Increased incidence of EBV-associated. lymphoproliferative disorders after. allogeneic stem cell transplantation from
|
|
|
- Walter Willis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 6 Increased incidence of EBV-associated lymphoproliferative disorders after allogeneic stem cell transplantation from matched unrelated donors due to a change of T cell depletion technique Ellen Meijer, Ineke C.M. Slaper-Cortenbach, Steven F.T. Thijsen, Adriaan W. Dekker, Leo F. Verdonck Bone Marrow Transplantation 2002; 29:
2 Abstract In this report the influence of T vs T and B cell depletion of grafts on the incidence of EBVassociated lymphoproliferative disorders (EBV-LPD) after bone marrow transplantation (BMT) from matched unrelated donors (MUD) is analysed. From 1982 to 1997 the Soy Bean Agglutinin/Sheep Red Blood Cell (SBA/SRBC) method, which has a risk of transmitting prions or viruses, was used for T cell depletion. Because of this risk a new T cell depletion method was introduced, using CD2 and CD3 monoclonal antibodies (CD2/3 method), which led to an unexpected increase in EBV-LPDs in MUD recipients. SBA depletion was reintroduced and combined with the CD2/3 method (SBA/CD2/3) in this patient population, later replaced by B cell specific (CD19 and CD22) antibodies (CD3/19/22 method). The number of T (x10 5 /kg) and B (x10 5 /kg) cells in the graft was 1.5 ± 0.8 and 2 ± 1 (T/B ratio 0.75), 2.2 ± 2.0 and 41 ± 21 (ratio 0.055), 5.0 ± 0.0 and 2 ± 1 (ratio 2.5), 2.5 ± 1.2 and 10 ± 6 (ratio 0.25) using the SBA/SRBC, CD2/3, SBA/CD2/3 and CD3/19/22 techniques, respectively. When B cell depletion was performed 4 out of 31 (13%) MUD recipients developed an EBV-LPD. Without B cell depletion (CD2/3 method) this occurred in 5 out of 7 patients (71%) (p<0.05). A T/B cell ratio in the graft of 0.25 seems sufficient to reduce significantly the incidence of EBV-LPD after BMT from MUDs. 78
3 Introduction After bone marrow transplantation (BMT) from a matched unrelated donor (MUD) transplant related morbidity and mortality are increased compared to BMT from a matched related donor (MRD). This is largely due to an increased incidence of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) and infectious complications 1,2. T cell depletion reduces the incidence and severity of GVHD but has also important side-effects 3. Curtis et al 4 showed that the risk of Epstein-Barr-virus-associated lymphoproliferative disorders (EBV-LPDs) was strongly associated with T cell depletion of donor marrow. Use of Antithymocyteglobulin (ATG) and of grafts from unrelated or HLA-mismatched related donors were other adverse risk factors for the development of EBV-LPD. The risk for EBV-LPD varied according to the techniques used for T cell depletion, being lowest when the Campath-1 method was used which, in contrast to T cell specific monoclonal antibodies (Moabs), removed both T and B cells 4. In this report the influence of the T vs T and B cell depletion method on the incidence of EBV-LPD among MUD transplant recipients is described, as was observed at our institute. From 1982 to 1997 the Soy Bean Agglutinin/Sheep Red Blood Cell (SBA/SRBC) method was used for T cell depletion. This technique has been well established, but the use of SRBC has a risk of transmitting prions or viruses. Therefore, a new T cell depletion method was introduced, the immunorosette (IR) technique, using tetrameric complexes with T cell specific CD2 and CD3 Moabs instead of sheep red blood cells. Unfortunately, this led to an unexpected high number of EBV-LPDs in patients receiving transplants from MUDs. Since it was suspected that this was caused by the relatively high number of B cells in the graft, SBA depletion -which results in B cell depletion of 1 to 1.5 log- was reintroduced and combined with CD2/3 depletion from May 1998 (SBA/CD2/3 method). In March 1999 SBA was replaced by B cell specific (CD19 and CD22) antibodies (CD3/19/22 method). Methods Patients From November 1985 to April 2000 a total of 313 patients received allogeneic BMT, 49 from a MUD and 264 from a Matched Related Donor (MRD). Eleven MUD and 63 MRD transplant recipients died within 6 months after BMT from relapse or transplant 79
4 related toxicity, apart from EBV-LPD and were therefore not evaluable for this study. The interval of 6 months was chosen because most EBV-LPDs develop during the first 6 months post-transplant 4. The distribution of patients according to T cell depletion used is shown in Table 1. Characteristics of recipients of MUD transplants are described in Table 2. All patients were treated with clinical protocols approved by the local investigation review board and gave informed consent. Transplantation procedure Conditioning regimens consisted of cyclophosphamide (60 mg/kg/day) on each of two successive days, followed by total body irradiation (600 cgray/day) on each 2 successive days. The graft was infused after the second TBI fraction (day 0). ATG (Thymoglobulin, Sangstat, Amstelveen, the Netherlands) was given to MUD patients before cyclophosphamide was started, at a total dose of 20 mg/kg intravenously. It was lowered to a total dose of 8 mg/kg since April All patients received cyclosporin from day -2 in a dose of 3 mg/kg/day by continuous infusion for 4 weeks, thereafter it was given orally for 4-6 weeks in a dose that gave comparable through levels, followed by tapering. Cyclosporin was discontinued within 3 months after transplantation if no active GVHD was observed. Infection prevention for all patients consisted of ciprofloxacin, fluconazole and amphotericin B given orally until granulocyte counts exceeded 500 cells/mm 3. Cephalothin was given intravenously for 10 days from day +3. Furthermore co-trimoxazole and valacyclovir were given orally from day +1 until 12 months post-bmt. GVHD was diagnosed according to the Seattle criteria 5. Acute GVHD grade I was treated with topical corticosteroids; grade II or higher was treated with systemic corticosteroids as described 6. Table 1 Number of BMTs according to depletion technique Depletion MUD NE MRD NE technique patients patients SBA/SRBC CD2/ SBA/CD2/3 6 0 CD3/19/ SBA/SRBC = soy bean agglutinin/sheep red blood cell; SBA/CD2/3 = SBA agglutination followed by depletion with anti CD2 and CD3 Moabs; CD2/3 = depletion with anti CD2 and CD3 Moabs; CD3/19/22 = depletion with anti CD3, CD19 and CD22 Moabs; NE = not evaluable because of early death. 80
5 Table 2 Characteristics of recipients of MUD transplants SBA/SRBC CD2/3 SBA/CD2/3 CD3/19/22 No. of patients Age, year (range) 29 (17-47) 28 (18-37) 31 (22-47) 32 (18-48) Diagnosis ALL AML CML MDS SAA Sex F/F M/M M/F F/M CMV serostatus R/D -/ / / / GVHD Acute I/II III/IV None Chronic L E NE None R/D = recipient/donor; NE = not evaluable; L = limited; E = extensive. Extensive chronic GVHD was treated with systemic corticosteroids, sometimes combined with cyclosporin. During the first 4 months post-transplant, CMV-seropositive patients who demonstrated reactivation of CMV infection or those who were treated with high-dose corti- 81
6 costeroids received pre-emptive or prophylactic therapy, respectively, with ganciclovir in a dose of 2.5 mg/kg intravenously twice a day for 14 days 7. HLA-matching In all MRD patient/donor pairs, class I antigens (A, B and Cw) were analysed by serological typing, in case of doubt low resolution molecular typing was performed. Class II antigens (DRB1, DRB3, DRB4, DRB5 and DQB1) were analysed by serological typing until 1993 and since 1993 by low resolution molecular typing with sequence specific primers. In MUD patient/donor pairs HLA analysis was performed as in MRD recipients until 1993, thereafter class I antigens (A, B) were analysed by serological typing, in case of doubt low resolution molecular typing was performed. Class I Cw and class II antigens (DRB1, DRB3, DRB4, DRB5 and DQB1) were analysed by low resolution molecular typing with sequence specific primers and DRB1, B3, B4 and B5 antigens were as well defined by high resolution typing since January T and B cell depletion SBA/SRBC T cell depletion was performed as described 8. The immunorosette depletion technique (CD2/3) was performed as described by Slaper- Cortenbach et al 9. In short, tetrameric complexes (CLB, Amsterdam, the Netherlands) were formed by addition of cross-linking RaMIgG1 Moabs to a mixture of murine IgG1 Moabs, one directed against glycophorin A in the membrane of human erythrocytes and another against T cell specific antigens (CD2 or CD3). These complexes were then bound to donor erythrocytes (in case of a MUD transplant obtained from a healthy O-rhesus negative donor from the blood bank) and the coated erythrocytes were washed. After addition of the coated erythrocytes to the bone marrow buffycoat cells, prepared using the COBE 2991, immunorosettes formed. These immunorosettes were removed using Ficoll density separation (d=1.077 g/cm 3 ). In the SBA/CD2/3 method Ficoll density separation was used to prepare mononuclear cells, subsequently SBA was used with the CD2 and CD3 tetrameric complexes instead of SRBC. The CD3/19/22 method used tetrameric complexes with CD3, CD19 and CD22 Moabs for depletion of T and B cells. All monoclonal antibodies were tested for viral and bacterial contamination and, therefore, biosafe. In all T/B cell depletion procedures the residual number of T cells was counted and nonmanipulated T cells (from a small BM fraction that was set apart before the stem cell manipulation started) were added to obtain a low fixed number of T cells 6. This fixed number of T cells in the graft differed per depletion technique (SBA/SRBC: 1 x 10 5 T cells/kg; CD2/3: 1 x 10 5 T cells/kg; SBA/CD2/3: 5 x 10 5 T cells/kg; CD3/19/22: 2 x 10 5 T cells/kg). In some grafts the residual number of T cells after depletion was above the fixed number, no T cell add-back was performed in these 82
