Introduction to. Arthritis. and
|
|
|
- Winifred Butler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction to Arthritis and Total Knee Replacement Knee replacement surgery has been available to arthritic patients for more than 30 years. Fortunately this surgical procedure has proven to be a very effective and reliable treatment for arthritis of the knee. The purpose of this pamphlet is to help you better understand knee replacement surgery. We will discuss how arthritis affects the knee and causes pain, stiffness, and disability. Further, we will describe knee replacement surgery and the usual recovery process. Finally, we will explain typical results of the operation and possible complications which may occur. It is our hope and intention that this knowledge will assist you in making an informed decision concerning your own need for knee replacement surgery. The physicians of Des Moines Orthopaedic Surgeons (DMOS) consist of a large group of orthopaedic subspecialists. In order to provide care for you that is as current and skilled as possible, each of the surgeons has chosen to emphasize surgical care of a limited number of orthopaedic conditions. The group has vast experience with the procedures of total hip and total knee replacement. Since the early 1970 s, surgeons of DMOS have performed over 10,000 total hip replacements and over 12,000 total knee replacements. This experience is unparalleled in our area.
2 Knee Anatomy and Function The knee joint is the largest joint in the body. It is a hinge-type joint formed by the meeting of two bones, the femur (thighbone) and the tibia (shinbone). The patella (kneecap) is also an important part of the knee joint. Ligaments and muscles secure these bones together and provide joint stability. All of the moving surfaces of the knee joint are covered with a smooth, firm lining known as articular or surface cartilage (Fig. 1). The contact of the cartilage on cartilage provides a cushioned, low friction surface. The combined structure of bone, cartilage, and muscle allows smooth, painless motion as you walk and bend and straighten your knee. EFFECTS OF ARTHRITIS Arthritis is the condition which results from gradual deterioration and loss of the joint surface cartilage (Fig. 2). This deterioration of cartilage may occur due to the effects of previous injury or from progressive wear, which occurs with aging. This process is called osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease. In addition, inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis may destroy joint surface cartilage. Mild arthritis causes joint stiffness and some discomfort. As the cartilage deterioration process progresses, nearly constant pain and permanent stiffness occur. At this point normal activities of daily living become difficult to carry out. Patients with advanced arthritis are only able to walk short distances before needing to rest, have difficulty going up and down stairs, and need assistance getting out of a chair or car. These patients often walk with a limp and may require the use of an assistance device such as a cane or walker. Femur Femur Surface Cartilage Patella Worn Surface Cartilage Patella Meniscus Cartilage Exposed Bone Tibia Tibia Fig. 1 Normal Knee Fig. 2 Arthritic Knee 2
3 Orthopaedic Evaluation & Treatment Alternatives In addition, ability to walk and the presence of a limp are noted. X-rays are very useful in determining the severity of arthritis (Fig. 3). As arthritis and cartilage deterioration progress the cartilage space between the bones decreases in size and may disappear altogether (bone rubbing on bone). This cartilage deterioration may be confined to a limited area of the knee joint (one compartment) or may involve the entire joint. After completion of the orthopaedic examination (symptoms, exam, x-rays), the various treatment options and specific recommendations will be discussed. Orthopaedic Consultation and Exam Your orthopaedic evaluation assesses the severity of your arthritis and leads to a treatment recommendation. With mild arthritis some moderation of activities and arthritis medications may be adequate. The occasional use of a cane may also be helpful. The evaluation begins with questions concerning the severity of your knee pain. We attempt to discover how your knee pain and stiffness limit your daily activities such as walking, stair climbing, and driving or riding in a car. We also ask about previous treatment such as medications, cortisone or other injections, and the use of a cane. Examination of the knee includes assessment of the knee range of motion (stiffness) and any knee deformity (bowlegged or knockkneed). Fig. 3 Normal Knee X-Ray (Note: Normal Cartilage Space) Arthritic Knee X-Ray (Note: Loss of Cartilage Space) 3
4 Injections of various substances into the knee joint may give temporary relief of arthritic symptoms. Cortisone injections have been utilized for more than 40 years and give very reliable, but temporary relief of arthritis pain. More recently lubricating substances (visco supplementation) have become available. These treatments are given in a series of three to five weekly injections into the knee joint. These injections can be very effective for patients with mild or moderate osteoarthritis, but are usually not effective for patients with severe osteoarthritis. Many patients ask about the use of the nutrients glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate. These two substances may promote the growth or regeneration of articular cartilage and may also have an anti-inflammatory effect. Like visco supplementation, the efficiency of this treatment is not well documented at this time. These substances appear to be very safe and can be obtained without prescription at most pharmacies and nutriceutical retailers. With more severe or constant pain and the inability to carry out daily activities, surgery with total knee replacement is often the recommended treatment. Age itself is not a major consideration in total knee replacement. The severity of the patient s pain and restriction in activities is the primary consideration. Younger patients must be aware that they need to moderate their activities if they are to enjoy comfortable use of their knee replacement for many years. Older patients whose health remains satisfactory should be able to tolerate a major operation and benefit from it. NONSURGICAL TREATMENT OF ARTHRITIS Weight Loss Moderation in Activity Arthritis Medication Glucosamine Cortisone Injection Visco Supplementation Injection Cane Knee Prosthesis Total knee replacement surgery requires replacement of the damaged cartilage joint surfaces with metal and plastic components (prosthesis). Metal on plastic artificial joints have proven to be selflubricating and show minimal effects of wear despite years of use. Nearly all knee replacements require the use of three parts or components (Fig. 4): 1) The femoral component is made of metal and covers the end of the femur (thighbone). Femoral Component Tibial Component Fig. 4 Total Knee Replacement 4
5 2) The tibial component is high-molecular weight polyethylene (plastic) that is reenforced by a metal base plate and sits on top of the tibia (shinbone). 3) The patellar component is polyethylene and covers the undersurface of the kneecap. In some circumstances the cartilage of the kneecap remains satisfactory and in that situation the patellar component may not be utilized. Actually very little bone is removed in the preparation for placement of the total knee components. The patient s own muscles and ligaments are preserved and continue to function and allow the new knee to work. Thus, the knee replacement provides new artificial surfaces to replace the worn cartilage. In selected circumstances, unicompartmental knee replacement (partial knee replacement) may be the best option (Fig. 5). Often the knee arthritis condition affects only one area of the knee severely and your surgeon may recommend that only that area of the joint be replaced. With this type of prosthesis, femoral and tibial components are smaller Femoral Component but still composed of the same materials. Unicompartmental knee replacement has the advantages of more normal function following recovery and a slightly easier recovery. This type of knee replacement has received considerable attention in the media in recent years and is one type of minimally invasive knee replacement. Surgeons at DMOS feel this type of knee replacement has significant advantages in appropriately selected cases. New design and materials utilized in knee joint replacement are slowly evolving. The plastic (ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene) material has been substantially improved in the last five years to enhance its wear resistance. This improvement has become standard in knee replacements at this time. Changes in the composition of the metal femoral component (zirconium) and design of the tibial component (mobile bearing) are occurring slowly and the appropriate use of these designs has yet to be fully determined. Your DMOS surgeon will discuss these options with you if they are felt to be appropriate in your case. Typically the artificial knee components are held to the bone with an acrylic cement. Fortunately this cement has been found to be very durable for years and years. In occasional cases knee components which allow fixation by bone ingrowth will be placed without cement. We will discuss these options with you prior to surgery. Tibial Component Fig. 5 Unicompartmental Knee Replacement 5
6 Results of Total Knee Replacement People with a complete knee replacement are typically able to bend their knee well beyond a right angle (90 degrees). Kneeling is certainly possible after knee replacement; however, many patients find this difficult and thus seldom kneel. Patient Walking After Knee Replacement ACTIVITIES AFTER TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Walking Bicycling Swimming Golf Bowling After knee replacement you can expect nearly complete relief of your knee pain. While an artificial knee is not a normal knee, you can expect to resume most activities of daily living with comfort and ease. Studies have confirmed that approximately 95% of all knee replacements can expect a very good result. Unlimited walking tolerance is the goal and is often achieved. Most patients are able to climb stairs foot over foot and get out of a chair or car without help. Excessive weight or other medical conditions can certainly affect these activities, however. Recreational activities such as walking, bicycling, swimming, bowling, and golf are likely to be possible. More strenuous activities such as jogging, tennis, racquet sports, and skiing could damage the artificial knee and are not recommended. Patient Golfing After Knee Replacement 6
7 Long Term Expectations of Knee Replacement Most patients wish to know how long they can expect their artificial knee replacement to last. Long term scientific studies have confirmed that over 90% of knee joint replacements are still functioning well at 10 years and over 80% of knee joint replacements are still functioning quite well at 20 years. Over time a knee replacement may deteriorate or fail for a number of reasons. Wear or deterioration of the plastic polyethylene component may cause inflammation within the joint, which can lead to discomfort, swelling, and some deterioration of the bone called osteolysis (Fig. 6). The risk of this occurrence may well be decreasing with the improved polyethylene materials now available. Knee joint failure may also occur if the cement bond between the component and the bone deteriorates. Infection of a total joint replacement is a particularly serious problem and may require several surgeries to resolve. Fortunately, this complication occurs in less than one half of 1% of knee replacement patients. Repeat surgery on a knee replacement is commonly called revision joint replacement surgery. These procedures are becoming more common due to the vast number of patients having completed knee joint replacement surgery in the last 40 years. Generally speaking, revision surgery is more complex and more difficult than the primary surgery and may often be associated with a longer recovery and less favorable results than the initial surgery. LONG TERM RESULTS 90% of knee joint replacements are still functioning well at ten years. Over 80% of knee replacements are still functioning well at 20 years. Fig. 6 Example of Osteolysis 7
