Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses. Short Answer. Figure 12.1
|
|
|
- Jody Lang
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses Short Answer Figure 12.1 Using Figure 12.1, identify the following: 1) A lymph capillary is indicated by letter. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 404 2) A lymph node is indicated by letter. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 404 3) The lymph duct is indicated by lettter. Answer: A Diff: 2 Page Ref: 404 4) Blood capillaries are indicated by letter. Answer: E Diff: 2 Page Ref: 404 5) Lymphatic collecting vessels are indicated by letter. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 404 1
2 Figure 12.2 Using Figure 12.2, identify the following: 6) The spleen is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 407 7) The tonsils are indicated by letter. Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref: 407 8) The thymus gland is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 407 9) The Peyer's patches are indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) The lymphoid organ that destroys worn-out blood cells is indicated by letter. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 407 2
3 11) The lymphoid tissues that trap and remove bacteria that enter the throat are indicated by letter. Answer: A Diff: 2 Page Ref: Fill in the blank or provide a short answer: 12) Lymph fluid and some plasma proteins originate (escape) from the. Answer: blood plasma Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Excess accumulations of fluid, which impair the exchange of materials within the tissues, is called. Answer: edema Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) The fibrous capsule of lymph nodes contains strands called that divide the node into compartments. Answer: trabeculae Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) Lymph exits the lymph node via the vessels. Answer: efferent lymphatic Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) The role of the in the lymphatic system is to remove worn-out blood cells and return some of the products to the liver. Answer: spleen Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Peyer's patches and the tonsils are part of the collection of small lymphoid tissues that protect the upper respiratory and digestive tracts from infection and are referred to as. Answer: MALT (mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue) Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) Harmful or disease-causing microorganisms from which nonspecific defenses protect the body are called. Answer: pathogens Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) The process by which WBCs and phagocytes migrate to an area experiencing acute inflammation is called. Answer: chemotaxis Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) The process by which neutrophils squeeze through capillary walls is called. Answer: diapedesis Diff: 2 Page Ref: 412 3
4 21) The binding of complement proteins to certain sugar or proteins on a foreign cell's surface is called. Answer: complement fixation Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) One effect of complement fixation that causes the cell membranes of foreign cells to become sticky so that they are easier to phagocytize is called. Answer: opsonization Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) Cells studded with protein molecules found on our own cells that do not trigger an immune response within us (but may within others) are called. Answer: self-antigens (autoantigens) Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) Troublesome small molecules or incomplete antigens that may mount an attack that is harmful rather than protective are called. Answer: haptens Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) When an antigen binds to B cell surface receptors, it becomes sensitized (activated) and undergoes. Answer: clonal selection Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) When B cells encounter antigens and produce antibodies against them, we exhibit. Answer: active immunity Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Antibodies constitute an important part of blood proteins and are also referred to as. Answer: immunoglobulins Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) The five major immunoglobulin classes are. Answer: IgM, IgA, IdD, IgG, IgE Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) The binding of antibodies to specific sites on bacterial exotoxins or viruses is called. Answer: neutralization Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) The clumping of foreign cells, a type of antigen-antibody reaction, is called. Answer: agglutination Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Killer T cells, which kill virus-invaded body cells, are also called. Answer: cytotoxic T cells Diff: 3 Page Ref: 425 4
5 32) Antigens that produce abnormally vigorous immune responses whereby the immune system causes tissue damage as it fights off a perceived threat that would otherwise be harmless are called. Answer: allergens or hypersensitivities Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Systemic (bodywide) acute allergic response caused by allergens that directly enter the blood, as with certain bee stings or spider bites, is called. Answer: anaphylactic shock Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) AIDS cripples the immune system by interfering with the activity of cells called. Answer: helper T cells Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) A tropical disease that results when parasitic worms clog the lymphatic vessels is called. Answer: elephantiasis Diff: 2 Page Ref: 431 Multiple Choice 1) The fluid that is forced out of the capillary beds by hydrostatic and osmotic pressures and into the tissue spaces is called: A) arterial blood B) venous blood C) plasma D) interstitial fluid E) lymph Answer: E Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) Lymph flows: A) in a circular pattern within the tissues B) away from the heart only C) toward the heart only D) both toward and away from the heart E) into the capillaries Diff: 1 Page Ref: 404 3) Lymph from the left arm would return to the heart through the: A) inferior vena cava B) thoracic duct C) right lymphatic duct D) left subclavian artery E) aorta Diff: 3 Page Ref: 404; 406 5
6 4) Which one of the following is NOT a mechanism that aids lymph return: A) milking action of skeletal muscles B) pressure changes within the thorax C) the pumping action of the heart D) smooth muscle contractions within the lymphatic vessels E) presence of valves within the larger lymph vessels Diff: 1 Page Ref: 404 5) Which one of the following is NOT true of lymph nodes: A) they remove foreign materials from the lymph fluid B) they have valves similar to those found in veins C) they contain lymphocytes D) they act as filters along the lymphatic vessels E) they contain macrophages Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Which lymphatic organ's major job is to destroy worn-out red blood cells and return some of the products to the liver: A) tonsils B) spleen C) thymus gland D) tonsils E) Peyer's patches Diff: 2 Page Ref: 407 7) Which lymphoid tissues trap and remove bacteria entering the throat: A) axillary lymph nodes B) cervical lymph nodes C) tonsils D) Peyer's patches E) thymus gland Diff: 2 Page Ref: 408 8) Which one of the following is NOT a type of lymphoid organ: A) spleen B) thymus gland C) tonsils D) appendix E) Peyer's patches Diff: 2 Page Ref:
7 9) The lymph organ that programs T cells and functions at peak levels only during youth is the: A) thymus B) spleen C) appendix D) tonsils E) Peyer's patches Answer: A Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) The lymph tissues found within the walls of the small intestine are called: A) tonsils B) appendix C) Peyer's patches D) thymus tissues E) intestinal nodes Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Which of these lymphoid organs is found along the left side of the abdominal cavity: A) spleen B) Peyer's patches C) thymus gland D) tonsils E) axillary lymph nodes Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) Musoca-associated lymphatic tissue (MALT) includes: A) spleen B) thymus gland C) tonsils only D) tonsils and Peyer's patches E) tonsils and spleen Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) The body's first line of defense against the invasion of disease-causing microorganisms is: A) phagocytes B) natural killer cells C) skin and mucous membranes D) inflammatory response E) fever Diff: 2 Page Ref: 409 7
8 14) Compared to the nonspecific chemicals that cover body surfaces and mucous membranes, the specific body defense system is: A) faster B) slower C) the same speed D) sometimes faster and sometimes slower E) not comparable in speed Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Which one of the following is NOT one of the nonspecific body defenses: A) intact skin B) antibody production C) the inflammatory response D) fever E) natural killer cells Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) The process by which neutrophils are squeezed through the capillary walls during the inflammatory process is called: A) agglutination B) chemotaxis C) diapedesis D) coagulation E) antibody production Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Which one of the following is NOT one of the four most common indicators of the inflammatory response: A) redness B) heat C) swelling D) fever E) pain Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) The migration of phagocytes and white blood cells to an inflamed area along a chemical gradient is called: A) diapedesis B) chemotaxis C) immunity D) perforins E) complement fixation Diff: 2 Page Ref: 411 8
9 19) The inflammatory process begins with release of chemicals, which do all of the following EXCEPT: A) dilate blood vessels B) attract phagocytes to the area C) stimulate release of lysozyme D) cause capillaries to become leaky E) activate pain receptors Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Tissues invaded by viruses, which attempt to replicate themselves by taking over cellular machinery, secrete small proteins called to protect nearby cells and hinder further multiplication of the viruses. A) histamine B) interferon C) kinins D) interleukins E) pyrogens Diff: 2 Page Ref: 413; ) The body's temperature-regulating "thermostat" that can be reset upward in response to pyrogens is located in the: A) hypothalamus B) thalamus C) pineal gland D) cerebellum E) medulla oblongata Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) Fever has the effect of doing all of the following EXCEPT: A) denaturing (scrambling) proteins B) stimulating the liver and spleen to gather up iron and zinc C) increasing metabolic rate of tissue cells D) stimulating complement fixation E) speeding up repair processes Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) The study of immunity is called: A) histology B) anatomy C) pathology D) immunology E) microbiology Diff: 1 Page Ref: 415 9