7 grafts. T/B cell depletion was evaluated by Facs analysis (FACScan, Becton Dickinson Immunocytometry Systems (BDIS), San Jose, CA) on unmanipulated bone marrow and depleted marrow using monoclonal antibodies (CD2-FITC, CD3-PE, CD19-PE, CD20-FITC, CD45-PERCP (Becton Dickinson)). EBV-LPD EBV-LPD was diagnosed by standard histological criteria 10. CD20 antibodies were used to assess the B cell origin of the LPD. The presence of EBV infection was determined immunohistochemically by detection of EBNA-2 and LMP-1 proteins and with in-situ hybridisation to detect EBV-encoded RNA (EBER). Statistics Data are expressed as mean ± SD. Mean differences between groups were assessed by the Mann Whitney U test or Chi square analysis. Calculations were performed using SPSS/PC+ 8.0 (SPSS Inc, Chicago Il, USA). Results Incidence of EBV-LPD The incidence of EBV-LPD is summarized in Table 3. When B cell depletion was performed (SBA/SRBC, SBA/CD2/3, CD3/19/22) 4 out of 31 patients (13%) receiving BMT from a MUD developed an EBV-LPD, being the cause of death in 3 patients. Without B cell depletion (CD2/3) 5 out of 7 patients (71%) receiving BMT from a MUD developed an EBV-LPD and two died of this disease. This resulted in a significant difference (p<0.05) between B cell depleting techniques and a non-b cell depleting technique concerning the incidence of EBV-LPDs. In contrast to MUD recipients, among patients receiving BMT from an HLA-identical sibling donor the incidence of EBV-LPD was similar when a T and B cell depletion method was used (SBA/SRBC) compared to a T without B cell depletion method (CD2/3). The incidence was 5 and 4%, respectively. T and B cell numbers in the graft T and B cell counts in the MUD grafts according to depletion technique are shown in Table 4. The SBA/CD2/3 group received significantly more T cells (p<0.05), compared to all other groups. This was not due to depletion failure as can be seen from the log depletion reached. In fact, the SBA/CD2/3 was the most efficient T cell depletion method. As has been described earlier, after T cell depletion the residual number of T cells was counted and nonmanipulated T cells were added to obtain a low fixed number of T cells (1-5 x 10 5 T cells/kg recipient weight). In the SBA/CD2/3 group this 83
8 number was set at 5 x 10 5 /kg. In the SBA/SRBC depleted grafts, B cell numbers were not measured. We can assume, however, that the SBA/SRBC method should yield a B cell depletion comparable to the SBA/CD2/3 method (confirmed by experiments in the laboratory). B cell numbers were not measured in CD2/3 depleted grafts of unrelated donors as well. When the incidence of EBV-LPD increased dramatically in MUD recipients and it was suspected to be due to the relatively high number of B cells in the graft, SBA agglutination was performed prior to CD2/3 depletion. Since then B cells were measured in all grafts (CD2/3 depleted grafts from MRDs, SBA/CD2/3 and CD3/19/22 depleted grafts from MUDs). The CD2/3 group (data derived from MRD transplants) received significantly more B cells compared to all other groups: 41 ± 21 x 10 5 /kg vs 2 ± 1 (SBA/CD2/3) and 10 ± 6 (CD3/19/22); p< The T/B cell ratio in the graft according to depletion method was 0.75 for the SBA/SRBC group (ratio was calculated using the B cell count from the SBA/CD2/3 method), for the CD2/3 method, 2.5 for the SBA/CD2/3 group and 0.25 for the CD3/19/22 technique. It should be noted that in this last group ATG dose was reduced. Therefore in vivo T cell depletion due to ATG in this group is expected to be less than in the other three groups 11. Table 3 EBV-LPD according to depletion technique Depletion MUD EBV-LPD DOD MRD patients EBV-LPD DOD technique patients (%) (%) SBA/SRBC 14 3 (21) (5) 5 CD2/3 7 5 (71) (4) 0 SBA/CD2/3 6 0 ( 0) 0 CD3/19/ ( 9) 1 EBV-LPD = EBV-associated lymphoproliferative disease; DOD = died of EBV-LPD. 84
9 Table 4 donors Depletion of T and B cells from marrow grafts of matched unrelated Technique T cell count Log B cell count Log ATG Ratio in graft depletion in graft depletion dose T/B (x10 5 /kg) T cells (x10 5 /kg) B cells SBA/SRBC a 1.5 ± ± 0.6 nd HD 0.75 CD2/3 b 2.2 ± ± ± ± 0.1 HD SBA/CD2/3 5.0 ± ± ± ± 0.2 HD 2.5 CD3/19/ ± ± ± ± 0.2 LD 0.25 a = to calculate the T/B cell ratio, B cell count from the SBA/CD2/3 group was taken; b = B cell count was measured in a group of 24 patients receiving a transplant from a MRD; HD = high dose (20 mg/kg); LD = low dose (8 mg/kg). Discussion The most important observation of this report is the significantly increased incidence of EBV- LPD in patients receiving BMT from an unrelated donor which was T but not B cell depleted with an immunorosette technique, using CD2 and CD3 Moabs. Among MRD patients the incidence of EBV-LPD was not influenced by B cell depletion. The SBA/SRBC depletion method was abandoned in 1997 because the use of SRBC has a risk of transmitting prions or viruses. The Moabs used in the immunorosette technique were biosafe (screened for viral and bacterial contamination). The CD2/3 depletion method had proven to result in a similar T cell depletion (Table 4). Engraftment and haematopoietic recovery were comparable for the two techniques (data not shown). Until 1998 there were no reports showing the importance of B cell depletion for prevention of EBV-LPD. Resting memory B cells are thought to be the natural reservoir of EBV within the body 12. The B cell load of patient origin has been largely destroyed due to the pre-transplant myeloablative conditioning regimen. Gratama et al 13,14 showed that also latently EBV-infected host cells can be eliminated after BMT. Therefore, theoretically, B cell depletion of the graft along with T cell depletion might improve immunological control of EBV infection post-transplant. Indeed, Cavazzana et al 15 showed that none of 19 patients receiving transplants from a partially matched related donor (PMRD) developed EBV-LPD when ex vivo T and B cell depletion was performed, 85
10 whereas 7 out of 19 historical controls developed EBV-LPD when only T cell depletion was performed. Two other studies showed that B cell depletion might be of benefit for decreasing the incidence of EBV-LPD 16,17. Our report emphasizes the importance of B cell depletion, in patients receiving T cell depleted grafts from matched unrelated donors. In MRD recipients T cell depletion without B cell depletion did not result in an increased incidence of EBV- LPD. Therefore, next to ex vivo T cell depletion, there have to be other factors which impair immune surveillance of the Epstein-Barr virus in MUD recipients. Recently it was shown that TCD together with the use of ATG were important factors influencing EBV reactivation posttransplant 18. All our MUD patients received ATG, giving in vivo T cell depletion as well 11. In MUD recipients the ratio of T and B cells in the graft seems to be very important for surveillance of EBV. When high dose ATG was used pre-transplant, a T/B cell ratio of 2.5 was sufficient to prevent EBV-LPD in 6 patients (SBA/CD2/3 group). When low dose ATG was used, a ratio of 0.25 did not prevent EBV-LPD totally: 1 out of 11 patients developed EBV-LPD (CD3/19/22 group). The actual T/B cell ratio in vivo might have been higher in this group due to a less severe in vivo T cell depletion. The optimal T/B cell ratio is not known at the moment and will be dependent on several factors such as use and dosage of ATG. The number of patients in our study is limited, so further studies are necessary to establish the degree of B cell depletion needed for efficient prevention of EBV-LPD in patients receiving T cell depleted grafts from donors other than HLA-matched siblings. In the study of Cavazzana et al 15 B and T cell counts in the grafts were 5 ± 8.5 x 10 5 /kg and 1.5 ± 1.7 x 10 5 /kg, respectively. This gave a ratio of 0.3 and no EBV-LPD was observed post-transplant. These and our data suggest that a ratio 0.25 can markedly reduce EBV-LPD in such patients. In conclusion, our data show that the incidence of EBV-associated lymphoproliferative disorders in recipients of allogeneic bone marrow transplants from matched unrelated donors is increased when T cell depletion of the graft is performed, without B cell depletion. We replaced the SBA/SRBC technique for a new technique, based on the use of Moabs instead of SRBC. This resulted in a disproportional higher number of residual B cells in the graft and, consequently, in a dramatic increase in EBV-LPD in recipients of T cell depleted stem cell transplant from matched unrelated donors. 86
