Tuberculosis. Impact of TB. Infectious Disease Epidemiology BMTRY 713 (A. Selassie, DrPH)
|
|
|
- Berenice Anastasia Griffin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Infectious Disease Epidemiology BMTRY 713 (A. Selassie, DrPH) Lecture 20 Tuberculosis Learning Objectives 1. Describe the biologic characteristics of the agent 2. Determine the epidemiologic characteristics of Tuberculosis 3. Identify the major risk factors of Tuberculosis Tuberculosis Caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis Suggestive identification in skeletons from 8,000-5,000 BC Additional evidence from Egyptian mummies Hypothesized it resulted from domestication of cattle Impact of TB 1999, WHO identified TB as among the most serious threats to the world ⅓ of the population of the world latently infected 7-9 million new cases annually ~2 million deaths annually Selassie AW (DPHS, MUSC) 1
2 Epidemiology Pandemic Seventh leading cause of death in the world Second leading infectious cause of death 95% of all cases are in the developing world, most victims between 15 and 55 Global variation in disease US and Europe Low prevalence Lowest in infancy, increasing with age Latin America and Caribbean Higher prevalence, incidence, and mortality Two peaks in incidence and mortality Infancy TB >Males Early adult TB>Females; Age 35 TB >Males Global variation in disease (2) Asia and Africa 60-70% adults have latent infection Two peaks in incidence Infancy TB >Males Late adolescence TB >Females Rates of women exceed men until age 60 Selassie AW (DPHS, MUSC) 2
3 The Organism (see table 14-1) Four are usual human pathogens Mycobacterium tuberculosis (1882 Koch) M. africanum M. canettii (1969; 1997) M. bovis M. kansaii M. leprae causes leprosy M. avium opportunistic infection in AIDS Selassie AW (DPHS, MUSC) 3
4 Clinical manifestations Initial latent infection Asymptomatic Clinical disease Usually pulmonary (80%) Extrapulmonary Can strike almost any organ system Pericardium, spine, GI tract, skin, kidney, lymph nodes More common in children and immunocompromised Clinical manifestations (2) Active disease Variable intensity Non-specific symptoms Cough, with or without bloody sputum, fatigue, anorexia and weight loss, fever, sweating and/or chills, chest pain Extrapulmonary fatigue and night sweats, other symptoms specific to organs Selassie AW (DPHS, MUSC) 4
5 Chest X-ray of Pulmonary TB b Tuberculous Pneumonia with consolidation Miliary Tuberculosis with shadowing on both lungs Diagnosis Latent Asymptomatic, based on clinical tests Tuberculin skin test (TST) purified protein derivative (PPD, Mantoux test) Intracutaneous injection Diagnosed by the size of the zone on induration surrounding the injection site hours >10 mm induration strongly suggestive Identifies disease in 98% of positives, only 5% of negatives BCG vaccine can produce false positive Selassie AW (DPHS, MUSC) 5
6 Techniques of Tuberculin Skin Test (TST) False negative tests Individuals with HIV or cancer Malnutrition Viral infection, such as measles Actively infected may have neg test Immune suppresion Cut points for positive test Dependent upon the size of induration, prior probability of infection, and clinical consequences of misreading the result. >=5 HIV+, close contact with known case >=10 Medical factors increase risk, high prevalence area >=15 Low risk Selassie AW (DPHS, MUSC) 6
7 Active disease 5-10% with latent infection develop active disease Diagnosis is based upon assessment of risk, clinical findings and symptoms, PPD test, chest X-ray, sputum culture Where medical tests are unavailable, diagnosis depends upon clinical symptoms and examination of sputum Therapy Three eras Pre-sanatorium (Pre-1850) Tumors cause by ill airs; Treatment living in a mild, seaside climate, bloodletting, rest Sanatorium 1850 s, rest, Isolation to decrease transmission Chemotherapeutic PAS (1940s),INH (1952),Streptomycin (1943) Early clinical trial 1940 England, multicenter, randomized, control trial Streptomycin vs. placebo (early 50s) Selassie AW (DPHS, MUSC) 7
8 Current treatment approach Slowly progressive disease; longer Rx Some drugs only kill actively growing bacteria Need to be taken for at least 6 months Risk of mutation with single drug therapy Usual treatment 2 or more drugs Patient adherence Main hurdle in TB therapy If non-adherent there is a risk of a antibiotic resistant strain developing Directly observed therapy (DOT) 6 month treatment, relapse 5%or less Natural History & Bacteriology Moderately infectious 20%-30% of exposed become infected Can remain dormant for years 5%-10% develop active disease, the rest have latent disease 5%-10% of those with latent disease develop active disease (reactivation TB) Facilitated by malnutrition, HIV, other medical Selassie AW (DPHS, MUSC) 8
9 Impact of natural history on population Reservoir of latent infection (stage1) Development of active infection (stage 2) People with active infection or reactivation transmit disease to others (stage 3) Impacted by prevalence of HIV Average of 10 contacts infected before case is treated 5-10% will develop TB in 12 months Transmit disease to their contacts Selassie AW (DPHS, MUSC) 9
10 The outer cover of M. Tuberculosis is a waxy layer (mycolic acid, phospho- and sulfolipids) that allows some of the bacilli not to fuse with lysosome. This allows some of the bacilli to remain alive indefinitely. Transmission of TB Airborne via respiratory tract People with active disease discharge minute particles of sputum when coughing, talking, sneezing, singing Smaller droplets are suspended in the air for long time periods Inhaled by uninfected people Infectivity of pulmonary TB Function of Virulence of the bacteria Frequency of cough Degree of pulmonary infiltration Bacterial load in the sputum Selassie AW (DPHS, MUSC) 10
11 Extrapulmonary TB Enters the body through mucous membranes in GI tract, genitourinary tract, conjunctiva, breaks in the skin Causes infection at the site of entry which can remain localized or spread to other organs Rarer transmission, esp. in developed countries Various sites of Tuberculosis Choroidal tuberculosis Vertebral tuberculosis Risk factors associated with infection Severity of disease in the index case is the most important factor Social factors Crowding and poverty May be related to probability of exposure Risk is a function of exposure Selassie AW (DPHS, MUSC) 11
12 Risk factors associated with development of disease 5%-10% of infected become diseased, usually within the first 2 years 1% in the first year 0.07% 8-10 years later Age, cohort effect Gender Peak in women during reproductive years maybe hormonal Peak in men at older ages a function of decrease immunity due to smoking and drinking Risk factors associated with development of disease (2) Genetics Twin studies infection of second twin more likely if monozygotic Some correlation of TB response and blood type OR for Types AB and B vs. O and A =3 Lean body build SES, but may reflect different exposure Risk factors associated with development of disease (3) Stress (Danish study) Lowest in married men Intermediate in single and widowed men Highest in divorced men Similar results but less dramatic for women Married people developed less severe disease Poverty Selassie AW (DPHS, MUSC) 12
