Ankylosaurus back sign: novel endoscopic finding in esophageal eosinophilia patients indicating proton pump inhibitor response
|
|
|
- Leonard Malone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ankylosaurus back sign: novel endoscopic finding in esophageal eosinophilia patients indicating proton pump inhibitor response Authors Norihisa Ishimura 1, Shohei Sumi 1, Mayumi Okada 1,DaisukeIzumi 1, Hironobu Mikami 1,EikoOkimoto 1,Nahoko Ishikawa 2, Yuji Tamagawa 1,TsuyoshiMishiro 1,NaokiOshima 1, Kotaro Shibagaki 1, Shunji Ishihara 1,Riruke Maruyama 2, Yoshikazu Kinoshita 1 Institutions 1 Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Shimane University School of Medicine, Izumo, Japan 2 Department of Pathology, Shimane University School of Medicine,Izumo,Japan submitted accepted after revision Bibliography DOI Endoscopy International Open 2018; 06: E165 E172 Georg Thieme Verlag KG Stuttgart New York ISSN Corresponding author Norihisa Ishimura, MD, PhD, Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Shimane University School of Medicine, 89-1, Enya-cho, Izumo, Shimane, , Japan Fax: ishimura@med.shimane-u.ac.jp ABSTRACT Background and study aims Characteristic endoscopic findings, such as linear furrows, rings, and whitish exudates, indicate the presence of esophageal eosinophilia (EE), though no specific findings are known to distinguish eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) from proton pump inhibitorresponsive esophageal eosinophilia (PPI-REE). Here, we present a novel endoscopic finding in some EE patients possessing a linear longitudinal arrangement of whitish nodules with the appearance of the back of an Ankylosaurus dinosaur, termed Ankylosaurus back sign (ABS), and evaluations of its significance in affected patients. Patients and methods Fifty-five patients diagnosed with EE ( 15 eosinophils/high power field) who were treated at our hospital and shown to evaluate a PPI response were enrolled. Endoscopic findings at baseline and clinical parameters were retrospectively reviewed. Furthermore, the clinicopathological features of patients with ABS, as well as the relationship between its presence and PPI response were evaluated. Results Fifty-five patients (47 males, 8 females) with EE (17withEoE,38withPPI-REE)wereevaluated,ofwhom50 (90.9 %) had linear furrows, the most frequently found feature, while ABS was found in 9 (16.4 %). Inter-observer agreement was substantial for ABS (κ 0.77). Interestingly, all patients with ABS had PPI-REE. Our findings revealed that the presence of ABS was closely associated with reflux esophagitis (RE) in patients with PPI-REE. Conclusions Although ABS was less frequent than typical endoscopic findings such as linear furrows in EE, this novel finding was closely associated with PPI-REE accompanied with RE. The clinical implications of ABS in patients with EE should be investigated further. Introduction Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is characterized by chronic inflammation along with dense eosinophile infiltration in the esophageal epithelial layer, as well as esophageal symptoms including dysphagia and heartburn, and is thought to be based on an allergic and immunological pathogenesis [1, 2]. Pathological identification of esophageal eosinophilia (EE) is considered to be the most important and critical step for diagnosis of EoE. However, the presence of EE is not specific for EoE, thus consensus guidelines require clinical and/or histologic unresponsiveness to acid-suppressive therapy with a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) to exclude other causes of EE, such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). In addition, it has become apparent that some patients with a phenotype appearance of EoE and distinct from GERD respond histologically to PPIs. To distinguish them from EoE patients, these are described as having PPI-responsive esophageal eosinophilia (PPI-REE) [3, 4]. On Ishimura Norihisa et al. Ankylosaurus back sign: Endoscopy International Open 2018; 06: E165 E172 E165
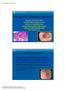
2 Fig.1 a,b Representative endoscopic findings of Ankylosaurus back sign, defined as a linear longitudinal arrangement of whitish nodules at uniform intervals in the esophagus. a Air deflated condition. b fully insufflated condition. c Image of Ankylosaurus, a genus of armored dinosaur. (Quelle: AdobeStock_ ) [rerif] the other hand, several studies have shown that PPI-REE and EoE are virtually indistinguishable from one another and called into question methods used to make a proper distinction between EoE and PPI-REE [5,6]. Therefore, the term PPI-REE is retracted and PPI use is recommended for therapeutic agent but not for diagnostic criterion in the most recently updated guidelines [7]. However, the underlying pathogenic mechanism of PPI response for EoE patients remains poorly understood. The associated endoscopic features of EE and EoE include linear furrows, rings, whitish exudates or plaque, strictures, diffuse narrowing, decreased vascularity or edema, and fragile mucosa (crepe paper appearance) [8, 9], which are increasingly being recognized as signs of EoE. Furthermore, recent prospective studies conducted in both Western and Asian countries have found that at least 1 of these abnormalities is detected by endoscopy in over 90 % of examined EoE patients [9 11]. The presence or absence of such endoscopic findings is used to make a diagnosis of EoE, as well as to guide biopsy decisions and assess response to therapy, though no specific endoscopic findings to distinguish EoE from PPI-REE have been presented. Recently, we noted a novel endoscopic finding in some patients with EE, which was recognized as the presence of a linear longitudinal arrangement of whitish nodules, such as the back of an Ankylosaurus dinosaur ( Fig. 1), which we termed Ankylosaurus back sign (ABS). However, it remains unknown whether this finding has diagnostic utility for EE. The aim of the current study was to evaluate the significance of ABS in patients with EE and also determine its association with PPI treatment for EE. E166 Ishimura Norihisa et al. Ankylosaurus back sign: Endoscopy International Open 2018; 06: E165 E172
3 Patients and methods Enrolled subjects and data collection Between July 2013 and January 2016, 70 adult patients with suspected EoE, who had symptoms of esophageal dysfunction and EE, visited our hospital. Histological diagnosis of EE was defined as the presence of 15 eosinophils per high power field (HPF) in biopsy samples obtained with endoscopy. Gastric and duodenal biopsy specimens were also collected to exclude concomitant eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Patients with a systemic cause of EE, including eosinophilic gastroenteritis, Crohn s disease, parasites, drug hypersensitivity, and hypereosinophilic syndrome, were excluded. Information regarding endoscopic findings and clinical parameters, including symptoms, allergy comorbid rate, laboratory findings, and response to PPI administration, was obtained and reviewed. EoE was defined clinically by symptoms of esophageal dysfunction and histologically by the presence of EE, as well as lack of response to a course of PPI therapy administered according to current guidelines [3, 4]. Furthermore, PPI-REE was defined as presentation of clinical symptoms similar to those of EoE, with both symptoms and eosinophile infiltration disappearing with PPI treatment at a standard or double dose within 2 months after beginning administration. Of the 70 patient charts initially reviewed, 15 were excluded because of an unfulfilled PPI trial, thus 55 cases were enrolled in this study. The clinical parameters described above were compared between patients with EoE and those with PPI-REE. The protocol of this study was evaluated and approved by the Ethical Committee of Shimane University School of Medicine. Assessment of endoscopic findings and inter-observer agreement Images obtained with endoscopy were separately reviewed by 3 expert endoscopists (N. I., E. O., N. O.) to determine the presence and location of ABS, as well as other typical findings including linear furrows, rings, and whitish exudates, in each case. ABS was defined as linear arrangement of whitish nodules with uniform intervals in the esophagus clearly detected by white light endoscopy ( Fig. 1a). One of the authors (Y. K.) explained representative endoscopic findings indicating EoE, including ABS before assessment, while endoscopic images used for instruction were not included inthisstudy.theexaminers were blinded in regard to the clinical diagnosis of each case and the endoscopic diagnosis was established by consensus of at least 2 of the 3. To evaluate the reliability of ABS, we estimated the inter-observer agreement for the identification of ABS among these 3 endoscopists. The kappa statistics with 95 % confidence interval (CI) were calculated according to Fleiss kappa calculation. The kappa value were evaluated as follows: kappa value below 0.20 considered to be poor, fair, moderate, substantial, and almost perfect. Mucosal breaks in patients with reflux esophagitis (RE) were graded according to the Los Angeles classification. The presence or absence of a hiatal hernia [12], as well as gastric mucosal atrophy [13] were also investigated in each case using endoscopic findings. Statistical analysis Statistical analyses were carried out using chi-squared and Mann Whitney U-tests, with Fisher s exact test used when necessary. P values<0.05 were considered to indicate statistical significance. All statistical analyses were performed using the SPSS statistical analysis software package (version 22.0 for the PC,Chicago,IL,USA). Results Clinical characteristics of enrolled patients The 55 enrolled patients consisted of 47 males and 8 females, with a mean (± SD) age of 46.8± 13.2 years (range years). Of 55 patients with EE, 17 were diagnosed with EoE, while 38 were diagnosed with PPI-REE. The demographic and clinical characteristics of each group are shown in Table 1. The EoE and PPI-REE groups were similar with respect to age (42.0 ±14.4 vs. 49.0± 12.3 years, P =0.09), gender (males 82.4% vs %, P =0.48), and frequency of concurrent allergic disease (82.4% vs. 78.9%, P = 0.54). In