Enluxtra Self-Adaptive Wound Dressing
|
|
|
- Rose Griffith
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Enluxtra Self-Adaptive Wound Dressing Case Studies OSNovation Systems, Inc. Enluxtra is the registered trademark of BASF, Inc. OSNovative Systems, Inc. 500 Laurelwood Rd, Ste 1 & 4, Santa Clara, CA
2 Self-Adaptive Advanced Wound Dressing Study Randall D. Wolcott, MD, Vicki Fischenich, GNP The Southwest Regional Wound Care Center, Lubbock, TX Abstract of presentation at The Symposium on Advanced Wound Care (SAWC) Spring 2012 The purpose of this study was to determine the effectiveness of a self-adaptive advanced wound dressing for achieving optimal moisture balance in multiple wound types. The subject dressing had the unique property of being able to sequester large amounts of exudate or conversely prevent desiccation of a dry wound. This allowed the dressing to be used throughout the healing of a wound. A total of 15 patients from a variety of settings (clinic and nursing homes) were selected. The types of wounds in the study included venous, diabetic, and decubitus ulcers as well as acute traumatic and chronic wounds. The dressing was applied one to three times per week either in clinic or in home settings, based on the wound and in conjunction with local best practices throughout the entire study. Our overall approach was to use this dressing on any wound regardless of etiology or the amount of exudate, and to decrease dressing changes to a minimum (once a week) until the wound was completely re-epithelialized. Our conclusion was that this dressing was effective on all types of wounds with minimal to heavy exudate and with no need for dressing customization. We observed notable improvements of wound edge conditions. The dressing demonstrated excellent properties with regard to preservation of peri-wound skin. Dressing removal was painless and non-traumatic. It also seemed that this dressing minimized formation of biofilm, therefore reducing the need for debridement. We had promising results with extended use in patients with once a week dressing changes with moderate drainage. The utilization of one-fit-all dressing for multiple wound types, which exhibit minimal to severe exudate, simplified wound care. This dressing improved the quality consistency of practical moist wound healing and facilitated care continuum in the clinic, home and facility settings. * Enluxtra Wound Dressing, OSNovation Systems, Inc., BASF,Inc. OSNovative Systems, Inc. 500 Laurelwood Rd, Ste 1 & 4, Santa Clara, CA Page 2 of 16
3 Case study 1: Chronic lower extremity venous stasis ulcer Enluxtra Wound Dressing Clinical Results Patient: A 53-year-old male presented with a draining lateral venous stasis ulcer on his left lower leg that had been present for several months. Patient is a heavy smoker (1pack a day) with a history of untreated hypertension, arterial compromise, and refused revascularization (ankle/brachial index:.82). Wound Description: Upon presentation to the clinic, the venous stasis ulcer appeared weepy and stalled in the inflammation phase of wound healing. Healing was further complicated by frequent recurrence of fungal/yeast infection on the periwound skin, which caused constant pruritus and inflammation. Patient complained of sleep loss due to itching and discomfort throughout the day. Initial goals in this case were to reduce wound drainage and edema. Initial Wound Treatment: In addition to triamcinolone, anti-fungal ointments and topical antibiotics, a variety of dressings were applied to the wound during the first four months of treatment, including foams, alginates, silver alginates, and polymeric membrane dressings. Unfortunately, the quantity and consistency of drainage from the wound did not change with application of any of these dressings. After 4 months of advanced wound care, the ulcer remained weepy and hypergranulated with raised wound edges above peri-wound skin level. Condition of the periwound skin was bright red, erythematous, edematous, and with scaly dry drainage adding to the pruritus (Fig. A). Application of Enluxtra: Prior to the first application of Enluxtra Humifiber wound dressing, following debridement, the ulcer measured 4.0 x 4.0 x 0.5 cm. Topical antibiotics and anti-fungal ointment were applied. Enluxtra was placed over the ulcer, overlapping 2 to 3 cm onto intact skin, and secured with circumferential gauze wrap. Wound Progression with Enluxtra: Two weeks following initial application of Enluxtra, drainage was noticeably reduced, the periwound erythema was resolved, and the wound was granulating normally with only a small, slightly raised area (Fig. B). The dressing prevented transfer of exudate to the peri-wound skin, ending prolonged skin irritation and itching after only one week of Enluxtra. Fig. A. Chronic venous leg ulcer with edematous raised bed after 4 months of advanced wound care and prior to Enluxtra application B Fig. B. Two weeks following initial use of Enluxtra, drainage is considerably decreased and peri-wound erythema is completely resolved. Signs of inflammation are no longer present and the wound is nearly level with the peri-wound skin. A OSNovative Systems, Inc. 500 Laurelwood Rd, Ste 1 & 4, Santa Clara, CA Page 3 of 16
4 After 4 weeks of Enluxtra, the wound bed was completely level with the periwound skin and reepithelializing normally. The wound measured only 0.5 x 0.25 x 0.25 cm with no periwound edema (Fig. C). No dressing adjustment or cutting was required during course of wound healing. After 2 months, the wound was completely closed and re-epithelialized (Fig. D). Dressings were discontinued and the patient was released from care. User Experience: The patient was very satisfied with the Enluxtra dressing, particularly with respect to painless, nonadherent dressing removal and the rapid rate of erythema resolution and wound closure. Patient reported no dressing leakage or fluid strike-through. Itchiness stopped within one week of application, and the patient was relieved to finally sleep through the night. His wound that had been open and draining for 4 months was nearly closed within 1 month of Enluxtra use, allowing him to return to his normal daily activities. Clinical Outcomes/Conclusion: In this case, Enluxtra appeared to contain all the properties needed to reverse the impediments in ulcer healing that were evident during the previous four months, including edema, uncontrolled drainage, and moisture imbalances. Compared to all previous dressings used in this chronic ulcer, Enluxtra was the only dressing that facilitated effective and efficient wound closure. Drainage was controlled, locked in and reduced with this dressing, resulting in edema reduction and optimal moisture balance throughout the wound and periwound skin. The dressing appeared to absorb exudate from the central area of the draining wound while maintaining moist wound edges, and to provide a moist healing environment during the low-/non-exuding final stages of wound healing. The final cosmetic appearance of the healed wound was excellent. From a clinician s perspective, Enluxtra greatly simplifies the tedious process of choosing appropriate wound care dressings, because this one dressing type is suited for the entire wound healing continuum and does not need to be switched according to changing wound conditions. Enluxtra was effective throughout all conditions and dimensions of the wound in this case. Reference: Vicki Fischenich, GNP-BC; Dr. Randall Wolcott Southwest Regional Wound Care Center, Lubbock, TX D Fig. C. After 1 month of Enluxtra, wound size was reduced to 0.5 x 0.25 x 0.25 cm with no edema or drainage. The wound appeared optimally moist and mostly re-epithelialized. Fig. D. Venous stasis ulcer is completely closed with excellent aesthetic result after 2 months of Enluxtra dressings C 2014 OSNovative Systems, Inc.. All rights reserved. Trademarks and services marks herein are the property of BASF, Inc. Enluxtra wound dressing is subject to patents and/or pending patents. OSNovative Systems, Inc. 500 Laurelwood Rd, Ste 1 & 4, Santa Clara, CA Page 4 of 16
5 Case study 2: Basal cell carcinoma of the temporal region Enluxtra Wound Dressing Clinical Results Patient: A 62-year-old male presented with a nonhealing soft tissue radionecrosis wound of the left facial and temporal region following severe radiation damage post basal cell carcinoma. Patient s medical history also included hypertension and stage II chronic kidney disease. Wound Description: Continual drainage from the exposed frontal sinus was contaminating and causing inflammation to the surrounding soft tissue, prolonging wound healing process. Wound healing was further complicated by desiccation of wound edges and non-exudative portions of the wound, as well as formation of necrotic tissue and biofilms. Initial Wound Treatment: A range of absorbent dressings, including hydrocellular and self-adherent polyurethane foams, were tried in the wound and were unsuccessful in controlling drainage of the sinus fluid and necrotic tissue formation. The wound required weekly debridements to remove necrotic tissue, which was increasing the wound size and traumatizing the wound edges, exposed bone, and the fragile thin tissue layer over the brain. Brain pulsating movement could be observed in the center of the wound. Continual debriding of this fragile area due to drainage deterred the healing process. Application of Enluxtra: Ten weeks after the patient initially presented to our clinic, the wound measured 10.0 x 13.0 x 1.0 cm with exposed bone (Fig. A). Debridement was performed, and Enluxtra was placed on the wound, overlapping 2 to 3 cm onto intact skin, and secured with non-woven cotton tape at the first dressing change. On follow-up visit, additional folded gauze was added to the outer Enluxtra dressing and cotton tape to ensure wound bed contact with the Enluxtra and aid drainage absorption and biofilm elimination. Fig. A. Chronic soft tissue radionecrosis wound prior to use of Enluxtra is filled with necrotic tissue and contaminated with sinus fluid Areas of exudation Dressing absorbs and contains exudate. Dry tissue Dressing hydrates. Exposed bone prone to dryness Dressing hydrates. Wound edge prone to dryness Dressing hydrates. OSNovative Systems, Inc. 500 Laurelwood Rd, Ste 1 & 4, Santa Clara, CA Page 5 of 16
6 Wound Progression with Enluxtra: Two weeks following initial placement of Enluxtra, the wound displayed marked signs of improvement. Drainage was controlled and isolated within the dressing, and healthy pink tissue was present in the wound bed and on wound edges (Fig. B). Exudate containment and maintenance of correct moisture balance throughout the entire wound led to a drastic reduction in sharp debridements and associated trauma to the exposed bone and healing tissues. The layer of tissue covering brain tissue continuously retained its moisture, and appeared strengthened within one month of Enluxtra use (Fig. C). After 3 months of Enluxtra, wound size was decreased, sinus fluid remained contained, and granulation buds were present throughout the wound bed (Fig. D). User Experience: The patient reported increased comfort with the dressing, particularly with respect to painless dressing removal, leak-free dressing and decreased debridement frequency. Other dressings applied prior to Enluxtra leaked drainage into the eye and inner ear, requiring frequent debridement and use of antibiotic eye drops for inflammation and irritation. Clinical Outcomes/Conclusion: All areas of this complex soft tissue radionecrosis wound responded positively underneath the Enluxtra dressing throughout the 12-week application period. Improved moisture balance and considerably reduced necrotic tissue and biofilm formation were observed with application of Enluxtra, compared to previous dressings used in this wound. Enluxtra appeared to assist in autolytic debridement, which greatly decreased the need for sharp debridement and allowed the underlying healthy tissue to consistently remain on a positive wound-healing trajectory. Fig. B. Two weeks following initial use of Enluxtra, sinus drainage is controlled and pink granulation buds are present in the wound bed Fig.C. After 1 month s use of Enluxtra, the need for debridement was drastically reduced and the thin tissue over the brain remained optimally moist and granulated Reference: Vicki Fischenich, GNP-BC Dr. Randall Wolcott Southwest Regional Wound Care Center Lubbock, TX Fig,D. After 3 months of Enluxtra, wound edges appear healthy, and all dimensions are smaller 2014 OSNovative Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and services marks herein are the property of BASF, Inc. Enluxtra wound dressing is subject to patents and/or pending patents. OSNovative Systems, Inc. 500 Laurelwood Rd, Ste 1 & 4, Santa Clara, CA Page 6 of 16
