N-Region Addition in Immunoglobulin Kappa Light Chains in B Cell Subsets in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Evidence for Over-expression of TDT in B Lineage
|
|
|
- Carol Mason
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 N-Region Addition in Immunoglobulin Kappa Light Chains in B Cell Subsets in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Evidence for Over-expression of TDT in B Lineage Choong Won Lee 1 and S. Louis Bridges, Jr 2 1 Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Wallace Memorial Baptist Hospital, Busan, Korea, and 2 Division of Immunology and Rheumatology, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, Alabama, U.S.A ABSTRACT Background: Unusually high amounts of N region addition and CDR3 length diversity were found in immunoglobulin (Ig) light chain Vk and Jk joins in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). We sought to determine whether this finding is due to excessive activity of the enzyme responsible for N region addition (terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase [TdT]) in B lineage cells in bone marrow or from positive antigenic selection of B cells with long CDR3 lengths. Methods: We used FACS to isolate IgM + /IgD + B cells (predominantly naive) and IgM - IgD - B cells (predominantly class-switched) B cells from peripheral blood of a patient with RA known to have enrichment for long Vk CDR3s and from that of two normal controls. RT-PCR of VkIII transcripts was performed, followed by sequencing of individual cdna clones. We analyzed the CDR3 lengths and N region additions in 97 clones. Results: There was enrichment for long CDR3 lengths (11 or 12 amino acids) in both IgM + /IgD + and IgM - IgD - B cells in RA compared to B cell subsets in the normal controls. The IgM + /IgD + B cell subset in RA was markedly enriched for N region addition and was similar to that seen in the IgM - /IgD - subset. Conclusion: These data suggest that enrichment for N region addition and long CDR3 lengths in RA may result from unusually high or prolonged activity of TdT in bone marrow. (Immune Network 23;3(2):89-95) Key Words: Rheumatoid arthritis, N region, CDR3 Introduction Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic disease marked by synovial inflammation and hyperplasia that often destroys involved joints (1,2). Infiltration of the synovium by antibody secreting plasma cells is a hallmark of the disease (3,4). Immunoglobulins are heteromeric proteins consisting of two heavy and two light chains, each of which is divided into a variable domain (V) that defines the antigen specificity of the molecule. V domains contain 3 hypervariable intervals of the complementary-determining regions (CDR1, CDR2, and CDR3) that are divided into 3 relatively constant domains of the framework regions (FR1, Correspondence to: Choong Won Lee, Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Wallace Memorial Baptist Hospital, Gumjung-gu P.O Box 1, Namsan-dong, Geumjeong-gu, Busan 69-34, Korea. (Tel) , (Fax) , ( ) choong@wmbh.co.kr FR2, and FR3)(5-7). The V H -D H -J H and V L -J L and non-germline-encoded (N) nucleotides additionally define CDR3. The CDRs are usually directly involved in antigen binding, with CDR3 at the center of antigen binding sites (6). Previous studies showed high levels of non- germline encoded nucleotides (N regions) in VJ joins of kappa light chain from RA synovia and unsorted cells of RA peripheral blood (PB)(8,9). N-nucleotides enhance antibody diversity by encoding additional amino acid residues in CDR3. This finding may be due to positive antigenic selection or rearrangement abnormality from the bone marrow or lymph nodes. In order to clarify these matters, we separated IgM + IgD + B cells, which come from bone marrow without contacting antigen, and IgM - IgD - B cells (presumably IgG + or IgA + ) in order to compare CDR3 and N-nucleotides between RA and normal individuals. We choose the IgM + IgD + B cells subset as a precursor of GC B cells and the IgM - IgD - cells Immune Network 89
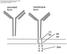
2 9 Choong Won Lee and S. Louis Bridges, Jr subset as GC derived memory B cells. To clarify whether abnormal N-nucleotides and CDR3 in RA comes from rearrangement abnormality or positive antigen selectivity, we compared N-nucleotides and CDR3 in those B cells subsets through sequencing of the V light chain. Materials and Methods Patient and control characteristics and cell separation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBC). PBC from patient AS, a 46-year-old black female with a 1-year history of RF-positive RA, and from two normal healthy individuals, a 35-year-white female SB and a 37-year old Asian male CL, were isolated by Ficoll- Isopaque density centrifugation. PBC were incubated with anti-cd19-microbeads for 15 min at 4 o C. CD19 + B cells were enriched by magnetic cell separation using the MiniMACS system (Miltenyi Biotec, Auburn, CA, USA). B cells were enriched 98% by a single step of magnetic sorting for analysis by immunofluorescence staining with anti-human CD19 FITC (PharMingen, San Diego, CA, USA). Cells of the CD19-enriched fraction were incubated with anti-human IgM-PE (PharMingen, San Diego, CA, USA)) and anti-human IgD-FITC for 2 min on ice, then sorted into IgM + IgD + and IgM - IgD - fractions on a FACS advantage SE (Becton Dickson, Franklin lakes, NJ, USA). Generation of cdna and PCR amplification of V -containing transcripts. Total RNA was isolated from each IgM + IgD + subset and from IgM - IgD - subset B cells using Tri-zol reagent (Molecular Research Center, Inc., Cincinnati, OH, USA). Oligo d(t)- primed first-strand cdna was generated from total RNA using SuperScript II for RNase H - Reverse transcriptase kit (GibcoBRL, Gaithersburg, MD, USA). PCR amplifications were performed on 2- l aliquots of first-strand cdna, using Taq DNA polymerase. PCR conditions were: 35 cycles of denaturation at 94 o C for 2 min, annealing at 55 o C for 3 sec, extension at 72 o C for 1 min, with a final extension at 72 o C for 7 min. PCR amplifications were designed to C sequence as an anti-sense 3' primer (LSK-19: 5'- GCGCCGTCTAGAATTAACACTCTCCCCTGTTGA A-3') and the leader and FR1 of germline Humkv325 as a sense 5' primer (LSK-16: 5'- CCACCGGAGAGC TCGTGTTGACGCAGTCTCCA-3'). To control for possible contamination, a mock PCR reaction mixture, lacking a template and containing products of the first strand cdna reaction without reverse transcriptase were prepared. None of the controls contained amplified product as assessed by ethidium-stained agarose gel electrophoresis. Cloning, transformation and sequencing of PCR products. Aliquots of PCR products were subcloned with pgem-t vector using TA cloning kit (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). Plasmids were transformed into DH5 E.Coli by 37 o C heat shock. For colonies that were digested with EcoR1 restriction enzyme, plasmid DNA was obtained and sequenced by dye terminator cycle sequencing using an automated sequencer (Applied Biosystems, Inc., Model ABI373, Foster, CA, USA). Sequence analysis. Sequences were analyzed with a sequence aliment (DNAPLOT) and SAW (Sequences Analysis Workshop) software (1). Nucleotide exchanges in V were considered for the analysis of somatic mutation. Levels of somatic hypermutation were assessed by comparing the number of nucleotides from the codon 2 of FR1 throughout the CDR3 domains (6). Non-germline encoded nucleotides at the V -J joint, which represent N-region insertion, and P nucleotides, which are palindromic to terminal nucleotides of the coding sequence, were not counted as somatic mutations (11). Statistical analysis. The results are presented as the A B C IgM PE IgM PE IgM PE IgD FITC IgD FITC IgD FITC Figure 1. Fluorescence analysis and gate for sorting of B cell subsets derived from peripheral lymphocytes of the rheumatoid arthritis (A) and normal controls (B and C).
3 N-Region Addition in Immunoglobulin Kappa Light Chains in B Cell Subsets in Rheumatoid Arthritis 91 mean±sd. Differences in the amounts of somatic mutation, N-region addition, and CDR3-length heterogeneity between RA patients and normal individuals were analyzed using the Chi-square test, Fisher exact test (two-tailed), or Student t-test, as appropriate. Results V transcripts from PBC of IgM + IgD + B cells had no, or fewer, somatic mutations than those from IgM - IgD - B cells. Following enrichment of CD19 + B cell by microbeads magnetic cell separation, IgM + IgD + and IgM - IgD - B cells were purified by fluorescence activated cell sorting (Fig. 1). The levels of somatic mutation, as reflected by divergence from germline, among the transcripts from the different samples are shown in Fig. 2. The transcripts from IgM + IgD + B cells of the RA patient and normal individuals (AS, CL and SB, n=46) were significantly less mutated (.54±.12%) than their transcripts from IgM - IgD - B cells (4.51±.42%, n=52) (P.1). Somatic mutation level of the IgM - IgD - B cells (memory cells) in RA was also significantly higher than those in the two normal controls (P=.4). No. of Mutated Nucleotide 2 1 CP SP AP(RA) CN SN AN(RA) IgM+IgD+ IgM-IgD- Figure 2. Somatic mutation in IgM + IgD + and IgM - IgD - B cells between rheumatoid arthritis (AP, AN) and normal controls (CP, CN, SP and SN). P=.4: AN versus CN & SN. * Twenty-seven (59%) of 46 V transcripts from IgM + IgD + B cells were completely germline in the V region, compared with none of 52 colonies from IgM - IgD - B cells. N-region addition. The nucleotide sequences of N regions of each clone in RA are shown in Fig. 3. The percentages of clones with at least one nucleotide of N region addition in IgM + IgD + B cells were: SB 2 of 13 (15%), CL 3 of 13 (23%), and AS 1 of 19 (53%). Those of N region addition in IgM - IgD - B cells were: SB 4 of 14 (29%), CL 7 of 17 (41%), and AS 12 of 21 (57%)(Table I). The nucleotides of N-region addition in the RA patient (1.3±.3, n=4) were significantly higher than those of the two normal controls (.4±.1, n=58)(p=.3), as in previous report (9)(Fig. 3). The nucleotides of N region addition in IgM + IgD + B cells in the RA patient (1.5±.4) were significantly higher than those of the two normal individuals (.3±.1) (P=.4). But those in IgM - IgD - B cells did not differ significantly between RA and normal controls. CDR3 lengths of V transcripts. The V repertoires of the RA patient are compared with those of the normal controls in Table I and Fig. 4, in order to demonstrate CDR3 length. Clones with unusually long CDR3s (one 11 and two 12 amino acid codons) were found in 3 of 4 (7.5%) transcripts from the RA patient, but in none of 58 transcripts from the normal controls. One 11 and one 12 amino acid codons were found in 19 transcripts of IgM + IgD + B cells (naive cells) in RA (Fig. 5). One 12 amino acid codons was also found in 21 transcripts of IgM - IgD - B cells in RA. Each of 3 long CDR3s came from Humkv325, Vg, and Humkv328 V gene segments. Germline derivation of light chains amplified with Humkv325 and C primers. The majority of transcripts amplified with Humkv325 and C primers were derived from Humkv325 (A27) (36%). Most of the remaining clones were derived from two other members of the V III family, 29% from Humkv328 (L2) and 21% from Vg (L6). One clone, AN22, was Table I. N region addition and CDR3 length in IgM + IgD + and IgM - IgD - cells in the rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and normal controls. B cell subset CDR3 1 aa Avg. CDR3 N addition Avg. No. of N RA IgM + /IgD + 2/19 (1%) 9.3 aa 1/19 (53%) 1. IgM - /IgD - 1/21 (5%) 9.3 aa 12/21 (57%) 1.1 Normal 1 IgM + /IgD + /13 (%) 9. aa 2/13 (15%).2 IgM - /IgD - /14 (%) 9.2 aa 4/14 (29%).4 Normal 2 IgM + /IgD + /13 (%) 9.2 aa 3/13 (23%).3 IgM - /IgD - /17 (%) 9. aa 7/17 (41%).7 aa: amino acid.
