XWH-5-- TITLE: Development of Antigen Presenting Cells for adoptive immunotherapy in prostate cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Mathias Oelke,. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Johns Hopkins
AD Award Number: W8-XWH-5-- TITLE: Development of Antigen Presenting Cells for adoptive immunotherapy in prostate cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Mathias Oelke,. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Johns Hopkins
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material accompanying the manuscript Interleukin 37 is a fundamental inhibitor of innate immunity Marcel F Nold, Claudia A Nold-Petry, Jarod A Zepp, Brent E Palmer, Philip Bufler & Charles
Supplementary Material accompanying the manuscript Interleukin 37 is a fundamental inhibitor of innate immunity Marcel F Nold, Claudia A Nold-Petry, Jarod A Zepp, Brent E Palmer, Philip Bufler & Charles
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. NKT ligand-loaded tumour antigen-presenting B cell- and monocyte-based vaccine induces NKT, NK and CD8 T cell responses. (A) The cytokine profiles of liver
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. NKT ligand-loaded tumour antigen-presenting B cell- and monocyte-based vaccine induces NKT, NK and CD8 T cell responses. (A) The cytokine profiles of liver
Avidity for antigen shapes clonal dominance in CD8 T cell populations specific for persistent DNA viruses
 Avidity for antigen shapes clonal dominance in CD8 T cell populations specific for persistent DNA viruses David A. Price, 1 Jason M. Brenchley, 1 Laura E. Ruff, 1 Michael R. Betts, 2 Brenna J. Hill, 1
Avidity for antigen shapes clonal dominance in CD8 T cell populations specific for persistent DNA viruses David A. Price, 1 Jason M. Brenchley, 1 Laura E. Ruff, 1 Michael R. Betts, 2 Brenna J. Hill, 1
Minor H Antigen-Specific T Cells -The Black Box of the GVL Effect
 Minor H Antigen-Specific T Cells -The Black Box of the GVL Effect All Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplants Are Blind Doctor Donor Patient Genetic polymorphism gives rise to unique peptides in donor and recipient
Minor H Antigen-Specific T Cells -The Black Box of the GVL Effect All Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplants Are Blind Doctor Donor Patient Genetic polymorphism gives rise to unique peptides in donor and recipient
<10. IL-1β IL-6 TNF + _ TGF-β + IL-23
 3 ns 25 ns 2 IL-17 (pg/ml) 15 1 ns ns 5 IL-1β IL-6 TNF
3 ns 25 ns 2 IL-17 (pg/ml) 15 1 ns ns 5 IL-1β IL-6 TNF
Journal of Immunological Methods
 Journal of Immunological Methods 338 (2008) 31 39 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Immunological Methods journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jim Research paper Detection of low
Journal of Immunological Methods 338 (2008) 31 39 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Immunological Methods journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jim Research paper Detection of low
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Science. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2008 March 12.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Science. 2006 October 6; 314(5796): 126 129. Cancer Regression in Patients After Transfer of Genetically Engineered Lymphocytes Richard
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Science. 2006 October 6; 314(5796): 126 129. Cancer Regression in Patients After Transfer of Genetically Engineered Lymphocytes Richard
Supplementary Fig. 1: Ex vivo tetramer enrichment with anti-c-myc beads
 Supplementary Fig. 1: Ex vivo tetramer enrichment with anti-c-myc beads Representative example of comparative ex vivo tetramer enrichment performed in three independent experiments with either conventional
Supplementary Fig. 1: Ex vivo tetramer enrichment with anti-c-myc beads Representative example of comparative ex vivo tetramer enrichment performed in three independent experiments with either conventional
