Osteolytic Phaeohyphomycosis in a German Shepherd Dog Caused by Phialemonium obovatum
|
|
|
- Thomasine Montgomery
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, May 1986, p Vol. 23, No /86/ $02.00/0 Copyright C) 1986, American Society for Microbiology Osteolytic Phaeohyphomycosis in a German Shepherd Dog Caused by Phialemonium obovatum LARRY G. LOMAX,1t JOHN R. COLE,1 ARVIND A. PADHYE,2* LIBERO AJELLO,2 FRANCIS W. CHANDLER,3 AND BRON R. SMITH4 Veterinary Diagnostic and Investigational Laboratory, University of Georgia, Tifton, Georgia ; Division of Mycotic Diseases2 and Division of Host Factors,3 Center for Infectious Diseases, Centers for Disease Control, Atlanta, Georgia 30333; and Scenic Plaza Animal Clinic, Lawrenceville, Georgia Received 26 December 1985/Accepted 13 February 1986 Phialemonium obovatum was found to be the cause of osteomyelitis in a German shepherd dog. Histologic examination of the biopsied material from the left tibia revealed septate, irregularly branched hyphae, swollen cells, and ovate-to-spherical cells divided by a transverse septum. The majority of the fungal elements were hyaline, but a few had lightly pigmented cell walls that had a greenish yellow tint. The presence of melanin in the cell walls of the hyphae and especially in their septa was verified by the use of the Fontana-Masson silver stain. P. obovatum formed moist, off-white-to-ochraceous, spreading colonies with a characteristic green pigment on their reverse side. The pigment was more prominent in cultures grown at 37 C than in those grown at 25 C. The isolate also grew at 40 C. The dog isolate produced characteristic adelophialides without conspicuous collarettes and also basal septa from the creeping vegetative hyphae growing on the surface of the medium. The numerous obovate phialoconidia were smooth and one-celled. Phaeohyphomycosis encompasses a distinct, heterogenous, and important group of infections in which the etiologic agents in tissue occur as dematiaceous, yeastlike cells, pseudohyphal-like elements, toruloid hyphae, small chains of cells, distorted to swollen cells, or any combinations of these forms (1, 2, 7). Even though fungal elements in tissue are generally described as dematiaceous, not all elements present in the tissue manifest their pigmented nature. In some instances, several tissue sections have to be carefully examined before the dematiaceous nature of the fungal elements is recognized. In phaeohyphomycotic infections caused by Alternaria alternata, Bipolaris spicifera (syn. Drechslera spicifera) (3, 4), Exophiala jeanselmei (4), or E. spinifera (9), the majority of the fungal elements in tissue may be hyaline. At times, a careful search of unstained or hematoxylin and eosin (H & E)-stained tissue sections is needed to reveal the pigmented nature of the fungal elements present. Currently, 62 species of dematiaceous fungi belonging to 33 genera have been described in the literature under a wide variety of confusing disease names, all of which, in fact, are agents of phaeohyphomycosis. We describe here another agent of phaeohyphomycotic infection, namely, Phialemonium obovatum (6), which infected the tibial bone of a dog. Case report. In November 1982, a 3-year-old female German shepherd dog was admitted to a veterinary clinic with a 2-week history of weakness and pain in the left hind leg. Upon palpation of this limb, pain was elicited from the proximal thigh region to just proximal of the tarsus. There was soft-tissue swelling over the entire length of the tibia. This was most prominent over the mid-tibial region. The dog was in good body condition otherwise and appeared to be alert. Her rectal temperature was 38.9 C. A tentative diag- * Corresponding author. t Present address: Mammalian and Environmental Toxicology Research Laboratory, Dow Chemical Company, Midland, MI nosis of local soft-tissue and possibly bone inflammation was made. Therapy consisted of 200 mg of butazolidin administered twice a day for 7 days, followed by 100 mg of this drug twice a day for an additional 7 days. The owner was encouraged to return the dog in 14 days for reexamination. Nineteen days later, the dog was readmitted to the clinic because of poor appetite and severe lameness in the left rear leg. Physical examination revealed a painful, firm swelling over the mid-tibial region of this leg. A similar lesion was palpated over the midregion of the left radius, and the entire diaphyseal length of both femurs was firm, painful, and thick. In addition, the dog had a head tilt to the left side. Blood was obtained for hematologic and serum enzyme chemistry determinations. Radiographs of the pelvis (ventrodorsal view), right femur, left tibia, and left radius (lateral and anteroposterior views) were obtained. A punch biopsy from the lesion in the tibia (the site of the original swelling) was also obtained. Portions of the biopsy were placed into 10% neutral buffered Formalin, and the remainder of the specimens was placed in sterile 0.9% saline (NaCl). This material was submitted to the University of Georgia Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory at Tifton, Ga. The dog died shortly thereafter, but permission for necropsy was denied. Radiographic findings included soft-tissue swelling, irregular periosteal proliferation, lysis of cortical bone, and increased medullary density in the mid-shaft regions of the left tibia (Fig. 1) and the left radius (Fig. 2). There was also a diffuse periosteal proliferation and increased medullary density throughout the diaphyses of both femurs. The periosteal reaction in the femurs extended from the proximal to the distal metaphyses. The coxofemoral, stifle, tarsal, and elbow joints showed no radiologic signs. Additional laboratory findings included neutrophilic leukocytosis with left shift and moderate monocytosis. The serum alkaline phosphatase was elevated (274 U/liter), whereas the other enzyme chemistry values were within normal ranges. Histologic findings. Histologic examination of the biopsy material from the left tibia revealed a diffuse granulomatous
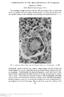
2 988 NOTES FIG. 1. Lateral view of left tibia and femur. There is soft-tissue swelling, irregular periosteal proliferation, lysis of cortical bone, and increased medullary density in the mid-shaft region of the tibia. The distal metaphysis of the femur has periosteal proliferation and increased medullary density. inflammation characterized by multinodular foci of macrophages and multinucleated giant cells among areas of hemorrhage and necrotic trabecular bone. The centers of most of the granulomas contained microabscesses and necrotic debris. Replicate tissue sections stained with Gomori methenamine silver revealed numerous pleomorphic fungal elements that were either scattered or arranged in loose aggregates within the areas of inflammation and necrosis (Fig. 3 through 5). The fungal elements consisted of septate, irregularly branched hyphae that ranged from 3 to 4.5,um in diameter. They varied considerably in length. The narrow hyphae were frequently constricted at their prominent, thick septations. They sometimes had terminal and intercalary chlamydoconidialike swellings up to 15,um in diameter (Fig. 3). Budding yeastlike cells were also present, along with hyphal elements, single thick-walled cells up to 20,um in diameter, and spherical to oval cells that were transversely septate (Fig. 4 and 5). Most of the fungal elements in H & E-stained sections appeared hyaline, but a few had lightly pigmented greenish yellow cell walls. The Fontana-Masson silver procedure for melanin stained the cell walls and the prominent septa of the fungal elements. It accentuated their light pigmentation (10). Certain other fungal elements that appeared hyaline in replicate H & E-stained sections also gave a positive reaction for melanin (Fig. 5, inset). Mycological findings. Examination of the smears of the biopsy material and KOH preparations by microscope revealed fungal hyphae. The biopsy fluid and tissue were J. CLIN. MICROBIOL. cultured on Sabouraud dextrose agar and Sabouraud dextrose agar containing chloramphenicol and cycloheximide. The cultures were incubated at 25 C for 2 weeks. Glabrous, dirty white to grayish white colonies with dark green pigment grew within 2 weeks of incubation. Based on an initial examination of the colony and examination of teased preparations by microscope, the isolate was tentatively identified as an Acremonium sp. The majority of the fungal elements in the tissue sections were hyaline in the H & E-stained sections, but in their morphology, they closely resembled the agents of phaeohyphomycosis. The green-pigmented colonies were unlike any of the known pathogenic species of Acremonium. Because of the unusual features of the causal agent observed both in vivo and in vitro, a subculture and tissue slides were sent to the Division of Mycotic Diseases, Centers for Disease Control, Atlanta, Ga., for specific identification of the causal agent. There, upon futher mycologic examination, the colonies on Sabouraud dextrose agar were noted to be moist, flat, and spreading. Initially they were white, but they soon became ochraceous and slightly greenish, reaching a diameter of 28 to 30 mm in 2 weeks at 25 C. As the colonies became older, a green diffusible pigment became prominent on their reverse side. In 4-week-old cultures, aerial hyphae FIG. 2. Lateral view of the left radius and ulna showing overlying soft-tissue swelling and periosteal proliferation on both the radius and ulna. The mid-shaft region of the radius also has cortical lysis and increased medullary density.
