Sir William Dunn School of Pathology, South Parks Road, Oxford 0X1 3RE, U.K.
|
|
|
- Coleen Singleton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J. Cell Sci. 66, (1984) 189 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1984 THE MONONUCLEAR PHAGOCYTE SYSTEM OF THE MOUSE DEFINED BY IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL LOCALIZATION OF ANTIGEN F4/80: MACROPHAGES OF BONE AND ASSOCIATED CONNECTIVE TISSUE DAVID A. HUME Department of Medicine and Clinical Science, John Curtin School of Medical Research, Canberra, Australia JOHN F. L0UT1T MRC Radiobiology Unit, Harwell, Didcot, U.K. AND SIAMON GORDON* Sir William Dunn School of Pathology, South Parks Road, Oxford 0X1 3RE, U.K. SUMMARY The macrophage-specific antigen F4/80 has been localized in adult mouse bone and connective tissue. F4/80 positive cells form the centre of haemopoietic islands, line the periosteal and subendosteal bone surfaces and are a major component of connective tissue and the synovial membrane (presumptive type A cells). F4/80 is absent from fibroblasts, chondrocytes, osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteoclasts and a subpopulation of synovial lining cells (presumptive type B cells). INTRODUCTION F4/80 is a rat hybridoma secreting a monoclonal antibody directed against the 160 X 10 3 molecular weight plasma membrane component of mouse mononuclear phagocytes (Austyn & Gordon, 1981). Previous reports have provided evidence that F4/80 antigen is a differentiation marker for macrophages (Hirsch, Austyn & Gordon, 1981) and is restricted to this cell lineage in major lymphoid and non-lymphoid tissues (Hume & Gordon, 1983; Hume, Robinson, MacPherson & Gordon, 1983a; Hume, Perry & Gordon, 19836). The present paper is concerned with the immunohistochemical localization of the antigen in mouse bone and associated-connective tissue and investigates the origins of synovial lining cells and osteoclasts. MATERIALS AND METHODS Adult male Balb/c mice were perfused through their aortas with f>5 % (v/v) glutaraldehyde in 1 % (w/v) sucrose/01 M-cacodylate as described by Hume & Gordon (1983). The femur and knee joint were excised and decalcified by incubation (24 48 h) in several changes of acid/citrate buffer (13% (w/v) sodium citrate in 2% (v/v) formaldehyde; ph4-7 with formic acid). Tissue was embedded in Polywax (Difco, U.K.) and 6/Jm sections were cut and stained for F4/80 antigen by Author for correspondence.
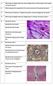
2 190 D. A. Hume, J. F. Loutit and S. Gordon the indirect ABC immunoperoxidase technique of Hsu, Raine & Fanger (1981) as modified by Hume & Gordon (1983). Reagents were supplied by Vector Laboratories (Kit PK4004) through Sera-Lab, U.K. Control sections with irrelevant rat monoclonal antibodies, or without first antibody, were devoid of reaction product. Sections were counterstained with Mayer's haematoxylin and photographed with a blue (Ilford 303) filter to increase contrast. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Previous immunohistochemical studies using F4/80 have led to the proposal that the antigen is restricted to mononuclear phagocytes and is absent from all other welldefined cell types (Hume & Gordon, 1983; Humee* al. 1983a,6). The present study adds to the latter category in that chondrocytes, fibroblasts, osteocytes, bone-lining cells, osteoblasts and osteoclasts are unstained by immunohistochemical localization of F4/80 (see below). Although these cells are unstained, bone and adjacent connective tissue contain an abundant population of F4/80 + cells. F4/80 + cells share the common features of stellate morphology (apart from occasional cells resembling monocytes) and a tendency to spread on surfaces or to intercalate with other cells. As noted elsewhere (Hume et al. 1983a), the most prominent population of F4/80 + cells is found in the marrow forming the centre of haemopoietic islands. The distribution of these cells appears uniform throughout the marrow and there is no evidence of differential association with erythropoietic versus granulopoietic islands. Examples of such cells can be seen in Fig. 1. The surfaces of the bone are coated with a narrow layer of bone-lining cells, which may be quiescent osteoblasts (Jee, 1983). Immediately adjacent to the bone lining, on both the subendosteal and periosteal faces, is an extensive layer of F4/80 + cells spread in the plane of the surface. These cells are difficult to see in vertical sections because Fig. 1. Metaphyseal growth plate: numerous F4/80 positive cells (dark precipitate) can be seen in the marrow in the upper half of the field. Note the stellate morphology of the F4/80 + cells and the apparent attachment of numerous smaller developing haemopoietic cells. F4/80 + cells cannot be seen immediately adjacent to the bone surface. Large arrow indicates a multinucleate osteoclast that is unstained with F4/80. The ruffled border of the cell faces an indentation in the bone surface (asterisk indicates lacuna). F4/80 is also absent from bone-forming cells in the lower half of the field. Bar, 25 ^m. Fig. 2. An oblique section of the subendosteal bone surface showing an almost continuous layer of F4/80 + cells (dark precipitate) spread in the plane of the bone. Bar, 10/tm. Fig. 3. An oblique section of the periosteal bone surface. The angle of section is greater than in Fig. 2 so that the periosteal F4/80 + cell lining appears as a line of stained stellate cells (arrows). These cells lie outside the bone-lining cells (left of field) and inside a layer of fibrous connective tissue (right of field). Bar, 10;um. Fig. 4. Highly vascularized (asterisks indicate vessels) loose connective tissue of the synovial lining contains many F4/80 + cells (arrows) frequently associated with the blood vessels. The left of the field contains a more ordered array of fibrous connective tissue with F4/80 + cells flattened like fibroblasts between the fibres. The field also contains many F4/80 negative cells, most of which are fibroblasts. Bar, 10 fim. Fig. 5. Synovial membrane: F4/80 + (small arrows) and F4/80" cells (large arrows) are present in roughly equal numbers. The contrast is difficult to demonstrate unequivocally in black and white micrographs but is obvious in the original colours. Bar, 10;im.