11 References 1 Kernan NA, Bartsch G, Ash RC et al. Analysis of 462 transplantations from unrelated donors facilitated by the national marrow donor program. N Engl J Med 1993; 328: Arnold R, de Witte T, van Biezen A et al. Unrelated bone marrow transplantation in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes and secondary acute myeloid leukaemia: an EBMT study. Bone Marrow Transplant 1998; 21: Ferrara JLM, Deeg HJ. Graft-versus-host disease. N Eng J Med 1991; 324: Curtis RE, Travis LB, Rowlings PA et al. Risk of lymphoproliferative disorders after bone marrow transplantation: a multiinstitutional study. Blood 1999; 94: Thomas ED, Storb R, Clift RA et al. Bone marrow transplantation. N Engl J Med 1975; 292: Verdonck LF, Dekker AW, de Gast GC et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation with a fixed low number of T cells in the marrow graft. Blood 1994; 83: Verdonck LF, Dekker AW, Rozenberg-Arska M, van den Hoek MR. A risk adapted approach with a short course of ganciclovir to prevent cytomegalovirus (CMV) pneumonia in CMV-seropositive recipients of allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Clin Infect Dis 1997; 24: Reisner Y, Kirkpatrick D, Dupont B et al. Transplantation for acute leukaemia with HLA-A and B nonidentical parental marrow cells fractionated with soybean agglutinin and sheep red blood cells. Lancet 1981; 15: Slaper-Cortenbach ICM, Wijngaarden-du Bois MJGJ, de Vries-van Rossen A et al. The depletion of T cells from haematopoietic stem cell transplants. Rheumatology 1999; 38: Knowles DM, Cesarman E, Chadburn A et al. Correlative morphologic and molecular genetic analysis demonstrates three distinct categories of posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disorders. Blood 1995; 85: Baurmann H, Revillard JP, Bonnefoy-Berard N, Schwerdtfeger R. Potent effects of ATG used as part of the conditioning in matched unrelated donor transplantation. Blood 1998; 92: S290a. Abstract. 12 Cohen JI. Epstein-Barr Virus infection. N Engl J Med 2000; 343: Gratama JW, Oosterveer MAP, Zwaan FE et al. Eradication of Epstein-Barr virus by allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: Implications for sites of viral latency. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1988; 8: Gratama JW, Oosterveer MAP, Lepoutre J et al. Serological and molecular studies of Epstein-Barr virus infection in allogeneic marrow graft recipients. Transplantation 1990; 49: Cavazzana M, Bensoussan D, Jabado N et al. Prevention of EBV-induced Blymphoproliferative disorder by ex vivo marrow B cell depletion in HLA-phenoidentical or non-identical Tdepleted bone marrow transplantation. Br J Haematol 1998; 103: Liu Z, Wilson JM, Jones MC et al. Addition of B cell depletion of donor marrow with anti-cd20 antibody to a T cell depletion regimen for prevention of EBV lymphoma after bone marrow transplantation. Blood 1999; 94: S638a. Abstract. 17. Hale G, Waldmann H. Risks of developing Epstein-Barr virus-related lymphoproliferative disorders after T cell-depleted marrow transplants. Blood 1998; 91: van Esser JWJ, van der Holt B, Meijer E et al. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) reactivation is a frequent event after allogeneic stem cell transplantation (SCT) and quantitatively predicts EBV-lymphoproliferative disease following T cell depleted SCT. Blood 2001; 98:
12 88
Rob Wynn RMCH & University of Manchester, UK. HCT in Children
 Rob Wynn RMCH & University of Manchester, UK HCT in Children Summary Indications for HCT in children Donor selection for Paediatric HCT Using cords Achieving engraftment in HCT Conditioning Immune action
Rob Wynn RMCH & University of Manchester, UK HCT in Children Summary Indications for HCT in children Donor selection for Paediatric HCT Using cords Achieving engraftment in HCT Conditioning Immune action
MUD SCT. Pimjai Niparuck Division of Hematology, Department of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University
 MUD SCT Pimjai Niparuck Division of Hematology, Department of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University Outlines Optimal match criteria for unrelated adult donors Role of ATG in MUD-SCT Post-transplant
MUD SCT Pimjai Niparuck Division of Hematology, Department of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University Outlines Optimal match criteria for unrelated adult donors Role of ATG in MUD-SCT Post-transplant
Back to the Future: The Resurgence of Bone Marrow??
 Back to the Future: The Resurgence of Bone Marrow?? Thomas Spitzer, MD Director. Bone Marrow Transplant Program Massachusetts General Hospital Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School Bone Marrow
Back to the Future: The Resurgence of Bone Marrow?? Thomas Spitzer, MD Director. Bone Marrow Transplant Program Massachusetts General Hospital Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School Bone Marrow
EBV in HSCT 2015 update of ECIL guidelines
 ECIL-6 EBV in HSCT 2015 update of ECIL guidelines Jan Styczynski (Poland, chair), Walter van der Velden (Netherlands), Christopher Fox (United Kingdom), Dan Engelhard (Israel), Rafael de la Camara (Spain),
ECIL-6 EBV in HSCT 2015 update of ECIL guidelines Jan Styczynski (Poland, chair), Walter van der Velden (Netherlands), Christopher Fox (United Kingdom), Dan Engelhard (Israel), Rafael de la Camara (Spain),
Multi-Virus-Specific T cell Therapy for Patients after HSC and CB Transplant
 Multi-Virus-Specific T cell Therapy for Patients after HSC and CB Transplant Hanley PJ, Krance BR, Brenner MK, Leen AM, Rooney CM, Heslop HE, Shpall EJ, Bollard CM Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Multi-Virus-Specific T cell Therapy for Patients after HSC and CB Transplant Hanley PJ, Krance BR, Brenner MK, Leen AM, Rooney CM, Heslop HE, Shpall EJ, Bollard CM Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Clinical Study CMV Serostatus of Donor-Recipient Pairs Influences the Risk of CMV Infection/Reactivation in HSCT Patients
 Bone Marrow Research Volume 22, Article ID 37575, 8 pages doi:.55/22/37575 Clinical Study CMV Serostatus of Donor-Recipient Pairs Influences the Risk of CMV Infection/Reactivation in HSCT Patients Emilia
Bone Marrow Research Volume 22, Article ID 37575, 8 pages doi:.55/22/37575 Clinical Study CMV Serostatus of Donor-Recipient Pairs Influences the Risk of CMV Infection/Reactivation in HSCT Patients Emilia
Severe Viral Related Complications Following Allo-HCT for Severe Aplastic Anemia
 Severe Viral Related Complications Following Allo-HCT for Severe Aplastic Anemia Liat Shragian Alon, MD Rabin Medical Center, ISRAEL #EBMT15 www.ebmt.org Patient: 25-year-old male No prior medical history
Severe Viral Related Complications Following Allo-HCT for Severe Aplastic Anemia Liat Shragian Alon, MD Rabin Medical Center, ISRAEL #EBMT15 www.ebmt.org Patient: 25-year-old male No prior medical history
The National Marrow Donor Program. Graft Sources for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Simon Bostic, URD Transplant Recipient
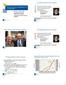 1988 199 1992 1994 1996 1998 2 22 24 26 28 21 212 214 216 218 Adult Donors Cord Blood Units The National Donor Program Graft Sources for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Dennis L. Confer, MD Chief Medical
1988 199 1992 1994 1996 1998 2 22 24 26 28 21 212 214 216 218 Adult Donors Cord Blood Units The National Donor Program Graft Sources for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Dennis L. Confer, MD Chief Medical
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/20898 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Jöris, Monique Maria Title: Challenges in unrelated hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/20898 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Jöris, Monique Maria Title: Challenges in unrelated hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
Anne H. Blaes, 1,2 Qing Cao, 1 John E. Wagner, 1,3 Jo-Anne H. Young, 1,4 Daniel J. Weisdorf, 1,2 Claudio G. Brunstein 1,2