3 VOL. 23, 1986 NOTES 989 ~ -..~~~~~~~. PI 9/ WF 0A * 'V _ 0 6 _ 0 ~~~~~Id I* 0p 0' tv -I_ -0. v *.. av, t e~~~~~~~~f *- R le C..d.. Q~~~~ _l S. A':s i* FIG. 3. Scattered and loosely aggregated hyphae of P. obovatum in a section of the tibial lesion stained with Gomori methenamine silver. Arrows, Two hyphae with terminal chlamydoconidiumlike swellings. Magnification, x700. in the central areas of the colonies became evident (Fig. 6). The isolate grew at 37 and 40 C. Examination of the slide culture preparations on potato dextrose agar by microscope after 2 weeks at 25 C revealed adelophialides which developed as small pegs from the sides of the vegetative hyphae. These adelophialides lacked the basal septa and collarettes which are typical of discrete phialides (Fig. 7). Some well-developed discrete phialides with a basal septum were produced, but only rarely. The conidia were hyaline, one-celled, obovate, and smooth. They measured 3.0 to 6.0 plm by 1.4 to 2.0,um. Chlamydoconidia were abundant in older cultures. They were oval to almost cylindrical, thin walled, and hyaline. i *** t. ov They were intercalary or terminal and measured 5 to 8,um by 2.5 to 4.5 plm (Fig. 8). A subculture of the dog isolate was sent to Walter Gams, Centraalbureau voor Schimmelcultures (CBS), Baarn, The Netherlands, who identified it as P. obovatum. It was accessioned at the CBS under CBS number It is also deposited in the Centers for Disease Control Division of Mycotic Diseases' culture collection under accession number B Discussion. The genus Phialemonium was proposed by Gams and McGinnis (6) as being intermediate between the genera Acremonium and Phialophora. It is characterized by the production of adelophialides arising from vegetative b soit 0 I CC) IV~~~~' f 0) %_ # C FIG. 4. Budding yeastlike cells and pseudohyphae in the necrotic center of a granuloma. Arrows, Spherical-to-oval fungal cells, stained with Gomori methenamine silver, with a single, thin septation. Magnification, x700.
4 990 NOTES J. CLIN. MICROBIOL..4 a go *db 4. 1%, il v 4 '. t irli 4-r ' gah.r.s j".41- V..; "..T 1.,.:.!".k 401il. :.:7; A -,c y 7 ("'N40 FIG. 5. Pleomorphic fungal elements of P. obovatum, stained with Gomori methenamine silver, in a tibial abscess. Magnification, x700. Inset: Replicate section shows positive staining of some elements for melanin with the Fontana-Masson silver procedure. Magnification, x700. hyphae close to the agar surface. The term adelophialide, as defined by Gams (5), is applied to a reduced phialide that arises from intercalary hyphal cells as a lateral, phialidic neck. There are no basal septa that separate these phialidic necks from their supporting hyphal cells. Occasionally, discrete phialides, which are well developed and have basal septa, are produced by the species of Phialemonium. The adelophialides lack conspicuous collarettes and inner periclinal wall thickenings. In the species belonging to the genus Phialophora, a continuous series of phialide types that range from discrete phialides with basal septa to adelophilides is observed. But discrete phialides with basal septa predominate in I i iw '.. " q' Is * Phialophora spp. They are considered to be the characteristic conidiogenous cell for the genus. The same type of conidiogenous cell with discrete phialides is also considered typical for members of the genus Acremonium. Some species of Phialophora and Acremonium may produce adelophialides mainly from submerged hyphae in addition to the characteristic discrete phialides which characterize the two genera. Gams and McGinnis (6) described three species of Phialemonium, namely, P. obovatum, P. curvatum, and P. dimorphosporum. In P. obovatum, the conidia are obovate and colonies develop a greenish pigment with age. Phialemonium curvatum is distinguished by its conidia,..wasf 19 FIG. 6. Colony of P. obovatum on Sabouraud dextrose agar after 2 weeks at 25 C. FIG. 7. Photomicrograph showing an adelophialide and conidia of P. obovatum. Lactophenol cotton blue; magnification, x1,560.
5 VOL. 23, 1986 FIG. 8. Photomicrograph showing conidia and intercalary chlamydoconidia of P. obovatum. Lactophenol cotton blue; magnification, x 1,560. which are uniformly allantoid, and colonies that do not turn vinaceous buff. The conidia of P. dimorphosporum are partly allantoid, partly ellipsoidal, and straight. The colonies of P. dimorphosporum form pale, vinaceous buff pigment on their reverse side. The colonies of P. obovatum and P. curvatum have been isolated from clinical specimens. P. curvatum and P. dimorphosporum have been isolated from soil, sewage, air samples, and water (6). Recently, McGinnis et al. (8) described P. obovatum as an opportunistic pathogen in a 4.5-month-old child that died of thermal burns. In antemortem and postmortem examinations of the skin and subcutaneous tissue from the burn wounds, they observed hyaline, septate, irregularly branched hyphae. Yeastlike cells and pseudohyphae were absent. In the tissues of the present case, P. obovatum was polymorphic. The fungal elements consisted of septate, irregularly branched hyphae, narrow hyphae with terminal or intercalary chlamydoconidialike swellings, budding yeastlike cells, and spherical-to-oval cells that were transversely septate. When NOTES 991 tissue sections were stained by the Fontana-Masson silver procedure (10) for melanin, the light or previously undetectable pigmentation in hyphal cell walls and especially their septations was markedly accentuated. As more species of dematiaceous fungi are reported as etiologic agents of phaeohyphomycosis, it is becoming clear that the innate brown pigmentation of their mycelia may not always be readily apparent in tissue sections. In most instances, a careful search almost always reveals at least some dematiaceous hyphae in unstained (cleared and mounted) or H & E-stained sections. In the case of P. obovatum, a special staining procedure proved useful to confirm the presence of melanin in its tissue cells. We thank Walter Gams, Centraalbureau voor Schimmelcultures, Baarn, The Netherlands, for identifying the dog isolate; Ray Simons, Laboratory Training and Consultation Division, Laboratory Program Office, Centers for Disease Control, for some of the photomicrographs; and the Mycology Section, Georgia Department of Human Resources, Atlanta, for their mycological studies. LITERATURE CITED 1. Ajello, L Phaeohyphomycosis: definition and etiology. Pan Am. Health Organ. Sci. Publ. 304: Ajello, L The gamut of human infections caused by dematiaceous fungi. Jpn. J. Med. Mycol. 22: Alcorn, J. L Generic concepts in Drechslera, Bipolaris and Exserohilum. Mycotaxon 17: Chandler, F. W., W. Kaplan, and L. Ajello A colour atlas and textbook of the histopathology of mycotic diseases, p and Wolfe Medical Publications Ltd., London, England. 5. Gams, W Cephalosporium-artige Schimmelpilze (Hyphomycetes), p G. Fischer, Stuttgart, Federal Republic of Germany. 6. Gams, W., and M. R. McGinnis Phialemonium, a new anamorph genus intermediate between Phialophora and Acremonium. Mycologia 75: McGinnis, M. R Chromoblastomycosis and phaeohyphomycosis: new concepts, diagnosis and mycology. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 8: McGinnis, M. R., W. Gams, and M. N. Goodwin Phialemonium obovatum infection in a burned child. Sabouraudia 24: Padhye, A. A., W. Kaplan, M. A. Neuman, P. Case, and G. N. Radcliffe Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused by Exophiala spinifera. Sabouraudia 22: Wood, C., and B. Russel-Bell Characterization of pigmented fungi by melanin staining. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 5:77-81.
