Clinical significance of interleukin-32 expression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
|
|
|
- Darren Daniel
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original article Clinical significance of interleukin-32 expression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis Ming Gui, Hao Zhang, Kuangbiao Zhong, Ying Li, Jian Sun and Li Wang Summary Objective To explore the clinical significance of interleukin (IL)-32 in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients and analyze the correlations of IL-32 with C-reactive protein (CRP), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and rheumatoid factor (RF). Methods A total of 97 patients with RA and 36 patients with non-ra connective tissue diseases (CTD) were included. The mrna levels of IL-32 and TNF-α in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were determined using a quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. The plasma concentrations of IL-32 and TNF-α were determined using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA and Spearman s method. Results The mrna levels of IL-32 and TNF-α in the active RA groups were significantly higher than those in the healthy control, stable RA, and non-ra CTD groups (P <0.01). There was no significant difference between the stable RA, healthy control, and non-ra CTD groups (P > 0.05). The concentrations of IL-32 and TNF-α in the active RA groups were significantly higher than those in the stable RA and control groups (P <0.01). IL-32 expression was positively correlated with TNF-α, ESR, CRP, RF, and DAS28 in patients with RA (P <0.01). From Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, the Third Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha , China Corresponding author: Hao Zhang haozhangcn@126.com Submitted date: 14/5/2012 Accepted date: 23/7/2012 Conclusion The levels of IL-32 and TNF-α in the peripheral blood of patients with active RA are significantly higher than in that of patients with stable RA and healthy people. The IL-32 level in peripheral blood may provide a reference for the detection of RA activity. (Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol 2012;31:73-8) Key words: rheumatoid arthritis, interleukin-32, tumor necrosis factor-α, C-reactive protein, connective tissue diseases Introduction Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease characterized by chronic articular inflammation. 1 Although the pathogenesis of RA remains unclear, T cells, B cells, macrophages, and synovial membrane fibroblasts are known to play a crucial roles in the development of articular inflammation and disease. 2-5 IL-32 is a relatively newly discovered cytokine and studies on it are still in their infancy. Studies on the correlation between IL-32 and RA are very limited. IL-32 induces the generation of pro-inflammatory factors (TNF-α, IL- 1, and IL-6) and chemokines via the mitogenactivated protein kinases NF-κB and p38 in human and rat cells. 6-9 Recent studies have shown that IL- 32 is closely correlated with the genesis of RA. 10,11.IL-32 is highly expressed in RA synovial living tissues, but is poorly expressed in osteoarthritis (OA) synovial tissues. 11 There is no study on IL-32 expression in the serum of RA patients. IL-32 synovial staining is correlated with disease activity, synovitis indices, and other synovial inflammatory factors. IL-32 also has a close correlation with TNFα, which plays an important role in the aggravation of TNF-α-related inflammatory arthritis and enteritis. These associations led us to question whether similar changes in IL-32 occur in the peripheral blood of patients with RA. In the present study, the levels of IL-32 and TNF-α in the peripheral blood of patients with RA were determined. Correlation analyses of these data and clinical data were performed to explore the possible role of IL-32 in the genesis of RA. 73
2 Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol 2012;31:73-8 Methods Patients A total of 97 patients in the Third Xiangya Hospital were diagnosed with RA between August 2010 and January All patients met the 1987 American College of Rheumatology diagnostic criteria for RA. 12 Among the patients, 23 were males and 74 were females with an approximate male to female ratio of 1:3. Their ages ranged from 23 years to 75 years with a mean age of 45 ± 13 years. Their duration of disease ranged from four months to twenty years. RA activity was evaluated according to the Disease Activity Score in 28 joints (DAS28). DAS28 > 2.6 was regarded as the threshold for RA in an active phase. Patients with DAS28 > 5.1 constituted the highly active RA group, and those with DAS28 between 2.6 and 5.1 were considerd to be the moderately active RA group. Patients with stable-phase RA must have DAS28 < 2.6, lasting at least two months according to the RA clinical remission criteria. 13 The steroid, NSAIDs and DMARDs taken by patients are shown in Table 1. A total of 36 patients constituted the non-ra CTD group. They received treatment in the Third Xiangya Hospital during the same period. There were 8 males and 28 females. Their ages ranged from 22 years to 55 years with a mean of 42 ± 7 years. There were 16 who had SLE and were taking prednisone (generic) (<20 mg/day) at the time ; 8 Table 1. The drugs used by patients in the RA group Item Highly active RA group (n=36) Moderately active RA group (n=33) RA remission group (n=28) No Only prednisone Methotrexate Leflunomide NSAIDs Methotrexate and prednisone Methotrexate and leflunomide Methotrexate and leflunomide and prednisone Anti-TNF and Methotrexate Anti-TNF and Methotrexate and leflunomide NSAIDs and one or more DMARDs had AS and were taking methotrexate plus an anti- TNF agent; 5 had dermatomyositis and were taking prednisone (generic) (<15 mg/day) plus methotrexate, 3 had Sjgren s syndromes, 2 had systemic sclerosis but were not taking NSAIDs, steroid or DMARDs, and 2 had adult Still s disease and were taking prednisone (generic) (<10 mg/day) plus methotrexate. All cases met the corresponding diagnostic criteria and were in an active phase. A total of 30 healthy volunteers constituted the healthy control group. There were 8 males and 22 females. Their ages ranged from 23 years to 60 years with a mean of 48 ± 10 years. They were free of heart diseases, diabetes, tumors, chronic obstructive lung diseases, inflammatory bowel diseases, and recent infectious diseases. This study was conducted in accordance with the declaration of Helsinki. This study was conducted with approval from the Ethics Committee of the Third Xiangya Hospital of Central South University. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants. Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) About 3 ml of venous blood was extracted from fasting subjects and was placed into a coagulationpromoting tube in the morning. Total mrna was extracted from the isolated PBMCs using an RNA extraction kit (Shanghai Biotechnology, China). cdna was synthesized according to the instructions indicated in arevertra Ace qpcr RT kit (TOYOBO, Japan). Based on the sequences in Genbank, target genes were designed using Primer 5.0 software. Syntheses were performed by Shanghai Biology Engineering. The sequences are listed in Table 2. The previously prepared cdna was used as the template. The optimal specific amplification conditions were as follows: the reaction system with a volume of 10 µl contained 5 µl of SYBR GreenER qpcrsupermix, 0.6 µl of cdna, 0.2 µl of the upstream primers, 0.2 µl of the downstream primers, and 4 µl of Rnase free water.the amplification conditions consisted of a pre-denaturation step at 94 C for 1 min, 40 cycles at 94 C for 15 s, 56 C for 15 s and 72 C for 45s, and a final extension step at 72 C for 7 min. Target gene expression was determined using an Eppendorf quantitative PCR analyzer. The expression of IL-32, TNF-α, and β-actin (the internal standard) was determined using quantitative real-time (QRT)-PCR, and 2 CT values were calculated. The QRT-PCR products were analyzed 74
