Chapter 21 The Lymphatic System Pearson Education, Inc.
|
|
|
- Pearl Carson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 21 The Lymphatic System
2 Overview of the Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System Protects us against disease Lymphatic system cells respond to: Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells, such as cancers
3 22-1 Overview of the Lymphatic System Specific Defenses Lymphocytes Part of the immune response Identify, attack, and develop immunity To a specific pathogen
4 An Introduction to the Lymphatic System and Immunity Pathogens Microscopic organisms that cause disease: Viruses Bacteria Fungi Parasites Each attacks in a specific way
5 22-1 Overview of the Lymphatic System The Immune System Immunity The ability to resist infection and disease All body cells and tissues involved in production of immunity Not just lymphatic system
6 22-1 Overview of the Lymphatic System Nonspecific Defenses Block or attack any potential infectious organism Cannot distinguish one attack from another
7 Structures of Body Defenses Organization of the Lymphatic System 1. Lymph A fluid similar to plasma but does not have plasma proteins 2. Lymphatic vessels (lymphatics) Carry lymph from peripheral tissues to the venous system 3. Lymphoid tissues and lymphoid organs 4. Lymphocytes, phagocytes, and other immune system cells
8 Figure 22-1 An Overview of the Lymphatic System (Part 1 of 2) Lymph Lymphocyte Lymphatic Vessels and Lymph Nodes Cervical lymph nodes Thoracic duct Right lymphatic duct Axillary lymph nodes Lymphatics of mammary gland Cisterna chyli Lymphatics of upper limb Lumbar lymph nodes Lymphoid Tissues and Organs Tonsil Thymus Spleen Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) in digestive, respiratory, urinary, and reproductive tracts
9 Figure 22-1 An Overview of the Lymphatic System (Part 2 of 2) Lymphoid Tissues and Organs Appendix Lymphatic Vessels and Lymph Nodes Inguinal lymph nodes Lymphatics of lower limb
10 Structures of Body Defenses Function of the Lymphatic System To produce, maintain, and distribute lymphocytes Lymphocyte Production Lymphocytes are produced In lymphoid tissues (e.g., tonsils) Lymphoid organs (e.g., spleen, thymus) In red bone marrow Lymphocyte distribution Detects problems Travels into site of injury or infection
11 Lymphocyte Circulation From blood to interstitial fluid through capillaries Returns to venous blood through lymphatic vessels The Circulation of Fluids From blood plasma to lymph and back to the venous system Transports hormones, nutrients, and waste products
12 Lymphatic Vessels Are vessels that carry lymph Lymphatic system begins with smallest vessels Lymphatic capillaries (terminal lymphatics)
13 Lymphatic Capillaries Differ from blood capillaries in four ways 1. Start as pockets rather than tubes 2. Have larger diameters 3. Have thinner walls 4. Flat or irregular outline in sectional view
14 Figure 22-2a Lymphatic Capillaries Smooth muscle Arteriole Venule Endothelial cells Lymphatic capillary Interstitial fluid Lymph flow Blood capillaries Loose connective tissue The interwoven network formed by blood capillaries and lymphatic capillaries.
15 WHAT S IN A LYMPHATIC VESSEL?
16 Figure 22-2b Lymphatic Capillaries Incomplete basement membrane Lymph flow Loose connective tissue Lymphocyte To larger lymphatics Interstitial fluid Lymphatic capillary Blood capillary Interstitial fluid A sectional view indicating the movement of fluid from the plasma, through the tissues as interstitial fluid, and into the lymphatic system as lymph.
17 Lymphatic Capillaries Endothelial cells loosely bound together with overlap Overlap acts as one-way valve Allows fluids, solutes, viruses, and bacteria to enter Prevents return to intercellular space
18 Lymph Flow From lymphatic capillaries to larger lymphatic vessels containing one-way valves Lymphatic vessels travel with veins Lacteals Are special lymphatic capillaries in small intestine Transport lipids from digestive tract
19 Figure 22-3a Lymphatic Vessels and Valves Vein Artery Artery Vein Lymphatic vessel Lymphatic valve Toward venous system Lymphatic vessel From lymphatic capillaries
20 Figure 22-3b Lymphatic Vessels and Valves Lymphatic valve Lymphatic vessel Like valves in veins, each lymphatic valve consists of a pair of flaps that permit movement of fluid in only one direction. Lymphatic vessel and valve LM 63
21 Structures of Body Defenses Lymphatic Vessels Superficial lymphatics Deep lymphatics Are located in: Skin Mucous membranes Serous membranes lining body cavities
22 Structures of Body Defenses Superficial and Deep Lymphatics The deep lymphatics Are larger vessels that accompany deep arteries and veins Superficial and deep lymphatics Join to form large lymphatic trunks Trunks empty into two major collecting vessels 1. Thoracic duct 2. Right lymphatic duct
23 Structures of Body Defenses Major Lymph-Collecting Vessels The base of the thoracic duct Expands into cisterna chyli Cisterna chyli receives lymph from: Right and left lumbar trunks Intestinal trunk
24 Structures of Body Defenses The Inferior Segment of Thoracic Duct Collects lymph from: Left bronchomediastinal trunk Left subclavian trunk Left jugular trunk Empties into left subclavian vein
25 Structures of Body Defenses The Right Lymphatic Duct Collects lymph from: Right jugular trunk Right subclavian trunk Right bronchomediastinal trunk Empties into right subclavian vein
26 Figure 22-4 The Relationship between the Lymphatic Ducts and the Venous System Right internal jugular vein Right jugular trunk Right lymphatic duct Right subclavian trunk Right subclavian vein Right bronchomediastinal trunk Superior vena cava (cut) Azygos vein Rib (cut) Brachiocephalic veins Left internal jugular vein Left jugular trunk Thoracic duct Left subclavian trunk Left bronchomediastinal trunk Left subclavian vein First rib (cut) Highest intercostal vein Drainage of right lymphatic duct Drainage of thoracic duct Thoracic duct Thoracic lymph nodes Hemiazygos vein Parietal pleura (cut) Diaphragm Inferior vena cava (cut) Right lumbar trunk Intestinal trunk Left lumbar trunk Cisterna chyli
27 Figure 22-4b The Relationship between the Lymphatic Ducts and the Venous System (Part 1 of 2) Brachiocephalic veins Right internal jugular vein Right jugular trunk Right lymphatic duct Right subclavian trunk Right subclavian vein Right bronchomediastinal trunk Superior vena cava (cut) Azygos vein Rib (cut) Inferior vena cava (cut) Right lumbar trunk The thoracic duct empties into the left subclavian vein. The right lymphatic duct drains into the right subclavian vein.
28 Figure 22-4b The Relationship between the Lymphatic Ducts and the Venous System (Part 2 of 2) Brachiocephalic veins Left internal jugular vein Left jugular trunk Thoracic duct Left subclavian trunk Left bronchomediastinal trunk Left subclavian vein First rib (cut) Highest intercostal vein Thoracic duct Thoracic lymph nodes Hemiazygos vein Parietal pleura (cut) Diaphragm Intestinal trunk Cisterna chyli Left lumbar trunk The thoracic duct empties into the left subclavian vein. The right lymphatic duct drains into the right subclavian vein.
