Supplementary Information. Supplementary Figure 1
|
|
|
- Branden Bryan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 1
2 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional assay of the hcas9-2a-mcherry construct (a) Gene correction of a mutant EGFP reporter cell line mediated by hcas9 or hcas9-2a-mcherry gene targeting. Schematic representation of the EGFP gene correction by Cas9-mediated homologous recombination (HR). The mutant EGFP gene harbors an insertion of a 35bp fragment containing a translational stop codon. The repair donor (tgfp) has a 5 truncated EGFP coding sequence. A guided RNA (grna-s35 or gs35) was designed to target the 35bp insertion. For EGFP gene correction, gs35 and tgfp were co-transfected with hcas9 or its derivative hcas9-mcherry into a mutated EGFP integrated cell line. Once the HR-mediated repair occurs, the expression of the EGFP can be detected. The upper right figure shows fluorescence microscopy of the mutant EGFP reporter cells at 4 days after transfection. Inset shows that no GFP+ cells are observed under fluorescence microscopy in the absence of hcas9. Lower panels: FACS analysis of the efficiency of hcas9 and hcas9-2a-mcherry mediated EGFP gene correction in mutated EGFP HEK293 cell line. hcas9-2a-mcherry shows similar efficiency of EGFP gene correction as wild-type hcas9. We used this hcas9-2a-mcherry (also named hcas9-mcherry) in the majority of the subsequent experiments in order to evaluate the efficiency of transfection. (b,c) No significant reduction of virus expression in control experiments with only grna but not hcas9 supplementary to Fig. 1b,c. (b) Fluorescence microscopy images of EGFP reporter lentivirus expression with only individual grnas used, which were the same as those shown in Figure 1. Insets show bright field images of HEK293 cells. (c) The bar graph represents the average of MFI (mean fluorescence intensity) from triplicates of Supplementary Fig. 1b. (d-i) HEK293A cells were pretreated with hcas9-mcherry and grnas for 20~24 hours, and then were challenged by either lentivirus (d,f,h) for 4 days or foreign plasmid (e,g,i) for 2 days with EGFP reporter. (d,e) Fluorescence microscopy images of EGFP reporter expression from lentivirus (d) or foreign plasmid (e) with only individual grnas used, which were the same as those shown in Figure 1. Insets show bright field images of HEK293 cells. (f,g) Decreased EGFP expressions of infected lentivirus (f) or foreign plasmid (g) were measured by flow-cytometric analysis. The bar graph represents the average of MFI (mean fluorescence intensity) from triplicates. (h,i) Confocal images represent the reduction of EGFP expression from lentivirus (h) or foreign plasmid (i) by gmock and gegfp-t1 guided hcas9-mcherry. GFP expression of EGFP reporter (left lane), RFP expression of hcas9-mcherry (middle lane) and overlapped image with nucleic DAPI staining (right lane) were shown with scale bar as 50 microns. 2
3 Supplementary Figure 2 3
4 Supplementary Figure 2. Specificity of the CRISPR/Cas9 mediated disruption or excision of infectious lentivirus or pre-integrated proviruses The CRISPR/Cas9 system can direct targeted disruption of infectious or pre-integrated lentiviruses with targeting specificity. (a,b) Antiviral specificity of the CRISPR/Cas9 system directed disruption of infectious lentivirus. Multiple grnas can independently disrupt two types of lentivirus, which shared the same LTR sequences but different fluorescence reporter genes. When working together with hcas9, each grna specifically targets its cognate region. (a) Expression of Lenti-EGFP can be inhibited by the grna targeting EGFP (gegfp-t1 and gegfp-t2) and the common LTR regions (gltr-t1 and gltr-t2), but not the negative controls (gempty and gmock) or mcherry (gmcherry-t1 and gmcherry-t2). (b) Expression of Lenti-mCherry can be inhibited by the grna targeting mcherry and common LTR regions but not the other sequences. Scale bar in fluorescent microscopy images: 500 microns. (c,d) Multiple grnas can independently disrupt or excise two types of fluorescent provirus from integrated HEK293 cells. The copy numbers of EGFP and mcherry provirus cell lines are shown in Fig. 2b. The high copy number EGFP integrated line was used in this experiment. When working together with hcas9 protein, each grna specifically targets its cognate region but not nonspecific sequences. (c) Expression of the EGFP provirus can be disrupted by hcas9 co-transfected with the grna targeting EGFP (gegfp-t1 and gegfp-t2) and common LTR regions (gltr-t1 and gltr-t2), but not the negative controls (gempty and gmock) or mcherry (gmcherry-t1 and gmcherry-t2). (d) Expression of mcherry provirus can be inhibited by the grna targeting mcherry and common LTR regions but not the others. Scale bar in fluorescent microscopy images: 200 microns. 4
5 Supplementary Figure 3 Supplementary Figure 3. CRISPR/Cas9 directed reduction of HIV-1 provirus in latently infected T cell lines and disruption against lentiviral infection by stable expression of hcas9/grnas in human cells (a) FACS analysis of EGFP expression from two types of J-Lat lentivirus T cell lines. Treatment with grna against HIV-1 LTR-U3-T1 and hcas9 resulted in a 6~7 fold increase of the GFP negative population in A2 and 10.6 J-Lat cells after reactivation by PMA + TNF-α. (b) DNA sequencing analysis of the disruption of the EGFP reporter virus from the provirus integration sites. The indel mutations and proviral excisions were only detected from the cells treated with gu3-t1 but not other controls. 5
