Module 9 Medicine CIWA
|
|
|
- Diane Gaines
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Module 9 Medicine CIWA
2 Table of Contents Reader s Notes... 1 Introduction... 3 Types of Medicine... 7 Prescription Medicine or Over-the-Counter Medicine How to take Medicines Medicine Label Medicine Label - How to Use Medicine Label - Drug Facts Asking a Pharmacist Giving Medicine to Children Overdose Overdose - Calling the Poison Control Centre Medicine Facts Additional References... 50
3 Reader s Notes The Medicine module explains the proper use and administration of medicine. It reviews various types of medicines, their packaging, dosages, the difference between over-thecounter and prescription medicines, label reading and directions to administer medicines. It also emphasizes on the potential side-effects, allergic reactions, over-dosages, abusage and precautions. An overview of the material covered in the module is provided in the introduction. This covers the salient features of the module and serves as a useful source of information for the facilitators. We recommend that the facilitators read the introduction so that they have complete information before going to the class. The introduction is written in plain language so that it can be incorporated into effective lesson delivery. Activity sheets that support the learning objectives are included in the module to reinforce the key health concepts that are being explored. A sample lesson plan which includes; the targeted Canadian Language Benchmark (CLB) level of the learners, delivery time estimation and additional information about the topic has been provided with all activities. A visual glossary has been provided to assist the facilitator in explaining new vocabulary. It is up to the facilitator to include, omit or adapt the activities according to the needs and level of the learners. Keeping in mind the limited literacy level of the learners, the preferred method for teaching the curriculum envisages the following stages: 1. Introduce the subject and prompt a discussion, through brainstorm questions provided in the facilitator s notes. This reveals the existing knowledge the learners possess on the topic. Guide learners to relate their experiences and opinions about the topic. These discussions kindle interest and gain the attention of the learners, while providing an assessment to the teacher. 2. Introduce vocabulary by writing the key words on the board and teaching their meanings by showing pictures. When feasible, use of transparencies/ PowerPoint/ real life objects (realia)/ models/ charts can be made to augment the learning. 3. Actively maintain learner participation by miming, choral repetition, role play, questioning, inviting opinions etc. 4. Review the activity sheet thoroughly and address learners questions. This is achieved by active questioning, hinting at answers, allowing the learners come to a conclusive solution and then revealing the correct answer. 5. Ask the learners to attempt the activity and clarify as much as possible, without giving the answers. Facilitators should use their discretion to select the activity sheets that best align with the level of their learners. Recapitulation and repetition is important at all stages. During facilitation, handouts and activities should be distributed to the learners. They should be prompted to seek clarifications about the handout contents. 1
4 Learners should be encouraged and motivated to obtain more information about health through reading, internet, suitable television/radio news and documentary programs in their first language and discussions with their family members and friends. Focus Questions Facilitators should review the effectiveness of learning by focusing on some key questions and adapting the lessons according to the specific need of the learners. Focus questions include: Is the lesson appropriate for the learners literacy level? Will the learners find the lesson interesting and useful? Does the lesson connect to the learning goals of the learners? Are the lessons being tailored to meet the needs of the learners? Is feedback being used to assess the effectiveness of learning by the class? Are the learners able to do what is expected of them at the end of instruction? Have the needs of the low literacy level learners been catered for to enable them to keep abreast with the rest of the class? Are lessons being recapitulated and reviewed regularly in the class? Are the learners acquiring adequate vocabulary about items related to health care? Can the learners describe problems related to health, hygiene, illness, sickness, injuries and symptoms orally and in writing? Have the learners been provided sufficient practice on what they will be assessed on? 2
5 Introduction Medicines Medicines are also called drugs. A pharmacy is also called drugstore. Medicines come in various forms and shapes like: Tablets (pill; powder pressed into a solid) Capsules (a small, gel container that has medicine inside. It melts in the stomach.) Caplets (a solid, long pill/medicine, coated to make it easy to swallow) Pills (medicine) Drops (medicine that is in a liquid form; for eyes or ears or nose) Patches (a bandage that has medicine on it) Syrups (a thick liquid medicine that you drink) Inhalers (breathing medicine, for asthma/breathing disease, medicine, helps give medicine into the breathing tubes) Ointments (a thick cream that you apply to the skin to soothe aches or relieve itch) Creams (a thick liquid form of medication; like lotion) Injections (medicine given through a needle) Sprays (liquid medicine that is squirted; i.e. nose spray is inhaled through the nose) Some of the different reasons why people need to take medication is they have: Heart problems (when your heart is weak or hurt) Blood pressure (the pressure of made by blood in the tubes in your body) Diabetes (too much sugar in the blood) Depression (sadness or unhappiness that lasts for a long time) Allergies (something that you eat, touch or breathe that makes you sick) Infection (illness; sickness you get from germs) Fever (body temperature is too high) Pain Asthma (disease that makes it hard to breathe) There are two types of medicines: over-the-counter and prescription. You need a prescription (a note) from a doctor to get prescription medicines. You do not need a note from the doctor for over-the-counter medicines. You can get over-the-counter drugs at grocery stores and drug stores. Medicines can have brand names or generic (common) names. The generic name is the chemical name. The brand name is the name given by the company that makes the medicine. A medicine can have only one generic name but many brand names. For example, Ibuprofen is the generic name but many companies sell it under their own brand names such as Advil or Motrin. Generic medicines are cheaper than brand name medicines, and work just as well. Knowing how to take medicine is important. You should ask certain questions before you start taking a new medicine, like: When should I take it? How long should I take it for? How much should I take each day? 3
6 Should I take it with food or on an empty stomach? It is important to read the labels on medicines. It can be bad for your health if you do not understand this. There is information about: How and when to take the medicine Expiry dates (it is the date that tells you when a medicine is no longer good to take) Side effects (reaction to medicine; such as rash, breathing problem, cough, etc.) Safety warnings (how to keep your medicine safe) Number of refills (how many times you can get the medicine again) Storage instructions (where to put your medicine in your house; fridge or cupboard) The label tells you about how much medicine you should take; and how to take the medicine: The label tells you how much medicine you should take and how many times a day. For example, take 2 tablets, 3 times a day. The label may tell you to do special things when taking the medicine. For example, take the medicine on an empty stomach. This means you should take it 1 hour before eating or 2 hours after eating. The label tells you how to take the medicine. For example by mouth, chewing, swallowing, applying on skin, putting drops in eyes or ears, etc. The label tells you how long you should take the medicine for. For example, if the directions are Take the medicine as needed, then you will take it only when the pain is very bad. If the directions are Take 3 tablets a day for 7 days then you must take the medicine for the 7 days even if you feel better after 5 days. The label tells you about side effects. Some medicines can make you sleepy, sick, upset your stomach, give you diarrhea (watery stool), make it hard to sleep etc. For example, the medicine may make you sleepy, so it will tell you not to drive or work on machinery after you take it. Instructions may also tell you not to drink alcohol with the medicine. Information about the expiry date is on the label. An expiry date tells you when a medicine is no longer good to take. Do not keep medicines past their expiry date. If they are old, they do not work as well. Old medicine should not be flushed down a toilet or a sink or thrown in the garbage. You should take your old medicines to the pharmacy. They can dispose of the medicine properly. Other warnings you may see are: 1. Do not take too much medicine. 2. Women who are pregnant or nursing (breast feeding) should not use some medicines. 3. Do not take a medicine if you have another health problem. For example, people with high blood pressure should not take some medicines for colds because they can raise your blood pressure. 4
7 4. Do not take medicine if you are taking some other medicines. New medicines taken with the old medicine can make you feel worse or can cause side effects (a reaction someone might have to medicine like a rash, breathing problems, throwing up or a cough). The old drug may also make the new drug not work as well. 5. What you should do in case of an overdose. An overdose is when you take too much medicine. Taking too much medicine, more than your doctor tell you too, can make you very sick. 6. You should not share your medicine with other people. If the doctor has told you to finish all of the medicine, you should. 7. Take the medicine that is past its expiry date to the pharmacist. 8. For children you should: Know how much your child weighs so that you give them the correct amount of medicine. Use a measuring spoon or dropper specially made for children s medicine. Do not call medicine candy. Always keep medicine out of reach of children. For example, up high or in a locked cabinet. You should ask your doctor or pharmacist questions about your medicine. You can ask: What is the name of the medicine? How much medicine should I take? How many times a day should I take this medicine? How long do I take this medicine for? What are the side effects (reaction to the medicine; such as rash, breathing problem; cough) of this medicine? I am allergic (bad reaction; danger) to (name the medicine). Is this medicine okay for me? I also take (name the medicine you are already taking). Is that a problem? Where should I store the medicine in my house? Should I store it in a cool dry place, refrigerate, protect from heat/ light etc? Are there any instructions for taking this medicine? All medicines in Canada have a Drug Identification Number (DIN). This number shows the instructions of use, preparation and labelling of the medicine are correct. If a medicine does not have a DIN, Canadian law does not approve it. Women should always tell their doctor if they are pregnant or nursing (breast feeding) a baby. Some medicines are not good for the baby. When travelling, you should keep medicines in your carry-on luggage (what you take with you onto the plane where you sit) because you may lose your checked-in luggage (luggage that the airline stores in the cargo). 5