4 92 Choong Won Lee and S. Louis Bridges, Jr No. of Nucleotides IgM-IgD- B Cells * No. of Nucleotides IgM+IgD+ B cells ** AN ( RA) CN SN AP (RA) CP SP Figure 3. N-region addition in IgM + IgD + and IgM - IgD - B cells between rheumatoid arthritis (AP, AN) and normal controls (CP, CN, SP and SN). P=.4: AP versus CP & SP, P=not significant: AN versus CN & SN. % AS (RA) CL SB IgM+IgD IgM-IgD Figure 4. Percentage of V clones containing CDR3 length of 11 and 12 amino acids between rheumatoid arthritis (AS) and normal controls (SB, CL). derived from the V III gene segment Humkv35 (A11). None of the other potentially functional members of the V III family were represented in this analysis. Seven clones (7%) were derived from V I gene segment Vd (DPK8), 12 (DPK9), and 18(DPK1), and six (6%) from the single member of the V IV family DPK24 (B3). The J 4 and J 1 were frequently used in RA and normal controls. The incidence of J in 3 sequences in RA were 11 of J 1(36%), 11 of J 4 (36%), 8 of J 2 (27%), 6 of J 5 (2%), and 4 of J 3 (13%). The incidence of J in 58 sequences in normal controls were 22 of J 4 (38%), 16 of J 1 (28%), 13 of J 3 (22%), 4 of J 3 (7%), and 3 of J 5 (5%). Analysis of clones from the IgM - IgD - B cells (memory B cells) in normal controls revealed two sets of 4 closely related sequences. SN 17, SN 32, CN3, and CN34 were completely identical to each other. Analysis from the IgM - IgD - B cells in RA revealed two sets of 5 related sequences. AN6, AN14, and AN17 were completely identical and AN2 and AN5 were completely identical to each other. But none of IgM + IgD + B cells of RA and normal controls revealed an identical sequence. Discussion During B cell development, a series of highly regulated gene rearrangements generates a function antibody molecule. In the pro-b cell stage, the heavy chain locus undergoes rearrangement. Variable heavychain domains are encoded by variable (V H ), diversity (D H ), and joining (J H ) gene segments, which undergo sequential somatic rearrangement to become juxtaposed in the genomic DNA (5). Initially, one or more D H gene segments are rearranged to a J H gene segment, followed by rearrangement of the V H gene segment to the D H -J H join. After heavy chain rearrangement, the kappa light chain segment undergoes rearrangements of V L and J L gene segments to generate light chain variable domains, presumably in the pre-b cell stage (7). During the pro-b cell stage, the enzyme responsible for N-region addition, TdT is present in the nucleus of the cell. Although functional TdT has not been shown to be present at the time of kappa light chain rearrangement, N region addition is clearly present in kappa light chains from normal individuals and patients with RA (1-12,16). Therefore, TdT appears to be active throughout all stages of immunoglobulin gene rearrangements in human B cells. Most PB B cells express IgM throughout their life and these cells are distinguished into IgM + IgD + and IgM + IgD - B cells (14,15). Sequence analysis of the V genes expressed by the B-cell subset revealed most IgM only cells while IgM - IgD - cells were mutated, but the IgM + IgD + cells in PB had no, or few somatic mutations (13,14). Therefore, IgM + IgD + B lymphocytes establish the naive, unmutated antibody repertoire, and if a somatically mutated subset exists among IgD-expressing PB B cells, it must be small
5 N-Region Addition in Immunoglobulin Kappa Light Chains in B Cell Subsets in Rheumatoid Arthritis 93 A Length Ig M+Ig D+ <--- CDR3 ----> P <-N ----> P <--- Jk <---- Fram ework > of Codon aa codo Humnkv325 CAG CAG TAT GGT AGC TCA CCT CC G TGG ACG TTC GGC CAA GGG ACC AAG GTG GAA ATC AAA J k 1 AP AG J k 1 9 AP J k 1 TG TAC ACT TTT GGC CAG GGG ACC AAG CTG GAG ATC AAA J k 2 AP g a J k 2 11 AP J k 2 9 AP CGG J k 2 8 AP TTC C gc J k 4 1 G ATC ACC TTC GGC CAA GGG ACA CGA CTG GAG ATT AAA J k 5 9 AP J k 5 9 AP J k 5 9 Humnkv328 CAG CAG TAT AAT AAC TGG CCT CC G TGG ACG TTC GGC CAA GGG ACC AAG GTG GAA ATC AAA J k 1 AP J k 1 9 AP J k 1 8 AP TG J k 1 9 G ATC ACC TTC GGC CAA GGG ACA CGA CTG GAG ATT AAA J k 5 AP CCT C J k 5 1 AP J k 5 9 Vg CAG CAG CGT AGC AAC TGG CCT CC TG TAC ACT TTT GGC CAG GGG ACC AAG CTG GAG ATC AAA J k 2 AP CC - A- - GAA J k 2 9 AP CT c J k 2 9 AP TCC A - T G J k 4 9 AP CT J k 4 6 G ATC ACC TTC GGC CAA GGG ACA CGA CTG GAG ATT AAA J k 5 AP gg GGG c J k 5 12 AP g J k 5 1 B Ig M-Ig D- <--- CDR ----> P <-N ----> P<--- Jk <----- Fram ework 4 ---> Codon aa codo Length of Humnkv325 CAG CAG TAT GGT AGC TCA CCT CC G TGG ACG TTC GGC CAA GGG ACC AAG GTG GAA ATC AAA J k 1 AN G T - C J k 1 9 AN C G G J k 1 9 TG TAC ACT TTT GGC CAG GGG ACC AAG CTG GAG ATC AAA J k 2 AN T - G J k 2 1 AN T - G J k 2 1 A TTC ACT TTC GGC CCT GGG ACC AAA GTG GAT ATC AAA J k 3 AN11 - -A GA J k 3 9 AN T T J k 3 AN A - - A - C GA G A C J k 4 9 AN C TCT GG G G J k 4 9 Humnkv328 CAG CAG TAT AAT AAC TGG CCT CC G TGG ACG TTC GGC CAA GGG ACC AAG GTG GAA ATC AAA J k 1 AN6 - - A C - - G G G J k 1 9 AN A C - - G G G J k 1 9 AN A C - - G G G J k 1 9 TG TAC ACT TTT GGC CAG GGG ACC AAG CTG GAG ATC AAA J k 2 AN G C C J k 2 9 A TTC ACT TTC GGC CCT GGG ACC AAA GTG GAT ATC AAA J k 3 AN T - C ACG GCC J k 3 12 AN T - - G - G CC G J k 3 1 AN G T J k 4 1 AN C C T J k 4 1 Vg CAG CAG CGT AGC AAC TGG CCT CC AN C - - G g g J k 4 9 AN J k 4 9 AN C - - G g g J k 4 9 AN TA tt C G G J k Humnkv35 CAG CAG TAT GGT AGC TCA CCT CC G TGG ACG TTC GGC CAA GGG ACC AAG GTG GAA ATC AAA J k 1 AN G C C GCG T TG T J k 1 9 Figure 5. Nucleotide sequences of CDR3 regions of clones in IgM + IgD + B cells (A) and those of clones in IgM - IgD - B cells (B) in rheumatoid arthritis. fraction of CD27-expressing B cells (16). The memory B-cell compartment in humans consists of somatically mutated, class-switched, which represent IgM - IgD - such as IgG + and IgA + PB cells, and IgM bearing B cells (17). If B cells succeed in generating a functional,
6 94 Choong Won Lee and S. Louis Bridges, Jr non-autoreactive, antigen receptor, they come into the peripheral B cell pool as naive cells. Upon encountering antigen, the antibodies expressed by a B cell are modified by class-switch recombination and somatic hypermutation (18,19). Somatic hypermutation appears to B cells proliferating within the microenvironment of germinal center (GC)(2,21). Thus somatic mutation of V-region gene is a hallmark of GC B cell and their descendants. V transcripts from IgM - IgD - B cells of a patient with RA is higher somatically mutated than those from normal individuals. The V genes of human PB IgM - IgD - lymphocytes, which are thought to be GC-derived memory B cells, are highly diversified by somatic mutation and independent of the age of an individual (13,22). We also found high levels of somatic mutation among V transcripts derived from the IgM - IgD - B cells of the two normal individuals (3.93% and 3.74%), similar to the 3.9% reported for V gene of IgM - IgD - B cells of a 67-year-old female (13). But the somatic mutation level of those cells was significant higher in the RA patient than in the normal controls (5.5%, P=.4). Differences in the proportions of different B cell subsets between RA and normal individuals may explain the increase in somatic mutation in IgM - IgD - B cells in the RA patient. RA may have a higher proportion of circulating memory B cells that have been exposed to antigen, which are more likely than nave cells to express mutated antigen receptor. Abnormal CDR3 regions encoding 11 or 12 amino acids of V expressed in IgM - IgD - B cells in RA. We found that V transcripts of the RA patient contain distinctively long CDR3 regions (Fig. 4). Data from other investigators show that V CDR3 regions with more than 1 codons were very rare in normal individuals (6,12,13,23). Most data showed less than 5% of CDR3 domains of 11 amino acids from normal PB. Nobody has reported CDR3 domains of 12 amino acids in V transcripts. Our data also showed no CDR3 domains of 11 or 12 amino acids among the 59 V transcripts of two normal controls. However, there were two CDR3 domains of 12 amino acids and one of 11 amino acids expressed among the 4 V transcripts (7.5%) of the RA patient. Our previous data from unsorted peripheral B cells