3 Clinical significance of IL-32 in RA patients Table 2. PCR primer sequences, PCR product length of IL-32, TNF-α, β-actin Primer sequences PCR product length (bp) IL-32 Upstream: 5'-TGAGGAGCAGCACCCAGAGC-3' 310 Downstream: 5'-CCGTAGGACTGGAAAGAGGA-3' TNF-α Upstream: 5'-TC AGCCTCTTCTCCTTCCTG-3' 324 Downstream: 5'-TGAAGAGGACCTGGGAGTAG-3' β-actin Upstream: 5'-TGGACTTCGAGCAAGAGATGG-3' 298 Downstream: 5'-ATCTCCTTCTGCATCCTGTCG-3' in an electrophoresis gel and then observed using an ultraviolet projectoscope. The mobility rates were compared with the marker, and their molecular weights were estimated. The products were found to be the fragments of the target genes. Related Clinical Indexes Serum IL-32 and TNF-α concentrations were determined using a human IL-32 (R&D, USA) and TNF-α (Neo Bioscience, China) ELISA kit. Rheumatoid factor (RF) and C-reactive protein (CRP) were detected by the nephrometry scoring system. The ESR was determined by the Westergren method. Statistical Analysis Data were analyzed using the SPSS17.0 software. Data with normal distribution were presented as means ± standard errors ( x ± s). Onefactor ANOVA was performed for comparison among groups and Spearman s analysis was performed for correlation analysis. P <0.05 was considered statistically significant. Results Patients There was no significant differences between the gender, age, and body weights of the different groups (P >0.05) (Table 3). PCR Amplification PCR amplifications were performed using the previously mentioned cdna as templates. The electrophoresis results are shown in Figure 1. Expression of IL-32 and TNF-α The mrna expression of IL-32 and TNF-α in the active RA groups, which including highly active RA (n=36) and moderately active RA (n=33) was significantly higher than that in the stable RA (n=28) and healthy control groups (n=30) (P <0.05). No significant difference was observed between the stable RA and control groups (P >0.05). The results are shown in Table 4. Correlation Analysis In the active groups, the IL-32 mrna expression in PBMCs was positively correlated with TNF-α mrna expression (r = 0.587, P <0.01), ESR, RF, and DAS28, but had no correlation with age, disease course, or CRP (Table 5). The protein concentrations of serum IL-32 and TNF-α in the active RA groups were noticeably higher than those in the other three groups (P <0.05) (Table 4). The protein concentrations were positively correlated with ESR, CRP, RF, and DAS28, but not with age or disease course (Table 6). Table 3. General data for the different groups Item Highly active Moderately Stable RA Healthy control Non-RA RA active RA (n=28) (n=30) control(n=36) (n=36) (n=33) Age, years (mean ± SD) ± ± ± ± ± Sex Male 9 (25) 8 (4.2) 6 (1.4) 8 (6.7) 8 (2.2) Female 27 (75) 25 (75.8) 22 (78.6) 22 (73.3) 28 (77.8) Weight, kg (mean ± SD) 53.2 ± ± ± ± ±
4 Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol 2012;31:73-8 Figure 1. PCR products of the serum target genes (IL-32 and TNF-α) in the RA and control groups. A: β-actin corresponded by IL-32 and TNF-α in different groups; B and C: IL-32, in which 1-5 are for patients with highly active RA, 6-10 for those with moderately active RA, for those with stable RA, for the healthy control group, and for the non-ra CTD group. Discussion RA is a systemic inflammatory disease that affects multiple peripheral joints. The correlations of RA with numerous inflammatory cells (T, B, synovial, and antigen-presenting cells) and their produced inflammatory factors (TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, IL-15, IL-17, and IL-18) have been previously demonstrated. However, the patho-mechanism of RA remains unclear. The pathology of RA synovial tissues is mainly characterized by the penetration of numerous macrophages and T-lymphocytes, synovial lining hyperplasia, angiogenesis, as well as pannus formation. TNF-α is a pro-inflammatory factor that plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of RA and is the most often studied cytokine. TNF-α can be produced by different types of inflammatory cells, such as macrophages, mononuclear cells, T- lymphocytes, and synovial membrane fibroblasts. TNF-α induces the production of other inflammatory factors and promotes the generation of osteoclasts that lead to bone destruction. Inflammatory arthropathy can develop spontaneously in TNF-α transgenic rats. By contrast, TNF-α inhibitors can mitigate the severity of arthritis and TNF-α monoclonal antibodies, as well as soluble TNF-α receptor analogs, have been applied in the treatment of RA and other types of inflammatory arthropathy. 16 IL-32 is a recently discovered cytokine and performs an important role in the development of autoimmune diseases. It is highly expressed in chronic obstructive lung disease, Crohn s disease, psoriasis, and RA IL-32 is closely correlated with the development of these diseases. It is highly expressed in RA synovial tissues but weakly expressed in OA synovial tissues. It has noticeable correlations with the ESR, as well as local TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-18 in RA synovial tissues. An animal experiment has revealed that recombinant human IL-32γ can stimulate the production of TNF-α, IL- 1β, and macrophage inflammatory protein-2 to aggravate joint swelling, invasion of numerous inflammatory cells, and bone destruction in rats. 18 IL-32 γ can also promote the differentiation of osteoclast precursors into osteoclasts. 19 Therefore, IL-32 exhibits a pro-inflammatory feature and plays an important role in the pathogenesis of RA. IL-32 is maintained at a stable level in human PBMCs when there is no stimulation and only low levels of IL-32 protein can be detected in supernatant liquid. However, the level increases significantly after lipopolysaccharide stimulation. Table 4. Comparisons of the mrna expression and protein concentrations of IL-32 and TNF-α in PBMCs and serum among different groups ( x ± s) mrna Protein (pg/ml) Groups Cases IL-32 TNF-α IL-32 TNF-α Highly active RA ± 0.072*# ± 0.022*# 107 ± 42*# 261 ± 77*# Moderately active RA ± *# ± 0.006*# 66 ± 27*# 186 ± 84*# Stable RA ± ± ± 9 73 ± 24 Healthy control ± ± ± ± 20 Non-RA CTD ± ± ± 9 92 ± 22 F value P value * P <0.01, compared with the stable RA group; # P < 0.01, compared with the healthy control group; and P < 0.01, compared with the non-ra CTD group. 76
5 Clinical significance of IL-32 in RA patients Table 5. Correlation analyses of the mrna expression of PBMC IL-32 and TNF-α and age, disease course, ESR, CRP, RF, and DAS28 in the active RA groups Indexes IL-32 TNF-α r value P value r value P value Age (year) Disease course (year) ESR (mm/h) 0.321** ** CRP(mg/L) 0.185** ** RF (U/ml) 0.325** ** DAS * ** TNF-α 0.568** ** P <0.01, and * P <0.05. In TNF-α-free rats, joint swelling caused by IL-32 cannot be observed and cell invasion is greatly reduced. By contrast, such effects cannot be observed after proteoglycan loss. 16 These findings suggest that IL-32 activity partially depends on TNF-α. To clarify whether IL-32 is highly expressed in the PBMCs of RA patients, whether IL-32 in peripheral blood is correlated with RA activity, and whether IL-32 expression is correlated with TNF-α expression, active RA, stable RA and control groups were compared in the present study. The results show that IL-32 mrna expression in the PBMCs of patients with active RA is significantly higher than that in patients with stable RA and healthy people. Serum IL-32 protein expression in patients with active RA is also significantly higher. Serum IL-32 expression in patients with active RA is positively correlated with the RA activity indices ESR, CRP, RF, and DAS28. The mrna and protein expression of IL-32 is significantly correlated with that of TNFα in patients with active RA. Interestingly, IL-32 mrna expression is significantly higher than that of TNF-α mrna expression. However, the serum IL-32 protein levels are two times lower than the TNF-α protein level in both the RA and healthy control groups. This result can be explained as follows. First, an animal experiment has demonstrated an aggravation in collagen-induced arthritis after the transposition of IL-32β into CD4+ T cells, in contrast to the disappearance of the amplification effect of IL-32β after TNF-α removal. This finding suggests that the performance of IL-32 may be partially dependent on TNF-α. 18 Hence, IL-32 Table 6. Correlation analyses of the mrna expression of serum TNF-α and age, disease course, ESR, CRP, RF, and DAS28 in the active RA groups Indexes IL-32(pg/ml) TNF-α(pg/ml) r value P value r value P value Age (year) Disease course (year) ESR (mm/h) 0.401** ** CRP (mg/l) 0.334** ** RF (U/ml) 0.325** ** DAS ** ** TNF-α 0.527** ** P < presumably regulates TNF-α expression upstream and then promotes the occurrence of inflammation. Second, the present study detected IL-32 total mrna in cells. However, there is a possibility that some IL-32 subtypes have been secreted out of the cells to perform external pro-inflammatory roles, leaving others inside. This possibility can be clarified by further exploring the intra- and extracellular subtypes of IL-32. Intracellular IL-32 protein was not detected in this study due to the limited volume of each blood sample. To the best of our knowledge, there has been no reported study on IL-32 expression in patients with non-ra CTDs, such as SLE, AS, dermatomyositis and systemic sclerosis. In this study, the expression of IL-32 and TNF-α in the peripheral blood of patients with active non-ra CTDs was also detected. No significant difference is found between the IL-32 expression of the non-ra CTD and healthy control groups. However, only a small sample size of each non-ra disease was included in this study. Thus, the possible correlations between IL-32 and the development of these diseases cannot be completely excluded. In conclusion, IL-32 is highly expressed in patients with active RA and its expression is positively correlated with the RA activity indices ESR, CRP, RF, and DAS28. These results are consistent with high IL-32 expression in RA synovial tissues, which further demonstrates the possible important role of IL-32 in the pathogenesis of RA. Therefore, the detection of IL-32 and TNF-α expression in patients with RA greatly aids studies on the role of IL-32 in RA pathogenesis and provides new ideas for the targeted treatment of RA. 77