both groups, the most frequently reported symptom was dysphagia (70.6 % vs. 50.0%, P =0.13) and the frequency was not significantly different between them. None of the enrolled patients had a history of food impaction, in contrast to Western EoE patients in whom that frequently occurs [14]. For both the EoE and PPI-REE groups, the number of peripheral eosinophils (17 and 36 cases, respectively) and plasma total IgE level (15 and 28 cases, respectively) were evaluated in most of the patients. There was no significant difference in frequency of peripheral eosinophilia (> 500 eosinophil/microliter) (35.3 % vs %, P =0.31) or total IgE elevation (> 173IU/mL) (60.0 % vs %, P =0.96). In addition, the rate of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection, which has been reported to be inversely associated with EoE [15, 16], was not significantly different between the groups (35.3 % vs. 31.6%, P = 0.79). Collectively, demographic and clinical features were similar between the present patients with PPI-REE and those with EoE, consistent with our recently reported findings [17]. As for endoscopic findings, linear furrows, whitish exudates, and rings were frequently observed, and at least 1 of those findings was seen in every case. Of them, linear furrows was the most frequently found endoscopic abnormality in both the EoE and PPI-REE groups (88.2 % vs %, P = 0.49). Mucosal breaks with grade A or B were also found in both the EoE and PPI-REE groups (11.8 % vs %, P = 0.43). In contrast, ABS was found in 9 (16.4 %) patients with EE. Interestingly, all patients with ABS had PPI-REE. Furthermore, ABS was the only significant parameter to distinguish between the EoE and PPI-REE groups (0 % vs %, P = 0.03). Endoscopic and histological features of ABS Next, we focused on the endoscopic features of ABS in our patients. ABS was found to be positioned in a longitudinal manner, and widespread throughout the lower to middle or upper Ishimura Norihisa et al. Ankylosaurus back sign: Endoscopy International Open 2018; 06: E165 E172 E167
4 Table1 Clinical characteristics of patients with EoE and PPI-REE. EoE patients (n= 17) PPI-REE patients (n= 38) P value Age, y, mean ± SD 42.0 ± ± Male, no. (%) 14 (82.4) 33 (86.8) 0.48 Concurrent allergic disease, no.(%) 14 (82.4) 30 (78.9) 0.54 Symptom, no. (%) dysphagia 12 (70.6) 19 (50.0) 0.13 heartburn/regurgitation 5 (29.4) 13 (34.2) 0.49 Laboratory findings, no. (%) peripheral eosinophilia 1 6 (35.3) 8 (22.2) 0.31 total IgE elevation 1 9 (60.0) 17 (60.7) 0.96 H. pylori infection 6 (35.3) 12 (31.6) 0.79 Endoscopic findings, no. (%) linear furrows 15 (88.2) 35 (92.1) 0.49 whitish exudates 10 (58.8) 18 (47.4) 0.43 rings 9 (52.9) 28 (73.7) 0.13 ABS 0(0) 9(23.7) 0.03 Reflux esophagitis 2 (11.8) 7 (18.4) Peripheral eosinophil count and total IgE were not evaluated in all of the enrolled subjects. EoE, eosinophilic esophagitis; PPI-REE, proton pump-inhibitor responsive esophageal eosinophilia; ABS, Ankylosaurus back sign esophagus in all cases. Representative endoscopic findings of ABS are shown in Fig.2a, Fig.2c, and Fig.2e. Asforcircumferential location, ABS was seen in all circumferential directions in a radial pattern in each of these patients. The position of ABS in relation to esophageal longitudinal folds was also assessed. We recently reported that linear furrows were found to be located in mucosal fold valleys in all affected patients [18]. Interestingly, in all of the present patients with ABS, that was found in esophageal longitudinal mucosal fold ridges, where it did not appear in the valleys. In addition, this finding was more clearly observed under an air deflated than fully insufflated condition ( Fig. 1a and Fig.1b). To assess changes in the characteristics of ABS induced by treatment, specific endoscopic findings obtained after at least 2 months of PPI treatment were evaluated. In all cases with ABS, histological remission of eosinophile infiltration was confirmed following PPI treatment, whereas ABS remained with similar characteristics in 5 of 9 cases with ABS after 2 months of treatment ( Fig.2b, Fig.2 d and Fig.2f). Thereafter, with longer treatment, ABS gradually disappeared in 2 of those 5cases. We obtained biopsy specimens from the ABS area in some of the affected patients and representative histological findings of those are shown in Fig.3. In that representative case, dense eosinophile infiltration (120 eosinophils/hpf) and spongiosis were found in the esophageal epithelial layer. On the other hand, other specific findings were not detected and the histological findings were not different from adjacent mucosa in the valley (data not shown). Therefore, the cause of formation of the whitish nodules remains unclear. Inter-observer agreement for the identification of ABS The kappa value of inter-observer agreement for the identification of ABS among 3 endoscopists were 0.77 (95 %CI ), showing substantial diagnostic agreement. This suggested that ABS could be identified substantially by white light endoscopy as well as other characteristic endoscopic findings for EoE, such as rings, as previously reported [19]. Clinical significance of ABS Because ABS was only found in patients with PPI-REE, we compared the clinical and endoscopic features between those with PPI-REE and with or without ABS ( Table2). All PPI-REE cases positive for ABS (n= 9) were male (mean age 46.3± 9.0, range years). Clinical data including demographics (age, gender), presenting symptom, concurrent allergic diseases, and laboratory findings were similar between the ABS-positive and -negative PPI-REE cases. As for endoscopic findings, linear furrows were frequently observed in both groups (88.9% vs. 93.1%, P = 0.87). In contrast, whitish exudates were not present in the ABS-positive cases, while that was present in 18 of the 29 ABS-negative cases, a significant difference (0% vs. 62.1%, P = 0.001). Also, mucosal breaks were significantly more frequent E168 Ishimura Norihisa et al. Ankylosaurus back sign: Endoscopy International Open 2018; 06: E165 E172
5 Fig.2 a,c,erepresentative endoscopic findings of Ankylosaurus back sign (ABS). b, d, f ABS remained with similar characteristics after 2 months of PPI treatment, though histological remission of eosinophile infiltration was confirmed in all cases. a and b, c and d, e and f show findings obtained from the same cases. Fig.3 Representative histopathological findings for biopsy specimen obtained from patient with Ankylosaurus back sign. Dense eosinophile infiltration (120 eosinophils/high power field) and spongiosis in the esophageal epithelial layer were found. a Hematoxylin-eosin stain, 100. b Hematoxylin-eosin stain, 200. in the ABS-positive group (55.6% vs. 6.9 %, P = 0.004), suggesting that the presence of ABS is closely associated with gastric acid reflux in patients with PPI-REE. Discussion This is the first known study to present and evaluate a novel endoscopic finding, termed ABS, in patients with EE. To date, several characteristic endoscopic findings, including linear furrows, rings, and whitish exudates, have been reported as useful Ishimura Norihisa et al. Ankylosaurus back sign: Endoscopy International Open 2018; 06: E165 E172 E169
6 Table2 Clinical characteristics of patients with PPI-REE with/without ABS. ABS-positive PPI-REE (n =9) ABS-negative PPI-REE (n= 29) P value Age, y, mean ± SD 46.3 ± ± Male, no. (%) 9 (100) 24 (82.8) 0.24 Concurrent allergic disease, no.(%) 6 (66.7) 24 (82.8) 0.28 Symptom, no. (%) dysphagia 5 (55.6) 14 (48.3) 0.50 heartburn/regurgitation 3 (33.3) 10 (34.5) 0.61 Laboratory findings, no. (%) peripheral eosinophilia 1 2 (22.2) 6 (22.2) 0.69 total IgE elevation 1 3 (37.5) 14 (70.0) 0.12 H. pylori infection 4 (44.4) 8 (27.6) 0.91 Endoscopic findings, no. (%) linear furrows 8 (88.9) 27 (93.1) 0.87 whitish exudates 0 (0) 18 (62.1) rings 7 (77.8) 21 (72.4) 0.56 Reflux esophagitis 5(55.6) 2 (6.9) Peripheral eosinophil count and total IgE were not evaluated in all of the enrolled subjects. ABS, Ankylosaurus back sign; PPI-REE, proton pump-inhibitor responsive esophageal eosinophilia; H. pylori, helicobacter pylori for diagnosis of EoE [18,20, 21]. In addition, a new classification system to standardize the endoscopic assessment of esophageal signs of EoE (EREFS) was recently introduced [8]. This classification consists of the 5 most common and reproducibly identifiable findings, including edema (or decreased vascularity), rings, exudates, furrows, and strictures. EREFS has been validated in studies performed in Western countries, and shown to have usefulness for diagnosis as well as monitoring treatment response in patients with EoE [19,22, 23]. In addition, several minor endoscopic findings have been reported, such as esophageal polyps [24 26] and cobblestone-like appearance [27]. ABS also features nodular formation, though the linear arrangement occurs at uniform intervals and is completely different from those previously reported findings. The prevalence of EoE has been rapidly increasing in both Western and Asian countries, including Japan [10,28], leading to increased recognition of characteristic endoscopic findings among Japanese endoscopists. According to a recent systematic review, linear furrows are the most frequently reported abnormality in Asian patients with EoE [10]. Although most typical endoscopic findings reported in studies conducted in Western and Asian countries are similar, there may be ethnic differences in regard to EoE-related endoscopic findings. For example, as compared with Caucasian patients, Asians rarely have stenotic-type endoscopic findings, such as strictures or diffuse narrowing, which are associated with food impaction, a typical symptom of Western EoE patients, suggesting that the clinical presentation of EoE in Asian patients might be milder. We speculate that ABS may be a finding specific for Asian patients. Nonetheless, a large scale multi-center study is needed to confirm the precise prevalence of this finding in EE and EoE cases. In the current study, we evaluated detailed endoscopic features of ABS in our patients. ABS was found to occur in all circumferential directions in a radial pattern and appeared in esophageal longitudinal mucosal fold ridges in every affected patient, whereas none were found in valleys between ridges. Since esophageal mucosa and submucosa form longitudinal folds, and the cross-section of the esophageal lumen is starshaped, positioning in relation to esophageal longitudinal folds (ridge or valley) may be important in regard to the pathogenesis of ABS. In previous studies, we demonstrated that mucosal breaks seen in RE cases were located on mucosal fold ridges, mainly on the right anterior wall of the esophagus [18,29]. The mucosal breaks found on esophageal fold ridges in patients with RE suggest a more pronounced effect of refluxed gastric acid on those ridges. Therefore, the preferential presence of ABS on the fold ridges indicates a possible role of refluxed acid for its formation. In addition, awareness of the localization of ABS on esophageal fold ridge with air deflated condition can help to detect lesions during endoscopic procedures. Indeed, ABS was able to be identified with substantial inter-observer agreement among expert endoscopists after instruction regarding the endoscopic characteristics of ABS. ABS was found only in patients with PPI-REE in the current study. Moreover, mucosal breaks suggesting increased gastric acid reflux were more frequently found in the ABS-positive PPI- REE group.these findings indicate that gastroesophageal reflux may play an important role in formation of ABS. While, ABS was E170 Ishimura Norihisa et al. Ankylosaurus back sign: Endoscopy International Open 2018; 06: E165 E172
