Collin College. BIOL Chapter 4. Tissue Levels CONNECTIVE TISSUE. C.T. derives from Mesenchyme embryonic tissue.
|
|
|
- Roderick Rich
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Collin College BIOL Chapter 4 Tissue Levels. CONNECTIVE TISSUE C.T. derives from Mesenchyme embryonic tissue. Depending on the stimuli, mesenchyme develops into specific cells that give rise to the different C.T. types The cells of each C.T. type secrete a surrounding matrix The majority of connective tissue is the matrix; it is made out of ground substance extra-cellular protein fibers Depending on the type of C.T., the matrix will be fluid and flexible with few or many cells solid and rigid with few or many cells 1
2 CONNECTIVE TISSUE Functions Establishes structural frameworks Transport fluids and dissolved materials Protect delicate organs Support, surround and interconnect tissues Store energy reserves and minerals Defend the body from microorganisms CLASSIFICATIONS 2
3 CLASSIFICATIONS COMPOSITION AND ORGANIZATION Connective tissue proper Contains largest variety of cells, has viscous ground substance and different fibers Fibroblasts produce the fibers Macrophage engulf pathogens Adipocytes fat-storing cells Mesenchymal cells stem cells Types of Cells Types of Fibers Collagen fibers flexible, high strength Melanocytes pigment producers Mast cells trigger inflammation Lymphocytes attack foreign antigens Microphages engulf cell remnants Elastic Fibers coiled fibers with elastic properties Reticular supporting network fibers 3
4 Cells of Connective Tissue Proper Fibroblasts The most abundant cell type: Found in all connective tissue proper Secrete proteins and hyaluronan (cellular cement) Fibrocytes The second most abundant cell type Found in all connective tissue proper Maintain the fibers of connective tissue proper Adipocytes Fat cells : each cell stores a single, large fat droplet Mesenchymal Cells Stem cells that respond to injury or infection Differentiate into fibroblasts, macrophages, etc. Cells of Connective Tissue Proper Macrophages Large, amoeba-like cells of the immune system Eat pathogens and damaged cells. Fixed macrophages stay in tissue, Free macrophages migrate Mast Cells Stimulate inflammation after injury or infection Release histamine and heparin Lymphocytes Specialized immune cells in lymphatic (lymphoid) system For example, lymphocytes may develop into plasma cells (plasmocytes) that produce antibodies 4
5 Fibers of Connective Tissue Proper Collagen Fibers Most common fibers in connective tissue proper Long, straight, and unbranched Strong and flexible ; resist force in one direction For example, tendons and ligaments Reticular Fibers Network of interwoven fibers (stroma) Strong and flexible as well ; resist force in many directions Stabilize functional cells (parenchyma) and structures For example, sheaths around organs Elastic Fibers Contain elastin Branched and wavy; return to original length after stretching For example, elastic ligaments of vertebrae Ground Substance Connective Tissue Proper Ground Substance Is clear, colorless, and viscous Fills spaces between cells and slows pathogen movement Important note : fibers and ground substance are found in all connective tissues. Connective tissue proper just has a lot more variety of cells 5
6 CELLS AND FIBERS OF C.T. PROPER Reticular fibers Melanocyte Fixed macrophage Plasma cell Mast cell Elastic fibers Free macrophage Collagen fibers Blood in vessel Fibroblast Adipocytes (fat cells) Mesenchymal cell Ground substance Lymphocyte COMPOSITION AND ORGANIZATION Connective tissue Proper Classified as Loose or Dense Loose Embryonic mesenchyme, mucous connective tissues Areolar tissue Adipose tissue Reticular tissue Dense Dense regular CT Dense irregular CT 6
7 Mesenchyme Mesenchyme Tissue is Embryonic Connective Tissues Is not found in adults, but mesenchyme cells remain in many connective tissue proper It can differentiate into new connective tissues when properly stimulated Blood vessel Mesenchymal cells LM 136 This is the first connective tissue to appear in an embryo. Areolar Connective Tissue Areolar Tissue Least specialized Open framework with Viscous ground substance Elastic and collagen fibers Found under many simple epithelial tissues (in lamina propria)- holds blood vessels and capillary beds LOCATIONS: Within and deep to the dermis of skin, and covered by the epithelial lining of the digestive, respiratory, and urinary tracts; between muscles; around joints, blood vessels, and nerves FUNCTIONS: Cushions organs; provides support but permits independent movement; phagocytic cells provide defense against pathogens Fibrocytes or fibroblasts Macrophage Collagen fibers Mast cell Elastic fibers 7
8 ADIPOSE AND RETICULAR C.T. Adipose Tissue Contains many adipocytes (fat cells) Two types of adipose tissue 1. White fat Most common and Stores fat Absorbs shocks/slows heat loss (insulation) 2. Brown fat More vascularized tissue Adipocytes have many mitochondria When stimulated by nervous system, fat breakdown accelerates, releasing energy Absorbs energy from surrounding tissues Reticular Tissue Provides support via complex, three-dimensional network Supportive fibers (stroma) support functional cells (parenchyma) The form structural Reticular organs such as spleen, liver, lymph nodes, and bone marrow ADIPOSE AND RETICULAR C.T. Adipose Tissue LOCATIONS: Deep to the skin, especially at sides, buttocks, and breasts; padding around eyes and kidneys FUNCTIONS: Provides padding and cushions shocks; insulates (reduces heat loss); stores energy Adipocytes (white adipose cells) Adipose tissue LM 300 Reticular Tissue LOCATIONS: Liver, kidney, spleen, lym ph nodes, and bone m ar r ow FUNCTIONS: fr am ewor k Provides supporting Reticular fibers Reticular tissue from liver Reticular tissue LM 375 8
9 DENSE C.T. DenseRegular Connective Tissue Tightly packed, parallel collagen fibers Tendons attach muscles to bones Ligaments connect bone to bone and stabilize organs Aponeuroses attach in sheets to large, flat muscles Dense Irregular Connective Tissue Interwoven networks of collagen fibers Typical in the dermis of the skin Around cartilages (perichondrium) and bones (periosteum) Form capsules around some organs (e.g., liver, kidneys) DENSE C.T. 9