10 24) Which of the following substances is NOT typically perceived as an antigen: A) pollen grains B) bacteria C) self-antigens D) fungi E) virus particles Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Which one of the following CANNOT be said about the history of immunity: A) the ancient Greeks knew something existed within the body to protect it from infectious disease B) scientists of the 1800s discovered "factors" now called antibodies C) scientists of the 1800s demonstrated that immune serum could protect another animal from disease D) scientists of the mid-1900s discovered the viral origin of AIDS E) scientists of the mid-1900s discovered that injection of serum containing antibodies did NOT always protect a recipient from disease Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Regardless of whether it matures into a B cell or a T cell, a lymphocyte that is capable of responding to a specific antigen by binding to it is said to be: A) clonal B) incompetent C) immune D) immunocompetent E) complemented Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) The specific foreign substances that an individual's immune system has the ability to recognize and resist is determined by: A) individual exposure to the specific foreign substance B) individual genetic makeup C) the total number of lymphocytes present at a given time D) the total number of macrophages at a given time E) the total number of self-antigens at a given time Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) Which one of the following is NOT true of macrophages: A) they are considered the "big eaters" of the immune system B) they engulf foreign particles C) they circulate continuously throughout the body D) they act as antigen presenters E) they secrete monokines Diff: 2 Page Ref:
11 29) B cells develop immunocompetence in the: A) thymus gland B) bone marrow C) spleen D) thyroid gland E) lymph nodes Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) The specific type of acquired immunity that a fetus obtains from maternal antibodies that cross the placenta is called: A) naturally acquired active immunity B) naturally acquired passive immunity C) artificially acquired active immunity D) artificially acquired passive immunity E) artificially acquired natural immunity Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) What specific type of acquired immunity do vaccines provide: A) naturally acquired active immunity B) naturally acquired passive immunity C) artificially acquired active immunity D) artificially acquired passive immunity E) naturally acquired artificial immunity Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) Vaccines are NOT for: A) pneumonia B) tetanus C) measles D) snake bites E) polio Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Immune sera are used for all of the following EXCEPT: A) tuberculosis B) rabies C) snake bites D) botulism E) tetanus Answer: A Diff: 2 Page Ref:
12 34) Which one of the following is NOT true of basic antibody structure: A) they consist of four amino acid chains B) they are linked together by disulfide bonds C) the heavy chains are identical D) the heavy chains are about 400 amino acids long E) the light chains are often of differing lengths Answer: E Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) Which one of the following is NOT true of the constant (C) regions of antibodies: A) they are the same or nearly the same B) they form the "stem" of an antibody C) they determine the specific type of antibody class formed D) they form an antigen-binding site E) they determine how an antibody class will carry out its immune role Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) Which one of the following is NOT one of the antibody classes: A) IgA B) IgB C) IgD D) IgG E) IgE Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) IgA: A) is mainly found in mucus and secretions such as tears and saliva B) is passed from mother to fetus during pregnancy C) is the most abundant antibody in blood plasma D) can fix complement E) is involved in allergies Answer: A Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) Which one of the following is NOT a method by which antibodies inactivate antigens: A) agglutination B) chemotaxis C) complement fixation D) neutralization E) precipitation Diff: 2 Page Ref:
13 39) The specific antibody class that has the ability to cross the placental barrier and provide immunity to the fetus is: A) IgM B) IgA C) IgD D) IgG E) IgE Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) The process by which antibodies bind to specific sites on bacterial exotoxins (toxic chemicals secreted by bacteria) to block their harmful effects is called: A) agglutination B) chemotaxis C) complement fixation D) neutralization E) precipitation Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Antigen presentation is essential for the activation and clonal selection of: A) T cells B) B cells C) plasma cell D) antigen-presenting cells E) antibodies Answer: A Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) An isograft is a tissue graft donated by: A) an unrelated person B) a parent C) a different animal species D) the same person E) an identical twin Answer: E Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Which one of the following is NOT a type of immunosuppressive therapy given after surgery to prevent rejection of a graft: A) corticosteroids B) radiation C) antiproliferative drugs D) gamma globulin E) immunosuppressive drugs Diff: 2 Page Ref:
14 True/False 44) With immediate hypersensitivy, the antibody class that binds to mast cells and basophils that trigger the release of histamine and other chemicals is: A) IgM B) IgA C) IgD D) IgG E) IgE Answer: E Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Allergic contact dermatitis following skin contact with poison ivy would normally lead to: A) immediate hypersensitivity B) acute hypersensitivity C) delayed hypersensitivity D) anaphylactic shock E) immunodeficiency Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) The relatively common autoimmune disease in which the thyroid gland produces excessive amounts of thyroxine is called: A) multiple sclerosis B) Graves' disease C) myasthenia gravis D) glomerulonephritis E) systemic lupus erythematosis Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Which one of the following is NOT an autoimmune disease: A) AIDS B) multiple sclerosis C) Graves' disease D) type I diabetes mellitus E) rheumatoid arthritis Answer: A Diff: 2 Page Ref: 429 1) The flaplike minivalves of the lymph capillaries act like one-way swinging doors that allow lymph fluid to enter the lymph capillaries but not exit. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 404 2) The daughter cells of B cells, called plasma cells, release antibodies. Diff: 2 Page Ref:
15 3) Lymph in the right arm is returned to the heart via the right lymphatic duct. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 404 4) The thymus gland, found around the trachea, programs certain lymphocytes. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 408 5) The tonsils, spleen, thymus gland, and Peyer's patches are referred to as mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue (MALT). Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 408 6) Natural killers are unique phagocytic defense cells that can kill cancer cells and virusinfected body cells well before the immune system is activated. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 410 7) Some pathologists consider limitation of joint movement to be an additional fifth cardinal sign of inflammation. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 412 8) The final disposal of cell debris as inflammation subsides is performed by neutrophils. Answer: FALSE Diff: 3 Page Ref: 412 9) The nonspecific defense by which complement proteins attach to sugars or proteins on the surface of foreign cells is called complement fixation. Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) Chemicals secreted by white blood cells and macrophages exposed to foreign substances that can increase body temperature are called pyrogens. Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) Fever is a systemic response triggered by pyrogens. Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Like all blood cells, lymphocytes originate from hemocytoblasts contained within red bone marrow. Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) Macrophages arise from monoctyes formed within the bone marrow. Diff: 2 Page Ref:
16 14) Extremely weakened pathogens that are still alive are attenuated. Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Artificially acquired passive immunity is conferred when one receives immune serum for poisonous snake bites. Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) Antibodies are also referred to as immunoglobulins. Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) There are three major immunoglobulin classes: IgM, IgA, and IgD. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) The antibody a mother passes to her fetus is IgM. Answer: FALSE Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) The process that occurs when antibodies clump foreign cells is called agglutination. Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Memory cells are descendants of an activated B or T cell. Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) An antibody is a substance capable of provoking an immune response. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Tissue grafts harvested from an unrelated person are called xenografts. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) Allografts are tissue grafts taken from an unrelated person. Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Allergies, or hypersensitivities, are normal immune responses. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system loses its ability to tolerate selfantigens while still recognizing and attaching foreign antigens. Diff: 3 Page Ref:
17 Matching 26) Our immune system can be affected by severe stress. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 435 Match the following descriptions with the appropriate lymphoid organ or tissue: 1) Located on the left side of the A) thymus gland abdominal cavity Diff: 1 Page Ref: 407 B) spleen 2) Trap and remove bacteria C) Peyer's patches and pathogens entering the throat Diff: 2 Page Ref: 408 D) tonsils 3) Located overlying the heart Diff: 1 Page Ref: 408 4) Filters and cleanses the blood of bacteria, viruses, and other debris Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Located in the wall of the small intestines Diff: 1 Page Ref: 408 6) Located in the pharynx (throat) Diff: 1 Page Ref: 408 1) B 2) D 3) A 4) B 5) C 6) D 17