3 Bone macrophages 191 w * *T 2 % ' ~ "' X, 4 Figs 1-5
4 192 D. A. Hume, J. F. Loutit and S. Gordon of their thin cytoplasm. The density of the covering can be assessed from Figs 2 and 3, where oblique sections have grazed the subendosteal and periosteal surfaces, respectively. The tendency of F4/80 + cells to associate with bone surfaces is also seen on bone spicules within the marrow (not shown) but is less evident than in the vicinity of the growth plate (Fig. 1). Towards the joint the periosteum becomes lined with connective tissue. In dense fibrous connective tissue the F4/80 + macrophages, like the unlabelled fibroblasts that are present in roughly equal numbers, lie flattened between the ordered collagen fibres (see Fig. 6). In loose, well-vascularized connective tissue including that underlying the synovial membrane (Fig. 4) F4/80 + cells are equally numerous and often have cell bodies immediately adjacent to the blood vessels (pericytes) as noted in many other tissues (Hume et al. unpublished). The synovial membrane itself contains an F4/80 + population. Approximately 40-50% of the synovial lining cells express the antigen. The cells extend membrane processes between the unlabelled cells so that the staining appears almost continuous (Fig. 5). The identification of F4/80 on a subpopulation of synovial lining cells is in agreement with its restriction to mononuclear phagocytes, since synovial type A cells have morphological and functional features of macrophages and are of bone marrow origin (Edwards, 1982). The presence of an F4/80 negative population of synovial cells (presumed to be the type B cells) argues \ ^! * Fig. 6. High-power view of F4/80 negative multinucleate osteoclast (arrow) with ruffled border (asterisk). F4/80 + cells (dark precipitate) can be seen in dense disordered connective tissue on the right and flattened between collagen fibres on the lower side of the field. Bar, 6 Jim.
5 Bone macrophages 193 against the concept expressed by Ghadially (1978) that 'type A and type B cells are not distinct and different races of cells with distinct and different functions, but merely cells whose morphology reflects the function they are performing at a given moment'. Type B cells have the morphological appearance of fibroblasts (Jee, 1983) and this would be their most obvious source. The absence of F4/80 from osteoclasts is of particular importance because of continued debate over the origin of these cells (Loutit & Nisbet, 1982). Figs 1 and 6 contain F4/80 negative osteoclasts identifiable by their morphology (including ruffled border), multinuclearity and location adjacent to a lacuna in the bone surface. An examination of over 40 such cells failed to identify any staining with F4/80. Some authors favour the view that osteoclasts are polykaryons formed by the fusion of mature mononuclear phagocytes (see Loutit & Nisbet, 1982; Ericsson, 1980). Support for this view can be taken from the observed ability of isolated macrophage populations to degrade bone matrix (Mundy, Altman, Gondek & Bandellin, 1977; Rifkin, Baker & Coleman, 1979; Holtrop, Cox & Glowacki, 1982) but macrophages resorbing bone do not form osteoclasts (RifkineZ al. 1979; Burger et al. 1982). Burger et al. (1982) found that the osteoclast progenitor was contained in the weakly adherent fraction of proliferating bone marrow cultures composed primarily of macrophages. They concluded that the most likely precursor was the monoblast or promonocyte. F4/80 antigen is present on immature, non-adherent, macrophage progenitors in marrow cultures (Hirsch et al. 1981) and on immature macrophages in bone marrow in vivo (Hume et al. 1983a). Thus the pathway suggested by Burger et al. (1982) would probably involve loss of F4/80 antigen during osteoclast formation. Alternatively, the results of Burger et al. (1982) do not eliminate the possibility that bone marrow cultures contain a specialized osteoclast 'stem cell' (Loutit & Nisbet, 1982) and that the absence of F4/80 from osteoclasts is a reflection of its restriction to mononuclear phagocytes. This work was supported in part by a grant from the Medical Research Council, U.K. We thank N. W. Nisbet for advice and materials; Mr Don Etheridge for assistance with histology, Mr Stan Buckingham and Miss Gill Roberts for photography and Mrs Pam Woodward for typing the manuscript. REFERENCES AUSTYN, J. M. & GORDON, S. (1981). F4/80: a monoclonal antibody directed specifically against the mouse macrophage. Eur.J. Immun. 11, BURGER, E. H., VAN DER MEER, J. V. M., VAN DE GEVEL, J. S., GRIBNAU, J. C, THESINGH, C. W. & VAN FURTH, R. (1982). In vitro formation of osteoclasts from long-term cultures of bone marrow mononuclear phagocytes..7. exp. Med. 156, EDWARDS, J. C. W. (1982). The origin of type A synovial-lining cells. Immunobiology 161, ERICSSON, J. L. E. (1980). Origin and structure of the osteoclast. In Mononuclear Phagocytes - Functional Aspects (ed. R. Van Furth), pp Amsterdam: Martinus Nijhoff. GHADIALLY, F. N. (1978). Fine structure of joints. inthe Joints and Synovial Fluid, vol. 10 (ed. L. Sokoloff), pp New York: Academic Press. HIRSCH, S., AUSTYN, J. M. & GORDON, S. (1981). Expression of the macrophage-specific antigen F4/80 during differentiation of mouse bone marrow cells in culture. J. exp. Med. 154,