10 DENSE ELASTIC TISSUE Made mostly of elastic fibers For example, elastic ligaments between spinal vertebrae FLUID CONNECTIVE TISSUE Blood and lymph = a watery matrix of dissolved proteins Carry specific cell types (formed elements) Formed elements of blood RBC s(erythrocytes), WBC s(leukocytes), Platelets Lymphatic system returns extra interstitial fluid back to blood fluid it monitored by immune system 10
11 SUPPORTING CONNECTIVE TISSUE Cartilage and bone support soft tissues and the rest of the body Cartilages : Matrix is a firm gel containing chondroitin sulfate and protein fibers Cells are called chondrocytes Cells are found in lacunae ( living areas ) Perichondrium separates cartilage from surrounding tissues Chondrocytes produce an anti-angiogenesis factor prevents the development of blood vessels into cartilage ( they are thus avascular) Cannot get too thick nutrients passage and healing factors are dependent on diffusion Three types: hyaline, elastic and fibrocartilage SUPPORTING CONNECTIVE TISSUE Hyaline Cartilage Stiff, flexible support most common cartilage Reduces friction between bones and protects Found in synovial joints, rib tips, sternum, Keeps the trachea open Usually, lacunae are large and not touching, fibers not visible 11
12 SUPPORTING CONNECTIVE TISSUE Elastic cartilge Supportive but bends easily Found in external ear and epiglottis Lacunae very close to each other with visible thin elastic fibers between Fibrocartilage (Fibrous Cartilage) Limits movement - Prevents bone-to-bone contact Found between pubic bones and intervertebral discs Lacunae are tiny and occur in small groups far apart Fibers sometimes visible as smears Elastic Cartilage LOCATIONS: Auricle of external ear; epiglottis; auditory canal; cuneiform cartilages of larynx FUNCTIONS: Provides support, but tolerates distortion without damage and returns to original shape Chondrocytes in lacunae Elastic fibers in matrix Elastic cartilage LM 358 Fibrocartilage LOCATIONS: Pads within knee joint; between pubic bones of pelvis; intervertebral discs FUNCTIONS: Resists compression; prevents bone-to-bone contact; limits movement Chondrocytes in lacunae Fibrous matrix LM 400 Fibrocartilage 12
13 SUPPORTING CONNECTIVE TISSUE BONE Has osteocytes located in lacunae In compact bone, they are located in concentric circles around a central canal containing blood vessels Cells depend on diffusion through canaliculi for nutrients Little ground substance but dominating collagen protein fibers provide limited flexibility within a dense mineralized matrix hard to break unless changes occur within matrix Surrounded by periosteum BONE CONNECTIVE TISSUE Osteon Canaliculi Osteocytes in lacunae Matrix Central canal Fibrous layer Cellular layer Periosteum Blood vessels Osteon LM
14 MUSCLE TISSUE Specialized for contraction Three types Skeletal muscle : Striated and voluntary Cardiac muscle : Striated and involuntary Smooth muscle : not striated and involuntary Striations in muscle are due to a very organized arrangement of the two contractile protein strands : actin and myosin MUSCLE TISSUE Skeletal Muscle Tissue Cells are long, cylindrical, striated, and multinucleate. LOCATIONS: Combined with connective tissues and neural tissue in skeletal muscles Striations Nuclei FUNCTIONS: Moves or stabilizes the position of the skeleton; guards entrances and exits to the digestive, respiratory, and urinary tracts; generates heat; protects internal organs a Skeletal muscle Muscle fiber LM 180 Very long/thin cells that are multinucleate They have a striated appearance They are our voluntary muscle Divide/regenerate via satellite cells 14
15 MUSCLE TISSUE Cardiocytes occur only in the heart Microscopic short cells that are branched and connect via intercalated discs They are striated involuntary muscle Rely on pacemaker cells for regular contraction MUSCLE TISSUE They are not striated and short, tapered cells ---- involuntary muscle Found everywhere motion is needed inside the body 15
16 NEURAL TISSUE Conducts electrical impulses Conveys information from one area to another CONTAINS TWO MAIN TYPES OF CELLS Neurons Transmit electrochemical signals Organized into a cell body, axon, and dendrites Dendrites receive the information and electrical information is guided down the axon to other neurons Neuroglia : Support neural tissue and help supply nutrients to neurons NEURAL Tissue 16
17 BODY SYSTEM MEMBRANES They Form barriers to protect organs They are Composed of epithelium and connective tissue Four types Cutaneous Synovial Serous Mucous Body membranes 17
18 Cutaneous Membranes Cutaneous membrane = skin A dry membrane Outermost protective boundary Superficial epidermis Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium Underlying dermis Mostly dense irregular connective tissue Mucous Membranes Lines passage ways that communicate with the exterior Must be kept moist to reduce friction The epithelial layer is lubricated by mucus from goblet cells or via multicellular glands The epithelial layer can be simple (ex : lining of intestine) or stratified (ex: lining of mouth) The connective tissue layer under these membranes is called the lamina propria and is mostly areolar C.T. 18
19 Serous Membranes Line the sealed internal subdivisions of the ventral body cavity ( cavities that DO NOT open to the exterior) 3 main types of serous membranes are The pericardium The pleura The peritoneum Each serous membrane has two layers to it The parietal portion : attaches to the inner surface of the body cavity ( body wall) The visceral portion or serosa : covers the outer surface of the organ involved. The epithelial layer is lubricated by mucus from goblet cells or via multicellular glands Serous Membranes Serous layers are separated by serous fluid 19
20 Synovial Membranes Composed out of only Connective tissue only Lines fibrous capsules surrounding joints CONNECTIVE TISSUE FRAMEWORK Layers of CT connect the organs within the dorsal and ventral body cavities The layers provide strength, maintain position of organs and provide routing areas for bloodvessesl and nerves Fasciae are connective tissue layers that support and surround organs Superficial Fascia or Subcutaneous layer also called the Hypo dermis ( located under the dermis layer) areolar CT and fat Deep fascia dense irregular CT Subserous fascia layer of areolar CT between deep fascia and serous membranes 20