6 (c-g) The CRISPR/Cas9 system stably expresses in HEK293 cells by piggybac-mediated transposon integration to perform antiviral activity. (c) hcas9-mcherry and grnas were cloned into piggybac transposon elements with a puromycin selection marker. The coding sequence of hcas9 is linked to mcherry and puromycin by 2A sequences and the expression is driven by the CMV promoter. The single or double grna expression cassettes are driven by the U6 promoter and put in the opposite orientation to that of hcas9. PB-ITR: piggybac inverted terminal repeat sequence. (d) Schematic illustration of the experimental design. Stable expression of hcas9-mcherry-grna HEK293 cells was established by co-transfection of PB-hCas9-mCherry-gRNA with PiggyBac transposase for 24 hours. After puromycin selection for two weeks, mcherry positive cells were split into two groups, some underwent single cell sorting by flow cytometry and others were unsorted. Then the cells were challenged by lenti-egfp for 4 days. The efficiency of targeted disruption was analyzed by fluorescent microscopy or determined by FACS. (e) Fluorescence microscopy images of unsorted cells with knock-in hcas9-mcherry and grnas for targeted disruption of infected lentivirus. Insets: bright field images of transduced 293A-hCas9-gRNA cells. Scale bars, 200 microns. (f,g) Decreased expressions of EGFP lentivirus from hcas9-mcherry-grna 293 cells were measured by FACS analysis. (f) Overlay histograms depicting gempty as non-targeting control in the first panel. Numbers in each panel represent the percentage of GFP-positive cells. (g) FACS analysis of EGFP expression by different type of knock-in hcas9-tandem grnas. The EGFP expressions from the treatment of hcas9-gegfp-t1 were further decreased by combination with either EGFP coding region grna (gegfp-t1-gegfp-t3) or non-coding region gltr-t2 (gegfp-t1-gltr-t2), but not with the gegfp-t1-gmock. Overlay histogram depicts gempty as non-targeting control in the first panel. Numbers in each panel represent the percentage of GFP-positive cells. 6
7 Supplementary Figure 4 7
8 Supplementary Figure 4. Cas9 and dcas9-krab establishes intracellular defense against retrovirus, adenovirus and HIV-1 in human cells (a-d) Retroviruses can cause tumor growth (ex. Rous sarcoma virus). In order to test whether the CRISPR/Cas9 system can function against viruses other than lentiviruses, we examined the antiviral activity of the CRISPR/Cas9 system against retroviral infections. (a) Eight grnas were designed and used with hcas9 to target corresponding regions on the EGFP retroviral reporter, including gegfp-t1 to -T6 against coding region of EGFP, and gretro-ltr-t1 and -T2 to target the long-terminal repeat (LTR) region of the retrovirus. (b) Schematic illustration showing the design of the experiment. HEK293 cells were pretreated with hcas9-mcherry and grnas for 20~24 hours, and then challenged by retroviruses with the EGFP reporter. FACS analysis was implemented 4 days after infection of EGFP retrovirus. (c) Fluorescence microscopy images of transduced 293 cells containing grnas to guide hcas9-mcherry to target and disrupt infected retrovirus. gempty is used as the empty target grna vector and gmock is used as a non-targeting mock grna. Six grnas were designed to target against the EGFP coding region, two grnas against retrovirus LTR, and the other two grnas against HIV-1 lentivirus LTR, but not the retrovirus LTR as the control. Inset shows bright field images of transduced HEK293 cells. Scale bar, 500 microns. (d,e) Decreased infected EGFP retroviral expressions were measured by FACS analysis. (d) Overlay histogram depicts gempty as a non-targeting control in the first panel. The dashed blue line in the first panel indicates the untreated HEK293 cells. Numbers in each panel represent the percentage of GFP-positive cells. (e) The bar graph represents the average of MFI from triplicates. (f-j) Adenoviruses are non-enveloped viruses composed of a nucleocapsid and a double-stranded linear DNA viral genome. Adenovirus infections most commonly can cause illness in the respiratory system. In order to examine the antiviral efficiency of CRISPR/Cas9 against this DNA virus, helper-dependent adenovirus 35 (HdAd35) was used as a model. (f) Five grnas were designed and used with hcas9 to target corresponding regions on the HdAd35 with Venus reporter, including gvenus-t1 to -T5 against the coding region of Venus coding sequence on HdAd35. (g) Schematic illustration showing the design of the experiment. HEK293 cells were pretreated with hcas9-mcherry and grnas for 20~24 hours, and then challenged by HdAd35 with Venus reporter. FACS analysis was implemented 2 days after infection of HdAd35-Venus. (h) Fluorescence microscopy images of transduced 293 cells containing grnas used to guide hcas9-mcherry to target and disrupt infected HdAd35. Five grnas were designed to target against the Venus coding region. Insets: bright field images of transduced HEK293 cells. Scale bar, 500 microns. (i,j) Decreased infected Venus expressions from HdAd35 were measured by 8
9 FACS analysis. (i) Overlay histogram depicts gempty as a non-targeting control in the first panel. Dashed blue line: untreated HEK293 cells. Numbers in each panel represent the percentage of Venus-positive cells. (j) The bar graph represents the average of MFI from triplicates. (k-m) Inactivated form of Cas9 fused with a transcriptional repressor, KRAB (dcas9-krab) can repress HIV-1 expression in 293T.CD4.CCR5 cells. (k) A model of repression of HIV-1 expression by dcas9-krab. (l,m) Decreased EGFP expressions of pseudo-type VSV.G-HIV-1 NL4-3- E-GFP (l) and wild-type HIV-1 NL43-GFP (m) reporter viruses were measured by FACS analysis. 9
10 Supplementary Figure 5 Supplementary Figure 5. Full western blot images (a) Full western blot of the selected portion shown in Figure 3e. (b) Full western blot of the selected portion shown in Figure 4d. 10
11 Supplementary Table 1: grna against fluorescent reporter sequence Number Name Target Sequence 1 gegfp-t1 GTCGCCACCATGGTGAGCAAGGG 2 gegfp-t2 GAGCTGGACGGCGACGTAAACGG 3 gegfp-t3 GGCGAGGGCGATGCCACCTACGG 4 gegfp-t4 GGAGCGCACCATCTTCTTCAAGG 5 gegfp-t5 GGGCGAGGAGCTGTTCACCGGGG 6 gegfp-t6 GGCCACAAGTTCAGCGTGTCCGG 7 gs35 (gmock) GCGCGAAGCTTAGGGATAACAGG 8 gmch-t1 GCCCTTCACCATGGTGAGCAAGG 9 gmch-t2 GGCCACGAGTTCGAGATCGAGGG 10 gretro-ltr-t1 GCAGTTCCTGCCCCGGCTCAGGG 11 gretro-ltr-t2 GAGCCCACAACCCCTCACTCGGG 12 gvenus-t1 GGGCGAGGAGCTGTTCACCGGGG 13 gvenus-t2 GTCGCCACCATGGTGAGCAAGGG 14 gvenus-t3 GAGCTGGACGGCGACGTAAACGG 15 gvenus-t4 GGCGAGGGCGATGCCACCTACGG 16 gvenus-t5 GGAGCGCACCATCTTCTTCAAGG
12 Supplementary Table 2: grna against HIV genome sequence Number Name Position* Target Sequence (inclulding PAM) 1 gu3-t1 78 GATTGGCAGAACTACACACCAGG 2 gu3-t2 221 GCATGGGATGGAGGACCCGGAGG 3 gu3-t3 380 GTGTGGCCTGGGCGGGACTGGGG 4 gltr-t1 (R region) 464 GGTTAGACCAGATCTGAGCCTGG 5 gltr-t2 (R region) 485 GGGAGCTCTCTGGCTAACTAGGG 6 gu5-t1 562 GCCCGTCTGTTGTGTGACTCTGG 7 gltr-t3 (U5 region) 627 GATTTTCCACACTGACTAAAAGG 8 gp17-t1 798 GAGAGCGTCGGTATTAAGCGGGG 9 gp17-t2 952 GAAGGCTGTAGACAAATACTGGG 10 gp24-t GGTAAAAGTAGTAGAAGAGAAGG 11 gp24-t GGCCAGATGAGAGAACCAAGGGG 12 gp24-t GAAATGATGACAGCATGTCAGGG 13 gpol-t GATGGAAACCAAAAATGATAGGG 14 gpol-t GAGACAACATCTGTTGAGGTGGG 15 gpol-t GTGATAAATGTCAGCTAAAAGGG 16 gvif-t GGAGAAAGAGACTGGCATTTGGG 17 gvif-t GGTAGGATCTCTACAGTACTTGG 18 genv-t GTATCAGCACTTGTGGAGATGGG 19 genv-t GTGGGTCACAGTCTATTATGGGG 20 genv-t GCACAGTTTTAATTGTGGAGGGG 21 grev-t GACCCACCTCCCAATCCCGAGGG 22 grev-t GTGGAACTTCTGGGACGCAGGGG *The position is based on the sequence number of HIV-NL4-3