18 Match the following protective mechanism with its associated element: 7) Traps microorganisms in A) nasal hairs respiratory and digestive tracts Diff: 1 Page Ref: 409 B) mucus C) acid mantle 8) Inhibits growth of bacteria D) lacrimal secretions and fungi in female reproductive tract Diff: 1 Page Ref: 409 E) keratin 9) Contains lysozyme Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Provides resistance against acids, alkalis, and bacterial enzymes Diff: 1 Page Ref: 409 F) cilia G) gastric juice 11) Filters and traps microorganisms within inhaled air Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) Contains concentrated hydrochloric acid and protein-digested enzymes that destroy pathogens within the stomach Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) Propels debris-laden mucus away from lower respiratory passages Diff: 1 Page Ref: 409 7) B 8) C 9) D 10) E 11) A 12) G 13) F 18
19 Match the following biological function with its antibody class: 14) Believed to be cell surface A) IgD receptor of immunocompetent B cell Diff: 3 Page Ref: B) IgG C) IgA 15) First immunoglobulin class D) IgM released to plasma by plasma cells during primary response Diff: 3 Page Ref: E) IgE 16) Main antibody of primary and secondary responses Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) Bathes and protects mucosal surfaces from attachment of pathogens Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) Triggers the release of histamine Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) Potent agglutinating agent Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) Crosses placenta and provides passive immunity to fetus Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) A 15) D 16) B 17) C 18) E 19) D 20) B Essay 1) Explain the origin and pathway of lymph. Answer: Lymph fluid arises from blood plasma that has been forced out of the capillary beds by osmotic and hydrostatic pressures. The fluid left behind is called interstitial fluid. The interstitial fluid is then picked up by lymph capillaries, after which it is called lymph. Lymph is routed up the lymphatic vessels until it is finally returned to the venous system through either the right lymphatic duct or the thoracic duct. Diff: 2 Page Ref:
20 2) Describe the methods the body uses to help return lymph to the heart. Answer: The return of lymph to the heart is aided by: 1. the milking action of the skeletal muscles, 2. pressure changes in the thorax during breathing, 3. smooth muscles in the walls of the larger lymphatics contract rhythmically. Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) Describe several of the protective chemicals produced by the skin and mucous membranes. Answer: Skin produces acid secretions that inhibit bacterial growth, and sebum contains chemicals that are toxic to bacteria. Vaginal secretions are highly acidic. The stomach mucosa secretes hydrochloric acid and protein-digesting enzymes, both of which can kill pathogens. Saliva and tears contain lysozyme, an enzyme that destroys bacteria. Mucus is a sticky mucous membrane secretion that traps microorganisms. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 409 4) Identify the four most common indicators and major symptoms of an acute inflammatory response and explain their origins. Answer: The four most common indicators of the inflammatory response are redness, heat, swelling, and pain. Redness and heat are a result of dilation of blood vessels that increase blood flow to the injured area. Swelling occurs when increased permeability of the capillaries allows plasma to leak from the bloodstream into the tissue spaces. The excess fluid, or edema, triggers the activation of pain receptors in the area, accounting for the pain associated with an injury. Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) List and describe the cells and chemicals the body uses as its second line of defense. Answer: 1. Phagocytes, such as neutrophils or macrophages, engulf foreign particles. These cells are in nearly every body organ and confront pathogens that make it through the surface membrane barriers. 2. Natural killer cells, found in blood and lymph, are lymphocytes. They can lyse and kill cancer cells and virus-infected body cells. 3. The inflammatory response is a nonspecific response that occurs when body tissues are injured. Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Describe the four major types of transplant grafts. Answer: Autografts are tissue grafts transplanted from one site to another within the same person. Isografts are tissue grafts harvested from a genetically identical person (identical twin). Allografts are tissue grafts harvested from an unrelated person. Xenografts are tissue grafts harvested from different animal species. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 427 7) Explain three current theories that attempt to explain why self-tolerance breaks down in autoimmune disorders. Answer: Inefficient lymphocyte programming is one theory that suggests self-reactive B or T cells escape to the rest of the body. Another theory is that self-proteins appear within the circulation that were not previously exposed to the immune system, thus initiating an immune response. These "hidden" antigens are found in sperm cells, the eye lens, and thyroid proteins. Another theory is that antibodies produced against foreign antigens cross-react with self-antigens such as when streptococcal bacteria crossreact with heart antigens causing rheumatic fever. Diff: 3 Page Ref:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses. Short Answer. Figure 12.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses Short Answer Figure 12.1 Using Figure 12.1, identify the following: 1) A lymph capillary is indicated
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses Short Answer Figure 12.1 Using Figure 12.1, identify the following: 1) A lymph capillary is indicated
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e (Marieb) Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses Multiple Choice Part I Questions
 Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e (Marieb) Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses 12.1 Multiple Choice Part I Questions Using Figure 12.1, identify the following: 1) A lymph capillary
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e (Marieb) Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses 12.1 Multiple Choice Part I Questions Using Figure 12.1, identify the following: 1) A lymph capillary
Unit 12: The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
 Unit 12: The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses I. The Lymphatic System A. Consists of two semi-independent parts 1. Lymphatic vessels 2. Lymphoid tissues and organs B. Lymphatic system functions 1. Transports
Unit 12: The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses I. The Lymphatic System A. Consists of two semi-independent parts 1. Lymphatic vessels 2. Lymphoid tissues and organs B. Lymphatic system functions 1. Transports
Unit 12 - The Lymphatic System and 1
 Unit 12 - The Lymphatic System and 1 I. Unit 12: The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses A. The Lymphatic System 1. Consists of two semi-independent parts a) Lymphatic vessels b) Lymphoid tissues and organs
Unit 12 - The Lymphatic System and 1 I. Unit 12: The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses A. The Lymphatic System 1. Consists of two semi-independent parts a) Lymphatic vessels b) Lymphoid tissues and organs
The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses 12PART B Adaptive Defense System: Third Line of Defense Immune
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses 12PART B Adaptive Defense System: Third Line of Defense Immune
Chapter 12- The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
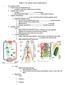 Chapter 12- The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses I. The Lymphatic System a. Consists of two semi-independent parts i. Lymphatic vessels and Lymphoid tissues and organs b. Lymphatic system functions i.
Chapter 12- The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses I. The Lymphatic System a. Consists of two semi-independent parts i. Lymphatic vessels and Lymphoid tissues and organs b. Lymphatic system functions i.
The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
 12 PART A The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
12 PART A The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses Slides 12.1 12.22 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Lymphatic
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses Slides 12.1 12.22 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Lymphatic
Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System
 Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System Immune System Composed of many nonspecific and specific defenses Lymphatic System also plays an important role in establishing immunity Lymphatic System Major components
Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System Immune System Composed of many nonspecific and specific defenses Lymphatic System also plays an important role in establishing immunity Lymphatic System Major components
2/28/18. Lymphatic System and Immunity. Introduction. Anatomy. Chapter 27. Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system
 Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 1 Introduction Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 1 Introduction Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
- Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body. - Has disease-fighting functions - Helps maintain homeostasis
 Introduction Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
Introduction Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
immunity produced by an encounter with an antigen; provides immunologic memory. active immunity clumping of (foreign) cells; induced by crosslinking
 active immunity agglutination allografts immunity produced by an encounter with an antigen; provides immunologic memory. clumping of (foreign) cells; induced by crosslinking of antigenantibody complexes.
active immunity agglutination allografts immunity produced by an encounter with an antigen; provides immunologic memory. clumping of (foreign) cells; induced by crosslinking of antigenantibody complexes.