7 Case study 3: Fourth metatarsal head following amputation Enluxtra Wound Dressing Clinical Results Patient: A 67-year-old male presented with a diabetic wound of the right foot fourth metatarsal head following toe amputation. Patient was a healthy, insulin-dependent diabetic with hypertension. Wound Description: Patient with a diabetic wound of the right foot fourth metatarsal had been unsuccessfully treated by a local physician for 1 month. Patient was admitted to a local hospital for amputation of foot and intravenous antibiotics. Patient sought second opinion from our wound clinic and it was determined that amputation of only the fourth digit was necessary. Three days after amputation, the incision dehisced and the wound began producing copious amounts of drainage. At initial presentation post dehiscence, wound edges were macerated and erythematous, due to the uncontrolled wound drainage. Application of Enluxtra: Following debridement, the ulcer measured 3.0 x 1.5 x 1.0 cm with exposed bone (Fig. A). A small piece of Enluxtra was cut and placed between the toes and over the wound, overlapping 2 to 3 cm onto intact skin (Fig. B), then secured with gauze wrap. The aim of the dressing was to absorb and reduce wound drainage as well as facilitate recovery of the macerated periwound skin. Wound Progression with Enluxtra: The drainage was well absorbed by the dressing. After one week of Enluxtra application, drainage was reduced and maceration around the wound was decreased (Fig. C). The periwound area was healthy and completely recovered at week 3 (Fig. D). After 6 weeks of Enluxtra, edema and erythema were no longer present and the wound appeared optimally moist. The wound was smaller (0.5 x 0.5 x 1.0 cm) and well-granulated, including over previously exposed bone (Fig. E). The wound was Fig.A. Diabetic wound post amputation and debridement with copious drainage and wound edge maceration Fig.B. Enluxtra dressing applied between toes and overlapping onto intact skin Fig. C. After 1 week of Enluxtra, wound edge maceration is resolving due to dressing absorption capabilities. Slight erythema is present at the wound edges. OSNovative Systems, Inc. 500 Laurelwood Rd, Ste 1 & 4, Santa Clara, CA Page 7 of 16
8 completely closed after 4 months of Enluxtra application (Fig. F), and the patient was discharged from wound care services. User Experience: The patient appreciated the ease of application and removal of the Enluxtra dressing, and was encouraged at each dressing change by consistent progress toward closure. Clinical Outcomes/Conclusion: The diabetic foot ulcer showed steady progression toward closure at each dressing change with use of Enluxtra, and was completely closed at 4 months. Drainage and edema were decreased and periwound maceration was eliminated with this dressing. Enluxtra appears to be a viable, simplified dressing option for diabetic wounds due to its effectiveness over different tissue types and throughout the wound healing continuum. Fig. D. Peri-wound is free of maceration and erythema after 3 weeks of Enluxtra. Wound edges remain moist and begin coming together Reference: Vicki Fischenich, GNP-BC Dr. Randall Wolcott Southwest Regional Wound Care Center Lubbock, TX Fig. E. After 6 weeks of Enluxtra, the wound was well granulated over tissue and bone Fig. F. At 4-months, the diabetic wound is completely closed 2014 OSNovative Systems, Inc.. All rights reserved. Trademarks and services marks herein are the property of BASF, Inc. Enluxtra wound dressing is subject to patents and/or pending patents. OSNovative Systems, Inc. 500 Laurelwood Rd, Ste 1 & 4, Santa Clara, CA Page 8 of 16
9 Case study 4: Diabetic foot ulcer secondary to gout Enluxtra Wound Dressing Clinical Results A Patient: A 60-year-old female presented with a diabetic foot ulcer secondary to gout and neuropathy on the lateral side of her right foot great toe. Patient is morbidly obese with an existing diabetic plantar ulcer of 7 months duration. Patient comorbidities include type 2 diabetes mellitus, gout, arthritis, venous insufficiency, hypertension, neuropathy, and Charcot foot disease. Wound Description: Upon presentation to the clinic, the wound was copiously draining, and inflammation extended to the periwound areas. The periwound skin was erythematous, edematous and warm to the touch. Wound secondary to gout at initial presentation, following debridement. Edges were undermined, edematous, and erythematous. B Initial Wound Treatment: Patient restarted allopurinol dosages and started on topical antibiotic and IV daptomycin. Sharp debridement was performed and continued weekly. The wound measured 2.0 x 4.0 x 1.0 cm with undermined edges (Fig. A). Application of Enluxtra: Enluxtra was placed over the ulcer, overlapping 2 to 3 cm onto intact skin, and secured with circumferential gauze wrap. Dressing changes were ordered once daily and performed by a family member. Wound Progression with Enluxtra: One week after initial application of Enluxtra, drainage was drastically reduced and the periwound erythema was largely resolved. Wound margins and undermining were reduced, and debridement of devitalized tissue revealed exposed tendon (Fig. B). After 2 weeks of Enluxtra, the wound size was reduced to 1.5 x 3.0 x 0.25 cm and the wound bed was 100% granulated over tendon (Fig. C). Periwound redness was no longer present, drainage was slight, and the wound edges remained optimally moist. After one month of Enluxtra, wound edges remained moist and approximating. The wound measured 1.0 x 1.0 x.25 and was re-epithelializing One week after initial use of Enluxtra, wound margins and periwound erythema are considerably decreased. After 2 weeks of Enluxtra, the wound was 100% granulated, including over tendon, with no edema or drainage. Wound and peri-wound area remained optimally moist. C OSNovative Systems, Inc. 500 Laurelwood Rd, Ste 1 & 4, Santa Clara, CA Page 9 of 16
10 normally (Fig. D). At 2 months post initial Enluxtra application, the wound was fully re-epithialized and dressings were discontinued (Fig. E). D User Experience: No dressing adjustment or cutting was required during course of wound healing. The patient was very satisfied with the Enluxtra dressing, particularly with respect to drainage containment, the rapid rate of erythema resolution and wound closure. Enluxtra contained the large amount of drainage early on, decreasing exacerbation of the peri-wound area and facilitating healing. Clinical Outcomes/Conclusion: During application of Enluxtra in this case, edema and drainage were reduced, and an optimal wound healing environment was maintained, despite multiple patient co-morbidities. After 2 weeks with the Enluxtra dressing, the wound was 100% granulated over exposed tendon, and within 2 months, the wound was closed without further complications. Enluxtra maintained effectiveness throughout all stages of healing in this diabetic foot ulcer. Reference: Vicki Fischenich, GNP-BC Randall Wolcott, MD Southwest Regional Wound Care Center Lubbock, TX At 1 month after initial presentation, wound edges are approximating; periwound is healthy with no edema. After 2 months of Enluxtra dressings, the wound was fully re-epithelialized and the dressings were discontinued. E D 2014 OSNovative Systems, Inc.. All rights reserved. Trademarks and services marks herein are the property of BASF, Inc. Enluxtra wound dressing is subject to patents and/or pending patents. OSNovative Systems, Inc. 500 Laurelwood Rd, Ste 1 & 4, Santa Clara, CA Page 10 of 16
11 Case study 5: Chronic lower extremity venous stasis ulcer Enluxtra Wound Dressing Clinical Results Patient: A 49-year-old female presented with a draining venous stasis ulcer on her right shin. Patient s medical history included coronary bypass graft surgery, hypertension, hyperlipidemia and coronary disease. Pyoderma was suspected but not diagnosed. Wound Description: This venous stasis ulcer had been present for 6 months, and appeared weepy and edematous at the initial clinic visit. Areas of wound edges were raised with undermining. Peri-wound skin was red and erythematous, and exhibited multiple scabs due to patient scratching and spreading contact dermatitis. The wound area was warm, and the patient complained of itchiness and pain. Initial goals in this case were to reduce wound drainage and edema, and to resolve wound edge erythema. Initial Wound Treatment: In addition to topical antibiotics, a range of dressings, including hydrocellular and hydropolymer foams, were applied to the ulcer during the first 6 months of treatment. However, the wound continued to drain copiously and the condition of the peri-wound skin remained red and irritated throughout treatment, even with daily dressing changes (Fig. A). The patient continued to complain of discomfort during dressing changes, and requested a dressing that could be changed less frequently than daily. A decision was made to apply Enluxtra Humifiber wound dressing. Application of Enluxtra: Prior to the first application of Enluxtra and following debridement, the ulcer measured 5.5 x 7.0 x 0.5 cm with exposed tendon (Fig. A). Topical antibiotics were applied. Enluxtra was placed over the ulcer, overlapping 2 to 3 cm onto intact skin, and secured with circumferential gauze wrap. Daily dressing changes were ordered initially. However, after 3 days, dressing could be left in place for up to 2 days. Wound Progression with Enluxtra: Two weeks following initial application of Enluxtra, drainage and peri-wound erythema were decreased. Edema was considerably reduced, wound edges were no longer raised, and the wound bed was level with the peri-wound skin. Healthy granulation buds appeared over the tendon (Fig. B). The patient reported no itching and less pain during or between dressing changes. Dressing change frequency was further reduced to every 3-4 days. Chronic, edematous venous leg ulcer with raised wound edges and exposed tendon after 6 months of advanced wound care and prior to Enluxtra application Areas of exudation Dressing absorbs and contains exudate. A Exposed tendon at risk for desiccation. Dressing hydrates. OSNovative Systems, Inc. 500 Laurelwood Rd, Ste 1 & 4, Santa Clara, CA Page 11 of 16
