Immune System. Biol 105 Chapter 13
|
|
|
- Loraine Holland
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Immune System Biol 105 Chapter 13
2 Outline Immune System I. Function of the Immune system II. Barrier Defenses III. Nonspecific Defenses A. Immune system cells B. Inflammatory response C. Complementary proteins IV. Specific Defenses A. B cells Antibody mediated response B. T cells Cell mediated response V. Disorders of the immune system
3 Function of the Immune System Defend the body against foreign invaders. Must be able to discriminate between the body s own cells & tissues versus foreign material.
4 Distinguishing Self from Foreign Organisms To defend against foreign invaders, the body needs to identify its own cells. All the cells in your body have proteins in their plasma membrane that identify them as part of your body. These proteins are major histocompatibility complex (MHC) markers. Your MHC markers are unique to you.
5 MHC Markers Figure 13.8
6 Terminology Antigen any object or substance that is perceived as foreign and therefore elicits an immune response. Antibodies proteins produced by B-cells in response to an antigen. Pathogen microorganism or parasite that causes disease.
7 Barrier Defenses 1. Skin 2. Tears and saliva have Lysozymes 3. Cilia and mucus 4. Stomach acid 5. Beneficial bacteria 6. Acidic urine
8 Barrier Defenses 1. The skin is an excellent barrier keeping many things out of the body. 2. Tears and saliva have lysozymes which are enzymes that can kill bacteria.
9 Barrier Defenses 3. The respiratory tract has cilia and mucus that help to trap foreign objects and transport them out of the respiratory system. 4. Stomach acid helps to kill bacteria that has been ingested.
10 Barrier Defenses 5. Beneficial bacteria in the large intestine out compete harmful bacteria. 6. Acidic urine kills bacteria and washes bacteria from urethra.
11 Two Types of Immune Defense 1. Nonspecific defenses: Part of the immune system that attacks any antigen (cell or object it identifies as foreign). 2. Specific defenses: Other immune cells will only respond to one specific antigen. Leads to an immunity = a long lasting protection from that specific antigen.
12 Non Specific Defenses 1. Immune system cells A. Neutrophils B. Monocytes/Macrophages (APC) C. Eosinophils D. Natural killer cells nonspecific lymphocyte 2. Inflammatory response 3. Proteins
13 Non Specific Defenses - Cells 1. Immune system cells A. Neutrophils B. Monocytes/Macrophages C. Eosinophils D. Natural Killer Cells See Blood Lecture for descriptions of these cells.
14 Inflammatory Response When the body is injured or damaged then the body mounts an inflammatory response. Mast cells in the tissue release histamine. Histamine causes: blood vessels to dilate blood vessels to become more permeable
15 Inflammatory Response Now that the blood vessels are wider (dilated), more blood flows to the site of injury and brings more immune cells and proteins to the injury. Increased blood flow causes increased temperature and redness.
16 Inflammatory Response The blood vessels become more permeable so the defense cells, fluid and proteins can get out of the vessels to reach the site of injury. This causes swelling and stimulates nerve receptors leading to pain Proteins, including complement proteins and clotting factors, arrive.
17 Inflammatory Response Figure 13.6 (1 of 2)
18 Inflammatory Response Figure 13.6 (2 of 2)
19 Defense Proteins - Complement proteins Complement Proteins: Proteins that enhance the immune response. Effects: Punch hole in invading cell. Attract phagocytes and coat bacteria to make them easier to phagocytize.
20 Complement proteins Figure 13.5 (1 of 3)
21 Complement proteins Figure 13.5 (2 of 3)
22 Complement proteins Figure 13.5 (3 of 3)
23 Defense Proteins - Interferons Interferons: Cells infected with viruses secrete interferon proteins. Effects: Attract Macrophages and Natural Killer Cells. Protect other cells from viral infections. Inhibit cell division in cancer cells
24 Specific Defenses Specific defenses are acquired immunity If our body come in contact with an antigen, it remembers that antigen so the next time it comes in contact with it, the body can quickly mount a defense and attack the antigen.
25 How do we acquire immunity? In the specific defenses there are two ways we fight invaders: Antibody-mediated immunity B lymphocytes Cell-mediated immunity T lymphocytes
26 Lymphocytes - T cells T cells are produced in the bone marrow They travel to the Thymus where they develop into mature T-Cells. These cells are important in the cell mediated part of our acquired immunity.
27 Lymphocytes - B cells B-Cells are produced in the bone marrow. They stay and mature in the bone marrow. They are important in antibody mediated immunity.
28 Lymphocytes - B cells and T cells Both mature B cells and T cells will go to the lymphatic system and the circulatory system.
29
30 Antibody Mediated Immunity Antibodies are proteins that circulate through the body and bind onto a particular antigen (foreign object). Antibodies start out as receptors on the surface of B cells. The antibody is specific it will only bind to one type of antigen. Antibodies are released from B cells and circulate throughout the body.
31 Antibodies An antibody is specific to a particular antigen. How can we have so many different types of receptors (antibodies) on our B cells?
32 Antibodies The B-cells have DNA sequences that are constantly being shuffled to create new B- cells with new types of receptors. DNA is transcribed to make mrna. mrna is translated to make proteins. The proteins are receptors (antibodies).
33 Antibodies B cells are diverse, they differ in the type of receptor they have, each B cell only has one type of receptor. When a B cell receptor comes into contact with the antigen it is specific for, the B cell starts to make identical copies of itself through mitosis. These copies are called clones = clonal selection.
34 Antibodies Some of these B cells will shed their receptors: Plasma cells. Other B cells will keep their receptors, and will remain in the body, ready to defend against the antigen in the future: Memory cells.
35 B Cells Produce Antibodies B-cell receptor There is a tremendous variety of B cells. Each B cell has receptors for a different antigen on its surface. B cells This B cell has receptors specific for this particular antigen. Antigen The antigen binds to the B cell with appropriate receptors. The selected B cell divides, producing a clone of cells all bearing receptors specific for that particular antigen. Figure (1 of 2)
36 B Cells Produce Antibodies Step 5: Building specific defenses The B cell divides and forms plasma cells and memory cells. B cell Memory B cell Plasma cell Step 6: Defense Plasma cells secrete antibodies specific for that antigen. Plasma cell Antibodies Step 7: Continued surveillance Memory B cells remain and mount a quick response if the invader is encountered again. Memory B cells Figure (2 of 2)
37 Immune Response Steps Figure 13.15
38 How do antibodies defend against antigens? The antibodies that are free floating in your body will bind to the antigen. This has many effects on the antigen.
