Supplemental Data. Wu et al. (2010). Plant Cell /tpc
|
|
|
- Ralph Gordon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplemental Figure 1. FIM5 is preferentially expressed in stamen and mature pollen. The expression data of FIM5 was extracted from Arabidopsis efp browser ( which was represented as GCOS (Gene Chip Operating Software) expression signal, and plotted against different Arabidopsis tissues. Tissues labeled by numbers are as follows: (1) Dry seed; (2) Imbibed seed, 24 h; (3) 1st node; (4) Flower stage 12, stamens; (5) Cauline leaf; (6) Cotyledon; (7) Root; (8) Entire rosette after transition to flowering; (9) Flower stage 9; (10) Flower stage 10/11; (11) Flower stage 12; (12) Flower stage 15; (13) Flower stage 12, carpels; (14) Flower stage 12, petals; (15) Flower stage 12, sepals; (16) Flower stage 15, carpels; (17) Flower stage 15, petals; (18) Flower stage 15, sepals; (19) Flower stage 15, stamen; (20) Flowers stage 15, pedicels; (21) Leaf 1 + 2; (22) Leaf 7, petiole; (23) Leaf 7, distal half; (24) Leaf 7, proximal half; (25) Hypocotyl; (26) Root; (27) Rosette leaf 2; (28) Rosette leaf 4; (29) Rosette leaf 6; (30) Rosette leaf 8; (31) Rosette leaf 10; (32) Rosette leaf 12; (33) Senescing leaf; (34) Shoot apex, inflorescence; (35) Shoot apex, transition; (36) Shoot apex, vegetative; (37) Stem, 2nd internode; (38) Mature pollen; (39) Seeds stage 3 w/ siliques; (40) Seeds stage 4 w/ siliques; (41) Seeds stage 5 w/ siliques;(42) Seeds stage 6 w/o siliques;(43) Seeds stage 7 w/o siliques; (44) Seeds stage 8 w/o siliques; (45) Seeds stage 9 w/o siliques; (46) Seeds stage 10 w/o siliques; (47) Vegetative rosette. Column represented for expression in mature pollen is highlighted in red.
2 Supplemental Figure 2. Alignment of the FIM5 protein sequence with sequences of other fimbrin family members. Protein sequences were aligned using DNAMAN. α-helices in each CH domain are indicated by bars above the alignment. The color of the bar indicates the CH domain: CH1, orange; CH2, yellow; CH3, green; and CH4, blue. Linker regions between CH domains are colored light blue. Residues that constitute putative actin binding sites are underlined in pink. The actin binding sites included ABS1 (residues in ABD1; in ABD2), ABS2 (residues in ABD1; in ABD2), and ABS3 (residues in ABD1; in ABD2). The numbers shown
3 above the alignment correspond to the FIM1 sequence. Identical amino acids (100% identity) and similar amino acids (greater than 75% identity) are colored olive and orange, respectively. Note that both FIM1 and FIM5 have an extended C-terminus. Names and database accession numbers for the sequences are as follows: FIM1 (Arabidopsis thaliana fimbrin1, NP_194400), FIM5 (NP_198420), Sac6p (Saccharomyces cerevisiae, NP_010414) and L-plastin (NP_002289).
4 Supplemental Figure 3. Pollen tube growth defects in fim5 mutants were rescued by expression of FIM5-GFP driven by the FIM5 native promoter. (A) RT-PCR analysis showed that FIM5 expression was restored in fim5 mutants after transformation with the complementation construct (C-fim5-1 and C-fim5-2 refer to transformants carrying the complementation construct in the fim5-1 and fim5-2 backgrounds, respectively). eif4a was amplified as an internal control. Forty PCR cycles were performed for both transcripts, and three replicates were conducted. (B) The defect in pollen tube growth of fim5 mutants was rescued by complementation. Pollen tube lengths were measured after 3 h of in vitro germination at 25ºC. A minimum of 100 pollen tubes were measured in each experiment, and three replicates were conducted. Data represent the mean ± SE. An Anova test revealed that no significant difference was present between C-fim5 lines and WT (p = 0.828).
5 Supplemental Figure 4. FIM5-GFP, driven by the FIM5 promoter, decorates actin filaments in both pollen grains and pollen tubes. FIM5-GFP decorates actin filaments in pollen grains (A-B) and in pollen tubes (C-I). In some pollen tubes, FIM5-GFP accumulates behind the tip, corresponding to the fringe or collar region. The step size of optical section was 0.5 µm for pollen grains and 0.4 µm for pollen tubes. Maximal projection of confocal optical sections throughout the entire pollen grain or pollen tube was performed. Scale bars = 10 µm in (A-I).
6 Supplemental Figure 5. Filamentous structures decorated by FIM5-GFP are dispersed by LatB treatment. To determine whether filamentous structures decorated by FIM5-GFP were actin filaments, fim5 pollen tubes carrying FIM5-GFP constructs were subjected to LatB treatment. (A) Pollen tubes expressing FIM5-GFP constructs contain filamentous structures. (B) Pollen tubes subjected to treatment with the vehicle (DMSO) exhibit similar structures after 30 min of treatment. (C) Filamentous structures dispersed after 30 min of 100 nm LatB treatment. (D) Filamentous structures returned after LatB wash out. Scale bar = 20 µm.
7 Supplemental Figure 6. FIM5-GFP co-localizes with actin filaments in pollen grains and pollen tubes. Pollen grains from fim5-1 lines complemented with FIM5-GFP driven by FIM5 promoter were dipped onto the pollen germination medium and germinated for 2 h at 25ºC. Pollen grains and pollen tubes were then processed for fixation with the addition of 300 µm MBS followed by staining with Alexa-568 phalloidin (see the details in the method section of F-actin staining with fluorescent phalloidin). (A-B) Representative Images showing FIM5 co-localizes with all F-actin structures in pollen grains; (C-I) Representative Images showing FIM5 co-localizes with all F-actin structures in pollen tubes of differing lengths. The red panels in (a) show actin filaments labeled with Alexa-568 phalloidin; the green panels in (b) show distribution of FIM5-GFP; the panels in (c) represent merged signals of corresponding (a) and (b) panels. Scale bars = 5 µm in (A-B) or 10 µm in (C-I).