8 Write all types of medicines that you take in a list; for example vitamins, herbal medicine, over-the-counter medicine etc. You should tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking any other medicine. This is important because some medicines may cause side effects (reaction to medicine; such as rash, breathing problem, cough, etc.) or not work as well when you take them at the same time. All medicines should be taken for as long as your doctor tells you. If you feel better before completing your medicine, you should not stop taking the medicines. If you finish your prescription medicine, you should check the label to see if there are refills. If you don t have enough medicine, you cannot take half dose. You should get a refill. It is not safe to take medicine after the expiry date. Side Effects & Allergic Reactions Medicines may have side effects. A side effect is a reaction someone might have to medicine. There are many side effects but some of these are a rash, throwing up or a cough. If you have any side effects, you should call Health Link Alberta or your doctor or pharmacist. If the side effects are very bad, then call 911 or go to the emergency department. Not all people have side effects. Some people are allergic (bad reaction; i.e. rash, trouble breathing) to certain medicines. An allergic reaction means their body reacts in a bad way. They may get a rash or not feel well. You should always tell your doctor/ pharmacist if you have any allergies. This can make you very sick and cause death. Having an allergy is different from getting a side effect. Signs of allergy to a medicine can include swelling (bump; enlargement) of lips, tongue or face, trouble breathing, rash (red spots on skin), itching etc. An allergic reaction to a medicine can be an emergency. Get advice right away from a health care professional. Do not take medicines with tea, coffee or other hot drinks. This may make them not work well. If you find that someone has taken too much medicine or poison, stay calm. If the person does not respond Call 911.If the person is able to speak, call Poison Control Center. Their toll-free number is (Alberta only). Poison Control can help you 24 hours a day. Tell them what the person ate and the time when they ate it. Tell them the age and weight of that person. Tell them what the person ate and the time when he/she ate it. 6
9 Types of Medicine Facilitator s Notes Level: Pre-benchmark, CLB 1, CLB 2 Time: minutes Targeted Language Skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing Objective: To familiarize learners with different types of medicines. Materials: Copy of activity sheet (one per learner) Pencils and erasers Vocabulary: Information: Brainstorm: spray, capsules, lotion, eye drops, syrup, ointment, tablets, patch, ear drops, cream, caplets, inhaler Medicines come in various forms and shapes like: Tablets (pill; powder pressed into a solid) Capsules (a small, gel container that has medicine inside. It melts in the stomach.) Caplets (a solid, long pill/medicine, coated to make it easy to swallow) Pills (medicine) Drops (medicine that is in a liquid form; for eyes or ears or nose) Patches (a bandage that has medicine on it) Syrups (a thick liquid medicine that you drink) Inhalers (breathing medicine, for asthma/breathing disease, medicine, helps give medicine into the breathing tubes) Ointments (a thick cream that you apply to the skin to soothe aches or relieve itch) Creams (a thick liquid form of medication; like lotion) injections (medicine given through a needle) Sprays (liquid medicine that is squirted; i.e. nose spray is inhaled through the nose) Ask learners: Do you take medicines? What type of medicine do you take? Is the medicine always in the form of tablets? Instructions: 1. Introduce new vocabulary by showing pictures (cut out from the activity sheet). 2. Have learners repeat the words for pronunciation practice. 3. Distribute activity sheet, Types of Medicine (part `A only). 4. Circulate to assist where needed. 5. Distribute part B of the activity. 6. Read the words aloud repeating frequently. 7. Ask the learners to find the relevant picture and write just the alphabet given under the picture. 7
10 Extension: Use the listening script for dictation. Answer Key: A: a. Capsules b. Syrup c. Ointment d. Tablets e. Spray f. Lotion B: a. Inhaler b. Cream c. Patch d. Caplets e. Eye drops f. Ear drops C: 1. D 2. B 3. H 4. C 5. E 6. A 7. G 8. F 8
11 Activity: Types of Medicines There are different types of medicines. A. Look at the pictures. Label them with the words given in the box. a. d. b. e. c. f. spray capsules lotion syrup ointment tablets 9
12 Activity: Types of Medicines B. Look at the pictures. Label them with the words given in the box. a. d. b. e. c. f. inhaler cream eye drops ear drops patch caplets 10
13 Listening: Types of Medicine C. Listen to the words. Identify the picture. Write the alphabets given under the pictures in the blanks. 1. eye drops 2. pills 3. ointment 4. inhaler 5. capsules 6. syrup 7. tablets 8. nasal spray 11
14 Activity: Types of Medicine C. Listen to your teacher. Find the picture. Write the alphabets given under the pictures in the blanks. A B C D E F G H
15 Prescription Medicine or Over-the-Counter Medicine Facilitator s Notes Level: Pre-benchmark, CLB 1, CLB 2 Time: minutes Targeted Language Skill: reading Objective: To enable learners to differentiate between prescription medicine and overthe-counter medicine. Materials: Copy of activity sheet (one per learner) Pencils and erasers Some empty containers for prescription and over-the-counter medicines Vocabulary: Information: Brainstorm: prescription medicine, over-the-counter medicine There are two types of medicines: over-the-counter and prescription. You need a prescription (a note) from a doctor to get prescription medicines. You do not need a note from the doctor for over-the-counter medicines. You can get over-the-counter drugs at grocery stores and drug stores. Ask Learners: Do you always go to your doctor if you need a medicine? Can you buy some medicines without a prescription? Instructions: 1. Write the words Prescription Medicine and Over-the-counter Medicine on the board. Explain with the help of examples and pictures. 2. Distribute the cut out cards Prescription Medicine and Over-thecounter Medicine. 3. Show learners different medicines and ask them to show the relevant card and say if it s prescription or over-the- counter. 4. Have the higher level learners write the name of the medicines in the relevant column in the activity sheet. 5. Circulate to assist where needed. 13
16 Activity: Prescription Medicine or Over-the-counter Medicine Prescription Medicine Over-the-counter Medicine 14
17 Activity: Prescription Medicine or Over-the-counter Medicine Listen to your teacher and write the name in the relevant column. PRESCRIPTION MEDICINE OVER-THE-COUNTER MEDICINE 15
18 How to take Medicines Facilitator s Notes Level: Pre-benchmark, CLB 1, CLB 2 Time: minutes Targeted Language Skills: reading Objective: To enable learners to follow the directions to take medicines. Materials: Copy of activity sheet (one per learner) Pencils and erasers Vocabulary: Information: morning, afternoon, evening, a.m., p.m., Saturday, Sunday, Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday Knowing how to take medicine is important. You should ask certain questions when starting new medicine such as: When should I take it? How long should I take it for? How much should I take each day? Should I take it with food or on an empty stomach? Different reasons why people need to take medication are: Heart problems (when your heart is weak or hurt) Blood pressure (the pressure of made by blood in the tubes in your body) Diabetes (too much sugar in the blood) Depression (sadness or unhappiness that lasts for a long time) Allergies (something that you eat, touch or breathe that makes you sick) Infections (illness; sickness you get from germs) Fever (body temperature is too high) Pain Asthma (disease that makes it hard to breathe) Brainstorm: Ask Learners: Have you ever had to take medication? When did you take it? (i.e. in the morning or afternoon or evening) Instructions: 1. Introduce new vocabulary. 2. Distribute part A of the activity sheet, How to take Medicines. 3. Explain the procedure of the activity. 4. Circulate to assist where needed. 5. Distribute part B of the activity sheet, How to take Medicines. 6. Explain the procedure of the activity by giving an example. 7. Circulate to assist where needed. 16
19 Activity: How to take Medicines Jill has health problems. She has to take many medicines. Every day she takes 2 tablets for diabetes. She takes one in the morning and one at night. On Monday, Wednesday and Friday she takes 1 capsule for cholesterol. She takes it at night. On Sunday and Thursday, she takes 1 caplet for osteoporosis. She takes it in the morning. 17
20 Activity: How to take Medicines A. Draw the shapes of medicines Jill has to take. DAYS AM PM MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY SATURDAY SUNDAY 18
21 B. Fill up the pill card for a patient. Activity: How to take Medicines Used For Instructions Morning Afternoon Evening Night Heart Take 1 pill in the morning and 1 pill in the evening Blood Pressure Take 1 pill in the morning Diabetes/ Sugar Take 1 pill in the morning and 1 pill at night Pain Take 1 pill in the morning, 1 pill in afternoon and 1 pill at night Depression Take 1 pill in the morning and 1 pill at night 19
22 Medicine Label Facilitator s Notes Level: Pre-benchmark, CLB 1, CLB 2 Time: minutes Targeted Language Skills: reading, writing Objective: To enable learners to read and understand the cautions given with the medicines. Materials: Copy of activity sheet (one per learner) Pencils and erasers Vocabulary: Information: machinery, refill, drowsiness, stomach It is important to read the prescription labels on medicines. It can be bad for your health if you do not understand this. There is information about: How and when to take the medicine Expiry dates (it is the date that tells you when a medicine is no longer good to take) Side effects (reaction to medicine; such as rash, breathing problem, cough, etc.) Safety warnings (how to keep your medicine safe) Number of refills (how many times you can get the medicine again) Storage instructions (where to put your medicine in your house) The label tells you about how much medicine you should take; and how to take the medicine: The label tells you how much medicine you should take and how many times a day. For example, take 2 tablets, 3 times a day. The label may tell you to do special things when taking the medicine. For example, take the medicine on an empty stomach. This means you should take it 1 hour before eating or 2 hours after eating. The label tells you how to take the medicine. For example by mouth, chewing, swallowing, applying on skin, putting drops in eyes or ears, etc. The label tells you how long you should take the medicine for. For example, if the directions are Take the medicine as needed, then you will take it only when the pain is very bad. If the directions are Take 3 tablets a day for 7 days then you must take the medicine for the 7 days even if you feel better after 5 days. 20