39 Effects of Antibodies Binding to Antigen 1. To mark it so the body knows to destroy it with its nonspecific defenses. 2. Attracts phagocytes to the area. The phagocytes will engulf and destroy the antigen. 3. Coats the antigen, making it easier to phagocytize. 4. Binds the antigens, causing them to clump together this will cause them fall out of solution. 5. Neutralize toxins and viruses. 6. Activate the complement proteins which cause the bacteria to lyse open.
40 Antigen-presenting cells Macrophages can also be antigen presenting cells (APCs) which pick up antigens (foreign material) and bring them to the lymph nodes and the spleen. The lymph nodes and spleen store huge numbers of immune system cells. One type of cell they meet there are Helper T cells.
41 Cell Mediated Immunity T Cells Remember that some lymphocytes go to the thymus to develop into T cells. These cells are important players in cell mediated immunity. There are two types of T cells Helper (CD4) T cells Killer (cytotoxic) T cells
42 T cells When a helper T cell meets a APC cell with the correct antigen, it becomes activated meaning it starts to make copies or clones of itself. The helper T cells also activate cytotoxic T cells to also start making clones, and the helper T cells activate B cells. The cytotoxic T cells kill virus infected cells and tumor cells.
43
44 Function of the Immune System Defend the body against foreign invaders. Must be able to discriminate between the body s own cells and tissues versus foreign material.
45 Autoimmune Disorders Remember that an antigen is something the immune system recognizes as foreign. Sometimes the body recognizes parts of the body as foreign. Systemic lupus erythematosus connective tissue Rheumatoid arthritis - joints Multiple sclerosis myelin sheath Myasthenia gravis - acetylcholine receptors at the neuromuscular junction
46 Immune system disorders Sometimes the body recognizes harmless foreign objects as harmful. Allergies, including food allergies
47 Important Concepts Read Chapter 13a for next lecture What are the examples of barrier defenses What are the Nonspecific defenses and the Specific defenses, what are the differences. What are the functions of all the white blood cells discussed in this lecture and in the blood lecture.
48 Important Concepts What are the three types of lymphocytes, which are part of the specific and which are part of the nonspecific defense system. How does the body mount an inflammatory response and what is the effect on the body. What are the functions of complement proteins and interferons. What is the function of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) markers
49 Important Concepts T cells and B cells where are they produced, where do they mature, where are they found once they have matured, are they part of the cell mediated or antibody mediated defenses? What are the types of T cells, what is the function of T cells? What are antibodies, how are they produced, What effect do they have. What are memory cells, plasma cells, and how does clonal selection work?
50 Important Concepts What are antigen-presenting cells (APCs). What is the target of HIV How does HIV replicate itself (seven steps, including the enzymes needed) What are the targets of HIV drugs What are examples of autoimmune and immune system disease, what is the target of the autoimmune disease, what is the effect of allergies on the body.
51 Definitions Antigen, antibodies, immunity, pathogen, lysozymes, histamines, permeable, transcription, translation, acquired immunity
Immune System. Biol 105 Lecture 16 Chapter 13
 Immune System Biol 105 Lecture 16 Chapter 13 Outline Immune System I. Function of the Immune system II. Barrier Defenses III. Nonspecific Defenses A. Immune system cells B. Inflammatory response C. Complementary
Immune System Biol 105 Lecture 16 Chapter 13 Outline Immune System I. Function of the Immune system II. Barrier Defenses III. Nonspecific Defenses A. Immune system cells B. Inflammatory response C. Complementary
Immune System. Biology 105 Lecture 16 Chapter 13
 Immune System Biology 105 Lecture 16 Chapter 13 Outline: Immune System I. Functions of the immune system II. Barrier defenses III. Non-specific defenses A. Immune system cells B. Inflammatory response
Immune System Biology 105 Lecture 16 Chapter 13 Outline: Immune System I. Functions of the immune system II. Barrier defenses III. Non-specific defenses A. Immune system cells B. Inflammatory response
Body Defense Mechanisms
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 13 Body Defense Mechanisms Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 13 Body Defense Mechanisms Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of
Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 The Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems 1 The Lymphatic Vessels Lymphoid Organs Three functions contribute to homeostasis 1. Return excess tissue fluid to the bloodstream 2. Help defend the body against
The Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems 1 The Lymphatic Vessels Lymphoid Organs Three functions contribute to homeostasis 1. Return excess tissue fluid to the bloodstream 2. Help defend the body against
Chapter 43. Immune System. phagocytosis. lymphocytes. AP Biology
 Chapter 43. Immune System phagocytosis lymphocytes 1 Why an immune system? Attack from outside lots of organisms want you for lunch! animals must defend themselves against unwelcome invaders viruses protists
Chapter 43. Immune System phagocytosis lymphocytes 1 Why an immune system? Attack from outside lots of organisms want you for lunch! animals must defend themselves against unwelcome invaders viruses protists
Chapter 38- Immune System
 Chapter 38- Immune System First Line of Defense: Barriers Nonspecific defenses, such as the skin and mucous membranes, are barriers to potential pathogens. In addition to being a physical barrier to pathogens,
Chapter 38- Immune System First Line of Defense: Barriers Nonspecific defenses, such as the skin and mucous membranes, are barriers to potential pathogens. In addition to being a physical barrier to pathogens,
Warm-up. Parts of the Immune system. Disease transmission. Disease transmission. Why an immune system? Chapter 43 3/9/2012.
 Warm-up Objective: Explain how antigens react with specific lymphocytes to induce immune response and immunological memory. Warm-up: Which of the following would normally contain blood with the least amount
Warm-up Objective: Explain how antigens react with specific lymphocytes to induce immune response and immunological memory. Warm-up: Which of the following would normally contain blood with the least amount
What are bacteria? Microbes are microscopic(bacteria, viruses, prions, & some fungi etc.) How do the sizes of our cells, bacteria and viruses compare?