12 After 2 months of Enluxtra, the wound was approximately 85% granulated and erythema in periwound was nearly resolved (Fig. C). At 12 weeks, use of Enluxtra was discontinued due to original time limits set forth in the clinical trial. The wound bed was 100% granulated and re-epithelializing normally. Peri-wound erythema remained controlled and the wound size was decreased to 3.5 x 5.0 x 0.25 cm (Fig. D). User Experience: The patient described the Enluxtra dressing as having a soothing and cooling effect on her wound, and was particularly satisfied with the rapid decrease in drainage, pain, and itchiness that resulted with the dressing. Because the patient was uninsured, the reduction in dressing change frequency with Enluxtra had huge cost benefits for her. Non-adherent dressing changes every 3-4 days were well tolerated by the patient. Patient reported no dressing leakage or fluid strike-through. Exudate containment, wound size reduction and increased comfort allowed the patient to return faster to normal daily activities. Clinicians appreciated ease of dressing removal and longer 2-year shelf life of dressing. Clinical Outcomes/Conclusion: Compared to prior dressings used in this wound, use of Enluxtra resulted in a decreased frequency of debridements and dressing changes both of which favorably impacted healthcare costs for this patient. Use of Enluxtra facilitated conversion of this stalled chronic ulcer to a wound that showed positive wound healing progression at every dressing change. The dressing was effective in controlling exudate removal throughout all phases of wound healing, ending prolonged skin irritation and itching within 2 weeks of Enluxtra use. Enluxtra appeared to maintain a positive moisture balance throughout the wound and peri-wound skin for the duration of its use, resulting in a well-granulated venous stasis ulcer in a patient with considerable comorbidities. Two weeks following initial application of Enluxtra, drainage and edema are considerably decreased, and wound edges are level with the peri-wound skin. The wound is granulating normally. After 2 months of Enluxtra dressings, ulcer is 85% granulated, including over tendon. Peri-wound skin is healthy with very slight erythema. B C D Reference: Vicki Fischenich, GNP-BC; Randall Wolcott, MD Southwest Regional Wound Care Center Lubbock, TX Venous stasis ulcer is completely granulated over tendon after 3 months of Enluxtra dressings OSNovative Systems, Inc.. All rights reserved. Trademarks and services marks herein are the property of BASF, Inc. Enluxtra wound dressing is subject to patents and/or pending patents. OSNovative Systems, Inc. 500 Laurelwood Rd, Ste 1 & 4, Santa Clara, CA Page 12 of 16
13 Case study 6: First metatarsal head following amputation Enluxtra Wound Dressing Clinical Results A Patient: A 75-year-old male presented with a diabetic wound of the left foot first metatarsal head following toe amputation performed prior to presentation at our clinic. Patient s past medical history significant for insulin-dependent diabetes, hypertension, neuropathy, and mild chronic obstructive pulmonary disease treated with prednisone. Wound Description: The patient was referred to our clinic with a dehisced incision over the first metatarsal head. The wound was edematous with copious drainage and maceration to the periwound area. Initial goals in this case were to reduce wound drainage and edema. Initial Wound Treatment: Culture-specific topical antibiotics, as well as numerous dressings and grafts were applied to this amputation wound during the first 7 months of treatment. Dressings applied to the wound included hydropolymer foam and oxidized regenerated cellulose/collagen matrix. Human fibroblast-derived dermal substitute was applied 5 times, and tissueengineered skin was applied 6 times. Despite the wide array of advanced wound care products used, the ulcer continued to drain on to the peri-wound area, causing severe maceration of wound edges and loss of surrounding tissue. After 7 months of care, the wound had a foul odor and was covered with a thin biofilm layer (Fig. A). A decision was made to apply Enluxtra Humifiber wound dressing to contain the drainage and maintain moisture balance throughout the wound and peri-wound. Application of Enluxtra: Prior to the first application of Enluxtra Humifiber wound dressing, following debridement, the ulcer measured 5.0 x 3.0 x0.5 cm. A topical, culturespecific antibiotic solution was applied, then Enluxtra was placed over the debrided area, overlapping 2 to 3 cm onto intact skin, and secured with a gauze wrap. Wound Progression with Enluxtra: After 3 weeks of 3-times weekly dressing changes with Enluxtra, peri-wound maceration was greatly reduced. Wound odor and signs of biofilm in the wound bed were no longer present. The wound bed was healthy, beefy red and epithelializing (Fig. B). Diabetic foot ulcer with severe peri-wound maceration after 7 months of advanced wound care and prior to Enluxtra application Three weeks following initial use of Enluxtra, maceration is considerably decreased, and the wound odor and signs of biofilm are no longer present. After 6 weeks of Enluxtra, ulcer area was reduced by greater than 60% with minimal drainage. C B OSNovative Systems, Inc. 500 Laurelwood Rd, Ste 1 & 4, Santa Clara, CA Page 13 of 16
14 A sheet of tissue-engineered skin was applied to the ulcer, over which the Enluxtra dressing was applied. Dressing change frequency was reduced from 3 times to 1 time per week. After 6 weeks of Enluxtra dressings, the wound was considerably smaller and re-epithelializing normally (Fig. C). Tissue-engineered skin and Enluxtra were re-applied. At 8 weeks, skin islands were visible within the wound bed, indicating that the tissueengineered skin graft was successful (Fig. D). Wound edges appeared moist, even over calloused skin of the patient who refused to offload or wear a boot. After 12 weeks of Enluxtra dressings and tissueengineered skin grafts, the wound bed remained optimally moist, and was 100% granulated. The wound size had been reduced to 1.5 x 1.5 x 0.25 cm (Fig. E). Use of Enluxtra was discontinued due to the 12-week time limit for the clinical evaluation. The patient subsequently lost home health services due to non-compliance and was lost to follow-up. User Experience: Patient preferred the Enluxtra dressing over all previously used dressings due to the dramatically decreased peri-wound maceration and reduction in dressing change frequency facilitated by the dressing. Clinicians reported excellent moisture control with Enluxtra, as the wound remained optimally moist without peri-wound maceration or leakage. Patient was also able to change his own dressing and provider care was cancelled. Clinical Outcomes/Conclusion: During use of Enluxtra, this previously stalled diabetic wound progressed to a clean, wellgranulated wound that showed consistent size reduction at each weekly visit. The dressing maintained good contact with the wound and periwound areas, facilitating moisture control throughout, despite the patient s refusal to off-load his foot. Reduction in dressing change frequency with Enluxtra also led to cost savings and increased patient satisfaction. Compared to all dressings previously used in this wound, Enluxtra provided the most optimal moist wound healing environment needed to progress the wound and maximize the effectiveness of tissueengineered grafts. After 8 weeks of Enluxtra and two tissueengineered skin grafts, skin islands are visible within the wound bed. Wound edges appear moist, even over calloused skin. Following a regimen of 12 weeks of Enluxtra and 3 tissue-engineered grafts, the wound bed remains optimally moist and 100% granulated. E D Reference: Vicki Fischenich, GNP-BC; Randall Wolcott, MD Southwest Regional Wound Care Center Lubbock, TX 2014 OSNovative Systems, Inc.. All rights reserved. Trademarks and services marks herein are the property of BASF, Inc. Enluxtra Humifiber wound dressing is subject to patents and/or pending patents. OSNovative Systems, Inc. 500 Laurelwood Rd, Ste 1 & 4, Santa Clara, CA Page 14 of 16
15 Utilizing the Self Regulating Moisture Control of a Self-Adaptive Dressing to Manage a Single Complex Wound Randall Wolcott, MD, Vicki Fischenich, GNP-BC Southwest Regional Wound Care Center, Lubbock, TX Abstract of presentation at The Symposium on Advanced Wound Care (SAWC) Spring 2012 Chronic wounds are often complex and have clearly been shown not to be homogeneous. The wound biofilm which covers the vast majority of the chronic wound shows significant differences in the constituent microbes at different locations within the wound. This heterogeneity of wound biofilm combined with the different tissue types that are often contributing to the wound bed along with different degrees of degradation of the host tissue can present significant problems for most traditional dressings. Certain areas, such as the wound edge that struggles with active wound biofilm producing marked inflammation and therefore exudate, have different moisture control needs versus areas of exposed bone or low inflammation. Currently, available dressings tend to be engineered to solve a single problem, such as too much exudate (absorption) or wound desiccation (hydration), which can limit their overall effectiveness in a complex wound. Complex wounds with areas of different properties therefore may benefit from a self-regulating dressing. An Enluxtra advanced wound dressing has a unique feature of self-adjusting its material properties in response to specific moisture conditions encountered within the wound. This material is able to simultaneously sequester large amounts of exudate over highly exudative regions and donate moisture to prevent desiccation of nondraining portions of the wound. The use of self-adaptive dressings simplifies wound care by assuring optimal moisture balance for the ever changing wound conditions within the complex chronic wound. * Enluxtra Wound Dressing, OSNovative Systems, Inc., BASF,Inc. OSNovative Systems, Inc. 500 Laurelwood Rd, Ste 1 & 4, Santa Clara, CA Page 15 of 16
16 OSNovative Systems, Inc. 500 Laurelwood Rd., Ste 1 & 4, Santa Clara, CA (888) OSNovative Systems, Inc. 500 Laurelwood Rd, Ste 1 & 4, Santa Clara, CA Page 16 of 16
Appropriate Dressing Selection For Treating Wounds
 Appropriate Dressing Selection For Treating Wounds Criteria to Consider for an IDEAL DRESSING Exudate Management Be able to provide for moist wound healing by absorbing exudate or adding moisture Secure
Appropriate Dressing Selection For Treating Wounds Criteria to Consider for an IDEAL DRESSING Exudate Management Be able to provide for moist wound healing by absorbing exudate or adding moisture Secure
The Power of a Hydroconductive Wound Dressing with LevaFiber Technology
 The Power of a Hydroconductive Wound Dressing with LevaFiber Technology The first step in healing a chronic wound is to detoxify it by removing slough, necrotic tissue, exudate and bacteria, while keeping
The Power of a Hydroconductive Wound Dressing with LevaFiber Technology The first step in healing a chronic wound is to detoxify it by removing slough, necrotic tissue, exudate and bacteria, while keeping
Agenda (45 minutes) Some questions for you. Which wound dressing? Dressing categories/types. Summary
 Dressing selection Agenda (45 minutes) Some questions for you. Which wound dressing? Dressing categories/types Summary Which wound dressing poster Ref: Which wound dressing? Practice Nursing, September
Dressing selection Agenda (45 minutes) Some questions for you. Which wound dressing? Dressing categories/types Summary Which wound dressing poster Ref: Which wound dressing? Practice Nursing, September
CASE 1: TYPE-II DIABETIC FOOT ULCER
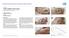 CASE 1: TYPE-II DIABETIC FOOT ULCER DIABETIC FOOT ULCER 48 YEAR-OLD MALE Mr. C., was a 48-year old man with a history of Type-II diabetes over the past 6 years. The current foot ulcer with corresponding
CASE 1: TYPE-II DIABETIC FOOT ULCER DIABETIC FOOT ULCER 48 YEAR-OLD MALE Mr. C., was a 48-year old man with a history of Type-II diabetes over the past 6 years. The current foot ulcer with corresponding
ENLUXTRA E-LEARNING VIDEO COURSE TRANSCRIPT
 ENLUXTRA E-LEARNING VIDEO COURSE TRANSCRIPT #1. Welcome to the Enluxtra Knowledge Base. #2. This video is about: Enluxtra technology Dressing application key points, including Sizing Peri-wound coverage
ENLUXTRA E-LEARNING VIDEO COURSE TRANSCRIPT #1. Welcome to the Enluxtra Knowledge Base. #2. This video is about: Enluxtra technology Dressing application key points, including Sizing Peri-wound coverage
Case 1. July 14, th week wound gel 3 cm x 2.5 cm = 7.5 cm². May 25, st wound gel on 290 days PI treatment 4 cm x 2.4 cm = 9.