8 Risks of Knee Replacement No surgery is without risk. Understanding the risks of surgery is necessary in order for you to make an informed decision about your desire for surgery. Medical Complications. Anesthesia and surgery place increased stress on the body. Serious complications such as heart attack, stroke, or even death may occur. Fortunately, these events only occur very rarely. A thorough medical examination prior to surgery minimizes these risks. Infection. Infection is a very serious complication of any joint replacement surgery. Many precautions are taken to avoid infection and as a result the risk of infection is very low (less than a half a percent). These precautions include the use of antibiotics at the time of surgery, use of designated operating rooms with special air handling filters, and in some instances the use of space suits by the physician and nurses. Further surgery would be necessary if an infection should occur and the successful treatment of infection could require many months of treatment. Blood Loss. Following knee replacement surgery, and particularly following bilateral knee joint replacement surgery, a blood transfusion may be required. Patients undergoing a single joint replacement have less than a 10% risk of requiring a transfusion. Patients undergoing bilateral (right and left) replacements, however, have a greater than 50% chance of requiring blood transfusion. Blood-borne disease (AIDS, hepatitis, etc.) and adverse allergic reactions are the major hazards of blood transfusion. Our blood bank screening is as modern and thorough as Example of Space Suits That May Be Worn by Physician and Staff During Surgery. 8
9 possible and therefore the risks are exceedingly small. In fact, the risk of dying from a blood transfusion is hundreds of times lower than that when driving your car for one day. There are many options available to lower your chance of needing a blood transfusion. Obesity. Excessive weight can make the actual surgical procedure more difficult and increases your risk of complications such as wound healing and infection. Excessive weight may also shorten the life of the prosthesis; however, patients with excessive weight generally do very well following knee replacement surgery and this has been confirmed by numerous scientific studies. Blood Clots. Blood clots can occur after knee surgery, but this occurrence has been considerably decreased by the routine use of blood thinners after surgery. Generally you will be required to take small injections of blood thinner medications daily or you will use an oral blood thinner medication called Coumadin. Nerve, Artery or Bone Injury. Even rarer complications could include artery or nerve damage or fractures of the bones near the knee. Bilateral Surgery Frequently both the right and left knee are affected by similar serious arthritis. Under these circumstances, the best results are only obtained if each knee undergoes a total knee replacement. We have found that it is sometimes desirable to complete both knee replacements during the same hospitalization although certainly the second knee replacement can be delayed many months. Replacing both knees in one operation on the same day is occasionally possible, but generally we find it is too stressful for most patients and has a higher risk of anesthesia related complications such as heart and lung problems, blood loss, and blood clots. We have found, however, that two knee replacements can be completed during the same hospitalization, four to seven days apart, with great success. This option will be discussed by your surgeon if both of your knees are severely affected by the arthritis. This of course will prolong your hospital stay four to six days. 9
10 Preparations for Surgery Medical Consultation and Exam Once you have made a decision to proceed with knee replacement surgery, a number of necessary events will be scheduled. A date for surgery will be determined and scheduled at the hospital by your surgeon. A presurgical medical examination will be scheduled. Your own primary care physician will typically complete this examination. This examination should be carried out at the physician s office in the weeks prior to the scheduled surgery. Many patients will complete this presurgical medical evaluation at a special clinic and instructional session held at Iowa Methodist Medical Center. We will provide additional information concerning these sessions and schedule your evaluation. Routine laboratory tests are performed in the weeks prior to surgery. These include necessary blood tests, possibly x-rays, and an EKG. Iowa Methodist Medical Center provides a very helpful presurgical instructional session. Nurses, occupational therapists, physical therapists, and anesthesiologists provide useful information concerning your hospitalization for your total knee replacement and are also able to answer your questions. We strongly encourage you to attend this session if possible. Many patients will complete this instruction in conjunction with their presurgical medical evaluation. You will be contacted approximately two weeks prior to your surgery date and invited to attend this class. Please call Powell 5 staff at (515) if you have questions about this class. If scheduled to arrive at 7 a.m., please park in the Younker lot off Woodland Avenue. Enter the Powell Building under the blue canopy. You will find the orthopaedic clinic at the second door to the left as you enter the Powell building. This class will last approximately three hours. If arriving at 9 a.m., please park in the Younker lot off Woodland Avenue. Enter the Powell Building under the blue canopy. This class is held on the fifth floor of the Powell Building in the Powell 5 West conference room. The classroom is to your right as you come off the elevators. Please follow the signs to the classroom. You will be in the class until noon. Presurgical Instructional Session 10
11 Blood Donation. Blood transfusion may be necessary with knee joint replacement. However, we cannot predict the exact need for blood transfusions. Several options are available to lower your risk of needing blood bank blood. 1) No blood donations prior to surgery. Not everyone requires a blood transfusion following total joint replacement. In fact, less than 10% of patients undergoing a single knee joint replacement require a blood transfusion. If you would require blood after surgery, it will be supplied from the blood bank. The blood is carefully screened for disease and cross-matched to you prior to transfusion. As a result the risk of disease transmission or allergic reaction is extremely rare. 2) Autologous Donation. If your medical health allows, you can donate your own blood (autologous) which is stored and given back to you following surgery if necessary. In giving autologous blood donations, you may donate one unit of blood per week. We recommend avoiding autologous blood donation in the final two weeks prior to your surgery. Generally you may donate a maximum of three units of blood. We strongly encourage you to take an iron supplement if you are going to donate your own blood. If you do not utilize your own blood, it will be discarded, as it cannot be utilized in the general blood donation pool. Donating your own blood is not a guarantee that you will not need a blood bank transfusion. Autologous donation is being used less now because often the pre-donated blood is not used. In fact, many insurance companies will no longer cover the cost of obtaining blood that is not used. 3) Direct Donation. This is a process where you select specific people to donate blood for you. They will be screened and crossmatched to see if they are a compatible donor. Obtaining a blood transfusion from a friend or relative does not decrease your risk of a transfusion problem and in fact may slightly increase your risk. We will provide the necessary paperwork, but it is your responsibility to contact the blood center to make arrangements. 4) Epoetin alfa Procrit. This medication has been used for years for people with chronic anemic conditions. It is now being used occasionally for people undergoing total joint replacement to increase their blood count prior to surgery. You may only choose this option upon the recommendation of your physician and if your blood count falls within a certain range. This treatment consists of a series of subcutaneous injections beginning approximately three weeks prior to your surgery. 5) Cell Saver Transfusion. In cases where we expect more than the usual amount of blood loss or often with bilateral knee replacements, special drains may be utilized that allow us to save some of your own blood drainage and return the blood to you. 6) If you choose to have blood available through autologous donation, it is recommended to have: one unit for a total knee replacement one or two units for a total hip replacement more than two units for a revision or complex procedure or bilateral procedures Please remember that even with autologous or direct donation, the possibility of needing additional blood from the blood bank still exists. HOME MEDICATIONS Medications Prior to Surgery. If you are taking aspirin or anti-inflammatory medications, please discontinue their use two weeks prior to surgery. If you have donated your own blood or if you are anemic, we strongly encourage iron supplements beginning three weeks prior to surgery (one tablet twice daily). 11
12 Surgery & Hospital Stay DAY OF SURGERY Patients are usually admitted to the hospital on the day of surgery. You will be contacted by Iowa Methodist Medical Center the day before your surgery to confirm the time of your surgery and what time to arrive. Surgery times are available by noon the day before surgery. If you have not received a call by 2 p.m., call Powell 5 at (515) Please expect to arrive 2-1/2 hours prior to your surgery time. You should report to the Powell Building, fifth floor (the same floor where you participated in the pre-admission testing and teaching course). Check in at the nurse s station and you will be assigned a room. If you are not initially assigned to a private room, you will be moved to one as soon as one becomes available. We are not able to hold private rooms in advance. Seventy-five percent of the rooms on Powell Five are private at the present time. The patient should bring sleepwear, a good pair of walking shoes and personal hygiene supplies with them. You should not eat or drink after midnight the evening before surgery. If you take medications every morning, discuss these medications with your primary care physician or surgeon as we may have you take these medications with a small sip of water on the morning of surgery. Patients that live a long distance from the hospital or prefer to stay close by on the preoperative night can stay at the Care Inn just south of the hospital for a nominal fee. To reach the Care Inn, please call (515) to make a reservation. The Care Inn is located on the hospital campus. Family members may also keep a room at the Care Inn during the patient s hospital stay. Total knee replacement is either performed under a spinal anesthetic or a general anesthetic. You will have an opportunity to discuss these options with an anesthesiologist prior to your surgery. There are several factors that determine the type of anesthetic that should be used, but the patient s preference is also taken into account. The surgical procedure, including the time for preparation, is approximately two hours. You will also spend about 1-1/2 hours in the recovery room area before you are taken to your room. Following completion of the knee replacement surgery, your leg is placed in a bandage that extends from the toes to the upper thigh. Patient with Knee Bandage When you return to your room, you will begin to experience pain in your knee. The onset of this pain can vary considerably depending on whether you had a general anesthetic or a spinal anesthetic. This pain can be greatly relieved by the use of a PCA pump, which allows you to administer your own pain relieving medication. By simply pressing a button, a predetermined amount of pain medication is pumped into your IV line. This provides rapid relief of pain without the usual discomfort and delay of a hypo. Only the patient should operate 12