 7.1 Microbes, pathogens and you Chp. 7 Lymphatic System & Immunity The interaction between microbes and humans? Microbes are very abundant in the environment and as well as in and on our bodies GOOD: We
7.1 Microbes, pathogens and you Chp. 7 Lymphatic System & Immunity The interaction between microbes and humans? Microbes are very abundant in the environment and as well as in and on our bodies GOOD: We
Topics in Parasitology BLY Vertebrate Immune System
 Topics in Parasitology BLY 533-2008 Vertebrate Immune System V. Vertebrate Immune System A. Non-specific defenses against pathogens 1. Skin - physical barrier a. Tough armor protein KERATIN b. Surface
Topics in Parasitology BLY 533-2008 Vertebrate Immune System V. Vertebrate Immune System A. Non-specific defenses against pathogens 1. Skin - physical barrier a. Tough armor protein KERATIN b. Surface
Chapter Pages Transmission
 Chapter 19.2 Pages 442-448 Transmission Immunity There are three lines of defense: 1 The skin and mucous membranes are a nonspecific barrier to infection. 2 Macrophages attack pathogens that enter the
Chapter 19.2 Pages 442-448 Transmission Immunity There are three lines of defense: 1 The skin and mucous membranes are a nonspecific barrier to infection. 2 Macrophages attack pathogens that enter the
Immune System AP SBI4UP
 Immune System AP SBI4UP TYPES OF IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY ACQUIRED IMMUNITY EXTERNAL DEFENCES INTERNAL DEFENCES HUMORAL RESPONSE Skin Phagocytic Cells CELL- MEDIATED RESPONSE Mucus layer Antimicrobial
Immune System AP SBI4UP TYPES OF IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY ACQUIRED IMMUNITY EXTERNAL DEFENCES INTERNAL DEFENCES HUMORAL RESPONSE Skin Phagocytic Cells CELL- MEDIATED RESPONSE Mucus layer Antimicrobial
AP Biology. Why an immune system? Chapter 43. Immune System. Lines of defense. 1st: External defense. 2nd: Internal, broad range patrol
 Chapter 43. Immune System lymphocytes attacking cancer cell lymph phagocytic leukocyte Why an immune system? Attack from outside lots of organisms want you for lunch! animals must defend themselves against
Chapter 43. Immune System lymphocytes attacking cancer cell lymph phagocytic leukocyte Why an immune system? Attack from outside lots of organisms want you for lunch! animals must defend themselves against
Immune System Notes Innate immunity Acquired immunity lymphocytes, humoral response Skin lysozyme, mucus membrane
 Immune System Notes I. The immune system consists of innate and acquired immunity. A. An animal must defend itself against unwelcome intruders the many potentially dangerous viruses, bacteria, and other
Immune System Notes I. The immune system consists of innate and acquired immunity. A. An animal must defend itself against unwelcome intruders the many potentially dangerous viruses, bacteria, and other
The Immune System. These are classified as the Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses. Innate Immunity
 The Immune System Biological mechanisms that defend an organism must be 1. triggered by a stimulus upon injury or pathogen attack 2. able to counteract the injury or invasion 3. able to recognise foreign
The Immune System Biological mechanisms that defend an organism must be 1. triggered by a stimulus upon injury or pathogen attack 2. able to counteract the injury or invasion 3. able to recognise foreign
I. Lines of Defense Pathogen: Table 1: Types of Immune Mechanisms. Table 2: Innate Immunity: First Lines of Defense
 I. Lines of Defense Pathogen: Table 1: Types of Immune Mechanisms Table 2: Innate Immunity: First Lines of Defense Innate Immunity involves nonspecific physical & chemical barriers that are adapted for
I. Lines of Defense Pathogen: Table 1: Types of Immune Mechanisms Table 2: Innate Immunity: First Lines of Defense Innate Immunity involves nonspecific physical & chemical barriers that are adapted for
The Immune System. Specific Immunity
 The Immune System Specific Immunity What You Should Know Immune surveillance A range of white blood cells constantly circulate monitoring the tissues. If tissues become damaged or invaded, cells release
The Immune System Specific Immunity What You Should Know Immune surveillance A range of white blood cells constantly circulate monitoring the tissues. If tissues become damaged or invaded, cells release
The Lymphatic System and Immunity. Chapters 20 & 21
 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapters 20 & 21 Objectives 1. SC.912.L.14.52 - Explain the basic functions of the human immune system, including specific and nonspecific immune response, vaccines, and
The Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapters 20 & 21 Objectives 1. SC.912.L.14.52 - Explain the basic functions of the human immune system, including specific and nonspecific immune response, vaccines, and
Chapter 17. The Lymphatic System and Immunity. Copyright 2010, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 17 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Immunity Innate Immunity Fast, non-specific and no memory Barriers, ph extremes, Phagocytes & NK cells, fever, inflammation, complement, interferon Adaptive
Chapter 17 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Immunity Innate Immunity Fast, non-specific and no memory Barriers, ph extremes, Phagocytes & NK cells, fever, inflammation, complement, interferon Adaptive
NOTES: CH 43, part 1 The Immune System - Nonspecific & Specific Defenses ( )
 NOTES: CH 43, part 1 The Immune System - Nonspecific & Specific Defenses (43.1-43.2) The lymphatic system is closely associated with the cardiovascular system. LYMPHATIC PATHWAYS Lymphatic capillaries
NOTES: CH 43, part 1 The Immune System - Nonspecific & Specific Defenses (43.1-43.2) The lymphatic system is closely associated with the cardiovascular system. LYMPHATIC PATHWAYS Lymphatic capillaries
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 13 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Internal Defense Notes
 Internal environment of animals provides attractive area for growth of bacteria, viruses, fungi Harm via: 1. destruction of cells 2. production of toxic chemicals To protect against foreign invaders, humans
Internal environment of animals provides attractive area for growth of bacteria, viruses, fungi Harm via: 1. destruction of cells 2. production of toxic chemicals To protect against foreign invaders, humans
PATHOGENS AND DEFENCE AGAINST INFECTIOUS DISEASE. By: Stephanie, Emily, Cem, and Julie
 PATHOGENS AND DEFENCE AGAINST INFECTIOUS DISEASE By: Stephanie, Emily, Cem, and Julie Pathogen Pathogen: an organism or virus that causes a disease. Examples: bacteria, fungi, protozoa, virus Disease Cause
PATHOGENS AND DEFENCE AGAINST INFECTIOUS DISEASE By: Stephanie, Emily, Cem, and Julie Pathogen Pathogen: an organism or virus that causes a disease. Examples: bacteria, fungi, protozoa, virus Disease Cause
CH. 24. The Immune System
 CH. 24 The Immune System The immune systems consists of organs, cells, and molecules that fight infections and protect us from invaders. Pathogens: Bacteria, Viruses, Parasites, Fungi 1. Innate (nonspecific)
CH. 24 The Immune System The immune systems consists of organs, cells, and molecules that fight infections and protect us from invaders. Pathogens: Bacteria, Viruses, Parasites, Fungi 1. Innate (nonspecific)
Immune System. Presented by Kazzandra Anton, Rhea Chung, Lea Sado, and Raymond Tanaka
 Immune System Presented by Kazzandra Anton, Rhea Chung, Lea Sado, and Raymond Tanaka Content Standards 35.1 In innate immunity, recognition and response rely on traits common to groups of pathogens 35.2
