THE ROLE OF MAST CELLS IN CARBON TETRACHLORIDE INDUCED RAT SKELETAL MUSCLE TISSUE DAMAGE
|
|
|
- Rafe Daniel
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original article UDC: XXXX doi: /amm THE ROLE OF MAST CELLS IN CARBON TETRACHLORIDE INDUCED RAT SKELETAL MUSCLE TISSUE DAMAGE Ljubiša M. Lilić 1, Dragan Toskić 1, Rade Ž. Stefanović 1, Branimir B. Mekić 1, Ivan R. Ilić 2, Nikola M. Stojanović 3 Animal models demonstrating skeletal muscle (SM) disorders are rarely investigated, although these disorders accompany liver disorders and can occur during prolonged exercise/training. It is speculated that mast cells, normally present in the interstitial SM tissue, are involved in the pathophysiology of different SM disorders. Thus, the present study aims to analyze, on histopathological level, the involvement of mast cells in acute rat intoxication with carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). Biceps and gastrocnemius muscle were obtained from male Wistar rats acutely exposed to CCl4 (1 ml/kg) and the pathological analysis was performed on Toluidine blue stained tissue sections. The obtained results were statically compared with those from control group using Student s t-test. In SM tissue obtained form the control group mast cells were found only in the interstitium, while in those that received CCl4 they were located mainly near the blood vessels. Also, in the experimental group treated with CCl4 mast cells were more abundant and were percenutally more degranulated than those found in the control group. Thus, one can say that herein presented model of CCl4-induced SM damage is partially dependent on the activity of mast cells. Acta Medica Medianae 2019;58(2):XX-XX. Key words: Carbon tetrachloride, Skeletal muscles, Mast cells 1 Faculty of Sport and Physical Education in Leposavić, University of Priština, Priština, Serbia 2 Institute of Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Niš, Zorana Đinđića 81, Niš, Serbia 3 Faculty of Medicine, University of Niš, Zorana Đinđića 81, Niš, Serbia Contact: : Nikola M Stojanović, Faculty of Medicine, University of Niš Zorana Đinđića Niš, Serbia nikola.st90@yahoo.com Introduction Our body is consisted of three distinct types of muscles, from which the skeletal muscles (SM) are the only ones that can contract under our will (deliberately) maintaining body posture and enabling locomotion. Skeletal muscle specific anatomical and physiological organization allows SM to function (1). Each SM is consisted of a large number of myofibrils (muscle cells) that represent the smallest functional unit (1). Body and SM tissue mass can be significantly affected under different underlaying conditions and these changes occur due to tissue protein degradation (2). Changes in SM mass and function can be seen in several liver disorders, as well as under various physiological conditions that involve significant production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) (3,4). Carbon tetrachloride (CCl 4), a synthetic chemical often used in paints, solvents and extinguishers (5), is known to be a useful in inducing ROS mediated tissue damage in laboratory animals. When applied it causes liver, kidneys, brain, muscles, lungs, testis, etc. oxidative damage (6), via trichloromethyl free radicals generated in liver (6,7). The mechanism by which CCl 4 damages cell structures is relatively well studied, however the role of mast cells in SM injury caused by CCl 4 are still not fully investigated. Mast cells are mesenchymal cell, stained metachromatically with some blue dyes, that contain numerous granules which contain the majority of the body s histamine. These cells play a crucial role in body inflammatory and allergic reaction (8). Before their final migration and differentiation in tissue, mast cells (type of leukocytes) circulate in the blood as immature cells derived from hematopoietic progenitor cells. All tissues of the body possess different percent of mast cells, while they are more abundant in tissues that are coming in close contact with external environment (skin, intestinal and airway mucosa) (8).
2 Aim of the study Although the toxic effects of CCl4 on SM tissue have been investigated, the specifics pathogenetic role of mast cells are not completely investigated. Thus, the goal of the present study was to detect and describe on histopathological level the changes in mast cells occurring in rat SM after acute administration of CCl4. Material and methods Animals and housing Male Wistar rats, weighting g, were housed in groups of 6 and obtained from the Vivarium of the Institute of Biomedical Research, Faculty of Medicine, University of Niš, Serbia. The animals were maintained under standard laboratory conditions: temperature 22±2 ºC and humidity 60%, with food and water available ad libitum. All experimental procedures with the animals were conducted in compliance with the declaration of Helsinki and European Community guidelines for the ethical handling of laboratory animals (EU Directive of 2010; 2010/63/EU) and were also approved by the local Ethics Committee. Muscle tissue damage induction Before the experiment, all animals were divided into two groups of 6 rats each: the control group where the animals were administered only the vehicle (olive oil) in the dose of 10 ml/kg, and the experimental group with CCl 4-treated animals. Acute administration of CCl 4 (1 ml/kg), known to cause significant liver damage (6), was given to rats via an intraperitoneal injection 24 h before the animals were sacrificed by an overdose of ketamine. Skeletal muscle tissue samples collected, using scissors and tweezers, for histological analyses included the left gastrocnemius (GCM) and biceps (BM) muscles. Histopathological observations The GCM and BM tissue specimens separated for histopathological examination were fixed in buffered formaldehyde solution (10%, w/v). The fixed tissues were then dehydrated with ethanol solutions of differing concentration (50-100%, v/v), embedded in paraffin, cut into 4-5 μm thick sections, stained with Toluidine Blue (TB) and further examined under an Olympus BH2 light microscope. The average number of mast cells per high-power field (x40) was counted on 10 randomly selected fields for each muscle specimen stained with TB. Also, the percent of degranulated mast cells was counted on each examined high-power field. Statistical analysis The results were expressed as mean values ± SD. Statistically significant differences were determined by Student s t-test (Graph pad Prism version 5.03, San Diego, CA, USA) and the obtained results were tested for correlation as well. Probability values (p) less than or equal to 0.05 were considered to be statistically significant. Results The number and % of degranulated mast cells, found in GCM and BM tissue sections stained with TB, were found to be statistically significantly higher in both investigated muscles originating from animals exposed to CCl4 compared to the control animals (Table 1 and Figure 1). In the investigated TB stained tissue mast cells granules appeared red-purple (metachromatic granules), while their cytoplasm and background appeared pale blue (ortochromatic). The mast cell shape varied from ovoid to spindle-shaped and one could clearly distinguish preserved (not degranulated) and degranulated mast cells that appeared deep and light blue, respectively (Figure 1). In healthy (control group) animal mast cells were observed only in the interstitial connective tissue that normally separates skeletal muscle into separate fascicles. On the other hand, in animals treated with CCl 4 mast cells appeared in the interstitial connective tissue as well, however they were more frequently found around blood vessels. Table 1. Number and % of degranulated mast cells obtained for each of the two studied muscles from the two different animal groups Tracked parameter Average number of mast cells/high power field (x40) Degranulated mast cells (%) Gastrocnemius muscle Biceps muscle Control 0.6 ± ± 0 CCl4 treated 1.4 ± 0.2* 66.5 ± 16.1* Control 0.9 ± ± 0 CCl4 treated 1.2 ± 0.05* 62.7 ± 14.2* The results are presented as mean±sd (n=6); *p<0.001 vs. control group.