23 The label tells you about side effects. Some medicines can make you sleepy, sick, upset your stomach, give you diarrhea (watery stool), make it hard to sleep etc. For example, the medicine may make you sleepy, so it will tell you not to drive or work on machinery after you take it. Instructions may also tell you not to drink alcohol with the medicine. Information about the expiry date is on the label. An expiry date tells you when a medicine is no longer good to take. Do not keep medicines past their expiry date. If they are old, they do not work as well. Old medicine should not be flushed down a toilet or a sink or thrown in the garbage. You should take your old medicines to the pharmacy. They can dispose of the medicine properly. Brainstorm: Ask learners: What cautions do you get with the medicines? Do you ask someone about the cautions with the medicines you have to take? Instructions: 1. Show a few caution labels and ask questions to elicit understanding. 2. Introduce new vocabulary. 3. Distribute activity sheet, Medicine Label Cautions. 4. Read each safety warning with the learners explaining it to them. 5. Use some examples to explain the task to learners. 6. Circulate to assist where needed. Answer Key: a. No b. Yes c. Yes d. No e. No f. No g. Yes h. No 21
24 Activity: Medicine Label - Cautions Circle the correct answer: a) You can run machines after taking this medicine. Yes No b) There are no refills left. Contact your doctor. Yes No c) Before taking this medicine, shake the bottle Yes No d) You can drink alcohol after taking this medicine Yes No 22
25 e) Keep this medicine in your cabinet. Yes No f) You may drive after taking this medicine. Yes No g) Take the medicine with water. Yes No h) Do not take this medicine with food. Yes No 23
26 Medicine Label - How to Use Facilitator s Notes Level: CLB 1, CLB 2 Time: minutes Targeted Language Skills: reading, writing Objective: To enable learners to read and understand the labels on prescription drugs. Materials: Copy of activity sheet (one per learner) Pencils and erasers Pictures for new vocabulary Vocabulary: Information: eye drops, alcohol, tablets, refill, expiry It is important to read the prescription labels on medicines. It can be bad for your health if you do not understand this. There is information about: How and when to take the medicine Expiry dates (it is the date that tells you when a medicine is no longer good to take) Side effects (reaction to medicine; such as rash, breathing problem, cough, etc.) Safety warnings (how to keep your medicine safe) Number of refills (how many times you can get the medicine again) Storage instructions (where to put your medicine in your house) The label tells you about how much medicine you should take; and how to take the medicine: The label tells you how much medicine you should take and how many times a day. For example, take 2 tablets, 3 times a day. The label may tell you to do special things when taking the medicine. For example, take the medicine on an empty stomach. This means you should take it 1 hour before eating or 2 hours after eating. The label tells you how to take the medicine. For example by mouth, chewing, swallowing, applying on skin, putting drops in eyes or ears, etc. The label tells you how long you should take the medicine for. For example, if the directions are Take the medicine as needed, then you will take it only when the pain is very bad. If the directions are Take 3 tablets a day for 7 days then you must take the medicine for the 7 days even if you feel better after 5 days. 24
27 The label tells you about side effects. Some medicines can make you sleepy, sick, upset your stomach, give you diarrhea (watery stool), make it hard to sleep etc. For example, the medicine may make you sleepy, so it will tell you not to drive or work on machinery after you take it. Instructions may also tell you not to drink alcohol with the medicine. Information about the expiry date is on the label. An expiry date tells you when a medicine is no longer good to take. Do not keep medicines past their expiry date. If they are old, they do not work as well. Old medicine should not be flushed down a toilet or a sink or thrown in the garbage. You should take your old medicines to the pharmacy. They can dispose of the medicine properly. Brainstorm: Ask learners: Do you read the labels on your medicines? What kind of warnings appear on prescription medicines? Instructions: 1. Introduce new vocabulary. Write the words on the board and show pictures. 2. Distribute part A of the activity sheet, Medicine Labels How to Use? 3. Read the activity with the learners explaining all the difficult words. 4. Circulate to assist where needed. 5. Repeat the same procedure with part B of the activity. Answer Key: 1. Tablet 2. Four 3. May One 5. Alcohol 6. Two 7. April
28 Activity: Medicine Label - How to Use GLENMORE PHARMACY RX: Dr Jim Crow Brad Long 25 June 2009 Otex Ear Drops 8 ml DIN: Use two drops every four hours Refills: None Expiry: May 2010 SANDSTONE PHARMACY RX: Dr Lisa Chow Beck Liang 15 July 2009 Norvasc 5mg 30 tablets DIN: One tablet daily Refills: 2 times Expiry: April 2011 Do not take alcohol when using this medicine A. Read the medicine labels. Circle the correct words. 1. Dr. Lisa Chow has given ear drops / tablets. 2. Brad should use two ear drops every four / two hours. 3. Brad should throw away the medicine in May 2010 / May Beck has to take one / two tablets at a time. 5. Beck should not drink water / alcohol when using the medicine. 6. Beck can refill the prescription two / three times. 7. Beck should not use her medicine after May 2010/April
29 Activity: Medicine Label How to Use B. Look at the picture. Circle the correct answers. 1. The name of the patient is Lee Wang/Sally Jones. 2. This is a prescription/over-the-counter medicine. 3. You can get this medicine from a grocery store/pharmacy. 4. Do not use the medicine after August 2004/August The name of the medicine is Allegra /Aventis. 6. The medicine can/cannot be refilled. 7. This medicine must be taken 2 / 1 times daily. 27
30 Medicine Label - Drug Facts Facilitator s Notes Level: CLB 2 Time: minutes Targeted Language Skills: reading Objective: To enable learners to read and comprehend the drug labels before use. Materials: Copy of activity sheet (one per learner) Pencils and erasers Pictures for new vocabulary Vocabulary: Information: dosages, warning, sneezing, hay fever, sedative, overdose, neighbours, exercise It is important to read the prescription labels on medicines. It can be bad for your health if you do not understand this. There is information about: How and when to take the medicine Expiry dates (it is the date that tells you when a medicine is no longer good to take) Side effects (reaction to medicine; such as rash, breathing problem, cough, etc.) Safety warnings (how to keep your medicine safe) Number of refills (how many times you can get the medicine again) Storage instructions (where to put your medicine in your house) Information about the expiry date is on the label. An expiry date tells you when a medicine is no longer good to take. Do not keep medicines past their expiry date. If they are old, they do not work as well. Old medicine should not be flushed down a toilet or a sink or thrown in the garbage. You should take your old medicines to the pharmacy. They can dispose of the medicine properly. Allergies (something that you eat, touch or breathe that makes you sick) Brainstorm: Ask learners: Do you read labels on the medicine you get? What is written on the label? Do you think it is important to read the label? Instructions: 1. Introduce new vocabulary with the help of pictures or simple definitions. 2. Bring the real medicine labels to the class if possible. 3. Distribute activity sheet, Medicine Label Drug Facts. 4. Read the activity with the learners explaining all the difficult words. 5. Circulate to assist where needed. 28
31 Answer Key: 1. pain 2. sprains 3. Poison Control Centre 4. children 5. outside/external 6. sicker 29
32 Activity: Medicine Label Drug Facts Read the following. Drug Facts Active Ingredients Purpose Camphor 3.1 % External Analgesic Uses: Lessens pains of muscles and joints for a short time Lessens pains because of bruises, sprains and backache. Warnings: For outside use only Do not put in eyes Do not bandage tightly Do not put on wounds Stop and ask a doctor if you feel sicker Symptoms do not go for more than 7 days Symptoms go away and come back in a few days KEEP OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN Directions: People 2 years of age and older should not use more than 3-4 times a day Children under 2 years of age do not use Consult a doctor In case someone eats it, contact Poison Control Centre. 30
33 Activity: Medicine Label Drug Facts Fill in the blanks. 1. This medicine is to lessen. 2. This medicine is to treat. 3. If someone eats it, contact. 4. Keep this medicine out of the reach of. 5. The medicine is for use only. 6. Call your doctor if you feel. 31
34 Asking a Pharmacist Facilitator s Notes Level: CLB 1, CLB 2 Time: minutes Targeted Language Skills: listening, speaking Objective: To enable learners to communicate with a pharmacist. Materials: Copy of activity sheet (one per learner) Pencils and erasers Pictures for new vocabulary Vocabulary: Information: Brainstorm: antibiotic, infection, side effects, teething You should ask your doctor or pharmacist questions about your medicine. You can ask: What is the name of the medicine? How much medicine should I take? How many times a day should I take this medicine? How long do I take this medicine for? What are the side effects (reaction to the medicine; such as rash, breathing problem; cough) of this medicine? I am allergic (bad reaction; danger) to (name the medicine). Is this medicine okay for me? I also take (name the medicine you are already taking). Is that a problem? Where should I store the medicine in my house? Should I store it in a cool dry place, refrigerate, protect from heat/ light etc? Are there any instructions for taking this medicine? Ask learners: Do you ask questions when you take medicine from a pharmacist? What type of questions do you ask? Instructions: 1. Write new vocabulary on the board and explain their meanings with the help of pictures and definitions. 2. Distribute the activity sheet, Asking a Pharmacist. 3. Read the dialogue with the learners explaining any difficult words. 4. Demonstrate the dialogue with the help of a volunteer. 5. Allow time for the learners to practice dialogues with a partner. 6. Have them present it in front of the class. 7. Repeat the same procedure with the next dialogue. 32
35 Activity: Asking a Pharmacist Salma went to a pharmacy to buy medicine. Practice the dialogue he had with the pharmacist. Pharmacist: May I help you? Salma: I have a prescription to fill. Pharmacist: Let s see. Ok, it s Amoxyl. Salma: What does this medicine do? Pharmacist: It s an antibiotic which fights germs. Salma: How much should I take? Pharmacist: You should take 1 capsule 3 times a day. Salma: For how many days? Pharmacist: Take it for 7 days and until its finished. Salma: Should I continue taking it even if I feel better? 33
36 Activity: Asking a Pharmacist Pharmacist: You should finish the medicine even if you feel better. Salma: How should I take it? Pharmacist: Take it with a glass of water. Salma: Ok. Salma: Are their any side effects? Pharmacist: You may have upset stomach. Drink plenty of water. Salma: I also take multivitamins. Is that a problem? Pharmacist: No, you can take them. Pharmacist: Your prescription will be ready in about 30 minutes. Salma: Thanks, I will wait. 34
37 Activity: Asking a Pharmacist Sheila s son is teething. She asks a pharmacist about the medicine. Sheila: Pharmacist: I have some questions about this medicine. Yes, go ahead. Sheila: My son is teething. I want to know if this medicine will help him with his pain. Pharmacist: How old is your son? Sheila: Pharmacist: He is nine months. Yes, this is good medicine. Give it twice a day until his tooth comes out. Sheila: Pharmacist: Are there any side effects? He will be sleepy. Call your doctor if the pain lasts more than 5 days. 35
38 Activity: Asking a Pharmacist Sheila: Pharmacist: Anything else? Yes, you can also try to give him a teething ring. Sheila: Pharmacist: Are their any side effects? He will be sleepy. Call your doctor if the pain lasts more than 5 days. Sheila: Pharmacist: Anything else? Yes, you can also try to give him a teething ring. Sheila: Pharmacist: Thanks. Bye. Bye. 36