7 not found localized on the right anterior wall, and did not disappear after 2 months of PPI administration, despite confirmation of remission of eosinophil infiltration shown by histological findings. Persistent eosinophil infiltration is associated with tissue remodeling and fibrosis, resulting in decreased esophageal compliance, increased esophageal stiffness, and increased smooth muscle mass with smooth muscle dysfunction [30, 31]. Although no specific histological findings were detected in biopsied esophageal epithelium samples in the present cases, subepithelial fibrosis may be associated with formation of whitish nodules associated with ABS in the esophagus. Endoscopic ultrasonography may be useful to clarify the pathogenesis of ABS. A recent systematic review revealed that approximately half of investigated patients with symptomatic EE showed findings suggestive of histological remission of EoE achieved with PPI therapy [32]. Currently, EoE and PPI-REE remain indistinguishable without administration of PPI therapy, and there is concern regarding whether these should be considered as different diseases, especially when considering that they share similar or nearly identical genetic, phenotypic and mechanistic features [17, 33]. Therefore, PPI therapy should be considered as the first step, with diet/steroid treatment representing a further step up in therapy in the absence of clinical or histological response to PPI therapy as recommended in the updated guidelines [7]. PPI use is generally considered to be safe, though there is increasing information showing the potential of adverse effects with prolonged exposure to the drugs [34,35]. To reduce that concern, factors associated with favorable PPI response in patients with EE should be clarified. We consider that ABS may identify a PPI responsive phenotype of EE, as it was found only in patients with PPI-REE. This study has some limitations. It was performed in a retrospective manner at a single tertiary referral center. Also, the number of patients with EoE may not be adequate to compare with PPI-REE patients in regard to clinical characteristics, because of the lower number of cases in Asian populations. All the endoscopic images were based on still images, which may different from the real -time endoscopic assessment. In addition, this finding may be subjective nature of the sign, and was not clearly visible in fully air-insufflated condition. Substantial inter-observer agreement for the identification of ABS was shown among expert endoscopists, however the reliability of this finding should be evaluated among large number of endoscopists including non-expert endoscopists. Although these limitations necessitate future prospective studies before drawing any definite conclusions in this study, the present findings provide important information for better understanding of these diseases. Conclusion In summary, we report a new endoscopic feature termed ABS, which was found in 16.4 % of patients with EE. Although ABS was less frequent than typical endoscopic findings such as linear furrows in those patients, it was closely associated with PPI- REE accompanied with RE. Further studies are needed to investigate the clinical implications of ABS in patients with EE. Acknowledgements This study was supported by Health and Labour Sciences Research Grants for research on intractable diseases from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan. Competing interests None References [1] Rothenberg ME. Molecular, genetic, and cellular bases for treating eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2015; 148: [2] Furuta GT, Katzka DA. Eosinophilic Esophagitis. N Engl J Med 2015; 373: [3] Dellon ES, Gonsalves N, Hirano I et al. ACG clinical guideline: Evidenced based approach to the diagnosis and management of esophageal eosinophilia and eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE). Am J Gastroenterol 2013; 108: [4] Liacouras CA, Furuta GT, Hirano I et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: updated consensus recommendations for children and adults. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2011; 128: 3 20 [5] Molina-Infante J, Bredenoord AJ, Cheng E et al. Proton pump inhibitorresponsive oesophageal eosinophilia: an entity challenging current diagnostic criteria for eosinophilic oesophagitis. Gut 2016; 65: [6] Warners MJ, van Rhijn BD, Curvers WL et al. PPI-responsive esophageal eosinophilia cannot be distinguished from eosinophilic esophagitis by endoscopic signs. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015; 27: [7] Lucendo AJ, Molina-Infante J, Arias A et al. Guidelines on eosinophilic esophagitis: evidence-based statements and recommendations for diagnosis and management in children and adults. United European Gastroenterol J 2017; 5: [8] Hirano I, Moy N, Heckman MG et al. Endoscopic assessment of the oesophageal features of eosinophilic oesophagitis: validation of a novel classification and grading system. Gut 2013; 62: [9] Kim HP, Vance RB, Shaheen NJ et al. The prevalence and diagnostic utility of endoscopic features of eosinophilic esophagitis: a meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012; 10: [10] Kinoshita Y, Ishimura N, Oshima N et al. Systematic review: Eosinophilic esophagitis in Asian countries. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21: [11] Ishimura N, Shimura S, Jiao D et al. Clinical features of eosinophilic esophagitis: Differences between Asian and Western populations. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015; 30: [12] Amano K, Adachi K, Katsube T et al. Role of hiatus hernia and gastric mucosal atrophy in the development of reflux esophagitis in the elderly. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2001; 16: [13] Kimura K, Takemoto T. An Endoscopic Recognition of the Atrophic Border and its Significance in Chronic Gastritis. Endoscopy 1969; 1: [14] Hiremath GS, Hameed F, Pacheco A et al. Esophageal Food Impaction and Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Retrospective Study, Systematic Review, and Meta-Analysis. Dig Dis Sci 2015; 60: Ishimura Norihisa et al. Ankylosaurus back sign: Endoscopy International Open 2018; 06: E165 E172 E171
8 [15] von Arnim U, Wex T, Link A et al. Helicobacter pylori infection is associated with a reduced risk of developing eosinophilic oesophagitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2016; 43: [16] Furuta K, Adachi K, Aimi M et al. Case-control study of association of eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders with Helicobacter pylori infection in Japan. J Clin Biochem Nutr 2013; 53: [17] Jiao D, Ishimura N, Maruyama R et al. Similarities and differences among eosinophilic esophagitis, proton-pump inhibitor-responsive esophageal eosinophilia, and reflux esophagitis: comparisons of clinical, endoscopic, and histopathological findings in Japanese patients. J Gastroenterol 2017; 52: [18] Okimoto E, Ishimura N, Okada M et al. Specific locations of linear furrows in patients with esophageal eosinophilia. Dig Endosc 2017; 29: [19] van Rhijn BD, Warners MJ, Curvers WL et al. Evaluating the endoscopic reference score for eosinophilic esophagitis: moderate to substantial intra- and interobserver reliability. Endoscopy 2014; 46: [20] Peery AF, Cao H, Dominik R et al. Variable reliability of endoscopic findings with white-light and narrow-band imaging for patients with suspected eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011; 9: [21] Shimura S, Ishimura N, Tanimura T et al. Reliability of Symptoms and Endoscopic Findings for Diagnosis of Esophageal Eosinophilia in a Japanese Population. Digestion 2014; 90: [22] van Rhijn BD, Verheij J, Smout AJ et al. The Endoscopic Reference Score shows modest accuracy to predict histologic remission in adult patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2016; 28: [23] Dellon ES, Cotton CC, Gebhart JH et al. Accuracy of the Eosinophilic Esophagitis Endoscopic Reference Score in Diagnosis and Determining Response to Treatment. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016; 14: [24] Gill JA, Shutter J, Brady P. A rare endoscopic feature of eosinophilic esophagitis. Endoscopy 2011; 43: Unusual cases and technical notes: E17 [25] Goyal A, Poulik J, Chang CH et al. Esophageal polyp in a boy with eosinophilic esophagitis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2010; 51: 541 [26] Mulder DJ, Gander S, Hurlbut DJ et al. Multiple squamous hyperplastic-fibrous inflammatory polyps of the oesophagus: a new feature of eosinophilic oesophagitis? J Clin Pathol 2009; 62: [27] Muller S, Puhl S, Vieth M et al. Analysis of symptoms and endoscopic findings in 117 patients with histological diagnoses of eosinophilic esophagitis. Endoscopy 2007; 39: [28] Arias A, Perez-Martinez I, Tenias JM et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: the incidence and prevalence of eosinophilic oesophagitis in children and adults in population-based studies. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2016; 43: 3 15 [29] Katsube T, Adachi K, Furuta K et al. Difference in localization of esophageal mucosal breaks among grades of esophagitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2006; 21: [30] Beppu LY, Anilkumar AA, Newbury RO et al. TGF-beta1-induced phospholamban expression alters esophageal smooth muscle cell contraction in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2014; 134: [31] Lucendo AJ, Arias A, De Rezende LC et al. Subepithelial collagen deposition, profibrogenic cytokine gene expression, and changes after prolonged fluticasone propionate treatment in adult eosinophilic esophagitis: a prospective study. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2011; 128: [32] Lucendo AJ, Arias A, Molina-Infante J. Efficacy of Proton Pump Inhibitor Drugs for Inducing Clinical and Histologic Remission in Patients With Symptomatic Esophageal Eosinophilia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016; 14: [33] Shoda T, Morita H, Nomura I et al. Comparison of gene expression profiles in eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) between Japan and Western countries. Allergol Int 2015; 64: [34] Freedberg DE, Kim LS, Yang YX. The Risks and Benefits of Long-term Use of Proton Pump Inhibitors: Expert Review and Best Practice Advice From the American Gastroenterological Association. Gastroenterology 2017; 152: [35] Reimer C. Safety of long-term PPI therapy. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2013; 27: E172 Ishimura Norihisa et al. Ankylosaurus back sign: Endoscopy International Open 2018; 06: E165 E172
Evaluating the Endoscopic Reference Score for eosinophilic esophagitis: moderate to substantial intra- and interobserver reliability
 Original article 1049 Evaluating the Endoscopic Reference Score for eosinophilic esophagitis: moderate to substantial intra- and interobserver reliability Authors Institution submitted 29. January 2014
Original article 1049 Evaluating the Endoscopic Reference Score for eosinophilic esophagitis: moderate to substantial intra- and interobserver reliability Authors Institution submitted 29. January 2014
Recent Progress in the Research of Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Gastroenteritis
 Review Published online: January 14, 2016 Recent Progress in the Research of Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Gastroenteritis Yoshikazu Kinoshita Norihisa Ishimura Naoki Oshima Hironobu Mikami Eiko Okimoto
Review Published online: January 14, 2016 Recent Progress in the Research of Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Gastroenteritis Yoshikazu Kinoshita Norihisa Ishimura Naoki Oshima Hironobu Mikami Eiko Okimoto
ACG Clinical Guideline: Evidenced Based Approach to the Diagnosis and Management of Esophageal Eosinophilia and Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE)
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Evidenced Based Approach to the Diagnosis and Management of Esophageal Eosinophilia and Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) Evan S. Dellon, MD, MPH, 1,6 Nirmala Gonsalves, MD, 2,6 Ikuo
ACG Clinical Guideline: Evidenced Based Approach to the Diagnosis and Management of Esophageal Eosinophilia and Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) Evan S. Dellon, MD, MPH, 1,6 Nirmala Gonsalves, MD, 2,6 Ikuo
Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE)
 Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) 01.06.2016 EoE: immune-mediated disorder food or environmental antigens => Th2 inflammatory response. Key cytokines: IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 stimulate the production of eotaxin-3
Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) 01.06.2016 EoE: immune-mediated disorder food or environmental antigens => Th2 inflammatory response. Key cytokines: IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 stimulate the production of eotaxin-3
Mucosal breaks show same circumferential distribution in majority of patients with recurrent reflux esophagitis
 Original article Mucosal breaks show same circumferential distribution in majority of patients with recurrent reflux esophagitis Authors Naoki Fukuda 1,, Norihisa Ishimura 1,MayumiOkada 1,Daisuke Izumi
Original article Mucosal breaks show same circumferential distribution in majority of patients with recurrent reflux esophagitis Authors Naoki Fukuda 1,, Norihisa Ishimura 1,MayumiOkada 1,Daisuke Izumi
Esophageal Eosinophilia and Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Bible Class 09. Mai 2018
 Esophageal Eosinophilia and Eosinophilic Esophagitis Bible Class 09. Mai 2018 61 yo male No upper-gi symptoms Gastroscopy vor bariatric Operation Lesion: Papilloma Histology of the surrounding mucosa:
Esophageal Eosinophilia and Eosinophilic Esophagitis Bible Class 09. Mai 2018 61 yo male No upper-gi symptoms Gastroscopy vor bariatric Operation Lesion: Papilloma Histology of the surrounding mucosa:
Webinar Presenter: Marijn J. Warners, MD, PhD. Department Gastroenterology & Hepatology, Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam
 Efficacy of Amino Acid-based diet on Histologic Remission and Restoring Esophageal Mucosal Integrity in Adult Patients with Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) Dr. Marijn Warners June 23, 2016 Webinar Presenter:
Efficacy of Amino Acid-based diet on Histologic Remission and Restoring Esophageal Mucosal Integrity in Adult Patients with Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) Dr. Marijn Warners June 23, 2016 Webinar Presenter:
Rings in the esophagus are not always eosinophilic esophagitis: Case series of ring forming lymphocytic esophagitis and review of the literature
 Rings in the esophagus are not always eosinophilic esophagitis: Case series of ring forming lymphocytic esophagitis and review of the literature Authors Julia L. Pleet 1,SofiaTaboada 2, Arvind Rishi 2,
Rings in the esophagus are not always eosinophilic esophagitis: Case series of ring forming lymphocytic esophagitis and review of the literature Authors Julia L. Pleet 1,SofiaTaboada 2, Arvind Rishi 2,
Faculty Disclosures Research Support Consultant
 Faculty Disclosures Research Support Shire clinical area: eosinophilic esophagitis Regeneron clinical area: eosinophilic esophagitis Allakos clinical area: eosinophilic gastritis Consultant Shire clinical
Faculty Disclosures Research Support Shire clinical area: eosinophilic esophagitis Regeneron clinical area: eosinophilic esophagitis Allakos clinical area: eosinophilic gastritis Consultant Shire clinical
pissn: eissn: Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility
 JNM J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 24 No. 2 April, 2018 pissn: 2093-0879 eissn: 2093-0887 https://doi.org/10.5056/jnm17047 Original Article Diagnostic Trends and Clinical Characteristics of Eosinophilic
JNM J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 24 No. 2 April, 2018 pissn: 2093-0879 eissn: 2093-0887 https://doi.org/10.5056/jnm17047 Original Article Diagnostic Trends and Clinical Characteristics of Eosinophilic
MEDICAL NECESSITY GUIDELINE
 PAGE: 1 of 7 IMPORTANT REMINDER This Clinical Policy has been developed by appropriately experienced and licensed health care professionals based on a thorough review and consideration of generally accepted
PAGE: 1 of 7 IMPORTANT REMINDER This Clinical Policy has been developed by appropriately experienced and licensed health care professionals based on a thorough review and consideration of generally accepted
Learning Objectives. Disclaimer 9/8/2015. Jean Marie Osborne MS, RN, ANP-C
 Jean Marie Osborne MS, RN, ANP-C Learning Objectives 1. Understand the pathophysiologic process of EoE. 2. Dietary indiscretions 3. Management None to report Disclaimer 1 History EoE as an allergic disease
Jean Marie Osborne MS, RN, ANP-C Learning Objectives 1. Understand the pathophysiologic process of EoE. 2. Dietary indiscretions 3. Management None to report Disclaimer 1 History EoE as an allergic disease
When Food Keeps Getting Stuck: Recognizing and Understanding Eosinophilic Esophagitis in Children
 When Food Keeps Getting Stuck: Recognizing and Understanding Eosinophilic Esophagitis in Children Jenifer R. Lightdale, MD, MPH, FASGE Division Chief, Pediatric Gastroenterology UMass Memorial Children
When Food Keeps Getting Stuck: Recognizing and Understanding Eosinophilic Esophagitis in Children Jenifer R. Lightdale, MD, MPH, FASGE Division Chief, Pediatric Gastroenterology UMass Memorial Children
Disclosure. Learning Objectives 4/25/2014. I have no disclosures
 Alka Goyal MD Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology and Nutrition Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh of UPMC Disclosure I have no disclosures Learning Objectives Diagnosis of Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Alka Goyal MD Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology and Nutrition Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh of UPMC Disclosure I have no disclosures Learning Objectives Diagnosis of Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: The New Kid on the Block
 6/9/215 Eosinophilic Esophagitis: The New Kid on the Block Consultant: Takeda Disclosures Stuart Jon Spechler, M.D. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology, VA North Texas Healthcare System; Co-Director, Esophageal
6/9/215 Eosinophilic Esophagitis: The New Kid on the Block Consultant: Takeda Disclosures Stuart Jon Spechler, M.D. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology, VA North Texas Healthcare System; Co-Director, Esophageal
Eosinophilic oesophagitis
 Eosinophilic oesophagitis Food Allergy (Allergic food hypersensitivity) Mike Levin Paediatric Allergy Red Cross Hospital UCT IgE mediated Mixed Non IgE mediated Disease Mechanisms in EGID Rothenberg, JACI,
Eosinophilic oesophagitis Food Allergy (Allergic food hypersensitivity) Mike Levin Paediatric Allergy Red Cross Hospital UCT IgE mediated Mixed Non IgE mediated Disease Mechanisms in EGID Rothenberg, JACI,
Dysphagia What Else Should Allergists Consider?
