Elucidation of Viral Replication Mechanisms in an Animal Model for Multiple Sclerosis
|
|
|
- Dora Cole
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Elucidation of Viral Replication Mechanisms in an Animal Model for Multiple Sclerosis Introduction It is often difficult to research human diseases due to obvious ethical implications. However, when an acceptable animal model of a disease is found, the medical world is given a rare window of opportunity to conduct crucial research at low risk. At the University of Tampa, I have been given the opportunity to work with my research mentor, Dr. Eric Freundt on a murine virus that causes similar disease pathology to human multiple sclerosis. Theiler s murine encephalomyelitis virus (TMEV), is a member of the Picornaviridae family and Cardiovirus genus. This virus was initially isolated from mice by virologist Max Theiler in 1937 at the Rockefeller Institute [1], and has since been described as one of the best models for multiple sclerosis. Once infected with TMEV, mice are susceptible to a chronic infection, which causes progressive demyelination throughout the central nervous system [2]. This pathology is an excellent model for multiple sclerosis, a disease known to be associated with axonal demyelination within the central nervous system. Multiple sclerosis has been recognized to cause severe cognitive impairments, as well as muscle weakness and other physical deficits in human patients, but remains incurable [3]. Although much is known about the effects of multiple sclerosis, what actually causes the demyelination within the human central nervous system remains unanswered, making the TMEV model a highly coveted research tool. Being in the same family as poliovirus, a highly studied and documented disease-causing virus, insight has been given to the replication of TMEV. As documented with poliovirus, TMEV replicates at intracellular vesicles that are used as docking sites for viral replication [4]. However, unlike poliovirus, the composition and origin of these replication vesicles is unknown. The primary motivation of my research is to elucidate the origin and of these vesicles at which TMEV replicates. By solving the question of how these viruses replicate, it may also be possible to trace the route of TMEV-induced demyelination and pathogenesis. If this pathological pathway of demyelination could be hindered in mice, and then applied to the human condition of multiple sclerosis, it may be possible to develop a cure or treatment. With any research project, it is necessary to identify a logical starting point. After completing an in-depth analysis of primary research on TMEV, my research mentor and I identified that there is a relationship between viral replication proteins and proteins of the trans- Golgi apparatus [5]. This finding opens up many questions about the nature of TMEV replication because the trans-golgi apparatus is responsible for sending secretory vesicles to intracellular organelles, and the cellular plasma membrane for exocytosis. Serving as a factory of modification and packaging for protein, the Golgi apparatus is a highly important part of cellular metabolism, and thus interplay with viral replication is a point of interest. The Golgi apparatus is a common target for cytopathic damage, or damage to the cell caused by viral infiltration, by numerous viruses, but has an unknown response to TMEV [6]. My initial experiments were targeted at answering how the Golgi apparatus is actually affected by infection with TMEV. Previous research points to the trans-golgi as providing vesicles for replication, but does not rule out other locations of the Golgi as vesicle origins. Thus, along with answering the issue of Golgi
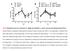
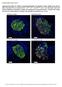
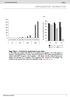
2 apparatus insult, it was necessary to establish if only the trans-golgi apparatus, or if other locations within the Golgi are involved in co-localization with viral replication proteins. Thanks to the generosity of Dr. Freundt and the University of Tampa Department of Biology, I was able develop a protocol to answer my aforementioned questions using technical equipment. Materials and Methods There was no risk of harming live murine species in experimentation, as a continuous cell line of baby hamster kidney cells (BHKs) was passaged and used for infection, rather than live animals. The first question of how infection with TMEV affects the Golgi apparatus was answered through the process of indirect immunofluorescence staining, a technique commonly used to detect the presence and location of specific proteins within a cell. BHK cells were seeded onto coverslips in a 24-well plate, and allowed 24 hours to reach a point of 60-70% confluence. At this point, 16 of the wells were infected with the GDVII strain of TMEV at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 10, while 8 wells were left as uninfected controls. To allow determination of the rate of Golgi apparatus insult, the infection was stopped at different time intervals using 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA), a reagent that cross links cellular proteins. Specifically, the infection was halted at 6, 9, 12, and 24 hours, while uninfected cells were halted at 6 and 24 hours to generate a baseline of normal uninfected Golgi formation at different time points post seeding. After the full time plot, cells were made permeable with 0.1% Triton-X 100 in PBS. Once the cells were made permeable, a common immunofluorescence protocol [7] was used to indirectly label all cover slips with DAPI, a marker specific for the nucleus, and GM130 a marker specific for the cis-golgi [8]. Half of the wells were labeled with anti-tmev capsid antibodies, a specific marker for viral capsid proteins. The remaining 12 wells were labeled with anti-3d antibodies, a marker for the viral 3D polymerase, which is a necessary viral replication protein, that docks with the replication vesicle. All coverslips were mounted onto glass slides using Vectashield mounting media to prevent photobleaching by the fluorescence microscope. The next step was to view the cells with fluorescence microscopy and quantify the amount of Golgi fragmentation at different times post infection. Results Quantification of presence or absence of Golgi insult was collected in 10 randomly selected fields for each coverslip at 60x magnification. A total of 597 nuclei were examined for Golgi insult from the 12 coverslips stained with DAPI, GM130, and anti-capsid, and presented in Figure 1, with calculated standard error of the mean. The graph depicts two bars for each time point from quantification of two different cover slips per condition. Images of infected and uninfected cells at different time points are presented in Figure 2. The 12 wells treated with 3D polymerase were extensively examined at all-time points. However, as depicted in Figure 3, there were no examples of co-localization between the cis-golgi marker (GM130), and the viral polymerase (anti-3d).
3 Percentage of Cells with Fragmented Golgi Compared to a Popula@on of Uninfected Cells 100 % of Cells with Fragmented Golgi Hour Control 6 HPI 9 HPI 12 HPI 24 HPI 24 HPI Figure 1: Percentage of cells with insulted Golgi at different time points. (HPI = hours post infection) A) 6 hour control B) 6 hour post infection C) 9 hour post infection D) 24 hour post infection E) 12 hour post infection F) 24 hour control Figures 2. TMEV infection correlates with Golgi fragmentation. Images are shown that represent staining with anti- GM130 (shown in green), DAPI (shown in blue), and anti- TMEV capsid (shown in red).