13 the PCA pump. Family or friends should not administer, this could cause overmedication. Your IV line is usually left in place for 48 hours so that you can be given adequate fluids and also so that necessary antibiotics can be given. Antibiotics help to prevent infection in your knee. You will be allowed to sit or stand at the bedside or you will be allowed to get up to a commode to void. Many patients do require the use of a catheter for a short period of time if they are unable to void. Physical Therapist with Patient Bending Knee Patient Walking with Crutches DAY 1 Most patients will be allowed and encouraged to get up out of bed the first day after surgery. Your diet will be progressed as long as you are not nauseated. An IV line will be continued through which fluids and antibiotics are given for the first 24 hours. Blood transfusions, if necessary, will be given through the same IV. You will continue the use of the PCA machine to alleviate pain in the operated knee. You will now begin the important rehabilitation process. The success of this program greatly depends on the cooperation and enthusiasm of the patient. The goals of physical therapy are to increase knee range of motion, build muscle strength and endurance, learn to walk with crutches, and to become independent with daily activities. Physical therapists will work with you each day emphasizing the importance of muscle strengthening and knee mobility. You will be instructed in a limited number of exercises, which you will continue throughout your hospitalization and upon your return home. They will also initiate walking with a walker or crutches. Finally, they will teach you to negotiate stairs safely. Occupational therapists will also see you each day. They will assist you in many activities including getting in and out of bed or a chair, dressing, bathing, and getting in and out of a car. They will also review more specific home instructions and safety recommendations. Nurses and other personnel will assist the patient in walking with either a walker or crutches at least three times per day. Some patients may use a CPM (Continuous Passive Motion) machine, which is a motorized device, which helps you bend your knee. Typically this device will be used twice a day for one to two hours. The knee motion allowed by the CPM will be increased with each use. It is very important that you fully extend or straighten your knee while using the CPM. Continuous Passive Motion Machine 13
14 Use of blood thinner begins on the day of surgery. This will either require a small shot daily or the use of Coumadin by mouth. In addition, many patients will use foot pumps which enhance circulation and diminish the risk of blood clots. These foot pumps are used at all times while in bed. DAY 2 The intravenous (IV) line will be discontinued on the second day. The full leg dressing, which was applied immediately after surgery, will be removed and replaced by a TED compression sock and an elastic sleeve around the knee. The knee dressing will be changed each day and the wound cleaned with alcohol. You can expect a moderate amount of swelling and bruising of the knee at this time. It takes several months for this to completely resolve. A physical therapist will again work with you each day on knee mobility and strengthening exercises. Occupational therapists will continue your instruction in activities of daily living. Nursing staff will continue your walking activities at least three times per day. It is our hope that you will be able to walk a greater distance each time. You are allowed and encouraged to place as much weight as is comfortable on the operated leg. A walker or crutches are merely for balance and security. At this point we will discourage the use of a bed pan as we want you to become more active and use the bathroom. Additional blood tests will be obtained periodically during your hospitalization. DAYS 3 5 Your rehabilitation program including physical therapy, occupational therapy, and ambulation with a walker or crutches will progress. Elastic TED stockings are continued to minimize the risk of blood clots and to control swelling in the lower leg and foot. If possible, these stockings should be worn during the day, but they may be removed at night for comfort. The patients will be ready for discharge from the hospital when they have demonstrated satisfactory independence with their walking and their necessary daily activities. This typically occurs three to five days after surgery. Nurses and social services will begin to help you make plans for any additional help you might need after returning home. If you need further assistance with your rehabilitation, you may go to a skilled nursing facility at your physician s recommendation. Patients who live alone or who have undergone bilateral knee replacement surgery are more likely to require a short stay in a skilled nursing facility. At the skilled nursing facility, you are given assistance with your activities of daily living and physical therapy until you become independent with the necessary activities. Your length of stay in the skilled nursing facility is determined by your progress. Most people are there for 7 to 14 days. These arrangements are completed at the hospital by a social worker. Upon your physician s recommendation, the social worker will make contact with you and discuss skilled nursing facility options. Whenever possible, the social worker will take your facility preferences into consideration. Transportation to the skilled facility is generally not covered by insurance companies and is the responsibility of the patient and their family. 14
15 Returning Home The Ride Home Most patients are ready to return home three to five days after surgery. At this time we expect you to be able to walk independently with crutches (or a walker), bend your knee to nearly 90 degrees (right angle), and lift your leg with the knee extended straight. The following instructions are intended to help make your return home as comfortable as possible. Since everyone s home situation varies, some patients may require additional assistance upon returning home. Either social services or home health care can arrange this assistance. If considerable help is necessary and if you live alone, transfer to an extended care facility where both nursing care and physical therapy are available may be required. Activity. We encourage you to be as active as possible. You should not spend too much time in bed other than at night to sleep. You should walk several times daily. These walks are by far the most important exercise you can do. As your recovery progresses, you should be able to walk longer distances and with less fatigue. Be careful not to push yourself too hard too quickly. You should continue to use your crutches until you obtain further instructions at your first office visit. Most patients are ready to progress to the use of crutches or a cane after only two weeks following surgery. Exercises. As noted previously, walking is the most important exercise. In addition, you should continue to work on the exercises that were started in the hospital under the direction of the physical therapist. These exercises are again described in a later section of this pamphlet. Physical Therapy. Supervised physical therapy following discharge after total knee replacement is generally not warranted. Numerous follow-up studies have shown that patients do just as well with a home exercise program and without the use of a home CPM machine. If special needs require, however, we will certainly arrange for outpatient physical therapy. Bathing. You may begin to shower as soon as four days after surgery. Bathing in a tub is acceptable after your staples are out, but is usually difficult for one to two months until your knee becomes more comfortable. Neither a shower nor a bath is harmful to your incision. 15
16 Incision. Usually the incision is healing well at the time of discharge and requires no special care at home. In most cases the skin staples will be removed at an office visit in the near future, or at home by a visiting nurse. If the incision becomes excessively swollen, red, or begins to drain, you should notify us. It is not unusual for the knee to remain swollen and feel warm and tight for several months after surgery. Elastic Stockings (TEDs). Please continue to wear the elastic stockings during the day when you are up. You do not need to wear them at night. You can discontinue these stockings when your foot and ankle swelling is gone. Return Appointment. Your first return examination in our office will occur about 7-10 days after discharge for the purpose of removing staples and to assess your progress. In most instances you will be given an appointment card at the time of discharge. If for some reason you do not receive an appointment or if your appointment time is not convenient, please call our office during normal office hours for an appointment time. Driving. You need to be able to control your leg well before resuming driving. Typically this occurs four to six weeks after surgery. We will advise you when we feel it is appropriate for you to resume driving. Traveling. It is reasonable to travel by car or plane soon after leaving the hospital. When traveling long distances you will be more comfortable if you stop and walk a little every hour. The artificial joints often set off airport security metal detectors. Your physician can supply you with a card as proof of your joint replacement if necessary. Medications. Most patients will require the occasional use of pain medications following discharge from the hospital. We will provide a prescription for an appropriate medication. In addition, you should resume any other medications you were taking prior to hospitalization unless otherwise instructed by a physician. Some patients will be also given a prescription for Coumadin (blood thinner) at the time of discharge. Patients requiring the use of Coumadin for an extended period of time will be asked to have their blood monitored with a blood test (PT/INR). Other patients will receive a low molecular weight heparin, such as Fragmin or Lovenox, that requires continuing the small injections under the skin. You will be provided with specific home instructions for the use of these injections if you are required to use them. Dental Care. When you require dental work (teeth cleaned, cavities filled, tooth pulled, root canal) we suggest the use of protective antibiotics. We generally recommend Keflex 500 mg tablets. Four tablets should be taken one hour prior to your dental care and no antibiotics are required after your dental care. Either your dentist or your physician can provide this prescription. It is generally recommended that you continue this precaution for two years after your surgery. Recovery. Keep in mind that although we expect a patient to be able to walk without crutches or a cane within four to six weeks of their surgery, full recovery and maximum comfort often require six or more months to occur. 16