29 Lymphedema Blockage of lymph drainage from a limb Causes severe swelling Interferes with immune system function Lymphocytes Make up 20 30% of circulating leukocytes Most are stored, not circulating
30 Types of Lymphocytes 1. T cells Thymus-dependent 2. B cells Bone marrow derived 3. NK cells Natural killer cells
31 T Cells Make up 80% of circulating lymphocytes Main Types of T Cells Cytotoxic T (T C ) cells Memory T cells Helper T (T H ) cells Suppressor T (T S ) cells
32 Cytotoxic T Cells Attack cells infected by viruses Produce cell-mediated immunity Memory T Cells Formed in response to foreign substance Remain in body to give immunity Helper T Cells Stimulate function of T cells and B cells
33 Suppressor T Cells Inhibit function of T cells and B cells Regulatory T Cells Are helper and suppressor T cells Control sensitivity of immune response
34 Other T Cells Inflammatory T cells Suppressor/inducer T cells B Cells Make up 10 15% of circulating lymphocytes Differentiate (change) into plasma cells Plasma cells Produce and secrete antibodies (immunoglobulin proteins)
35 Antigens Targets that identify any pathogen or foreign compound Immunoglobulins (Antibodies) The binding of a specific antibody to its specific target antigen initiates antibody-mediated immunity
36 Antibody-Mediated Immunity A chain of events that destroys the target compound or organism Natural Killer (NK) Cells Also called large granular lymphocytes Make up 5 10% of circulating lymphocytes Responsible for immunological surveillance Attack foreign cells, virus-infected cells, and cancer cells
37 Figure 22-5 Classes of Lymphocytes (Part 1 of 2) Classes of Lymphocytes subdivided into T Cells Approximately 80% of circulating lymphocytes are classified as T cells. can differentiate into Cytotoxic T Cells Helper T Cells Suppressor T Cells Memory T Cells Cytotoxic T cells attack foreign cells or body cells infected by viruses. Helper T cells stimulate the activation and function of both T cells and B cells. Suppressor T cells inhibit the activation and function of both T cells and B cells. Memory T cells are a subset of T cells that respond to a previously encountered antigen.
38 Figure 22-5 Classes of Lymphocytes (Part 2 of 2) Classes of Lymphocytes subdivided into B Cells B cells make up 10-15% of circulating lymphocytes. NK Cells NK cells make up the remaining 5-10% of circulating lymphocytes. Plasma Cells When stimulated, B cells can differentiate into plasma cells, which produce and secrete antibodies.
39 Lymphocyte Distribution Tissues maintain different T cell and B cell populations Lymphocytes wander through tissues Enter blood vessels or lymphatics for transport Can survive many years
40 Lymphocyte Production Also called lymphopoiesis, involves: Bone marrow Thymus Peripheral lymphoid tissues Hemocytoblasts In bone marrow, divide into two types of lymphoid stem cells
41 Lymphoid Stem Cells Group 1 Remains in bone marrow and develop with help of stromal cells Produces B cells and natural killer cells Group 2 Migrates to thymus Produces T cells in environment isolated by blood thymus barrier
42 Figure 22-6a The Derivation and Distribution of Lymphocytes Red Bone Marrow One group of lymphoid stem cells remains in the bone marrow, producing daughter cells that mature into B cells and NK cells that Hemocytoblasts enter peripheral tissues. Interleukin-7 Lymphoid stem cells Lymphoid stem cells Transported in the bloodstream Mature T cell B cells NK cells
43 Figure 22-6b The Derivation and Distribution of Lymphocytes Thymus The second group of lymphoid stem cells migrates to the thymus, where subsequent divisions produce daughter cells that mature into T cells. Thymic hormones Migrate to thymus Lymphoid stem cells Production and differentiation of T cells Mature T cell
44 T Cells and B Cells Migrate throughout the body To defend peripheral tissues Retaining their ability to divide Is essential to immune system function
45 Differentiation B cells differentiate With exposure to hormone called cytokine (interleukin-7) T cells differentiate With exposure to several thymic hormones
46 Lymphoid Tissues Connective tissues dominated by lymphocytes Lymphoid Nodules Areolar tissue with densely packed lymphocytes Germinal center contains dividing lymphocytes
47 Figure 22-7a Lymphoid Nodules (Part 1 of 2) Intestinal lumen Aggregated lymphoid nodule Underlying connective tissue Aggregated lymphoid nodules in large intestine LM 40 Aggregated lymphoid nodules in section
48 Figure 22-7a Lymphoid Nodules (Part 2 of 2) Intestinal lumen Mucous membrane Germinal center Aggregated lymphoid nodule Underlying connective tissue Aggregated lymphoid nodules in section
49 Figure 22-7b Lymphoid Nodules Pharyngeal epithelium Pharyngeal tonsil Palate Palatine tonsil Lingual tonsil Germinal centers within nodules Pharyngeal tonsil LM 20 The positions of the tonsils and a tonsil in section. Notice the pale germinal centers, where lymphocyte cell divisions occur.
