Spore-Forming Gram-Positive Bacilli: Bacillus & Clostridium Species: Introduction
|
|
|
- Tyler Wheeler
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Spore-Forming Gram-Positive Bacilli: Bacillus & Clostridium Species: Introduction The gram-positive spore-forming bacilli are the bacillus and clostridium species. These bacilli are ubiquitous, and because they form spores they can survive in the environment for many years. Bacillus species are aerobes, whereas clostridia are anaerobes. Of the many species of both bacillus and clostridium genera, most do not cause disease and are not well characterized in medical microbiology. Several species, however, cause important disease in humans. Anthrax, a prototype disease in the history of microbiology, is caused by Bacillus anthracis. Anthrax remains an important disease of animals and occasionally of humans, Bacillus cereus causes food poisoning and occasionally eye or other localized infections. Clostridia cause several important toxin-mediated diseases: Clostridium tetani, tetanus; Clostridium botulinum, botulism; Clostridium perfringens, gas gangrene; and Clostridium difficile, pseudomembranous colitis. Other clostridia are also found in mixed anaerobic infections in humans Bacillus species The genus bacillus includes large aerobic, gram-positive rods occurring in chains. Most members of this genus are saprophytic organisms prevalent in soil, water, and air and on vegetation, such as Bacillus cereus and Bacillus subtilis. B.cereus can grow in foods and produce an enterotoxins which cause food poisoning. Such organisms may occasionally produce disease in immunocompromised humans (eg, meningitis, endocarditis, endophthalmitis, conjunctivitis, or acute gastroenteritis). B. anthracis a major pathogen in this genus which cause anthrax. Typical Organisms & Growth Characteristics The typical cells, measuring 1 x 3 4µm, have square ends and are arranged in long chains; spores are located in the center of the nonmotile bacilli. Colonies of B. anthracis are round and have a "cut glass" appearance in transmitted light. Hemolysis is uncommon with B anthracis but common with the saprophytic bacilli. Gelatin is liquefied. 1
2 The saprophytic bacilli utilize simple sources of nitrogen and carbon for energy and growth. The spores are resistant to environmental changes, withstand dry heat and certain chemical disinfectants for moderate periods. Animal products contaminated with anthrax spores (eg, hides, bristles, hair, wool, bone) can be sterilized only by autoclaving. Bacillus Anthracis Pathogenesis Anthrax is primarily a disease of herbivores goats, sheep, cattle, horses, etc; other animals (e.g., rats) are relatively resistant to the infection. Humans become infected incidentally by contact with infected animals or their products. In humans, the infection is usually acquired by the entry of spores through injured skin (cutaneous anthrax) or rarely the mucous membranes (gastrointestinal anthrax), or by inhalation of spores into the lung (inhalation anthrax). The spores germinate in the tissue at the site of entry, and growth of the vegetative organisms results in formation of a gelatinous edema and congestion. Bacilli spread via lymphatics to the bloodstream, and they multiply freely in the blood and tissues shortly before and after death. B anthracis that does not produce a capsule is not virulent and does not induce anthrax in test animals. The poly-d-glutamic acid capsule (protein in nature) is antiphagocytic. The capsule gene is on a plasmid.anthrax toxin is made up of three proteins: protective antigen (PA), edema factor (EF), and lethal factor (LF). PA binds to specific cell receptors, and following proteolytic activation it forms a membrane channel that mediates entry of EF and LF into the cell. EF is an adenylate cyclase; with PA it forms a toxin known as edema toxin. LF plus PA form lethal toxin, which is a major virulence factor and cause of death in infected animals. 2
3 Clinical Findings In humans, approximately 95% of cases are cutaneous anthrax and 5% are inhalation. Gastrointestinal anthrax is very rare.cutaneous anthrax generally occurs on exposed surfaces of the arms or hands, followed in frequency by the face and neck. A pruritic papule develops 1 7 days after entry of the organisms or spores through a scratch. The papule rapidly changes into a vesicle or small ring of vesicles that coalesce, and necrotic ulcer develops. The lesions and have a characteristic central black eschar. Marked edema occurs. Lymphangitis and lymphadenopathy and systemic signs and symptoms of fever, malaise, and headache may occur. After 7 10 days the eschar is fully developed. Eventually it dries, loosens, and separates; healing is by granulation and leaves a scar. In as many as 20% of patients, cutaneous anthrax can lead to sepsis, systemic infection including meningitis and death. The incubation period in inhalation anthrax may be as long as 6 weeks. The early clinical manifestations are associated with marked hemorrhagic 3
4 necrosis and edema of the mediastinum, Substernal pain may be prominent, hemorrhagic pleural effusions and cough. Sepsis occurs, and there may be hematogenous spread to the gastrointestinal tract, causing bowel ulceration, or to the meninges, causing hemorrhagic meningitis. The fatality rate in inhalation anthrax is high. Diagnostic Laboratory Tests Specimens to be examined are fluid or pus from a local lesion, blood, and sputum. Stained smears from the local lesion or of blood from dead animals often show chains of large gram-positive rods. Anthrax can be identified in dried smears by immunofluorescence staining techniques. When grown on blood agar plates, the organisms produce nonhemolytic gray to white colonies with a rough texture and a groundglass appearance. Comma-shaped outgrowths (Medusa head) may project from the colony. Gram stain shows large gram-positive rods. Carbohydrate fermentation is not useful. In semisolid medium, anthrax bacilli are always nonmotile, whereas related nonpathogenic organisms (eg, B cereus) exhibit motility by "swarming." Virulent anthrax cultures kill mice or guinea pigs upon intraperitoneal injection. An enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA) has been developed to measure antibodies against edema and lethal toxins. Treatment Many antibiotics are effective against anthrax in humans, but treatment must be started early. Ciprofloxacin is recommended for treatment of anthrax. Many antibiotics are active against B anthracis; penicillin G, along with gentamicin or streptomycin, has previously been used to treat anthrax. In the setting of potential exposure to B. anthracis as an agent of biologic warfare, prophylaxis with ciprofloxacin or doxycycline should be continued for 4 weeks while three doses of vaccine are being given, or for 8 weeks if no vaccine is administered. Some other gram-positive bacilli, such as B cereus, are resistant to penicillin by virtue of β-lactamase production. Doxycycline, erythromycin, or ciprofloxacin may be effective alternatives to penicillin. Epidemiology, Prevention, & Control 4
5 Soil is contaminated with anthrax spores from the carcasses of dead animals. These spores remain viable for decades. Perhaps spores can germinate in soil at ph 6.5 at proper temperature. Control measures include (1) disposal of animal carcasses by burning or by deep burial in lime pits, (2) decontamination (usually by autoclaving) of animal products, (3) protective clothing and gloves for handling potentially infected materials, and (4) active immunization of domestic animals with live attenuated vaccines. Persons with high occupational risk should be immunized. Bacillus Cereus Food poisoning caused by Bacillus cereus has two distinct forms: the emetic type, associated with fried rice, and the diarrheal type, associated with meat dishes and sauces. B cereus produces toxins that cause disease that is more an intoxication than a food-borne infection. The emetic form is manifested by nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, and occasionally diarrhea and is self-limiting, with recovery occurring within 24 hours. It begins 1 5 hours after ingestion of rice and occasionally pasta dishes. B cereus is a soil organism that commonly contaminates rice. When large amounts of rice are cooked and allowed to cool slowly, the B cereus spores germinate and the vegetative cells produce the toxin during logphase growth or during sporulation. The diarrheal form has an incubation period of 1 24 hours and is manifested by profuse diarrhea with abdominal pain and cramps; fever and vomiting are uncommon. The enterotoxin may be preformed in the food or produced in the intestine. The presence of B cereus in a patient's stool is not sufficient to make a diagnosis of B cereus disease. B cereus is an important cause of eye infections, severe keratitis, endophthalmitis, etc. Typically, the organisms are introduced into the eye by foreign bodies associated with trauma. B cereus has also been associated with localized infections and with systemic infections, including endocarditis, meningitis, osteomyelitis, and pneumonia. 5
Anthrax and Anthrax Vaccine
 Anthrax and Anthrax Vaccine Under Supervision of : Prof. Dr\ Ekram M. El-Shabrawy Team Work : Mostafa Emad Ahmed Mohammed Bahaa El-Din Mostafa Abd-Elsamee Ahmed Mohamed Taha Contents Causative Organism.