3 Figure 1. Microscopic appearance of degranulated and non-degranulated mast cells present in skeletal muscle tissue stained with Toluidine blue (x400). Discussion The two muscles evaluated in our study, GCM and BFM, represent important hind-limb muscles that enable animal movement. Biceps femoris muscle is the largest muscle in the hind limb and has multiple functions that involve thigh abduction, hip extension and knee flexion, while GCM is responsible for plantar flexion (9). Since their discovery, back in 1877, mast cells are considered as normal constituents of interstitial tissue of different vertebrates (10). Later they were recognized as cells important in triggering and/or maintenance of different inflammatory and immunological processes (10). These cells represent the source of inflammatory mediators such as histamine, nitric oxide, proteases tryptase and chymase, and pre-formed tumor necrosis factoralpha (TNF-α), as well as other toxic mediators by which the muscle tissue can be injured (11, 8). When mast cells are triggered to degranulate, the secretory granules located within the cell are released, exocytosis, resulting in the release of their internal contents (8). The importance of mast cells in the pathophysiology of muscle disorders was previously shown in the ischemia/reperfusion muscle injury model (11) and the present research proves the involvement of these cells in acute CCl 4-induced muscle damage (Table 1, Figure 1), as well. Also, these cells were found to be significantly increased in different myopathic disorders, e.g. Duchenne muscular dystrophy, where it was suggested that grouped necrosis of extrafusal fibers occurs possibly due to the activity of these cells (10). Thus, the increase in both the number of mast cells and % of their degranulation indicates that their involvement in acute CCl 4-induced muscle damage should not be neglected. Additionally, there is a possibility that a much higher number of mast cells were involved in tissue damage, both resident and mobilized, however due to their degranulation TB staining might not have stained all of mast cells. The consequence of degranulation can probably be brought in connection with inflammatory cell infiltrate, seen after CCl 4 application, that is comprised mainly of neutrophils. Namely these neutrophils secrete an enzyme, myeloperoxidase, that causes the onset of degranulation (histamine release) form isolated mast cells (12). On the other hand, SM resident mast cells are known to provoke a significant increase in the number of neutrophils in injured SM tissue (13). Similar results were obtained in the study where mast cell membrane stabilizing agent, cromolyn, was administer prior to neutrophil attracting agent, bupivacaine, thus causing a decrease in neutrophil infiltration by 70% (14). All of the results, relating to the presence and state of mast cells, represent an important addition to the overall conclusion concerning the involvement of these cells in muscle tissue damage induced by an acute application of CCl 4. Also, one can say that the damage caused by CCl 4 seems more significant in GCM than in BM (Table 1), and such slight differences in the extent of CCl 4 injury in GCM and BM are not completely unexpected. Namely, a previous study revealed different degrees of protein catabolism, estimated based on tyrosine release, in various muscle tissues after CCl 4 application (3). Thus, it is not surprising that the two muscles do not suffer identical damage, since their vascularisation, structure (fibers size, mitochondria amount, myoglobin concentration, etc.) and function are not the same.
4 Conclusion The herein presented model of CCl 4-induced skeletal muscle damage can be considered a useful model that could mimic both mild ROS-mediated muscle damage seen in strenuous physical exercise and/or muscle damage (waste) that frequently accompanies liver diseases. The results unequivocally demonstrated the involvement of mast cells in skeletal muscle tissue damage caused by CCl 4 after an acute application. Acknowledgment This work was funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of Serbia (grant No. III 43012). References 1. Thews G, Mutschler E, Vaupel P. Skelett. Muskulatur und Bindegewebe. In: Vaupel P, Schaible HG, Mutschler E (Eds). Anatomie, Physiologie, Pathophysiologie des Menschen. Stuttgart: Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft mbh; 1999, pp Wolfe, RR. The underappreciated role of muscle in health and disease. Am J Clin Nutr 2006;84(3): Weber FL Jr, Macechko PT, Kelson SR, Karajiannis E, Hassan MO. Increased muscle protein catabolism caused by carbon tetrachloride hepatic injury in rats. Gastroenterology. 1992;102(5): Bentley DJ, Ackerman J, Clifford T, Slattery KS. Acute and chronic effects of antioxidant supplementation on exercise performance. In: Lamprecht M (Ed). Antioxidants in sport nutrition. Boca Raton: CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2015, pp Pope AM, Rall DP. Environmental Medicine. Washington D.C.: National Academy Press; Radulović NS, Randjelović PJ, Stojanović NM, Ilić IR, Miltojević AB. Influence of methyl and isopropyl n- methyl antranilates on carbon tetrachloride-induced changes in rat liver morphology and function. FU Phys Chem Tech 2013;11(1): Vural DF, Cebesoy S, Ozerkan D, Eyison HM. The effect of melatonine on rats gastrocnemius muscle applied with carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). J Entomol Zool Stud 2017;5(3): Dawicki W, Marshall JS. New and emerging roles for mast cells in host defence. Curr Opin Immunol. 2007; 19: Armstrong RB, Phelps RO. Muscle fiber type composition of the rat hindlimb. Am J Anat 1984;171(3): Nahirney PC, Dow PR, Ovalle WK. Quantitative morphology of mast cells in skeletal muscle of normal and genetically dystrophic mice. Anat Rec. 1997; 247(3): Bortolotto SK, Morrison WA, Han XL, Messina A. Mast cells play a pivotal role in ischaemia reperfusion injury to skeletal muscles. Lab Invest 2004;84(9): Stendahl O, Molin L, Lindroth M. Granulocytemediated release of histamine from mast cells. Effect of myeloperoxidase and its inhibition by antiinflammatory sulfone compounds. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol 1983;70(3): Dumont N, Lepage K, Côté CH, Frenette J. Mast cells can modulate leukocyte accumulation and skeletal muscle function following hindlimb unloading. J Appl Physiol. 2007; 103(1): Côte CH, Tremblay MH, Duchesne E, Lapoite BM. Inflammation-induced leukocyte accumulation in injured skeletal muscle: role of mast cells. Muscle Nerve. 2008; 37(6):
5 Originalni rad UDC: XXXX doi: /amm ULOGA MASTOCITA U MODELU UGLJEN TETRAHLORIDOM INDUKOVANOG OŠTEĆENJA SKELETNOG MIŠIĆNOG TKIVA PACOVA Ljubiša M. Lilić 1, Dragan Toskić 1, Rade Ž. Stefanović 1, Branimir B. Mekić 1, Ivan R. Ilić 2, Nikola M. Stojanović 3 1 Fakultet sporta i fizičke aktivnosti u Leposaviću, Univerzitet u Prištini, Priština, Srbija 2 Institut za Patologiju, Medicinski fakultet, Univerzitet u Nišu, Niš, Srbija 3 Medicinski fakultet, Univerzitet u Nišu, Niš, Srbija Kontakt: Nikola M. Stojanović, Medicinski fakultet, Univerzitet u Nišu Zorana Đinđića 81, Niš, Srbija nikola.st90@yahoo.com Animalni modeli koji imitiraju oštećenja skeletnih mišića (SM) su retko predmet istraživanja, iako poremećaji SM često prate druge poremećaje organa, kao što su oštećenja jetre. Takođe, oštećenja SM mogu da se jave nakon duge i intenzivne fizičke aktivnosti. Smatra se da su mastociti, deo normalne ćelije populacije intersticijuma SM, uključeni u patofiziološki mehanizam nastanaka SM oboljenja. Ova studija ima za cilj da na patohistološkom nivou pokaže ulogu mastocita u akutnom oštećenju SM pacova koji su izloženi ugljen-tetrahloridu (CCl4). Od životinja koje su tretirane akutno CCl4 (1 ml/kg) uzimani su uzorci m. biceps i m. gastrocnemius za dalju patohistološku obradu, bojenje (Toludin blue) i analziu. Dobijeni rezultati su upoređeni korišćenjem Studentovog t-testa. U uzorcima SM koji su dobijeni od životinja iz kontrolne grupe mastociti su bili prisutni najčešće u intersticijumu, dok kod životinja koje su bile izložene CCl4 mastociti su se nalazili većinom u blizini krvnih sudova. Takođe, u eksperimentalnoj grupi životinja tretiranih CCl4 mastociti su bili mnogo više zastupljeniji nego u kontrolnoj, a i procenat onih koji su bili degranulisani je bio statistički značajno veći. Na osnovu rezultata ove studije može se zaključiti da u oštećenja SM koje je indukovano CCl4 delimično zavisi i od aktivnosti mastocita. Acta Medica Medianae 2019;58(2):XX-XX. Ključne reči: Ugljen-tetrahlorid, Skeletni mišići, Mastociti
LYMPH GLAND. By : Group 1
 LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Role of Mast Cells in Appendicitis Dr. Jyoti Sharma 1*, Dr. Nitin Chaudhary 2*, Dr. Sunita
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Role of Mast Cells in Appendicitis Dr. Jyoti Sharma 1*, Dr. Nitin Chaudhary 2*, Dr. Sunita
Yara Saddam. Amr Alkhatib. Ihsan
 1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
MAST CELLS IN ORAL LICHEN PLANUS
 MAST CELLS IN ORAL LICHEN PLANUS Mahija Janardhanan* V.Ramesh. ** *Reader, Department of Oral Pathology & Microbiology, Amrita school of Dentistry, Kochi. **Professor & HOD, Department of Oral Pathology
MAST CELLS IN ORAL LICHEN PLANUS Mahija Janardhanan* V.Ramesh. ** *Reader, Department of Oral Pathology & Microbiology, Amrita school of Dentistry, Kochi. **Professor & HOD, Department of Oral Pathology
Muscular System. IB Sports, exercise and health science 1.2
 Muscular System IB Sports, exercise and health science 1.2 Characteristics Common to Contractility-ability to shorten the muscles length Extensibility-ability to lengthen the muscles length Elasticity-muscle
Muscular System IB Sports, exercise and health science 1.2 Characteristics Common to Contractility-ability to shorten the muscles length Extensibility-ability to lengthen the muscles length Elasticity-muscle
1 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II PLATELETS. Mature Stage: No nucleus. Only 2-3 µm in diameter: significantly smaller than RBCs
 1 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II LAB BLOOD PLATES EOSINOPHIL Contains large red-staining granules Usually 2 lobes 12-17 µm: about the size of neutrophils (2X erythrocytes) regulation/reduction of Histamine.
1 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II LAB BLOOD PLATES EOSINOPHIL Contains large red-staining granules Usually 2 lobes 12-17 µm: about the size of neutrophils (2X erythrocytes) regulation/reduction of Histamine.
Cell Adaptation, Cell Injury and Cell Death
 Cell Adaptation, Cell Injury and Cell Death Pathology:- is the study of structural and functional abnormalities that are expressed as diseases of organs and systems. Modern pathology, proposed that injury
Cell Adaptation, Cell Injury and Cell Death Pathology:- is the study of structural and functional abnormalities that are expressed as diseases of organs and systems. Modern pathology, proposed that injury
Agenda. Components of blood. Blood is Fluid Connective Tissue. Blood: General functions
 Agenda Chapter 19: Blood Major functions Major Components Structure of RBCs and WBCs ABO Blood Types, and Rh Factor Lab 34.1 and Blood Typing Blood: General functions Transport of dissolved gases, nutrients,
Agenda Chapter 19: Blood Major functions Major Components Structure of RBCs and WBCs ABO Blood Types, and Rh Factor Lab 34.1 and Blood Typing Blood: General functions Transport of dissolved gases, nutrients,
Individual cells Extracellular matrix
 Connective Tissue Connective Tissue Elements Individual cells Extracellular matrix»fibers» Collagen» Elastic» Reticular»Ground Substance» PG (proteoglycans)» GAG (glycosaminoglycan)» GP (glycoprotein)
Connective Tissue Connective Tissue Elements Individual cells Extracellular matrix»fibers» Collagen» Elastic» Reticular»Ground Substance» PG (proteoglycans)» GAG (glycosaminoglycan)» GP (glycoprotein)
How I Handle Mast Cells in GI Biopsies
 How I Handle Mast Cells in GI Biopsies Dora Lam-Himlin, MD Mayo Clinic Scottsdale, AZ Rodger C. Haggitt Gastrointestinal Pathology Society Forum United States and Canadian Academy of Pathologists Seattle,
How I Handle Mast Cells in GI Biopsies Dora Lam-Himlin, MD Mayo Clinic Scottsdale, AZ Rodger C. Haggitt Gastrointestinal Pathology Society Forum United States and Canadian Academy of Pathologists Seattle,
Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, University of Florida College of Medicine-Jacksonville, Jacksonville, FL 32209, USA
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Dermatology Volume 2012, Article ID 759630, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2012/759630 Research Article A Comparative Analysis of Mast Cell Quantification in Five Common
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Dermatology Volume 2012, Article ID 759630, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2012/759630 Research Article A Comparative Analysis of Mast Cell Quantification in Five Common
Sheet #7. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh
 Sheet #7 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Connective tissue The differences between epithelial and connective tissue - Epithelial cells are tightly packed (no or minimal spaces
Sheet #7 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Connective tissue The differences between epithelial and connective tissue - Epithelial cells are tightly packed (no or minimal spaces
Cell-Derived Inflammatory Mediators
 Cell-Derived Inflammatory Mediators Introduction about chemical mediators in inflammation Mediators may be Cellular mediators cell-produced or cell-secreted derived from circulating inactive precursors,
Cell-Derived Inflammatory Mediators Introduction about chemical mediators in inflammation Mediators may be Cellular mediators cell-produced or cell-secreted derived from circulating inactive precursors,
G. Types of White Blood Cells
 1. White blood cells are also called leukocytes. G. Types of White Blood Cells 2. White blood cells function to protect against diseases. 3. Two hormones that stimulate white blood cell production are
1. White blood cells are also called leukocytes. G. Types of White Blood Cells 2. White blood cells function to protect against diseases. 3. Two hormones that stimulate white blood cell production are
Prepared by Cyrus H. Nozad, MD, University of Tennessee and John Seyerle, MD, Ohio State University
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 21 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, Seventh Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 21: Antigen-Presenting Dendritic Cells (Pages
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 21 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, Seventh Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 21: Antigen-Presenting Dendritic Cells (Pages
How I Handle Mast Cells in GI Biopsies
 How I Handle Mast Cells in GI Biopsies Dora Lam-Himlin, MD Rodger C. Haggitt Gastrointestinal Pathology Society Forum United States and Canadian Academy of Pathologists Seattle, Washington, March 12, 2016
How I Handle Mast Cells in GI Biopsies Dora Lam-Himlin, MD Rodger C. Haggitt Gastrointestinal Pathology Society Forum United States and Canadian Academy of Pathologists Seattle, Washington, March 12, 2016
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi
 number 11 Done by Husam Abu-Awad Corrected by Muhammad Tarabieh Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi The possible outcomes of an acute inflammation are the following: 1- A complete resolution in which the tissue returns
number 11 Done by Husam Abu-Awad Corrected by Muhammad Tarabieh Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi The possible outcomes of an acute inflammation are the following: 1- A complete resolution in which the tissue returns
Mast Cells in the Rat Tongue
 Institute of Experimental Morphology, Pathology and Anthropology with Museum Bulgarian Anatomical Society Acta morphologica et anthropologica, 25 (3-4) Sofia 2018 Mast Cells in the Rat Tongue Nikola Pirovski
Institute of Experimental Morphology, Pathology and Anthropology with Museum Bulgarian Anatomical Society Acta morphologica et anthropologica, 25 (3-4) Sofia 2018 Mast Cells in the Rat Tongue Nikola Pirovski
Dragan Toskić 1, Ljubiša Lilić 1 and Lazar Toskić 2. Master student, Belgrade, Serbia. Resaarch in Kinesiology 2014, Vol. 4, No. 1, pp.
 Resaarch in Kinesiology 2014, Vol. 4, No. 1, pp. 55-59 55 A COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF THE MORPHOLOGICAL STRUCTURES AND DIFFERENCES AMONG ELEMENTARY SCHOOL STUDENTS CAUSED BY THE EFFECTS OF VARIOUS PHYSICAL
Resaarch in Kinesiology 2014, Vol. 4, No. 1, pp. 55-59 55 A COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF THE MORPHOLOGICAL STRUCTURES AND DIFFERENCES AMONG ELEMENTARY SCHOOL STUDENTS CAUSED BY THE EFFECTS OF VARIOUS PHYSICAL
Succinic Dehydrogenase Activity of Skeltral Muscle and Its Electrophysiological Function
 26 Succinic Dehydrogenase Activity of Skeltral Muscle and Its Electrophysiological Function Shusaku TSUICAMOTO and Masahiko MORI Department of Oral Surgery, Osaka University Dental School, Osaka. Introduction
26 Succinic Dehydrogenase Activity of Skeltral Muscle and Its Electrophysiological Function Shusaku TSUICAMOTO and Masahiko MORI Department of Oral Surgery, Osaka University Dental School, Osaka. Introduction
Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system. Answer Sheet
 Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system Answer Sheet Q1 Which areas of the lymph node have most CD3 staining? A1 Most CD3 staining is present in the paracortex (T cell areas). This is towards the outside
Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system Answer Sheet Q1 Which areas of the lymph node have most CD3 staining? A1 Most CD3 staining is present in the paracortex (T cell areas). This is towards the outside
Chapter 14. Blood. Blood Volume. Blood Composition. Blood
 Blood connective tissue transports vital substances maintains stability of interstitial fluid distributes heat Chapter 14 Blood Blood Cells form mostly in red bone marrow red blood cells white blood cells
Blood connective tissue transports vital substances maintains stability of interstitial fluid distributes heat Chapter 14 Blood Blood Cells form mostly in red bone marrow red blood cells white blood cells
HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS D R S H O AI B R AZ A
 HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS D R S H O AI B R AZ A HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS Are exaggerated immune response upon antigenic stimulation Individuals who have been previously exposed to an antigen are said
HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS D R S H O AI B R AZ A HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS Are exaggerated immune response upon antigenic stimulation Individuals who have been previously exposed to an antigen are said
Human Anatomy and Physiology- Problem Drill 04: Tissues of the Body
 Human Anatomy and Physiology- Problem Drill 04: Tissues of the Body Question No. 1 of 10 A biopsy sample is obtained from a lesion on the right cheek of a male patient. A technician in the histology lab
Human Anatomy and Physiology- Problem Drill 04: Tissues of the Body Question No. 1 of 10 A biopsy sample is obtained from a lesion on the right cheek of a male patient. A technician in the histology lab
Medical School Histology Basics Introduction to Microscopy. VIBS 289 lab
 Medical School Histology Basics Introduction to Microscopy VIBS 289 lab Larry Johnson Texas A&M University Objectives Learn the difference in magnification and resolution Learn about different types of
Medical School Histology Basics Introduction to Microscopy VIBS 289 lab Larry Johnson Texas A&M University Objectives Learn the difference in magnification and resolution Learn about different types of
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL. Sample preparation for light microscopy
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Sample preparation for light microscopy To characterize the granulocytes and melanomacrophage centers, cross sections were prepared for light microscopy, as described in Material
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Sample preparation for light microscopy To characterize the granulocytes and melanomacrophage centers, cross sections were prepared for light microscopy, as described in Material
LECTURE TOPIC ASSIGNMENTS
 BASICS LECTURE TOPIC ASSIGNMENTS LECTURE TOPIC: ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY Read the textbook: Ch. 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go To: Web Site > Folder: AnatTerm > A25terms09.pdf. Download the file &
BASICS LECTURE TOPIC ASSIGNMENTS LECTURE TOPIC: ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY Read the textbook: Ch. 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go To: Web Site > Folder: AnatTerm > A25terms09.pdf. Download the file &
Research Article Cytological Evaluation of Hyaluronic Acid on Wound Healing Following Extraction
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS DENTAL SCIENCE Research Article Cytological Evaluation of Hyaluronic Acid on Wound Healing Following Extraction Gocmen Gokhan 1 *, Gonul O 1, Oktay NS 2, Pisiriciler R 2 and Goker
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS DENTAL SCIENCE Research Article Cytological Evaluation of Hyaluronic Acid on Wound Healing Following Extraction Gocmen Gokhan 1 *, Gonul O 1, Oktay NS 2, Pisiriciler R 2 and Goker
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR
 INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Lecture 7 Chemical Mediators of Inflammation Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Course Outline i. Inflammation: Introduction and generalities (lecture
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Lecture 7 Chemical Mediators of Inflammation Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Course Outline i. Inflammation: Introduction and generalities (lecture
HISTOLOGY Lecture TWO DR. ASHRAF SAID
 HISTOLOGY Lecture TWO DR. ASHRAF SAID Start Of this lecture TISSUES TISSUE: A DEFINITION A group of connected and interdependent cells that cooperate to perform a specific function CONNECTIVE TISSUE The
HISTOLOGY Lecture TWO DR. ASHRAF SAID Start Of this lecture TISSUES TISSUE: A DEFINITION A group of connected and interdependent cells that cooperate to perform a specific function CONNECTIVE TISSUE The
Comparing Bones, Joints, and Muscles
 Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Comparing Bones, Joints, and Muscles You may want to refer students to Chapter 36 in the textbook for a general discussion of skeletal and muscular
Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Comparing Bones, Joints, and Muscles You may want to refer students to Chapter 36 in the textbook for a general discussion of skeletal and muscular
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences
 Research Article Pharmacognosy International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 HEPATOPROTECTIVE ACTIVITY OF SEMECARPUS ANACARDIUM FRUIT EXTRACTS AGAINST CARBON TETRACHLORIDE INDUCED HEPATOTOXICITY
Research Article Pharmacognosy International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 HEPATOPROTECTIVE ACTIVITY OF SEMECARPUS ANACARDIUM FRUIT EXTRACTS AGAINST CARBON TETRACHLORIDE INDUCED HEPATOTOXICITY
Quantitative analysis of mast cells in invasive ductal carcinoma
 ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 2 Number 12 (December-2014) pp. 91-96 www.ijcrar.com Quantitative analysis of mast cells in invasive ductal carcinoma M.N.Divyarani*, M.L.Harendra Kumar, B.V.Swaroop raj, and U.D.Manoranjan
ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 2 Number 12 (December-2014) pp. 91-96 www.ijcrar.com Quantitative analysis of mast cells in invasive ductal carcinoma M.N.Divyarani*, M.L.Harendra Kumar, B.V.Swaroop raj, and U.D.Manoranjan
Skeletal muscle. General features :
 Muscular tissues In the first embryonic life the muscular tissues arise from mesoderm, The function of movement in multicellular organisms is usually assumed by specialized cells called muscle fibers which
Muscular tissues In the first embryonic life the muscular tissues arise from mesoderm, The function of movement in multicellular organisms is usually assumed by specialized cells called muscle fibers which
The Muscular System and Homeostasis
 Chapter 10 Chapter 10 The Muscular System and Homeostasis The Muscular System and Homeostasis 10.1 Movement and Muscle Tissue 10.2 Muscles, Health, and Homeostasis 10.1 Movement and Muscle Tissue Muscles
Chapter 10 Chapter 10 The Muscular System and Homeostasis The Muscular System and Homeostasis 10.1 Movement and Muscle Tissue 10.2 Muscles, Health, and Homeostasis 10.1 Movement and Muscle Tissue Muscles
Practical Histology. Lab 3: Connective tissue
 Practical Histology Lab 3: Connective tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue provides structural support for the body by binding cells and tissues together to form organs. It also provides metabolic
Practical Histology Lab 3: Connective tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue provides structural support for the body by binding cells and tissues together to form organs. It also provides metabolic
Hematopoiesis. Hematopoiesis. Hematopoiesis
 Chapter. Cells and Organs of the Immune System Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis- formation and development of WBC and RBC bone marrow. Hematopoietic stem cell- give rise to any blood cells (constant number,
Chapter. Cells and Organs of the Immune System Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis- formation and development of WBC and RBC bone marrow. Hematopoietic stem cell- give rise to any blood cells (constant number,
Composition of Blood
 Blood is a connective tissue, specialized to transport the respiratory gasses as well as hormones, nutrients, and wastes, and the distribution of heat. The various cells of the blood perform specific functions.
Blood is a connective tissue, specialized to transport the respiratory gasses as well as hormones, nutrients, and wastes, and the distribution of heat. The various cells of the blood perform specific functions.
Blood: Functions. Liquid connective tissue 3 general functions 1. Transportation. 2. Regulation. 3. Protection
 Blood Elements Lecture Objectives List blood components. Classify formed elements of blood. Discuss the scientific basis of the above classification. Describe the basic structure of erythrocytes and criteria
Blood Elements Lecture Objectives List blood components. Classify formed elements of blood. Discuss the scientific basis of the above classification. Describe the basic structure of erythrocytes and criteria
Dr. Hany M. Abo-Haded
 BY Dr. Hany M. Abo-Haded Pediatric Cardiology Unit, Mansoura Universty Children Hospital, Mansoura, Egypt Co-authors: Dina S El-Agamy and Mohamed A Elkablawy Background Doxorubicin (DOX) is an anthracycline
BY Dr. Hany M. Abo-Haded Pediatric Cardiology Unit, Mansoura Universty Children Hospital, Mansoura, Egypt Co-authors: Dina S El-Agamy and Mohamed A Elkablawy Background Doxorubicin (DOX) is an anthracycline
Muscle tissues. Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD
 Muscle tissues Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Muscle tissue is a soft tissue that composes muscles in animal bodies, and gives rise to muscles' ability to contract. Muscle tissue
Muscle tissues Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Muscle tissue is a soft tissue that composes muscles in animal bodies, and gives rise to muscles' ability to contract. Muscle tissue
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. The Muscular System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscles are responsible for all types of body movement they contract or shorten and are the machine of the body Three basic
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscles are responsible for all types of body movement they contract or shorten and are the machine of the body Three basic
PRACTICAL ROADMAP. MUSCLE WJ van der Spuy
 PRACTICAL ROADMAP MUSCLE WJ van der Spuy MUSCLE Skeletal (striated) Cardiac (striated) Smooth Identification based on Fiber size, shape and presence/absence of branching Number, shape and position of nuclei
PRACTICAL ROADMAP MUSCLE WJ van der Spuy MUSCLE Skeletal (striated) Cardiac (striated) Smooth Identification based on Fiber size, shape and presence/absence of branching Number, shape and position of nuclei
ANTI-OXIDANT ACTIVITY OF MORINDA CITRIFOLIA ON LYMPHOMA-BEARING MICE
 Ancient Science of Life Vol. : XXVI (1&) July, August, September, October, November, December 006 ANTI-OXIDANT ACTIVITY OF MORINDA CITRIFOLIA ON LYMPHOMA-BEARING MICE T.ANITHA AND S.MOHANDASS Received
Ancient Science of Life Vol. : XXVI (1&) July, August, September, October, November, December 006 ANTI-OXIDANT ACTIVITY OF MORINDA CITRIFOLIA ON LYMPHOMA-BEARING MICE T.ANITHA AND S.MOHANDASS Received
Anti-inflammatory properties of SM04690, a small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway as a potential treatment for knee osteoarthritis
 Anti-inflammatory properties of SM04690, a small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway as a potential treatment for knee osteoarthritis V. Deshmukh 1, T. Seo 1, C. Swearingen 1, Y. Yazici 1 1 Samumed,
Anti-inflammatory properties of SM04690, a small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway as a potential treatment for knee osteoarthritis V. Deshmukh 1, T. Seo 1, C. Swearingen 1, Y. Yazici 1 1 Samumed,
CHAPTER 6 2/9/2016. Learning Objectives List the four traits that all muscle types have in common.
 Learning Objectives List the four traits that all muscle types have in common. CHAPTER 6 The Muscular System Demonstrate and explain the use of antagonistic muscle pairs. Describe the attachment of muscle
Learning Objectives List the four traits that all muscle types have in common. CHAPTER 6 The Muscular System Demonstrate and explain the use of antagonistic muscle pairs. Describe the attachment of muscle
Mast cells in leprosy
 Original article: Mast cells in leprosy *Dr. Navdeep Kaur, 1 Dr. S.S. Hiremath, 2 Dr. Suresh K.K. 3 1Post Graduate, 2 Professor, 3 Professor, Department of Pathology, JJM Medical College, Davangere, Karnataka,
Original article: Mast cells in leprosy *Dr. Navdeep Kaur, 1 Dr. S.S. Hiremath, 2 Dr. Suresh K.K. 3 1Post Graduate, 2 Professor, 3 Professor, Department of Pathology, JJM Medical College, Davangere, Karnataka,
shehab Moh Tarek ... ManarHajeer
 3 shehab Moh Tarek... ManarHajeer In the previous lecture we discussed the accumulation of oxygen- derived free radicals as a mechanism of cell injury, we covered their production and their pathologic
3 shehab Moh Tarek... ManarHajeer In the previous lecture we discussed the accumulation of oxygen- derived free radicals as a mechanism of cell injury, we covered their production and their pathologic
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted form Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 20 The Cardiovascular System: Blood
 Adapted form Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 20 The Cardiovascular System: Blood Introduction The cardiovascular system functions as a system to transport numerous substances throughout the body
Adapted form Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 20 The Cardiovascular System: Blood Introduction The cardiovascular system functions as a system to transport numerous substances throughout the body
INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response. Physiology Unit 3
 INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response Physiology Unit 3 Protection Against Infection The body has several defenses to protect itself from getting an infection Skin Mucus membranes Serous membranes
INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response Physiology Unit 3 Protection Against Infection The body has several defenses to protect itself from getting an infection Skin Mucus membranes Serous membranes
Perioperative and Early Postoperative Outcome of Proximal Femoral Nailing for Stable and Unstable Trochanteric Fractures
 ACTA FACULTATIS MEDICAE NAISSENSIS DOI: 10.1515/afmnai-2016-0005 UDC: 616.718.4-001.5-089 Perioperative and Early Postoperative Outcome of Proximal Femoral Nailing for Stable and Unstable Trochanteric
ACTA FACULTATIS MEDICAE NAISSENSIS DOI: 10.1515/afmnai-2016-0005 UDC: 616.718.4-001.5-089 Perioperative and Early Postoperative Outcome of Proximal Femoral Nailing for Stable and Unstable Trochanteric
STARS. Mini-Symposium. Skeletal Muscle: Development, Adaptation & Disease. Gain Without Pain
 STARS Mini-Symposium Skeletal Muscle: Development, Adaptation & Disease Gain Without Pain Rhonda Bassel-Duby, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Molecular Biology Diagram of Skeletal Muscle Myoglobin Immunohistochemistry
STARS Mini-Symposium Skeletal Muscle: Development, Adaptation & Disease Gain Without Pain Rhonda Bassel-Duby, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Molecular Biology Diagram of Skeletal Muscle Myoglobin Immunohistochemistry
Whole Blood. Lab 29A. Blood. Plasma. Whole Blood. Formed Elements. Plasma: Fluid component. Formed elements: Cells and fragments
 Whole Blood Lab 29A. Blood Plasma: Fluid component Water (90%) Dissolved plasma proteins Other solutes Formed elements: Cells and fragments RBCs (carry Oxygen) WBCs (immunity) Platelets (cell fragments
Whole Blood Lab 29A. Blood Plasma: Fluid component Water (90%) Dissolved plasma proteins Other solutes Formed elements: Cells and fragments RBCs (carry Oxygen) WBCs (immunity) Platelets (cell fragments
VIRULENCE FACTORS AND SUSCEPTIBILITY OF CANDIDA SPP. CAUSATIVE AGENTS OF NEONATAL INFECTIONS
 VIRULENCE FACTORS AND SUSCEPTIBILITY OF CANDIDA SPP. CAUSATIVE AGENTS OF NEONATAL INFECTIONS Nikola Stojanović, Predrag Stojanović, Suzana Otašević, Valentina Arsić-Arsenijević What do we know? - Third
VIRULENCE FACTORS AND SUSCEPTIBILITY OF CANDIDA SPP. CAUSATIVE AGENTS OF NEONATAL INFECTIONS Nikola Stojanović, Predrag Stojanović, Suzana Otašević, Valentina Arsić-Arsenijević What do we know? - Third
The Skinny of the Immune System
 The Skinny of the Immune System Robert Hostoffer, DO, FACOP, FAAP Associate Professor of Pediatrics Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio Overview 1. Immune system of the skin 2. Immune Players
The Skinny of the Immune System Robert Hostoffer, DO, FACOP, FAAP Associate Professor of Pediatrics Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio Overview 1. Immune system of the skin 2. Immune Players
Ch.10 Muscle Tissue. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
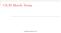 Ch.10 Muscle Tissue Preview Chapter 10 In groups we will define the following terms 1. Skeletal muscle 2. Smooth muscle 3. Cardiac muscle 4. Sarcomere 5. Myofibril 6. Myofilament 7. Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Ch.10 Muscle Tissue Preview Chapter 10 In groups we will define the following terms 1. Skeletal muscle 2. Smooth muscle 3. Cardiac muscle 4. Sarcomere 5. Myofibril 6. Myofilament 7. Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Human Anatomy & Physiology. Unit 1: Introduction and Biochemistry / Cells Review. 3 weeks A&P1, A&P2
 Unit 1: Introduction and Biochemistry / Cells Review A&P1, A&P2 Does the study of anatomy at the molecular and cellular level support a creationist theory about our origins? List and describe the major
Unit 1: Introduction and Biochemistry / Cells Review A&P1, A&P2 Does the study of anatomy at the molecular and cellular level support a creationist theory about our origins? List and describe the major
Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/-
 Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 19 The Cardiovascular System: The Blood Functions and Properties of Blood Blood is a liquid connective tissue consisting of cells surrounded by
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 19 The Cardiovascular System: The Blood Functions and Properties of Blood Blood is a liquid connective tissue consisting of cells surrounded by
Cardiac Muscle Tissue. Cardiac Muscle Tissue
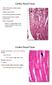 Walls of the heart (cardia: heart); myocardium. Cardiac muscle fibers not as densely packed as skeletal cardiac muscle tissue is highly vascularized Other components; dense C.T. septa, larger blood vessels,
Walls of the heart (cardia: heart); myocardium. Cardiac muscle fibers not as densely packed as skeletal cardiac muscle tissue is highly vascularized Other components; dense C.T. septa, larger blood vessels,
APPENDIX 1 ETHICAL CLEARANCE
 APPENDIX 1 ETHICAL CLEARANCE 75 APPENDIX 2 76 PROCEDURE FOR PREPARING OF LIVER HISTOLOGY SLIDES Overview: Histology involves the use of a set of techniques to examine the morphology, architecture and composition
APPENDIX 1 ETHICAL CLEARANCE 75 APPENDIX 2 76 PROCEDURE FOR PREPARING OF LIVER HISTOLOGY SLIDES Overview: Histology involves the use of a set of techniques to examine the morphology, architecture and composition
BMS101 INTRODUCTION TO THE HUMAN BODY STUDY NOTES EXTRACTS FOR SAMPLE
 BMS101 INTRODUCTION TO THE HUMAN BODY STUDY NOTES EXTRACTS FOR SAMPLE What is anatomy? Anatomy is the study of structure. Greek for to cut up or cut open What is physiology? Physiology studies the function
BMS101 INTRODUCTION TO THE HUMAN BODY STUDY NOTES EXTRACTS FOR SAMPLE What is anatomy? Anatomy is the study of structure. Greek for to cut up or cut open What is physiology? Physiology studies the function
Muscle Tissue. General concepts. Classification of muscle. I. Functional classification is based on the type of neural control.
 Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
******************************************************************************************************* MUSCLE CYTOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ******************************************************************************************************* MUSCLE CYTOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY *******************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ******************************************************************************************************* MUSCLE CYTOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY *******************************************************************************************************
The Muscular System. Myology the study of muscles
 The Muscular System Myology the study of muscles Functions of muscles: 1. Movement 2. Stability /support posture 3. Heat production 85% of our body heat 4. Communication 5. Constriction of organs and vessels
The Muscular System Myology the study of muscles Functions of muscles: 1. Movement 2. Stability /support posture 3. Heat production 85% of our body heat 4. Communication 5. Constriction of organs and vessels
DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES, ONDO DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY BLOOD AND BODY FLUID PHYSIOLOGY LECTURER: MR A.O. AKINOLA OBJECTIVES Leukopoiesis Thrombopoiesis Leukopoiesis and Lymphopoiesis White blood
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES, ONDO DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY BLOOD AND BODY FLUID PHYSIOLOGY LECTURER: MR A.O. AKINOLA OBJECTIVES Leukopoiesis Thrombopoiesis Leukopoiesis and Lymphopoiesis White blood
Chapter 10 -Muscle Tissue
 Chapter 10 -Muscle Tissue Muscles: 1. Overview of Muscle Tissue A. Review 5 functions of muscle tissue. B. Review the 5 properties of muscle tissue. WHICH do they share with nervous tissue? (2, plus the
Chapter 10 -Muscle Tissue Muscles: 1. Overview of Muscle Tissue A. Review 5 functions of muscle tissue. B. Review the 5 properties of muscle tissue. WHICH do they share with nervous tissue? (2, plus the
Immunology 2011 Lecture 23 Immediate Hypersensitivity 26 October
 Immunology 2011 Lecture 23 Immediate Hypersensitivity 26 October Allergic Reactions ( Immediate Hypersensitivity ) Hay fever, food, drug & animal allergies, reactions to bee stings, etc. Symptoms may include
Immunology 2011 Lecture 23 Immediate Hypersensitivity 26 October Allergic Reactions ( Immediate Hypersensitivity ) Hay fever, food, drug & animal allergies, reactions to bee stings, etc. Symptoms may include
4. TEXTBOOK: ABUL K. ABBAS. ANDREW H. LICHTMAN. CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR IMMUNOLOGY. 5 TH EDITION. Chapter 2. pg
 LECTURE: 03 Title: CELLS INVOLVED IN THE IMMUNE RESPONSE LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Identify the organs where the process of the blood formation occurs. Identify the main cell
LECTURE: 03 Title: CELLS INVOLVED IN THE IMMUNE RESPONSE LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Identify the organs where the process of the blood formation occurs. Identify the main cell
Mast cell profile in appendicitis
 Original Research Article DOI: 10.18231/2394-6792.2017.0120 Mast cell profile in appendicitis G. Patil Anuradha 1, AM Anita 2, Saini Kr. Seemant 3,*, S. Pratima 4 1 HOD, 2 Associate Professor, 3 PG Student,
Original Research Article DOI: 10.18231/2394-6792.2017.0120 Mast cell profile in appendicitis G. Patil Anuradha 1, AM Anita 2, Saini Kr. Seemant 3,*, S. Pratima 4 1 HOD, 2 Associate Professor, 3 PG Student,
Evaluation of the Protective Effect of Plant Extracts Against Pheophorbide a-induced Photosensitive Damage
 Trace Nutrients Research 26 : 88 92 (2009) Evaluation of the Protective Effect of Plant Extracts Against Pheophorbide a-induced Photosensitive Damage Amy TOMITA, Tomoyo KAJIURA and Shuichi KIMURA Showa
Trace Nutrients Research 26 : 88 92 (2009) Evaluation of the Protective Effect of Plant Extracts Against Pheophorbide a-induced Photosensitive Damage Amy TOMITA, Tomoyo KAJIURA and Shuichi KIMURA Showa
GENERAL HISTOLOGY 4. Muscular Tissue
 Biology-232 GENERAL HISTOLOGY 4. Muscular Tissue Dr. Manal Othman Anatomy Department CMMS, AGU Responsible for MOST types of BODY MOVEMENT Made up of groups of elongated MUSCLE cells with contractile filaments
Biology-232 GENERAL HISTOLOGY 4. Muscular Tissue Dr. Manal Othman Anatomy Department CMMS, AGU Responsible for MOST types of BODY MOVEMENT Made up of groups of elongated MUSCLE cells with contractile filaments
HIF-P4H-2 deficiency protects against skeletal muscle ischemia-reperfusion injury
 J Mol Med 2015 HIF-P4H-2 deficiency protects against skeletal muscle ischemia-reperfusion injury Sara Karsikas; Mikko Myllymäki; Minna Heikkilä; Raija Sormunen; Kari I Kivirikko; Johanna Myllyharju; Raisa
J Mol Med 2015 HIF-P4H-2 deficiency protects against skeletal muscle ischemia-reperfusion injury Sara Karsikas; Mikko Myllymäki; Minna Heikkilä; Raija Sormunen; Kari I Kivirikko; Johanna Myllyharju; Raisa
Immunology 2011 Lecture 23 Immediate Hypersensitivity 26 October
 Immunology 2011 Lecture 23 Immediate Hypersensitivity 26 October Allergic Reactions ( Immediate Hypersensitivity ) Hay fever, food, drug & animal allergies, reactions to bee stings, etc. Symptoms may include
Immunology 2011 Lecture 23 Immediate Hypersensitivity 26 October Allergic Reactions ( Immediate Hypersensitivity ) Hay fever, food, drug & animal allergies, reactions to bee stings, etc. Symptoms may include
BLOOD. EEI n: t.ee# Required Name : Due : April 12,2018 COMPOSITION AND FUNCTIONS OF BLOOD. Beginningof Class
 t.ee# Required Name : Due : April 12,2018 Beginningof Class BLOOD Blood, the "life fluid" that courses through the body's blood vessels, provides the means by which the body's cells receive vital nutrients
t.ee# Required Name : Due : April 12,2018 Beginningof Class BLOOD Blood, the "life fluid" that courses through the body's blood vessels, provides the means by which the body's cells receive vital nutrients
CONNECTIVE TISSUE (C.T.)
 CONNECTIVE TISSUE (C.T.) Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Enumerate the general characteristics of C.T. 2. Classify C.T into C.T. proper and special types of C.T.
CONNECTIVE TISSUE (C.T.) Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Enumerate the general characteristics of C.T. 2. Classify C.T into C.T. proper and special types of C.T.
Connective tissue Histology lab 6 Notes by Omar Sami
 Connective tissue Histology lab 6 Notes by Omar Sami The connective tissue is composed of: 1- Cells. 2- Extra Cellular Matrix; fibers & ground substance. Ground substance is where you find both Cells &
Connective tissue Histology lab 6 Notes by Omar Sami The connective tissue is composed of: 1- Cells. 2- Extra Cellular Matrix; fibers & ground substance. Ground substance is where you find both Cells &
shquld be regarded as tension per unit cross-section of the muscle because,
 267 J. Physiol. (I944) I03, 267-273 6I2.74I ABSOLUTE MUSCLE FORCE IN THE ANKLE FLEXORS OF MAN By H. A. HAXTON, From the Radcliffe Infirmary, Oxford, and the Anatomy Department, University of St Andrews
267 J. Physiol. (I944) I03, 267-273 6I2.74I ABSOLUTE MUSCLE FORCE IN THE ANKLE FLEXORS OF MAN By H. A. HAXTON, From the Radcliffe Infirmary, Oxford, and the Anatomy Department, University of St Andrews
Ethanol-Induced Neuroinflammation in the Developing Hippocampus: Mast Cells and Microglia
 Ethanol-Induced Neuroinflammation in the Developing Hippocampus: Mast Cells and Microglia Derick H. Lindquist, Ph.D. The Ohio State University March 2, 2017 Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders FASD afflicts
Ethanol-Induced Neuroinflammation in the Developing Hippocampus: Mast Cells and Microglia Derick H. Lindquist, Ph.D. The Ohio State University March 2, 2017 Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders FASD afflicts
Outline. Bio 105: Muscular System. Muscular System. Types of Muscles. Smooth Muscle. Cardiac Muscle 4/6/2016
 Outline Bio 105: Muscular System Lecture 11 Chapter 6 Characteristics of muscles 3 types of muscles Functions of muscles Structure of skeletal muscles Mechanics of muscle contraction Energy sources for
Outline Bio 105: Muscular System Lecture 11 Chapter 6 Characteristics of muscles 3 types of muscles Functions of muscles Structure of skeletal muscles Mechanics of muscle contraction Energy sources for
Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell?
 Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
UVOD. itakokompenzujesmaweweppo 2. ppo 2. skevisinesmatrasezonompotpunekompenzacije. ppo 2 uarterijskoj. mm Hg), a ppo 2 mm Hg
 PREGLEDI IZ LITERATURE BIBLID: 0370-8179, 133(2005) 5-6 p. 307-311 1 2 1 Institut za fiziologiju, Medicinski fakultet, Niš; 2 UVOD ppo 2 skevisinesmatrasezonompotpunekompenzacije mm Hg), a ppo 2 mm Hg
PREGLEDI IZ LITERATURE BIBLID: 0370-8179, 133(2005) 5-6 p. 307-311 1 2 1 Institut za fiziologiju, Medicinski fakultet, Niš; 2 UVOD ppo 2 skevisinesmatrasezonompotpunekompenzacije mm Hg), a ppo 2 mm Hg
Immunology. Prof. Nagwa Mohamed Aref (Molecular Virologist & Immunology)
 Host Defenses Overview and Nonspecific Defenses I Immunology Prof. Nagwa Mohamed Aref (Molecular Virologist & Immunology) The Nature of Host Defenses 2 3 4 1st line of defense - intact skin mucous membranes
Host Defenses Overview and Nonspecific Defenses I Immunology Prof. Nagwa Mohamed Aref (Molecular Virologist & Immunology) The Nature of Host Defenses 2 3 4 1st line of defense - intact skin mucous membranes
Special Staining (I)
 Special Staining (I) Carbohydrates 1- PERIODIC ACID SCHIFF'S (PAS ) Purpose: Glycogen is present in liver, kidney, skeletal and cardiac muscle. The PAS stain is used to demonstrate neutral polysaccharides
Special Staining (I) Carbohydrates 1- PERIODIC ACID SCHIFF'S (PAS ) Purpose: Glycogen is present in liver, kidney, skeletal and cardiac muscle. The PAS stain is used to demonstrate neutral polysaccharides
Anatomy & Physiology. An Introduction
 Anatomy & Physiology An Introduction An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy - The study of the structure of the human body Physiology - The study of body function Branches of Anatomy Surface anatomy Gross anatomy
Anatomy & Physiology An Introduction An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy - The study of the structure of the human body Physiology - The study of body function Branches of Anatomy Surface anatomy Gross anatomy
I. Concepts: Fill in the following sections with information from the text and lecture.
 Name: Period: 10 Blood Study Guide I. Concepts: Fill in the following sections with information from the text and lecture. 1. Composition and Function of Blood: 2. Hematopoiesis: 1 Miss School, Miss Out
Name: Period: 10 Blood Study Guide I. Concepts: Fill in the following sections with information from the text and lecture. 1. Composition and Function of Blood: 2. Hematopoiesis: 1 Miss School, Miss Out
Session 3-Part 2: Skeletal Muscle
 Session 3-Part 2: Skeletal Muscle Course: Introduction to Exercise Science-Level 2 (Exercise Physiology) Presentation Created by Ken Baldwin, M.ED, ACSM-H/FI Copyright EFS Inc. All Rights Reserved. Skeletal
Session 3-Part 2: Skeletal Muscle Course: Introduction to Exercise Science-Level 2 (Exercise Physiology) Presentation Created by Ken Baldwin, M.ED, ACSM-H/FI Copyright EFS Inc. All Rights Reserved. Skeletal
Warm Up! Test review (already! ;))
 Warm Up! Test review (already! ;)) Write a question you might find on the Unit 5 test next week! (Multiple choice, matching, fill in, or short answer!) - challenge yourself and be ready to share!!! PowerPoint
Warm Up! Test review (already! ;)) Write a question you might find on the Unit 5 test next week! (Multiple choice, matching, fill in, or short answer!) - challenge yourself and be ready to share!!! PowerPoint
Exercise associated muscle cramps & Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness
 Exercise associated muscle cramps & Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness Dr Rob Collins Sports Physician www.ilovesport.co.za Exercise Associated Muscle Cramps Definition Painful, spasmodic, involuntary contractions
Exercise associated muscle cramps & Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness Dr Rob Collins Sports Physician www.ilovesport.co.za Exercise Associated Muscle Cramps Definition Painful, spasmodic, involuntary contractions
Introduction to Immunopathology
 MICR2209 Introduction to Immunopathology Dr Allison Imrie 1 Allergy and Hypersensitivity Adaptive immune responses can sometimes be elicited by antigens not associated with infectious agents, and this
MICR2209 Introduction to Immunopathology Dr Allison Imrie 1 Allergy and Hypersensitivity Adaptive immune responses can sometimes be elicited by antigens not associated with infectious agents, and this
Hypersensitivity is the term used when an immune response results in exaggerated or inappropriate reactions harmful to the host.
 Hypersensitivity is the term used when an immune response results in exaggerated or inappropriate reactions harmful to the host. Hypersensitivity vs. allergy Hypersensitivity reactions require a pre-sensitized
Hypersensitivity is the term used when an immune response results in exaggerated or inappropriate reactions harmful to the host. Hypersensitivity vs. allergy Hypersensitivity reactions require a pre-sensitized
Green tea extract Its potential protective effect on bleomycin induced lung injuries in rats
 Green tea extract Its potential protective effect on bleomycin induced lung injuries in rats Azza H. EL-Medany, Jamila EL-Medany The interest in the use of plant extracts in the treatment of several diseases
Green tea extract Its potential protective effect on bleomycin induced lung injuries in rats Azza H. EL-Medany, Jamila EL-Medany The interest in the use of plant extracts in the treatment of several diseases
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
ulcer healing role 118 Bicarbonate, prostaglandins in duodenal cytoprotection 235, 236
 Subject Index Actin cellular forms 48, 49 epidermal growth factor, cytoskeletal change induction in mucosal repair 22, 23 wound repair 64, 65 polyamine effects on cytoskeleton 49 51 S-Adenosylmethionine
Subject Index Actin cellular forms 48, 49 epidermal growth factor, cytoskeletal change induction in mucosal repair 22, 23 wound repair 64, 65 polyamine effects on cytoskeleton 49 51 S-Adenosylmethionine
Muscles, muscle fibres and myofibrils
 Muscles, muscle fibres and myofibrils Properties of Muscle Fiber Types Fast fibers Slow fibers Characteristic IIb IIx IIa Type I V max (speed of shortening) Highest Intermediate Low Resistance to fatigue
Muscles, muscle fibres and myofibrils Properties of Muscle Fiber Types Fast fibers Slow fibers Characteristic IIb IIx IIa Type I V max (speed of shortening) Highest Intermediate Low Resistance to fatigue
Blood consists of red and white blood cells suspended in plasma Blood is about 55% plasma and 45% cellular elements Plasma 90% water 10% dissolved
 Bio 100 Guide 21 Blood consists of red and white blood cells suspended in plasma Blood is about 55% plasma and 45% cellular elements Plasma 90% water 10% dissolved inorganic ions, proteins, nutrients,
Bio 100 Guide 21 Blood consists of red and white blood cells suspended in plasma Blood is about 55% plasma and 45% cellular elements Plasma 90% water 10% dissolved inorganic ions, proteins, nutrients,
Dr/ Sherein Saeid AbdElgayed, ph.d
 هللامسب Dr/ Sherein Saeid AbdElgayed, ph.d Professor of Veterinary Pathology, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt. Chairman of the Editorial Board of Arab Journal of Science & Research Publishing (AJSRP) http://www.ajsrp.com
هللامسب Dr/ Sherein Saeid AbdElgayed, ph.d Professor of Veterinary Pathology, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt. Chairman of the Editorial Board of Arab Journal of Science & Research Publishing (AJSRP) http://www.ajsrp.com
OBJECTIVES. Unit 7:5 PROPERTIES OR CHARACTERISTICS OF MUSCLES. Introduction. 3 Kinds of Muscles. 3 Kinds of Muscles 4/17/2018 MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 OBJECTIVES Unit 7:5 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Compare the three main kinds of muscles by describing the action of each Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles List at least three functions of muscles
OBJECTIVES Unit 7:5 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Compare the three main kinds of muscles by describing the action of each Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles List at least three functions of muscles
Atlas of Stains. Special Stains on Artisan Link Pro
 Atlas of Stains Special Stains on Artisan Link Pro Intended use Routinely processed samples (paraffin-embedded) may be used. The preferred fixative is neutral buffered formalin. The clinical interpretation
Atlas of Stains Special Stains on Artisan Link Pro Intended use Routinely processed samples (paraffin-embedded) may be used. The preferred fixative is neutral buffered formalin. The clinical interpretation
The Human Body: An Orientation
 The Human Body: An Orientation Activity Booklet Name: Per: #: Label the following diagram with the levels of structural organization and the examples of each: 1 Identify the following body systems and
The Human Body: An Orientation Activity Booklet Name: Per: #: Label the following diagram with the levels of structural organization and the examples of each: 1 Identify the following body systems and