4 A) 6 hour control B) 6 hour post infection C) 9 hour post infection D) 12 hour post infection E) 24 hour post infection F) 24 hour control Figures 3. TMEV 3D polymerase does not colocalize with cis- Golgi protein GM130. Images are shown that represent staining with anti- GM130 (shown in green), DAPI (shown in blue), and anti- 3D polymerase (shown in red). Discussion The uninfected controls at both 6 and 24 hours in this experiment have established a baseline of approximately 10% of uninfected cells have fragmented Golgi, and this may be caused by natural cell death or mitotic events. The most noticeable cytopathic effect of infected cells is Golgi fragmentation. Figure 1 depicts a direct correlation between time post infection and amount of fragmented Golgi within infected cells. There is not a substantial increase in fragmentation after 12 hours, indicating that at a high MOI, 12 hours is sufficient time to cause Golgi fragmentation within infected cells. This result points strongly to the conclusion that infection with GDVII strain of TMEV causes fragmentation of the Golgi apparatus. Additionally, Figure 2 shows an increase in distance of fragmented Golgi protein spread throughout the cell as time post infection increases. Data from the coverslips exposed to anti-3d polymerase (Figure 3) strongly supports that GM130 cis-golgi protein marker does not co-localize with the replication vesicles. This data introduces the possibility that TMEV selectively utilizes trans-golgi proteins for replication vesicles, and may even suggest that TMEV has evolved to utilize vesicles sent from the trans-golgi to be secreted from the cell. If this hypothetical mechanism of replication is correct, it will identify a novel mechanism of viral replication, and potentially, provide a more efficient release pathway for the virus, requiring further research on viral release. Disruption of the trans-golgi by TMEV may also provide insight into the pathology of demyelination. Myelination of neurons in the central nervous system (CNS) is not a fully understood process. However, it is known that neuronal cells have the capacity to communicate with Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes, which are responsible for neuronal myelination, through axonal connections and cues [9]. If TMEV replication blocks the normal neuronal exocytosis and secretory pathway used for communication between neurons in the CNS and oligodendrocytes, a demyelination mechanism may result. Additionally, disruption of the Golgi of oligodendrocytes could prevent trafficking of myelin proteins and lead to oligodendrocyte cell
5 death. My next steps are to experimentally test this hypothesis of pathology with immunofluorescence staining specifically for secretory vesicle protein, and viral 3D polymerase. High co-localization of secretory vesicle proteins, and 3D polymerase in an immunofluorescence stain will strongly support my proposed mechanism of viral replication on sequestered post- Golgi vesicles in the secretory pathway. Reference List Theiler, M., (1937). Spontaneous Encephalomyelitis of Mice, a New Virus Disease. The Journal of Experimental Medicine, 65, Mecha, M., Carrillo-Salinas, F.J., Mestre, L., Feliú, A., & Guaza, C., (2013). Viral Models of Multiple Sclerosis: Neurodegeneration and Demyelination in Mice Infected with Theiler's Virus. Progress in Neurobiology, 101, doi: /j.pneurobio Moreno, M.J., Garcia, C.M., Gonzales, P.A., & Benito, A.Y., (2013). Neuropsychological Syndromes in Multiple Sclerosis. Psicothema, 25, doi: /psicothema Richards, A.L., & Jackson W.T., (2012). Intracellular Vesicle Acidification Promotes Maturation of Infectious Poliovirus Particles. PLoS, 9. doi: /journal.ppat Jauka, T., Mutsvunguma, L., Boshoff, L., Edkins, A.L., & Knox, C., (2010). Localisation of Theiler's Murine Encephalomyelitis Virus Protein 2C to the Golgi Apparatus Using Antibodies Generated against a Peptide Region. Journal of Virology Methods, 168, doi: /j.jviromet Beske, O., Reichelt, M., Taylor, M.P., Kirkegaard, K., & Andino, R. (2007). Poliovirus infection blocks ERGIC-to-Golgi trafficking and induces microtubule-dependent disruption of the Golgi complex. Journal of Cell Science, 120, doi: / jcs Najm, F.J., Zaremba, A., Caprariello, A.V., Nayak, S., Freundt, E.C., Scacheri, P.C., Miller, R.H., & Tesar, P.J. (2011). Rapid and robust generation of functional oligodendrocyte progenitor cells from epiblast stem cells. Nature Methods, doi: /nmeth.1712 Nakamura, N., Rabouille, C., Watson, R., Nilsson, T., Hui, N., Slusarewicz, P., Kreis, T.E., & Warren, G., (1995). Characterization of a cis-golgi matrix protein, GM130. Journal of Cell Biology 131, doi: /jcb Simons, M., & Trotter, J., (2007). Wrapping it up: the cell biology of myelination. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 17,
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4322
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Predicted RNA structure of 3 UTR and sequence alignment of deleted nucleotides. (a) Predicted RNA secondary structure of ZIKV 3 UTR. The stem-loop structure
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Predicted RNA structure of 3 UTR and sequence alignment of deleted nucleotides. (a) Predicted RNA secondary structure of ZIKV 3 UTR. The stem-loop structure
The pathogenesis of nervous distemper
 Veterinary Sciences Tomorrow - 2004 The pathogenesis of nervous distemper Marc Vandevelde Canine distemper is a highly contagious viral disease of dogs and of all animals in the Canidae, Mustellidae and
Veterinary Sciences Tomorrow - 2004 The pathogenesis of nervous distemper Marc Vandevelde Canine distemper is a highly contagious viral disease of dogs and of all animals in the Canidae, Mustellidae and
What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord
 What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord Jennifer LaVail, Ph.D. (http://anatomy.ucsf.edu/pages/lavaillab/index.html) What kinds of cells are these?" Neuron?" Epithelial cell?" Glial cell?" What makes
What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord Jennifer LaVail, Ph.D. (http://anatomy.ucsf.edu/pages/lavaillab/index.html) What kinds of cells are these?" Neuron?" Epithelial cell?" Glial cell?" What makes
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S2. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of dnscs.
 Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread
 Supplementary Information Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread Amrita Kumar 1, Jin Hyang Kim 1, Priya Ranjan 1, Maureen G. Metcalfe 2, Weiping Cao 1, Margarita Mishina 1,
Supplementary Information Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread Amrita Kumar 1, Jin Hyang Kim 1, Priya Ranjan 1, Maureen G. Metcalfe 2, Weiping Cao 1, Margarita Mishina 1,
D. J. Dargan,* C. B. Gait and J. H. Subak-Sharpe
 Journal of General Virology (1992), 73, 407-411. Printed in Great Britain 407 The effect of cicloxolone sodium on the replication in cultured cells of adenovirus type 5, reovirus type 3, poliovirus type
Journal of General Virology (1992), 73, 407-411. Printed in Great Britain 407 The effect of cicloxolone sodium on the replication in cultured cells of adenovirus type 5, reovirus type 3, poliovirus type
The Infectious Cycle. Lecture 2 Biology W3310/4310 Virology Spring You know my methods, Watson --SIR ARTHUR CONAN DOYLE
 The Infectious Cycle Lecture 2 Biology W3310/4310 Virology Spring 2016 You know my methods, Watson --SIR ARTHUR CONAN DOYLE The Infectious Cycle Virologists divide the infectious cycle into steps to facilitate
The Infectious Cycle Lecture 2 Biology W3310/4310 Virology Spring 2016 You know my methods, Watson --SIR ARTHUR CONAN DOYLE The Infectious Cycle Virologists divide the infectious cycle into steps to facilitate
Theiler s Murine Encephalomyelitis Virus-Induced CNS Autoimmunity
 Theiler s Murine Encephalomyelitis Virus-Induced CNS Autoimmunity Virus-induced molecular mimicry is part of a mouse model of multiple sclerosis that is providing insights about the disease in humans Julie
Theiler s Murine Encephalomyelitis Virus-Induced CNS Autoimmunity Virus-induced molecular mimicry is part of a mouse model of multiple sclerosis that is providing insights about the disease in humans Julie
Supplementary Figure 1: GFAP positive nerves in patients with adenocarcinoma of
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND MOVIE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1: GFAP positive nerves in patients with adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. (A) Images of nerves stained for GFAP (green), S100 (red) and DAPI
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND MOVIE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1: GFAP positive nerves in patients with adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. (A) Images of nerves stained for GFAP (green), S100 (red) and DAPI
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni eee Supplementary Figure 1
 eee Supplementary Figure 1 Hyphae induce NET release, but yeast do not. (a) NET release by human peripheral neutrophils stimulated with a hgc1 yeast-locked C. albicans mutant (yeast) or pre-formed WT C.
eee Supplementary Figure 1 Hyphae induce NET release, but yeast do not. (a) NET release by human peripheral neutrophils stimulated with a hgc1 yeast-locked C. albicans mutant (yeast) or pre-formed WT C.
Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML)
 Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML) By Jamie Meier Introduction: Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) occurs when change in an individual s immune status triggers reactivation
Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML) By Jamie Meier Introduction: Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) occurs when change in an individual s immune status triggers reactivation
Quantifying Lipid Contents in Enveloped Virus Particles with Plasmonic Nanoparticles
 Quantifying Lipid Contents in Enveloped Virus Particles with Plasmonic Nanoparticles Amin Feizpour Reinhard Lab Department of Chemistry and the Photonics Center, Boston University, Boston, MA May 2014
Quantifying Lipid Contents in Enveloped Virus Particles with Plasmonic Nanoparticles Amin Feizpour Reinhard Lab Department of Chemistry and the Photonics Center, Boston University, Boston, MA May 2014
Lecture Readings. Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell
 October 26, 2006 1 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
October 26, 2006 1 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the
 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the location of the transmembrane (TM), FRM binding (FB)
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the location of the transmembrane (TM), FRM binding (FB)
Cells of the Nervous System
 Cells of the Nervous System Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal Cord (in the spine) Interprets sensory input, initiates movement, and mediates complex
Cells of the Nervous System Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal Cord (in the spine) Interprets sensory input, initiates movement, and mediates complex
Cell Biology Research
 Wheaton Journal of Cell Biology Research Issue 6, Spring 2016: "Living Architecture" R.L. Morris, Editor. Wheaton College, Norton Massachusetts. Living Architecture logo by R.L.Morris using image of skeletal
Wheaton Journal of Cell Biology Research Issue 6, Spring 2016: "Living Architecture" R.L. Morris, Editor. Wheaton College, Norton Massachusetts. Living Architecture logo by R.L.Morris using image of skeletal
Chapter 12 The Nervous System INTRODUCTION TO THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. Central Nervous System (CNS): STRUCTURE BRAIN SPINAL CORD NERVES
 Chapter 12 The Nervous System PowerPoint by John McGill Supplemental Notes by Beth Wyatt INTRODUCTION TO THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURE BRAIN SPINAL CORD NERVES Central Nervous System (CNS): Brain Spinal
Chapter 12 The Nervous System PowerPoint by John McGill Supplemental Notes by Beth Wyatt INTRODUCTION TO THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURE BRAIN SPINAL CORD NERVES Central Nervous System (CNS): Brain Spinal
Temperature-Sensitive Mutants Isolated from Hamster and
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Nov. 1975, p. 1332-1336 Copyright i 1975 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 16, No. 5 Printed in U.S.A. Temperature-Sensitive Mutants Isolated from Hamster and Canine Cell Lines
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Nov. 1975, p. 1332-1336 Copyright i 1975 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 16, No. 5 Printed in U.S.A. Temperature-Sensitive Mutants Isolated from Hamster and Canine Cell Lines
Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies?
 Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies? The standard test for rabies testing is dfa. This test has been thoroughly evaluated for more than 40 years, and is recognized as the most rapid and reliable
Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies? The standard test for rabies testing is dfa. This test has been thoroughly evaluated for more than 40 years, and is recognized as the most rapid and reliable
Chemokine Regulation of Oligodendrocyte Development in the Spinal Cord. Bob Avino Saint Louis University Senior Honors Thesis April 19, 2011
 Chemokine Regulation of Oligodendrocyte Development in the Spinal Cord Bob Avino Saint Louis University Senior Honors Thesis April 19, 2011 Richard J. Miller, PhD Northwestern University Feinberg School
Chemokine Regulation of Oligodendrocyte Development in the Spinal Cord Bob Avino Saint Louis University Senior Honors Thesis April 19, 2011 Richard J. Miller, PhD Northwestern University Feinberg School
Project report October 2012 March 2013 CRF fellow: Principal Investigator: Project title:
 Project report October 2012 March 2013 CRF fellow: Gennaro Napolitano Principal Investigator: Sergio Daniel Catz Project title: Small molecule regulators of vesicular trafficking to enhance lysosomal exocytosis
Project report October 2012 March 2013 CRF fellow: Gennaro Napolitano Principal Investigator: Sergio Daniel Catz Project title: Small molecule regulators of vesicular trafficking to enhance lysosomal exocytosis
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURE AND MAINTENANCE OF NEURONS (a) (b) Dendrites Cell body Initial segment collateral terminals (a) Diagrammatic representation of a neuron. The break in
STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURE AND MAINTENANCE OF NEURONS (a) (b) Dendrites Cell body Initial segment collateral terminals (a) Diagrammatic representation of a neuron. The break in
Supplementary materials
 Supplementary materials Chemical library from ChemBridge 50,240 structurally diverse small molecule compounds dissolved in DMSO Hits Controls: No virus added μ Primary screening at 20 g/ml of compounds
Supplementary materials Chemical library from ChemBridge 50,240 structurally diverse small molecule compounds dissolved in DMSO Hits Controls: No virus added μ Primary screening at 20 g/ml of compounds
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Replication Defective Enterovirus Infections: Implications for Type I Diabetes
 Replication Defective Enterovirus Infections: Implications for Type I Diabetes N. M. Chapman Department of Pathology & Microbiology University of Nebraska Medical Center Enterovirus Genome and 2 Capsid
Replication Defective Enterovirus Infections: Implications for Type I Diabetes N. M. Chapman Department of Pathology & Microbiology University of Nebraska Medical Center Enterovirus Genome and 2 Capsid
33VASTVNGATSANNHGEPPS51PADARPR58
 Pro-rich region Trans-membrane region 214 246 359 381 UL50 1 397 211SSRTAS216PPPPPR222 NLS CR1 CR2 CR3 CR4 UL53 1 376 11RERRS15ALRS19LLRKRRR25 33VASTVNGATSANNHGEPPS51PADARPR58 FIG S1. UL97 phosphorylation
Pro-rich region Trans-membrane region 214 246 359 381 UL50 1 397 211SSRTAS216PPPPPR222 NLS CR1 CR2 CR3 CR4 UL53 1 376 11RERRS15ALRS19LLRKRRR25 33VASTVNGATSANNHGEPPS51PADARPR58 FIG S1. UL97 phosphorylation
Chapter 13: Vesicular Traffic
 Chapter 13: Vesicular Traffic Know the terminology: ER, Golgi, vesicle, clathrin, COP-I, COP-II, BiP, glycosylation, KDEL, microtubule, SNAREs, dynamin, mannose-6-phosphate, M6P receptor, endocytosis,
Chapter 13: Vesicular Traffic Know the terminology: ER, Golgi, vesicle, clathrin, COP-I, COP-II, BiP, glycosylation, KDEL, microtubule, SNAREs, dynamin, mannose-6-phosphate, M6P receptor, endocytosis,
 I.Tsunoda et al. Table 3 Three viral abilities determine neuropathogenesis Viral ability Mumps Rabies HTLV WNV TMEV Neurotropism Neurovirulence Neuroinvasiveness ZIKV adult mouse adult fetus? human fetus
I.Tsunoda et al. Table 3 Three viral abilities determine neuropathogenesis Viral ability Mumps Rabies HTLV WNV TMEV Neurotropism Neurovirulence Neuroinvasiveness ZIKV adult mouse adult fetus? human fetus
Relative SOD1 activity. Relative SOD2 activity. Relative SOD activity (Infected:Mock) + CP + DDC
 Supplementary Figure 1. SOD1 activity is significantly increased relative to SOD1 levels. SOD1 and SOD2 activities in the infected mork13 cells are shown normalised to their corresponding levels and relative
Supplementary Figure 1. SOD1 activity is significantly increased relative to SOD1 levels. SOD1 and SOD2 activities in the infected mork13 cells are shown normalised to their corresponding levels and relative
The GDVII Strain of Theiler s Virus Spreads via Axonal Transport
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, July 1999, p. 6093 6098 Vol. 73, No. 7 0022-538X/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. The GDVII Strain of Theiler s Virus Spreads via
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, July 1999, p. 6093 6098 Vol. 73, No. 7 0022-538X/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. The GDVII Strain of Theiler s Virus Spreads via
Microglia-derived extracellular vesicles regulate the proliferation and differentiation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells
 University of Turin CNR Institute of Neuroscience Microglia-derived extracellular vesicles regulate the proliferation and differentiation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells Roberta Parolisi Turin, December
University of Turin CNR Institute of Neuroscience Microglia-derived extracellular vesicles regulate the proliferation and differentiation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells Roberta Parolisi Turin, December
Animal hosts Natural host Laboratory animals Rabbits Mice Rats Hamsters Newborn or suckling rodents Animal models for viral pathogenesis 4 Growth of v
 Principles of Virology Department of Molecular Genetics & Microbiology Univ ersity of Florida, Gainesv ille, FL 1 Outline Virus cultivation Assay of viruses Virus genetics 2 Virus isolation Evidence of
Principles of Virology Department of Molecular Genetics & Microbiology Univ ersity of Florida, Gainesv ille, FL 1 Outline Virus cultivation Assay of viruses Virus genetics 2 Virus isolation Evidence of
FIG S1 Replication rates of S. suis strain 10, 10Δsly, and 10cpsΔEF on mono- and virus pre-infected porcine PCLS.
 A strain 10 10cps EF B strain 10 H1N1 + strain 10 10cps EF H1N1 + 10cps EF 10 8 10 sly 10 7 H3N2 + strain 10 H3N2 + 10cps EF CFU/ml media 10 7 10 6 10 5 10 4 CFU/ml media 10 6 10 5 10 4 10 3 0 2 4 8 12
A strain 10 10cps EF B strain 10 H1N1 + strain 10 10cps EF H1N1 + 10cps EF 10 8 10 sly 10 7 H3N2 + strain 10 H3N2 + 10cps EF CFU/ml media 10 7 10 6 10 5 10 4 CFU/ml media 10 6 10 5 10 4 10 3 0 2 4 8 12
Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology
 The cell III. Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology Size and Biology Biology is a visually rich subject many of the biological events and structures are smaller than the unaided human
The cell III. Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology Size and Biology Biology is a visually rich subject many of the biological events and structures are smaller than the unaided human
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/283/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for JNK3 Couples the Neuronal Stress Response to Inhibition of Secretory Trafficking Guang Yang,* Xun Zhou, Jingyan Zhu,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/283/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for JNK3 Couples the Neuronal Stress Response to Inhibition of Secretory Trafficking Guang Yang,* Xun Zhou, Jingyan Zhu,
The Brain Symphony of Science
 The Brain Symphony of Science https://www.youtube.com/watch?t=2&v=jb7jsfevz1u!! Mosby items and derived items 2012 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 The Brain Symphony of Science https://www.youtube.com/watch?t=2&v=jb7jsfevz1u!!
The Brain Symphony of Science https://www.youtube.com/watch?t=2&v=jb7jsfevz1u!! Mosby items and derived items 2012 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 The Brain Symphony of Science https://www.youtube.com/watch?t=2&v=jb7jsfevz1u!!
Supplementary Figure S1. Distinct compartmentalization of proinsulin in obese db/db mouse islet ß- cells.