Anthrax and Anthrax Vaccine Under Supervision of : Prof. Dr\ Ekram M. El-Shabrawy Team Work : Mostafa Emad Ahmed Mohammed Bahaa El-Din Mostafa Abd-Elsamee Ahmed Mohamed Taha Contents Causative Organism.
Medical Bacteriology - Lecture 7. Spore- forming Gram Positive Rods. Bacillus
 Medical Bacteriology - Lecture 7 Spore- forming Gram Positive Rods Bacillus 1 Bacillus Characteristics - Gram positive - Large rod. - Arranged in long chain - Spore forming - Aerobic or facultative anaerobic
Medical Bacteriology - Lecture 7 Spore- forming Gram Positive Rods Bacillus 1 Bacillus Characteristics - Gram positive - Large rod. - Arranged in long chain - Spore forming - Aerobic or facultative anaerobic
Lecture (14) Amiedi Ph.D.Microbiology
 AEROBIC BACILLUS Lecture (14) Dr. Baha,H,AL-Amiedi Amiedi Ph.D.Microbiology General Characteristics of Bacillus 60 species; Gram-positive or Gram-variable bacilli Large (0.5 x 1.2 to 2.5 x 10 um) Most
AEROBIC BACILLUS Lecture (14) Dr. Baha,H,AL-Amiedi Amiedi Ph.D.Microbiology General Characteristics of Bacillus 60 species; Gram-positive or Gram-variable bacilli Large (0.5 x 1.2 to 2.5 x 10 um) Most
species; Gram-positive or Gram-variable bacilli 60 (Large (0.5 x 1.2 to 2.5 x 10 um Most are saprophytic contaminants or normal flora
 AEROBIC BACILLUS (Lecture (15 Dr. Baha,H,AL-Amiedi Ph.D.Microbiology General Characteristics of Bacillus species; Gram-positive or Gram-variable bacilli 60 (Large (0.5 x 1.2 to 2.5 x 10 um Most are saprophytic
AEROBIC BACILLUS (Lecture (15 Dr. Baha,H,AL-Amiedi Ph.D.Microbiology General Characteristics of Bacillus species; Gram-positive or Gram-variable bacilli 60 (Large (0.5 x 1.2 to 2.5 x 10 um Most are saprophytic
Dr.Baha,Hamdi AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology
 BACILLUS ANTHRAX Dr.Baha,Hamdi AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology BACILLUS ANTHRACIS BACILLUS ANTHRAX Dr.Baha,Hamdi AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology Bacillus:General characters Anthrax is a zoonotic disease (could
BACILLUS ANTHRAX Dr.Baha,Hamdi AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology BACILLUS ANTHRACIS BACILLUS ANTHRAX Dr.Baha,Hamdi AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology Bacillus:General characters Anthrax is a zoonotic disease (could
Spore-Forming Gram-Positive Bacilli: Bacillus and Clostridium Species. By : Nader Alaridah MD, PhD
 Spore-Forming Gram-Positive Bacilli: Bacillus and Clostridium Species By : Nader Alaridah MD, PhD Bacillus Species The genus Bacillus includes large aerobic or facultatively anaerobic, gram-positive, spore
Spore-Forming Gram-Positive Bacilli: Bacillus and Clostridium Species By : Nader Alaridah MD, PhD Bacillus Species The genus Bacillus includes large aerobic or facultatively anaerobic, gram-positive, spore
Infection Control Protocol for the Management of Anthrax Cases in Health Care settings
 State of Kuwait Ministry of Health Infection Control Directorate Infection Control Protocol for the Management of Anthrax Cases in Health Care settings 2002 Introduction: Anthrax is a bacterial infectious
State of Kuwait Ministry of Health Infection Control Directorate Infection Control Protocol for the Management of Anthrax Cases in Health Care settings 2002 Introduction: Anthrax is a bacterial infectious
Anthrax: An Epidemiologic Perspective. Denise Dietz Public Health Epidemiologist
 Anthrax: An Epidemiologic Perspective Denise Dietz Public Health Epidemiologist Outline Overview of anthrax Explain different types of anthrax Clinical Why a good weapon Epidemiology Bacillus anthracis
Anthrax: An Epidemiologic Perspective Denise Dietz Public Health Epidemiologist Outline Overview of anthrax Explain different types of anthrax Clinical Why a good weapon Epidemiology Bacillus anthracis
ANTHRAX (Malignant Edema, Malignant Pustule, Woolsorter's Disease, Charbon, Ragpicker's Disease)
 ANTHRAX (Malignant Edema, Malignant Pustule, Woolsorter's Disease, Charbon, Ragpicker's Disease) REPORTING INFORMATION Class A: Report immediately via telephone the case or suspected case and/or a positive
ANTHRAX (Malignant Edema, Malignant Pustule, Woolsorter's Disease, Charbon, Ragpicker's Disease) REPORTING INFORMATION Class A: Report immediately via telephone the case or suspected case and/or a positive
Medical Bacteriology Dr. Ibtisam
 Clostridium (An aerobic Bacilli) Most Clostridium species decompose proteins or form toxins and some do both. Their natural habitat is the soil or intestinal tract as saprophytes. The important pathogenic
Clostridium (An aerobic Bacilli) Most Clostridium species decompose proteins or form toxins and some do both. Their natural habitat is the soil or intestinal tract as saprophytes. The important pathogenic
Answers to these questions are available on LF is a zinc-dependent protease EF is a calmodulin-dependent adenylate cyclase
 21 Bacillus Two hours after a dinner, a family of four developed acute abdominal cramps with nausea and vomiting. The illness lasted for less than a day. 1. Bacillus cereus is associated with two forms
21 Bacillus Two hours after a dinner, a family of four developed acute abdominal cramps with nausea and vomiting. The illness lasted for less than a day. 1. Bacillus cereus is associated with two forms
FOOD BORNE DISEASES Lectures