13 Risk factors associated with development of disease (4) Nutrition Specific micronutrients Low vitamin A and selenium associated with increased risk of developing disease Malnutrition Higher among malnourished, thinner people Occupation Silica in the work site, health care workers Risk factors associated with development of disease (5) HIV infection and AIDS Most potent biologic risk factor for developing TB Reactivation is 3%-14% New infection 40% of HIV + develop Tb within several years Can occur even with relatively high CD4 counts HIV epidemic severely undermines TB control, especially in developing countries BCG vaccination Developed in 1921 Common in Europe until Lubeck disaster In 1930, 251/412 German children vaccinated contracted TB Accidentally vaccinated with live, virulent culture Decreased usage followed by increase in TB Safe vaccine, efficacy range 22% to 85% WHO standard vaccine, except US and Netherlands Selassie AW (DPHS, MUSC) 13
14 BCG response at 6 weeks: Clinical evidence of a cell-mediated immune response Control strategies Case finding and treatment Strong surveillance system, sufficient laboratory components, effective treatments (DOT), reliable supply of drugs Goal is to identify 70% of smear positive patients and to treat 85% successfully Current estimate is 1/3 of cases identified and treated Epidemiologic basis of control Reproductive rate to be <1 Developing countries BCG vaccination Case detection and treatment Preventive therapy Treatment of latent disease reduces the risk by 60%-90% Offering preventive treatment o high risk patients Close contacts, HIV, recent converters Selassie AW (DPHS, MUSC) 14
15 Increasing prevalence of drugresistant TB Patients without prior therapy 9.9% History of therapy 35.6% Multi-drug resistance Treatment is more toxic and expensive Hot spots Russia, Dominican Republic, China Various lesions of Tuberculosis Cavitary Tuberculosis from Mycobacterium avium 60-year-old male smoker Bilateral Tuberculosis from Mycobacterium kansaii 42-year-old male smoker Selassie AW (DPHS, MUSC) 15
Fundamentals of Tuberculosis (TB)
 TB in the United States Fundamentals of Tuberculosis (TB) From 1953 to 1984, reported cases decreased by approximately 5.6% each year From 1985 to 1992, reported cases increased by 20% 25,313 cases reported
TB in the United States Fundamentals of Tuberculosis (TB) From 1953 to 1984, reported cases decreased by approximately 5.6% each year From 1985 to 1992, reported cases increased by 20% 25,313 cases reported
Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Lecture (14) Dr.Baha, AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology
 Mycobacterium tuberculosis Lecture (14) Dr.Baha, AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology Robert Koch 1843-1910 German physician Became famous for isolating the anthrax bacillus (1877), tuberculosis bacillus (1882)
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Lecture (14) Dr.Baha, AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology Robert Koch 1843-1910 German physician Became famous for isolating the anthrax bacillus (1877), tuberculosis bacillus (1882)
What is tuberculosis? What causes tuberculosis?
 What is tuberculosis? What causes tuberculosis? Last updated: Thursday 4 September 2014 Tuberculosis Infectious Diseases / Bacteria / Viruses Respiratory / Asthma Some may see Tuberculosis as a historical
What is tuberculosis? What causes tuberculosis? Last updated: Thursday 4 September 2014 Tuberculosis Infectious Diseases / Bacteria / Viruses Respiratory / Asthma Some may see Tuberculosis as a historical
Tuberculosis What you need to know. James Zoretic M.D., M.P.H. Regions 2 and 3 Director
 Tuberculosis What you need to know James Zoretic M.D., M.P.H. Regions 2 and 3 Director What is Tuberculosis? Tuberculosis, (TB) is a communicable disease caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacillus
Tuberculosis What you need to know James Zoretic M.D., M.P.H. Regions 2 and 3 Director What is Tuberculosis? Tuberculosis, (TB) is a communicable disease caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacillus
CHAPTER 3: DEFINITION OF TERMS
 CHAPTER 3: DEFINITION OF TERMS NOTE: TB bacteria is used in place of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in most of the definitions presented here. 3.1 Acid-fast bacteria
CHAPTER 3: DEFINITION OF TERMS NOTE: TB bacteria is used in place of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in most of the definitions presented here. 3.1 Acid-fast bacteria
Descriptive Epidemiology Project: Tuberculosis in the. United States. MPH 510: Applied Epidemiology. Summer A 2014
 Descriptive Epidemiology Project: Tuberculosis in the United States MPH 510: Applied Epidemiology Summer A 2014 June 1, 2014 1 The white plague affected thousands upon thousands of people in the 18 th
Descriptive Epidemiology Project: Tuberculosis in the United States MPH 510: Applied Epidemiology Summer A 2014 June 1, 2014 1 The white plague affected thousands upon thousands of people in the 18 th
Tuberculosis Elimination: The Role of the Infection Preventionist
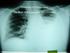 Tuberculosis Elimination: The Role of the Infection Preventionist Preface: What Happens when Health Care Professionals are not familiar with TB? A 15 year old student was diagnosed with highly infectious
Tuberculosis Elimination: The Role of the Infection Preventionist Preface: What Happens when Health Care Professionals are not familiar with TB? A 15 year old student was diagnosed with highly infectious
Tuberculosis (TB) Fundamentals for School Nurses
 Tuberculosis (TB) Fundamentals for School Nurses June 9, 2015 Kristin Gall, RN, MSN/Pat Infield, RN-TB Program Manager Marsha Carlson, RN, BSN Two Rivers Public Health Department Nebraska Department of
Tuberculosis (TB) Fundamentals for School Nurses June 9, 2015 Kristin Gall, RN, MSN/Pat Infield, RN-TB Program Manager Marsha Carlson, RN, BSN Two Rivers Public Health Department Nebraska Department of
Characteristics of Mycobacterium
 Mycobacterium Characteristics of Mycobacterium Very thin, rod shape. Culture: Aerobic, need high levels of oxygen to grow. Very slow in grow compared to other bacteria (colonies may be visible in up to
Mycobacterium Characteristics of Mycobacterium Very thin, rod shape. Culture: Aerobic, need high levels of oxygen to grow. Very slow in grow compared to other bacteria (colonies may be visible in up to
Chapter 22. Pulmonary Infections
 Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
TB IN EMERGENCIES. Disease Control in Humanitarian Emergencies (DCE)
 TB IN EMERGENCIES Department of Epidemic and Pandemic Alert and Response (EPR) Health Security and Environment Cluster (HSE) (Acknowledgements WHO Stop TB Programme WHO/STB) 1 Why TB? >33% of the global
TB IN EMERGENCIES Department of Epidemic and Pandemic Alert and Response (EPR) Health Security and Environment Cluster (HSE) (Acknowledgements WHO Stop TB Programme WHO/STB) 1 Why TB? >33% of the global
SWABCHA Fact Sheet: Tuberculosis (TB)
 SWABCHA (TB) Text sourced from the SWABCHA Change Agent Training Guide - 2012 Introduction to TB Microscopic bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis causes TB Only TB of the lungs or throat may be infectious.