6 194 D. A. Hume, J. F. Loutit and S. Gordon HOLTROP, M. E., Cox, K. A. & GLOWACKI, J. (1982). Cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system resorb implanted bone matrix: A histologic and ultrastructural study. Calc. Tissue Int. 34, Hsu, S. M., RAINE, L. & FANGER, H. (1981). The use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase (ABC) complex in immunoperoxidase techniques: A comparison between ABC and unlabelled antibody (PAP) procedures, j. Histochem. Cytochem. 29, HUME, D. A. & GORDON, S. (1983). The mononuclear phagocyte system of the mouse defined by immunohistochemical localisation of antigen F4/80. Identification of resident macrophages in renal medullary and cortical interstitium and the juxtaglomerular complex. J. exp. Med. 157, HUME, D. A., ROBINSON, A. P., MACPHERSON, G. G. & GORDON, S. (1983n). The mononuclear phagocyte system of the mouse defined by immunohistochemical localisation of antigen F4/80. The relationship between macrophages, Langerhans cells, reticular cells and dendritic cells in lymphoid and hematopoietic organs. J. exp. Med. (in press). HUME, D. A., PERRY, V. H. & GORDON, S. (19836). Immunohistochemical localisation of a macrophage-specific antigen in developing mouse retina: phagocytosis of dying neurons and differentiation of microglial cells to form a regular array in the plexiform layers. J. Cell Biol. 97, JEE, W. J. S. (1983). The Skeletal Tissues. In Histology, Cell and Tissue Biology (ed. L. Weiss), pp New York: Elsevier. LOUTIT, J. F. & NISBET, N. W. (1982). The origin of osteoclasts. Immunobiology 161, MUNDY, G. R., ALTMAN, A. J., GONDEK, M. D. & BANDELLIN, J. G. (1977). Direct resorption of bone by human monocytes. Science, N.Y. 196, RIFKIN, B. R., BAKER, R. L. & COLEMAN, S. J. (1979). An ultrastructural study of macrophage mediated resorption of calcified tissue. Cell Tiss. Res. 202, (Received 1 September J983-Accepted 12 September 1983)
Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
Edinburgh Research Explorer
 Edinburgh Research Explorer Immunohistochemical localization of a macrophage-specific antigen in developing mouse retina Citation for published version: Hume, DA, Perry, VH & Gordon, S 1983, 'Immunohistochemical
Edinburgh Research Explorer Immunohistochemical localization of a macrophage-specific antigen in developing mouse retina Citation for published version: Hume, DA, Perry, VH & Gordon, S 1983, 'Immunohistochemical
BONE TISSUE. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
The purpose of this practical session is to demonstrate cartilage and bone as specialized connective tissues to the student.
 1 CARTILAGE AND BONE The purpose of this practical session is to demonstrate cartilage and bone as specialized connective tissues to the student. 1. Hyaline cartilage Slide 73 This is a cross section through
1 CARTILAGE AND BONE The purpose of this practical session is to demonstrate cartilage and bone as specialized connective tissues to the student. 1. Hyaline cartilage Slide 73 This is a cross section through
Quiz 6. Cartilage and Bone
 Quiz 6 Cartilage and Bone MCQs X type (true or false): 1. Cartilage tissue: a. Has a rich blood supply. b. Develops from mesenchyme. c. Has ability for a quick regeneration. d. Has chondrocytes as precursor
Quiz 6 Cartilage and Bone MCQs X type (true or false): 1. Cartilage tissue: a. Has a rich blood supply. b. Develops from mesenchyme. c. Has ability for a quick regeneration. d. Has chondrocytes as precursor
Practical Histology. Lab 3: Connective tissue
 Practical Histology Lab 3: Connective tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue provides structural support for the body by binding cells and tissues together to form organs. It also provides metabolic
Practical Histology Lab 3: Connective tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue provides structural support for the body by binding cells and tissues together to form organs. It also provides metabolic
BONE LABORATORY DEMONSTRATIONS. These demonstrations are found on the bulletin boards outside the MCO Bookstore.
 BONE LABORATORY DEMONSTRATIONS These demonstrations are found on the bulletin boards outside the MCO Bookstore. COMPACT & TRABECULAR BONE - LM When viewed under the polarizing light microscope, the layering
BONE LABORATORY DEMONSTRATIONS These demonstrations are found on the bulletin boards outside the MCO Bookstore. COMPACT & TRABECULAR BONE - LM When viewed under the polarizing light microscope, the layering
LYMPH GLAND. By : Group 1
 LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
Deposition of Bone by the Osteoblasts. Bone is continually being deposited by osteoblasts, and it is continually being resorbed where osteoclasts are
 Bone remodeling Deposition of Bone by the Osteoblasts. Bone is continually being deposited by osteoblasts, and it is continually being resorbed where osteoclasts are active. This mechanism is always is
Bone remodeling Deposition of Bone by the Osteoblasts. Bone is continually being deposited by osteoblasts, and it is continually being resorbed where osteoclasts are active. This mechanism is always is
Lab Animal Tissue. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: To understand the relationship between the structure and function of different animal tissues
 Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Lab Exercise 6a-2. Classification of connective tissues. Connective Tissue. Connective tissues. Areolar. Areolar tissue
 Classification of connective tissues Lab Exercise 6a-2 Connective Tissue Nervous Muscle Connective Tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue proper Fluid connective tissue Supportive connecting tissue
Classification of connective tissues Lab Exercise 6a-2 Connective Tissue Nervous Muscle Connective Tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue proper Fluid connective tissue Supportive connecting tissue
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue
 Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
Connective Tissue Nervous Muscle. Classification of connective tissues
 Connective Tissue Nervous Muscle Lab Exercise 6a-2 Classification of connective tissues 1 Connective Tissue Connective tissue proper Fluid connective tissue Supportive connecting tissue Connective tissues
Connective Tissue Nervous Muscle Lab Exercise 6a-2 Classification of connective tissues 1 Connective Tissue Connective tissue proper Fluid connective tissue Supportive connecting tissue Connective tissues
Variations in the Appearance of Human Elastic Cartilage
 The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 69, Issue 6 (November, 1969) 1969-11 Variations in the Appearance of
The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 69, Issue 6 (November, 1969) 1969-11 Variations in the Appearance of
Flow Cytometry. What is flow cytometry?