 FOOD BORNE DISEASES Lectures Nur Hidayat Jur TIP FTP UB http://nurhidayat.lecture.ub.ac.id/mikrobiolologi-bioproses/ FOOD BORNE INTOXICATIONS These are diseases caused by consumption of food containing:
FOOD BORNE DISEASES Lectures Nur Hidayat Jur TIP FTP UB http://nurhidayat.lecture.ub.ac.id/mikrobiolologi-bioproses/ FOOD BORNE INTOXICATIONS These are diseases caused by consumption of food containing:
GENUS: BACILLUS. Genus Features. Gram-positive rods Spore forming Aerobic. Species of Medical Importance. Bacillus anthracis Bacillus cereus
 GENUS: BACILLUS Genus Features Gram-positive rods Spore forming Aerobic Species of Medical Importance Bacillus anthracis Bacillus cereus Bacillus anthracis 1. Distinguishing Features Large, boxcar-like,
GENUS: BACILLUS Genus Features Gram-positive rods Spore forming Aerobic Species of Medical Importance Bacillus anthracis Bacillus cereus Bacillus anthracis 1. Distinguishing Features Large, boxcar-like,
Yersinia pestis. Yersinia and plague. Dr. Hala Al Daghistani
 Yersinia pestis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Yersinia species Short, pleomorphic gram-negative rods that can exhibit bipolar staining. Catalase positive, and microaerophilic or facultatively anaerobic. Animals
Yersinia pestis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Yersinia species Short, pleomorphic gram-negative rods that can exhibit bipolar staining. Catalase positive, and microaerophilic or facultatively anaerobic. Animals
Shapes and Genera of cocci-shaped organisms:
 BIO230 Microbiology 19: Pathogenic Gram-Positive Cocci and Bacilli 1. Gram-positive pathogens Color reaction Shapes and Genera of cocci-shaped organisms: Genera of bacilli-shaped organisms: 2. Staphylococcus
BIO230 Microbiology 19: Pathogenic Gram-Positive Cocci and Bacilli 1. Gram-positive pathogens Color reaction Shapes and Genera of cocci-shaped organisms: Genera of bacilli-shaped organisms: 2. Staphylococcus
Gram Positive Coccus Staphylococci Dr. Hala Al Daghistani
 Medical bacteriology Gram Positive Coccus Staphylococci Dr. Hala Al Daghistani The Staphylococci are gram-positive spherical cells, nonmotile, usually arranged in grapelike irregular clusters. Some are
Medical bacteriology Gram Positive Coccus Staphylococci Dr. Hala Al Daghistani The Staphylococci are gram-positive spherical cells, nonmotile, usually arranged in grapelike irregular clusters. Some are
Anthrax. Department of Child Health Medical Faculty University of Sumatera Utara
 Anthrax Malignant pustule, malignant edema, Woolsorters Disease, Ragpickers Disease, Maladi Charbon, Splenic Fever Infectious and Tropical Pediatric Division Department of Child Health Medical Faculty
Anthrax Malignant pustule, malignant edema, Woolsorters Disease, Ragpickers Disease, Maladi Charbon, Splenic Fever Infectious and Tropical Pediatric Division Department of Child Health Medical Faculty
Characteristics of Mycobacterium
 Mycobacterium Characteristics of Mycobacterium Very thin, rod shape. Culture: Aerobic, need high levels of oxygen to grow. Very slow in grow compared to other bacteria (colonies may be visible in up to
Mycobacterium Characteristics of Mycobacterium Very thin, rod shape. Culture: Aerobic, need high levels of oxygen to grow. Very slow in grow compared to other bacteria (colonies may be visible in up to
Salmonella, Shigella, and Campylobacter
 1 Salmonella, Shigella, and Campylobacter Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Salmonella and enteritis Salmonellae are often pathogenic for humans or animals when acquired by the oral route. They are transmitted from
1 Salmonella, Shigella, and Campylobacter Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Salmonella and enteritis Salmonellae are often pathogenic for humans or animals when acquired by the oral route. They are transmitted from
GI Bacterial Infections (part-1)
 GI Bacterial Infections (part-1) Mohammed Abdulla Mehdi FIBMS (internal medicine), FIBMS (Gastroenterology & Hepatology) Acute diarrhea and vomiting Acute diarrhea, sometimes with vomiting, is the predominant
GI Bacterial Infections (part-1) Mohammed Abdulla Mehdi FIBMS (internal medicine), FIBMS (Gastroenterology & Hepatology) Acute diarrhea and vomiting Acute diarrhea, sometimes with vomiting, is the predominant
True Pathogens of the Enterobacteriaceae: Salmonella, Shigella & Yersinia Salmonella
 Lec. 6 Oral Microbiology Dr. Chatin True Pathogens of the Enterobacteriaceae: Salmonella, Shigella & Yersinia Salmonella General Characteristics of Salmonella جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان Coliform bacilli
Lec. 6 Oral Microbiology Dr. Chatin True Pathogens of the Enterobacteriaceae: Salmonella, Shigella & Yersinia Salmonella General Characteristics of Salmonella جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان Coliform bacilli
Anthrax is ancient. It's been around since biblical times, and is mentioned by Homer, Virgil & Hippocrates.
 Anthrax I. Introduction & history: Anthrax is ancient. It's been around since biblical times, and is mentioned by Homer, Virgil & Hippocrates. - Some people attribute the sixth plague (in Exodus) to Anthrax.
Anthrax I. Introduction & history: Anthrax is ancient. It's been around since biblical times, and is mentioned by Homer, Virgil & Hippocrates. - Some people attribute the sixth plague (in Exodus) to Anthrax.