 Supplementary Figure S1. Distinct compartmentalization of proinsulin in obese db/db mouse islet ß- cells. Pancreata from 16-weeks-old 6J +/+, 6J db/db, KS +/+ and KS db/db mice were harvested, fixed with
Supplementary Figure S1. Distinct compartmentalization of proinsulin in obese db/db mouse islet ß- cells. Pancreata from 16-weeks-old 6J +/+, 6J db/db, KS +/+ and KS db/db mice were harvested, fixed with
Lab 3: Pathogenesis of Virus Infections & Pattern 450 MIC PRACTICAL PART SECTION (30397) MIC AMAL ALGHAMDI 1
 Lab 3: Pathogenesis of Virus Infections & Pattern 450 MIC PRACTICAL PART SECTION (30397) 2018 450 MIC AMAL ALGHAMDI 1 Learning Outcomes The pathogenesis of viral infection The viral disease pattern Specific
Lab 3: Pathogenesis of Virus Infections & Pattern 450 MIC PRACTICAL PART SECTION (30397) 2018 450 MIC AMAL ALGHAMDI 1 Learning Outcomes The pathogenesis of viral infection The viral disease pattern Specific
Lecture 2: Virology. I. Background
 Lecture 2: Virology I. Background A. Properties 1. Simple biological systems a. Aggregates of nucleic acids and protein 2. Non-living a. Cannot reproduce or carry out metabolic activities outside of a
Lecture 2: Virology I. Background A. Properties 1. Simple biological systems a. Aggregates of nucleic acids and protein 2. Non-living a. Cannot reproduce or carry out metabolic activities outside of a
The Neuron by Richard H. Hall, 1998
 The Neuron by Richard H. Hall, 1998 External Structure A neuron can be defined as a nerve cell. The neuron is often thought of as the "building block" of the nervous system, and for good reason. The neuron
The Neuron by Richard H. Hall, 1998 External Structure A neuron can be defined as a nerve cell. The neuron is often thought of as the "building block" of the nervous system, and for good reason. The neuron
Annexin V-PE Apoptosis Detection Kit
 Annexin V-PE Apoptosis Detection Kit Catalog Number KA0716 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
Annexin V-PE Apoptosis Detection Kit Catalog Number KA0716 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
Detection of Tissue Culture-Adapted Theiler's Virus RNA in
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Aug. 1982, p. 763-770 Vol. 37, No. 2 0019-9567/82/080763-08$02.00/0 Detection of Tissue Culture-Adapted Theiler's Virus RNA in Spinal Cord White Matter Cells Throughout Infection
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Aug. 1982, p. 763-770 Vol. 37, No. 2 0019-9567/82/080763-08$02.00/0 Detection of Tissue Culture-Adapted Theiler's Virus RNA in Spinal Cord White Matter Cells Throughout Infection
Lack of Correlation of Central Nervous System Inflammation and Neuropathology with the Development of Seizures following Acute Virus Infection
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Aug. 2011, p. 8149 8157 Vol. 85, No. 16 0022-538X/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jvi.00730-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Lack of Correlation of
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Aug. 2011, p. 8149 8157 Vol. 85, No. 16 0022-538X/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jvi.00730-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Lack of Correlation of
Annexin V-Cy3 Apoptosis Detection Reagent
 ab14143 Annexin V-Cy3 Apoptosis Detection Reagent Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples This product is for research use only and is not
ab14143 Annexin V-Cy3 Apoptosis Detection Reagent Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples This product is for research use only and is not
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Fig. S1. Overexpression of Rpr causes progenitor cell death. (A) TUNEL assay of control intestines. No progenitor cell death could be observed, except that some ECs are undergoing
Supporting Information Fig. S1. Overexpression of Rpr causes progenitor cell death. (A) TUNEL assay of control intestines. No progenitor cell death could be observed, except that some ECs are undergoing
LEC 2, Medical biology, Theory, prepared by Dr. AYAT ALI
 General Characteristics, Structure and Taxonomy of Viruses Viruses A virus is non-cellular organisms made up of genetic material and protein that can invade living cells. They are considered both a living
General Characteristics, Structure and Taxonomy of Viruses Viruses A virus is non-cellular organisms made up of genetic material and protein that can invade living cells. They are considered both a living
Chapter 6- An Introduction to Viruses*
 Chapter 6- An Introduction to Viruses* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. 6.1 Overview of Viruses
Chapter 6- An Introduction to Viruses* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. 6.1 Overview of Viruses
For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples.
 ab14082 500X Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Reagent Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples. This product is for research use only and
ab14082 500X Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Reagent Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples. This product is for research use only and
ab CytoPainter Golgi/ER Staining Kit
 ab139485 CytoPainter Golgi/ER Staining Kit Instructions for Use Designed to detect Golgi bodies and endoplasmic reticulum by microscopy This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab139485 CytoPainter Golgi/ER Staining Kit Instructions for Use Designed to detect Golgi bodies and endoplasmic reticulum by microscopy This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES ON EQUINE ENCEPHALOSIS VIRUS
 Onderstepoort]. vet. Res. 40 (2), 53-58 (1973) ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES ON EQUINE ENCEPHALOSIS VIRUS G. LECATSAS, B. J. ERASMUS and H. J. ELS, Veterinary Research Institute, Onderstepoort ABSTRACT
Onderstepoort]. vet. Res. 40 (2), 53-58 (1973) ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES ON EQUINE ENCEPHALOSIS VIRUS G. LECATSAS, B. J. ERASMUS and H. J. ELS, Veterinary Research Institute, Onderstepoort ABSTRACT
A Tour of the Cell Period
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Name Date Period California State standard covered within this chapter: Cell Biology 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Name Date Period California State standard covered within this chapter: Cell Biology 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical
Supplemental Materials. STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle
 Supplemental Materials STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle Juanjuan Liu 1,2,3, Xingxing Yang 1,3, Binhua Li 1, Junjun Wang 1,2, Wenchao Wang 1, Jing Liu 1, Qingsong
Supplemental Materials STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle Juanjuan Liu 1,2,3, Xingxing Yang 1,3, Binhua Li 1, Junjun Wang 1,2, Wenchao Wang 1, Jing Liu 1, Qingsong
ROCK/Cdc42-mediated microglial motility and gliapse formation lead to phagocytosis of degenerating dopaminergic neurons in vivo