in the same RA patient (AS) showed two CDR3 domains of 1 sequences with 11 amino acids (9). Interestingly, two of 3 abnormally long CDR3 domains in RA were expressed in IgM - IgD - B cells (memory B cells). Three factors influence the number of nucleotides at the V -J join and thus determine the CDR3 length: the rearrangement site of the V gene segment, that of the J gene segment, and the presence of N nucleotides. Since abnormally long CDR3 was expressed in IgM + IgD + B cells (naive B cell), the mechanism responsible for generation of CDR3 regions of unusual length in RA maybe unusual V and J rearrangement or abnormal N region addition in bone marrow. But we couldn't exclude peripheral antigen selection because of the 2 abnormally long CDR3 in IgM - IgD - B cells in RA. N-region addition is extensively higher in IgM + IgD + B cells in RA than those in normal individuals. Insertion of non-germline encoded nucleotides (N-regions) during Ig gene rearrangement was first described as a mechanism for the generation of junctional diversity in heavy chain CDR3 (24,25). A previous study with unsorted PBC in normal individuals and the same RA patient has shown N-region addition was present in kappa light chains with a similar proportion (9). In our present study with sorted IgM + IgD + B cells in RA, N-region addition was extensively higher than in normal controls. There are several possible explanations for the presence of non-germline encoded nucleotides at the V-J junctions of light chains. Most likely, TdT in an amount sufficient to introduce N regions into the light chains junction is expressed from the pro-b cell to pre-b cell stage (26,27). Alternatively, light chain rearrangement can potentially precede heavy chain rearrangement in normal pro-b cells that express TdT (28). Thus, this high proportional N-nucleotides addition of IgM + IgD + B cells in RA may result from abnormal regulation of TdT or light chain rearrangement in bone marrow level. In conclusion, these data suggest that enrichment for N region addition and long CDR3 lengths in RA may be from unusually high or prolonged activity of TdT in bone marrow B lineage cells. Acknowledgments We thank Stephanie Bayer for technical assistance. References 1. Zvaifler NJ: The immunopathology of joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Adv Immunol 16; , Harris ED Jr: Rheumatoid arthritis. Pathophysiology and implications for therapy. N Engl J Med 322; , Mellors RC, Heimer R, Corcos J, Korngold L: Cellular origin of rheumatoid factor. J Exp Med 11; , Smiley JD, Sachs C, Ziff M: In vitro synthesis of immunoglobulin by rheumatoid synovial membrane. J Clin Invest 47; , Tonegawa S: Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature 32; , Kabat EA, Wu TT: Identical V region amino acid sequences and segments of sequences in antibodies of different specificities. Relative contributions of VH and VL genes, minigenes, and complementarity-determining regions to binding of antibody-combining sites. J Immunol 147; , Max EE: Immunoglobulins: molecular genetics. In: Paul WE
7 N-Region Addition in Immunoglobulin Kappa Light Chains in B Cell Subsets in Rheumatoid Arthritis 95 (ed). Fundamental Immunology, 3 rd ed. Raven Press, New York, p , Lee SK, Bridges SL, Jr., Koopman WJ, Schroeder HW Jr: The immunoglobulin kappa light chain repertoire expressed in the synovium of a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 35;95-913, Bridges SL, Jr., Lee SK, Johnson ML, Johnson ML, Lavelle JC, Fowler PG, Koopman WJ, Schroeder HW Jr: Somatic mutation and CDR3 lengths of immunoglobulin kappa light chains expressed in patient s with rheumatoid arthritis and normal individuals. J Clin Invest 96; , Elgavish RA, Schroeder HW Jr: SAW: a graphical user interface for the analysis of immunoglobulin variable domain sequences. Biotechniques 15; , Lafaille JJ, DeCloux A, Bonneville M, Takagaki Y, Tonegawa S: Junctional sequences of T cell receptor gamma delta genes: implications for gamma delta T cell lineages and for a novel intermediate of V-(d)-J joining. Cell 59;859-87, Victor KD, Capra JD: An apparently common mechanism of generating antibody diversity: length variation of the VL-JL junction. Mol Immunol 31;39-46, Klein U, Kppers R, Rajewsky K: Human IgM + IgD + B cell, the major B cell subset in the peripheral blood, express V kappa genes with no or little somatic mutation throughout life. Eur J Immunol 23; , Chapple MR, MacLennan IC, Johson GD: A phenotypic study of B lymphocyte subpopulations in human bone marrow. Clin Exp Immunol 81; , Rajewsky K: Clonal selection and learning in the antibody system. Nature 381; , Jelinek DF, Splawski JB, Lipsky PE: Human peripheral blood B lymphocyte subpopulations: functional and phenotypic analysis of surface IgD positive and negative subsets. J Immunol 136;83-92, Agematsu K, Nayumo H, Yang FC, Nakazawa T, Fukushima K, Ito S, Sugita K, Moris T, Kobata T, Morimoto C, Komiyama A: B cell subpopulations separated by CD27 and crucial collaboration of CD27 + B cells and helper T cells in immunoglobulin production. Eur J Immunol 27; , Klein U, Goossens T, Fischer M, Kanzler H, Braeuniner A, Rajewsky K, Kppers R: Somatic hypermutation in normal and transformed human B cells. Immunol Rev 162; , Liu YJ, Malisan F, de Bouteiller O, Gurest C, Lebecque S, Banchereau J, Mills FC, Max EE, Martinez-Valdez H: Within germinal centers, isotype switching of immunoglobulin genes occurs after the onset of somatic mutation. Immunity 4;241-25, Berek C, Berger A, Apel M: Maturation of the immune response in germinal centers. cell 67; , Kroses FG, Timens W, Niewenhuis P: Germinal center reaction and B lymphocytes: morphology and function. Curr Top Pathol 84; Weber JC, Blaison G, Martin T, Knapp AM: Evidence that the VkIII gene usage is nonstochastic in both adult and newborn peripheral B cells and that peripheral CD5 + adult B cells are oligoclonal. J Clin Invest 93; , Kurosawa Y, Tonegawa S: Organization, structure, and assembly of immunoglobulin heavy chain diversity DNA segments. J Exp Med 155;21-218, Alt FW, Baltimore D: Joining of immunoglobulin heavy chain gene segments: implications from a chromosome with evidence of three D-JH fusions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79; , George JF Jr, Schroeder HW Jr: Developmental regulation of D reading frame and junctional diversity in TCR transcripts from human thymus. J Immunol 148; , Nishimoto N, Kubagawa H, Cooper MD: Comparison of pre-b cell differentiation in normal and X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA) individuals. Fed Proc 5;1346a (Abstract), Kubagawa H, Cooper AJ, Burrows PD: Light-chain gene expression before heavy chain rearrangement in pre-b cells transformed by Epstein-Barr virus. Proc Natl Acd Sci USA 86; , 1989
c Tuj1(-) apoptotic live 1 DIV 2 DIV 1 DIV 2 DIV Tuj1(+) Tuj1/GFP/DAPI Tuj1 DAPI GFP
 Supplementary Figure 1 Establishment of the gain- and loss-of-function experiments and cell survival assays. a Relative expression of mature mir-484 30 20 10 0 **** **** NCP mir- 484P NCP mir- 484P b Relative
Supplementary Figure 1 Establishment of the gain- and loss-of-function experiments and cell survival assays. a Relative expression of mature mir-484 30 20 10 0 **** **** NCP mir- 484P NCP mir- 484P b Relative
Toluidin-Staining of mast cells Ear tissue was fixed with Carnoy (60% ethanol, 30% chloroform, 10% acetic acid) overnight at 4 C, afterwards
 Toluidin-Staining of mast cells Ear tissue was fixed with Carnoy (60% ethanol, 30% chloroform, 10% acetic acid) overnight at 4 C, afterwards incubated in 100 % ethanol overnight at 4 C and embedded in
Toluidin-Staining of mast cells Ear tissue was fixed with Carnoy (60% ethanol, 30% chloroform, 10% acetic acid) overnight at 4 C, afterwards incubated in 100 % ethanol overnight at 4 C and embedded in
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Sherman SI, Wirth LJ, Droz J-P, et al. Motesanib diphosphate
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Sherman SI, Wirth LJ, Droz J-P, et al. Motesanib diphosphate
Supplementary Table 3. 3 UTR primer sequences. Primer sequences used to amplify and clone the 3 UTR of each indicated gene are listed.
