PAIN SYNDROMES
|
|
|
- Edmund Fitzgerald
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PAIN SYNDROMES 1) Fibromyalgia Syndrome Synonyms Fibromyalgia is a diffuse idiopathic musculoskeletal pain syndrome. Fibromyalgia is a disease causing widespread musculoskeletal pain, tender areas in soft tissues (muscles and tendons), and severe fatigue. Fibromyalgia occurs mainly in adults. It occurs rarely in children, predominatly in adolescents. Females are more frequently affected than males. Children with this disease share many characteristics with children suffering from localized idiopathic musculoskeletal pain syndrome. What are the typical clinical characteristics? The patients complain of wide-soread pain in deep tissue. The severity of the pain is subjective. The pain occurs in both sides of the body, and in the upper and lower extremities. Patients find it difficult to sleep and patients feel unrefreshing when they wake up. Another main complaint is severe fatigue, accompanyed by the decrease of physical capacities. Patients with the disease frequently report generalized complaints, such as headaches, a sense of swelling of the limbs (not present), and numbness. These symptoms cause anxiety, depression, and these patients tend to miss a lot of school. Diagnosis is made when there is a history of generalized aching in four body areas, lasting more than three months and when a physical examination reveals pain in 11 out of 18 tender points. Tender points are clinically measurable by thumb pressure, which is equally as reliable as the dolorimeter, a special tool that measures the pain. What is the treatment? It is important to address is the anxiety produced by the disease. This needs to be eleviated by explaining to the patient and family that, although the pain is severe and real, there is no damage to the joints, nor a serious physical disease. is done by a multidisciplinary team approach (specialists in different areas working together), and is based on treating three areas. 1
2 The most important one is to initiate a progressive cardiovascular fitness training program, the best exercise being swimming. The second step is to start a cognitive behavioral therapy, individually or in a group. Finally, some patients may need to begin a drug therapy course, aimed to restore sleep. The use of a special pillow that maintains neck support during sleep may also be of help. Prognosis It is not easy to recover from the disease, requiring a major effort by the patient and essential support from the family. Generally, the outcome in children is much better than in adults and most will recover fully. Compliance with the regular physical exercise program is the most important factor in recovery. 2) Localized Idiopathic Musculoskeletal Pain Syndrome Synonyms Reflex Sympathetic Distrophy of the Complex Regional Pain Syndrome type. This is a disease consisting of extremely severe limb pain with no obvious clinical cause. It is frequently associated with skin changes. There is no reliable data on the frequency of this disease. It is known, however, that it is more common in adolescents (the average age of onset is around 12 years of age), and in girls. Usually there is a long lasting history of very severe limb pain that increases over time and is unresponsive to different therapies. It can results in a loss of use in the affected limb. The patient will suffer pain from the lightest of touch, called allodynia. The combination of these symptoms will affect the daily activities of affected children, who usually miss a lot of school. Some children will develop changes in skin color (pallid or purple mottled appearance), changes in temperature (usually reduced), or perspiration. Sometimes the child will hold the limb in an unusual posture, refusing to move it. Until a few years ago these syndromes received different names. Considering that most are of unknown origin and that their therapy is the same, the current trend is to put them under the same umbrella as localized musculoskeletal pain syndromes. A set of criteria is used for the diagnosis of this set of diseases. The diagnosis is clinical, based on the type of pain (severe, prolonged, limiting activity, unresponsive to therapy and the presence of allodynia) and the findings of a physical examination. The diagnosis also requires that other diseases b ruled out. Most of the time these diseases have been discarded before the patient sees a pediatric rheumatologist. Laboratory studies are normal. 2
3 The approach that works the best is the initiation of a substantial therapeutic physical exercise program, supervised by physical and occupational therapists, sometime with psychotherapy. Psychological intervention is usually necessary because of the stress produced by the disease. Treatment is hard for everyone involved, the children, the family and the medical team. Lots of different kinds of treatments, alone or in combination (antidepressants, biofeedback, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, behavioural modification) have been proposed without definite results. Prognosis This disease has a better prognosis in children than in adults. Almost all children eventually will recover Every day life Children should be encouraged to maintain a normal level of activity. Attending school regulary and socializing with their peers. 3) Erythromelalgia It is also known as Erythermalgia. It is extremely uncommon, although it may run in families. Most children are around 10 years of age when they present with the disease. It is more frequent in girls. The disease is characterized by burning sensation with warm, red and swollen feet or, less commonly, hands. The symptoms worsen upon exposure to heat and are relieved by cooling the extremity, to the point that some children refuse to remove their feet from ice water. The course is unrelenting. Avoiding heat and vigorous exercise seem the most useful therapeutical measures. The disease in children does not usually respond to nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs, which have proved useful in adults. Vasodilators may help. 4) Growing Pains Growing pains is a benign syndrome that refers to a characteristic pattern of pain in the limbs, which usually occurs in children younger than 10 years of age. Pains in the limbs are among the leading causes for seeking specialist care in pediatrics. Among them growing pains are the most common % of children worldwide experience growing pains, mainly between the ages 3-12 years. Boys and girls are similarly affected. The pain appears mostly in the legs (skins, calves, behind the knees or thighs), and is usually bilateral. The pain appears late in the day or at night, often awakening the child. 3
4 Parents commonly report that chidren develop the pain on days of increased physical activity. The duration of the pain is usually between 10 and 30 minutes, although it might range from minutes to hours. Its intensity can be mild or very severe. Growing pains are intermittent, with pain-free intervals from days to months. In some cases the pain can occur daily. The characteristic pain manifestations combined with a normal physical examination lead to diagnosis. There is no need to perform laboratory tests and X rays studies, which are all normal. What is the treatment? Explaining the benign nature of the process reduces the anxiety in the child and the family. During pain episodes local massage and mild analgesics may help. In children with frequent episodes an evening dose of ibuprofen might diminishe or prevent the pain. Prognosis Growing pains are not associated with any serious organic disease, and usually resolve by late childhood. In 100% of children the pain disappears as they grow older. 5) Benign Hypermobility Syndrome Benign Hypermobility Syndrome (BHS) refers to pain in the extremities due to an increased mobility (range of motion) of the joints, without any associated congenital or conective tissue disease. Therefore, BHS is not a disease but rather a normal finding. BHS is extremely common in children, having being reported in 25 to 50% of those younger than 10 years of age. Its frequency decreases with age. BHS frequently runs in families. Hypermobility frequently results in intermittent, deep aching, recurrent pains at the end of the day or at night in the knees, feet and/or ankles. In children playing piano, violin, etc. it might affect the fingers instead. Physical activity and exercise trigger or increase the pain. Rarely mild joint swelling may be present. On the basis of a predefined set of criteria that quantify joint hypermobility. 4