8 Supplemental Figure 7. Actin filaments become redistributed, form thick bundles and display diverse patterns in fim5 pollen grains. Besides the patterns of actin filaments distribution shown in Figure 5B-D, actin filaments also display other patterns in fim5 pollen grains and form thick bundles. (A-D) Actin distribution in fim5-1 pollen grains; (E-H) Actin distribution in fim5-2 pollen grains. Scale bar = 5 µm.
9 Supplemental Figure 8. Thicker actin bundles are present in fim5-1 pollen grains. The appearance of thicker actin bundles in fim5-1 pollen grains was confirmed by analyzing the fluorescence pixel intensity of actin filaments along the long axis of pollen grains using Image J. (A) WT Col-0 pollen grain. A total of 94 fluorescence peaks were identified. (B) fim5-1 pollen grain. A total of 72 fluorescence peaks were identified. (C) Plot of average peak number. Black column represents the number of fluorescence peak of WT col-0 pollen; white column represents the number of fluorescence peak of fim5-1. Five pollens for each genotype were selected randomly to analyze the number of fluorescence peak, and error bars represent mean ± SE. *P < 0.05, by a students test. (D) Black column represents the width of fluorescence peak of WT col-0 pollen; white column represents the width of fluorescence peak of fim5-1. Five pollens for each genotype were selected randomly to analyze the width of fluorescence peak, and at least 25 fluorescence peaks were measured for each pollen. Peak width was determined at half height of the fluorescence peak. Error bars represent mean ± SE. *P < 0.05, by nested ANOVA test.
10 Supplemental Figure 9. Actin filaments are reorganized and form thicker bundles in fim5-1 pollen grains revealed by fluorescent phalloidin staining fixed with paraformaldehyde. Pollen grains were dipped onto the surface of pollen germination medium, rinsed for five minutes in PEM (0.1 M PIPES, ph 7.0, 1 mm MgCl 2, 5 mm EGTA) containing 18% sucrose and fixed for 1h with 4% paraformaldehyde in the same buffer. The following procedure was similar to that of F-actin staining with MBS fixation described in the method section. The occurrence of thick actin bundles are confirmed by analyzing the fluorescence peak number and average fluorescence peak width by Image J as described in Supplemental Figure 8. (A) Pollen grains stained with Alexa-488 phalloidin. (a-b) WT Col-0 pollen grains; (c-h) fim5-1 pollen grains. Scale bars = 5 µm in (a-h). (B) Plot of peak number. Five pollen grains for each genotype were selected randomly to identify the peak number, and error bars represent mean ±
11 SE. *P <0.05 (Student s t-test). (C) Plot of average fluorescence peak width. Five pollen grains were selected randomly and at least 40 fluorescence peaks were measured for each pollen grain. Peak width was determined at half height. Error bars represent mean ± SE. **P <0.01 (Nested ANOVA test).
12 Supplemental Figure 10. Uniform normal distribution of actin filaments was restored in complemented fim5-1 pollen grains carrying the FIM5-GFP construct. (A) In WT Col-0 pollen, actin filaments were uniformly distributed. (B) In fim5-1 pollen, actin filaments were disorganized, as shown in Figure 5. (C D) In fim5-1 pollen grains carrying pcambia1301fim5 pro :Fim5-EGFP-NOS, actin filaments displayed a uniform, normal organization indistinguishable from WT Col-0 pollen grains. Scale bar = 5 µm.
13 Supplemental Table 1. Primer information used in this study Primer name Primer sequence fim5-1 LP 5 -TTTAGGACGGTGAGGCATATG-3 fim5-1 RP 5 -GCGAGTGTGATCTCAAGTTCC-3 fim5-2 LP 5 -GTGGGACTGGACTCGGAAGC-3 fim5-2 RP 5 -GACATAGTGGACGGCTCAG-3 LB 5 -AACGTCCGCAATGTGTTATTAAGTTGTC-3 F5f1 5 -GCGGCCGCATGTCTAGTTACGTTG-3 F5r1 5 -TCTAGACCGCCTGCATCTTTATTATTC-3 F5f2 5 -GACATAGTGGACGGCTCAG-3 F5r2 5 -GTGGGACTGGACTCGGAAGC-3 F5f3 5 -GAGCCTCCAACAACAATCAGACA-3 F5r3 5 -GCATCTTTATTATTCTCACCATC-3 eif4afor 5 -GGGTATCTATGCTTACGGTTTCG-3 eif4arev 5 -CAGAGAACACTCCAA CCTGAATC-3 FIM5For 5 -GGATCCATGTCTAGTTACGTTGGTGTT-3 (with the BamH I site underlined) FIM5Rev 5 -CCCGGGTGCATCTTTATTATTCTCA-3 (with the Sma I site underlined) FIM5proFor 5 -GTCGACCTAACATTAACATCTACAA-3 (with the Sal I site underlined) FIM5proRev (5 -GGATCCTTTTTCTAATCGATTTCT-3 ) (with the BamH I site underlined) EGFPFor 5 -CCCGGGATGGTGAGCAAGGGCGAGGAG-3 (with the Sma I site underlined) EGFPRev 5 -GTGAATTCTTACTTGTACAGCTCGTCCATG-3 (with the EcoR I site underlined) FIM5KGFor 5 -GAATTCTAATGTCTAGTTACGTTGGTGT-3 (underlined EcoRⅠ site) FIM5KGRev 5 -GAATTCTCATGCATCTTTATTATTCTC-3 (underlined EcoRⅠ site)
Supplemental Data. Müller-Xing et al. (2014). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. Phenotypes of iclf (clf-28 swn-7 CLF pro :CLF-GR) plants. A, Late rescue of iclf plants by renewed DEX treatment; senescent inflorescence with elongated siliques (arrow; 90 DAG,
Supplemental Figure 1. Phenotypes of iclf (clf-28 swn-7 CLF pro :CLF-GR) plants. A, Late rescue of iclf plants by renewed DEX treatment; senescent inflorescence with elongated siliques (arrow; 90 DAG,
Testing the ABC floral-organ identity model: expression of A and C function genes
 Objectives: Testing the ABC floral-organ identity model: expression of A and C function genes To test the validity of the ABC model for floral organ identity we will: 1. Use the model to make predictions
Objectives: Testing the ABC floral-organ identity model: expression of A and C function genes To test the validity of the ABC model for floral organ identity we will: 1. Use the model to make predictions
Flowers, Fruit and Seeds Notes Flower Structure and Reproduction Taken from
 Flowers, Fruit and Seeds Notes Flower Structure and Reproduction Taken from http://www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/flower_coloring.html Flowers are the plant's reproductive structures. Angiosperms are