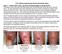 2.5% Sodium Hyaluronate Wound Gel Study Cases Case 1 Patient with Lower Leg Ulcer Not Responding to Compression This patient was a 50-year old male patient with nonhealing right lower leg since January
2.5% Sodium Hyaluronate Wound Gel Study Cases Case 1 Patient with Lower Leg Ulcer Not Responding to Compression This patient was a 50-year old male patient with nonhealing right lower leg since January
WOUND CARE. By Laural Aiesi, RN, BSN Alina Kisiel RN, BSN Summit ElderCare
 WOUND CARE By Laural Aiesi, RN, BSN Alina Kisiel RN, BSN Summit ElderCare PRESSURE ULCER DIABETIC FOOT ULCER VENOUS ULCER ARTERIAL WOUND NEW OR WORSENING INCONTINENCE CHANGE IN MENTAL STATUS DECLINE IN
WOUND CARE By Laural Aiesi, RN, BSN Alina Kisiel RN, BSN Summit ElderCare PRESSURE ULCER DIABETIC FOOT ULCER VENOUS ULCER ARTERIAL WOUND NEW OR WORSENING INCONTINENCE CHANGE IN MENTAL STATUS DECLINE IN
Your guide to wound debridement and assessment. Michelle Greenwood. Lorraine Grothier. Lead Nurse, Tissue Viability, Walsall Healthcare NHS Trust
 Your guide to wound debridement and assessment Michelle Greenwood Lead Nurse, Tissue Viability, Walsall Healthcare NHS Trust Lorraine Grothier Clinical Nurse Specialist, Tissue Viability, Central Essex
Your guide to wound debridement and assessment Michelle Greenwood Lead Nurse, Tissue Viability, Walsall Healthcare NHS Trust Lorraine Grothier Clinical Nurse Specialist, Tissue Viability, Central Essex
Topical antimicrobials (antiseptics) Iodine, Silver, Honey
 Topical antimicrobials (antiseptics) Iodine, Silver, Honey Iodine Honey Silver Enzymatic debridement Proteolytic enzyme, also called Proteinase Proteinase breaks the long chainlike molecules of proteins
Topical antimicrobials (antiseptics) Iodine, Silver, Honey Iodine Honey Silver Enzymatic debridement Proteolytic enzyme, also called Proteinase Proteinase breaks the long chainlike molecules of proteins
The Proven Multifunctional Dressing
 The Proven Multifunctional Dressing belongs to an innovative class of multifunctional wound care dressings. dressings effectively cleanse, fill, absorb and moisten wounds throughout the healing continuum.
The Proven Multifunctional Dressing belongs to an innovative class of multifunctional wound care dressings. dressings effectively cleanse, fill, absorb and moisten wounds throughout the healing continuum.
Consider the possibility of pressure ulcer development
 Douglas Fronzaglia II, DO, MS LECOM Institute for Successful Aging LECOM Institute for Advanced Wound Care and Hyperbaric Medicine Consider the possibility of pressure ulcer development 1 Identify ulcer
Douglas Fronzaglia II, DO, MS LECOM Institute for Successful Aging LECOM Institute for Advanced Wound Care and Hyperbaric Medicine Consider the possibility of pressure ulcer development 1 Identify ulcer
Nanogen Aktiv. Naz Wahab MD, FAAFP, FAPWCA Nexderma
 Nanogen Aktiv Naz Wahab MD, FAAFP, FAPWCA Nexderma Patient BM 75 y.o female with a history of Type 2 Diabetes, HTN, Hypercholesterolemia, Renal insufficiency, Chronic back Pain, who had undergone a L3-L4
Nanogen Aktiv Naz Wahab MD, FAAFP, FAPWCA Nexderma Patient BM 75 y.o female with a history of Type 2 Diabetes, HTN, Hypercholesterolemia, Renal insufficiency, Chronic back Pain, who had undergone a L3-L4
Wound Dressing. Choosing the Right Dressing
 Wound Dressing Choosing the Right Dressing Benefits of using the correct Drsg Helps create the optimal wound environment Increases healing rates Reduces pain Decreases infection rates Cost effective Care
Wound Dressing Choosing the Right Dressing Benefits of using the correct Drsg Helps create the optimal wound environment Increases healing rates Reduces pain Decreases infection rates Cost effective Care
Wound Jeopardy: Name That Wound Session 142 Saturday, September 10 th 2011
 Initial Wound Care Consult History Physical Examination Detailed examination of the wound Photographs Cultures Procedures TCOM ABI Debridement Management Decisions A Detailed History and Physical (wound)
Initial Wound Care Consult History Physical Examination Detailed examination of the wound Photographs Cultures Procedures TCOM ABI Debridement Management Decisions A Detailed History and Physical (wound)
Acute and Chronic WOUND ASSESSMENT. Wound Assessment OBJECTIVES ITEMS TO CONSIDER
 WOUND ASSESSMENT Acute and Chronic OBJECTIVES Discuss classification systems and testing methods for pressure ulcers, venous, arterial and diabetic wounds List at least five items to be assessed and documented
WOUND ASSESSMENT Acute and Chronic OBJECTIVES Discuss classification systems and testing methods for pressure ulcers, venous, arterial and diabetic wounds List at least five items to be assessed and documented
Wound Care Program for Nursing Assistants-
 Wound Care Program for Nursing Assistants- Wound Cleansing,Types & Presentation Elizabeth DeFeo, RN, WCC, OMS, CWOCN Wound, Ostomy, & Continence Specialist ldefeo@cornerstonevna.org Outline/Agenda At completion
Wound Care Program for Nursing Assistants- Wound Cleansing,Types & Presentation Elizabeth DeFeo, RN, WCC, OMS, CWOCN Wound, Ostomy, & Continence Specialist ldefeo@cornerstonevna.org Outline/Agenda At completion
Genadyne A4 and foam to treat a postoperative debridment flank abscess
 Genadyne A4 and foam to treat a postoperative debridment flank abscess Michael S. DO, The Wound Healing Center Indianapolis, IN Cynthia Peebles RN D.O.N., Becky Beck RN Heartland at Prestwick NH Avon,
Genadyne A4 and foam to treat a postoperative debridment flank abscess Michael S. DO, The Wound Healing Center Indianapolis, IN Cynthia Peebles RN D.O.N., Becky Beck RN Heartland at Prestwick NH Avon,
Wound Care Evaluation by Kris Dalseg MS PT CWS CLT
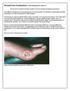 Wound Care Evaluation by Kris Dalseg MS PT CWS CLT This document is intended to describe a standard wound care evaluation for healthcare practitioners. In healthcare, all aspects of our treatment have
Wound Care Evaluation by Kris Dalseg MS PT CWS CLT This document is intended to describe a standard wound care evaluation for healthcare practitioners. In healthcare, all aspects of our treatment have
Advazorb. Hydrophilic foam dressing range
 Advazorb Hydrophilic foam dressing range Advazorb A comprehensive range of patient friendly, absorbent foam dressings Non-adhesive and atraumatic silicone adhesive options Designed to manage exudate whilst
Advazorb Hydrophilic foam dressing range Advazorb A comprehensive range of patient friendly, absorbent foam dressings Non-adhesive and atraumatic silicone adhesive options Designed to manage exudate whilst
V.A.C. Therapy Safety Information
 Bringing Safety Home V.A.C. Therapy Safety Information Bleeding Precautions Dressing Change Frequency Foam Removal Important Information 2 Prior to use of V.A.C. Therapy System it is important for the
Bringing Safety Home V.A.C. Therapy Safety Information Bleeding Precautions Dressing Change Frequency Foam Removal Important Information 2 Prior to use of V.A.C. Therapy System it is important for the
Disclosures for Tarik Alam. Wound Bed Preparation. Wound Prognosis. Session Objectives. Debridement 4/26/2015
 Disclosures for Tarik Alam Challenges in Managing Bioburden and Devitalized Tissue Tarik Alam RN, BScN, ET, MClSc(WH) Enterostomal Therapy Nurse tarikalam@hotmail.com Clinical Affairs Manager for Hollister
Disclosures for Tarik Alam Challenges in Managing Bioburden and Devitalized Tissue Tarik Alam RN, BScN, ET, MClSc(WH) Enterostomal Therapy Nurse tarikalam@hotmail.com Clinical Affairs Manager for Hollister
DRESSING SELECTION. Rebecca Aburn MN NP Candidate
 DRESSING SELECTION Rebecca Aburn MN NP Candidate Should be individually tailored in conjunction with the patient to meet their individual needs. WOUND MANAGEMENT: Comprehensive health assessment Wound
DRESSING SELECTION Rebecca Aburn MN NP Candidate Should be individually tailored in conjunction with the patient to meet their individual needs. WOUND MANAGEMENT: Comprehensive health assessment Wound