Structural and kinetic basis for heightened immunogenicity of T cell vaccines
 Structural and kinetic basis for heightened immunogenicity of T cell vaccines Ji-Li Chen, 1 Guillaume Stewart-Jones, 2 Giovanna Bossi, 3 Nikolai M. Lissin, 4 Linda Wooldridge, 5 Ed Man Lik Choi, 1 Gerhard
Structural and kinetic basis for heightened immunogenicity of T cell vaccines Ji-Li Chen, 1 Guillaume Stewart-Jones, 2 Giovanna Bossi, 3 Nikolai M. Lissin, 4 Linda Wooldridge, 5 Ed Man Lik Choi, 1 Gerhard
TCR-ligand dissociation rate is a robust and stable biomarker of CD8 + T cell potency
 TCR-ligand dissociation rate is a robust and stable biomarker of CD8 + T cell potency Mathilde Allard,, Michael Hebeisen, Nathalie Rufer JCI Insight. 2017;2(14):e92570.. Research Article Immunology Therapeutics
TCR-ligand dissociation rate is a robust and stable biomarker of CD8 + T cell potency Mathilde Allard,, Michael Hebeisen, Nathalie Rufer JCI Insight. 2017;2(14):e92570.. Research Article Immunology Therapeutics
Challenges in Development and Validation of an Intracellular Cytokine Staining assay
 Challenges in Development and Validation of an Intracellular Cytokine Staining assay Jenny Hendriks, Crucell Hatching @ EBF, Brussels, June 202 www.crucell.com Vaccines vs Protein therapeutics Protein
Challenges in Development and Validation of an Intracellular Cytokine Staining assay Jenny Hendriks, Crucell Hatching @ EBF, Brussels, June 202 www.crucell.com Vaccines vs Protein therapeutics Protein
MHC Class I Molecules with Superenhanced CD8 Binding Properties Bypass the Requirement for Cognate TCR Recognition and Nonspecifically Activate CTLs
 The Journal of Immunology MHC Class I Molecules with Superenhanced CD8 Binding Properties Bypass the Requirement for Cognate TCR Recognition and Nonspecifically Activate CTLs Linda Wooldridge,*,1 Mathew
The Journal of Immunology MHC Class I Molecules with Superenhanced CD8 Binding Properties Bypass the Requirement for Cognate TCR Recognition and Nonspecifically Activate CTLs Linda Wooldridge,*,1 Mathew
TITLE: Development of Antigen Presenting Cells for adoptive immunotherapy in prostate cancer
 AD Award Number: W8XWH-5-- TITLE: Development of Antigen Presenting Cells for adoptive immunotherapy in prostate cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Mathias Oelke Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Johns Hopkins
AD Award Number: W8XWH-5-- TITLE: Development of Antigen Presenting Cells for adoptive immunotherapy in prostate cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Mathias Oelke Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Johns Hopkins
BD CBA on the BD Accuri C6: Bringing Multiplexed Cytokine Detection to the Benchtop
 BD CBA on the BD Accuri C6: Bringing Multiplexed Cytokine Detection to the Benchtop Maria Dinkelmann, PhD Senior Marketing Applications Specialist BD Biosciences, Ann Arbor, MI 23-14380-00 Cellular Communication
BD CBA on the BD Accuri C6: Bringing Multiplexed Cytokine Detection to the Benchtop Maria Dinkelmann, PhD Senior Marketing Applications Specialist BD Biosciences, Ann Arbor, MI 23-14380-00 Cellular Communication
T Cell Differentiation
 T Cell Differentiation Ned Braunstein, MD MHC control of Immune Responsiveness: Concept Whether or not an individual makes an immune response to a particular antigen depends on what MHC alleles an individual
T Cell Differentiation Ned Braunstein, MD MHC control of Immune Responsiveness: Concept Whether or not an individual makes an immune response to a particular antigen depends on what MHC alleles an individual
Junko Matsuzaki 1, Takemasa Tsuji 1*, Thinle Chodon 1, Courtney Ryan 2, Richard C. Koya 1 and Kunle Odunsi 1,3*
 Matsuzaki et al. Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer (2019) 7:7 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40425-018-0467-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access A rare population of tumor antigen-specific CD4 + CD8 + double-positive