21 CONNECTIVE TISSUE FRAMEWORK 21
The Tissue Level of Organization
 Tissue The Tissue Level of Organization Chapter 3 Definition an aggregation of cells in which each cooperates with all others in the performance of a given function Examples of general functions Movement
Tissue The Tissue Level of Organization Chapter 3 Definition an aggregation of cells in which each cooperates with all others in the performance of a given function Examples of general functions Movement
Connective Tissue. Consists of two basic elements: Cells and Extra-cellular matrix
 Connective Tissue Consists of two basic elements: Cells and Extra-cellular matrix True Connective Tissue Cells Fibroblasts: Secrete both fibers and ground substance of the matrix (wandering) Macrophages:
Connective Tissue Consists of two basic elements: Cells and Extra-cellular matrix True Connective Tissue Cells Fibroblasts: Secrete both fibers and ground substance of the matrix (wandering) Macrophages:
Bio& 241 Unit 1 / Lecture 4
 Bio& 241 Unit 1 / Lecture 4 Connective Tissue Consists of two basic elements: Cells and Extra-cellular matrix 1 True Connective Tissue Cells Fibroblasts: Secrete both fibers and ground substance of the
Bio& 241 Unit 1 / Lecture 4 Connective Tissue Consists of two basic elements: Cells and Extra-cellular matrix 1 True Connective Tissue Cells Fibroblasts: Secrete both fibers and ground substance of the
Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and
 CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
8/30/2017. Tissue: The Living Fabric. 4.3 Connective Tissue
 Chapter 4 Part B Tissue: The Living Fabric Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College 4.3 Connective Tissue Connective tissue
Chapter 4 Part B Tissue: The Living Fabric Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College 4.3 Connective Tissue Connective tissue
Most abundant and widely distributed tissues in the body Binds, support, and strengthen body tissues, protect and insulate internal organ, serve as
 Connective tissue Most abundant and widely distributed tissues in the body Binds, support, and strengthen body tissues, protect and insulate internal organ, serve as major transport system, compartmentalizes
Connective tissue Most abundant and widely distributed tissues in the body Binds, support, and strengthen body tissues, protect and insulate internal organ, serve as major transport system, compartmentalizes
HOLE S ANATOMY CHAPTER 5, PART II Lecture notes
 HOLE S ANATOMY CHAPTER 5, PART II Lecture notes I. Connective Tissue A. Structure 1. have few cells that are spaced apart and can divide; two categories: a. fixed cells cells that are present in tissue
HOLE S ANATOMY CHAPTER 5, PART II Lecture notes I. Connective Tissue A. Structure 1. have few cells that are spaced apart and can divide; two categories: a. fixed cells cells that are present in tissue
4 Types of Tissue. Epithelial Connective Muscle Neural
 Connective Tissue 4 Types of Tissue Epithelial Connective Muscle Neural Connective Tissue Fills internal spaces Supports & binds other tissues Transports materials Stores energy Classification of Connective
Connective Tissue 4 Types of Tissue Epithelial Connective Muscle Neural Connective Tissue Fills internal spaces Supports & binds other tissues Transports materials Stores energy Classification of Connective
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 4 Part 2 SI All connective tissues arise from, an embryonic tissue.
 BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 4 Part 2 SI 1 1. All connective tissues arise from, an embryonic tissue. 2. Describe the vascularity of connective tissues, which are very diverse. 3. Describe the innervation of connective
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 4 Part 2 SI 1 1. All connective tissues arise from, an embryonic tissue. 2. Describe the vascularity of connective tissues, which are very diverse. 3. Describe the innervation of connective
4 Types of Tissue. Epithelial Connective Muscle Neural
 Connective Tissue 4 Types of Tissue Epithelial Connective Muscle Neural Connective Tissue Fills internal spaces Supports & binds other tissues Transports materials Stores energy Classification of Connective
Connective Tissue 4 Types of Tissue Epithelial Connective Muscle Neural Connective Tissue Fills internal spaces Supports & binds other tissues Transports materials Stores energy Classification of Connective
The Tissue Level of Organization
 The Tissue Level of Organization 4.5-4.11 August 31, 2012 4.5 Connective Tissues Describe the general features of connective Describe the structure, location, and function of the various types of connective
The Tissue Level of Organization 4.5-4.11 August 31, 2012 4.5 Connective Tissues Describe the general features of connective Describe the structure, location, and function of the various types of connective
Chapter 5. Tissues. 4 Types of Body Tissues. Tissues
 Chapter 5 Tissues Tissues Tissues - groups of cells that are similar in structure & function RBC, WBC, & platelets are a group of cells working together to form BLOOD tissue Histology Pathohistology study
Chapter 5 Tissues Tissues Tissues - groups of cells that are similar in structure & function RBC, WBC, & platelets are a group of cells working together to form BLOOD tissue Histology Pathohistology study
Connective Tissue. Found everywhere in the body. Most abundant and widely distributed. Never exposed to the outside environment.
 Connective Tissue Found everywhere in the body. Most abundant and widely distributed. Never exposed to the outside environment. Connective Tissue Functions Binding and support Protection Insulation Transportation
Connective Tissue Found everywhere in the body. Most abundant and widely distributed. Never exposed to the outside environment. Connective Tissue Functions Binding and support Protection Insulation Transportation
Body Tissues Pearson Education, Inc.
 Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types: Epithelial tissue (epithelium).1 Connective tissue.2 Muscle tissue.3 Nervous tissue.4 Epithelial Tissues Locations:
Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types: Epithelial tissue (epithelium).1 Connective tissue.2 Muscle tissue.3 Nervous tissue.4 Epithelial Tissues Locations:
Tejido Conectivo Parte B. Informe #3 Laboratorio Biología # 240 Profesor: Javier Cabello
 Tejido Conectivo Parte B Informe #3 Laboratorio Biología # 240 Profesor: Javier Cabello Figure 4-8 The Cells and Fibers of Connective Tissue Proper Areolar Elastic fibers Collagen fibers Fibroblast Free
Tejido Conectivo Parte B Informe #3 Laboratorio Biología # 240 Profesor: Javier Cabello Figure 4-8 The Cells and Fibers of Connective Tissue Proper Areolar Elastic fibers Collagen fibers Fibroblast Free
Basic Histology. By Mrs. Bailey
 Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 5 Tissues Four major tissue types 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial Tissues General characteristics - cover organs and the body
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 5 Tissues Four major tissue types 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial Tissues General characteristics - cover organs and the body
Epithelia of Coverings and Linings. Tissues. Tissue
 Tissue Tissues Chapter 3 Definition an aggregation of cells in which each cooperates with all others in the performance of a given function Examples of general functions Movement Protection Support Production
Tissue Tissues Chapter 3 Definition an aggregation of cells in which each cooperates with all others in the performance of a given function Examples of general functions Movement Protection Support Production
Tissue = groups of cells that are similar in structure and function
 Tissue = groups of cells that are similar in structure and function Types Epithelial - covering Connective - support Muscle - movement Nervous - control Membranes line body cavities and hold organs together
Tissue = groups of cells that are similar in structure and function Types Epithelial - covering Connective - support Muscle - movement Nervous - control Membranes line body cavities and hold organs together
Histology. Study of body tissues
 Histology Study of body tissues 2 Introduction to Body Tissues 1. Composed of specialized cells of similar structure and perform a common function 2. Four major types (4 Cs) a. Epithelial - Cover b. Connective
Histology Study of body tissues 2 Introduction to Body Tissues 1. Composed of specialized cells of similar structure and perform a common function 2. Four major types (4 Cs) a. Epithelial - Cover b. Connective
10/3/2012. Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part B. Extracellular matrix Ground substance Fibers Collagen fiber Elastic fiber Reticular fiber.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part B Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part B Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Function: Provides reserve food fuel; Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. White blood cell (lymphocyte)
 Adipose Tissue Closely packed adipocytes Have nucleus pushed to one side by fat droplet Richly vascularized Provides reserve food fuel Insulates against heat loss Supports and protects organs Under skin
Adipose Tissue Closely packed adipocytes Have nucleus pushed to one side by fat droplet Richly vascularized Provides reserve food fuel Insulates against heat loss Supports and protects organs Under skin
HISTOLOGY. Simple squamal lungs
 HISTOLOGY Lab Objectives: Students should be able to... 1. Visually identify each class of tissue and examples within each class 2. Indicate the location (in the human body and/or organ) and function of
HISTOLOGY Lab Objectives: Students should be able to... 1. Visually identify each class of tissue and examples within each class 2. Indicate the location (in the human body and/or organ) and function of
A. cells that perform related functions and are similar in structure. B. extracellular material - made by cells and secreted into interstitial space
 I. tissue components A. cells that perform related functions and are similar in structure B. extracellular material - made by cells and secreted into interstitial space II. tissue types A. epithelium (e.)
I. tissue components A. cells that perform related functions and are similar in structure B. extracellular material - made by cells and secreted into interstitial space II. tissue types A. epithelium (e.)
Epithelial Tissue. Simple Cuboidal Function: secretion and absorption. Simple Squamous
 Epithelial Tissue General Functions: Lines and covers organs Absorbs / secretes substances Gas exchange Protection Special Characteristics: - have an apical surface on top - have a basement membrane below
Epithelial Tissue General Functions: Lines and covers organs Absorbs / secretes substances Gas exchange Protection Special Characteristics: - have an apical surface on top - have a basement membrane below
Tissues Chapter 5...Tissue - a group or mass of similar cells working together to perform certain common functions
 Tissues Chapter 5...Tissue - a group or mass of similar cells working together to perform certain common functions There are 4 major types of tissue Epithelial Connective Muscle Nervous 1. Epithelial Tissue
Tissues Chapter 5...Tissue - a group or mass of similar cells working together to perform certain common functions There are 4 major types of tissue Epithelial Connective Muscle Nervous 1. Epithelial Tissue
Chapter 05. Review. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 05 Review 5.1: Introduction Similar cells with a common function are called tissues. The study of tissues is called histology. There are four (4) primary or major tissue types: 1. Epithelial Tissue
Chapter 05 Review 5.1: Introduction Similar cells with a common function are called tissues. The study of tissues is called histology. There are four (4) primary or major tissue types: 1. Epithelial Tissue
Lab 1 ANIMAL TISSUES
 Lab 1 ANIMAL TISSUES Levels of Organization Animals are multicellular heterotrophs whose cells lack cell walls. Most animals exhibit a hierarchical level of organization: Cells are organized into tissues
Lab 1 ANIMAL TISSUES Levels of Organization Animals are multicellular heterotrophs whose cells lack cell walls. Most animals exhibit a hierarchical level of organization: Cells are organized into tissues
Tissues 10/21/2016. Epithelial Tissue
 Tissues This is a generalized cell diagram. It shows the anatomy of a cell, but most cells do not actually look like this. Cells can have a wide variety of shapes and sizes, depending on their function.
Tissues This is a generalized cell diagram. It shows the anatomy of a cell, but most cells do not actually look like this. Cells can have a wide variety of shapes and sizes, depending on their function.
Connective Tissues. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
 C.T. are found in all parts of the body & diverse in structure & function. C.T. Functions: -connect structures -provide support -protect vital organs -fill space b/w structures -stores fat -defends body
C.T. are found in all parts of the body & diverse in structure & function. C.T. Functions: -connect structures -provide support -protect vital organs -fill space b/w structures -stores fat -defends body
What is histology? HISTOLOGY
 Introduction to Histology What is histology? HISTOLOGY histo = tissue ogy = study So HISTOLOGY = the study of tissues! What is a TISSUE? Tissues are groups of cells with specialized structural and functional
Introduction to Histology What is histology? HISTOLOGY histo = tissue ogy = study So HISTOLOGY = the study of tissues! What is a TISSUE? Tissues are groups of cells with specialized structural and functional
Anatomy &- Physiology Histology Worksheet
 Anatomy &- Physiology Histology Worksheet 1. The four primary tissue types found in the human body are a) squamous, cuboidal, columnar, glandular b) adipose, elastic, reticular, cartilage c) skeletal,
Anatomy &- Physiology Histology Worksheet 1. The four primary tissue types found in the human body are a) squamous, cuboidal, columnar, glandular b) adipose, elastic, reticular, cartilage c) skeletal,
Histology. The study of tissues.