13 Supplementary Table 3: Off-target analysis of CRISPR-gRNA against HIV-LTR in human stable cell lines Top 5 exonic off-target sites to gltr-t1 (GGTTAGACCAGATCTGAGCC TGG) Off-target ratio* Sequence Mismatches UCSC gene Locus Gene Forward primer Reverse primer HEK GGTAAGACCAGATCTGAGGGAGG 3MMs [4:19:20] NM_ chr1: KLHL12 ctgctccacttcaaaaagctc tgggcatgaggatttaccac 0/12 2 GGTTACACCAGAACGGAGCCAGG 3MMs [6:13:15] NM_ chr10: TLL2 agctttggggatgacagtga gggccacattggaagaaga 0/12 3 GGTTAGAGCAGTTCTGGGCCGGG 3MMs [8:12:17] NM_ chr12: ITGA7 tggggagagggctagaaaga gggaggggacatccagagta 0/11 4 TGGTAGACCACATCTGAGGCTAG 4MMs [1:3:11:19] NM_ chr13: METTL21C gccaaggctaaggaatccag ttgtgaaaggcattttgttgg 0/9 5 GGTTGGCCCAGCTCTGAGGCTGG 4MMs [5:7:12:19] NM_ chr14: PLEKHD1 agcaggtggctctggaatct gtgtgccaagcttcttccag 0/12 Top 5 exonic off-target sites to gltr-t2 ( GGGAGCTCTCTGGCTAACTA GGG) Off-target ratio* Sequence Mismatches UCSC gene Locus Gene Forward primer Reverse primer HEK-293 hpsc 1 GGGAACTGTTTGGCTAACAAGAG 4MMs [5:8:10:19] NM_ chr1: IFFO2 tctgggtttcactgggattg cctcgaggaaacggaaaatc 0/23 0/31 2 GTGTGCTCTGTGGCTAATTAAAG 4MMs [2:4:10:18] NM_ chr1: CSMD2 caggaggctgctgagtgtg cgttcttgatggaaccagga 0/12 0/29 3 GGGATCACACTGGCTAACAAAGG 4MMs [5:7:9:19] NR_ chr12: SYT1 ggcaaaacgaaaccaatagaaa tgaggtactccgagtcagattca 0/29 0/31 4 GGGATCTCTCAGGCTCACAACGG 4MMs [5:11:16:19] NR_ chr21: DSCAM ataggatggggagggaacaa ttgcttgaatttgggaggtg 0/11 0/30 5 GGGAGCTCGCTGGCTGCCCATGG 4MMs [9:16:17:19] NM_ chr9: PHF2 ttgtgcaggagtttgtgcag ctgagctgaggcctgctgta 0/21 0/26 *Off-target ratio is calculated by the in/del sequence analysis of anti-hiv CRISPR/Cas9 stable cell clones with top 5 sequence similarity to exonic off-target sites in human genome
Use of the CRISPR/Cas9 system as an intracellular defense against HIV-1 infection in human cells
 Received 3 Jul 214 Accepted 27 Jan 215 Published 1 Mar 215 DOI: 1.138/ncomms7413 Use of the CRISPR/Cas9 system as an intracellular defense against HIV-1 infection in human cells Hsin-Kai Liao 1, Ying Gu
Received 3 Jul 214 Accepted 27 Jan 215 Published 1 Mar 215 DOI: 1.138/ncomms7413 Use of the CRISPR/Cas9 system as an intracellular defense against HIV-1 infection in human cells Hsin-Kai Liao 1, Ying Gu
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.2109
 HIV 1 Infects Multipotent Progenitor Cells Causing Cell Death and Establishing Latent Cellular Reservoirs Christoph C. Carter, Adewunmi Onafuwa Nuga, Lucy A. M c Namara, James Riddell IV, Dale Bixby, Michael
HIV 1 Infects Multipotent Progenitor Cells Causing Cell Death and Establishing Latent Cellular Reservoirs Christoph C. Carter, Adewunmi Onafuwa Nuga, Lucy A. M c Namara, James Riddell IV, Dale Bixby, Michael
Host Double Strand Break Repair Generates HIV-1 Strains Resistant to CRISPR/Cas9
 Host Double Strand Break Repair Generates HIV-1 Strains Resistant to CRISPR/Cas9 Kristine E. Yoder, a * and Ralf Bundschuh b a Department of Molecular Virology, Immunology and Medical Genetics, Center
Host Double Strand Break Repair Generates HIV-1 Strains Resistant to CRISPR/Cas9 Kristine E. Yoder, a * and Ralf Bundschuh b a Department of Molecular Virology, Immunology and Medical Genetics, Center
Choosing Between Lentivirus and Adeno-associated Virus For DNA Delivery
 Choosing Between Lentivirus and Adeno-associated Virus For DNA Delivery Presenter: April 12, 2017 Ed Davis, Ph.D. Senior Application Scientist GeneCopoeia, Inc. Outline Introduction to GeneCopoeia Lentiviral
Choosing Between Lentivirus and Adeno-associated Virus For DNA Delivery Presenter: April 12, 2017 Ed Davis, Ph.D. Senior Application Scientist GeneCopoeia, Inc. Outline Introduction to GeneCopoeia Lentiviral
Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids and viruses Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR Generation of molecular standard for quantitative PCR
 Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids and viruses To generate pseudotyped viruses, the previously described recombinant plasmids pnl4-3-δnef-gfp or pnl4-3-δ6-drgfp and a vector expressing HIV-1 X4
Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids and viruses To generate pseudotyped viruses, the previously described recombinant plasmids pnl4-3-δnef-gfp or pnl4-3-δ6-drgfp and a vector expressing HIV-1 X4
Supplementary Information. Novel lentiviral vectors with mutated reverse transcriptase for mrna delivery of TALE nucleases
 Supplementary Information Novel lentiviral vectors with mutated reverse transcriptase for mrna delivery of TALE nucleases Ulrike Mock 1, Kristoffer Riecken 1, Belinda Berdien 1, Waseem Qasim 2, Emma Chan
Supplementary Information Novel lentiviral vectors with mutated reverse transcriptase for mrna delivery of TALE nucleases Ulrike Mock 1, Kristoffer Riecken 1, Belinda Berdien 1, Waseem Qasim 2, Emma Chan
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system
 Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
Conditional and reversible disruption of essential herpesvirus protein functions
 nature methods Conditional and reversible disruption of essential herpesvirus protein functions Mandy Glaß, Andreas Busche, Karen Wagner, Martin Messerle & Eva Maria Borst Supplementary figures and text:
nature methods Conditional and reversible disruption of essential herpesvirus protein functions Mandy Glaß, Andreas Busche, Karen Wagner, Martin Messerle & Eva Maria Borst Supplementary figures and text:
VIROLOGY. Engineering Viral Genomes: Retrovirus Vectors
 VIROLOGY Engineering Viral Genomes: Retrovirus Vectors Viral vectors Retrovirus replicative cycle Most mammalian retroviruses use trna PRO, trna Lys3, trna Lys1,2 The partially unfolded trna is annealed
VIROLOGY Engineering Viral Genomes: Retrovirus Vectors Viral vectors Retrovirus replicative cycle Most mammalian retroviruses use trna PRO, trna Lys3, trna Lys1,2 The partially unfolded trna is annealed
Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Introduction retroposon
 17.1 - Introduction A retrovirus is an RNA virus able to convert its sequence into DNA by reverse transcription A retroposon (retrotransposon) is a transposon that mobilizes via an RNA form; the DNA element
17.1 - Introduction A retrovirus is an RNA virus able to convert its sequence into DNA by reverse transcription A retroposon (retrotransposon) is a transposon that mobilizes via an RNA form; the DNA element
CRISPRaTest Functional dcas9-activator Assay Kit v1 Last update: 2018/07/04 Cellecta, Inc.