39 Giving Medicine to Children Facilitator s Notes Level: Pre-benchmark, CLB 1, CLB 2 Time: minutes Targeted Language Skills: reading, writing Objective: To familiarize learners with the things to take care of while giving medicine to the children. Materials: Copy of activity sheet (one per learner) Pencils and erasers Pictures for new vocabulary Vocabulary: Information: Brainstorm: measuring device, dose, weight, safely, confused For children you should: Know how much your child weighs so that you give them the correct amount of medicine. Use a measuring spoon or dropper specially made for children s medicine. Do not call medicine candy. Always keep medicine out of reach of children. For example, up high or in a locked cabinet. Ask learners: What things do you consider while giving medicines to your children? Instructions: 1. Introduce new vocabulary with the help of pictures or simple definitions. 2. Distribute activity sheet, Giving medicine to Children. 3. Read the paragraph with the class explaining any difficult words. 4. Ask learners to fill in the blanks. 5. Circulate to assist where needed. Answer Key: 1. measuring device 2. less 3. pharmacist 4. dose 5. candy 37
40 Activity: Giving Medicine to Children Giving medicine safely to children Be careful when you give medicine to your child. If you are confused ask a doctor or a pharmacist. A pharmacist will tell you the right dose for your child. Children need less medicine than their mother or father. Use small measuring cups or droppers to give medicine to your child. Do not tell your child that medicine is candy. Do not tell your child that it tastes good, if it doesn t. 38
41 Activity: Giving Medicine to Children Fill in the blanks by choosing the words from the box. 1. Use a when giving medicine to children. 2. They need medicine than a mother or father. 3. If you are confused ask a doctor or a. 4. A pharmacist can tell you the right for your child. 5. Do not tell your child that medicine is. dose less measuring device candy pharmacist 39
42 Overdose Facilitator s Notes Level: CLB 1, CLB 2 Time: minutes Targeted Language Skills: reading, writing Objective: To educate learners on what to do when someone has taken an overdose. Materials: Copy of activity sheet (one per learner) Pencils and erasers Vocabulary: Information: overdose, weight, poison, calm If you find that someone has taken too much medicine or poison, stay calm. If the person does not respond Call 911.If the person is able to speak, call Poison Control Center. Their toll-free number is (Alberta only). They can help you 24 hours a day. Tell them what the person ate and the time when they ate it. Tell them the age and weight of that person. Tell them what the person ate and the time when he/she ate it. Brainstorm: Ask learners: Where should we keep our medicine? What happens when someone takes a lot of medicine? Instructions: 1. Distribute activity sheet, Overdose. 2. Read the sentences clarifying any difficult words or phrases. 3. Allow time for the learners to fill in the blanks. 4. Circulate to assist where needed. Answer Key: 1. Poison Calm 4. Age 5. Ate 40
43 Activity: Overdose Read the sentences below. If you find that someone has taken too much medicine/ poison. Stay calm. If the person does not respond. Call 911. If the person is able to speak, call Poison Control Center. Their toll-free number is (Alberta only). They can help you 24 hours a day. Tell them the age and weight of that person. Tell them what the person ate and the time when he/she ate it. 41
44 Activity: Overdose Fill in the blanks with the help of the sentences you read. 1. The Control Center is available 24 hours a day. 2. Their toll-free number is. 3. You should stay. 4. You have to tell them and weight of the person. 5. You should know what the person. 42
45 Overdose - Calling the Poison Control Centre Facilitator s Notes Level: CLB 1, CLB 2 Time: minutes Targeted Language Skills: listening, speaking Objective: To familiarize learners with how to call Poison Control Centre in case of an overdosing. Materials: Copy of activity sheet (one per learner) Pencils and erasers Pictures for new vocabulary Vocabulary: Information: weigh, already, hesitate If you find that someone has taken too much medicine or poison, stay calm. If the person does not respond Call 911.If the person is able to speak, call Poison Control Center. Their toll-free number is (Alberta only). They can help you 24 hours a day. Tell them what the person ate and the time when they ate it. Tell them the age and weight of that person. Tell them what the person ate and the time when he/she ate it. Brainstorm: Ask learners: Where should we keep our medicine? What happens when someone take a lot of medicine? Who should we call? Instructions: 1. Explain new vocabulary with the help of pictures or illustrations. 2. Distribute the activity sheet, Overdose Calling the Poison Control Centre 3. Read the dialogue with the learners explaining any difficult words. 4. Demonstrate the dialogue with the help of a volunteer. 5. Allow time for the learners to practice dialogue with a partner. 6. Have them present it in front of the class. 43
46 Activity: Overdose Calling the Poison Control Centre Jenna found her son with a spilled bottle of medicine. She did not know if the boy was safe. So she dialled the Poison Control Centre at (toll free). Operator: Jenna: May I help you? My child has taken too much of a medicine. What should I do? Operator: May I have your name and phone number? Jenna: My name is Jenna. My telephone number is Operator: Jenna: What was the medicine? It was Calpox for babies. Operator: Jenna: When did this happen? About 5 minutes ago. 44
47 Activity: Overdose Calling the Poison Control Centre Operator: Jenna: How old is the child and how much does he weigh? He is 18 months old and weighs 20 pounds. Operator: Jenna: How much did he drink? Was the bottle full? It was a new bottle. It s still more than half full. Operator: Jenna: Did the doctor give him this medicine? No. Operator: Give him something to eat and drink. Do not worry, he will be ok. Jenna: Thanks, I feel much better after talking to you. Operator: Jenna: You can call again if you want. Bye Bye. 45
48 Medicine Facts Facilitator s Notes Level: CLB 1, CLB 2 Time: minutes Targeted Language Skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing Objective: To familiarize learners with some facts about medicines. Materials: Copy of activity sheet (one per learner) Pencils and erasers Pictures for new vocabulary Vocabulary: Information: expiry, refill It is important to ask your pharmacist about side effects (reaction to medicine; such as rash, breathing problem, cough, etc.) of the medicines. Never call medicine candy when you give it to your child. Your child might want to eat more of them which could make them very sick. Write all types of medicines that you take in your medicine list. For example vitamins, herbal medicine, over-the-counter medicine etc. All medicines should be taken for as long as your doctor tells you. If you feel better before completing your medicine, you should not stop taking the medicines. If you finish your prescription medicine, you should check the label to see if there are refills. If you don t have enough medicine, you cannot take half dose. You should get a refill. It is not safe to take medicine after the expiry date. If you are not sure which over-the-counter medicine to buy, you can ask the pharmacist. The directions on over-the-counter medicines will tell you if it is safe for children. Phone number for Calgary Poison Control Center is Brainstorm: Ask Learners: What is the difference between prescription medicine and over-thecounter medicine? What do side effects mean? Instructions: 1. Write new vocabulary on the board and explain their meanings with the help of pictures. 2. Distribute activity sheet, Medicine Facts. 3. Read the sentences with the class explaining them. 4. Obtain class consensus on answers. 46
49 Answer Key: A: B: 1. Yes 2. Yes 3. Yes 4. No 5. No 1. Yes 2. Yes 3. Yes 4. No 5. No 47
50 Activity: Medicine Facts A. Read the sentences and circle Yes or No. 1. Write all types of medicines that you take in your medicine list. Yes No 2. Phone number for Calgary Poison Control Center is Yes No 3. It is important to ask your pharmacist about side effects of the medicines. Yes No 4. Is it a good idea to call medicine candy when giving it to children? Yes No 5. If you feel better before completing your medicine, you should stop taking the medicines. Yes No 48
51 Activity: Medicine Facts B. Read the sentences and circle Yes or No. 1. If you are not sure which over-the-counter medicine to buy, you can ask the pharmacist. Yes No 2. The directions on over-the-counter medicines will tell you if it is safe for children. Yes No 3. If you finish your prescription medicine, you should check the label to see if there are refills. Yes No 4. If you don t have enough medicine, you can take half dose until you can get refills. Yes No 5. It is safe to take medicine after the expiry date. Yes No 49
52 Additional References Poison Prevention (City of Calgary) /content.calgary.ca/cca/city+living/safety+and+health/safety+tips/in+the+home/p oison+prevention.htme Medication Poison Prevention Tips (Safe Kids USA) 50
Module 6 Navigating a Health Facility CIWA
 Module 6 Navigating a Health Facility CIWA Table of Contents Reader s Notes... 1 Introduction... 3 Directions... 5 Hospital Directions... 9 Hospital Departments... 12 Hospital Departments What are they
Module 6 Navigating a Health Facility CIWA Table of Contents Reader s Notes... 1 Introduction... 3 Directions... 5 Hospital Directions... 9 Hospital Departments... 12 Hospital Departments What are they
CHAPTER 3 Medicines 35
 P CHA TER 3 Medicines 35 Learning About Medicines Medicines medicines Medicines are something you use when you are sick and want to get better. You can also use medicines to stay healthy. Medicines are
P CHA TER 3 Medicines 35 Learning About Medicines Medicines medicines Medicines are something you use when you are sick and want to get better. You can also use medicines to stay healthy. Medicines are
Medicines are Drugs. changes how your body works, or. treats or prevents a disease or symptom
 1 Welcome to Medicines in My Home. Today, we are going to talk about over-the-counter (or OTC) medicines and how to use OTC medicine labels. To use OTC medicines safely and correctly, you need to read
1 Welcome to Medicines in My Home. Today, we are going to talk about over-the-counter (or OTC) medicines and how to use OTC medicine labels. To use OTC medicines safely and correctly, you need to read
Advice from the pharmacist
 ESOL TOPIC 4 THEME 6 LEARNING OUTCOMES To consult a pharmacist about minor health concerns To follow instructions from a pharmacist about medicines RESOURCES Copies of Resources 1 3 Cards for instructions
ESOL TOPIC 4 THEME 6 LEARNING OUTCOMES To consult a pharmacist about minor health concerns To follow instructions from a pharmacist about medicines RESOURCES Copies of Resources 1 3 Cards for instructions
Lesson 8 Using Medicines in Safe Ways
 Lesson 8 Using Medicines in Safe Ways Overview Students identify symptoms or signals the body sends when a person is sick. They define medicine and learn the difference between prescription and over-the-counter
Lesson 8 Using Medicines in Safe Ways Overview Students identify symptoms or signals the body sends when a person is sick. They define medicine and learn the difference between prescription and over-the-counter
Do Not Reproduce. Things to Tell Your Health Care Provider
 Note: This CareKit does not replace expert medical care. 2 Things to Tell Your Health Care Provider Before medicine is prescribed, tell him or her: Medicines on your health plan s preferred drug list (formulary).