 Dysphagia What Else Should Allergists Consider? Seema Aceves MD, PhD Associate Professor, Pediatrics and Medicine Director, EGID Clinic University of California, San Diego Rady Children s Hospital, San
Dysphagia What Else Should Allergists Consider? Seema Aceves MD, PhD Associate Professor, Pediatrics and Medicine Director, EGID Clinic University of California, San Diego Rady Children s Hospital, San
Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Kristine J. Krueger M.D. June 2014
 Eosinophilic Esophagitis Kristine J. Krueger M.D. June 2014 A Most Interesting Patient 36 year old self employed tree surgeon with long standing history of intermittent dysphagia and atypical GERD, NOT
Eosinophilic Esophagitis Kristine J. Krueger M.D. June 2014 A Most Interesting Patient 36 year old self employed tree surgeon with long standing history of intermittent dysphagia and atypical GERD, NOT
D DAVID PUBLISHING. 1. Introduction. Augusto Fey 1, 2, Lorete Maria da Silva Kotze 2 and Mônica Serapião 1
 Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 5 (2017) 834-839 doi: 10.17265/2328-2150/2017.11.007 D DAVID PUBLISHING A Novel Therapy of Eosinophilic Esophagitis-Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis Using a Single
Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 5 (2017) 834-839 doi: 10.17265/2328-2150/2017.11.007 D DAVID PUBLISHING A Novel Therapy of Eosinophilic Esophagitis-Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis Using a Single
Nicholas J. Shaheen, MD. MPH Center for Esophageal Diseases and Swallowing University of North Carolina SOM
 Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Are We There Yet? Nicholas J. Shaheen, MD. MPH Center for Esophageal Diseases and Swallowing University of North Carolina SOM Learning Objectives Understand current definition
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Are We There Yet? Nicholas J. Shaheen, MD. MPH Center for Esophageal Diseases and Swallowing University of North Carolina SOM Learning Objectives Understand current definition
Proton-pump inhibitor-responsive esophageal eosinophilia
 REVIEW C URRENT OPINION Proton-pump inhibitor-responsive esophageal eosinophilia Javier Molina-Infante a and David A. Katzka b Purpose of review Proton-pump inhibitor-responsive esophageal eosinophilia
REVIEW C URRENT OPINION Proton-pump inhibitor-responsive esophageal eosinophilia Javier Molina-Infante a and David A. Katzka b Purpose of review Proton-pump inhibitor-responsive esophageal eosinophilia
Helicobacter pylori Improved Detection of Helicobacter pylori
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2016.17.4.2099 RESEARCH ARTICLE Improved Detection of Helicobacter pylori Infection and Premalignant Gastric Mucosa Using Conventional White Light Source Gastroscopy
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2016.17.4.2099 RESEARCH ARTICLE Improved Detection of Helicobacter pylori Infection and Premalignant Gastric Mucosa Using Conventional White Light Source Gastroscopy
Research Article Prevalence of Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Lymphocytic Esophagitis in Adults with Esophageal Food Bolus Impaction
 Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2016, Article ID 9303858, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9303858 Research Article Prevalence of Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Lymphocytic Esophagitis
Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2016, Article ID 9303858, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9303858 Research Article Prevalence of Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Lymphocytic Esophagitis
Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Another Reason Not to Swallow
 Eosinophilic Esophagitis Another Reason Not to Swallow Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted in any form or
Eosinophilic Esophagitis Another Reason Not to Swallow Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted in any form or
IgE antibodies and response to cow's milk elimination diet in pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis
 IgE antibodies and response to cow's milk elimination diet in pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis Elizabeth A. Erwin, Nationwide Children's Hospital Patrice Kruszewski, Emory University John M. Russo, Nationwide
IgE antibodies and response to cow's milk elimination diet in pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis Elizabeth A. Erwin, Nationwide Children's Hospital Patrice Kruszewski, Emory University John M. Russo, Nationwide
Prevalence of Multiple White and Flat Elevated Lesions in Individuals Undergoing a Medical Checkup
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.9808-17 http://internmed.jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prevalence of Multiple White and Flat Elevated Lesions in Individuals Undergoing a Medical Checkup Kyoichi Adachi 1, Tomoko Mishiro
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.9808-17 http://internmed.jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prevalence of Multiple White and Flat Elevated Lesions in Individuals Undergoing a Medical Checkup Kyoichi Adachi 1, Tomoko Mishiro
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a poorly understood disease ENDOSCOPY CORNER
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2011;9:475 480 ENDOSCOPY CORNER Variable Reliability of Endoscopic Findings With White-Light and Narrow-Band Imaging for Patients With Suspected Eosinophilic Esophagitis
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2011;9:475 480 ENDOSCOPY CORNER Variable Reliability of Endoscopic Findings With White-Light and Narrow-Band Imaging for Patients With Suspected Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Eosinophilic Oesophagitis Bruce McLain Consultant Paediatric Gastroenterologist University Hospital North Tees
 Eosinophilic Oesophagitis Bruce McLain Consultant Paediatric Gastroenterologist University Hospital North Tees Eosinophilic oesophagitis Outline Definition Incidence and prevalence Pathology Presentation
Eosinophilic Oesophagitis Bruce McLain Consultant Paediatric Gastroenterologist University Hospital North Tees Eosinophilic oesophagitis Outline Definition Incidence and prevalence Pathology Presentation
GERD DIAGNOSIS & TREATMENT DISCLOSURES 4/18/2018
 GERD DIAGNOSIS & TREATMENT Subhash Chandra MBBS Assistant Professor CHI Health Clinic Gastroenterology Creighton University, School of Medicine April 28, 2018 DISCLOSURES None 1 OBJECTIVES Review update
GERD DIAGNOSIS & TREATMENT Subhash Chandra MBBS Assistant Professor CHI Health Clinic Gastroenterology Creighton University, School of Medicine April 28, 2018 DISCLOSURES None 1 OBJECTIVES Review update
Eosinophilic esophagitis. Kathleen Boynton MD University of Utah Gastroenterology Division
 Eosinophilic esophagitis Kathleen Boynton MD University of Utah Gastroenterology Division Financial disclosures: Janssen Genetech UCB All for research support Learning Objectives To identify the clinical
Eosinophilic esophagitis Kathleen Boynton MD University of Utah Gastroenterology Division Financial disclosures: Janssen Genetech UCB All for research support Learning Objectives To identify the clinical
Fibrosis and Remodeling in EoE
 Fibrosis and Remodeling in EoE Seema S. Aceves, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Allergy, Immunology University of California, San Diego Rady Children s Hospital, San Diego Faculty Disclosure Co-inventor of OVB
Fibrosis and Remodeling in EoE Seema S. Aceves, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Allergy, Immunology University of California, San Diego Rady Children s Hospital, San Diego Faculty Disclosure Co-inventor of OVB
Thermo Fisher IMMUNODAYS 2015 Lucerne, November 5 th EOSINOPHILIC ESOPHAGITIS: An emerging disease
 Thermo Fisher IMMUNODAYS 2015 Lucerne, November 5 th 2015 EOSINOPHILIC ESOPHAGITIS: An emerging disease Alain Schoepfer, MD, PD + MER1 Divison de Gastroentérologie et d Hépatologie CHUV, Lausanne Outline
Thermo Fisher IMMUNODAYS 2015 Lucerne, November 5 th 2015 EOSINOPHILIC ESOPHAGITIS: An emerging disease Alain Schoepfer, MD, PD + MER1 Divison de Gastroentérologie et d Hépatologie CHUV, Lausanne Outline
Relationship between Esophageal Cardiac Glands and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Relationship between Esophageal Cardiac Glands and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Kozue Hanada 1, Kyoichi Adachi 1, Tomoko Mishiro 1, Shino Tanaka 1, Yoshiko Takahashi 1, Kazuaki Yoshikawa
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Relationship between Esophageal Cardiac Glands and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Kozue Hanada 1, Kyoichi Adachi 1, Tomoko Mishiro 1, Shino Tanaka 1, Yoshiko Takahashi 1, Kazuaki Yoshikawa
Complex EoE patients. EoE is complicated
 Complex EoE patients ACG Annual Meeting 10/17/2016 Evan S. Dellon, MD, MPH Center for Esophageal Diseases And Swallowing EoE is complicated Page 1 of 21 Overview 4 complex cases EoE non-response a diagnostic
Complex EoE patients ACG Annual Meeting 10/17/2016 Evan S. Dellon, MD, MPH Center for Esophageal Diseases And Swallowing EoE is complicated Page 1 of 21 Overview 4 complex cases EoE non-response a diagnostic
Does Helicobacter pylori Protect against Eosinophilic Esophagitis in Children?
 Marshall University From the SelectedWorks of Deborah L Preston October, 2014 Does Helicobacter pylori Protect against Eosinophilic Esophagitis in Children? Yoram Elitsur, MD, Joan C Edwards School of
Marshall University From the SelectedWorks of Deborah L Preston October, 2014 Does Helicobacter pylori Protect against Eosinophilic Esophagitis in Children? Yoram Elitsur, MD, Joan C Edwards School of
What is Eosinophilic Esophagitis, how is it treated, and will it go away?
 Panelists What is Eosinophilic Esophagitis, how is it treated, and will it go away? Bradley A. Becker, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics and Internal Medicine Division of Allergy and Immunology Saint Louis
Panelists What is Eosinophilic Esophagitis, how is it treated, and will it go away? Bradley A. Becker, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics and Internal Medicine Division of Allergy and Immunology Saint Louis
A Chronic or Recurring Pattern of Esophagitis Resembling Allergic Contact Dermatitis
 Anatomic Pathology / Lymphocytic Esophagitis Lymphocytic Esophagitis A Chronic or Recurring Pattern of Esophagitis Resembling Allergic Contact Dermatitis Julianne K. Purdy, MD, Henry D. Appelman, MD, Christopher
Anatomic Pathology / Lymphocytic Esophagitis Lymphocytic Esophagitis A Chronic or Recurring Pattern of Esophagitis Resembling Allergic Contact Dermatitis Julianne K. Purdy, MD, Henry D. Appelman, MD, Christopher
A visual analogue scale and a Likert scale are simple and responsive tools for assessing dysphagia in eosinophilic oesophagitis
 Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics A visual analogue scale and a Likert scale are simple and responsive tools for assessing dysphagia in eosinophilic oesophagitis C. C. Reed, W. A. Wolf, C. C. Cotton
Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics A visual analogue scale and a Likert scale are simple and responsive tools for assessing dysphagia in eosinophilic oesophagitis C. C. Reed, W. A. Wolf, C. C. Cotton
Relationship between Kyphosis and Barrett s Esophagus in Japanese Patients
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Relationship between Kyphosis and Barrett s Esophagus in Japanese Patients Goichi Uno 1, Yuji Amano 1, Takafumi Yuki 1, Akihiko Oka 2, Norihisa Ishimura 2, Shunji Ishihara 2 and Yoshikazu
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Relationship between Kyphosis and Barrett s Esophagus in Japanese Patients Goichi Uno 1, Yuji Amano 1, Takafumi Yuki 1, Akihiko Oka 2, Norihisa Ishimura 2, Shunji Ishihara 2 and Yoshikazu
The efficacy of step-down therapy in adult patients with proton pump inhibitor-responsive oesophageal eosinophilia
 Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics The efficacy of step-down therapy in adult patients with proton pump inhibitor-responsive oesophageal eosinophilia E. Gomez-Torrijos*, R. Garcıa-Rodrıguez*, A.
Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics The efficacy of step-down therapy in adult patients with proton pump inhibitor-responsive oesophageal eosinophilia E. Gomez-Torrijos*, R. Garcıa-Rodrıguez*, A.
Eosinophilic Esophagitis No Relevant Disclosures
 Eosinophilic Esophagitis No Relevant Disclosures Rabindra R Watson, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine Director, Career Development in Advanced Endoscopy Division of Digestive Diseases David Geffen
Eosinophilic Esophagitis No Relevant Disclosures Rabindra R Watson, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine Director, Career Development in Advanced Endoscopy Division of Digestive Diseases David Geffen
Eosinophilic Esophagitis Medical versus Dietary Therapy
 Eosinophilic Esophagitis Medical versus Dietary Therapy Kathryn A. Peterson MD, MSci University of Utah Gastroenterology ACG Clinical Guideline: 2013 Genetic profiles support an allergic pathogenesis TH2
Eosinophilic Esophagitis Medical versus Dietary Therapy Kathryn A. Peterson MD, MSci University of Utah Gastroenterology ACG Clinical Guideline: 2013 Genetic profiles support an allergic pathogenesis TH2
JNM Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility
 JNM Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 19 No. 1 January, 2013 pissn: 2093-0879 eissn: 2093-0887 http://dx.doi.org/10.5056/jnm.2013.19.1.42 Original Article Observations
JNM Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 19 No. 1 January, 2013 pissn: 2093-0879 eissn: 2093-0887 http://dx.doi.org/10.5056/jnm.2013.19.1.42 Original Article Observations
Thermo Fisher IMMUNODAY Lausanne, December 1 st Diagnosis and Management of Eosinophilic Esophagitis
 Thermo Fisher IMMUNODAY Lausanne, December 1 st 2016 Diagnosis and Management of Eosinophilic Esophagitis Alain Schoepfer, MD, PD + MERClin Division de Gastroentérologie et d Hépatologie CHUV, Lausanne
Thermo Fisher IMMUNODAY Lausanne, December 1 st 2016 Diagnosis and Management of Eosinophilic Esophagitis Alain Schoepfer, MD, PD + MERClin Division de Gastroentérologie et d Hépatologie CHUV, Lausanne
EGD. John M. Wo, M.D. University of Louisville July 3, 2008
 EGD John M. Wo, M.D. University of Louisville July 3, 2008 Different Ways to do an EGD Which scope? Pediatric, regular, jumbo EGD endoscope or pediatric colonoscope Transnasal vs. transoral insertion Sedation
EGD John M. Wo, M.D. University of Louisville July 3, 2008 Different Ways to do an EGD Which scope? Pediatric, regular, jumbo EGD endoscope or pediatric colonoscope Transnasal vs. transoral insertion Sedation
Management Strategies for the Newly Diagnosed Patient with Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Diet, Medications, or Both?
 Management Strategies for the Newly Diagnosed Patient with Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Diet, Medications, or Both? Jonathan E. Markowitz, MD, MSCE Chief, Pediatric Gastroenterology Greenville Children s
Management Strategies for the Newly Diagnosed Patient with Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Diet, Medications, or Both? Jonathan E. Markowitz, MD, MSCE Chief, Pediatric Gastroenterology Greenville Children s
Gastric mucosal status in patients with reflux esophagitis
 Gastric mucosal status in patients with reflux esophagitis Riyadh Mohamad Hasan 1, Batool Mutar Mahdi 2 1. Department of Surgery, Al-Kindy College of Medicine, University of Baghdad, Iraq 2. Department
Gastric mucosal status in patients with reflux esophagitis Riyadh Mohamad Hasan 1, Batool Mutar Mahdi 2 1. Department of Surgery, Al-Kindy College of Medicine, University of Baghdad, Iraq 2. Department
Gastrooesophageal reflux disease. Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia
 Gastrooesophageal reflux disease Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia Reflux esophagitis (RE) GERD: a spectrum of clinical conditions and histologic alterations resulting
Gastrooesophageal reflux disease Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia Reflux esophagitis (RE) GERD: a spectrum of clinical conditions and histologic alterations resulting
Accepted Manuscript. CGH Editorial: Sound the Alarm for Barrett s Screening! Tarek Sawas, M.D., M.P.H., David A. Katzka, M.D
 Accepted Manuscript CGH Editorial: Sound the Alarm for Barrett s Screening! Tarek Sawas, M.D., M.P.H., David A. Katzka, M.D PII: S1542-3565(18)31093-0 DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.10.010 Reference: YJCGH 56132
Accepted Manuscript CGH Editorial: Sound the Alarm for Barrett s Screening! Tarek Sawas, M.D., M.P.H., David A. Katzka, M.D PII: S1542-3565(18)31093-0 DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.10.010 Reference: YJCGH 56132
Linked color imaging improves detection of minimal change esophagitis in non-erosive reflux esophagitis patients
 Linked color imaging improves detection of minimal change esophagitis in non-erosive reflux esophagitis patients Authors Pei Deng *,MinMin *, Tenghui Dong, Yiliang Bi, Airong Tang, Yan Liu Institution
Linked color imaging improves detection of minimal change esophagitis in non-erosive reflux esophagitis patients Authors Pei Deng *,MinMin *, Tenghui Dong, Yiliang Bi, Airong Tang, Yan Liu Institution
Review Article Eosinophilic Esophagitis for the Otolaryngologist
 International Otolaryngology Volume 2012, Article ID 181402, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/181402 Review Article Eosinophilic Esophagitis for the Otolaryngologist Petros D. Karkos, R. Srivastava, S. Kaptanis,
International Otolaryngology Volume 2012, Article ID 181402, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/181402 Review Article Eosinophilic Esophagitis for the Otolaryngologist Petros D. Karkos, R. Srivastava, S. Kaptanis,
Proton Pump Inhibitor Induction of Gastric Cobblestone-like Lesions in the Stomach
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.7964-16 Intern Med Advance Publication http://internmed.jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Proton Pump Inhibitor Induction of Gastric Cobblestone-like Lesions in the Stomach Kosuke Takahari
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.7964-16 Intern Med Advance Publication http://internmed.jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Proton Pump Inhibitor Induction of Gastric Cobblestone-like Lesions in the Stomach Kosuke Takahari
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is an emerging condition
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:1305 1313 Clinical, Endoscopic, and Histologic Findings Distinguish Eosinophilic Esophagitis From Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease EVAN S. DELLON,*, WOOD
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:1305 1313 Clinical, Endoscopic, and Histologic Findings Distinguish Eosinophilic Esophagitis From Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease EVAN S. DELLON,*, WOOD
Systematic review: Eosinophilic esophagitis in Asian countries
 Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 0.3748/wjg.v2.i27.8433 World J Gastroenterol 205 July 2; 2(27): 8433-8440 ISSN 007-9327 (print)
Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 0.3748/wjg.v2.i27.8433 World J Gastroenterol 205 July 2; 2(27): 8433-8440 ISSN 007-9327 (print)
Objectives. Disclosures. Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Nutritional Consequences. Food Allergy In Schools
 Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Nutritional Consequences Douglas T. Johnston, DO, FACAAI, FAAAAI Assistant Professor of Internal Medicine / Allergy & Immunology Edward Via College of Osteopathic Medicine
Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Nutritional Consequences Douglas T. Johnston, DO, FACAAI, FAAAAI Assistant Professor of Internal Medicine / Allergy & Immunology Edward Via College of Osteopathic Medicine
Gastrointestinal Imaging
 Endoscopic Imaging of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Kerry B Dunbar, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Abstract
Endoscopic Imaging of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Kerry B Dunbar, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Abstract
Magnifying image-enhanced endoscopy for collagenous colitis
 Magnifying image-enhanced endoscopy for collagenous colitis Authors Masaaki Kobayashi 1, Takahiro Hoshi 1, Shin-ich Morita 1,TsutomuKanefuji 1, Takeshi Suda 1,GoHasegawa 2, Shuji Terai 3 Institutions 1
Magnifying image-enhanced endoscopy for collagenous colitis Authors Masaaki Kobayashi 1, Takahiro Hoshi 1, Shin-ich Morita 1,TsutomuKanefuji 1, Takeshi Suda 1,GoHasegawa 2, Shuji Terai 3 Institutions 1
Relationship of Helicobacter pylori Infection with Gastric Black Spots Shown by Endoscopy
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1751-18 http://internmed.jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Relationship of Helicobacter pylori Infection with Gastric Black Spots Shown by Endoscopy Kyoichi Adachi 1, Takumi Notsu 1, Tomoko
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1751-18 http://internmed.jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Relationship of Helicobacter pylori Infection with Gastric Black Spots Shown by Endoscopy Kyoichi Adachi 1, Takumi Notsu 1, Tomoko
Barrett s Esophagus. Abdul Sami Khan, M.D. Gastroenterologist Aurora Healthcare Burlington, Elkhorn, Lake Geneva, WI
 Barrett s Esophagus Abdul Sami Khan, M.D. Gastroenterologist Aurora Healthcare Burlington, Elkhorn, Lake Geneva, WI A 58 year-old, obese white man has had heartburn for more than 20 years. He read a magazine
Barrett s Esophagus Abdul Sami Khan, M.D. Gastroenterologist Aurora Healthcare Burlington, Elkhorn, Lake Geneva, WI A 58 year-old, obese white man has had heartburn for more than 20 years. He read a magazine
Endoscopic atrophic classification before and after H. pylori eradication is closely associated with histological atrophy and intestinal metaplasia
 E311 before and after H. pylori eradication is closely associated with histological atrophy and intestinal metaplasia Authors Institution Masaaki Kodama, Tadayoshi Okimoto, Ryo Ogawa, Kazuhiro Mizukami,
E311 before and after H. pylori eradication is closely associated with histological atrophy and intestinal metaplasia Authors Institution Masaaki Kodama, Tadayoshi Okimoto, Ryo Ogawa, Kazuhiro Mizukami,
Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGIDs) are
 G&H CLINICAL CASE STUDIES Esophageal Obstruction as a Result of Isolated Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis Petros C. Benias, MD Ayaz Matin, MD Gil Ignacio Ascunce, MD David L. Carr-Locke, MD Division of Digestive
G&H CLINICAL CASE STUDIES Esophageal Obstruction as a Result of Isolated Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis Petros C. Benias, MD Ayaz Matin, MD Gil Ignacio Ascunce, MD David L. Carr-Locke, MD Division of Digestive
Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks
 Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks Stuart Jon Spechler, M.D. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology, VA North Texas Healthcare System; Co-Director, Esophageal Diseases Center, Professor of Medicine,
Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks Stuart Jon Spechler, M.D. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology, VA North Texas Healthcare System; Co-Director, Esophageal Diseases Center, Professor of Medicine,
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: helicobacter_pylori_testing 01/01/2019 N/A 01/01/2020 01/01/2019 Policy Effective April 1, 2019 Description
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: helicobacter_pylori_testing 01/01/2019 N/A 01/01/2020 01/01/2019 Policy Effective April 1, 2019 Description
Eosinophilic Esophagitis in Children and Adults
 Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 37:S23 S28 November/December 2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia Eosinophilic Esophagitis in Children and Adults Chris A. Liacouras
Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 37:S23 S28 November/December 2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia Eosinophilic Esophagitis in Children and Adults Chris A. Liacouras
Can esophageal dilation be avoided in the treatment of severe esophageal stricture caused by eosinophilic esophagitis?