 CRISPRaTest Functional dcas9-activator Assay Kit v1 Last update: 2018/07/04 Cellecta, Inc. Copyright (c) 2018 Cellecta, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Table of Contents 1. CRISPRaTest Functional dcas9-activator
CRISPRaTest Functional dcas9-activator Assay Kit v1 Last update: 2018/07/04 Cellecta, Inc. Copyright (c) 2018 Cellecta, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Table of Contents 1. CRISPRaTest Functional dcas9-activator
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein
 Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Retroviruses. ---The name retrovirus comes from the enzyme, reverse transcriptase.
 Retroviruses ---The name retrovirus comes from the enzyme, reverse transcriptase. ---Reverse transcriptase (RT) converts the RNA genome present in the virus particle into DNA. ---RT discovered in 1970.
Retroviruses ---The name retrovirus comes from the enzyme, reverse transcriptase. ---Reverse transcriptase (RT) converts the RNA genome present in the virus particle into DNA. ---RT discovered in 1970.
CRISPR/Cas9 cleavage of viral DNA efficiently suppresses hepatitis B virus
 0 0 CRISPR/Cas cleavage of viral DNA efficiently suppresses hepatitis B virus Authors: Vyas Ramanan,, Amir Shlomai,, David B.T. Cox,,,, Robert E. Schwartz,,, Eleftherios Michailidis, Ankit Bhatta, David
0 0 CRISPR/Cas cleavage of viral DNA efficiently suppresses hepatitis B virus Authors: Vyas Ramanan,, Amir Shlomai,, David B.T. Cox,,,, Robert E. Schwartz,,, Eleftherios Michailidis, Ankit Bhatta, David
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. DNA-methylation machinery is essential for silencing of Cd4 in cytotoxic T cells.
 Supplementary Figure 1 DNA-methylation machinery is essential for silencing of Cd4 in cytotoxic T cells. (a) Scheme for the retroviral shrna screen. (b) Histogram showing CD4 expression (MFI) in WT cytotoxic
Supplementary Figure 1 DNA-methylation machinery is essential for silencing of Cd4 in cytotoxic T cells. (a) Scheme for the retroviral shrna screen. (b) Histogram showing CD4 expression (MFI) in WT cytotoxic
Tel: ; Fax: ;
 Tel.: +98 216 696 9291; Fax: +98 216 696 9291; E-mail: mrasadeghi@pasteur.ac.ir Tel: +98 916 113 7679; Fax: +98 613 333 6380; E-mail: abakhshi_e@ajums.ac.ir A Soluble Chromatin-bound MOI 0 1 5 0 1 5 HDAC2
Tel.: +98 216 696 9291; Fax: +98 216 696 9291; E-mail: mrasadeghi@pasteur.ac.ir Tel: +98 916 113 7679; Fax: +98 613 333 6380; E-mail: abakhshi_e@ajums.ac.ir A Soluble Chromatin-bound MOI 0 1 5 0 1 5 HDAC2
Pre-made Lentiviral Particles for Fluorescent Proteins
 Pre-made Lentiviral Particles for Fluorescent Proteins Catalog# Product Name Amounts Fluorescent proteins expressed under sucmv promoter: LVP001 LVP001-PBS LVP002 LVP002-PBS LVP011 LVP011-PBS LVP012 LVP012-PBS
Pre-made Lentiviral Particles for Fluorescent Proteins Catalog# Product Name Amounts Fluorescent proteins expressed under sucmv promoter: LVP001 LVP001-PBS LVP002 LVP002-PBS LVP011 LVP011-PBS LVP012 LVP012-PBS
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells
 MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
Development of 5 LTR DNA methylation of latent HIV-1 provirus in cell line models and in long-term-infected individuals
 Trejbalová et al. Clinical Epigenetics (2016) 8:19 DOI 10.1186/s13148-016-0185-6 RESEARCH Development of 5 LTR DNA methylation of latent HIV-1 provirus in cell line models and in long-term-infected individuals
Trejbalová et al. Clinical Epigenetics (2016) 8:19 DOI 10.1186/s13148-016-0185-6 RESEARCH Development of 5 LTR DNA methylation of latent HIV-1 provirus in cell line models and in long-term-infected individuals
Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid.
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
Right view a copy of this license, visit
 Title Harnessing the CRISPR/Cas9 system t provirus. Author(s) Ebina, Hirotaka; Misawa, Naoko; Kan Yoshio Citation Scientific reports (2013), 3 Issue Date 2013-08-26 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/178737
Title Harnessing the CRISPR/Cas9 system t provirus. Author(s) Ebina, Hirotaka; Misawa, Naoko; Kan Yoshio Citation Scientific reports (2013), 3 Issue Date 2013-08-26 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/178737
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4322
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Predicted RNA structure of 3 UTR and sequence alignment of deleted nucleotides. (a) Predicted RNA secondary structure of ZIKV 3 UTR. The stem-loop structure
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Predicted RNA structure of 3 UTR and sequence alignment of deleted nucleotides. (a) Predicted RNA secondary structure of ZIKV 3 UTR. The stem-loop structure
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
DNA context and promoter activity affect gene expression in lentiviral vectors
 ACTA BIOMED 2008; 79: 192-196 Mattioli 1885 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E DNA context and promoter activity affect gene expression in lentiviral vectors Gensheng Mao 1, Francesco Marotta 2, Jia Yu 3, Liang
ACTA BIOMED 2008; 79: 192-196 Mattioli 1885 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E DNA context and promoter activity affect gene expression in lentiviral vectors Gensheng Mao 1, Francesco Marotta 2, Jia Yu 3, Liang
Supplementary information. MARCH8 inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins
 Supplementary information inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins Takuya Tada, Yanzhao Zhang, Takayoshi Koyama, Minoru Tobiume, Yasuko Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Shoji
Supplementary information inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins Takuya Tada, Yanzhao Zhang, Takayoshi Koyama, Minoru Tobiume, Yasuko Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Shoji
File Name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Tables. File Name: Peer Review File Description:
 File Name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Tables File Name: Peer Review File Description: Primer Name Sequence (5'-3') AT ( C) RT-PCR USP21 F 5'-TTCCCATGGCTCCTTCCACATGAT-3'
File Name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Tables File Name: Peer Review File Description: Primer Name Sequence (5'-3') AT ( C) RT-PCR USP21 F 5'-TTCCCATGGCTCCTTCCACATGAT-3'
Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent Protein.
 prfp-vector RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 prfp-mir-124 mir-93/124 RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 Untransfected prfp-vector prfp-mir-93 prfp-mir-124 Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent
prfp-vector RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 prfp-mir-124 mir-93/124 RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 Untransfected prfp-vector prfp-mir-93 prfp-mir-124 Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent
Screening for Complex Phenotypes
 Screening for Complex Phenotypes Michael Hemann hemann@mit.edu Screening for cancer phenotypes in mice How do we typically model cancer in mice? Tumor Suppressor KO Oncogene transgenesis Problems with
Screening for Complex Phenotypes Michael Hemann hemann@mit.edu Screening for cancer phenotypes in mice How do we typically model cancer in mice? Tumor Suppressor KO Oncogene transgenesis Problems with
Fayth K. Yoshimura, Ph.D. September 7, of 7 HIV - BASIC PROPERTIES
 1 of 7 I. Viral Origin. A. Retrovirus - animal lentiviruses. HIV - BASIC PROPERTIES 1. HIV is a member of the Retrovirus family and more specifically it is a member of the Lentivirus genus of this family.