 Flow Cytometry Flow Cytometry What is flow cytometry? Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology to analyze the characteristics of cells or particles. It is predominantly used to measure fluorescence
Flow Cytometry Flow Cytometry What is flow cytometry? Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology to analyze the characteristics of cells or particles. It is predominantly used to measure fluorescence
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH. 8 - BONE AND CARTILAGE.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: BONE CLASSIFICATIONS There are four classifications of bones based on their 1. Long bones are greater in length than in width - Found in the upper and lower limbs (ex: arm,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: BONE CLASSIFICATIONS There are four classifications of bones based on their 1. Long bones are greater in length than in width - Found in the upper and lower limbs (ex: arm,
What are the parts of the skeletal system? Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues. Growth of Cartilage. Bones come in many shapes
 Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues Components of the skeletal system Classification of Bone (bone shapes) Functions of bone Bone structure Microscopic structure of bone and bone cells What are
Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues Components of the skeletal system Classification of Bone (bone shapes) Functions of bone Bone structure Microscopic structure of bone and bone cells What are
Lab 1 ANIMAL TISSUES
 Lab 1 ANIMAL TISSUES Levels of Organization Animals are multicellular heterotrophs whose cells lack cell walls. Most animals exhibit a hierarchical level of organization: Cells are organized into tissues
Lab 1 ANIMAL TISSUES Levels of Organization Animals are multicellular heterotrophs whose cells lack cell walls. Most animals exhibit a hierarchical level of organization: Cells are organized into tissues
Cartilage & bone. Red: important. Black: in male female slides. Gray: notes extra. Editing File
 Cartilage & bone Red: important. Black: in male female slides. Gray: notes extra. Editing File OBJECTIVES describe the microscopic structure, distribution and growth of the different types of Cartilage
Cartilage & bone Red: important. Black: in male female slides. Gray: notes extra. Editing File OBJECTIVES describe the microscopic structure, distribution and growth of the different types of Cartilage
Functions of the Skeletal System. Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Chapter 4. Cartilage and Bone. Li Shu-Lei instructor. Dept. Histology and Embryology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Jilin University
 Chapter 4 Cartilage and Bone Li Shu-Lei instructor Dept. Histology and Embryology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Jilin University I Cartilage a specialized connective tissue Characterizers: Cartilage
Chapter 4 Cartilage and Bone Li Shu-Lei instructor Dept. Histology and Embryology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Jilin University I Cartilage a specialized connective tissue Characterizers: Cartilage
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
Due in Lab. Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary
 Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Skeletal Tissue: Cartilage and Bone This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Overview of the Skeleton, Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Skeletal Tissue: Cartilage and Bone This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Overview of the Skeleton, Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages,
HISTOLOGY Lecture TWO DR. ASHRAF SAID
 HISTOLOGY Lecture TWO DR. ASHRAF SAID Start Of this lecture TISSUES TISSUE: A DEFINITION A group of connected and interdependent cells that cooperate to perform a specific function CONNECTIVE TISSUE The
HISTOLOGY Lecture TWO DR. ASHRAF SAID Start Of this lecture TISSUES TISSUE: A DEFINITION A group of connected and interdependent cells that cooperate to perform a specific function CONNECTIVE TISSUE The
SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM TYPES OF BONES
 SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 By John McGill Supplement Outlines: Beth Wyatt Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STRUCTURE Organs: Bones Related Tissues: Cartilage and Ligaments
SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 By John McGill Supplement Outlines: Beth Wyatt Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STRUCTURE Organs: Bones Related Tissues: Cartilage and Ligaments
FORMATION OF BONE. Intramembranous Ossification. Bone-Lec-10-Prof.Dr.Adnan Albideri
 FORMATION OF BONE All bones are of mesodermal origin. The process of bone formation is called ossification. We have seen that formation of most bones is preceded by the formation of a cartilaginous model,
FORMATION OF BONE All bones are of mesodermal origin. The process of bone formation is called ossification. We have seen that formation of most bones is preceded by the formation of a cartilaginous model,
Graefe's Archive. Ophthalmology Springer-Verlag Artificial anterior chamber for the growing of membranes on lens implants*
 Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (1983) 221:55-60 Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology Springer-Verlag 1983 Artificial anterior chamber for the growing of membranes on lens implants*
Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (1983) 221:55-60 Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology Springer-Verlag 1983 Artificial anterior chamber for the growing of membranes on lens implants*
BONE HISTOLOGY SLIDE PRESENTATION
 BONE HISTOLOGY SLIDE PRESENTATION PRESENTED BY: SKELETECH, INC. Clients and Friends: SkeleTech invites you to use these complimentary images for your own presentations or as teaching slides for bone biology.
BONE HISTOLOGY SLIDE PRESENTATION PRESENTED BY: SKELETECH, INC. Clients and Friends: SkeleTech invites you to use these complimentary images for your own presentations or as teaching slides for bone biology.
Compact bone; Many parallel Haversian canals contain: small blood vessels. very small nerve. Interconnected by Volkmann s canals.
 Special characteristics of COMPACT BONE (dense bone) Thick; well vascularized Osteocytes and lamellae Concentric rings around blood vessels Most bones: outer compact bone inner spongy bone Marrow cavity
Special characteristics of COMPACT BONE (dense bone) Thick; well vascularized Osteocytes and lamellae Concentric rings around blood vessels Most bones: outer compact bone inner spongy bone Marrow cavity
By Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud
 By Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud Part I Introduction Types of White Blood Cells Genesis of the White Blood Cells Life Span of the White Blood Cells Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud 2 Leucocytes Introduction: Infectious
By Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud Part I Introduction Types of White Blood Cells Genesis of the White Blood Cells Life Span of the White Blood Cells Dr. Mohamed Saad Daoud 2 Leucocytes Introduction: Infectious
Connective Tissue. Found everywhere in the body. Most abundant and widely distributed. Never exposed to the outside environment.