SWABCHA (TB) Text sourced from the SWABCHA Change Agent Training Guide - 2012 Introduction to TB Microscopic bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis causes TB Only TB of the lungs or throat may be infectious.
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10. Mycobacterium. Actinomycetes. Nocardia
 Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Nocardia 1 Mycobacterium Characteristics - Large, very weakly gram positive rods - Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes - Catalase positive
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Nocardia 1 Mycobacterium Characteristics - Large, very weakly gram positive rods - Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes - Catalase positive
Disease-causing organisms
 1 of 41 2 of 41 Disease-causing organisms Organisms that cause disease are called pathogens. What are the four major types of pathogen? bacteria fungi protozoa virus 3 of 41 How do pathogens cause illness?
1 of 41 2 of 41 Disease-causing organisms Organisms that cause disease are called pathogens. What are the four major types of pathogen? bacteria fungi protozoa virus 3 of 41 How do pathogens cause illness?
Communicable Disease Control Manual Chapter 4: Tuberculosis
 Provincial TB Services 655 West 12th Avenue Vancouver, BC V5Z 4R4 www.bccdc.ca Communicable Disease Control Manual Definitions Page 1 2.0 DEFINITIONS Many of the definitions that follow are taken from
Provincial TB Services 655 West 12th Avenue Vancouver, BC V5Z 4R4 www.bccdc.ca Communicable Disease Control Manual Definitions Page 1 2.0 DEFINITIONS Many of the definitions that follow are taken from
New Entrant Screening and Latent TB Get screened and find out if you have TB infection before you develop TB disease!
 New Entrant Screening and Latent TB Get screened and find out if you have TB infection before you develop TB disease! Screening and treatment for TB are free. What does this leaflet cover? What is Tuberculosis
New Entrant Screening and Latent TB Get screened and find out if you have TB infection before you develop TB disease! Screening and treatment for TB are free. What does this leaflet cover? What is Tuberculosis
Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13. Mycobacterium Actinomycetes
 Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Mycobacterium tuberculosis Large, very weakly gram positive rods, Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes, non spore forming, non motile
Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Mycobacterium tuberculosis Large, very weakly gram positive rods, Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes, non spore forming, non motile
All you need to know about Tuberculosis
 All you need to know about Tuberculosis What is tuberculosis? Tuberculosis is an infectious disease that usually affects the lungs. Doctors make a distinction between two kinds of tuberculosis infection:
All you need to know about Tuberculosis What is tuberculosis? Tuberculosis is an infectious disease that usually affects the lungs. Doctors make a distinction between two kinds of tuberculosis infection:
Self-Study Modules on Tuberculosis
 Self-Study Modules on Tuberculosis Transmission and Pathogenesis of Tube rc ulos is U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for HIV/AIDS,
Self-Study Modules on Tuberculosis Transmission and Pathogenesis of Tube rc ulos is U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for HIV/AIDS,
TB the basics. (Dr) Margaret (DHA) and John (INZ)
 TB the basics (Dr) Margaret (DHA) and John (INZ) Question 1 The scientist who discovered M. tuberculosis was: A: Louis Pasteur B: Robert Koch C: Jean-Antoine Villemin D: Calmette and Guerin Question 2
TB the basics (Dr) Margaret (DHA) and John (INZ) Question 1 The scientist who discovered M. tuberculosis was: A: Louis Pasteur B: Robert Koch C: Jean-Antoine Villemin D: Calmette and Guerin Question 2
Symptoms Latent TB Active TB
 1 Tuberculosis Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease that can spread through the air. It is caused by a bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It usually affect the lungs. However, it can also affect other
1 Tuberculosis Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease that can spread through the air. It is caused by a bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It usually affect the lungs. However, it can also affect other
CHAPTER:1 TUBERCULOSIS. BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY
 CHAPTER:1 TUBERCULOSIS BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY GLOBAL EMERGENCY: * Tuberculosis kills 5,000 people a day! * 2.3 million die each year!
CHAPTER:1 TUBERCULOSIS BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY GLOBAL EMERGENCY: * Tuberculosis kills 5,000 people a day! * 2.3 million die each year!
Chapter 7 Tuberculosis (TB)
 Chapter 7 Tuberculosis (TB) TB infection vs. TB disease Information about TB TB skin testing Active TB disease TB risk factors Role of Peel Public Health in TB prevention and control Environmental and
Chapter 7 Tuberculosis (TB) TB infection vs. TB disease Information about TB TB skin testing Active TB disease TB risk factors Role of Peel Public Health in TB prevention and control Environmental and
"GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS IN INSTITUTIONAL FACILITIES"
 MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS IN INSTITUTIONAL FACILITIES" Training For THE CDC "TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTION GUIDELINES" "Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today...and Tomorrow"
MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS IN INSTITUTIONAL FACILITIES" Training For THE CDC "TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTION GUIDELINES" "Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today...and Tomorrow"
Mycobacteria & Tuberculosis PROF.HANAN HABIB & PROF ALI SOMILY DEPRTMENT OF PATHOLOGY, MICROBIOLOGY UNIT COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
 Mycobacteria & Tuberculosis PROF.HANAN HABIB & PROF ALI SOMILY DEPRTMENT OF PATHOLOGY, MICROBIOLOGY UNIT COLLEGE OF MEDICINE Objectives l Recognize that tuberculosis as a chronic disease mainly affecting
Mycobacteria & Tuberculosis PROF.HANAN HABIB & PROF ALI SOMILY DEPRTMENT OF PATHOLOGY, MICROBIOLOGY UNIT COLLEGE OF MEDICINE Objectives l Recognize that tuberculosis as a chronic disease mainly affecting
Tuberculosis & Refugees in Philadelphia
 Tuberculosis & Refugees in Philadelphia Philadelphia TB Control Program Daniel P. Dohony, MPH Philadelphia TB Control Program Health Information Portal Website: hip.phila.gov Contains Information On» Disease
Tuberculosis & Refugees in Philadelphia Philadelphia TB Control Program Daniel P. Dohony, MPH Philadelphia TB Control Program Health Information Portal Website: hip.phila.gov Contains Information On» Disease
TB facts & figures Microbiology of TB Transmission of TB Infection control in health care settings Special cases Resistant TB Masks
 1 TB facts & figures Microbiology of TB Transmission of TB Infection control in health care settings Special cases Resistant TB Masks 2 Page 1 4 NHS Lothian Infection Prevention and Control Study Day On
1 TB facts & figures Microbiology of TB Transmission of TB Infection control in health care settings Special cases Resistant TB Masks 2 Page 1 4 NHS Lothian Infection Prevention and Control Study Day On
TUBERCULOSIS. Presented By: Public Health Madison & Dane County
 TUBERCULOSIS Presented By: Public Health Madison & Dane County What is Tuberculosis? Tuberculosis, or TB, is a disease caused by a bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The bacteria can attack any
TUBERCULOSIS Presented By: Public Health Madison & Dane County What is Tuberculosis? Tuberculosis, or TB, is a disease caused by a bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The bacteria can attack any
"GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS IN HEALTHCARE FACILITIES"
 MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS IN HEALTHCARE FACILITIES" Training For THE CDC "TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTION GUIDELINES" "Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today...and Tomorrow" Outline
MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS IN HEALTHCARE FACILITIES" Training For THE CDC "TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTION GUIDELINES" "Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today...and Tomorrow" Outline
TB 2015 burden, challenges, response. Dr Mario RAVIGLIONE Director
 TB 2015 burden, challenges, response Dr Mario RAVIGLIONE Director Addis Ababa, Ethiopia 11-13 November 2015 Overview TB basics TB burden & challenges Response: End TB Strategy DAY 1 What is TB? Definition
TB 2015 burden, challenges, response Dr Mario RAVIGLIONE Director Addis Ababa, Ethiopia 11-13 November 2015 Overview TB basics TB burden & challenges Response: End TB Strategy DAY 1 What is TB? Definition
Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update
 Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update CAPA Conference 2014 JoAnn Deasy, PA-C. MPH, DFAAPA jadeasy@sbcglobal.net Adjunct Faculty Touro PA Program Learning Objectives Outline the pathogenesis of active pulmonary
Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update CAPA Conference 2014 JoAnn Deasy, PA-C. MPH, DFAAPA jadeasy@sbcglobal.net Adjunct Faculty Touro PA Program Learning Objectives Outline the pathogenesis of active pulmonary
Core Curriculum on Tuberculosis: What the Clinician Should Know
 Core Curriculum on Tuberculosis: What the Clinician Should Know Sixth Edition 2013 National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention Division of Tuberculosis Elimination 1 Chapters
Core Curriculum on Tuberculosis: What the Clinician Should Know Sixth Edition 2013 National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention Division of Tuberculosis Elimination 1 Chapters
TB & HIV CO-INFECTION IN CHILDREN. Reené Naidoo Paediatric Infectious Diseases Broadreach Healthcare 19 April 2012
 TB & HIV CO-INFECTION IN CHILDREN Reené Naidoo Paediatric Infectious Diseases Broadreach Healthcare 19 April 2012 Introduction TB & HIV are two of the leading causes of morbidity & mortality in children
TB & HIV CO-INFECTION IN CHILDREN Reené Naidoo Paediatric Infectious Diseases Broadreach Healthcare 19 April 2012 Introduction TB & HIV are two of the leading causes of morbidity & mortality in children
Contracts Carla Chee, MHS May 8, 2012
 Moving Past the Basics of Tuberculosis Phoenix, Arizona May 8-10, 2012 Contracts Carla Chee, MHS May 8, 2012 Carla Chee, MHS has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
Moving Past the Basics of Tuberculosis Phoenix, Arizona May 8-10, 2012 Contracts Carla Chee, MHS May 8, 2012 Carla Chee, MHS has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
Tuberculosis 6/7/2018. Objectives. What is Tuberculosis?
 Tuberculosis Understanding, Investigating, Eliminating Jeff Maupin, RN Tuberculosis Control Nurse Sedgwick County Division of Health Objectives At the conclusion of this presentation, you will be able
Tuberculosis Understanding, Investigating, Eliminating Jeff Maupin, RN Tuberculosis Control Nurse Sedgwick County Division of Health Objectives At the conclusion of this presentation, you will be able
Mycobacterial Infections: What the Primary Provider Should Know about Tuberculosis
 Mycobacterial Infections: What the Primary Provider Should Know about Tuberculosis Henry F. Chambers, M.D Professor of Medicine, UCSF Topics for Discussion Epidemiology Diagnosis of active TB Screening
Mycobacterial Infections: What the Primary Provider Should Know about Tuberculosis Henry F. Chambers, M.D Professor of Medicine, UCSF Topics for Discussion Epidemiology Diagnosis of active TB Screening
Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis. Dr: Salah Ahmed
 Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis Dr: Salah Ahmed Is a chronic granulomatous disease, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (hominis) Usually it involves lungs but may affect any organ or tissue Transmission:
Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis Dr: Salah Ahmed Is a chronic granulomatous disease, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (hominis) Usually it involves lungs but may affect any organ or tissue Transmission:
Transmission and Pathogenesis of Tuberculosis. Transmission and Pathogenesis of Tuberculosis. Mycobacteria. Introduction to the pathogen Transmission
 Transmission and Pathogenesis of Tuberculosis Adithya Cattamanchi MD, MAS Assistant Professor of Medicine University of California San Francisco Slides adapted from James Watts, Phil Hopewell Transmission
Transmission and Pathogenesis of Tuberculosis Adithya Cattamanchi MD, MAS Assistant Professor of Medicine University of California San Francisco Slides adapted from James Watts, Phil Hopewell Transmission
Etiological Agent: Pulmonary Tuberculosis. Debra Mercer BSN, RN, RRT. Definition
 Pulmonary Tuberculosis Debra Mercer BSN, RN, RRT Definition Tuberculosis is a contagious bacterial infection of the lungs caused by Mycobacterium Tuberculosis (TB) Etiological Agent: Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
Pulmonary Tuberculosis Debra Mercer BSN, RN, RRT Definition Tuberculosis is a contagious bacterial infection of the lungs caused by Mycobacterium Tuberculosis (TB) Etiological Agent: Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 6 Tuberculosis. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 6-1 through 6-11. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 6-1. Identify the characteristics, signs/ symptoms,
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 6 Tuberculosis. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 6-1 through 6-11. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 6-1. Identify the characteristics, signs/ symptoms,
Transmission and Pathogenesis of Tuberculosis
 Transmission and Pathogenesis of Tuberculosis Adithya Cattamanchi MD, MAS Associate Professor of Medicine University of California San Francisco Slides adapted from James Watts, Phil Hopewell Transmission
Transmission and Pathogenesis of Tuberculosis Adithya Cattamanchi MD, MAS Associate Professor of Medicine University of California San Francisco Slides adapted from James Watts, Phil Hopewell Transmission
What Drug Treatment Centers Can do to Prevent Tuberculosis
 What Drug Treatment Centers Can do to Prevent Tuberculosis Tuberculosis (TB) is alive and well Learn what you can do to prevent TB among your clients and protect yourself! Transmission TB is spread through
What Drug Treatment Centers Can do to Prevent Tuberculosis Tuberculosis (TB) is alive and well Learn what you can do to prevent TB among your clients and protect yourself! Transmission TB is spread through
A Review on Prevalence of TB and HIV Co-infection
 Human Journals Review Article May 2015 Vol.:1, Issue:1 All rights are reserved by Jyoti P. Waghmode et al. A Review on Prevalence of TB and HIV Co-infection Keywords: tuberculosis, HIV, co-infection, prevalence
Human Journals Review Article May 2015 Vol.:1, Issue:1 All rights are reserved by Jyoti P. Waghmode et al. A Review on Prevalence of TB and HIV Co-infection Keywords: tuberculosis, HIV, co-infection, prevalence
HEALTHWEST PROCEDURE. No Revised by: Effective: December 1, 1995 Revised: April 19, 2017 Environment of Care Committee
 HEALTHWEST PROCEDURE Revised by: Effective: December 1, 1995 Revised: April 19, 2017 Environment of Care Committee Approved by: Subject: Tuberculosis Infection Control Julia Rupp, Executive Director I.