1 of 7 I. Viral Origin. A. Retrovirus - animal lentiviruses. HIV - BASIC PROPERTIES 1. HIV is a member of the Retrovirus family and more specifically it is a member of the Lentivirus genus of this family.
Certificate of Analysis
 Certificate of Analysis Catalog No. Amount Lot Number 631987 10 μg Specified on product label. Product Information plvx-ef1α-ires-mcherry is a bicistronic lentiviral expression vector that can be used
Certificate of Analysis Catalog No. Amount Lot Number 631987 10 μg Specified on product label. Product Information plvx-ef1α-ires-mcherry is a bicistronic lentiviral expression vector that can be used
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supp. Fig. 1. Autoimmunity. Tolerance APC APC. T cell. T cell. doi: /nature06253 ICOS ICOS TCR CD28 TCR CD28
 Supp. Fig. 1 a APC b APC ICOS ICOS TCR CD28 mir P TCR CD28 P T cell Tolerance Roquin WT SG Icos mrna T cell Autoimmunity Roquin M199R SG Icos mrna www.nature.com/nature 1 Supp. Fig. 2 CD4 + CD44 low CD4
Supp. Fig. 1 a APC b APC ICOS ICOS TCR CD28 mir P TCR CD28 P T cell Tolerance Roquin WT SG Icos mrna T cell Autoimmunity Roquin M199R SG Icos mrna www.nature.com/nature 1 Supp. Fig. 2 CD4 + CD44 low CD4
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
IKK-dependent activation of NF-κB contributes to myeloid and lymphoid leukemogenesis by BCR-ABL1
 Supplemental Figures BLOOD/2014/547943 IKK-dependent activation of NF-κB contributes to myeloid and lymphoid leukemogenesis by BCR-ABL1 Hsieh M-Y and Van Etten RA Supplemental Figure S1. Titers of retroviral
Supplemental Figures BLOOD/2014/547943 IKK-dependent activation of NF-κB contributes to myeloid and lymphoid leukemogenesis by BCR-ABL1 Hsieh M-Y and Van Etten RA Supplemental Figure S1. Titers of retroviral
Highly Significant Antiviral Activity of HIV-1 LTR-Specific Tre-
 Supporting Information Hauber et al. page 1 Text S1 - Supporting Information Highly Significant Antiviral Activity of HIV-1 LTR-Specific Tre- Recombinase in Humanized Mice Ilona Hauber 1, Helga Hofmann-Sieber
Supporting Information Hauber et al. page 1 Text S1 - Supporting Information Highly Significant Antiviral Activity of HIV-1 LTR-Specific Tre- Recombinase in Humanized Mice Ilona Hauber 1, Helga Hofmann-Sieber
Hepatitis B Antiviral Drug Development Multi-Marker Screening Assay
 Hepatitis B Antiviral Drug Development Multi-Marker Screening Assay Background ImQuest BioSciences has developed and qualified a single-plate method to expedite the screening of antiviral agents against
Hepatitis B Antiviral Drug Development Multi-Marker Screening Assay Background ImQuest BioSciences has developed and qualified a single-plate method to expedite the screening of antiviral agents against
Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
 open reading frame 1565 (segment 5) 47 (-) 3 5 (+) 76 101 125 149 173 197 221 246 287 open reading frame 890 (segment 8) 60 (-) 3 5 (+) 172 Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
open reading frame 1565 (segment 5) 47 (-) 3 5 (+) 76 101 125 149 173 197 221 246 287 open reading frame 890 (segment 8) 60 (-) 3 5 (+) 172 Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
Overview: Chapter 19 Viruses: A Borrowed Life
 Overview: Chapter 19 Viruses: A Borrowed Life Viruses called bacteriophages can infect and set in motion a genetic takeover of bacteria, such as Escherichia coli Viruses lead a kind of borrowed life between
Overview: Chapter 19 Viruses: A Borrowed Life Viruses called bacteriophages can infect and set in motion a genetic takeover of bacteria, such as Escherichia coli Viruses lead a kind of borrowed life between
UNDERSTANDING THE ROLES OF NUCLEAR RECEPTORS IN THE MAINTENANCE OF HIV PROVIRAL LATENCY USING NOVEL GENE EDITING TECHONOLOGY STEPHANIE C.
 UNDERSTANDING THE ROLES OF NUCLEAR RECEPTORS IN THE MAINTENANCE OF HIV PROVIRAL LATENCY USING NOVEL GENE EDITING TECHONOLOGY By STEPHANIE C. MILNE Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for
UNDERSTANDING THE ROLES OF NUCLEAR RECEPTORS IN THE MAINTENANCE OF HIV PROVIRAL LATENCY USING NOVEL GENE EDITING TECHONOLOGY By STEPHANIE C. MILNE Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for
Supplementary Figure 1 IL-27 IL
 Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Module 2 In vivo gene therapy. Lecture 7. In-situ, in-vivo and ex-vivo gene therapy (part I)
 Module 2 In vivo gene therapy Lecture 7 In-situ, in-vivo and ex-vivo gene therapy (part I) Somatic cell gene therapy involves the transfer of gene to a diseased somatic cell either within the body or outside
Module 2 In vivo gene therapy Lecture 7 In-situ, in-vivo and ex-vivo gene therapy (part I) Somatic cell gene therapy involves the transfer of gene to a diseased somatic cell either within the body or outside
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice. (a) Gene expression profile in the resting CD4 + T cells were analyzed by an Affymetrix microarray
Supplementary Figure 1 Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice. (a) Gene expression profile in the resting CD4 + T cells were analyzed by an Affymetrix microarray
Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2)
 Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. EBV-gB 23-431 mainly exists as trimer in HEK 293FT cells. (a) Western blotting analysis for DSS crosslinked FLAG-gB 23-431. HEK 293FT cells transfected
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. EBV-gB 23-431 mainly exists as trimer in HEK 293FT cells. (a) Western blotting analysis for DSS crosslinked FLAG-gB 23-431. HEK 293FT cells transfected
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study
 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
Viral Vectors In The Research Laboratory: Just How Safe Are They? Dawn P. Wooley, Ph.D., SM(NRM), RBP, CBSP
 Viral Vectors In The Research Laboratory: Just How Safe Are They? Dawn P. Wooley, Ph.D., SM(NRM), RBP, CBSP 1 Learning Objectives Recognize hazards associated with viral vectors in research and animal
Viral Vectors In The Research Laboratory: Just How Safe Are They? Dawn P. Wooley, Ph.D., SM(NRM), RBP, CBSP 1 Learning Objectives Recognize hazards associated with viral vectors in research and animal
Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the
 Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the targeted allele in ES cells, and the mutant allele in
Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the targeted allele in ES cells, and the mutant allele in
Supplementary Figure 1 The plasmids used for the GPCR-CRISPR ChaCha and the GPCR-CRISPR Tango systems. (a) The plasmids for the GPCR-CRISPR ChaCha
 Supplementary Figure 1 The plasmids used for the GPCR-CRISPR ChaCha and the GPCR-CRISPR Tango systems. (a) The plasmids for the GPCR-CRISPR ChaCha system. The dcas9-vpr effector is fused to the C-terminus
Supplementary Figure 1 The plasmids used for the GPCR-CRISPR ChaCha and the GPCR-CRISPR Tango systems. (a) The plasmids for the GPCR-CRISPR ChaCha system. The dcas9-vpr effector is fused to the C-terminus
Fig. S1. Subcellular localization of overexpressed LPP3wt-GFP in COS-7 and HeLa cells. Cos7 (top) and HeLa (bottom) cells expressing for 24 h human
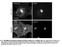 Fig. S1. Subcellular localization of overexpressed LPP3wt-GFP in COS-7 and HeLa cells. Cos7 (top) and HeLa (bottom) cells expressing for 24 h human LPP3wt-GFP, fixed and stained for GM130 (A) or Golgi97
Fig. S1. Subcellular localization of overexpressed LPP3wt-GFP in COS-7 and HeLa cells. Cos7 (top) and HeLa (bottom) cells expressing for 24 h human LPP3wt-GFP, fixed and stained for GM130 (A) or Golgi97
Supplementary Figure 1 Induction of cellular senescence and isolation of exosome. a to c, Pre-senescent primary normal human diploid fibroblasts
 Supplementary Figure 1 Induction of cellular senescence and isolation of exosome. a to c, Pre-senescent primary normal human diploid fibroblasts (TIG-3 cells) were rendered senescent by either serial passage
Supplementary Figure 1 Induction of cellular senescence and isolation of exosome. a to c, Pre-senescent primary normal human diploid fibroblasts (TIG-3 cells) were rendered senescent by either serial passage
mock! A3AC106S! A3BE255Q! 86.7! 90.1! 88.0! 89.8! 89.0!