Flowers, Fruit and Seeds Notes Flower Structure and Reproduction Taken from http://www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/flower_coloring.html Flowers are the plant's reproductive structures. Angiosperms are
Open Flower. Juvenile leaf Flowerbud. Carpel 35 NA NA NA NA 61 NA 95 NA NA 15 NA 41 3 NA
 PaxDB Root Juvenile leaf Flowerbud Open Flower Carpel Mature Pollen Silique Seed Sec3a Sec3b Sec5a Sec5b Sec6 Sec8 Sec10a/b Sec15a Sec15b Exo84a Exo84b Exo84c Exo70A1 Exo70A2 Exo70A3 49 47 8 75 104 79
PaxDB Root Juvenile leaf Flowerbud Open Flower Carpel Mature Pollen Silique Seed Sec3a Sec3b Sec5a Sec5b Sec6 Sec8 Sec10a/b Sec15a Sec15b Exo84a Exo84b Exo84c Exo70A1 Exo70A2 Exo70A3 49 47 8 75 104 79
3/18/2012. Chapter 36. Flower Parts. Flower Parts. Reproduction in Angiosperms
 Chapter 36 Reproduction in Angiosperms Bryophytes >450mya 360 mya Fig. 27-4, p. 584 Lily Flower Flower Parts Sepals cover and protect flower parts in bud Collectively calyx Petals Can attract animal pollinators
Chapter 36 Reproduction in Angiosperms Bryophytes >450mya 360 mya Fig. 27-4, p. 584 Lily Flower Flower Parts Sepals cover and protect flower parts in bud Collectively calyx Petals Can attract animal pollinators
Arabidopsis FIMBRIN5, an Actin Bundling Factor, Is Required for Pollen Germination and Pollen Tube Growth W
 The Plant Cell, Vol. 22: 3745 3763, November 2010, www.plantcell.org ã 2010 American Society of Plant Biologists Arabidopsis FIMBRIN5, an Actin Bundling Factor, Is Required for Pollen Germination and Pollen
The Plant Cell, Vol. 22: 3745 3763, November 2010, www.plantcell.org ã 2010 American Society of Plant Biologists Arabidopsis FIMBRIN5, an Actin Bundling Factor, Is Required for Pollen Germination and Pollen
Regulation of Floral Organ Identity. Dr. Chloe Diamond Mara
 Regulation of Floral Organ Identity Dr. Chloe Diamond Mara Flower Development Angiosperms (flowering plants) are the most widespread group of land plants Flowers are the reproductive organs that consist
Regulation of Floral Organ Identity Dr. Chloe Diamond Mara Flower Development Angiosperms (flowering plants) are the most widespread group of land plants Flowers are the reproductive organs that consist
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
Chapter 38 Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology
 Chapter 38 Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology Concept 38.1 Pollination enables gametes to come together within a flower Diploid (2n) sporophytes produce spores by meiosis; these grow into haploid
Chapter 38 Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology Concept 38.1 Pollination enables gametes to come together within a flower Diploid (2n) sporophytes produce spores by meiosis; these grow into haploid
Supplemental Information. Figures. Figure S1
 Supplemental Information Figures Figure S1 Identification of JAGGER T-DNA insertions. A. Positions of T-DNA and Ds insertions in JAGGER are indicated by inverted triangles, the grey box represents the
Supplemental Information Figures Figure S1 Identification of JAGGER T-DNA insertions. A. Positions of T-DNA and Ds insertions in JAGGER are indicated by inverted triangles, the grey box represents the
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites.
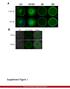
 Supplementary Figure 1 Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites. Staining with fluorescence antibodies to detect GFP (Green), β-galactosidase (magenta/white). (a, b) Class
Supplementary Figure 1 Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites. Staining with fluorescence antibodies to detect GFP (Green), β-galactosidase (magenta/white). (a, b) Class
NOTES: CH 38 Plant Reproduction
 NOTES: CH 38 Plant Reproduction *Modifications in reproduction were key adaptations enabling plants to spread into a variety of terrestrial habitats. * Water has been replaced by wind and animals as a
NOTES: CH 38 Plant Reproduction *Modifications in reproduction were key adaptations enabling plants to spread into a variety of terrestrial habitats. * Water has been replaced by wind and animals as a
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM. (a-c) Heterozygous c.216ga mice displayed normal hair bundle morphology at P18. (d-i) Disorganized hair bundles
Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM. (a-c) Heterozygous c.216ga mice displayed normal hair bundle morphology at P18. (d-i) Disorganized hair bundles
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction. AP Biology
 Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction. AP Biology
 Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated
 Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated from 7 day-old seedlings treated with or without
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated from 7 day-old seedlings treated with or without
Nyla Phillips-Martin 2013 mscraftynyla.blogspot.com
 1 Here are exciting ways to teach your students about the parts of a flower and the function of each part. It includes: A DIY craft activity for assembling the flower parts together to make a complete
1 Here are exciting ways to teach your students about the parts of a flower and the function of each part. It includes: A DIY craft activity for assembling the flower parts together to make a complete
Safety Dissection tools are very sharp. Use appropriately and do not leave unattended in the presence of children.
 Plant Dissection Consider the lilies, how they grow: they labour not, neither do they spin. But I say to you, not even Solomon in all his glory was clothed like one of these. Luke 12:27 Introduction In
Plant Dissection Consider the lilies, how they grow: they labour not, neither do they spin. But I say to you, not even Solomon in all his glory was clothed like one of these. Luke 12:27 Introduction In
We will learn to label the parts of a plant and flower.