 Supplemental Figure 1. DLKI-DIO3 mirna/mrna complementarity. Complementarity between the indicated DLK1-DIO3 cluster mirnas and the UTR of SOX2, SOX9, HIF1A, ZEB1, ZEB2, STAT3 and CDH1with mirsvr and PhastCons
Supplemental Figure 1. DLKI-DIO3 mirna/mrna complementarity. Complementarity between the indicated DLK1-DIO3 cluster mirnas and the UTR of SOX2, SOX9, HIF1A, ZEB1, ZEB2, STAT3 and CDH1with mirsvr and PhastCons
Supplemental Data. Shin et al. Plant Cell. (2012) /tpc YFP N
 MYC YFP N PIF5 YFP C N-TIC TIC Supplemental Data. Shin et al. Plant Cell. ()..5/tpc..95 Supplemental Figure. TIC interacts with MYC in the nucleus. Bimolecular fluorescence complementation assay using
MYC YFP N PIF5 YFP C N-TIC TIC Supplemental Data. Shin et al. Plant Cell. ()..5/tpc..95 Supplemental Figure. TIC interacts with MYC in the nucleus. Bimolecular fluorescence complementation assay using
Table S1. Oligonucleotides used for the in-house RT-PCR assays targeting the M, H7 or N9. Assay (s) Target Name Sequence (5 3 ) Comments
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION 2 3 Table S. Oligonucleotides used for the in-house RT-PCR assays targeting the M, H7 or N9 genes. Assay (s) Target Name Sequence (5 3 ) Comments CDC M InfA Forward (NS), CDC M
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION 2 3 Table S. Oligonucleotides used for the in-house RT-PCR assays targeting the M, H7 or N9 genes. Assay (s) Target Name Sequence (5 3 ) Comments CDC M InfA Forward (NS), CDC M
a) Primary cultures derived from the pancreas of an 11-week-old Pdx1-Cre; K-MADM-p53
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Supplementary Figure 1. Induction of p53 LOH by MADM. a) Primary cultures derived from the pancreas of an 11-week-old Pdx1-Cre; K-MADM-p53 mouse revealed increased p53 KO/KO (green,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Supplementary Figure 1. Induction of p53 LOH by MADM. a) Primary cultures derived from the pancreas of an 11-week-old Pdx1-Cre; K-MADM-p53 mouse revealed increased p53 KO/KO (green,
BIOLOGY 621 Identification of the Snorks
 Name: Date: Block: BIOLOGY 621 Identification of the Snorks INTRODUCTION: In this simulation activity, you will examine the DNA sequence of a fictitious organism - the Snork. Snorks were discovered on
Name: Date: Block: BIOLOGY 621 Identification of the Snorks INTRODUCTION: In this simulation activity, you will examine the DNA sequence of a fictitious organism - the Snork. Snorks were discovered on
Supplementary Document
 Supplementary Document 1. Supplementary Table legends 2. Supplementary Figure legends 3. Supplementary Tables 4. Supplementary Figures 5. Supplementary References 1. Supplementary Table legends Suppl.
Supplementary Document 1. Supplementary Table legends 2. Supplementary Figure legends 3. Supplementary Tables 4. Supplementary Figures 5. Supplementary References 1. Supplementary Table legends Suppl.
Supplementary Figure 1 a
 Supplementary Figure a Normalized expression/tbp (A.U.).6... Trip-br transcripts Trans Trans Trans b..5. Trip-br Ctrl LPS Normalized expression/tbp (A.U.) c Trip-br transcripts. adipocytes.... Trans Trans
Supplementary Figure a Normalized expression/tbp (A.U.).6... Trip-br transcripts Trans Trans Trans b..5. Trip-br Ctrl LPS Normalized expression/tbp (A.U.) c Trip-br transcripts. adipocytes.... Trans Trans
Abbreviations: P- paraffin-embedded section; C, cryosection; Bio-SA, biotin-streptavidin-conjugated fluorescein amplification.
 Supplementary Table 1. Sequence of primers for real time PCR. Gene Forward primer Reverse primer S25 5 -GTG GTC CAC ACT ACT CTC TGA GTT TC-3 5 - GAC TTT CCG GCA TCC TTC TTC-3 Mafa cds 5 -CTT CAG CAA GGA
Supplementary Table 1. Sequence of primers for real time PCR. Gene Forward primer Reverse primer S25 5 -GTG GTC CAC ACT ACT CTC TGA GTT TC-3 5 - GAC TTT CCG GCA TCC TTC TTC-3 Mafa cds 5 -CTT CAG CAA GGA
Supplementary Materials and Methods
 DD2 suppresses tumorigenicity of ovarian cancer cells by limiting cancer stem cell population Chunhua Han et al. Supplementary Materials and Methods Analysis of publicly available datasets: To analyze
DD2 suppresses tumorigenicity of ovarian cancer cells by limiting cancer stem cell population Chunhua Han et al. Supplementary Materials and Methods Analysis of publicly available datasets: To analyze
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1: Cryopreservation alters CD62L expression by CD4 T cells. Freshly isolated (left) or cryopreserved PBMCs (right) were stained with the mix of antibodies described
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1: Cryopreservation alters CD62L expression by CD4 T cells. Freshly isolated (left) or cryopreserved PBMCs (right) were stained with the mix of antibodies described
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 U1 inhibition causes a shift of RNA-seq reads from exons to introns. (a) Evidence for the high purity of 4-shU-labeled RNAs used for RNA-seq. HeLa cells transfected with control
Supplementary Figure 1 U1 inhibition causes a shift of RNA-seq reads from exons to introns. (a) Evidence for the high purity of 4-shU-labeled RNAs used for RNA-seq. HeLa cells transfected with control
Supplementary Figure 1 MicroRNA expression in human synovial fibroblasts from different locations. MicroRNA, which were identified by RNAseq as most
 Supplementary Figure 1 MicroRNA expression in human synovial fibroblasts from different locations. MicroRNA, which were identified by RNAseq as most differentially expressed between human synovial fibroblasts
Supplementary Figure 1 MicroRNA expression in human synovial fibroblasts from different locations. MicroRNA, which were identified by RNAseq as most differentially expressed between human synovial fibroblasts
Supplementary Figure 1. ROS induces rapid Sod1 nuclear localization in a dosagedependent manner. WT yeast cells (SZy1051) were treated with 4NQO at
 Supplementary Figure 1. ROS induces rapid Sod1 nuclear localization in a dosagedependent manner. WT yeast cells (SZy1051) were treated with 4NQO at different concentrations for 30 min and analyzed for
Supplementary Figure 1. ROS induces rapid Sod1 nuclear localization in a dosagedependent manner. WT yeast cells (SZy1051) were treated with 4NQO at different concentrations for 30 min and analyzed for
Chapter 5. Generation of lymphocyte antigen receptors
 Chapter 5 Generation of lymphocyte antigen receptors Structural variation in Ig constant regions Isotype: different class of Ig Heavy-chain C regions are encoded in separate genes Initially, only two of
Chapter 5 Generation of lymphocyte antigen receptors Structural variation in Ig constant regions Isotype: different class of Ig Heavy-chain C regions are encoded in separate genes Initially, only two of
Plasmids Western blot analysis and immunostaining Flow Cytometry Cell surface biotinylation RNA isolation and cdna synthesis
 Plasmids psuper-retro-s100a10 shrna1 was constructed by cloning the dsdna oligo 5 -GAT CCC CGT GGG CTT CCA GAG CTT CTT TCA AGA GAA GAA GCT CTG GAA GCC CAC TTT TTA-3 and 5 -AGC TTA AAA AGT GGG CTT CCA GAG
Plasmids psuper-retro-s100a10 shrna1 was constructed by cloning the dsdna oligo 5 -GAT CCC CGT GGG CTT CCA GAG CTT CTT TCA AGA GAA GAA GCT CTG GAA GCC CAC TTT TTA-3 and 5 -AGC TTA AAA AGT GGG CTT CCA GAG
Supplementary Figure 1
 Metastatic melanoma Primary melanoma Healthy human skin Supplementary Figure 1 CD22 IgG4 Supplementary Figure 1: Immunohisochemical analysis of CD22+ (left) and IgG4 (right), cells (shown in red and indicated
Metastatic melanoma Primary melanoma Healthy human skin Supplementary Figure 1 CD22 IgG4 Supplementary Figure 1: Immunohisochemical analysis of CD22+ (left) and IgG4 (right), cells (shown in red and indicated
Principles of Adaptive Immunity
 Principles of Adaptive Immunity Chapter 3 Parham Hans de Haard 17 th of May 2010 Agenda Recognition molecules of adaptive immune system Features adaptive immune system Immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors
Principles of Adaptive Immunity Chapter 3 Parham Hans de Haard 17 th of May 2010 Agenda Recognition molecules of adaptive immune system Features adaptive immune system Immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors
*To whom correspondence should be addressed. This PDF file includes:
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.1212182/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Partial Retraction to Detection of an Infectious Retrovirus, XMRV, in Blood Cells of Patients with Chronic Fatigue
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.1212182/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Partial Retraction to Detection of an Infectious Retrovirus, XMRV, in Blood Cells of Patients with Chronic Fatigue
CD31 5'-AGA GAC GGT CTT GTC GCA GT-3' 5 ' -TAC TGG GCT TCG AGA GCA GT-3'
 Table S1. The primer sets used for real-time RT-PCR analysis. Gene Forward Reverse VEGF PDGFB TGF-β MCP-1 5'-GTT GCA GCA TGA ATC TGA GG-3' 5'-GGA GAC TCT TCG AGG AGC ACT T-3' 5'-GAA TCA GGC ATC GAG AGA
Table S1. The primer sets used for real-time RT-PCR analysis. Gene Forward Reverse VEGF PDGFB TGF-β MCP-1 5'-GTT GCA GCA TGA ATC TGA GG-3' 5'-GGA GAC TCT TCG AGG AGC ACT T-3' 5'-GAA TCA GGC ATC GAG AGA
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.3836
 Supplementary Figure 1 Recombinant LIGHT-VTP induces pericyte contractility and endothelial cell activation. (a) Western blot showing purification steps for full length murine LIGHT-VTP (CGKRK) protein:
Supplementary Figure 1 Recombinant LIGHT-VTP induces pericyte contractility and endothelial cell activation. (a) Western blot showing purification steps for full length murine LIGHT-VTP (CGKRK) protein:
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 3 3 3 1 1 Bregma -1.6mm 3 : Bregma Ref) Http://www.mbl.org/atlas165/atlas165_start.html Bregma -.18mm Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of the utilized brain slice