Vibrio cholera. Dr. Hala Al Daghistani
 Vibrio cholera Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Vibrios are among the most common bacteria in surface waters worldwide. V. cholerae is a comma-shaped, curved rod that are all widely distributed in nature. It produce
Vibrio cholera Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Vibrios are among the most common bacteria in surface waters worldwide. V. cholerae is a comma-shaped, curved rod that are all widely distributed in nature. It produce
Food Borne Diseases Complete List: Symptoms & Preventions
 Food Borne Diseases Complete List: Symptoms & Preventions Food borne diseases are acute illnesses caused by harmful bacteria or toxins that usually develop within hours of consuming contaminated or poisonous
Food Borne Diseases Complete List: Symptoms & Preventions Food borne diseases are acute illnesses caused by harmful bacteria or toxins that usually develop within hours of consuming contaminated or poisonous
Anthrax. Dr.T.V.Rao MD. Dr.T.V.Rao MD 1
 Anthrax Dr.T.V.Rao MD Dr.T.V.Rao MD 1 General Characteristics of Bacillus ~ 60 species; Gram-positive or Gram-variable bacilli Large (0.5 x 1.2 to 2.5 x 10 um) Most are saprophytic contaminants or normal
Anthrax Dr.T.V.Rao MD Dr.T.V.Rao MD 1 General Characteristics of Bacillus ~ 60 species; Gram-positive or Gram-variable bacilli Large (0.5 x 1.2 to 2.5 x 10 um) Most are saprophytic contaminants or normal
Small living organism Not visible to the naked eye Must be viewed under a microscope Found everywhere in the environment, including on and in the
 Small living organism Not visible to the naked eye Must be viewed under a microscope Found everywhere in the environment, including on and in the human body Many Microorganisms are part of normal flora
Small living organism Not visible to the naked eye Must be viewed under a microscope Found everywhere in the environment, including on and in the human body Many Microorganisms are part of normal flora
Spore forming bacteria
 Spore forming bacteria !Spore former!bacillus!clostridium!desulfotomaculans Spore forming bacteria!gram negative!converse sulfate to sulfide!sporolactobacillus!rod shape, microaerophilic bacteria!sporpsarcina!cocci,
Spore forming bacteria !Spore former!bacillus!clostridium!desulfotomaculans Spore forming bacteria!gram negative!converse sulfate to sulfide!sporolactobacillus!rod shape, microaerophilic bacteria!sporpsarcina!cocci,
A Reference Guide for Foodborne Pathogens 1
 FSHN05-16 1 Ronald H. Schmidt 2 The following is a general summary of the characteristics of certain pathogens commonly involved in foodborne illness, and is provided as a quick reference guide. It is
FSHN05-16 1 Ronald H. Schmidt 2 The following is a general summary of the characteristics of certain pathogens commonly involved in foodborne illness, and is provided as a quick reference guide. It is
Medical Microbiology
 Lecture 5!!!!!!ƒš!!Œ!!! š!!œ!! Œ!!!! Dr. Ismail I. Daood Medical Microbiology!! Systematic Bacteriology Gram-Positive Cocci : GENUS : Staphylococcus : The general properties of Staphylococcus are Gram-
Lecture 5!!!!!!ƒš!!Œ!!! š!!œ!! Œ!!!! Dr. Ismail I. Daood Medical Microbiology!! Systematic Bacteriology Gram-Positive Cocci : GENUS : Staphylococcus : The general properties of Staphylococcus are Gram-
UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS FIELD MEDICAL TRAINING BATTALION Camp Lejeune, NC
 UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS FIELD MEDICAL TRAINING BATTALION Camp Lejeune, NC 28542-0042 FMST 304 Manage Biological Agent Casualties TERMINAL LEARNING OBJECTIVE 1. Given a casualty and the absence of a
UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS FIELD MEDICAL TRAINING BATTALION Camp Lejeune, NC 28542-0042 FMST 304 Manage Biological Agent Casualties TERMINAL LEARNING OBJECTIVE 1. Given a casualty and the absence of a
YERSINIA MODULE 26.1 INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES 26.2 YERSINIA PESTIS. Notes
 MODULE Yersinia 26 YERSINIA 26.1 INTRODUCTION Genus Yersinia belongs to tribe Yersinieae of the family Enterobacteriaceae. Yersinia are Gram-negative rod shaped bacteria and are facultative anaerobes.
MODULE Yersinia 26 YERSINIA 26.1 INTRODUCTION Genus Yersinia belongs to tribe Yersinieae of the family Enterobacteriaceae. Yersinia are Gram-negative rod shaped bacteria and are facultative anaerobes.
Shigella and salmonella
 Sulaimani University College of Pharmacy Microbiology Lec. 9 & 10 Shigella and salmonella Dr. Abdullah Ahmed Hama PhD. Microbiology/Molecular Parasitology abdullah.hama@spu.edu.iq 1 Shigella Shigella species
Sulaimani University College of Pharmacy Microbiology Lec. 9 & 10 Shigella and salmonella Dr. Abdullah Ahmed Hama PhD. Microbiology/Molecular Parasitology abdullah.hama@spu.edu.iq 1 Shigella Shigella species
Enteric bacteria(pseudomonas+salmonella) Dr.Asem shihabi. Jumanah Nayef Abu Asbeh
 15 Microbiology sheet #15 1. Gram-negative facultative anaerobic rapidly growing bacteria are divided into 2 major Lactose fermenter group which is represented by the Coliforms. 2. Lactose non-fermenter
15 Microbiology sheet #15 1. Gram-negative facultative anaerobic rapidly growing bacteria are divided into 2 major Lactose fermenter group which is represented by the Coliforms. 2. Lactose non-fermenter
Robert Koch's original micrographs of the anthrax bacillus. mail, that will work, but then you can't read that letter from Aunt Marge.
 [Previous] [Next] Introduction Chapters-> Search Send us your comments Host Defenses Normal Flora Constiuitive Defenses Constiuitive Def. (cont.) Inducible Defenses Antimicrobial Agents Resistance to Defenses
[Previous] [Next] Introduction Chapters-> Search Send us your comments Host Defenses Normal Flora Constiuitive Defenses Constiuitive Def. (cont.) Inducible Defenses Antimicrobial Agents Resistance to Defenses
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10. Mycobacterium. Actinomycetes. Nocardia
 Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Nocardia 1 Mycobacterium Characteristics - Large, very weakly gram positive rods - Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes - Catalase positive
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Nocardia 1 Mycobacterium Characteristics - Large, very weakly gram positive rods - Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes - Catalase positive
Chapter 38 Pt. II. Human Diseases Caused by Bacteria
 Chapter 38 Pt. II Human Diseases Caused by Bacteria Arthropod-Borne Diseases generally rare some are of historical interest some newly emerged Yersinia pestis nonenteric tiny, gram-negative rod, unusual
Chapter 38 Pt. II Human Diseases Caused by Bacteria Arthropod-Borne Diseases generally rare some are of historical interest some newly emerged Yersinia pestis nonenteric tiny, gram-negative rod, unusual
Microbial Hazard. Microorganisms. Microbial Hazard. Some microorganisms can be pathogenic (concerns food processors and public health officials).
