Function of the skeleton
|
|
|
- Linette Leonard
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Function of the skeleton Yr9 Biology Revision The skeleton has four main functions: to support the body to protect some of the vital organs of the body to help the body move to make blood cells Label the diagram
2 Joints Bones are linked together by joints. Most joints allow different parts of the skeleton to move. The human skeleton has joints calledsynovial joints. The synovial joint If two bones just moved against each other, they would eventually wear away. This can happen in people who have a condition called arthritis. To stop this happening, the ends of the bones in a joint are covered with a tough, smooth substance called cartilage. This is kept slippery by a liquid called synovial fluid. Tough ligaments join the two bones in the joint and stop the joint falling apart. The main features of a synovial joint Movement Different types of synovial joint allow different types of movement. The table describes two types of joint: Type of joint Examples Movement allowed Hinge joint Ball and socket Knee, elbow Hip, shoulder The same as opening and closing a door, with no rotation (turning) Back and forth in all directions, and rotation The bones cannot move on their own - they need muscles for this to happen.
3 Complete the table Type of joint Type of movement Example Fixed Hinge Ball and socket Sliding Muscles Muscles work by getting shorter. We say that they contract, and the process is called contraction. Muscles are attached to bones by strongtendons. When a muscle contracts, it pulls on the bone, and the bone can move if it is part of a joint. Antagonistic muscles Muscles can only pull and cannot push. This would be a problem if a joint were controlled by just one muscle. As soon as the muscle had contracted and pulled on a bone, that would be it, with no way to move the bone back again. This problem is solved by having muscles in pairs, called antagonistic muscles. For example, your elbow joint has two muscles that move your forearm up or down. These are the biceps on the front of the upper arm and the triceps on the back of the upper arm: to raise the forearm, the biceps contracts and the triceps relaxes to lower the forearm again, the triceps contracts and the biceps relaxes Describe 2 different antagonistic muscle pairs by filling in this table Biceps and triceps Antagonistic muscle pair Quadriceps and hamstring Description of movement The biceps the arm at the elbow. The triceps the arm at the elbow. The quadriceps the leg at the knee. The hamstring the leg at the knee.
4 Reflex actions When a receptor is stimulated, it sends a signal to the central nervous system, where the brain coordinates the response. But sometimes a very quick response is needed, one that does not need the involvement of the brain. This is a reflex action. Reflex actions are rapid and happen without us thinking. For example, you would pull your hand away from a hot flame without thinking about it. This is what happens: 1. receptor detects a stimulus - change in the environment 2. sensory neurone sends signal to relay neurone 3. motor neurone sends signal to effector 4. effector produces a response For example, the way the iris in our eye adjusts the size of the pupil in response to bright or dim light is also a reflex action. In bright light: Radial muscles of the iris relax. Circular muscles of the iris contract. Less light enters the eye through the contracted pupil. In dim light: Radial muscles of the iris contract. Circular muscles of the iris relax. More light enters the eye through the dilated pupil. Complete the following table Stimulus Response Dust in eye Touching a hot surface Being hit below the kneecap Loud "bang" Smelling nice food
5 Temperature regulation If you become too hot or too cold, there are several ways in which your temperature can be controlled. They involve sweating, shivering, skin capillaries and hairs. Too hot When we get too hot: Sweat glands in the skin release more sweat. This evaporates, removing heat energy from the skin. Blood vessels leading to the skin capillaries become wider - they dilate - allowing more blood to flow through the skin, and more heat to be lost. Too cold When we get too cold: Muscles contract rapidly - we shiver. These contractions need energy from respiration, and some of this is released as heat. Blood vessels leading to the skin capillaries become narrower - they constrict - letting less blood flow through the skin and conserving heat in the body. The hairs on the skin also help to control body temperature. They lie flat when we are warm, and rise when we are cold. The hairs trap a layer of air above the skin, which helps to insulate the skin against heat loss. Controlling temperature Too cold Too hot A - Hair muscles pull hairs on end. B - Erect hairs trap air. C - Blood flow in capillaries decreases. D - Hair muscles relax. Hairs lie flat so heat can escape. E - Sweat secreted by sweat glands. Cools skin by evaporation. F - Blood flow in capillaries increases.
6 The urinary system overview The urinary system is designed to remove waste products such as urea, as well as excess ions and water from our blood. The kidneys contain many nephrons which remove any waste, before reabsorbing any substances the body needs. Waste is stored in the bladder before being removed as urine. Waste products are produced by our cells. These include carbon dioxide fromrespiration and urea from the breakdown of excess amino acids in the liver. Carbon dioxide is removed by our lungs. Our urinary system is responsible for producing, storing and removing urine from our bodies. Our urine contains urea and any excess water. The kidneys The kidneys are part of the urinary system, together with the ureter, urethraand bladder. Humans have two kidneys. They are bean-shaped organs - approximately 11.5 cm long which are found just below our ribcage, one on either side of our spine. location of kidneys in abdominal cavity.
7 Variety within a species Natural selection Within a population of animals, plants or any living organisms, there will be variations. Variation has two causes; Inherited (genetic) and environment. Complete the table:- Characteristic Cause Eye colour Accent Hair colour Age Selective breeding Artificial selection is when people use selective breeding to produce new varieties of a species. A variety is a type of a particular species that is different in some clear way from other varieties of that species. For example, pedigree dogs come in lots of different varieties, called breeds of dog. They may be different colours and sizes, but they are all still dogs. They are all still the same species. Different varieties of dog have been produced by selective breeding. Different breeds of dogs
8 Selective breeding of cows Suppose you wanted a variety of cow that produced a lot of milk. This is what you could do: choose or select the cows in your herd that produce the most milk let only these cows reproduce select the offspring that produce the most milk let only these offspring reproduce keep repeating the process of selection and breeding until you achieve your goal. Other examples of selective breeding The key here is to identify the feature you want, and only breed from the individuals that have that feature. Here are some examples of what selective breeding can produce: hens that lay big eggs of a particular colour cattle that produce lots of meat tomato plants that produce lots of tomatoes crops that are resistant to certain plant diseases. Chromosomes, DNA and genes The DNA in all of your cells is approximately two metres long, except red blood cells which have none and sperm or eggs which only have about one metre. Because it is so long it is very thin and coiled into structures called chromosomes. The chromosomes are found in thenucleus of each cell.