50 Distribution of Lymphoid Nodules Lymph nodes Spleen Respiratory tract (tonsils) Along digestive, urinary, and reproductive tracts
51 Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (MALT) Lymphoid tissues associated with the digestive system Aggregated Lymphoid Nodules Clustered deep to intestinal epithelial lining Appendix (Vermiform Appendix) Contains a mass of fused lymphoid nodules
52 The Five Tonsils In wall of pharynx Left and right palatine tonsils Pharyngeal tonsil (adenoid) Two lingual tonsils
53 Lymphoid Organs Lymph nodes Thymus Spleen Are separated from surrounding tissues by a fibrous connective tissue capsule
54 Lymph Nodes Trabeculae Bundles of collagen fibers Extend from capsule into interior of lymph node Hilum A shallow indentation where blood vessels and nerves reach the lymph node
55 Lymph Nodes Afferent lymphatics Carry lymph From peripheral tissues to lymph node Efferent lymphatics Leave lymph node at hilum Carry lymph to venous circulation
56 Figure 22-8 The Structure of a Lymph Node (Part 1 of 2) Lymph vessel Lymph nodes Efferent vessel Lymph node artery and vein Trabeculae Medulla Cortex Hilum Lymph nodes Medullary sinus Outer cortex (B cells) Subcapsular space Deep cortex (T cells) Capsule Medullary cord (B cells and plasma cells) Afferent vessel
57 Figure 22-8 The Structure of a Lymph Node (Part 2 of 2) Germinal center Outer cortex Subcapsular space Capsule Dividing B cell Dendritic cells Nuclei of B cells Capillary
58 Lymph Flow Flows through lymph node in a network of sinuses From subcapsular space Contains macrophages and dendritic cells Through outer cortex Contains B cells within germinal centers Through deep cortex Dominated by T cells Through the core (medulla) Contains B cells and plasma cells, organized into medullary cords Finally, into hilum and efferent lymphatics
59 Lymph Node Function A filter Purifies lymph before return to venous circulation Removes: Debris Pathogens 99% of antigens
60 Antigen Presentation First step in immune response Extracted antigens are presented to lymphocytes Or attached to dendritic cells to stimulate lymphocytes
61 Lymphatic Functions Lymphoid tissues and lymph nodes Distributed to monitor peripheral infections Respond before infections reach vital organs of trunk Lymph nodes of gut, trachea, lungs, and thoracic duct Protect against pathogens in digestive and respiratory systems
62 Lymph Nodes (Glands) Large lymph nodes at groin and base of neck Swell in response to inflammation Lymphadenopathy Chronic or excessive enlargement of lymph nodes May indicate infections, endocrine disorders, or cancer
63 The Thymus Located in mediastinum Atrophies after puberty Diminishing effectiveness of immune system Divisions of the Thymus Thymus is divided into two thymic lobes Septa divide lobes into smaller lobules
64 A Thymic Lobule Contains a dense outer cortex and a pale central medulla Lymphocytes Divide in the cortex T cells migrate into medulla Mature T cells leave thymus by medullary blood vessels
65 Reticular Epithelial Cells in the Cortex Surround lymphocytes in cortex Maintain blood thymus barrier Secrete thymic hormones that stimulate: Stem cell divisions T cell differentiation
66 Reticular Epithelial Cells in the Medulla Form concentric layers known as thymic (Hassall s) corpuscles The medulla has no blood thymus barrier T cells can enter or leave bloodstream Thymus Hormones Thymosin - an extract from the thymus that promotes development of lymphocytes
67 Figure 22-9a The Thymus Thyroid gland Trachea THYMUS Right lobe Right lung Left lung Left lobe Heart Diaphragm The appearance and position of the thymus in relation to other organs in the chest.
68 Figure 22-9b The Thymus Right lobe Left lobe Septa Lobule Anatomical landmarks on the thymus.
69 Figure 22-9c The Thymus Medulla Septa Cortex Lobule Lobule The thymus gland LM 50 Fibrous septa divide the tissue of the thymus into lobules resembling interconnected lymphoid nodules.
70 Figure 22-9d The Thymus Lymphocytes Thymic corpuscle Reticular cells A thymic corpuscle LM 550 Higher magnification reveals the unusual structure of thymic corpuscles. The small cells are lymphocytes in various stages of development.
71 Three Functions of the Spleen 1. Removal of abnormal blood cells and other blood components by phagocytosis 2. Storage of iron recycled from red blood cells 3. Initiation of immune responses by B cells and T cells In response to antigens in circulating blood
72 Anatomy of the Spleen Attached to stomach by gastrosplenic ligament Contacts diaphragm and left kidney Splenic veins, arteries, and lymphatic vessels Communicate with spleen at hilum
73 Histology of the Spleen Inside fibrous capsule Red pulp contains many red blood cells White pulp resembles lymphoid nodules
74 Trabecular Arteries Branch and radiate toward capsule Finer branches surrounded by white pulp Capillaries discharge red blood cells into red pulp Red Pulp Contains elements of circulating blood Plus fixed and free macrophages
75 Splenic Circulation Blood passes through: Network of reticular fibers Then enters large sinusoids (lined by macrophages) Which empty into trabecular veins
76 Figure 22-10a The Spleen Parietal peritoneum Spleen Rib Pancreas Aorta Liver Visceral peritoneum Stomach Diaphragm Gastrosplenic ligament Gastric area Diaphragmatic surface SPLEEN Hilum Renal area Kidneys
77 Figure 22-10b The Spleen SUPERIOR Gastric area Renal area Hilum Splenic vein Splenic artery Splenic lymphatic vessel INFERIOR A posterior view of the surface of an intact spleen, showing major anatomical landmarks.
78 Figure 22-10c The Spleen White pulp of splenic nodule Capsule Red pulp Trabecular artery The spleen LM 50 Central artery in splenic nodule The histological appearance of the spleen. White pulp is dominated by lymphocytes; it appears purple because the nuclei of lymphocytes stain very darkly. Red pulp contains a large number of red blood cells.
79 Spleen Function Phagocytes and other lymphocytes in spleen Identify and attack damaged and infected cells In circulating blood
The Lymphoid System Pearson Education, Inc.
 23 The Lymphoid System Introduction The lymphoid system consists of: Lymph Lymphatic vessels Lymphoid organs An Overview of the Lymphoid System Lymph consists of: Interstitial fluid Lymphocytes Macrophages
23 The Lymphoid System Introduction The lymphoid system consists of: Lymph Lymphatic vessels Lymphoid organs An Overview of the Lymphoid System Lymph consists of: Interstitial fluid Lymphocytes Macrophages
Overview of the Lymphoid System
 Overview of the Lymphoid System The Lymphoid System Protects us against disease Lymphoid system cells respond to Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells, such as cancers Overview of the Lymphoid
Overview of the Lymphoid System The Lymphoid System Protects us against disease Lymphoid system cells respond to Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells, such as cancers Overview of the Lymphoid
LYMPHATIC ANATOMY LAB. BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D.
 LYMPHATIC ANATOMY LAB BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM ORGANS PRIMARY BONE MARROW THYMUS SECONDARY LYMPH NODES SPLEEN FUNCTIONS CONTROL DISEASE TRANSPORT
LYMPHATIC ANATOMY LAB BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM ORGANS PRIMARY BONE MARROW THYMUS SECONDARY LYMPH NODES SPLEEN FUNCTIONS CONTROL DISEASE TRANSPORT
2/19/2018. Lymphatic System and Lymphoid Organs and Tissues. What is Lymph?