Subcutaneous Mycosis
 Subcutaneous Mycosis Fungal infections 1. Superficial mycosis. 2. Coetaneous mycosis: Dermatophytoses. 3. Subcutaneous mycosis. 4. Systemic mycosis. 5. Opportunistic mycosis. Subcutanus mycoses Fungal
Subcutaneous Mycosis Fungal infections 1. Superficial mycosis. 2. Coetaneous mycosis: Dermatophytoses. 3. Subcutaneous mycosis. 4. Systemic mycosis. 5. Opportunistic mycosis. Subcutanus mycoses Fungal
Phialophora repens, an Emerging Agent of Subcutaneous
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1989, p. 394-399 Vol. 27, No. 3 0095-1137/89/030394-06$02.00/0 Copyright 1989, American Society for Microbiology Phialophora repens, an Emerging Agent of Subcutaneous
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1989, p. 394-399 Vol. 27, No. 3 0095-1137/89/030394-06$02.00/0 Copyright 1989, American Society for Microbiology Phialophora repens, an Emerging Agent of Subcutaneous
Phialemonium Species and a Reevaluation of its Taxonomy
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, July 1993, p. 1804-1810 0095-1137/93/071804-07$02.00/0 Copyright X) 1993, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 31, No. 7 A Phaeohyphomycotic Cyst and Peritonitis Caused
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, July 1993, p. 1804-1810 0095-1137/93/071804-07$02.00/0 Copyright X) 1993, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 31, No. 7 A Phaeohyphomycotic Cyst and Peritonitis Caused
Subcutaneous Fungi 10/13/2009. General Characteristics. Pathogenesis. Epidemiology. Laboratory Diagnosis. Specimens. Growth rate: 1-4 weeks
 General Characteristics Growth rate: 1-4 weeks Subcutaneous Fungi Clinical Laboratory Science Program Carol Larson MSEd, MT(ASCP) Dematiaceous septate hyphae Hyaline septate hyphae Branching GPR Epidemiology
General Characteristics Growth rate: 1-4 weeks Subcutaneous Fungi Clinical Laboratory Science Program Carol Larson MSEd, MT(ASCP) Dematiaceous septate hyphae Hyaline septate hyphae Branching GPR Epidemiology
The Differentiation of Yeast and Yeast-Like Forms in Human Tissues. Introduction. Histochemical Stains Used to Detect Fungi. Histopathologic Diagnoses
 The Differentiation of Yeast and Yeast-Like Forms in Human Tissues Gary W. Procop, MD Chair, Clinical Pathology Staff, Anatomic Pathology Director, Molecular Microbiology, Mycology, and Parasitology Cleveland
The Differentiation of Yeast and Yeast-Like Forms in Human Tissues Gary W. Procop, MD Chair, Clinical Pathology Staff, Anatomic Pathology Director, Molecular Microbiology, Mycology, and Parasitology Cleveland
Definition. Phaeohyphomycosis
 Phaeohyphomycosis Synonyms: Cerebral chromomycosis, chromoblastomycosis, chromomycosis, cladosporiosis, phaeomycotic cyst, phaeosporotrichosis, subcutaneous mycotic cyst. Definition Phaeohyphomycosis consists
Phaeohyphomycosis Synonyms: Cerebral chromomycosis, chromoblastomycosis, chromomycosis, cladosporiosis, phaeomycotic cyst, phaeosporotrichosis, subcutaneous mycotic cyst. Definition Phaeohyphomycosis consists
Cutaneous phaeohyphomycosis in an immunocompromised host
 Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2014) 22, 85-89 Case Report Cutaneous phaeohyphomycosis in an immunocompromised host YXE Tay, JY Pan, SSJ Lee Phaeohyphomycosis is an infection caused by dematiaceous
Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2014) 22, 85-89 Case Report Cutaneous phaeohyphomycosis in an immunocompromised host YXE Tay, JY Pan, SSJ Lee Phaeohyphomycosis is an infection caused by dematiaceous
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Introduction to Medical Mycology. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 1 Introduction to Medical Mycology. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 1-1 through 1-7. TASKS OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 1-1. Select the statement
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 1 Introduction to Medical Mycology. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 1-1 through 1-7. TASKS OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 1-1. Select the statement
Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis:
 J Clin Pathol 1985;38:288-292 Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis: a histopathological study of nine cases from Malawi PJ O'DONNELL, MSR HUTT From the Department ofhistopathology, St Thomas's Hospital Medical
J Clin Pathol 1985;38:288-292 Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis: a histopathological study of nine cases from Malawi PJ O'DONNELL, MSR HUTT From the Department ofhistopathology, St Thomas's Hospital Medical
Histopathology: skin pathology
 Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology Description:
 2013-2-1 CANINE HEART Ahmed M. Abubakar BOVINE PATHOLOGY CONTRIBUTING INSTITUTION : The Royal Veterinary college, Dept. of Pathology and Biology Signalment: 11-month-old male Border Collie dog (Canis familiaris)
2013-2-1 CANINE HEART Ahmed M. Abubakar BOVINE PATHOLOGY CONTRIBUTING INSTITUTION : The Royal Veterinary college, Dept. of Pathology and Biology Signalment: 11-month-old male Border Collie dog (Canis familiaris)
Evaluation of an alternative slide culture technique for the morphological identification of fungal species
 Research Article Evaluation of an alternative slide culture technique for the morphological identification of fungal species Abstract M H Wijedasa 1, L V C Liyanapathirana 1. Sri Lanka Journal of Infectious
Research Article Evaluation of an alternative slide culture technique for the morphological identification of fungal species Abstract M H Wijedasa 1, L V C Liyanapathirana 1. Sri Lanka Journal of Infectious
Mycology. BioV 400. Subcutaneous Mycoses. Ecological associations. Geographic distribution World-wide
 BioV 400 Mycology Handout 8 Subcutaneous Mycoses Lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis Chromoblastomycosis Phaeohyphomycosis Zygomycosis Mycetoma Lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis Sporothrix schenckii Chronic infection
BioV 400 Mycology Handout 8 Subcutaneous Mycoses Lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis Chromoblastomycosis Phaeohyphomycosis Zygomycosis Mycetoma Lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis Sporothrix schenckii Chronic infection
Diagnosis of Invasive Septate Mold Infections A Correlation of Microbiological Culture and Histologic or Cytologic Examination
 Microbiology and Infectious Disease / DIAGNOSIS OF SEPTATE MOLD INFECTIONS Diagnosis of Invasive Septate Mold Infections A Correlation of Microbiological Culture and Histologic or Cytologic Examination
Microbiology and Infectious Disease / DIAGNOSIS OF SEPTATE MOLD INFECTIONS Diagnosis of Invasive Septate Mold Infections A Correlation of Microbiological Culture and Histologic or Cytologic Examination
Molecular and Phenotypic Characterization of Phialemonium and Lecythophora Isolates from Clinical Samples
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Apr. 2011, p. 1209 1216 Vol. 49, No. 4 0095-1137/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jcm.01979-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Molecular and
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Apr. 2011, p. 1209 1216 Vol. 49, No. 4 0095-1137/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jcm.01979-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Molecular and
. 1.5 cm, Fonsecaea pedrosoi. 1.5 cm, Fig. 1.. Bowen,. Phialophora. 240, Fukushiro 1. . Hepatitis C Virus. . Fig. 2.