9 Each cell with a nucleus contains chromosomes, which are made from DNA Human body cells each contain 23 pairs of chromosomes, half of which are from each parent. So, human gametes (eggs and sperm) each contain 23 chromosomes. When an egg is fertilised by a sperm, it becomes a cell with 23 pairs of chromosomes. This is why children resemble both their parents half of their chromosomes and DNA come from their mother, and half from their father.
10 A collection of human chromosomes A gene is a section of DNA that is responsible for a characteristic like eye colour or blood group. Humans have around 20,000 genes. DNA makes up genes, which makes up chromosomes. One copy of all your chromosomes is called your genome. Genetic diagrams (Punnett squares) Genetic diagrams or Punnett squares are used to show the possible outcomes of a particular cross. A dominant allele is shown by a capital letter, and a recessive allele by a lower case letter. Cystic fibrosis
11 Cystic fibrosis (CF) is caused by a recessive allele. In the genetic diagram below, it is written as f. People with CF produce abnormally thick and sticky mucus in their lungs and airways. As a result, they are more likely to get respiratory infections. Daily physiotherapy helps to relieve congestion, while antibiotics can fight infection. CF also affects the gut and pancreas, so food is not digested efficiently. Inheriting copies of the allele You need to inherit two copies of the faulty allele to be born with CF. If you have just one copy, you are a carrier, but will not experience any symptoms. If two carriers have a child together, there is a one in four chance (or 25 per cent) of it inheriting the disorder. The genetic diagrams below shows why. Cystic fibrosis is an inherited disorder caused by a recessive allele. This genetic diagram shows the possible outcomes when both parents are heterozygous for the faulty allele. There is a one in four chance or 25 percent of the offspring being homozygous for the faulty allele, and so having cystic fibrosis.
B1 Question 1 Foundation
 B1 Question 1 Foundation The nucleus controls the activities of a cell. The instructions for how an organism develops i.e. the genes are found in the nuclei of its cells B1 Question 2 Foundation The genes
B1 Question 1 Foundation The nucleus controls the activities of a cell. The instructions for how an organism develops i.e. the genes are found in the nuclei of its cells B1 Question 2 Foundation The genes
spinal cord P finger Q What is the sequence of nerve cells through which an impulse passes during a reflex action?
 1 The diagram represents a simple reflex arc. spinal cord P R pin finger Q muscle What is the sequence of nerve cells through which an impulse passes during a reflex action? PhysicsndMathsTutor.com 2 The
1 The diagram represents a simple reflex arc. spinal cord P R pin finger Q muscle What is the sequence of nerve cells through which an impulse passes during a reflex action? PhysicsndMathsTutor.com 2 The
Coordination and Responses Nervous System (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Coordination and Responses Nervous System (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Nervous System Nervous system Central Nervous System (CNS) Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Brain Spinal Cord Nerves and neurones
Coordination and Responses Nervous System (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Nervous System Nervous system Central Nervous System (CNS) Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Brain Spinal Cord Nerves and neurones
Name: Class Period: Due Date: Spring Final Exam Review 2015
 Name: Class Period: Due Date: Spring Final Exam Review 2015 Sources of Information: Use your notes, ppts and review material on teacher s website, and online resources. Cells 1. What are the 3 components
Name: Class Period: Due Date: Spring Final Exam Review 2015 Sources of Information: Use your notes, ppts and review material on teacher s website, and online resources. Cells 1. What are the 3 components
Homeostasis. Name (2) A response is caused when information in the nervous system reaches an effector.
 Homeostasis. Name. Thornton College Q.This question is about the nervous system. (a) Describe the function of receptors in the skin............. (2) (b) A response is caused when information in the nervous
Homeostasis. Name. Thornton College Q.This question is about the nervous system. (a) Describe the function of receptors in the skin............. (2) (b) A response is caused when information in the nervous
BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS:
 BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS: LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION smallest unit Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems largest unit Body TISSUES IN THE HUMAN BODY Tissue Function Example Muscle makes parts of the body
BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS: LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION smallest unit Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems largest unit Body TISSUES IN THE HUMAN BODY Tissue Function Example Muscle makes parts of the body
The Human Body. Mrs. Green
 The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015
 Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015 Biology Duration: 3.00 Hours Part 1 Index No:- Choose the correct or most appropriate answer and underline them 1) When
Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015 Biology Duration: 3.00 Hours Part 1 Index No:- Choose the correct or most appropriate answer and underline them 1) When
The Skeletal System. Functions of the Skeletal System
 Skeletal System The Skeletal System Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support Protect internal organs Allows your body to move Stores and produced materials that your body needs You have 206 bones
Skeletal System The Skeletal System Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support Protect internal organs Allows your body to move Stores and produced materials that your body needs You have 206 bones
REVISION BOOKLET. The Body Systems
 REVISION BOOKLET The Body Systems GCSE PE 2016 Skeletal System Functions of the skeleton Joints for movement Muscle attachment Protection of vital organs Red and white blood cell production platelets Storage
REVISION BOOKLET The Body Systems GCSE PE 2016 Skeletal System Functions of the skeleton Joints for movement Muscle attachment Protection of vital organs Red and white blood cell production platelets Storage
3.4.6 The Excretory System in the Human
 3.4.6 The Excretory System in the Human Objectives What you will need to know from this section Explain the role of the excretory system in homeostasis -- the ability and necessity to maintain constancy
3.4.6 The Excretory System in the Human Objectives What you will need to know from this section Explain the role of the excretory system in homeostasis -- the ability and necessity to maintain constancy
Excretion (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Excretion (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Structure of the Kidney Excretion is the removal from organisms of toxic materials, the waste products of metabolism and substances in excess of requirements
Excretion (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Structure of the Kidney Excretion is the removal from organisms of toxic materials, the waste products of metabolism and substances in excess of requirements
Glossary. Maintain keep up. Constant the same. Internal inside the body. Environment surroundings of the body.