Palliative Care. EPUAP/NPUAP Publish New Pressure Ulcer Guidelines for. Treatment. Improving Quality of Care Based on CMS Guidelines 39
 Treatment EPUAP/NPUAP Publish New Pressure Ulcer Guidelines for Palliative Care Dealing with the end of a loved one s life is difficult enough, but when wound and skin care issues are involved, the decisions
Treatment EPUAP/NPUAP Publish New Pressure Ulcer Guidelines for Palliative Care Dealing with the end of a loved one s life is difficult enough, but when wound and skin care issues are involved, the decisions
Supporting healthcare professionals in taking control of the infection risk with ACTICOAT Flex TAKE CONTROL. of the infection risk in chronic wound
 Supporting healthcare professionals in taking control of the infection risk with ACTICOAT Flex TAKE CONTROL of the infection risk in chronic wound Introduction The impact of infection on patients is well
Supporting healthcare professionals in taking control of the infection risk with ACTICOAT Flex TAKE CONTROL of the infection risk in chronic wound Introduction The impact of infection on patients is well
TIME CONCEPT AND LOCAL WOUND MANAGEMENT
 TIME CONCEPT AND LOCAL WOUND MANAGEMENT B. BRAUN WOUND CARE INTRODUCTION: TIME is a global care framework used to implement appropriate care plans and promote wound healing Tissue Management Inflammation
TIME CONCEPT AND LOCAL WOUND MANAGEMENT B. BRAUN WOUND CARE INTRODUCTION: TIME is a global care framework used to implement appropriate care plans and promote wound healing Tissue Management Inflammation
Wound Care per HHVNA Wound Product Formulary
 Venous Ulcers ABI of 0.9-1.2 = normal blood flow An ABI MUST be obtained prior to inititiation of compression therapy. Compression is the Gold Standard of care to promote wound of venous ulcers. Elevation
Venous Ulcers ABI of 0.9-1.2 = normal blood flow An ABI MUST be obtained prior to inititiation of compression therapy. Compression is the Gold Standard of care to promote wound of venous ulcers. Elevation
HydroTherapy: A simple approach to Wound Management
 Copyright Paul Hartmann Pty Ltd material may not be reproduced or used without written permission HydroTherapy: A simple approach to Wound Management HARTMANN Education Agenda Agenda Acute vs Chronic wounds:
Copyright Paul Hartmann Pty Ltd material may not be reproduced or used without written permission HydroTherapy: A simple approach to Wound Management HARTMANN Education Agenda Agenda Acute vs Chronic wounds:
V.A.C. Therapy Patient Guide. Are you suffering from a wound? Ask your doctor about V.A.C. Therapy and whether it may be right for you.
 V.A.C. Therapy Patient Guide Are you suffering from a wound? Ask your doctor about V.A.C. Therapy and whether it may be right for you. kci1.com 800.275.4524 Table of Contents Wound Healing is a Process...2
V.A.C. Therapy Patient Guide Are you suffering from a wound? Ask your doctor about V.A.C. Therapy and whether it may be right for you. kci1.com 800.275.4524 Table of Contents Wound Healing is a Process...2
WOUND DRESSING Daily Dressing Packets
 AMERIGEL WOUND DRESSING Daily Dressing Packets P R O D U C T I N F O R M AT I O N MSDS APPLICATION PROTOCOLS AmeriGel WOUND DRESSING Daily Dressing Packets A HYDROGEL WITH A UNIQUE AUTOLYTIC DEBRIDER Diabetic
AMERIGEL WOUND DRESSING Daily Dressing Packets P R O D U C T I N F O R M AT I O N MSDS APPLICATION PROTOCOLS AmeriGel WOUND DRESSING Daily Dressing Packets A HYDROGEL WITH A UNIQUE AUTOLYTIC DEBRIDER Diabetic
o Venous edema o Stasis ulcers o Varicose veins (not including spider veins) o Lipodermatosclerosis
 Wound Care Equipment and Supply Benefits to Change for Texas Medicaid July 1, 2018 Effective for dates of service on or after July 1, 2018, wound care equipment and supply benefits will change for Texas
Wound Care Equipment and Supply Benefits to Change for Texas Medicaid July 1, 2018 Effective for dates of service on or after July 1, 2018, wound care equipment and supply benefits will change for Texas
MANAGEMENT OF DIABETIC WOUNDS : HEALTH CLINIC SETTING DR NORLIZAH PAIDI FAMILY MEDICINE SPECIALIST KLINIK KESIHATAN BANDAR MAS KOTA TINGGI JOHOR
 MANAGEMENT OF DIABETIC WOUNDS : HEALTH CLINIC SETTING DR NORLIZAH PAIDI FAMILY MEDICINE SPECIALIST KLINIK KESIHATAN BANDAR MAS KOTA TINGGI JOHOR OUTLINE DEFINITION FACTORS CONTRIBUTING TO WOUND DEVELOPMENT
MANAGEMENT OF DIABETIC WOUNDS : HEALTH CLINIC SETTING DR NORLIZAH PAIDI FAMILY MEDICINE SPECIALIST KLINIK KESIHATAN BANDAR MAS KOTA TINGGI JOHOR OUTLINE DEFINITION FACTORS CONTRIBUTING TO WOUND DEVELOPMENT
Foam dressings have frequently
 The practical use of foam dressings Efficient and cost-effective management of excessive exudate continues to challenge clinicians. Foam dressings are commonly used in the management of moderate to heavily
The practical use of foam dressings Efficient and cost-effective management of excessive exudate continues to challenge clinicians. Foam dressings are commonly used in the management of moderate to heavily
Determining Wound Diagnosis and Documentation Tips Job Aid
 Determining Wound Diagnosis and Job Aid 1 Coding Is this a traumatic injury from an accident? 800 Codes - Injury Section of the Coding Manual Code by specific site of injury. Only use for accidents or
Determining Wound Diagnosis and Job Aid 1 Coding Is this a traumatic injury from an accident? 800 Codes - Injury Section of the Coding Manual Code by specific site of injury. Only use for accidents or
The Risk. Background / Bias. Integrating Wound Care into a Limb Preservation Initiative 4/24/2009
 Stimulating Wound Granulation: Advances in NPWT and other Measures (Wound Bed Preparation) Charles Andersen MD, FACS, FAPWCA Clinical Prof of Surgery UW, USUHS Chief Vascular/Endovascular/ Limb Preservation
Stimulating Wound Granulation: Advances in NPWT and other Measures (Wound Bed Preparation) Charles Andersen MD, FACS, FAPWCA Clinical Prof of Surgery UW, USUHS Chief Vascular/Endovascular/ Limb Preservation
INTRODUCTION TO WOUND DRESSINGS
 WOUND CARE INTRODUCTION TO WOUND DRESSINGS JEC 2017 Wound Care Successfully completed specialized skills training in Wound Management. WOUND CONDITIONS & SYMBOLS BY COLOURS Yellow Black Necrotic tissue
WOUND CARE INTRODUCTION TO WOUND DRESSINGS JEC 2017 Wound Care Successfully completed specialized skills training in Wound Management. WOUND CONDITIONS & SYMBOLS BY COLOURS Yellow Black Necrotic tissue
ULCERS 1/12/ million diabetics in the US (2012) Reamputation Rate 26.7% at 1 year 48.3% at 3 years 60.7% at 5 years
 Jay Christensen D.P.M Advanced Foot and Ankle of Wisconsin 2-4% of the population at any given time will have ulcers 0.06-0.20% of the total population Average age of patients 70 years increased as more
Jay Christensen D.P.M Advanced Foot and Ankle of Wisconsin 2-4% of the population at any given time will have ulcers 0.06-0.20% of the total population Average age of patients 70 years increased as more
Regenerative Tissue Matrix in Treatment of Wounds
 Regenerative Tissue Matrix in Treatment of Wounds Learning Objectives Differentiate between reparative and regenerative healing Review surgical techniques for applying a regenerative tissue scaffold to
Regenerative Tissue Matrix in Treatment of Wounds Learning Objectives Differentiate between reparative and regenerative healing Review surgical techniques for applying a regenerative tissue scaffold to
Surgical Wounds & Incisions
 Surgical Wounds & Incisions A Comprehensive Review Assessment & Management Alex Khan APRN ACNS-BC MSN CWCN CFCN WCN-C Advanced Practice Nurse / Adult Clinical Nurse Specialist www.woundcarenurses.org 1
Surgical Wounds & Incisions A Comprehensive Review Assessment & Management Alex Khan APRN ACNS-BC MSN CWCN CFCN WCN-C Advanced Practice Nurse / Adult Clinical Nurse Specialist www.woundcarenurses.org 1
We look forward to serving you.