Note: This CareKit does not replace expert medical care. 2 Things to Tell Your Health Care Provider Before medicine is prescribed, tell him or her: Medicines on your health plan s preferred drug list (formulary).
Oral Systemic Therapy
 Oral Systemic Therapy This information does not take the place of the care and advice of your Cancer Care Team. Talk to your Cancer Care Team about your health concerns, treatment options and any questions
Oral Systemic Therapy This information does not take the place of the care and advice of your Cancer Care Team. Talk to your Cancer Care Team about your health concerns, treatment options and any questions
Medicines and You: A Guide for Older Adults
 Medicines and You: A Guide for Older Adults Council on Family Health Provided in cooperation with U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration and the Administration on Aging
Medicines and You: A Guide for Older Adults Council on Family Health Provided in cooperation with U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration and the Administration on Aging
Oral Systemic Therapy
 Patient & Family Guide 2018 Oral Systemic Therapy www.nscancercare.ca Patient s Name: Type of Treatment: Cancer Doctor: Cancer Clinic: Phone Number: Emergency Department Phone Number: Who do I call if
Patient & Family Guide 2018 Oral Systemic Therapy www.nscancercare.ca Patient s Name: Type of Treatment: Cancer Doctor: Cancer Clinic: Phone Number: Emergency Department Phone Number: Who do I call if
Sorafenib (Nexavar ) ( sor-af-e-nib )
 Sorafenib (Nexavar ) ( sor-af-e-nib ) How the drug is given: by mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer, liver cancer, and other cancers How to take the drug by mouth Take on
Sorafenib (Nexavar ) ( sor-af-e-nib ) How the drug is given: by mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer, liver cancer, and other cancers How to take the drug by mouth Take on
Your Medicine: Be Smart. Be Safe.
 Your Medicine: Be Smart. Be Safe. Learn more about how to take medicines safely. Use the wallet card at the back of this booklet to keep track of your medicines. Keep this booklet with your medicines and
Your Medicine: Be Smart. Be Safe. Learn more about how to take medicines safely. Use the wallet card at the back of this booklet to keep track of your medicines. Keep this booklet with your medicines and
More about using medicines safely. Quick info. Doctor s phone number: Pharmacy phone number: 24 hour Poison Control Center
 More about using medicines safely Medicines in My Home: FDA Consumer Medicine Education: www.fda.gov/usemedicinesafely National Council on Patient Information and Education: www.bemedwise.org Medline Plus,
More about using medicines safely Medicines in My Home: FDA Consumer Medicine Education: www.fda.gov/usemedicinesafely National Council on Patient Information and Education: www.bemedwise.org Medline Plus,
It is used to treat or prevent upset stomach and throwing up. What do I need to tell my doctor BEFORE I take this drug?
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Ondansetron Brand Names: US Zofran; Zofran ODT [DSC]; Zuplenz Brand Names: Canada Ondissolve ODF; Zofran ODT What is this drug used for? It is used to treat or prevent upset
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Ondansetron Brand Names: US Zofran; Zofran ODT [DSC]; Zuplenz Brand Names: Canada Ondissolve ODF; Zofran ODT What is this drug used for? It is used to treat or prevent upset
TRIPROLIDINE. Please read this leaflet and the packaging of the medicine you purchased, carefully before you start using triprolidine.
 TRIPROLIDINE New Zealand Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet The medicine you have purchased contains triprolidine. This leaflet is intended to provide information on the active ingredient
TRIPROLIDINE New Zealand Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet The medicine you have purchased contains triprolidine. This leaflet is intended to provide information on the active ingredient
Everolimus (Afinitor )
 Everolimus (Afinitor ) ( e-ver-oh-li-mus ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: to slow the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer and other cancers How to take the drug Take with or without food and
Everolimus (Afinitor ) ( e-ver-oh-li-mus ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: to slow the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer and other cancers How to take the drug Take with or without food and
Eltrombopag (Promacta )
 Eltrombopag (Promacta ) ( el TROM boe pag ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: to treat aplastic anemia and increase low platelet counts in some conditions How to take this drug 1. Take this medication
Eltrombopag (Promacta ) ( el TROM boe pag ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: to treat aplastic anemia and increase low platelet counts in some conditions How to take this drug 1. Take this medication
What are some things I need to know or do while I take
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Cyclophosphamide Brand Names: Canada Procytox What is this drug used for? It is used to treat cancer. It is used to treat nephrotic syndrome. It may be g iven to you for other
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Cyclophosphamide Brand Names: Canada Procytox What is this drug used for? It is used to treat cancer. It is used to treat nephrotic syndrome. It may be g iven to you for other
It is very common to get symptoms like cough, sore throat, runny nose and watery eyes. Usually when you
 A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health Let s Learn about Respiratory Infections It is very common to get symptoms like cough, sore throat, runny nose and watery eyes. Usually when you
A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health Let s Learn about Respiratory Infections It is very common to get symptoms like cough, sore throat, runny nose and watery eyes. Usually when you
Medication Safety Presentation
 Appendix E Aid 1: Sample Event Poster Medication Safety Presentation Do YOU know your role on the healthcare team? Do YOU know the questions to ask your pharmacist? Do YOU know safe medication practices?
Appendix E Aid 1: Sample Event Poster Medication Safety Presentation Do YOU know your role on the healthcare team? Do YOU know the questions to ask your pharmacist? Do YOU know safe medication practices?
All medicines have risks and benefits. Your doctor has weighed the risks of you taking Triprim against the benefits he or she expects it will have.
 Triprim Tablets Trimethoprim Tablets Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet? The leaflet answers some common questions about Triprim tablets. It does not contain all the available information
Triprim Tablets Trimethoprim Tablets Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet? The leaflet answers some common questions about Triprim tablets. It does not contain all the available information
It is used to prevent or treat soft, brittle bones (osteoporosis). It may be g iven to you for other reasons. Talk with the doctor.
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Alendronate Brand Names: US Binosto; Fosamax Brand Names: Canada Fosamax What is this drug used for? It is used to prevent or treat soft, brittle bones (osteoporosis). It
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Alendronate Brand Names: US Binosto; Fosamax Brand Names: Canada Fosamax What is this drug used for? It is used to prevent or treat soft, brittle bones (osteoporosis). It
Acetylcysteine Injection; Acetylcysteine Solution; Mucomyst; Parvolex. It is used to thin mucus so it can be taken from the body by coughing.
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Acetylcysteine Brand Names: US Acetadote; Cetylev Brand Names: Canada Acetylcysteine Injection; Acetylcysteine Solution; Mucomyst; Parvolex What is this drug used for? It
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Acetylcysteine Brand Names: US Acetadote; Cetylev Brand Names: Canada Acetylcysteine Injection; Acetylcysteine Solution; Mucomyst; Parvolex What is this drug used for? It
It does not contain all the available information. It does not take the place of talking to your doctor or pharmacist.
 STILNOX zolpidem tartrate Consumer Medicine Information WARNING: ZOLPIDEM MAY BE ASSOCIATED WITH UNUSUAL AND POTENTIALLY DANGEROUS BEHAVIOURS WHILST APPARENTLY ASLEEP. THESE HAVE INCLUDED SLEEP WALKING,
STILNOX zolpidem tartrate Consumer Medicine Information WARNING: ZOLPIDEM MAY BE ASSOCIATED WITH UNUSUAL AND POTENTIALLY DANGEROUS BEHAVIOURS WHILST APPARENTLY ASLEEP. THESE HAVE INCLUDED SLEEP WALKING,
Dabrafenib (Tafinlar )
 Dabrafenib (Tafinlar ) ( da-braf-e-nib ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in melanoma and other cancers. How to take this drug Take this medication on an empty stomach
Dabrafenib (Tafinlar ) ( da-braf-e-nib ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in melanoma and other cancers. How to take this drug Take this medication on an empty stomach
This leaflet answers some common questions about ATIVAN. It does not contain all of the available information.
 Ativan Lorazepam Tablets Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about ATIVAN. It does not contain all of the available information. It does not
Ativan Lorazepam Tablets Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about ATIVAN. It does not contain all of the available information. It does not
THE FACTS ABOUT PRESCRIPTION MEDICINE MISUSE
 JUNE This month, Health is Primary is focusing on safe use of prescription medicines. We are sharing the facts about the risks of medicine misuse and the importance of using medicines as prescribed along
JUNE This month, Health is Primary is focusing on safe use of prescription medicines. We are sharing the facts about the risks of medicine misuse and the importance of using medicines as prescribed along
How Entecavir GH Works
 entecavir monohydrate tablets ENTECAVIR GH Tablets Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet Read this leaflet carefully before taking. This leaflet answers some common questions about. It
entecavir monohydrate tablets ENTECAVIR GH Tablets Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet Read this leaflet carefully before taking. This leaflet answers some common questions about. It
Health Talk with your partner about a time when you were sick Discuss:
 Health Talk with your partner about a time when you were sick Discuss: What was the matter? How did you feel? What did you do? How long were you ill? Fill in the gaps with the correct vocabulary backache
Health Talk with your partner about a time when you were sick Discuss: What was the matter? How did you feel? What did you do? How long were you ill? Fill in the gaps with the correct vocabulary backache
Medication Administration Curriculum INSTRUCTOR S MANUAL. Name State Date
 Instructions: Circle the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. If select modules were presented, only fill out the questions related to those modules. MODULE 1
Instructions: Circle the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. If select modules were presented, only fill out the questions related to those modules. MODULE 1
Chemists Own Strong Pain Extra Paracetamol and Codeine Phosphate
 Chemists Own Strong Pain Extra Paracetamol and Codeine Phosphate Consumer Medicine Information(CMI) Please read this information before you start taking this medicine. What is in this CMI? This CMI answers
Chemists Own Strong Pain Extra Paracetamol and Codeine Phosphate Consumer Medicine Information(CMI) Please read this information before you start taking this medicine. What is in this CMI? This CMI answers
Imatinib (Gleevec ) ( eye-mat-eh-nib )
 Imatinib (Gleevec ) ( eye-mat-eh-nib ) How drug is given: by mouth Purpose: stops growth of cancer cells in leukemia, gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST), and other cancers How to take the drug by mouth
Imatinib (Gleevec ) ( eye-mat-eh-nib ) How drug is given: by mouth Purpose: stops growth of cancer cells in leukemia, gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST), and other cancers How to take the drug by mouth
Medication Information for Parents and Teachers
 Medication Information for Parents and Teachers General Information About Medication Hydroxyzine Vistaril Each child and adolescent is different. No one has exactly the same combination of medical and
Medication Information for Parents and Teachers General Information About Medication Hydroxyzine Vistaril Each child and adolescent is different. No one has exactly the same combination of medical and
health care quality Your Medicine: Play It Safe Medicine Record Form at the Learn more about how to take medicines safely. Use the
 Your Medicine: Play It Safe Learn more about how to take medicines safely. Use the Medicine Record Form at the back of this booklet to keep track of your medicines. Logo Here health care quality Have you
Your Medicine: Play It Safe Learn more about how to take medicines safely. Use the Medicine Record Form at the back of this booklet to keep track of your medicines. Logo Here health care quality Have you
PHOLCODINE. Please follow the instructions on the packaging of the medicine you purchased and in this leaflet before you start using pholcodine.