 Homeostasis Glossary Maintain keep up. Constant the same. Internal inside the body. Environment surroundings of the body. What is Homeostasis? Body cells work best if they have the correct Temperature
Homeostasis Glossary Maintain keep up. Constant the same. Internal inside the body. Environment surroundings of the body. What is Homeostasis? Body cells work best if they have the correct Temperature
PREDICTING INHERITED TRAITS & PUNNETT SQUARE ANALYSIS
 PREDICTING INHERITED TRAITS & PUNNETT SQUARE ANALYSIS GENETICS TERMS AND VOCABULARY DNA- Deoxyribonucleic acid. It is the molecule that codes for our traits. CHROMOSOME - A structure found in the nucleus
PREDICTING INHERITED TRAITS & PUNNETT SQUARE ANALYSIS GENETICS TERMS AND VOCABULARY DNA- Deoxyribonucleic acid. It is the molecule that codes for our traits. CHROMOSOME - A structure found in the nucleus
14 Coordination and response
 oordination and response Question Paper Level IGSE Subject iology Exam oard ambridge International Examinations Unit 14 oordination and response ooklet Question Paper 2 Time llowed: 30 minutes Score: /25
oordination and response Question Paper Level IGSE Subject iology Exam oard ambridge International Examinations Unit 14 oordination and response ooklet Question Paper 2 Time llowed: 30 minutes Score: /25
Wednesday 11 January 2017 Afternoon Time: 2 hours
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Centre Number Human Biology Unit: 4HB0 Paper: 01 Candidate Number Wednesday 11 January 2017 Afternoon Time: 2 hours You must
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Centre Number Human Biology Unit: 4HB0 Paper: 01 Candidate Number Wednesday 11 January 2017 Afternoon Time: 2 hours You must
B1 Revision You and Your Genes. You and Your Genes (B1) Revision for Exam
 B1 Revision You and Your Genes You and Your Genes (B1) Revision for Exam What makes us all different? Organisms inherit information from their parents. This controls how they develop, so children look
B1 Revision You and Your Genes You and Your Genes (B1) Revision for Exam What makes us all different? Organisms inherit information from their parents. This controls how they develop, so children look
Genetics and Diversity Punnett Squares
 Genetics and Diversity Punnett Squares 1 OUTCOME QUESTION(S): S1-1-12: How are the features of the parents inherited to create unique offspring? Vocabulary & Concepts Allele Dominant Recessive Genotype
Genetics and Diversity Punnett Squares 1 OUTCOME QUESTION(S): S1-1-12: How are the features of the parents inherited to create unique offspring? Vocabulary & Concepts Allele Dominant Recessive Genotype
Homeostasis. Mark Scheme 1. Save My Exams! The Home of Revision. Level GCSE (9-1) Exam Board 4.5 Homeostasis and Response. Booklet Mark Scheme 1
 Homeostasis Mark Scheme Level GCSE (9-) Subject Biology Exam Board AQA Topic 4.5 Homeostasis and Response Sub-Topic Homeostasis Difficulty Level Silver Level Booklet Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 60 minutes
Homeostasis Mark Scheme Level GCSE (9-) Subject Biology Exam Board AQA Topic 4.5 Homeostasis and Response Sub-Topic Homeostasis Difficulty Level Silver Level Booklet Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 60 minutes
Two copies of each autosomal gene affect phenotype.
 UNIT 3 GENETICS LESSON #34: Chromosomes and Phenotype Objective: Explain how the chromosomes on which genes are located can affect the expression of traits. Take a moment to look at the variety of treats
UNIT 3 GENETICS LESSON #34: Chromosomes and Phenotype Objective: Explain how the chromosomes on which genes are located can affect the expression of traits. Take a moment to look at the variety of treats
Cell Division and Inheritance Revision 7
 Cell Division and Inheritance Revision 7 65 minutes 65 marks Page of 20 Q. Cystic fibrosis is a disease which affects in 600 babies. (a) What are the symptoms of cystic fibrosis? (3) Two parents with normal
Cell Division and Inheritance Revision 7 65 minutes 65 marks Page of 20 Q. Cystic fibrosis is a disease which affects in 600 babies. (a) What are the symptoms of cystic fibrosis? (3) Two parents with normal
Science 1.9 AS WORKBOOK. Working to Excellence
 Science 1.9 AS 90948 Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to genetic variation WORKBOOK Working to Excellence CONTENTS 1. Writing Excellence answers to DNA and Genes questions 2. Writing
Science 1.9 AS 90948 Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to genetic variation WORKBOOK Working to Excellence CONTENTS 1. Writing Excellence answers to DNA and Genes questions 2. Writing
What are sex cells? How does meiosis help explain Mendel s results?
 CHAPTER 5 3 Meiosis SECTION Heredity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are sex cells? How does meiosis help explain Mendel s results? National
CHAPTER 5 3 Meiosis SECTION Heredity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are sex cells? How does meiosis help explain Mendel s results? National
Unit B2, B2.7. Cell division and inheritance. Stage 1. Ovary. Cell Q. Cell P. Cell R. Cell S. 7 Embryo A B C
 Cell division and inheritance 1. A woman gives birth to triplets. Two of the triplets are boys and the third is a girl. The triplets developed from two egg cells released from the ovary at the same time.