 5 th level CS We will learn to label the parts of a plant and flower. We will learn that plants produce flowers which have male and female organs. We will learn that seeds are formed when pollen from the
5 th level CS We will learn to label the parts of a plant and flower. We will learn that plants produce flowers which have male and female organs. We will learn that seeds are formed when pollen from the
Flowering Plant Reproduction
 Lab Exercise Flowering Plant Reproduction Objectives - To be able to identify the parts of a flower - Be able to distinguish between dicots and monocots based on flower morphology - Become familiar with
Lab Exercise Flowering Plant Reproduction Objectives - To be able to identify the parts of a flower - Be able to distinguish between dicots and monocots based on flower morphology - Become familiar with
plant reproduction chapter 40 Alternation of Generations
 Alternation of Generations plant reproduction chapter 40 Haploid (n) Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) Archegonium Antheridium Sperm Sporangium Mature sporophyte (2n) New
Alternation of Generations plant reproduction chapter 40 Haploid (n) Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) Archegonium Antheridium Sperm Sporangium Mature sporophyte (2n) New
plant reproduction Alternation of Generations chapter 38
 Alternation of Generations Haploid (n) plant reproduction chapter 38 Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) ARCHEGONIUM ANTHERIDIUM Sperm Mature Sorus Sporangium sporophyte
Alternation of Generations Haploid (n) plant reproduction chapter 38 Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) ARCHEGONIUM ANTHERIDIUM Sperm Mature Sorus Sporangium sporophyte
2014 Pearson Education, Inc. 1
 1 Stamen Anther Filament Stigma Carpel Style Ovary Petal Sepal Ovule 2 A B Sepals Petals Stamens Carpels C A + B gene activity B + C gene activity C gene activity Carpel Petal (a) A schematic diagram of
1 Stamen Anther Filament Stigma Carpel Style Ovary Petal Sepal Ovule 2 A B Sepals Petals Stamens Carpels C A + B gene activity B + C gene activity C gene activity Carpel Petal (a) A schematic diagram of
Arabidopsis: Flower Development and Patterning
 Arabidopsis: Flower Development and Patterning John L Bowman, University of California, Davis, California, USA The development of flowers and floral organs is directed by genetic programmes likely to be
Arabidopsis: Flower Development and Patterning John L Bowman, University of California, Davis, California, USA The development of flowers and floral organs is directed by genetic programmes likely to be
Figure legends of supplementary figures
 Figure legends of supplementary figures Figure 1. Phenotypic analysis of rice early flowering1 () plants and enhanced expression of floral identity genes in.. Leaf emergence of,, and plants with complementary
Figure legends of supplementary figures Figure 1. Phenotypic analysis of rice early flowering1 () plants and enhanced expression of floral identity genes in.. Leaf emergence of,, and plants with complementary
Floral Organ Mutants and the Study of Organ Morphogenesis
 Floral Organ Mutants and the Study of Organ Morphogenesis Objectives: 1. How does one use mutants to understand floral organ morphogenesis? 2. What are the phenotypes of some floral organ mutants? 3. What
Floral Organ Mutants and the Study of Organ Morphogenesis Objectives: 1. How does one use mutants to understand floral organ morphogenesis? 2. What are the phenotypes of some floral organ mutants? 3. What
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS WITH SEEDS
 There are several stages in the process of sexual reproduction in plants with seeds (spermatophytes): gamete formation, pollintation, fertilisation, seed and fruit formation, seed disemination and seed
There are several stages in the process of sexual reproduction in plants with seeds (spermatophytes): gamete formation, pollintation, fertilisation, seed and fruit formation, seed disemination and seed
Supplemental Information. Spatial Auxin Signaling. Controls Leaf Flattening in Arabidopsis
 Current Biology, Volume 27 Supplemental Information Spatial Auxin Signaling Controls Leaf Flattening in Arabidopsis Chunmei Guan, Binbin Wu, Ting Yu, Qingqing Wang, Naden T. Krogan, Xigang Liu, and Yuling
Current Biology, Volume 27 Supplemental Information Spatial Auxin Signaling Controls Leaf Flattening in Arabidopsis Chunmei Guan, Binbin Wu, Ting Yu, Qingqing Wang, Naden T. Krogan, Xigang Liu, and Yuling
Plants Provision for Life. Chapter 2 7 th Grade
 Plants Provision for Life Chapter 2 7 th Grade Lesson 2.1- Structure of Flowers Pistil- female reproductive structure Stigma- sticky top part. Traps pollen. Style- slender tube connecting stigma and ovary.
Plants Provision for Life Chapter 2 7 th Grade Lesson 2.1- Structure of Flowers Pistil- female reproductive structure Stigma- sticky top part. Traps pollen. Style- slender tube connecting stigma and ovary.
MII. Supplement Figure 1. CapZ β2. Merge. 250ng. 500ng DIC. Merge. Journal of Cell Science Supplementary Material. GFP-CapZ β2 DNA
 A GV GVBD MI DNA CapZ β2 CapZ β2 Merge B DIC GFP-CapZ β2 Merge CapZ β2-gfp 250ng 500ng Supplement Figure 1. MII A early MI late MI Control RNAi CapZαβ DNA Actin Tubulin B Phalloidin Intensity(A.U.) n=10
A GV GVBD MI DNA CapZ β2 CapZ β2 Merge B DIC GFP-CapZ β2 Merge CapZ β2-gfp 250ng 500ng Supplement Figure 1. MII A early MI late MI Control RNAi CapZαβ DNA Actin Tubulin B Phalloidin Intensity(A.U.) n=10
Chapter 31: Plant Reproduction
 Chapter 31: Plant Reproduction Plants and Pollinators Pollen had evolved by 390 million years ago Sperm packed inside a nutritious package Transferred first by wind currents Later transferred by insects
Chapter 31: Plant Reproduction Plants and Pollinators Pollen had evolved by 390 million years ago Sperm packed inside a nutritious package Transferred first by wind currents Later transferred by insects
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Lee et al. 10.1073/pnas.0910950106 Fig. S1. Fe (A), Zn (B), Cu (C), and Mn (D) concentrations in flag leaves from WT, osnas3-1, and OsNAS3-antisense (AN-2) plants. Each measurement
Supporting Information Lee et al. 10.1073/pnas.0910950106 Fig. S1. Fe (A), Zn (B), Cu (C), and Mn (D) concentrations in flag leaves from WT, osnas3-1, and OsNAS3-antisense (AN-2) plants. Each measurement
Supporting Information
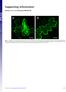 Supporting Information Harries et al. 1.173/pnas.9923916 A Fig. S1. Disruption of microfilaments within epidermal cells after treatment with 5 M Lat. Images of N. benthamiana cells are from plants expressing
Supporting Information Harries et al. 1.173/pnas.9923916 A Fig. S1. Disruption of microfilaments within epidermal cells after treatment with 5 M Lat. Images of N. benthamiana cells are from plants expressing