 Monitoring and Preemptive Rituximab Therapy for Epstein-Barr Virus Reactivation after Antithymocyte Globulin Containing Nonmyeloablative Conditioning for Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation Anne H. Blaes,
Monitoring and Preemptive Rituximab Therapy for Epstein-Barr Virus Reactivation after Antithymocyte Globulin Containing Nonmyeloablative Conditioning for Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation Anne H. Blaes,
MUD HSCT as first line Treatment in Idiopathic SAA. Dr Sujith Samarasinghe Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children, London, UK
 MUD HSCT as first line Treatment in Idiopathic SAA Dr Sujith Samarasinghe Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children, London, UK No Financial Disclosures Guidelines for management of aplastic anaemia British
MUD HSCT as first line Treatment in Idiopathic SAA Dr Sujith Samarasinghe Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children, London, UK No Financial Disclosures Guidelines for management of aplastic anaemia British
HLA-DR-matched Parental Donors for Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Patients with High-risk Acute Leukemia
 BRIEF COMMUNICATION HLA-DR-matched Parental Donors for Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Patients with High-risk Acute Leukemia Shang-Ju Wu, Ming Yao,* Jih-Luh Tang, Bo-Sheng Ko, Hwei-Fang
BRIEF COMMUNICATION HLA-DR-matched Parental Donors for Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Patients with High-risk Acute Leukemia Shang-Ju Wu, Ming Yao,* Jih-Luh Tang, Bo-Sheng Ko, Hwei-Fang
Haploidentical Transplantation: The Answer to our Donor Problems? Mary M. Horowitz, MD, MS CIBMTR, Medical College of Wisconsin January 2017
 Haploidentical Transplantation: The Answer to our Donor Problems? Mary M. Horowitz, MD, MS CIBMTR, Medical College of Wisconsin January 2017 Allogeneic Transplant Recipients in the US, by Donor Type 9000
Haploidentical Transplantation: The Answer to our Donor Problems? Mary M. Horowitz, MD, MS CIBMTR, Medical College of Wisconsin January 2017 Allogeneic Transplant Recipients in the US, by Donor Type 9000
3.1 Clinical safety of chimeric or humanized anti-cd25 (ch/anti-cd25)
 3 Results 3.1 Clinical safety of chimeric or humanized anti-cd25 (ch/anti-cd25) Five infusions of monoclonal IL-2 receptor antibody (anti-cd25) were planned according to protocol between day 0 and day
3 Results 3.1 Clinical safety of chimeric or humanized anti-cd25 (ch/anti-cd25) Five infusions of monoclonal IL-2 receptor antibody (anti-cd25) were planned according to protocol between day 0 and day
One Day BMT Course by Thai Society of Hematology. Management of Graft Failure and Relapsed Diseases
 One Day BMT Course by Thai Society of Hematology Management of Graft Failure and Relapsed Diseases Piya Rujkijyanont, MD Division of Hematology-Oncology Department of Pediatrics Phramongkutklao Hospital
One Day BMT Course by Thai Society of Hematology Management of Graft Failure and Relapsed Diseases Piya Rujkijyanont, MD Division of Hematology-Oncology Department of Pediatrics Phramongkutklao Hospital
Immune recovery and the risk of CMV/ EBV reactivation in children post allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation
 Clinical immunology DOI: 1.5114/ceji.216.63129 Immune recovery and the risk of CMV/ EBV reactivation in children post allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation MAŁGORZATA JANECZKO, MONIKA MIELCAREK,
Clinical immunology DOI: 1.5114/ceji.216.63129 Immune recovery and the risk of CMV/ EBV reactivation in children post allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation MAŁGORZATA JANECZKO, MONIKA MIELCAREK,
5/9/2018. Bone marrow failure diseases (aplastic anemia) can be cured by providing a source of new marrow
 5/9/2018 or Stem Cell Harvest Where we are now, and What s Coming AA MDS International Foundation Indianapolis IN Luke Akard MD May 19, 2018 Infusion Transplant Conditioning Treatment 2-7 days STEM CELL
5/9/2018 or Stem Cell Harvest Where we are now, and What s Coming AA MDS International Foundation Indianapolis IN Luke Akard MD May 19, 2018 Infusion Transplant Conditioning Treatment 2-7 days STEM CELL
Trends in Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. AAMAC Patient Education Day Oct 2014
 Trends in Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation AAMAC Patient Education Day Oct 2014 Objectives Review the principles behind allogeneic stem cell transplantation Outline the process of transplant, some of
Trends in Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation AAMAC Patient Education Day Oct 2014 Objectives Review the principles behind allogeneic stem cell transplantation Outline the process of transplant, some of
Stem Cell Transplantation for Severe Aplastic Anemia
 Number of Transplants 10/24/2011 Stem Cell Transplantation for Severe Aplastic Anemia Claudio Anasetti, MD Professor of Oncology and Medicine Chair, Blood and Marrow Transplant Dpt Moffitt Cancer Center
Number of Transplants 10/24/2011 Stem Cell Transplantation for Severe Aplastic Anemia Claudio Anasetti, MD Professor of Oncology and Medicine Chair, Blood and Marrow Transplant Dpt Moffitt Cancer Center
The future of HSCT. John Barrett, MD, NHBLI, NIH Bethesda MD
 The future of HSCT John Barrett, MD, NHBLI, NIH Bethesda MD Transplants today Current approaches to improve SCT outcome Optimize stem cell dose and source BMT? PBSCT? Adjusting post transplant I/S to minimize
The future of HSCT John Barrett, MD, NHBLI, NIH Bethesda MD Transplants today Current approaches to improve SCT outcome Optimize stem cell dose and source BMT? PBSCT? Adjusting post transplant I/S to minimize
Acknowledgements. Department of Hematological Malignancy and Cellular Therapy, University of Kansas Medical Center
 The Addition of Extracorporeal Photopheresis (ECP) to Tacrolimus and Methotrexate to Prevent Acute and Chronic Graft- Versus Host Disease in Myeloablative Hematopoietic Cell Transplant (HCT) Anthony Accurso,
The Addition of Extracorporeal Photopheresis (ECP) to Tacrolimus and Methotrexate to Prevent Acute and Chronic Graft- Versus Host Disease in Myeloablative Hematopoietic Cell Transplant (HCT) Anthony Accurso,
Chronic Kidney Disease after Myeloablative Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
 Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 13:1169-1175 (2007) 2007 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation 1083-8791/07/1310-0001$32.00/0 doi:10.1016/j.bbmt.2007.06.008 Chronic Kidney Disease
Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 13:1169-1175 (2007) 2007 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation 1083-8791/07/1310-0001$32.00/0 doi:10.1016/j.bbmt.2007.06.008 Chronic Kidney Disease
Haplo vs Cord vs URD Debate
 3rd Annual ASBMT Regional Conference for NPs, PAs and Fellows Haplo vs Cord vs URD Debate Claudio G. Brunstein Associate Professor University of Minnesota Medical School Take home message Finding a donor
3rd Annual ASBMT Regional Conference for NPs, PAs and Fellows Haplo vs Cord vs URD Debate Claudio G. Brunstein Associate Professor University of Minnesota Medical School Take home message Finding a donor
Haploidentical Stem Cell Transplantation with post transplantation Cyclophosphamide for the treatment of Fanconi Anemia
 Haploidentical Stem Cell Transplantation with post transplantation Cyclophosphamide for the treatment of Fanconi Anemia Carmem Bonfim Director Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplantation Program HC Federal
Haploidentical Stem Cell Transplantation with post transplantation Cyclophosphamide for the treatment of Fanconi Anemia Carmem Bonfim Director Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplantation Program HC Federal
Comparable Outcome with T-Cell Depleted Unrelated-Donor versus Related-Donor Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplantation
 Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 8:601-607 (2002) 2002 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation ASBMT Comparable Outcome with T-Cell Depleted Unrelated-Donor versus Related-Donor
Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 8:601-607 (2002) 2002 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation ASBMT Comparable Outcome with T-Cell Depleted Unrelated-Donor versus Related-Donor
Transplantation with unrelated bone marrow in leukaemic patients above 40 years of age
 Bone Marrow Transplantation, (1998) 21, 43 49 1998 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0268 3369/98 $12.00 Transplantation with unrelated bone marrow in leukaemic patients above 40 years of age O Ringdén
Bone Marrow Transplantation, (1998) 21, 43 49 1998 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0268 3369/98 $12.00 Transplantation with unrelated bone marrow in leukaemic patients above 40 years of age O Ringdén