Cell division and inheritance 1. A woman gives birth to triplets. Two of the triplets are boys and the third is a girl. The triplets developed from two egg cells released from the ovary at the same time.
Assessment Schedule 2015 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of genetic variation and change (91157)
 NCEA Level 2 Biology (91157) 2015 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2015 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of genetic variation and change (91157) Assessment Criteria Achievement Achievement with Merit
NCEA Level 2 Biology (91157) 2015 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2015 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of genetic variation and change (91157) Assessment Criteria Achievement Achievement with Merit
Human Biology *P41558A0128* P41558A. Unit: 4HB0 Paper: 01. Edexcel International GCSE. Tuesday 7 May 2013 Morning Time: 2 hours.
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel International GCSE Centre Number Human Biology Unit: 4HB0 Paper: 01 Candidate Number Tuesday 7 May 2013 Morning Time: 2 hours You must have: Ruler Candidates
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel International GCSE Centre Number Human Biology Unit: 4HB0 Paper: 01 Candidate Number Tuesday 7 May 2013 Morning Time: 2 hours You must have: Ruler Candidates
B1 You and Your Genes Q3 Question: What are alleles?
 Q1 : Where are chromosomes found within a cell? Inside the nucleus. Q2 : Put the following in size order starting with the smallest first: nucleus, chromosome, cell, gene. Gene, chromosome, nucleus, cell.
Q1 : Where are chromosomes found within a cell? Inside the nucleus. Q2 : Put the following in size order starting with the smallest first: nucleus, chromosome, cell, gene. Gene, chromosome, nucleus, cell.
Laughter and the Body Systems
 Laughter and the Body Systems Laughter causes the lungs to pump out carbon dioxide, the eyes to cleanse themselves with tears, the muscles to relax, the flow of adrenaline to increase, and the cardiovascular
Laughter and the Body Systems Laughter causes the lungs to pump out carbon dioxide, the eyes to cleanse themselves with tears, the muscles to relax, the flow of adrenaline to increase, and the cardiovascular
Homeostasis 1 of 26 Boardworks Ltd 2011
 Homeostasis 1 of 26 Boardworks Ltd 2011 2 of 26 Boardworks Ltd 2011 A day at the sauna 3 of 26 Boardworks Ltd 2011 How does the body react to change? Saving energy? 4 of 26 Boardworks Ltd 2011 Sayid has
Homeostasis 1 of 26 Boardworks Ltd 2011 2 of 26 Boardworks Ltd 2011 A day at the sauna 3 of 26 Boardworks Ltd 2011 How does the body react to change? Saving energy? 4 of 26 Boardworks Ltd 2011 Sayid has
Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view
 Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
EB Education Revision Guide. How to work with Homeostasis: Part 1 Thermoregulation
 EB Education Revision Guide How to work with Homeostasis: Part 1 Thermoregulation Basics of homeostasis Thermoregulation a) Why your body regulates temperature What you need to know about Homeostasis:
EB Education Revision Guide How to work with Homeostasis: Part 1 Thermoregulation Basics of homeostasis Thermoregulation a) Why your body regulates temperature What you need to know about Homeostasis:
15/12/2011. You and your genes (OCR)
 You and your genes (OCR) Variation Variation is the name given to differences between individuals of the SAME species. Variation is due to GENETIC or ENVIRONMENTAL causes. For example, consider dogs: 1)
You and your genes (OCR) Variation Variation is the name given to differences between individuals of the SAME species. Variation is due to GENETIC or ENVIRONMENTAL causes. For example, consider dogs: 1)
Conditions inside the body must be kept constant. Urea must be removed from the body. Name the organ which makes urea.
 Conditions inside the body must be kept constant. (a) Urea must be removed from the body. (i) Name the organ which makes urea. () Which organ removes urea from the body? () (iii) What is urea made from?
Conditions inside the body must be kept constant. (a) Urea must be removed from the body. (i) Name the organ which makes urea. () Which organ removes urea from the body? () (iii) What is urea made from?
Nervous System. Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body
 Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
To meet the expectations of this unit, students should already be able to describe the skeleton s role in movement, support and protection.
 GRADE 9: Life science 4 Movement UNIT 9L.4 4 hours About this unit This unit is the fourth of six units on life science for Grade 9. This unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching of lessons
GRADE 9: Life science 4 Movement UNIT 9L.4 4 hours About this unit This unit is the fourth of six units on life science for Grade 9. This unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching of lessons
5. Maintaining the internal environment. Homeostasis
 5. Maintaining the internal environment Homeostasis Blood and tissue fluid derived from blood, flow around or close to all cells in the body. Blood and tissue fluid form the internal environment of the
5. Maintaining the internal environment Homeostasis Blood and tissue fluid derived from blood, flow around or close to all cells in the body. Blood and tissue fluid form the internal environment of the
Name: Period: Review for Animal Systems Test II - KEY
 Name: Period: Review for Animal Systems Test II - KEY Questions 1-9: Write the main functions of the following body s in the spaces below. Then, write the levels of organization for each body. Give specific
Name: Period: Review for Animal Systems Test II - KEY Questions 1-9: Write the main functions of the following body s in the spaces below. Then, write the levels of organization for each body. Give specific
Lab Report Sheet. Title: Hypothesis (What I Think Will Happen) Materials (What We Used) Procedure (What We Did)
 Appendix 107 108 Lab Report Sheet Title: Hypothesis (What I Think Will Happen) Materials (What We Used) Procedure (What We Did) Observations and Results (What I Saw and Measured) Worksheet prepared by
Appendix 107 108 Lab Report Sheet Title: Hypothesis (What I Think Will Happen) Materials (What We Used) Procedure (What We Did) Observations and Results (What I Saw and Measured) Worksheet prepared by
By Helen and Mark Warner
 By Helen and Mark Warner www.teachingpacks.co.uk Teaching Packs - The Human Body - Page 1 Image ThinkStock In this section, you will learn about... 1. The major systems and organs in the human body. 2.