5 Treatment is very seldom necessary. If the child plays certain repetitive impact sports such as football or gymnastics, and develops recurrent sprains / torn joints, muscle strengthening and joint protection (functional braces) should be used. Every day life Hypermobility is a benign condition that decreases with age. Families should be aware that its main risk comes from preventing children to live normal lives. Children should be encouraged to maintain a normal level of activity, including playing any sports they are interested in. 6) Transient Synovitis Toxic synovitis, Irritable hip. Effusion of the hip joint of unknown cause that resolves by itself leaving no damage. It is the most common cause of hip pain in children. It affects 2 to 3% of children aged 3-10 years of age. It is more common in boys, to the extent that for each girl, there are three or four boys affected. Hip pain and a limp. Hip pain may be present as pain in the groin, upper thigh, or occasionally, in the knee. The pain usually comes on suddenly. The most common first sign is a child who awakens with a limp or who refuses to walk. A physical examination will reveal a limp with decreased and painful hip motion. In 5% of the cases both hips are affected. X-rays are normal, so are usually not performed. The basis of treatment is rest, which should be proportionate to the degree of pain. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, are of help to decrease pain. In very severe episodes, traction of the leg may be used. The condition usually resolves without therapy after an average of six to eight days Prognosis (predicted outcome and course of the disease) Full recovery is achieved in more than 99% of children. It is not uncommon to develop subsequent episodes of transient synovitis, usually milder and shorter than the first. 7) Patellofemoral Pain - Knee pain Introduction Patellofemoral pain is the most common pediatric Overuse Syndrome. This group of disorders result from repetitive motion or sustained exercise-related injury to a particular part of the body. 5
6 These disorders are much more common in adults (tennis or golf elbow, carpal tunnel syndrome, etc) than in children. Synonyms Patellofemoral Syndrome, Chondromalacia of the patella, Chondromalacia, Anterior knee pain. Patellofemoral pain refers to the development of anterior knee pain from activities that place additional load over the patellofemoral joint (joint formed by the knee cap and the lower part of the thigh bone or femur). When the pain is accompanied by changes in the inner-looking surface tissue (cartilage) of the patella the term chondromalacia of patella or chondromalacia patellae is used. It is very uncommon in children younger than eight years of age, becoming progressively more common in adolescents. Patellofemoral pain is more common in girls. It can also be more common in children with a significant angulation of the knees such as knock-knees, or bow legs, as well as in those with a disease of the knee cap (recurrent instability and malalignment). The characteristic symptoms are anterior knee pain that worsens with activities such as running, climbing up or down stairs, squatting, or jumping. Pain is also worsened by prolonged sitting with the knee bent. Patellofemoral pain in healthy children is diagnoses from a clinical examination. Lab tests and imaging studies are not necessary. Pain may be reproduced by compression of the knee cap, or by restraining the upward movement of the knee cap when the thigh muscle is contracted. Usually, therapy is not needed, in most children with no associated diseases. It is a benign condition that resolves by itself. If the pain interferes with sports, or daily activities, the initiation of a program to strengthen the thigh muscles may be of help. Ice may relieve pain after exercise. Every day life Children should lead a normal life, but their level of physical activity should be adjusted to keep them pain-free. Children very active in sports may use a knee sleeve with a knee cap strap. 8) Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis 6
7 Displacement of the femoral head (the part of the thigh bone closest to the hip) through the growth plate, with no known cause, such as an accident. The growth plate is a slide of cartilage sandwiched between bone tissue. This the weakest part of the bone and, once it has mineralized and becomes bone itself, the bones stop growing It is an uncommon disease that affects 3-10 in children. It is more frequent in adolescents and boys. Obesity seems to be a predisposing factor. Limp and hip pain that gets worse with physical activity, with decrease mobility of the hip. Pain may be felt in the upper (two thirds) or lower (one third) thigh, and increases with activity. In 15% of children, the disease affects both hips. It is diagnosed through assessment of the findings of a physical examination, with the presence of decreased hip mobility. The diagnosis is confirmed by x-ray. Surgical pinning, where the femoral head is stabilised by placing pins to keep it in place). Prognosis (predicted outcome and course of the disease) Depends on the length of time between the femoral head slipping and diagnosis and on the degree of slippage. 9) Osteochondroses (Synonyms Osteonechroses, Avascular necroses). Introduction The word Osteochondroses means bone death. It is a diverse group of diseases, the causes of which are unknown. Bones are mostly made of cartilage at birth, a softer tissue that is replaced over time by a more mineralized and resistant tissue, the bone. This replacement begins at specific sites within each bone, the so called ossification centers, spreading out to the rest of the bone over time. In these diseases there is an interruption of the blood flow to the primary or secondary ossification center of the affected bones. Osteochondrosis refers to the process associated with the loss of blood supply to the ossification center of the bones, and its replacement by reparative bone tissue. Pain is the main symptom of these disorders. Diagnosis is confirmed by imaging studies. X-rays show, in sequence fragmentation ( islands within the bone), collapse (break down), sclerosis (increased density, the bone looks whiter on the films) and reossification (new bone formation) with reconstitution of the bone contour. Although it sounds like a serious disease, it is quite common in children and, with the possible exception of extensive involvement of the hip, has an excellent prognosis. Some 7
8 forms of osteochondroses are so frequent that they are considered normal variants of bone development. Others may be included under the overuse syndromes. 9.1) Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease Avascular necrosis of the femoral head (the part of the thigh bone closest to the hip). It is not a common disease, seen in ine in 10,000 children. It is more frequent in boys (four or five boys for each girl) between the ages of three and 12 years, but particularly in children between four and nine years old. Most children present with a limp and variable degrees of hip pain, sometimes none. Usually only one hip is involved, but in about 10% of cases the disease affects both. The mobility of the hip is impaired and may be painful. X-rays may be normal at the beginning, but later show the progression stated in the introduction. Bone scans and Magnetic Resonance detect the disease earlier than plain films. Children with Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease should always be referred to a Pediatric Orthopedic Department. Treatment depends on the severity of the disease. In very mild cases observation may be sufficient. In more severe cases the therapy is aimed at keeping the affected femoral head within the hip joint, so that, when the formation of new bone starts, the femoral head recover its spherical form. This goal may be achieved, to variable degrees, by wearing an abduction brace, for younger children, or by surgically reshaping the femur (osteotomy, cutting a wedge of bone to keep the head in a better position), in older children. Prognosis (predicted outcome and course of the disease) It depends on how extensive the femoral head involvement is and on the age of the child. It is better if younger than six. The whole process (from fragmentation to regeneration) takes between 12 and 18months. Overall, about two thirds of hips have a good long-term radiographic result. Every day life Depends on the treatment applied. Children under observation should avoid heavy impact on the hip (jumping, running). However, they should carry an otherwise normal school life and participate in all other activities that do not involve heavy weigth-bearing. 9.2) Osgood-Schlatter Disease 8