 ADVANCED CARE GEMCORE360 offers healthcare professionals a simple, clear and cost-effective wound care range while ensuring excellent clinical outcomes for their patients. 1 At GEMCO Medical, we strive
ADVANCED CARE GEMCORE360 offers healthcare professionals a simple, clear and cost-effective wound care range while ensuring excellent clinical outcomes for their patients. 1 At GEMCO Medical, we strive
Management of Complex Wounds with Vacuum Assisted Closure
 Management of Complex Wounds with Vacuum Assisted Closure Wendy McInnes Vascular / Wound Nurse Practitioner The Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Adelaide, South Australia Treasurer ANZSVN wendy.mcinnes@health.sa.gov.au
Management of Complex Wounds with Vacuum Assisted Closure Wendy McInnes Vascular / Wound Nurse Practitioner The Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Adelaide, South Australia Treasurer ANZSVN wendy.mcinnes@health.sa.gov.au
Skin Integrity and Wound Care
 Skin Integrity and Wound Care By Dr. Amer Hasanien & Dr. Ali Saleh Skin Integrity and Wound Care Skin integrity: the presence of normal Skin & Uninterrupted skin layers by wounds. Factors affecting appearance
Skin Integrity and Wound Care By Dr. Amer Hasanien & Dr. Ali Saleh Skin Integrity and Wound Care Skin integrity: the presence of normal Skin & Uninterrupted skin layers by wounds. Factors affecting appearance
Dressings do not heal wounds properly selected dressings enhance the body s ability to heal the wound. Progression Towards Healing
 Dressings in Wound Care: They Do Matter John S. Steinberg, DPM FACFAS Associate Professor, Department of Plastic Surgery Georgetown University School of Medicine Dressings do not heal wounds properly selected
Dressings in Wound Care: They Do Matter John S. Steinberg, DPM FACFAS Associate Professor, Department of Plastic Surgery Georgetown University School of Medicine Dressings do not heal wounds properly selected
Uncovering the Pressure Ulcer Coverup Rhonda Kistler RN MS CWON Wound Care Concepts Gentell
 Uncovering the Pressure Ulcer Coverup Rhonda Kistler RN MS CWON Wound Care Concepts Gentell Objectives Identify the stages of pressure ulcer according to the depth of tissue destruction. Discuss the differences
Uncovering the Pressure Ulcer Coverup Rhonda Kistler RN MS CWON Wound Care Concepts Gentell Objectives Identify the stages of pressure ulcer according to the depth of tissue destruction. Discuss the differences
Use of Non-Contact Low Frequency Ultrasound in Wound Care
 Use of Non-Contact Low Frequency Ultrasound in Wound Care BLAIRE CHANDLER SEPTEMBER 29, 2015 VCU DPT CLASS OF 2016 Objectives Patient case overview Examine clinical evidence Review intervention of interest
Use of Non-Contact Low Frequency Ultrasound in Wound Care BLAIRE CHANDLER SEPTEMBER 29, 2015 VCU DPT CLASS OF 2016 Objectives Patient case overview Examine clinical evidence Review intervention of interest
CLINICAL EVIDENCE Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT)
 CLINICAL EVIDENCE Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT) Endoform forms part of the NPWT strategy Endoform fits seamlessly with NPWT approaches. Utilize Endoform within the wound bed to help stabilize,
CLINICAL EVIDENCE Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT) Endoform forms part of the NPWT strategy Endoform fits seamlessly with NPWT approaches. Utilize Endoform within the wound bed to help stabilize,
Pressure ulcer. Dressing Selection Guide, Protocol, & Procedure
 Pressure ulcer Dressing Selection Guide, Protocol, & Procedure Sponsored by: Ferris Mfg. Corp. 16W300 83rd Street, Burr Ridge, IL 60527 USA Toll Free U.S.A.:800-765-9636 International: +1 630-887-9797
Pressure ulcer Dressing Selection Guide, Protocol, & Procedure Sponsored by: Ferris Mfg. Corp. 16W300 83rd Street, Burr Ridge, IL 60527 USA Toll Free U.S.A.:800-765-9636 International: +1 630-887-9797
Successful Wound Management Strategies : An Introduction. Alex Khan, APRN ACNS-BC. Organization of Wound Care Nurses
 Successful Wound Management Strategies : An Introduction Alex Khan, APRN ACNS-BC Organization of Wound Care Nurses www.woundcarenurses.org Goals & Objectives The role and importance of wound care management
Successful Wound Management Strategies : An Introduction Alex Khan, APRN ACNS-BC Organization of Wound Care Nurses www.woundcarenurses.org Goals & Objectives The role and importance of wound care management
Basic Dressing Categories
 Category of Dressing Examples Advantages/Indications Disadvantages/Contraindications Hydrofiber Aquacel AG - ConvaTec Aquacel - Convatec Excellent for absorbing excess exudate These dressings form a gel
Category of Dressing Examples Advantages/Indications Disadvantages/Contraindications Hydrofiber Aquacel AG - ConvaTec Aquacel - Convatec Excellent for absorbing excess exudate These dressings form a gel
Galen ( A.D) Advanced Wound Dressing
 Galen (120-201A.D) Advanced Wound Dressing Wounds heal optimally in a moist environment นพ.เก งกาจ ว น ยโกศล Wound assessment Ideal wound dressing Type of wound Clinical appearance Wound location Measurement
Galen (120-201A.D) Advanced Wound Dressing Wounds heal optimally in a moist environment นพ.เก งกาจ ว น ยโกศล Wound assessment Ideal wound dressing Type of wound Clinical appearance Wound location Measurement
ACOFP 55th Annual Convention & Scientific Seminars. New Physicians and Residents: Introduction to Wound Care. Katherine Lincoln, DO, FAAFP
 8 ACOFP 55th Annual Convention & Scientific Seminars New Physicians and Residents: Introduction to Wound Care Katherine Lincoln, DO, FAAFP Introduction to Wound Care KATHERINE LINCOLN, DO, FAAFP ACOFP
8 ACOFP 55th Annual Convention & Scientific Seminars New Physicians and Residents: Introduction to Wound Care Katherine Lincoln, DO, FAAFP Introduction to Wound Care KATHERINE LINCOLN, DO, FAAFP ACOFP
Essity Internal. Taking the fear out of wound infection: conquering everyday issues
 Taking the fear out of wound infection: conquering everyday issues Learning objectives 1. Identifying the cost which wound infection can have on both the patient and healthcare organisations 2. Understanding
Taking the fear out of wound infection: conquering everyday issues Learning objectives 1. Identifying the cost which wound infection can have on both the patient and healthcare organisations 2. Understanding
Lower Extremity Wound Evaluation and Treatment
 Lower Extremity Wound Evaluation and Treatment Boni-Jo Silbernagel, DPM Describe effective lower extremity wound evaluation and treatment. Discuss changes in theories of treatment in wound care and implications
Lower Extremity Wound Evaluation and Treatment Boni-Jo Silbernagel, DPM Describe effective lower extremity wound evaluation and treatment. Discuss changes in theories of treatment in wound care and implications
Advancing the science of wound bed preparation
 Advancing the science of wound bed preparation How Drawtex wound dressing works LevaFiber Technology provides three different types of action. Mechanisms of Action Capillary Action Hydroconductive Action
Advancing the science of wound bed preparation How Drawtex wound dressing works LevaFiber Technology provides three different types of action. Mechanisms of Action Capillary Action Hydroconductive Action
Venous Leg Ulcers. Care for Patients in All Settings
 Venous Leg Ulcers Care for Patients in All Settings Summary This quality standard focuses on care for people who have developed or are at risk of developing a venous leg ulcer. The scope of the standard
Venous Leg Ulcers Care for Patients in All Settings Summary This quality standard focuses on care for people who have developed or are at risk of developing a venous leg ulcer. The scope of the standard
Wound Classification. Overview
 Overview Jeffrey A. Niezgoda, MD FACHM, MAPWCA, CHWS Review of Initial Wound Care Consultation Rational for Classification Wound Appearance Wound Etiology Management Algorithms Initial Wound Care Consult
Overview Jeffrey A. Niezgoda, MD FACHM, MAPWCA, CHWS Review of Initial Wound Care Consultation Rational for Classification Wound Appearance Wound Etiology Management Algorithms Initial Wound Care Consult
Wound Assessment Report
 Wound Assessment Report Single Assessment, Single Wound Mary Taylor Assessment Patient ID MT4367147 Date of Birth 1939-4-18 Left Foot, Sole: Wound A Image taken 16-45-43 Area 1.7cm2 Perimeter 48mm Maximum
Wound Assessment Report Single Assessment, Single Wound Mary Taylor Assessment Patient ID MT4367147 Date of Birth 1939-4-18 Left Foot, Sole: Wound A Image taken 16-45-43 Area 1.7cm2 Perimeter 48mm Maximum
Many patients with chronic wounds. Case reports. The use of Prontosan in combination with Askina Calgitrol : an independent case series
 Case reports The use of Prontosan in combination with Askina Calgitrol : an independent case series Author: Liezl Naude Many patients with chronic wounds will develop infection (Landis et al, 2007; Sibbald
Case reports The use of Prontosan in combination with Askina Calgitrol : an independent case series Author: Liezl Naude Many patients with chronic wounds will develop infection (Landis et al, 2007; Sibbald
The Triangle of Wound Assessment
 The Triangle of Wound Assessment A simple and holistic framework for wound management CPWSC_TOWA_Brochure_210x210_2018.indd 1 10/01/2018 15.13 ? We asked healthcare professionals around the world about
The Triangle of Wound Assessment A simple and holistic framework for wound management CPWSC_TOWA_Brochure_210x210_2018.indd 1 10/01/2018 15.13 ? We asked healthcare professionals around the world about
2008 American Medical Association and National Committee for Quality Assurance. All Rights Reserved. CPT Copyright 2007 American Medical Association
 Chronic Wound Care ASPS #1: Use of wound surface culture technique in patients with chronic skin ulcers (overuse measure) This measure may be used as an Accountability measure Clinical Performance Measure
Chronic Wound Care ASPS #1: Use of wound surface culture technique in patients with chronic skin ulcers (overuse measure) This measure may be used as an Accountability measure Clinical Performance Measure
NovoSorb BTM. A unique synthetic biodegradable wound scaffold. Regenerating tissue. Changing lives.