The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses Outline PART 1: INNATE DEFENSES 21.1 Surface barriers act as the first line of defense to keep
 The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses Outline PART 1: INNATE DEFENSES 21.1 Surface barriers act as the first line of defense to keep invaders out of the body (pp. 772 773; Fig. 21.1; Table
The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses Outline PART 1: INNATE DEFENSES 21.1 Surface barriers act as the first line of defense to keep invaders out of the body (pp. 772 773; Fig. 21.1; Table
CHAPTER 16: LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY OBJECTIVES. Transport dietary fat. Transport excess tissue fluid back to blood stream
 CHAPTER 16: LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY OBJECTIVES 1. Name the organs that compose the lymphatic system and give three general functions performed by this system. Bone Marrow Control Disease Thymus Lymph
CHAPTER 16: LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY OBJECTIVES 1. Name the organs that compose the lymphatic system and give three general functions performed by this system. Bone Marrow Control Disease Thymus Lymph
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 11 AND 12
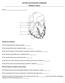 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 11 AND 12 Name Identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label. 2) The sinoatrial (SA) node is indicated by letter. 3) The specific chamber
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 11 AND 12 Name Identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label. 2) The sinoatrial (SA) node is indicated by letter. 3) The specific chamber
(b) fluid returns to venous end of capillary due to hydrostatic pressure and osmotic pressure
 (Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Lymphatic System and Immunity (Body Defenses) I. (Slide 2) Introduction A) General 1) Lymphatic System performs 2 basic functions: 2) Organs of the Lymphatic System (a) lymphatic
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Lymphatic System and Immunity (Body Defenses) I. (Slide 2) Introduction A) General 1) Lymphatic System performs 2 basic functions: 2) Organs of the Lymphatic System (a) lymphatic
Body Defense Mechanisms
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 13 Body Defense Mechanisms Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 13 Body Defense Mechanisms Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 13 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
What are bacteria? Microbes are microscopic(bacteria, viruses, prions, & some fungi etc.) How do the sizes of our cells, bacteria and viruses compare?
 7.1 Microbes, pathogens and you Chp. 7 Lymphatic System & Immunity The interaction between microbes and humans? Microbes are very abundant in the environment and as well as in and on our bodies GOOD: We
7.1 Microbes, pathogens and you Chp. 7 Lymphatic System & Immunity The interaction between microbes and humans? Microbes are very abundant in the environment and as well as in and on our bodies GOOD: We
Topics in Parasitology BLY Vertebrate Immune System
 Topics in Parasitology BLY 533-2008 Vertebrate Immune System V. Vertebrate Immune System A. Non-specific defenses against pathogens 1. Skin - physical barrier a. Tough armor protein KERATIN b. Surface
Topics in Parasitology BLY 533-2008 Vertebrate Immune System V. Vertebrate Immune System A. Non-specific defenses against pathogens 1. Skin - physical barrier a. Tough armor protein KERATIN b. Surface
Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 The Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems 1 The Lymphatic Vessels Lymphoid Organs Three functions contribute to homeostasis 1. Return excess tissue fluid to the bloodstream 2. Help defend the body against
The Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems 1 The Lymphatic Vessels Lymphoid Organs Three functions contribute to homeostasis 1. Return excess tissue fluid to the bloodstream 2. Help defend the body against
Chapter 14. Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Chapter 14 Lymphatic System and Immunity 1 Introduction A. The lymphatic system is comprised of a network of vessels that transport body fluids, the cells and chemicals in those vessels and the organs
Chapter 14 Lymphatic System and Immunity 1 Introduction A. The lymphatic system is comprised of a network of vessels that transport body fluids, the cells and chemicals in those vessels and the organs
Immune system. Aims. Immune system. Lymphatic organs. Inflammation. Natural immune system. Adaptive immune system
 Aims Immune system Lymphatic organs Inflammation Natural immune system Adaptive immune system Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) Disorders of the immune system 1 2 Immune system Lymphoid organs Immune
Aims Immune system Lymphatic organs Inflammation Natural immune system Adaptive immune system Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) Disorders of the immune system 1 2 Immune system Lymphoid organs Immune
1. Lymphatic vessels recover about of the fluid filtered by capillaries. A. ~1% C. ~25% E. ~85% B. ~10% D. ~50%
 BIOL2030 Huaman A&P II -- Exam 3 -- XXXX -- Form A Name: 1. Lymphatic vessels recover about of the fluid filtered by capillaries. A. ~1% C. ~25% E. ~85% B. ~10% D. ~50% 2. Special lymphatic vessels called
BIOL2030 Huaman A&P II -- Exam 3 -- XXXX -- Form A Name: 1. Lymphatic vessels recover about of the fluid filtered by capillaries. A. ~1% C. ~25% E. ~85% B. ~10% D. ~50% 2. Special lymphatic vessels called
3/17/2014. The Lymphatic System. Lymphatic System Overview Lymphatic Vessels and Flow of Lymph Lymphoid Cells, Tissues, and Organs
 The Lymphatic System Lymphatic System Overview Lymphatic Vessels and Flow of Lymph Lymphoid Cells, Tissues, and Organs Overview of the Lymphatic System Slide 2 Major Components of the Lymphatic System
The Lymphatic System Lymphatic System Overview Lymphatic Vessels and Flow of Lymph Lymphoid Cells, Tissues, and Organs Overview of the Lymphatic System Slide 2 Major Components of the Lymphatic System
Chapter 23 Immunity Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 23 Immunity Exam Study Questions 1. Define 1) Immunity 2) Neutrophils 3) Macrophage 4) Epitopes 5) Interferon 6) Complement system 7) Histamine 8) Mast cells 9) Antigen 10) Antigens receptors 11)
Chapter 23 Immunity Exam Study Questions 1. Define 1) Immunity 2) Neutrophils 3) Macrophage 4) Epitopes 5) Interferon 6) Complement system 7) Histamine 8) Mast cells 9) Antigen 10) Antigens receptors 11)
Overview of the Lymphoid System
 Overview of the Lymphoid System The Lymphoid System Protects us against disease Lymphoid system cells respond to Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells, such as cancers Overview of the Lymphoid
Overview of the Lymphoid System The Lymphoid System Protects us against disease Lymphoid system cells respond to Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells, such as cancers Overview of the Lymphoid
Immune System. Biol 105 Lecture 16 Chapter 13
 Immune System Biol 105 Lecture 16 Chapter 13 Outline Immune System I. Function of the Immune system II. Barrier Defenses III. Nonspecific Defenses A. Immune system cells B. Inflammatory response C. Complementary
Immune System Biol 105 Lecture 16 Chapter 13 Outline Immune System I. Function of the Immune system II. Barrier Defenses III. Nonspecific Defenses A. Immune system cells B. Inflammatory response C. Complementary
Chapter 21: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses
 Chapter 21: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses I. 2 main types of body defenses A. Innate (nonspecific) defense: not to a specific microorganism or substance B. Adaptive (specific) defense: immunity to
Chapter 21: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses I. 2 main types of body defenses A. Innate (nonspecific) defense: not to a specific microorganism or substance B. Adaptive (specific) defense: immunity to
Lymphatic System and Immune System. Blood capillaries. Lymphatic vessels/ lymph nodes. Then, identify by labeling these specific structures in part B.