Reduced-intensity Conditioning Transplantation
 Reduced-intensity Conditioning Transplantation Current Role and Future Prospect He Huang M.D., Ph.D. Bone Marrow Transplantation Center The First Affiliated Hospital Zhejiang University School of Medicine,
Reduced-intensity Conditioning Transplantation Current Role and Future Prospect He Huang M.D., Ph.D. Bone Marrow Transplantation Center The First Affiliated Hospital Zhejiang University School of Medicine,
Samples Available for Recipient Only. Samples Available for Recipient and Donor
 Unrelated HCT Research Sample Inventory - Summary for First Allogeneic Transplants in CRF and TED with biospecimens available through the CIBMTR Repository stratified by availability of paired samples,
Unrelated HCT Research Sample Inventory - Summary for First Allogeneic Transplants in CRF and TED with biospecimens available through the CIBMTR Repository stratified by availability of paired samples,
UKALL14. Non-Myeloablative Conditioning Regimen (1/1) Date started (dd/mm/yyyy) (Day 7) Weight (kg) BSA (m 2 )
 Non-Myeloablative Conditioning Regimen (1/1) started (dd/mm/yyyy) (Day 7) BSA (m 2 ) Weight (kg) Please enter the daily dose given in the table below: Day Fludarabine (mg) Melphalan (mg) Alemtuzumab (mg)
Non-Myeloablative Conditioning Regimen (1/1) started (dd/mm/yyyy) (Day 7) BSA (m 2 ) Weight (kg) Please enter the daily dose given in the table below: Day Fludarabine (mg) Melphalan (mg) Alemtuzumab (mg)
Samples Available for Recipient Only. Samples Available for Recipient and Donor
 Unrelated HCT Research Sample Inventory - Summary for First Allogeneic Transplants in CRF and TED with biospecimens available through the CIBMTR Repository stratified by availability of paired samples,
Unrelated HCT Research Sample Inventory - Summary for First Allogeneic Transplants in CRF and TED with biospecimens available through the CIBMTR Repository stratified by availability of paired samples,
Samples Available for Recipient and Donor
 Unrelated HCT Research Sample Inventory - Summary for First Allogeneic Transplants in CRF and TED with biospecimens available through the CIBMTR Repository stratified by availability of paired samples,
Unrelated HCT Research Sample Inventory - Summary for First Allogeneic Transplants in CRF and TED with biospecimens available through the CIBMTR Repository stratified by availability of paired samples,
CHAPTER 3 LABORATORY PROCEDURES
 CHAPTER 3 LABORATORY PROCEDURES CHAPTER 3 LABORATORY PROCEDURES 3.1 HLA TYPING Molecular HLA typing will be performed for all donor cord blood units and patients in the three reference laboratories identified
CHAPTER 3 LABORATORY PROCEDURES CHAPTER 3 LABORATORY PROCEDURES 3.1 HLA TYPING Molecular HLA typing will be performed for all donor cord blood units and patients in the three reference laboratories identified
Haploidentical Transplantation today: and the alternatives
 Haploidentical Transplantation today: and the alternatives Daniel Weisdorf MD University of Minnesota February, 2013 No matched sib: where to look? URD donor requires close HLA matching and 3-12 weeks
Haploidentical Transplantation today: and the alternatives Daniel Weisdorf MD University of Minnesota February, 2013 No matched sib: where to look? URD donor requires close HLA matching and 3-12 weeks
T-CELL DEPLETION: ALEMTUZUMAB IN THE BAG
 UCT T-CELL DEPLETION: ALEMTUZUMAB IN THE BAG Nicolas Novitzky PhD, FCP(SA) Engraftment variables in Allo SCT Host HLA identity Integrity of marrow stroma Disease type and status Previous chemotherapy Graft
UCT T-CELL DEPLETION: ALEMTUZUMAB IN THE BAG Nicolas Novitzky PhD, FCP(SA) Engraftment variables in Allo SCT Host HLA identity Integrity of marrow stroma Disease type and status Previous chemotherapy Graft
Introduction to Clinical Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation (HCT) George Chen, MD Thursday, May 03, 2018
 Introduction to Clinical Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation (HCT) George Chen, MD Thursday, May 03, 2018 The transfer of hematopoietic progenitor and stem cells for therapeutic purposes Hematopoietic Cell
Introduction to Clinical Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation (HCT) George Chen, MD Thursday, May 03, 2018 The transfer of hematopoietic progenitor and stem cells for therapeutic purposes Hematopoietic Cell
Therapeutic Advances in Treatment of Aplastic Anemia. Seiji Kojima MD. PhD.
 Therapeutic Advances in Treatment of Aplastic Anemia Seiji Kojima MD. PhD. Department of Pediatrics Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine Chairman of the Severe Aplastic Anemia Working Party Asia-Pacific
Therapeutic Advances in Treatment of Aplastic Anemia Seiji Kojima MD. PhD. Department of Pediatrics Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine Chairman of the Severe Aplastic Anemia Working Party Asia-Pacific
CMV pneumonia in allogeneic BMT recipients undergoing early treatment or pre-emptive ganciclovir therapy
 (2000) 26, 413 417 2000 Macmillan Publishers Ltd All rights reserved 0268 3369/00 $15.00 www.nature.com/bmt CMV pneumonia in allogeneic BMT recipients undergoing early treatment or pre-emptive ganciclovir
(2000) 26, 413 417 2000 Macmillan Publishers Ltd All rights reserved 0268 3369/00 $15.00 www.nature.com/bmt CMV pneumonia in allogeneic BMT recipients undergoing early treatment or pre-emptive ganciclovir
AIH, Marseille 30/09/06
 ALLOGENEIC STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION FOR MYELOID MALIGNANCIES Transplant and Cellular Therapy Unit Institut Paoli Calmettes Inserm U599 Université de la Méditerranée ée Marseille, France AIH, Marseille
ALLOGENEIC STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION FOR MYELOID MALIGNANCIES Transplant and Cellular Therapy Unit Institut Paoli Calmettes Inserm U599 Université de la Méditerranée ée Marseille, France AIH, Marseille
Revista Cubana de Hematología, Inmunología y Hemoterapia. 2017; 36 (Suplemento).
 Depletion of TCR alpha/beta+ T-lymphocytes from grafts for haplo haematopoietic CELL transplantation (HCT) in children Heilmann C, Ifversen M, Haastrup E, Fischer-Nielsen A. Haematopoietic Cell Transplantation
Depletion of TCR alpha/beta+ T-lymphocytes from grafts for haplo haematopoietic CELL transplantation (HCT) in children Heilmann C, Ifversen M, Haastrup E, Fischer-Nielsen A. Haematopoietic Cell Transplantation
Carol Cantwell Blood Transfusion Laboratory Manager St Mary s Hospital, ICHNT
 Carol Cantwell Blood Transfusion Laboratory Manager St Mary s Hospital, ICHNT History Why is blood transfusion involved? What tests are performed in blood transfusion and why? What does a protocol look
Carol Cantwell Blood Transfusion Laboratory Manager St Mary s Hospital, ICHNT History Why is blood transfusion involved? What tests are performed in blood transfusion and why? What does a protocol look
An Introduction to Bone Marrow Transplant
 Introduction to Blood Cancers An Introduction to Bone Marrow Transplant Rushang Patel, MD, PhD, FACP Florida Hospital Medical Group S My RBC Plt Gran Polycythemia Vera Essential Thrombocythemia AML, CML,
Introduction to Blood Cancers An Introduction to Bone Marrow Transplant Rushang Patel, MD, PhD, FACP Florida Hospital Medical Group S My RBC Plt Gran Polycythemia Vera Essential Thrombocythemia AML, CML,
Retrospective evaluation of serum Epstein Barr virus DNA levels in 406 allogeneic stem cell transplant patients
 Retrospective evaluation of serum Epstein Barr virus DNA levels in 406 allogeneic stem cell transplant patients Eeva Juvonen, Sanna Aalto, Jussi Tarkkanen, Liisa Volin, Klaus Hedman, Tapani Ruutu Original
Retrospective evaluation of serum Epstein Barr virus DNA levels in 406 allogeneic stem cell transplant patients Eeva Juvonen, Sanna Aalto, Jussi Tarkkanen, Liisa Volin, Klaus Hedman, Tapani Ruutu Original
PUO in the Immunocompromised Host: CMV and beyond
 PUO in the Immunocompromised Host: CMV and beyond PUO in the immunocompromised host: role of viral infections Nature of host defect T cell defects Underlying disease Treatment Nature of clinical presentation
PUO in the Immunocompromised Host: CMV and beyond PUO in the immunocompromised host: role of viral infections Nature of host defect T cell defects Underlying disease Treatment Nature of clinical presentation
CMV Infection after Transplant from Cord Blood Compared to Other Alternative Donors: The Importance of Donor-Negative CMV Serostatus
 CMV Infection after Transplant from Cord Blood Compared to Other Alternative Donors: The Importance of Donor-Negative CMV Serostatus Małgorzata Mikulska, 1 Anna Maria Raiola, 2 Paolo Bruzzi, 3 Riccardo
CMV Infection after Transplant from Cord Blood Compared to Other Alternative Donors: The Importance of Donor-Negative CMV Serostatus Małgorzata Mikulska, 1 Anna Maria Raiola, 2 Paolo Bruzzi, 3 Riccardo
What s a Transplant? What s not?