Matsuzaki et al. Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer (2019) 7:7 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40425-018-0467-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access A rare population of tumor antigen-specific CD4 + CD8 + double-positive
T cell Receptor. Chapter 9. Comparison of TCR αβ T cells
 Chapter 9 The αβ TCR is similar in size and structure to an antibody Fab fragment T cell Receptor Kuby Figure 9-3 The αβ T cell receptor - Two chains - α and β - Two domains per chain - constant (C) domain
Chapter 9 The αβ TCR is similar in size and structure to an antibody Fab fragment T cell Receptor Kuby Figure 9-3 The αβ T cell receptor - Two chains - α and β - Two domains per chain - constant (C) domain
LAB 1, Immunology. Laboratory manual Immunology and Infection Biology Biomedicine course Autumn 2007
 LAB 1, Immunology Laboratory manual Immunology and Infection Biology Biomedicine course Autumn 2007 QUANTIFICATION OF CYTOTOXIC T LYMPHOCYTE ACTIVITY AND DETECTION OF FAS/TRAILR INDUCED APOPTOSIS RESPONSIBLE:
LAB 1, Immunology Laboratory manual Immunology and Infection Biology Biomedicine course Autumn 2007 QUANTIFICATION OF CYTOTOXIC T LYMPHOCYTE ACTIVITY AND DETECTION OF FAS/TRAILR INDUCED APOPTOSIS RESPONSIBLE:
Naive CD8 + T-cell precursors display structured TCR repertoires and composite antigen-driven selection dynamics
 OPEN (2015) 93, 625 633 & 2015 Australasian Society for Immunology Inc. All rights reserved 0818-9641/15 www.nature.com/icb ORIGINAL ARTICLE Naive CD8 + T-cell precursors display structured TCR repertoires
OPEN (2015) 93, 625 633 & 2015 Australasian Society for Immunology Inc. All rights reserved 0818-9641/15 www.nature.com/icb ORIGINAL ARTICLE Naive CD8 + T-cell precursors display structured TCR repertoires
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION
 Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Effector Responses: Cell- and Antibody-Mediated Immunity Copyright 2013 by W. H.
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Effector Responses: Cell- and Antibody-Mediated Immunity Copyright 2013 by W. H.
Potential cross reactions between HIV 1 specific T cells and the microbiome. Andrew McMichael Suzanne Campion
 Potential cross reactions between HIV 1 specific T cells and the microbiome Andrew McMichael Suzanne Campion Role of the Microbiome? T cell (and B cell) immune responses to HIV and Vaccines are influenced
Potential cross reactions between HIV 1 specific T cells and the microbiome Andrew McMichael Suzanne Campion Role of the Microbiome? T cell (and B cell) immune responses to HIV and Vaccines are influenced
New technologies for studying human immunity. Lisa Wagar Postdoctoral fellow, Mark Davis lab Stanford University School of Medicine
 New technologies for studying human immunity Lisa Wagar Postdoctoral fellow, Mark Davis lab Stanford University School of Medicine New strategies: Human immunology is ideal for a systems approach We have
New technologies for studying human immunity Lisa Wagar Postdoctoral fellow, Mark Davis lab Stanford University School of Medicine New strategies: Human immunology is ideal for a systems approach We have
Supplementalgfigureg1gSchematicgdiagramgofgtumor1modellingg
 SChinjectionh F:LuchLCLsh IVhinjectionh T:cellsh Monitorhforhtumorh growthhandhxeno: reactivehgvhd GVLgexperimentg kcbgvsgpbgt1cellse Xeno1reactiveg experimentg kcbgvsgpbgt1cellse IVhinjectionh 5xh,N^6
SChinjectionh F:LuchLCLsh IVhinjectionh T:cellsh Monitorhforhtumorh growthhandhxeno: reactivehgvhd GVLgexperimentg kcbgvsgpbgt1cellse Xeno1reactiveg experimentg kcbgvsgpbgt1cellse IVhinjectionh 5xh,N^6
A Novel HLA-B18 Restricted CD8+ T Cell Epitope Is Efficiently Cross-Presented by Dendritic Cells from Soluble Tumor Antigen
 A Novel HLA-B18 Restricted CD8+ T Cell Epitope Is Efficiently Cross-Presented by Dendritic Cells from Soluble Tumor Antigen Rona Y. Zhao 1., Nicole A. Mifsud 1., Kun Xiao 1., Kok-Fei Chan 1, Sara Oveissi
A Novel HLA-B18 Restricted CD8+ T Cell Epitope Is Efficiently Cross-Presented by Dendritic Cells from Soluble Tumor Antigen Rona Y. Zhao 1., Nicole A. Mifsud 1., Kun Xiao 1., Kok-Fei Chan 1, Sara Oveissi
Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells Inhibit Cytomegalovirus Inflammation through Interleukin-27 and B7-H4
 Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells Inhibit Cytomegalovirus Inflammation through Interleukin-27 and B7-H4 Ankita Garg, Rodney Trout and Stephen A. Spector,,* Department
Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells Inhibit Cytomegalovirus Inflammation through Interleukin-27 and B7-H4 Ankita Garg, Rodney Trout and Stephen A. Spector,,* Department
Alternate Antibody-Based Therapeutic Strategies To Purge the HIV Cell Reservoir
 Alternate Antibody-Based Therapeutic Strategies To Purge the HIV Cell Reservoir Giuseppe Pantaleo, M.D. Professor of Medicine Head, Division of Immunology and Allergy Executive Director, Swiss Vaccine
Alternate Antibody-Based Therapeutic Strategies To Purge the HIV Cell Reservoir Giuseppe Pantaleo, M.D. Professor of Medicine Head, Division of Immunology and Allergy Executive Director, Swiss Vaccine
Relating TCR-peptide-MHC affinity to immunogenicity for the design of tumor vaccines
 Research article Relating TCR-peptide-MHC affinity to immunogenicity for the design of tumor vaccines Rachel H. McMahan, 1 Jennifer A. McWilliams, 1 Kimberly R. Jordan, 1 Steven W. Dow, 2 Darcy B. Wilson,
Research article Relating TCR-peptide-MHC affinity to immunogenicity for the design of tumor vaccines Rachel H. McMahan, 1 Jennifer A. McWilliams, 1 Kimberly R. Jordan, 1 Steven W. Dow, 2 Darcy B. Wilson,
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice. (a) Gene expression profile in the resting CD4 + T cells were analyzed by an Affymetrix microarray
Supplementary Figure 1 Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice. (a) Gene expression profile in the resting CD4 + T cells were analyzed by an Affymetrix microarray
Th17 and Th17/Treg ratio at early HIV infection associate with protective HIV-specific CD8 + T-cell responses and disease progression
 Th17 and Th17/Treg ratio at early HIV infection associate with protective HIV-specific CD8 T-cell responses and disease progression Juliana Falivene 1, Yanina Ghiglione 1, Natalia Laufer 1,3, María Eugenia
Th17 and Th17/Treg ratio at early HIV infection associate with protective HIV-specific CD8 T-cell responses and disease progression Juliana Falivene 1, Yanina Ghiglione 1, Natalia Laufer 1,3, María Eugenia
HLA-E restricted responses in Tuberculosis
 HLA-E restricted responses in Tuberculosis Simone A. Joosten Dept. of Infectious Diseases LEIDEN UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTER Unconventional immunity Conventional immunity: T cells reactive to complexes of
HLA-E restricted responses in Tuberculosis Simone A. Joosten Dept. of Infectious Diseases LEIDEN UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTER Unconventional immunity Conventional immunity: T cells reactive to complexes of
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Valkenburg et al. 10.1073/pnas.1403684111 SI Materials and Methods ELISA and Microneutralization. Sera were treated with Receptor Destroying Enzyme II (RDE II, Accurate) before ELISA
Supporting Information Valkenburg et al. 10.1073/pnas.1403684111 SI Materials and Methods ELISA and Microneutralization. Sera were treated with Receptor Destroying Enzyme II (RDE II, Accurate) before ELISA
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR. (R)-Profens Are Substrate-Selective Inhibitors of Endocannabinoid Oxygenation. by COX-2
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR (R)-Profens Are Substrate-Selective Inhibitors of Endocannabinoid Oxygenation by COX-2 Kelsey C. Duggan, Daniel J. Hermanson, Joel Musee, Jeffery J. Prusakiewicz, Jami L.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR (R)-Profens Are Substrate-Selective Inhibitors of Endocannabinoid Oxygenation by COX-2 Kelsey C. Duggan, Daniel J. Hermanson, Joel Musee, Jeffery J. Prusakiewicz, Jami L.