 PHOLCODINE New Zealand Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet The medicine you have purchased contains pholcodine. This leaflet is intended to provide information on the active ingredient
PHOLCODINE New Zealand Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet The medicine you have purchased contains pholcodine. This leaflet is intended to provide information on the active ingredient
For the Patient: Trastuzumab emtansine Other names: KADCYLA
 For the Patient: Trastuzumab emtansine Other names: KADCYLA Trastuzumab emtansine (tras tooz' ue mab em tan' seen) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. Trastuzumab emtansine is a clear
For the Patient: Trastuzumab emtansine Other names: KADCYLA Trastuzumab emtansine (tras tooz' ue mab em tan' seen) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. Trastuzumab emtansine is a clear
F O R Y O U R H E A L T H. Nicotine and Your Health. Vocabulary Emphysema Addicted Toxic Secondhand smoke
 Do you have a family member or a friend who smokes cigarettes or chews tobacco? Have you heard that person say, I am OK... I have been smoking for 20 Vocabulary Emphysema Addicted Toxic Secondhand smoke
Do you have a family member or a friend who smokes cigarettes or chews tobacco? Have you heard that person say, I am OK... I have been smoking for 20 Vocabulary Emphysema Addicted Toxic Secondhand smoke
Valsartan and Hydrochlorothiazide
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Valsartan and Hydrochlorothiazide Brand Names: US Diovan HCT Brand Names: Canada Diovan HCT; Valsartan-HCT; Valsartan-HCTZ Warning Do not take if you are preg nant. Use during
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Valsartan and Hydrochlorothiazide Brand Names: US Diovan HCT Brand Names: Canada Diovan HCT; Valsartan-HCT; Valsartan-HCTZ Warning Do not take if you are preg nant. Use during
How will you know if you ate contaminated food? Diarrhea Stomach cramps Fever Nausea/Vomiting
 A H E A L T H Y H O U S E You Can Prevent Food Poisoning! The food you eat can make you sick. Many people go to the hospital each year because they get food poisoning. Learn what you can do to prevent
A H E A L T H Y H O U S E You Can Prevent Food Poisoning! The food you eat can make you sick. Many people go to the hospital each year because they get food poisoning. Learn what you can do to prevent
Pain and Ways to Manage It
 Pain and Ways to Manage It FM.850.M311.PHC (R.Jul-15) 1 Contents This page intentionally left blank. What the words mean............................. 2 Why is it important to manage your pain?............
Pain and Ways to Manage It FM.850.M311.PHC (R.Jul-15) 1 Contents This page intentionally left blank. What the words mean............................. 2 Why is it important to manage your pain?............
MEDICATION GUIDE. ACTIQ (AK-tik) CII (fentanyl citrate) oral transmucosal lozenge 200 mcg, 400 mcg, 600 mcg, 800 mcg, 1200 mcg, 1600 mcg
 MEDICATION GUIDE ACTIQ (AK-tik) CII (fentanyl citrate) oral transmucosal lozenge 200 mcg, 400 mcg, 600 mcg, 800 mcg, 1200 mcg, 1600 mcg IMPORTANT: Do not use ACTIQ unless you are regularly using another
MEDICATION GUIDE ACTIQ (AK-tik) CII (fentanyl citrate) oral transmucosal lozenge 200 mcg, 400 mcg, 600 mcg, 800 mcg, 1200 mcg, 1600 mcg IMPORTANT: Do not use ACTIQ unless you are regularly using another
CIPROXIN HC Ear Drops
 CIPROXIN HC Ear Drops Ciprofloxacin and Hydrocortisone CONSUMER MEDICINE INFORMATION What is in this leaflet Please read this leaflet carefully before you use. This leaflet answers some common questions
CIPROXIN HC Ear Drops Ciprofloxacin and Hydrocortisone CONSUMER MEDICINE INFORMATION What is in this leaflet Please read this leaflet carefully before you use. This leaflet answers some common questions
Medication Information for Parents and Teachers
 Medication Information for Parents and Teachers General Information About Medication Melatonin Each child and adolescent is different. No one has exactly the same combination of medical and psychological
Medication Information for Parents and Teachers General Information About Medication Melatonin Each child and adolescent is different. No one has exactly the same combination of medical and psychological
ZOLPIDEM PHARMACOR Zolpidem tartrate
 Zolpidem tartrate Consumer Medicine Information Warning: Zolpidem may be associated with unusual and potentially dangerous behavior whilst apparently asleep. These have included sleep walking, driving
Zolpidem tartrate Consumer Medicine Information Warning: Zolpidem may be associated with unusual and potentially dangerous behavior whilst apparently asleep. These have included sleep walking, driving
Tips for Teaching ARISE Life Management Skills...3. Introduction...6 Lessons...7. Introduction...12 Lessons Introduction...19 Lessons...
 ARISE Life-Skills for Middle School - Volume 4 Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Tips for Teaching ARISE Life Management Skills...3 SECTION ONE: Health care is self-care Introduction...6 Lessons...7
ARISE Life-Skills for Middle School - Volume 4 Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Tips for Teaching ARISE Life Management Skills...3 SECTION ONE: Health care is self-care Introduction...6 Lessons...7
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Pulmicort Turbohaler budesonide. 1. What Pulmicort Turbohaler is and what it is used for
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Pulmicort Turbohaler budesonide Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine. Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again. If
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Pulmicort Turbohaler budesonide Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine. Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again. If
Ibrutinib (Imbruvica )
 Ibrutinib (Imbruvica ) ( eye BROO ti nib ) How drug is given: by mouth Purpose: to stop the growth of cancer cells in lymphoma and other cancers How to take the drug Take each dose at the same time every
Ibrutinib (Imbruvica ) ( eye BROO ti nib ) How drug is given: by mouth Purpose: to stop the growth of cancer cells in lymphoma and other cancers How to take the drug Take each dose at the same time every
APOHEALTH Diarrhoea Relief PLUS
 APOHEALTH Diarrhoea Relief PLUS Chewable Tablets Contains the active ingredient Loperamide hydrochloride and Simethicone Consumer Medicine Information For a copy of a large print leaflet, Ph: 1800 195
APOHEALTH Diarrhoea Relief PLUS Chewable Tablets Contains the active ingredient Loperamide hydrochloride and Simethicone Consumer Medicine Information For a copy of a large print leaflet, Ph: 1800 195
For the Patient: Fludarabine injection Other names: FLUDARA
 For the Patient: Fludarabine injection Other names: FLUDARA Fludarabine (floo-dare-a-been) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell
For the Patient: Fludarabine injection Other names: FLUDARA Fludarabine (floo-dare-a-been) is a drug that is used to treat many types of cancer. It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein. Tell
For the Patient: Bendamustine Other names: TREANDA
 For the Patient: Bendamustine Other names: TREANDA Bendamustine (ben'' da mus' teen) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer (lymphoma). It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein.
For the Patient: Bendamustine Other names: TREANDA Bendamustine (ben'' da mus' teen) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer (lymphoma). It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein.
CONSUMER MEDICINE INFORMATION
 CONSUMER MEDICINE INFORMATION 250 mg, 500 mg and 1000 mg Levetiracetam WHAT IS IN THIS LEAFLET This leaflet answers some common questions about. It does not contain all the available information. It does
CONSUMER MEDICINE INFORMATION 250 mg, 500 mg and 1000 mg Levetiracetam WHAT IS IN THIS LEAFLET This leaflet answers some common questions about. It does not contain all the available information. It does
Zovirax Ophthalmic (eye) Ointment Acyclovir
 Zovirax Ophthalmic (eye) Ointment Acyclovir Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about Zovirax ophthalmic ointment. It does not contain all the
Zovirax Ophthalmic (eye) Ointment Acyclovir Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about Zovirax ophthalmic ointment. It does not contain all the
Head. ing. More about using medicines safely. Quick info. Doctor s phone number: Pharmacy phone number: 24 hour Poison Control Center
 More about using medicines safely Medicines in My Home: www.fda.gov/medsinmyhome Visit the resources in the Student Room Department of Health and Human Services U.S. Food and Drug Administration FDA Consumer
More about using medicines safely Medicines in My Home: www.fda.gov/medsinmyhome Visit the resources in the Student Room Department of Health and Human Services U.S. Food and Drug Administration FDA Consumer
If you have any concerns about taking this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
 CHAMPIX Varenicline tartrate What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about CHAMPIX. It does not contain all the available information. It does not take the place of talking to
CHAMPIX Varenicline tartrate What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about CHAMPIX. It does not contain all the available information. It does not take the place of talking to
It is used to lower blood sugar in patients with high blood sugar (diabetes). What do I need to tell my doctor BEFORE I take this drug?