 Connective Tissue Found everywhere in the body. Most abundant and widely distributed. Never exposed to the outside environment. Connective Tissue Functions Binding and support Protection Insulation Transportation
Connective Tissue Found everywhere in the body. Most abundant and widely distributed. Never exposed to the outside environment. Connective Tissue Functions Binding and support Protection Insulation Transportation
Chapter 5. Tissues. 4 Types of Body Tissues. Tissues
 Chapter 5 Tissues Tissues Tissues - groups of cells that are similar in structure & function RBC, WBC, & platelets are a group of cells working together to form BLOOD tissue Histology Pathohistology study
Chapter 5 Tissues Tissues Tissues - groups of cells that are similar in structure & function RBC, WBC, & platelets are a group of cells working together to form BLOOD tissue Histology Pathohistology study
Flow Cytometry. Hanan Jafar (2017)
 1 Flow Cytometry Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology to analyze the characteristics of cells or particles. It is predominantly used to measure fluorescence intensity produced by fluorescent-labeled
1 Flow Cytometry Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology to analyze the characteristics of cells or particles. It is predominantly used to measure fluorescence intensity produced by fluorescent-labeled
What is histology? HISTOLOGY
 Introduction to Histology What is histology? HISTOLOGY histo = tissue ogy = study So HISTOLOGY = the study of tissues! What is a TISSUE? Tissues are groups of cells with specialized structural and functional
Introduction to Histology What is histology? HISTOLOGY histo = tissue ogy = study So HISTOLOGY = the study of tissues! What is a TISSUE? Tissues are groups of cells with specialized structural and functional
Histology Final Exam Done by:maha AbuAjamieh
 Histology Final Exam Done by:maha AbuAjamieh 1) Which of the following is the least valuable when distinguishing between bone and hyaline cartilage?? A- lacunae B-canaliculi C-lamella D-cell nest E- harversian
Histology Final Exam Done by:maha AbuAjamieh 1) Which of the following is the least valuable when distinguishing between bone and hyaline cartilage?? A- lacunae B-canaliculi C-lamella D-cell nest E- harversian
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen
 PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/14752
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/14752
Fig Articular cartilage. Epiphysis. Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line. Marrow cavity. Yellow bone marrow. Periosteum. Nutrient foramen Diaphysis
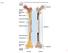 Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
OpenStax-CNX module: m Bone Structure * Ildar Yakhin. Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax. Abstract
 OpenStax-CNX module: m63474 1 Bone Structure * Ildar Yakhin Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By
OpenStax-CNX module: m63474 1 Bone Structure * Ildar Yakhin Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By
2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION
 2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION ENDOCHONDRAL OSSIFICATION 6 STEPS 1. CARTILAGE ENLARGES, BY APPOSITIONAL GROWTH; CHONDROCYTES AT CENTER OF CARTILAGE GROW IN SIZE; MATRIX REDUCES IN SIZE & SPICULES CALCIFY;
2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION ENDOCHONDRAL OSSIFICATION 6 STEPS 1. CARTILAGE ENLARGES, BY APPOSITIONAL GROWTH; CHONDROCYTES AT CENTER OF CARTILAGE GROW IN SIZE; MATRIX REDUCES IN SIZE & SPICULES CALCIFY;
Ossification and Bone Remodeling
 Ossification and Bone Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation) 1.
Ossification and Bone Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation) 1.
Pathophysiology of fracture healing
 Pathophysiology of fracture healing Bone anatomy and biomechanics Fracture patterns Bone healing and blood supply Influence of implants 1 What is the structure of bone? 2 Bone structure Four levels: Chemical
Pathophysiology of fracture healing Bone anatomy and biomechanics Fracture patterns Bone healing and blood supply Influence of implants 1 What is the structure of bone? 2 Bone structure Four levels: Chemical
36 1 The Skeletal System Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
HOLE S ANATOMY CHAPTER 5, PART II Lecture notes
 HOLE S ANATOMY CHAPTER 5, PART II Lecture notes I. Connective Tissue A. Structure 1. have few cells that are spaced apart and can divide; two categories: a. fixed cells cells that are present in tissue
HOLE S ANATOMY CHAPTER 5, PART II Lecture notes I. Connective Tissue A. Structure 1. have few cells that are spaced apart and can divide; two categories: a. fixed cells cells that are present in tissue
Bone (2) Chapter 8. The bone is surrounded by the periosteum, the periosteum consists of two layers: a fibrous outer layer and an innercellular layer.