 Histology The study of tissues. Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types Epithelium Connective tissue Nervous
Histology The study of tissues. Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types Epithelium Connective tissue Nervous
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 4 Outline Tissues and Membranes
 Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 4 Outline Tissues and Membranes 1 Tissue group of cells with similar structure and function o 4 major groups epithelial, connective, muscle, nerve Epithelial tissue (Fig
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 4 Outline Tissues and Membranes 1 Tissue group of cells with similar structure and function o 4 major groups epithelial, connective, muscle, nerve Epithelial tissue (Fig
Lecture Overview. Connective Tissues. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Connective Tissues Lecture 10
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Connective Tissues Lecture 10 Lecture Overview General composition and function of connective tissue Components of
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Connective Tissues Lecture 10 Lecture Overview General composition and function of connective tissue Components of
The Tissue Level of Organization
 4 The Tissue Level of Organization PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris 4-1 Four Types of Tissue Tissue Are collections of cells and cell products that
4 The Tissue Level of Organization PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris 4-1 Four Types of Tissue Tissue Are collections of cells and cell products that
Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues
 Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in
Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in
Outline. Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory. Organization of the Human Body. Tissue - Epithelium. Tissues 3/2/ Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc
 Outline Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory Laboratory 5 Reading: Chapter 4 I. Cell to cell contact II. Body Cavities III. Membranes IV. Homeostasis V. Integumentary System I. Includes skin, hair and nails 1 2
Outline Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory Laboratory 5 Reading: Chapter 4 I. Cell to cell contact II. Body Cavities III. Membranes IV. Homeostasis V. Integumentary System I. Includes skin, hair and nails 1 2
Biology 325 Fall 2003
 Name: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following is not one of the primary tissue types? A) germinative tissue B) muscle
Name: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following is not one of the primary tissue types? A) germinative tissue B) muscle
Tissues are: group of similar or identical cells that share a common function. used to build organs
 Tissues: Four classes Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous Tissues are: group of similar or identical cells that share a common function. used to build organs Overview: Epithelial o Line body cavities
Tissues: Four classes Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous Tissues are: group of similar or identical cells that share a common function. used to build organs Overview: Epithelial o Line body cavities
Basic Tissue Types and Functions
 Tissues Histology Basic Tissue Types and Functions 1) Epithelial tissue covering 2) Connective tissue support 3) Muscle tissue movement 4) Nervous tissue control Epithelial Tissue 1) Covers a body surface
Tissues Histology Basic Tissue Types and Functions 1) Epithelial tissue covering 2) Connective tissue support 3) Muscle tissue movement 4) Nervous tissue control Epithelial Tissue 1) Covers a body surface
Unit II: Tissues and Integumentary System
 Unit II: Tissues and Integumentary System 2.1 - Tissues Chapter 4 Written Response #1 1. What is a tissue? 2. What are four major types of tissues? Tissue Definition: a group or mass of similar cells working
Unit II: Tissues and Integumentary System 2.1 - Tissues Chapter 4 Written Response #1 1. What is a tissue? 2. What are four major types of tissues? Tissue Definition: a group or mass of similar cells working
Study of Tissues Dr. A. Ebneshahidi
 Study of Tissues Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Tissues Tissues are composed of cells similar in structure and specialized to perform a specific function for the body. The human body is made of four general types
Study of Tissues Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Tissues Tissues are composed of cells similar in structure and specialized to perform a specific function for the body. The human body is made of four general types
Tissue Outline (chapter 4) Tissues group of cells that perform structural and roles. List the 4 types:
 Tissue Outline (chapter 4) Tissues group of cells that perform structural and roles. List the 4 types: 1. 2. 3. 4. I. Epithelial Tissue covers all the surfaces, inside & out. Are the major tissues of,
Tissue Outline (chapter 4) Tissues group of cells that perform structural and roles. List the 4 types: 1. 2. 3. 4. I. Epithelial Tissue covers all the surfaces, inside & out. Are the major tissues of,
Lab Exercise 6a-2. Classification of connective tissues. Connective Tissue. Connective tissues. Areolar. Areolar tissue
 Classification of connective tissues Lab Exercise 6a-2 Connective Tissue Nervous Muscle Connective Tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue proper Fluid connective tissue Supportive connecting tissue
Classification of connective tissues Lab Exercise 6a-2 Connective Tissue Nervous Muscle Connective Tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue proper Fluid connective tissue Supportive connecting tissue
B. Classification of epithelium: by number of cell layers present and by shape of the superficial cell layers.
 I. Introduction - tissue: group of cells that are closely associated, similar in structure and function, and perform a common or related function. - four primary tissues: epithelial tissue, connective
I. Introduction - tissue: group of cells that are closely associated, similar in structure and function, and perform a common or related function. - four primary tissues: epithelial tissue, connective
Body Tissues. Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues - groups of cells with similar structure. and function Four primary tissue types:
 Chapter 3 Tissues Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues - groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary tissue types: Epithelium Connective tissue Nervous
Chapter 3 Tissues Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues - groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary tissue types: Epithelium Connective tissue Nervous
Cells and Tissues 3PART D. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART D Connective Tissue Found everywhere in the body Includes the most abundant
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART D Connective Tissue Found everywhere in the body Includes the most abundant
Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues
 Histology Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Extracellular Matrix cell glue between cells Histology study of tissue
Histology Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Extracellular Matrix cell glue between cells Histology study of tissue
Tissues. Group of cells that are similar in structure and function. 4 primary types. Epithelium (covering) Connective (support) Nervous(control)
 Tissues Tissues Group of cells that are similar in structure and function 4 primary types Epithelium (covering) Connective (support) Nervous(control) Epithelial tissue (epithelium) Lining, covering, and
Tissues Tissues Group of cells that are similar in structure and function 4 primary types Epithelium (covering) Connective (support) Nervous(control) Epithelial tissue (epithelium) Lining, covering, and
Tissues. Tissues. Four basic tissues. A collection of cells with a common function. 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscular 4.