 Lymphatic System and Lymphoid Organs and Tissues Lymphatic system a transport system for tissue fluids 1. elaborate network of one-way drainage vessels returning lymph to systemic circulation 2. Lymph:
Lymphatic System and Lymphoid Organs and Tissues Lymphatic system a transport system for tissue fluids 1. elaborate network of one-way drainage vessels returning lymph to systemic circulation 2. Lymph:
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 20: Immunity and the Lymphatic System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 20: Immunity and the Lymphatic System Question No. 1 of 10 The lymphatic system is formed early during human development. Which of the following statements
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 20: Immunity and the Lymphatic System Question No. 1 of 10 The lymphatic system is formed early during human development. Which of the following statements
Returns fluids that leaked from blood vessels back to blood Consists of three parts
 Lymphatic System Returns fluids that leaked from blood vessels back to blood Consists of three parts 1. Network of lymphatic vessels (lymphatics) 2. Lymph fluid in vessels 3. Lymph cleanse lymph 1 Lymphoid
Lymphatic System Returns fluids that leaked from blood vessels back to blood Consists of three parts 1. Network of lymphatic vessels (lymphatics) 2. Lymph fluid in vessels 3. Lymph cleanse lymph 1 Lymphoid
The Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 21 Part 1 The Lymphatic and Immune Systems The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Lymphatic system Main function
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 21 Part 1 The Lymphatic and Immune Systems The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Lymphatic system Main function
The Lymphatic System
 The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic Systems Overview General Functions Organization Components Lymphatic System General Functions Transportation Excess fluid from capillary exchange Fats & fat soluble vitamins
The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic Systems Overview General Functions Organization Components Lymphatic System General Functions Transportation Excess fluid from capillary exchange Fats & fat soluble vitamins
The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues
 The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues : are the lymph nodes, spleen, Mucosal associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). All secondary lymphoid organs have one
The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues : are the lymph nodes, spleen, Mucosal associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). All secondary lymphoid organs have one
Sinusoids and venous sinuses
 LYMPHOID SYSTEM General aspects Consists of organs that are made of lymphoid tissue; Immune defense Breakdown of red blood cells. 1 Sinusoids In place of capillaries Endothelium; often fenestrated More
LYMPHOID SYSTEM General aspects Consists of organs that are made of lymphoid tissue; Immune defense Breakdown of red blood cells. 1 Sinusoids In place of capillaries Endothelium; often fenestrated More
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 11 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 11 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY Functions of the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system has three primary functions. First of all, it returns excess interstitial
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 11 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY Functions of the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system has three primary functions. First of all, it returns excess interstitial
3/17/2014. The Lymphatic System. Lymphatic System Overview Lymphatic Vessels and Flow of Lymph Lymphoid Cells, Tissues, and Organs
 The Lymphatic System Lymphatic System Overview Lymphatic Vessels and Flow of Lymph Lymphoid Cells, Tissues, and Organs Overview of the Lymphatic System Slide 2 Major Components of the Lymphatic System
The Lymphatic System Lymphatic System Overview Lymphatic Vessels and Flow of Lymph Lymphoid Cells, Tissues, and Organs Overview of the Lymphatic System Slide 2 Major Components of the Lymphatic System
Lymphoid Organs. Dr. Sami Zaqout. Dr. Sami Zaqout IUG Faculty of Medicine
 Lymphoid Organs Dr. Sami Zaqout Cells of the Immune System Lymphocytes Plasma cells Mast cells Neutrophils Eosinophils Cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system Distribution of cells of the immune system
Lymphoid Organs Dr. Sami Zaqout Cells of the Immune System Lymphocytes Plasma cells Mast cells Neutrophils Eosinophils Cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system Distribution of cells of the immune system
Lymphatic System and Immunity. Lymphatic System
 Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Lymphatic System High hydrostatic pressure in the arterioles and capillaries at the arterial part of the circulation leads to move plasma fluid from the capillaries
Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Lymphatic System High hydrostatic pressure in the arterioles and capillaries at the arterial part of the circulation leads to move plasma fluid from the capillaries
Lymphatic System. Where s your immunity idol?
 Lymphatic System Where s your immunity idol? Functions of the Lymphatic System Fluid Balance Drains excess fluid from tissues Lymph contains solutes from plasma Fat Absorption Lymphatic system absorbs
Lymphatic System Where s your immunity idol? Functions of the Lymphatic System Fluid Balance Drains excess fluid from tissues Lymph contains solutes from plasma Fat Absorption Lymphatic system absorbs
Chapter 16 Lymphatic System and Immunity. Lymphatic Pathways. Lymphatic Capillaries. network of vessels that assist in circulating fluids
 Chapter 16 Lymphatic System and Immunity network of vessels that assist in circulating fluids closely associated with the cardiovascular system transports excess fluid away from interstitial spaces transports
Chapter 16 Lymphatic System and Immunity network of vessels that assist in circulating fluids closely associated with the cardiovascular system transports excess fluid away from interstitial spaces transports
Introduction to Lesson 4 - The Lymphatic System
 Introduction to Lesson 4 - The Lymphatic System Your circulatory system is not your body s only vascular transport system. Closely associated with the blood vessels of the circulatory system is the lymphatic
Introduction to Lesson 4 - The Lymphatic System Your circulatory system is not your body s only vascular transport system. Closely associated with the blood vessels of the circulatory system is the lymphatic
Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students
 University of Baghdad College of Nursing Department of Basic Medical Sciences Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Electrolyte and
University of Baghdad College of Nursing Department of Basic Medical Sciences Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Electrolyte and
Chapt 21: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 Chapt 21: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Goals 1. Discuss the organization of the lymphatic system, including the vessels, principal lymph nodes, thymus, and spleen 2. Explain the relationship between
Chapt 21: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Goals 1. Discuss the organization of the lymphatic system, including the vessels, principal lymph nodes, thymus, and spleen 2. Explain the relationship between
Lymphatic System. Chapter 14. Introduction. Main Channels of Lymphatics. Lymphatics. Lymph Tissue. Major Lymphatic Vessels of the Trunk
 Lymphatic System Chapter 14 Components Lymph is the fluid Vessels lymphatics Structures & organs Functions Return tissue fluid to the bloodstream Transport fats from the digestive tract to the bloodstream
Lymphatic System Chapter 14 Components Lymph is the fluid Vessels lymphatics Structures & organs Functions Return tissue fluid to the bloodstream Transport fats from the digestive tract to the bloodstream
2/28/18. Lymphatic System and Immunity. Introduction. Anatomy. Chapter 27. Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system
 Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 1 Introduction Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 1 Introduction Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
- Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body. - Has disease-fighting functions - Helps maintain homeostasis
 Introduction Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
Introduction Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
The Lymphatic System and Immunity
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 14 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 14 Learning Outcomes 14-1 14-2 14-3 14-4 Distinguish between innate
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 14 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 14 Learning Outcomes 14-1 14-2 14-3 14-4 Distinguish between innate
The Lymphatic System
 الكلية االسالمية الجامعة قسم تقنيات التحليالت المرضية االسم التدريسي: ا.د.عبد الهادي صالل المرحلة الثانية المادة : التشريح / النظري 2018-2017 م. م. عباس حسين عبيد The Lymphatic System The lymphatic system