 Lecture Material - Food Safety Inneke Hantoro Microbial Hazard Microbial Hazard Microbial foodborne illness, also commonly called food poisoning, is illness caused by eating food contaminated with specific
Lecture Material - Food Safety Inneke Hantoro Microbial Hazard Microbial Hazard Microbial foodborne illness, also commonly called food poisoning, is illness caused by eating food contaminated with specific
Rapid and progressive necrosis of the tissue underlying epidermis (cellulitis)
 Table 1. Infections of the Skin, Eyes and Ears Folliculitis Furuncles (boils) & Carbuncles Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Scald Skin Syndrome Peeling skin on infants Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Impetigo Lesions
Table 1. Infections of the Skin, Eyes and Ears Folliculitis Furuncles (boils) & Carbuncles Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Scald Skin Syndrome Peeling skin on infants Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Impetigo Lesions
Bacteria. Major Food Poisoning Caused by Bacteria. Most Important Prevention Measure. Controlling time. Preventing cross-contamination
 Bacteria Major Food Poisoning Caused by Bacteria Most Important Prevention Measure Controlling time and temperature Preventing crosscontamination Practising personal hygiene Bacillus cereus gastroenteritis
Bacteria Major Food Poisoning Caused by Bacteria Most Important Prevention Measure Controlling time and temperature Preventing crosscontamination Practising personal hygiene Bacillus cereus gastroenteritis
Campylobacter jejuni
 U.S. Food & Drug Administration Center for Food Safety & Applied Nutrition Foodborne Pathogenic Microorganisms and Natural Toxins Handbook Campylobacter jejuni 1. Name of the Organism: Campylobacter jejuni
U.S. Food & Drug Administration Center for Food Safety & Applied Nutrition Foodborne Pathogenic Microorganisms and Natural Toxins Handbook Campylobacter jejuni 1. Name of the Organism: Campylobacter jejuni
GI tract bacterial infections Dr.Asem
 ** You don't have to refer to the slides, all of the info are included here.. Slides #7,8 : Campylobacter bacteria : - Gram negative microaerophilic bacteria. - Spiral (curved)-shaped as vibrio cholera
** You don't have to refer to the slides, all of the info are included here.. Slides #7,8 : Campylobacter bacteria : - Gram negative microaerophilic bacteria. - Spiral (curved)-shaped as vibrio cholera
Anaerobic bacteria and more. Stijn van der Veen
 Anaerobic bacteria and more Stijn van der Veen Anaerobic bacteria Anaerobic bacteria do not require oxygen for growth. Some anaerobic bacteria die in the presence of oxygen, while others are able to tolerate
Anaerobic bacteria and more Stijn van der Veen Anaerobic bacteria Anaerobic bacteria do not require oxygen for growth. Some anaerobic bacteria die in the presence of oxygen, while others are able to tolerate
4. The most common cause of traveller s diarrheoa is a. Rotavirus b. E coli c. Shigella d. Giardia e. Salmonella
 INFECTIOUS DISEASE 1. Mumps virus is a a. Adenovirus b. Herpes virus c. Paramyxovirus d. Pox virus e. Picornavirus 2. All of the following cause a clinical effect via the production of exotoxin except
INFECTIOUS DISEASE 1. Mumps virus is a a. Adenovirus b. Herpes virus c. Paramyxovirus d. Pox virus e. Picornavirus 2. All of the following cause a clinical effect via the production of exotoxin except
GRAM-NEGATIVE BACILLI THE ENTERICS: Family Enterobacteriaceae: Genus Escherichia & Genus Klebsiella
 DR. HUDA ABO- ALEES 214-2-15 Obgectives: GRAM-NEGATIVE BACILLI THE ENTERICS: Family Enterobacteriaceae: Genus Escherichia & Genus Klebsiella Describe the morphology & physiology for E.coli & Klebsiella
DR. HUDA ABO- ALEES 214-2-15 Obgectives: GRAM-NEGATIVE BACILLI THE ENTERICS: Family Enterobacteriaceae: Genus Escherichia & Genus Klebsiella Describe the morphology & physiology for E.coli & Klebsiella
Gram-Negative Cocci :Neisseria & Vibrio
 Sulaimani University College of Pharmacy Microbiology Lec. 7 Gram-Negative Cocci :Neisseria & Vibrio Dr. Abdullah Ahmed Hama PhD. Microbiology/Molecular Parasitology abdullah.hama@spu.edu.iq 1 Neisseria
Sulaimani University College of Pharmacy Microbiology Lec. 7 Gram-Negative Cocci :Neisseria & Vibrio Dr. Abdullah Ahmed Hama PhD. Microbiology/Molecular Parasitology abdullah.hama@spu.edu.iq 1 Neisseria
Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) Week 52 (Ending 30/12/2017)
 Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) Week 52 (Ending 30/12/2017) What is Clostridium difficile? Clostridium difficile is a Gram-positive anaerobic spore forming bacillus. It is ubiquitous in nature and
Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) Week 52 (Ending 30/12/2017) What is Clostridium difficile? Clostridium difficile is a Gram-positive anaerobic spore forming bacillus. It is ubiquitous in nature and
How to Respond to an Anthrax Threat
 How to Respond to an Anthrax Threat http://www.gsa.gov/mailpolicy Objectives Define - What is anthrax and what do I need to know. - The three forms of anthrax and treatment. Identify - What to look for
How to Respond to an Anthrax Threat http://www.gsa.gov/mailpolicy Objectives Define - What is anthrax and what do I need to know. - The three forms of anthrax and treatment. Identify - What to look for
DR. HUDA ABO- ALEES GRAM-NEGATIVE BACILLI THE ENTERICS:
 DR. HUDA ABO- ALEES 214-2-15 GRAM-NEGATIVE BACILLI THE ENTERICS: Family Enterobacteriaceae: Genus Escherichia & Genus Klebsiella OBJECTIVES Describe the morphology & physiology for E.coli & Klebsiella
DR. HUDA ABO- ALEES 214-2-15 GRAM-NEGATIVE BACILLI THE ENTERICS: Family Enterobacteriaceae: Genus Escherichia & Genus Klebsiella OBJECTIVES Describe the morphology & physiology for E.coli & Klebsiella
Clostridium difficile Essential information
 Clostridium difficile Essential information Clostridium difficile Origins Clostridium difficile (C. diff) is a Gram positive, spore forming, anaerobic bacterium with a rod structure. It was first identified
Clostridium difficile Essential information Clostridium difficile Origins Clostridium difficile (C. diff) is a Gram positive, spore forming, anaerobic bacterium with a rod structure. It was first identified
Spore forming bacteria
 Spore forming bacteria !Spore former!bacillus!clostridium!desulfotomaculans Spore forming bacteria!gram negative!converse sulfate to sulfide!sporolactobacillus!rod shape, microaerophilic bacteria!sporpsarcina!cocci,
Spore forming bacteria !Spore former!bacillus!clostridium!desulfotomaculans Spore forming bacteria!gram negative!converse sulfate to sulfide!sporolactobacillus!rod shape, microaerophilic bacteria!sporpsarcina!cocci,
GI Bacterial Infections (part-2)
 GI Bacterial Infections (part-2) Mohammed Abdulla Mehdi FIBMS (internal medicine), FIBMS (G&H) Clostridium difficile infection C. difficile is the most commonly diagnosed cause of antibioticassociated
GI Bacterial Infections (part-2) Mohammed Abdulla Mehdi FIBMS (internal medicine), FIBMS (G&H) Clostridium difficile infection C. difficile is the most commonly diagnosed cause of antibioticassociated
Principles of Infectious Disease Lecture #13 Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Principles of Infectious Disease Lecture #13 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Terminology Pathology study of disease Etiology cause of disease Pathogenesis disease process Infection colonization by microbes Disease illness
Principles of Infectious Disease Lecture #13 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Terminology Pathology study of disease Etiology cause of disease Pathogenesis disease process Infection colonization by microbes Disease illness
How to Respond to an Anthrax Threat
 How to Respond to an Anthrax Threat http://www.gsa.gov/mailpolicy Objectives U.S.GENERAL SERVICES ADMINISTRATION Define What is anthrax and what do I need to know. The three forms of anthrax and treatment.
How to Respond to an Anthrax Threat http://www.gsa.gov/mailpolicy Objectives U.S.GENERAL SERVICES ADMINISTRATION Define What is anthrax and what do I need to know. The three forms of anthrax and treatment.
Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
 Mechanisms of Pathogenicity The Microbes Fight Back Medically important bacteria Salmonella Bacillus anthracis Shigella dysenteriae Campylobacter Shigella sonnei Clostridium botulinum Staphylococcus aureus
Mechanisms of Pathogenicity The Microbes Fight Back Medically important bacteria Salmonella Bacillus anthracis Shigella dysenteriae Campylobacter Shigella sonnei Clostridium botulinum Staphylococcus aureus
Unit II Problem 2 Microbiology Lab: Pneumonia
 Unit II Problem 2 Microbiology Lab: Pneumonia - What are the steps needed to obtain a proper sputum specimen? You need the following: A wide-mouth labeled container. Gloves. Water. Mouth wash + tissues.