HEALTHWEST PROCEDURE Revised by: Effective: December 1, 1995 Revised: April 19, 2017 Environment of Care Committee Approved by: Subject: Tuberculosis Infection Control Julia Rupp, Executive Director I.
Summary of Key Points WHO Position Paper on BCG Vaccine, February 2018
 Summary of Key Points WHO Position Paper on BCG Vaccine, February 2018 1 Introduction This position paper replaces the 2004 WHO position paper on Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine and the 2007 WHO
Summary of Key Points WHO Position Paper on BCG Vaccine, February 2018 1 Introduction This position paper replaces the 2004 WHO position paper on Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine and the 2007 WHO
MODULE ONE" TB Basic Science" Treatment Action Group TB/HIV Advocacy Toolkit
 MODULE ONE" TB Basic Science" Treatment Action Group TB/HIV Advocacy Toolkit Topics to be covered What is Tuberculosis? TB bacteria and what is unique about it. How is TB different from HIV? How is TB
MODULE ONE" TB Basic Science" Treatment Action Group TB/HIV Advocacy Toolkit Topics to be covered What is Tuberculosis? TB bacteria and what is unique about it. How is TB different from HIV? How is TB
Understanding and Managing Latent TB Infection Arnold, Missouri October 5, 2010
 Understanding and Managing Latent TB Infection Arnold, Missouri October 5, 2010 What is Latent TB Infection (LTBI)? Traci Hadley, RN October 5, 2010 LTBI or TB Disease? Presented by : Traci Hadley, RN
Understanding and Managing Latent TB Infection Arnold, Missouri October 5, 2010 What is Latent TB Infection (LTBI)? Traci Hadley, RN October 5, 2010 LTBI or TB Disease? Presented by : Traci Hadley, RN
Diagnosis and Medical Management of Latent TB Infection
 Diagnosis and Medical Management of Latent TB Infection Marsha Majors, RN September 7, 2017 TB Contact Investigation 101 September 6 7, 2017 Little Rock, AR EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Marsha Majors,
Diagnosis and Medical Management of Latent TB Infection Marsha Majors, RN September 7, 2017 TB Contact Investigation 101 September 6 7, 2017 Little Rock, AR EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Marsha Majors,
TUBERCULOSIS. What you need to know BECAUSE...CARING COMES NATURALLY TO US
 TUBERCULOSIS What you need to know BECAUSE...CARING COMES NATURALLY TO US Are certain people more at risk of developing Tuberculosis Yes, while everyone exposed to the disease could develop TB, the following
TUBERCULOSIS What you need to know BECAUSE...CARING COMES NATURALLY TO US Are certain people more at risk of developing Tuberculosis Yes, while everyone exposed to the disease could develop TB, the following
(a) Infection control program. The facility must establish an infection control program under which it--
 420-5-10-.17 Infection Control. (1) The facility must establish and maintain an infection control program designed to provide a safe, sanitary, and comfortable environment and to help prevent the development
420-5-10-.17 Infection Control. (1) The facility must establish and maintain an infection control program designed to provide a safe, sanitary, and comfortable environment and to help prevent the development
Tuberculosis Populations at Risk
 Tuberculosis Populations at Risk One-third of the world is infected with TB, an average of one new infection per second Two million people died from tuberculosis in 2010, 1 every 20 seconds TB is the leading
Tuberculosis Populations at Risk One-third of the world is infected with TB, an average of one new infection per second Two million people died from tuberculosis in 2010, 1 every 20 seconds TB is the leading
"GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS AS A FIRST RESPONDER"
 MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS AS A FIRST RESPONDER" Training For THE CDC "TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTION GUIDELINES" "Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today...and Tomorrow" Outline
MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS AS A FIRST RESPONDER" Training For THE CDC "TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTION GUIDELINES" "Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today...and Tomorrow" Outline
Measles (Rubeola) Biology of measles virus. April 20, 2017 Department of Public Health Sciences
 Infectious Disease Epidemiology BMTRY 713 (A. Selassie, DrPH) Lecture 25 Measles Learning Objectives 1. Explain the disease burden of measles and why it still occurs 2. Identify the biologic characteristics
Infectious Disease Epidemiology BMTRY 713 (A. Selassie, DrPH) Lecture 25 Measles Learning Objectives 1. Explain the disease burden of measles and why it still occurs 2. Identify the biologic characteristics
Tuberculosis. By: Shefaa Q aqa
 Tuberculosis By: Shefaa Q aqa Tuberculosis is a communicable chronic granulomatous disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It usually involves the lungs but may affect any organ or tissue in the
Tuberculosis By: Shefaa Q aqa Tuberculosis is a communicable chronic granulomatous disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It usually involves the lungs but may affect any organ or tissue in the
Self-Study Modules on Tuberculosis
 Self-Study Modules on Tuberculosis Targe te d Te s ting and the Diagnosis of Latent Tuberculosis Infection and Tuberculosis Disease U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control
Self-Study Modules on Tuberculosis Targe te d Te s ting and the Diagnosis of Latent Tuberculosis Infection and Tuberculosis Disease U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control
New NICE guideline updates recommendations for diagnosing latent tuberculosis
 Tel: 0845 003 7782 www.nice.org.uk Ref: 2011/053 PRESS RELEASE New NICE guideline updates recommendations for diagnosing latent tuberculosis The National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE)
Tel: 0845 003 7782 www.nice.org.uk Ref: 2011/053 PRESS RELEASE New NICE guideline updates recommendations for diagnosing latent tuberculosis The National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE)