 Tissues Tissues A collection of cells with a common function Four basic tissues 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscular 4. Nervous Epithelia: cells in layers Types of epithelia 1) lining Layers of cells
Tissues Tissues A collection of cells with a common function Four basic tissues 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscular 4. Nervous Epithelia: cells in layers Types of epithelia 1) lining Layers of cells
Tissues Description Function(s) Locations Miscellaneous. avascular -thelium = covering
 Epithelial Tissue Simple Squamous flattened cells diffusion and Kidney glomeruli disc-shaped central filtration air sacs of lung Simple = Single layer nuclei secretes lubricating lining of heart, blood
Epithelial Tissue Simple Squamous flattened cells diffusion and Kidney glomeruli disc-shaped central filtration air sacs of lung Simple = Single layer nuclei secretes lubricating lining of heart, blood
Connective Tissue Nervous Muscle. Classification of connective tissues
 Connective Tissue Nervous Muscle Lab Exercise 6a-2 Classification of connective tissues 1 Connective Tissue Connective tissue proper Fluid connective tissue Supportive connecting tissue Connective tissues
Connective Tissue Nervous Muscle Lab Exercise 6a-2 Classification of connective tissues 1 Connective Tissue Connective tissue proper Fluid connective tissue Supportive connecting tissue Connective tissues
Tissues. Cells work together in functionally related groups called tissues Types of tissues: 1. Epithelial lining and covering. 2. Connective support
 Histology Tissues Cells work together in functionally related groups called tissues Types of tissues: 1. Epithelial lining and covering 2. Connective support 3. Muscle movement 4. Nervous control Epithelial
Histology Tissues Cells work together in functionally related groups called tissues Types of tissues: 1. Epithelial lining and covering 2. Connective support 3. Muscle movement 4. Nervous control Epithelial
What is a tissue? Points to ponder. Tissues Connective Tissue. 1. Connective tissue 2/23/2019. Organization and Regulation of Body Systems
 Organization and Regulation of Body Systems Chapter 04 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education.
Organization and Regulation of Body Systems Chapter 04 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education.
Anatomy and Physiology Tissue Review
 Anatomy and Physiology Tissue Review OVERVIEW Histology practicals can be rough, especially when access to slides is limited to the lab period. This resource provides an opportunity to learn or review
Anatomy and Physiology Tissue Review OVERVIEW Histology practicals can be rough, especially when access to slides is limited to the lab period. This resource provides an opportunity to learn or review
Air sacs of lungs and the lining of the heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels
 Cells Location Function Simple squamous epithelium Air sacs of lungs and the lining of the heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels Allows materials to pass through by diffusion and filtration, and
Cells Location Function Simple squamous epithelium Air sacs of lungs and the lining of the heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels Allows materials to pass through by diffusion and filtration, and
CONNECTIVE TISSUE (Refer to pp for specific characteristics of each) VAN (**Be familiar with exceptions**)
 CONNECTIVE TISSUE CHARACTERISTICS: *Most abundant tissue type; Composed of ECM (GS & Protein Fibers) + Cells (Refer to pp.129-131 for specific characteristics of each) *Highly equipped with VAN assists
CONNECTIVE TISSUE CHARACTERISTICS: *Most abundant tissue type; Composed of ECM (GS & Protein Fibers) + Cells (Refer to pp.129-131 for specific characteristics of each) *Highly equipped with VAN assists
Histology review. Histology. Slides. Epithelial tissue. Another example - kidney. Simple cuboidal epithelium. What to look for
 Histology review Histology What to look for Histology Practical = 50 pts Some slides set up on scopes (~10) Some Powerpoint pictures on the projector Questions I will ask: What kind of tissue? General
Histology review Histology What to look for Histology Practical = 50 pts Some slides set up on scopes (~10) Some Powerpoint pictures on the projector Questions I will ask: What kind of tissue? General
Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job).
 Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous Epithelial cells Epithelium
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous Epithelial cells Epithelium
Tissue Outline. Chapter 4. Tissue. Cellular Connections. I. Definitions II. Cellular Connections III. Tissue Types IV. Membranes V.
 Tissue Outline Chapter 4 The Tissue Level of Organization I. Definitions II. Cellular Connections III. Tissue Types IV. Membranes V. Tissue Repair 1 2 Tissue Cellular Connections Tissue Groups of cells
Tissue Outline Chapter 4 The Tissue Level of Organization I. Definitions II. Cellular Connections III. Tissue Types IV. Membranes V. Tissue Repair 1 2 Tissue Cellular Connections Tissue Groups of cells
Histology. There are four basic tissue types in the body are :-
 Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
The Tissue Level of Organization
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 4 The Tissue Level of Organization Chapter 4 Learning Outcomes 4-1 4-2 4-3 4-4 Identify the body's four basic types
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 4 The Tissue Level of Organization Chapter 4 Learning Outcomes 4-1 4-2 4-3 4-4 Identify the body's four basic types
NOTES: CH 40 Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology
 NOTES: CH 40 Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology THE HUMAN BODY Anatomy Physiology (= structures) (= functions or processes) Characteristics of LIFE: 1) Made up of 1 or more CELLS. 2) Obtain and
NOTES: CH 40 Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology THE HUMAN BODY Anatomy Physiology (= structures) (= functions or processes) Characteristics of LIFE: 1) Made up of 1 or more CELLS. 2) Obtain and
Histology 101! !! Name:! Block: Identify and describe the functions of major tissue types including their subclasses and varieties!