9 It results from repeated trauma to the ossification center of the tibial tuberosity (small bone crest present in the upper leg). It is present in about 1% of adolescents, being more common in those who play sports. Pain worsens with activities such as running, jumping, going up or downstairs and kneeling. The diagnosis is established by physical examination, with tenderness or pain, sometimes accompanied by swelling at the insertion of the patellar (knee cap) tendon into the tibia. X-rays might be normal, or show small fragments of bone in the tibial tuberosity region. Treatment is based on adjusting their level of activity to keep them pain-free, applying ice after sports and rest. This disease resolves over time. 9.3) Sever s Disease It is also called Calcaneal Apophysitis. It is an osteochondrosis of the calcaneal apophysis (the heel bone), probably related to the traction delivered by the Achilles tendon. It is one of the most common causes of heel pain in children. Sever s disease is activityrelated and more common in males. Its onset is usually around six to 10 years of age, with heel pain and occasional limping after exercise. The diagnosis is made by clinical examination. There is no need for therapy other than to adjust the level of activity to keep the children pain-free and, if it does not work, to use a heel cushion. This disease resolves over time. 9.4) Freiberg s Disease This is osteonechrosis of the head of the second metatarsal bone in the foot (The bones in the middle of the foot). Its cause is probably traumatic. It is uncommon and most cases involve adolescent girls. The pain increases with activity. Physical exam shows tenderness under the second metatarsal head and occasionally swelling. The diagnosis is confirmed by X-rays, although it may take two weeks from the beginning of the symptoms to show changes. Treatment includes rest and a metatarsal pad. 9.5) Scheuermann s Disease Scheuermann s disease, or juvenile kyphosis (roundback), is an osteonechrosis of the ring apophysis of the vertebral body. It is most common in adolescent boys. Most children have poor posture, with or without back pain. When present, the pain is activity related and may be relieved by rest. Diagnosis is confirmed by x-ray. To be considered Scheuermann s disease the child has to have irregularities of the vertebral plates and anterior wedging of 5º in at least three consecutive vertebrae. Scheuermann s disease does not usually require other therapy than to adjust the level of activity of the child, observation. Severe cases may require a bracing, however. 9
Non-inflammatory joint pain
 Non-inflammatory joint pain Lawrence Owino Okong o, Mmed (UoN); Mphil. (UCT). Lecturer, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, University of Nairobi. Paediatrician/ Rheumatologist. INTRODUCTION Musculoskeletal
Non-inflammatory joint pain Lawrence Owino Okong o, Mmed (UoN); Mphil. (UCT). Lecturer, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, University of Nairobi. Paediatrician/ Rheumatologist. INTRODUCTION Musculoskeletal
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL)
 Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the 4 major ligament stabilizers of the knee. ACL tears are among the most common major knee injuries in active people of
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the 4 major ligament stabilizers of the knee. ACL tears are among the most common major knee injuries in active people of
A Patient s Guide to Osgood-Schlatter Lesion of the Knee
 A Patient s Guide to Osgood-Schlatter Lesion of the Knee Anatomy What part of the knee is affected? Introduction An Osgood-Schlatter lesion involves pain and swelling in the small bump of bone on the front
A Patient s Guide to Osgood-Schlatter Lesion of the Knee Anatomy What part of the knee is affected? Introduction An Osgood-Schlatter lesion involves pain and swelling in the small bump of bone on the front
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
 What is patellofemoral pain syndrome? Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome Patellofemoral pain syndrome is pain behind the kneecap. It has been given many names, including patellofemoral disorder, patellar malalignment,
What is patellofemoral pain syndrome? Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome Patellofemoral pain syndrome is pain behind the kneecap. It has been given many names, including patellofemoral disorder, patellar malalignment,
7/1/2012. Repetitive valgus stresses cause microfractures in the apophyseal cartilage (weak link) Common in year olds
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 When growing pains are not growing pains David W. Gray,M.D. Medical Director Orthopedics Differential Diagnosis Fracture Ligament Injury Disloclation Cartilage Injury Apophysitis Inflammation
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 When growing pains are not growing pains David W. Gray,M.D. Medical Director Orthopedics Differential Diagnosis Fracture Ligament Injury Disloclation Cartilage Injury Apophysitis Inflammation
A Patient s Guide to Limping in Children
 A Patient s Guide to Limping in Children 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Limping in Children 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
Jumper s Knee in Children and Adolescents
 A Patient s Guide to Jumper s Knee in Children and Adolescents 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Jumper s Knee in Children and Adolescents 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Juvenile Osteochondroses
 Juvenile Osteochondroses Nathalie Gaulier, MD Sports Medicine Physician Cook Children s Medical Center Definition General term for disorders that affect one or more ossification centers in children Encompasses
Juvenile Osteochondroses Nathalie Gaulier, MD Sports Medicine Physician Cook Children s Medical Center Definition General term for disorders that affect one or more ossification centers in children Encompasses
Running Injuries in Children and Adolescents
 Running Injuries in Children and Adolescents Cook Children s SPORTS Symposium July 2, 2014 Running Injuries Overuse injuries Acute injuries Anatomic conditions 1 Overuse Injuries Pain that cannot be tied
Running Injuries in Children and Adolescents Cook Children s SPORTS Symposium July 2, 2014 Running Injuries Overuse injuries Acute injuries Anatomic conditions 1 Overuse Injuries Pain that cannot be tied
Rehabilitation for Patellar Tendinitis (jumpers knee) and Patellofemoral Syndrome (chondromalacia patella)
 Rehabilitation for Patellar Tendinitis (jumpers knee) and Patellofemoral Syndrome (chondromalacia patella) Patellar Tendinitis The most common tendinitis about the knee is irritation of the patellar tendon.
Rehabilitation for Patellar Tendinitis (jumpers knee) and Patellofemoral Syndrome (chondromalacia patella) Patellar Tendinitis The most common tendinitis about the knee is irritation of the patellar tendon.
A Patient s Guide to Transient Synovitis of the Hip in Children
 A Patient s Guide to Transient Synovitis of the Hip in Children 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
A Patient s Guide to Transient Synovitis of the Hip in Children 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
(Also known as a, Lateral Cartilage Tear,, Bucket Handle Tear of the Lateral Meniscus, Torn Cartilage)
 Lateral Meniscus Tear (Also known as a, Lateral Cartilage Tear,, Bucket Handle Tear of the Lateral Meniscus, Torn Cartilage) What is a lateral meniscus tear? The knee joint comprises of the union of two
Lateral Meniscus Tear (Also known as a, Lateral Cartilage Tear,, Bucket Handle Tear of the Lateral Meniscus, Torn Cartilage) What is a lateral meniscus tear? The knee joint comprises of the union of two
ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN. Explanation. Causes. Symptoms
 ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN Explanation Anterior knee pain is most commonly caused by irritation and inflammation of the patellofemoral joint of the knee (where the patella/kneecap connects to the femur/thigh bone).
ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN Explanation Anterior knee pain is most commonly caused by irritation and inflammation of the patellofemoral joint of the knee (where the patella/kneecap connects to the femur/thigh bone).
Knee Pain. Pain in the pressure on. the kneecap. well as being supported (retinaculum) quadricep. Abnormal. to the knee. or dislocate.