17 Total Knee Exercise Program The goals of any knee exercise program are to build muscle strength and endurance, and to increase lower extremity mobility and function. These exercises are taught during the postoperative recovery period by your physical therapist. Each exercise should be performed two to three times per day for at least three months following your surgery. Quadriceps Setting 1) Lie on your back with both knees out as straight as possible. 2) Tighten the muscles on top of your thigh by pressing the back of your knee down into the surface. 3) Keep your toes pointed straight up. 4) Hold for five seconds, then relax. 5) Repeat ten times. Sitting Knee Stretch Bending 1) Sit in a straight chair. Feet flat on floor. 2) Slide your operated foot back. 3) Scoot buttocks to the edge of chair until a stretch is felt in the knee. Keep both feet flat on floor. 4) Hold for ten seconds, then relax. 5) Repeat ten times. 6) To assist the knee in bending more, cross the opposite ankle over the operated ankle and use gentle pressure to push the foot back. Straight Leg Raise 1) Lie on back with opposite knee bent and foot flat on bed. 2) Tighten the muscles on top of your thigh (do a quad set). 3) Lift the leg about twelve inches off the bed. 4) Keep the knee straight and toes pointed up throughout the exercise. 5) Hold for five seconds. 6) Slowly return to the starting position and relax. 7) Repeat ten times. Sitting Knee Stretch Straightening 1) Sit in a chair with your lower leg placed on another chair or footstool of the same height. 2) Press knee down until fully straight. Keep foot pointed up throughout. 3) To do this, tighten the muscles on top of your thigh or gently press down on your thigh. 4) Hold for 30 seconds, then relax. 5) Repeat ten times. 6) Decrease the number or repetitions of any exercise that produces pain that is lasting. 17
18 Common Questions COMMON QUESTIONS AND CONCERNS FOLLOWING TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT 1) Patients will commonly experience a click in their knee. This is normal and should not cause concern, and typically disappears. 2) All patients will experience some numbness or diminished feeling over the front of their knee in the area along the scar following surgery. This numbness will gradually improve over the first year, but will never completely disappear. 3) Kneeling and squatting are perfectly acceptable activities but never become as easy as in a normal knee. 4) Stiffness or tightness in the knee is a very common concern, but also tends to diminish over time although it often never completely resolves. Patients particularly complain of stiffness after a period of sitting or inactivity. 5) It is unlikely that your knee will bend or flex any further than it did prior to your surgery. In some patients with a particularly stiff knee, flexion may improve. 6) Some patients experience continued swelling in their joint of a mild degree indefinitely. Rarely is there a good explanation for this situation, but fortunately it causes only mild symptoms. 7) Remember that you can expect some improvement in pain, swelling, comfort and motion for a minimum of 6 months and often 12 months after the surgery. 8) Patients who experience particular difficulty in regaining their knee flexion may benefit from a knee manipulation with anesthesia. This option will be discussed with you if necessary by your surgeon. SUMMARY Total knee replacement is extremely effective in relieving the pain of arthritis. Most people with a total knee will continue to enjoy pain-free activity for many years after their surgery. It is extremely important for you to return for periodic evaluation of your artificial knee. These examinations typically should occur every two to five years or sooner if you experience any unexpected difficulties. Patient Bicycling 18
19 NOTES 19
20 NOTES 20
Total Knee Replacement
 Total Knee Replacement Learn About: How Your Knee Works Knee Related Problems Candidates for Knee Replacement Surgery What to Expect From Your Artificial Knee Preparing for Knee Replacement Your Surgery
Total Knee Replacement Learn About: How Your Knee Works Knee Related Problems Candidates for Knee Replacement Surgery What to Expect From Your Artificial Knee Preparing for Knee Replacement Your Surgery
What is arthroscopy? Normal knee anatomy
 What is arthroscopy? Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure for examining and repairing the inside of your knee. It is a minimally invasive surgical procedure which uses an Arthroscope and other specialized
What is arthroscopy? Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure for examining and repairing the inside of your knee. It is a minimally invasive surgical procedure which uses an Arthroscope and other specialized
Knee Replacement PROGRAM. Nightingale. Home Healthcare
 Knee Replacement PROGRAM TM Nightingale Home Healthcare With the help of Nightingale s experienced and professional rehabilitation team, you will be guided through a more complete and successful recovery
Knee Replacement PROGRAM TM Nightingale Home Healthcare With the help of Nightingale s experienced and professional rehabilitation team, you will be guided through a more complete and successful recovery
Brian P. McKeon MD Jason D. Rand, PA-C, PT Patient Information Sheet: Total Knee Replacement
 Brian P. McKeon MD Jason D. Rand, PA-C, PT Patient Information Sheet: Total Knee Replacement This is a general information packet for patients undergoing Total Knee Replacement. Osteoarthritis (OA) is
Brian P. McKeon MD Jason D. Rand, PA-C, PT Patient Information Sheet: Total Knee Replacement This is a general information packet for patients undergoing Total Knee Replacement. Osteoarthritis (OA) is
Total Knee Replacement
 Total Knee Replacement If you and your surgeon have exhausted all non-surgical measures for treating your knee pain and inflammation, you might be a candidate for total knee replacement. This procedure
Total Knee Replacement If you and your surgeon have exhausted all non-surgical measures for treating your knee pain and inflammation, you might be a candidate for total knee replacement. This procedure
TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET
 TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET This leaflet has been produced to help answer some questions you may have following your knee replacement. However if you still have any concerns or queries
TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET This leaflet has been produced to help answer some questions you may have following your knee replacement. However if you still have any concerns or queries
Total hip replacement
 Total hip replacement 2 Hip pain Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States, and the most frequent cause of discomfort and chronic hip pain. In fact, it s estimated that 1 in 5 people
Total hip replacement 2 Hip pain Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States, and the most frequent cause of discomfort and chronic hip pain. In fact, it s estimated that 1 in 5 people
ACL Reconstruction. Role of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament. Treatment of ACL tears. ACL Reconstruction
 Role of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament The ACL stabilizes the knee when jumping, pivoting, or cutting. It prevents the shinbone (tibia) from sliding forward on the thigh bone (femur). ACL tears often occur
Role of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament The ACL stabilizes the knee when jumping, pivoting, or cutting. It prevents the shinbone (tibia) from sliding forward on the thigh bone (femur). ACL tears often occur
introduction jointunderstanding benefits of knee-replacement surgery
 introduction When knee pain becomes so severe that drugs do not provide relief or when knee problems make daily activities painful, difficult, or even impossible, surgeons can sometimes replace the damaged
introduction When knee pain becomes so severe that drugs do not provide relief or when knee problems make daily activities painful, difficult, or even impossible, surgeons can sometimes replace the damaged
A Patient s Guide to Partial Knee Resurfacing
 A Patient s Guide to Partial Knee Resurfacing Surgical Outcomes System (SOS ) www.orthoillustrated.com OrthoIllustrated is a leading Internet-based resource for patient education. Please visit this website
A Patient s Guide to Partial Knee Resurfacing Surgical Outcomes System (SOS ) www.orthoillustrated.com OrthoIllustrated is a leading Internet-based resource for patient education. Please visit this website
Information for Patients having Total Knee Replacement Surgery
 Information for Patients having Total Knee Replacement Surgery Hello You will be coming into hospital for your surgery and we hope your stay will be pleasant. We have written this booklet to give you information
Information for Patients having Total Knee Replacement Surgery Hello You will be coming into hospital for your surgery and we hope your stay will be pleasant. We have written this booklet to give you information
Brian P. McKeon MD Jason D. Rand, PA-C, PT Patient Information Sheet: Unicondylar Knee Replacement
 Brian P. McKeon MD Jason D. Rand, PA-C, PT Patient Information Sheet: Unicondylar Knee Replacement This is a general information packet for patients undergoing unicondylar knee replacement. Osteoarthritis
Brian P. McKeon MD Jason D. Rand, PA-C, PT Patient Information Sheet: Unicondylar Knee Replacement This is a general information packet for patients undergoing unicondylar knee replacement. Osteoarthritis
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO REHABILITATION POST KNEE REPLACEMENT SURGERY
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO REHABILITATION POST KNEE REPLACEMENT SURGERY Georgia Bouffard Student Physiotherapist Colin Walker Orthopaedic Knee Specialist Frank Gilroy BSc MSCP 1 CONTENTS Anatomy of the knee
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO REHABILITATION POST KNEE REPLACEMENT SURGERY Georgia Bouffard Student Physiotherapist Colin Walker Orthopaedic Knee Specialist Frank Gilroy BSc MSCP 1 CONTENTS Anatomy of the knee
Knee Replacement Surgery
 To print: Use your web browser's print feature. Close this window after printing. Knee Replacement Surgery Table of Contents Knee Replacement Surgery Appendix Topic Images Knee Replacement Surgery Knee
To print: Use your web browser's print feature. Close this window after printing. Knee Replacement Surgery Table of Contents Knee Replacement Surgery Appendix Topic Images Knee Replacement Surgery Knee
Total Knee Replacement
 Total Knee Replacement If your knee is severely damaged by arthritis or injury, it may be hard for you to perform simple activities, such as walking or climbing stairs. You may even begin to feel pain
Total Knee Replacement If your knee is severely damaged by arthritis or injury, it may be hard for you to perform simple activities, such as walking or climbing stairs. You may even begin to feel pain
The Shoulder. The Shoulder Joint:
 The Shoulder The board certified physicians and surgeons at Orthopaedic Associates of Central Texas (OACT) are leaders in caring for the joints of the body. The shoulder joint is a complex and dynamic
The Shoulder The board certified physicians and surgeons at Orthopaedic Associates of Central Texas (OACT) are leaders in caring for the joints of the body. The shoulder joint is a complex and dynamic
Unicompartmental Knee Resurfacing
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage knee pain. All decisions about the management of knee pain must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage knee pain. All decisions about the management of knee pain must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed
Total Hip Replacement
 PATIENT EDUCATION Total Hip Replacement A guide to understanding total hip replacement surgery, featuring The George Archer Story. BACK TO MOBILITY George Archer s Personal Adventure On April16, 1996,
PATIENT EDUCATION Total Hip Replacement A guide to understanding total hip replacement surgery, featuring The George Archer Story. BACK TO MOBILITY George Archer s Personal Adventure On April16, 1996,
Advantage Orthopaedics, P.C.
 TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Whether you have just begun exploring treatment options or have already decided with your orthopaedic surgeon to undergo hip replacement surgery, this booklet will help you understand
TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Whether you have just begun exploring treatment options or have already decided with your orthopaedic surgeon to undergo hip replacement surgery, this booklet will help you understand
Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty
![Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty](/thumbs/90/102636395.jpg) Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty Introduction Hip arthritis is a common problem, most often due to osteoarthritis. In hip arthritis affects a patient,
Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty Introduction Hip arthritis is a common problem, most often due to osteoarthritis. In hip arthritis affects a patient,
MENISCUS TEAR. Description
 MENISCUS TEAR Description Expected Outcome The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage structure in the knee that sits on top of the leg bone (tibia). Each knee has two menisci, an inner and outer meniscus. The
MENISCUS TEAR Description Expected Outcome The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage structure in the knee that sits on top of the leg bone (tibia). Each knee has two menisci, an inner and outer meniscus. The
PHASE ONE: THE FIRST SIX WEEKS AFTER INJURY
 Exercises After Injury to the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) of the Knee Dr. Abigail R. Hamilton, M.D. PHASE ONE: THE FIRST SIX WEEKS AFTER INJURY Initially, the knee needs to be protected-use the knee
Exercises After Injury to the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) of the Knee Dr. Abigail R. Hamilton, M.D. PHASE ONE: THE FIRST SIX WEEKS AFTER INJURY Initially, the knee needs to be protected-use the knee
Knee Replacement Recovery Guide
 Knee Replacement Recovery Guide Table of Contents Congratulations!... 2 Recuperating At home... 2 Range of Motion... 2 Wound Care... 3 Important Signs & Symptoms... 3 Bathing and Showering... 3 Bruising...
Knee Replacement Recovery Guide Table of Contents Congratulations!... 2 Recuperating At home... 2 Range of Motion... 2 Wound Care... 3 Important Signs & Symptoms... 3 Bathing and Showering... 3 Bruising...
REHABILITATION AFTER ARTHROSCOPIC KNEE SURGERY
 REHABILITATION AFTER ARTHROSCOPIC KNEE SURGERY This protocol is a guideline for your rehabilitation after arthroscopic knee surgery. You may vary in your ability to do these exercises and to progress to
REHABILITATION AFTER ARTHROSCOPIC KNEE SURGERY This protocol is a guideline for your rehabilitation after arthroscopic knee surgery. You may vary in your ability to do these exercises and to progress to
What is a total knee replacement?
 What is a total knee replacement? If you and your surgeon have exhausted all non-surgical measures for treating your knee pain and inflammation, you might be a candidate for total knee replacement. This
What is a total knee replacement? If you and your surgeon have exhausted all non-surgical measures for treating your knee pain and inflammation, you might be a candidate for total knee replacement. This
A Patient s Guide to Artificial Joint Replacement of the Ankle
 A Patient s Guide to Artificial Joint Replacement of the Ankle Introduction Surgery to replace the ankle joint with an artificial joint (called ankle arthroplasty) is becoming more common. This surgery
A Patient s Guide to Artificial Joint Replacement of the Ankle Introduction Surgery to replace the ankle joint with an artificial joint (called ankle arthroplasty) is becoming more common. This surgery
Physiotherapy Information following Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction
 Physiotherapy Information following Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction Name:... Surgery Date:... Graft:... Orthopaedic Outpatient Appointment Date: Time: Location: Contact Number: Contacting
Physiotherapy Information following Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction Name:... Surgery Date:... Graft:... Orthopaedic Outpatient Appointment Date: Time: Location: Contact Number: Contacting
HIP REPLACEMENT SURGERY
 HIP REPLACEMENT SURGERY HOW TO PREPARE FOR SURGERY AND REC0VERY Before surgery: Arrange for someone to help you around the house for a week or two after coming home from the hospital. Arrange for transportation
HIP REPLACEMENT SURGERY HOW TO PREPARE FOR SURGERY AND REC0VERY Before surgery: Arrange for someone to help you around the house for a week or two after coming home from the hospital. Arrange for transportation
Total Hip Replacement Exercise Booklet Cemented Femoral Stem Weight Bearing As Tolerated
 Total Hip Replacement Exercise Booklet Cemented Femoral Stem Weight Bearing As Tolerated Patient Name: Surgeon: Date of Surgery: Physiotherapist: Department of Rehabilitation (416) 967-8650 ext. PR 99506
Total Hip Replacement Exercise Booklet Cemented Femoral Stem Weight Bearing As Tolerated Patient Name: Surgeon: Date of Surgery: Physiotherapist: Department of Rehabilitation (416) 967-8650 ext. PR 99506
Knee Replacement , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. op Last reviewed: 06/01/2017 1
 Knee Replacement Introduction Severe arthritis in the knee can lead to serious pain and loss of motion. Health care providers may recommend surgery for people suffering from severe arthritis in the knee.
Knee Replacement Introduction Severe arthritis in the knee can lead to serious pain and loss of motion. Health care providers may recommend surgery for people suffering from severe arthritis in the knee.
Mosaicplasty and OATS Rehabilitation Protocol
 Mosaicplasty and OATS Rehabilitation Protocol PHASE 1: 0 2 weeks after surgery You will go home with crutches, cryocuff cold therapy unit and a CPM machine. GOALS: 1. Protect the cartilage transfer avoid
Mosaicplasty and OATS Rehabilitation Protocol PHASE 1: 0 2 weeks after surgery You will go home with crutches, cryocuff cold therapy unit and a CPM machine. GOALS: 1. Protect the cartilage transfer avoid
It s your knee. Help keep it that way PERSONALIZED TOTAL KNEE IMPLANTS
 It s your knee Help keep it that way PERSONALIZED TOTAL KNEE IMPLANTS Osteoarthritis the disease Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis, affecting tens of millions of people worldwide.
It s your knee Help keep it that way PERSONALIZED TOTAL KNEE IMPLANTS Osteoarthritis the disease Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis, affecting tens of millions of people worldwide.
Total Hip Replacement. Find out why Total Hip Replacement may be right for you.
 Total Hip Replacement Find out why Total Hip Replacement may be right for you. UNDERSTANDING TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT This brochure offers a brief overview of hip anatomy, arthritis and total hip arthroplasty.
Total Hip Replacement Find out why Total Hip Replacement may be right for you. UNDERSTANDING TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT This brochure offers a brief overview of hip anatomy, arthritis and total hip arthroplasty.
Total Knee Replacement: Your Guide to Preparation and Recovery
 Total Knee Replacement: Your Guide to Preparation and Recovery Table of Contents Preparing For Your Surgery...................... 1 During Your Hospital Stay...................... 5 After Surgery.............................
Total Knee Replacement: Your Guide to Preparation and Recovery Table of Contents Preparing For Your Surgery...................... 1 During Your Hospital Stay...................... 5 After Surgery.............................