الكلية االسالمية الجامعة قسم تقنيات التحليالت المرضية االسم التدريسي: ا.د.عبد الهادي صالل المرحلة الثانية المادة : التشريح / النظري 2018-2017 م. م. عباس حسين عبيد The Lymphatic System The lymphatic system
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II THE BODY SYSTEMS Anatomy & Physiology II The Body Systems Michelle Cochrane 2014 All rights reserved. This material is subject to copyright and may not be reprinted or reproduced
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II THE BODY SYSTEMS Anatomy & Physiology II The Body Systems Michelle Cochrane 2014 All rights reserved. This material is subject to copyright and may not be reprinted or reproduced
Chapter10 Immune system
 Chapter10 Immune system Lyu Zhengmei Department of Histology and Embryology, Anhui Medical University Ⅰ.General Introduction Function ------ Defense The human body immune system has the ability to distinguish
Chapter10 Immune system Lyu Zhengmei Department of Histology and Embryology, Anhui Medical University Ⅰ.General Introduction Function ------ Defense The human body immune system has the ability to distinguish
8: Lymphatic vessels and lymphoid tissue. nur
 8: Lymphatic vessels and lymphoid tissue nur Lymphatic vascular system Functions return to the blood extracellular fluid (Lymph) from connective tissue spaces. ensures the return of water, electrolytes
8: Lymphatic vessels and lymphoid tissue nur Lymphatic vascular system Functions return to the blood extracellular fluid (Lymph) from connective tissue spaces. ensures the return of water, electrolytes
Chapter 17. The Lymphatic System and Immunity. Copyright 2010, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 17 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Immunity Innate Immunity Fast, non-specific and no memory Barriers, ph extremes, Phagocytes & NK cells, fever, inflammation, complement, interferon Adaptive
Chapter 17 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Immunity Innate Immunity Fast, non-specific and no memory Barriers, ph extremes, Phagocytes & NK cells, fever, inflammation, complement, interferon Adaptive
Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System
 Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System Immune System Composed of many nonspecific and specific defenses Lymphatic System also plays an important role in establishing immunity Lymphatic System Major components
Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System Immune System Composed of many nonspecific and specific defenses Lymphatic System also plays an important role in establishing immunity Lymphatic System Major components
Chapter 14. Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Chapter 14 Lymphatic System and Immunity 1 Introduction A. The lymphatic system is comprised of a network of vessels that transport body fluids, the cells and chemicals in those vessels and the organs
Chapter 14 Lymphatic System and Immunity 1 Introduction A. The lymphatic system is comprised of a network of vessels that transport body fluids, the cells and chemicals in those vessels and the organs
Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 Lymphatic and Immune www.vastaccess.com 2 Specialized component of circulatory system Lymphatic system functions: Maintenance of internal fluid balance Immunity Lymph derived from blood and tissue fluid
Lymphatic and Immune www.vastaccess.com 2 Specialized component of circulatory system Lymphatic system functions: Maintenance of internal fluid balance Immunity Lymph derived from blood and tissue fluid
The Lymphatic System and Immunity. Chapters 20 & 21
 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapters 20 & 21 Objectives 1. SC.912.L.14.52 - Explain the basic functions of the human immune system, including specific and nonspecific immune response, vaccines, and
The Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapters 20 & 21 Objectives 1. SC.912.L.14.52 - Explain the basic functions of the human immune system, including specific and nonspecific immune response, vaccines, and
LYMPHOID ORGANS. Dr. Iram Tassaduq
 LYMPHOID ORGANS Dr. Iram Tassaduq COMPONENTS OF IMMUNE SYSTEM Lymphocytes Diffuse Lymphatic Tissue Lymphatic Nodules Lymph node Spleen Bone marrow Thymus Functions of Immune System Has the ability to distinguish
LYMPHOID ORGANS Dr. Iram Tassaduq COMPONENTS OF IMMUNE SYSTEM Lymphocytes Diffuse Lymphatic Tissue Lymphatic Nodules Lymph node Spleen Bone marrow Thymus Functions of Immune System Has the ability to distinguish
Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Immunity- ability to resist infection and disease through the activation of specific defenses These defenses can be found in the lymphatic system Lymphatic
Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Immunity- ability to resist infection and disease through the activation of specific defenses These defenses can be found in the lymphatic system Lymphatic
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 13 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
1. Lymphatic vessels recover about of the fluid filtered by capillaries. A. ~1% C. ~25% E. ~85% B. ~10% D. ~50%
 BIOL2030 Huaman A&P II -- Exam 3 -- XXXX -- Form A Name: 1. Lymphatic vessels recover about of the fluid filtered by capillaries. A. ~1% C. ~25% E. ~85% B. ~10% D. ~50% 2. Special lymphatic vessels called
BIOL2030 Huaman A&P II -- Exam 3 -- XXXX -- Form A Name: 1. Lymphatic vessels recover about of the fluid filtered by capillaries. A. ~1% C. ~25% E. ~85% B. ~10% D. ~50% 2. Special lymphatic vessels called
Lymph I: The Peripheral Lymph System
 Lymph I: The Peripheral Lymph System Peripheral = Secondary Primary Immune Organs = bone marrow, thymus Site of maturation of cells of the immune system Secondary Immune Organs = Nodes, MALT, spleen Filter
Lymph I: The Peripheral Lymph System Peripheral = Secondary Primary Immune Organs = bone marrow, thymus Site of maturation of cells of the immune system Secondary Immune Organs = Nodes, MALT, spleen Filter
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 7 Lymphatic System & Immune System Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions and Structure of the lymphatic
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 7 Lymphatic System & Immune System Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions and Structure of the lymphatic
The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
 12 PART A The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
12 PART A The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
KEY - Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems - KEY
 KEY - Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems - KEY Note: Not all of the lymphatic system will be on the actual exam next Monday so disregard any questions that deal with something that
KEY - Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems - KEY Note: Not all of the lymphatic system will be on the actual exam next Monday so disregard any questions that deal with something that
LYMPH GLAND. By : Group 1
 LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 The Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems 1 The Lymphatic Vessels Lymphoid Organs Three functions contribute to homeostasis 1. Return excess tissue fluid to the bloodstream 2. Help defend the body against
The Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems 1 The Lymphatic Vessels Lymphoid Organs Three functions contribute to homeostasis 1. Return excess tissue fluid to the bloodstream 2. Help defend the body against
A Rough look at the tonsils and adenoids, for Bonny Peppa!
 A Rough look at the tonsils and adenoids, for Bonny Peppa! tonsils (two oval masses in the back of the throat) Lymphoid organs include: adenoids (two glands located at the back of the nasal passage) appendix
A Rough look at the tonsils and adenoids, for Bonny Peppa! tonsils (two oval masses in the back of the throat) Lymphoid organs include: adenoids (two glands located at the back of the nasal passage) appendix
Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems
 Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems Note: Not all of the lymphatic system will be on the actual exam next Monday so disregard any questions that deal with something that wasn t covered
Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems Note: Not all of the lymphatic system will be on the actual exam next Monday so disregard any questions that deal with something that wasn t covered
BIO 116 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 3 - The Lymphatic, Immune and Digestive Systems This is not a required assignment
 BIO 116 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 3 - The Lymphatic, Immune and Digestive Systems This is not a required assignment 1. Which are components of the lymphatic system? a: Thyroid gland b:
BIO 116 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 3 - The Lymphatic, Immune and Digestive Systems This is not a required assignment 1. Which are components of the lymphatic system? a: Thyroid gland b:
Anatomy. Lymph: Tissue fluid that enters a lymphatic capillary (clear fluid that surrounds new piercings!)