 Knee Pain in Children and Adolescents Description Pain in the knee can occur from various causess but is usually from increased pressure on the kneecap (patella) or abnormal motion. Softening of the cartilage
Knee Pain in Children and Adolescents Description Pain in the knee can occur from various causess but is usually from increased pressure on the kneecap (patella) or abnormal motion. Softening of the cartilage
Hip Pain. Anatomy of the hip
 Hip Pain Anatomy of the hip The hip is a ball and socket joint, the ball is on the head of femur (the top of the thigh bone) and the socket (acetabulum) is a part of the pelvis. It s surrounded by tendons
Hip Pain Anatomy of the hip The hip is a ball and socket joint, the ball is on the head of femur (the top of the thigh bone) and the socket (acetabulum) is a part of the pelvis. It s surrounded by tendons
Patellofemoral Osteoarthritis
 Patellofemoral Osteoarthritis Arthritis of the patellofemoral joint refers to degeneration (wearing out) of the cartilage on the underside of the patella (kneecap) and the trochlea (groove) of the femur.
Patellofemoral Osteoarthritis Arthritis of the patellofemoral joint refers to degeneration (wearing out) of the cartilage on the underside of the patella (kneecap) and the trochlea (groove) of the femur.
Joint involment in orthopedic diseases
 Joint involment in orthopedic diseases PReS Latin America Basic Pediatric Rheumatology Course 2015 Aguas de São Pedro, São Paulo, Brazil Carmen L. De Cunto carmen.decunto@hospitalitaliano.org.ar Sección
Joint involment in orthopedic diseases PReS Latin America Basic Pediatric Rheumatology Course 2015 Aguas de São Pedro, São Paulo, Brazil Carmen L. De Cunto carmen.decunto@hospitalitaliano.org.ar Sección
Patella Instability in Children and Adolescents
 Patella Instability in Children and Adolescents Description Patella Instability is an injury to the kneecap (patella) affecting the joint it forms with the thigh bone (femur) Patella Instability can occur
Patella Instability in Children and Adolescents Description Patella Instability is an injury to the kneecap (patella) affecting the joint it forms with the thigh bone (femur) Patella Instability can occur
What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis?
 Shoulder Tendinitis, Bursitis, and Impingement Syndrome What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis? Two types of tendinitis can affect the shoulder. Biceps tendinitis causes pain in the front or side of the shoulder.
Shoulder Tendinitis, Bursitis, and Impingement Syndrome What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis? Two types of tendinitis can affect the shoulder. Biceps tendinitis causes pain in the front or side of the shoulder.
Servers Disease (Calcaneal Apophysitis ) 101
 Servers Disease (Calcaneal Apophysitis ) 101 Servers Disease Causes a disturbance to the growing area at the back of the heel bone (calcaneus) where the strong Achilles tendon attaches to it. It is most
Servers Disease (Calcaneal Apophysitis ) 101 Servers Disease Causes a disturbance to the growing area at the back of the heel bone (calcaneus) where the strong Achilles tendon attaches to it. It is most
Common Apophyseal Problems in the Athlete
 Disclosure Common Apophyseal Problems in the Athlete Mark Halstead, MD November 19, 2009 Faculty Disclosure Information In the past 12 months, I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturer
Disclosure Common Apophyseal Problems in the Athlete Mark Halstead, MD November 19, 2009 Faculty Disclosure Information In the past 12 months, I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturer
ARTHRITIS. What Is Arthritis?
 There are many types of arthritic processes that can cause joint changes, pain and loss of motion and strength in the hands. Many excellent and detailed resources are available and will be listed under
There are many types of arthritic processes that can cause joint changes, pain and loss of motion and strength in the hands. Many excellent and detailed resources are available and will be listed under
Anterior knee pain.
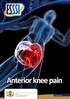 Anterior knee pain What are the symptoms? Anterior knee pain is very common amongst active adolescents and athletes participating in contact sports. It is one of the most common problems/injuries seen
Anterior knee pain What are the symptoms? Anterior knee pain is very common amongst active adolescents and athletes participating in contact sports. It is one of the most common problems/injuries seen
Bursitis. Other joints are found between the different bones of your fingers and toes. You also have joints that allow your vertebrae to move.
 Bursitis Introduction Bursitis is a common condition that causes swelling around muscles and bones. It happens most often in the shoulder, elbow, hip, or knee. Bursitis is usually caused by overusing a
Bursitis Introduction Bursitis is a common condition that causes swelling around muscles and bones. It happens most often in the shoulder, elbow, hip, or knee. Bursitis is usually caused by overusing a
Current Thinking of the Osteochondroses. Diego Jaramillo, M.D., M.P.H. Department of Radiology Stanford Children s Hospital
 Current Thinking of the Osteochondroses Diego Jaramillo, M.D., M.P.H. Department of Radiology Stanford Children s Hospital What is an osteochondrosis? Abnormal endochondral ossification and epiphyseal
Current Thinking of the Osteochondroses Diego Jaramillo, M.D., M.P.H. Department of Radiology Stanford Children s Hospital What is an osteochondrosis? Abnormal endochondral ossification and epiphyseal
Introduction. Anatomy
 the patella is called the quadriceps mechanism. Though we think of it as a single device, the quadriceps mechanism has two separate tendons, the quadriceps tendon on top of the patella and the patellar
the patella is called the quadriceps mechanism. Though we think of it as a single device, the quadriceps mechanism has two separate tendons, the quadriceps tendon on top of the patella and the patellar
Copyright Vanderbilt Sports Medicine. Table of Contents. The Knee Cap and Knee Joint...2. What is Patellofemoral Pain?...4
 Table of Contents The Knee Cap and Knee Joint...2 What is Patellofemoral Pain?....4 What to Expect From a Medical Evaluation....6 What to Expect After Therapy....7 1 The Kneecap and Knee Joint The knee
Table of Contents The Knee Cap and Knee Joint...2 What is Patellofemoral Pain?....4 What to Expect From a Medical Evaluation....6 What to Expect After Therapy....7 1 The Kneecap and Knee Joint The knee
tibial tubercle of the to 19 Compared pulling on inferior pole patella Cause subsequent pain The injury knee that is
 Osgood-Schlatter Disease Description Osgood Schlatter disease is an inflammatory injury of the growth plate on the tibia (shin bone) just below the level of the knee at the tibial tubercle This disease
Osgood-Schlatter Disease Description Osgood Schlatter disease is an inflammatory injury of the growth plate on the tibia (shin bone) just below the level of the knee at the tibial tubercle This disease
Osteoarthritis of the Hip
 Osteoarthritis of the Hip Sometimes called "wear-and-tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is a common condition that many people develop during middle age or older. Osteoarthritis of the hip causes pain and
Osteoarthritis of the Hip Sometimes called "wear-and-tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is a common condition that many people develop during middle age or older. Osteoarthritis of the hip causes pain and
Anterior Knee Pain in Children. Joseph Chorley, MD Associate Professor, Pediatrics Baylor College of Medicine
 Anterior Knee Pain in Children Joseph Chorley, MD Associate Professor, Pediatrics Baylor College of Medicine Goals and Objectives To learn how to care for patients with chronic knee pain To be able to
Anterior Knee Pain in Children Joseph Chorley, MD Associate Professor, Pediatrics Baylor College of Medicine Goals and Objectives To learn how to care for patients with chronic knee pain To be able to
The Child With a Limp
 KID WITH A LIMP Common in ED, common in Exams Differential diagnosis is very wide Most causes benign, but mustn't miss Septic arthritis Osteomyelitis Fractures / NAI SUFE (older, heavier children) The
KID WITH A LIMP Common in ED, common in Exams Differential diagnosis is very wide Most causes benign, but mustn't miss Septic arthritis Osteomyelitis Fractures / NAI SUFE (older, heavier children) The
Apply this knowledge into proper management strategies and referrals
 1 2 3 Lower Extremity Injuries Jason Kennedy, M.D. Disclosures I have no financial/ industry disclosures. Objectives Identify common lower extremity injury patterns in the child and adolescent Apply this
1 2 3 Lower Extremity Injuries Jason Kennedy, M.D. Disclosures I have no financial/ industry disclosures. Objectives Identify common lower extremity injury patterns in the child and adolescent Apply this
Patellar Instability. OrthoInfo Patella Instability Page 1 of 5
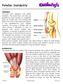 Patellar Instability OVERVIEW You have been diagnosed with patella instability. This means that your knee cap (patella) has been partially or completely going out of place and is not tracking well against
Patellar Instability OVERVIEW You have been diagnosed with patella instability. This means that your knee cap (patella) has been partially or completely going out of place and is not tracking well against
ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT INJURY
 ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT INJURY WHAT IS THE ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT? The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of four major ligaments that stabilizes the knee joint. A ligament is a tough band
ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT INJURY WHAT IS THE ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT? The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of four major ligaments that stabilizes the knee joint. A ligament is a tough band
Learning Objectives. Epidemiology 7/22/2016. What are the Medical Concerns for the Adolescent Female Athlete? Krystle Farmer, MD July 21, 2016
 What are the Medical Concerns for the Adolescent Female Athlete? Krystle Farmer, MD July 21, 2016 Learning Objectives Discuss why females are different than males in sports- the historical perspective.