Adoptive cell therapy using genetically modified antigen-presenting cells
 Adoptive cell therapy using genetically modified antigen-presenting cells Naoto Hirano Ontario Cancer Institute Princess Margaret Cancer Centre University of Toronto UofT-USP Oncology Conference November
Adoptive cell therapy using genetically modified antigen-presenting cells Naoto Hirano Ontario Cancer Institute Princess Margaret Cancer Centre University of Toronto UofT-USP Oncology Conference November
Supplementary Data. Treg phenotype
 Supplementary Data Additional Experiment An additional experiment was performed using cryopreserved peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) derived from five renal cell carcinoma (RCC) patients [see
Supplementary Data Additional Experiment An additional experiment was performed using cryopreserved peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) derived from five renal cell carcinoma (RCC) patients [see
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 A β-strand positions consistently places the residues at CDR3β P6 and P7 within human and mouse TCR-peptide-MHC interfaces. (a) E8 TCR containing V β 13*06 carrying with an 11mer
Supplementary Figure 1 A β-strand positions consistently places the residues at CDR3β P6 and P7 within human and mouse TCR-peptide-MHC interfaces. (a) E8 TCR containing V β 13*06 carrying with an 11mer
Use of Peptide-Major Histocompatibility Complex Tetramer Technology To Study Interactions between Staphylococcus aureus Proteins and Human Cells
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Dec. 2007, p. 5711 5715 Vol. 75, No. 12 0019-9567/07/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.00875-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Use of Peptide-Major
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Dec. 2007, p. 5711 5715 Vol. 75, No. 12 0019-9567/07/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.00875-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Use of Peptide-Major
TITLE: MODULATION OF T CELL TOLERANCE IN A MURINE MODEL FOR IMMUNOTHERAPY OF PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA
 AD Award Number: DAMD17-01-1-0085 TITLE: MODULATION OF T CELL TOLERANCE IN A MURINE MODEL FOR IMMUNOTHERAPY OF PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: ARTHUR A HURWITZ, Ph.d. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AD Award Number: DAMD17-01-1-0085 TITLE: MODULATION OF T CELL TOLERANCE IN A MURINE MODEL FOR IMMUNOTHERAPY OF PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: ARTHUR A HURWITZ, Ph.d. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
LG-APM s for MHC-Peptide Screening
 LG-APM s for MHC-Peptide Screening S. Stanley*, I. A. Dodi* #, C.R. Evans*, S. J. Paston #, R.C. Rees*, C.J. Percival $, Glen McHale* and M.I Newton* *School of Biomedical & Natural Sciences, Nottingham
LG-APM s for MHC-Peptide Screening S. Stanley*, I. A. Dodi* #, C.R. Evans*, S. J. Paston #, R.C. Rees*, C.J. Percival $, Glen McHale* and M.I Newton* *School of Biomedical & Natural Sciences, Nottingham
Other Clinical Diagnoses
 Donor Case ID 14 year old fe npod6342 24 year old npod6367 12 year old fe npod6268 6 year old fe npod69 22 year old fe npod6323 20 year old T1D.6 27 year old T1D.7 30 year old T1D.8 22 year old T1D.9 Duration
Donor Case ID 14 year old fe npod6342 24 year old npod6367 12 year old fe npod6268 6 year old fe npod69 22 year old fe npod6323 20 year old T1D.6 27 year old T1D.7 30 year old T1D.8 22 year old T1D.9 Duration