Immune System Presented by Kazzandra Anton, Rhea Chung, Lea Sado, and Raymond Tanaka Content Standards 35.1 In innate immunity, recognition and response rely on traits common to groups of pathogens 35.2
Immunity. Chapter 38
 Immunity Chapter 38 Impacts, Issues Frankie s Last Wish Infection with a common, sexually transmitted virus (HPV) causes most cervical cancers including the one that killed Frankie McCullogh 38.1 Integrated
Immunity Chapter 38 Impacts, Issues Frankie s Last Wish Infection with a common, sexually transmitted virus (HPV) causes most cervical cancers including the one that killed Frankie McCullogh 38.1 Integrated
Immune System. Before You Read. Read to Learn
 Immune System 37 section 2 The Immune System Biology/Life Sciences 10.b Students know the role of antibodies in the body s response to infection. Also covers: Biology/Life Sciences 10.a, 10.e, 10.f Components
Immune System 37 section 2 The Immune System Biology/Life Sciences 10.b Students know the role of antibodies in the body s response to infection. Also covers: Biology/Life Sciences 10.a, 10.e, 10.f Components
Chapter 24 The Immune System
 Chapter 24 The Immune System The Immune System Layered defense system The skin and chemical barriers The innate and adaptive immune systems Immunity The body s ability to recognize and destroy specific
Chapter 24 The Immune System The Immune System Layered defense system The skin and chemical barriers The innate and adaptive immune systems Immunity The body s ability to recognize and destroy specific
Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 24 The Immune System Multiple-Choice Questions
 Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 24 The Immune System 24.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The body's innate defenses against infection include A) several nonspecific
Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 24 The Immune System 24.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The body's innate defenses against infection include A) several nonspecific
1. Lymphatic vessels recover about of the fluid filtered by capillaries. A. ~1% C. ~25% E. ~85% B. ~10% D. ~50%
 BIOL2030 Huaman A&P II -- Exam 3 -- XXXX -- Form A Name: 1. Lymphatic vessels recover about of the fluid filtered by capillaries. A. ~1% C. ~25% E. ~85% B. ~10% D. ~50% 2. Special lymphatic vessels called
BIOL2030 Huaman A&P II -- Exam 3 -- XXXX -- Form A Name: 1. Lymphatic vessels recover about of the fluid filtered by capillaries. A. ~1% C. ~25% E. ~85% B. ~10% D. ~50% 2. Special lymphatic vessels called
Cell-mediated response (what type of cell is activated and what gets destroyed?)
 The Immune System Reading Guide (Chapter 43) Name Per 1. The immune response in animals can be divided into innate immunity and adaptive immunity. As an overview, complete this figure indicating the divisions
The Immune System Reading Guide (Chapter 43) Name Per 1. The immune response in animals can be divided into innate immunity and adaptive immunity. As an overview, complete this figure indicating the divisions
Diseases-causing agents, pathogens, can produce infections within the body.
 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II 1 CHAPTER 16 Lecture: Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. LYMPHATIC and IMMUNE Systems Body Defenses Against
BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II 1 CHAPTER 16 Lecture: Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. LYMPHATIC and IMMUNE Systems Body Defenses Against
All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 In innate immunity, recognition and
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 In innate immunity, recognition and
Ch. 11: Immune Physiology. 1. Review Immune Organs & Cells. Immune system = The cells and organs involved in defense against pathogens and cancer.
 Ch. 11: Immune Physiology Objectives: 1. Review immune organs & cells. 2. Two types of immunity. 3. Understand functions of immune cells (T-cells and B-cells) 4. Understand autoimmunity disorders. 1. Review
Ch. 11: Immune Physiology Objectives: 1. Review immune organs & cells. 2. Two types of immunity. 3. Understand functions of immune cells (T-cells and B-cells) 4. Understand autoimmunity disorders. 1. Review
Physiology Unit 3. ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY The Specific Immune Response
 Physiology Unit 3 ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY The Specific Immune Response In Physiology Today The Adaptive Arm of the Immune System Specific Immune Response Internal defense against a specific pathogen Acquired
Physiology Unit 3 ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY The Specific Immune Response In Physiology Today The Adaptive Arm of the Immune System Specific Immune Response Internal defense against a specific pathogen Acquired
Chapter 37 Section 1: Protecting Against Disease. Key Vocabulary Terms 9
 Chapter 37 Section 1: Protecting Against Disease Key Vocabulary Terms 9 Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Pathogen A microorganism, another organism, a virus, or a protein that causes disease; an infectious
Chapter 37 Section 1: Protecting Against Disease Key Vocabulary Terms 9 Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Pathogen A microorganism, another organism, a virus, or a protein that causes disease; an infectious
- Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body. - Has disease-fighting functions - Helps maintain homeostasis
 Introduction Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
Introduction Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
2/28/18. Lymphatic System and Immunity. Introduction. Anatomy. Chapter 27. Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system
 Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 1 Introduction Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 1 Introduction Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
Unit 23: Immunity from Disease
 Unit 5 The Human Body Unit 23 Immunity from Disease- Unit 23: Immunity from Disease Name: Period: Page 1 of 51 Unit 5 The Human Body Unit 23 Immunity from Disease- Chapter 23 assignments Pages/Sections
Unit 5 The Human Body Unit 23 Immunity from Disease- Unit 23: Immunity from Disease Name: Period: Page 1 of 51 Unit 5 The Human Body Unit 23 Immunity from Disease- Chapter 23 assignments Pages/Sections
The Lymphatic System. Innate Immunity
 The Lymphatic System Innate Immunity 1 Types of Immunity Innate (non-specific) immunity Adaptive (specific) immunity The human body has several different ways that it defends itself against infection by
The Lymphatic System Innate Immunity 1 Types of Immunity Innate (non-specific) immunity Adaptive (specific) immunity The human body has several different ways that it defends itself against infection by
4) What causes lymph to move? Skeletal muscle contraction; smooth muscle contraction, breathing (like blood moves through veins)
 NPHS Anatomy & Physiology UNIT 10 REVIEW GUIDE Lymphatic System 1) List the three functions of the lymphatic system. transports excess fluid to the bloodstream absorbs fats helps defend the body against
NPHS Anatomy & Physiology UNIT 10 REVIEW GUIDE Lymphatic System 1) List the three functions of the lymphatic system. transports excess fluid to the bloodstream absorbs fats helps defend the body against
The Immune System. Protective system that fight disease in the body. Includes parts of the circulatory system and lymph system.