Supplementary Figure 1 3 3 3 1 1 Bregma -1.6mm 3 : Bregma Ref) Http://www.mbl.org/atlas165/atlas165_start.html Bregma -.18mm Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of the utilized brain slice
Citation for published version (APA): Oosterveer, M. H. (2009). Control of metabolic flux by nutrient sensors Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Control of metabolic flux by nutrient sensors Oosterveer, Maaike IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
University of Groningen Control of metabolic flux by nutrient sensors Oosterveer, Maaike IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
Figure S1. Analysis of genomic and cdna sequences of the targeted regions in WT-KI and
 Figure S1. Analysis of genomic and sequences of the targeted regions in and indicated mutant KI cells, with WT and corresponding mutant sequences underlined. (A) cells; (B) K21E-KI cells; (C) D33A-KI cells;
Figure S1. Analysis of genomic and sequences of the targeted regions in and indicated mutant KI cells, with WT and corresponding mutant sequences underlined. (A) cells; (B) K21E-KI cells; (C) D33A-KI cells;
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials 1 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used for quantitative PCR analysis. Gene name Gene symbol Accession IDs Sequence range Product Primer sequences size (bp) β-actin Actb gi
Supplementary Materials 1 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used for quantitative PCR analysis. Gene name Gene symbol Accession IDs Sequence range Product Primer sequences size (bp) β-actin Actb gi
Innate immunity (rapid response) Dendritic cell. Macrophage. Natural killer cell. Complement protein. Neutrophil
 1 The immune system The immune response The immune system comprises two arms functioning cooperatively to provide a comprehensive protective response: the innate and the adaptive immune system. The innate
1 The immune system The immune response The immune system comprises two arms functioning cooperatively to provide a comprehensive protective response: the innate and the adaptive immune system. The innate
Antibodies and T Cell Receptor Genetics Generation of Antigen Receptor Diversity
 Antibodies and T Cell Receptor Genetics 2008 Peter Burrows 4-6529 peterb@uab.edu Generation of Antigen Receptor Diversity Survival requires B and T cell receptor diversity to respond to the diversity of
Antibodies and T Cell Receptor Genetics 2008 Peter Burrows 4-6529 peterb@uab.edu Generation of Antigen Receptor Diversity Survival requires B and T cell receptor diversity to respond to the diversity of
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. H3F3B expression in lung cancer. a. Comparison of H3F3B expression in relapsed and non-relapsed lung cancer patients. b. Prognosis of two groups of lung cancer
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. H3F3B expression in lung cancer. a. Comparison of H3F3B expression in relapsed and non-relapsed lung cancer patients. b. Prognosis of two groups of lung cancer
Beta Thalassemia Case Study Introduction to Bioinformatics
 Beta Thalassemia Case Study Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University San José, California, USA sami.khuri@sjsu.edu www.cs.sjsu.edu/faculty/khuri Outline v Hemoglobin v Alpha
Beta Thalassemia Case Study Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University San José, California, USA sami.khuri@sjsu.edu www.cs.sjsu.edu/faculty/khuri Outline v Hemoglobin v Alpha
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH THE IMMUNE SYSTEM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF HOST DEFENSES The human body contains three lines of against infectious agents (pathogens) 1. Mechanical and chemical boundaries (part of the innate immune system)
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF HOST DEFENSES The human body contains three lines of against infectious agents (pathogens) 1. Mechanical and chemical boundaries (part of the innate immune system)
Supplementary Table 2. Conserved regulatory elements in the promoters of CD36.
 Supplementary Table 1. RT-qPCR primers for CD3, PPARg and CEBP. Assay Forward Primer Reverse Primer 1A CAT TTG TGG CCT TGT GCT CTT TGA TGA GTC ACA GAA AGA ATC AAT TC 1B AGG AAA TGA ACT GAT GAG TCA CAG
Supplementary Table 1. RT-qPCR primers for CD3, PPARg and CEBP. Assay Forward Primer Reverse Primer 1A CAT TTG TGG CCT TGT GCT CTT TGA TGA GTC ACA GAA AGA ATC AAT TC 1B AGG AAA TGA ACT GAT GAG TCA CAG
all of the above the ability to impart long term memory adaptive immunity all of the above bone marrow none of the above
 1. (3 points) Immediately after a pathogen enters the body, it faces the cells and soluble proteins of the innate immune system. Which of the following are characteristics of innate immunity? a. inflammation
1. (3 points) Immediately after a pathogen enters the body, it faces the cells and soluble proteins of the innate immune system. Which of the following are characteristics of innate immunity? a. inflammation
Introduction. Introduction. Lymphocyte development (maturation)
 Introduction Abbas Chapter 8: Lymphocyte Development and the Rearrangement and Expression of Antigen Receptor Genes Christina Ciaccio, MD Children s Mercy Hospital January 5, 2009 Lymphocyte development
Introduction Abbas Chapter 8: Lymphocyte Development and the Rearrangement and Expression of Antigen Receptor Genes Christina Ciaccio, MD Children s Mercy Hospital January 5, 2009 Lymphocyte development
Ig light chain rearrangement: Rescue pathway
 B Cell Development Ig light chain rearrangement: Rescue pathway There is only a 1:3 chance of the join between the V and J region being in frame Vk Jk Ck Non-productive Rearrangement Light chain has a
B Cell Development Ig light chain rearrangement: Rescue pathway There is only a 1:3 chance of the join between the V and J region being in frame Vk Jk Ck Non-productive Rearrangement Light chain has a
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS. showed that all three replicates had similar growth trends (Figure 4.1) (p<0.05; p=0.0000)
 CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 4.1 Growth Characterization of C. vulgaris 4.1.1 Optical Density Growth study of Chlorella vulgaris based on optical density at 620 nm (OD 620 ) showed that all three replicates had similar
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 4.1 Growth Characterization of C. vulgaris 4.1.1 Optical Density Growth study of Chlorella vulgaris based on optical density at 620 nm (OD 620 ) showed that all three replicates had similar
Nucleotide Sequence of the Australian Bluetongue Virus Serotype 1 RNA Segment 10
 J. gen. Virol. (1988), 69, 945-949. Printed in Great Britain 945 Key words: BTV/genome segment lo/nucleotide sequence Nucleotide Sequence of the Australian Bluetongue Virus Serotype 1 RNA Segment 10 By
J. gen. Virol. (1988), 69, 945-949. Printed in Great Britain 945 Key words: BTV/genome segment lo/nucleotide sequence Nucleotide Sequence of the Australian Bluetongue Virus Serotype 1 RNA Segment 10 By
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature05883 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Figure 1 Prostaglandin agonists and antagonists alter runx1/cmyb expression. a-e, Embryos were exposed to (b) PGE2 and (c) PGI2 (20μM) and
doi: 10.1038/nature05883 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Figure 1 Prostaglandin agonists and antagonists alter runx1/cmyb expression. a-e, Embryos were exposed to (b) PGE2 and (c) PGI2 (20μM) and
Culture Density (OD600) 0.1. Culture Density (OD600) Culture Density (OD600) Culture Density (OD600) Culture Density (OD600)
 A. B. C. D. E. PA JSRI JSRI 2 PA DSAM DSAM 2 DSAM 3 PA LNAP LNAP 2 LNAP 3 PAO Fcor Fcor 2 Fcor 3 PAO Wtho Wtho 2 Wtho 3 Wtho 4 DTSB Low Iron 2 4 6 8 2 4 6 8 2 22 DTSB Low Iron 2 4 6 8 2 4 6 8 2 22 DTSB
A. B. C. D. E. PA JSRI JSRI 2 PA DSAM DSAM 2 DSAM 3 PA LNAP LNAP 2 LNAP 3 PAO Fcor Fcor 2 Fcor 3 PAO Wtho Wtho 2 Wtho 3 Wtho 4 DTSB Low Iron 2 4 6 8 2 4 6 8 2 22 DTSB Low Iron 2 4 6 8 2 4 6 8 2 22 DTSB
Supplemental Figures: Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figures: Supplemental Figure 1 Suppl. Figure 1. BM-DC infection with H. pylori does not induce cytotoxicity and treatment of BM-DCs with H. pylori sonicate, but not heat-inactivated bacteria,
Supplemental Figures: Supplemental Figure 1 Suppl. Figure 1. BM-DC infection with H. pylori does not induce cytotoxicity and treatment of BM-DCs with H. pylori sonicate, but not heat-inactivated bacteria,
Supplemental Information. Th17 Lymphocytes Induce Neuronal. Cell Death in a Human ipsc-based. Model of Parkinson's Disease
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 23 Supplemental Information Th17 Lymphocytes Induce Neuronal Cell Death in a Human ipsc-based Model of Parkinson's Disease Annika Sommer, Franz Maxreiter, Florian Krach, Tanja Fadler,
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 23 Supplemental Information Th17 Lymphocytes Induce Neuronal Cell Death in a Human ipsc-based Model of Parkinson's Disease Annika Sommer, Franz Maxreiter, Florian Krach, Tanja Fadler,
Generation of antibody diversity October 18, Ram Savan
 Generation of antibody diversity October 18, 2016 Ram Savan savanram@uw.edu 441 Lecture #10 Slide 1 of 30 Three lectures on antigen receptors Part 1 : Structural features of the BCR and TCR Janeway Chapter
Generation of antibody diversity October 18, 2016 Ram Savan savanram@uw.edu 441 Lecture #10 Slide 1 of 30 Three lectures on antigen receptors Part 1 : Structural features of the BCR and TCR Janeway Chapter
BHP 2-7 and Nthy-ori 3-1 cells were grown in RPMI1640 medium (Hyclone) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco), 2mM L-glutamine, and 100 U/mL
 1 2 3 4 Materials and Methods Cell culture BHP 2-7 and Nthy-ori 3-1 cells were grown in RPMI1640 medium (Hyclone) 5 supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco), 2mM L-glutamine, and 100 U/mL 6 penicillin-streptomycin.