RECOGNITION OF MYCOBACTERIAL ANTIGENS BY CONVENTIONAL AND UNCONVENTIONAL HUMAN T-CELLS. Johanne M. Pentier
 RECOGNITION OF MYCOBACTERIAL ANTIGENS BY CONVENTIONAL AND UNCONVENTIONAL HUMAN T-CELLS Johanne M. Pentier A thesis submitted to Cardiff University in fulfilment of the requirement for the Degree of Doctor
RECOGNITION OF MYCOBACTERIAL ANTIGENS BY CONVENTIONAL AND UNCONVENTIONAL HUMAN T-CELLS Johanne M. Pentier A thesis submitted to Cardiff University in fulfilment of the requirement for the Degree of Doctor
Defining the directionality and quality of influenza virus specific CD8 + T cell cross-reactivity in individuals infected with hepatitis C virus
 Research article Defining the directionality and quality of influenza virus specific CD8 + T cell cross-reactivity in individuals infected with hepatitis C virus Victoria Kasprowicz, 1 Scott M. Ward, 2
Research article Defining the directionality and quality of influenza virus specific CD8 + T cell cross-reactivity in individuals infected with hepatitis C virus Victoria Kasprowicz, 1 Scott M. Ward, 2
Commercially available HLA Class II tetramers (Beckman Coulter) conjugated to
 Class II tetramer staining Commercially available HLA Class II tetramers (Beckman Coulter) conjugated to PE were combined with dominant HIV epitopes (DRB1*0101-DRFYKTLRAEQASQEV, DRB1*0301- PEKEVLVWKFDSRLAFHH,
Class II tetramer staining Commercially available HLA Class II tetramers (Beckman Coulter) conjugated to PE were combined with dominant HIV epitopes (DRB1*0101-DRFYKTLRAEQASQEV, DRB1*0301- PEKEVLVWKFDSRLAFHH,
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Cytokine pattern in skin in response to urushiol.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Cytokine pattern in skin in response to urushiol. Wild-type (WT) and CD1a-tg mice (n = 3 per group) were sensitized and challenged with urushiol (uru) or vehicle (veh). Quantitative
Supplementary Figure 1 Cytokine pattern in skin in response to urushiol. Wild-type (WT) and CD1a-tg mice (n = 3 per group) were sensitized and challenged with urushiol (uru) or vehicle (veh). Quantitative
HD1 (FLU) HD2 (EBV) HD2 (FLU)
 ramer staining + anti-pe beads ramer staining a HD1 (FLU) HD2 (EBV) HD2 (FLU).73.11.56.46.24 1.12 b CD127 + c CD127 + d CD127 - e CD127 - PD1 - PD1 + PD1 + PD1-1 1 1 1 %CD127 + PD1-8 6 4 2 + anti-pe %CD127
ramer staining + anti-pe beads ramer staining a HD1 (FLU) HD2 (EBV) HD2 (FLU).73.11.56.46.24 1.12 b CD127 + c CD127 + d CD127 - e CD127 - PD1 - PD1 + PD1 + PD1-1 1 1 1 %CD127 + PD1-8 6 4 2 + anti-pe %CD127
Supplementary Table 1 Clinicopathological characteristics of 35 patients with CRCs
 Supplementary Table Clinicopathological characteristics of 35 patients with CRCs Characteristics Type-A CRC Type-B CRC P value Sex Male / Female 9 / / 8.5 Age (years) Median (range) 6. (9 86) 6.5 (9 76).95
Supplementary Table Clinicopathological characteristics of 35 patients with CRCs Characteristics Type-A CRC Type-B CRC P value Sex Male / Female 9 / / 8.5 Age (years) Median (range) 6. (9 86) 6.5 (9 76).95
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Mechanism of inactivation of -aminobutyric acid aminotransferase by (1S,3S)-3-amino-4-difluoromethylenyl-1- cyclopentanoic acid (CPP-115) Hyunbeom Lee, 1, Emma H. Doud, 1,2 Rui Wu,
Supporting Information Mechanism of inactivation of -aminobutyric acid aminotransferase by (1S,3S)-3-amino-4-difluoromethylenyl-1- cyclopentanoic acid (CPP-115) Hyunbeom Lee, 1, Emma H. Doud, 1,2 Rui Wu,
Supplemental Data Figure S1 Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells.
