Magnetic resonance imaging in ankylosing spondylitis
|
|
|
- Camron Gaines
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 REVIEW Magnetic resonance imaging in ankylosing spondylitis Xenofon Baraliakos, Robert Landewé & Juergen Braun Author for correspondence Ruhr-University, Rheumazentrum Ruhrgebiet Herne, Bochum, Germany Tel.: ; Fax: ; Keywords: ankylosing spondylitis, anti-tumor necrosis factor-α treatment, etanercept, gadolinium, infliximab, magnetic resonance imaging, spinal inflammation, sacroiliitis, short tau inversion recovery, x-rays Although x-rays are still the standard for the assessment of structural sacroiliac joint changes and the diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis (AS), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) sequences are necessary for assessment of active sacroiliitis. Conventional radiographs of the spine are the basis for the detection of AS-related structural spinal changes, such as syndesmophytes and ankylosis. MRI of the spine is useful for the assessment of inflammatory changes, and potentially for the diagnosis of early and active stages of the disease. MRI sequences useful for the assessment of active disease are the short tau inversion recovery, the T2-fat saturated and the T1 post-gadolinium MRI sequences. For assessment of structural changes, the T1-weighted MRI sequence is used. Both sacroiliac joint and spinal changes can be quantified by evaluated scoring systems. These systems are mostly used in clinical trials to quantify the impact of therapy, such as anti-tumor necrosis factor-α agents, on spinal inflammation. Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is the major subtype of the heterogeneous group of the spondyloarthritides (SpA), which comprises reactive SpA, psoriatic SpA, SpA associated with inflammatory bowel diseases and undifferentiated SpA (uspa). Imaging plays an important role in diagnosis, classification and monitoring of patients with AS. The standard imaging approach is conventional plain radiography of sacroiliac joints and spine. However, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ultrasound are of increasing importance in clinical practice and clinical trials. Many different anatomical structures may be involved in AS. The most characteristic features are inflammation of the sacroiliac joints (SIJ) and of spinal structures, as well as new bone formation leading to syndesmophytes and ankylosis. Various spinal sites may be affected, in part dependent on the stage of the disease [1]. In later stages of the disease, inflammatory lesions affect the spine in approximately 60 80% of the cases. There are different patterns of axial involvement. The vertebral bodies may be affected by spondylitis or, together with the intervertebral disks, by spondylodiskitis. Furthermore, the surrounding soft tissues may be affected by spinal enthesitis and zygoapophyseal, costovertebral and costosternal joints by spondylarthritis [2]. Peripheral manifestations of the musculoskeletal system are mainly seen in the peripheral joints and entheses. Imaging is an important part of classification criteria for AS. The modified New York criteria combine clinical features with definite radiological criteria [3]. This is relevant for the diagnosis in clinical practice and classification of AS and for the differentiation of AS from uspa [4]. MRI has clear advantages in the detection of active inflammatory lesions in the axial skeleton as well as in the peripheral joints and entheses, while for diagnosis and classification of AS, and also for the detection of chronic structural changes, conventional radiographs of the SIJ and the spine are still the gold standard [5]. In general, the musculoskeletal system in patients with AS may show two types of abnormalities on imaging: active inflammatory changes and chronic structural changes. The structural changes can be further differentiated in erosive changes and changes with bone proliferation. The different imaging techniques have different capacities to assess AS-related changes (Table 1). While, in general, conventional radiographs and computed tomography (CT) have advantages in the detection of structural changes [5], MRI is superior in detecting active changes. The indications for the use of the techniques differ, and therefore they are often used complementarily. Imaging of the sacroiliac joint in AS Imaging of the SIJ plays an important role in AS, since almost all patients with AS do have involvement of the SIJ. Furthermore, imaging of structural changes in the SIJ is the major item in the modified New York criteria for the classification and diagnosis of AS [3]. MRI of the sacroiliac joints in AS MRI of the SIJ is useful for visualization of the complicated anatomy of the SIJ, including abnormalities of the periarticular tissues, such as joint capsule, subchondral bone, entheses and ligaments, / Future Medicine Ltd ISSN Future Rheumatol. (2006) 1(4),
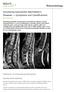
2 REVIEW Baraliakos, Landewé & Braun Table 1. Imaging techniques and sensitivity of assessment of acute and chronic changes in ankylosing spondylitis. Acute/inflammatory changes Chronic/bony changes Conventional radiographs + + Computed tomography + ++ Scintigraphy + - MRI ++ + MRI T1-weighted sequence + + MRI post-t1-weighted, STIR and T2 FS sequence ++ - FS: Fat saturated; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; STIR: Short tau inversion recovery. which are difficult to detect by other methods. MRI is especially valid for the detection of inflammation in the axial skeleton in AS patients. The MRI results correlate well with conventional histology and immunohistological findings [6]. By contrast with other imaging techniques, MRI is not associated with radiation exposure. This makes the technique favorable, especially in young women, children or patients who are likely to have repeated, frequent examinations. However, routine access to MRI, optimal technical equipment and skilled staff is not widely available, and costs of MRI are still rather high [7]. Furthermore, patients with a pacemaker or with older types of metal implants cannot be examined by MRI. In addition, the rather long duration of the procedure ( min) renders the technique poorly applicable for some patients because of intolerable pain and stiffness in the supine position [8]. In MRI examination of the SIJ, oblique transaxial sections should be used (Figure 1) [6]. Paraxial slices may provide additional information on the SIJ in a few patients [9]. For the assessment of inflammatory SIJ lesions, the appropriate MRI sequences are the short tau inversion recovery (STIR) technique (Figure 1A), the T1-weighted turbo spin echo sequence after application of a contrast agent (gadolinium diethylenetriamine-penta-acetic acid [T1/Gd-DTPA]) (Figure 1B) and the T2-weighted gradient echo sequence after fat suppression (FS) (Figure 1C) [10,11]. The T1/Gd-DTPA turbo spin echo sequence depicts inflammation in the SIJ by detection of enhancement of contrast agents, especially in areas with hypervascularization. The STIR and T2 FS techniques are able to assess inflammation by depiction of bone-marrow edema, thus, without the use of contrast agent. Although the T2 FS sequence has been used more frequently in the past, the new STIR technique is now often preferred because of its superior fat/water contrast obtained by total suppression of the fat signal [8]. In contrast to MRI of the spine [12], the question whether application of contrast agents provides additional information in the examination of the SIJ has not been resolved. Preliminary results suggest that STIR imaging is 90% compatible with techniques using post-gadolinium T1-weighted MRI [8]. The use of dynamic MRI of the SIJ on the basis of an early scoring proposal should not be widely used anymore because of its problematic performance in routine care with too many positive but nonspecific results [10]. The importance of MRI examinations of the SIJ for the diagnosis of early disease stages of SpA in patients with inflammatory back pain (IBP) was evaluated recently, among other diagnostic tools [13]. According to this evaluation, the highest likehood ratios for accurate diagnosis were obtained when MRI examinations together with the occurrence of HLA-B27 were taken into account. It was concluded that this approach may be used in clinical practice with a high degree of confidence in order to diagnose axial SpA at an early stage in patients who lack radiographic sacroiliitis but complain of IBP symptoms. MRI can also be useful for the assessment of chronic SIJ changes, since the grading of SIJ changes is essential for the classification of AS [14 16]. However, the performance of MRI for assessment of structural SIJ changes has not been standardized to date. There is recent evidence that plain radiography performs better in detecting chronic changes than MRI [5]. Currently, the most frequently used MRI sequences for quantification and assessment of structural SIJ lesions are the T1-weighted turbo spin echo sequence (usually performed before application of contrast material) (Figure 1d) and gradient echo techniques [8]. The whole topic has been extensively evaluated by the Assessment in Ankylosing Spondylitis (ASAS)/Outcome Measured 424 Future Rheumatol. (2006) 1(4)
3 Magnetic resonance imaging in ankylosing spondylitis REVIEW Figure 1. Magnetic resonance imaging examinations of the sacroiliac joints in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. A B C D (A) Short tau inversion recovery magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). (B) T1-weighted MRI of the sacroiliac joints (SIJ) after application of contrast agent with typical increased signal intensity due to contrast agent enhancement in inflammatory regions, (C) T2-weighted MRI of the SIJ after fat suppression. (D) T1-weighted MRI of the SIJ of the same patient as in (B), before application of contrast agent. Enhancement of contrast agent due to inflammation (hypervascularization) demonstrates the typical decreased signal intensity compared with post-gadolinium images. in Rheumatology Clinical Trials (OMERACT) MRI in AS working group. All available scoring systems for the use of MRI of the SIJ in AS have been validated recently, setting the conditions for further evaluation in this important field [17]. Several recent studies with biologicals, such as infliximab and etanercept [18,19], have shown definite clinical efficacy on disease activity and improvement of inflammation of the SI joints and the spine [18,20 22]. MRI of the pubic symphysis in AS Involvement of the pubic symphysis in AS occurs in up to 25% of patients. In most occasions this is only detected in late stages of the disease when advanced abnormalities in the SIJ have already been detected [23]. Involvement of the pubic symphysis detected by conventional radiography ranges from minimal changes to erosions, parasymphyseal osteosclerosis, apparent destruction and ankylosis [23]. Symphysitis in earlier stages of disease may be detected by scintigraphy or by MRI using T1/Gd-DTPA, T2 FS or STIR techniques where it appears as subcortical, anteriorly located bone-marrow edema, indicating either enthesitis or pelvic instability with a correspondingly decreased signal on T1-weighted images. Involvement of the symphysis may be of clinical relevance, but is not generally critical for the diagnosis of AS or SpA