 Name: Date: Period: Lymphatic System and Immune System 1. Figure 21.1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. In part A the relationship between lymphatic vessels and the blood vessels of the cardiovascular
Name: Date: Period: Lymphatic System and Immune System 1. Figure 21.1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. In part A the relationship between lymphatic vessels and the blood vessels of the cardiovascular
Immune System. Biol 105 Chapter 13
 Immune System Biol 105 Chapter 13 Outline Immune System I. Function of the Immune system II. Barrier Defenses III. Nonspecific Defenses A. Immune system cells B. Inflammatory response C. Complementary
Immune System Biol 105 Chapter 13 Outline Immune System I. Function of the Immune system II. Barrier Defenses III. Nonspecific Defenses A. Immune system cells B. Inflammatory response C. Complementary
Diseases-causing agents, pathogens, can produce infections within the body.
 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II 1 CHAPTER 16 Lecture: Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. LYMPHATIC and IMMUNE Systems Body Defenses Against
BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II 1 CHAPTER 16 Lecture: Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. LYMPHATIC and IMMUNE Systems Body Defenses Against
Chapter 24 The Immune System
 Chapter 24 The Immune System The Immune System Layered defense system The skin and chemical barriers The innate and adaptive immune systems Immunity The body s ability to recognize and destroy specific
Chapter 24 The Immune System The Immune System Layered defense system The skin and chemical barriers The innate and adaptive immune systems Immunity The body s ability to recognize and destroy specific
4/28/2016. Host Defenses. Unit 8 Microorganisms & The Immune System. Types of Innate Defenses. Defensive Cells Leukocytes
 Host Defenses Unit 8 Microorganisms & The Immune System CH 16-18 Host defenses that produce resistance can be either innate or adaptive: Innate: those that protect against any type of invading agent Adaptive:
Host Defenses Unit 8 Microorganisms & The Immune System CH 16-18 Host defenses that produce resistance can be either innate or adaptive: Innate: those that protect against any type of invading agent Adaptive:
Blood and Immune system Acquired Immunity
 Blood and Immune system Acquired Immunity Immunity Acquired (Adaptive) Immunity Defensive mechanisms include : 1) Innate immunity (Natural or Non specific) 2) Acquired immunity (Adaptive or Specific) Cell-mediated
Blood and Immune system Acquired Immunity Immunity Acquired (Adaptive) Immunity Defensive mechanisms include : 1) Innate immunity (Natural or Non specific) 2) Acquired immunity (Adaptive or Specific) Cell-mediated
Internal Defense Notes
 Internal environment of animals provides attractive area for growth of bacteria, viruses, fungi Harm via: 1. destruction of cells 2. production of toxic chemicals To protect against foreign invaders, humans
Internal environment of animals provides attractive area for growth of bacteria, viruses, fungi Harm via: 1. destruction of cells 2. production of toxic chemicals To protect against foreign invaders, humans
Outline. Animals: Immunity. Defenses Against Disease. Key Concepts:
 Animals: Immunity Defenses Against Disease Outline 1. Key concepts 2. Physical barriers: Skin, Mucus and HCL in stomach 3. Non-specific 4. Specific responses Immune System a. Components of Immune system
Animals: Immunity Defenses Against Disease Outline 1. Key concepts 2. Physical barriers: Skin, Mucus and HCL in stomach 3. Non-specific 4. Specific responses Immune System a. Components of Immune system
Immune System Notes Innate immunity Acquired immunity lymphocytes, humoral response Skin lysozyme, mucus membrane
 Immune System Notes I. The immune system consists of innate and acquired immunity. A. An animal must defend itself against unwelcome intruders the many potentially dangerous viruses, bacteria, and other
Immune System Notes I. The immune system consists of innate and acquired immunity. A. An animal must defend itself against unwelcome intruders the many potentially dangerous viruses, bacteria, and other
LYMPHATIC AND IMMUNE SYSTEMS. Chapter 33
 LYMPHATIC AND IMMUNE SYSTEMS Chapter 33 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM The lymphatic system has three main functions Take up excess tissue fluid and return it to the bloodstream Receive fats called lipoproteins
LYMPHATIC AND IMMUNE SYSTEMS Chapter 33 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM The lymphatic system has three main functions Take up excess tissue fluid and return it to the bloodstream Receive fats called lipoproteins
Immune System. Biology 105 Lecture 16 Chapter 13
 Immune System Biology 105 Lecture 16 Chapter 13 Outline: Immune System I. Functions of the immune system II. Barrier defenses III. Non-specific defenses A. Immune system cells B. Inflammatory response
Immune System Biology 105 Lecture 16 Chapter 13 Outline: Immune System I. Functions of the immune system II. Barrier defenses III. Non-specific defenses A. Immune system cells B. Inflammatory response
4) What causes lymph to move? Skeletal muscle contraction; smooth muscle contraction, breathing (like blood moves through veins)
 NPHS Anatomy & Physiology UNIT 10 REVIEW GUIDE Lymphatic System 1) List the three functions of the lymphatic system. transports excess fluid to the bloodstream absorbs fats helps defend the body against
NPHS Anatomy & Physiology UNIT 10 REVIEW GUIDE Lymphatic System 1) List the three functions of the lymphatic system. transports excess fluid to the bloodstream absorbs fats helps defend the body against
Lymphatic System. Where s your immunity idol?
 Lymphatic System Where s your immunity idol? Functions of the Lymphatic System Fluid Balance Drains excess fluid from tissues Lymph contains solutes from plasma Fat Absorption Lymphatic system absorbs
Lymphatic System Where s your immunity idol? Functions of the Lymphatic System Fluid Balance Drains excess fluid from tissues Lymph contains solutes from plasma Fat Absorption Lymphatic system absorbs
2. The normal of the gut, and vagina keep the growth of pathogens in check. 3. in the respiratory tract sweep out bacteria and particles.