Unit II Problem 2 Microbiology Lab: Pneumonia - What are the steps needed to obtain a proper sputum specimen? You need the following: A wide-mouth labeled container. Gloves. Water. Mouth wash + tissues.
FOODBORNE DISEASES. Why learning foodborne diseases is very important? What do you know about foodborne diseases? What do you want to know more?
 FOODBORNE DISEASES FOODBORNE DISEASES Why learning foodborne diseases is very important? What do you know about foodborne diseases? What do you want to know more? COURSES 1) Causes of foodborne diseases
FOODBORNE DISEASES FOODBORNE DISEASES Why learning foodborne diseases is very important? What do you know about foodborne diseases? What do you want to know more? COURSES 1) Causes of foodborne diseases
(Splenic fever, Siberian ulcer, Charbon, Milzbrand)
 MSD MANUAL Veterinary / Generalized Conditions / Anthrax Veterinary Manual Overview of Anthrax (Splenic fever, Siberian ulcer, Charbon, Milzbrand) By Martin E. Hugh Jones, VetMB, MPH, PhD, MRCVS, Professor
MSD MANUAL Veterinary / Generalized Conditions / Anthrax Veterinary Manual Overview of Anthrax (Splenic fever, Siberian ulcer, Charbon, Milzbrand) By Martin E. Hugh Jones, VetMB, MPH, PhD, MRCVS, Professor
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 13 Gram Negative Coccobacilli Haemophilus Bordetella
 Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 13 Gram Negative Coccobacilli Haemophilus Bordetella 1 Haemophilus "loves heme" Small gram-negative coccobacilli Non-spore forming Non-motile Growth is enhanced in CO2 Present
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 13 Gram Negative Coccobacilli Haemophilus Bordetella 1 Haemophilus "loves heme" Small gram-negative coccobacilli Non-spore forming Non-motile Growth is enhanced in CO2 Present
Podcast (Video Recorded Lecture Series): Soft Tissue Infections for the USMLE Step One Exam
 Podcast (Video Recorded Lecture Series): Soft Tissue Infections for the USMLE Step One Exam Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com Email: Howard@12daysinmarch.com MSK Infections Bone and Joint Infections
Podcast (Video Recorded Lecture Series): Soft Tissue Infections for the USMLE Step One Exam Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com Email: Howard@12daysinmarch.com MSK Infections Bone and Joint Infections
Chapter 7 8/23/2016. Asepsis and Infection Control. Asepsis. Asepsis (Cont.) Microorganisms. Infection control and prevention
 Chapter 7 Asepsis and Infection Control All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Asepsis Microorganisms Tiny microscopic entities capable
Chapter 7 Asepsis and Infection Control All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Asepsis Microorganisms Tiny microscopic entities capable
Campylobacter ENTERITIS SURVEILLANCE PROTOCOL
 Campylobacter ENTERITIS SURVEILLANCE PROTOCOL Public Health Action 1. Educate providers and laboratories to report stool cultures positive for Campylobacter jejuni or Campylobacter coli from patients within
Campylobacter ENTERITIS SURVEILLANCE PROTOCOL Public Health Action 1. Educate providers and laboratories to report stool cultures positive for Campylobacter jejuni or Campylobacter coli from patients within
DEFINITION AETIOLOGY EPIDEMIOLOGY
 ANTHRAX IN CAMELS DEFINITION Anthrax is a serious infectious bacterial disease affecting all wild and domestic hoofed animals caused by Bacillus anthracis and takes an acute or a peracute form leading
ANTHRAX IN CAMELS DEFINITION Anthrax is a serious infectious bacterial disease affecting all wild and domestic hoofed animals caused by Bacillus anthracis and takes an acute or a peracute form leading
Biological Warfare Agents
 Biological Warfare Agents Chapter 29 Biological Warfare Agents The reader is strongly advised to supplement material in this chapter with the following reference: US Army Medical Research Institute of
Biological Warfare Agents Chapter 29 Biological Warfare Agents The reader is strongly advised to supplement material in this chapter with the following reference: US Army Medical Research Institute of
Bacteria Affect Seafood Quality and Safety (part 3)
 Bacteria Affect Seafood Quality and Safety (part 3) Brian Himelbloom, PhD University of Alaska Fairbanks School of Fisheries and Ocean Sciences Kodiak Seafood and Marine Science Center Kodiak, AK 99615
Bacteria Affect Seafood Quality and Safety (part 3) Brian Himelbloom, PhD University of Alaska Fairbanks School of Fisheries and Ocean Sciences Kodiak Seafood and Marine Science Center Kodiak, AK 99615
General surgery department of SGMU Lecturer ass. Khilgiyaev R.H. Anaerobic infection. Gas gangrene
 Anaerobic infection Gas gangrene Anaerobic bacteria Anaerobic bacteria are the most numerous inhabitants of the normal gastrointestinal tract, including the mouth Bacteroides fragilis and Clostridium The
Anaerobic infection Gas gangrene Anaerobic bacteria Anaerobic bacteria are the most numerous inhabitants of the normal gastrointestinal tract, including the mouth Bacteroides fragilis and Clostridium The
Advisory on Gastroenteritis
 10 December 2018 Advisory on Gastroenteritis Background Singapore has seen a spate of four food poisoning outbreaks since November 2018, affecting more than 400 people. The most serious involved a fatality,
10 December 2018 Advisory on Gastroenteritis Background Singapore has seen a spate of four food poisoning outbreaks since November 2018, affecting more than 400 people. The most serious involved a fatality,
Ebola Virus Patient Advisory
 22 September 2014 Ebola Virus Patient Advisory Introduction Ebola virus was first identified in Sudan and Zaire in 1976. It belongs to the family of Filoviridae. It causes Ebola Virus Disease (EVD), formerly
22 September 2014 Ebola Virus Patient Advisory Introduction Ebola virus was first identified in Sudan and Zaire in 1976. It belongs to the family of Filoviridae. It causes Ebola Virus Disease (EVD), formerly
Medical Bacteriology Lecture 15
 Medical Bacteriology Lecture 15 Gram Negative Coccobacilli Haemophilus Bordetella pertussis Haemophilus "loves heme" small gram-negative coccobacilli, non-spore forming, non-motile, require enriched media
Medical Bacteriology Lecture 15 Gram Negative Coccobacilli Haemophilus Bordetella pertussis Haemophilus "loves heme" small gram-negative coccobacilli, non-spore forming, non-motile, require enriched media
Anthrax. Surveillance Protocol. Provider Responsibilities. Laboratory Responsibilities. Infectious Disease Epidemiology Program
 January 2007 may result from a naturally occurring, unintentional exposure such as from infected animals or from an intentional exposure such as from a bioterrorism (BT) event. When necessary this protocol
January 2007 may result from a naturally occurring, unintentional exposure such as from infected animals or from an intentional exposure such as from a bioterrorism (BT) event. When necessary this protocol
Gram-Negative rods Introduction to
 Lec 5 Oral Microbiology Dr. Chatin Gram-Negative rods Introduction to Enterobacteriaceae Characteristics: جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان Small gram-negative rods (2-5 by 0.5 microns) Most motile with peritrichous
Lec 5 Oral Microbiology Dr. Chatin Gram-Negative rods Introduction to Enterobacteriaceae Characteristics: جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان Small gram-negative rods (2-5 by 0.5 microns) Most motile with peritrichous
Erysipelothrix. Listeria 9/12/2011. General. Pathogenic Listeria species. Presumptive Identification
 General Listeria Erysipelothrix Grampositive, nonspore forming rods Facultative anaerobes Grow over a wide temperature range (4 ºC to 44 ºC) tolerate ph (5.5 ~9.5) and 10% NaCl Widely distributed in herbage,
General Listeria Erysipelothrix Grampositive, nonspore forming rods Facultative anaerobes Grow over a wide temperature range (4 ºC to 44 ºC) tolerate ph (5.5 ~9.5) and 10% NaCl Widely distributed in herbage,
The Chain of Infection
 The Chain of Infection As healthcare professionals, it is important to understand two facts about infection: 1.The various ways infection can be transmitted. 2. The ways the infection chain can be broken.