4 REVIEW Baraliakos, Landewé & Braun Imaging of the spine in AS The classification of AS is based on the modified 1984 New York criteria [3], which mainly rely on the detection and the degree of structural changes in the SIJ obtained by conventional x-rays. However, conventional radiographs are known to have a rather low sensitivity to detect sacroiliitis and spondylitis in early stages of disease [24]. This may cause diagnostic problems, since the mean time between the first symptoms and the diagnosis of AS ranged between 5 and 9 years in one study [25]. The other problem with the New York criteria is that approximately 3 5% of patients with AS do not have unequivocal structural changes in the SIJ [26], but only spinal changes (classical syndesmophytes). Similarly to the SIJ, conventional radiographs are still the gold standard for the assessment and quantification of structural spinal lesions. Recently, T1-weighted MRI has also been successfully used to assess structural changes [27]. Overall, spinal MRI performs best in the identification and quantification of active spinal lesions, where it has proved superior when compared with other imaging techniques [12,20,21,28 30]. MRI of the spine in AS MRI is currently considered the most sensitive method for imaging of spinal inflammation [1,12,28,29,31]. Positron emission tomography techniques have not been evaluated for this purpose to a sufficient degree. MRI is being increasingly tested to classify and diagnose patients with early AS [13]. In patients with AS, spinal MRI has been used to assess spinal inflammation as an indicator of disease activity and a possible predictor of response to therapy. The evaluation of MRI as a tool to define allocation to different therapeutic strategies, such as treatment with biologicals, is currently ongoing [20,21,28,30]. Spondylitis Inflammation of the vertebral body and adjacent structures (sspondylitis anterior, Romanus lesion, shiny corner sign and vertebral osteitis) has been considered as a rather early sign of spinal involvement in patients with AS. First described by Romanus in 1952 [28,32], it represents a rather typical radiographic sign of spinal involvement in AS, which was most frequently seen in the thoraco lumbar region at T10 T12 (Figure 2) [31]. When using MRI, spondylitis anterior is typically observed as a decreased signal in T1-weighted MRI and an increased signal in Figure 2. Romanus lesions in the anterior edge of the vertebral body, as depicted by STIR MRI in the lumbar spine of an AS patient. AS: Ankylosing spondylitis; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; STIR: Short tau inversion recovery. T1-weighted MRI after gadolinium contrast. Similar findings are obtained using the T2-weighted MRI or the STIR sequence. The typical appearance of spondylitis is not always limited to the vertebral edges, but may also spread to the entire vertebral body as a sign of generalized inflammation [33 35]. The signal intensity within the disk may remain normal during vertebral inflammation. High signal intensity on T1- and T2-weighted images with no enhancement following intravenous contrast is known to indicate fat accumulation [33]. Furthermore, diskovertebral junctions may display low signal intensity on T1- and T2-weighted images when a marginal sclerosis occurs after a spondylitis [33]. Spondylitis anterior is an active osteitis and enthesitis at the junction of the anulus fibrosus and the longitudinal ligaments with the anterior longitudinal ligament, the vertebral body and the intervertebral disk. Although the assumption that syndesmophytes occur as a consequence of the inflammation and repair reaction, it is still not proven whether, in later stages, active inflammation may result in erosive and later in sclerotic changes and reactive new bone formation, including syndesmophytes at the corner of the affected vertebral bodies. Less frequently, these 426 Future Rheumatol. (2006) 1(4)
5 Magnetic resonance imaging in ankylosing spondylitis REVIEW changes are also seen at the posterior vertebral edges [31,33]. Spondylitis is rare in SpA patients without an established diagnosis of AS [34]. Spondylodiskitis & diskitis Inflammation of the intervertebral space (diskitis) and the disk together with the vertebral body (spondylodiskitis, Andersson lesion, Figure 3A) are also rather typical signs of spinal inflammatiaon in patients with AS. In contrast to conventional radiographs, where only the consequences of spondylodiskitis are visible in later disease stages, MRI is able to detect such changes already in early phases [36,37]. Accordingly, negative radiographic findings are sometimes accompanied by positive MRI findings indicative of spondylodiskitis (Figure 3B) [36,37]. Asymptomatic spondylodiskitis may occur in multiple spinal segments Figure 3. Anderson lesion as detected in magnetic resonance imaging and conventional radiography in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. A B in approximately 8% of the patients in early disease [38]. The incidence of spondylodiskitis, which may occur without major clinical symptoms, has been estimated at 15% in patients with AS [24,38]. The first radiographic descriptions of spondylodiskitis were published by Andersson in 1937 [39] and later by Dihlmann in 1978 [40], who proposed to distinguish inflammatory and noninflammatory spondylodiskitis. Using MRI, spondylosdiskitis is characterized by a circumscript hemispherical erosive lesion, which is often surrounded by an area of low signal intensity in one of two neighbored vertebral bodies (Figure 3A). By the course of the disease, spondylodiskitis may develop into transdiskal proliferation processes without marginal syndesmophytes. By contrast, the noninflammatory spondylodiskal lesion is a transdiskal fracture for different reasons, such as advanced disk degeneration and inflammation or osteoporotic processes. It should be noted that the described early lesions, inflammatory or noninflammatory, are very similar to Modic I lesions which have been described to lead to erosive osteochondrosis [41], while late spondylodiskitis bear similarity to Modic II lesions in MRI. Therefore, they cannot be used for diagnostic purposes per se without clinical evidence of AS related symptoms [24]. Costovertebral joints Inflammatory lesions in the costovertebral joints are also characterized by low-density signals in T1-weighted MRI and high-density signals in MRI sequences sensitive to depict inflammation. Affection of costovertebral joints in AS leads to a reduced chest expansion a frequent finding in AS [3]. This symptom may be explained by both active and structural spinal changes. (A) Andersson lesion, as detected by contrast agent (Gd-DTPA)-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with the typical circumscribed hemispherical erosive lesion (dotted circle), which is often surrounded by an area of low signal intensity in one of two neighbored vertebral bodies. (B) In contrast to the MRI, the corresponding x-ray image does not show any pathological sign (continuous circle). Scoring of spinal MRI in AS MRI is now increasingly used for the evaluation of the influence of anti-inflammatory drugs (such as antitumor necrosis factor [TNF]-α agents) on spinal inflammation in randomized clinical trials (RCT) [28,30]. In order to quantify active spondylitic changes in patients with AS, MRI scoring methods have been developed: the best evaluated scoring system is the AS spinal MRI scoring system (ASspiMRI) [8,12,22,27,28,30,42,43]. This scoring system distinguishes disease activity (ASspiMRI-a) and chronicity (ASspiMRI-c). Scoring for both activity and chronicity is performed on a graded scale from 0 to 6. Inflammatory activity, as assessed by the ASspiMRI-a, quantifies either the enhancement after T1/Gd- DTPA, or the bone marrow edema detected by 427
6 REVIEW Baraliakos, Landewé & Braun the STIR or the T2 FS technique. The ASspiMRI-a values erosions as both inflammatory and chronic changes. Chronicity is assessed by the ASspiMRI-c by grading structural lesions in T1-weighted MRI sequences (before application of contrast agents). For the quantification of active and structural spinal lesions, the ASspiMRI evaluates vertebral units, which are defined as the region between two virtual lines drawn through the middle of each vertebral body. Almost the entire spine, from C2 to S1, is captured by the ASspiMRI, which comprises 23 vertebral units (VUs; the bony region above and below an intervertebral disk, including the disk region). Thus, the range of the scoring system is for both the activity and the chronicity index respectively. A modification of the ASspiMRI-a is described by investigators from Berlin, and omits erosions as a sign of inflammation [44]. Another scoring system available for scoring of spinal lesions in AS is the system developed by the Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada (SPARCC) [45]. This scoring system evaluates only six diskovertebral units (DVU) (the definition of DVU is similar to that of the VU in the ASspiMRI), selected on the basis of presence of inflammation (global judgement). It assigns additional scores to intensity and depth of inflammation. The ASAS/OMERACT MRI in AS Working Group is currently evaluating all available scoring methods and modifications, in order to find out whether it is possible to prioritize a scoring system for as the assessment of inflammation in clinical trials with AS patients. This is an important issue, since several recent studies with biologicals, such as infliximab and etanercept [18,45,46], have demonstrated definite clinical efficacy on disease activity, and improvement of inflammation in the spine [18,20 22]. Extravertebral manifestations of AS Peripheral extravertebral manifestations, such as enthesitis and bursitis, occur frequently in patients with spondyloarthritides. In active inflammatory lesions, MRI shows a decreased signal in T1-weighted sequences and increased signal in T2-weighted sequences or STIR sequences. Frequently affected sites of enthesitis in SpA are the Achilles tendon and the retrocalcanear bursa at the calcaneus (Figure 4), the Figure 4. Affection of the calcaneus in the STIR MRI sequence (A) and involvement of the retrocalcanear bursa in the gadolinium-enhanced MRI sequence (B) as an extraspinal manifestation in two patients with ankylosing spondylitits. A B MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; STIR: Short tau inversion recovery. Reprinted with permission from [49]. 428 Future Rheumatol. (2006) 1(4)