 Chapter 39 Immunity I. Three Lines of Defense A. Surface Barriers to Invasion 1. is an important barrier. 2. The normal of the gut, and vagina keep the growth of pathogens in check. 3. in the respiratory
Chapter 39 Immunity I. Three Lines of Defense A. Surface Barriers to Invasion 1. is an important barrier. 2. The normal of the gut, and vagina keep the growth of pathogens in check. 3. in the respiratory
3/28/2012. Immune System. Activation of Innate Immunity. Innate (non-specific) Immunity
 Chapter 5 Outline Defense Mechansims Functions of B Lymphocytes Functions of T Lymphocytes Active and Passive Immunity Tumor Immunology Diseases Caused By Immune System Immune System Anatomy - Lymphoid
Chapter 5 Outline Defense Mechansims Functions of B Lymphocytes Functions of T Lymphocytes Active and Passive Immunity Tumor Immunology Diseases Caused By Immune System Immune System Anatomy - Lymphoid
Chapter 16 Lymphatic System and Immunity. Lymphatic Pathways. Lymphatic Capillaries. network of vessels that assist in circulating fluids
 Chapter 16 Lymphatic System and Immunity network of vessels that assist in circulating fluids closely associated with the cardiovascular system transports excess fluid away from interstitial spaces transports
Chapter 16 Lymphatic System and Immunity network of vessels that assist in circulating fluids closely associated with the cardiovascular system transports excess fluid away from interstitial spaces transports
NOTES: CH 43, part 2 Immunity; Immune Disruptions ( )
 NOTES: CH 43, part 2 Immunity; Immune Disruptions (43.3-43.4) Activated B & T Lymphocytes produce: CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNE RESPONSE: involves specialized T cells destroying infected host cells HUMORAL IMMUNE
NOTES: CH 43, part 2 Immunity; Immune Disruptions (43.3-43.4) Activated B & T Lymphocytes produce: CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNE RESPONSE: involves specialized T cells destroying infected host cells HUMORAL IMMUNE
Physiology Unit 3. ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY The Specific Immune Response
 Physiology Unit 3 ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY The Specific Immune Response In Physiology Today The Adaptive Arm of the Immune System Specific Immune Response Internal defense against a specific pathogen Acquired
Physiology Unit 3 ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY The Specific Immune Response In Physiology Today The Adaptive Arm of the Immune System Specific Immune Response Internal defense against a specific pathogen Acquired
Chapter 17. The Lymphatic System and Immunity. Copyright 2010, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 17 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Immunity Innate Immunity Fast, non-specific and no memory Barriers, ph extremes, Phagocytes & NK cells, fever, inflammation, complement, interferon Adaptive
Chapter 17 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Immunity Innate Immunity Fast, non-specific and no memory Barriers, ph extremes, Phagocytes & NK cells, fever, inflammation, complement, interferon Adaptive
The Lymphatic System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
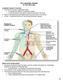 The Lymphatic System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Lymphatic System: Overview Consists of two semi-independent parts o A meandering network of lymphatic vessels o Lymphoid tissues and organs scattered throughout the
The Lymphatic System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Lymphatic System: Overview Consists of two semi-independent parts o A meandering network of lymphatic vessels o Lymphoid tissues and organs scattered throughout the
Chapter 07 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 07 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 07 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 24 The Immune System Multiple-Choice Questions
 Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 24 The Immune System 24.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The body's innate defenses against infection include A) several nonspecific
Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 24 The Immune System 24.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The body's innate defenses against infection include A) several nonspecific
The Immune System is the Third Line of Defense Against Infection. Components of Human Immune System
 Chapter 17: Specific Host Defenses: The Immune Response The Immune Response Immunity: Free from burden. Ability of an organism to recognize and defend itself against specific pathogens or antigens. Immune
Chapter 17: Specific Host Defenses: The Immune Response The Immune Response Immunity: Free from burden. Ability of an organism to recognize and defend itself against specific pathogens or antigens. Immune
Lymphatic System. Chapter 14. Introduction. Main Channels of Lymphatics. Lymphatics. Lymph Tissue. Major Lymphatic Vessels of the Trunk
 Lymphatic System Chapter 14 Components Lymph is the fluid Vessels lymphatics Structures & organs Functions Return tissue fluid to the bloodstream Transport fats from the digestive tract to the bloodstream
Lymphatic System Chapter 14 Components Lymph is the fluid Vessels lymphatics Structures & organs Functions Return tissue fluid to the bloodstream Transport fats from the digestive tract to the bloodstream
Chapter 43. Immune System. phagocytosis. lymphocytes. AP Biology
 Chapter 43. Immune System phagocytosis lymphocytes 1 Why an immune system? Attack from outside lots of organisms want you for lunch! animals must defend themselves against unwelcome invaders viruses protists
Chapter 43. Immune System phagocytosis lymphocytes 1 Why an immune system? Attack from outside lots of organisms want you for lunch! animals must defend themselves against unwelcome invaders viruses protists
All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 In innate immunity, recognition and
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 In innate immunity, recognition and
CHAPTER-VII IMMUNOLOGY R.KAVITHA, M.PHARM, LECTURER, DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACEUTICS, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY, SRM UNIVERSITY, KATTANKULATHUR.
 CHAPTER-VII IMMUNOLOGY R.KAVITHA, M.PHARM, LECTURER, DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACEUTICS, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY, SRM UNIVERSITY, KATTANKULATHUR. The Immune Response Immunity: Free from burden. Ability of an
CHAPTER-VII IMMUNOLOGY R.KAVITHA, M.PHARM, LECTURER, DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACEUTICS, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY, SRM UNIVERSITY, KATTANKULATHUR. The Immune Response Immunity: Free from burden. Ability of an
Chapter 38- Immune System
 Chapter 38- Immune System First Line of Defense: Barriers Nonspecific defenses, such as the skin and mucous membranes, are barriers to potential pathogens. In addition to being a physical barrier to pathogens,
Chapter 38- Immune System First Line of Defense: Barriers Nonspecific defenses, such as the skin and mucous membranes, are barriers to potential pathogens. In addition to being a physical barrier to pathogens,
Chapter 24 The Immune System
 Chapter 24 The Immune System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction: The Kissing Disease?!?
Chapter 24 The Immune System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction: The Kissing Disease?!?
Warm-up. Parts of the Immune system. Disease transmission. Disease transmission. Why an immune system? Chapter 43 3/9/2012.
 Warm-up Objective: Explain how antigens react with specific lymphocytes to induce immune response and immunological memory. Warm-up: Which of the following would normally contain blood with the least amount
Warm-up Objective: Explain how antigens react with specific lymphocytes to induce immune response and immunological memory. Warm-up: Which of the following would normally contain blood with the least amount
The Lymphatic System and Immunity. Chapters 20 & 21
 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapters 20 & 21 Objectives 1. SC.912.L.14.52 - Explain the basic functions of the human immune system, including specific and nonspecific immune response, vaccines, and
The Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapters 20 & 21 Objectives 1. SC.912.L.14.52 - Explain the basic functions of the human immune system, including specific and nonspecific immune response, vaccines, and
Defense & the Immune System. Immune System Agenda 4/28/2010. Overview. The bigger picture Non specific defenses Specific defenses (Immunity)
 Defense &The Immune System Overview Immune System Agenda The bigger picture Non specific defenses Specific defenses (Immunity) Defense & the Immune System Big Picture Defense Any means of preventing or
Defense &The Immune System Overview Immune System Agenda The bigger picture Non specific defenses Specific defenses (Immunity) Defense & the Immune System Big Picture Defense Any means of preventing or
Chapter Pages Transmission
 Chapter 19.2 Pages 442-448 Transmission Immunity There are three lines of defense: 1 The skin and mucous membranes are a nonspecific barrier to infection. 2 Macrophages attack pathogens that enter the
Chapter 19.2 Pages 442-448 Transmission Immunity There are three lines of defense: 1 The skin and mucous membranes are a nonspecific barrier to infection. 2 Macrophages attack pathogens that enter the
I. Defense Mechanisms Chapter 15
 10/24/11 I. Defense Mechanisms Chapter 15 Immune System Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Defense Mechanisms Protect against
10/24/11 I. Defense Mechanisms Chapter 15 Immune System Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Defense Mechanisms Protect against
I. Lines of Defense Pathogen: Table 1: Types of Immune Mechanisms. Table 2: Innate Immunity: First Lines of Defense
 I. Lines of Defense Pathogen: Table 1: Types of Immune Mechanisms Table 2: Innate Immunity: First Lines of Defense Innate Immunity involves nonspecific physical & chemical barriers that are adapted for
I. Lines of Defense Pathogen: Table 1: Types of Immune Mechanisms Table 2: Innate Immunity: First Lines of Defense Innate Immunity involves nonspecific physical & chemical barriers that are adapted for
AP Biology. Why an immune system? Chapter 43. Immune System. Lines of defense. 1st: External defense. 2nd: Internal, broad range patrol
 Chapter 43. Immune System lymphocytes attacking cancer cell lymph phagocytic leukocyte Why an immune system? Attack from outside lots of organisms want you for lunch! animals must defend themselves against
Chapter 43. Immune System lymphocytes attacking cancer cell lymph phagocytic leukocyte Why an immune system? Attack from outside lots of organisms want you for lunch! animals must defend themselves against
Unit 5 The Human Immune Response to Infection
 Unit 5 The Human Immune Response to Infection Unit 5-page 1 FOM Chapter 21 Resistance and the Immune System: Innate Immunity Preview: In Chapter 21, we will learn about the branch of the immune system
Unit 5 The Human Immune Response to Infection Unit 5-page 1 FOM Chapter 21 Resistance and the Immune System: Innate Immunity Preview: In Chapter 21, we will learn about the branch of the immune system
3. Lymphocyte proliferation (fig. 15.4): Clones of responder cells and memory cells are derived from B cells and T cells.