 NovoSorb BTM A unique synthetic biodegradable wound scaffold Regenerating tissue. Changing lives. Overview NovoSorb BTM is a unique synthetic biodegradable wound scaffold that delivers good cosmetic and
NovoSorb BTM A unique synthetic biodegradable wound scaffold Regenerating tissue. Changing lives. Overview NovoSorb BTM is a unique synthetic biodegradable wound scaffold that delivers good cosmetic and
Diabetic Foot Ulcer Treatment and Prevention
 Diabetic Foot Ulcer Treatment and Prevention Alexander Reyzelman DPM, FACFAS Associate Professor California School of Podiatric Medicine at Samuel Merritt University Diabetic Foot Ulcers One of the most
Diabetic Foot Ulcer Treatment and Prevention Alexander Reyzelman DPM, FACFAS Associate Professor California School of Podiatric Medicine at Samuel Merritt University Diabetic Foot Ulcers One of the most
Evaluation of the Use of a Silver Collagen Amorphous Gel in the Healing of Post Surgical and Dehisced Lesions
 Evaluation of the Use of a Silver Collagen Amorphous Gel in the Healing of Post Surgical and Dehisced Lesions Presented by: Kathryn Khandaker, RN, BSN, CWCN and Deanna Sue Kohl, RN, BSN, CWOCN, CFCN Introduction:
Evaluation of the Use of a Silver Collagen Amorphous Gel in the Healing of Post Surgical and Dehisced Lesions Presented by: Kathryn Khandaker, RN, BSN, CWCN and Deanna Sue Kohl, RN, BSN, CWOCN, CFCN Introduction:
THERAPIES. HAND IN HAND. Need safe and efficient infection prevention and management? 1 The Cutimed. Closing wounds. Together.
 Closing wounds. Together. Need safe and efficient infection prevention and management? 1 The Cutimed Sorbact range. A responsible choice. THERAPIES. HAND IN HAND. www.bsnmedical.co.uk TOGETHER WE CAN MAKE
Closing wounds. Together. Need safe and efficient infection prevention and management? 1 The Cutimed Sorbact range. A responsible choice. THERAPIES. HAND IN HAND. www.bsnmedical.co.uk TOGETHER WE CAN MAKE
Lower Extremity Venous Disease (LEVD)
 Lower Extremity Venous Disease (LEVD) Lower Extremity Venous Disease (LEVD) Wounds Etiology Lower extremity venous leg ulcers are caused by chronic venous hypertension. Failure of valves in the veins or
Lower Extremity Venous Disease (LEVD) Lower Extremity Venous Disease (LEVD) Wounds Etiology Lower extremity venous leg ulcers are caused by chronic venous hypertension. Failure of valves in the veins or
Pressure Ulcer Staging. Staging of Wounds are based on the deepest level of tissue damage
 Pressure Ulcer Staging Staging of Wounds are based on the deepest level of tissue damage Pressure Ulcer Staging New Pressure Ulcer Staging Stage I Stage II Stage III Stage IV Unstageable Suspected Deep
Pressure Ulcer Staging Staging of Wounds are based on the deepest level of tissue damage Pressure Ulcer Staging New Pressure Ulcer Staging Stage I Stage II Stage III Stage IV Unstageable Suspected Deep
Definitions and criteria
 Several disciplines are involved in the management of diabetic foot disease and having a common vocabulary is essential for clear communication. Thus, based on a review of the literature, the IWGDF has
Several disciplines are involved in the management of diabetic foot disease and having a common vocabulary is essential for clear communication. Thus, based on a review of the literature, the IWGDF has
DRESSING SELECTION SIMPLIFIED
 10 DRESSING SELECTION SIMPLIFIED It must be recognised that no one dressing provides the optimum environment for the healing of all wounds (Mahoney, 2015) DRESSING SELECTION SIMPLIFIED Selecting the correct
10 DRESSING SELECTION SIMPLIFIED It must be recognised that no one dressing provides the optimum environment for the healing of all wounds (Mahoney, 2015) DRESSING SELECTION SIMPLIFIED Selecting the correct
How Wounds Heal: A Guide for the Wound-care Novice
 C L I N I C A L P R A C T I C E How Wounds Heal: A Guide for the Wound-care Novice BY Christine Pearson Christine Pearson, RN, IIWCC, is a wound clinician for Vancouver Coastal Health and has worked in
C L I N I C A L P R A C T I C E How Wounds Heal: A Guide for the Wound-care Novice BY Christine Pearson Christine Pearson, RN, IIWCC, is a wound clinician for Vancouver Coastal Health and has worked in
VACUUM ASSISTED CLOSURE (V.A.C.) THERAPY: Mr. Ismazizi Zaharudin Jabatan pembedahan Am Hospital Kuala Lumpur
 VACUUM ASSISTED CLOSURE (V.A.C.) THERAPY: Mr. Ismazizi Zaharudin Jabatan pembedahan Am Hospital Kuala Lumpur Learning Objectives Define Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT) Discuss guidelines for the
VACUUM ASSISTED CLOSURE (V.A.C.) THERAPY: Mr. Ismazizi Zaharudin Jabatan pembedahan Am Hospital Kuala Lumpur Learning Objectives Define Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT) Discuss guidelines for the
The use of MEDIHONEY in Palliative Wound Care and the Advanced Aging Patient
 The use of MEDIHONEY in Palliative Wound Care and the Advanced Aging Patient Presenter: Angel Sutton, RN, MSN/Ed, CWCN, CFCN, CCCN Wound Care Nurse Consultant Click here to view detailed product descriptions
The use of MEDIHONEY in Palliative Wound Care and the Advanced Aging Patient Presenter: Angel Sutton, RN, MSN/Ed, CWCN, CFCN, CCCN Wound Care Nurse Consultant Click here to view detailed product descriptions
If both a standardized, validated screening tool and an evaluation of clinical factors are utilized, select Response 2.
 (M1300) Pressure Ulcer Assessment: Was this patient assessed for Risk of Developing Pressure Ulcers? 0 - No assessment conducted [Go to M1306 ] 1 - Yes, based on an evaluation of clinical factors (for
(M1300) Pressure Ulcer Assessment: Was this patient assessed for Risk of Developing Pressure Ulcers? 0 - No assessment conducted [Go to M1306 ] 1 - Yes, based on an evaluation of clinical factors (for
Hemostasis Inflammatory Phase Proliferative/rebuilding Phase Maturation Phase
 The presenters are staff members of the CHI Health St. Elizabeth Burn and Wound Center. Many of the products discussed are used in our current practice but we have no conflict of interest to disclose.
The presenters are staff members of the CHI Health St. Elizabeth Burn and Wound Center. Many of the products discussed are used in our current practice but we have no conflict of interest to disclose.
South West Regional Wound Care Toolkit F. PRINCIPLES OF TREATMENT BASED ON ETIOLOGY (TREAT THE CAUSE)
 F. PRINCIPLES OF TREATMENT BASED ON ETIOLOGY (TREAT THE CAUSE) F.5 SURGICAL WOUND (CLOSED AND OPEN) 5.1 Background to Etiology Closed surgical wounds are well-approximated with a palpable healing ridge
F. PRINCIPLES OF TREATMENT BASED ON ETIOLOGY (TREAT THE CAUSE) F.5 SURGICAL WOUND (CLOSED AND OPEN) 5.1 Background to Etiology Closed surgical wounds are well-approximated with a palpable healing ridge
Ms Prudence Lennox. Ms Liz Milner. 15:30-16:00 Wound Management in Primary Care. Nurse Manager Healthcare Rehabilitation Auckland
 Ms Liz Milner Nurse Manager Healthcare Rehabilitation Auckland Ms Prudence Lennox President NZ Wound Care Society 15:30-16:00 Wound Management in Primary Care Overview Wounds we see in primary care Flap
Ms Liz Milner Nurse Manager Healthcare Rehabilitation Auckland Ms Prudence Lennox President NZ Wound Care Society 15:30-16:00 Wound Management in Primary Care Overview Wounds we see in primary care Flap
Prontosan. Clean. Easy Wound Healing. Wound Cleansing
 Prontosan Clean. Easy Wound Healing. Wound Cleansing CoE Infection Control Prontosan the unique combination of Betaine & Polihexanide reduces healing time removes and prevents biofilm prevents infections
Prontosan Clean. Easy Wound Healing. Wound Cleansing CoE Infection Control Prontosan the unique combination of Betaine & Polihexanide reduces healing time removes and prevents biofilm prevents infections
Assessment & Management of Wounds in primary practice.
 Assessment & Management of Wounds in primary practice. Nutrition Successful wound management depends on appropriate nutritional support. Poor nutrition is recognised as one of the major causes of poor
Assessment & Management of Wounds in primary practice. Nutrition Successful wound management depends on appropriate nutritional support. Poor nutrition is recognised as one of the major causes of poor
Venous. Arterial. Neuropathic (e.g. diabetic foot ulcer) Describe Wound Types & Stages of. Pressure Ulcers. Identify Phases of Healing & Wound Care
 A dressing the situation at hand Describe Wound Types & Stages of Pressure Ulcers Identify Phases of Healing & Wound Care Goals Clarify Referral Protocol Lacerations- The goal is nearest to complete approximation
A dressing the situation at hand Describe Wound Types & Stages of Pressure Ulcers Identify Phases of Healing & Wound Care Goals Clarify Referral Protocol Lacerations- The goal is nearest to complete approximation
4-layer compression bandaging system (includes microbe binding wound contact layer) Latex-free, 4-layer compression bandaging system
 JOBST Comprifore JOBST Comprifore at a glance: provides effective levels of sustained graduated compression provides built in safety and ease of application Insures compliance and maximum healing for cost
JOBST Comprifore JOBST Comprifore at a glance: provides effective levels of sustained graduated compression provides built in safety and ease of application Insures compliance and maximum healing for cost
Wound Management. E. Foy White-Chu, MD, CWSP
 Wound Management E. Foy White-Chu, MD, CWSP E. Foy White-Chu, MD, CWSP Assistant Professor, OHSU Wound Medical Director, VAPORHCS List the Four Principles of Wound Bed Preparation Determine safe debridement
Wound Management E. Foy White-Chu, MD, CWSP E. Foy White-Chu, MD, CWSP Assistant Professor, OHSU Wound Medical Director, VAPORHCS List the Four Principles of Wound Bed Preparation Determine safe debridement
A Pilot Study of Oxygen Therapy for Acute Leg Ulcers
 A Pilot Study of Oxygen Therapy for Acute Leg Ulcers Background: The concept of increasing the oxygen concentration in healing wounds developed originally with hyperbaric oxygen therapy and from the fact
A Pilot Study of Oxygen Therapy for Acute Leg Ulcers Background: The concept of increasing the oxygen concentration in healing wounds developed originally with hyperbaric oxygen therapy and from the fact
Beyond the Basics ImprovingYour Wound Care Knowledge. Berna Goldentyer RN, BSN, CWOCN Kathy Hugen RN, BSN, CWOCN
 Beyond the Basics ImprovingYour Wound Care Knowledge Berna Goldentyer RN, BSN, CWOCN Kathy Hugen RN, BSN, CWOCN Projects and Posters These resources were developed by creative VA nurses who had no special
Beyond the Basics ImprovingYour Wound Care Knowledge Berna Goldentyer RN, BSN, CWOCN Kathy Hugen RN, BSN, CWOCN Projects and Posters These resources were developed by creative VA nurses who had no special
Welcome to NuMed! Our Commitment: Quality Products, Cost Savings, Exceptional Service
 It s a New Day in Wound Care Welcome to NuMed! Our Commitment: Quality Products, Cost Savings, Exceptional Service NuMed Industries is a manufacturing company that specializes in Advanced Wound Care products.