1 2 3 4 Materials and Methods Cell culture BHP 2-7 and Nthy-ori 3-1 cells were grown in RPMI1640 medium (Hyclone) 5 supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco), 2mM L-glutamine, and 100 U/mL 6 penicillin-streptomycin.
A smart acid nanosystem for ultrasensitive. live cell mrna imaging by the target-triggered intracellular self-assembly
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 A smart ZnO@polydopamine-nucleic acid nanosystem for ultrasensitive live cell mrna imaging
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 A smart ZnO@polydopamine-nucleic acid nanosystem for ultrasensitive live cell mrna imaging
Adaptive Immune System
 Short Course on Immunology Adaptive Immune System Bhargavi Duvvuri Ph.D IIIrd Year (Immunology) bhargavi@yorku.ca Supervisor Dr.Gillian E Wu Professor, School of Kinesiology and Health Sciences York University,
Short Course on Immunology Adaptive Immune System Bhargavi Duvvuri Ph.D IIIrd Year (Immunology) bhargavi@yorku.ca Supervisor Dr.Gillian E Wu Professor, School of Kinesiology and Health Sciences York University,
HCV Persistence and Immune Evasion in the Absence of Memory T Cell Help.
 SOM Text HCV Persistence and Immune Evasion in the Absence of Memory T Cell Help. Arash Grakoui 1, Naglaa H. Shoukry 2, David J. Woollard 2, Jin-Hwan Han 1, Holly L. Hanson 1, John Ghrayeb 3, Krishna K.
SOM Text HCV Persistence and Immune Evasion in the Absence of Memory T Cell Help. Arash Grakoui 1, Naglaa H. Shoukry 2, David J. Woollard 2, Jin-Hwan Han 1, Holly L. Hanson 1, John Ghrayeb 3, Krishna K.
Astaxanthin prevents and reverses diet-induced insulin resistance and. steatohepatitis in mice: A comparison with vitamin E
 Supplementary Information Astaxanthin prevents and reverses diet-induced insulin resistance and steatohepatitis in mice: A comparison with vitamin E Yinhua Ni, 1,2 Mayumi Nagashimada, 1 Fen Zhuge, 1 Lili
Supplementary Information Astaxanthin prevents and reverses diet-induced insulin resistance and steatohepatitis in mice: A comparison with vitamin E Yinhua Ni, 1,2 Mayumi Nagashimada, 1 Fen Zhuge, 1 Lili
TetR repressor-based bioreporters for the detection of doxycycline using Escherichia
 Supplementary materials TetR repressor-based bioreporters for the detection of doxycycline using Escherichia coli and Acinetobacter oleivorans Hyerim Hong and Woojun Park * Department of Environmental
Supplementary materials TetR repressor-based bioreporters for the detection of doxycycline using Escherichia coli and Acinetobacter oleivorans Hyerim Hong and Woojun Park * Department of Environmental
 www.lessonplansinc.com Topic: Protein Synthesis - Sentence Activity Summary: Students will simulate transcription and translation by building a sentence/polypeptide from words/amino acids. Goals & Objectives:
www.lessonplansinc.com Topic: Protein Synthesis - Sentence Activity Summary: Students will simulate transcription and translation by building a sentence/polypeptide from words/amino acids. Goals & Objectives:
Molecular Pathology of Lymphoma (Part 1) Rex K.H. Au-Yeung Department of Pathology, HKU
 Molecular Pathology of Lymphoma (Part 1) Rex K.H. Au-Yeung Department of Pathology, HKU Lecture outline Time 10:00 11:00 11:15 12:10 12:20 13:15 Content Introduction to lymphoma Review of lymphocyte biology
Molecular Pathology of Lymphoma (Part 1) Rex K.H. Au-Yeung Department of Pathology, HKU Lecture outline Time 10:00 11:00 11:15 12:10 12:20 13:15 Content Introduction to lymphoma Review of lymphocyte biology
Immunobiology 7. The Humoral Immune Response
 Janeway Murphy Travers Walport Immunobiology 7 Chapter 9 The Humoral Immune Response Copyright Garland Science 2008 Tim Worbs Institute of Immunology Hannover Medical School 1 The course of a typical antibody
Janeway Murphy Travers Walport Immunobiology 7 Chapter 9 The Humoral Immune Response Copyright Garland Science 2008 Tim Worbs Institute of Immunology Hannover Medical School 1 The course of a typical antibody
T cell Receptor. Chapter 9. Comparison of TCR αβ T cells
 Chapter 9 The αβ TCR is similar in size and structure to an antibody Fab fragment T cell Receptor Kuby Figure 9-3 The αβ T cell receptor - Two chains - α and β - Two domains per chain - constant (C) domain
Chapter 9 The αβ TCR is similar in size and structure to an antibody Fab fragment T cell Receptor Kuby Figure 9-3 The αβ T cell receptor - Two chains - α and β - Two domains per chain - constant (C) domain
Andrea s SI Session PCB Practice Test Test 3
 Practice Test Test 3 READ BEFORE STARTING PRACTICE TEST: Remember to please use this practice test as a tool to measure your knowledge, and DO NOT use it as your only tool to study for the test, since
Practice Test Test 3 READ BEFORE STARTING PRACTICE TEST: Remember to please use this practice test as a tool to measure your knowledge, and DO NOT use it as your only tool to study for the test, since
The development of clonality testing for lymphomas in the Bristol Genetics Laboratory. Dr Paula Waits Bristol Genetics Laboratory
 The development of clonality testing for lymphomas in the Bristol Genetics Laboratory Dr Paula Waits Bristol Genetics Laboratory Introduction The majority of lymphoid malignancies belong to the B cell
The development of clonality testing for lymphomas in the Bristol Genetics Laboratory Dr Paula Waits Bristol Genetics Laboratory Introduction The majority of lymphoid malignancies belong to the B cell
Cross-talk between mineralocorticoid and angiotensin II signaling for cardiac
 ONLINE SUPPLEMENT TO Crosstalk between mineralocorticoid and angiotensin II signaling for cardiac remodeling An Di ZHANG,,3, Aurelie NGUYEN DINH CAT*,,3, Christelle SOUKASEUM *,,3, Brigitte ESCOUBET, 4,
ONLINE SUPPLEMENT TO Crosstalk between mineralocorticoid and angiotensin II signaling for cardiac remodeling An Di ZHANG,,3, Aurelie NGUYEN DINH CAT*,,3, Christelle SOUKASEUM *,,3, Brigitte ESCOUBET, 4,
Supplementary Figure 1a
 Supplementary Figure 1a Hours: E-cadherin TGF-β On TGF-β Off 0 12 24 36 48 24 48 72 Vimentin βactin Fig. S1a. Treatment of AML12 cells with TGF-β induces EMT. Treatment of AML12 cells with TGF-β results
Supplementary Figure 1a Hours: E-cadherin TGF-β On TGF-β Off 0 12 24 36 48 24 48 72 Vimentin βactin Fig. S1a. Treatment of AML12 cells with TGF-β induces EMT. Treatment of AML12 cells with TGF-β results
Recommended laboratory tests to identify influenza A/H5 virus in specimens from patients with an influenza-like illness
 World Health Organization Recommended laboratory tests to identify influenza A/H5 virus in specimens from patients with an influenza-like illness General information Highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI)
World Health Organization Recommended laboratory tests to identify influenza A/H5 virus in specimens from patients with an influenza-like illness General information Highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI)
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Lats1/2 deleted ihbs and ihps showed decreased transcripts of hepatocyte related genes (a and b) Western blots (a) and recombination PCR (b) of control and
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Lats1/2 deleted ihbs and ihps showed decreased transcripts of hepatocyte related genes (a and b) Western blots (a) and recombination PCR (b) of control and
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for qrt-pcr
 Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for qrt-pcr Gene PRDM16 UCP1 PGC1α Dio2 Elovl3 Cidea Cox8b PPARγ AP2 mttfam CyCs Nampt NRF1 16s-rRNA Hexokinase 2, intron 9 β-actin Primer Sequences 5'-CCA CCA GCG
Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for qrt-pcr Gene PRDM16 UCP1 PGC1α Dio2 Elovl3 Cidea Cox8b PPARγ AP2 mttfam CyCs Nampt NRF1 16s-rRNA Hexokinase 2, intron 9 β-actin Primer Sequences 5'-CCA CCA GCG
The Adaptive Immune Response. B-cells
 The Adaptive Immune Response B-cells The innate immune system provides immediate protection. The adaptive response takes time to develop and is antigen specific. Activation of B and T lymphocytes Naive
The Adaptive Immune Response B-cells The innate immune system provides immediate protection. The adaptive response takes time to develop and is antigen specific. Activation of B and T lymphocytes Naive
Lezione 10. Sommario. Bioinformatica. Lezione 10: Sintesi proteica Synthesis of proteins Central dogma: DNA makes RNA makes proteins Genetic code
 Lezione 10 Bioinformatica Mauro Ceccanti e Alberto Paoluzzi Lezione 10: Sintesi proteica Synthesis of proteins Dip. Informatica e Automazione Università Roma Tre Dip. Medicina Clinica Università La Sapienza
Lezione 10 Bioinformatica Mauro Ceccanti e Alberto Paoluzzi Lezione 10: Sintesi proteica Synthesis of proteins Dip. Informatica e Automazione Università Roma Tre Dip. Medicina Clinica Università La Sapienza
Immunology - Lecture 2 Adaptive Immune System 1
 Immunology - Lecture 2 Adaptive Immune System 1 Book chapters: Molecules of the Adaptive Immunity 6 Adaptive Cells and Organs 7 Generation of Immune Diversity Lymphocyte Antigen Receptors - 8 CD markers
Immunology - Lecture 2 Adaptive Immune System 1 Book chapters: Molecules of the Adaptive Immunity 6 Adaptive Cells and Organs 7 Generation of Immune Diversity Lymphocyte Antigen Receptors - 8 CD markers
Beta Thalassemia Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University Spring 2015
 Bioinformatics in Medical Product Development SMPD 287 Three Beta Thalassemia Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University Hemoglobin Outline Anatomy of a gene Hemoglobinopathies
Bioinformatics in Medical Product Development SMPD 287 Three Beta Thalassemia Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University Hemoglobin Outline Anatomy of a gene Hemoglobinopathies
Antigen-Independent B-Cell Development Bone Marrow
 Antigen-Independent B-Cell Development Bone Marrow 1. DNA rearrangements establish the primary repertoire, creating diversity 2. Allelic exclusion ensures that each clone expresses a single antibody on