 Supplementary Information ROCK/Cdc42-mediated microglial motility and gliapse formation lead to phagocytosis of degenerating dopaminergic neurons in vivo Carlos Barcia* 1,2, Carmen M Ros 1,2, Valentina
Supplementary Information ROCK/Cdc42-mediated microglial motility and gliapse formation lead to phagocytosis of degenerating dopaminergic neurons in vivo Carlos Barcia* 1,2, Carmen M Ros 1,2, Valentina
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 b 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 Number of organoids per well 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 R0 R50 R100 R500 1st 2nd 3rd Noggin 100 ng/ml Noggin 10 ng/ml Noggin
b 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 Number of organoids per well 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 R0 R50 R100 R500 1st 2nd 3rd Noggin 100 ng/ml Noggin 10 ng/ml Noggin
<20 <20 <20 < <20 <20 <20 <20. Mock
 Cross-Lineage Neutralization PRNT 80 Titers Asian Asian West African Indian Ocean Group NHP Strain 181/25 Strain 99659 Strain 37997 Strain LR 142590 80 80 20 40 EILV/CHIKV 150844 640 640 160 320 Mock 150849
Cross-Lineage Neutralization PRNT 80 Titers Asian Asian West African Indian Ocean Group NHP Strain 181/25 Strain 99659 Strain 37997 Strain LR 142590 80 80 20 40 EILV/CHIKV 150844 640 640 160 320 Mock 150849
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues. Short Answer. Figure 3.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Short Answer Figure 3.1 Using Figure 3.1, match the following: 1) The illustration of simple cuboidal epithelium is. Answer:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Short Answer Figure 3.1 Using Figure 3.1, match the following: 1) The illustration of simple cuboidal epithelium is. Answer:
Evidence for a biphasic mode of respiratory syncytial virus transmission in permissive HEp2 cell monolayers
 Huong et al. Virology Journal (2016) 13:12 DOI 10.1186/s12985-016-0467-9 RESEARCH Open Access Evidence for a biphasic mode of respiratory syncytial virus transmission in permissive HEp2 cell monolayers
Huong et al. Virology Journal (2016) 13:12 DOI 10.1186/s12985-016-0467-9 RESEARCH Open Access Evidence for a biphasic mode of respiratory syncytial virus transmission in permissive HEp2 cell monolayers
Suppl Video: Tumor cells (green) and monocytes (white) are seeded on a confluent endothelial
 Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Dynamic Interaction of Stress Granule, DDX3X and IKK-α Mediates Multiple Functions in
 Dynamic Interaction of Stress Granule, and Mediates Multiple Functions in Hepatitis C Virus Infection Véronique Pène, Qisheng Li#, Catherine Sodroski, Ching-Sheng Hsu, T. Jake Liang# Liver Diseases Branch,
Dynamic Interaction of Stress Granule, and Mediates Multiple Functions in Hepatitis C Virus Infection Véronique Pène, Qisheng Li#, Catherine Sodroski, Ching-Sheng Hsu, T. Jake Liang# Liver Diseases Branch,
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 17: Intracellular Vesicular Traffic
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 17: Intracellular Vesicular Traffic Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about clathrin-coated vesicles is correct? Question #1 (A) There are
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 17: Intracellular Vesicular Traffic Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about clathrin-coated vesicles is correct? Question #1 (A) There are
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4547
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
RayBio Annexin V-Cy5 Apoptosis Detection Kit
 RayBio Annexin V-Cy5 Apoptosis Detection Kit User Manual Version 1.0 Mar 20, 2014 (Cat#: 68C5-AnnV-S) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent Support And Service Tel:(Toll Free)1-888-494-8555 or
RayBio Annexin V-Cy5 Apoptosis Detection Kit User Manual Version 1.0 Mar 20, 2014 (Cat#: 68C5-AnnV-S) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent Support And Service Tel:(Toll Free)1-888-494-8555 or
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
Supplemental Information. Ca V 2.2 Gates Calcium-Independent. but Voltage-Dependent Secretion. in Mammalian Sensory Neurons
 Neuron, Volume 96 Supplemental Information Ca V 2.2 Gates Calcium-Independent but Voltage-Dependent Secretion in Mammalian Sensory Neurons Zuying Chai, Changhe Wang, Rong Huang, Yuan Wang, Xiaoyu Zhang,
Neuron, Volume 96 Supplemental Information Ca V 2.2 Gates Calcium-Independent but Voltage-Dependent Secretion in Mammalian Sensory Neurons Zuying Chai, Changhe Wang, Rong Huang, Yuan Wang, Xiaoyu Zhang,
Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES Generalized Cell All cells: Human cells have three basic parts: Plasma membrane flexible outer boundary Cytoplasm intracellular fluid containing organelles Nucleus control center
Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES Generalized Cell All cells: Human cells have three basic parts: Plasma membrane flexible outer boundary Cytoplasm intracellular fluid containing organelles Nucleus control center
Cryptosporidium Proficiency Test Program for Laboratories using US EPA Method 1623: Cryptosporidium and Giardia
 Cryptosporidium Proficiency Test Program for Laboratories using US EPA Method 1623: Cryptosporidium and Giardia in Water by Filtration/IMS/FA, December 2005 version Preferable Specifications to Establish
Cryptosporidium Proficiency Test Program for Laboratories using US EPA Method 1623: Cryptosporidium and Giardia in Water by Filtration/IMS/FA, December 2005 version Preferable Specifications to Establish
The Regulated Secretory Pathway in CD4 + T cells Contributes to Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 Cell-to-Cell Spread at the Virological Synapse
 The Regulated Secretory Pathway in CD4 + T cells Contributes to Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 Cell-to-Cell Spread at the Virological Synapse Clare Jolly 1 *, Sonja Welsch 2,3, Stefanie Michor 4,
The Regulated Secretory Pathway in CD4 + T cells Contributes to Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 Cell-to-Cell Spread at the Virological Synapse Clare Jolly 1 *, Sonja Welsch 2,3, Stefanie Michor 4,
Tunneling nanotubes (TNT) as a novel route of cell-to-cell spread of herpesviruses
 JVI Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 28 February 2018 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.00090-18 Copyright 2018 American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 Tunneling nanotubes (TNT) as a novel route
JVI Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 28 February 2018 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.00090-18 Copyright 2018 American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 Tunneling nanotubes (TNT) as a novel route
Cell Biology. A discipline of biology: 1. Cell structure 2. Cellular processes 3. Cell division
 The Cell Cell Biology 1 A discipline of biology: 1. Cell structure 2. Cellular processes 3. Cell division Tight connection with 1. Molecular biology 2. Biochemistry Cell theory 2 1838, 1839 Theodor Schwann