 a A3A A3Bi7 A3Btok A3Bwh A3Blan mock V5 DAPI merge 5 µm b edited A3A A3Bi7 A3Btok A3Blan A3Bwh A3BF38L A3BW359L mock A3AC16S A3BE255Q 79.5 79.7 8.4 81.3 82.5 83.9 85.3 86.7 88. 89. 89.8 9.1 HBV 3DPCR Td/
a A3A A3Bi7 A3Btok A3Bwh A3Blan mock V5 DAPI merge 5 µm b edited A3A A3Bi7 A3Btok A3Blan A3Bwh A3BF38L A3BW359L mock A3AC16S A3BE255Q 79.5 79.7 8.4 81.3 82.5 83.9 85.3 86.7 88. 89. 89.8 9.1 HBV 3DPCR Td/
Supplementary Figure 1. Properties of various IZUMO1 monoclonal antibodies and behavior of SPACA6. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) .
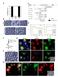 Supplementary Figure 1. Properties of various IZUMO1 monoclonal antibodies and behavior of SPACA6. (a) The inhibitory effects of new antibodies (Mab17 and Mab18). They were investigated in in vitro fertilization
Supplementary Figure 1. Properties of various IZUMO1 monoclonal antibodies and behavior of SPACA6. (a) The inhibitory effects of new antibodies (Mab17 and Mab18). They were investigated in in vitro fertilization
Supplementary Fig. 1 No relative growth advantage of Foxp3 negative cells.
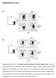 Supplementary Fig. 1 Supplementary Figure S1: No relative growth advantage of Foxp3 negative cells. itreg were induced from WT (A) or FIR (B) CD4 + T cells. FIR itregs were then removed from the TCR signal
Supplementary Fig. 1 Supplementary Figure S1: No relative growth advantage of Foxp3 negative cells. itreg were induced from WT (A) or FIR (B) CD4 + T cells. FIR itregs were then removed from the TCR signal
Chapter13 Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids, and Prions
 Chapter13 Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids, and Prions 11/20/2017 MDufilho 1 Characteristics of Viruses Viruses Minuscule, acellular, infectious agent having either DNA or RNA Cause infections
Chapter13 Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids, and Prions 11/20/2017 MDufilho 1 Characteristics of Viruses Viruses Minuscule, acellular, infectious agent having either DNA or RNA Cause infections
Jumpstart your research with ViraPower Lentiviral Expression Systems
 ViraPower Lentiviral Expression Systems Jumpstart your research with ViraPower Lentiviral Expression Systems With ViraPower Lentiviral Systems you can: Efficiently transduce both dividing and non-dividing
ViraPower Lentiviral Expression Systems Jumpstart your research with ViraPower Lentiviral Expression Systems With ViraPower Lentiviral Systems you can: Efficiently transduce both dividing and non-dividing
LESSON 4.6 WORKBOOK. Designing an antiviral drug The challenge of HIV
 LESSON 4.6 WORKBOOK Designing an antiviral drug The challenge of HIV In the last two lessons we discussed the how the viral life cycle causes host cell damage. But is there anything we can do to prevent
LESSON 4.6 WORKBOOK Designing an antiviral drug The challenge of HIV In the last two lessons we discussed the how the viral life cycle causes host cell damage. But is there anything we can do to prevent
Pre-made Reporter Lentivirus for NF-κB Signal Pathway
 Pre-made Reporter for NF-κB Signal Pathway Cat# Product Name Amounts LVP965-P or: LVP965-P-PBS NFKB-GFP (Puro) LVP966-P or: LVP966-P-PBS NFKB-RFP (Puro) LVP967-P or: LVP967-P-PBS NFKB-Luc (Puro) LVP968-P
Pre-made Reporter for NF-κB Signal Pathway Cat# Product Name Amounts LVP965-P or: LVP965-P-PBS NFKB-GFP (Puro) LVP966-P or: LVP966-P-PBS NFKB-RFP (Puro) LVP967-P or: LVP967-P-PBS NFKB-Luc (Puro) LVP968-P
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1! a! b! Nfatc1!! Nfatc1"! P1! P2! pa1! pa2! ex1! ex2! exons 3-9! ex1! ex11!!" #" Nfatc1A!!" Nfatc1B! #"!" Nfatc1C! #" DN1! DN2! DN1!!A! #A!!B! #B!!C! #C!!A!
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1! a! b! Nfatc1!! Nfatc1"! P1! P2! pa1! pa2! ex1! ex2! exons 3-9! ex1! ex11!!" #" Nfatc1A!!" Nfatc1B! #"!" Nfatc1C! #" DN1! DN2! DN1!!A! #A!!B! #B!!C! #C!!A!