 Jpn. J. Med. Mycol. Vol. 48, 85 89, 2007 ISSN 0916 4804 Fonsecaea pedrosoi 1 1 2 2 2 1 1 2 3 17, 2006. 12 15, 2006 67 1. 1.5 cm. Fonsecaea pedrosoi., Phialophora., 5 mm,. 3., 1955 1981 Fukushiro 296, 1982
Jpn. J. Med. Mycol. Vol. 48, 85 89, 2007 ISSN 0916 4804 Fonsecaea pedrosoi 1 1 2 2 2 1 1 2 3 17, 2006. 12 15, 2006 67 1. 1.5 cm. Fonsecaea pedrosoi., Phialophora., 5 mm,. 3., 1955 1981 Fukushiro 296, 1982
Introduction. Study of fungi called mycology.
 Fungi Introduction Study of fungi called mycology. Some fungi are beneficial: ex a) Important in production of some foods, ex: cheeses, bread. b) Important in production of some antibiotics, ex: penicillin
Fungi Introduction Study of fungi called mycology. Some fungi are beneficial: ex a) Important in production of some foods, ex: cheeses, bread. b) Important in production of some antibiotics, ex: penicillin
First Report of Penicillium adametzioides from Decayed Grapes (Vitis vinifera) in Pakistan
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 12 (2016) pp. 316-320 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.512.034
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 12 (2016) pp. 316-320 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.512.034
FRACTURE CALLUS ASSOCIATED WITH BENIGN AND MALIGNANT BONE LESIONS AND MIMICKING OSTEOSARCOMA
 THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PATHOLOGY Vol. 52, No. 1 Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Printed in U.S.A. FRACTURE CALLUS ASSOCIATED WITH BENIGN AND MALIGNANT BONE LESIONS AND MIMICKING
THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PATHOLOGY Vol. 52, No. 1 Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Printed in U.S.A. FRACTURE CALLUS ASSOCIATED WITH BENIGN AND MALIGNANT BONE LESIONS AND MIMICKING
Histopathology: granulomatous inflammation, including tuberculosis
 Histopathology: granulomatous inflammation, including tuberculosis These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: granulomatous inflammation, including tuberculosis These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Phialemonium: An Emerging Mold Pathogen That Caused 4 Cases of Hemodialysis-Associated Endovascular Infection
 MAJOR ARTICLE Phialemonium: An Emerging Mold Pathogen That Caused 4 Cases of Hemodialysis-Associated Endovascular Infection Laurie A. Proia, 1 Mary K. Hayden, 1 Patricia L. Kammeyer, 2 Joanna Ortiz, 3
MAJOR ARTICLE Phialemonium: An Emerging Mold Pathogen That Caused 4 Cases of Hemodialysis-Associated Endovascular Infection Laurie A. Proia, 1 Mary K. Hayden, 1 Patricia L. Kammeyer, 2 Joanna Ortiz, 3
Mycology. BioV 400. Clinical classification. Clinical classification. Fungi as Infectious Agents. Thermal dimorphism. Handout 6
 BioV 400 Mycology Handout 6 Fungi as Infectious Agents True or primary fungal pathogens invades and grows in a healthy, noncompromise d host Most striking adaptation to survival and growth in the human
BioV 400 Mycology Handout 6 Fungi as Infectious Agents True or primary fungal pathogens invades and grows in a healthy, noncompromise d host Most striking adaptation to survival and growth in the human
Identification of Yeasts. Medical Mycology Training Network 15 November 2018 Dr Tan Ai Ling Department of Microbiology, Singapore General Hospital
 Identification of Yeasts Medical Mycology Training Network 15 November 2018 Dr Tan Ai Ling Department of Microbiology, Singapore General Hospital Definition of Yeasts Eukaryote cells have defined nucleus
Identification of Yeasts Medical Mycology Training Network 15 November 2018 Dr Tan Ai Ling Department of Microbiology, Singapore General Hospital Definition of Yeasts Eukaryote cells have defined nucleus
What s Your Diagnosis? Catherine Donewald, Class of 2016
 What s Your Diagnosis? Catherine Donewald, Class of 2016 Signalment: 9 ½ year old, male castrate Greyhound dog History: The patient presented to referring veterinarian with a history of decreased energy
What s Your Diagnosis? Catherine Donewald, Class of 2016 Signalment: 9 ½ year old, male castrate Greyhound dog History: The patient presented to referring veterinarian with a history of decreased energy
VPM 201: Veterinary Bacteriology and Mycology 23-24/11/2011 LABORATORY 11: MYCOLOGY
 VPM 201: Veterinary Bacteriology and Mycology 23-24/11/2011 LABORATORY 11: MYCOLOGY I. Overview of Major Groups of Pathogenic Fungi. Although the Kingdom Fungi have been undergoing considerable phylogenetic
VPM 201: Veterinary Bacteriology and Mycology 23-24/11/2011 LABORATORY 11: MYCOLOGY I. Overview of Major Groups of Pathogenic Fungi. Although the Kingdom Fungi have been undergoing considerable phylogenetic
Morphology and Ultrastructure of Fungi in Extended-Wear
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, July 1986, p. 21-25 0095-1137/86/070021-05$02.00/0 Copyright D 1986, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 24, No. 1 Morphology and Ultrastructure of Fungi in Extended-Wear
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, July 1986, p. 21-25 0095-1137/86/070021-05$02.00/0 Copyright D 1986, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 24, No. 1 Morphology and Ultrastructure of Fungi in Extended-Wear
Goosiomyces bambusicola - A new cheirosporous anamorphic species from Western Ghats, India.
 Current Research in Environmental & Applied Mycology 4 (2): 211 216 (2014) ISSN 2229-2225 www.creamjournal.org Article CREAM Copyright 2014 Doi 10.5943/cream/4/2/8 Online Edition Goosiomyces bambusicola
Current Research in Environmental & Applied Mycology 4 (2): 211 216 (2014) ISSN 2229-2225 www.creamjournal.org Article CREAM Copyright 2014 Doi 10.5943/cream/4/2/8 Online Edition Goosiomyces bambusicola
7/13/09. Definition. Infections Due to Malassezia. Case Report 1. Case Report 1 (cont.) Case Report 1 (cont.)
 Definition Infections Due to Malassezia Various species of Malassezia cause both opportunistic, superficial infections and occasionally systemic infections Common superficial infections include: Pityriasis
Definition Infections Due to Malassezia Various species of Malassezia cause both opportunistic, superficial infections and occasionally systemic infections Common superficial infections include: Pityriasis
The Radiology Assistant : Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions
 Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
7-002b: Malt agar method for the detection of Alternaria radicina on Daucus carota (carrot)
 International Rules for Seed Testing Annexe to Chapter 7: Seed Health Testing Methods 7-002b: Malt agar method for the detection of Alternaria radicina on Daucus carota (carrot) Published by: International
International Rules for Seed Testing Annexe to Chapter 7: Seed Health Testing Methods 7-002b: Malt agar method for the detection of Alternaria radicina on Daucus carota (carrot) Published by: International
Inflammation Laboratory 1
 Inflammation Laboratory 1 Lab1 Emphasis: The exudates of acute inflammation Descriptions Morphologic Diagnoses Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: February 2012 Describing Lesions
Inflammation Laboratory 1 Lab1 Emphasis: The exudates of acute inflammation Descriptions Morphologic Diagnoses Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: February 2012 Describing Lesions
This is the written version of our Hot Topic video presentation available at: MayoMedicalLaboratories.com/hot-topics
 This is the written version of our Hot Topic video presentation available at: MayoMedicalLaboratories.com/hot-topics Welcome to Mayo Medical Laboratories hot topics. These presentations provide short discussion
This is the written version of our Hot Topic video presentation available at: MayoMedicalLaboratories.com/hot-topics Welcome to Mayo Medical Laboratories hot topics. These presentations provide short discussion
HISTOPATHOLOGY. Shannon Martinson
 HISTOPATHOLOGY Shannon Martinson March 2013 Case #1 History: 8 year old beagle Neck pain for the past couple of weeks Paresis, followed by paralysis developed over the past few days Gross Description courtesy
HISTOPATHOLOGY Shannon Martinson March 2013 Case #1 History: 8 year old beagle Neck pain for the past couple of weeks Paresis, followed by paralysis developed over the past few days Gross Description courtesy
Inflammation Laboratory 3 Emphasis: Chronic inflammation and healing. Shannon Martinson: VPM 152: April 2013
 Inflammation Laboratory 3 Emphasis: Chronic inflammation and healing Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: April 2013 Example A Reproductive tract and colon/rectum from a sheep Previous
Inflammation Laboratory 3 Emphasis: Chronic inflammation and healing Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: April 2013 Example A Reproductive tract and colon/rectum from a sheep Previous
Departments o/ Botany and Dermatology, University o/ Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, U.S.A.)