 The Immune System Protective system that fight disease in the body. Includes parts of the circulatory system and lymph system. The immune system recognizes, attacks, destroys, and remembers each kind of
The Immune System Protective system that fight disease in the body. Includes parts of the circulatory system and lymph system. The immune system recognizes, attacks, destroys, and remembers each kind of
Chapter 07 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 07 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 07 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Immunity. Innate & Adaptive
 Immunity Innate & Adaptive Immunity Innate: response to attack is always the same Mechanical mechanisms Chemical mediators Cellular response Inflammatory response Adaptive: response to attack improves
Immunity Innate & Adaptive Immunity Innate: response to attack is always the same Mechanical mechanisms Chemical mediators Cellular response Inflammatory response Adaptive: response to attack improves
Guided Reading Activities
 Name Period Chapter 24: The Immune System Guided Reading Activities Big idea: Innate immunity Answer the following questions as you read modules 24.1 24.2: 1. Bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms
Name Period Chapter 24: The Immune System Guided Reading Activities Big idea: Innate immunity Answer the following questions as you read modules 24.1 24.2: 1. Bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms
2. The normal of the gut, and vagina keep the growth of pathogens in check. 3. in the respiratory tract sweep out bacteria and particles.
 Chapter 39 Immunity I. Three Lines of Defense A. Surface Barriers to Invasion 1. is an important barrier. 2. The normal of the gut, and vagina keep the growth of pathogens in check. 3. in the respiratory
Chapter 39 Immunity I. Three Lines of Defense A. Surface Barriers to Invasion 1. is an important barrier. 2. The normal of the gut, and vagina keep the growth of pathogens in check. 3. in the respiratory
phagocytic leukocyte Immune System lymphocytes attacking cancer cell lymph system
 phagocytic leukocyte Immune System lymphocytes attacking cancer cell lymph system 2006-2007 1) recognizing the presence of an infection; 2) containing the infection and working to eliminate it; 3) regulating
phagocytic leukocyte Immune System lymphocytes attacking cancer cell lymph system 2006-2007 1) recognizing the presence of an infection; 2) containing the infection and working to eliminate it; 3) regulating
Overview. Barriers help animals defend against many dangerous pathogens they encounter.
 Immunity Overview Barriers help animals defend against many dangerous pathogens they encounter. The immune system recognizes foreign bodies and responds with the production of immune cells and proteins.
Immunity Overview Barriers help animals defend against many dangerous pathogens they encounter. The immune system recognizes foreign bodies and responds with the production of immune cells and proteins.
Unit 3 Dynamic Equilibrium Chapter Immune System
 Biology 2201 Unit 3 Dynamic Equilibrium Chapter 11.4 - Immune System Compiled by S. Whalen What is Immunity? Immunity Immunity The ability of the body to fight infection and/or foreign invaders by producing
Biology 2201 Unit 3 Dynamic Equilibrium Chapter 11.4 - Immune System Compiled by S. Whalen What is Immunity? Immunity Immunity The ability of the body to fight infection and/or foreign invaders by producing
The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses Slides 12.1 12.22 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Lymphatic
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses Slides 12.1 12.22 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Lymphatic
Chapter 22: The Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Bio40C schedule Lecture Immune system Lab Quiz 2 this week; bring a scantron! Study guide on my website (see lab assignments) Extra credit Critical thinking questions at end of chapters 5 pts/chapter Due
Bio40C schedule Lecture Immune system Lab Quiz 2 this week; bring a scantron! Study guide on my website (see lab assignments) Extra credit Critical thinking questions at end of chapters 5 pts/chapter Due
Outline. Animals: Immunity. Defenses Against Disease. Key Concepts:
 Animals: Immunity Defenses Against Disease Outline 1. Key concepts 2. Physical barriers: Skin, Mucus and HCL in stomach 3. Non-specific 4. Specific responses Immune System a. Components of Immune system
Animals: Immunity Defenses Against Disease Outline 1. Key concepts 2. Physical barriers: Skin, Mucus and HCL in stomach 3. Non-specific 4. Specific responses Immune System a. Components of Immune system
Lymphatic System. The targets of the immune defenses are infectious organisms such as,, parasites, fungi, and some protists.
 Lymphatic System I. Non-specific Defenses The immune system is a body wide network of cells and organs that have evolved to defend the body against attacks by invaders. The targets of the immune defenses
Lymphatic System I. Non-specific Defenses The immune system is a body wide network of cells and organs that have evolved to defend the body against attacks by invaders. The targets of the immune defenses
Blood and Immune system Acquired Immunity
 Blood and Immune system Acquired Immunity Immunity Acquired (Adaptive) Immunity Defensive mechanisms include : 1) Innate immunity (Natural or Non specific) 2) Acquired immunity (Adaptive or Specific) Cell-mediated
Blood and Immune system Acquired Immunity Immunity Acquired (Adaptive) Immunity Defensive mechanisms include : 1) Innate immunity (Natural or Non specific) 2) Acquired immunity (Adaptive or Specific) Cell-mediated
35.2 Defenses against Infection
 35.2 Defenses against Infection Key Questions At the end of this section you should be able to answer the following questions: What are the two types of infections? What are examples of each? How does
35.2 Defenses against Infection Key Questions At the end of this section you should be able to answer the following questions: What are the two types of infections? What are examples of each? How does
Chapter 23 Immunity Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 23 Immunity Exam Study Questions 1. Define 1) Immunity 2) Neutrophils 3) Macrophage 4) Epitopes 5) Interferon 6) Complement system 7) Histamine 8) Mast cells 9) Antigen 10) Antigens receptors 11)
Chapter 23 Immunity Exam Study Questions 1. Define 1) Immunity 2) Neutrophils 3) Macrophage 4) Epitopes 5) Interferon 6) Complement system 7) Histamine 8) Mast cells 9) Antigen 10) Antigens receptors 11)
The immune system is made up of a complex and vital network of cells and organs that protect the body from infection.