MYCOBACTERIUM. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis (Mtb) nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) Mycobacterium lepray
 MYCOBACTERIUM nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) Mycobacterium Tuberculosis (Mtb) Mycobacterium lepray 1-tubercle bacilli are thin 2- straight rods 3- obligate aerobes 4- derive energy from the oxidation
MYCOBACTERIUM nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) Mycobacterium Tuberculosis (Mtb) Mycobacterium lepray 1-tubercle bacilli are thin 2- straight rods 3- obligate aerobes 4- derive energy from the oxidation
PREVALENCE OF HIV INFECTION AND RISK FACTORS OF TUBERCULIN INFECTION AMONG HOUSEHOLD CONTACTS IN AN HIV EPIDEMIC AREA: CHIANG RAI PROVINCE, THAILAND
 JOURNAL OF SCIENCE, Hue University, N 0 61, 2010 PREVALENCE OF HIV INFECTION AND RISK FACTORS OF TUBERCULIN INFECTION AMONG HOUSEHOLD CONTACTS IN AN HIV EPIDEMIC AREA: CHIANG RAI PROVINCE, THAILAND Pornnapa
JOURNAL OF SCIENCE, Hue University, N 0 61, 2010 PREVALENCE OF HIV INFECTION AND RISK FACTORS OF TUBERCULIN INFECTION AMONG HOUSEHOLD CONTACTS IN AN HIV EPIDEMIC AREA: CHIANG RAI PROVINCE, THAILAND Pornnapa
#114 - Tuberculosis Update [1]
![#114 - Tuberculosis Update [1] #114 - Tuberculosis Update [1]](/thumbs/96/128750142.jpg) Published on Excellence In Learning (https://excellenceinlearning.net) Home > #114 - Tuberculosis Update #114 - Tuberculosis Update [1] Please login [2] or register [3] to take this course. $8.00 Course
Published on Excellence In Learning (https://excellenceinlearning.net) Home > #114 - Tuberculosis Update #114 - Tuberculosis Update [1] Please login [2] or register [3] to take this course. $8.00 Course
Running head: TUBERCULOSIS 1
 Running head: TUBERCULOSIS 1 Tuberculosis Erin Burdi Ferris State University TUBERCULOSIS 2 Abstract Tuberculosis is one of the world s oldest infectious diseases. It is a disease that continues to affect
Running head: TUBERCULOSIS 1 Tuberculosis Erin Burdi Ferris State University TUBERCULOSIS 2 Abstract Tuberculosis is one of the world s oldest infectious diseases. It is a disease that continues to affect
Questions and Answers About
 Questions and Answers About TB 2002 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES n Questions and Answers About TB 2002 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National
Questions and Answers About TB 2002 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES n Questions and Answers About TB 2002 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National
TUBERCULOSIS. Pathogenesis and Transmission
 TUBERCULOSIS Pathogenesis and Transmission TUBERCULOSIS Pathogenesis and Transmission Infection to Disease Diagnostic & Isolation Updates Treatment Updates Pathogenesis Droplet nuclei of 5µm or less are
TUBERCULOSIS Pathogenesis and Transmission TUBERCULOSIS Pathogenesis and Transmission Infection to Disease Diagnostic & Isolation Updates Treatment Updates Pathogenesis Droplet nuclei of 5µm or less are
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 TB Partial Update Appendix 1 - Scope NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Tuberculosis: interferon gamma tests for the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis (partial
TB Partial Update Appendix 1 - Scope NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Tuberculosis: interferon gamma tests for the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis (partial
DIAGNOSIS AND MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF TB DISEASE
 DIAGNOSIS AND MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF TB DISEASE Annie Kizilbash MD, MPH Assistant Professor University of Texas Health Science Center Staff Physician, Texas Center for Infectious Diseases TB Nurse Case
DIAGNOSIS AND MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF TB DISEASE Annie Kizilbash MD, MPH Assistant Professor University of Texas Health Science Center Staff Physician, Texas Center for Infectious Diseases TB Nurse Case
ESCMID Online Lecture Library. by author
 Tuberculosis prevention in immunodepressed patients M. Carmen Fariñas Álvarez Infectious Diseases.H.U.Marqués de Valdecilla University of Cantabria, Spain DISCLOSURES I have no potential conflicts with
Tuberculosis prevention in immunodepressed patients M. Carmen Fariñas Álvarez Infectious Diseases.H.U.Marqués de Valdecilla University of Cantabria, Spain DISCLOSURES I have no potential conflicts with
Targeted Testing and the Diagnosis of. Latent Tuberculosis. Infection and Tuberculosis Disease
 Self-Study Study Modules on Tuberculosis Targeted Testing and the Diagnosis of Latent Tuberculosis Infection and Tuberculosis Disease 1 Module 3: Objectives At completion of this module, learners will
Self-Study Study Modules on Tuberculosis Targeted Testing and the Diagnosis of Latent Tuberculosis Infection and Tuberculosis Disease 1 Module 3: Objectives At completion of this module, learners will
What the Primary Physician Should Know about Tuberculosis. Topics for Discussion. Life Cycle of M. tuberculosis
 What the Primary Physician Should Know about Tuberculosis Henry F. Chambers, M.D Professor of Medicine, UCSF Topics for Discussion Microbiology Epidemiology Common disease presentations Diagnosis of active
What the Primary Physician Should Know about Tuberculosis Henry F. Chambers, M.D Professor of Medicine, UCSF Topics for Discussion Microbiology Epidemiology Common disease presentations Diagnosis of active
PREVENTION OF TUBERCULOSIS. Dr Amitesh Aggarwal
 PREVENTION OF TUBERCULOSIS Dr Amitesh Aggarwal 25 to 50 % of persons exposed to intimate contact with active PTB - latent infection with TB. Exposure to index case for 12 hours - high risk of infection.
PREVENTION OF TUBERCULOSIS Dr Amitesh Aggarwal 25 to 50 % of persons exposed to intimate contact with active PTB - latent infection with TB. Exposure to index case for 12 hours - high risk of infection.