 EFFECT OF LIGHT AND MEDIA UPON GROWTH AND MELANIN FORMATION IN CLADOSPORIUM MANSONI by A. S. SUSSMAN, YAMUNA LINGAPPA & I. A. BERNSTEIN Departments o/ Botany and Dermatology, University o/ Michigan, Ann
EFFECT OF LIGHT AND MEDIA UPON GROWTH AND MELANIN FORMATION IN CLADOSPORIUM MANSONI by A. S. SUSSMAN, YAMUNA LINGAPPA & I. A. BERNSTEIN Departments o/ Botany and Dermatology, University o/ Michigan, Ann
Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations
 Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
العصوي الوعاي ي الورام = angiomatosis Bacillary
 1 / 7 BACILLARY ANGIOMATOSIS Epidemiology BA is most commonly seen in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and a CD4 count less than 50 cells/mm 3, with an incidence of 1.2 cases per
1 / 7 BACILLARY ANGIOMATOSIS Epidemiology BA is most commonly seen in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and a CD4 count less than 50 cells/mm 3, with an incidence of 1.2 cases per
7-001b: Malt agar method for the detection of Alternaria dauci on Daucus carota (carrot)
 International Rules for Seed Testing Annexe to Chapter 7: Seed Health Testing Methods 7-001b: Malt agar method for the detection of Alternaria dauci on Daucus carota (carrot) Published by: International
International Rules for Seed Testing Annexe to Chapter 7: Seed Health Testing Methods 7-001b: Malt agar method for the detection of Alternaria dauci on Daucus carota (carrot) Published by: International
RAFI, M. AND SAJJAD-UR-RAHMAN Department of Veterinary Microbiology, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad 38040, Pakistan
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF AGRICULTURE & BIOLOGY 1560 8530/00/04 4 553 558 http://www.ijab.org Isolation and Identification of Indigenous Penicillium chrysogenum Series RAFI, M. AND SAJJAD-UR-RAHMAN Department
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF AGRICULTURE & BIOLOGY 1560 8530/00/04 4 553 558 http://www.ijab.org Isolation and Identification of Indigenous Penicillium chrysogenum Series RAFI, M. AND SAJJAD-UR-RAHMAN Department
World Journal of Microbiology Vol. 1(2), pp , September, ISSN: XXXX-XXXX
 World Journal of Microbiology Vol. 1(2), pp. 013-016, September, 2014. www.premierpublishers.org, ISSN: XXXX-XXXX WJM Research Article Study of Fungal Genus Gyrothrix Corda from the forest flora of Indian
World Journal of Microbiology Vol. 1(2), pp. 013-016, September, 2014. www.premierpublishers.org, ISSN: XXXX-XXXX WJM Research Article Study of Fungal Genus Gyrothrix Corda from the forest flora of Indian
EXPERIMENTAL THERMAL BURNS I. A study of the immediate and delayed histopathological changes of the skin.
 EXPERIMENTAL THERMAL BURNS I A study of the immediate and delayed histopathological changes of the skin. RJ Brennan, M.D. and B. Rovatti M.D. The purpose of this study was to determine the progressive
EXPERIMENTAL THERMAL BURNS I A study of the immediate and delayed histopathological changes of the skin. RJ Brennan, M.D. and B. Rovatti M.D. The purpose of this study was to determine the progressive
Phaeohyphomycosis of the Nasal Sinuses Caused by a New Species of Exserohilum
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Aug. 1986, p. 245-249 0095-1137/86/080245-05$02.00/0 Copyright 1986, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 24, No. 2 Phaeohyphomycosis of the Nasal Sinuses Caused by
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Aug. 1986, p. 245-249 0095-1137/86/080245-05$02.00/0 Copyright 1986, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 24, No. 2 Phaeohyphomycosis of the Nasal Sinuses Caused by
Allergic Fungal Sinusitis Report of Three Cases Associated with Dematiaceous Fungi
 CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY Original Article Report of Three Cases Associated with Dematiaceous Fungi GLEN C. FRIEDMAN, M.D., 1 R. WARREN J. HARTWICK, M.D., F.R.C.P.C., 1 JAE Y. RO, M.D., 1 GEORGE Y. SALEH,
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY Original Article Report of Three Cases Associated with Dematiaceous Fungi GLEN C. FRIEDMAN, M.D., 1 R. WARREN J. HARTWICK, M.D., F.R.C.P.C., 1 JAE Y. RO, M.D., 1 GEORGE Y. SALEH,
CONSULTATION DURING SURGERY / NOT A FINAL DIAGNOSIS. FROZEN SECTION DIAGNOSIS: - A. High grade sarcoma. Wait for paraffin sections results.
 Pathology Report Date: 3/5/02 A, B. Biopsy right distal femur- high grade spindle cell sarcoma Immunohistochemistry studies are pending to further classify the nature of the tumor. CONSULTATION DURING
Pathology Report Date: 3/5/02 A, B. Biopsy right distal femur- high grade spindle cell sarcoma Immunohistochemistry studies are pending to further classify the nature of the tumor. CONSULTATION DURING
MYCOBACTERIA. Pulmonary T.B. (infect bird)
 MYCOBACTERIA SPP. Reservoir Clinical Manifestation Mycobacterium tuberculosis Human Pulmonary and dissem. T.B. M. lepra Human Leprosy M. bovis Human & cattle T.B. like infection M. avium Soil, water, birds,
MYCOBACTERIA SPP. Reservoir Clinical Manifestation Mycobacterium tuberculosis Human Pulmonary and dissem. T.B. M. lepra Human Leprosy M. bovis Human & cattle T.B. like infection M. avium Soil, water, birds,
Nursing college, Second stage Microbiology Dr.Nada Khazal K. Hendi Medical Microbiology
 1 Nursing college, Second stage Microbiology Medical Microbiology Lecture-1- Fungi (Mycosis) They are a diverse group of saprophytic and parasitic eukaryotic organisms. Human fungal diseases (mycoses)
1 Nursing college, Second stage Microbiology Medical Microbiology Lecture-1- Fungi (Mycosis) They are a diverse group of saprophytic and parasitic eukaryotic organisms. Human fungal diseases (mycoses)
Headaches and hemiparesis in an immunocompetent inmate
 Virginia Commonwealth University VCU Scholars Compass Pathology Publications Dept. of Pathology 2014 Headaches and hemiparesis in an immunocompetent inmate Andrea Gilbert Jelinek Virginia Commonwealth
Virginia Commonwealth University VCU Scholars Compass Pathology Publications Dept. of Pathology 2014 Headaches and hemiparesis in an immunocompetent inmate Andrea Gilbert Jelinek Virginia Commonwealth
This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very
 This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very basic response to injury inflammation. We ll look at examples
This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very basic response to injury inflammation. We ll look at examples
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
8/2/10. Sanaz Jalali, Jennifer Demler, Jeremy King. Histoplasmosis is an intracellular mycotic infection of the reticuloendothelial system.