Antigen-Independent B-Cell Development Bone Marrow 1. DNA rearrangements establish the primary repertoire, creating diversity 2. Allelic exclusion ensures that each clone expresses a single antibody on
Formylpeptide receptor2 contributes to colon epithelial homeostasis, inflammation, and tumorigenesis
 Supplementary Data Formylpeptide receptor2 contributes to colon epithelial homeostasis, inflammation, and tumorigenesis Keqiang Chen, Mingyong Liu, Ying Liu, Teizo Yoshimura, Wei Shen, Yingying Le, Scott
Supplementary Data Formylpeptide receptor2 contributes to colon epithelial homeostasis, inflammation, and tumorigenesis Keqiang Chen, Mingyong Liu, Ying Liu, Teizo Yoshimura, Wei Shen, Yingying Le, Scott
Supplemental Information. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Neutralize. the Anti-tumor Effect of CSF1 Receptor Blockade
 Cancer Cell, Volume 32 Supplemental Information Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Neutralize the Anti-tumor Effect of CSF1 Receptor Blockade by Inducing PMN-MDSC Infiltration of Tumors Vinit Kumar, Laxminarasimha
Cancer Cell, Volume 32 Supplemental Information Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Neutralize the Anti-tumor Effect of CSF1 Receptor Blockade by Inducing PMN-MDSC Infiltration of Tumors Vinit Kumar, Laxminarasimha
Antigen Receptor Structures October 14, Ram Savan
 Antigen Receptor Structures October 14, 2016 Ram Savan savanram@uw.edu 441 Lecture #8 Slide 1 of 28 Three lectures on antigen receptors Part 1 (Today): Structural features of the BCR and TCR Janeway Chapter
Antigen Receptor Structures October 14, 2016 Ram Savan savanram@uw.edu 441 Lecture #8 Slide 1 of 28 Three lectures on antigen receptors Part 1 (Today): Structural features of the BCR and TCR Janeway Chapter
CIRCRESAHA/2004/098145/R1 - ONLINE 1. Validation by Semi-quantitative Real-Time Reverse Transcription PCR
 CIRCRESAHA/2004/098145/R1 - ONLINE 1 Expanded Materials and Methods Validation by Semi-quantitative Real-Time Reverse Transcription PCR Expression patterns of 13 genes (Online Table 2), selected with respect
CIRCRESAHA/2004/098145/R1 - ONLINE 1 Expanded Materials and Methods Validation by Semi-quantitative Real-Time Reverse Transcription PCR Expression patterns of 13 genes (Online Table 2), selected with respect
Malignant Amelanotic Melanoma of the Pleura without Primary Skin Lesion: An Autopsy Case Report. a a*
 2009 63 6 379 384 Malignant Amelanotic Melanoma of the Pleura without Primary Skin Lesion: An Autopsy Case Report a b a a a* a b 380 63 6 Chest x ray and computed tomography (CT). A, Chest x ray on admission
2009 63 6 379 384 Malignant Amelanotic Melanoma of the Pleura without Primary Skin Lesion: An Autopsy Case Report a b a a a* a b 380 63 6 Chest x ray and computed tomography (CT). A, Chest x ray on admission
Frequency of mosaicism points towards mutation prone early cleavage cell divisions.
 Frequency of mosaicism points towards mutation prone early cleavage cell divisions. Chad Harland, Wouter Coppieters, Latifa Karim, Carole Charlier, Michel Georges Germ-line de novo mutations Definition:
Frequency of mosaicism points towards mutation prone early cleavage cell divisions. Chad Harland, Wouter Coppieters, Latifa Karim, Carole Charlier, Michel Georges Germ-line de novo mutations Definition:
IMGT Collier de Perles: the New Look for IgSF and MhcSF in IMGT
 IMGT Collier de Perles: the New Look for IgSF and MhcSF in IMGT Quentin Kaas and Marie-Paule Lefranc Laboratoire d ImmunoGénétique Moléculaire Université Montpellier, UPR CNRS 1142, IGH Institut Universitaire
IMGT Collier de Perles: the New Look for IgSF and MhcSF in IMGT Quentin Kaas and Marie-Paule Lefranc Laboratoire d ImmunoGénétique Moléculaire Université Montpellier, UPR CNRS 1142, IGH Institut Universitaire
membrane form secreted form 13 aa 26 aa K K V V K K 3aa
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv Pillai secreted form membrane form 13 aa 26 aa K K V V K K 3aa Hapten monosaccharide
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv Pillai secreted form membrane form 13 aa 26 aa K K V V K K 3aa Hapten monosaccharide
L I F E S C I E N C E S
 1a L I F E S C I E N C E S 5 -UUA AUA UUC GAA AGC UGC AUC GAA AAC UGU GAA UCA-3 5 -TTA ATA TTC GAA AGC TGC ATC GAA AAC TGT GAA TCA-3 3 -AAT TAT AAG CTT TCG ACG TAG CTT TTG ACA CTT AGT-5 OCTOBER 31, 2006
1a L I F E S C I E N C E S 5 -UUA AUA UUC GAA AGC UGC AUC GAA AAC UGU GAA UCA-3 5 -TTA ATA TTC GAA AGC TGC ATC GAA AAC TGT GAA TCA-3 3 -AAT TAT AAG CTT TCG ACG TAG CTT TTG ACA CTT AGT-5 OCTOBER 31, 2006
ice-cold 70% ethanol with gentle vortexing, incubated at -20 C for 4 hours, and washed with PBS.
 Cell cycle analysis For cell cycle analysis, single cell suspensions of E12.5 fetal liver cells were suspended in 4 ml ice-cold 7% ethanol with gentle vortexing, incubated at -2 C for 4 hours, and washed
Cell cycle analysis For cell cycle analysis, single cell suspensions of E12.5 fetal liver cells were suspended in 4 ml ice-cold 7% ethanol with gentle vortexing, incubated at -2 C for 4 hours, and washed
κ λ Antigen-Independent B-Cell Development Bone Marrow Ordered Rearrangement of Ig Genes During B-Cell Development in the Bone Marrow
 Antigen-Independent B-Cell Development Bone Marrow 1. DNA rearrangements establish the primary repertoire, creating diversity 2. Allelic exclusion ensures that each clone expresses a single antibody on
Antigen-Independent B-Cell Development Bone Marrow 1. DNA rearrangements establish the primary repertoire, creating diversity 2. Allelic exclusion ensures that each clone expresses a single antibody on
Integration Solutions
 Integration Solutions (1) a) With no active glycosyltransferase of either type, an ii individual would not be able to add any sugars to the O form of the lipopolysaccharide. Thus, the only lipopolysaccharide
Integration Solutions (1) a) With no active glycosyltransferase of either type, an ii individual would not be able to add any sugars to the O form of the lipopolysaccharide. Thus, the only lipopolysaccharide
Expression of Selected Inflammatory Cytokine Genes in Bladder Biopsies
 Borneo Journal of Resource Science and Technology (2013) 3(2): 15-20 Expression of Selected Inflammatory Cytokine Genes in Bladder Biopsies EDMUND UI-HANG SIM *1, NUR DIANA ANUAR 2, TENG-AIK ONG 3, GUAN-
Borneo Journal of Resource Science and Technology (2013) 3(2): 15-20 Expression of Selected Inflammatory Cytokine Genes in Bladder Biopsies EDMUND UI-HANG SIM *1, NUR DIANA ANUAR 2, TENG-AIK ONG 3, GUAN-
Received 29 December 1998/Accepted 9 March 1999
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, June 1999, p. 4794 4805 Vol. 73, No. 6 0022-538X/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Molecular Requirements for Human Immunodeficiency
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, June 1999, p. 4794 4805 Vol. 73, No. 6 0022-538X/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Molecular Requirements for Human Immunodeficiency
Mutation Screening and Association Studies of the Human UCP 3 Gene in Normoglycemic and NIDDM Morbidly Obese Patients
 Mutation Screening and Association Studies of the Human UCP 3 Gene in Normoglycemic and NIDDM Morbidly Obese Patients Shuichi OTABE, Karine CLEMENT, Séverine DUBOIS, Frederic LEPRETRE, Veronique PELLOUX,
Mutation Screening and Association Studies of the Human UCP 3 Gene in Normoglycemic and NIDDM Morbidly Obese Patients Shuichi OTABE, Karine CLEMENT, Séverine DUBOIS, Frederic LEPRETRE, Veronique PELLOUX,
Adaptive Immunity: Humoral Immune Responses
 MICR2209 Adaptive Immunity: Humoral Immune Responses Dr Allison Imrie 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will review the different mechanisms which constitute the humoral immune response, and examine the antibody
MICR2209 Adaptive Immunity: Humoral Immune Responses Dr Allison Imrie 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will review the different mechanisms which constitute the humoral immune response, and examine the antibody
Development of B and T lymphocytes
 Development of B and T lymphocytes What will we discuss today? B-cell development T-cell development B- cell development overview Stem cell In periphery Pro-B cell Pre-B cell Immature B cell Mature B cell
Development of B and T lymphocytes What will we discuss today? B-cell development T-cell development B- cell development overview Stem cell In periphery Pro-B cell Pre-B cell Immature B cell Mature B cell
Commercially available HLA Class II tetramers (Beckman Coulter) conjugated to
 Class II tetramer staining Commercially available HLA Class II tetramers (Beckman Coulter) conjugated to PE were combined with dominant HIV epitopes (DRB1*0101-DRFYKTLRAEQASQEV, DRB1*0301- PEKEVLVWKFDSRLAFHH,
Class II tetramer staining Commercially available HLA Class II tetramers (Beckman Coulter) conjugated to PE were combined with dominant HIV epitopes (DRB1*0101-DRFYKTLRAEQASQEV, DRB1*0301- PEKEVLVWKFDSRLAFHH,
Helminth worm, Schistosomiasis Trypanosomes, sleeping sickness Pneumocystis carinii. Ringworm fungus HIV Influenza
 Helminth worm, Schistosomiasis Trypanosomes, sleeping sickness Pneumocystis carinii Ringworm fungus HIV Influenza Candida Staph aureus Mycobacterium tuberculosis Listeria Salmonella Streptococcus Levels
Helminth worm, Schistosomiasis Trypanosomes, sleeping sickness Pneumocystis carinii Ringworm fungus HIV Influenza Candida Staph aureus Mycobacterium tuberculosis Listeria Salmonella Streptococcus Levels
IMMUNE CELL SURFACE RECEPTORS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS
 LECTURE: 07 Title: IMMUNE CELL SURFACE RECEPTORS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: The chemical nature of the cellular surface receptors. Define the location of the
LECTURE: 07 Title: IMMUNE CELL SURFACE RECEPTORS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: The chemical nature of the cellular surface receptors. Define the location of the
Chapter 11. B cell generation, Activation, and Differentiation. Pro-B cells. - B cells mature in the bone marrow.