 Histology 101 Identify and describe the functions of major tissue types including their subclasses and varieties Name: Block: "1 Introduction to Tissues Histology Notes Tissue (living fabric) : groups
Histology 101 Identify and describe the functions of major tissue types including their subclasses and varieties Name: Block: "1 Introduction to Tissues Histology Notes Tissue (living fabric) : groups
Simple Squamous Epithelium
 Histology Simple Squamous Epithelium One layer of flattened cells. Protective characteristics are diminished because of this. Examples: Alveoli in the lungs Capillaries where diffusion of nutrients and
Histology Simple Squamous Epithelium One layer of flattened cells. Protective characteristics are diminished because of this. Examples: Alveoli in the lungs Capillaries where diffusion of nutrients and
Tissues. groups of cells similar in structure and function 4 types. epithelium connective muscle nervous
 Tissues groups of cells similar in structure and function 4 types epithelium connective muscle nervous Epithelial Tissue lining covering glandular Functions protection absorption filtration secretion Epithelium
Tissues groups of cells similar in structure and function 4 types epithelium connective muscle nervous Epithelial Tissue lining covering glandular Functions protection absorption filtration secretion Epithelium
Chapter 4. The Tissue Level of Organization
 Chapter 4 The Tissue Level of Organization 1 Tissue Outline I. Definitions II. Cellular Connections III.Tissue Types IV. Membranes V. Tissue Repair 2 Tissue Tissue Groups of cells that are similar in structure
Chapter 4 The Tissue Level of Organization 1 Tissue Outline I. Definitions II. Cellular Connections III.Tissue Types IV. Membranes V. Tissue Repair 2 Tissue Tissue Groups of cells that are similar in structure
THE TISSUE LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION PART I: EPITHELIAL TISSUE
 THE TISSUE LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION PART I: EPITHELIAL TISSUE 4 Main Tissue Types Epithelium Covers surfaces, lines cavities, forms glands Connective Tissue Support and protects body Muscular Tissue Movement
THE TISSUE LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION PART I: EPITHELIAL TISSUE 4 Main Tissue Types Epithelium Covers surfaces, lines cavities, forms glands Connective Tissue Support and protects body Muscular Tissue Movement
Lab Animal Tissue. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: To understand the relationship between the structure and function of different animal tissues
 Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture
 I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body
 Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Chapter 4 :Organization & Regulation of Body Systems
 Chapter 4 :Organization & Regulation of Body Systems 4.1 Types of tissues What is a tissue? A collection of cells of the same type that perform a common function There are 4 major tissue types in the body:
Chapter 4 :Organization & Regulation of Body Systems 4.1 Types of tissues What is a tissue? A collection of cells of the same type that perform a common function There are 4 major tissue types in the body:
Name: Test Date: Chapter 4- Tissues. Use the choices to identify the major tissue types found below:
 Name: Test Date: Chapter 4- Tissues Use the choices to identify the major tissue types found below: A. Connective B. Epithelium C. Muscle D. Nervous 1. B Lines body cavities and covers the body s external
Name: Test Date: Chapter 4- Tissues Use the choices to identify the major tissue types found below: A. Connective B. Epithelium C. Muscle D. Nervous 1. B Lines body cavities and covers the body s external
ACTIVITY 2: HISTOLOGY AND INTEGUMENT
 ACTIVITY 2: HISTOLOGY AND INTEGUMENT Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 4 and 5, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify each tissue (26 tissues)
ACTIVITY 2: HISTOLOGY AND INTEGUMENT Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 4 and 5, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify each tissue (26 tissues)
Tissues, Glands, and Membranes. Chapter Five Mrs. Hornacek
 Tissues, Glands, and Membranes Chapter Five Mrs. Hornacek Objectives 1. Name the four main groups of tissues and give the location and general characteristics of each. 2. Differentiate between voluntary
Tissues, Glands, and Membranes Chapter Five Mrs. Hornacek Objectives 1. Name the four main groups of tissues and give the location and general characteristics of each. 2. Differentiate between voluntary
Connec<ve Tissue. Major Func<ons of Connec<ve Tissue 9/8/14. Most and widely distributed <ssue type Four classes. Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part B
 Connec
Connec
Connec<ve Tissue 9/8/14. Major Func<ons of Connec<ve Tissue. of Connec<ve Tissue. Characteris<cs of Connec<ve Tissue
 Connec
Connec
Tissues and Membranes
 I. In the Beginning a. Egg + sperm! Tissues and Membranes b. 1 cell divides to make 2, 2 divide to make 4, 4 divide to make 8, and then? c. d. e. Totipotent: f. Pluripotent: II. III. Tissues a. Tissues
I. In the Beginning a. Egg + sperm! Tissues and Membranes b. 1 cell divides to make 2, 2 divide to make 4, 4 divide to make 8, and then? c. d. e. Totipotent: f. Pluripotent: II. III. Tissues a. Tissues
The Tissue Level of Organization
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 4 The Tissue Level of Organization Chapter 4 Learning Outcomes 4-1 4-2 4-3 4-4 Identify the body's four basic types
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 4 The Tissue Level of Organization Chapter 4 Learning Outcomes 4-1 4-2 4-3 4-4 Identify the body's four basic types
Epithelial Tissue lining, covering, glandular tissue > Function protect, absorption, filtration, secretion, excretion
 Chapter 4: TISSUES IX. Tissues Intro Epithelial Tissue lining, covering, glandular tissue > Function protect, absorption, filtration, secretion, excretion Connective Tissue most widespread tissue type
Chapter 4: TISSUES IX. Tissues Intro Epithelial Tissue lining, covering, glandular tissue > Function protect, absorption, filtration, secretion, excretion Connective Tissue most widespread tissue type
Introduction to Types of Body Tissue Putting it All Together. Packet #12
 Introduction to Types of Body Tissue Putting it All Together Packet #12 Introduction Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types Epithelial tissue (epithelium)
Introduction to Types of Body Tissue Putting it All Together Packet #12 Introduction Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types Epithelial tissue (epithelium)
Connexons: hollow connective tubes
 Chapter 3 1. tight junctions: like a zipper, these junctions hold the cells tightly together making them impermeable to the extracellular fluid that surrounds them. 2. desmosomes: like buttons, these
Chapter 3 1. tight junctions: like a zipper, these junctions hold the cells tightly together making them impermeable to the extracellular fluid that surrounds them. 2. desmosomes: like buttons, these
I. Introduction. Unit One. Tendons of the hand. The white glistening appearance results from the collagen of which tendons are composed.