The Cell Cell Biology 1 A discipline of biology: 1. Cell structure 2. Cellular processes 3. Cell division Tight connection with 1. Molecular biology 2. Biochemistry Cell theory 2 1838, 1839 Theodor Schwann
Annexin V-Cy3 Apoptosis Detection Kit
 ab14142 Annexin V-Cy3 Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples. This product is for research use only and is not intended
ab14142 Annexin V-Cy3 Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples. This product is for research use only and is not intended
The Leader Polypeptide of Theiler s Virus Is Essential for Neurovirulence but Not for Virus Growth in BHK Cells
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Sept. 1995, p. 5544 5549 Vol. 69, No. 9 0022-538X/95/$04.00 0 Copyright 1995, American Society for Microbiology The Leader Polypeptide of Theiler s Virus Is Essential for Neurovirulence
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Sept. 1995, p. 5544 5549 Vol. 69, No. 9 0022-538X/95/$04.00 0 Copyright 1995, American Society for Microbiology The Leader Polypeptide of Theiler s Virus Is Essential for Neurovirulence
Lahore University of Management Sciences. BIO314 Virology and Microbiology (Spring 2015)
 BIO314 Virology and Microbiology (Spring 2015) Instructor Room. Office Hours Email Telephone Secretary/TA TA Office Hours Course URL (if any) Shaper Mirza and Sadia Hamera Shaper.Mirza@uth.tmc.edu Course
BIO314 Virology and Microbiology (Spring 2015) Instructor Room. Office Hours Email Telephone Secretary/TA TA Office Hours Course URL (if any) Shaper Mirza and Sadia Hamera Shaper.Mirza@uth.tmc.edu Course
Determination of the temporal pattern and importance of BALF1 expression in Epstein-Barr viral infection
 Determination of the temporal pattern and importance of BALF1 expression in Epstein-Barr viral infection Melissa Mihelidakis May 6, 2004 7.340 Research Proposal Introduction Apoptosis, or programmed cell
Determination of the temporal pattern and importance of BALF1 expression in Epstein-Barr viral infection Melissa Mihelidakis May 6, 2004 7.340 Research Proposal Introduction Apoptosis, or programmed cell
The Cell. The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes.
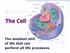 The Cell The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes. Life is macromolecules that can perform unique functions because they are enclosed in a structural compartment that is separate from
The Cell The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes. Life is macromolecules that can perform unique functions because they are enclosed in a structural compartment that is separate from
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 11: Neural Tissue & The Nervous System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 11: Neural Tissue & The Nervous System Question No. 1 of 10 The human body contains different types of tissue. The tissue is formed into organs and organ systems.
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 11: Neural Tissue & The Nervous System Question No. 1 of 10 The human body contains different types of tissue. The tissue is formed into organs and organ systems.
RayBio Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit
 RayBio Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit User Manual Version 1.0 May 25, 2014 (Cat#: 68FT-AnnV-S) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent Support And Service Tel:(Toll Free)1-888-494-8555 or
RayBio Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit User Manual Version 1.0 May 25, 2014 (Cat#: 68FT-AnnV-S) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent Support And Service Tel:(Toll Free)1-888-494-8555 or
Laboratory 10 Factors Controlling Phagocytosis in Tetrahymena,
 BIO354: Cell Biology Laboratory 1 Laboratory 1 Factors Controlling Phagocytosis in Tetrahymena, I. Introduction A characteristic feature of all eukaryotic cells is the ability to pinch off portions of
BIO354: Cell Biology Laboratory 1 Laboratory 1 Factors Controlling Phagocytosis in Tetrahymena, I. Introduction A characteristic feature of all eukaryotic cells is the ability to pinch off portions of
Cell Overview. Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD
 Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
10 The Golgi Apparatus: The First 100 Years
 2 Structure With no cell compartment or organelle has morphology served such a pivotal role in its discovery and investigation as with the apparatus of Golgi. The original description of the apparato reticulo
2 Structure With no cell compartment or organelle has morphology served such a pivotal role in its discovery and investigation as with the apparatus of Golgi. The original description of the apparato reticulo
Cellular compartments
 Cellular compartments 1. Cellular compartments and their function 2. Evolution of cellular compartments 3. How to make a 3D model of cellular compartment 4. Cell organelles in the fluorescent microscope
Cellular compartments 1. Cellular compartments and their function 2. Evolution of cellular compartments 3. How to make a 3D model of cellular compartment 4. Cell organelles in the fluorescent microscope
LESSON 4.4 WORKBOOK. How viruses make us sick: Viral Replication
 DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Eukaryotic: Non-bacterial cell type (bacteria are prokaryotes).. LESSON 4.4 WORKBOOK How viruses make us sick: Viral Replication This lesson extends the principles we learned in Unit
DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Eukaryotic: Non-bacterial cell type (bacteria are prokaryotes).. LESSON 4.4 WORKBOOK How viruses make us sick: Viral Replication This lesson extends the principles we learned in Unit
The Cell. Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 The Cell Cell Theory The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life The organism activity depends on individual and collective activity of cells Biochemical activities of cells are dictated
The Cell Cell Theory The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life The organism activity depends on individual and collective activity of cells Biochemical activities of cells are dictated
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen Mechanisms of Hemagglutinin Targeted Influenza Virus Neutralization Brandenburg, Boerries; Koudstaal, Wouter; Goudsmit, Jaap; Klaren, Vincent; Tang, Chan; Bujny, Miriam V.; Korse,
University of Groningen Mechanisms of Hemagglutinin Targeted Influenza Virus Neutralization Brandenburg, Boerries; Koudstaal, Wouter; Goudsmit, Jaap; Klaren, Vincent; Tang, Chan; Bujny, Miriam V.; Korse,
Vesicle Transport. Vesicle pathway: many compartments, interconnected by trafficking routes 3/17/14
 Vesicle Transport Vesicle Formation Curvature (Self Assembly of Coat complex) Sorting (Sorting Complex formation) Regulation (Sar1/Arf1 GTPases) Fission () Membrane Fusion SNARE combinations Tethers Regulation