Genome-editing via Oviductal Nucleic Acids Delivery (GONAD) system: a novel microinjection-independent genome engineering method in mice
 Supplementary Information Genome-editing via Oviductal Nucleic Acids Delivery (GONAD) system: a novel microinjection-independent genome engineering method in mice Gou Takahashi, Channabasavaiah B Gurumurthy,
Supplementary Information Genome-editing via Oviductal Nucleic Acids Delivery (GONAD) system: a novel microinjection-independent genome engineering method in mice Gou Takahashi, Channabasavaiah B Gurumurthy,
Pre-made Reporter Lentivirus for MAPK/ERK Signal Pathway
 Pre-made Reporter for MAPK/ERK Signal Pathway Cat# Product Name Amounts LVP957-P or: LVP957-P-PBS SRE-GFP (Puro) LVP958-P or: LVP958-P-PBS SRE-RFP (Puro) LVP959-P or: LVP959-P-PBS SRE-Luc (Puro) LVP960-P
Pre-made Reporter for MAPK/ERK Signal Pathway Cat# Product Name Amounts LVP957-P or: LVP957-P-PBS SRE-GFP (Puro) LVP958-P or: LVP958-P-PBS SRE-RFP (Puro) LVP959-P or: LVP959-P-PBS SRE-Luc (Puro) LVP960-P
Oxford Expression Technologies Ltd
 Oxford Expression Technologies Ltd Founded in 2007 as a spin out from Oxford Brookes University and Natural Environment Research Council Technology based on the insect baculovirus expression vectors (BEVs)
Oxford Expression Technologies Ltd Founded in 2007 as a spin out from Oxford Brookes University and Natural Environment Research Council Technology based on the insect baculovirus expression vectors (BEVs)
Lecture 2: Virology. I. Background
 Lecture 2: Virology I. Background A. Properties 1. Simple biological systems a. Aggregates of nucleic acids and protein 2. Non-living a. Cannot reproduce or carry out metabolic activities outside of a
Lecture 2: Virology I. Background A. Properties 1. Simple biological systems a. Aggregates of nucleic acids and protein 2. Non-living a. Cannot reproduce or carry out metabolic activities outside of a
Pre-made Reporter Lentivirus for JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway
 Pre-made Reporter for JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway Cat# Product Name Amounts LVP937-P or: LVP937-P-PBS ISRE-GFP (Puro) LVP938-P or: LVP938-P-PBS ISRE-RFP (Puro) LVP939-P or: LVP939-P-PBS ISRE-Luc (Puro)
Pre-made Reporter for JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway Cat# Product Name Amounts LVP937-P or: LVP937-P-PBS ISRE-GFP (Puro) LVP938-P or: LVP938-P-PBS ISRE-RFP (Puro) LVP939-P or: LVP939-P-PBS ISRE-Luc (Puro)
Identification of Mutation(s) in. Associated with Neutralization Resistance. Miah Blomquist
 Identification of Mutation(s) in the HIV 1 gp41 Subunit Associated with Neutralization Resistance Miah Blomquist What is HIV 1? HIV-1 is an epidemic that affects over 34 million people worldwide. HIV-1
Identification of Mutation(s) in the HIV 1 gp41 Subunit Associated with Neutralization Resistance Miah Blomquist What is HIV 1? HIV-1 is an epidemic that affects over 34 million people worldwide. HIV-1
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material accompanying the manuscript Interleukin 37 is a fundamental inhibitor of innate immunity Marcel F Nold, Claudia A Nold-Petry, Jarod A Zepp, Brent E Palmer, Philip Bufler & Charles
Supplementary Material accompanying the manuscript Interleukin 37 is a fundamental inhibitor of innate immunity Marcel F Nold, Claudia A Nold-Petry, Jarod A Zepp, Brent E Palmer, Philip Bufler & Charles
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 sirna pool: Control Tetherin -HA-GFP HA-Tetherin -Tubulin Supplementary Figure S1. Knockdown of HA-tagged tetherin expression by tetherin specific sirnas. HeLa cells were cotransfected with plasmids expressing
sirna pool: Control Tetherin -HA-GFP HA-Tetherin -Tubulin Supplementary Figure S1. Knockdown of HA-tagged tetherin expression by tetherin specific sirnas. HeLa cells were cotransfected with plasmids expressing
Helper virus-free transfer of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 vectors
 Journal of General Virology (1995), 76, 691 696. Printed in Great Britabz 691 Helper virus-free transfer of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 vectors Jennifer H. Riehardson,~ Jane F. Kaye, Lisa A. Child
Journal of General Virology (1995), 76, 691 696. Printed in Great Britabz 691 Helper virus-free transfer of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 vectors Jennifer H. Riehardson,~ Jane F. Kaye, Lisa A. Child
Direct non-productive HIV-1 infection in a T-cell line is driven by cellular activation state and NFκB
 Dahabieh et al. Retrovirology 2014, 11:17 RESEARCH Open Access Direct non-productive HIV-1 infection in a T-cell line is driven by cellular activation state and NFκB Matthew S Dahabieh 1, Marcel Ooms 2*,
Dahabieh et al. Retrovirology 2014, 11:17 RESEARCH Open Access Direct non-productive HIV-1 infection in a T-cell line is driven by cellular activation state and NFκB Matthew S Dahabieh 1, Marcel Ooms 2*,
Supplementary Figure 1. BMS enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a
 Supplementary Figure 1. BMS98662 enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a concentration-dependent manner. Jurkat T cells were activated with anti-cd3 and anti-cd28 antibody in the presence of titrated
Supplementary Figure 1. BMS98662 enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a concentration-dependent manner. Jurkat T cells were activated with anti-cd3 and anti-cd28 antibody in the presence of titrated
Expanded View Figures
 PEX13 functions in selective autophagy Ming Y Lee et al Expanded View Figures Figure EV1. PEX13 is required for Sindbis virophagy. A, B Quantification of mcherry-capsid puncta per cell (A) and GFP-LC3
PEX13 functions in selective autophagy Ming Y Lee et al Expanded View Figures Figure EV1. PEX13 is required for Sindbis virophagy. A, B Quantification of mcherry-capsid puncta per cell (A) and GFP-LC3
Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria
 Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria What is Microbiology? Microbiology is the science that studies microorganisms = living things that are too small to be seen with the naked eye Microorganisms
Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria What is Microbiology? Microbiology is the science that studies microorganisms = living things that are too small to be seen with the naked eye Microorganisms
EGFR shrna A: CCGGCGCAAGTGTAAGAAGTGCGAACTCGAGTTCGCACTTCTTACACTTGCG TTTTTG. EGFR shrna B: CCGGAGAATGTGGAATACCTAAGGCTCGAGCCTTAGGTATTCCACATTCTCTT TTTG
 Supplementary Methods Sequence of oligonucleotides used for shrna targeting EGFR EGFR shrna were obtained from the Harvard RNAi consortium. The following oligonucleotides (forward primer) were used to
Supplementary Methods Sequence of oligonucleotides used for shrna targeting EGFR EGFR shrna were obtained from the Harvard RNAi consortium. The following oligonucleotides (forward primer) were used to
Human Immunodeficiency Virus
 Human Immunodeficiency Virus Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Viruses and hosts Lentivirus from Latin lentis (slow), for slow progression of disease
Human Immunodeficiency Virus Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Viruses and hosts Lentivirus from Latin lentis (slow), for slow progression of disease
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures S1-S9. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
A. Generation and characterization of Ras-expressing autophagycompetent
 Supplemental Material Supplemental Figure Legends Fig. S1 A. Generation and characterization of Ras-expressing autophagycompetent and -deficient cell lines. HA-tagged H-ras V12 was stably expressed in
Supplemental Material Supplemental Figure Legends Fig. S1 A. Generation and characterization of Ras-expressing autophagycompetent and -deficient cell lines. HA-tagged H-ras V12 was stably expressed in
VIRUSES. 1. Describe the structure of a virus by completing the following chart.