 Bone (2) Chapter 8 The bone is surrounded by the periosteum, the periosteum consists of two layers: a fibrous outer layer and an innercellular layer. The innercellular layer contains osteoprogenitor cells,
Bone (2) Chapter 8 The bone is surrounded by the periosteum, the periosteum consists of two layers: a fibrous outer layer and an innercellular layer. The innercellular layer contains osteoprogenitor cells,
Osteology. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College
 Osteology Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions of the Skeletal System: Support Movement Protection Hemopoiesis Electrolyte balance (Ca ++ /PO -3 4 ) Acid-base balance Storage
Osteology Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions of the Skeletal System: Support Movement Protection Hemopoiesis Electrolyte balance (Ca ++ /PO -3 4 ) Acid-base balance Storage
Epithelia of Coverings and Linings. Tissues. Tissue
 Tissue Tissues Chapter 3 Definition an aggregation of cells in which each cooperates with all others in the performance of a given function Examples of general functions Movement Protection Support Production
Tissue Tissues Chapter 3 Definition an aggregation of cells in which each cooperates with all others in the performance of a given function Examples of general functions Movement Protection Support Production
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
Bones. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
 Bones Osteocytes : Are responsible for maintenance of bones Present in lacunae, and send processes. Unable to divide. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
Bones Osteocytes : Are responsible for maintenance of bones Present in lacunae, and send processes. Unable to divide. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
Individual cells Extracellular matrix
 Connective Tissue Connective Tissue Elements Individual cells Extracellular matrix»fibers» Collagen» Elastic» Reticular»Ground Substance» PG (proteoglycans)» GAG (glycosaminoglycan)» GP (glycoprotein)
Connective Tissue Connective Tissue Elements Individual cells Extracellular matrix»fibers» Collagen» Elastic» Reticular»Ground Substance» PG (proteoglycans)» GAG (glycosaminoglycan)» GP (glycoprotein)
Connective Tissue. Consists of two basic elements: Cells and Extra-cellular matrix
 Connective Tissue Consists of two basic elements: Cells and Extra-cellular matrix True Connective Tissue Cells Fibroblasts: Secrete both fibers and ground substance of the matrix (wandering) Macrophages:
Connective Tissue Consists of two basic elements: Cells and Extra-cellular matrix True Connective Tissue Cells Fibroblasts: Secrete both fibers and ground substance of the matrix (wandering) Macrophages:
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
Anatomy &- Physiology Histology Worksheet
 Anatomy &- Physiology Histology Worksheet 1. The four primary tissue types found in the human body are a) squamous, cuboidal, columnar, glandular b) adipose, elastic, reticular, cartilage c) skeletal,
Anatomy &- Physiology Histology Worksheet 1. The four primary tissue types found in the human body are a) squamous, cuboidal, columnar, glandular b) adipose, elastic, reticular, cartilage c) skeletal,
Lecture 2: Skeletogenesis
 Jilin University School of Stomatology Skeletogenesis Lecture 2: Skeletogenesis Aug. 18, 2015 Yuji Mishina, Ph.D. mishina@umich.edu Student will describe Development of Bone - the general anatomy of bone
Jilin University School of Stomatology Skeletogenesis Lecture 2: Skeletogenesis Aug. 18, 2015 Yuji Mishina, Ph.D. mishina@umich.edu Student will describe Development of Bone - the general anatomy of bone
Most abundant and widely distributed tissues in the body Binds, support, and strengthen body tissues, protect and insulate internal organ, serve as
 Connective tissue Most abundant and widely distributed tissues in the body Binds, support, and strengthen body tissues, protect and insulate internal organ, serve as major transport system, compartmentalizes
Connective tissue Most abundant and widely distributed tissues in the body Binds, support, and strengthen body tissues, protect and insulate internal organ, serve as major transport system, compartmentalizes
Bio& 241 Unit 1 / Lecture 4
 Bio& 241 Unit 1 / Lecture 4 Connective Tissue Consists of two basic elements: Cells and Extra-cellular matrix 1 True Connective Tissue Cells Fibroblasts: Secrete both fibers and ground substance of the
Bio& 241 Unit 1 / Lecture 4 Connective Tissue Consists of two basic elements: Cells and Extra-cellular matrix 1 True Connective Tissue Cells Fibroblasts: Secrete both fibers and ground substance of the
Skeletal Tissues. Skeletal tissues. Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs.
 Skeletal Tissues Functions 1) support 2) protection 3) movement Skeletal tissues Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs. Aids muscle contraction; generate
Skeletal Tissues Functions 1) support 2) protection 3) movement Skeletal tissues Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs. Aids muscle contraction; generate
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues
 An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
Blood. Hematopoietic Tissue
 Blood Hematopoietic Tissue Is a type of connective tissue in which its cells are suspended in a circulating fluid. Erythrocytes+ leukocytes + platelets (thrombocytes) =formed elements of blood. These formed
Blood Hematopoietic Tissue Is a type of connective tissue in which its cells are suspended in a circulating fluid. Erythrocytes+ leukocytes + platelets (thrombocytes) =formed elements of blood. These formed
Derived copy of Bone *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m57739 1 Derived copy of Bone * Shannon McDermott Based on Bone by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By
OpenStax-CNX module: m57739 1 Derived copy of Bone * Shannon McDermott Based on Bone by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By
Skeletal System Module 4: Bone Structure
 Connexions module: m47981 1 Skeletal System Module 4: Bone Structure Donna Browne Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax College This work is produced by The Connexions Project and licensed under the Creative
Connexions module: m47981 1 Skeletal System Module 4: Bone Structure Donna Browne Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax College This work is produced by The Connexions Project and licensed under the Creative
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL SECOND EDITION
 VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
Which compound is reponsible for the viscous character of the ground substance?
 1 2 Which type of collagen forms the coarse collagen fibres in dense regular and irregular connective tissues? Which compound is reponsible for the viscous character of the ground substance? 3 Which class
1 2 Which type of collagen forms the coarse collagen fibres in dense regular and irregular connective tissues? Which compound is reponsible for the viscous character of the ground substance? 3 Which class
The Skeletal System PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
Human Biology Chapter 15.3: Bone Structure *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m58082 1 Human Biology Chapter 15.3: Bone Structure * Willy Cushwa Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
OpenStax-CNX module: m58082 1 Human Biology Chapter 15.3: Bone Structure * Willy Cushwa Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
Car$lage and Bone. Kris$ne Kra0s, M.D.
 Car$lage and Bone Kris$ne Kra0s, M.D. Car$lage and Bone Lecture Objec$ves Describe the general func$ons of car$lage and bone. Compare the func$on and composi$on of the three types of car$lage. Describe
Car$lage and Bone Kris$ne Kra0s, M.D. Car$lage and Bone Lecture Objec$ves Describe the general func$ons of car$lage and bone. Compare the func$on and composi$on of the three types of car$lage. Describe
MONOCYTES FROM CIRCULATING BLOOD FUSE IN VITRO WITH PURIFIED OSTEOCLASTS IN PRIMARY CULTURE
 J. Cell Set. 66, 335-342 (1984) 335 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1984 MONOCYTES FROM CIRCULATING BLOOD FUSE IN VITRO WITH PURIFIED OSTEOCLASTS IN PRIMARY CULTURE A. ZAMBONIN
J. Cell Set. 66, 335-342 (1984) 335 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1984 MONOCYTES FROM CIRCULATING BLOOD FUSE IN VITRO WITH PURIFIED OSTEOCLASTS IN PRIMARY CULTURE A. ZAMBONIN
Basic Histology. By Mrs. Bailey
 Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
Periodontal ligament
 Periodontal ligament The periodontium The periodontium includes: The gingiva Cementum Periodontal ligament Alveolar bone Def: The periodontal ligament is the dense fibrous connective tissue that occupies
Periodontal ligament The periodontium The periodontium includes: The gingiva Cementum Periodontal ligament Alveolar bone Def: The periodontal ligament is the dense fibrous connective tissue that occupies
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen
 PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen This full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/1737
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen This full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/1737
Megakaryoblastic Leukemia in a Dog A. Hillström 1, H. Tvedten 1, M. Kiupel 2.