 IMMUNE SYSTEM Viruses, bacteria and other germs are all around us. Most of the time, a healthy immune system keeps us well. The purpose of the immune system is to keep infectious micro-organisms, such
IMMUNE SYSTEM Viruses, bacteria and other germs are all around us. Most of the time, a healthy immune system keeps us well. The purpose of the immune system is to keep infectious micro-organisms, such
BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Spring 2011 Section A. Steve Thompson:
 BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Spring 2011 Section A Steve Thompson: stthompson@valdosta.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net 1 Keeping the bad guys at bay immunology The vertebrate immune
BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Spring 2011 Section A Steve Thompson: stthompson@valdosta.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net 1 Keeping the bad guys at bay immunology The vertebrate immune
11/25/2017. THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS BARRIER DEFENSES INNATE IMMUNITY OF VERTEBRATES
 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS Exoskeleton made of chitin forms the first barrier to pathogens Digestive system is protected by a chitin-based barrier and lysozyme,
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS Exoskeleton made of chitin forms the first barrier to pathogens Digestive system is protected by a chitin-based barrier and lysozyme,
Immune system. Aims. Immune system. Lymphatic organs. Inflammation. Natural immune system. Adaptive immune system
 Aims Immune system Lymphatic organs Inflammation Natural immune system Adaptive immune system Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) Disorders of the immune system 1 2 Immune system Lymphoid organs Immune
Aims Immune system Lymphatic organs Inflammation Natural immune system Adaptive immune system Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) Disorders of the immune system 1 2 Immune system Lymphoid organs Immune
Defense mechanism against pathogens
 Defense mechanism against pathogens Immune System What is immune system? Cells and organs within an animal s body that contribute to immune defenses against pathogens ( ) Bacteria -Major entry points ;open
Defense mechanism against pathogens Immune System What is immune system? Cells and organs within an animal s body that contribute to immune defenses against pathogens ( ) Bacteria -Major entry points ;open
Nonspecific External Barriers skin, mucous membranes
 Immune system Chapter 36 BI 103 Plant-Animal A&P Levels of Defense Against Disease Nonspecific External Barriers skin, mucous membranes Physical barriers? Brainstorm with a partner If these barriers are
Immune system Chapter 36 BI 103 Plant-Animal A&P Levels of Defense Against Disease Nonspecific External Barriers skin, mucous membranes Physical barriers? Brainstorm with a partner If these barriers are
LYMPHATIC AND IMMUNE SYSTEMS. Chapter 33
 LYMPHATIC AND IMMUNE SYSTEMS Chapter 33 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM The lymphatic system has three main functions Take up excess tissue fluid and return it to the bloodstream Receive fats called lipoproteins
LYMPHATIC AND IMMUNE SYSTEMS Chapter 33 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM The lymphatic system has three main functions Take up excess tissue fluid and return it to the bloodstream Receive fats called lipoproteins
The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately
 The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 INNATE IMMUNITY (all animals) Recognition of traits shared
The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 INNATE IMMUNITY (all animals) Recognition of traits shared
Overview of the Lymphoid System
 Overview of the Lymphoid System The Lymphoid System Protects us against disease Lymphoid system cells respond to Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells, such as cancers Overview of the Lymphoid
Overview of the Lymphoid System The Lymphoid System Protects us against disease Lymphoid system cells respond to Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells, such as cancers Overview of the Lymphoid
Chapter 12- The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
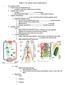 Chapter 12- The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses I. The Lymphatic System a. Consists of two semi-independent parts i. Lymphatic vessels and Lymphoid tissues and organs b. Lymphatic system functions i.
Chapter 12- The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses I. The Lymphatic System a. Consists of two semi-independent parts i. Lymphatic vessels and Lymphoid tissues and organs b. Lymphatic system functions i.
Immunity and Infection. Chapter 17
 Immunity and Infection Chapter 17 The Chain of Infection Transmitted through a chain of infection (six links) Pathogen: Disease causing microorganism Reservoir: Natural environment of the pathogen Portal
Immunity and Infection Chapter 17 The Chain of Infection Transmitted through a chain of infection (six links) Pathogen: Disease causing microorganism Reservoir: Natural environment of the pathogen Portal
phagocytic leukocyte Fighting the Enemy Within Immune System lymphocytes attacking cancer cell lymph system
 Fighting the Enemy Within phagocytic leukocyte Immune System lymphocytes attacking cancer cell lymph system AP Biology 2006-2007 Avenues of attack Points of entry digestive system respiratory system urinary
Fighting the Enemy Within phagocytic leukocyte Immune System lymphocytes attacking cancer cell lymph system AP Biology 2006-2007 Avenues of attack Points of entry digestive system respiratory system urinary
White Blood Cells (WBCs)
 YOUR ACTIVE IMMUNE DEFENSES 1 ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE 2! Innate Immunity - invariant (generalized) - early, limited specificity - the first line of defense 1. Barriers - skin, tears 2. Phagocytes - neutrophils,
YOUR ACTIVE IMMUNE DEFENSES 1 ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSE 2! Innate Immunity - invariant (generalized) - early, limited specificity - the first line of defense 1. Barriers - skin, tears 2. Phagocytes - neutrophils,
Lymphatic System. Chapter 14. Introduction. Main Channels of Lymphatics. Lymphatics. Lymph Tissue. Major Lymphatic Vessels of the Trunk
 Lymphatic System Chapter 14 Components Lymph is the fluid Vessels lymphatics Structures & organs Functions Return tissue fluid to the bloodstream Transport fats from the digestive tract to the bloodstream
Lymphatic System Chapter 14 Components Lymph is the fluid Vessels lymphatics Structures & organs Functions Return tissue fluid to the bloodstream Transport fats from the digestive tract to the bloodstream
The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses 12PART B Adaptive Defense System: Third Line of Defense Immune
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses 12PART B Adaptive Defense System: Third Line of Defense Immune
Defense & the Immune System. Immune System Agenda 4/28/2010. Overview. The bigger picture Non specific defenses Specific defenses (Immunity)
 Defense &The Immune System Overview Immune System Agenda The bigger picture Non specific defenses Specific defenses (Immunity) Defense & the Immune System Big Picture Defense Any means of preventing or