 Lymphatic System Anatomy Lymphatic vessels: meet up in capillaries of of tissues to collect extra water, and have an end point of meeting up with lymphatic ducts that empty fluid into large veins in the
Lymphatic System Anatomy Lymphatic vessels: meet up in capillaries of of tissues to collect extra water, and have an end point of meeting up with lymphatic ducts that empty fluid into large veins in the
Equine biological systems
 Equine biological systems Pack 20 The lymphatic system Pack Code: EBS20 This pack will help you to: List the functions of the lymphatic system. Describe the components of the lymphatic system.. www.lbcnc.org.uk
Equine biological systems Pack 20 The lymphatic system Pack Code: EBS20 This pack will help you to: List the functions of the lymphatic system. Describe the components of the lymphatic system.. www.lbcnc.org.uk
Lymphatic Vessels & Lymph lymphatic vessels. 20 The Lymphatic System. They can't all be superstars! The Lymphatic System. Keeps us healthy!
 They can't all be superstars! The Lymphatic System Lymphatic System: 1. lymphatic vessels 2. lymph 3. irculation, P, Supports immune & clotting, etc... cardiovascular system! Lymphoid Organs & Tissues:
They can't all be superstars! The Lymphatic System Lymphatic System: 1. lymphatic vessels 2. lymph 3. irculation, P, Supports immune & clotting, etc... cardiovascular system! Lymphoid Organs & Tissues:
LYMPHATIC SYSTEM LAB WORKSHEET
 NAME: Pd 4 DATE: LYMPHATIC SYSTEM LAB WORKSHEET ACTIVITY 1: Answer the following questions 1. What is lymph? What is the normal composition of lymph? How does the composition of lymph differs from that
NAME: Pd 4 DATE: LYMPHATIC SYSTEM LAB WORKSHEET ACTIVITY 1: Answer the following questions 1. What is lymph? What is the normal composition of lymph? How does the composition of lymph differs from that
Cardiovascular & lymphatic system both are supply fluid flow in to the body. but bothe are deferent type of fluid..
 Hap unit 6th Introduction:- All body tissues are bathed in tissue fluid, consisting of the diffusible constituent of blood & waste material from cell. Some tissue fluid returnes to capillaries at their
Hap unit 6th Introduction:- All body tissues are bathed in tissue fluid, consisting of the diffusible constituent of blood & waste material from cell. Some tissue fluid returnes to capillaries at their
CHAPTER VI PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY. Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer.
 CHAPTER VI PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. Lymphatic System: Lymphatic System which consists of vessels and organs plays two vital roles in our lives: 1) The vessels
CHAPTER VI PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. Lymphatic System: Lymphatic System which consists of vessels and organs plays two vital roles in our lives: 1) The vessels
PBS Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs , 27-30
 PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
Portal System & Lymphatic System. When the vein of any organ of the body does not open in the caval vein or heart.
 1. Introduction of portal system 2. Renal portal system 3. Hepatic portal system 4. Hypophysial portal system 5. Introduction of lymphatic system 6. The lymph 7. Lymph vessels 8. Lymph nodes 9. Lymphoid
1. Introduction of portal system 2. Renal portal system 3. Hepatic portal system 4. Hypophysial portal system 5. Introduction of lymphatic system 6. The lymph 7. Lymph vessels 8. Lymph nodes 9. Lymphoid
Cardiovascular system:
 Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
Lymphatic System. Organs, vessels and a fluid called lymph. Organs and structures involved. similar to interstitial fluid
 Lymphatic System Organs, vessels and a fluid called lymph similar to interstitial fluid Organs and structures involved red bone marrow thymus spleen lymph nodes diffuse lymphatic tissue tonsils, adenoids
Lymphatic System Organs, vessels and a fluid called lymph similar to interstitial fluid Organs and structures involved red bone marrow thymus spleen lymph nodes diffuse lymphatic tissue tonsils, adenoids
Lymphatic System. The most important functions of the lymphatic system are: Maintenance of fluid balance in the internal environment
 Lymphatic System Lymphatic System The lymphatic system is a complex network of connective tissue that is composed of: Lymphoid organs Lymph nodes Lymph ducts Lymph vessels Lymph capillaries Lymphatic System
Lymphatic System Lymphatic System The lymphatic system is a complex network of connective tissue that is composed of: Lymphoid organs Lymph nodes Lymph ducts Lymph vessels Lymph capillaries Lymphatic System
CHAPTER 16: LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY OBJECTIVES. Transport dietary fat. Transport excess tissue fluid back to blood stream
 CHAPTER 16: LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY OBJECTIVES 1. Name the organs that compose the lymphatic system and give three general functions performed by this system. Bone Marrow Control Disease Thymus Lymph
CHAPTER 16: LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY OBJECTIVES 1. Name the organs that compose the lymphatic system and give three general functions performed by this system. Bone Marrow Control Disease Thymus Lymph
Return tissue fluid to the bloodstream (fluid balance) Immunity. Transport fats from the digestive tract to the bloodstream
 Lymphatic System L Y M P H A T I C C O M P O N E N T S What is a Lymphatic System? The lymphatic system is a complex system of fluid drainage and transport, immune response, and disease resistance. Fluid
Lymphatic System L Y M P H A T I C C O M P O N E N T S What is a Lymphatic System? The lymphatic system is a complex system of fluid drainage and transport, immune response, and disease resistance. Fluid
CIRCULATORY SYSTEMS. Has a pump (heart)
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEMS Cardiovascular Derived from mesoderm Transport System Has a pump (heart) Arteries Veins for return Veins have valves Carries RC, WBC, plasma Lymphatic Derived from mesoderm Transport
CIRCULATORY SYSTEMS Cardiovascular Derived from mesoderm Transport System Has a pump (heart) Arteries Veins for return Veins have valves Carries RC, WBC, plasma Lymphatic Derived from mesoderm Transport
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 28 The Immune System Lesson 1: The Immune System Lesson Objectives Upon completion of this lesson,
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 28 The Immune System Lesson 1: The Immune System Lesson Objectives Upon completion of this lesson,
Ch. 22 The Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Ch. 22 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Above: macrophage (gray), T lymphocyte (pink), and bacteria (orange) The lymphatic system General functions: It acts with other organ systems to help provide immunity
Ch. 22 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Above: macrophage (gray), T lymphocyte (pink), and bacteria (orange) The lymphatic system General functions: It acts with other organ systems to help provide immunity
The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses Slides 12.1 12.22 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Lymphatic
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses Slides 12.1 12.22 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Lymphatic
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 11 AND 12
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 11 AND 12 Name Identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label. 2) The sinoatrial (SA) node is indicated by letter. 3) The specific chamber
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 11 AND 12 Name Identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label. 2) The sinoatrial (SA) node is indicated by letter. 3) The specific chamber
Clinical Lymphatic System
 Quiz Description Clinical Lymphatic System Q.1) Q.2) The right lymphatic duct and the thoracic duct empty into the jugular vein inferior vena cava portal vein subclavian veins Lymph from the right arm
Quiz Description Clinical Lymphatic System Q.1) Q.2) The right lymphatic duct and the thoracic duct empty into the jugular vein inferior vena cava portal vein subclavian veins Lymph from the right arm
Cardiovascular System. Chapters 11, 12
 Cardiovascular System Chapters 11, 12 Oxygen enters the cardiovascular system by diffusing from alveoli into blood cells in the capillaries, then binding to hemoglobin in red blood cells. Blood Hematology-
Cardiovascular System Chapters 11, 12 Oxygen enters the cardiovascular system by diffusing from alveoli into blood cells in the capillaries, then binding to hemoglobin in red blood cells. Blood Hematology-
Immune - lymphatic system
 Immune system - organisation: Immune - lymphatic system - histology & embryology organised lymphoid structures cell components lymphocytes event. lymphatic follicles accessory cells monocytes-macrophages
Immune system - organisation: Immune - lymphatic system - histology & embryology organised lymphoid structures cell components lymphocytes event. lymphatic follicles accessory cells monocytes-macrophages
Mediastinum and pericardium
 Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
When an ordinary man attains knowledge, he becomes a sage. When a sage attains knowledge, he becomes an ordinary man. -Zen saying.