 Supplemental Data Figure S1. Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells. (A) Specific lysis of IFN-γ-treated SKBR-3 cells in the absence
Supplemental Data Figure S1. Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells. (A) Specific lysis of IFN-γ-treated SKBR-3 cells in the absence
Supplementary Figure 1. Efficient DC depletion in CD11c.DOG transgenic mice
 Supplementary Figure 1. Efficient DC depletion in CD11c.DOG transgenic mice (a) CD11c.DOG transgenic mice (tg) were treated with 8 ng/g body weight (b.w.) diphtheria toxin (DT) i.p. on day -1 and every
Supplementary Figure 1. Efficient DC depletion in CD11c.DOG transgenic mice (a) CD11c.DOG transgenic mice (tg) were treated with 8 ng/g body weight (b.w.) diphtheria toxin (DT) i.p. on day -1 and every
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Notes 1: accuracy of prediction algorithms for peptide binding affinities to HLA and Mamu alleles For each HLA and Mamu allele we have analyzed the accuracy of four predictive algorithms
Supplementary Notes 1: accuracy of prediction algorithms for peptide binding affinities to HLA and Mamu alleles For each HLA and Mamu allele we have analyzed the accuracy of four predictive algorithms
Tumors arise from accumulated genetic mutations. Tumor Immunology (Cancer)
 Tumor Immunology (Cancer) Tumors arise from accumulated genetic mutations Robert Beatty MCB150 Mutations Usually have >6 mutations in both activation/growth factors and tumor suppressor genes. Types of
Tumor Immunology (Cancer) Tumors arise from accumulated genetic mutations Robert Beatty MCB150 Mutations Usually have >6 mutations in both activation/growth factors and tumor suppressor genes. Types of
x Lymphocyte count /µl CD8+ count/µl 800 Calculated
 % Lymphocyte in CBC A. 50 40 30 20 10 Lymphocyte count /µl B. x10 3 2.5 1.5 C. 50 D. 1000 % CD3+CD8+ Cells 40 30 20 Calculated CD8+ count/µl 800 600 400 200 10 0 #61 #63 #64 #65 #68 #71 #72 #75 Figure
% Lymphocyte in CBC A. 50 40 30 20 10 Lymphocyte count /µl B. x10 3 2.5 1.5 C. 50 D. 1000 % CD3+CD8+ Cells 40 30 20 Calculated CD8+ count/µl 800 600 400 200 10 0 #61 #63 #64 #65 #68 #71 #72 #75 Figure
Tumor Antigen, Tumor Immunogenicity and Immunization
 Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer 2012 Primer in Tumor Immunology and Biological Therapy of Cancer October 25 th, 2012, Bethesda, MD Tumor Antigen, Tumor Immunogenicity and Immunization Pedro Romero
Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer 2012 Primer in Tumor Immunology and Biological Therapy of Cancer October 25 th, 2012, Bethesda, MD Tumor Antigen, Tumor Immunogenicity and Immunization Pedro Romero
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION
 Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 11 T-Cell Activation, Differentiation, and Memory Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 11 T-Cell Activation, Differentiation, and Memory Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and
IOM Immunization Safety Review 11/12/2001. Immunological Competition and the Infant Immune Response to Vaccines
 IOM Immunization Safety Review 11/12/2001 Immunological Competition and the Infant Immune Response to Vaccines Richard Insel University of Rochester Goals Neonatal and Infant Immune System Broad Effects
IOM Immunization Safety Review 11/12/2001 Immunological Competition and the Infant Immune Response to Vaccines Richard Insel University of Rochester Goals Neonatal and Infant Immune System Broad Effects
Narrowed TCR repertoire and viral escape as a consequence of heterologous immunity
 Research article Narrowed TCR repertoire and viral escape as a consequence of heterologous immunity Markus Cornberg, 1,2 Alex T. Chen, 1 Lee A. Wilkinson, 1 Michael A. Brehm, 1 Sung-Kwon Kim, 1 Claudia
Research article Narrowed TCR repertoire and viral escape as a consequence of heterologous immunity Markus Cornberg, 1,2 Alex T. Chen, 1 Lee A. Wilkinson, 1 Michael A. Brehm, 1 Sung-Kwon Kim, 1 Claudia
EBV Infection and Immunity. Andrew Hislop Institute for Cancer Studies University of Birmingham
 EBV Infection and Immunity Andrew Hislop Institute for Cancer Studies University of Birmingham EBV Introduction Large ds DNA virus Spread by saliva contact Lifelong infection Predominantly B-lymphotropic
EBV Infection and Immunity Andrew Hislop Institute for Cancer Studies University of Birmingham EBV Introduction Large ds DNA virus Spread by saliva contact Lifelong infection Predominantly B-lymphotropic
Todd D. Prickett Ph.D. Surgery Branch/NCI/NIH. Dr. Steven A. Rosenberg Branch Chief Dr. Paul F. Robbins Surgery Branch/NCI/NIH
 Durable Complete Response in a Patient with Metastatic Melanoma Following Adoptive Transfer of Autologous T cells Recognizing 1 Mutated Tumor Antigens Todd D. Prickett Ph.D. Surgery Branch/NCI/NIH Dr.
Durable Complete Response in a Patient with Metastatic Melanoma Following Adoptive Transfer of Autologous T cells Recognizing 1 Mutated Tumor Antigens Todd D. Prickett Ph.D. Surgery Branch/NCI/NIH Dr.