6 Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol 2012;31:73-8 However, IL-32 has six subtypes. The subtype that performs a major role in the peripheral blood of patients with RA is still uncertain at present. IL-32- related receptors and their action mechanisms also remain to be explored. Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest concerning this article. References 1. Andersson AK, Li C, Brennan FM. Recent developments in the immunobiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008;10: Singh K, Deshpande P, Pryshchep S, Colmegna I, Liarski V, Weyand CM, et al. ERK-dependent T-cell receptor threshold calibration in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol. 2009;183: Gottenberg JE, Miceli-Richard C, Ducot B, Goupille P, Combe B, Mariette X. Markers of B-lymphocyte activation are elevated in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis and correlated with disease activity in the ESPOIR cohort. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11:R Tanaka M, Nagai T, Tsuneyoshi Y, Sunahara N, Matsuda T, Nakamura T, et al. Expansion of a unique macrophage subset in rheumatoid arthritis synovial lining layer. Clin Exp Immunol. 2008;154: Bartok B, Firestein GS. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes: key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Rev. 2010; 233: Li W, Liu Y, Mukhtar MM, Gong R, Pan Y, Rasool ST, et al. Activation of Interleukin-32 Pro-Inflammatory Pathway in Response to Influenza A Virus Infection. PLoS One. 2008;3:e Marcondes AM, Ramakrishnan A, Deeg HJ. Myeloid Malignancies and the Marrow Microenvironment: Some Recent Studies in Patients with MDS. Curr Cancer Ther Rev. 2009;5: Kobayashi H, Yazlovitskaya EM, Lin PC. Interleukin-32 positively regulates radiation-induced vascular inflammation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009;74: Gabay C, McInnes IB. The biological and clinical importance of the 'new generation' cytokines in rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11: Cagnard N, Letourneur F, Essabbani A, Devauchelle V, Mistou S, Rapinat A, et al. Interleukin-32, CCL2, PF4F1 and GFD10 are the only cytokine/chemokine genes differentially expressed by in vitro cultured rheumatoid and osteoarthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2005;16: Joosten LA, Netea MG, Kim SH, Yoon DY, Oppers-Walgreen B, Radstake TR, et al. IL-32, a proinflammatory cytokine in rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103: Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988;31: Prevoo ML, van t Hof MA, Kuper HH,, van Leeuwen MA, van de Putte LB, et al. Modified disease activity scores that include twenty-eight-joint counts. Development and validation in a prospective longitudinal study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995;38: Lipsky PE, van der Heijde DM, St Clair EW, Furst DE, Breedveld FC, Kalden JR, et al. Infliximab and methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Trial in Rheumatoid Arthritis with Concomitant Therapy Study Group. N Engl J Med. 2000; 343: Choi JD, Bae SY, Hong JW, Azam T, Dinarello CA, Her E, et al. Identification of the most active interleukin-32isoform. Immunol. 2009;126: Carter KL, Cahir-McFarland E, Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus-induced changes n B-lymphocyte gene expression. J Virol. 2002; 76: Park GH, Choe J, Choo HJ, Park YG, Sohn J, Kim MK. Genomewide expression profiling of 8-chloroadenosine-and 8-chlorocAMP-treated human neuroblastoma cells using radioactive human cdna microarray. Exp Mol Med. 2002;34: Kim SH, Han SY, Azam T, Yoon DY, Dinarello CA. Interleukin- 32: a cytokine and inducer of TNFalpha. Immunity. 2005:22: Brown J, Matutes E, Singleton A, Price C, Molgaard H, Buttle D, et al. Lymphopain a cytotoxic T and naturalkiller cell-associated cysteine proteinase. Leukemia. 1998;12:
Autoimmune Diseases. Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic
 Autoimmune Diseases Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic Disclosures (financial) No relevant disclosures Learning Objectives Explain the pathophysiology of autoimmune disease Discuss safe administration
Autoimmune Diseases Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic Disclosures (financial) No relevant disclosures Learning Objectives Explain the pathophysiology of autoimmune disease Discuss safe administration
Immunological Aspect of Ozone in Rheumatic Diseases
 Immunological Aspect of Ozone in Rheumatic Diseases Prof. Dr. med. Z. Fahmy Chief Consulting Rheumatologist Augusta Clinic for Rheumatic Diseases And Rehabilitation Bad Kreuznach Germany Rheumatoid arthritis
Immunological Aspect of Ozone in Rheumatic Diseases Prof. Dr. med. Z. Fahmy Chief Consulting Rheumatologist Augusta Clinic for Rheumatic Diseases And Rehabilitation Bad Kreuznach Germany Rheumatoid arthritis
Introduction ORIGINAL ARTICLE
 Mod Rheumatol (2007) 17:28 32 Japan College of Rheumatology 2007 DOI 10.1007/s10165-006-0532-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hisashi Yamanaka Yoshiya Tanaka Naoya Sekiguchi Eisuke Inoue Kazuyoshi Saito Hideto Kameda
Mod Rheumatol (2007) 17:28 32 Japan College of Rheumatology 2007 DOI 10.1007/s10165-006-0532-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hisashi Yamanaka Yoshiya Tanaka Naoya Sekiguchi Eisuke Inoue Kazuyoshi Saito Hideto Kameda
Potential Role of Sphingosine 1-Phosphate in the. Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Potential Role of Sphingosine 1-Phosphate in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis COMMENTARY for Zhao, C., Fernandes, M.J., Turgeon, M., Tancrede, S., Di Battista, J., Poubelle, P.E. and Bourgoin,
Potential Role of Sphingosine 1-Phosphate in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis COMMENTARY for Zhao, C., Fernandes, M.J., Turgeon, M., Tancrede, S., Di Battista, J., Poubelle, P.E. and Bourgoin,
Lack of association of IL-2RA and IL-2RB polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis in a Han Chinese population
 Lack of association of IL-2RA and IL-2RB polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis in a Han Chinese population J. Zhu 1 *, F. He 2 *, D.D. Zhang 2 *, J.Y. Yang 2, J. Cheng 1, R. Wu 1, B. Gong 2, X.Q. Liu
Lack of association of IL-2RA and IL-2RB polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis in a Han Chinese population J. Zhu 1 *, F. He 2 *, D.D. Zhang 2 *, J.Y. Yang 2, J. Cheng 1, R. Wu 1, B. Gong 2, X.Q. Liu
1.0 Abstract. Title. Keywords. Rationale and Background
 1.0 Abstract Title A Prospective, Multi-Center Study in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients on Adalimumab to Evaluate its Effect on Synovitis Using Ultrasonography in an Egyptian Population Keywords Synovitis
1.0 Abstract Title A Prospective, Multi-Center Study in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients on Adalimumab to Evaluate its Effect on Synovitis Using Ultrasonography in an Egyptian Population Keywords Synovitis
A. Kopchev, S.Monov, D. Kyurkchiev, I.Ivanova, T. Georgiev (UMHAT St. Ivan Rilski, Medical University - Sofia, Bulgaria)
 International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6718, ISSN (Print): 2319 670X Volume 6 Issue 7 July 2017 PP. 08-12 Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), cartilage oligomeric
International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6718, ISSN (Print): 2319 670X Volume 6 Issue 7 July 2017 PP. 08-12 Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), cartilage oligomeric
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Correlation between Plasma Interleukin-18 Level and Disease Activity in Jordanian Patients
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Correlation between Plasma Interleukin-18 Level and Disease Activity in Jordanian Patients
MAF Shalaby Prof. Rheumatology Al Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt.
 MAF Shalaby Prof. Rheumatology Al Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt. AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE RA SLE VASCULITIS RELAPSING POLYCHONDRITIS SS DM/PM SJOGREN S SYNDROME RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Classically immune mediated
MAF Shalaby Prof. Rheumatology Al Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt. AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE RA SLE VASCULITIS RELAPSING POLYCHONDRITIS SS DM/PM SJOGREN S SYNDROME RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Classically immune mediated
IL-17 in health and disease. March 2014 PSO13-C051n
 IL-17 in health and disease March 2014 PSO13-C051n Originally Researchers Suggested That IL-12 and IL-4 drove Th Cell Differentiation Naïve CD4 + T cell Question: Which of these cell types is responsible
IL-17 in health and disease March 2014 PSO13-C051n Originally Researchers Suggested That IL-12 and IL-4 drove Th Cell Differentiation Naïve CD4 + T cell Question: Which of these cell types is responsible
SIGNIFICANCE OF ELEVATED INTERLEUKIN-6 LEVEL IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS PATIENTS
 SIGNIFICANCE OF ELEVATED INTERLEUKIN-6 LEVEL IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS PATIENTS Essam Tewfik Attwa and S. Al-Beltagy* Rheumatology & Rehabilitation Department, Zagazig University Faculty of Medicine
SIGNIFICANCE OF ELEVATED INTERLEUKIN-6 LEVEL IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS PATIENTS Essam Tewfik Attwa and S. Al-Beltagy* Rheumatology & Rehabilitation Department, Zagazig University Faculty of Medicine
B cells: a fundamental role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis?