 Chapter 15 Adaptive, Specific Immunity and Immunization* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. Specific
Chapter 15 Adaptive, Specific Immunity and Immunization* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. Specific
~ons~ecific Bod~ Defenses and Immunity
 ~ons~ecific Bod~ Defenses and Immunity The human body continually attempts to maintain homeostasis by counteracting harmful or disease-producing organisms called pathoqens or the toxins they produce. The
~ons~ecific Bod~ Defenses and Immunity The human body continually attempts to maintain homeostasis by counteracting harmful or disease-producing organisms called pathoqens or the toxins they produce. The
Immune System. Before You Read. Read to Learn
 Immune System 37 section 2 The Immune System Biology/Life Sciences 10.b Students know the role of antibodies in the body s response to infection. Also covers: Biology/Life Sciences 10.a, 10.e, 10.f Components
Immune System 37 section 2 The Immune System Biology/Life Sciences 10.b Students know the role of antibodies in the body s response to infection. Also covers: Biology/Life Sciences 10.a, 10.e, 10.f Components
phagocytic leukocyte Immune System lymphocytes attacking cancer cell lymph system
 phagocytic leukocyte Immune System lymphocytes attacking cancer cell lymph system 2006-2007 1) recognizing the presence of an infection; 2) containing the infection and working to eliminate it; 3) regulating
phagocytic leukocyte Immune System lymphocytes attacking cancer cell lymph system 2006-2007 1) recognizing the presence of an infection; 2) containing the infection and working to eliminate it; 3) regulating
General Biology. A summary of innate and acquired immunity. 11. The Immune System. Repetition. The Lymphatic System. Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.
 A summary of innate and acquired immunity General iology INNATE IMMUNITY Rapid responses to a broad range of microbes Course No: NG00 Credits:.00 External defenses Invading microbes (pathogens). The Immune
A summary of innate and acquired immunity General iology INNATE IMMUNITY Rapid responses to a broad range of microbes Course No: NG00 Credits:.00 External defenses Invading microbes (pathogens). The Immune
Overview. Barriers help animals defend against many dangerous pathogens they encounter.
 Immunity Overview Barriers help animals defend against many dangerous pathogens they encounter. The immune system recognizes foreign bodies and responds with the production of immune cells and proteins.
Immunity Overview Barriers help animals defend against many dangerous pathogens they encounter. The immune system recognizes foreign bodies and responds with the production of immune cells and proteins.
The Immune System. These are classified as the Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses. Innate Immunity
 The Immune System Biological mechanisms that defend an organism must be 1. triggered by a stimulus upon injury or pathogen attack 2. able to counteract the injury or invasion 3. able to recognise foreign
The Immune System Biological mechanisms that defend an organism must be 1. triggered by a stimulus upon injury or pathogen attack 2. able to counteract the injury or invasion 3. able to recognise foreign
Ch. 11: Immune Physiology. 1. Review Immune Organs & Cells. Immune system = The cells and organs involved in defense against pathogens and cancer.
 Ch. 11: Immune Physiology Objectives: 1. Review immune organs & cells. 2. Two types of immunity. 3. Understand functions of immune cells (T-cells and B-cells) 4. Understand autoimmunity disorders. 1. Review
Ch. 11: Immune Physiology Objectives: 1. Review immune organs & cells. 2. Two types of immunity. 3. Understand functions of immune cells (T-cells and B-cells) 4. Understand autoimmunity disorders. 1. Review
The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately
 The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 INNATE IMMUNITY (all animals) Recognition of traits shared
The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 INNATE IMMUNITY (all animals) Recognition of traits shared
Lymphatic System. The targets of the immune defenses are infectious organisms such as,, parasites, fungi, and some protists.
 Lymphatic System I. Non-specific Defenses The immune system is a body wide network of cells and organs that have evolved to defend the body against attacks by invaders. The targets of the immune defenses
Lymphatic System I. Non-specific Defenses The immune system is a body wide network of cells and organs that have evolved to defend the body against attacks by invaders. The targets of the immune defenses
LYMPHATIC SYSTEM LAB WORKSHEET
 NAME: Pd 4 DATE: LYMPHATIC SYSTEM LAB WORKSHEET ACTIVITY 1: Answer the following questions 1. What is lymph? What is the normal composition of lymph? How does the composition of lymph differs from that
NAME: Pd 4 DATE: LYMPHATIC SYSTEM LAB WORKSHEET ACTIVITY 1: Answer the following questions 1. What is lymph? What is the normal composition of lymph? How does the composition of lymph differs from that
NOTES: CH 43, part 1 The Immune System - Nonspecific & Specific Defenses ( )
 NOTES: CH 43, part 1 The Immune System - Nonspecific & Specific Defenses (43.1-43.2) The lymphatic system is closely associated with the cardiovascular system. LYMPHATIC PATHWAYS Lymphatic capillaries
NOTES: CH 43, part 1 The Immune System - Nonspecific & Specific Defenses (43.1-43.2) The lymphatic system is closely associated with the cardiovascular system. LYMPHATIC PATHWAYS Lymphatic capillaries
Immune System. Presented by Kazzandra Anton, Rhea Chung, Lea Sado, and Raymond Tanaka
 Immune System Presented by Kazzandra Anton, Rhea Chung, Lea Sado, and Raymond Tanaka Content Standards 35.1 In innate immunity, recognition and response rely on traits common to groups of pathogens 35.2
Immune System Presented by Kazzandra Anton, Rhea Chung, Lea Sado, and Raymond Tanaka Content Standards 35.1 In innate immunity, recognition and response rely on traits common to groups of pathogens 35.2
Immunity. Chapter 38
 Immunity Chapter 38 Impacts, Issues Frankie s Last Wish Infection with a common, sexually transmitted virus (HPV) causes most cervical cancers including the one that killed Frankie McCullogh 38.1 Integrated
Immunity Chapter 38 Impacts, Issues Frankie s Last Wish Infection with a common, sexually transmitted virus (HPV) causes most cervical cancers including the one that killed Frankie McCullogh 38.1 Integrated
Guided Reading Activities
 Name Period Chapter 24: The Immune System Guided Reading Activities Big idea: Innate immunity Answer the following questions as you read modules 24.1 24.2: 1. Bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms
Name Period Chapter 24: The Immune System Guided Reading Activities Big idea: Innate immunity Answer the following questions as you read modules 24.1 24.2: 1. Bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms
The Lymphatic System. Innate Immunity
 The Lymphatic System Innate Immunity 1 Types of Immunity Innate (non-specific) immunity Adaptive (specific) immunity The human body has several different ways that it defends itself against infection by
The Lymphatic System Innate Immunity 1 Types of Immunity Innate (non-specific) immunity Adaptive (specific) immunity The human body has several different ways that it defends itself against infection by
Section 9: Lymphatic system and immunity A. Definitions Bacteria Viruses Prions Lines of Defence: How we fight the invaders
 Section 9: Lymphatic system and immunity A. Definitions 1. Microbes = microscopic organisms such as bacteria Some microbes are useful to humans: contribute to production of yogurt, cheese, bread, beer,
Section 9: Lymphatic system and immunity A. Definitions 1. Microbes = microscopic organisms such as bacteria Some microbes are useful to humans: contribute to production of yogurt, cheese, bread, beer,
Unit 3 Dynamic Equilibrium Chapter Immune System
 Biology 2201 Unit 3 Dynamic Equilibrium Chapter 11.4 - Immune System Compiled by S. Whalen What is Immunity? Immunity Immunity The ability of the body to fight infection and/or foreign invaders by producing
Biology 2201 Unit 3 Dynamic Equilibrium Chapter 11.4 - Immune System Compiled by S. Whalen What is Immunity? Immunity Immunity The ability of the body to fight infection and/or foreign invaders by producing
Anatomy. Lymph: Tissue fluid that enters a lymphatic capillary (clear fluid that surrounds new piercings!)