7 Magnetic resonance imaging in ankylosing spondylitis REVIEW trochanter major and the pes anserinus. Enthesitis is depicted as hyperintensity in the STIR or the T2-weighted sequence, with strong enhancement after contrast [24]. Peripheral enthesitis may clinically appear as arthritis, and differentiation can be achieved by MRI using inflammation-sensitive sequences [47]. Human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-B27-positive SpA patients are predicted to develop higher peripheral pathology with respect to extravertebraldisease-related manifestations, such as plantar fasciitis, as compared with HLA-B27 negative patients [48]. Conclusion In summary, x-rays are still the standard for the assessment of structural SIJ changes and the diagnosis of AS. For assessment of active sacroiliitis, MRI sequences are necessary. Conventional radiographs of the spine are the basis for the detection of AS-related structural spinal changes, such as syndesmophytes and ankylosis. MRI of the spine is useful for the assessment of inflammatory changes, and potentially for the diagnosis of early and active stages of the disease. MRI sequences useful for the assessment of active disease are the STIR, the T2-fat saturated and the T1 post-gadolinium MRI sequences. For assessment of structural changes, the T1-weighted MRI sequence is used. Both SIJ and spinal changes can be quantified by evaluated scoring systems. These systems are mostly used in clinical trials to quantify the impact of therapy, such as anti-tnf-α agents, on spinal inflammation. Future perspective MRI will be extensively used for the diagnosis and monitoring of treatment in ankylosing spondylitis. Inflammatory spinal lesions and sacroiliitis will become pathognomonic for the diagnosis of the disease and will contribute, together with other clinical and laboratory tools, for setting the diagnosis of AS in early stages. Executive summary Imaging of the sacroiliac joint in ankylosing spondylitis Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the sacroiliac joints (SIJ) is accurate for detection of acute and chronic SIJ lesions in ankylosing spondylitis (AS) patients. MRI results correlate well with conventional histology and immunohistological findings. MRI examinations together with the presence of human leukocyte antigen-b27 have the highest likelihood ratio for the accurate diagnosis of AS already in early stages. Imaging of the spine in AS MRI is currently considered the most sensitive method for imaging of spinal inflammation. Short tau inversion recovery (STIR) and Gd-DTPA sequences are both able to detect spinal inflammation in AS patients. T1-weighted MRI can be used for assessment of chronic spinal lesions, but conventional x-rays still represent the gold standard for depiction of such changes. Extravertebral manifestations of AS Enthesitis is depicted as hyperintensity in the STIR or the T2-weighted sequence, with strong enhancement after application of contrast agent. Bibliography 1. Bollow M, Enzweiler C, Taupitz M et al.: Use of contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging to detect spinal inflammation in patients with spondyloarthritides. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 20(6 Suppl. 28), S167 S174 (2002). 2. Hermann KG, Bollow M: Magnetic resonance imaging of the axial skeleton in rheumatoid disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 18(6) (2004). 3. van der Linden S, Valkenburg HA, Cats A: Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum. 27(4) (1984). 4. Brandt J, Bollow M, Haberle J et al.: Studying patients with inflammatory back pain and arthritis of the lower limbs clinically and by magnetic resonance imaging: many, but not all patients with sacroiliitis have spondyloarthropathy. Rheumatology (Oxford) 38(9) (1999). 5. Heuft-Dorenbosch L, Landewe R, Weijers R et al.: Combining information obtained from MRI and conventional radiographs in order to detect sacroiliitis in patients with recent-onset inflammatory back pain. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 65(6), (2005). 6. Puhakka KB, Melsen F, Jurik AG, Boel LW, Vesterby A, Egund N: MR imaging of the normal sacroiliac joint with correlation to histology. Skeletal Radiol. 33(1) (2004)
8 REVIEW Baraliakos, Landewé & Braun 7. Fenton P: Magnetic resonance imaging of the sacroiliac joints: worth the cost? J. Rheumatol. 23(12) (1996). 8. Braun J, van der Heijde D: Imaging and scoring in ankylosing spondylitis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 16(4) (2002). 9. Remy M, Bouillet P, Bertin P et al.: Evaluation of magnetic resonance imaging for the detection of sacroiliitis in patients with early seronegative spondylarthropathy. Rev. Rheum. Engl. Ed. 63(9) (1996). 10. Braun J, Bollow M, Eggens U, Konig H, Distler A, Sieper J: Use of dynamic magnetic resonance imaging with fast imaging in the detection of early and advanced sacroiliitis in spondylarthropathy patients. Arthritis Rheum. 37(7) (1994). 11. Bollow M, Braun J, Hamm B et al.: Early sacroiliitis in patients with spondyloarthropathy: evaluation with dynamic gadolinium-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 194(2) (1995). 12. Baraliakos X, Hermann KG, Landewe R et al.: Assessment of acute spinal inflammation in patients with ankylosing spondylitis by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): a comparison between contrast enhanced T1 and short-tau inversion recovery (STIR) sequences. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 64(8) (2005). 13. Rudwaleit M, van der Heijde D, Khan MA, Braun J, Sieper J: How to diagnose axial spondyloarthritis early. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 63(5) (2004). 14. Braun J, Bollow M, Seyrekbasan F et al.: Computed tomography guided corticosteroid injection of the sacroiliac joint in patients with spondyloarthropathy with sacroiliitis: clinical outcome and follow up by dynamic magnetic resonance imaging. J. Rheumatol.. 23(4) (1996). 15. Marzo-Ortega H, Braun J, Maksymowych WP et al.: Interreader agreement in the assessment of magnetic resonance imaging of the sacroiliac joints in spondyloarthropathy-the 1st MISS study. Arthritis Rheum. 46, S428 (2002) (Abstract). 16. Braun J, Sieper J, Bollow M: Imaging of sacroiliitis. Clin. Rheumatol. 19(1) (2000). 17. Landewé R, Hermann KG, van der Heijde D et al.: Scoring sacro-iliac joints by magnetic resonance imaging a multiplereader reliability experiment. J. Rheumatol. 32(10) (2005). 18. Braun J, Brandt J, Listing J et al.: Treatment of active ankylosing spondylitis with infliximab: a randomised controlled multicentre trial. Lancet 359(9313) (2002). 19. Brandt J, Khariouzov A, Listing J et al.: Six-month results of a double-blind, placebocontrolled trial of etanercept treatment in patients with active ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 48(6) (2003). 20. Marzo-Ortega H, McGonagle D, O Connor P, Emery P: Efficacy of etanercept in the treatment of the entheseal pathology in resistant spondylarthropathy: a clinical and magnetic resonance imaging study. Arthritis Rheum. 44(9) (2001). 21. Stone M, Salonen D, Lax M, Payne U, Lapp V, Inman R: Clinical and imaging correlates of response to treatment with infliximab in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. J. Rheumatol. 28(7) (2001). 22. Rudwaleit M, Baraliakos X, Listing J, Brandt J, Sieper J, Braun J: Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine and the sacroiliac joints in ankylosing spondylitis before and during therapy with etanercept. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 64(9) (2005). 23. Jajic Z, Jajic I, Grazio S: Radiological changes of the symphysis in ankylosing spondylitis. Acta Radiol. 41(4) (2000). 24. Bollow M: Magnetic resonance imaging in ankylosing spondylitis (Marie-Struempell- Bechterewdisease). Rofo. 174(12) (2002). 25. Feldtkeller E: Age at disease on set and delayed diagnosis of spondylo arthropathies. J. Rheumatol. 58(1) (1999). 26. Khan MA, van der Linden SM, Kushner I, Valkenburg HA, Cats A: Spondylitic disease without radiologic evidence of sacroiliitis in relatives of HLA-B27 positive ankylosing spondylitis patients. Arthritis Rheum. 28(1) (1985). 27. Braun J, Baraliakos X, Golder W et al.: Analysing chronic spinal changes in ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic comparison of conventional x rays with magnetic resonance imaging using established and new scoring systems. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 63(9) (2004). 28. Baraliakos X, Davis J, Tsuji W, Braun J: Magnetic resonance imaging examinations of the spine in patients with ankylosing spondylitis before and after therapy with the tumor necrosis factor alpha receptor fusion protein etanercept. Arthritis Rheum. 52(4) (2005). 29. Baraliakos X, Landewe R, Hermann KG et al.: Inflammation in ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic description of the extent and frequency of acute spinal changes using magnetic resonance imaging. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 64(5) (2005). 30. Braun J, Baraliakos X, Golder W et al.: Magnetic resonance imaging examinations of the spine in patients with ankylosing spondylitis, before and after successful therapy with infliximab: evaluation of a new scoring system. Arthritis and Rheumatism. 48(4) (2003). 31. Braun J, Bollow M, Sieper J: Radiologic diagnosis and pathology of the spondyloarthropathies. Rheum. Dis. Clin. North Am. 24(4) (1998). 32. Romanus R, Yden S: Destructive and ossifying spondylitic changes in rheumatoid ankylosing spondylitis. Acta Orthop. Scand. 22, 89 (1952). 33. Jevtic V, Kos-Golja M, Rozman B, McCall I: Marginal erosive discovertebral Romanus lesions in ankylosing spondylitis demonstrated by contrast enhanced Gd-DTPA magnetic resonance imaging. Skeletal Radiol. 29(1) (2000). 34. Kurugoglu S, Kanberoglu K, Kanberoglu A, Mihmanli I, Cokyuksel O: MRI appearances of inflammatory vertebral osteitis in early ankylosing spondylitis. Pediatr. Radiol. 32(3) (2002). 35. Remedios D, Natali C, Saifuddin A: Case report: MRI of vertebral osteitis in early ankylosing spondylitis. Clin. Radiol. 53(7) (1998). 36. Rasker JJ, Prevo RL, Lanting PJ: Spondylodiscitis in ankylosing spondylitis, inflammation or trauma? A description of six cases. Scand J. Rheumatol. 25(1) (1996). 37. Wienands K, Lukas P, Albrecht HJ: Clinical value of MR tomography of spondylodiscitis in ankylosing spondylitis. J. Rheumatol. 49(6) (1990). 38. Kabasakal Y, Garrett SL, Calin A: The epidemiology of spondylodiscitis in ankylosing spondylitis a controlled study. Br. J. Rheumatol. 35(7) (1996). 39. Andersson O: Röntgenbilden vid spondylarthritis ankylopoetica. Nord. Med. Tidskr. 14, 2000 (1937). 40. Dihlmann W, Delling G: Disco-vertebral destructive lesions (so called Andersson lesions) associated with ankylosing spondylitis. Skeletal Radiol. 3, (1978). 41. Modic MT, Steinberg PM, Ross JS, Masaryk TJ, Carter JR: Degenerative disk disease: assessment of changes in vertebral body marrow with MR imaging. Radiology 166(1 Pt 1) (1988). 42. Baraliakos X, Landewe R, Hermann KG et al.: Inflammation in ankylosing spondylitis a systematic description of the extension and frequency of acute spinal changes using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Ann. Rheum. Dis. (2004). 430 Future Rheumatol. (2006) 1(4)