 Megakaryoblastic Leukemia in a Dog A. Hillström 1, H. Tvedten 1, M. Kiupel 2. 1 University Animal Hospital, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences and Strömsholm Referral Animal Hospital, Sweden 2
Megakaryoblastic Leukemia in a Dog A. Hillström 1, H. Tvedten 1, M. Kiupel 2. 1 University Animal Hospital, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences and Strömsholm Referral Animal Hospital, Sweden 2
The U ltrastructure of Bone
 ANNALS O F CLIN IC A L AND LABORATORY SCIEN CE, Vol. 5, No. 4 Copyright 1975, Institute for Clinical Science The U ltrastructure of Bone MARIJKE E. HOLTROP, M D., Ph D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery,
ANNALS O F CLIN IC A L AND LABORATORY SCIEN CE, Vol. 5, No. 4 Copyright 1975, Institute for Clinical Science The U ltrastructure of Bone MARIJKE E. HOLTROP, M D., Ph D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery,
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 4 Part 2 SI All connective tissues arise from, an embryonic tissue.
 BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 4 Part 2 SI 1 1. All connective tissues arise from, an embryonic tissue. 2. Describe the vascularity of connective tissues, which are very diverse. 3. Describe the innervation of connective
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 4 Part 2 SI 1 1. All connective tissues arise from, an embryonic tissue. 2. Describe the vascularity of connective tissues, which are very diverse. 3. Describe the innervation of connective
4. TEXTBOOK: ABUL K. ABBAS. ANDREW H. LICHTMAN. CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR IMMUNOLOGY. 5 TH EDITION. Chapter 2. pg
 LECTURE: 03 Title: CELLS INVOLVED IN THE IMMUNE RESPONSE LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Identify the organs where the process of the blood formation occurs. Identify the main cell
LECTURE: 03 Title: CELLS INVOLVED IN THE IMMUNE RESPONSE LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Identify the organs where the process of the blood formation occurs. Identify the main cell
Oral Histology. Alveolar bone or process: Functions of alveolar bone: Chemical composition: Development of the alveolar process: Dr.
 Oral Histology Lec.12 Alveolar bone or process: Dr. Nada Al-Ghaban Alveolar bone is a specialized part of the mandibular and maxillary bones that forms the primary support structure for teeth. Although
Oral Histology Lec.12 Alveolar bone or process: Dr. Nada Al-Ghaban Alveolar bone is a specialized part of the mandibular and maxillary bones that forms the primary support structure for teeth. Although
Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1
 Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1 Bone Functions Support Protection Assistance in movement Mineral storage and release Blood cell production Triglyceride storage 5-2 Bone Chemistry Water (25%) Organic Constituent
Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1 Bone Functions Support Protection Assistance in movement Mineral storage and release Blood cell production Triglyceride storage 5-2 Bone Chemistry Water (25%) Organic Constituent
8/30/2017. Tissue: The Living Fabric. 4.3 Connective Tissue
 Chapter 4 Part B Tissue: The Living Fabric Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College 4.3 Connective Tissue Connective tissue
Chapter 4 Part B Tissue: The Living Fabric Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College 4.3 Connective Tissue Connective tissue
The Skeletal System PART A
 5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 6 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 6 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
Using the Ch6diak-Higashi Marker
 A Study of the Origin of Pulmonary Macrophages Using the Ch6diak-Higashi Marker Kent J. Johnson, MD, Peter A. Ward, MD, Gary Striker, MD, and Robin Kunkel, MS Using bone marrow reconstitution techniques
A Study of the Origin of Pulmonary Macrophages Using the Ch6diak-Higashi Marker Kent J. Johnson, MD, Peter A. Ward, MD, Gary Striker, MD, and Robin Kunkel, MS Using bone marrow reconstitution techniques
Demonstration of bone marrow derived cells in synovial lining by means of giant intracellular granules as genetic markers
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 177-182 Demonstration of bone marrow derived cells in synovial lining by means of giant intracellular granules as genetic markers J. C. W. EDWARDS AND D. A.
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 177-182 Demonstration of bone marrow derived cells in synovial lining by means of giant intracellular granules as genetic markers J. C. W. EDWARDS AND D. A.