Supplemental Data. Hiruma et al. Plant Cell. (2010) /tpc Col-0. pen2-1
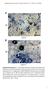 A Ch B Col-0 Cg pen2-1 Supplemental Figure 1. Trypan Blue Staining of Leaves Inoculated with Adapted and Nonadapted Colletotrichum Species.(A) Conidial suspensions of C. higginsianum MAFF305635 (Ch) were
A Ch B Col-0 Cg pen2-1 Supplemental Figure 1. Trypan Blue Staining of Leaves Inoculated with Adapted and Nonadapted Colletotrichum Species.(A) Conidial suspensions of C. higginsianum MAFF305635 (Ch) were
Supplemental Data. Beck et al. (2010). Plant Cell /tpc
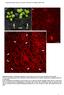 Supplemental Figure 1. Phenotypic comparison of the rosette leaves of four-week-old mpk4 and Col-0 plants. A mpk4 vs Col-0 plants grown in soil. Note the extreme dwarfism of the mpk4 plants (white arrows)
Supplemental Figure 1. Phenotypic comparison of the rosette leaves of four-week-old mpk4 and Col-0 plants. A mpk4 vs Col-0 plants grown in soil. Note the extreme dwarfism of the mpk4 plants (white arrows)
Supplemental Data. Candat et al. Plant Cell (2014) /tpc Cytosol. Nucleus. Mitochondria. Plastid. Peroxisome. Endomembrane system
 Cytosol Nucleus 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 PSORT MultiLoc YLoc SubLoc BaCelLo WoLF PSORT
Cytosol Nucleus 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 PSORT MultiLoc YLoc SubLoc BaCelLo WoLF PSORT
A -GLS Arabidopsis Cuscuta gronovii
 -GLS Arabidopsis Cuscuta gronovii internal standard 4MS Wildtype Arabidopsis Cuscuta gronovii base Cuscuta gronovii apex 3MSP internal standard MSP 4MT 8MSO 4MO 1MO Figure S1. Representative HPLC-DAD chromatograms
-GLS Arabidopsis Cuscuta gronovii internal standard 4MS Wildtype Arabidopsis Cuscuta gronovii base Cuscuta gronovii apex 3MSP internal standard MSP 4MT 8MSO 4MO 1MO Figure S1. Representative HPLC-DAD chromatograms
The Flower, Pollination, and Seeds
 The Flower, Pollination, and Seeds Class 9 th Chapters 6,7,8 1 The Flower A complete or a perfect flower, has all the four Whorls. If, even one whorl is missing, it is an Incomplete Flower. The fourth
The Flower, Pollination, and Seeds Class 9 th Chapters 6,7,8 1 The Flower A complete or a perfect flower, has all the four Whorls. If, even one whorl is missing, it is an Incomplete Flower. The fourth
The Rab GTPase RabA4d Regulates Pollen Tube Tip Growth in Arabidopsis thaliana W
 The Plant Cell, Vol. 21: 526 544, February 2009, www.plantcell.org ã 2009 American Society of Plant Biologists The Rab GTPase RabA4d Regulates Pollen Tube Tip Growth in Arabidopsis thaliana W Amy L. Szumlanski
The Plant Cell, Vol. 21: 526 544, February 2009, www.plantcell.org ã 2009 American Society of Plant Biologists The Rab GTPase RabA4d Regulates Pollen Tube Tip Growth in Arabidopsis thaliana W Amy L. Szumlanski
Past Questions on Plant Reproduction
 Past Questions on Plant Reproduction Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D in figure 1 State one function for each A and B. Figure 1 Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D,E and F in figure 2 What is the function
Past Questions on Plant Reproduction Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D in figure 1 State one function for each A and B. Figure 1 Name the parts labelled A, B, C, D,E and F in figure 2 What is the function
Supplemental Data. Di Giorgio et al. (2016). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. Synteny analysis of NIP4;1 and NIP4;2. Examination of the NIP4;1-NIP4;2 region in rabidopsis thaliana and equivalent evolutionary regions in other dicot genomes are shown on the
Supplemental Figure 1. Synteny analysis of NIP4;1 and NIP4;2. Examination of the NIP4;1-NIP4;2 region in rabidopsis thaliana and equivalent evolutionary regions in other dicot genomes are shown on the
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge Ordinary Level. Published
 Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge Ordinary Level BIOLOGY 5090/31 Paper 3 Practical Test MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 0 Published This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers and
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge Ordinary Level BIOLOGY 5090/31 Paper 3 Practical Test MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 0 Published This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers and
Botany Physiology. Due Date Code Period Earned Points
 Name Botany Physiology C/By Due Date Code Period Earned Points Bot Phys 4W1 Flowers (divide by 6.5) Completion Complete each sentence or statement. 1. (4 points) The female reproductive organs are the
Name Botany Physiology C/By Due Date Code Period Earned Points Bot Phys 4W1 Flowers (divide by 6.5) Completion Complete each sentence or statement. 1. (4 points) The female reproductive organs are the
Flower Morphology. Flower Structure
 wrong 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5
wrong 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5
Introduction. Copyright 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
Operation Flower Dissection
 Operation Flower Dissection Classroom Activity: K-4 Time: One to two 50-minute class periods Overview: In this activity, students will observe the similarities and differences between flowers of different
Operation Flower Dissection Classroom Activity: K-4 Time: One to two 50-minute class periods Overview: In this activity, students will observe the similarities and differences between flowers of different
CHAPTER 2 Reproduction of Flowering Plants. Bui Tan Anh College of Natural Sciences
 CHAPTER 2 Reproduction of Flowering Plants Bui Tan Anh College of Natural Sciences Rafflesiaarnoldii in Indonesia Asexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Seeds and Fruits Flower Plant Reproduction Many
CHAPTER 2 Reproduction of Flowering Plants Bui Tan Anh College of Natural Sciences Rafflesiaarnoldii in Indonesia Asexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Seeds and Fruits Flower Plant Reproduction Many
Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al
 Supplementary Material Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al Supplementary Figure 1. AICAR improves P23H rod opsin
Supplementary Material Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al Supplementary Figure 1. AICAR improves P23H rod opsin
Supplemental Data. Wang et al. (2013). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Data. Wang et al. (2013). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.112.108993 Supplemental Figure 1. 3-MA Treatment Reduces the Growth of Seedlings. Two-week-old Nicotiana benthamiana seedlings germinated on
Supplemental Data. Wang et al. (2013). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.112.108993 Supplemental Figure 1. 3-MA Treatment Reduces the Growth of Seedlings. Two-week-old Nicotiana benthamiana seedlings germinated on
Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid.