 Rheumatology 2005;44(Suppl. 2):ii3 ii7 B cells: a fundamental role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis? doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keh616 The role of T cells in the pathogenesis of RA is well established,
Rheumatology 2005;44(Suppl. 2):ii3 ii7 B cells: a fundamental role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis? doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keh616 The role of T cells in the pathogenesis of RA is well established,
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Marge Beckman FALU, FLMI Vice President RGA Underwriting Quarterly Underwriting Meeting March 24, 2011
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Marge Beckman FALU, FLMI Vice President RGA Underwriting Quarterly Underwriting Meeting March 24, 2011 The security of experience. The power of innovation. www.rgare.com Case Study
Rheumatoid Arthritis Marge Beckman FALU, FLMI Vice President RGA Underwriting Quarterly Underwriting Meeting March 24, 2011 The security of experience. The power of innovation. www.rgare.com Case Study
Treating Rheumatologic Disease in Arizona: Good News, Bad News
 Treating Rheumatologic Disease in Arizona: Good News, Bad News Jeffrey R. Lisse, M.D. Ethel P. McChesney Bilby Professor of Medicine Chief, Section of Rheumatology University of Arizona School of Medicine
Treating Rheumatologic Disease in Arizona: Good News, Bad News Jeffrey R. Lisse, M.D. Ethel P. McChesney Bilby Professor of Medicine Chief, Section of Rheumatology University of Arizona School of Medicine
TIPE2 expression is increased in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis
 /, 2017, Vol. 8, (No.50), pp: 87472-87479 TIPE2 expression is increased in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis Zhu Shi-Bai 1, Liu Rui-Min 2, Sun Ying-Chuan 2, Zhai
/, 2017, Vol. 8, (No.50), pp: 87472-87479 TIPE2 expression is increased in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis Zhu Shi-Bai 1, Liu Rui-Min 2, Sun Ying-Chuan 2, Zhai
APRIL is increased in serum of patients with brain glioblastoma multiforme
 276 Eur. Cytokine Netw., Vol. 17 n 4, December 06, 276-80 APRIL is increased in serum of patients with brain glioblastoma multiforme Joanna Iłżecka 1, Marek Iłżecki 2 1 Department of Neurology, Medical
276 Eur. Cytokine Netw., Vol. 17 n 4, December 06, 276-80 APRIL is increased in serum of patients with brain glioblastoma multiforme Joanna Iłżecka 1, Marek Iłżecki 2 1 Department of Neurology, Medical
Analysis of regulatory T cell subsets in the peripheral blood of immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) patients
 Analysis of regulatory T cell subsets in the peripheral blood of immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) patients S. Yang, B. Chen, J. Shi, F. Chen, J. Zhang and Z. Sun Department of Nephrology, Huaihe Hospital
Analysis of regulatory T cell subsets in the peripheral blood of immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) patients S. Yang, B. Chen, J. Shi, F. Chen, J. Zhang and Z. Sun Department of Nephrology, Huaihe Hospital
Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA)
 Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA) Spondyloarthritis: Characteristic Parameters Used for Diagnosis I Symptoms Inflammatory back pain Imaging Lab ESR/CRP Patient s history Good response to NSAIDs Spondyloarthritis-Characteristic
Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA) Spondyloarthritis: Characteristic Parameters Used for Diagnosis I Symptoms Inflammatory back pain Imaging Lab ESR/CRP Patient s history Good response to NSAIDs Spondyloarthritis-Characteristic
Apolipoprotein A-I and cholesterol in synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and osteoarthritis
 Apolipoprotein A-I and cholesterol in synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and osteoarthritis F. Oliviero 1, P. Sfriso 1, G. Baldo 2, J.-M. Dayer 4, S. Giunco 2, A.
Apolipoprotein A-I and cholesterol in synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and osteoarthritis F. Oliviero 1, P. Sfriso 1, G. Baldo 2, J.-M. Dayer 4, S. Giunco 2, A.
Index. Index 439. Aequorin, 84, 94 Affinity precipitation, 372, AP-1, 100 Asthma, 170, 305
 Index 439 Index A Aequorin, 84, 94 Affinity precipitation, 372, 376 381 AP-1, 100 Asthma, 170, 305 B Bioassay, 185, comparison with ELISA, 318 GM-CSF bioassay, 351 IL-2 bioassay, 185 192, 300 IL-3 IL-6
Index 439 Index A Aequorin, 84, 94 Affinity precipitation, 372, 376 381 AP-1, 100 Asthma, 170, 305 B Bioassay, 185, comparison with ELISA, 318 GM-CSF bioassay, 351 IL-2 bioassay, 185 192, 300 IL-3 IL-6
Elevated level of interleukin-29: A proinflammatory role in synovial inflammation of rheumatoid arthritis
 Advances in Biochemistry 2014; 2(2): 29-33 Published online April 20, 2014 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ab) doi: 10.11648/j.ab.20140202.11 Elevated level of interleukin-29: A proinflammatory
Advances in Biochemistry 2014; 2(2): 29-33 Published online April 20, 2014 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ab) doi: 10.11648/j.ab.20140202.11 Elevated level of interleukin-29: A proinflammatory
Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Past, the Present and the Future
 Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Past, the Present and the Future Lai-Ling Winchow FCP(SA) Cert Rheum(SA) Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital University of the Witwatersrand Outline of presentation
Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Past, the Present and the Future Lai-Ling Winchow FCP(SA) Cert Rheum(SA) Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital University of the Witwatersrand Outline of presentation
Clinical Policy: Tocilizumab (Actemra) Reference Number: ERX.SPMN.44
 Clinical Policy: (Actemra) Reference Number: ERX.SPMN.44 Effective Date: 10/16 Last Review Date: 09/16 Coding Implications Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory
Clinical Policy: (Actemra) Reference Number: ERX.SPMN.44 Effective Date: 10/16 Last Review Date: 09/16 Coding Implications Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory
Efficacy of Anakinra in Bone: Comparison to Other Biologics
 Advances In Therapy Volume 19 No. 1 January/February 2002 Efficacy of Anakinra in Bone: Comparison to Other Biologics Stephen A. Paget, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery Department of Rheumatic Disease
Advances In Therapy Volume 19 No. 1 January/February 2002 Efficacy of Anakinra in Bone: Comparison to Other Biologics Stephen A. Paget, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery Department of Rheumatic Disease
Cell-Mediated Immunity and T Lymphocytes
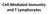 Cell-Mediated Immunity and T Lymphocytes T helper (Th) Cells Peripheral lymhoid tissue thymus Lymphoid stem cell CD8+ CD4+ CD4+ Treg CD8+ CTL + antigen Cytotoxic T lymphocyte CD4+ Th Helper T cell CD4+
Cell-Mediated Immunity and T Lymphocytes T helper (Th) Cells Peripheral lymhoid tissue thymus Lymphoid stem cell CD8+ CD4+ CD4+ Treg CD8+ CTL + antigen Cytotoxic T lymphocyte CD4+ Th Helper T cell CD4+
Interleukin-32 in Inflammatory Autoimmune Diseases
 http://dx.doi.org/10.4110/in.2014.14.3.123 pissn 1598-2629 eissn 2092-6685 REVIEW ARTICLE Interleukin-32 in Inflammatory Autoimmune Diseases * Department of Biomedical Sciences and Technology, Konkuk University,
http://dx.doi.org/10.4110/in.2014.14.3.123 pissn 1598-2629 eissn 2092-6685 REVIEW ARTICLE Interleukin-32 in Inflammatory Autoimmune Diseases * Department of Biomedical Sciences and Technology, Konkuk University,
Comparison between ESR and C-Reactive Protein(CRP) as a Marker of Disease activity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Original Article Comparison between ESR and C-Reactive Protein(CRP) as a Marker of Disease activity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Ali M.E. Yousef 1, Fatemah A. Elshabacy 2, Sherry K. Abdelrahman
Original Article Comparison between ESR and C-Reactive Protein(CRP) as a Marker of Disease activity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Ali M.E. Yousef 1, Fatemah A. Elshabacy 2, Sherry K. Abdelrahman
Serum chemokines in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with etanercept
 Serum chemokines in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with etanercept Piotr Adrian Klimiuk, Stanislaw Sierakowski, Izabela Domyslawska, Justyna Chwiecko To cite this version: Piotr Adrian Klimiuk,
Serum chemokines in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with etanercept Piotr Adrian Klimiuk, Stanislaw Sierakowski, Izabela Domyslawska, Justyna Chwiecko To cite this version: Piotr Adrian Klimiuk,
MANUAL IL-1alpha (mouse) ELISA Kit Cat. No. AG-45B-0003-KI01 [Interleukin-1 alpha (mouse) ELISA Kit]
![MANUAL IL-1alpha (mouse) ELISA Kit Cat. No. AG-45B-0003-KI01 [Interleukin-1 alpha (mouse) ELISA Kit] MANUAL IL-1alpha (mouse) ELISA Kit Cat. No. AG-45B-0003-KI01 [Interleukin-1 alpha (mouse) ELISA Kit]](/thumbs/75/71629507.jpg) MANUAL IL-1alpha (mouse) ELISA Kit [Interleukin-1 alpha (mouse) ELISA Kit] For research use only. Not for diagnostic use Version 1 (March-5-2013) Cat. No. AG-45B-0003-KI01 www.adipogen.com Table of Contents
MANUAL IL-1alpha (mouse) ELISA Kit [Interleukin-1 alpha (mouse) ELISA Kit] For research use only. Not for diagnostic use Version 1 (March-5-2013) Cat. No. AG-45B-0003-KI01 www.adipogen.com Table of Contents
ankylosing spondylitis Department of Clinical Immunology, Xijing Hospital, The Fourth Military
 Functional defects in CD4 + CD25 high FoxP3 + regulatory cells in ankylosing spondylitis Huifang Guo 1, 2, 3, Ming Zheng 1, 2, 3, Kui Zhang 1, 3, Fengfan Yang 1, 3, Xin Zhang 1, 3, Qing Han 1, 3, Zhi-Nan
Functional defects in CD4 + CD25 high FoxP3 + regulatory cells in ankylosing spondylitis Huifang Guo 1, 2, 3, Ming Zheng 1, 2, 3, Kui Zhang 1, 3, Fengfan Yang 1, 3, Xin Zhang 1, 3, Qing Han 1, 3, Zhi-Nan