TB and Respiratory Protection
 Slide 1 TB and Respiratory Protection Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease present throughout the United States. Lehigh Valley Health Network is concerned about your health and needs your help to prevent the
Slide 1 TB and Respiratory Protection Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease present throughout the United States. Lehigh Valley Health Network is concerned about your health and needs your help to prevent the
Respiratory System الفريق الطبي االكاديمي
 Respiratory System الفريق الطبي االكاديمي Pathology sheet 5 Tuberculosis Done by: Ahmad Al-Sahele Introduction: as we know TB is caused by mycobacterium tubercolosis; now keep in your mind another microorganism
Respiratory System الفريق الطبي االكاديمي Pathology sheet 5 Tuberculosis Done by: Ahmad Al-Sahele Introduction: as we know TB is caused by mycobacterium tubercolosis; now keep in your mind another microorganism
Primer on Tuberculosis (TB) in the United States
 Primer on Tuberculosis (TB) in the United States The purpose of this primer is to provide instructors who have no prior background in TB research or clinical care with basic knowledge that they may find
Primer on Tuberculosis (TB) in the United States The purpose of this primer is to provide instructors who have no prior background in TB research or clinical care with basic knowledge that they may find
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Tuberculosis: interferon gamma tests for the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis (partial update) 1.1 Short title Tuberculosis
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Tuberculosis: interferon gamma tests for the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis (partial update) 1.1 Short title Tuberculosis
What Is TB? 388 How TB Is Spread 388 How to Know if a Person Has TB 389 How to Treat TB 389 Resistance to TB medicines 390
 386 Chapter 25 In this chapter: What Is TB? 388 How TB Is Spread 388 How to Know if a Person Has TB 389 How to Treat TB 389 Resistance to TB medicines 390 Preventing TB 391 Working for Change 391 387 (TB)
386 Chapter 25 In this chapter: What Is TB? 388 How TB Is Spread 388 How to Know if a Person Has TB 389 How to Treat TB 389 Resistance to TB medicines 390 Preventing TB 391 Working for Change 391 387 (TB)
Tuberculosis - clinical forms. Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases
 Tuberculosis - clinical forms Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases 1 TB DISEASE Primary Post-primary (Secondary) Common primary forms Primary complex Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic
Tuberculosis - clinical forms Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases 1 TB DISEASE Primary Post-primary (Secondary) Common primary forms Primary complex Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic
Proposed Regs.pdf
 Kansas Wesleyan University TB testing Policy In Compliance with Kansas Statue KSA 2009 Supp. 65-129, all Kansas Wesleyan University students who have traveled, resided in for more than three months, or
Kansas Wesleyan University TB testing Policy In Compliance with Kansas Statue KSA 2009 Supp. 65-129, all Kansas Wesleyan University students who have traveled, resided in for more than three months, or
Learning Objectives: Case 1 11/12/2015. Tuberculosis: Focus on Transmission and Pathogenesis. TB: Some Important Terms
 A 11/12/2015 Learning Objectives: Tuberculosis: Focus on Transmission and Pathogenesis Henry Fraimow, M ivision of Infectious iseases ooper School of Medicine at Rowan University Medical onsultant, Southern
A 11/12/2015 Learning Objectives: Tuberculosis: Focus on Transmission and Pathogenesis Henry Fraimow, M ivision of Infectious iseases ooper School of Medicine at Rowan University Medical onsultant, Southern
What the Primary Physician Should Know about Tuberculosis. Topics for Discussion. Global Impact of TB
 What the Primary Physician Should Know about Tuberculosis Henry F. Chambers, M.D Professor of Medicine, UCSF Topics for Discussion Epidemiology Common disease presentations Diagnosis of active TB Screening
What the Primary Physician Should Know about Tuberculosis Henry F. Chambers, M.D Professor of Medicine, UCSF Topics for Discussion Epidemiology Common disease presentations Diagnosis of active TB Screening
Replaces: 02/11/16. Formulated: 7/95 EMPLOYEE TB TESTING
 Effective : 02/09/17 Page 1 of 4 PURPOSE: To describe the process where by employees may obtain routine TB skin testing by facility medical staff. POLICY: Employees of the Texas Department of Criminal
Effective : 02/09/17 Page 1 of 4 PURPOSE: To describe the process where by employees may obtain routine TB skin testing by facility medical staff. POLICY: Employees of the Texas Department of Criminal
TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas December 1-3, 2010
 TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas December 1-3, 2010 TB Pathogenesis and Transmission Lynn Horvath, MD; TCID December 1, 2010 Tuberculosis Pathogenesis Lynn L. Horvath, MD, FACP, FIDSA Associate Professor
TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas December 1-3, 2010 TB Pathogenesis and Transmission Lynn Horvath, MD; TCID December 1, 2010 Tuberculosis Pathogenesis Lynn L. Horvath, MD, FACP, FIDSA Associate Professor
Tuberculosis Facts. TB is not spread by: Sharing food and drink Shaking someone s hand Touching bed lines or toilet seats
 Tuberculosis Facts Below are frequently asked questions about TB, and their answers. If you have additional questions you may contact the City of Ennis Department of Health Services at 972-875-1234 or
Tuberculosis Facts Below are frequently asked questions about TB, and their answers. If you have additional questions you may contact the City of Ennis Department of Health Services at 972-875-1234 or
Questions and Answers About
 Questions and Answers About TB 2005 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES TB Elimination Questions and Answers About TB 2005 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Questions and Answers About TB 2005 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES TB Elimination Questions and Answers About TB 2005 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Gary Reubenson 16 October 2012 PAEDIATRIC TUBERCULOSIS: AN OVERVIEW IN 40 MINUTES!!
 Gary Reubenson 16 October 2012 PAEDIATRIC TUBERCULOSIS: AN OVERVIEW IN 40 MINUTES!! DECLARATION No relevant conflicts of interest to declare OVERVIEW Burden of disease & epidemiology Pathogenesis (not
Gary Reubenson 16 October 2012 PAEDIATRIC TUBERCULOSIS: AN OVERVIEW IN 40 MINUTES!! DECLARATION No relevant conflicts of interest to declare OVERVIEW Burden of disease & epidemiology Pathogenesis (not
The Air We Share: Principles and Practices of TB Infection Control
 The Air We Share: Principles and Practices of TB Infection Control Session Four of a Four-Part Webinar Series Presented in Partnership with the BC Lung Association January 10, 2014 Facilitators: Nash Dhalla,
The Air We Share: Principles and Practices of TB Infection Control Session Four of a Four-Part Webinar Series Presented in Partnership with the BC Lung Association January 10, 2014 Facilitators: Nash Dhalla,
Why need to havetb Clearance. To Control and Prevent Tuberculosis
 Why need to havetb Clearance To Control and Prevent Tuberculosis How to ID Tuberculosis There are two kinds of tests that are used to determine if a person has been infected with TB bacteria: the tuberculin
Why need to havetb Clearance To Control and Prevent Tuberculosis How to ID Tuberculosis There are two kinds of tests that are used to determine if a person has been infected with TB bacteria: the tuberculin
TB In Detroit 2011* Early TB: Smudge Sign. Who is at risk for exposure to or infection with TB? Who is at risk for TB after exposure or infection?