 What s a Transplant? What s not? How to report the difference? Daniel Weisdorf MD University of Minnesota Anti-cancer effects of BMT or PBSCT [HSCT] Kill the cancer Save the patient Restore immunocompetence
What s a Transplant? What s not? How to report the difference? Daniel Weisdorf MD University of Minnesota Anti-cancer effects of BMT or PBSCT [HSCT] Kill the cancer Save the patient Restore immunocompetence
Leukaemia Section Short Communication
 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology OPEN ACCESS JOURNAL INIST-CNRS Leukaemia Section Short Communication Ding-Bao Chen Department of Pathology, Peking University People's Hospital,
Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology OPEN ACCESS JOURNAL INIST-CNRS Leukaemia Section Short Communication Ding-Bao Chen Department of Pathology, Peking University People's Hospital,
Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: State of the Art in 2018 RICHARD W. CHILDS M.D. BETHESDA MD
 Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: State of the Art in 2018 RICHARD W. CHILDS M.D. BETHESDA MD Overview: Update on allogeneic transplantation for malignant and nonmalignant diseases: state
Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: State of the Art in 2018 RICHARD W. CHILDS M.D. BETHESDA MD Overview: Update on allogeneic transplantation for malignant and nonmalignant diseases: state
HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0
 HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0 Centre Identification EBMT Code (CIC): Contact person: Hospital: Email: Unit: Patient Data Date of this report: First transplant for this patient?:
HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0 Centre Identification EBMT Code (CIC): Contact person: Hospital: Email: Unit: Patient Data Date of this report: First transplant for this patient?:
ALLOGENEIC STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION FOR ACUTE MYELOBLASTIC LEUKEMIAS
 ALLOGENEIC STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION FOR ACUTE MYELOBLASTIC LEUKEMIAS Didier Blaise, MD Transplant and Cellular Therapy Unit (U2T) Department of Hematology Centre de Recherche en Cancérologie, Inserm U891
ALLOGENEIC STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION FOR ACUTE MYELOBLASTIC LEUKEMIAS Didier Blaise, MD Transplant and Cellular Therapy Unit (U2T) Department of Hematology Centre de Recherche en Cancérologie, Inserm U891
Stem cells. -Dr Dinesh Bhurani, MD, DM, FRCPA. Rajiv Gandhi Cancer Institute, Delhi, -Director, Department of Haematology and BMT
 Stem cells -Dr Dinesh Bhurani, MD, DM, FRCPA -Director, Department of Haematology and BMT Rajiv Gandhi Cancer Institute, Delhi, Flow of presentation Update on stem cell uses Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Stem cells -Dr Dinesh Bhurani, MD, DM, FRCPA -Director, Department of Haematology and BMT Rajiv Gandhi Cancer Institute, Delhi, Flow of presentation Update on stem cell uses Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation
A.M.W. van Marion. H.M. Lokhorst. N.W.C.J. van de Donk. J.G. van den Tweel. Histopathology 2002, 41 (suppl 2):77-92 (modified)
 chapter 4 The significance of monoclonal plasma cells in the bone marrow biopsies of patients with multiple myeloma following allogeneic or autologous stem cell transplantation A.M.W. van Marion H.M. Lokhorst
chapter 4 The significance of monoclonal plasma cells in the bone marrow biopsies of patients with multiple myeloma following allogeneic or autologous stem cell transplantation A.M.W. van Marion H.M. Lokhorst
Clinical Aspect and Application of Laboratory Test in Herpes Virus Infection. Masoud Mardani M.D,FIDSA
 Clinical Aspect and Application of Laboratory Test in Herpes Virus Infection Masoud Mardani M.D,FIDSA Shahidhid Bh BeheshtiMdi Medical lui Universityit Cytomegalovirus (CMV), Epstein Barr Virus(EBV), Herpes
Clinical Aspect and Application of Laboratory Test in Herpes Virus Infection Masoud Mardani M.D,FIDSA Shahidhid Bh BeheshtiMdi Medical lui Universityit Cytomegalovirus (CMV), Epstein Barr Virus(EBV), Herpes
& 2004 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved /04 $
 (2004) 33, 197 204 & 2004 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0268-3369/04 $25.00 www.nature.com/bmt Viral infections Influence of cytomegalovirus (CMV) sero-positivity on CMV infection, lymphocyte
(2004) 33, 197 204 & 2004 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0268-3369/04 $25.00 www.nature.com/bmt Viral infections Influence of cytomegalovirus (CMV) sero-positivity on CMV infection, lymphocyte
2016 BMT Tandem Meetings
 ASBMT CIBMTR 2016 BMT Tandem Meetings for Prevention of Cytomegalovirus after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation in CMV-Seropositive Patients A Randomized, Double-Blind, -Controlled, Parallel-Group
ASBMT CIBMTR 2016 BMT Tandem Meetings for Prevention of Cytomegalovirus after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation in CMV-Seropositive Patients A Randomized, Double-Blind, -Controlled, Parallel-Group
Please submit supporting medical documentation, notes and test results.
 Pharmacy Prior Authorization AETA BETTER HEALTH FLORIDA Valcyte (Medicaid) This fax machine is located in a secure location as required by HIPAA regulations. Complete/review information, sign and date.
Pharmacy Prior Authorization AETA BETTER HEALTH FLORIDA Valcyte (Medicaid) This fax machine is located in a secure location as required by HIPAA regulations. Complete/review information, sign and date.
Dr. Joseph McGuirk Professor of Medicine, BMT Medical Director, Interim Director, Division of Hematology/Oncology
 Advances in Autologous and Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation Dr. Joseph McGuirk Professor of Medicine, BMT Medical Director, Interim Director, Division of Hematology/Oncology April 12, 2014 Disclosures
Advances in Autologous and Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation Dr. Joseph McGuirk Professor of Medicine, BMT Medical Director, Interim Director, Division of Hematology/Oncology April 12, 2014 Disclosures
Diagnosis of CMV infection UPDATE ECIL
 UPDATE ECIL-4 2011 Recommendations for CMV and HHV-6 management in patients with hematological diseases Per Ljungman, Rafael de la Camara, Hermann Einsele, Dan Engelhard, Pierre Reusser, Jan Styczynski,
UPDATE ECIL-4 2011 Recommendations for CMV and HHV-6 management in patients with hematological diseases Per Ljungman, Rafael de la Camara, Hermann Einsele, Dan Engelhard, Pierre Reusser, Jan Styczynski,
Effect of Conditioning Regimen Intensity on CMV Infection in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation
 Version 3-30-2009 Effect of Conditioning Regimen Intensity on CMV Infection in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Authors: Hirohisa Nakamae, 1 Katharine A. Kirby, 1 Brenda M. Sandmaier, 1,2
Version 3-30-2009 Effect of Conditioning Regimen Intensity on CMV Infection in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Authors: Hirohisa Nakamae, 1 Katharine A. Kirby, 1 Brenda M. Sandmaier, 1,2
What s new in Blood and Marrow Transplant? Saar Gill, MD PhD Jan 22, 2016
 What s new in Blood and Marrow Transplant? Saar Gill, MD PhD Jan 22, 2016 Division of Hematology-Oncology University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine 1 Who should be transplanted and how? Updates
What s new in Blood and Marrow Transplant? Saar Gill, MD PhD Jan 22, 2016 Division of Hematology-Oncology University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine 1 Who should be transplanted and how? Updates
Alloreattività e Tolleranza nei Trapianti di Cellule Staminali Emopoietiche Allogeniche
 Alloreattività e Tolleranza nei Trapianti di Cellule Staminali Emopoietiche Allogeniche Massimo Fabrizio Martelli Ematologia ed Immunologia Clinica Università degli Studi di Perugia 41 Congresso Nazionale
Alloreattività e Tolleranza nei Trapianti di Cellule Staminali Emopoietiche Allogeniche Massimo Fabrizio Martelli Ematologia ed Immunologia Clinica Università degli Studi di Perugia 41 Congresso Nazionale
Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation with Peripheral Blood Stem Cells Mobilized by Pegylated G-CSF
 Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 12:63-67 (26) 26 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation 183-8791/6/126-2$32./ doi:1.116/j.bbmt.26.3.1 Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation with
Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 12:63-67 (26) 26 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation 183-8791/6/126-2$32./ doi:1.116/j.bbmt.26.3.1 Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation with
EBMT Complications and Quality of Life Working Party Educational Course
 EBMT Complications and Quality of Life Working Party Educational Course Organisers: R. Duarte, G. Basak 23-24 October 2014, Warsaw, Poland #EBMT2014 www.ebmt.org EBMT Complications and Quality of Life
EBMT Complications and Quality of Life Working Party Educational Course Organisers: R. Duarte, G. Basak 23-24 October 2014, Warsaw, Poland #EBMT2014 www.ebmt.org EBMT Complications and Quality of Life
HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0
 HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0 Centre Identification EBMT Code (CIC): Contact person: Hospital: Email: Unit: Patient Data Date of this report: First transplant for this patient?:
HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0 Centre Identification EBMT Code (CIC): Contact person: Hospital: Email: Unit: Patient Data Date of this report: First transplant for this patient?:
Haploidentical Transplants for Lymphoma. Andrea Bacigalupo Universita Cattolica Policlinico Gemelli Roma - Italy
 Haploidentical Transplants for Lymphoma Andrea Bacigalupo Universita Cattolica Policlinico Gemelli Roma - Italy HODGKIN NON HODGKIN Non Myelo Ablative Regimen Luznik L et al BBMT 2008 Comparison of Outcomes
Haploidentical Transplants for Lymphoma Andrea Bacigalupo Universita Cattolica Policlinico Gemelli Roma - Italy HODGKIN NON HODGKIN Non Myelo Ablative Regimen Luznik L et al BBMT 2008 Comparison of Outcomes
Hematology and Oncology, The Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio; 3 Department of Biostatistics, The Ohio State University Hospitals, Columbus, Ohio
 Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 12:61-67 (2006) 2006 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation 1083-8791/06/1201-0004$32.00/0 doi:10.1016/j.bbmt.2005.06.004 High Disease Burden
Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 12:61-67 (2006) 2006 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation 1083-8791/06/1201-0004$32.00/0 doi:10.1016/j.bbmt.2005.06.004 High Disease Burden
Outcomes of Transplantation with Related- and Unrelated-Donor Stem Cells in Children with Severe Thalassemia
 Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 12:683-687 (2006) 2006 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation 1083-8791/06/1206-0011$32.00/0 doi:10.1016/j.bbmt.2006.02.008 Outcomes of Transplantation
Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 12:683-687 (2006) 2006 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation 1083-8791/06/1206-0011$32.00/0 doi:10.1016/j.bbmt.2006.02.008 Outcomes of Transplantation
Acute GVHD. ESH-EBMT 2009 Latimer A. Devergie
 Acute GVHD ESH-EBMT 2009 Latimer A. Devergie Acute GVHD Activated Donor T cells damage host epithelial cells after an inflammatory cascade that begins after the preparative regimen GVHD is the major barrier
Acute GVHD ESH-EBMT 2009 Latimer A. Devergie Acute GVHD Activated Donor T cells damage host epithelial cells after an inflammatory cascade that begins after the preparative regimen GVHD is the major barrier
2017 CST-Astellas Canadian Transplant Fellows Symposium. EBV Post Transplantation Implications and Approach to Management
 2017 CST-Astellas Canadian Transplant Fellows Symposium EBV Post Transplantation Implications and Approach to Management Atul Humar, MD Atul Humar is a Professor in the Department of Medicine, University
2017 CST-Astellas Canadian Transplant Fellows Symposium EBV Post Transplantation Implications and Approach to Management Atul Humar, MD Atul Humar is a Professor in the Department of Medicine, University
Acute leukemia Bone marrow transplantation from partially HLA-mismatched family donors for acute leukemia: single-center experience of 201 patients
 (2004) 33, 389 396 & 2004 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0268-3369/04 $25.00 www.nature.com/bmt Acute leukemia Bone marrow transplantation from partially HLA-mismatched family donors for acute
(2004) 33, 389 396 & 2004 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0268-3369/04 $25.00 www.nature.com/bmt Acute leukemia Bone marrow transplantation from partially HLA-mismatched family donors for acute
Objectives. What is Aplastic Anemia. SAA 101: An Introductory Course to Severe Aplastic Anemia
 SAA 101: An Introductory Course to Severe Aplastic Anemia David A. Margolis, MD Professor of Pediatrics/Medical College of Wisconsin Program Director/ Children s Hospital of Wisconsin BMT Program Objectives
SAA 101: An Introductory Course to Severe Aplastic Anemia David A. Margolis, MD Professor of Pediatrics/Medical College of Wisconsin Program Director/ Children s Hospital of Wisconsin BMT Program Objectives
Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease (agvhd) Udomsak Bunworasate Chulalongkorn University
 Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease (agvhd) Udomsak Bunworasate Chulalongkorn University Graft-versus-Host Disease (GVHD) Background GVHD is an immunologic reaction of the donor immune cells (Graft) against
Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease (agvhd) Udomsak Bunworasate Chulalongkorn University Graft-versus-Host Disease (GVHD) Background GVHD is an immunologic reaction of the donor immune cells (Graft) against
The role of HLA in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation and Platelet Refractoriness.
 The role of HLA in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation and Platelet Refractoriness. Robert Liwski, MD, PhD, FRCPC Medical Director HLA Typing Laboratory Department of Pathology Dalhousie
The role of HLA in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation and Platelet Refractoriness. Robert Liwski, MD, PhD, FRCPC Medical Director HLA Typing Laboratory Department of Pathology Dalhousie
Graft Versus Tumour Effect
 Graft Versus Tumour Effect Mairéad NíChonghaile 12 Abstract The treatment of relapsed disease remains challenging, and it is well accepted that concept of allogeneic HSCT relies upon both the conditioning
Graft Versus Tumour Effect Mairéad NíChonghaile 12 Abstract The treatment of relapsed disease remains challenging, and it is well accepted that concept of allogeneic HSCT relies upon both the conditioning
AML:Transplant or ChemoTherapy?
 AML:Transplant or ChemoTherapy? 1960 s: Importance of HLA type in Animal Models Survival of Dogs Given 1000 RAD TBI and a Marrow Infusion from a Littermate Matched or Mismatched for Dog Leucocyte Antigens
AML:Transplant or ChemoTherapy? 1960 s: Importance of HLA type in Animal Models Survival of Dogs Given 1000 RAD TBI and a Marrow Infusion from a Littermate Matched or Mismatched for Dog Leucocyte Antigens
T cell manipulation of the graft: Yes
 T cell manipulation of the graft: Yes J.H. Frederik Falkenburg Department of Hematology L M U C Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (SCT) for non-malignant disorders: no need for anti-tumor
T cell manipulation of the graft: Yes J.H. Frederik Falkenburg Department of Hematology L M U C Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (SCT) for non-malignant disorders: no need for anti-tumor
KEY WORDS: Alternative donor stem cell transplantation, Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, GVHD, Leukemia relapse
 Comparable Outcome of Alternative Donor and Matched Sibling Donor Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant for Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in First or Second Remission Using Alemtuzumab in a Myeloablative
Comparable Outcome of Alternative Donor and Matched Sibling Donor Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant for Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in First or Second Remission Using Alemtuzumab in a Myeloablative
Myeloablative and Reduced Intensity Conditioning for HSCT Annalisa Ruggeri, MD, Hôpital Saint Antoine Eurocord- Hôpital Saint Louis, Paris
 Myeloablative and Reduced Intensity Conditioning for HSCT Annalisa Ruggeri, MD, Hôpital Saint Antoine Eurocord- Hôpital Saint Louis, Paris 18th ESH - EBMT Training Course on HSCT 8-10 May 2014, Vienna,
Myeloablative and Reduced Intensity Conditioning for HSCT Annalisa Ruggeri, MD, Hôpital Saint Antoine Eurocord- Hôpital Saint Louis, Paris 18th ESH - EBMT Training Course on HSCT 8-10 May 2014, Vienna,
EBMT2008_22_44:EBMT :29 Pagina 454 CHAPTER 30. HSCT for Hodgkin s lymphoma in adults. A. Sureda
 EBMT2008_22_44:EBMT2008 6-11-2008 9:29 Pagina 454 * CHAPTER 30 HSCT for Hodgkin s lymphoma in adults A. Sureda EBMT2008_22_44:EBMT2008 6-11-2008 9:29 Pagina 455 CHAPTER 30 HL in adults 1. Introduction
EBMT2008_22_44:EBMT2008 6-11-2008 9:29 Pagina 454 * CHAPTER 30 HSCT for Hodgkin s lymphoma in adults A. Sureda EBMT2008_22_44:EBMT2008 6-11-2008 9:29 Pagina 455 CHAPTER 30 HL in adults 1. Introduction
Cord-Blood Transplantation in Patients with Minimal Residual Disease
 The new england journal of medicine Original Article Cord-Blood Transplantation in Patients with Minimal Residual Disease Filippo Milano, M.D., Ph.D., Ted Gooley, Ph.D., Brent Wood, M.D., Ann Woolfrey,
The new england journal of medicine Original Article Cord-Blood Transplantation in Patients with Minimal Residual Disease Filippo Milano, M.D., Ph.D., Ted Gooley, Ph.D., Brent Wood, M.D., Ann Woolfrey,
Manipulation of T Cells in the Thnsplant Inoculum
 International Journal of Cell Cloning 4: 122-126 Suppl 1 (1986) Manipulation of T Cells in the Thnsplant Inoculum J. Kersey Bone Marrow Transplantation Program, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN,
International Journal of Cell Cloning 4: 122-126 Suppl 1 (1986) Manipulation of T Cells in the Thnsplant Inoculum J. Kersey Bone Marrow Transplantation Program, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN,
MAJOR ARTICLE. (See the editorial commentary by Bitan on pages )