 Lymphatic System Anatomy Lymphatic vessels: meet up in capillaries of of tissues to collect extra water, and have an end point of meeting up with lymphatic ducts that empty fluid into large veins in the
Lymphatic System Anatomy Lymphatic vessels: meet up in capillaries of of tissues to collect extra water, and have an end point of meeting up with lymphatic ducts that empty fluid into large veins in the
Unit 23: Immunity from Disease
 Unit 5 The Human Body Unit 23 Immunity from Disease- Unit 23: Immunity from Disease Name: Period: Page 1 of 51 Unit 5 The Human Body Unit 23 Immunity from Disease- Chapter 23 assignments Pages/Sections
Unit 5 The Human Body Unit 23 Immunity from Disease- Unit 23: Immunity from Disease Name: Period: Page 1 of 51 Unit 5 The Human Body Unit 23 Immunity from Disease- Chapter 23 assignments Pages/Sections
Third line of Defense
 Chapter 15 Specific Immunity and Immunization Topics -3 rd of Defense - B cells - T cells - Specific Immunities Third line of Defense Specific immunity is a complex interaction of immune cells (leukocytes)
Chapter 15 Specific Immunity and Immunization Topics -3 rd of Defense - B cells - T cells - Specific Immunities Third line of Defense Specific immunity is a complex interaction of immune cells (leukocytes)
Ch. 22 The Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Ch. 22 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Above: macrophage (gray), T lymphocyte (pink), and bacteria (orange) The lymphatic system General functions: It acts with other organ systems to help provide immunity
Ch. 22 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Above: macrophage (gray), T lymphocyte (pink), and bacteria (orange) The lymphatic system General functions: It acts with other organ systems to help provide immunity
The Immune System. by Dr. Carmen Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College
 The Immune System by Dr. Carmen Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College What is the immune system? defense system found in vertebrates Two categories Nonspecific specific provides protection from pathogens
The Immune System by Dr. Carmen Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College What is the immune system? defense system found in vertebrates Two categories Nonspecific specific provides protection from pathogens
Instructor s Guide. Films for the. Humanities & Sciences i A Wealth of Information. A World of Ideas. The Human Body: How It Works THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
 i A Wealth of Information. A World of Ideas. Instructor s Guide The Human Body: How It Works Introduction This program is part of the nine-part series The Human Body: How It Works. The series uses physiologic
i A Wealth of Information. A World of Ideas. Instructor s Guide The Human Body: How It Works Introduction This program is part of the nine-part series The Human Body: How It Works. The series uses physiologic
Immune System AP SBI4UP
 Immune System AP SBI4UP TYPES OF IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY ACQUIRED IMMUNITY EXTERNAL DEFENCES INTERNAL DEFENCES HUMORAL RESPONSE Skin Phagocytic Cells CELL- MEDIATED RESPONSE Mucus layer Antimicrobial
Immune System AP SBI4UP TYPES OF IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY ACQUIRED IMMUNITY EXTERNAL DEFENCES INTERNAL DEFENCES HUMORAL RESPONSE Skin Phagocytic Cells CELL- MEDIATED RESPONSE Mucus layer Antimicrobial
IMMUNITY AND DISEASE II
 IMMUNITY AND DISEASE II A. Evolution of the immune system. 1. Figure 1--57.25, p. 1167 from Raven and Johnson Biology 6 th ed. shows how the immune system evolved. Figure 1. How the immune system evolved.
IMMUNITY AND DISEASE II A. Evolution of the immune system. 1. Figure 1--57.25, p. 1167 from Raven and Johnson Biology 6 th ed. shows how the immune system evolved. Figure 1. How the immune system evolved.
1. Specificity: specific activity for each type of pathogens. Immunity is directed against a particular pathogen or foreign substance.
 L13: Acquired or adaptive (specific) immunity The resistance, which absent at the time of first exposure to a pathogen, but develops after being exposed to the pathogen is called acquired immunity. It
L13: Acquired or adaptive (specific) immunity The resistance, which absent at the time of first exposure to a pathogen, but develops after being exposed to the pathogen is called acquired immunity. It
Chapter 15 Adaptive, Specific Immunity and Immunization
 Chapter 15 Adaptive, Specific Immunity and Immunization Adaptive Immunity: The third line of defense Third line of defense acquired and specific. Dual System of B and T lymphocytes- Immunocompetence Antigen
Chapter 15 Adaptive, Specific Immunity and Immunization Adaptive Immunity: The third line of defense Third line of defense acquired and specific. Dual System of B and T lymphocytes- Immunocompetence Antigen
CH. 24. The Immune System
 CH. 24 The Immune System The immune systems consists of organs, cells, and molecules that fight infections and protect us from invaders. Pathogens: Bacteria, Viruses, Parasites, Fungi 1. Innate (nonspecific)
CH. 24 The Immune System The immune systems consists of organs, cells, and molecules that fight infections and protect us from invaders. Pathogens: Bacteria, Viruses, Parasites, Fungi 1. Innate (nonspecific)
2/19/2018. Lymphatic System and Lymphoid Organs and Tissues. What is Lymph?
 Lymphatic System and Lymphoid Organs and Tissues Lymphatic system a transport system for tissue fluids 1. elaborate network of one-way drainage vessels returning lymph to systemic circulation 2. Lymph:
Lymphatic System and Lymphoid Organs and Tissues Lymphatic system a transport system for tissue fluids 1. elaborate network of one-way drainage vessels returning lymph to systemic circulation 2. Lymph:
Lymphatic System. Organs, vessels and a fluid called lymph. Organs and structures involved. similar to interstitial fluid
 Lymphatic System Organs, vessels and a fluid called lymph similar to interstitial fluid Organs and structures involved red bone marrow thymus spleen lymph nodes diffuse lymphatic tissue tonsils, adenoids
Lymphatic System Organs, vessels and a fluid called lymph similar to interstitial fluid Organs and structures involved red bone marrow thymus spleen lymph nodes diffuse lymphatic tissue tonsils, adenoids
Fluid movement in capillaries. Not all fluid is reclaimed at the venous end of the capillaries; that is the job of the lymphatic system
 Capillary exchange Fluid movement in capillaries Not all fluid is reclaimed at the venous end of the capillaries; that is the job of the lymphatic system Lymphatic vessels Lymphatic capillaries permeate
Capillary exchange Fluid movement in capillaries Not all fluid is reclaimed at the venous end of the capillaries; that is the job of the lymphatic system Lymphatic vessels Lymphatic capillaries permeate
Chapter 40 Section 2 The Immune System
 Chapter 40 Section 2 The Immune System Science Standard 10a What is the role of the skin in providing nonspecific defenses against infection? What is the function of the immune system? The immune system
Chapter 40 Section 2 The Immune System Science Standard 10a What is the role of the skin in providing nonspecific defenses against infection? What is the function of the immune system? The immune system
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 28 The Immune System Lesson 1: The Immune System Lesson Objectives Upon completion of this lesson,
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 28 The Immune System Lesson 1: The Immune System Lesson Objectives Upon completion of this lesson,