What are the Medical Concerns for the Adolescent Female Athlete? Krystle Farmer, MD July 21, 2016 Learning Objectives Discuss why females are different than males in sports- the historical perspective.
Orthopedics. 1. GOAL: Understand the pediatrician's role in preventing and screening for
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Orthopedics 1. GOAL: Understand the pediatrician's role in preventing and screening for orthopedic injury, disease and dysfunction.
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Orthopedics 1. GOAL: Understand the pediatrician's role in preventing and screening for orthopedic injury, disease and dysfunction.
Achilles Tendonitis and Tears
 Achilles Tendonitis and Tears The Achilles tendon is an important structure for normal ankle motion and normal function, even for daily activities such as walking. Achilles tendonitis can occur in patients
Achilles Tendonitis and Tears The Achilles tendon is an important structure for normal ankle motion and normal function, even for daily activities such as walking. Achilles tendonitis can occur in patients
DISCOID MENISCUS. Description
 DISCOID MENISCUS Description For participation in jumping (basketball, volleyball) or The meniscus is a cartilage structure in the knee that sits on contact sports, protect the knee joint with supportive
DISCOID MENISCUS Description For participation in jumping (basketball, volleyball) or The meniscus is a cartilage structure in the knee that sits on contact sports, protect the knee joint with supportive
ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN. Expected Outcome. Causes
 Montefiore Pediatric Orthopedic and Scoliosis Center Children s Hospital at Montefiore Norman Otsuka MD Eric Fornari MD Jacob Schulz MD Jaime Gomez MD Christine Moloney PA 3400 Bainbridge Avenue, 6 th
Montefiore Pediatric Orthopedic and Scoliosis Center Children s Hospital at Montefiore Norman Otsuka MD Eric Fornari MD Jacob Schulz MD Jaime Gomez MD Christine Moloney PA 3400 Bainbridge Avenue, 6 th
Other Culprits in Knee Dysfunction
 Unraveling the Mystery of Knee Pain #6: Other Culprits in Knee Dysfunction 1 Webinar Goals Explore the assessment and treatment of other culprits in knee dysfunction. 2 Time: 60 minutes Schedule: Logistics
Unraveling the Mystery of Knee Pain #6: Other Culprits in Knee Dysfunction 1 Webinar Goals Explore the assessment and treatment of other culprits in knee dysfunction. 2 Time: 60 minutes Schedule: Logistics
An understanding of the components of the normal gait cycle will aid in describing abnormalities of gait.
 Approach to the Child with a Limp: Student writer: Brian Mayson Resident editor: Elmine Statham Background The child with a limp is a common problem seen in pediatrics. A limp is defined as any deviation
Approach to the Child with a Limp: Student writer: Brian Mayson Resident editor: Elmine Statham Background The child with a limp is a common problem seen in pediatrics. A limp is defined as any deviation
Spondylolisthesis DESCRIPTION EXPECTED OUTCOME POSSIBLE COMPLICATIONS COMMON SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS GENERAL TREATMENT CONSIDERATIONS CAUSES
 DESCRIPTION is the slippage of one or more vertebrae, the bones of the spine. Many causes of slippage of the vertebra are possible; these include stress fracture (spondylolysis), which is often seen in
DESCRIPTION is the slippage of one or more vertebrae, the bones of the spine. Many causes of slippage of the vertebra are possible; these include stress fracture (spondylolysis), which is often seen in
Spondylolysis DESCRIPTION EXPECTED OUTCOME POSSIBLE COMPLICATIONS COMMON SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS GENERAL TREATMENT CONSIDERATIONS CAUSES
 DESCRIPTION is a stress or fatigue fracture of the bones of the spine (vertebrae) that does not involve the main weight-bearing part of those bones, the body of the vertebra. Instead, it involves an area
DESCRIPTION is a stress or fatigue fracture of the bones of the spine (vertebrae) that does not involve the main weight-bearing part of those bones, the body of the vertebra. Instead, it involves an area
PAIN. Headache. enstrual Pain. Low Back Pain. Osteoarthritis. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Sprains and Strains. Taking Care of. Pain of
 Low Back Pain Sprains and Strains Taking Care of PAIN TIPS FOR UNDERSTANDING, AVOIDING, AND CARING FOR COMMON TYPES OF PAIN Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain of Osteoarthritis enstrual Pain Headache BROUGHT
Low Back Pain Sprains and Strains Taking Care of PAIN TIPS FOR UNDERSTANDING, AVOIDING, AND CARING FOR COMMON TYPES OF PAIN Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain of Osteoarthritis enstrual Pain Headache BROUGHT
MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg)
 MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg) Description Expected Outcome Medial head gastrocnemius tear is a strain of the inner part (medial head) of the major calf muscle (gastrocnemius muscle). Muscle
MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg) Description Expected Outcome Medial head gastrocnemius tear is a strain of the inner part (medial head) of the major calf muscle (gastrocnemius muscle). Muscle
.org. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. Anatomy. Cause. Symptoms
 Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
DISCOID MENISCUS. Description
 Montefiore Pediatric Orthopedic and Scoliosis Center Children s Hospital at Montefiore Norman Otsuka MD Eric Fornari MD Jacob Schulz MD Jaime Gomez MD Christine Moloney PA 3400 Bainbridge Avenue, 6 th
Montefiore Pediatric Orthopedic and Scoliosis Center Children s Hospital at Montefiore Norman Otsuka MD Eric Fornari MD Jacob Schulz MD Jaime Gomez MD Christine Moloney PA 3400 Bainbridge Avenue, 6 th
BATES VISUAL GUIDE TO PHYSICAL EXAMINATION. OSCE 4: Knee Pain
 BATES VISUAL GUIDE TO PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OSCE 4: Knee Pain This video format is designed to help you prepare for objective structured clinical examinations, or OSCEs. You are going to observe and participate
BATES VISUAL GUIDE TO PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OSCE 4: Knee Pain This video format is designed to help you prepare for objective structured clinical examinations, or OSCEs. You are going to observe and participate
PHASE ONE: THE FIRST SIX WEEKS AFTER INJURY
 Exercises After Injury to the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) of the Knee Dr. Abigail R. Hamilton, M.D. PHASE ONE: THE FIRST SIX WEEKS AFTER INJURY Initially, the knee needs to be protected-use the knee
Exercises After Injury to the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) of the Knee Dr. Abigail R. Hamilton, M.D. PHASE ONE: THE FIRST SIX WEEKS AFTER INJURY Initially, the knee needs to be protected-use the knee
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
 Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome This article is also available in Spanish: El síndrome de dolor patelofemoral (Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome) (topic.cfm?topic=a00763). Patellofemoral pain syndrome is a broad
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome This article is also available in Spanish: El síndrome de dolor patelofemoral (Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome) (topic.cfm?topic=a00763). Patellofemoral pain syndrome is a broad
Case. 5 year old with 2 weeks leg pain and now refusing to walk + Fevers, lower leg swelling, warmth Denies and history of trauma or wounds