 C A S E R E P O R T S Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol Vol 47, N 4, 132-136, 2015 D. Silva 1,2, F. Santos 3, S. Piedade 1, M. Morais-Almeida 1 Can esophageal dilation be avoided in the treatment of severe
C A S E R E P O R T S Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol Vol 47, N 4, 132-136, 2015 D. Silva 1,2, F. Santos 3, S. Piedade 1, M. Morais-Almeida 1 Can esophageal dilation be avoided in the treatment of severe
Last Revised: September 15 Last Reviewed: September EOSINOPHILIC ESOPHAGITIS (EOE)/PPI-RESPONSIVE ESOPHAGEAL EOSINOPHILIA (PPI-REE)
 7.0 GASTROENTEROLOGY Last Revised: September 5 Last Reviewed: September 5 7. EOSINOPHILIC ESOPHAGITIS (EOE)/PPI-RESPONSIVE ESOPHAGEAL EOSINOPHILIA (PPI-REE) Significant changes: ) Addition of PPI-REE as
7.0 GASTROENTEROLOGY Last Revised: September 5 Last Reviewed: September 5 7. EOSINOPHILIC ESOPHAGITIS (EOE)/PPI-RESPONSIVE ESOPHAGEAL EOSINOPHILIA (PPI-REE) Significant changes: ) Addition of PPI-REE as
New Developments in the Endoscopic Diagnosis and Management of Barrett s Esophagus
 New Developments in the Endoscopic Diagnosis and Management of Barrett s Esophagus Prateek Sharma, MD Key Clinical Management Points: Endoscopic recognition of a columnar lined distal esophagus is crucial
New Developments in the Endoscopic Diagnosis and Management of Barrett s Esophagus Prateek Sharma, MD Key Clinical Management Points: Endoscopic recognition of a columnar lined distal esophagus is crucial
Risk Factors for Helicobacter pylori Infection and Endoscopic Reflux Esophagitis in Healthy Young Japanese Volunteers
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8669-16 Intern Med 56: 2979-2983, 2017 http://internmed.jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Risk Factors for Helicobacter pylori Infection and Endoscopic Reflux in Healthy Young Japanese
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8669-16 Intern Med 56: 2979-2983, 2017 http://internmed.jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Risk Factors for Helicobacter pylori Infection and Endoscopic Reflux in Healthy Young Japanese
Common Inflammatory Gastrointestinal Disorders: Endoscopic and Pathologic Correlations
 Common Inflammatory Gastrointestinal Disorders: Endoscopic and Pathologic Correlations Nicole C. Panarelli, M.D. Attending Pathologist Montefiore Medical Center Associate Professor of Pathology - Albert
Common Inflammatory Gastrointestinal Disorders: Endoscopic and Pathologic Correlations Nicole C. Panarelli, M.D. Attending Pathologist Montefiore Medical Center Associate Professor of Pathology - Albert
Faculty Disclosure for Seema Aceves, MD, PhD
 Faculty Disclosure for Seema Aceves, MD, PhD For the 12 months preceding this CME activity, I disclose the following types of financial relationships: Honoraria received from: None Consulted for: None
Faculty Disclosure for Seema Aceves, MD, PhD For the 12 months preceding this CME activity, I disclose the following types of financial relationships: Honoraria received from: None Consulted for: None
The skinny on eosinophilic esophagitis
 MEDICAL GRAND ROUNDS CME CREDIT EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVE: Readers will distinguish eosinophilic esophagitis from reflux disease based on specific clinical symptoms and histologic features DAVID A. KATZKA,
MEDICAL GRAND ROUNDS CME CREDIT EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVE: Readers will distinguish eosinophilic esophagitis from reflux disease based on specific clinical symptoms and histologic features DAVID A. KATZKA,
Eosinophilic esophagi.s- Diagnosis and Treatment. The Atopic poor eater. The Fearful Carnivore 2/24/13. 3 yo Male
 Eosinophilic esophagi.s- Diagnosis and Treatment Big Sky Pulmonary Conference Bozeman, MT March 8, 2013 Glenn T. Furuta Diges.ve Health Ins.tute Children s Hospital Colorado, Aurora, CO Na.onal Jewish
Eosinophilic esophagi.s- Diagnosis and Treatment Big Sky Pulmonary Conference Bozeman, MT March 8, 2013 Glenn T. Furuta Diges.ve Health Ins.tute Children s Hospital Colorado, Aurora, CO Na.onal Jewish
Eosinophilic Oesphagitis
 Eosinophilic Oesphagitis Eosinophilic oesophagitis results in an inflamed oesophagus, the muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach. Most cases are seen in people with other allergies such as
Eosinophilic Oesphagitis Eosinophilic oesophagitis results in an inflamed oesophagus, the muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach. Most cases are seen in people with other allergies such as
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic inflammatory disorder
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE: GASTROENTEROLOGY Early Life Exposures as Risk Factors for Pediatric Eosinophilic Esophagitis Elizabeth T. Jensen, y Michael D. Kappelman, z Hannah P. Kim, Tamar Ringel-Kulka, and z Evan
ORIGINAL ARTICLE: GASTROENTEROLOGY Early Life Exposures as Risk Factors for Pediatric Eosinophilic Esophagitis Elizabeth T. Jensen, y Michael D. Kappelman, z Hannah P. Kim, Tamar Ringel-Kulka, and z Evan
Case discussions. Case 1
 Case discussions Arzu Ensari 12 year old teen Case 1 Progressive cough and dysphagia following flu-like symptoms Family history of asthma Erythema in lower oesophagus 1 40 eos/hpf 2 What is Eosinophilic
Case discussions Arzu Ensari 12 year old teen Case 1 Progressive cough and dysphagia following flu-like symptoms Family history of asthma Erythema in lower oesophagus 1 40 eos/hpf 2 What is Eosinophilic
ORIGINAL ARTICLES ALIMENTARY TRACT. Esophageal Eosinophilic Infiltration Responds to Proton Pump Inhibition in Most Adults
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2011;9:110 117 ORIGINAL ARTICLES ALIMENTARY TRACT Esophageal Eosinophilic Infiltration Responds to Proton Pump Inhibition in Most Adults JAVIER MOLINA INFANTE,*
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2011;9:110 117 ORIGINAL ARTICLES ALIMENTARY TRACT Esophageal Eosinophilic Infiltration Responds to Proton Pump Inhibition in Most Adults JAVIER MOLINA INFANTE,*
Ethnic Distribution of Atrophic Autoimmune Gastritis in the United States
 Ethnic Distribution of Atrophic Autoimmune Gastritis in the United States Robert M. Genta, Regan Allen, Massimo Rugge Miraca Life Sciences Research Institute, Miraca Life Sciences, Irving, Texas UTSW University
Ethnic Distribution of Atrophic Autoimmune Gastritis in the United States Robert M. Genta, Regan Allen, Massimo Rugge Miraca Life Sciences Research Institute, Miraca Life Sciences, Irving, Texas UTSW University
ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Barrett s Esophagus
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Barrett s Esophagus Nicholas J. Shaheen, MD, MPH, FACG 1, Gary W. Falk, MD, MS, FACG 2, Prasad G. Iyer, MD, MSc, FACG 3 and Lauren Gerson, MD, MSc, FACG
ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Barrett s Esophagus Nicholas J. Shaheen, MD, MPH, FACG 1, Gary W. Falk, MD, MS, FACG 2, Prasad G. Iyer, MD, MSc, FACG 3 and Lauren Gerson, MD, MSc, FACG
Dupilumab Efficacy and Safety in Adult Patients With Active Eosinophilic Esophagitis: a Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Phase 2 Trial
 Dupilumab Efficacy and Safety in Adult Patients With Active Eosinophilic Esophagitis: a Randomized Double-Blind -Controlled Phase 2 Trial Ikuo Hirano, Evan S. Dellon, Jennifer D. Hamilton, Margaret H.