Vesicle Transport Vesicle Formation Curvature (Self Assembly of Coat complex) Sorting (Sorting Complex formation) Regulation (Sar1/Arf1 GTPases) Fission () Membrane Fusion SNARE combinations Tethers Regulation
Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
 open reading frame 1565 (segment 5) 47 (-) 3 5 (+) 76 101 125 149 173 197 221 246 287 open reading frame 890 (segment 8) 60 (-) 3 5 (+) 172 Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
open reading frame 1565 (segment 5) 47 (-) 3 5 (+) 76 101 125 149 173 197 221 246 287 open reading frame 890 (segment 8) 60 (-) 3 5 (+) 172 Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
Starch grains - excess sugars
 (a) Membrane system - site of light reactions (photosynthesis) - chlorpophyll pigments - enzymes - electron carriers - flattened, fluid-filled sacs (called thylakoids which are stacked to form grana) -
(a) Membrane system - site of light reactions (photosynthesis) - chlorpophyll pigments - enzymes - electron carriers - flattened, fluid-filled sacs (called thylakoids which are stacked to form grana) -
ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE FORMATION OF BLUETONGUE VIRUS*
 Onderstepoort J. vet. Res. (1968), 35 (1), 139-150 Printed in the Repub. of S. Afr. by The Government Printer, Pretoria ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE FORMATION OF BLUETONGUE VIRUS* G. LECATSAS, Veterinary
Onderstepoort J. vet. Res. (1968), 35 (1), 139-150 Printed in the Repub. of S. Afr. by The Government Printer, Pretoria ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE FORMATION OF BLUETONGUE VIRUS* G. LECATSAS, Veterinary
Human Anatomy and Physiology- Problem Drill 04: Tissues of the Body
 Human Anatomy and Physiology- Problem Drill 04: Tissues of the Body Question No. 1 of 10 A biopsy sample is obtained from a lesion on the right cheek of a male patient. A technician in the histology lab
Human Anatomy and Physiology- Problem Drill 04: Tissues of the Body Question No. 1 of 10 A biopsy sample is obtained from a lesion on the right cheek of a male patient. A technician in the histology lab
Overview of virus life cycle
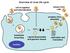 Overview of virus life cycle cell recognition and internalization release from cells progeny virus assembly membrane breaching nucleus capsid disassembly and genome release replication and translation
Overview of virus life cycle cell recognition and internalization release from cells progeny virus assembly membrane breaching nucleus capsid disassembly and genome release replication and translation
L* Protein of the DA Strain of Theiler s Murine Encephalomyelitis Virus Is Important for Virus Growth in a Murine Macrophage-Like Cell Line
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, June 1998, p. 4950 4955 Vol. 72, No. 6 0022-538X/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology L* Protein of the DA Strain of Theiler s Murine Encephalomyelitis Virus
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, June 1998, p. 4950 4955 Vol. 72, No. 6 0022-538X/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology L* Protein of the DA Strain of Theiler s Murine Encephalomyelitis Virus
Poliovirus infection blocks ERGIC-to-Golgi trafficking and induces microtubule-dependent disruption of the Golgi complex
 Research Article 3207 Poliovirus infection blocks ERGIC-to-Golgi trafficking and induces microtubule-dependent disruption of the Golgi complex Oren Beske 1, *, Mike Reichelt 2, *, Matthew P. Taylor 2,
Research Article 3207 Poliovirus infection blocks ERGIC-to-Golgi trafficking and induces microtubule-dependent disruption of the Golgi complex Oren Beske 1, *, Mike Reichelt 2, *, Matthew P. Taylor 2,
Gastroenteritis Viruses Prof. Mary K. Estes
 Gastroenteritis Viruses Mary K. Estes, Ph.D. Professor of Molecular Virology and Microbiology and Medicine-GI, BCM Director, Texas Medical Center DDC 1 Outline Gastrointestinal viruses Rotaviruses Noroviruses
Gastroenteritis Viruses Mary K. Estes, Ph.D. Professor of Molecular Virology and Microbiology and Medicine-GI, BCM Director, Texas Medical Center DDC 1 Outline Gastrointestinal viruses Rotaviruses Noroviruses
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Lu et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201012063/dc1 Figure S1. Kinetics of nuclear envelope assembly, recruitment of Nup133
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Lu et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201012063/dc1 Figure S1. Kinetics of nuclear envelope assembly, recruitment of Nup133
Thursday, October 16 th
 Thursday, October 16 th Good morning. Those of you needing to take the Enzymes and Energy Quiz will start very soon. Students who took the quiz Wednesday: Please QUIETLY work on the chapter 6 reading guide.
Thursday, October 16 th Good morning. Those of you needing to take the Enzymes and Energy Quiz will start very soon. Students who took the quiz Wednesday: Please QUIETLY work on the chapter 6 reading guide.
Essential Cell Biology
 Alberts Bray Hopkin Johnson Lewis Raff Roberts Walter Essential Cell Biology FOURTH EDITION Chapter 15 Intracellular Compartments and Protein Transport Copyright Garland Science 2014 CHAPTER CONTENTS MEMBRANE-ENCLOSED
Alberts Bray Hopkin Johnson Lewis Raff Roberts Walter Essential Cell Biology FOURTH EDITION Chapter 15 Intracellular Compartments and Protein Transport Copyright Garland Science 2014 CHAPTER CONTENTS MEMBRANE-ENCLOSED
Principles of Molecular Virology STAGE / YEAR: 3 CREDITS: 10. PROGRAMME COMMITTEE: Biomedical Sciences. VERSION: 4th March 2015
 MODULE: MODULE NUMBER: JACS CODE: Principles of Molecular Virology BIO00041H C540 STAGE / YEAR: 3 CREDITS: 10 ORGANISER: Nathalie Signoret PROGRAMME COMMITTEE: Biomedical Sciences VERSION: 4th March 2015
MODULE: MODULE NUMBER: JACS CODE: Principles of Molecular Virology BIO00041H C540 STAGE / YEAR: 3 CREDITS: 10 ORGANISER: Nathalie Signoret PROGRAMME COMMITTEE: Biomedical Sciences VERSION: 4th March 2015
Recent Findings from Analysis of HIV Clade C in India
 Recent Findings from Analysis of HIV Clade C in India Pankaj Seth, Ph.D Associate Professor, Molecular & Cellular Neuroscience National Brain Research Centre (NBRC) Manesar, INDIA pseth@nbrc.res.in NeuroAIDS
Recent Findings from Analysis of HIV Clade C in India Pankaj Seth, Ph.D Associate Professor, Molecular & Cellular Neuroscience National Brain Research Centre (NBRC) Manesar, INDIA pseth@nbrc.res.in NeuroAIDS
Endomembrane system, *Chloroplasts, *Mitochondria. *Learn these from text/connect1. Fertilization of a human cell
 Key Concepts: - Cells are the Basic Unit of Life Cell Theory, Surface to Volume - 2 Cell Types Prokaryotic, Eukaryotic - Cell Membrane Membrane Structure - Cell Organelles Endomembrane system, *Chloroplasts,
Key Concepts: - Cells are the Basic Unit of Life Cell Theory, Surface to Volume - 2 Cell Types Prokaryotic, Eukaryotic - Cell Membrane Membrane Structure - Cell Organelles Endomembrane system, *Chloroplasts,