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Semaglutide Brand Names: US Ozempic Brand Names: Canada Ozempic Warning This drug has been shown to cause thyroid cancer in some animals. It is not known if this happens in
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Semaglutide Brand Names: US Ozempic Brand Names: Canada Ozempic Warning This drug has been shown to cause thyroid cancer in some animals. It is not known if this happens in
MEDICATION GUIDE ZUBSOLV (Zub-solve) (buprenorphine and naloxone) Sublingual Tablet (CIII)
 MEDICATION GUIDE ZUBSOLV (Zub-solve) (buprenorphine and naloxone) Sublingual Tablet (CIII) IMPORTANT: Keep ZUBSOLV in a secure place away from children. If a child accidentally takes ZUBSOLV, this is a
MEDICATION GUIDE ZUBSOLV (Zub-solve) (buprenorphine and naloxone) Sublingual Tablet (CIII) IMPORTANT: Keep ZUBSOLV in a secure place away from children. If a child accidentally takes ZUBSOLV, this is a
For the Patient: PROTOCOL SMAVTMZ Other Names: Palliative Therapy for Malignant Melanoma with Brain Metastases Using Temozolomide
 For the Patient: PROTOCOL SMAVTMZ Other Names: Palliative Therapy for Malignant Melanoma with Brain Metastases Using Temozolomide SM = Melanoma AV = Advanced TMZ = Temozolomide ABOUT THIS MEDICATION What
For the Patient: PROTOCOL SMAVTMZ Other Names: Palliative Therapy for Malignant Melanoma with Brain Metastases Using Temozolomide SM = Melanoma AV = Advanced TMZ = Temozolomide ABOUT THIS MEDICATION What
Divulging drug differences
 Lesson 2 Divulging drug differences SPECIFIC OUTCOMES Expand practices that provide safety for self and others by identifying a variety of drugs recognizing three different categories of drugs (legally
Lesson 2 Divulging drug differences SPECIFIC OUTCOMES Expand practices that provide safety for self and others by identifying a variety of drugs recognizing three different categories of drugs (legally
MODULE 3 How to Administer Medication
 MODULE 3 How to Administer Medication Introduction: top common errors 5 Rights Identifying as needed conditions Universal/standard precautions Preparing to administer medication Medication administration
MODULE 3 How to Administer Medication Introduction: top common errors 5 Rights Identifying as needed conditions Universal/standard precautions Preparing to administer medication Medication administration
Simplotan* tablets Tinidazole (tin-id-azole)
 Simplotan* tablets Tinidazole (tin-id-azole) Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about Simplotan. It does not contain all the available information.
Simplotan* tablets Tinidazole (tin-id-azole) Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about Simplotan. It does not contain all the available information.
SANDOMIGRAN. 0.5mg tablet Pizotifen malate
 SANDOMIGRAN 0.5mg tablet Pizotifen malate What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about Sandomigran. It does not contain all the available information. It does not take the place
SANDOMIGRAN 0.5mg tablet Pizotifen malate What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about Sandomigran. It does not contain all the available information. It does not take the place
Midostaurin (Rydapt )
 Midostaurin (Rydapt ) ( mye doe STAW rin ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and other cancers. How to take this drug 1. Take this
Midostaurin (Rydapt ) ( mye doe STAW rin ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and other cancers. How to take this drug 1. Take this
A Guide to Help You Reduce and Stop Using Tobacco
 Let s Talk Tobacco A Guide to Help You Reduce and Stop Using Tobacco Congratulations for taking this first step towards a healthier you! 1-866-710-QUIT (7848) albertaquits.ca It can be hard to stop using
Let s Talk Tobacco A Guide to Help You Reduce and Stop Using Tobacco Congratulations for taking this first step towards a healthier you! 1-866-710-QUIT (7848) albertaquits.ca It can be hard to stop using
Medicines. Let s Talk About. health literacy. wisconsin. A division of Wisconsin Literacy, Inc.
 Let s Talk About Medicines Supported by a grant from the Wisconsin Department of Health Services Minority Health Program wisconsin health literacy A division of Wisconsin Literacy, Inc. What is a pharmacy?
Let s Talk About Medicines Supported by a grant from the Wisconsin Department of Health Services Minority Health Program wisconsin health literacy A division of Wisconsin Literacy, Inc. What is a pharmacy?
Shopping List for Knee Arthroscopy
 inserts 8-08.qxp 9/16/2008 3:41 PM Page 1 Shopping List for Knee Arthroscopy The following is a list of supplies which you should have at home following your surgery: Adhesive bandages (Band-Aids ) Helpful
inserts 8-08.qxp 9/16/2008 3:41 PM Page 1 Shopping List for Knee Arthroscopy The following is a list of supplies which you should have at home following your surgery: Adhesive bandages (Band-Aids ) Helpful
Beclazone 50, 100, 250 micrograms CFC-Free Inhaler
 NEW ZEALAND CONSUMER MEDICINE INFORMATION Beclazone 50, 100, 250 micrograms CFC-Free Inhaler Beclometasone dipropionate 50, 100, or 250 micrograms per metered dose ( puff ) Please read this leaflet carefully
NEW ZEALAND CONSUMER MEDICINE INFORMATION Beclazone 50, 100, 250 micrograms CFC-Free Inhaler Beclometasone dipropionate 50, 100, or 250 micrograms per metered dose ( puff ) Please read this leaflet carefully
Information Sheet 10. Medication Hints and Tips (Updated August 2014)
 An information sheet on Medication problems and how to prevent them. Memory Loss... People who suffer from dementia or Alzheimer s disease may simply forget to take their medications, causing them to skip
An information sheet on Medication problems and how to prevent them. Memory Loss... People who suffer from dementia or Alzheimer s disease may simply forget to take their medications, causing them to skip
MEDICATION GUIDE SUBOXONE (Sub OX own) (buprenorphine and naloxone) Sublingual Tablets (CIII)
 MEDICATION GUIDE SUBOXONE (Sub OX own) (buprenorphine and naloxone) Sublingual Tablets (CIII) IMPORTANT: Keep SUBOXONE in a secure place away from children. Accidental use by a child is a medical emergency
MEDICATION GUIDE SUBOXONE (Sub OX own) (buprenorphine and naloxone) Sublingual Tablets (CIII) IMPORTANT: Keep SUBOXONE in a secure place away from children. Accidental use by a child is a medical emergency
What do I need to tell my doctor BEFORE I take this drug?
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Benzoin Brand Names: US Benz-Protect Swabs [OTC]; Sprayzoin [OTC] What is this drug used for? It is used to treat or prevent certain skin problems. It is used to treat canker
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Benzoin Brand Names: US Benz-Protect Swabs [OTC]; Sprayzoin [OTC] What is this drug used for? It is used to treat or prevent certain skin problems. It is used to treat canker
For the Patient: ULUAVPMTN
 ABOUT THIS MEDICATION For the Patient: ULUAVPMTN Other Names: Maintenance Therapy of Advanced n-small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) with Pemetrexed U = Undesignated (requires special approval) LU = LUng AV
ABOUT THIS MEDICATION For the Patient: ULUAVPMTN Other Names: Maintenance Therapy of Advanced n-small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) with Pemetrexed U = Undesignated (requires special approval) LU = LUng AV
Fluticasone propionate, 50 mcg per spray. Please read this leaflet carefully before you use FLIXONASE ALLERGY & HAYFEVER 24 HOUR.
 FLIXONASE ALLERGY & HAYFEVER 24 HOUR Fluticasone propionate, 50 mcg per spray Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet? Please read this leaflet carefully before you use FLIXONASE ALLERGY
FLIXONASE ALLERGY & HAYFEVER 24 HOUR Fluticasone propionate, 50 mcg per spray Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet? Please read this leaflet carefully before you use FLIXONASE ALLERGY
Zoster Vaccine (Recombinant)
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Zoster Vaccine (Recombinant) Brand Names: US Shing rix What is this drug used for? It is used to prevent shingles. What do I need to tell my doctor BEFORE I take this drug?
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Zoster Vaccine (Recombinant) Brand Names: US Shing rix What is this drug used for? It is used to prevent shingles. What do I need to tell my doctor BEFORE I take this drug?
Ceclor CD cefaclor monohydrate sustained release tablets
 Ceclor CD cefaclor monohydrate sustained release tablets Consumer Medicine Information (CMI) What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about Ceclor CD. It does not contain all
Ceclor CD cefaclor monohydrate sustained release tablets Consumer Medicine Information (CMI) What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about Ceclor CD. It does not contain all
2. Describing Ailments and Symptoms
 HEALTH LITERACY CURRICULUM 2. Describing Ailments and Symptoms Materials Needed Warmup/Review Check homework Activity 1 Listening Activity 2 Treatments Board or chart paper Markers Pictures of ailments/symptoms:
HEALTH LITERACY CURRICULUM 2. Describing Ailments and Symptoms Materials Needed Warmup/Review Check homework Activity 1 Listening Activity 2 Treatments Board or chart paper Markers Pictures of ailments/symptoms:
Share the important information in this Medication Guide with members of your household.
 Medication Guide BUPRENORPHINE (BUE-pre-NOR-feen) and NALOXONE (nal-ox-one) Sublingual Tablets, CIII IMPORTANT: Keep buprenorphine and naloxone sublingual tablets in a secure place away from children.
Medication Guide BUPRENORPHINE (BUE-pre-NOR-feen) and NALOXONE (nal-ox-one) Sublingual Tablets, CIII IMPORTANT: Keep buprenorphine and naloxone sublingual tablets in a secure place away from children.
FLIXOTIDE ACCUHALER Fluticasone propionate 50, 100, 250 micrograms per inhalation
 FLIXOTIDE ACCUHALER Fluticasone propionate 50, 100, 250 micrograms per inhalation Consumer Medicine Information Please read this leaflet carefully before you start taking Flixotide What is in this leaflet?
FLIXOTIDE ACCUHALER Fluticasone propionate 50, 100, 250 micrograms per inhalation Consumer Medicine Information Please read this leaflet carefully before you start taking Flixotide What is in this leaflet?
Medication Use safety Training FOR SENIORS
 www.mustforseniors.org Medication Use safety Training FOR SENIORS Medication Use Safety Training for Seniors A National Education Campaign for Older Adults and Caregivers developed by the National Council
www.mustforseniors.org Medication Use safety Training FOR SENIORS Medication Use Safety Training for Seniors A National Education Campaign for Older Adults and Caregivers developed by the National Council
Legal and Illegal Substances
 Learning Goals By the end of this lesson, students will be able to: demonstrate an understanding of the abuse of different types of legal and illegal substances demonstrate an understanding of the impact
Learning Goals By the end of this lesson, students will be able to: demonstrate an understanding of the abuse of different types of legal and illegal substances demonstrate an understanding of the impact
It may be g iven to you for other reasons. Talk with the doctor. What do I need to tell my doctor BEFORE I take this drug?