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2294 Figure S1 Localization and function of cell wall polysaccharides in root hair cells. (a) Spinning-disk confocal sections of seven day-old A. thaliana seedlings stained with 0.1% S4B
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2294 Figure S1 Localization and function of cell wall polysaccharides in root hair cells. (a) Spinning-disk confocal sections of seven day-old A. thaliana seedlings stained with 0.1% S4B
Reproduction and Development in Flowering Plants
 Reproduction and Development in Flowering Plants Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants The flower functions in sexual reproduction of plants and precedes the development of seeds and fruits. Flowers
Reproduction and Development in Flowering Plants Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants The flower functions in sexual reproduction of plants and precedes the development of seeds and fruits. Flowers
El Azzouzi et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb /DC1
 Supplemental material JCB El Azzouzi et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201510043 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Acquisition of -phluorin correlates negatively with podosome
Supplemental material JCB El Azzouzi et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201510043 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Acquisition of -phluorin correlates negatively with podosome
Flowering plants can be pollinated by wind or animals.
 Wed 4/5 Activities Learning Target Class Activities *attached below (scroll down)* Website: my.hrw.com Username: bio678 Password:a4s5s Describe the reproductive organs and fertilization of flowering plants.
Wed 4/5 Activities Learning Target Class Activities *attached below (scroll down)* Website: my.hrw.com Username: bio678 Password:a4s5s Describe the reproductive organs and fertilization of flowering plants.
CLAVATA1, a regulator of meristem and flower development in Arabidopsis
 Development 119, 397-418 (1993) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1993 397 CLAVATA1, a regulator of meristem and flower development in Arabidopsis Steven E. Clark, Mark P. Running
Development 119, 397-418 (1993) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1993 397 CLAVATA1, a regulator of meristem and flower development in Arabidopsis Steven E. Clark, Mark P. Running
BIOLOGI UMUM Priyambodo, M.Sc.
 BIOLOGI UMUM Priyambodo, M.Sc. KONSEP REPRODUKSI TUMBUHAN KONSEP REPRODUKSI TUMBUHAN Vegetatif vs generatif VEGETATIF VS GENERATIF Menurut pendapat Anda, makanah jenis reproduksi yang lebih baik bagi tumbuhan?
BIOLOGI UMUM Priyambodo, M.Sc. KONSEP REPRODUKSI TUMBUHAN KONSEP REPRODUKSI TUMBUHAN Vegetatif vs generatif VEGETATIF VS GENERATIF Menurut pendapat Anda, makanah jenis reproduksi yang lebih baik bagi tumbuhan?
The Flower - what is it? 1/31/18. Magnoliophyta - Flowering Plants. Magnoliophyta - Flowering Plants. Magnoliophyta - Flowering Plants
 - what is it? Floral structure will be examined in lab next Mon/Tues save space in your notes! Introduction to Angiosperms "angio-" = vessel; so "angiosperm" means "vessel for the seed [seed encased in
- what is it? Floral structure will be examined in lab next Mon/Tues save space in your notes! Introduction to Angiosperms "angio-" = vessel; so "angiosperm" means "vessel for the seed [seed encased in
Serafino et al. Thymosin α1 activates complement receptor-mediated phagocytosis in human monocyte-derived macrophages. SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 Supplementary Fig. S1. Evaluation of the purity and maturation of macrophage cultures tested by flow cytometry. The lymphocytic/monocytic cellular fraction was isolated from buffy coats of healthy donors
Supplementary Fig. S1. Evaluation of the purity and maturation of macrophage cultures tested by flow cytometry. The lymphocytic/monocytic cellular fraction was isolated from buffy coats of healthy donors
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures a miel1-2 (SALK_41369).1kb miel1-1 (SALK_978) b TUB MIEL1 Supplementary Figure 1. MIEL1 expression in miel1 mutant and S:MIEL1-MYC transgenic plants. (a) Mapping of the T-DNA insertion
Supplementary Figures a miel1-2 (SALK_41369).1kb miel1-1 (SALK_978) b TUB MIEL1 Supplementary Figure 1. MIEL1 expression in miel1 mutant and S:MIEL1-MYC transgenic plants. (a) Mapping of the T-DNA insertion
Plant Terminology. Floral Symmetry
 Plant Terminology Parts of a Flower Pedicel--the stalk of an individual flower Calyx--outermost whorl of a flower Sepal--one member of the calyx Corolla--second whorl of a flower Petal--one member of the
Plant Terminology Parts of a Flower Pedicel--the stalk of an individual flower Calyx--outermost whorl of a flower Sepal--one member of the calyx Corolla--second whorl of a flower Petal--one member of the
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Old plants are more resistant to insect herbivores than young plants. (a) Image of young (1-day-old, 1D) and old (-day-old, D) plants of Arabidopsis
Supplementary Figures 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Old plants are more resistant to insect herbivores than young plants. (a) Image of young (1-day-old, 1D) and old (-day-old, D) plants of Arabidopsis
Introduction. Copyright 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
CLAVATA3 is a specific regulator of shoot and floral meristem development
 Development 2, 20572067 (995) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 995 2057 CLAVATA3 is a specific regulator of shoot and floral meristem development affecting the same processes
Development 2, 20572067 (995) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 995 2057 CLAVATA3 is a specific regulator of shoot and floral meristem development affecting the same processes
A putative MYB35 ortholog is a candidate for the sex-determining genes in Asparagus
 Supplementary figures for: A putative MYB35 ortholog is a candidate for the sex-determining genes in Asparagus officinalis Daisuke Tsugama, Kohei Matsuyama, Mayui Ide, Masato Hayashi, Kaien Fujino, and
Supplementary figures for: A putative MYB35 ortholog is a candidate for the sex-determining genes in Asparagus officinalis Daisuke Tsugama, Kohei Matsuyama, Mayui Ide, Masato Hayashi, Kaien Fujino, and
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS)
 Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Regulation of Floral-Organ- Type by SUPERMAN