 Histoplasmosis is an intracellular mycotic infection of the reticuloendothelial system. Type of chronic respiratory infection http://www.eregimens.com/regimens/antifungal%20general.htm Sanaz Jalali, Jennifer
Histoplasmosis is an intracellular mycotic infection of the reticuloendothelial system. Type of chronic respiratory infection http://www.eregimens.com/regimens/antifungal%20general.htm Sanaz Jalali, Jennifer
REINWARDTIA Published by Herbarium Bogoriense LBN, Bogor Vol. 10, Part 2, pp (1985) THE ANAMORPH OF SARAWAKUS SUCCISUS RIFAI
 REINWARDTIA Published by Herbarium Bogoriense LBN, Bogor Vol. 10, Part 2, pp. 265 270 (1985) THE ANAMORPH OF SARAWAKUS SUCCISUS RIFAI MIEN A. RIFAI, KARTINI KRAMADIBRATA Herbarium Bogorievnc LBN, Bogor,
REINWARDTIA Published by Herbarium Bogoriense LBN, Bogor Vol. 10, Part 2, pp. 265 270 (1985) THE ANAMORPH OF SARAWAKUS SUCCISUS RIFAI MIEN A. RIFAI, KARTINI KRAMADIBRATA Herbarium Bogorievnc LBN, Bogor,
Sporotrichosis Centering Siliguri and its Sub-Himalayan Neighbours
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 2 (2017) pp. 817-822 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.602.091
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 2 (2017) pp. 817-822 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.602.091
PROBABLE HODGKIN'S DISEASE IN A DOG: REPORT OF A CASE 1
 PROBABLE HODGKIN'S DISEASE IN A DOG: REPORT OF A CASE 1 LEONARD K. STALKER, M.D. Fellow in Surgery, The Mayo Foundation CARL F. SCHLOTTHAUER, D.V.M. AND WILLIAM H. FELDMAN, D.V.M., M.S. Division of Experimental
PROBABLE HODGKIN'S DISEASE IN A DOG: REPORT OF A CASE 1 LEONARD K. STALKER, M.D. Fellow in Surgery, The Mayo Foundation CARL F. SCHLOTTHAUER, D.V.M. AND WILLIAM H. FELDMAN, D.V.M., M.S. Division of Experimental
A Cladosarum-like spontaneous mutant of Aspergillus aureolatus
 A Cladosarum-like spontaneous mutant of Aspergillus aureolatus By M. Muntanjola-Cvetkovic & J. Bata Institute for Biological Research Botanicki Zavod, Takovska 43, Belgrade, Yugoslavia Summary. A spontaneous
A Cladosarum-like spontaneous mutant of Aspergillus aureolatus By M. Muntanjola-Cvetkovic & J. Bata Institute for Biological Research Botanicki Zavod, Takovska 43, Belgrade, Yugoslavia Summary. A spontaneous
Fungi. Eucaryotic Rigid cell wall(chitin, glucan) Cell membrane ergosterol Unicellular, multicellular Classic fungus taxonomy:
 MYCOLOGY Mycology I Fungi Eucaryotic Rigid cell wall(chitin, glucan) Cell membrane ergosterol Unicellular, multicellular Classic fungus taxonomy: Morphology Spore formation FFungi Yeast Mold Yeastlike
MYCOLOGY Mycology I Fungi Eucaryotic Rigid cell wall(chitin, glucan) Cell membrane ergosterol Unicellular, multicellular Classic fungus taxonomy: Morphology Spore formation FFungi Yeast Mold Yeastlike
Cellular Pathology. Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018
 Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
Autopsy findings in 51 year-old man with mantle cell lymphoma
 Autopsy findings in 51 year-old man with mantle cell lymphoma Bobbi S. Pritt, MD, MSc Professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires
Autopsy findings in 51 year-old man with mantle cell lymphoma Bobbi S. Pritt, MD, MSc Professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires
Disseminated Infection by Fusarium moniliforme During Treatment for Malignant Lymphoma
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, June 1978, p. 589-594 0095-1137/78/0007-0589$02.00/0 Copyright ( 1978 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 7, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. Disseminated Infection by Fusarium
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, June 1978, p. 589-594 0095-1137/78/0007-0589$02.00/0 Copyright ( 1978 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 7, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. Disseminated Infection by Fusarium
CASE REPORT CHROMOBLASTOMYCOSIS MASQUERADING AS DERMATOPHYTOSIS, WITH THE DESCRIPTION OF A NEW OPPORTUNISTIC SPECIES
 CASE REPORT CHROMOBLASTOMYCOSIS MASQUERADING AS DERMATOPHYTOSIS, WITH THE DESCRIPTION OF A NEW OPPORTUNISTIC SPECIES Kowit Kampirapap 1, Sutthirat Reangchainam 1, Pornpit Ornpaew 2 and Poohglin Tresukosol
CASE REPORT CHROMOBLASTOMYCOSIS MASQUERADING AS DERMATOPHYTOSIS, WITH THE DESCRIPTION OF A NEW OPPORTUNISTIC SPECIES Kowit Kampirapap 1, Sutthirat Reangchainam 1, Pornpit Ornpaew 2 and Poohglin Tresukosol
New, Special Stain for Histopathological Diagnosis of Cryptococcosis
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1981, p. 383-387 0095-1137/81/020383-05$02.00/0 Vol. 13, No. 2 New, Special Stain for Histopathological Diagnosis of Cryptococcosis KYUNG J. KWON-CHUNG,* WILLIAM
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1981, p. 383-387 0095-1137/81/020383-05$02.00/0 Vol. 13, No. 2 New, Special Stain for Histopathological Diagnosis of Cryptococcosis KYUNG J. KWON-CHUNG,* WILLIAM
Epidemiology and Laboratory Diagnosis of Fungal Diseases
 Medical Mycology (BIOL 4849) Summer 2007 Dr. Cooper Epidemiology of Mycoses Epidemiology and Laboratory Diagnosis of Fungal Diseases Mycosis (pl., mycoses) - an infection caused by a fungus Two broad categories
Medical Mycology (BIOL 4849) Summer 2007 Dr. Cooper Epidemiology of Mycoses Epidemiology and Laboratory Diagnosis of Fungal Diseases Mycosis (pl., mycoses) - an infection caused by a fungus Two broad categories
MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR. Physician-in-Chief, AIRP. Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging
 ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR Physician-in-Chief, AIRP Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE Giant cell tumor (GCT) Unicameral
ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR Physician-in-Chief, AIRP Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE Giant cell tumor (GCT) Unicameral
7-002a: Blotter method for the detection of Alternaria radicina on Daucus carota (carrot)
 International Rules for Seed Testing Annexe to Chapter 7: Seed Health Testing Methods 7-002a: Blotter method for the detection of Alternaria radicina on Daucus carota (carrot) Published by: International
International Rules for Seed Testing Annexe to Chapter 7: Seed Health Testing Methods 7-002a: Blotter method for the detection of Alternaria radicina on Daucus carota (carrot) Published by: International
Actinomycosis and aspergillosis in the nose of a diabetic: A case report
 Volume 2 Issue 3 2012 ISSN 2250-0359 Actinomycosis and aspergillosis in the nose of a diabetic: A case report 1 Meenu Khurana Cherian 1*, Rajarajeswari 2 1 Department of ENT, Gulf Medical College Hospital
Volume 2 Issue 3 2012 ISSN 2250-0359 Actinomycosis and aspergillosis in the nose of a diabetic: A case report 1 Meenu Khurana Cherian 1*, Rajarajeswari 2 1 Department of ENT, Gulf Medical College Hospital
Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2, Patrick Smith, M.D. 2, and Larry S. Matthews, M.D. 2
 Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
A Change in the Type of Lesion Produced by the Fibroma Virus
 A CHANGE IN RABBIT FIBROMA VIRUS SUGGESTING MUTATION II. BEHAVIOR 0]~ THE VARIANT VIRUS IN COTTONTAIL RABBITS BY RICHARD E. SHOPE, M.D. (From the Department of Animal and Plant Pathology of The Rockefeller
A CHANGE IN RABBIT FIBROMA VIRUS SUGGESTING MUTATION II. BEHAVIOR 0]~ THE VARIANT VIRUS IN COTTONTAIL RABBITS BY RICHARD E. SHOPE, M.D. (From the Department of Animal and Plant Pathology of The Rockefeller
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
Fungi and their pathogenesis
 Fungi and their pathogenesis -Important -Extra -Notes -In boy s slides -In girl s slides In this link, you will find any correction or notes unmentioned in the team s work. Please check the link below
Fungi and their pathogenesis -Important -Extra -Notes -In boy s slides -In girl s slides In this link, you will find any correction or notes unmentioned in the team s work. Please check the link below
Stilbella holubovae, a new synnematous hyphomycete species on driftwood from the Philippines and South Africa
 Stilbella holubovae, a new synnematous hyphomycete species on driftwood from the Philippines and South Africa Keith A. Seifert 1, Susan J. Stanley 2 and Kevin D. Hyde 2 Centre for Land and Biological Resources
Stilbella holubovae, a new synnematous hyphomycete species on driftwood from the Philippines and South Africa Keith A. Seifert 1, Susan J. Stanley 2 and Kevin D. Hyde 2 Centre for Land and Biological Resources
Impression smear from a nasal mass on a 2 year old cat Presented with: one month duration of epistaxis
 Impression smear from a nasal mass on a 2 year old cat Presented with: one month duration of epistaxis Identify the structures neutrophils macrophages x40 Organisms 8 30 micron in size, with variable capsule
Impression smear from a nasal mass on a 2 year old cat Presented with: one month duration of epistaxis Identify the structures neutrophils macrophages x40 Organisms 8 30 micron in size, with variable capsule
Inflammation Laboratory 1
 Inflammation Laboratory 1 Lab1 Emphasis: The exudates of acute inflammation Descriptions Morphologic Diagnoses Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: March 2013 Describing Lesions
Inflammation Laboratory 1 Lab1 Emphasis: The exudates of acute inflammation Descriptions Morphologic Diagnoses Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: March 2013 Describing Lesions
Mass Histology Service
 Mass Histology Service A complete anatomical pathology laboratory www.masshistology.com Telephone: (877) 286-6004 Report on Pathology A Time Course Study of the Local Effects of Intramuscular XXXXXXX Injection
Mass Histology Service A complete anatomical pathology laboratory www.masshistology.com Telephone: (877) 286-6004 Report on Pathology A Time Course Study of the Local Effects of Intramuscular XXXXXXX Injection
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE RHINOCEREBRAL MUCORMYCOSIS DUE TO RHIZOPUS IN A RECENTLY DIAGNOSED DIABETIC FEMALE: A CASE REPORT KULKARNI KV 1, PATHAK NP 2 1. Assistant
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE RHINOCEREBRAL MUCORMYCOSIS DUE TO RHIZOPUS IN A RECENTLY DIAGNOSED DIABETIC FEMALE: A CASE REPORT KULKARNI KV 1, PATHAK NP 2 1. Assistant
Nyamdolgor.U, Usuhgerel.S, Baatarjargal.P, others, Journal of agricultural sciences 15 (02): 51-55, 2015
 51 HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY FOR USING OF POX INACTIVATED VACCINE IN GOATS Nyamdolgor.U 1*, Usuhgerel.S 2, Baatarjargal.P 1, Altanchimeg.A 1, Odbileg.R 1 1-Institute of Veterinary Medicine, MULS, Mongolia
51 HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY FOR USING OF POX INACTIVATED VACCINE IN GOATS Nyamdolgor.U 1*, Usuhgerel.S 2, Baatarjargal.P 1, Altanchimeg.A 1, Odbileg.R 1 1-Institute of Veterinary Medicine, MULS, Mongolia
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR
 INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Histopath Laboratory 1 Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Goals: Examine Tissue and Identify the Organ Describe the lesion, grossly and histologically
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Histopath Laboratory 1 Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Goals: Examine Tissue and Identify the Organ Describe the lesion, grossly and histologically
7-001a: Blotter method for the detection of Alternaria dauci on Daucus carota (carrot)
 International Rules for Seed Testing Annexe to Chapter 7: Seed Health Testing Methods 7-001a: Blotter method for the detection of Alternaria dauci on Daucus carota (carrot) Published by: International
International Rules for Seed Testing Annexe to Chapter 7: Seed Health Testing Methods 7-001a: Blotter method for the detection of Alternaria dauci on Daucus carota (carrot) Published by: International
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL SECOND EDITION
 VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
LYMPHOBLASTOMA OF THE SPLEEN
 LYMPHOBLASTOMA OF THE SPLEEN By ELLIS KELLERT, M.D. (From the Ellis Hospital Laboratory, Schenectady, N. Y.) Several recently reported cases have stimulated interest in a newly described form of the ever
LYMPHOBLASTOMA OF THE SPLEEN By ELLIS KELLERT, M.D. (From the Ellis Hospital Laboratory, Schenectady, N. Y.) Several recently reported cases have stimulated interest in a newly described form of the ever
Fatal Case of Trichoderma harzianum Infection in a Renal Transplant Recipient
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 1999, p. 3751 3755 Vol. 37, No. 11 0095-1137/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Fatal Case of Trichoderma harzianum
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 1999, p. 3751 3755 Vol. 37, No. 11 0095-1137/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Fatal Case of Trichoderma harzianum
Histopathology: chronic inflammation
 Histopathology: chronic inflammation These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: chronic inflammation These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
GIANT CELL TUMOR OF TENDON SHEATH A CYTO HISTO CORRELATION
 GIANT CELL TUMOR OF TENDON SHEATH A CYTO HISTO CORRELATION Dr.S.SRIKANTH, Assistant Professor.Dept of Patholgy. Dr.SMITHA VADANA, Resident.Dept of pathology. Dr.R.SUHELA. Resident.Dept Of Pathology. Prathima
GIANT CELL TUMOR OF TENDON SHEATH A CYTO HISTO CORRELATION Dr.S.SRIKANTH, Assistant Professor.Dept of Patholgy. Dr.SMITHA VADANA, Resident.Dept of pathology. Dr.R.SUHELA. Resident.Dept Of Pathology. Prathima
ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF A SMALL PIGMENTED CUTANEOUS LESION*
 ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF A SMALL PIGMENTED CUTANEOUS LESION* The description of the lesion in the title of this rcport is intentionally non-committal. Diagnosed clinically as a lentigo, it was removed as
ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF A SMALL PIGMENTED CUTANEOUS LESION* The description of the lesion in the title of this rcport is intentionally non-committal. Diagnosed clinically as a lentigo, it was removed as
CONTRIBUTION TO THE HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FILARIASIS
 CONTRIBUTION TO THE HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FILARIASIS PHILIP H. HARTZ Public Health Service, Curacao, N.W.I. The histologic changes caused by filariasis (Wucheria Bancrofti) are considered to be non-specific
CONTRIBUTION TO THE HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FILARIASIS PHILIP H. HARTZ Public Health Service, Curacao, N.W.I. The histologic changes caused by filariasis (Wucheria Bancrofti) are considered to be non-specific
1. Supplementary Prevention Experiment Additional Results
 1. Supplementary 1. 1. Prevention Experiment Additional Results Figure 1 presents the NMR measurements of tibiae and femurs bones, which were measured 6 weeks post operation at the central zone of bone
1. Supplementary 1. 1. Prevention Experiment Additional Results Figure 1 presents the NMR measurements of tibiae and femurs bones, which were measured 6 weeks post operation at the central zone of bone
BONE TISSUE. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
Fungal ball.. Clinical and radiological features DR. AHMED ALTUWAIJRI 1/5/2017
 Fungal ball.. Clinical and radiological features DR. AHMED ALTUWAIJRI 1/5/2017 Fungal Rhinosinusitis (FRS) Rhinosinusitis, is a common disorder affecting approximately 20% of the population at some time
Fungal ball.. Clinical and radiological features DR. AHMED ALTUWAIJRI 1/5/2017 Fungal Rhinosinusitis (FRS) Rhinosinusitis, is a common disorder affecting approximately 20% of the population at some time
Dermatophytes Dr. Hala Al Daghistani
 Dermatophytes Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Dermatophytoses are superficial infections of the skin and its appendages, commonly known as ringworm, athlete s foot, and jock itch. They are caused by species of
Dermatophytes Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Dermatophytoses are superficial infections of the skin and its appendages, commonly known as ringworm, athlete s foot, and jock itch. They are caused by species of
Blotter method for the detection of Alternaria radicina on Daucus carota
 International Rules for Seed Testing Annexe to Chapter 7: Seed Health Testing Methods 7-002a: Blotter method for the detection of Alternaria radicina on Daucus carota Published by: International Seed Testing
International Rules for Seed Testing Annexe to Chapter 7: Seed Health Testing Methods 7-002a: Blotter method for the detection of Alternaria radicina on Daucus carota Published by: International Seed Testing
Title. Author(s)KANAGAWA, Hiroshi; ISHIKAWA, Tsune; KAWATA, Keiichir. CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 13(1): Issue Date
 Title A CASE OF CANINE TESTICULAR SERTOLI CELL TUMOR Author(s)KANAGAWA, Hiroshi; ISHIKAWA, Tsune; KAWATA, Keiichir CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 13(1): 11-1 Issue Date 1965-03 DOI 10.14943/jjvr.13.1.11
Title A CASE OF CANINE TESTICULAR SERTOLI CELL TUMOR Author(s)KANAGAWA, Hiroshi; ISHIKAWA, Tsune; KAWATA, Keiichir CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 13(1): 11-1 Issue Date 1965-03 DOI 10.14943/jjvr.13.1.11
LGM International, Inc.