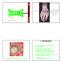 5 Tendons of the hand tendons The white glistening appearance results from the collagen of which tendons are composed. Chapter 5 Karen Webb Smith Unit One I. Introduction A. Cells are arranged in tissues
5 Tendons of the hand tendons The white glistening appearance results from the collagen of which tendons are composed. Chapter 5 Karen Webb Smith Unit One I. Introduction A. Cells are arranged in tissues
TISSUE. A group of cells that perform a similar function within an organism. Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous CREDITS
 TISSUE A group of cells that perform a similar function within an organism. Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous CREDITS Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous Epithelium Composed of a layer of cells. Lines
TISSUE A group of cells that perform a similar function within an organism. Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous CREDITS Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous Epithelium Composed of a layer of cells. Lines
Tissues. How do cells form tissues?
 Tissues How do cells form tissues? Using cell junctions Tissues Epithelial tissue Connective tissue Muscle tissue Nervous tissue Epithelial Tissue Closely packed cells in continuous sheets connected by
Tissues How do cells form tissues? Using cell junctions Tissues Epithelial tissue Connective tissue Muscle tissue Nervous tissue Epithelial Tissue Closely packed cells in continuous sheets connected by
Anatomy Chapter 4 Tissues
 4 Principle Tissue Types Epithelial tissue Covering and lining Glandular Connective tissue Highly variable Most abundant tissue type Muscular tissue 3 major types Produce force through contraction Nervous
4 Principle Tissue Types Epithelial tissue Covering and lining Glandular Connective tissue Highly variable Most abundant tissue type Muscular tissue 3 major types Produce force through contraction Nervous
Lesson 9A Tissues in Animals
 Lesson 9A Tissues in Animals Levels of Organization in the Human Body Similar types of cells Different types of tissues Different organs Many organ systems cell tissue organ organ system organism Levels
Lesson 9A Tissues in Animals Levels of Organization in the Human Body Similar types of cells Different types of tissues Different organs Many organ systems cell tissue organ organ system organism Levels
Histology= the study of tissues
 Unit 3-Histology Histology= the study of tissues A tissue is a group of cells that have a similar shape and function. Different types of tissues can be found in different organs. In humans, there are four
Unit 3-Histology Histology= the study of tissues A tissue is a group of cells that have a similar shape and function. Different types of tissues can be found in different organs. In humans, there are four
Tissues- of cells with similar and
 Tissues- of cells with similar and. Four types of tissues 1. 2. 3. 4. Characteristics of Epithelial Tissue -Highly Cellular -Special contacts -Polar (apical and basal surfaces) -Supported by connective
Tissues- of cells with similar and. Four types of tissues 1. 2. 3. 4. Characteristics of Epithelial Tissue -Highly Cellular -Special contacts -Polar (apical and basal surfaces) -Supported by connective
Classification of Tissues
 6 R e v i e w S h e e t Exercise Classification of Tissues NAME LAB TIME/DATE Tissue Structure and Function General Review 1. Define tissue. A group of cells similar to one another in structure that perform
6 R e v i e w S h e e t Exercise Classification of Tissues NAME LAB TIME/DATE Tissue Structure and Function General Review 1. Define tissue. A group of cells similar to one another in structure that perform
Epithelial Tissues. Types of Epithelial Tissues: Lining of Kidney
 Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
Human anatomy Unit III. Tissue
 Human anatomy Unit III Tissue Definition of Tissues Biological tissue is a collection of interconnected cells that perform a similar function within an organism. In other words, it is a group of cells
Human anatomy Unit III Tissue Definition of Tissues Biological tissue is a collection of interconnected cells that perform a similar function within an organism. In other words, it is a group of cells
Tissues and Structures to Know for the Lab Practical
 Ch. 3 - Cells and Tissues Tissues and Structures to Know for the Lab Practical Miss School, Miss Out! Simple squamous epithelium line and cover; site of diffusion Simple squamous epithelium apical surface
Ch. 3 - Cells and Tissues Tissues and Structures to Know for the Lab Practical Miss School, Miss Out! Simple squamous epithelium line and cover; site of diffusion Simple squamous epithelium apical surface
Use for reference if needed:
 A- 2.5 Describe how structure and function are related in terms of cell and tissue types. I can recognize different types of body tissue. I can explain how different tissue structures affect their functions.
A- 2.5 Describe how structure and function are related in terms of cell and tissue types. I can recognize different types of body tissue. I can explain how different tissue structures affect their functions.
TISSUES. Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 TISSUES Dr. Gary Mumaugh Tissues Tissues - Groups of cells similar in structure and function and perform a common function Histology The study of tissues The four types of tissues Epithelial Connective
TISSUES Dr. Gary Mumaugh Tissues Tissues - Groups of cells similar in structure and function and perform a common function Histology The study of tissues The four types of tissues Epithelial Connective
6a A&P: Introduction to the Human Body - Tissues
 6a A&P: Introduction to the Human Body - Tissues 6a A&P: Introduction to the Human Body - Tissues! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture: AOIs of
6a A&P: Introduction to the Human Body - Tissues 6a A&P: Introduction to the Human Body - Tissues! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture: AOIs of
UNIT 4 T I S S U E S
 UNIT 4 T I S S U E S WHAT IS A TISSUE Group of cells that work together to do a function Cells are similar Extracellular fluid around them is similar Histology EPITHELIAL TISSUE Also called epithelium
UNIT 4 T I S S U E S WHAT IS A TISSUE Group of cells that work together to do a function Cells are similar Extracellular fluid around them is similar Histology EPITHELIAL TISSUE Also called epithelium
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
The Tissue Level of Organization_professor edit
 4 The Tissue Level of Organization_professor edit PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Tissues Learning Outcomes 4-1 Identify the
4 The Tissue Level of Organization_professor edit PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Tissues Learning Outcomes 4-1 Identify the