9 Magnetic resonance imaging in ankylosing spondylitis REVIEW 43. Hermann KG, Landewe RB, Braun J, van der Heijde D: Magnetic resonance imaging of inflammatory lesions in the spine in ankylosing spondylitis clinical trials: is paramagnetic contrast medium necessary? J. Rheumatol. 32(10) (2005). 44. Haibel H, Rudwaleit M, Brandt HC et al.: Preliminary MRI results in patients with active ankylosing spondylitis treated with adalimumab for 12 weeks. Arthritis & Rheum. 50(9 Suppl.) S618 (2004). 45. Maksymowych WP, Inman RD, Salonen D et al.: Spondyloarthritis research Consortium of Canada magnetic resonance imaging index for assessment of sacroiliac joint inflammation in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 53(5) (2005). 46. Baraliakos X, Brandt J, Listing J et al.: Outcome of patients with active ankylosing spondylitis after two years of therapy with etanercept: Clinical and magnetic resonance imaging data. Arthritis Rheum. 53(6) (2005). 47. McGonagle D, Gibbon W, O Connor P, Green M, Pease C, Emery P: Characteristic magnetic resonance imaging entheseal changes of knee synovitis in spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 41(4) (1998). 48. McGonagle D, Marzo-Ortega H, O Connor P et al.: The role of biomechanical factors and HLA-B27 in magnetic resonance imaging-determined bone changes in plantar fascia enthesopathy. Arthritis Rheum. 46(2) (2002). 49. Braun J, Baraliakos X: Ankylosing spondylitis. In: Ankylosing Spondylitis and the Spondyloarthropathies (Volume 1). Weisman van der Heijde, Reveille (Eds), Elsevier, UK (2006) Affiliations Xenofon Baraliakos Rheumazentrum Ruhrgebiet, Ruhr-University Bochum, Landgrafenstr. 19, Herne, Germany Tel.: ; Fax: ; xenob@onlinehome.de Robert Landewé University Hospital Maastricht, Department of Internal Medicine/Rheumatology, PO Box 5800, 6202AZ Maastricht, The Netherlands Tel.: ; Fax: ; rlan@sint.azm.nl Juergen Braun Rheumazentrum Ruhrgebiet, Ruhr-University Bochum, Landgrafenstr. 19, Herne, Germany Tel.: ; Fax: ; j.braun@rheumazentrum-ruhrgebiet.de 431
T he spondyloarthritides (SpA) comprise five subtypes:
 1305 EXTENDED REPORT Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine and the sacroiliac joints in ankylosing spondylitis and undifferentiated spondyloarthritis during treatment with etanercept M Rudwaleit*, X
1305 EXTENDED REPORT Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine and the sacroiliac joints in ankylosing spondylitis and undifferentiated spondyloarthritis during treatment with etanercept M Rudwaleit*, X
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/43590 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Machado, Pedro Title: Health and imaging outcomes in axial spondyloarthritis Issue
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/43590 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Machado, Pedro Title: Health and imaging outcomes in axial spondyloarthritis Issue
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Inflammatory Lesions in the Spine in Ankylosing Spondylitis Clinical Trials: Is Paramagnetic Contrast Medium Necessary?
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Inflammatory Lesions in the Spine in Ankylosing Spondylitis Clinical Trials: Is Paramagnetic Contrast Medium Necessary? KAY-GEERT A. HERMANN, ROBERT B.M. LANDEWÉ, JÜRGEN BRAUN,
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Inflammatory Lesions in the Spine in Ankylosing Spondylitis Clinical Trials: Is Paramagnetic Contrast Medium Necessary? KAY-GEERT A. HERMANN, ROBERT B.M. LANDEWÉ, JÜRGEN BRAUN,
A nkylosing spondylitis (AS) is a common chronic
 1046 EXTENDED REPORT Analysing chronic spinal changes in ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic comparison of conventional x rays with magnetic resonance imaging using established and new scoring systems
1046 EXTENDED REPORT Analysing chronic spinal changes in ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic comparison of conventional x rays with magnetic resonance imaging using established and new scoring systems
Department of Radiology, Aarhus University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark; 4. Key words MRI, sacroiliitis, ankylosing spondylitis, axial spondyloarthritis.
 Gadolinium contrast-enhanced MRI sequence does not have an incremental value in the assessment of sacroiliitis in patients with early inflammatory back pain by using MRI in combination with pelvic radiographs:
Gadolinium contrast-enhanced MRI sequence does not have an incremental value in the assessment of sacroiliitis in patients with early inflammatory back pain by using MRI in combination with pelvic radiographs:
Discovertebral (Andersson) lesions in severe ankylosing spondylitis: a study using MRI and conventional radiography
 Clin Rheumatol (2010) 29:1433 1438 DOI 10.1007/s10067-010-1480-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Discovertebral (Andersson) lesions in severe ankylosing spondylitis: a study using MRI and conventional radiography Mirjam
Clin Rheumatol (2010) 29:1433 1438 DOI 10.1007/s10067-010-1480-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Discovertebral (Andersson) lesions in severe ankylosing spondylitis: a study using MRI and conventional radiography Mirjam
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies
 Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as /ard
 ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2005.044206 Combining information obtained from MRI and conventional radiographs in order to detect sacroiliitis in patients with recent-onset
ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2005.044206 Combining information obtained from MRI and conventional radiographs in order to detect sacroiliitis in patients with recent-onset
MRI of the Sacroiliac Joints in Patients with Moderate to Severe Ankylosing Spondylitis
 MRI of Sacroiliac Joints in Patients with nkylosing Spondylitis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research M E D E N T U R I L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1420 1426 0361 803X/06/1876 1420 merican Roentgen
MRI of Sacroiliac Joints in Patients with nkylosing Spondylitis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research M E D E N T U R I L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1420 1426 0361 803X/06/1876 1420 merican Roentgen
MRI of the sacroiliac joints: what to report and its pitfalls
 MRI of the sacroiliac joints: what to report and its pitfalls Poster No.: C-1920 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Goncalves, A. Y. Aihara, C. Longo, H. Guidorizzi, P. Aguiar, 1
MRI of the sacroiliac joints: what to report and its pitfalls Poster No.: C-1920 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Goncalves, A. Y. Aihara, C. Longo, H. Guidorizzi, P. Aguiar, 1
Diagnostic value of pelvic enthesitis on MRI of the sacroiliac joints in spondyloarthritis
 Eur Radiol (2014) 24:866 871 DOI 10.1007/s00330-013-3074-9 MUSCULOSKELETAL Diagnostic value of pelvic enthesitis on MRI of the sacroiliac joints in spondyloarthritis L. Jans & C. van Langenhove & L. Van
Eur Radiol (2014) 24:866 871 DOI 10.1007/s00330-013-3074-9 MUSCULOSKELETAL Diagnostic value of pelvic enthesitis on MRI of the sacroiliac joints in spondyloarthritis L. Jans & C. van Langenhove & L. Van
The evidence for whole-spine MRI in the assessment of axial spondyloarthropathy
 RHEUMATOLOGY Rheumatology 2010;49:426 432 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kep427 Advance Access publication 11 January 2010 Review The evidence for whole-spine MRI in the assessment of axial spondyloarthropathy
RHEUMATOLOGY Rheumatology 2010;49:426 432 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kep427 Advance Access publication 11 January 2010 Review The evidence for whole-spine MRI in the assessment of axial spondyloarthropathy
37 year old male with several year history of back pain
 37 year old male with several year history of back pain Inflammatory Low Back Pain Clues onset before the age of 40 years insidious onset, chronic (>3 months) pain morning stiffness for longer than 30
37 year old male with several year history of back pain Inflammatory Low Back Pain Clues onset before the age of 40 years insidious onset, chronic (>3 months) pain morning stiffness for longer than 30
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Curr Opin Rheumatol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 January 20.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2010 September ; 22(5): 603 607. doi:10.1097/bor.0b013e32833c7255. Early axial spondyloarthritis Robert A Colbert
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2010 September ; 22(5): 603 607. doi:10.1097/bor.0b013e32833c7255. Early axial spondyloarthritis Robert A Colbert
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint. Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital
 Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
Current Concept of Spondyloarthritis: Special Emphasis on Early Referral and Diagnosis
 DOI 10.1007/s11926-012-0274-2 SERONEGATIVE ARTHRITIS (MA KHAN, SECTION EDITOR) Current Concept of Spondyloarthritis: Special Emphasis on Early Referral and Diagnosis Salih Ozgocmen & Muhammad Asim Khan
DOI 10.1007/s11926-012-0274-2 SERONEGATIVE ARTHRITIS (MA KHAN, SECTION EDITOR) Current Concept of Spondyloarthritis: Special Emphasis on Early Referral and Diagnosis Salih Ozgocmen & Muhammad Asim Khan
Imaging of axial spondyloarthritis including ankylosing spondylitis
 Imaging of axial spondyloarthritis including ankylosing spondylitis ACR 2012 Prof. Dr. med. J. Braun Rheumazentrum Ruhrgebiet, Herne Ruhr-Universität Bochum Germany Modified New York Criteria 1984 for
Imaging of axial spondyloarthritis including ankylosing spondylitis ACR 2012 Prof. Dr. med. J. Braun Rheumazentrum Ruhrgebiet, Herne Ruhr-Universität Bochum Germany Modified New York Criteria 1984 for
C. Imaging the spine in arthritis
 C. Imaging the spine in arthritis Poster No.: A-173 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Invited Speaker Topic: Musculoskeletal - Without Subtopic Authors: A. G. Jurik; Århus C/DK Keywords: arthritis, spondyloarthritis,
C. Imaging the spine in arthritis Poster No.: A-173 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Invited Speaker Topic: Musculoskeletal - Without Subtopic Authors: A. G. Jurik; Århus C/DK Keywords: arthritis, spondyloarthritis,
Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA)
 Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA) Spondyloarthritis: Characteristic Parameters Used for Diagnosis I Symptoms Inflammatory back pain Imaging Lab ESR/CRP Patient s history Good response to NSAIDs Spondyloarthritis-Characteristic
Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA) Spondyloarthritis: Characteristic Parameters Used for Diagnosis I Symptoms Inflammatory back pain Imaging Lab ESR/CRP Patient s history Good response to NSAIDs Spondyloarthritis-Characteristic
ACR Appropriateness Criteria Chronic Back Pain Suspected Sacroiliitis Spondyloarthropathy EVIDENCE TABLE
 1. Underwood MR, Dawes P. Inflammatory back pain in primary care. Br J Rheumatol. 1995;(11):107-1077.. Sieper J, van der Heijde D, Landewe R, et al. New criteria for inflammatory back pain in patients
1. Underwood MR, Dawes P. Inflammatory back pain in primary care. Br J Rheumatol. 1995;(11):107-1077.. Sieper J, van der Heijde D, Landewe R, et al. New criteria for inflammatory back pain in patients
What is Axial Spondyloarthritis?