Synoviocytes. Macrophage. B cell C H R O N I C. Neutrophil. Mast cell I N F L A M M A T I O N. Tissue cell. Endothelial cell. Th1/Th17 IL17 IL22
 DC IL12, IL23 chemokines, ECM, Co-stimulation IL17, IL22 IFNγ ± Macrophage peptidoglycan lipopolysaccharide heat shock proteins Th1/Th17 IL17 IL22 Cell contact, co-stimulation immune complexes acute phase
DC IL12, IL23 chemokines, ECM, Co-stimulation IL17, IL22 IFNγ ± Macrophage peptidoglycan lipopolysaccharide heat shock proteins Th1/Th17 IL17 IL22 Cell contact, co-stimulation immune complexes acute phase
Mechanisms of Autontibodies
 Mechanisms of Autontibodies Production in Rheumatic Diseases Eisa Salehi PhD Tehran University of Medical Sciences Immunology Department Introduction Rheumatic diseases: Cause inflammation, swelling, and
Mechanisms of Autontibodies Production in Rheumatic Diseases Eisa Salehi PhD Tehran University of Medical Sciences Immunology Department Introduction Rheumatic diseases: Cause inflammation, swelling, and
Abstract. , Eugene J. Kucharz. Magdalena Kopec-Medrek A D, F A, E, F
 Original papers Fibulin-3 and other cartilage metabolism biomarkers in relationship to calprotectin (MRP8/14) and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with anti-tnf therapy Magdalena
Original papers Fibulin-3 and other cartilage metabolism biomarkers in relationship to calprotectin (MRP8/14) and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with anti-tnf therapy Magdalena
Kun Jiang 1, He-Bin Chen 1, Ying Wang 1, Jia-Hui Lin 2, Yan Hu 1, Yu-Rong Fang 1
 Original Article Changes in interleukin-17 and transforming growth factor beta 1 levels in serum and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and their clinical significance among children with asthma Kun Jiang 1,
Original Article Changes in interleukin-17 and transforming growth factor beta 1 levels in serum and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and their clinical significance among children with asthma Kun Jiang 1,
Requirements in the Development of an Autoimmune Disease Amino Acids in the Shared Epitope
 + T cell MHC/self-peptide MHC/Vβ Induction of + T H 1 mediated autoimmunity: A paradigm for the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis and type I diabetes APC Activated autoreactive +
+ T cell MHC/self-peptide MHC/Vβ Induction of + T H 1 mediated autoimmunity: A paradigm for the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis and type I diabetes APC Activated autoreactive +
The Role of IL-1 and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α in Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 RHEUMATOID THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE ARTHRITIS MEDICAL JOURNAL The Role of IL-1 and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α in Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Eman Sh.Al-Obeidy*, Shatha F. Abdullah** ABSTRACT: BACKGROUND:
RHEUMATOID THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE ARTHRITIS MEDICAL JOURNAL The Role of IL-1 and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α in Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Eman Sh.Al-Obeidy*, Shatha F. Abdullah** ABSTRACT: BACKGROUND:
Judging disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis by serum free kappa and lambda light chain levels
 Kaohsiung Journal of Medical Sciences (2013) 29, 547e553 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: http://www.kjms-online.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Judging disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis
Kaohsiung Journal of Medical Sciences (2013) 29, 547e553 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: http://www.kjms-online.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Judging disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis
C. Assess clinical response after the first three months of treatment.
 Government Health Plan (GHP) of Puerto Rico Authorization Criteria Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNFα) Adalimumab (Humira ) Managed by MCO Section I. Prior Authorization Criteria A. Physician must submit
Government Health Plan (GHP) of Puerto Rico Authorization Criteria Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNFα) Adalimumab (Humira ) Managed by MCO Section I. Prior Authorization Criteria A. Physician must submit
The GPs role with biologics for immune-mediated inflammatory diseases David Gardner Rheumatologist GPCME 2015
 The GPs role with biologics for immune-mediated inflammatory diseases David Gardner Rheumatologist GPCME 2015 The views and opinions expressed in the following presentation are those of the presenter and
The GPs role with biologics for immune-mediated inflammatory diseases David Gardner Rheumatologist GPCME 2015 The views and opinions expressed in the following presentation are those of the presenter and
of 0.20) and Health assessment questionnaire disability index (HAQ-DI) (r partial
 IL-6 receptor inhibition modulates type III collagen and C-reactive protein degradation in rheumatoid arthritis patients with an inadequate response to anti-tumour necrosis factor therapy: analysis of
IL-6 receptor inhibition modulates type III collagen and C-reactive protein degradation in rheumatoid arthritis patients with an inadequate response to anti-tumour necrosis factor therapy: analysis of
Scintigraphic Findings and Serum Matrix Metalloproteinase 3 and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Levels in Patients with Polymyalgia Rheumatica
 The Open General and Internal Medicine Journal, 29, 3, 53-57 53 Open Access Scintigraphic Findings and Serum Matrix Metalloproteinase 3 and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Levels in Patients with Polymyalgia
The Open General and Internal Medicine Journal, 29, 3, 53-57 53 Open Access Scintigraphic Findings and Serum Matrix Metalloproteinase 3 and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Levels in Patients with Polymyalgia
Wei-Tso Chia a,b, Li-Tzu Yeh b, Yuan-Wu Chen b, Herng-Sheng Lee b, Deh-Ming Chang b and Huey-Kang Sytwu b, 1. Introduction
 Disease Markers 26 (2009) 1 7 1 DOI 10.3233/DMA-2009-0593 IOS Press IL-1β in irrigation fluid and mrna expression in synovial tissue of the knee joint as therapeutic markers of inflammation in collagen
Disease Markers 26 (2009) 1 7 1 DOI 10.3233/DMA-2009-0593 IOS Press IL-1β in irrigation fluid and mrna expression in synovial tissue of the knee joint as therapeutic markers of inflammation in collagen
Comparison of long-term clinical outcome with etanercept and adalimumab treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with respect to immunogenicity
 7 Comparison of long-term clinical outcome with etanercept and adalimumab treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with respect to immunogenicity Charlotte Krieckaert* Anna Jamnitski* Mike Nurmohamed Piet Kostense
7 Comparison of long-term clinical outcome with etanercept and adalimumab treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with respect to immunogenicity Charlotte Krieckaert* Anna Jamnitski* Mike Nurmohamed Piet Kostense
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Rheumatoid arthritis : of mice and men : towards the development of innovative therapies for rheumatoid arthritis Gerlag, D.M.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Rheumatoid arthritis : of mice and men : towards the development of innovative therapies for rheumatoid arthritis Gerlag, D.M. Link to publication Citation for published
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Rheumatoid arthritis : of mice and men : towards the development of innovative therapies for rheumatoid arthritis Gerlag, D.M. Link to publication Citation for published
12/10/2009. Department of Pathology, Case Western Reserve University. Mucosal Cytokine Network in IBD
 Cytokine-Mediated Inflammation in IBD Theresa T. Pizarro Department of Pathology, Case Western Reserve University Mucosal Cytokine Network in IBD Andoh, et al., 2008 1 Interleukin-1 (IL-1) Family Cytokine
Cytokine-Mediated Inflammation in IBD Theresa T. Pizarro Department of Pathology, Case Western Reserve University Mucosal Cytokine Network in IBD Andoh, et al., 2008 1 Interleukin-1 (IL-1) Family Cytokine
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Rituximab for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: rituximab_for_the_treatment_of_rheumatoid_arthritis 4/2008
Corporate Medical Policy Rituximab for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: rituximab_for_the_treatment_of_rheumatoid_arthritis 4/2008
The Correlation between Increased Serum Concentrations of Interleukin-6 Family Cytokines and Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
 Original Article DOI 10.3349/ymj.2011.52.1.113 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 52(1):113-120, 2011 The Correlation between Increased Serum Concentrations of Interleukin-6 Family Cytokines
Original Article DOI 10.3349/ymj.2011.52.1.113 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 52(1):113-120, 2011 The Correlation between Increased Serum Concentrations of Interleukin-6 Family Cytokines
High serum and synovial fluid granulocyte colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) concentrations in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
 Hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenocortical and -gonadal axis in RA / M. Cutolo The role of different fixatives for ANCA testing / EDITORIAL A. Radice et al. High serum and synovial fluid granulocyte colony
Hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenocortical and -gonadal axis in RA / M. Cutolo The role of different fixatives for ANCA testing / EDITORIAL A. Radice et al. High serum and synovial fluid granulocyte colony
Sarcoidosis: is there a role for anti-tnf-α?