The Chain of Infection As healthcare professionals, it is important to understand two facts about infection: 1.The various ways infection can be transmitted. 2. The ways the infection chain can be broken.
Chapter 19. Pathogenic Gram-Positive Bacteria. Staphylococcus & Streptococcus
 Chapter 19 Pathogenic Gram-Positive Bacteria Staphylococcus & Streptococcus Staphylococcus Normal members of every human's microbiota Can be opportunistic pathogens Facultative anaerobes Cells occur in
Chapter 19 Pathogenic Gram-Positive Bacteria Staphylococcus & Streptococcus Staphylococcus Normal members of every human's microbiota Can be opportunistic pathogens Facultative anaerobes Cells occur in
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
 Corynebacterium diphtheriae Aerobic gram-positive bacillus Toxin production occurs only when C. diphtheriae infected by virus (phage) carrying tox gene If isolated, must be distinguished from normal diphtheroid
Corynebacterium diphtheriae Aerobic gram-positive bacillus Toxin production occurs only when C. diphtheriae infected by virus (phage) carrying tox gene If isolated, must be distinguished from normal diphtheroid
SUMMARY OF FOODBORNE AND WATERBORNE DISEASE CHARACTERISTICS
 SUMMARY OF FOODBNE AND WATERBNE DISEASE CHARACTERISTICS BACTERIAL Bacillus cereus Vomiting toxin Diarrheal toxin Brucella species Campylobacter species Clostridium botulinum Clostridium perfringens 1-6
SUMMARY OF FOODBNE AND WATERBNE DISEASE CHARACTERISTICS BACTERIAL Bacillus cereus Vomiting toxin Diarrheal toxin Brucella species Campylobacter species Clostridium botulinum Clostridium perfringens 1-6
Anthrax. Nina Marano DVM, MPH, Dipl. ACVPM Meningitis and Special Pathogens Branch National Center for Infectious Diseases
 Anthrax Nina Marano DVM, MPH, Dipl. ACVPM Meningitis and Special Pathogens Branch National Center for Infectious Diseases Overview History, etiology, pathogenesis Burden of natural disease Disease forms
Anthrax Nina Marano DVM, MPH, Dipl. ACVPM Meningitis and Special Pathogens Branch National Center for Infectious Diseases Overview History, etiology, pathogenesis Burden of natural disease Disease forms
Top 8 Pathogens. Print this document and study these pathogens. You will be better prepared to challenge the ADVANCED.fst exam.
 Top 8 Pathogens The top 8 pathogens outlined in this document often cause foodborne illness in Canada. Take particular note of the bolded/underlined sections, as they are especially important. Print this
Top 8 Pathogens The top 8 pathogens outlined in this document often cause foodborne illness in Canada. Take particular note of the bolded/underlined sections, as they are especially important. Print this
Firmicutes: The Low G + C Gram-Positive Bacteria
 23 Firmicutes: The Low G + C Gram-Positive Bacteria Copyright McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Great practical importance Genus Clostridium
23 Firmicutes: The Low G + C Gram-Positive Bacteria Copyright McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Great practical importance Genus Clostridium
Basic Epi: Differential Diagnosis of Foodborne Illnesses. One Foodborne Investigation Strategy. Second Strategy: Differential Diagnosis
 Basic Epi: Differential Diagnosis of Foodborne Illnesses John Kobayashi MD, MPH August 12, 2009 One Foodborne Investigation Strategy Pathogen known look for the source using the known incubation period.
Basic Epi: Differential Diagnosis of Foodborne Illnesses John Kobayashi MD, MPH August 12, 2009 One Foodborne Investigation Strategy Pathogen known look for the source using the known incubation period.
An Overview of Bioterrorism. SAEMS January 30, Charles A. Schable, M.S. Institutional Biosafety Committee University of Arizona
 An Overview of Bioterrorism SAEMS January 30, 2008 Charles A. Schable, M.S. Institutional Biosafety Committee University of Arizona Bioterrorism Intentional or threatened use of viruses, bacteria, fungi,
An Overview of Bioterrorism SAEMS January 30, 2008 Charles A. Schable, M.S. Institutional Biosafety Committee University of Arizona Bioterrorism Intentional or threatened use of viruses, bacteria, fungi,
12 June The average EVD case fatality rate has been around 50 per cent.
 12 June 2015 Ebola virus was first identified in Sudan and Zaire in 1976. It belongs to the family of Filoviridae. It causes Ebola Virus Disease (EVD), formerly known as Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever. EVD is
12 June 2015 Ebola virus was first identified in Sudan and Zaire in 1976. It belongs to the family of Filoviridae. It causes Ebola Virus Disease (EVD), formerly known as Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever. EVD is
PATHOGENICITY OF MICROORGANISMS
 PATHOGENICITY OF MICROORGANISMS Some microorganisms are : 1- Harmless microorganism, as normal flora 2- Harmfull microorganism, as pathogenic. A pathogenic microorganism is defined as one that causes or
PATHOGENICITY OF MICROORGANISMS Some microorganisms are : 1- Harmless microorganism, as normal flora 2- Harmfull microorganism, as pathogenic. A pathogenic microorganism is defined as one that causes or
Fundamental Principles about Bioterrorism
 Fundamental Principles about Bioterrorism The following discussion provides a useful framework for putting into perspective the enormous volume of information being disseminated regarding health and Bioterrorism.
Fundamental Principles about Bioterrorism The following discussion provides a useful framework for putting into perspective the enormous volume of information being disseminated regarding health and Bioterrorism.
Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13. Mycobacterium Actinomycetes
 Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Mycobacterium tuberculosis Large, very weakly gram positive rods, Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes, non spore forming, non motile
Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Mycobacterium tuberculosis Large, very weakly gram positive rods, Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes, non spore forming, non motile
The incubation period is unknown. However; the onset of clinical disease is typically 5-10 days after initiation of antimicrobial treatment.