 Case 5 year old with 2 weeks leg pain and now refusing to walk + Fevers, lower leg swelling, warmth Denies and history of trauma or wounds Exam I: Swelling over entire tibia extending to foot P: Tenderness
Case 5 year old with 2 weeks leg pain and now refusing to walk + Fevers, lower leg swelling, warmth Denies and history of trauma or wounds Exam I: Swelling over entire tibia extending to foot P: Tenderness
MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM. What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders
 MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders Every year more than 1.8 million workers in the United States suffer painful back and repetitive strain injuries,
MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders Every year more than 1.8 million workers in the United States suffer painful back and repetitive strain injuries,
P R O D U C T C A T A L O G
 2015 PRODUCT CATALOG AT igo, WE PUT PEOPLE FIRST. Our staff of medical personnel and engineers work tirelessly to take groundbreaking orthopedic technology and turn it into intentionally designed, innovative
2015 PRODUCT CATALOG AT igo, WE PUT PEOPLE FIRST. Our staff of medical personnel and engineers work tirelessly to take groundbreaking orthopedic technology and turn it into intentionally designed, innovative
PATELLAR DISLOCATION AND SUBLUXATION
 PATELLAR DISLOCATION AND SUBLUXATION Description For jumping (basketball, volleyball) or contact sports, Patellar dislocation and subluxation are injuries to the protect the patella with supportive devices,
PATELLAR DISLOCATION AND SUBLUXATION Description For jumping (basketball, volleyball) or contact sports, Patellar dislocation and subluxation are injuries to the protect the patella with supportive devices,
SEMIMEMBRANOSUS TENDINITIS
 SEMIMEMBRANOSUS TENDINITIS Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: Semimembranosus tendinitis is characterized by inflammation and pain at the knee joint on the back part of the inner side of the
SEMIMEMBRANOSUS TENDINITIS Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: Semimembranosus tendinitis is characterized by inflammation and pain at the knee joint on the back part of the inner side of the
Lower Extremity Sports Injuries
 Lower Extremity Sports Injuries AAP Musculoskeletal Boot Camp Sigrid F. Wolf, MD Pediatric Sports Medicine Fellow Northwestern University Lurie Children s Hospital Disclosure I have no relevant financial
Lower Extremity Sports Injuries AAP Musculoskeletal Boot Camp Sigrid F. Wolf, MD Pediatric Sports Medicine Fellow Northwestern University Lurie Children s Hospital Disclosure I have no relevant financial
A Patient s Guide to Patellofemoral Problems
 A Patient s Guide to Patellofemoral Problems 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Patellofemoral Problems 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Guide to Common Ankle Injuries
 A Guide to Common Ankle Injuries Learn About: Common ankle injuries Feet and Ankle Diagnosis and Treatment Ankle exercises Beginning your recovery Frequently asked questions Do s and Don t s Arthroscopy
A Guide to Common Ankle Injuries Learn About: Common ankle injuries Feet and Ankle Diagnosis and Treatment Ankle exercises Beginning your recovery Frequently asked questions Do s and Don t s Arthroscopy
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 Dr. S. Matthew Hollenbeck, MD Kansas Orthopaedic Center, PA 7550 West Village Circle, Wichita, KS 67205 2450 N Woodlawn, Wichita, KS 67220 Phone: (316) 838-2020 Fax: (316) 838-7574 Description ILIOTIBIAL
Dr. S. Matthew Hollenbeck, MD Kansas Orthopaedic Center, PA 7550 West Village Circle, Wichita, KS 67205 2450 N Woodlawn, Wichita, KS 67220 Phone: (316) 838-2020 Fax: (316) 838-7574 Description ILIOTIBIAL
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the
Mr. Siva Chandrasekaran Orthopaedic Surgeon MBBS MSpMed MPhil (surg) FRACS
 Sprained Ankle An ankle sprain occurs when the strong ligaments that support the ankle stretch beyond their limits and tear. Ankle sprains are common injuries that occur among people of all ages. They
Sprained Ankle An ankle sprain occurs when the strong ligaments that support the ankle stretch beyond their limits and tear. Ankle sprains are common injuries that occur among people of all ages. They
Iliotibial (IT) Band Syndrome
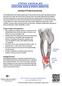 Iliotibial (IT) Band Syndrome The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon passes
Iliotibial (IT) Band Syndrome The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon passes
Will She Still Make the WNBA? Sports Injuries & Fractures
 Will She Still Make the WNBA? Sports Injuries & Fractures Aharon Z. Gladstein MD Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery Pediatric Sports Medicine Sports Injuries Chronic (overuse) Acute Who can be treated in PCP
Will She Still Make the WNBA? Sports Injuries & Fractures Aharon Z. Gladstein MD Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery Pediatric Sports Medicine Sports Injuries Chronic (overuse) Acute Who can be treated in PCP
Evaluation of the Hip and Knee
 Evaluation of the Hip and Knee Causes of hip pain RA Osteoarthritis Psoriatic arthritis Septic arthritis Bursitis Hip fx Labral tear Tendinitis Referred back pain Cancer AVN Legg-Calve-Perthes Paget's
Evaluation of the Hip and Knee Causes of hip pain RA Osteoarthritis Psoriatic arthritis Septic arthritis Bursitis Hip fx Labral tear Tendinitis Referred back pain Cancer AVN Legg-Calve-Perthes Paget's
Anterior knee pain causes and treatments
 INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Anterior knee pain causes and treatments This leaflet aims to provide you with information regarding anterior knee pain (a common knee complaint where pain is felt in or around
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Anterior knee pain causes and treatments This leaflet aims to provide you with information regarding anterior knee pain (a common knee complaint where pain is felt in or around
UNIT 2.- SPORT INJURIES: SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENT
 UNIT 2.- SPORT INJURIES: SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENT Every year, millions of teenagers participate in high school sports. An injury to a high school athlete can be a significant disappointment for the teen,
UNIT 2.- SPORT INJURIES: SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENT Every year, millions of teenagers participate in high school sports. An injury to a high school athlete can be a significant disappointment for the teen,
Your Joint Pain and Treatment Options
 Your Joint Pain and Treatment Options Pinnacle Orthopedics Pinnacle Medical Network About Pinnacle Orthopedics and Pinnacle Medical Network South Louisiana s Premier System for the Delivery of Musculoskeletal
Your Joint Pain and Treatment Options Pinnacle Orthopedics Pinnacle Medical Network About Pinnacle Orthopedics and Pinnacle Medical Network South Louisiana s Premier System for the Delivery of Musculoskeletal
A Patient s Guide to Bipartite Patella
 A Patient s Guide to Bipartite Patella 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Bipartite Patella 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
ANTERIOR ANKLE IMPINGEMENT
 ANTERIOR ANKLE IMPINGEMENT Description Possible Complications Pinching of bone or soft tissue, including scar tissue, at the Frequent recurrence of symptoms, resulting in chronically front of the ankle