 Sarcoidosis: is there a role for anti-tnf-α? Abstract In severe cases of sarcoidosis treatment can be very difficult. The common treatment strategies might be failing. Tumour necrosis factor (TNF) α therapy
Sarcoidosis: is there a role for anti-tnf-α? Abstract In severe cases of sarcoidosis treatment can be very difficult. The common treatment strategies might be failing. Tumour necrosis factor (TNF) α therapy
Summary. Introduction. Materials and methods
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2002) 10, 277 281 2002 OsteoArthritis Research Society International 1063 4584/02/040277+05 $22.00/0 doi:10.1053/joca.2001.0509, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2002) 10, 277 281 2002 OsteoArthritis Research Society International 1063 4584/02/040277+05 $22.00/0 doi:10.1053/joca.2001.0509, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com
Clinical Policy: Certolizumab (Cimzia) Reference Number: PA.CP.PHAR.247 Effective Date: 01/18 Last Review Date: 08/17 Line of Business: Medicaid
 Clinical Policy: (Cimzia) Reference Number: PA.CP.PHAR.247 Effective Date: 01/18 Last Review Date: 08/17 Line of Business: Medicaid Coding Implications Revision Log Description (Cimzia ) is a tumor necrosis
Clinical Policy: (Cimzia) Reference Number: PA.CP.PHAR.247 Effective Date: 01/18 Last Review Date: 08/17 Line of Business: Medicaid Coding Implications Revision Log Description (Cimzia ) is a tumor necrosis
Remicade (Infliximab)
 Remicade (Infliximab) Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.04.016 11/18/2003 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 07/26/2013 Section: Prescription Drugs Place(s)
Remicade (Infliximab) Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.04.016 11/18/2003 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 07/26/2013 Section: Prescription Drugs Place(s)
Received: 27 May 2003 Revisions requested: 26 Jun 2003 Revisions received: 14 Aug 2003 Accepted: 19 Aug 2003 Published: 1 Oct 2003
 Research article Etanercept versus etanercept plus methotrexate: a registrybased study suggesting that the combination is clinically more efficacious Ronald F van Vollenhoven 1, Sofia Ernestam 2, Anders
Research article Etanercept versus etanercept plus methotrexate: a registrybased study suggesting that the combination is clinically more efficacious Ronald F van Vollenhoven 1, Sofia Ernestam 2, Anders
PATHOGENESIS OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 PATHOGENESIS OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Division of Rheumatology Department of Internal Medicine College of Medicine Seoul National University Seoul National University Bundang Hospital Yun Jong Lee Rheumatoid
PATHOGENESIS OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Division of Rheumatology Department of Internal Medicine College of Medicine Seoul National University Seoul National University Bundang Hospital Yun Jong Lee Rheumatoid
Patient #1. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatoid Arthritis. 45 y/o female Morning stiffness in her joints >1 hour
 Patient #1 Rheumatoid Arthritis Essentials For The Family Medicine Physician 45 y/o female Morning stiffness in her joints >1 hour Hands, Wrists, Knees, Ankles, Feet Polyarticular, symmetrical swelling
Patient #1 Rheumatoid Arthritis Essentials For The Family Medicine Physician 45 y/o female Morning stiffness in her joints >1 hour Hands, Wrists, Knees, Ankles, Feet Polyarticular, symmetrical swelling
Effect of High-fat or High-glucose Diet on Obesity and Visceral Adipose Tissue in Mice
 ACTA ACADEMIAE MEDICINAE SINICAE 410011 0731-85295846 lixia2014@vip. 163. com 4 C57BL /6 20-1 mrna 20 P < 0. 05 O 20 P > 0. 05 M2 P < 0. 05-1 mrna P < 0. 05 P > 0. 05 R589. 2 DOI 10. 3881 /j. issn. 1000-503X.
ACTA ACADEMIAE MEDICINAE SINICAE 410011 0731-85295846 lixia2014@vip. 163. com 4 C57BL /6 20-1 mrna 20 P < 0. 05 O 20 P > 0. 05 M2 P < 0. 05-1 mrna P < 0. 05 P > 0. 05 R589. 2 DOI 10. 3881 /j. issn. 1000-503X.
Following T-cell activation and differentiation with HTRF reagents: IL-2, IFN-γ and IL-17
 Following T-cell activation and differentiation with HTRF reagents: IL-2, IFN-γ and IL-17 4 th HTRF Symposium for Drug Discovery Avignon, Sept. 24-26, 28 Introduction: T-cells have effector and helper
Following T-cell activation and differentiation with HTRF reagents: IL-2, IFN-γ and IL-17 4 th HTRF Symposium for Drug Discovery Avignon, Sept. 24-26, 28 Introduction: T-cells have effector and helper
Immunology for the Rheumatologist
 Immunology for the Rheumatologist Rheumatologists frequently deal with the immune system gone awry, rarely studying normal immunology. This program is an overview and discussion of the function of the
Immunology for the Rheumatologist Rheumatologists frequently deal with the immune system gone awry, rarely studying normal immunology. This program is an overview and discussion of the function of the
Serum levels of soluble ST2 and interleukin-33 in patients with dermatomyositis and polymyositis
 Serum levels of soluble ST2 and interleukin-33 in patients with dermatomyositis and polymyositis L. Yuan 1, L. Yao 2, L. Zhao 1, L. Xia 1, H. Shen 1, J. Lu 1 1 Department of Rheumatology, First Affiliated
Serum levels of soluble ST2 and interleukin-33 in patients with dermatomyositis and polymyositis L. Yuan 1, L. Yao 2, L. Zhao 1, L. Xia 1, H. Shen 1, J. Lu 1 1 Department of Rheumatology, First Affiliated
 Targeting Adipose Tissue in Rheumatoid Arthritis TARA study HOFFA L SCAPTIPL 0.1013606 0.270906 0.3759505 0.3373511 0.4050987 0.404667 11.6 DISCUSSIONS The study targeted the serum levels of adipokines
Targeting Adipose Tissue in Rheumatoid Arthritis TARA study HOFFA L SCAPTIPL 0.1013606 0.270906 0.3759505 0.3373511 0.4050987 0.404667 11.6 DISCUSSIONS The study targeted the serum levels of adipokines
Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 2011; 29:
 Soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor as a useful biomarker to predict the response to adalimumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in a Japanese population T. Koga 1, A. Okada 1, S. Kawashiri
Soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor as a useful biomarker to predict the response to adalimumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in a Japanese population T. Koga 1, A. Okada 1, S. Kawashiri
Mechanism of mirna-21-5p on apoptosis of IL-1β- induced rat. synovial cells
 Mechanism of mirna-21-5p on apoptosis of IL-1β- induced rat synovial cells Zhen Li 1,2,3,4, Xiaofu Li 4, Yi Wang 4, Qingjun Wei 1,2,3,* 1 Orthopaedic Department, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi
Mechanism of mirna-21-5p on apoptosis of IL-1β- induced rat synovial cells Zhen Li 1,2,3,4, Xiaofu Li 4, Yi Wang 4, Qingjun Wei 1,2,3,* 1 Orthopaedic Department, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi
Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 2 Volume Set. Text with Internet Access Code for Premium Consult Edition
 Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 2 Volume Set. Text with Internet Access Code for Premium Consult Edition Firestein, G ISBN-13: 9781437717389 Table of Contents VOLUME I STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BONE,
Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 2 Volume Set. Text with Internet Access Code for Premium Consult Edition Firestein, G ISBN-13: 9781437717389 Table of Contents VOLUME I STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BONE,
Amino acid sequences in the β chain HLA- DRB*0401 molecules dictate susceptibility to RA Amino Acids in the Shared Epitope
 MHC/self-peptide MHC/Vβ TCR Vβx + Vβx T cell Induction of + TH1 mediated autoimmunity: A paradigm for the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis and APC type I diabetes TCR Vβx Activated
MHC/self-peptide MHC/Vβ TCR Vβx + Vβx T cell Induction of + TH1 mediated autoimmunity: A paradigm for the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis and APC type I diabetes TCR Vβx Activated
Monoclonal Antibodies in the Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis Prof. John D. Isaacs