 Physiotherapist Module 2 What is Axial Spondyloarthritis? How does it apply to physiotherapists? Claire Harris, Senior Physiotherapist, London North West Healthcare NHS Trust Susan Gurden, Advanced Physiotherapy
Physiotherapist Module 2 What is Axial Spondyloarthritis? How does it apply to physiotherapists? Claire Harris, Senior Physiotherapist, London North West Healthcare NHS Trust Susan Gurden, Advanced Physiotherapy
Chapter 2. Overview of ankylosing spondylitis
 Chapter 2 Overview of ankylosing spondylitis The concept and classification of spondyloarthritis The term spondyloarthritis (SpA) comprises AS, reactive arthritis, arthritis/spondylitis associated with
Chapter 2 Overview of ankylosing spondylitis The concept and classification of spondyloarthritis The term spondyloarthritis (SpA) comprises AS, reactive arthritis, arthritis/spondylitis associated with
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE. Proposed Health Technology Appraisal
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Secukinumab for treating ankylosing spondylitis after inadequate response to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Secukinumab for treating ankylosing spondylitis after inadequate response to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
The Andersson lesion in ankylosing spondylitis
 SPINE The Andersson lesion in ankylosing spondylitis DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN THE INFLAMMATORY AND TRAUMATIC SUBTYPES Y.-S. Park, J.-H. Kim, J.-A. Ryu, T.-H. Kim From Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College
SPINE The Andersson lesion in ankylosing spondylitis DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN THE INFLAMMATORY AND TRAUMATIC SUBTYPES Y.-S. Park, J.-H. Kim, J.-A. Ryu, T.-H. Kim From Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College
A mong the inflammatory rheumatic diseases
 659 REVIEW Early referral recommendations for ankylosing spondylitis (including pre-radiographic and radiographic forms) in primary care J Sieper, M Rudwaleit... An earlier diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis
659 REVIEW Early referral recommendations for ankylosing spondylitis (including pre-radiographic and radiographic forms) in primary care J Sieper, M Rudwaleit... An earlier diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis
Sacroiliac joints MR: Finally a universal language for the sacroiliitis diagnosis
 Sacroiliac joints MR: Finally a universal language for the sacroiliitis diagnosis Poster No.: C-1836 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. E. Banegas Illescas, C. López Menéndez, M. L.
Sacroiliac joints MR: Finally a universal language for the sacroiliitis diagnosis Poster No.: C-1836 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. E. Banegas Illescas, C. López Menéndez, M. L.
SpA non-radiografica: fase precoce di spondilite anchilosante o altro?
 Rheumatology Department of Lucania, S. Carlo Hospital of Potenza and Madonna delle Grazie Hospital of Matera SpA non-radiografica: fase precoce di spondilite anchilosante o altro? Ignazio Olivieri Disclosures
Rheumatology Department of Lucania, S. Carlo Hospital of Potenza and Madonna delle Grazie Hospital of Matera SpA non-radiografica: fase precoce di spondilite anchilosante o altro? Ignazio Olivieri Disclosures
Spondylarthropathies. Outline. Introduction. Spondylarthropathy other than AS. Mimickers of spondylarthropathy. Conclusions.
 Spondylarthropathies Filip M. Vanhoenacker Johan Van Goethem General Hospital St-Maarten Duffel-Mechelen Universities of Antwerp and Ghent Outline Introduction Spondylarthropathy other than AS Mimickers
Spondylarthropathies Filip M. Vanhoenacker Johan Van Goethem General Hospital St-Maarten Duffel-Mechelen Universities of Antwerp and Ghent Outline Introduction Spondylarthropathy other than AS Mimickers
UPDATE ON MRI OF SPONDYLOARTHRITIS. PART ONE: THE SACRO-ILIAC JOINT
 JR TR, 2014, 97: 222-227. UPDTE ON MRI OF SPONDYLORTHRITIS. PRT ONE: THE SCRO-ILIC JOINT.C. Vande erg, P. Omoumi,. Larbi, F. Lecouvet, J. Malghem 1 In recent years, there has been an increased trend toward
JR TR, 2014, 97: 222-227. UPDTE ON MRI OF SPONDYLORTHRITIS. PRT ONE: THE SCRO-ILIC JOINT.C. Vande erg, P. Omoumi,. Larbi, F. Lecouvet, J. Malghem 1 In recent years, there has been an increased trend toward
What rheumathologist expect from radiologist in spinal MRI studies: Imaging findings in Spondiloarthritis
 What rheumathologist expect from radiologist in spinal MRI studies: Imaging findings in Spondiloarthritis Poster No.: C-2383 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: B. Gutierrez, V. Familiar
What rheumathologist expect from radiologist in spinal MRI studies: Imaging findings in Spondiloarthritis Poster No.: C-2383 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: B. Gutierrez, V. Familiar
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive
 Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive Poster No.: C-1816 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Shindi, H. Nejadhamzeeigilani, P. Nagtode, C. Nel ; 1 1 2 2 3
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive Poster No.: C-1816 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Shindi, H. Nejadhamzeeigilani, P. Nagtode, C. Nel ; 1 1 2 2 3
ORIGINAL ARTICLE INTRODUCTION
 Arthritis & Rheumatism (Arthritis Care & Research) Vol. 53, No. 5, October 15, 2005, pp 703 709 DOI 10.1002/art.21445 2005, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Spondyloarthritis Research
Arthritis & Rheumatism (Arthritis Care & Research) Vol. 53, No. 5, October 15, 2005, pp 703 709 DOI 10.1002/art.21445 2005, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Spondyloarthritis Research
New developments in the diagnosis and treatment of axial spondyloarthritis
 Review: Clinical Trial Outcomes New developments in the diagnosis and treatment of axial spondyloarthritis Clin. Invest. (2013) 3(2), 153 171 Spondyloarthritis (SpA) is an umbrella term for a group of
Review: Clinical Trial Outcomes New developments in the diagnosis and treatment of axial spondyloarthritis Clin. Invest. (2013) 3(2), 153 171 Spondyloarthritis (SpA) is an umbrella term for a group of
Active (acute) inflammation on MRI highly suggestive of sacroiliitis associated with SpA
 MRI findings of active and chronic sacroiliitis in light of recent ASAS criteria for diagnosing axial spondyloarthritis: what the radiologist should know Poster No.: C-1955 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational
MRI findings of active and chronic sacroiliitis in light of recent ASAS criteria for diagnosing axial spondyloarthritis: what the radiologist should know Poster No.: C-1955 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational
Do HLA-B27 positive patients differ from HLA-B27 negative patients in clinical presentation
 Do HLA-B27 positive patients differ from HLA-B27 negative patients in clinical presentation and imaging? Results from the DESIR cohort of patients with recent onset axial spondyloarthritis Ho Yin Chung
Do HLA-B27 positive patients differ from HLA-B27 negative patients in clinical presentation and imaging? Results from the DESIR cohort of patients with recent onset axial spondyloarthritis Ho Yin Chung
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29572 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Berg, Rosaline van den Title: Spondyloarthritis : recognition, imaging, treatment
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29572 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Berg, Rosaline van den Title: Spondyloarthritis : recognition, imaging, treatment
ABSTRACT Objective: To validate and refine two sets of candidate criteria for the classification/diagnosis of axial spondyloarthritis
 1 Rheumatology, Med Klinik I, Charité, Campus Benjamin Franklin, Berlin, Germany; 2 Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, The Netherlands; 3 Maastricht University Medical Center, Maastricht, The Netherlands;
1 Rheumatology, Med Klinik I, Charité, Campus Benjamin Franklin, Berlin, Germany; 2 Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, The Netherlands; 3 Maastricht University Medical Center, Maastricht, The Netherlands;
Ankylosing spondylitis: A Pictorial Review
 Ankylosing spondylitis: A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0009 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1 2 Hernandez Muñiz,
Ankylosing spondylitis: A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0009 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1 2 Hernandez Muñiz,
Sacroiliac Joint Imaging
 Sacroiliac Joint Imaging Jacob Jaremko, MD, PhD Edmonton, Canada SPR, May 2017 Longview, Alberta Overview SI joint anatomy Sacroiliitis pathophysiology Sacroiliitis imaging Disease features Imaging protocols
Sacroiliac Joint Imaging Jacob Jaremko, MD, PhD Edmonton, Canada SPR, May 2017 Longview, Alberta Overview SI joint anatomy Sacroiliitis pathophysiology Sacroiliitis imaging Disease features Imaging protocols
Introduction SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE
 Skeletal Radiol (2017) 46:633 639 DOI 10.1007/s00256-017-2581-1 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Prevalence and clinical significance of lumbosacral transitional vertebra (LSTV) in a young back pain population with
Skeletal Radiol (2017) 46:633 639 DOI 10.1007/s00256-017-2581-1 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Prevalence and clinical significance of lumbosacral transitional vertebra (LSTV) in a young back pain population with
Netherlands, Atrium Medical Center, Heerlen, the Netherlands. Rheumatology Unit, Department of Medicine DIMED, University of Padova, Italy
 DR. SOFIA RAMIRO (Orcid ID : 0000-0002-8899-9087) Article type : Full Length Is it useful to repeat MRI of the sacroiliac joints after three months or one year in the diagnostic process of patients with
DR. SOFIA RAMIRO (Orcid ID : 0000-0002-8899-9087) Article type : Full Length Is it useful to repeat MRI of the sacroiliac joints after three months or one year in the diagnostic process of patients with