Total Knee Replacement
 Total Knee Replacement STEPHEN M. DESIO, M.D. Hospital Stay Most patients are in the hospital for two to three days. A Case Manager is part of our team whom you will meet after surgery. We will work together
Total Knee Replacement STEPHEN M. DESIO, M.D. Hospital Stay Most patients are in the hospital for two to three days. A Case Manager is part of our team whom you will meet after surgery. We will work together
ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT INFORMATION PACKET
 ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT INFORMATION PACKET Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) Michael Angeline, MD Orthopedic and Sports Medicine Mercy Health System - 1 - Instructions
ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT INFORMATION PACKET Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) Michael Angeline, MD Orthopedic and Sports Medicine Mercy Health System - 1 - Instructions
KUCHING SPECIALIST HOSPITAL - Arthritis and Sports Injury Centre -
 KUCHING SPECIALIST HOSPITAL - Arthritis and Sports Injury Centre - ARTHROSCOPY FOR TORN MENISCI You have had problems with your knee and your orthopaedic surgeon suspects that you may have a torn meniscus,
KUCHING SPECIALIST HOSPITAL - Arthritis and Sports Injury Centre - ARTHROSCOPY FOR TORN MENISCI You have had problems with your knee and your orthopaedic surgeon suspects that you may have a torn meniscus,
Knee Arthroscopy: Postoperative Instructions
 Knee Arthroscopy: Postoperative Instructions John P. Woll, MD Knee arthroscopy is a commonly performed procedure that is much less invasive than previous open techniques, but it is still an operation,
Knee Arthroscopy: Postoperative Instructions John P. Woll, MD Knee arthroscopy is a commonly performed procedure that is much less invasive than previous open techniques, but it is still an operation,
A Guide to Common Ankle Injuries
 A Guide to Common Ankle Injuries Learn About: Common ankle injuries Feet and Ankle Diagnosis and Treatment Ankle exercises Beginning your recovery Frequently asked questions Do s and Don t s Arthroscopy
A Guide to Common Ankle Injuries Learn About: Common ankle injuries Feet and Ankle Diagnosis and Treatment Ankle exercises Beginning your recovery Frequently asked questions Do s and Don t s Arthroscopy
PILGRIM HOSPITAL Department of Orthopaedics TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT. Patient Information & Exercise Folder
 PILGRIM HOSPITAL Department of Orthopaedics TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Patient Information & Exercise Folder Mr D Raj FRCS (Tr & Orth) Consultant Lower Limb Orthopaedic Surgeon Pilgrim Hospital, Boston Lincolnshire
PILGRIM HOSPITAL Department of Orthopaedics TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Patient Information & Exercise Folder Mr D Raj FRCS (Tr & Orth) Consultant Lower Limb Orthopaedic Surgeon Pilgrim Hospital, Boston Lincolnshire
TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (Total Knee Replacement) The Knee Joint
 (Total Knee Replacement) The Knee Joint The knee is a hinge joint, formed by the end of the femur (thighbone) and the end of the tibia (shinbone). The bones are coated in cartilage, which acts as a cushion
(Total Knee Replacement) The Knee Joint The knee is a hinge joint, formed by the end of the femur (thighbone) and the end of the tibia (shinbone). The bones are coated in cartilage, which acts as a cushion
Total Knee Replacement. University Hospital Ahuja Medical Center
 Total Knee Replacement University Hospital Ahuja Medical Center Total Knee Replacement If your knee is severely damaged by arthritis or injury, it may be hard for you to perform simple activities, such
Total Knee Replacement University Hospital Ahuja Medical Center Total Knee Replacement If your knee is severely damaged by arthritis or injury, it may be hard for you to perform simple activities, such
Activities After Knee Replacement
 Activities After Knee Replacement After undergoing knee replacement, you may expect your lifestyle to be a lot like it was before surgery but without the pain. In many ways, you are right, but returning
Activities After Knee Replacement After undergoing knee replacement, you may expect your lifestyle to be a lot like it was before surgery but without the pain. In many ways, you are right, but returning
Anterior Approach to Hip Replacement Surgery
 Anterior Approach to Hip Replacement Surgery Introduction When debilitating pain and stiffness in your hip limits your daily activities, you may need a total hip replacement. The development of total hip
Anterior Approach to Hip Replacement Surgery Introduction When debilitating pain and stiffness in your hip limits your daily activities, you may need a total hip replacement. The development of total hip
Physical & Occupational Therapy
 In this section you will find our recommendations for exercises and everyday activities around your home. We hope that by following our guidelines your healing process will go faster and there will be
In this section you will find our recommendations for exercises and everyday activities around your home. We hope that by following our guidelines your healing process will go faster and there will be
GETTING READY FOR TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT
 GETTING READY FOR TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Pre-Op Exercises for a Better Recovery Your Recovery Begins Now Even if your hip replacement surgery is weeks or months away, start getting ready now. People who
GETTING READY FOR TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Pre-Op Exercises for a Better Recovery Your Recovery Begins Now Even if your hip replacement surgery is weeks or months away, start getting ready now. People who
CEC ARTICLE: Special Medical Conditions Part 3: Hip and Knee Replacement C. Eggers
 CEC ARTICLE: Special Medical Conditions Part 3: Hip and Knee Replacement C. Eggers Joint replacement surgery removes a damaged joint and replaces it with a prosthesis or artificial joint. The purpose of
CEC ARTICLE: Special Medical Conditions Part 3: Hip and Knee Replacement C. Eggers Joint replacement surgery removes a damaged joint and replaces it with a prosthesis or artificial joint. The purpose of
YOUR TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT SURGERY STEPS TO RETURNING TO A LIFESTYLE YOU DESERVE
 YOUR TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT SURGERY STEPS TO RETURNING TO A LIFESTYLE YOU DESERVE IMPORTANT. PLEASE NOTE. This brochure offers a brief overview of hip anatomy, arthritis and hip replacement surgery. The
YOUR TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT SURGERY STEPS TO RETURNING TO A LIFESTYLE YOU DESERVE IMPORTANT. PLEASE NOTE. This brochure offers a brief overview of hip anatomy, arthritis and hip replacement surgery. The
Rehabilitation for Patellar Tendinitis (jumpers knee) and Patellofemoral Syndrome (chondromalacia patella)
 Rehabilitation for Patellar Tendinitis (jumpers knee) and Patellofemoral Syndrome (chondromalacia patella) Patellar Tendinitis The most common tendinitis about the knee is irritation of the patellar tendon.
Rehabilitation for Patellar Tendinitis (jumpers knee) and Patellofemoral Syndrome (chondromalacia patella) Patellar Tendinitis The most common tendinitis about the knee is irritation of the patellar tendon.
TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY (Total Hip Replacement)
 (Total Hip Replacement) The Hip Joint The hip is a ball and socket joint. The joint is formed by the head of the femur (thighbone) and the acetabulum (pelvis). The bones are coated in cartilage, which
(Total Hip Replacement) The Hip Joint The hip is a ball and socket joint. The joint is formed by the head of the femur (thighbone) and the acetabulum (pelvis). The bones are coated in cartilage, which
Total Shoulder Replacement Patient Guide
 About Your Surgery and Recovery WELCOME This booklet has been designed to answer your questions about what to expect if you will need surgery. I truly hope that this will make your surgery an easier and
About Your Surgery and Recovery WELCOME This booklet has been designed to answer your questions about what to expect if you will need surgery. I truly hope that this will make your surgery an easier and
Rehabilitation After Patellar Tendon Debridement Surgery
 Katherine J. Coyner, MD UCONN Musculoskeletal Institute Medical Arts & Research Building 263 Farmington Ave. Farmington, CT 06030 Office: (860) 679-6600 Fax: (860) 679-6649 www.drcoyner.com Avon Office
Katherine J. Coyner, MD UCONN Musculoskeletal Institute Medical Arts & Research Building 263 Farmington Ave. Farmington, CT 06030 Office: (860) 679-6600 Fax: (860) 679-6649 www.drcoyner.com Avon Office
Rehabilitation. Walking after Total Knee Replacement. Continuous Passive Motion Device
 Walking after Total Knee Replacement After your TKR, continue using your walker or crutches until your surgeons tells you it is okay to stop using them. When turning with a walker or crutches DO NOT PIVOT
Walking after Total Knee Replacement After your TKR, continue using your walker or crutches until your surgeons tells you it is okay to stop using them. When turning with a walker or crutches DO NOT PIVOT
YOUR TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT SURGERY
 YOUR TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT SURGERY STEPS TO RETURNING TO A LIFESTYLE YOU DESERVE Exactech_030H Rev A_Total Hip Replacement Surgery_PRINT.indd 1 IMPORTANT. PLEASE NOTE. This brochure offers a brief overview
YOUR TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT SURGERY STEPS TO RETURNING TO A LIFESTYLE YOU DESERVE Exactech_030H Rev A_Total Hip Replacement Surgery_PRINT.indd 1 IMPORTANT. PLEASE NOTE. This brochure offers a brief overview
TIBIAL PLATEAU FRACTURE
 TIBIAL PLATEAU FRACTURE Description Preventive Measures A tibial plateau fracture is a complete or incomplete break Appropriately warm up and stretch before practice or in the larger of the two leg bones
TIBIAL PLATEAU FRACTURE Description Preventive Measures A tibial plateau fracture is a complete or incomplete break Appropriately warm up and stretch before practice or in the larger of the two leg bones
Rehabilitation. Walkers, Crutches, Canes
 Walkers, Crutches, Canes These devices provide support through your arms to limit the amount of weight on your operated hip. Initially, after a total hip replacement you will use a walker to get around.