 John D Isaacs Professor of Clinical Rheumatology Director, Wilson Horne Immunotherapy Centre Newcastle University, UK 1 Rheumatoid arthritis Targeting T-cells Targeting B-cells Costimulation blockade Novel
John D Isaacs Professor of Clinical Rheumatology Director, Wilson Horne Immunotherapy Centre Newcastle University, UK 1 Rheumatoid arthritis Targeting T-cells Targeting B-cells Costimulation blockade Novel
Role of BAFF in B cell Biology and Autoimmunity
 Role of BAFF in B cell Biology and Autoimmunity B cell development in health and disease: B-lymphocytes or B cells, and the antibodies they produce, are crucial mediators of humoral immunity, providing
Role of BAFF in B cell Biology and Autoimmunity B cell development in health and disease: B-lymphocytes or B cells, and the antibodies they produce, are crucial mediators of humoral immunity, providing
Rheumatoid arthritis
 Rheumatoid arthritis 1 Definition Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most common inflammatory disorders affecting the population worldwide. It is a systemic inflammatory disease which affects not only
Rheumatoid arthritis 1 Definition Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most common inflammatory disorders affecting the population worldwide. It is a systemic inflammatory disease which affects not only
Possible roles of adiponectin in inflammatory process of rheumatoid arthritis
 193 Mini Review Possible roles of adiponectin in inflammatory process of rheumatoid arthritis Miho Suzuki and Masahiko Mihara Product Research Department, Fuji-Gotemba Research Laboratories, Chugai Pharmaceutical
193 Mini Review Possible roles of adiponectin in inflammatory process of rheumatoid arthritis Miho Suzuki and Masahiko Mihara Product Research Department, Fuji-Gotemba Research Laboratories, Chugai Pharmaceutical
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Manish Relan, MD FACP RhMSUS Arthritis & Rheumatology Care Center. Jacksonville, FL (904)
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Manish Relan, MD FACP RhMSUS Arthritis & Rheumatology Care Center. Jacksonville, FL (904) 503-6999. 1 Disclosures Speaker Bureau: Abbvie 2 Objectives Better understand the pathophysiology
Rheumatoid Arthritis Manish Relan, MD FACP RhMSUS Arthritis & Rheumatology Care Center. Jacksonville, FL (904) 503-6999. 1 Disclosures Speaker Bureau: Abbvie 2 Objectives Better understand the pathophysiology
Anti-inflammatory properties of SM04690, a small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway as a potential treatment for knee osteoarthritis
 Anti-inflammatory properties of SM04690, a small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway as a potential treatment for knee osteoarthritis V. Deshmukh 1, T. Seo 1, C. Swearingen 1, Y. Yazici 1 1 Samumed,
Anti-inflammatory properties of SM04690, a small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway as a potential treatment for knee osteoarthritis V. Deshmukh 1, T. Seo 1, C. Swearingen 1, Y. Yazici 1 1 Samumed,
Animal Models to Understand Immunity
 Animal Models to Understand Immunity Hussein El Saghire hesaghir@sckcen.be Innate Adaptive immunity Immunity MAPK and NF-kB TLR pathways receptors Fast Slow Non-specific Specific NOD-like receptors T-cell
Animal Models to Understand Immunity Hussein El Saghire hesaghir@sckcen.be Innate Adaptive immunity Immunity MAPK and NF-kB TLR pathways receptors Fast Slow Non-specific Specific NOD-like receptors T-cell
1. Background: Infliximab is administered parenterally; therefore, it is not covered under retail pharmacy benefits.
 Subject: Infliximab (Remicade ) Original Original Committee Approval: October 13, 2006 Revised Last Committee Approval: December 3, 2008 Last Review: October 19, 2007 1. Background: Infliximab is a genetically
Subject: Infliximab (Remicade ) Original Original Committee Approval: October 13, 2006 Revised Last Committee Approval: December 3, 2008 Last Review: October 19, 2007 1. Background: Infliximab is a genetically
Correlations between CXCL13, IL-24 genes and wrist arthritis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 25-30 Correlations between CXCL13, IL-24 genes and wrist arthritis G. ZHAO 1,2, J.-Y. MI 2, X.-Y. PAN 2, X. ZHANG 2, Y.-J. RUI 1,2 1 Department
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 25-30 Correlations between CXCL13, IL-24 genes and wrist arthritis G. ZHAO 1,2, J.-Y. MI 2, X.-Y. PAN 2, X. ZHANG 2, Y.-J. RUI 1,2 1 Department
Materials and Methods
 Short term hyperthermia prevents activation of proinflammatory genes in type B synoviocytes by blocking the activation of the transcription factor NF-κB Marica Markovic Institute of Medical Biochemistry,
Short term hyperthermia prevents activation of proinflammatory genes in type B synoviocytes by blocking the activation of the transcription factor NF-κB Marica Markovic Institute of Medical Biochemistry,
Research Article Association between Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Level and Rheumatoid Arthritis
 BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 913804, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/913804 Research Article Association between Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Level and Rheumatoid Arthritis
BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 913804, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/913804 Research Article Association between Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Level and Rheumatoid Arthritis
J. van Aken* H. van Dongen* S. le Cessie F.C. Breedveld T.W.J. Huizinga. * both authors contributed equally
 CHAPTER Comparison of long term outcome of patients with rheumatoid arthritis presenting with undifferentiated arthritis or with rheumatoid arthritis: an observational cohort study J. van Aken* H. van
CHAPTER Comparison of long term outcome of patients with rheumatoid arthritis presenting with undifferentiated arthritis or with rheumatoid arthritis: an observational cohort study J. van Aken* H. van
AUTOIMMUNITY CLINICAL CORRELATES
 AUTOIMMUNITY CLINICAL CORRELATES Pamela E. Prete, MD, FACP, FACR Section Chief, Rheumatology VA Healthcare System, Long Beach, CA Professor of Medicine, Emeritus University of California, Irvine Colonel
AUTOIMMUNITY CLINICAL CORRELATES Pamela E. Prete, MD, FACP, FACR Section Chief, Rheumatology VA Healthcare System, Long Beach, CA Professor of Medicine, Emeritus University of California, Irvine Colonel
AUTOIMMUNITY TOLERANCE TO SELF
 AUTOIMMUNITY CLINICAL CORRELATES Pamela E. Prete, MD, FACP, FACR Section Chief, Rheumatology VA Healthcare System, Long Beach, CA Professor of Medicine, Emeritus University of California, Irvine Colonel
AUTOIMMUNITY CLINICAL CORRELATES Pamela E. Prete, MD, FACP, FACR Section Chief, Rheumatology VA Healthcare System, Long Beach, CA Professor of Medicine, Emeritus University of California, Irvine Colonel
Performance of the Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) in patients under biological therapies
 Performance of the Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) in patients under biological therapies 1. Introduction The Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) is a new instrument
Performance of the Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) in patients under biological therapies 1. Introduction The Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) is a new instrument
p. 70 p. 94 p. 102 p. 105 p. 108
 European League Against Rheumatism EULAR - a vehicle for communication p. 3 EULAR - a vehicle for communication; the role of ILAR p. 8 Overview on the Scientific Basis of Rheumatic Diseases Molecular and
European League Against Rheumatism EULAR - a vehicle for communication p. 3 EULAR - a vehicle for communication; the role of ILAR p. 8 Overview on the Scientific Basis of Rheumatic Diseases Molecular and
MATERIALS AND METHODS. Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
Elevated risk of tuberculosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in Japan
 ARD Online First, published on July 12, 2006 as 10.1136/ard.2005.047274 Concise report Elevated risk of tuberculosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in Japan Toru Yamada, Ayako Nakajima, Eisuke Inoue,