M Bollow, T Fischer, H Reiβhauer, M Backhaus, J Sieper, B Hamm, J Braun
 Ann Rheum Dis 2000;59:135 140 135 Radiology, Klinikum Charité, Humboldt University, Berlin, Germany M Bollow T Fischer B Hamm Pathology, Klinikum Charité, Humboldt University H Reiβhauer Rheumatology and
Ann Rheum Dis 2000;59:135 140 135 Radiology, Klinikum Charité, Humboldt University, Berlin, Germany M Bollow T Fischer B Hamm Pathology, Klinikum Charité, Humboldt University H Reiβhauer Rheumatology and
MR findings that can be confused with spondyloarthritis lesions
 MR findings that can be confused with spondyloarthritis lesions Poster No.: C-1608 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Zabala Martín-Gil, E. M. Ocón Alonso, N. Gómez León, P. 1 2 2
MR findings that can be confused with spondyloarthritis lesions Poster No.: C-1608 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Zabala Martín-Gil, E. M. Ocón Alonso, N. Gómez León, P. 1 2 2
Evaluation of MRI diffusion in spondylarthropathy axial skeleton lesions
 Evaluation of MRI diffusion in spondylarthropathy axial skeleton lesions Poster No.: C-2353 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: B. Dallaudiere, R. Dautry, A. Felter, J. LINCOT, P. Koch,
Evaluation of MRI diffusion in spondylarthropathy axial skeleton lesions Poster No.: C-2353 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: B. Dallaudiere, R. Dautry, A. Felter, J. LINCOT, P. Koch,
Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review
 Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0008 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1
Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0008 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1
MUSCULOSKELETAL RADIOLOGY
 MUSCULOSKELETAL RADOLOGY SECTON www.cambridge.org Achilles tendonopathy/rupture Characteristics Describes pathology of the combined tendon of the gastro-soleus complex, which inserts onto the calcaneum.
MUSCULOSKELETAL RADOLOGY SECTON www.cambridge.org Achilles tendonopathy/rupture Characteristics Describes pathology of the combined tendon of the gastro-soleus complex, which inserts onto the calcaneum.
The effect of two golimumab doses on radiographic progression in ankylosing spondylitis: results through 4 years of the GO-RAISE trial
 Handling editor Tore K Kvien 1 Department of Rheumatology, Rheumazentrum Ruhrgebiet, Herne, Germany 2 Department of Radiology, Charité Medical School, Berlin, Germany 3 Division of Arthritis & Rheumatic
Handling editor Tore K Kvien 1 Department of Rheumatology, Rheumazentrum Ruhrgebiet, Herne, Germany 2 Department of Radiology, Charité Medical School, Berlin, Germany 3 Division of Arthritis & Rheumatic
Overview of axial spondyloarthritis
 Chapter 2 Overview of axial spondyloarthritis The concept and classification of spondyloarthritis The term spondyloarthritis (SpA) comprises ankylosing spondylitis (AS), reactive arthritis, arthritis/spondylitis
Chapter 2 Overview of axial spondyloarthritis The concept and classification of spondyloarthritis The term spondyloarthritis (SpA) comprises ankylosing spondylitis (AS), reactive arthritis, arthritis/spondylitis
Clinical and Imaging Efficacy of Infliximab in HLA B27 Positive Patients With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Determined Early Sacroiliitis
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 60, No. 4, April 2009, pp 946 954 DOI 10.1002/art.24408 2009, American College of Rheumatology Clinical and Imaging Efficacy of Infliximab in HLA B27 Positive Patients With
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 60, No. 4, April 2009, pp 946 954 DOI 10.1002/art.24408 2009, American College of Rheumatology Clinical and Imaging Efficacy of Infliximab in HLA B27 Positive Patients With
Certolizumab pegol (Cimzia) for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis second or third line
 Certolizumab pegol (Cimzia) for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis second or third line August 2011 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited
Certolizumab pegol (Cimzia) for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis second or third line August 2011 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited
Clinical and MRI responses to etanercept in early non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis: 48-week results from the EMBARK study
 EXTENDED REPORT Clinical and MRI responses to etanercept in early non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis: 48-week results from the EMBARK study Walter P Maksymowych, 1 Maxime Dougados, 2 Désirée van
EXTENDED REPORT Clinical and MRI responses to etanercept in early non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis: 48-week results from the EMBARK study Walter P Maksymowych, 1 Maxime Dougados, 2 Désirée van
Axial Spondyloarthritis: Issues & Controversies
 Axial Spondyloarthritis: Issues & Controversies Atul Deodhar, MD Professor of Medicine Oregon Health & Science University Portland, OR WRA 2018 Annual Meeting, Leavenworth, WA. 16 th September, 2018 Disclosures:
Axial Spondyloarthritis: Issues & Controversies Atul Deodhar, MD Professor of Medicine Oregon Health & Science University Portland, OR WRA 2018 Annual Meeting, Leavenworth, WA. 16 th September, 2018 Disclosures:
Progression of Nonradiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis to Ankylosing Spondylitis
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY Vol. 68, No. 6, June 2016, pp 1415 1421 DOI 10.1002/art.39542 VC 2016, American College of Rheumatology Progression of Nonradiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis to Ankylosing Spondylitis
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY Vol. 68, No. 6, June 2016, pp 1415 1421 DOI 10.1002/art.39542 VC 2016, American College of Rheumatology Progression of Nonradiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis to Ankylosing Spondylitis
I n 1995, the ASsessment in Ankylosing Spondylitis
 127 EXTENDED REPORT Assessment of enthesitis in ankylosing spondylitis L Heuft-Dorenbosch, A Spoorenberg, A van Tubergen, R Landewé, H van der Tempel, H Mielants, M Dougados, D van der Heijde... See end
127 EXTENDED REPORT Assessment of enthesitis in ankylosing spondylitis L Heuft-Dorenbosch, A Spoorenberg, A van Tubergen, R Landewé, H van der Tempel, H Mielants, M Dougados, D van der Heijde... See end
 www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Peak onset between 20 and 30 years Form of spondyloarthritis (cause inflammation around site of ligament insertion into bone) and association with HLA-B27 Prevalence as high
www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Peak onset between 20 and 30 years Form of spondyloarthritis (cause inflammation around site of ligament insertion into bone) and association with HLA-B27 Prevalence as high
Evaluation of treatments for sacroiliitis in spondyloarthropathy using the Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium Canada scoring system
 Cui et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2016) 18:38 DOI 10.1186/s13075-016-0916-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Evaluation of treatments for sacroiliitis in spondyloarthropathy using the Spondyloarthritis
Cui et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2016) 18:38 DOI 10.1186/s13075-016-0916-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Evaluation of treatments for sacroiliitis in spondyloarthropathy using the Spondyloarthritis
Walter P. Maksymowych, Robert G. Lambert, L. Steven Brown and Aileen L. Pangan
 The Journal of Rheumatology Defining the Minimally Important Change for the SpondyloArthritis Research Consortium of Canada Spine and Sacroiliac Joint Magnetic Resonance Imaging Indices for Ankylosing
The Journal of Rheumatology Defining the Minimally Important Change for the SpondyloArthritis Research Consortium of Canada Spine and Sacroiliac Joint Magnetic Resonance Imaging Indices for Ankylosing
Gender differences in effectiveness of treatment in rheumatic diseases
 Gender differences in effectiveness of treatment in rheumatic diseases Irene van der Horst-Bruinsma Associate Professor Rheumatology Center of Excellence of Axial Spondyloarthritis ARC/VU University Medical
Gender differences in effectiveness of treatment in rheumatic diseases Irene van der Horst-Bruinsma Associate Professor Rheumatology Center of Excellence of Axial Spondyloarthritis ARC/VU University Medical
Diagnostic imaging of sacroiliac joints and the spine in the course of spondyloarthropathies
 Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2013; 78(2): 43-49 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.889039 REVIEW RTICLE Received: 2013.02.11 ccepted: 2013.04.08 Diagnostic imaging of sacroiliac joints and the spine in the course of spondyloarthropathies
Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2013; 78(2): 43-49 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.889039 REVIEW RTICLE Received: 2013.02.11 ccepted: 2013.04.08 Diagnostic imaging of sacroiliac joints and the spine in the course of spondyloarthropathies
All that glitters is not inflammatory - a review of the differential diagnosis of spondyloarthritis in the spine and sacroiliac joints
 All that glitters is not inflammatory - a review of the differential diagnosis of spondyloarthritis in the spine and sacroiliac joints Poster No.: C-0468 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
All that glitters is not inflammatory - a review of the differential diagnosis of spondyloarthritis in the spine and sacroiliac joints Poster No.: C-0468 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
Axial Spondyloarthritis. Doug White, Rheumatologist Waikato Hospital
 Axial Spondyloarthritis Doug White, Rheumatologist Waikato Hospital Disclosures Presentations / Consulting Abbott Laboratories AbbVie MSD Novartis Roche Clinical Trials Abbott Laboratories AbbVie Actelion
Axial Spondyloarthritis Doug White, Rheumatologist Waikato Hospital Disclosures Presentations / Consulting Abbott Laboratories AbbVie MSD Novartis Roche Clinical Trials Abbott Laboratories AbbVie Actelion