ANTERIOR ANKLE IMPINGEMENT Description Possible Complications Pinching of bone or soft tissue, including scar tissue, at the Frequent recurrence of symptoms, resulting in chronically front of the ankle
SPORTS INJURIES IN CYCLING. dr. Luthfi Hidayat, Sp. OT (K)
 SPORTS INJURIES IN CYCLING dr. Luthfi Hidayat, Sp. OT (K) But, injury can happen Acute traumatic injuries due to fall Overuse injuries develop gradually overtime (due to repeated movement patterns or
SPORTS INJURIES IN CYCLING dr. Luthfi Hidayat, Sp. OT (K) But, injury can happen Acute traumatic injuries due to fall Overuse injuries develop gradually overtime (due to repeated movement patterns or
Anterior Shoulder Instability
 Anterior Shoulder Instability Anterior shoulder instability typically results from a dislocation injury to the shoulder joint when the humeral head (ball) of the humerus (upper arm bone) is displaced from
Anterior Shoulder Instability Anterior shoulder instability typically results from a dislocation injury to the shoulder joint when the humeral head (ball) of the humerus (upper arm bone) is displaced from
Overcoming joint pain and arthritis
 Overcoming joint pain and arthritis The 9 things you need to know to get moving again This guide provides an overview about managing joint pain, stiffness and swelling without sacrificing your quality
Overcoming joint pain and arthritis The 9 things you need to know to get moving again This guide provides an overview about managing joint pain, stiffness and swelling without sacrificing your quality
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings. ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders. Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS
 ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2120 ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2120 ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal
MEDIAL TIBIAL STRESS SYNDROME (Shin Splints)
 MEDIAL TIBIAL STRESS SYNDROME (Shin Splints) Description Expected Outcome Shin splints is a term broadly used to describe pain in the lower extremity brought on by exercise or athletic activity. Most commonly
MEDIAL TIBIAL STRESS SYNDROME (Shin Splints) Description Expected Outcome Shin splints is a term broadly used to describe pain in the lower extremity brought on by exercise or athletic activity. Most commonly
Pediatric Athletic Overuse Injuries. Susan Haralabatos, MD OPSC Annual Meeting 2018
 Pediatric Athletic Overuse Injuries Susan Haralabatos, MD OPSC Annual Meeting 2018 Text I have no disclosures Overview Etiology, Physiology &Anatomy Common Physeal Overuse Injuries Stress Fractures Concussion
Pediatric Athletic Overuse Injuries Susan Haralabatos, MD OPSC Annual Meeting 2018 Text I have no disclosures Overview Etiology, Physiology &Anatomy Common Physeal Overuse Injuries Stress Fractures Concussion
Low-Back Strain DESCRIPTION POSSIBLE COMPLICATIONS COMMON SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS GENERAL TREATMENT CONSIDERATIONS CAUSES FACTORS THAT INCREASE RISK
 Page Number: 0 Date:13/6/11 Time:20:10:06 Low-Back Strain DESCRIPTION POSSIBLE COMPLICATIONS Low-back strain is an injury to the muscles and tendons of the lower back. These muscles require great force
Page Number: 0 Date:13/6/11 Time:20:10:06 Low-Back Strain DESCRIPTION POSSIBLE COMPLICATIONS Low-back strain is an injury to the muscles and tendons of the lower back. These muscles require great force
THE HIP. Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness.
 THE HIP Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness. Objectives Hip anatomy Causes of hip pain Hip exam Anatomy Bones Ilium Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
THE HIP Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness. Objectives Hip anatomy Causes of hip pain Hip exam Anatomy Bones Ilium Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
AMERICAN RED CROSS FIRST AID RESPONDING TO EMERGENCIES FOURTH EDITION Copyright 2006 by The American National Red Cross All rights reserved.
 Musculoskeletal injuries are most commonly caused by Mechanical forms of energy. Chemicals. Electrical energy. Heat Mechanical energy produces direct, indirect, twisting and contracting forces. Can be
Musculoskeletal injuries are most commonly caused by Mechanical forms of energy. Chemicals. Electrical energy. Heat Mechanical energy produces direct, indirect, twisting and contracting forces. Can be
Knee Replacement PROGRAM. Nightingale. Home Healthcare
 Knee Replacement PROGRAM TM Nightingale Home Healthcare With the help of Nightingale s experienced and professional rehabilitation team, you will be guided through a more complete and successful recovery
Knee Replacement PROGRAM TM Nightingale Home Healthcare With the help of Nightingale s experienced and professional rehabilitation team, you will be guided through a more complete and successful recovery
Sports Medicine. A Guide to Overuse Knee Injuries
 Sports Medicine A Guide to Overuse Knee Injuries We re a national leader in the care and management of knee injuries. Nationwide Children s Hospital Sports Medicine understands the specialized health
Sports Medicine A Guide to Overuse Knee Injuries We re a national leader in the care and management of knee injuries. Nationwide Children s Hospital Sports Medicine understands the specialized health
MENISCUS TEAR. Description
 MENISCUS TEAR Description Expected Outcome The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage structure in the knee that sits on top of the leg bone (tibia). Each knee has two menisci, an inner and outer meniscus. The
MENISCUS TEAR Description Expected Outcome The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage structure in the knee that sits on top of the leg bone (tibia). Each knee has two menisci, an inner and outer meniscus. The
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN
 CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN Description Cervical strain/sprain is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or forward. The structures involved are the muscles, ligaments,
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN Description Cervical strain/sprain is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or forward. The structures involved are the muscles, ligaments,
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN (Whiplash)
 CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN (Whiplash) Description time and using proper technique decrease the frequency of Whiplash is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN (Whiplash) Description time and using proper technique decrease the frequency of Whiplash is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or
Pediatric Fractures. Objectives. Epiphyseal Complex. Anatomy and Physiology. Ligaments. Bony matrix
 1 Pediatric Fractures Nicholas White, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Eastern Virginia Medical School Attending, Pediatric Emergency Department Children s Hospital of The King s Daughters Objectives
1 Pediatric Fractures Nicholas White, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Eastern Virginia Medical School Attending, Pediatric Emergency Department Children s Hospital of The King s Daughters Objectives
ANKLE SPRAIN, ACUTE. Description
 Description ANKLE SPRAIN, ACUTE An acute ankle sprain involves the stretching and tearing of one or more ligaments in the ankle. A two-ligament sprain causes more disability than a single-ligament sprain.