 When an ordinary man attains knowledge, he becomes a sage. When a sage attains knowledge, he becomes an ordinary man. -Zen saying Lymphatic System Lesson Plan: Lymphatic System 5 minutes: Breath of Arrival
When an ordinary man attains knowledge, he becomes a sage. When a sage attains knowledge, he becomes an ordinary man. -Zen saying Lymphatic System Lesson Plan: Lymphatic System 5 minutes: Breath of Arrival
Lymphatic vessels purpose arterial side of the capillaries lose more fluid then venous end reabsorbs
 Chapter 22 The Lymphatic System and Immunity composed of 1. lymphatic vessels 2. specialized cells called lymphocytes 2. numerous lymphoid tissues and organs function of the lymphatic system 1. production,
Chapter 22 The Lymphatic System and Immunity composed of 1. lymphatic vessels 2. specialized cells called lymphocytes 2. numerous lymphoid tissues and organs function of the lymphatic system 1. production,
Chapter 22. The Lymphatic System. AP2 Chapter 22 1
 Chapter 22 The Lymphatic System AP2 Chapter 22 1 Chapter 22 Outline I. Lymphatic System II. Immunity III. Innate Immunity IV. Adaptive Immunity V. Immune Interactions VI. Immunotherapy VII. Acquired Immunity
Chapter 22 The Lymphatic System AP2 Chapter 22 1 Chapter 22 Outline I. Lymphatic System II. Immunity III. Innate Immunity IV. Adaptive Immunity V. Immune Interactions VI. Immunotherapy VII. Acquired Immunity
10. Figure 22.3 C. Lymphatic Tissue and Organs: 1. Lymphatic organs contain lymphatic tissue which consists primarily of lymphocytes, but also include
 Chapter 22 Lymphatic Systems & Immunity I. Lymphatic System: a) includes lymph, lymphatic vessels, lymphatic tissue, lymphatic nodes, tonsils, the spleen, and the thymus. A. Functions of the Lymphatic
Chapter 22 Lymphatic Systems & Immunity I. Lymphatic System: a) includes lymph, lymphatic vessels, lymphatic tissue, lymphatic nodes, tonsils, the spleen, and the thymus. A. Functions of the Lymphatic
Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University. Systematic Anatomy
 Systematic Anatomy Department of Anatomy,Histology & Embryology Shanghai Medical College,Fudan University Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: Zhanghq58@126.com Office: Building 9,Room308, 54237151-9308 Mobile:13761809799
Systematic Anatomy Department of Anatomy,Histology & Embryology Shanghai Medical College,Fudan University Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: Zhanghq58@126.com Office: Building 9,Room308, 54237151-9308 Mobile:13761809799
LYMPHATIC AND IMMUNE SYSTEMS. Chapter 33
 LYMPHATIC AND IMMUNE SYSTEMS Chapter 33 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM The lymphatic system has three main functions Take up excess tissue fluid and return it to the bloodstream Receive fats called lipoproteins
LYMPHATIC AND IMMUNE SYSTEMS Chapter 33 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM The lymphatic system has three main functions Take up excess tissue fluid and return it to the bloodstream Receive fats called lipoproteins
Lymphatic System & Immunity
 Lymphatic System & Immunity Arteriole Venule Tissue Blood Lymph cells capilla capillaries ries Lymphatic System -closely related to cardiovascular system -conducting system that carries fluid from extracellular
Lymphatic System & Immunity Arteriole Venule Tissue Blood Lymph cells capilla capillaries ries Lymphatic System -closely related to cardiovascular system -conducting system that carries fluid from extracellular
Chapter 12- The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
 Chapter 12- The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses I. The Lymphatic System a. Consists of two semi-independent parts i. Lymphatic vessels and Lymphoid tissues and organs b. Lymphatic system functions i.
Chapter 12- The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses I. The Lymphatic System a. Consists of two semi-independent parts i. Lymphatic vessels and Lymphoid tissues and organs b. Lymphatic system functions i.
The Lymphatic System. General Functions of Lymphatic System:
 The Lymphatic System network of tissues, organs and vessels that help to maintain the body s fluid balance & protect it from pathogens lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils, etc without
The Lymphatic System network of tissues, organs and vessels that help to maintain the body s fluid balance & protect it from pathogens lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils, etc without
Anatomy & Physiology Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Anatomy & Physiology Lymphatic System and Immunity BELL WORK: DEFINE THE TERMS USING YOUR NEW BOOKS (PAGES 335-336): LYMPHOCYTE PHAGOCYTE PATHOGEN A NTIGEN A NTIBODIES A&P State Standards 33) Describe
Anatomy & Physiology Lymphatic System and Immunity BELL WORK: DEFINE THE TERMS USING YOUR NEW BOOKS (PAGES 335-336): LYMPHOCYTE PHAGOCYTE PATHOGEN A NTIGEN A NTIBODIES A&P State Standards 33) Describe
Lymphatic System and Immune System. Blood capillaries. Lymphatic vessels/ lymph nodes. Then, identify by labeling these specific structures in part B.
 Name: Date: Period: Lymphatic System and Immune System 1. Figure 21.1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. In part A the relationship between lymphatic vessels and the blood vessels of the cardiovascular
Name: Date: Period: Lymphatic System and Immune System 1. Figure 21.1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. In part A the relationship between lymphatic vessels and the blood vessels of the cardiovascular
Lymphatic System. Where s your immunity idol?