Heel pain in spondyloarthritis: results of a cross-sectional study of 275 patients
 Heel pain in spondyloarthritis: results of a cross-sectional study of 275 patients E. Koumakis, L. Gossec, M. Elhai, V. Burki, A. Durnez, I. Fabreguet, M. Meyer, J. Payet, F. Roure, S. Paternotte, M. Dougados
Heel pain in spondyloarthritis: results of a cross-sectional study of 275 patients E. Koumakis, L. Gossec, M. Elhai, V. Burki, A. Durnez, I. Fabreguet, M. Meyer, J. Payet, F. Roure, S. Paternotte, M. Dougados
Spondyloarthritis. Key messages
 To cite: Baraliakos X, Kiltz U, Appel H, et al. Chronic but not inflammatory changes at the Achilles tendon differentiate patients with peripheral spondyloarthritis from other diagnoses Results from a
To cite: Baraliakos X, Kiltz U, Appel H, et al. Chronic but not inflammatory changes at the Achilles tendon differentiate patients with peripheral spondyloarthritis from other diagnoses Results from a
The Challenge of Diagnosis and Classification in Early Ankylosing Spondylitis
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 52, No. 4, April 2005, pp 1000 1008 DOI 10.1002/art.20990 2005, American College of Rheumatology COMMENTARY The Challenge of Diagnosis and Classification in Early Ankylosing
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 52, No. 4, April 2005, pp 1000 1008 DOI 10.1002/art.20990 2005, American College of Rheumatology COMMENTARY The Challenge of Diagnosis and Classification in Early Ankylosing
Identification of Psoriatic Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis Early Detection to Facilitate Appropriate Care
 Identification of Psoriatic Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis Early Detection to Facilitate Appropriate Care Joy Schechtman D.O. Professor Midwestern University 64C-1876207 Disclosures None 3 64C-1876207
Identification of Psoriatic Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis Early Detection to Facilitate Appropriate Care Joy Schechtman D.O. Professor Midwestern University 64C-1876207 Disclosures None 3 64C-1876207
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Ho Yin Chung & Chak Sing Lau & Ka Pik Wu & Woon Sing Wong & Mo Yin MOK
 Clin Rheumatol (2011) 30:947 953 DOI 10.1007/s10067-011-1693-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of performance of the Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society, the European Spondyloarthropathy
Clin Rheumatol (2011) 30:947 953 DOI 10.1007/s10067-011-1693-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of performance of the Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society, the European Spondyloarthropathy
Imaging the spine in arthritis a pictorial review
 Insights Imaging (2011) 2:177 191 DOI 10.1007/s13244-010-0061-4 PICTORIAL REVIEW Imaging the spine in arthritis a pictorial review Anne Grethe Jurik Received: 3 August 2010 /Revised: 6 November 2010 /Accepted:
Insights Imaging (2011) 2:177 191 DOI 10.1007/s13244-010-0061-4 PICTORIAL REVIEW Imaging the spine in arthritis a pictorial review Anne Grethe Jurik Received: 3 August 2010 /Revised: 6 November 2010 /Accepted:
Spine MRI in SpA What is the rheumatologist interested in? Personal use only
 Spine MRI in SpA What is the rheumatologist interested in? 4th Musculoskeletal MRI Meeting 2017: Spine MRI Ospedale Regionale di Lugano May 6th 2017 Ulrich Weber MD Consultant, King Christian 10th Hospital,
Spine MRI in SpA What is the rheumatologist interested in? 4th Musculoskeletal MRI Meeting 2017: Spine MRI Ospedale Regionale di Lugano May 6th 2017 Ulrich Weber MD Consultant, King Christian 10th Hospital,
Introduction. Natural Progression of AS. Sacroiliac Joint. Clinical Features and Assessment of Ankylosing Spondylitis
 Clinical Features and Assessment of Ankylosing Spondylitis Dr. YIM, Cheuk Wan Specialist in Rheumatology United Christian Hospital Introduction Ankylo=fusion Spondylitis=inflammation of spine Affect 0.1-0.5%
Clinical Features and Assessment of Ankylosing Spondylitis Dr. YIM, Cheuk Wan Specialist in Rheumatology United Christian Hospital Introduction Ankylo=fusion Spondylitis=inflammation of spine Affect 0.1-0.5%
A nkylosing spondylitis (AS), the prototype of the
 EXTENDED REPORT Staging of patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a preliminary proposal J Braun, D van der Heijde, M Dougados, P Emery, M A Khan, J Sieper, Sj van der Linden... See end of article for authors
EXTENDED REPORT Staging of patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a preliminary proposal J Braun, D van der Heijde, M Dougados, P Emery, M A Khan, J Sieper, Sj van der Linden... See end of article for authors
8/29/2012. Outline Juvenile idiopathic arthritis. 1. Classification-ILAR. 1. Classification-clinical diagnosis. 1. JIA classification
 Outline Juvenile idiopathic arthritis 1. Classification and symptoms (ILAR-International league of Associations for Rheumatology) 2. Imaging J. Herman Kan, M.D. Section chief, musculoskeletal imaging Edward
Outline Juvenile idiopathic arthritis 1. Classification and symptoms (ILAR-International league of Associations for Rheumatology) 2. Imaging J. Herman Kan, M.D. Section chief, musculoskeletal imaging Edward
Feasibility and reliability of the Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada sacroiliac joint inflammation score in children
 Weiss et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2018) 20:56 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1543-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Feasibility and reliability of the Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada sacroiliac
Weiss et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2018) 20:56 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1543-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Feasibility and reliability of the Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada sacroiliac
Medical Science. MRI Analogue Signs in the Imaging of the Spine and Sacroiliac Joints in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis...
 Volume : 5 Issue : 9 Septemer 2016 ISSN No 2277-8179 IF : 3.508 IC Value : 69.48 MRI Analogue Signs in the Imaging of the Spine and Sacroiliac Joints in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis...the Many
Volume : 5 Issue : 9 Septemer 2016 ISSN No 2277-8179 IF : 3.508 IC Value : 69.48 MRI Analogue Signs in the Imaging of the Spine and Sacroiliac Joints in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis...the Many
Clinical and spinal radiographic outcome in axial spondyloarthritis Maas, Fiona
 University of Groningen Clinical and spinal radiographic outcome in axial spondyloarthritis Maas, Fiona IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
University of Groningen Clinical and spinal radiographic outcome in axial spondyloarthritis Maas, Fiona IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies. Dr. M Jokar
 Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies Dr. M Jokar 1 Definition The spondyloarthropathies are a group of disorders that share certain clinical features and an association with the HLA-B27 allele 2 Spondyloarthropathies
Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies Dr. M Jokar 1 Definition The spondyloarthropathies are a group of disorders that share certain clinical features and an association with the HLA-B27 allele 2 Spondyloarthropathies
SPARCC Abstracts and Publications
 SPARCC Abstracts and Publications 2006 Papers 1. Siannis F, Farewell VT, Cook RJ, Schentag CT, Gladman DD. Clinical and radiological damage in psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis online 2006;65 478-481
SPARCC Abstracts and Publications 2006 Papers 1. Siannis F, Farewell VT, Cook RJ, Schentag CT, Gladman DD. Clinical and radiological damage in psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis online 2006;65 478-481
Rheumatology. Ankylosing Spondylitis (Bechterew s Disease) Symptoms and Classifications. Definition of Ankylosing Spondylitis. Spondyloarthropathies
 Rheumatology Ankylosing Spondylitis (Bechterew s Disease) Symptoms and Classifications See online here Ankylosing spondylitis, formerly known as Bechterew s disease or Marie- Strümpell disease, is a type
Rheumatology Ankylosing Spondylitis (Bechterew s Disease) Symptoms and Classifications See online here Ankylosing spondylitis, formerly known as Bechterew s disease or Marie- Strümpell disease, is a type
Anja Weiß 1*, In-Ho Song 2, Hildrun Haibel 2, Joachim Listing 1 and Joachim Sieper 1,2
 Weiß et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy 2014, 16:R35 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Good correlation between changes in objective and subjective signs of inflammation in patients with short- but not long
Weiß et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy 2014, 16:R35 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Good correlation between changes in objective and subjective signs of inflammation in patients with short- but not long
Indirect comparison of anti-tnf-α agents for active ankylosing spondylitis: mixed treatment comparison of randomised controlled trials
 Indirect comparison of anti-tnf-α agents for active ankylosing spondylitis: mixed treatment comparison of randomised controlled trials T. Shu 1, G.H. Chen 2, L. Rong 1, F. Feng 1, B. Yang 1, R. Chen 1,
Indirect comparison of anti-tnf-α agents for active ankylosing spondylitis: mixed treatment comparison of randomised controlled trials T. Shu 1, G.H. Chen 2, L. Rong 1, F. Feng 1, B. Yang 1, R. Chen 1,
COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP)
 European Medicines Agency Pre-Authorisation Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 23 April 2009 Doc. Ref. CPMP/EWP/4891/03 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON CLINICAL
European Medicines Agency Pre-Authorisation Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 23 April 2009 Doc. Ref. CPMP/EWP/4891/03 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON CLINICAL