By Helen and Mark Warner www.teachingpacks.co.uk Teaching Packs - The Human Body - Page 1 Image ThinkStock In this section, you will learn about... 1. The major systems and organs in the human body. 2.
Page 2. Q1.Figure 1 shows a human body cell. Figure 1. Which part in Figure 1 contains chromosomes? Tick one box. A B C
 Q1.Figure 1 shows a human body cell. Figure 1 (a) Which part in Figure 1 contains chromosomes? Tick one box. A B C (b) Humans have pairs of chromosomes in their body cells. Draw one line from each type
Q1.Figure 1 shows a human body cell. Figure 1 (a) Which part in Figure 1 contains chromosomes? Tick one box. A B C (b) Humans have pairs of chromosomes in their body cells. Draw one line from each type
CIE Biology A-level Topic 14: Homeostasis
 CIE Biology A-level Topic 14: Homeostasis Notes Communication is essential for the survival of organism as all living organisms must be able to detect and respond to changes in both their internal and
CIE Biology A-level Topic 14: Homeostasis Notes Communication is essential for the survival of organism as all living organisms must be able to detect and respond to changes in both their internal and
Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view
 Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Hormones are involved in controlling the menstrual cycle and fertility. (a) (i) Use the correct answer from the box to complete the sentence.
 Hormones are involved in controlling the menstrual cycle and fertility. (a) (i) Use the correct answer from the box to complete the sentence. auxin follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) thalidomide A hormone
Hormones are involved in controlling the menstrual cycle and fertility. (a) (i) Use the correct answer from the box to complete the sentence. auxin follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) thalidomide A hormone
M1. (a) pupils dilated (at B) allow converse for A 1. in dim light / low light levels 1. because circular muscles (in iris) relax 1
 M. (a) pupils dilated (at B) allow converse for A in dim light / low light levels because circular muscles (in iris) relax (and) radial muscles contract (b) figure 2 shows myopia where light does not focus
M. (a) pupils dilated (at B) allow converse for A in dim light / low light levels because circular muscles (in iris) relax (and) radial muscles contract (b) figure 2 shows myopia where light does not focus
Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete)
 Activity #12 What s happening inside? Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete) Act #12 pg 1 of 3 Analysis
Activity #12 What s happening inside? Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete) Act #12 pg 1 of 3 Analysis
A response is caused when information in the nervous system reaches an effector. the response each type of effector makes.
 This question is about the nervous system. (a) Describe the function of receptors in the skin. (2) (b) A response is caused when information in the nervous system reaches an effector. (i) There are two
This question is about the nervous system. (a) Describe the function of receptors in the skin. (2) (b) A response is caused when information in the nervous system reaches an effector. (i) There are two
* If a person is badly burnt the hairs on the skin are lost and blisters can cover the surface of the skin.
 Questions Q1. * If a person is badly burnt the hairs on the skin are lost and blisters can cover the surface of the skin. Explain how burns to the skin affect temperature regulation in the human body.
Questions Q1. * If a person is badly burnt the hairs on the skin are lost and blisters can cover the surface of the skin. Explain how burns to the skin affect temperature regulation in the human body.
M1. (a) (concentration high) in the hepatic portal vein is blood with glucose absorbed from the intestine 1
 M. (a) (concentration high) in the hepatic portal vein is blood with glucose absorbed from the intestine concentration is lower in the hepatic vein because insulin (has caused) glucose to be converted
M. (a) (concentration high) in the hepatic portal vein is blood with glucose absorbed from the intestine concentration is lower in the hepatic vein because insulin (has caused) glucose to be converted
Questions Q1. ) in the box next to your answer. (1) A FF B Ff C ff. D ff (ii) Explain why a person with cystic fibrosis (CF) may lose body mass.
 Questions Q1. Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a recessive genetic disorder. The recessive allele is shown as f and the dominant allele as F. (a) (i) What is the genotype of a person with cystic fibrosis? Put a
Questions Q1. Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a recessive genetic disorder. The recessive allele is shown as f and the dominant allele as F. (a) (i) What is the genotype of a person with cystic fibrosis? Put a
A day at the sauna. Boardworks Ltd How does the body react to change?
 1 of 40 2 of 40 A day at the sauna 3 of 40 How does the body react to change? Saving energy? 4 of 40 Sayid has decided to save energy by staying in bed all day. How much of his energy do you think this
1 of 40 2 of 40 A day at the sauna 3 of 40 How does the body react to change? Saving energy? 4 of 40 Sayid has decided to save energy by staying in bed all day. How much of his energy do you think this
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet
 Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
Chapter 22. Body Organization & Structure
 Chapter 22 Body Organization & Structure Start-Up Activity Too Cold for Comfort Hold a few pieces of ice in one hand. Hold the ice until the cold is uncomfortable. Then release the ice into the dish. Compare
Chapter 22 Body Organization & Structure Start-Up Activity Too Cold for Comfort Hold a few pieces of ice in one hand. Hold the ice until the cold is uncomfortable. Then release the ice into the dish. Compare
Warm Up Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells?
 Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
Guided Notes: Simple Genetics
 Punnett Squares Guided Notes: Simple Genetics In order to determine the a person might inherit, we use a simple diagram called a o Give us of an offspring having particular traits Pieces of the Punnett
Punnett Squares Guided Notes: Simple Genetics In order to determine the a person might inherit, we use a simple diagram called a o Give us of an offspring having particular traits Pieces of the Punnett
3. A process that occurs in the human body is represented in the diagram below.
 1. Molecules in a certain medication attach to receptors on nerve cells. This prevents the normal chemical signal from binding to the receptor. One immediate result of taking this medication might be a
1. Molecules in a certain medication attach to receptors on nerve cells. This prevents the normal chemical signal from binding to the receptor. One immediate result of taking this medication might be a
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 45-1 The Human Body Plan
 STUDY GUIDE SECTION 45-1 The Human Body Plan Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank 1. Nervous tissue contains specialized cells called a. Transmitters. b. neurons c. messenger
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 45-1 The Human Body Plan Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank 1. Nervous tissue contains specialized cells called a. Transmitters. b. neurons c. messenger
SUPPORT, MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION
 SUPPORT, MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION Overview Bones Joints Antagonistic Muscles Forelimbs Bones Functions of the skeleton Locomotion The ability to move from place to place Support Holds the body off the ground
SUPPORT, MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION Overview Bones Joints Antagonistic Muscles Forelimbs Bones Functions of the skeleton Locomotion The ability to move from place to place Support Holds the body off the ground
Core 1. Coordination, Response & Homeostasis. page 1.
 Core 1 Coordination, Response & Homeostasis page 1 Core 2 1 1 1. Coordination, Response & Homeostasis page 2 Core 3 Fig. 2 Fig. 2 Coordination, Response & Homeostasis page 3 Alternative to practical 1
Core 1 Coordination, Response & Homeostasis page 1 Core 2 1 1 1. Coordination, Response & Homeostasis page 2 Core 3 Fig. 2 Fig. 2 Coordination, Response & Homeostasis page 3 Alternative to practical 1
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *8954733823* BIOLOGY 0610/21 Paper 2 Core October/November 2014 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates answer
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *8954733823* BIOLOGY 0610/21 Paper 2 Core October/November 2014 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates answer
The Circulatory System. Lesson 4. Quick Check. Trace the path of blood after it is pumped from the heart. 22. First
 Lesson 4 The Circulatory System How does blood transport materials? Your circulatory system is a delivery system. Red blood cells travel in the blood, bringing things to and from your body cells. The main
Lesson 4 The Circulatory System How does blood transport materials? Your circulatory system is a delivery system. Red blood cells travel in the blood, bringing things to and from your body cells. The main
Homeostasis involves maintaining the volume, chemical make up and other factors of blood and tissue fluid within restricted limits and set-points.
 = The maintenance of a constant internal environment Homeostasis involves maintaining the volume, chemical make up and other factors of blood and tissue fluid within restricted limits and set-points. The
= The maintenance of a constant internal environment Homeostasis involves maintaining the volume, chemical make up and other factors of blood and tissue fluid within restricted limits and set-points. The
Science Olympiad Heredity
 Science Olympiad Heredity Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A Punnett square shows you all the ways in which can combine. a.
Science Olympiad Heredity Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A Punnett square shows you all the ways in which can combine. a.
Answer Acceptable answers Mark. Answer Acceptable answers Mark. Answer Acceptable answers Mark. accept: 3 : 1. Answer Acceptable answers Mark
 1a(i) answers must be in this order. dominant HH 1a(ii) 1a(iii) H h H HH Hh h Hh hh 1 mark for correct gametes 1 mark for correct offspring If incorrect gametes allow 1 mark for correct Punnett square
1a(i) answers must be in this order. dominant HH 1a(ii) 1a(iii) H h H HH Hh h Hh hh 1 mark for correct gametes 1 mark for correct offspring If incorrect gametes allow 1 mark for correct Punnett square
Body Systems Notes. Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive
 Body Systems Notes Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive Homeostasis: maintaining a balance. Examples: temperature,
Body Systems Notes Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive Homeostasis: maintaining a balance. Examples: temperature,
CADASIL is an inherited disorder caused by a dominant allele. CADASIL leads to weakening of blood vessels in the brain.
 REPRODUCTION PART II Q1. CADASIL is an inherited disorder caused by a dominant allele. CADASIL leads to weakening of blood vessels in the brain. The diagram shows the inheritance of CADASIL in one family.
REPRODUCTION PART II Q1. CADASIL is an inherited disorder caused by a dominant allele. CADASIL leads to weakening of blood vessels in the brain. The diagram shows the inheritance of CADASIL in one family.
Nervous System. Skeletal System. Muscular System. Reproductive System. Circulatory System. Endocrine System. Respiratory System. Integumentary System
 The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
Mendelian Genetics. Activity. Part I: Introduction. Instructions
 Activity Part I: Introduction Some of your traits are inherited and cannot be changed, while others can be influenced by the environment around you. There has been ongoing research in the causes of cancer.
Activity Part I: Introduction Some of your traits are inherited and cannot be changed, while others can be influenced by the environment around you. There has been ongoing research in the causes of cancer.
What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body.
 Excretion What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body. Excretion in Plants Plants produce very little waste products. Plants lose oxygen and water vapour through the stomata.
Excretion What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body. Excretion in Plants Plants produce very little waste products. Plants lose oxygen and water vapour through the stomata.
National Know that stem cells in animals are cells which can divide.
 National 5 Biology Multicellular Organisms Unit Success Criteria Success Criteria Multicellular Organisms National 5 Colour the box at the side of each objective: RED I don t know much about this or am
National 5 Biology Multicellular Organisms Unit Success Criteria Success Criteria Multicellular Organisms National 5 Colour the box at the side of each objective: RED I don t know much about this or am
London Examinations IGCSE
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference 4 4 3 7 4 H Surname Signature Paper Reference(s) 4437/4H London Examinations IGCSE Science (Double Award) Biology Paper 4H Higher Tier Wednesday 17 November 2010
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference 4 4 3 7 4 H Surname Signature Paper Reference(s) 4437/4H London Examinations IGCSE Science (Double Award) Biology Paper 4H Higher Tier Wednesday 17 November 2010
Department of Science Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones
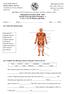 Department of Science 2018-2019 Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones Grade 4... Name:... Date:.../.../2019 Q.1 Label each muscle group. neck muscles shoulder muscles thigh
Department of Science 2018-2019 Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones Grade 4... Name:... Date:.../.../2019 Q.1 Label each muscle group. neck muscles shoulder muscles thigh
December 3, Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow?