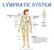 Lymphatic System Where s your immunity idol? Lymph Parts of the Lymphatic Lymphatic Vessels Lymphatic Tissue Lymphatic Organs System Functions of the Lymphatic Fluid Balance System Drains excess fluid
Lymphatic System Where s your immunity idol? Lymph Parts of the Lymphatic Lymphatic Vessels Lymphatic Tissue Lymphatic Organs System Functions of the Lymphatic Fluid Balance System Drains excess fluid
You see it every rainy day water, water everywhere, rushing along gutters and down
 Chapter 11 Keeping Up Your Defenses: The Lymphatic System In This Chapter Delving into lymphatic ducts Noodling around with nodes Exploring the lymphatic organs You see it every rainy day water, water
Chapter 11 Keeping Up Your Defenses: The Lymphatic System In This Chapter Delving into lymphatic ducts Noodling around with nodes Exploring the lymphatic organs You see it every rainy day water, water
The Spleen. Dr Fahad Ullah
 The Spleen BY Dr Fahad Ullah Spleen The spleen is an largest lymphoid organ shaped like a shoe that lies relative to the 9th and 11th ribs and is located in the left hypochondrium. Thus, the spleen is
The Spleen BY Dr Fahad Ullah Spleen The spleen is an largest lymphoid organ shaped like a shoe that lies relative to the 9th and 11th ribs and is located in the left hypochondrium. Thus, the spleen is
Organ Systems (ch21-26) Practice Questions. Name:
 1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
Bio& 242, Unit 3/ Lab 4 Blood Vessels, Lymphatic System and Blood Pressure G. Blevins/ G. Brady Summer 2009
 Bio& 242, Unit 3/ Lab 4 Blood Vessels, Lymphatic System and Blood Pressure G. Blevins/ G. Brady Summer 2009 Major Arteries and for arteries and veins with common names your answer must include either artery
Bio& 242, Unit 3/ Lab 4 Blood Vessels, Lymphatic System and Blood Pressure G. Blevins/ G. Brady Summer 2009 Major Arteries and for arteries and veins with common names your answer must include either artery
OBJECTIVES. The Amazing Immune System
 The Amazing Immune System Graphic source: (l) Jeanne Kelly, NIAID; (r) Wikimedia Commons OBJECTIVES Describe at least three components of the immune system Describe the role in our immune response of at
The Amazing Immune System Graphic source: (l) Jeanne Kelly, NIAID; (r) Wikimedia Commons OBJECTIVES Describe at least three components of the immune system Describe the role in our immune response of at
Lab Activity 25. Blood Vessels & Circulation. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 25 Blood Vessels & Circulation Portland Community College BI 232 Artery and Vein Histology Walls have 3 layers: Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa 2 Tunica Intima Is the innermost layer
Lab Activity 25 Blood Vessels & Circulation Portland Community College BI 232 Artery and Vein Histology Walls have 3 layers: Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa 2 Tunica Intima Is the innermost layer
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Arteries Arteries Arteries
 CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
Flow Cytometry. Hanan Jafar (2017)
 1 Flow Cytometry Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology to analyze the characteristics of cells or particles. It is predominantly used to measure fluorescence intensity produced by fluorescent-labeled
1 Flow Cytometry Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology to analyze the characteristics of cells or particles. It is predominantly used to measure fluorescence intensity produced by fluorescent-labeled
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
5 Lymphatic System. Chapter
 67 Chapter 5 Lymphatic System Overview -The lymphatic system consists of the following components (Figure 5.1, Derrickson): (i) lymphatic vessels, which contain a fluid called lymph, (ii) lymphatic organs,
67 Chapter 5 Lymphatic System Overview -The lymphatic system consists of the following components (Figure 5.1, Derrickson): (i) lymphatic vessels, which contain a fluid called lymph, (ii) lymphatic organs,
The Urinary System Pearson Education, Inc.
 26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
HUMAN HEART. Learn the following structures on the heart models.
 HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
The Lymphatic System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Lymphatic System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Lymphatic System Lymphatic capillaries reabsorb excessive tissue fluid and transport the fluid through the lymphatic pathway, and ultimately dispose
The Lymphatic System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Lymphatic System Lymphatic capillaries reabsorb excessive tissue fluid and transport the fluid through the lymphatic pathway, and ultimately dispose
GENERAL ANATOMY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
 GENERAL ANATOMY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM 1 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM - A SYSTEM WHICH CONTROLS PRESERVE GENETIC INTEGRITY OF THE ORGANISM. BODILY FUNCTIONS PROTECTION OF ANTIGENS CALLED IMMUNITY (FROM THE LATIN WORD
GENERAL ANATOMY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM 1 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM - A SYSTEM WHICH CONTROLS PRESERVE GENETIC INTEGRITY OF THE ORGANISM. BODILY FUNCTIONS PROTECTION OF ANTIGENS CALLED IMMUNITY (FROM THE LATIN WORD
Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N
 Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N 2015 Welcome to the Anatomy Workbook. This directed learning has been developed to prepare you for lectures designed to study
Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N 2015 Welcome to the Anatomy Workbook. This directed learning has been developed to prepare you for lectures designed to study
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures. The Large Arteries. The Aorta. Ascending aorta
 Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
The Lymphatic System
 94 The Lymphatic System Lymph Lymph is the name for tissue fluid that enters lymph capillaries. Filtration in capillaries creates tissue fluid, most of which returns almost immediately to the blood in
94 The Lymphatic System Lymph Lymph is the name for tissue fluid that enters lymph capillaries. Filtration in capillaries creates tissue fluid, most of which returns almost immediately to the blood in
Chapter 2 (pages 22 33): Cells and Tissues of the Immune System. Prepared by Kristen Dazy, MD, Scripps Clinic Medical Group
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS; Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD; and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 2 (pages 22 33): Cells and
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS; Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD; and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 2 (pages 22 33): Cells and
What are bacteria? Microbes are microscopic(bacteria, viruses, prions, & some fungi etc.) How do the sizes of our cells, bacteria and viruses compare?
 7.1 Microbes, pathogens and you Chp. 7 Lymphatic System & Immunity The interaction between microbes and humans? Microbes are very abundant in the environment and as well as in and on our bodies GOOD: We
7.1 Microbes, pathogens and you Chp. 7 Lymphatic System & Immunity The interaction between microbes and humans? Microbes are very abundant in the environment and as well as in and on our bodies GOOD: We
Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System And Body Defenses Key
 Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System And Body Defenses Key CHAPTER 12 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND BODY DEFENSES KEY PDF - Are you looking for chapter 12 the lymphatic system and body defenses key Books? Now, you
Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System And Body Defenses Key CHAPTER 12 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND BODY DEFENSES KEY PDF - Are you looking for chapter 12 the lymphatic system and body defenses key Books? Now, you
NOTES: CH 43, part 1 The Immune System - Nonspecific & Specific Defenses ( )
 NOTES: CH 43, part 1 The Immune System - Nonspecific & Specific Defenses (43.1-43.2) The lymphatic system is closely associated with the cardiovascular system. LYMPHATIC PATHWAYS Lymphatic capillaries
NOTES: CH 43, part 1 The Immune System - Nonspecific & Specific Defenses (43.1-43.2) The lymphatic system is closely associated with the cardiovascular system. LYMPHATIC PATHWAYS Lymphatic capillaries