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Bendamustine Brand Names: US Bendeka; Treanda Brand Names: Canada Treanda What is this drug used for? It is used to treat a type of leukemia. It is used to treat a type of
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Bendamustine Brand Names: US Bendeka; Treanda Brand Names: Canada Treanda What is this drug used for? It is used to treat a type of leukemia. It is used to treat a type of
It may be g iven to your child for other reasons. Talk with the doctor.
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Gabapentin Brand Names: US Gralise; Gralise Starter; Neurontin Brand Names: Canada Neurontin What is this drug used for? It is used to treat seizures. It may be g iven to
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Gabapentin Brand Names: US Gralise; Gralise Starter; Neurontin Brand Names: Canada Neurontin What is this drug used for? It is used to treat seizures. It may be g iven to
Otezla (apremilast) film coated tablets
 New Zealand Consumer Medicine Information Otezla (apremilast) film coated tablets WHAT IS IN THIS LEAFLET This leaflet answers some common questions about Otezla. It does not contain all the available
New Zealand Consumer Medicine Information Otezla (apremilast) film coated tablets WHAT IS IN THIS LEAFLET This leaflet answers some common questions about Otezla. It does not contain all the available
Cosudex. Bicalutamide 50 mg Tablets CONSUMER MEDICINE INFORMATION
 Cosudex Bicalutamide 50 mg Tablets CONSUMER MEDICINE INFORMATION What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some of the common questions people ask about Cosudex. It does not contain all the information
Cosudex Bicalutamide 50 mg Tablets CONSUMER MEDICINE INFORMATION What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some of the common questions people ask about Cosudex. It does not contain all the information
APO-Olopatadine Eye Drops Contains the active ingredient olopatadine (as olopatadine hydrochloride)
 APO-Olopatadine Eye Drops Contains the active ingredient olopatadine (as olopatadine hydrochloride) Consumer Medicine Information For a copy of a large print leaflet, Ph: 1800 195 055 What is in this leaflet
APO-Olopatadine Eye Drops Contains the active ingredient olopatadine (as olopatadine hydrochloride) Consumer Medicine Information For a copy of a large print leaflet, Ph: 1800 195 055 What is in this leaflet
Medication Guide Fentanyl transdermal system, CII Rx Only Fentanyl transdermal system is: A strong prescription pain medicine that contains an opioid
 Medication Guide Fentanyl transdermal system, CII Rx Only Fentanyl transdermal system is: A strong prescription pain medicine that contains an opioid (narcotic) that is used to manage pain severe enough
Medication Guide Fentanyl transdermal system, CII Rx Only Fentanyl transdermal system is: A strong prescription pain medicine that contains an opioid (narcotic) that is used to manage pain severe enough
6. Never give SUBSYS to anyone else, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them or even cause death.
 Medication Guide SUBSYS (sub sis) CII (fentanyl) sublingual spray 100 mcg, 200 mcg, 400 mcg, 600 mcg, 800 mcg IMPORTANT: Do not use SUBSYS unless you are regularly using another opioid pain medicine around-the-clock
Medication Guide SUBSYS (sub sis) CII (fentanyl) sublingual spray 100 mcg, 200 mcg, 400 mcg, 600 mcg, 800 mcg IMPORTANT: Do not use SUBSYS unless you are regularly using another opioid pain medicine around-the-clock
MEDICINES AND PRESCRIPTIONS
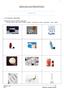 1 MEDICINES AND PRESCRIPTIONS MEDICINES I VOCABULARY: MEDICINES 1. Match the picture and the medication. capsule - cream - drip - drops - inhaler - injection - ointment - pill - spray - suppository - syrup
1 MEDICINES AND PRESCRIPTIONS MEDICINES I VOCABULARY: MEDICINES 1. Match the picture and the medication. capsule - cream - drip - drops - inhaler - injection - ointment - pill - spray - suppository - syrup
Module II Medication Basics
 Module II Medication Basics Kinds of Medications People make different choices about medications and remedies. Today, there are more than 11,000 medications available to the consumer. There are also hundreds
Module II Medication Basics Kinds of Medications People make different choices about medications and remedies. Today, there are more than 11,000 medications available to the consumer. There are also hundreds
Lenvatinib (Lenvima ) ( len-va-ti-nib )
 Lenvatinib (Lenvima ) ( len-va-ti-nib ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To treat thyroid cancer or other cancers How to take this drug This medicine can be taken with or without food. Take each dose
Lenvatinib (Lenvima ) ( len-va-ti-nib ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To treat thyroid cancer or other cancers How to take this drug This medicine can be taken with or without food. Take each dose
For the Patient: LUAVPG (Carboplatin Option)
 For the Patient: LUAVPG (Carboplatin Option) Other Names: Treatment of Advanced n-small Cell Lung Cancer with Carboplatin and Gemcitabine LU = LUng AV = AdVanced PG = CarboPlatin, Gemcitabine ABOUT THIS
For the Patient: LUAVPG (Carboplatin Option) Other Names: Treatment of Advanced n-small Cell Lung Cancer with Carboplatin and Gemcitabine LU = LUng AV = AdVanced PG = CarboPlatin, Gemcitabine ABOUT THIS
What do I need to tell my doctor BEFORE I take this drug? If you have an allerg y to ofatumumab or any other part of this drug.
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Ofatumumab Brand Names: US Arzerra Brand Names: Canada Arzerra Warning If you have had hepatitis B before or carry the virus, this drug can cause the virus to become active.
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Ofatumumab Brand Names: US Arzerra Brand Names: Canada Arzerra Warning If you have had hepatitis B before or carry the virus, this drug can cause the virus to become active.
MEDICATION GUIDE SUBOXONE (Sub OX own) (buprenorphine and naloxone) Sublingual Film for sublingual or buccal administration (CIII)
 MEDICATION GUIDE SUBOXONE (Sub OX own) (buprenorphine and naloxone) Sublingual Film for sublingual or buccal administration (CIII) IMPORTANT: Keep SUBOXONE in a secure place away from children. Accidental
MEDICATION GUIDE SUBOXONE (Sub OX own) (buprenorphine and naloxone) Sublingual Film for sublingual or buccal administration (CIII) IMPORTANT: Keep SUBOXONE in a secure place away from children. Accidental
In-Patient Radioactive Iodine ( 131 I) Treatment
 In-Patient Radioactive Iodine ( 131 I) Treatment Information for patients and families Princess Margaret Read this booklet to learn: what radioactive iodine treatment is what to expect instructions to
In-Patient Radioactive Iodine ( 131 I) Treatment Information for patients and families Princess Margaret Read this booklet to learn: what radioactive iodine treatment is what to expect instructions to
Tuscarawas County Health Department. Vivitrol Treatment Consent
 Tuscarawas County Health Department Vivitrol Treatment Consent I. Vivitrol Medication Guide: a. VIVITROL (viv-i-trol) (naltrexone for extended-release injectable suspension) b. Read this Medication Guide
Tuscarawas County Health Department Vivitrol Treatment Consent I. Vivitrol Medication Guide: a. VIVITROL (viv-i-trol) (naltrexone for extended-release injectable suspension) b. Read this Medication Guide
Flu: What You Can Do. Caring for People at Home
 Flu: What You Can Do Caring for People at Home Flu: What You Can Do Caring for People at Home For more information, please visit: www.mass.gov/dph/flu CONTENTS: What is the flu? 2 table of contents Flu
Flu: What You Can Do Caring for People at Home Flu: What You Can Do Caring for People at Home For more information, please visit: www.mass.gov/dph/flu CONTENTS: What is the flu? 2 table of contents Flu
If you have any concerns about taking this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
 EZETROL ezetimibe 10 mg tablet What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about EZETROL. It does not contain all the available information. It does not take the place of talking
EZETROL ezetimibe 10 mg tablet What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about EZETROL. It does not contain all the available information. It does not take the place of talking
Apo-Ciclopirox ciclopirox USP 8% w/w Nail Lacquer (Topical Solution)
 New Zealand Consumer Medicine Information Apo-Ciclopirox ciclopirox USP 8% w/w Nail Lacquer (Topical Solution) What is in this leaflet Please read this leaflet carefully before you start using Apo-Ciclopirox.
New Zealand Consumer Medicine Information Apo-Ciclopirox ciclopirox USP 8% w/w Nail Lacquer (Topical Solution) What is in this leaflet Please read this leaflet carefully before you start using Apo-Ciclopirox.
Living with Congestive Heart Failure
 Living with Congestive Heart Failure EPICORE CENTRE Division of Cardiology 213 Heritage Medical Research Centre University of Alberta Edmonton, AB T6G 2S2 Phone: (780) 492-8525 Fax: (780) 492-6059 Website:
Living with Congestive Heart Failure EPICORE CENTRE Division of Cardiology 213 Heritage Medical Research Centre University of Alberta Edmonton, AB T6G 2S2 Phone: (780) 492-8525 Fax: (780) 492-6059 Website:
Ezetimibe Sandoz Ezetimibe 10 mg tablet
 Consumer Medicine Information Ezetimibe Sandoz Ezetimibe 10 mg tablet WHAT IS IN THIS LEAFLET This leaflet answers some common questions about Ezetimibe Sandoz. It does not contain all the available information.
Consumer Medicine Information Ezetimibe Sandoz Ezetimibe 10 mg tablet WHAT IS IN THIS LEAFLET This leaflet answers some common questions about Ezetimibe Sandoz. It does not contain all the available information.
This leaflet answers some common questions about Momex SR Tablets.
 Momex SR Modified (Sustained) Release Tablets [Morphine sulphate] CONSUMER MEDICINE INFORMATION What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about Momex SR Tablets. It does not contain
Momex SR Modified (Sustained) Release Tablets [Morphine sulphate] CONSUMER MEDICINE INFORMATION What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about Momex SR Tablets. It does not contain
Medication Information for Parents and Teachers
 Medication Information for Parents and Teachers Modafinil Provigil Armodafinil Nuvigil General Information About Medication Each child and adolescent is different. No one has exactly the same combination
Medication Information for Parents and Teachers Modafinil Provigil Armodafinil Nuvigil General Information About Medication Each child and adolescent is different. No one has exactly the same combination