ARD Online First, published on July 12, 2006 as 10.1136/ard.2005.047274 Concise report Elevated risk of tuberculosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in Japan Toru Yamada, Ayako Nakajima, Eisuke Inoue,
Elevated Levels of T Helper 17 Cells Are Associated with Disease Activity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Original Article Diagnostic Immunology Ann Lab Med 2013;33:52-59 ISSN 2234-3806 eissn 2234-3814 Elevated Levels of T Helper 17 Cells Are Associated with Disease Activity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Original Article Diagnostic Immunology Ann Lab Med 2013;33:52-59 ISSN 2234-3806 eissn 2234-3814 Elevated Levels of T Helper 17 Cells Are Associated with Disease Activity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Vol. 41 No Journal of Jiangxi Normal University Natural Science Sep. 2017
 41 5 Vol 41 No 5 2017 9 Journal of Jiangxi Normal University Natural Science Sep 2017 1000-5862 2017 05-0516-05 II 1 2 2 3 1 2* 1 518001 2 518060 3 518020 II ELISA IgE IgG IL-6 TNF-α IFN-γ 5 10 mg kg -
41 5 Vol 41 No 5 2017 9 Journal of Jiangxi Normal University Natural Science Sep 2017 1000-5862 2017 05-0516-05 II 1 2 2 3 1 2* 1 518001 2 518060 3 518020 II ELISA IgE IgG IL-6 TNF-α IFN-γ 5 10 mg kg -
Cytokines (II) Dr. Aws Alshamsan Department of Pharmaceu5cs Office: AA87 Tel:
 Cytokines (II) Dr. Aws Alshamsan Department of Pharmaceu5cs Office: AA87 Tel: 4677363 aalshamsan@ksu.edu.sa Learning Objectives By the end of this lecture you will be able to: 1 Understand the physiological
Cytokines (II) Dr. Aws Alshamsan Department of Pharmaceu5cs Office: AA87 Tel: 4677363 aalshamsan@ksu.edu.sa Learning Objectives By the end of this lecture you will be able to: 1 Understand the physiological
Non-commercial use only
 Reumatismo, 2016; 68 (2): 90-96 Real-world experiences of folic acid supplementation (5 versus 30 mg/week) with methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis patients: a comparison study K.T. Koh 1, C.L. Teh 2,
Reumatismo, 2016; 68 (2): 90-96 Real-world experiences of folic acid supplementation (5 versus 30 mg/week) with methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis patients: a comparison study K.T. Koh 1, C.L. Teh 2,
Rheumatoid arthritis: A heterogeneous disease with a heterogeneous response to treatment
 Rheumatoid arthritis: A heterogeneous disease with a heterogeneous response to treatment Pr Pierre Miossec MD PhD Clinical Immunology Unit Hôpital Edouard Herriot Lyon miossec@univ-lyon1.fr Pathogenesis
Rheumatoid arthritis: A heterogeneous disease with a heterogeneous response to treatment Pr Pierre Miossec MD PhD Clinical Immunology Unit Hôpital Edouard Herriot Lyon miossec@univ-lyon1.fr Pathogenesis
Efficacy and Safety of Tocilizumab in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
 New Evidence reports on presentations given at EULAR 2010 Efficacy and Safety of Tocilizumab in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Report on EULAR 2010 presentations
New Evidence reports on presentations given at EULAR 2010 Efficacy and Safety of Tocilizumab in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Report on EULAR 2010 presentations
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information M1 macrophage-derived nanovesicles potentiate the anticancer efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors Yeon Woong Choo, 1, Mikyung Kang, 2, Han Young Kim, 1 Jin Han, 1 Seokyung Kang,
Supporting Information M1 macrophage-derived nanovesicles potentiate the anticancer efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors Yeon Woong Choo, 1, Mikyung Kang, 2, Han Young Kim, 1 Jin Han, 1 Seokyung Kang,
The BeSt way of withdrawing biologic agents
 The BeSt way of withdrawing biologic agents C.F. Allaart 1, W.F. Lems 2, T.W.J. Huizinga 1 1 Department of Rheumatology, Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden; 2 Department of Rheumatology, Free University
The BeSt way of withdrawing biologic agents C.F. Allaart 1, W.F. Lems 2, T.W.J. Huizinga 1 1 Department of Rheumatology, Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden; 2 Department of Rheumatology, Free University
Biologic agents in Internal Medicine-2018: Targeted therapies for.
 Biologic agents in Internal Medicine-2018: Targeted therapies for. Chronic inflammatory diseases affecting the skin Chronic inflammatory diseases affecting the gut Chronic inflammatory diseases affecting
Biologic agents in Internal Medicine-2018: Targeted therapies for. Chronic inflammatory diseases affecting the skin Chronic inflammatory diseases affecting the gut Chronic inflammatory diseases affecting
F or the management of rheumatoid arthritis, there is
 1294 EXTENDED REPORT Effectiveness of systematic monitoring of rheumatoid arthritis disease activity in daily practice: a multicentre, cluster randomised controlled trial J Fransen, H Bernelot Moens, I
1294 EXTENDED REPORT Effectiveness of systematic monitoring of rheumatoid arthritis disease activity in daily practice: a multicentre, cluster randomised controlled trial J Fransen, H Bernelot Moens, I
Case Report Pulmonary Sarcoidosis following Etanercept Treatment
 Case Reports in Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 724013, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/724013 Case Report Pulmonary Sarcoidosis following Etanercept Treatment Kuljeet Bhamra and Richard Stevens Department
Case Reports in Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 724013, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/724013 Case Report Pulmonary Sarcoidosis following Etanercept Treatment Kuljeet Bhamra and Richard Stevens Department
Role of JAKs in myeloid cells and autoimmune diseases. Satoshi Kubo, Kunihiro Yamaoka and Yoshiya Tanaka
 131 Mini Review Role of JAKs in myeloid cells and autoimmune diseases Satoshi Kubo, Kunihiro Yamaoka and Yoshiya Tanaka The First Department of Internal Medicine, University of Occupational and Environmental
131 Mini Review Role of JAKs in myeloid cells and autoimmune diseases Satoshi Kubo, Kunihiro Yamaoka and Yoshiya Tanaka The First Department of Internal Medicine, University of Occupational and Environmental
NBQX, An AMPA/Kainate Glutamate Receptor Antagonist, Alleviates Joint Disease In Models Of Inflammatory- And Osteo- Arthritis.
 NBQX, An AMPA/Kainate Glutamate Receptor Antagonist, Alleviates Joint Disease In Models Of Inflammatory- And Osteo- Arthritis. Cleo S. Bonnet, PhD 1, Anwen S. Williams, PhD 1, Sophie J. Gilbert, PhD 1,
NBQX, An AMPA/Kainate Glutamate Receptor Antagonist, Alleviates Joint Disease In Models Of Inflammatory- And Osteo- Arthritis. Cleo S. Bonnet, PhD 1, Anwen S. Williams, PhD 1, Sophie J. Gilbert, PhD 1,
PATHOGENESIS OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 PATHOGENESIS OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Division of Rheumatology Department of Internal Medicine College of Medicine Seoul National University Seoul National University Bundang Hospital Yun Jong Lee Rheumatoid
PATHOGENESIS OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Division of Rheumatology Department of Internal Medicine College of Medicine Seoul National University Seoul National University Bundang Hospital Yun Jong Lee Rheumatoid
Interleukin-6; pathogenesis and treatment of autoimmune inflammatory diseases
 54 Review Article Interleukin-6; pathogenesis and treatment of autoimmune inflammatory diseases Toshio Tanaka 1, 2), Masashi Narazaki 3), Kazuya Masuda 4) and Tadamitsu Kishimoto 4, ) 1) Department of
54 Review Article Interleukin-6; pathogenesis and treatment of autoimmune inflammatory diseases Toshio Tanaka 1, 2), Masashi Narazaki 3), Kazuya Masuda 4) and Tadamitsu Kishimoto 4, ) 1) Department of
Expression and clinical significance of the obesity-related gene TNFAIP9 in obese children
 Expression and clinical significance of the obesity-related gene TNFAIP9 in obese children L.Y. Gui 1, Y.L. Hu 1, Z.L. Hou 2 and P. Wang 1 1 Department of Pediatrics, Pediatrics, Women & Infants Hospital
Expression and clinical significance of the obesity-related gene TNFAIP9 in obese children L.Y. Gui 1, Y.L. Hu 1, Z.L. Hou 2 and P. Wang 1 1 Department of Pediatrics, Pediatrics, Women & Infants Hospital