 Regulation of Floral-Organ- Type by SUPERMAN 1. Need for regulators of the organ-identity genes. 2. The Superman mutant phenotype-predicting the role of SUPERMAN. 3. Testing our hypothesis of the role
Regulation of Floral-Organ- Type by SUPERMAN 1. Need for regulators of the organ-identity genes. 2. The Superman mutant phenotype-predicting the role of SUPERMAN. 3. Testing our hypothesis of the role
Flower Morphology. Flower Structure. Name
 right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5 83.3 82.1 81.0 79.8 Flower Morphology Name You are already familiar
right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5 83.3 82.1 81.0 79.8 Flower Morphology Name You are already familiar
Biology Journal Volume I
 BI 101 Fall 2018 Monday Oct. 8 2018 5:00 p.m. 131 Weniger 1. Journals can be turned in early 2. Late Portfolio? Can be turned in to 131 Weniger either: (A) Monday Oct. 8 5:01 p.m. - Tuesday Oct. 9 12:00
BI 101 Fall 2018 Monday Oct. 8 2018 5:00 p.m. 131 Weniger 1. Journals can be turned in early 2. Late Portfolio? Can be turned in to 131 Weniger either: (A) Monday Oct. 8 5:01 p.m. - Tuesday Oct. 9 12:00
33VASTVNGATSANNHGEPPS51PADARPR58
 Pro-rich region Trans-membrane region 214 246 359 381 UL50 1 397 211SSRTAS216PPPPPR222 NLS CR1 CR2 CR3 CR4 UL53 1 376 11RERRS15ALRS19LLRKRRR25 33VASTVNGATSANNHGEPPS51PADARPR58 FIG S1. UL97 phosphorylation
Pro-rich region Trans-membrane region 214 246 359 381 UL50 1 397 211SSRTAS216PPPPPR222 NLS CR1 CR2 CR3 CR4 UL53 1 376 11RERRS15ALRS19LLRKRRR25 33VASTVNGATSANNHGEPPS51PADARPR58 FIG S1. UL97 phosphorylation
Key Anatomical Directions
 Dissection Anatomical Direction Before beginning a dissection, it is important to have an understanding of some of the basic directional terminology associated with the dissection of specimens. Some of
Dissection Anatomical Direction Before beginning a dissection, it is important to have an understanding of some of the basic directional terminology associated with the dissection of specimens. Some of
The Structure of a Flower Information Sheet
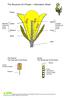 The Structure of a Flower Information Sheet Petals stigma Stamen anther Carpel male part female part of the of the flower filament ovary flower sepal stalk The Stamen Carpel The male part of the flower
The Structure of a Flower Information Sheet Petals stigma Stamen anther Carpel male part female part of the of the flower filament ovary flower sepal stalk The Stamen Carpel The male part of the flower
Student Exploration: Pollination: Flower to Fruit
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Pollination: Flower to Fruit Vocabulary: anther, cross pollination, filament, fruit, nectar, ovary, ovule, pedicel, petal, pistil, pollen, pollen tube, pollination, receptacle,
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Pollination: Flower to Fruit Vocabulary: anther, cross pollination, filament, fruit, nectar, ovary, ovule, pedicel, petal, pistil, pollen, pollen tube, pollination, receptacle,
Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread
 Supplementary Information Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread Amrita Kumar 1, Jin Hyang Kim 1, Priya Ranjan 1, Maureen G. Metcalfe 2, Weiping Cao 1, Margarita Mishina 1,
Supplementary Information Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread Amrita Kumar 1, Jin Hyang Kim 1, Priya Ranjan 1, Maureen G. Metcalfe 2, Weiping Cao 1, Margarita Mishina 1,
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
Supplemental Data. Hao et al. (2014). Plant Cell /tpc
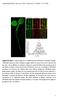 Supplemental Figure 1. Confocal Images and VA-TIRFM Analysis of GFP-RbohD in Arabidopsis Seedlings. (A) RbohD expression in whole Arabidopsis seedlings. RbohD was expressed in the leaves, hypocotyl, and
Supplemental Figure 1. Confocal Images and VA-TIRFM Analysis of GFP-RbohD in Arabidopsis Seedlings. (A) RbohD expression in whole Arabidopsis seedlings. RbohD was expressed in the leaves, hypocotyl, and
Plant Reproduction. In a nutshell
 Plant Reproduction In a nutshell 2007-2008 Plant Diversity mosses ferns conifers flowering plants Bryophytes non-vascular land plants Pteridophytes seedless vascular plants Gymnosperm pollen & naked seeds
Plant Reproduction In a nutshell 2007-2008 Plant Diversity mosses ferns conifers flowering plants Bryophytes non-vascular land plants Pteridophytes seedless vascular plants Gymnosperm pollen & naked seeds
ASSESSMENT OF CELLULAR OXYGEN GRADIENTS WITH A PANEL OF PHOSPHORESCENT OXYGEN-SENSITIVE PROBES
 ASSESSMENT OF CELLULAR OXYGEN GRADIENTS WITH A PANEL OF PHOSPHORESCENT OXYGEN-SENSITIVE PROBES Ruslan I. Dmitriev, Alexander V. Zhdanov, Greg Jasionek, Dmitri B. Papkovsky Biochemistry Department, University
ASSESSMENT OF CELLULAR OXYGEN GRADIENTS WITH A PANEL OF PHOSPHORESCENT OXYGEN-SENSITIVE PROBES Ruslan I. Dmitriev, Alexander V. Zhdanov, Greg Jasionek, Dmitri B. Papkovsky Biochemistry Department, University
Transient β-hairpin Formation in α-synuclein Monomer Revealed by Coarse-grained Molecular Dynamics Simulation
 Transient β-hairpin Formation in α-synuclein Monomer Revealed by Coarse-grained Molecular Dynamics Simulation Hang Yu, 1, 2, a) Wei Han, 1, 3, b) Wen Ma, 1, 2 1, 2, 3, c) and Klaus Schulten 1) Beckman
Transient β-hairpin Formation in α-synuclein Monomer Revealed by Coarse-grained Molecular Dynamics Simulation Hang Yu, 1, 2, a) Wei Han, 1, 3, b) Wen Ma, 1, 2 1, 2, 3, c) and Klaus Schulten 1) Beckman
Supplemental Data. Deinlein et al. Plant Cell. (2012) /tpc
 µm Zn 2+ 15 µm Zn 2+ Growth (% of control) empty vector NS1 NS2 NS3 NS4 S. pombe zhfδ Supplemental Figure 1. Functional characterization of. halleri NS genes in Zn 2+ hypersensitive S. pombe Δzhf mutant
µm Zn 2+ 15 µm Zn 2+ Growth (% of control) empty vector NS1 NS2 NS3 NS4 S. pombe zhfδ Supplemental Figure 1. Functional characterization of. halleri NS genes in Zn 2+ hypersensitive S. pombe Δzhf mutant
Plant Life Cycles. Plant life cycles alternate between. producing gametes. Life cycle phases look different among various
 Plant Life Cycles Plant life cycles alternate between two cycles: Producing spores and producing gametes A two phase life cycle is called alternation of generations Diploid phase Haploid phase Alternates
Plant Life Cycles Plant life cycles alternate between two cycles: Producing spores and producing gametes A two phase life cycle is called alternation of generations Diploid phase Haploid phase Alternates