 Those oral antibiotics are just not working! Inpatient Standards of Care & Discharge Planning S/He s in the Hospital: Now What Do I Do? Dana G. Kissner, MD TB Intensive Workshop, Lansing, MI 2012 Objectives:
Those oral antibiotics are just not working! Inpatient Standards of Care & Discharge Planning S/He s in the Hospital: Now What Do I Do? Dana G. Kissner, MD TB Intensive Workshop, Lansing, MI 2012 Objectives:
Tuberculosis Pathogenesis
 Tuberculosis Pathogenesis Renuka Khurana, MD, MPH May 12, 2015 TB for Community Providers May 12, 2015 Phoenix, Arizona EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Renuka Khurana, MD, MPH has the following disclosures
Tuberculosis Pathogenesis Renuka Khurana, MD, MPH May 12, 2015 TB for Community Providers May 12, 2015 Phoenix, Arizona EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Renuka Khurana, MD, MPH has the following disclosures
Tuberculosis Intensive
 Tuberculosis Intensive San Antonio, Texas April 3 6, 2012 Tuberculosis Pathogenesis Lynn Horvath, MD April 3, 2012 Lynn Horvath, MD has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
Tuberculosis Intensive San Antonio, Texas April 3 6, 2012 Tuberculosis Pathogenesis Lynn Horvath, MD April 3, 2012 Lynn Horvath, MD has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
Stop TB Poster (laminated copies are available from TB Control: )
 Tuberculosis Prevention and Control Recommendations For Homeless Shelters in Maine Tool Kit What Your Shelter Can Do to Prevent TB Assessing Your Shelter Guests Risk for TB Cough Alert Policy Think TB
Tuberculosis Prevention and Control Recommendations For Homeless Shelters in Maine Tool Kit What Your Shelter Can Do to Prevent TB Assessing Your Shelter Guests Risk for TB Cough Alert Policy Think TB
Interpretation of Chest Radiographs Paul Christensen, MD 10/21/09. Diagnostic Evaluation. Medical Evaluation & CXR Interpretation.
 Diagnostic Evaluation Medical Evaluation & CXR Interpretation University of Michigan TB Consultant Washtenaw County Medical history Physical examination Testing for TB exposure (previously covered) Radiologic
Diagnostic Evaluation Medical Evaluation & CXR Interpretation University of Michigan TB Consultant Washtenaw County Medical history Physical examination Testing for TB exposure (previously covered) Radiologic
PATHOLOGY & PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
 PATHOLOGY & PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DISORDERS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Disorders of the Respiratory System Infections Degenerative Tumours Immune Trauma Congenital Upper respiratory
PATHOLOGY & PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DISORDERS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Disorders of the Respiratory System Infections Degenerative Tumours Immune Trauma Congenital Upper respiratory
INDEX CASE INFORMATION
 Instructions for Completing the MDH Tuberculosis Contact Investigation Report Form Please provide as much information as possible. Each field represents information that is important to the contact investigation.
Instructions for Completing the MDH Tuberculosis Contact Investigation Report Form Please provide as much information as possible. Each field represents information that is important to the contact investigation.
MYCOBACTERIA. Pulmonary T.B. (infect bird)
 MYCOBACTERIA SPP. Reservoir Clinical Manifestation Mycobacterium tuberculosis Human Pulmonary and dissem. T.B. M. lepra Human Leprosy M. bovis Human & cattle T.B. like infection M. avium Soil, water, birds,
MYCOBACTERIA SPP. Reservoir Clinical Manifestation Mycobacterium tuberculosis Human Pulmonary and dissem. T.B. M. lepra Human Leprosy M. bovis Human & cattle T.B. like infection M. avium Soil, water, birds,
Advanced Management of Patients with Tuberculosis Little Rock, Arkansas August 13 14, 2014
 Advanced Management of Patients with Tuberculosis Little Rock, Arkansas August 13 14, 2014 Tuberculosis Pathogenesis and Treatment of Latent TB Infection Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD August 13, 2014 Lisa Armitige,
Advanced Management of Patients with Tuberculosis Little Rock, Arkansas August 13 14, 2014 Tuberculosis Pathogenesis and Treatment of Latent TB Infection Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD August 13, 2014 Lisa Armitige,
1966 CDC assessment of US Health
 Infectious Disease Epidemiology BMTRY 713 (A. Selassie, DrPH) Lecture 14 Emerging and New IDs Learning Objectives 1. Describe the threat of emerging and new infectious agents 2. Identify the contributing
Infectious Disease Epidemiology BMTRY 713 (A. Selassie, DrPH) Lecture 14 Emerging and New IDs Learning Objectives 1. Describe the threat of emerging and new infectious agents 2. Identify the contributing
Infection Prevention Prevention and Contr
 Infection Prevention and Control o What is an infection? An infection is an illness caused by microorganisms A disease producing micro organism is called a pathogen Most microorganisms are classified as:
Infection Prevention and Control o What is an infection? An infection is an illness caused by microorganisms A disease producing micro organism is called a pathogen Most microorganisms are classified as:
Tuberculosis Procedure ICPr016. Table of Contents
 Tuberculosis Procedure ICPr016 Table of Contents Tuberculosis Procedure ICPr016... 1 What is Tuberculosis?... 2 Any required definitions/explanations... 2 NHFT... 2 Tuberculosis (TB)... 3 Latent TB...
Tuberculosis Procedure ICPr016 Table of Contents Tuberculosis Procedure ICPr016... 1 What is Tuberculosis?... 2 Any required definitions/explanations... 2 NHFT... 2 Tuberculosis (TB)... 3 Latent TB...
결핵 전남대학교병원 호흡기내과 권용수
 결핵 전남대학교병원호흡기내과 권용수 History of TB Skeletal TB Prehistoric humans in 8000 B.C. Egyptian mummies in 2500-1000 B.C. From Tuberculosis 2007. Classification of Mycobacterial Species M. tuberculosis complex
결핵 전남대학교병원호흡기내과 권용수 History of TB Skeletal TB Prehistoric humans in 8000 B.C. Egyptian mummies in 2500-1000 B.C. From Tuberculosis 2007. Classification of Mycobacterial Species M. tuberculosis complex
OSHA INSERVICE. Tuberculosis and Bloodborne Pathogens
 OSHA INSERVICE Tuberculosis and Bloodborne Pathogens Tuberculosis Airborne contagious disease caused by bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis How it is spread: TB Infection TB Disease TB bacteria
OSHA INSERVICE Tuberculosis and Bloodborne Pathogens Tuberculosis Airborne contagious disease caused by bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis How it is spread: TB Infection TB Disease TB bacteria