Generation of monocytederived Dendritic Cells (modcs)
 monocytederived Dendritic (modcs) Application Note Background Dendritic (DCs) are so called because of their characteristic cell surface projections that resemble the dendrites of neurons (see Fig 1 and
monocytederived Dendritic (modcs) Application Note Background Dendritic (DCs) are so called because of their characteristic cell surface projections that resemble the dendrites of neurons (see Fig 1 and
Connective tissue Histology lab 6 Notes by Omar Sami
 Connective tissue Histology lab 6 Notes by Omar Sami The connective tissue is composed of: 1- Cells. 2- Extra Cellular Matrix; fibers & ground substance. Ground substance is where you find both Cells &
Connective tissue Histology lab 6 Notes by Omar Sami The connective tissue is composed of: 1- Cells. 2- Extra Cellular Matrix; fibers & ground substance. Ground substance is where you find both Cells &
Mast Cell. Mast Cells. James W. Truman, Ph.D. Howard Hughes Medical Institute Chevy Chase, Maryland
 5 th ANNUAL SINAUER ASSOCIATES DISTINGUISHED SCIENTIST LECTURE James W. Truman, Ph.D. Howard Hughes Medical Institute Chevy Chase, Maryland Neuronal Lineages in the CNS of Drosophila: Units of Development,
5 th ANNUAL SINAUER ASSOCIATES DISTINGUISHED SCIENTIST LECTURE James W. Truman, Ph.D. Howard Hughes Medical Institute Chevy Chase, Maryland Neuronal Lineages in the CNS of Drosophila: Units of Development,
Tissue Outline (chapter 4) Tissues group of cells that perform structural and roles. List the 4 types:
 Tissue Outline (chapter 4) Tissues group of cells that perform structural and roles. List the 4 types: 1. 2. 3. 4. I. Epithelial Tissue covers all the surfaces, inside & out. Are the major tissues of,
Tissue Outline (chapter 4) Tissues group of cells that perform structural and roles. List the 4 types: 1. 2. 3. 4. I. Epithelial Tissue covers all the surfaces, inside & out. Are the major tissues of,
Tissues. Tissues - Overview. Bio211 Laboratory 2. Epithelial and Connective Tissues
 Bio211 Laboratory 2 Epithelial and Connective Tissues 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue (p. 79 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Connective Tissue (p. 93 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Muscle/Nervous
Bio211 Laboratory 2 Epithelial and Connective Tissues 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue (p. 79 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Connective Tissue (p. 93 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Muscle/Nervous
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Cell and Developmental Biology License: Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons
Author(s): University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Cell and Developmental Biology License: Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons
physical properties depend on: electrostatic bonds between collagen/elastic fibers and GAGs water bound to negatively charged sulfated GAG chains
 connective/supporting tissue bears mechanical stress without distortion -> shock absorption smooth surface -> facilitates movements of joints guides development of bones chondrocytes extracellular matrix
connective/supporting tissue bears mechanical stress without distortion -> shock absorption smooth surface -> facilitates movements of joints guides development of bones chondrocytes extracellular matrix
Histology review. Histology. Slides. Epithelial tissue. Another example - kidney. Simple cuboidal epithelium. What to look for
 Histology review Histology What to look for Histology Practical = 50 pts Some slides set up on scopes (~10) Some Powerpoint pictures on the projector Questions I will ask: What kind of tissue? General
Histology review Histology What to look for Histology Practical = 50 pts Some slides set up on scopes (~10) Some Powerpoint pictures on the projector Questions I will ask: What kind of tissue? General
Module 2:! Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A! Semester 1! !!! !!!! Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb!
 Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A Module 2: Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb Semester 1 1 18. Bone Tissue & Growth of Bones 18.1 Describe the structure of bone tissue
Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A Module 2: Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb Semester 1 1 18. Bone Tissue & Growth of Bones 18.1 Describe the structure of bone tissue
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure I. An Introduction to the Skeletal System, p. 180 Objective: Describe the functions of the skeletal system The skeletal system includes: - bones of the skeleton
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure I. An Introduction to the Skeletal System, p. 180 Objective: Describe the functions of the skeletal system The skeletal system includes: - bones of the skeleton
NOTES: Skeletal System (Ch 5, part 1)
 NOTES: Skeletal System (Ch 5, part 1) Individual bones are the organs of the skeletal system. A bone contains very active tissues. BONE STRUCTURE: *Bone structure reflects its function. Parts of a long
NOTES: Skeletal System (Ch 5, part 1) Individual bones are the organs of the skeletal system. A bone contains very active tissues. BONE STRUCTURE: *Bone structure reflects its function. Parts of a long
Rama Nada. - Mousa Al-Abbadi. 1 P a g e
 - 1 - Rama Nada - - Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 P a g e Bones, Joints and Soft tissue tumors Before we start: the first 8 minutes was recalling to Dr.Mousa s duties, go over them in the slides. Wherever you see
- 1 - Rama Nada - - Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 P a g e Bones, Joints and Soft tissue tumors Before we start: the first 8 minutes was recalling to Dr.Mousa s duties, go over them in the slides. Wherever you see
Formation of Blood Cells
 Hematopoiesis Lecture Objectives Name organs responsible for hematopoiesis in the fetus. List the developmental stages of hematopoiesis both prenatally and postnatally. Outline the major steps of post
Hematopoiesis Lecture Objectives Name organs responsible for hematopoiesis in the fetus. List the developmental stages of hematopoiesis both prenatally and postnatally. Outline the major steps of post
Edinburgh Research Explorer
 Edinburgh Research Explorer The mononuclear phagocyte system of the mouse defined by immunohistochemical localization of antigen F4/80 Citation for published version: Hume, DA, Halpin, D, Charlton, H &
Edinburgh Research Explorer The mononuclear phagocyte system of the mouse defined by immunohistochemical localization of antigen F4/80 Citation for published version: Hume, DA, Halpin, D, Charlton, H &
Chapter10 Immune system
 Chapter10 Immune system Lyu Zhengmei Department of Histology and Embryology, Anhui Medical University Ⅰ.General Introduction Function ------ Defense The human body immune system has the ability to distinguish
Chapter10 Immune system Lyu Zhengmei Department of Histology and Embryology, Anhui Medical University Ⅰ.General Introduction Function ------ Defense The human body immune system has the ability to distinguish
The Tissue Level of Organization
 The Tissue Level of Organization 4.5-4.11 August 31, 2012 4.5 Connective Tissues Describe the general features of connective Describe the structure, location, and function of the various types of connective
The Tissue Level of Organization 4.5-4.11 August 31, 2012 4.5 Connective Tissues Describe the general features of connective Describe the structure, location, and function of the various types of connective
Tissues and Membranes
 I. In the Beginning a. Egg + sperm! Tissues and Membranes b. 1 cell divides to make 2, 2 divide to make 4, 4 divide to make 8, and then? c. d. e. Totipotent: f. Pluripotent: II. III. Tissues a. Tissues
I. In the Beginning a. Egg + sperm! Tissues and Membranes b. 1 cell divides to make 2, 2 divide to make 4, 4 divide to make 8, and then? c. d. e. Totipotent: f. Pluripotent: II. III. Tissues a. Tissues