 December 3, 2013 Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow? Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Chapter 36: Biology II The Skeleton
December 3, 2013 Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow? Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Chapter 36: Biology II The Skeleton
HOMEOSTASIS 37 C. ph of % blood sugar
 HOMEOSTASIS ph of 7.35 37 C 0.1% blood sugar Homeostasis an equilibrium (steady state) between an organism s various physiological functions, and between the organism and the environment. This is a balance
HOMEOSTASIS ph of 7.35 37 C 0.1% blood sugar Homeostasis an equilibrium (steady state) between an organism s various physiological functions, and between the organism and the environment. This is a balance
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin. KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body.
 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS WHAT MOVES YOU!
 SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS WHAT MOVES YOU! WHAT ARE THE MAIN FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM? THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeletal system is the organ system that supports and protects the body and allows
SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS WHAT MOVES YOU! WHAT ARE THE MAIN FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM? THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeletal system is the organ system that supports and protects the body and allows
Chapter 6 Heredity The Big Idea Heredity is the passing of the instructions for traits from one generation to the next.
 Chapter 6 Heredity The Big Idea Heredity is the passing of the instructions for traits from one generation to the next. Section 1 Mendel and His Peas Key Concept The work of Gregor Mendel explains the
Chapter 6 Heredity The Big Idea Heredity is the passing of the instructions for traits from one generation to the next. Section 1 Mendel and His Peas Key Concept The work of Gregor Mendel explains the
ANSWERS AND MARK SCHEMES. (a) excretion; 1. kidneys; 2. (c) (i) respiration; 1. (ii) lungs; 1. (iii) kidney; 1. kidney; lungs; 2
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 excretion; 1 skin; kidneys; 2 (i) respiration; 1 (ii) lungs; 1 (d) (iii) kidney; 1 2 of: skin; kidney; lungs; 2 QUESTIONSHEET 2 2500 cm 3 ; 1 1550 cm 3 ; 1 500 x 100; 1 2500 = 20%; 1 (d)
QUESTIONSHEET 1 excretion; 1 skin; kidneys; 2 (i) respiration; 1 (ii) lungs; 1 (d) (iii) kidney; 1 2 of: skin; kidney; lungs; 2 QUESTIONSHEET 2 2500 cm 3 ; 1 1550 cm 3 ; 1 500 x 100; 1 2500 = 20%; 1 (d)
Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems
 Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems 1. The locomotor system 2. The skeletal system 2.1. The human skeleton 2.2. Bones 2.3. Joints 2.4. Tendons and ligaments 3. The muscular system 3.1. Muscles of the
Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems 1. The locomotor system 2. The skeletal system 2.1. The human skeleton 2.2. Bones 2.3. Joints 2.4. Tendons and ligaments 3. The muscular system 3.1. Muscles of the
Genetics. by their offspring. The study of the inheritance of traits is called.
 Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a part of DNA, which has enough bases to make for many different proteins. These specific proteins made by a gene decide the of an
Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a part of DNA, which has enough bases to make for many different proteins. These specific proteins made by a gene decide the of an
4-5 Homeostasis and response Biology
 4-5 Homeostasis and response Biology.0 Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose (sugar) concentration may rise more than normal.. Which organ in the body monitors this rise in blood sugar? Tick one
4-5 Homeostasis and response Biology.0 Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose (sugar) concentration may rise more than normal.. Which organ in the body monitors this rise in blood sugar? Tick one
(2) A response is caused when information in the nervous system reaches an effector. the two different types of effector
 NERVOUS SYSTEM. NAME.. Q.This question is about the nervous system. (a) Describe the function of receptors in the skin. A response is caused when information in the nervous system reaches an effector.
NERVOUS SYSTEM. NAME.. Q.This question is about the nervous system. (a) Describe the function of receptors in the skin. A response is caused when information in the nervous system reaches an effector.
MCAS Biology: Human Systems Review
 MCAS Biology: Human Systems Review This booklet is designed to introduce or review the human biology concepts tested on the MCAS exam. Since this unit comes at the end of the year, it is often a rushed
MCAS Biology: Human Systems Review This booklet is designed to introduce or review the human biology concepts tested on the MCAS exam. Since this unit comes at the end of the year, it is often a rushed
New GCSE 4461/01 SCIENCE A FOUNDATION TIER BIOLOGY 1
 Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number New GCSE 4461/01 SCIENCE A FOUNDATION TIER BIOLOGY 1 ADDITIONAL MATERIALS A.M. THURSDAY, 12 January 2012 1 hour In addition to this paper you may require
Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number New GCSE 4461/01 SCIENCE A FOUNDATION TIER BIOLOGY 1 ADDITIONAL MATERIALS A.M. THURSDAY, 12 January 2012 1 hour In addition to this paper you may require
Cells. Dissolved substances pass into and out of cells by diffusion. Water passes into and out of cells by osmosis.
 Biology Cells All animals and plants are made of cells. Animal cells and plant cells have features in common, such as nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, mitochondria and ribosomes. Plant cells also have
Biology Cells All animals and plants are made of cells. Animal cells and plant cells have features in common, such as nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, mitochondria and ribosomes. Plant cells also have
Chapter 32 Excretion
 Chapter 32 Excretion 3.4 Learning Objectives 3.4.6 The Excretory System in Humans 1. Role of the excretory system in homeostasis. 2. Importance of temperature regulation within the body. 3. Outline the
Chapter 32 Excretion 3.4 Learning Objectives 3.4.6 The Excretory System in Humans 1. Role of the excretory system in homeostasis. 2. Importance of temperature regulation within the body. 3. Outline the
Karen Storey. Multiple Choice: Draw a Complete Circle around the ONE BEST answer.