Walkers, Crutches, Canes These devices provide support through your arms to limit the amount of weight on your operated hip. Initially, after a total hip replacement you will use a walker to get around.
Knee Replacement Patient Information
 Knee Replacement Patient Information This information sheet is designed to help you to understand what a knee replacement involves. I perform knee replacements frequently, several times each week, and
Knee Replacement Patient Information This information sheet is designed to help you to understand what a knee replacement involves. I perform knee replacements frequently, several times each week, and
Total Hip Replacement: Your Guide to Preparation and Recovery
 Total Hip Replacement: Your Guide to Preparation and Recovery Table of Contents Preparing For Your Surgery...................... 1 During Your Hospital Stay...................... 6 After Surgery.............................
Total Hip Replacement: Your Guide to Preparation and Recovery Table of Contents Preparing For Your Surgery...................... 1 During Your Hospital Stay...................... 6 After Surgery.............................
your guide to Total Knee replacement surgery
 your guide to Total Knee replacement surgery Arthritis and Knee understanding replacement Joint deterioration can affect every aspect of a person s life. In its early stages, it is common for people to
your guide to Total Knee replacement surgery Arthritis and Knee understanding replacement Joint deterioration can affect every aspect of a person s life. In its early stages, it is common for people to
Patellofemoral Replacement
 Patellofemoral Replacement During knee replacement surgery, damaged bone and cartilage is resurfaced with metal and plastic components. Patellofemoral replacement is a type of "partial" knee replacement
Patellofemoral Replacement During knee replacement surgery, damaged bone and cartilage is resurfaced with metal and plastic components. Patellofemoral replacement is a type of "partial" knee replacement
TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT
 TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Patient Information Realistic Expectations about Knee Replacement Surgery An important factor in deciding whether to have total knee replacement surgery is understanding what the
TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Patient Information Realistic Expectations about Knee Replacement Surgery An important factor in deciding whether to have total knee replacement surgery is understanding what the
GG10Rehabilitation Programme for Arthroscopically Assisted Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction
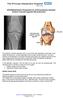 GG10Rehabilitation Programme for Arthroscopically Assisted Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Femur ACL Graft Fibula Tibia The Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) is one of the main ligaments in the
GG10Rehabilitation Programme for Arthroscopically Assisted Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Femur ACL Graft Fibula Tibia The Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) is one of the main ligaments in the
RISKS AND COMPLICATIONS
 PATIENT INFORMATION SHEET RISKS AND COMPLICATIONS TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Page 1 of 12 RISKS AND COMPLICATIONS - TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Index Pages INTRODUCTION 3 (1) ANAESTHETIC AND MEDICAL: 4 (2) BLOOD
PATIENT INFORMATION SHEET RISKS AND COMPLICATIONS TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Page 1 of 12 RISKS AND COMPLICATIONS - TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Index Pages INTRODUCTION 3 (1) ANAESTHETIC AND MEDICAL: 4 (2) BLOOD
PATIENT HANDBOOK AND JOURNAL FAQ
 PATIENT HANDBOOK AND JOURNAL FAQ FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS What is the recovery time for a total hip replacement? This generally takes about three months. Everyone heals at a different pace so this time
PATIENT HANDBOOK AND JOURNAL FAQ FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS What is the recovery time for a total hip replacement? This generally takes about three months. Everyone heals at a different pace so this time
Patient Education Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Explanation of Diagnosis and Procedure The knee is the largest joint in the body. Normal knee function is required to perform most everyday activities. The knee is made up of the lower end of the thighbone
Explanation of Diagnosis and Procedure The knee is the largest joint in the body. Normal knee function is required to perform most everyday activities. The knee is made up of the lower end of the thighbone
Lumbar Decompression GUIDELINES FOR PATIENTS HAVING A. Lumbar Decompression
 ORTHOPAEDIC UNIT: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 UPMC BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 GUIDELINES FOR PATIENTS HAVING A Lumbar Decompression Please stick addresograph
ORTHOPAEDIC UNIT: 01-293 8687 /01-293 6602 UPMC BEACON CENTRE FOR ORTHOPAEDICS: 01-2937575 PHYSIOTHERAPY DEPARTMENT: 01-2936692 GUIDELINES FOR PATIENTS HAVING A Lumbar Decompression Please stick addresograph
A Patient s Guide to Artificial Joint Replacement of the Knee
 A Patient s Guide to Artificial Joint Replacement of the Knee 12911 120th NE, Ste H210 Kirkland, WA 98034 Phone: 425-823-4000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Artificial Joint Replacement of the Knee 12911 120th NE, Ste H210 Kirkland, WA 98034 Phone: 425-823-4000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
Osteoarthritis of the Hip
 Osteoarthritis of the Hip Sometimes called "wear-and-tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is a common condition that many people develop during middle age or older. Osteoarthritis of the hip causes pain and
Osteoarthritis of the Hip Sometimes called "wear-and-tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is a common condition that many people develop during middle age or older. Osteoarthritis of the hip causes pain and
DISCOID MENISCUS. Description
 DISCOID MENISCUS Description For participation in jumping (basketball, volleyball) or The meniscus is a cartilage structure in the knee that sits on contact sports, protect the knee joint with supportive
DISCOID MENISCUS Description For participation in jumping (basketball, volleyball) or The meniscus is a cartilage structure in the knee that sits on contact sports, protect the knee joint with supportive
ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN. Explanation. Causes. Symptoms
 ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN Explanation Anterior knee pain is most commonly caused by irritation and inflammation of the patellofemoral joint of the knee (where the patella/kneecap connects to the femur/thigh bone).
ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN Explanation Anterior knee pain is most commonly caused by irritation and inflammation of the patellofemoral joint of the knee (where the patella/kneecap connects to the femur/thigh bone).
A Patient s Guide. ACL Injury: Ø Frequently asked questions on injury, Ø Preoperative and postoperative. surgery and recovery.
 ACL Injury: A Patient s Guide Ø Frequently asked questions on injury, surgery and recovery Ø Preoperative and postoperative guidelines Mia S. Hagen, M.D. Assistant Professor Department of Orthopaedics
ACL Injury: A Patient s Guide Ø Frequently asked questions on injury, surgery and recovery Ø Preoperative and postoperative guidelines Mia S. Hagen, M.D. Assistant Professor Department of Orthopaedics
Total Hip Replacement Surgery
 Total Hip Replacement Surgery On this page: Overview What is Total hip replacement (THA)? Anatomy Preparing for surgery The Operation Post-Operative Possible Complications Exercise Restrictions Overview
Total Hip Replacement Surgery On this page: Overview What is Total hip replacement (THA)? Anatomy Preparing for surgery The Operation Post-Operative Possible Complications Exercise Restrictions Overview
Integra. Salto Talaris Total Ankle Prosthesis PATIENT INFORMATION
 Integra Salto Talaris Total Ankle Prosthesis PATIENT INFORMATION Fibula Articular Surface Lateral Malleolus Tibia Medial Malleolus Talus Anterior view of the right ankle region Talo-fibular Ligament Calcaneal
Integra Salto Talaris Total Ankle Prosthesis PATIENT INFORMATION Fibula Articular Surface Lateral Malleolus Tibia Medial Malleolus Talus Anterior view of the right ankle region Talo-fibular Ligament Calcaneal
Understanding treatments for knee pain.
 Understanding treatments for knee pain. 2 Table of Contents Why does my knee hurt? 2 Diagnosis 4 Nonsurgical treatments 5 Surgical treatments 9 Arthroscopy Partial Knee Replacement 10 What is knee replacement?
Understanding treatments for knee pain. 2 Table of Contents Why does my knee hurt? 2 Diagnosis 4 Nonsurgical treatments 5 Surgical treatments 9 Arthroscopy Partial Knee Replacement 10 What is knee replacement?
Move your ankle inward toward your other foot and then outward away from your other foot.
 TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT POST OPERATIVE EXERCISES Regular exercises to restore your normal hip motion and strength and a gradual return to everyday activities are important for your full recovery. Dr. Robertson
TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT POST OPERATIVE EXERCISES Regular exercises to restore your normal hip motion and strength and a gradual return to everyday activities are important for your full recovery. Dr. Robertson
Computer Aided Knee Reconstruction
 Computer Aided Knee Reconstruction INCREASING SURGICAL ACCURACY WITH INFRARED KNEE MAPPING SYSTEM Von Kilaghbian, M.D. KNEE REPLACEMENT SURGERY COMPUTER AIDED TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY In addition to suggestions
Computer Aided Knee Reconstruction INCREASING SURGICAL ACCURACY WITH INFRARED KNEE MAPPING SYSTEM Von Kilaghbian, M.D. KNEE REPLACEMENT SURGERY COMPUTER AIDED TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY In addition to suggestions
RISKS AND COMPLICATIONS
 PATIENT INFORMATION SHEET RISKS AND COMPLICATIONS TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Page 1 of 8 INTRODUCTION A hip replacement is an extremely successful operation. At least 95% of patients are satisfied with their
PATIENT INFORMATION SHEET RISKS AND COMPLICATIONS TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Page 1 of 8 INTRODUCTION A hip replacement is an extremely successful operation. At least 95% of patients are satisfied with their
Information and exercises following a proximal femoral replacement
 Physiotherapy Department Information and exercises following a proximal femoral replacement Introduction The hip joint is a type known as a ball and socket joint. The cup side of the joint is known as
Physiotherapy Department Information and exercises following a proximal femoral replacement Introduction The hip joint is a type known as a ball and socket joint. The cup side of the joint is known as
A Customized Knee Replacement. Provides the Perfect Fit
 A Customized Knee Replacement Provides the Perfect Fit You Can Return to Your Active Lifestyle in No Time You re struggling with a debilitating knee problem like arthritis. You can t climb the stairs without
A Customized Knee Replacement Provides the Perfect Fit You Can Return to Your Active Lifestyle in No Time You re struggling with a debilitating knee problem like arthritis. You can t climb the stairs without
Information and exercises following dynamic hip screw
 Physiotherapy Department Information and exercises following dynamic hip screw Introduction A dynamic hip screw is performed where the neck of femur has been fractured and where there is a good chance
Physiotherapy Department Information and exercises following dynamic hip screw Introduction A dynamic hip screw is performed where the neck of femur has been fractured and where there is a good chance
Patient Education GANZ PERIACETABULAR OSTEOTOMY
 GANZ PERIACETABULAR OSTEOTOMY Thank you for the opportunity of allowing us to take care of you. We understand that there are many questions regarding your hip surgery for you and your parents. This information
GANZ PERIACETABULAR OSTEOTOMY Thank you for the opportunity of allowing us to take care of you. We understand that there are many questions regarding your hip surgery for you and your parents. This information
Hip Replacement Recovery Guide
 Hip Replacement Recovery Guide Table of Contents Congratulations!... 2 Recuperating At home... 2 Safe Activities & Movements... 2 Wound Care... 3 Important Signs & Symptoms... 3 Bathing and Showering...
Hip Replacement Recovery Guide Table of Contents Congratulations!... 2 Recuperating At home... 2 Safe Activities & Movements... 2 Wound Care... 3 Important Signs & Symptoms... 3 Bathing and Showering...
Arthritis. What is arthritis? Who is affected? What treatment options are available?
 Arthritis What is arthritis? Who is affected? What treatment options are available? What is Arthritis? arth - joint itis inflammation Arthritis inflammation of the joint(s). What is Inflammation? Inflammation
Arthritis What is arthritis? Who is affected? What treatment options are available? What is Arthritis? arth - joint itis inflammation Arthritis inflammation of the joint(s). What is Inflammation? Inflammation
YOUR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT
 YOUR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT General Guide to getting you back to function. Topics to Cover Walking, step climbing, functional mobility and using assistive devices Transfers in and out of chairs, car, bed
YOUR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT General Guide to getting you back to function. Topics to Cover Walking, step climbing, functional mobility and using assistive devices Transfers in and out of chairs, car, bed
DISCOID MENISCUS. Description
 Montefiore Pediatric Orthopedic and Scoliosis Center Children s Hospital at Montefiore Norman Otsuka MD Eric Fornari MD Jacob Schulz MD Jaime Gomez MD Christine Moloney PA 3400 Bainbridge Avenue, 6 th
Montefiore Pediatric Orthopedic and Scoliosis Center Children s Hospital at Montefiore Norman Otsuka MD Eric Fornari MD Jacob Schulz MD Jaime Gomez MD Christine Moloney PA 3400 Bainbridge Avenue, 6 th
UNICOMPARTMENTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT (UKR) PATIENT INFORMATION
 UNICOMPARTMENTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT (UKR) PATIENT INFORMATION The following information is to help you understand what is going to happen when you have a UKR. It is only a guide and some aspects will vary
UNICOMPARTMENTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT (UKR) PATIENT INFORMATION The following information is to help you understand what is going to happen when you have a UKR. It is only a guide and some aspects will vary
AFTER KNEE REPLACEMENT
 AFTER KNEE REPLACEMENT Living in Comfort with Your New Knee Stepping into Recovery Before knee replacement surgery, your painful knee may have limited your activity. Replacing your knee joint was your
AFTER KNEE REPLACEMENT Living in Comfort with Your New Knee Stepping into Recovery Before knee replacement surgery, your painful knee may have limited your activity. Replacing your knee joint was your
While it s unlikely you ll meet all of us you can expect to see more than one physio during your stay in hospital.
 Introduction: This information is provided to give you and your family a basic knowledge of the total hip replacement operation, outlining the things you should know, both before and after surgery. The
Introduction: This information is provided to give you and your family a basic knowledge of the total hip replacement operation, outlining the things you should know, both before and after surgery. The
The S.T.A.R. Scandinavian Total Ankle Replacement. Patient Information
 The S.T.A.R. Scandinavian Total Ankle Replacement Patient Information Patient Information This patient education brochure is presented by Small Bone Innovations, Inc. Patient results may vary. Please
The S.T.A.R. Scandinavian Total Ankle Replacement Patient Information Patient Information This patient education brochure is presented by Small Bone Innovations, Inc. Patient results may vary. Please
Patellofemoral Osteoarthritis
 Patellofemoral Osteoarthritis Arthritis of the patellofemoral joint refers to degeneration (wearing out) of the cartilage on the underside of the patella (kneecap) and the trochlea (groove) of the femur.
Patellofemoral Osteoarthritis Arthritis of the patellofemoral joint refers to degeneration (wearing out) of the cartilage on the underside of the patella (kneecap) and the trochlea (groove) of the femur.
Total Knee Replacements
 Total Knee Replacements Historical Information: End-stage osteoarthritis (Degenerative Joint Disease) makes it very difficult for patients to perform simple activities of daily living such as walking or
Total Knee Replacements Historical Information: End-stage osteoarthritis (Degenerative Joint Disease) makes it very difficult for patients to perform simple activities of daily living such as walking or
Total Hip Replacement Exercise Guide
 Total Hip Replacement Exercise Guide Regular exercise to restore strength and mobility to your hip and a gradual return to everyday activities are important for your full recovery after hip replacement.
Total Hip Replacement Exercise Guide Regular exercise to restore strength and mobility to your hip and a gradual return to everyday activities are important for your full recovery after hip replacement.
What is an ACL Tear?...2. Treatment Options...3. Surgical Techniques...4. Preoperative Care...5. Preoperative Requirements...6
 Table of Contents What is an ACL Tear?....2 Treatment Options...3 Surgical Techniques...4 Preoperative Care...5 Preoperative Requirements...6 Postoperative Care...................... 7 Crutch use...8 Initial
Table of Contents What is an ACL Tear?....2 Treatment Options...3 Surgical Techniques...4 Preoperative Care...5 Preoperative Requirements...6 Postoperative Care...................... 7 Crutch use...8 Initial
The aim of this booklet is to provide you with information about your operation and the treatment you will receive.
 Patient Information Physiotherapy after Total Knee Replacement Physiotherapy Department Introduction The aim of this booklet is to provide you with information about your operation and the treatment you
Patient Information Physiotherapy after Total Knee Replacement Physiotherapy Department Introduction The aim of this booklet is to provide you with information about your operation and the treatment you
TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT. Surgical Treatment for Advanced Pain due to Arthritis. Dr. Adam S. Rosen
 TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Surgical Treatment for Advanced Pain due to Arthritis Dr. Adam S. Rosen What is Arthritis? How do you treat Arthritis? Arthritis is an inflammation of the joint due to loss of cartilage.
TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Surgical Treatment for Advanced Pain due to Arthritis Dr. Adam S. Rosen What is Arthritis? How do you treat Arthritis? Arthritis is an inflammation of the joint due to loss of cartilage.
TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT
 TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Knee pain When debilitating pain, accompanied by stiffness, swelling and limited motion in your knee keep you from your daily activities, it may be time to consider total knee replacement.
TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Knee pain When debilitating pain, accompanied by stiffness, swelling and limited motion in your knee keep you from your daily activities, it may be time to consider total knee replacement.
PATIENT GUIDE TO CARTILAGE INJURIES
 Lucas Wymore, MD Sports Medicine 23000 Moakley Street Suite 102 Leonardtown MD 20650 Office Phone: 301-475-5555 Office Fax: 301-475- 5914 Email: lwymore@somdortho.com PATIENT GUIDE TO CARTILAGE INJURIES
Lucas Wymore, MD Sports Medicine 23000 Moakley Street Suite 102 Leonardtown MD 20650 Office Phone: 301-475-5555 Office Fax: 301-475- 5914 Email: lwymore@somdortho.com PATIENT GUIDE TO CARTILAGE INJURIES
Knee arthroscopy surgery
 Patient information Knee arthroscopy surgery i Important information for all orthopaedic patients undergoing knee arthroscopy surgery. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY
Patient information Knee arthroscopy surgery i Important information for all orthopaedic patients undergoing knee arthroscopy surgery. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY
