PedsCases Podcast Scripts
|
|
|
- Darlene Shepherd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Drug Allergy. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics. The audio versions are accessible on itunes or at Drug Allergy Introduction Hi everyone! Our names are Dr. Lucy Duan and Dr. Stephanie Erdle, and we are both paediatric allergy fellows. Thank you to Dr. Vy Kim for supervising us for this podcast. In this podcast, we will be discussing drug allergies. This is an issue that comes up in all areas of paediatrics, so developing a clear approach to drug allergies is important. Part 1. Objectives After listening to this podcast, the listener should be able to: 1. Differentiate allergic drug reactions from other adverse drug reactions 2. Develop an approach to drug allergy diagnosis 3. Understand the four main categories of drug allergies and their clinical manifestations 4. Develop a differential diagnosis of other conditions to consider 5. Understand a general treatment approach to drug allergies Part 2. Generic cases We will begin with a few cases to start us off. Case 1. A 10-year-old girl with acute lymphoblastic leukemia is undergoing IV chemotherapy with Cisplatin. 10 minutes after the infusion starts, she develops diffuse urticaria, swelling of the lips and eyes, and difficulty breathing. Is this an allergic reaction? If so, what type? Case 2. A 16-year-old male hospitalized on the Neurosurgery ward developed high fever, skin blistering and sloughing, and mucosal erosions, following the 4th dose of phenytoin prescribed for new onset seizures following head trauma. Is this a drug reaction, if so, what type? Case 3. A 5-year-old boy presents to his primary care provider with cough, runny nose and fever. His left tympanic membrane looks red on examination, so he is started on amoxicillin for a suspected acute otitis media. Three days after starting the antibiotic he wakes up with an itchy red rash. Is this an allergic reaction? Part 3. Adverse drug reactions
2 Adverse drug reactions are defined as a harmful or unintended reaction to a drug. These reactions can be classified as Type A or Type B reactions. Type A reactions are considered to be predictable events that are usually dose dependent and can occur in anyone. An example of a type A reaction is diarrhea from an antibiotic. Type B reactions are unpredictable reactions generally unrelated to the pharmacologic actions of the drug, that only occur in susceptible individuals. Examples of type B reactions include drug allergy, non-allergic drug hypersensitivity reactions, intolerance, and idiosyncratic reactions. This podcast will focus on true drug allergy. Drug allergy is a Type B adverse drug reaction that results from a specific immunologic response to a medication with varying mechanisms and clinical presentations. Drug allergies account for about 5-10% of all adverse drug reactions and are commonly seen in all areas of medicine. Diagnosis of drug allergy relies on a careful history and physical examination. In some instances, additional testing including skin testing and oral challenges are helpful and may be required. Risk factors for developing a drug allergy include female sex, certain genetic polymorphisms, viral infections, and drug-related factors. Susceptibility to drug allergy is also influenced by the route of administration. Topical, intramuscular, and intravenous routes are more likely to cause allergic drug reactions than oral administration. Part 4. Drug allergies There are four major categories of drug allergies, which are most commonly classified based on the Gell and Coombs classification system. We will first give a brief overview of each category, then go into each category in more detail. Type I reactions are a typical IgE-mediated allergy. This is what people typically think of when they hear the word allergy. These reactions are immediate in onset, typically in less than one hour and can develop into anaphylaxis. Type II, III and IV are all delayed onset allergic reactions with different mechanisms. Type II reactions are delayed in onset and caused by antibody-mediated cell destruction. Patients may present with hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia or neutropenia. Type III reactions are delayed in onset and caused by IgG:drug immune complex deposition and complement activation. Patients may present with serum-sickness like reaction, which we will describe in more detail. Type IV reactions are delayed in onset and T-cell mediated. These patients can present in many different ways ranging from contact dermatitis, to severe reactions like SJS or TEN, DRESS syndrome, and many more. We will now go through each type in more detail. For each type, we will briefly cover the pathophysiology, the timing of the reaction, the classic presentation, and some examples of drugs that are known to cause the reaction type. Type I
3 Of the four types, type I reactions are the most common. As we mentioned, type I reactions are what we think of as classic allergic reactions. These reactions require the presence of a drugspecific IgE. Once formed, these IgE bind to mast cells and basophils throughout the body. If the drug or its metabolite is encountered again, it can bind to the IgE, forming drug-ige complexes that then cause degranulation, with release of histamine and other inflammatory mediators, causing an allergic reaction. These reactions are rapid in onset, typically within one hour of drug administration. The timing can vary depending on how the drug is given - for example, a drug given intravenously may lead to a more rapid reaction than the same drug given orally. The reaction may be even later if the oral medication is given with food, causing delayed absorption. These patients classically present with symptoms caused from the histamine release. These reactions can include urticaria, angioedema, respiratory symptoms, GI symptoms or hypotension and may develop into anaphylaxis. Diagnosis is guided by detailed history, physical examination, and in some cases, skin-prick testing and oral challenge. Skin-prick testing is only useful in type 1 drug allergy reactions, and not the other types of reactions. Patients with type I reaction need to be treated in the same way you would treat any other IgEmediated allergic reaction. If the patient presents with anaphylaxis, they need to be given IM epinephrine immediately. You can listen to the PedCases podcast on anaphylaxis for more detail on the management of anaphylaxis. The drugs that most commonly cause these reactions include beta-lactams, such as penicillins or cephalosporins, chemotherapeutic agents, and foreign proteins such as monoclonal antibodies. Type II Type II reactions are much less common than type I reactions. Type II reactions are caused by antibody-mediated cell destruction. In these cases, the drug binds to the surface of certain cell types, and acts as an antigen. Specific IgG or IgM antibodies that match these drug antigens then bind to them, causing them to be destroyed. These reactions are delayed, with patients presenting at least 5-8 days after drug exposure, however, then can occur much more quickly if the causative drug is stopped then restarted. The cell types that are most commonly affected are RBCs, platelets and neutrophils. Patients therefore classically present with either hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia or neutropenia. There are many drugs that can cause a type II hypersensitivity reaction, some commonly seen drugs include cephalosporins, penicillins, anti-convulsants, NSAIDs, heparin, and sulfonamides. Type III Type III reactions are caused by IgG-drug immune complex deposition. In this type of reaction, the drug can bind IgG and form immune complexes. Immune complexes can activate complement and an inflammatory cascade, and precipitate in different tissues including blood
4 vessels, joints, and renal glomeruli. Re-exposure to the same drug can lead to more rapid and severe effects. These reactions are delayed and typically manifest 1-3 weeks following drug exposure. Patients with type III reactions can present in several different ways including serum sickness and vasculitis. Serum sickness is an immune-complex reaction where patients present with fever, arthralgia, lymphadenopathy, cutaneous lesions, and in some cases acute glomerulonephritis. Commonly encountered agents that can cause a type III hypersensitivity reaction include heterologous antibodies, antibiotics, thiazides, allopurinol. Type IV Type IV reactions are T-cell mediated hypersensitivity reactions, and in contrast to the other 3 types, are not caused by antibodies. These reactions are also known as delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions, and can be further subdivided, however that is beyond the scope of this podcast. These reactions are caused by drug-specific T cells that recognize drugs through their T-cell receptors in an MHC-dependent way. This leads to subsequent cytokine and inflammatory mediator release, and can be associated with the recruitment of eosinophils, monocytes, and neutrophils. Type IV reactions are typically delayed by at least 1-3 days, and can occur days to weeks following exposure to the offending drug. If following a repeat exposure to a drug, symptoms may appear within 24 hours. Clinically, this group of reactions is highly variable and range from mild skin reactions, to lifethreatening conditions. An example of a common type IV hypersensitivity reaction is allergic contact dermatitis, which is characterized by erythema and edema with/without vesicles and bullae. It is caused by a wide variety of topical medications, and is the most frequent occupational skin disease. Patch testing can be used to aid in the diagnosis of contact dermatitis. There are 3 other type IV hypersensitivity reactions which are much more severe: Stevens- Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) and drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, known as DRESS. SJS/TEN is characterized by detachment and necrosis of the epidermis. Patients present with fever, mucous membrane involvement, and epidermal skin sloughing. Symptoms appear 1-4 weeks following drug exposure, but re-exposure can lead to symptom onset in 2-3 days. SJS is when skin detachment is less than 10% of the body surface, and TEN is when skin detachment affects greater than 30% of the body surface area. SJS/TEN overlap describes patients with skin detachment of 10-30%. Common offending drugs include allopurinol, sulfonamides, NSAIDs, and anticonvulsants including lamotrigine, carbamazepine, phenytoin, and phenobarbital. Patients with SJS/TEM can become very sick and often require intensive care admission or burn unit admission, for initiation of supportive treatment. Management includes prompt discontinuation of the drug, wound care, fluid and electrolyte management, nutritional support, pain control, and treatment of any superinfections.
5 DRESS is a rare but potentially life-threatening type IV hypersensitivity reaction. Clinically, patients present with fever, skin rash, malaise, hematologic abnormalities including eosinophilia and atypical lymphocytosis, increased lymphadenopathy, and multi-organ involvement. In most patients, symptoms begin 2-6 weeks following the initiation of the offending drug. The most common category of medications that cause DRESS are antiepileptics including carbamazepine, lamotrigine, phenytoin, and phenobarbital. Other medications include allopurinol and sulfonamides. Management is similar to that of SJS/TEN and involves removal of the offending drug and supportive care. Part 5. Differential Diagnosis Since the clinical manifestations of drug allergy are variable, it is important to consider and exclude other medical conditions in the differential diagnosis. This list is broad, but we have included some important diagnoses to think about. For immediate onset allergic reactions consider other allergies such as food allergy or latex allergy, asthma, infectious causes such as EBV or hepatitis, insect bites, and mastocytosis. For delayed onset reactions consider viral infections, bacterial infections such as streptococcal infection, autoimmune conditions such as psoriasis, Kawasaki Disease, or Still s disease, and insect bites. Part 6. Approach to Diagnosis On history, information should be obtained about what medication was taken, the dose and duration, the route of administration, if this was the first time this medication was being used, and any concurrent prescription and non-prescription medications (in particular, NSAIDs). It is important to obtain a detailed timeline of the reaction, description of clinical symptoms, any treatment that was given, and any previous or subsequent exposures to the medication. A detailed review of systems including looking for intercurrent illnesses such as viral infections, as well as past medical history of other allergic reactions also important. In addition to a detailed history, a careful physical examination should be conducted including examination of the cardiovascular, respiratory, gastrointestinal, and cutaneous symptoms. More detailed description of clinical findings of drug reactions will be discussed in the subsequent sections. Useful investigations depend on the type of adverse reaction. For immediate IgE-mediated hypersensitivity reactions, skin testing procedures such as skin prick testing (SPT) and intradermal testing (IDT) are useful and performed by allergists. Serum specific IgE tests are available for a limited number of medications, however in most clinical settings, serum specific IgE tests for medications are not used for the diagnosis of drug allergy and should not be ordered without consultation with allergists. For delayed hypersensitivity, patch testing by specialists can also be used. Part 7. Treatment Management of drug allergy varies depending on the type of reaction. In most cases, the most effective strategy is to avoid or discontinue the offending drug. Cross-reactivity amongst drugs should be considered when choosing alternative agents. In the event of anaphylaxis, the patient must be treated with epinephrine by intramuscular injection. Additional therapies involve
6 symptomatic and supportive care. The specific treatment for each type is outside the scope of this podcast. Part 8. Penicillin allergy One of the most common referrals we get in our allergy clinic is for concerns of penicillin, or amoxicillin, allergy. This most often presents with a vague history of rash sometime during the course of antibiotics. Over 95% of the time, the patients do not actually have a penicillin allergy, and this can largely be determined by history alone. The first thing to determine is whether the patient has received penicillin before. In order to have an IgE-mediated reaction, the patient needs to be sensitized to the antibiotic, which requires previous exposure to the antibiotics. If they have not had a previous course of the antibiotics, it is unlikely to be an IgE-mediated reaction. The next step is to determine the timing of the reaction. IgE-mediated reactions typically occur with an hour of the first dose on re-exposure. If the reaction occurs several hours after a dose, or after a few days into the course of antibiotic, it is unlikely to be an IgE-mediated reaction. Rashes while on antibiotics are extremely common, and are most often secondary to the infection itself such as a viral urticaria or other viral exanthem. If the reaction sounds like an IgE-mediated reaction, it is important to refer to an allergist for testing. This involves epicutaneous and intradermal testing, and if negative, an oral challenge. If the reaction is a rash that occurs several days into the course of antibiotics, it is unlikely to be IgE-mediated. In these cases, the families can be reassured that this is not a drug allergy. If the family is anxious to try the antibiotic again, we will often give them an ageappropriate dose of the antibiotic in clinic, and observe them for an hour, for reassurance. If no reaction develops, they can be reassured that they are not allergic to the drug. In a small subset of patients, they will have isolated rashes several days into the course of antibiotics on each re-exposure. As long as the child is well and only have a rash, this is not dangerous, and the families do not need to stop the antibiotics. Part 9. Returning to the cases Let s now return to the cases. As you recall, in the first case we had a 10-year-old girl undergoing IV chemotherapy with Cisplatin. 10 minutes after starting the drug infusion she developed diffuse urticaria, facial swelling and had difficulty breathing. Do you think this is an allergic reaction? If so, what type? If you guessed a type I IgE-mediated reaction, you are right! Remember, type I reactions are immediate, IgE-mediated reactions, causing histamine release, causing reactions ranging from urticaria development to anaphylaxis. This patient has developed an anaphylactic reaction from her chemotherapy, and requires immediate IM epinephrine. In our second case, a 16- year- old male developed fever, skin sloughing, and mucosal erosions following the 5th dose of phenytoin prescribed for new onset seizures following head trauma. Is this a drug reaction, if so, what type? This is an example SJS/TEN, a severe type IV hypersensitivity reaction that is a T-cell mediated reaction. Phenytoin and other aromatic antiepileptic medications are known offending agents for SJS/TEN and should been on your differential diagnosis if you see a patient with a similar clinical presentation. Remember that it is
7 important to obtain a detailed medication history in patients! This patient needs immediate removal of the offending drug, and active supportive care. In our third case, a 5 year old boy developed an itchy red rash after being treated with amoxicillin for three days for a suspected acute otitis media. Is this an allergic reaction? Does this reaction fit with any of our above reaction types? Some people might think that this is a type I IgE-mediated reaction, but this reaction developed after 3 days of an antibiotic, and not immediately after receiving it. This patient most likely had a viral infection, and this is likely a viral exanthem, or a viral rash. Viral rashes are commonly mistaken for allergic reactions, and amoxicillin is the most commonly implicated antibiotic. Usually with a good history and timeline of the reaction, you can figure out if there is actually a concern for a true allergic reaction. Part 10. Summary In this podcast, we reviewed what adverse drug reactions are, and that drug allergy is an example of a type B adverse drug reaction. We discussed an approach to diagnosing drug allergy which includes the importance of obtaining a detailed history and careful physical examination. The Gell and Coombs classification system is commonly used to describe the 4 types of hypersensitivity reactions. We also discussed a broad differential diagnosis and general treatment approach. Here are few key take-home points: 1. A drug allergy is a Type B adverse drug reaction that results from a specific immunologic response to a medication with varying mechanisms and clinical presentations. 2. A detailed drug history including dates and route of administration, drug formulation, and timing and duration of clinical symptoms is the most important aspect in the diagnosis of drug allergy. 3. There are four major categories of drug allergies, which are most commonly classified based on the Gell and Coombs classification system. 4. The mainstay of treatment is avoidance of the offending drug. 5. Penicillin allergy is the most common labeled drug allergy in children, however most children do not have a true IgE mediate hypersensitivity reaction to penicillin. Thanks for listening! References 1. Khan D, Solensky R. Drug allergy. American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology. 2009: S Solensky R, Khan D. Drug allergy: an updated practice parameter. Annals of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology. 2010: 105; 273e Warrington R, Silviu-Dan F, Wong T. Drug allergy. Allergy, Asthma and Clinical Immunology. 2018: 14;
Drug Allergy A Guide to Diagnosis and Management
 Drug Allergy A Guide to Diagnosis and Management (Version 1 April 2015 updated April 2018) Author: Jed Hewitt Chief Pharmacist, Governance & Professional Practice Date of Preparation: April 2015 Updated:
Drug Allergy A Guide to Diagnosis and Management (Version 1 April 2015 updated April 2018) Author: Jed Hewitt Chief Pharmacist, Governance & Professional Practice Date of Preparation: April 2015 Updated:
8/8/2016. Overview. Back to Basics: Immunology. Adverse Reactions to Drugs: Dispelling Myths
 Adverse Reactions to Drugs: Dispelling Myths Allison Ramsey, MD NPA Annual Conference September 30, 2016 Overview Review of types of hypersensitivity reactions Penicillin allergy IV contrast allergy Local
Adverse Reactions to Drugs: Dispelling Myths Allison Ramsey, MD NPA Annual Conference September 30, 2016 Overview Review of types of hypersensitivity reactions Penicillin allergy IV contrast allergy Local
The mechanisms of common drug hypersensitivities and implications for testing
 The mechanisms of common drug hypersensitivities and implications for testing R J Heddle 17 May 2016 Adverse Drug Reactions (ADR) Type A 85-90% of ADR Any individual, given sufficient dose & exposure Predictable
The mechanisms of common drug hypersensitivities and implications for testing R J Heddle 17 May 2016 Adverse Drug Reactions (ADR) Type A 85-90% of ADR Any individual, given sufficient dose & exposure Predictable
Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs) Outline
 Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs) Outline 1. What are Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs)? WHAT WHY HOW 2. How important are ADRs and are they preventable? 3. What are the classifications and mechanisms of ADRs?
Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs) Outline 1. What are Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs)? WHAT WHY HOW 2. How important are ADRs and are they preventable? 3. What are the classifications and mechanisms of ADRs?
They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest version of this NICE Pathway see:
 bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
Immunology. Lecture- 8
 Immunology Lecture- 8 Immunological Disorders Immunodeficiency Autoimmune Disease Hypersensitivities Immunodeficiency 1. Immunodeficiency --> abnormal production or function of immune cells, phagocytes,
Immunology Lecture- 8 Immunological Disorders Immunodeficiency Autoimmune Disease Hypersensitivities Immunodeficiency 1. Immunodeficiency --> abnormal production or function of immune cells, phagocytes,
An unpredictable, dose-independent adverse drug reaction which is immunologically or IgEmediated.
 R H E U M A T I S M D I S O R D E R S A N D A L L E R G I E S APPROACH TO DRUG ALLERGY Dr Bernard Thong DEFINITION OF DRUG ALLERGY An unpredictable, dose-independent adverse drug reaction which is immunologically
R H E U M A T I S M D I S O R D E R S A N D A L L E R G I E S APPROACH TO DRUG ALLERGY Dr Bernard Thong DEFINITION OF DRUG ALLERGY An unpredictable, dose-independent adverse drug reaction which is immunologically
Antibiotic allergy in the Intensive Care. Sanjay Swaminathan Clinical Immunologist, Westmead and Blacktown Hospitals September 28, 2017
 Antibiotic allergy in the Intensive Care Sanjay Swaminathan Clinical Immunologist, Westmead and Blacktown Hospitals September 28, 2017 Outline of talk True or false? Case example Types of drug allergy
Antibiotic allergy in the Intensive Care Sanjay Swaminathan Clinical Immunologist, Westmead and Blacktown Hospitals September 28, 2017 Outline of talk True or false? Case example Types of drug allergy
Emergency Dermatology Dr Melissa Barkham
 Emergency Dermatology Dr Melissa Barkham Spotlight Seminar 30 th September 2010 Why is this important? Urgent recognition and treatment of dermatologic emergencies can be life saving and prevent long term
Emergency Dermatology Dr Melissa Barkham Spotlight Seminar 30 th September 2010 Why is this important? Urgent recognition and treatment of dermatologic emergencies can be life saving and prevent long term
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Shenoy E, Macy E, Rowe TA, Blumenthal KG. Evaluation and management of penicillin allergy. JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.19283 Table 1. Hypersensitivity reaction types Table
Supplementary Online Content Shenoy E, Macy E, Rowe TA, Blumenthal KG. Evaluation and management of penicillin allergy. JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.19283 Table 1. Hypersensitivity reaction types Table
Lecture 03: Drug allergy
 Lecture 03: Drug allergy 1. Basic Information Author: Netherlands Pharmacovigilance Centre Lareb Version date: 17 Nov 2017 Content: This hand-out describes Drug allergy and provides background information
Lecture 03: Drug allergy 1. Basic Information Author: Netherlands Pharmacovigilance Centre Lareb Version date: 17 Nov 2017 Content: This hand-out describes Drug allergy and provides background information
Drug induced allergy and hypersensitivity
 Drug induced allergy and hypersensitivity Yunita Sari Pane, Aznan Lelo Dept. Pharmacology & Therapeutic School of Medicine Universitas Sumatera Utara 13 Mei 2009, KBK-FK USU, Medan Drug Allergy Adverse
Drug induced allergy and hypersensitivity Yunita Sari Pane, Aznan Lelo Dept. Pharmacology & Therapeutic School of Medicine Universitas Sumatera Utara 13 Mei 2009, KBK-FK USU, Medan Drug Allergy Adverse
Objectives 8/30/2012. How Do I Deal with a Person s Multiple (and Single) Drug Allergies? Adverse Drug Reactions
 How Do I Deal with a Person s Multiple (and Single) Drug Allergies? Faoud Ishmael, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Medicine Section of Allergy and Immunology Penn State College of Medicine I have no conflicts
How Do I Deal with a Person s Multiple (and Single) Drug Allergies? Faoud Ishmael, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Medicine Section of Allergy and Immunology Penn State College of Medicine I have no conflicts
Chapter 65 Allergy and Immunology for the Internist. ingestion provoke an IgE antibody response and clinical symptoms in sensitive individuals.
 Chapter 65 Allergy and Immunology for the Internist 1 I. Basic Information A. Definition of Allergens: Proteins of appropriate size that after inhalation, injection (e.g. drug, venom) or ingestion provoke
Chapter 65 Allergy and Immunology for the Internist 1 I. Basic Information A. Definition of Allergens: Proteins of appropriate size that after inhalation, injection (e.g. drug, venom) or ingestion provoke
Anaphylactic response in rabbit Part II
 Anaphylactic response in rabbit Part II Introduction Four types of hypersensitivity reactions: Type I: allergy Type II: antibodies Type III: immune complex Type IV: T-cells Type I Hypersensitivity ALLERGY
Anaphylactic response in rabbit Part II Introduction Four types of hypersensitivity reactions: Type I: allergy Type II: antibodies Type III: immune complex Type IV: T-cells Type I Hypersensitivity ALLERGY
Pediatric Dermatology
 Pediatric Dermatology --------- Emergencies & Urgencies Nicholas V. Nguyen, M.D. Director, Pediatric Dermatology Disclosures In the past 12 months, I have had the following financial relationships with
Pediatric Dermatology --------- Emergencies & Urgencies Nicholas V. Nguyen, M.D. Director, Pediatric Dermatology Disclosures In the past 12 months, I have had the following financial relationships with
Al ergy: An Overview
 Allergy: An Overview Allergy Type of hypersensitivity reactions of the immune system. Allergy may involve more than one type of reaction. An allergy is a reaction to something that does not affect most
Allergy: An Overview Allergy Type of hypersensitivity reactions of the immune system. Allergy may involve more than one type of reaction. An allergy is a reaction to something that does not affect most
PedsCases Podcast Scripts
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Acute Otitis Media. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics. The
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Acute Otitis Media. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics. The
Adverse drug reactions
 Medications William Smith Adverse drug reactions Allergy? Side-effect? Intolerance? Background Adverse drug reactions (ADRs) vary from life-threatening anaphylaxis to minor common side-effects. Objective
Medications William Smith Adverse drug reactions Allergy? Side-effect? Intolerance? Background Adverse drug reactions (ADRs) vary from life-threatening anaphylaxis to minor common side-effects. Objective
KDIGO Conference San Francisco March KDIGO. Mechanisms of drug hypersensitivity. A. J. Bircher Dermatology/Allergology
 Conference San Francisco March 27 30 2014 Mechanisms of drug hypersensitivity A. J. Bircher Dermatology/Allergology University Hospital Basel Switzerland andreas.bircher@unibas.ch Disclosure of Interests
Conference San Francisco March 27 30 2014 Mechanisms of drug hypersensitivity A. J. Bircher Dermatology/Allergology University Hospital Basel Switzerland andreas.bircher@unibas.ch Disclosure of Interests
Emergency Dermatology. Emergency Dermatology
 Emergency Dermatology These are rapidly progressive skin conditions and some are potentially lifethreatening. Early recognition is important to implement prompt supportive care and therapy. Some are drug
Emergency Dermatology These are rapidly progressive skin conditions and some are potentially lifethreatening. Early recognition is important to implement prompt supportive care and therapy. Some are drug
PedsCases Podcast Scripts
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Urticaria These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics. The audio versions
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Urticaria These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics. The audio versions
Paediatric Food Allergy. Introduction to the Causes and Management
 Paediatric Food Allergy Introduction to the Causes and Management Allergic Reactions in Children Prevalence of atopic disorders in urbanized societies has increased significantly over the past several
Paediatric Food Allergy Introduction to the Causes and Management Allergic Reactions in Children Prevalence of atopic disorders in urbanized societies has increased significantly over the past several
Drug allergy and Skin Disorders. Timothy Craig, DO, FACOI Professor of Medicine and Pediatrics Distinguished Educator Penn State University, Hershey
 Drug allergy and Skin Disorders Timothy Craig, DO, FACOI Professor of Medicine and Pediatrics Distinguished Educator Penn State University, Hershey The best screening test for anaphylaxis is? A. histamine
Drug allergy and Skin Disorders Timothy Craig, DO, FACOI Professor of Medicine and Pediatrics Distinguished Educator Penn State University, Hershey The best screening test for anaphylaxis is? A. histamine
Allergy/Immunology Marshall University Pediatrics
 Allergy/Immunology Marshall University Pediatrics Description: This is a clinical rotation about the most common chronic diseases affecting both children and adults. Residents will be introduced to allergy,
Allergy/Immunology Marshall University Pediatrics Description: This is a clinical rotation about the most common chronic diseases affecting both children and adults. Residents will be introduced to allergy,
Adverse Drug Reactions. Navigating the World of. Adverse Drug Reactions. Definition. Essential History Taking. Essential History Taking
 Adverse Drug Reactions Navigating the World of Adverse Drug Reactions Jason Knuffman, M.D. Quincy Medical Group Quincy, IL Allergy and Immunology Section Upon completion of this activity, the participant
Adverse Drug Reactions Navigating the World of Adverse Drug Reactions Jason Knuffman, M.D. Quincy Medical Group Quincy, IL Allergy and Immunology Section Upon completion of this activity, the participant
Type III Hypersensitivity. Immune Complex Mediated Reaction
 Type III Hypersensitivity Immune Complex Mediated Reaction Type III: Immune Complex Mediated Reaction *When antibodies (Ig G or Ig M) and antigen coexist immune complexes are formed *Immune complexes are
Type III Hypersensitivity Immune Complex Mediated Reaction Type III: Immune Complex Mediated Reaction *When antibodies (Ig G or Ig M) and antigen coexist immune complexes are formed *Immune complexes are
Drug Allergy HSJ 19/09/2011
 Drug Allergy HSJ 19/09/2011 BSACI Guidelines Definitions Mechanisms Clinical Features Risk factors Diagnosis Investigations Criteria for referral/investigation Mirakian et al. Clin Exp All 2008 ; 39: 43-61
Drug Allergy HSJ 19/09/2011 BSACI Guidelines Definitions Mechanisms Clinical Features Risk factors Diagnosis Investigations Criteria for referral/investigation Mirakian et al. Clin Exp All 2008 ; 39: 43-61
VACCINE-RELATED ALLERGIC REACTIONS
 VACCINE-RELATED ALLERGIC REACTIONS Management of Anaphylaxis Public Health Immunization Program June 2018 VACCINE-RELATED ADVERSE EVENTS Local reactions pain, edema, erythema Systemic reactions fever,
VACCINE-RELATED ALLERGIC REACTIONS Management of Anaphylaxis Public Health Immunization Program June 2018 VACCINE-RELATED ADVERSE EVENTS Local reactions pain, edema, erythema Systemic reactions fever,
New product information wording Extracts from PRAC recommendations on signals
 20 July 2017 EMA/PRAC/406976/2017 Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) New product information wording Extracts from PRAC recommendations on signals Adopted at the 3-6 July 2017 PRAC The
20 July 2017 EMA/PRAC/406976/2017 Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) New product information wording Extracts from PRAC recommendations on signals Adopted at the 3-6 July 2017 PRAC The
VACCINE-RELATED ALLERGIC REACTIONS
 VACCINE-RELATED ALLERGIC REACTIONS Management of Anaphylaxis IERHA Immunization Program September 2016 VACCINE-RELATED ADVERSE EVENTS Local reactions pain, edema, erythema Systemic reactions fever, lymphadenopathy
VACCINE-RELATED ALLERGIC REACTIONS Management of Anaphylaxis IERHA Immunization Program September 2016 VACCINE-RELATED ADVERSE EVENTS Local reactions pain, edema, erythema Systemic reactions fever, lymphadenopathy
Managing Penicillin Allergy
 Managing Penicillin Allergy Brian T. Kelly, MD MA April 12, 2019 Objectives Review penicillin allergy prevalence, morbidity, and management Describe the penicillin testing and oral challenge process Provide
Managing Penicillin Allergy Brian T. Kelly, MD MA April 12, 2019 Objectives Review penicillin allergy prevalence, morbidity, and management Describe the penicillin testing and oral challenge process Provide
PACKAGE INSERT USP ANTIBIOTIC
 Pr AMPICILLIN for Injection USP ANTIBIOTIC ACTIONS AND CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY Ampicillin has a broad spectrum of bactericidal activity against many gram-positive and gramnegative aerobic and anaerobic bacteria.
Pr AMPICILLIN for Injection USP ANTIBIOTIC ACTIONS AND CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY Ampicillin has a broad spectrum of bactericidal activity against many gram-positive and gramnegative aerobic and anaerobic bacteria.
EPIPEN INSERVICE Emergency Administration of Epinephrine for the Basic EMT. Michael J. Calice MD, FACEP St. Mary Mercy Hospital
 EPIPEN INSERVICE Emergency Administration of Epinephrine for the Basic EMT Michael J. Calice MD, FACEP St. Mary Mercy Hospital Case #1 NR is an 8 yo male c/o hot mouth and stomach ache after eating jelly
EPIPEN INSERVICE Emergency Administration of Epinephrine for the Basic EMT Michael J. Calice MD, FACEP St. Mary Mercy Hospital Case #1 NR is an 8 yo male c/o hot mouth and stomach ache after eating jelly
Bugs and Drugs: What s New in Hypersensitivity Reactions?
 Bugs and Drugs: What s New in Hypersensitivity Reactions? Erin Mathes, MD Associate Professor of Dermatology and Pediatrics University of California, San Francisco DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY
Bugs and Drugs: What s New in Hypersensitivity Reactions? Erin Mathes, MD Associate Professor of Dermatology and Pediatrics University of California, San Francisco DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY
HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS D R S H O AI B R AZ A
 HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS D R S H O AI B R AZ A HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS Are exaggerated immune response upon antigenic stimulation Individuals who have been previously exposed to an antigen are said
HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS D R S H O AI B R AZ A HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS Are exaggerated immune response upon antigenic stimulation Individuals who have been previously exposed to an antigen are said
ANTIBIOTICS ACUTE RHINOSINUSITIS IN CHILDREN
 MARCH 2016 DRUG ANTIBIOTICS This optimal usage guide is mainly intended f primary care health professionnals. It is provided f infmation purposes only and should not replace the clinician s judgement.
MARCH 2016 DRUG ANTIBIOTICS This optimal usage guide is mainly intended f primary care health professionnals. It is provided f infmation purposes only and should not replace the clinician s judgement.
7/25/2016. Use of Epinephrine in the Community. Knowledge Amongst Paramedics. Knowledge Amongst Paramedics survey of 3479 paramedics
 Recognition & Management of Anaphylaxis in the Community S. Shahzad Mustafa, MD, FAAAAI Disclosures Speaker s bureau Genentech, Teva Consultant Genentech, Teva Outline Knowledge gap Definition Pathophysiology
Recognition & Management of Anaphylaxis in the Community S. Shahzad Mustafa, MD, FAAAAI Disclosures Speaker s bureau Genentech, Teva Consultant Genentech, Teva Outline Knowledge gap Definition Pathophysiology
Path2220 INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN DISEASE ALLERGY. Dr. Erika Bosio
 Path2220 INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN DISEASE ALLERGY Dr. Erika Bosio Research Fellow Centre for Clinical Research in Emergency Medicine, Harry Perkins Institute of Medical Research University of Western Australia
Path2220 INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN DISEASE ALLERGY Dr. Erika Bosio Research Fellow Centre for Clinical Research in Emergency Medicine, Harry Perkins Institute of Medical Research University of Western Australia
Immunology 2011 Lecture 23 Immediate Hypersensitivity 26 October
 Immunology 2011 Lecture 23 Immediate Hypersensitivity 26 October Allergic Reactions ( Immediate Hypersensitivity ) Hay fever, food, drug & animal allergies, reactions to bee stings, etc. Symptoms may include
Immunology 2011 Lecture 23 Immediate Hypersensitivity 26 October Allergic Reactions ( Immediate Hypersensitivity ) Hay fever, food, drug & animal allergies, reactions to bee stings, etc. Symptoms may include
International Consensus (ICON) on Drug Allergy
 International Consensus (ICON) on Drug Allergy Allergy 2014; 69: 420 437 Pascal Demoly, N. Franklin Adkinson, Knut Brockow, Mariana Castells, Anca M. Chiriac, Paul A. Greenberger, David A. Khan, David
International Consensus (ICON) on Drug Allergy Allergy 2014; 69: 420 437 Pascal Demoly, N. Franklin Adkinson, Knut Brockow, Mariana Castells, Anca M. Chiriac, Paul A. Greenberger, David A. Khan, David
Penicillin Allergy Guidance Document
 Key Points Penicillin Allergy Guidance Document Background Careful evaluation of antibiotic allergy and prior tolerance history is essential to providing optimal treatment The true incidence of penicillin
Key Points Penicillin Allergy Guidance Document Background Careful evaluation of antibiotic allergy and prior tolerance history is essential to providing optimal treatment The true incidence of penicillin
Cutaneous Drug Reactions
 Cutaneous Drug Reactions Andrei Metelitsa, MD, FRCPC, FAAD Co-Director, Institute for Skin Advancement Clinical Associate Professor, Dermatology University of Calgary, Canada Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses
Cutaneous Drug Reactions Andrei Metelitsa, MD, FRCPC, FAAD Co-Director, Institute for Skin Advancement Clinical Associate Professor, Dermatology University of Calgary, Canada Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses
Future of Pediatrics: Blisters, Hives and Other Tales from the Emergency Room June 14 th, 2016
 A. Yasmine Kirkorian MD Assistant Professor of Dermatology & Pediatrics Children s National Health System George Washington University School of Medicine & Health Sciences Future of Pediatrics: Blisters,
A. Yasmine Kirkorian MD Assistant Professor of Dermatology & Pediatrics Children s National Health System George Washington University School of Medicine & Health Sciences Future of Pediatrics: Blisters,
Immunologic Mechanisms of Tissue Damage. (Immuopathology)
 Immunologic Mechanisms of Tissue Damage (Immuopathology) Immunopathology Exaggerated immune response may lead to different forms of tissue damage 1) An overactive immune response: produce more damage than
Immunologic Mechanisms of Tissue Damage (Immuopathology) Immunopathology Exaggerated immune response may lead to different forms of tissue damage 1) An overactive immune response: produce more damage than
Penicillin Allergy and Use of Other Antibiotics
 Penicillin Allergy and Use of Other Antibiotics 7300-646PT Policy No.: 7310-646PT 8790-646PT Original Policy Date: 10/10/2016 Revision Date(s): Review Date(s): Approval: 11/17/16 Pharmacy & Therapeutics
Penicillin Allergy and Use of Other Antibiotics 7300-646PT Policy No.: 7310-646PT 8790-646PT Original Policy Date: 10/10/2016 Revision Date(s): Review Date(s): Approval: 11/17/16 Pharmacy & Therapeutics
The Diagnosis and Management of Anaphylaxis
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/focus-on-allergy/the-diagnosis-and-management-of-anaphylaxis/3919/
Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/focus-on-allergy/the-diagnosis-and-management-of-anaphylaxis/3919/
Body Defense Mechanisms
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 13 Body Defense Mechanisms Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 13 Body Defense Mechanisms Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of
Hypersensitivity is the term used when an immune response results in exaggerated or inappropriate reactions harmful to the host.
 Hypersensitivity is the term used when an immune response results in exaggerated or inappropriate reactions harmful to the host. Hypersensitivity vs. allergy Hypersensitivity reactions require a pre-sensitized
Hypersensitivity is the term used when an immune response results in exaggerated or inappropriate reactions harmful to the host. Hypersensitivity vs. allergy Hypersensitivity reactions require a pre-sensitized
PHM142 Autoimmune Disorders + Idiosyncratic Drug Reactions
 PHM142 Autoimmune Disorders + Idiosyncratic Drug Reactions 1 Autoimmune Disorders Auto-reactivity: low physiological levels (e.g. tolerance) vs. pathogenic levels 80+ types of autoimmune diseases affect
PHM142 Autoimmune Disorders + Idiosyncratic Drug Reactions 1 Autoimmune Disorders Auto-reactivity: low physiological levels (e.g. tolerance) vs. pathogenic levels 80+ types of autoimmune diseases affect
Scope of Practice Allergy Skin Testing in Australia In relation to revised Medicare Benefits Schedule item numbers effective 1 November 2018
 Scope of Practice Allergy Skin Testing in Australia In relation to revised Medicare Benefits Schedule item numbers effective 1 November 2018 A. Introduction The Australasian Society of Clinical Immunology
Scope of Practice Allergy Skin Testing in Australia In relation to revised Medicare Benefits Schedule item numbers effective 1 November 2018 A. Introduction The Australasian Society of Clinical Immunology
Immunology 2011 Lecture 23 Immediate Hypersensitivity 26 October
 Immunology 2011 Lecture 23 Immediate Hypersensitivity 26 October Allergic Reactions ( Immediate Hypersensitivity ) Hay fever, food, drug & animal allergies, reactions to bee stings, etc. Symptoms may include
Immunology 2011 Lecture 23 Immediate Hypersensitivity 26 October Allergic Reactions ( Immediate Hypersensitivity ) Hay fever, food, drug & animal allergies, reactions to bee stings, etc. Symptoms may include
Local Omalizumab Treatment Protocol (For children 6 to <12 years of age)
 Local Omalizumab Treatment Protocol (For children 6 to
Local Omalizumab Treatment Protocol (For children 6 to
4/28/2016. Host Defenses. Unit 8 Microorganisms & The Immune System. Types of Innate Defenses. Defensive Cells Leukocytes
 Host Defenses Unit 8 Microorganisms & The Immune System CH 16-18 Host defenses that produce resistance can be either innate or adaptive: Innate: those that protect against any type of invading agent Adaptive:
Host Defenses Unit 8 Microorganisms & The Immune System CH 16-18 Host defenses that produce resistance can be either innate or adaptive: Innate: those that protect against any type of invading agent Adaptive:
Hypersensitivity Reactions
 Color code: Important in red Extra in blue Hypersensitivity Reactions For team error adjustments, click here Objectives To know that hypersensitivity reactions are over and excessive immune responses that
Color code: Important in red Extra in blue Hypersensitivity Reactions For team error adjustments, click here Objectives To know that hypersensitivity reactions are over and excessive immune responses that
Status Epilepticus in Children
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Status Epilepticus in Children. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics.
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Status Epilepticus in Children. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics.
VI.2 Elements for a public summary. VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology
 VI.2 Elements for a public summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Sinus infection (Acute bacterial sinusitis) Sinus infection (upper respiratory infection) is short-lived infection of the sinuses,
VI.2 Elements for a public summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Sinus infection (Acute bacterial sinusitis) Sinus infection (upper respiratory infection) is short-lived infection of the sinuses,
Skin Manifestations of Drug Reactions
 Skin Manifestations of Drug Reactions Dr Carol Hlela, Division of Dermatology Department of Medicine, University of Cape Town and Red Cross Children s Hospital What are the Skin Manifestations of Drug
Skin Manifestations of Drug Reactions Dr Carol Hlela, Division of Dermatology Department of Medicine, University of Cape Town and Red Cross Children s Hospital What are the Skin Manifestations of Drug
Michaela Lucas. Clinical Immunologist/Immunopathologist. Pathwest, QE2 Medical Centre, Princess Margaret Hospital
 Michaela Lucas Clinical Immunologist/Immunopathologist Pathwest, QE2 Medical Centre, Princess Margaret Hospital School of Medicine and Pharmacology, School of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University
Michaela Lucas Clinical Immunologist/Immunopathologist Pathwest, QE2 Medical Centre, Princess Margaret Hospital School of Medicine and Pharmacology, School of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University
Diagnosis and management of suspected drug allergies
 Diagnosis and management of suspected drug allergies SPL Sophie Farooque MRCP Allergic reactions can be caused by commonly prescribed drugs and can lead to fatal anaphylaxis. Here, the author describes
Diagnosis and management of suspected drug allergies SPL Sophie Farooque MRCP Allergic reactions can be caused by commonly prescribed drugs and can lead to fatal anaphylaxis. Here, the author describes
A Retrospective Cross- sectional Study Evaluating Beta- lactam Allergy Labeling in Hospitalized Patients
 Pharmacy Residency Research Project Manuscript A Retrospective Cross- sectional Study Evaluating Beta- lactam Allergy Labeling in Hospitalized Patients Bingjie (Amy) Wang Pharmacy Resident Trillium Health
Pharmacy Residency Research Project Manuscript A Retrospective Cross- sectional Study Evaluating Beta- lactam Allergy Labeling in Hospitalized Patients Bingjie (Amy) Wang Pharmacy Resident Trillium Health
Annex I: Proposed Core Safety Profile (CSP) 4.3 Contraindications
 Annex I: Proposed Core Safety Profile (CSP) 4.3 Contraindications Hypersensitivity to cefuroxime or to any of the excipients listed in section 6.1. Patients with known hypersensitivity to cephalosporin
Annex I: Proposed Core Safety Profile (CSP) 4.3 Contraindications Hypersensitivity to cefuroxime or to any of the excipients listed in section 6.1. Patients with known hypersensitivity to cephalosporin
DERMATOLOGIC EMERGENCIES. Mary Evers D.O., F.A.O.C.D. Georgetown, Texas
 DERMATOLOGIC EMERGENCIES Mary Evers D.O., F.A.O.C.D. Georgetown, Texas SKIN EMERGENCIES??? Subclassifications: Autoimmune (Anaphylaxis, Vasculitis, Pemphigus) Erythroderma (AGEP, DRESS, SJS, TEN) Infectious
DERMATOLOGIC EMERGENCIES Mary Evers D.O., F.A.O.C.D. Georgetown, Texas SKIN EMERGENCIES??? Subclassifications: Autoimmune (Anaphylaxis, Vasculitis, Pemphigus) Erythroderma (AGEP, DRESS, SJS, TEN) Infectious
Allergy overview. Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Department of Paediatrics University of Cape Town Red Cross Hospital
 Allergy overview Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Department of Paediatrics University of Cape Town Red Cross Hospital Adaptive Immune Responses Adaptive immune responses allow responses against
Allergy overview Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Department of Paediatrics University of Cape Town Red Cross Hospital Adaptive Immune Responses Adaptive immune responses allow responses against
Immunological transfusion reactions
 Immunological transfusion reactions Immunological transfusion reactions can be hemolytic or non-hemolytic in nature. Both types can be separated into acute (those occurring immediately after transfusion)
Immunological transfusion reactions Immunological transfusion reactions can be hemolytic or non-hemolytic in nature. Both types can be separated into acute (those occurring immediately after transfusion)
SKIN REACTIONS WITH PSYCHOTROPICS: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
 SKIN REACTIONS WITH PSYCHOTROPICS: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW *Anderson Isaac, PharmD Candidate, 2019 Pooja Patel, PharmD Candidate, 2019 Katelyn Thomasson, PharmD Candidate, 2019 Erika Tillery, PharmD, BCPP,
SKIN REACTIONS WITH PSYCHOTROPICS: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW *Anderson Isaac, PharmD Candidate, 2019 Pooja Patel, PharmD Candidate, 2019 Katelyn Thomasson, PharmD Candidate, 2019 Erika Tillery, PharmD, BCPP,
Dilantin (phenytoin) ROBERT A. SCHWARTZ
 Dilantin (phenytoin) ROBERT A. SCHWARTZ Bailey & Galyen Attorney in Charge, Mass Tort Litigation Managing Attorney, Houston 18333 Egret Bay Blvd., Suite 120 Houston, Texas 77058 Toll Free: (866) 715-1529
Dilantin (phenytoin) ROBERT A. SCHWARTZ Bailey & Galyen Attorney in Charge, Mass Tort Litigation Managing Attorney, Houston 18333 Egret Bay Blvd., Suite 120 Houston, Texas 77058 Toll Free: (866) 715-1529
Drug Allergy: A Rash ionale for Treatment
 Drug Allergy: A Rash ionale for Treatment Heather A. Powell, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor of Clinical Sciences Roosevelt University College of Pharmacy Jordan O. Powell, PharmD Clinical Pharmacist
Drug Allergy: A Rash ionale for Treatment Heather A. Powell, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor of Clinical Sciences Roosevelt University College of Pharmacy Jordan O. Powell, PharmD Clinical Pharmacist
Disruptions in the Immune
 Disruptions in the Immune System Bởi: OpenStaxCollege A functioning immune system is essential for survival, but even the sophisticated cellular and molecular defenses of the mammalian immune response
Disruptions in the Immune System Bởi: OpenStaxCollege A functioning immune system is essential for survival, but even the sophisticated cellular and molecular defenses of the mammalian immune response
Cutaneous Conditions Associated with Systemic Disease
 Cutaneous Conditions Associated with Systemic Disease Johnnie M Woodson, M.D., F.A.A.D. Assistant Professor of Dermatology University of Nevada School of Medicine Director of J. Woodson Dermatology & Associates,
Cutaneous Conditions Associated with Systemic Disease Johnnie M Woodson, M.D., F.A.A.D. Assistant Professor of Dermatology University of Nevada School of Medicine Director of J. Woodson Dermatology & Associates,
Non-Beta-lactam Antibiotic: Testing and Desensitization
 Non-Beta-lactam Antibiotic: Testing and Desensitization David A. Khan, MD Professor of Medicine Allergy & Immunology Program Director Division of Allergy & Immunology 1 Disclosures n Research Grants n
Non-Beta-lactam Antibiotic: Testing and Desensitization David A. Khan, MD Professor of Medicine Allergy & Immunology Program Director Division of Allergy & Immunology 1 Disclosures n Research Grants n
Hypersensitivity diseases
 Hypersensitivity diseases Downloaded from: StudentConsult (on 18 July 2006 11:40 AM) 2005 Elsevier Type-I Hypersensitivity Basic terms Type-I = Early= IgE-mediated = Atopic = Anaphylactic type of hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity diseases Downloaded from: StudentConsult (on 18 July 2006 11:40 AM) 2005 Elsevier Type-I Hypersensitivity Basic terms Type-I = Early= IgE-mediated = Atopic = Anaphylactic type of hypersensitivity
IMMUNOLOGY. Referral Guidelines NATIONAL REFERRAL GUIDELINES : IMMUNOLOGY. As above Specialist assessment is essential.
 PAGE 1 IMMUNOLOGY National PRIMARY IMMUNODEFICIENCY Primary immunodeficiency should be suspected in any patient with recurrent or persistent infection or unusual infection. Recurrent sinopulmonary infections
PAGE 1 IMMUNOLOGY National PRIMARY IMMUNODEFICIENCY Primary immunodeficiency should be suspected in any patient with recurrent or persistent infection or unusual infection. Recurrent sinopulmonary infections
About the immune system
 The immune system and anaphylaxis edward.purssell@kcl.ac.uk About the immune system The immune system Protects the body from infectious organisms, foreign bodies and malignancies Surface barriers Innate
The immune system and anaphylaxis edward.purssell@kcl.ac.uk About the immune system The immune system Protects the body from infectious organisms, foreign bodies and malignancies Surface barriers Innate
Urticaria and Angioedema. Allergy and Immunology Awareness Program
 Urticaria and Angioedema Allergy and Immunology Awareness Program 1 Urticaria and Angioedema Allergy and Immunology Awareness Program Urticaria Commonly known as hives, urticarial is an itchy rash with
Urticaria and Angioedema Allergy and Immunology Awareness Program 1 Urticaria and Angioedema Allergy and Immunology Awareness Program Urticaria Commonly known as hives, urticarial is an itchy rash with
BOLSTRAN Injection (Omalizumab)
 Published on: 27 Feb 2017 BOLSTRAN Injection (Omalizumab) Composition Active Substance Omalizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody manufactured from a mammalian cell line. One vial of BOLSTRAN 150 mg
Published on: 27 Feb 2017 BOLSTRAN Injection (Omalizumab) Composition Active Substance Omalizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody manufactured from a mammalian cell line. One vial of BOLSTRAN 150 mg
To update the use of IVIG and CORTICOIDS IN management of SJS/ TEN To remind Doctors being careful when giving
 Present : Dr Pham Thi Minh Rang Internal Department No2-Hospital for children No2 AIMS To update the use of IVIG and CORTICOIDS IN management of SJS/ TEN To remind Doctors being careful when giving To
Present : Dr Pham Thi Minh Rang Internal Department No2-Hospital for children No2 AIMS To update the use of IVIG and CORTICOIDS IN management of SJS/ TEN To remind Doctors being careful when giving To
Medical Documentation/Records. ADVERSE DRUG REACTIONS (ADRs) AND ALLERGIES TO MEDICATIONS
 FLORIDA STATE HOSPITAL OPERATING PROCEDURE NO. 151-24 STATE OF FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF CHILDREN AND FAMILIES CHATTAHOOCHEE, April 26, 2017 Medical Documentation/Records ADVERSE DRUG REACTIONS (ADRs) AND
FLORIDA STATE HOSPITAL OPERATING PROCEDURE NO. 151-24 STATE OF FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF CHILDREN AND FAMILIES CHATTAHOOCHEE, April 26, 2017 Medical Documentation/Records ADVERSE DRUG REACTIONS (ADRs) AND
Food allergy in children. nice bulletin. NICE Bulletin Food Allergy in Chlidren.indd 1
 nice bulletin Food allergy in children NICE provided the content for this booklet which is independent of any company or product advertised NICE Bulletin Food Allergy in Chlidren.indd 1 23/01/2012 11:04
nice bulletin Food allergy in children NICE provided the content for this booklet which is independent of any company or product advertised NICE Bulletin Food Allergy in Chlidren.indd 1 23/01/2012 11:04
Chapter 8. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Anaphylaxis. List symptoms of anaphylactic shock
 Chapter 8 Anaphylaxis Learning Objectives List symptoms of anaphylactic shock Discuss role of immune system in fighting antigens Define allergic response Learning Objectives Describe body s response to
Chapter 8 Anaphylaxis Learning Objectives List symptoms of anaphylactic shock Discuss role of immune system in fighting antigens Define allergic response Learning Objectives Describe body s response to
This is lesson 6 What to expect when you take medication
 Welcome to the Pennsylvania Department of Public Welfare (DPW), Office of Developmental Programs (ODP) Medication Administration Course for life sharers. This course was developed by the ODP Office of
Welcome to the Pennsylvania Department of Public Welfare (DPW), Office of Developmental Programs (ODP) Medication Administration Course for life sharers. This course was developed by the ODP Office of
Sign up to receive ATOTW weekly -
 ANAPHYLAXIS ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 38 1 th DECEMBER 2006 Dr. Sara Rees Cardiff, UK Case History You are anaesthetising a fit and well 40 year old woman for total abdominal hysterectomy for menorrhagia.
ANAPHYLAXIS ANAESTHESIA TUTORIAL OF THE WEEK 38 1 th DECEMBER 2006 Dr. Sara Rees Cardiff, UK Case History You are anaesthetising a fit and well 40 year old woman for total abdominal hysterectomy for menorrhagia.
Lesson 17: Allergies & Anaphylaxis. Emergency Reference Guide p
 Lesson 17: Allergies & Anaphylaxis Emergency Reference Guide p. 25-30 Objectives Describe basics of allergic reactions & treatment Define anaphylaxis List signs & symptoms of anaphylaxis Describe conditions
Lesson 17: Allergies & Anaphylaxis Emergency Reference Guide p. 25-30 Objectives Describe basics of allergic reactions & treatment Define anaphylaxis List signs & symptoms of anaphylaxis Describe conditions
Hypersensitivity reactions. Immune responses which are damaging rather than helpful to the host.
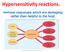 Hypersensitivity reactions. Immune responses which are damaging rather than helpful to the host. 1 Hypersensitivity reaction depends on: 1) chemical nature of allergen 2) route involved in sensitization
Hypersensitivity reactions. Immune responses which are damaging rather than helpful to the host. 1 Hypersensitivity reaction depends on: 1) chemical nature of allergen 2) route involved in sensitization
Immunocompetence The immune system responds appropriately to a foreign stimulus
 Functions of the immune system Protect the body s internal environment against invading organisms Maintain homeostasis by removing damaged cells from the circulation Serve as a surveillance network for
Functions of the immune system Protect the body s internal environment against invading organisms Maintain homeostasis by removing damaged cells from the circulation Serve as a surveillance network for
Perioperative Anaphylaxis. Aleena Banerji, MD AAAAI 2014 San Diego, California
 Perioperative Anaphylaxis Aleena Banerji, MD AAAAI 2014 San Diego, California Objectives Better understand the differential diagnosis of perioperative anaphylaxis Evaluate and manage patients with a history
Perioperative Anaphylaxis Aleena Banerji, MD AAAAI 2014 San Diego, California Objectives Better understand the differential diagnosis of perioperative anaphylaxis Evaluate and manage patients with a history
Developed by Stephanie Zachary, Sarah Weicker, Dr. Jeremy Friedman, Dr. Carolyn Beck, and Dr. Lauren Kitney for PedsCases.com.
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Primary Immune Thrombocytopenia (ITP) CPS Podcast These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Primary Immune Thrombocytopenia (ITP) CPS Podcast These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of
Transfusion and Allergy: What is it, and what is it not? Prof. Olivier GARRAUD INTS, Paris Université de Lyon/Saint-Etienne France
 Transfusion and Allergy: What is it, and what is it not? Prof. Olivier GARRAUD INTS, Paris Université de Lyon/Saint-Etienne France The commonest picture of Allergy Allergy is commonly sensed as an Antibody
Transfusion and Allergy: What is it, and what is it not? Prof. Olivier GARRAUD INTS, Paris Université de Lyon/Saint-Etienne France The commonest picture of Allergy Allergy is commonly sensed as an Antibody
December 3, 2015 Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock Antibiotic Guide
 Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock Antibiotic Guide Surviving Sepsis: The choice of empirical antimicrobial therapy depends on complex issues related to the patient s history, including drug intolerances,
Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock Antibiotic Guide Surviving Sepsis: The choice of empirical antimicrobial therapy depends on complex issues related to the patient s history, including drug intolerances,
Topic 9 (Ch16_18) Immune Disorders. Allergies. 4 Hypersensitivity Types. Topics - Allergies - Autoimmunity - Immunodeficiency
 Topic 9 (Ch16_18) Immune Disorders Topics - Allergies - Autoimmunity - Immunodeficiency 1 Allergies Allergens (antigens) cause an exaggerated immune response or hypersensitivity 4 types: Type I Type II
Topic 9 (Ch16_18) Immune Disorders Topics - Allergies - Autoimmunity - Immunodeficiency 1 Allergies Allergens (antigens) cause an exaggerated immune response or hypersensitivity 4 types: Type I Type II
Allergic rhinitis (Hay fever) Asthma Anaphylaxis Urticaria Atopic dermatitis
 Hypersensitivity Disorders Hypersensitivity Disorders Immune Response IgE Disease Example Ragweed hay fever IgG Cytotoxic Immune complex T Cell Hemolytic anemia Serum sickness Poison ivy IgE-mediated Diseases
Hypersensitivity Disorders Hypersensitivity Disorders Immune Response IgE Disease Example Ragweed hay fever IgG Cytotoxic Immune complex T Cell Hemolytic anemia Serum sickness Poison ivy IgE-mediated Diseases
ANAPHYLAXIS IN ANESTHESIA
 ANAPHYLAXIS IN ANESTHESIA Content I. Definition II. Epidemiology III. Etiology IV. Recognition V. Diagnosis VI. Observation and follow up VII.Drugs Definition Prophylaxis : protection Anaphylaxis : against
ANAPHYLAXIS IN ANESTHESIA Content I. Definition II. Epidemiology III. Etiology IV. Recognition V. Diagnosis VI. Observation and follow up VII.Drugs Definition Prophylaxis : protection Anaphylaxis : against
Is it allergy? Debbie Shipley
 Is it allergy? Debbie Shipley Topics Food Allergy and Eczema Hand Eczema and Patch Testing Urticaria Tackling Allergy Gell and Coombs classification Skin conditions with possible allergic component Allergy
Is it allergy? Debbie Shipley Topics Food Allergy and Eczema Hand Eczema and Patch Testing Urticaria Tackling Allergy Gell and Coombs classification Skin conditions with possible allergic component Allergy
Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Capsules, 200mg, 400mg, Oral suspensions, 90mg/5ml, 180mg/5ml, 36 mg/ml SI/H/PSUR/0002/002 Date of FAR:
 0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Ceftibuten Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Capsules, 200mg, 400mg, Oral suspensions, 90mg/5ml, 180mg/5ml, 36 mg/ml P-RMS: SI/H/PSUR/0002/002 Date of FAR: 14.02.2013
0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Ceftibuten Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Capsules, 200mg, 400mg, Oral suspensions, 90mg/5ml, 180mg/5ml, 36 mg/ml P-RMS: SI/H/PSUR/0002/002 Date of FAR: 14.02.2013
contact activation in formation diseases 67 endothelial cells and kinin formation 73 processing and degradation 68 70
 Subject Index Adenosine, mast cell activation modulation 60 Age, risk factor 17, 18 Allergen elicitors 9, 10 insects, see Insect venom-induced microarrays for 136 overview of characteristics 23 recognition
Subject Index Adenosine, mast cell activation modulation 60 Age, risk factor 17, 18 Allergen elicitors 9, 10 insects, see Insect venom-induced microarrays for 136 overview of characteristics 23 recognition
Disorders Associated with the Immune System
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 19 Disorders Associated with the Immune System Disorders of the Immune System Disorders of the
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 19 Disorders Associated with the Immune System Disorders of the Immune System Disorders of the
PedsCases Podcast Scripts
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Febrile Neutropenia. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics. The
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Febrile Neutropenia. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics. The
Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition
 Lecture PowerPoint to accompany Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition Talaro Chapter 16 To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn
Lecture PowerPoint to accompany Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition Talaro Chapter 16 To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn
Anaphylaxis: Treatment in the Community
 : Treatment in the Community is likely if a patient who, within minutes of exposure to a trigger (allergen), develops a sudden illness with rapidly progressing skin changes and life-threatening airway
: Treatment in the Community is likely if a patient who, within minutes of exposure to a trigger (allergen), develops a sudden illness with rapidly progressing skin changes and life-threatening airway
PedsCases Podcast Scripts
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Anaphylaxis in Children. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics.
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Anaphylaxis in Children. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics.