Defense &The Immune System Overview Immune System Agenda The bigger picture Non specific defenses Specific defenses (Immunity) Defense & the Immune System Big Picture Defense Any means of preventing or
Chapter 35 Active Reading Guide The Immune System
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 35 Active Reading Guide The Immune System Section 1 Phagocytosis plays an important role in the immune systems of both invertebrates and vertebrates. Review the process
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 35 Active Reading Guide The Immune System Section 1 Phagocytosis plays an important role in the immune systems of both invertebrates and vertebrates. Review the process
Fluid movement in capillaries. Not all fluid is reclaimed at the venous end of the capillaries; that is the job of the lymphatic system
 Capillary exchange Fluid movement in capillaries Not all fluid is reclaimed at the venous end of the capillaries; that is the job of the lymphatic system Lymphatic vessels Lymphatic capillaries permeate
Capillary exchange Fluid movement in capillaries Not all fluid is reclaimed at the venous end of the capillaries; that is the job of the lymphatic system Lymphatic vessels Lymphatic capillaries permeate
Human Immune Response. Part 1: innate immunity
 Human Immune Response Part 1: innate immunity Our bodies are under constant attack from pathogens A pathogen is an organism that can cause disease Pathogens include: Bacteria Viruses Protists Fungi 6.3.1
Human Immune Response Part 1: innate immunity Our bodies are under constant attack from pathogens A pathogen is an organism that can cause disease Pathogens include: Bacteria Viruses Protists Fungi 6.3.1
Immune System. Chapter 40
 Immune System Chapter 40 Germ Theory of Disease Idea that microorganisms can cause infectious disease. Disease: any change that disrupts normal body function. What are the 5 main agents that cause disease?
Immune System Chapter 40 Germ Theory of Disease Idea that microorganisms can cause infectious disease. Disease: any change that disrupts normal body function. What are the 5 main agents that cause disease?
Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System
 Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System Immune System Composed of many nonspecific and specific defenses Lymphatic System also plays an important role in establishing immunity Lymphatic System Major components
Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System Immune System Composed of many nonspecific and specific defenses Lymphatic System also plays an important role in establishing immunity Lymphatic System Major components
Immunology Lecture- 1
 Immunology Lecture- 1 Immunology and Immune System Immunology: Study of the components and function of the immune system Immune System a network collected from cells, tissues organs and soluble factors
Immunology Lecture- 1 Immunology and Immune System Immunology: Study of the components and function of the immune system Immune System a network collected from cells, tissues organs and soluble factors
Chapter 24 The Immune System
 Chapter 24 The Immune System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction: The Kissing Disease?!?
Chapter 24 The Immune System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction: The Kissing Disease?!?
Chapter 21: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses
 Chapter 21: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses I. 2 main types of body defenses A. Innate (nonspecific) defense: not to a specific microorganism or substance B. Adaptive (specific) defense: immunity to
Chapter 21: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses I. 2 main types of body defenses A. Innate (nonspecific) defense: not to a specific microorganism or substance B. Adaptive (specific) defense: immunity to
Anatomy. Lymph: Tissue fluid that enters a lymphatic capillary (clear fluid that surrounds new piercings!)
 Lymphatic System Anatomy Lymphatic vessels: meet up in capillaries of of tissues to collect extra water, and have an end point of meeting up with lymphatic ducts that empty fluid into large veins in the
Lymphatic System Anatomy Lymphatic vessels: meet up in capillaries of of tissues to collect extra water, and have an end point of meeting up with lymphatic ducts that empty fluid into large veins in the
Blood consists of red and white blood cells suspended in plasma Blood is about 55% plasma and 45% cellular elements Plasma 90% water 10% dissolved
 Bio 100 Guide 21 Blood consists of red and white blood cells suspended in plasma Blood is about 55% plasma and 45% cellular elements Plasma 90% water 10% dissolved inorganic ions, proteins, nutrients,
Bio 100 Guide 21 Blood consists of red and white blood cells suspended in plasma Blood is about 55% plasma and 45% cellular elements Plasma 90% water 10% dissolved inorganic ions, proteins, nutrients,
Innate Immunity. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Innate Immunity Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The vertebrate, including human, immune system is a complex multilayered system for defending against external and internal threats to the integrity of the body. The
Innate Immunity Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The vertebrate, including human, immune system is a complex multilayered system for defending against external and internal threats to the integrity of the body. The
immunity produced by an encounter with an antigen; provides immunologic memory. active immunity clumping of (foreign) cells; induced by crosslinking
 active immunity agglutination allografts immunity produced by an encounter with an antigen; provides immunologic memory. clumping of (foreign) cells; induced by crosslinking of antigenantibody complexes.
active immunity agglutination allografts immunity produced by an encounter with an antigen; provides immunologic memory. clumping of (foreign) cells; induced by crosslinking of antigenantibody complexes.
NOTES: CH 43, part 2 Immunity; Immune Disruptions ( )
 NOTES: CH 43, part 2 Immunity; Immune Disruptions (43.3-43.4) Activated B & T Lymphocytes produce: CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNE RESPONSE: involves specialized T cells destroying infected host cells HUMORAL IMMUNE
NOTES: CH 43, part 2 Immunity; Immune Disruptions (43.3-43.4) Activated B & T Lymphocytes produce: CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNE RESPONSE: involves specialized T cells destroying infected host cells HUMORAL IMMUNE
The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses Outline PART 1: INNATE DEFENSES 21.1 Surface barriers act as the first line of defense to keep
 The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses Outline PART 1: INNATE DEFENSES 21.1 Surface barriers act as the first line of defense to keep invaders out of the body (pp. 772 773; Fig. 21.1; Table
The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses Outline PART 1: INNATE DEFENSES 21.1 Surface barriers act as the first line of defense to keep invaders out of the body (pp. 772 773; Fig. 21.1; Table
Immune System.notebook March 07, Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium. Immune system 1st, 2nd and 3rd line of defense Immune disorders
 Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Immune system 1st, 2nd and 3rd line of defense Immune disorders Oct 11 3:27 PM p.382 386 Immune system A complex system involving several organs and tissues (e.g.
Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Immune system 1st, 2nd and 3rd line of defense Immune disorders Oct 11 3:27 PM p.382 386 Immune system A complex system involving several organs and tissues (e.g.
Instructor s Guide. Films for the. Humanities & Sciences i A Wealth of Information. A World of Ideas. The Human Body: How It Works THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
 i A Wealth of Information. A World of Ideas. Instructor s Guide The Human Body: How It Works Introduction This program is part of the nine-part series The Human Body: How It Works. The series uses physiologic
i A Wealth of Information. A World of Ideas. Instructor s Guide The Human Body: How It Works Introduction This program is part of the nine-part series The Human Body: How It Works. The series uses physiologic
Lecture 10 Immune System
 Lecture 10 Immune System Lecture 10 1. Introduction 2. Nonspecific External Defenses 3. Innate Immune Response 4. Acquired Immune Response 5. Antibiotics and Vaccines 1 The not-so-common cold A cold is
Lecture 10 Immune System Lecture 10 1. Introduction 2. Nonspecific External Defenses 3. Innate Immune Response 4. Acquired Immune Response 5. Antibiotics and Vaccines 1 The not-so-common cold A cold is
Unit 12: The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
 Unit 12: The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses I. The Lymphatic System A. Consists of two semi-independent parts 1. Lymphatic vessels 2. Lymphoid tissues and organs B. Lymphatic system functions 1. Transports
Unit 12: The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses I. The Lymphatic System A. Consists of two semi-independent parts 1. Lymphatic vessels 2. Lymphoid tissues and organs B. Lymphatic system functions 1. Transports
Immune System. How your body goes to war to keep you well
 Immune System How your body goes to war to keep you well WATCH OUT! Millions of bacteria and viruses are everywhere. Many aim to find a host and invade the body. HOW CAN WE DEFEND AGAINST IT? The Bad Guys
Immune System How your body goes to war to keep you well WATCH OUT! Millions of bacteria and viruses are everywhere. Many aim to find a host and invade the body. HOW CAN WE DEFEND AGAINST IT? The Bad Guys
Microbes which manage to evade the non-specific immune system are then met with the next level of defence known as the specific immune system.
 Higher Human Biology Unit 4 Key Area 2 Pupil Notes Microbes which manage to evade the non-specific immune system are then met with the next level of defence known as the specific immune system. Note: In
Higher Human Biology Unit 4 Key Area 2 Pupil Notes Microbes which manage to evade the non-specific immune system are then met with the next level of defence known as the specific immune system. Note: In
Unit 12 - The Lymphatic System and 1
 Unit 12 - The Lymphatic System and 1 I. Unit 12: The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses A. The Lymphatic System 1. Consists of two semi-independent parts a) Lymphatic vessels b) Lymphoid tissues and organs
Unit 12 - The Lymphatic System and 1 I. Unit 12: The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses A. The Lymphatic System 1. Consists of two semi-independent parts a) Lymphatic vessels b) Lymphoid tissues and organs
Immunity. Chapter 38 Part 1
 Immunity Chapter 38 Part 1 Impacts, Issues Frankie s Last Wish Infection with a common, sexually transmitted virus (HPV) causes most cervical cancers including the one that killed Frankie McCullogh 38.1
Immunity Chapter 38 Part 1 Impacts, Issues Frankie s Last Wish Infection with a common, sexually transmitted virus (HPV) causes most cervical cancers including the one that killed Frankie McCullogh 38.1
The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
 12 PART A The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
12 PART A The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
immunity defenses invertebrates vertebrates chapter 48 Animal defenses --
 defenses Animal defenses -- immunity chapter 48 invertebrates coelomocytes, amoebocytes, hemocytes sponges, cnidarians, etc. annelids basophilic amoebocytes, acidophilic granulocytes arthropod immune systems
defenses Animal defenses -- immunity chapter 48 invertebrates coelomocytes, amoebocytes, hemocytes sponges, cnidarians, etc. annelids basophilic amoebocytes, acidophilic granulocytes arthropod immune systems
KEY CONCEPT Germs cause many diseases in humans.
 31.1 40.1 Pathogens Infectious Diseases and Human Illness KEY CONCEPT Germs cause many diseases in humans. 31.1 40.1 Pathogens Infectious Diseases and Human Illness Germ theory states that microorganisms
31.1 40.1 Pathogens Infectious Diseases and Human Illness KEY CONCEPT Germs cause many diseases in humans. 31.1 40.1 Pathogens Infectious Diseases and Human Illness Germ theory states that microorganisms
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM. Dinithi Peiris Department of Zoology. The Lymphatic System. Lymphatic System: Components
 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Dinithi Peiris Department of Zoology The Lymphatic System A system of vessels, cells and organs Vessels originate blindly and the structure is similar to that of a vein with valves The
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Dinithi Peiris Department of Zoology The Lymphatic System A system of vessels, cells and organs Vessels originate blindly and the structure is similar to that of a vein with valves The
INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response. Physiology Unit 3
 INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response Physiology Unit 3 Protection Against Infection The body has several defenses to protect itself from getting an infection Skin Mucus membranes Serous membranes
INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response Physiology Unit 3 Protection Against Infection The body has several defenses to protect itself from getting an infection Skin Mucus membranes Serous membranes
Chapter 40 Section 2 The Immune System
 Chapter 40 Section 2 The Immune System Science Standard 10a What is the role of the skin in providing nonspecific defenses against infection? What is the function of the immune system? The immune system
Chapter 40 Section 2 The Immune System Science Standard 10a What is the role of the skin in providing nonspecific defenses against infection? What is the function of the immune system? The immune system
(b) fluid returns to venous end of capillary due to hydrostatic pressure and osmotic pressure
 (Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Lymphatic System and Immunity (Body Defenses) I. (Slide 2) Introduction A) General 1) Lymphatic System performs 2 basic functions: 2) Organs of the Lymphatic System (a) lymphatic
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Lymphatic System and Immunity (Body Defenses) I. (Slide 2) Introduction A) General 1) Lymphatic System performs 2 basic functions: 2) Organs of the Lymphatic System (a) lymphatic