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Seed Plants Lab. Learning Objectives. Procedure and Questions
 Seed Plants Lab Learning Objectives Define the terms (meanings of the names) angiosperm and gymnosperm State what type of cells create eggs and what type of cells create sperm in gymnosperms and angiosperms
Seed Plants Lab Learning Objectives Define the terms (meanings of the names) angiosperm and gymnosperm State what type of cells create eggs and what type of cells create sperm in gymnosperms and angiosperms
Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Supplemental Figures:
 Supplemental Figures: Figure 1: Intracellular distribution of VWF by electron microscopy in human endothelial cells. a) Immunogold labeling of LC3 demonstrating an LC3-positive autophagosome (white arrow)
Supplemental Figures: Figure 1: Intracellular distribution of VWF by electron microscopy in human endothelial cells. a) Immunogold labeling of LC3 demonstrating an LC3-positive autophagosome (white arrow)
Reproductive Development and Structure
 Reproductive Development and Structure Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction takes place with slight variations in different groups of plants. Plants have two distinct stages in their lifecycle: the
Reproductive Development and Structure Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction takes place with slight variations in different groups of plants. Plants have two distinct stages in their lifecycle: the
Chapter 38: Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology: To Seed or Not to Seed
 Chapter 38: Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology: To Seed or Not to Seed The parasitic plant Rafflesia arnoldi produces huge flowers that produce up to 4 million seeds Many angiosperms reproduce sexually
Chapter 38: Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology: To Seed or Not to Seed The parasitic plant Rafflesia arnoldi produces huge flowers that produce up to 4 million seeds Many angiosperms reproduce sexually
Teaching A2 Biology Practical Skills Appendix 2
 Practical 10 - T(a)(d) The structure of wind pollinated flowers and fruit. This practical focuses on recording accurately Biological drawings. You will be developing other assessed skills throughout the
Practical 10 - T(a)(d) The structure of wind pollinated flowers and fruit. This practical focuses on recording accurately Biological drawings. You will be developing other assessed skills throughout the
Supplemental Materials. STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle
 Supplemental Materials STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle Juanjuan Liu 1,2,3, Xingxing Yang 1,3, Binhua Li 1, Junjun Wang 1,2, Wenchao Wang 1, Jing Liu 1, Qingsong
Supplemental Materials STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle Juanjuan Liu 1,2,3, Xingxing Yang 1,3, Binhua Li 1, Junjun Wang 1,2, Wenchao Wang 1, Jing Liu 1, Qingsong
7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans.
 Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
Figure S1. (A) SDS-PAGE separation of GST-fusion proteins purified from E.coli BL21 strain is shown. An equal amount of GST-tag control, LRRK2 LRR
 Figure S1. (A) SDS-PAGE separation of GST-fusion proteins purified from E.coli BL21 strain is shown. An equal amount of GST-tag control, LRRK2 LRR and LRRK2 WD40 GST fusion proteins (5 µg) were loaded
Figure S1. (A) SDS-PAGE separation of GST-fusion proteins purified from E.coli BL21 strain is shown. An equal amount of GST-tag control, LRRK2 LRR and LRRK2 WD40 GST fusion proteins (5 µg) were loaded
Supplementary Information and Figure legends
 Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES Supplementary Figure S1: CaSR expression in neuroblastoma models. A. Proteins were isolated from three neuroblastoma cell lines and from the liver metastasis of a MYCN-non
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES Supplementary Figure S1: CaSR expression in neuroblastoma models. A. Proteins were isolated from three neuroblastoma cell lines and from the liver metastasis of a MYCN-non
Supplementary Figure S1 (a) (b)
 Supplementary Figure S1: IC87114 does not affect basal Ca 2+ level nor nicotineinduced Ca 2+ influx. (a) Bovine chromaffin cells were loaded with Fluo-4AM (1 μm) in buffer A containing 0.02% of pluronic
Supplementary Figure S1: IC87114 does not affect basal Ca 2+ level nor nicotineinduced Ca 2+ influx. (a) Bovine chromaffin cells were loaded with Fluo-4AM (1 μm) in buffer A containing 0.02% of pluronic
The Role of Lipids in Flowering Development of Arabidopsis Enhanced pah1pah2 Plants. Toshiro Ito 1 & Lee Lishi 2
 The Role of Lipids in Flowering Development of Arabidopsis Enhanced pah1pah2 Plants Toshiro Ito 1 & Lee Lishi 2 Department of Biological Sciences, Faculty of Science, National University of Singapore,
The Role of Lipids in Flowering Development of Arabidopsis Enhanced pah1pah2 Plants Toshiro Ito 1 & Lee Lishi 2 Department of Biological Sciences, Faculty of Science, National University of Singapore,
Supporting Information Table of Contents
 Supporting Information Table of Contents Supporting Information Figure 1 Page 2 Supporting Information Figure 2 Page 4 Supporting Information Figure 3 Page 5 Supporting Information Figure 4 Page 6 Supporting
Supporting Information Table of Contents Supporting Information Figure 1 Page 2 Supporting Information Figure 2 Page 4 Supporting Information Figure 3 Page 5 Supporting Information Figure 4 Page 6 Supporting
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth.4257
 Supplementary Figure 1 Screen for polypeptides that affect cellular actin filaments. (a) Table summarizing results from all polypeptides tested. Source shows organism, gene, and amino acid numbers used.
Supplementary Figure 1 Screen for polypeptides that affect cellular actin filaments. (a) Table summarizing results from all polypeptides tested. Source shows organism, gene, and amino acid numbers used.
16B Flower Dissection
 16B How does the design of flower help in its pollination? Do you know where the saying the birds and the bees came from? It all started with flowers. Plants require pollinators like birds and bees to
16B How does the design of flower help in its pollination? Do you know where the saying the birds and the bees came from? It all started with flowers. Plants require pollinators like birds and bees to