 Human Body Systems Test Review Karen Storey 7th Grade Science Multiple Choice: Draw a Complete Circle around the ONE BEST answer. 1. Which organ system makes blood cells? a. nervous system b. circulatory
Human Body Systems Test Review Karen Storey 7th Grade Science Multiple Choice: Draw a Complete Circle around the ONE BEST answer. 1. Which organ system makes blood cells? a. nervous system b. circulatory
Homeostasis and Osmoregulation
 Homeostasis and Osmoregulation Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Homeostasis refers to the relatively stable state inside the body of an animal. Animal organs and organ systems constantly adjust to internal and external
Homeostasis and Osmoregulation Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Homeostasis refers to the relatively stable state inside the body of an animal. Animal organs and organ systems constantly adjust to internal and external
In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions
 16 Support System: Bones, Joints and Muscles l a b o r at o ry In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions of the skeletal and muscular systems in supporting and moving your
16 Support System: Bones, Joints and Muscles l a b o r at o ry In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions of the skeletal and muscular systems in supporting and moving your
SECTION 45-1 REVIEW. VOCABULARY REVIEW Describe the functions of the tissues listed below.
 SECTION 45-1 REVIEW THE HUMAN BODY PLAN VOCABULARY REVIEW Describe the functions of the tissues listed below. 1. nervous tissue 2. muscular tissue 3. skeletal muscle 4. epithelial tissue 5. connective
SECTION 45-1 REVIEW THE HUMAN BODY PLAN VOCABULARY REVIEW Describe the functions of the tissues listed below. 1. nervous tissue 2. muscular tissue 3. skeletal muscle 4. epithelial tissue 5. connective
Department of Science Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones
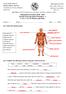 Department of Science 2018-2019 Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones Grade 4... Name:... Date:.../.../2019 Q.1 Label each muscle group. neck muscles shoulder muscles thigh
Department of Science 2018-2019 Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones Grade 4... Name:... Date:.../.../2019 Q.1 Label each muscle group. neck muscles shoulder muscles thigh
YR10. IGCSE Biology. Homeostasis
 YR10 IGCSE Biology Homeostasis Name: Prepared by William Green DBGS 2010 Homeostasis Body cells work best if they have the correct conditions e.g. 1. 2. 3. Write the definition of Homeostasis in the box
YR10 IGCSE Biology Homeostasis Name: Prepared by William Green DBGS 2010 Homeostasis Body cells work best if they have the correct conditions e.g. 1. 2. 3. Write the definition of Homeostasis in the box
1. understand that the internal skeleton of vertebrates is needed for support and movement
 B7.1 Peak performance movement and exercise 1. understand that the internal skeleton of vertebrates is needed for support and movement 2. understand that muscles can only move bones at a joint by contraction,
B7.1 Peak performance movement and exercise 1. understand that the internal skeleton of vertebrates is needed for support and movement 2. understand that muscles can only move bones at a joint by contraction,
Biology Notes. Homeostasis
 Biology Notes Homeostasis Homeostasis is defined as the maintenance of constant internal conditions within organisms. The principle can be developed in a wide range of contexts, including the maintenance
Biology Notes Homeostasis Homeostasis is defined as the maintenance of constant internal conditions within organisms. The principle can be developed in a wide range of contexts, including the maintenance
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *8889282829* BIOLOGY 0610/22 Paper 2 Core May/June 2013 Candidates answer on the Question Paper.
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *8889282829* BIOLOGY 0610/22 Paper 2 Core May/June 2013 Candidates answer on the Question Paper.
Genetics. the of an organism. The traits of that organism can then be passed on to, on
 Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a segment of DNA, which consists of enough bases to code for many different proteins. The specific proteins produced by a gene determine
Genetics DNA contains the genetic code for the production of. A gene is a segment of DNA, which consists of enough bases to code for many different proteins. The specific proteins produced by a gene determine
Chapter 11 introduction to genetics 11.1 The work of Gregor mendel
 Chapter 11 introduction to genetics 11.1 The work of Gregor mendel What is inheritance? Two uses of the word inheritance Things that are passed down through generations Factors we get from our parents
Chapter 11 introduction to genetics 11.1 The work of Gregor mendel What is inheritance? Two uses of the word inheritance Things that are passed down through generations Factors we get from our parents
Human Biology Unit: 4HB0 Paper: 01
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel IGCSE Centre Number Human Biology Unit: 4HB0 Paper: 01 Candidate Number Monday 9 May 2011 Afternoon Time: 2 hours You must have: Ruler Candidates may use
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel IGCSE Centre Number Human Biology Unit: 4HB0 Paper: 01 Candidate Number Monday 9 May 2011 Afternoon Time: 2 hours You must have: Ruler Candidates may use
*Hierarchical Organization of Multicellular Organisms
 *Hierarchical Organization of Multicellular Organisms 7.L.1.3 - Summarize the hierarchical organization of multicellular organisms from cells to tissues to organs to systems to organisms. Table of Contents
*Hierarchical Organization of Multicellular Organisms 7.L.1.3 - Summarize the hierarchical organization of multicellular organisms from cells to tissues to organs to systems to organisms. Table of Contents
2017 Version. Key Question types NCEA Science 1.9 Genetic Variation AS 90948
 2017 Version Key Question types NCEA Science 1.9 Genetic Variation AS 90948 Linking DNA, Alleles and Chromosomes Chromosomes are made up of DNA. DNA is a large molecule that is coiled into a double helix
2017 Version Key Question types NCEA Science 1.9 Genetic Variation AS 90948 Linking DNA, Alleles and Chromosomes Chromosomes are made up of DNA. DNA is a large molecule that is coiled into a double helix
(a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. B... (2)
 1 The diagrams show an animal cell and a bacterial cell. (a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. Use words from the box to name structures A and B. cell membrane
1 The diagrams show an animal cell and a bacterial cell. (a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. Use words from the box to name structures A and B. cell membrane