 Liqui-PREP TM Cytology Atlas Preface The following pictures are examples with descriptions of cytology slides processed with the Liqui-PREP TM System.. The descriptions are reviewed by Pathologists. It
Liqui-PREP TM Cytology Atlas Preface The following pictures are examples with descriptions of cytology slides processed with the Liqui-PREP TM System.. The descriptions are reviewed by Pathologists. It
HOW DO WE DIAGNOSE LAMENESS IN YOUR HORSE?
 HOW DO WE DIAGNOSE LAMENESS IN YOUR HORSE? To help horse owners better understand the tools we routinely use at VetweRx to evaluate their horse s soundness, the following section of this website reviews
HOW DO WE DIAGNOSE LAMENESS IN YOUR HORSE? To help horse owners better understand the tools we routinely use at VetweRx to evaluate their horse s soundness, the following section of this website reviews
Describing and interpreting gross lesions. Prepared for VPM 4600, May 2018; Shannon Martinson
 Describing and interpreting gross lesions Prepared for VPM 4600, May 2018; Shannon Martinson How to Describe (and Interpret) Lesions Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 Look at the specimen: Is it normal or abnormal
Describing and interpreting gross lesions Prepared for VPM 4600, May 2018; Shannon Martinson How to Describe (and Interpret) Lesions Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 Look at the specimen: Is it normal or abnormal
A rare complication of ear piercing: a case of subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused by Veronaea botryosa in China
 Medical Mycology April 2011, 49, 296 302 Case Reports A rare complication of ear piercing: a case of subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused by Veronaea botryosa in H. SANG *,1, X. E. ZHENG *, Q. T. KONG
Medical Mycology April 2011, 49, 296 302 Case Reports A rare complication of ear piercing: a case of subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused by Veronaea botryosa in H. SANG *,1, X. E. ZHENG *, Q. T. KONG
Colonial and Morphological Characteristics of various fungi Species Isolated from soil in Bangalore city
 Bulletin of Environment, Pharmacology and Life Sciences Bull. Env. Pharmacol. Life Sci., Vol 6[1] December 2016: 17-21 2016 Academy for Environment and Life Sciences, India Online ISSN 2277-1808 Journal
Bulletin of Environment, Pharmacology and Life Sciences Bull. Env. Pharmacol. Life Sci., Vol 6[1] December 2016: 17-21 2016 Academy for Environment and Life Sciences, India Online ISSN 2277-1808 Journal
Dermatomycosis is defined as nondermatophyte. Four Cases of Dermatomycosis: Superficial Cutaneous Infection by Alternaria or Bipolaris
 : Superficial Cutaneous Infection by Alternaria or Bipolaris Christopher W. Robb, PhD; Peter J. Malouf, DO; Ronald P. Rapini, MD Invasive dermal infections in immunosuppressed patients by a wide variety
: Superficial Cutaneous Infection by Alternaria or Bipolaris Christopher W. Robb, PhD; Peter J. Malouf, DO; Ronald P. Rapini, MD Invasive dermal infections in immunosuppressed patients by a wide variety
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton
 Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
Key words wild passion-fruit, Mycosphaerellaceae, tropical fruits, cercosporoid fungi
 A NEW FUNGAL DISEASE CAUSED BY A PSEUDOCERCOSPORA SPECIES ON PASSIFLORA SETACEA IN PLANALTINA-DF, BRAZIL Alexei C. Dianese 1, Ana M. Costa 1 & José C. Dianese 2 ( 1 Embrapa Cerrados, Br-020, Km 18, 73310-970
A NEW FUNGAL DISEASE CAUSED BY A PSEUDOCERCOSPORA SPECIES ON PASSIFLORA SETACEA IN PLANALTINA-DF, BRAZIL Alexei C. Dianese 1, Ana M. Costa 1 & José C. Dianese 2 ( 1 Embrapa Cerrados, Br-020, Km 18, 73310-970
Hyphomycetes & Coelomycetes Identification
 Hyphomycetes & Coelomycetes Identification Saccardo ~ 1880 devised the first practical scheme for identifying fungi based on structure (morphology) of the conidium. "Sylloge Fungorum IV" Vuillemin ~ 1910
Hyphomycetes & Coelomycetes Identification Saccardo ~ 1880 devised the first practical scheme for identifying fungi based on structure (morphology) of the conidium. "Sylloge Fungorum IV" Vuillemin ~ 1910
The Morphologic Identification of Common Organisms That May Look Alike in the General Pathology Practice: A Brief Review
 Ibnosina J Med BS 227 PATHOLOGY CORNER The Morphologic Identification of Common Organisms That May Look Alike in the General Pathology Practice: A Brief Review Jenna Boué 1, Basil M. Kahwash 2, Sean Kirby
Ibnosina J Med BS 227 PATHOLOGY CORNER The Morphologic Identification of Common Organisms That May Look Alike in the General Pathology Practice: A Brief Review Jenna Boué 1, Basil M. Kahwash 2, Sean Kirby
Prevalence of Oculomycosis in a Tertiary Care Centre
 AJMS Al Ameen J Med Sci (2 011 )4 (4 ):3 3 4-3 3 8 (A US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal) I S S N 0 9 7 4-1 1 4 3 C O D E N : A A J M B G ORIGI NAL ARTICLE Prevalence of Oculomycosis in a
AJMS Al Ameen J Med Sci (2 011 )4 (4 ):3 3 4-3 3 8 (A US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal) I S S N 0 9 7 4-1 1 4 3 C O D E N : A A J M B G ORIGI NAL ARTICLE Prevalence of Oculomycosis in a