Description ANKLE SPRAIN, ACUTE An acute ankle sprain involves the stretching and tearing of one or more ligaments in the ankle. A two-ligament sprain causes more disability than a single-ligament sprain.
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Patellar Tendon and Quadriceps Tendon Repair
 UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Patellar Tendon and Quadriceps Tendon Repair The knee consists of four bones that form three joints. The femur is the large bone in the thigh
UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Patellar Tendon and Quadriceps Tendon Repair The knee consists of four bones that form three joints. The femur is the large bone in the thigh
Osteoarthritis of the Hip
 Osteoarthritis of the Hip Information on hip osteoarthritis is also available in Spanish: Osteoartritis de cadera (topic.cfm?topic=a00608). Sometimes called "wear and tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is
Osteoarthritis of the Hip Information on hip osteoarthritis is also available in Spanish: Osteoartritis de cadera (topic.cfm?topic=a00608). Sometimes called "wear and tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is
A Patient s Guide to Quadriceps Tendonitis
 A Patient s Guide to Quadriceps Tendonitis 1436 Exchange Street Middlebury, VT 05753 Phone: 802-388-3194 Fax: 802-388-4881 cvo@champlainvalleyortho.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Quadriceps Tendonitis 1436 Exchange Street Middlebury, VT 05753 Phone: 802-388-3194 Fax: 802-388-4881 cvo@champlainvalleyortho.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Lateral Collateral Ligament Sprain
 What is lateral collateral ligament sprain? Lateral Collateral Ligament Sprain A sprain is a joint injury that causes a stretch or tear in a ligament, a strong band of tissue connecting one bone to another.
What is lateral collateral ligament sprain? Lateral Collateral Ligament Sprain A sprain is a joint injury that causes a stretch or tear in a ligament, a strong band of tissue connecting one bone to another.
In-toeing, Out-toeing, Growing Pains, Bowlegs, Knock-Knees and Flat Feet
 Jeffrey B. Neustadt, M.D. Scott W. Beck, M.D. Gregory V. Hahn, M.D. Drew E. Warnick, M.D. Paul L. Benfanti, M.D. Lee G. Phillips, M.D. Daniel C. Bland, M.D. Common Benign Orthopaedic Conditions In-toeing,
Jeffrey B. Neustadt, M.D. Scott W. Beck, M.D. Gregory V. Hahn, M.D. Drew E. Warnick, M.D. Paul L. Benfanti, M.D. Lee G. Phillips, M.D. Daniel C. Bland, M.D. Common Benign Orthopaedic Conditions In-toeing,
A Patient s Guide to Tendonitis. Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, P.C.
 A Patient s Guide to Tendonitis Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
A Patient s Guide to Tendonitis Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
BOW LEGS (GENU VARUM)
 BOW LEGS (GENU VARUM) By Dr John Ebnezar INTRODUCTION Have you noticed how your knees look like? If you observe carefully you will see that both your knees are not parallel but deviated slightly outwards
BOW LEGS (GENU VARUM) By Dr John Ebnezar INTRODUCTION Have you noticed how your knees look like? If you observe carefully you will see that both your knees are not parallel but deviated slightly outwards
What is an ACL Tear?...2. Treatment Options...3. Surgical Techniques...4. Preoperative Care...5. Preoperative Requirements...6
 Table of Contents What is an ACL Tear?....2 Treatment Options...3 Surgical Techniques...4 Preoperative Care...5 Preoperative Requirements...6 Postoperative Care...................... 7 Crutch use...8 Initial
Table of Contents What is an ACL Tear?....2 Treatment Options...3 Surgical Techniques...4 Preoperative Care...5 Preoperative Requirements...6 Postoperative Care...................... 7 Crutch use...8 Initial
Prevalence of childhood and adolescent soccer-related overuse injuries
 369 ORIGINAL Prevalence of childhood and adolescent soccer-related overuse injuries Naoto Suzue 1, Tetsuya Matsuura 1, Toshiyuki Iwame 2, Daisuke Hamada 1, Tomohiro Goto 1, Yoichiro Takata 1, Takenobu
369 ORIGINAL Prevalence of childhood and adolescent soccer-related overuse injuries Naoto Suzue 1, Tetsuya Matsuura 1, Toshiyuki Iwame 2, Daisuke Hamada 1, Tomohiro Goto 1, Yoichiro Takata 1, Takenobu
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery. By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4
 Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Recognizing common injuries to the lower extremity
 Recognizing common injuries to the lower extremity Bones Femur Patella Tibia Tibial Tuberosity Medial Malleolus Fibula Lateral Malleolus Bones Tarsals Talus Calcaneus Metatarsals Phalanges Joints - Knee
Recognizing common injuries to the lower extremity Bones Femur Patella Tibia Tibial Tuberosity Medial Malleolus Fibula Lateral Malleolus Bones Tarsals Talus Calcaneus Metatarsals Phalanges Joints - Knee
PT Final Exam. July 2018 Core Content Review 6 Presented by Mark. Copyright 2018 PT Final Exam
 PT Final Exam July 2018 Core Content Review 6 Presented by Mark A 34 year old male comes to your clinic with reoccurring hamstring tears. Upon examination, the therapist is able to achieve 130 degrees
PT Final Exam July 2018 Core Content Review 6 Presented by Mark A 34 year old male comes to your clinic with reoccurring hamstring tears. Upon examination, the therapist is able to achieve 130 degrees
Periarticular knee osteotomy
 Periarticular knee osteotomy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4803 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. Knee joint The knee consists of two joints which allow flexion (bending)
Periarticular knee osteotomy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4803 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. Knee joint The knee consists of two joints which allow flexion (bending)
Why choose Ottauquechee PT
 Why does your back hurt? Low back pain is one of the most common patient complaints affecting 80% of adults at some point in their lives. Generally the source of pain is in the spine and/or its supporting
Why does your back hurt? Low back pain is one of the most common patient complaints affecting 80% of adults at some point in their lives. Generally the source of pain is in the spine and/or its supporting