2004 Health Press Ltd.
 ... Ankylosing spondylitis Maxime Dougados MD Professor of Rheumatology Hôpital Cochin René Descartes University Paris, France Désirée van der Heijde MD PhD Professor of Rheumatology University Hospital
... Ankylosing spondylitis Maxime Dougados MD Professor of Rheumatology Hôpital Cochin René Descartes University Paris, France Désirée van der Heijde MD PhD Professor of Rheumatology University Hospital
MRI in Seronegative Spondyloarthritis: Imaging Features and Differential Diagnosis in the Spine and Sacroiliac Joints
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Review Canella et al. MRI in Seronegative Spondyloarthritis Musculoskeletal Imaging Review Clarissa Canella 1,2,3 runo Schau 4 Elisio Ribeiro 5 runa Sbaffi 2,6 Edson Marchiori 1
Musculoskeletal Imaging Review Canella et al. MRI in Seronegative Spondyloarthritis Musculoskeletal Imaging Review Clarissa Canella 1,2,3 runo Schau 4 Elisio Ribeiro 5 runa Sbaffi 2,6 Edson Marchiori 1
B Freundlich,7 M Rudwaleit,1 J Sieper 1
 1 Department of Rheumatology, Charité Medical University, Campus Benjamin Franklin, Berlin, Germany 2 Department of Radiology, Charité Medical University, Campus Charité Mitte, Berlin, Germany 3 German
1 Department of Rheumatology, Charité Medical University, Campus Benjamin Franklin, Berlin, Germany 2 Department of Radiology, Charité Medical University, Campus Charité Mitte, Berlin, Germany 3 German
6/6/2017. Spondyloarthritis and Osteopathic Primary Care: Facts and Challenges. Progression of Ankylosing Spondylitis Classic Disease
 1 Outline Talk 1 Introduction of spondyloarthritis (SpA) Clinical case challenge The problem of low back pain (LBP) in primary care and in osteopathic primary care Talk 2 What is SpA today? How many people
1 Outline Talk 1 Introduction of spondyloarthritis (SpA) Clinical case challenge The problem of low back pain (LBP) in primary care and in osteopathic primary care Talk 2 What is SpA today? How many people
Ankylosing spondylitis: Assessment and analysis of long-term outcome Ramiro, S.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Ankylosing spondylitis: Assessment and analysis of long-term outcome Ramiro, S. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Antunes da Cunha Oliveira
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Ankylosing spondylitis: Assessment and analysis of long-term outcome Ramiro, S. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Antunes da Cunha Oliveira
THE VEGF AND BMP-2 LEVELS IN PATIENTS WITH ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS AND THE RELATIONSHIP TO TREATMENT WITH TUMOUR NECROSIS FACTOR ALPHA INHIBITORS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES THE VEGF AND BMP-2 LEVELS IN PATIENTS WITH ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS AND THE RELATIONSHIP TO TREATMENT WITH TUMOUR NECROSIS FACTOR ALPHA INHIBITORS Marian Tošovský 1, Petr Bradna 1, Ctirad
ORIGINAL ARTICLES THE VEGF AND BMP-2 LEVELS IN PATIENTS WITH ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS AND THE RELATIONSHIP TO TREATMENT WITH TUMOUR NECROSIS FACTOR ALPHA INHIBITORS Marian Tošovský 1, Petr Bradna 1, Ctirad
Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 2013; 31:
 Scoring with the Berlin MRI method for assessment of spinal inflammatory activity in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a calibration exercise among rheumatologists L. Carmona 1, A. Sellas 2, C. Rodríguez-Lozano
Scoring with the Berlin MRI method for assessment of spinal inflammatory activity in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a calibration exercise among rheumatologists L. Carmona 1, A. Sellas 2, C. Rodríguez-Lozano
Summary. Background. The Role of MRI in the Criteria for Classification of Rheumatic Diseases
 Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2015; 80: 259-265 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.893670 REVIEW ARTICLE Received: 2015.01.25 Accepted: 2015.02.08 Published: 2015.05.16 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2015; 80: 259-265 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.893670 REVIEW ARTICLE Received: 2015.01.25 Accepted: 2015.02.08 Published: 2015.05.16 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Dr Tracey Kain. Associate Professor Ed Gane
 Associate Professor Ed Gane New Zealand Liver Transplant Unit Auckland Dr Tracey Kain Consultant Rheumatologist Grace Orthopaedic Centre Tauranga Hospital Tauranga 7:00-7:55 Abbvie Breakfast Session 1.
Associate Professor Ed Gane New Zealand Liver Transplant Unit Auckland Dr Tracey Kain Consultant Rheumatologist Grace Orthopaedic Centre Tauranga Hospital Tauranga 7:00-7:55 Abbvie Breakfast Session 1.
Ankylosing spondylitis (Bechterew's Disease) [Name of Writer] [Name of Institute]
![Ankylosing spondylitis (Bechterew's Disease) [Name of Writer] [Name of Institute] Ankylosing spondylitis (Bechterew's Disease) [Name of Writer] [Name of Institute]](/thumbs/96/128019585.jpg) Ankylosing spondylitis 1 Running Head: ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS Ankylosing spondylitis (Bechterew's Disease) [Name of Writer] [Name of Institute] Ankylosing spondylitis 2 Ankylosing spondylitis (Bechterew's
Ankylosing spondylitis 1 Running Head: ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS Ankylosing spondylitis (Bechterew's Disease) [Name of Writer] [Name of Institute] Ankylosing spondylitis 2 Ankylosing spondylitis (Bechterew's
Demonstration of evolution of hemispherical spondysclerosis by contrast enhanced Gd-DTPA magnetic resonance imaging
 Demonstration of evolution of hemispherical spondysclerosis by contrast enhanced Gd-DTPA magnetic resonance imaging Vladimir Jevtič 1, Natalija Majcen 2 1 Clinical Radiology Institute, University Clinical
Demonstration of evolution of hemispherical spondysclerosis by contrast enhanced Gd-DTPA magnetic resonance imaging Vladimir Jevtič 1, Natalija Majcen 2 1 Clinical Radiology Institute, University Clinical
Are gender-specific approaches needed in diagnosing early axial spondyloarthritis? Data from the SPondyloArthritis Caught Early cohort
 Ortolan et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2018) 20:218 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1705-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Are gender-specific approaches needed in diagnosing early axial spondyloarthritis? Data
Ortolan et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2018) 20:218 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1705-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Are gender-specific approaches needed in diagnosing early axial spondyloarthritis? Data
Diakonhjemmet Hospital, Oslo, Norway;
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY Vol. 70, No. 7, July 2018, pp 1042 1048 DOI 10.1002/art.40475 2018 The Authors. Arthritis & Rheumatology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American College of Rheumatology.
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY Vol. 70, No. 7, July 2018, pp 1042 1048 DOI 10.1002/art.40475 2018 The Authors. Arthritis & Rheumatology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American College of Rheumatology.
Disease Characteristics of Filipino Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients in Metro Manila Rheumatology Clinics
 Philippine Journal of Internal Medicine Original Paper Disease Characteristics of Filipino Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients in Metro Manila Rheumatology Clinics Ma. Lucila Dianongco, M.D.*; Marc Gregory
Philippine Journal of Internal Medicine Original Paper Disease Characteristics of Filipino Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients in Metro Manila Rheumatology Clinics Ma. Lucila Dianongco, M.D.*; Marc Gregory
Ankylosing Spondylitis. DR. Milt Baker SEA Courses 2017
 Ankylosing Spondylitis DR. Milt Baker SEA Courses 2017 Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted in any form or
Ankylosing Spondylitis DR. Milt Baker SEA Courses 2017 Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted in any form or
Nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis: clinical and therapeutic relevance
 Ghosh and Ruderman Arthritis Research & Therapy (2017) 19:286 DOI 10.1186/s13075-017-1493-8 REVIEW Nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis: clinical and therapeutic relevance Nilasha Ghosh and Eric M.
Ghosh and Ruderman Arthritis Research & Therapy (2017) 19:286 DOI 10.1186/s13075-017-1493-8 REVIEW Nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis: clinical and therapeutic relevance Nilasha Ghosh and Eric M.
Scottish Medicines Consortium
 Scottish Medicines Consortium etanercept 25mg vial of powder for subcutaneous injection (Enbrel ) (No. 212/05) Wyeth New indication: severe active ankylosing spondylitis inadequately controlled by conventional
Scottish Medicines Consortium etanercept 25mg vial of powder for subcutaneous injection (Enbrel ) (No. 212/05) Wyeth New indication: severe active ankylosing spondylitis inadequately controlled by conventional
Clinical and spinal radiographic outcome in axial spondyloarthritis Maas, Fiona
 University of Groningen Clinical and spinal radiographic outcome in axial spondyloarthritis Maas, Fiona IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
University of Groningen Clinical and spinal radiographic outcome in axial spondyloarthritis Maas, Fiona IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