It s a New Day in Wound Care Welcome to NuMed! Our Commitment: Quality Products, Cost Savings, Exceptional Service NuMed Industries is a manufacturing company that specializes in Advanced Wound Care products.
Slide 1. Slide 2 Disclosures. Slide 3 Objectives. Karen Rogge Miller, RN, BS, WCC Wound and Ostomy Clinician
 Slide 1 Karen Rogge Miller, RN, BS, WCC Wound and Ostomy Clinician Slide 2 Disclosures Wound and Ostomy RN at St. Vincent Healthcare and Billings Clinic, Billings, MT Former employee of KCI, a division
Slide 1 Karen Rogge Miller, RN, BS, WCC Wound and Ostomy Clinician Slide 2 Disclosures Wound and Ostomy RN at St. Vincent Healthcare and Billings Clinic, Billings, MT Former employee of KCI, a division
Integra Flowable Wound Matrix
 Integra Flowable Wound Matrix Table of Contents How Supplied...2 Storage...2 Product Information Disclosure...2 Symbols Used On Labeling...2 Instructions for Use... 3 Instructions for Use (Continued)...
Integra Flowable Wound Matrix Table of Contents How Supplied...2 Storage...2 Product Information Disclosure...2 Symbols Used On Labeling...2 Instructions for Use... 3 Instructions for Use (Continued)...
First Coast Service Options (FCSO) Medicare Policy Primer
 First Coast Service Options (FCSO) Medicare Policy Primer Medicare Jurisdiction (JN) Florida, Puerto Rico and U.S. Virgin Islands Application of Skin Substitute Grafts for the treatment of DFU and VLU
First Coast Service Options (FCSO) Medicare Policy Primer Medicare Jurisdiction (JN) Florida, Puerto Rico and U.S. Virgin Islands Application of Skin Substitute Grafts for the treatment of DFU and VLU
Ms Prudence Lennox. Director of Nursing IHC President of the NZ Wound Care Society Auckland. 8:45-9:15 Wound Management in Primary Care
 Ms Prudence Lennox Director of Nursing IHC President of the NZ Wound Care Society Auckland 8:45-9:15 Wound Management in Primary Care Wound management in primary care L I Z M I L N E R N U R S E M A N
Ms Prudence Lennox Director of Nursing IHC President of the NZ Wound Care Society Auckland 8:45-9:15 Wound Management in Primary Care Wound management in primary care L I Z M I L N E R N U R S E M A N
Traditional Silicone Technology
 Innovative Non-Silicone Low Trauma Adhesives versus Traditional Silicone Technology A Review and Comparison Alan Neil Medical Industry Consultant Advanced Wound Care Lohmann Corporation 2016 Chronic wound
Innovative Non-Silicone Low Trauma Adhesives versus Traditional Silicone Technology A Review and Comparison Alan Neil Medical Industry Consultant Advanced Wound Care Lohmann Corporation 2016 Chronic wound
DEBRIDEMENT. Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations
 DEBRIDEMENT Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations DEBRIDEMENT Principles - CSD Methods of Debridement Biopsy options PRINCIPLES OF WOUND MANAGEMENT
DEBRIDEMENT Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations DEBRIDEMENT Principles - CSD Methods of Debridement Biopsy options PRINCIPLES OF WOUND MANAGEMENT
Topical Oxygen Wound Therapy (MEDICAID)
 Topical Oxygen Wound Therapy (MEDICAID) Last Review Date: September 8, 2017 Number: MG.MM.DM.15C8v2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or
Topical Oxygen Wound Therapy (MEDICAID) Last Review Date: September 8, 2017 Number: MG.MM.DM.15C8v2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or
2/11/2016. Palliative Wound Management Workshop. Carolyn Brown BS, MEd, RN, ARM, CWS, FACCWS Carolyn Brown Consulting
 Palliative Wound Management Workshop Be the best that you can be! Carolyn Brown BS, MEd, RN, ARM, CWS, FACCWS Carolyn Brown Consulting 727-348-5856 cbjackwill@gmail.com Learner Objectives After attending
Palliative Wound Management Workshop Be the best that you can be! Carolyn Brown BS, MEd, RN, ARM, CWS, FACCWS Carolyn Brown Consulting 727-348-5856 cbjackwill@gmail.com Learner Objectives After attending
1/5. Introduction. Primary endpoint Time to reach readiness for closure by surgical intervention or left for closure by secondary intention
 1/5 Introduction Materials and methods Animal studies show that intermittent NPWT has potential to increase the rate of granulation tissue formation compared with adjustable intermittent (AI) NPWT 1 However,
1/5 Introduction Materials and methods Animal studies show that intermittent NPWT has potential to increase the rate of granulation tissue formation compared with adjustable intermittent (AI) NPWT 1 However,
CLINICAL EVIDENCE Partial and Deep Partial Burns
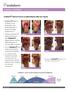 CLINICAL EVIDENCE Partial and Deep Partial Burns Endoform helps to improve re-epithelialization after burn injuries Endoform helps to facilitate tissue granulation and epithelialization in partial and
CLINICAL EVIDENCE Partial and Deep Partial Burns Endoform helps to improve re-epithelialization after burn injuries Endoform helps to facilitate tissue granulation and epithelialization in partial and
3M Cavilon Advanced Skin Protectant. Experience the power of ultimate protection.
 3M Cavilon Advanced Skin Protectant Experience the power of ultimate protection. The many challenges of skin integrity. Skin damage presents negative clinical outcomes resulting in potential complications
3M Cavilon Advanced Skin Protectant Experience the power of ultimate protection. The many challenges of skin integrity. Skin damage presents negative clinical outcomes resulting in potential complications
QUICK GUIDE SNAP THERAPY SYSTEM
 QUICK GUIDE SNAP THERAPY SYSTEM Clinical Pathway to SNAP System Full holistic assessment of patient and wound Is the wound type indicated for NPWT use without contraindications 1? SNAP System is indicated
QUICK GUIDE SNAP THERAPY SYSTEM Clinical Pathway to SNAP System Full holistic assessment of patient and wound Is the wound type indicated for NPWT use without contraindications 1? SNAP System is indicated
PROTEX HEALTHCARE (UK) LIMITED PRODUCT QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
 PROTEX HEALTHCARE (UK) LIMITED PRODUCT QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS Question What is Vacutex? How does Vacutex work? Does Vacutex prevent maceration to the surrounding skin? Does Vacutex adhere to the wound face?
PROTEX HEALTHCARE (UK) LIMITED PRODUCT QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS Question What is Vacutex? How does Vacutex work? Does Vacutex prevent maceration to the surrounding skin? Does Vacutex adhere to the wound face?
Total Contact Cast System
 Total Contact Cast System Instructions for Use Products Included in Cutimed Off-Loader Select kit Qty Cutimed Cavity Sterile 1 ea. Cutisorb Cotton Gauze 2" x 2" 4 ea. Delta-Lite Conformable Fiberglass
Total Contact Cast System Instructions for Use Products Included in Cutimed Off-Loader Select kit Qty Cutimed Cavity Sterile 1 ea. Cutisorb Cotton Gauze 2" x 2" 4 ea. Delta-Lite Conformable Fiberglass
BIOSORB GELLING FIBRE DRESSING. Key facts: In vitro evidence
 BIOSORB GELLING FIBRE DRESSING Key facts: In vitro evidence BIOSORB Gelling Fibre Dressing WHAT IS IT? BIOSORB Gelling Fibre Dressing is a soft, conformable non-woven dressing made from sodium carboxymethyl
BIOSORB GELLING FIBRE DRESSING Key facts: In vitro evidence BIOSORB Gelling Fibre Dressing WHAT IS IT? BIOSORB Gelling Fibre Dressing is a soft, conformable non-woven dressing made from sodium carboxymethyl
SAMPLE. HLTEN406A Undertake basic wound care. Learner resource. HLT07 Health Training Package. Version 2
 HLT07 Health Training Package HLTEN406A Undertake basic wound care Learner resource Version 2 Training and Education Support Industry Skills Unit Meadowbank Acknowledgments The TAFE NSW Training and Education
HLT07 Health Training Package HLTEN406A Undertake basic wound care Learner resource Version 2 Training and Education Support Industry Skills Unit Meadowbank Acknowledgments The TAFE NSW Training and Education
PALLIATIVE WOUND CARE
 PALLIATIVE WOUND CARE Scott Bolhack, MD, FACP President/CEO TLC HealthCare Companies Learning Objectives: Describe the aspects of palliative wound care.. Demonstrate palliative practices used in the care
PALLIATIVE WOUND CARE Scott Bolhack, MD, FACP President/CEO TLC HealthCare Companies Learning Objectives: Describe the aspects of palliative wound care.. Demonstrate palliative practices used in the care