Dupilumab Efficacy and Safety in Adult Patients With Active Eosinophilic Esophagitis: a Randomized Double-Blind -Controlled Phase 2 Trial Ikuo Hirano, Evan S. Dellon, Jennifer D. Hamilton, Margaret H.
Disclosures. GI Motility Disorders. Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders & Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders & Irritable Bowel Syndrome None Disclosures Jasmine Zia, MD Acting Assistant Professor Division of Gastroenterology, University of Washington 6 th Asian Health Symposium
Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders & Irritable Bowel Syndrome None Disclosures Jasmine Zia, MD Acting Assistant Professor Division of Gastroenterology, University of Washington 6 th Asian Health Symposium
Clinical Study Eosinophilic Esophagitis in a Developing Country: Is It Different from Developed Countries?
 Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2013, Article ID 526037, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/526037 Clinical Study Eosinophilic Esophagitis in a Developing Country: Is It Different from
Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2013, Article ID 526037, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/526037 Clinical Study Eosinophilic Esophagitis in a Developing Country: Is It Different from
INTRODUCTION. Key Words: Gastroesophageal reflux; Agreement; Experience. ORiginal Article
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 8, No. 2, March 2014, pp. 154-159 ORiginal Article Endoscopic Experience Improves Interobserver Agreement in the Grading of Esophagitis by Los Angeles Classification: Conventional Endoscopy
Gut and Liver, Vol. 8, No. 2, March 2014, pp. 154-159 ORiginal Article Endoscopic Experience Improves Interobserver Agreement in the Grading of Esophagitis by Los Angeles Classification: Conventional Endoscopy
Proton pump inhibitor-responsive esophageal eosinophilia: A historical perspective on a novel and evolving entity
 1130-0108/2015/107/1/29-36 Revista Española de Enfermedades Digestivas Copyright 2015 Arán Ediciones, S. L. Rev Esp Enferm Dig (Madrid Vol. 107, N.º 1, pp. 29-36, 2015 REVIEW Proton pump inhibitor-responsive
1130-0108/2015/107/1/29-36 Revista Española de Enfermedades Digestivas Copyright 2015 Arán Ediciones, S. L. Rev Esp Enferm Dig (Madrid Vol. 107, N.º 1, pp. 29-36, 2015 REVIEW Proton pump inhibitor-responsive
Module 2 Heartburn Glossary
 Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
AGA SECTION. Gastroenterology 2016;150:
 Gastroenterology 2016;150:1026 1030 April 2016 AGA Section 1027 Procedural intervention (3) Upper endoscopy indications 3 6 Non-response of symptoms to a 4 8 week empiric trial of twice-daily PPI Troublesome
Gastroenterology 2016;150:1026 1030 April 2016 AGA Section 1027 Procedural intervention (3) Upper endoscopy indications 3 6 Non-response of symptoms to a 4 8 week empiric trial of twice-daily PPI Troublesome
Management of Barrett s Esophagus. Case Presentation
 Management of Barrett s Esophagus Lauren B. Gerson MD, MSc Associate Clinical Professor, UCSF Director of Clinical Research Gastroenterology Fellowship Program California Pacific Medical Center San Francisco,
Management of Barrett s Esophagus Lauren B. Gerson MD, MSc Associate Clinical Professor, UCSF Director of Clinical Research Gastroenterology Fellowship Program California Pacific Medical Center San Francisco,
Esophageal Dysphagia prior to 1995: Structural Etiologies. Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Eosinophilic Esophagitis Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE)
 Case sentation 42 year old male presents with 12 years of intermittent dysphagia for solids that localizes to his mid sternum. Symptoms have been progressive; now occurring on a daily basis. He has had
Case sentation 42 year old male presents with 12 years of intermittent dysphagia for solids that localizes to his mid sternum. Symptoms have been progressive; now occurring on a daily basis. He has had
Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 2. Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath
 Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath Eosinophilic esophagitis Incidence of eosinophilic gastritis is increasing. Symptoms: food impaction and dysphagia. Histology: infiltration
Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath Eosinophilic esophagitis Incidence of eosinophilic gastritis is increasing. Symptoms: food impaction and dysphagia. Histology: infiltration
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Introduction. Original articles. Nicolás Rocha, 1 Sandra Huertas, 2 Rosario Albis, 3 Diego Aponte, 4 Luis Carlos Sabbagh. 5
 Original articles Correlation of endoscopic and histological findings in diagnosis of gastrointestinal metaplasia in patients referred to the Clinica Colombia for upper endoscopies Nicolás Rocha, 1 Sandra
Original articles Correlation of endoscopic and histological findings in diagnosis of gastrointestinal metaplasia in patients referred to the Clinica Colombia for upper endoscopies Nicolás Rocha, 1 Sandra
Effects of Metoclopramide on Esophageal Motor Activity and Esophagogastric Junction Compliance in Healthy Volunteers
 JNM J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 22 No. 1 January, 2016 pissn: 2093-0879 eissn: 2093-0887 http://dx.doi.org/10.5056/jnm15130 Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility Original Article Effects of
JNM J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 22 No. 1 January, 2016 pissn: 2093-0879 eissn: 2093-0887 http://dx.doi.org/10.5056/jnm15130 Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility Original Article Effects of
Definition of GERD American College of Gastroenterology
 Definition of GERD American College of Gastroenterology GERD is defined as chronic symptoms or mucosal damage produced by the abnormal reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus DeVault et al. Am J
Definition of GERD American College of Gastroenterology GERD is defined as chronic symptoms or mucosal damage produced by the abnormal reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus DeVault et al. Am J
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic inflammatory disorder
 Current Diagnostic and Treatment Strategies for Eosinophilic Esophagitis Anna M. Lipowska, MD, and Robert T. Kavitt, MD, MPH Dr Lipowska is a gastroenterology fellow and Dr Kavitt is an assistant professor
Current Diagnostic and Treatment Strategies for Eosinophilic Esophagitis Anna M. Lipowska, MD, and Robert T. Kavitt, MD, MPH Dr Lipowska is a gastroenterology fellow and Dr Kavitt is an assistant professor
Correlation between Gastric Mucosal Morphologic Patterns and Histopathological Severity of
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 808505, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/808505 Research Article Correlation between Gastric Mucosal Morphologic
Hindawi Publishing Corporation BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 808505, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/808505 Research Article Correlation between Gastric Mucosal Morphologic
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic allergic/immunemediated
 An Evolving Approach to the Diagnosis of Eosinophilic Esophagitis Hannah P. Kim, MD, and Evan S. Dellon, MD, MPH Dr Kim is a fellow and Dr Dellon is an associate professor at the Center for Esophageal
An Evolving Approach to the Diagnosis of Eosinophilic Esophagitis Hannah P. Kim, MD, and Evan S. Dellon, MD, MPH Dr Kim is a fellow and Dr Dellon is an associate professor at the Center for Esophageal
Eosinophilic esophagitis associated with celiac disease in children
 DOI 10.1186/s13104-015-1256-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Eosinophilic esophagitis associated with celiac disease in children Rajmohan Dharmaraj 1*, Karen Hagglund 2 and Hernando Lyons 3 Open Access Abstract Background:
DOI 10.1186/s13104-015-1256-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Eosinophilic esophagitis associated with celiac disease in children Rajmohan Dharmaraj 1*, Karen Hagglund 2 and Hernando Lyons 3 Open Access Abstract Background:
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children
 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children 4 Marzo 2017 Drssa Chiara Leoni Drssa Valentina Giorgio pediatriagastro@gmail.com valentinagiorgio1@gmail.com Definitions: GER GER is the passage
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children 4 Marzo 2017 Drssa Chiara Leoni Drssa Valentina Giorgio pediatriagastro@gmail.com valentinagiorgio1@gmail.com Definitions: GER GER is the passage
Eosinophilic esophagitis: An increasingly recognized cause of dysphagia, food impaction, and refractory heartburn
 REVIEW ILCHE T. NONEVSKI, MD, MBA Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Center for Swallowing and Esophageal Disorders, Cleveland Clinic ERINN DOWNS-KELLY, DO Department of Anatomic Pathology,
REVIEW ILCHE T. NONEVSKI, MD, MBA Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Center for Swallowing and Esophageal Disorders, Cleveland Clinic ERINN DOWNS-KELLY, DO Department of Anatomic Pathology,
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: From the Bench to the Bedside
 Summary of presentation Eosinophilic Esophagitis: From the Bench to the Bedside at the North American Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, October 22, 2005 Glenn T. Furuta,
Summary of presentation Eosinophilic Esophagitis: From the Bench to the Bedside at the North American Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, October 22, 2005 Glenn T. Furuta,