 Chapter B cell generation, Activation, and Differentiation - B cells mature in the bone marrow. - B cells proceed through a number of distinct maturational stages: ) Pro-B cell ) Pre-B cell ) Immature
Chapter B cell generation, Activation, and Differentiation - B cells mature in the bone marrow. - B cells proceed through a number of distinct maturational stages: ) Pro-B cell ) Pre-B cell ) Immature
The Major Histocompatibility Complex of Genes
 The Major Histocompatibility Complex of Genes Topic 4 The Major Histocompatibility Complex Outline of Lectures The immunological reasons for transplant rejection How the MHC was discovered using inbred
The Major Histocompatibility Complex of Genes Topic 4 The Major Histocompatibility Complex Outline of Lectures The immunological reasons for transplant rejection How the MHC was discovered using inbred
SPECIFIC IMMUNITY = ACQUIRED IMMUNITY = ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY SPECIFIC IMMUNITY - BASIC CHARACTERISTIC
 SPECIFIC IMMUNITY - BASIC CHARACTERISTIC SPECIFIC IMMUNITY = ACQUIRED IMMUNITY = ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY BASIC TERMINOLOGY SPECIFIC IMMUNITY humoral mediated with antibodies cellular mediated with T lymphocytes
SPECIFIC IMMUNITY - BASIC CHARACTERISTIC SPECIFIC IMMUNITY = ACQUIRED IMMUNITY = ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY BASIC TERMINOLOGY SPECIFIC IMMUNITY humoral mediated with antibodies cellular mediated with T lymphocytes
SUPPORTING INFORMATION
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Biology is different in small volumes: endogenous signals shape phenotype of primary hepatocytes cultured in microfluidic channels Amranul Haque, Pantea Gheibi, Yandong Gao, Elena
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Biology is different in small volumes: endogenous signals shape phenotype of primary hepatocytes cultured in microfluidic channels Amranul Haque, Pantea Gheibi, Yandong Gao, Elena
Finding protein sites where resistance has evolved
 Finding protein sites where resistance has evolved The amino acid (Ka) and synonymous (Ks) substitution rates Please sit in row K or forward The Berlin patient: first person cured of HIV Contracted HIV
Finding protein sites where resistance has evolved The amino acid (Ka) and synonymous (Ks) substitution rates Please sit in row K or forward The Berlin patient: first person cured of HIV Contracted HIV
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Unique polypharmacology nuclear receptor modulator blocks inflammatory signaling pathways Mi Ra Chang 1, Anthony Ciesla 1, Timothy S. Strutzenberg 1, Scott J. Novick 1, Yuanjun
Supplementary information Unique polypharmacology nuclear receptor modulator blocks inflammatory signaling pathways Mi Ra Chang 1, Anthony Ciesla 1, Timothy S. Strutzenberg 1, Scott J. Novick 1, Yuanjun
Chapter 11. B cell generation, Activation, and Differentiation. Pro-B cells. - B cells mature in the bone marrow.
 Chapter B cell generation, Activation, and Differentiation - B cells mature in the bone marrow. - B cells proceed through a number of distinct maturational stages: ) Pro-B cell ) Pre-B cell ) Immature
Chapter B cell generation, Activation, and Differentiation - B cells mature in the bone marrow. - B cells proceed through a number of distinct maturational stages: ) Pro-B cell ) Pre-B cell ) Immature
Cancer Genetics 204 (2011) 45e52
 Cancer Genetics 204 (2011) 45e52 Exon scanning by reverse transcriptaseepolymerase chain reaction for detection of known and novel EML4eALK fusion variants in nonesmall cell lung cancer Heather R. Sanders
Cancer Genetics 204 (2011) 45e52 Exon scanning by reverse transcriptaseepolymerase chain reaction for detection of known and novel EML4eALK fusion variants in nonesmall cell lung cancer Heather R. Sanders
Phylogenetic analysis of human and chicken importins. Only five of six importins were studied because
 Supplementary Figure S1 Phylogenetic analysis of human and chicken importins. Only five of six importins were studied because importin-α6 was shown to be testis-specific. Human and chicken importin protein
Supplementary Figure S1 Phylogenetic analysis of human and chicken importins. Only five of six importins were studied because importin-α6 was shown to be testis-specific. Human and chicken importin protein
L I F E S C I E N C E S
 1a L I F E S C I E N C E S 5 -UUA AUA UUC GAA AGC UGC AUC GAA AAC UGU GAA UCA-3 5 -TTA ATA TTC GAA AGC TGC ATC GAA AAC TGT GAA TCA-3 3 -AAT TAT AAG CTT TCG ACG TAG CTT TTG ACA CTT AGT-5 NOVEMBER 2, 2006
1a L I F E S C I E N C E S 5 -UUA AUA UUC GAA AGC UGC AUC GAA AAC UGU GAA UCA-3 5 -TTA ATA TTC GAA AGC TGC ATC GAA AAC TGT GAA TCA-3 3 -AAT TAT AAG CTT TCG ACG TAG CTT TTG ACA CTT AGT-5 NOVEMBER 2, 2006
Characterizing intra-host influenza virus populations to predict emergence
 Characterizing intra-host influenza virus populations to predict emergence June 12, 2012 Forum on Microbial Threats Washington, DC Elodie Ghedin Center for Vaccine Research Dept. Computational & Systems
Characterizing intra-host influenza virus populations to predict emergence June 12, 2012 Forum on Microbial Threats Washington, DC Elodie Ghedin Center for Vaccine Research Dept. Computational & Systems
Baseline clinical characteristics for the 81 CMML patients Routine diagnostic testing and statistical analyses... 3
 Next-Generation Sequencing Technology Reveals a Characteristic Pattern of Molecular Mutations in 72.8% of Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukemia (CMML) by Detecting Frequent Alterations in TET2, CBL, RAS, and
Next-Generation Sequencing Technology Reveals a Characteristic Pattern of Molecular Mutations in 72.8% of Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukemia (CMML) by Detecting Frequent Alterations in TET2, CBL, RAS, and
Third line of Defense
 Chapter 15 Specific Immunity and Immunization Topics -3 rd of Defense - B cells - T cells - Specific Immunities Third line of Defense Specific immunity is a complex interaction of immune cells (leukocytes)
Chapter 15 Specific Immunity and Immunization Topics -3 rd of Defense - B cells - T cells - Specific Immunities Third line of Defense Specific immunity is a complex interaction of immune cells (leukocytes)
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE 1
 SUPPLEMENTL FIGURE 1 C Supplemental Figure 1. pproach for removal of snorns from Rpl13a gene. () Wild type Rpl13a exonintron structure is shown, with exo in black and intronic snorns in red rectangles.
SUPPLEMENTL FIGURE 1 C Supplemental Figure 1. pproach for removal of snorns from Rpl13a gene. () Wild type Rpl13a exonintron structure is shown, with exo in black and intronic snorns in red rectangles.
Detection of 549 new HLA alleles in potential stem cell donors from the United States, Poland and Germany
 HLA ISSN 2059-2302 BRIEF COMMUNICATION Detection of 549 new HLA alleles in potential stem cell donors from the United States, Poland and Germany C. J. Hernández-Frederick 1, N. Cereb 2,A.S.Giani 1, J.
HLA ISSN 2059-2302 BRIEF COMMUNICATION Detection of 549 new HLA alleles in potential stem cell donors from the United States, Poland and Germany C. J. Hernández-Frederick 1, N. Cereb 2,A.S.Giani 1, J.