 AP BIOLOGY MOLECULAR GENETICS ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR VIRUSES 1. Describe the structure of a virus by completing the following chart. Viral Part Description of Part 2. Some viruses have an envelope
AP BIOLOGY MOLECULAR GENETICS ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR VIRUSES 1. Describe the structure of a virus by completing the following chart. Viral Part Description of Part 2. Some viruses have an envelope
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
CRISPR/CAS9 based high-throughput screening. Journal club Caihong Zhu
 CRISPR/CAS9 based high-throughput screening Journal club Caihong Zhu 29.04.2014 High Throughput Screening (HTS) HTS is a method for scientific experimentation especially used in drug discovery and relevant
CRISPR/CAS9 based high-throughput screening Journal club Caihong Zhu 29.04.2014 High Throughput Screening (HTS) HTS is a method for scientific experimentation especially used in drug discovery and relevant
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
Viral Genetics. BIT 220 Chapter 16
 Viral Genetics BIT 220 Chapter 16 Details of the Virus Classified According to a. DNA or RNA b. Enveloped or Non-Enveloped c. Single-stranded or double-stranded Viruses contain only a few genes Reverse
Viral Genetics BIT 220 Chapter 16 Details of the Virus Classified According to a. DNA or RNA b. Enveloped or Non-Enveloped c. Single-stranded or double-stranded Viruses contain only a few genes Reverse
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 3 3 3 1 1 Bregma -1.6mm 3 : Bregma Ref) Http://www.mbl.org/atlas165/atlas165_start.html Bregma -.18mm Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of the utilized brain slice
Supplementary Figure 1 3 3 3 1 1 Bregma -1.6mm 3 : Bregma Ref) Http://www.mbl.org/atlas165/atlas165_start.html Bregma -.18mm Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of the utilized brain slice
% of live splenocytes. STAT5 deletion. (open shapes) % ROSA + % floxed
 Supp. Figure 1. a 14 1 1 8 6 spleen cells (x1 6 ) 16 % of live splenocytes 5 4 3 1 % of live splenocytes 8 6 4 b 1 1 c % of CD11c + splenocytes (closed shapes) 8 6 4 8 6 4 % ROSA + (open shapes) % floxed
Supp. Figure 1. a 14 1 1 8 6 spleen cells (x1 6 ) 16 % of live splenocytes 5 4 3 1 % of live splenocytes 8 6 4 b 1 1 c % of CD11c + splenocytes (closed shapes) 8 6 4 8 6 4 % ROSA + (open shapes) % floxed
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author):
 Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): Nature Communications manuscript number NCOMMS-16-15882, by Miyakawa et al. presents an intriguing analysis of the effects of the tumor suppressor
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): Nature Communications manuscript number NCOMMS-16-15882, by Miyakawa et al. presents an intriguing analysis of the effects of the tumor suppressor
7.012 Quiz 3 Answers
 MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology - Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. Claudette Gardel Friday 11/12/04 7.012 Quiz 3 Answers A > 85 B 72-84
MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology - Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. Claudette Gardel Friday 11/12/04 7.012 Quiz 3 Answers A > 85 B 72-84
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. HOX fusions enhance self-renewal capacity.
 Supplementary Figure 1 HOX fusions enhance self-renewal capacity. Mouse bone marrow was transduced with a retrovirus carrying one of three HOX fusion genes or the empty mcherry reporter construct as described
Supplementary Figure 1 HOX fusions enhance self-renewal capacity. Mouse bone marrow was transduced with a retrovirus carrying one of three HOX fusion genes or the empty mcherry reporter construct as described
Fayth K. Yoshimura, Ph.D. September 7, of 7 RETROVIRUSES. 2. HTLV-II causes hairy T-cell leukemia
 1 of 7 I. Diseases Caused by Retroviruses RETROVIRUSES A. Human retroviruses that cause cancers 1. HTLV-I causes adult T-cell leukemia and tropical spastic paraparesis 2. HTLV-II causes hairy T-cell leukemia
1 of 7 I. Diseases Caused by Retroviruses RETROVIRUSES A. Human retroviruses that cause cancers 1. HTLV-I causes adult T-cell leukemia and tropical spastic paraparesis 2. HTLV-II causes hairy T-cell leukemia
HIV INFECTION: An Overview
 HIV INFECTION: An Overview UNIVERSITY OF PAPUA NEW GUINEA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL MBBS II SEMINAR VJ
HIV INFECTION: An Overview UNIVERSITY OF PAPUA NEW GUINEA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL MBBS II SEMINAR VJ
(a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable
 Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Electron micrograph of phosphotungstanic acid-stained exosomes derived from murine
 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. Physical properties of murine DC-derived exosomes. a, Electron micrograph of phosphotungstanic acid-stained exosomes derived from
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. Physical properties of murine DC-derived exosomes. a, Electron micrograph of phosphotungstanic acid-stained exosomes derived from
Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse
 Supplemental figure legends Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse hippocampus targets GFAP-positive but not NeuN-positive cells. (A) Stereotaxic
Supplemental figure legends Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse hippocampus targets GFAP-positive but not NeuN-positive cells. (A) Stereotaxic
Joint Department of Biomedical Engineering
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Biomaterials Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Data Systemic Delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 with PEG-PLGA Nanoparticles for
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Biomaterials Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Data Systemic Delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 with PEG-PLGA Nanoparticles for
2) What is the difference between a non-enveloped virion and an enveloped virion? (4 pts)
 Micro 260 SFCC Spring 2010 Name: All diagrams and drawings shall be hand drawn (do not photo-copied from a publication then cut and pasted into work sheet). Do not copy other student s answers. Para phase
Micro 260 SFCC Spring 2010 Name: All diagrams and drawings shall be hand drawn (do not photo-copied from a publication then cut and pasted into work sheet). Do not copy other student s answers. Para phase
7.012 Problem Set 6 Solutions
 Name Section 7.012 Problem Set 6 Solutions Question 1 The viral family Orthomyxoviridae contains the influenza A, B and C viruses. These viruses have a (-)ss RNA genome surrounded by a capsid composed
Name Section 7.012 Problem Set 6 Solutions Question 1 The viral family Orthomyxoviridae contains the influenza A, B and C viruses. These viruses have a (-)ss RNA genome surrounded by a capsid composed
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Palmisano et al. 10.1073/pnas.1202174109 Fig. S1. Expression of different transgenes, driven by either viral or human promoters, is up-regulated by amino acid starvation. (A) Quantification
Supporting Information Palmisano et al. 10.1073/pnas.1202174109 Fig. S1. Expression of different transgenes, driven by either viral or human promoters, is up-regulated by amino acid starvation. (A) Quantification
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Choi YL, Soda M, Yamashita Y, et al. EML4-ALK mutations in
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Choi YL, Soda M, Yamashita Y, et al. EML4-ALK mutations in
Reverse transcription and integration
 Reverse transcription and integration Lecture 9 Biology 3310/4310 Virology Spring 2018 One can t believe impossible things, said Alice. I dare say you haven t had much practice, said the Queen. Why, sometimes
Reverse transcription and integration Lecture 9 Biology 3310/4310 Virology Spring 2018 One can t believe impossible things, said Alice. I dare say you haven t had much practice, said the Queen. Why, sometimes
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/8/e1500296/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Transcriptional regulation of APOBEC3 antiviral immunity through the CBF- /RUNX axis This PDF file includes: Brett
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/8/e1500296/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Transcriptional regulation of APOBEC3 antiviral immunity through the CBF- /RUNX axis This PDF file includes: Brett