 MAJOR ARTICLE Management of Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Reactivation after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation by Simultaneous Analysis of EBV DNA Load and EBV-Specific T Cell Reconstitution Nicola E. Annels,
MAJOR ARTICLE Management of Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Reactivation after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation by Simultaneous Analysis of EBV DNA Load and EBV-Specific T Cell Reconstitution Nicola E. Annels,
KEY WORDS: Total body irradiation, acute myelogenous leukemia, relapse
 The Addition of 400 cgy Total Body Irradiation to a Regimen Incorporating Once-Daily Intravenous Busulfan, Fludarabine, and Antithymocyte Globulin Reduces Relapse Without Affecting Nonrelapse Mortality
The Addition of 400 cgy Total Body Irradiation to a Regimen Incorporating Once-Daily Intravenous Busulfan, Fludarabine, and Antithymocyte Globulin Reduces Relapse Without Affecting Nonrelapse Mortality
Disclosure. Objectives 1/22/2015
 Evaluation of the Impact of Anti Thymocyte Globulin (ATG) on Post Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant (HCT) Outcomes in Patients Undergoing Allogeneic HCT Katie S. Kaminski, PharmD, CPP University of North
Evaluation of the Impact of Anti Thymocyte Globulin (ATG) on Post Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant (HCT) Outcomes in Patients Undergoing Allogeneic HCT Katie S. Kaminski, PharmD, CPP University of North
KEY WORDS: Unrelated SCT, HLA-mismatch, ATG, Graft-versus-host disease
 HLA-Mismatched Unrelated Donors as an Alternative Graft Source for Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation after Antithymocyte Globulin-Containing Conditioning Regimen Nicolaus Kröger, 1 Tatjana Zabelina,
HLA-Mismatched Unrelated Donors as an Alternative Graft Source for Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation after Antithymocyte Globulin-Containing Conditioning Regimen Nicolaus Kröger, 1 Tatjana Zabelina,
Transplantation - Challenges for the future. Dr Gordon Cook S t James s Institute of Oncology, Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust
 Transplantation - Challenges for the future Dr Gordon Cook S t James s Institute of Oncology, Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust Bone Marrow Transplantation Timeline, 1957-2006 Appelbaum F. N Engl J Med 2007;357:1472-1475
Transplantation - Challenges for the future Dr Gordon Cook S t James s Institute of Oncology, Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust Bone Marrow Transplantation Timeline, 1957-2006 Appelbaum F. N Engl J Med 2007;357:1472-1475
HCT for Myelofibrosis
 Allogeneic HSCT for MDS and Myelofibrosis Sunil Abhyankar, MD Professor Medicine, Medical Director, Pheresis and Cell Processing University of Kansas Hospital BMT Program April 27 th, 213 HCT for Myelofibrosis
Allogeneic HSCT for MDS and Myelofibrosis Sunil Abhyankar, MD Professor Medicine, Medical Director, Pheresis and Cell Processing University of Kansas Hospital BMT Program April 27 th, 213 HCT for Myelofibrosis
UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD STEM CELLS EXPANDED IN THE PRESENCE OF NICOTINAMIDE (NICORD) PROVIDE LONG TERM MULITI-LINEAGE ENGRAFTMENT
 UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD STEM CELLS EXPANDED IN THE PRESENCE OF NICOTINAMIDE (NICORD) PROVIDE LONG TERM MULITI-LINEAGE ENGRAFTMENT Mitchell E. Horwitz, MD Duke University Medical Center Duke Cancer Institute
UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD STEM CELLS EXPANDED IN THE PRESENCE OF NICOTINAMIDE (NICORD) PROVIDE LONG TERM MULITI-LINEAGE ENGRAFTMENT Mitchell E. Horwitz, MD Duke University Medical Center Duke Cancer Institute
CD34+ Cell Enrichment High incidence of graft failure in children receiving CD34+ augmented elutriated allografts for nonmalignant diseases
 (2003) 31, 73 80 & 2003 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0268-3369/03 $25.00 www.nature.com/bmt CD34+ Cell Enrichment High incidence of graft failure in children receiving CD34+ augmented elutriated
(2003) 31, 73 80 & 2003 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0268-3369/03 $25.00 www.nature.com/bmt CD34+ Cell Enrichment High incidence of graft failure in children receiving CD34+ augmented elutriated
HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0
 CIC: HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0 Centre Identification EBMT Code (CIC): Contact person: Hospital: Email: Unit: Patient Data Date of this report: First transplant for this patient?:
CIC: HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0 Centre Identification EBMT Code (CIC): Contact person: Hospital: Email: Unit: Patient Data Date of this report: First transplant for this patient?:
MATCHMAKER, MATCHMAKER, MAKE ME A MATCH, FIND ME A MISMATCHED TRANSPLANT TO CATCH
 MATCHMAKER, MATCHMAKER, MAKE ME A MATCH, FIND ME A MISMATCHED TRANSPLANT TO CATCH TEJASWINI M. DHAWALE, M.D. HEME FELLOWS CONFERENCE NOVEMBER 08, 2013 CASE PRESENTATION 51 yo M with history of MDS (unilinear
MATCHMAKER, MATCHMAKER, MAKE ME A MATCH, FIND ME A MISMATCHED TRANSPLANT TO CATCH TEJASWINI M. DHAWALE, M.D. HEME FELLOWS CONFERENCE NOVEMBER 08, 2013 CASE PRESENTATION 51 yo M with history of MDS (unilinear
Original article Failure of pre-emptive treatment of cytomegalovirus infections and antiviral resistance in stem cell transplant recipients
 Antiviral Therapy ; 7: (doi:.8/imp899) Original article Failure of pre-emptive treatment of cytomegalovirus infections and antiviral resistance in stem cell transplant recipients Martha T van der Beek
Antiviral Therapy ; 7: (doi:.8/imp899) Original article Failure of pre-emptive treatment of cytomegalovirus infections and antiviral resistance in stem cell transplant recipients Martha T van der Beek
Role of NMDP Repository in the Evolution of HLA Matching and Typing for Unrelated Donor HCT
 Role of NMDP Repository in the Evolution of HLA Matching and Typing for Unrelated Donor HCT Stephen Spellman, MBS Director, Immunobiology and Observational Research Assistant Scientific Director CIBMTR,
Role of NMDP Repository in the Evolution of HLA Matching and Typing for Unrelated Donor HCT Stephen Spellman, MBS Director, Immunobiology and Observational Research Assistant Scientific Director CIBMTR,
Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation
 Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation Current Results John E. Wagner, M.D. Blood and Marrow Transplant Program and Stem Cell Institute University of Minnesota Donor Choices Unrelated Marrow/PBSC Results
Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation Current Results John E. Wagner, M.D. Blood and Marrow Transplant Program and Stem Cell Institute University of Minnesota Donor Choices Unrelated Marrow/PBSC Results
Donatore HLA identico di anni o MUD giovane?
 Donatore HLA identico di 60-70 anni o MUD giovane? Stella Santarone Dipartimento di Ematologia, Medicina Trasfusionale e Biotecnologie Pescara AGENDA 1. Stem Cell Donation: fatalities and severe events
Donatore HLA identico di 60-70 anni o MUD giovane? Stella Santarone Dipartimento di Ematologia, Medicina Trasfusionale e Biotecnologie Pescara AGENDA 1. Stem Cell Donation: fatalities and severe events
Virological Surveillance in Paediatric HSCT Recipients
 Virological Surveillance in Paediatric HSCT Recipients Dr Pamela Lee Clinical Assistant Professor Department of Paediatrics & Adolescent Medicine Queen Mary Hospital LKS Faculty of Medicine, The University
Virological Surveillance in Paediatric HSCT Recipients Dr Pamela Lee Clinical Assistant Professor Department of Paediatrics & Adolescent Medicine Queen Mary Hospital LKS Faculty of Medicine, The University
Bone Marrow Transplantation in Myelodysplastic Syndromes. An overview for the Myelodysplasia Support Group of Ottawa
 Bone Marrow Transplantation in Myelodysplastic Syndromes An overview for the Myelodysplasia Support Group of Ottawa Objectives Provide brief review of marrow failure Re emphasize the importance of predictions
Bone Marrow Transplantation in Myelodysplastic Syndromes An overview for the Myelodysplasia Support Group of Ottawa Objectives Provide brief review of marrow failure Re emphasize the importance of predictions
Current Status of Haploidentical Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
 Current Status of Haploidentical Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Annalisa Ruggeri, MD, PhD Hematology and BMT Unit Hôpital Saint Antoine, Paris, France #EBMTITC16 www.ebmt.org Hematopoietic SCT
Current Status of Haploidentical Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Annalisa Ruggeri, MD, PhD Hematology and BMT Unit Hôpital Saint Antoine, Paris, France #EBMTITC16 www.ebmt.org Hematopoietic SCT
Non-myeloablative allogeneic stem cell transplantation focusing on immunotherapy of life-threatening malignant and non-malignant diseases
 Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology 39 (2001) 25 29 www.elsevier.com/locate/critrevonc Non-myeloablative allogeneic stem cell transplantation focusing on immunotherapy of life-threatening malignant
Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology 39 (2001) 25 29 www.elsevier.com/locate/critrevonc Non-myeloablative allogeneic stem cell transplantation focusing on immunotherapy of life-threatening malignant