 C. DIFFICILE Case definition CONFIRMED CASE A patient is defined as a case if they are one year of age or older AND have one of the following requirements: A laboratory confirmation of a positive toxin
C. DIFFICILE Case definition CONFIRMED CASE A patient is defined as a case if they are one year of age or older AND have one of the following requirements: A laboratory confirmation of a positive toxin
Updated Recommendations for Management
 JAMA Vol. 287 No. 17, May 1, 2002 JAMA. 2002;287:2236-2252 Anthrax as a Biological Weapon, 2002 Updated Recommendations for Management Consensus Statement ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION CONSENSUS METHODS HISTORY
JAMA Vol. 287 No. 17, May 1, 2002 JAMA. 2002;287:2236-2252 Anthrax as a Biological Weapon, 2002 Updated Recommendations for Management Consensus Statement ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION CONSENSUS METHODS HISTORY
Giardia lamblia (flagellates)
 Giardia lamblia (flagellates) Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Giardia lamblia (Giardia duodenalis or Giardia intestinalis) is the causative agent of giardiasis and is the only common pathogenic protozoan found
Giardia lamblia (flagellates) Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Giardia lamblia (Giardia duodenalis or Giardia intestinalis) is the causative agent of giardiasis and is the only common pathogenic protozoan found
All are microbes except in red Phylogenic tree
 19 Pathogenic Gram-Positive Cocci and Bacilli http://www.healthmap.org/en The Three Domains of Life All are microbes except in red Phylogenic tree Domain characteristics 1 prokaryotes Figure 11.9 - Overview
19 Pathogenic Gram-Positive Cocci and Bacilli http://www.healthmap.org/en The Three Domains of Life All are microbes except in red Phylogenic tree Domain characteristics 1 prokaryotes Figure 11.9 - Overview
Manal AL khulaifi. Enterobacteriaceae
 Enterobacteriaceae Characteristics E.coli Most significant species in the genus Important potential pathogen in humans Common isolate from colon flora Dry, pink (lactose positive) pink colony with area
Enterobacteriaceae Characteristics E.coli Most significant species in the genus Important potential pathogen in humans Common isolate from colon flora Dry, pink (lactose positive) pink colony with area
MYCOBACTERIA. Pulmonary T.B. (infect bird)
 MYCOBACTERIA SPP. Reservoir Clinical Manifestation Mycobacterium tuberculosis Human Pulmonary and dissem. T.B. M. lepra Human Leprosy M. bovis Human & cattle T.B. like infection M. avium Soil, water, birds,
MYCOBACTERIA SPP. Reservoir Clinical Manifestation Mycobacterium tuberculosis Human Pulmonary and dissem. T.B. M. lepra Human Leprosy M. bovis Human & cattle T.B. like infection M. avium Soil, water, birds,
ا.م.د.هيفاء الحديثي. Enterobacteriaceae
 ا.م.د.هيفاء الحديثي Bacteriology Genus Salmonella Enterobacteriaceae - Pathogenic for human and animals - They are gram negative rods, motile with peritrichous flagella except Gallinarum-pullorum - Ferment
ا.م.د.هيفاء الحديثي Bacteriology Genus Salmonella Enterobacteriaceae - Pathogenic for human and animals - They are gram negative rods, motile with peritrichous flagella except Gallinarum-pullorum - Ferment
Bacterial pathogenesis. Bacterial pathogenesis. Host-microbe relationships. Chapters 14/15: Bacterial Pathogenesis & epidemiology
 Chapters 14/15: Bacterial Pathogenesis & epidemiology Dr. Amy Rogers Office Hours: Mondays & Wednesdays 9-10 AM or by request Bacterial pathogenesis How do we catch disease? How do bacteria cause disease?
Chapters 14/15: Bacterial Pathogenesis & epidemiology Dr. Amy Rogers Office Hours: Mondays & Wednesdays 9-10 AM or by request Bacterial pathogenesis How do we catch disease? How do bacteria cause disease?
FOOD BORNE INFECTIONS
 Food Poisoning Food poisoning Advisory commitee on Microbiological safety of food (ACMSF, UK) has defined food poisoning as : An acute illness with gastrointestinal or neurological manifestation affecting
Food Poisoning Food poisoning Advisory commitee on Microbiological safety of food (ACMSF, UK) has defined food poisoning as : An acute illness with gastrointestinal or neurological manifestation affecting
Bioterrorism: Medical and Public Health Perspectives
 Bioterrorism: Medical and Public Health Perspectives Overview and Historical Perspective Marcelle Layton As weapons, biological agents have a number of advantages. There is the potential for wide dissemination
Bioterrorism: Medical and Public Health Perspectives Overview and Historical Perspective Marcelle Layton As weapons, biological agents have a number of advantages. There is the potential for wide dissemination
Food Microbiology. The good, the bad and the ugly 10/13/13. Good-bacteria are important in food production. Bad-some bacteria cause food poisoning
 Food Microbiology The good, the bad and the ugly Good-bacteria are important in food production Bad-some bacteria cause food poisoning Ugly-some bacteria cause food spoilage Some factors that influence
Food Microbiology The good, the bad and the ugly Good-bacteria are important in food production Bad-some bacteria cause food poisoning Ugly-some bacteria cause food spoilage Some factors that influence
Bacillus anthracis meningitis during an outbreak of injectional anthrax in Scotland
 Bacillus anthracis meningitis during an outbreak of injectional anthrax in Scotland Dr Simon Dewar Microbiology Registrar and PhD Fellow University of Dundee SMA Free-paper session 31/10/15 Bacillis Anthraxis
Bacillus anthracis meningitis during an outbreak of injectional anthrax in Scotland Dr Simon Dewar Microbiology Registrar and PhD Fellow University of Dundee SMA Free-paper session 31/10/15 Bacillis Anthraxis
2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C
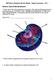 2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C Section A: Types of cells and their parts 1. Please state if the cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Then label the following molecular components
2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C Section A: Types of cells and their parts 1. Please state if the cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Then label the following molecular components
CNS module / 3 rd year medicine. Dr Hamed Al-Zoubi Associate Prof. / Department of Microbiology
 CNS module / 3 rd year medicine Dr Hamed Al-Zoubi Associate Prof. / Department of Microbiology Neuroscience 2 / Lecture 1 1. Clostridium botulinum 2. Clostridium tetani 3. Prion diseases Characteristics:
CNS module / 3 rd year medicine Dr Hamed Al-Zoubi Associate Prof. / Department of Microbiology Neuroscience 2 / Lecture 1 1. Clostridium botulinum 2. Clostridium tetani 3. Prion diseases Characteristics:
Welcome to Pathogen Group 4
 Welcome to Pathogen Group 4 Chlamydia trachomatis Trachoma Genital chlamydia Chlamydophila (Chlamydia) psittaci Bacillus anthracis Neisseria meningitidis Haemophilus influenzae, type B Helicobacter pylori
Welcome to Pathogen Group 4 Chlamydia trachomatis Trachoma Genital chlamydia Chlamydophila (Chlamydia) psittaci Bacillus anthracis Neisseria meningitidis Haemophilus influenzae, type B Helicobacter pylori
Fine mist or spray that may contain micro-organisms.
 additional precautions aerosol airborne precautions airborne transmission alimentary canal antibody antigen antimicrobial AS aseptic aseptic hand wash aseptic technique Extra infection control measures
additional precautions aerosol airborne precautions airborne transmission alimentary canal antibody antigen antimicrobial AS aseptic aseptic hand wash aseptic technique Extra infection control measures
