Bone and joint symptoms in Paget's disease
|
|
|
- Susanna Lindsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1984, 43, Bone and joint symptoms in Paget's disease J. WINFIELD AND T. C. B. STAMP From the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital, 234 Great Portland Street, London WI SUMMARY Fifty patients with Paget's disease of bone were reviewed with regard to the basis of their symptoms and the long-term results of treatment. Twenty-four patients (48%) presented with pain localised within bone, while 17 (34%) presented with symptoms of degenerative joint disease. Three patients presented with bone pain and arthritis and the remaining six with fractures, ataxia, or painless deformity. Symptomatic osteoarthritis of the hip (OA) developed in 25 patients (50%) with approximately half developing radiological changes identical to those of idiopathic OA. Among the other patients those with coxa vara tended to show medial (rather than superior) joint space narrowing and severe Paget's disease on both sides of the joint. Arthritic pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility in other joints (knee, ankle, and wrist) were associated clinically with bone deformity adjacent to the affected joint and radiologically with distorted articular surfaces and narrowed joint spaces; sclerosis, subarticular cyst formation, and osteophytosis were usually absent. Fifteen patients were treated with calcitonin for bone pain alone; all claimed long-term 'good to complete' relief. By contrast, none of the 14 with arthritic symptoms responded to calcitonin when assessed retrospectively. Results of surgical and other medical treatment were analysed. Careful clinical evaluation is a prerequisite for optimal treatment in Paget's disease. Paget's disease is a common bone disorder characterised by increased, disorganised bone turnover in affected areas with overgrowth of immature woven bone. It affects about 4% of the population over 40 years of age in the United Kingdom.' 2 Its incidence increases with age, but only 5% of the affected patients are symptomatic.3 Pain is the principal symptom4 and most frequently arises from bone or associated arthritis, while fracture, nerve compression, or sarcoma are less common. When Paget's disease and arthritis are adjacent, it is easy to overlook the exact source of symptoms. Now that different therapy is available for each of these conditions, accurate evaluation is clearly important.5 We therefore undertook to review the frequency, origin, and features of pain and to record the pattern of joint involvement. Since chronic, polyostotic disease may produce a variety of symptoms, we initially analysed only presenting com- Accepted for publication 16 February Correspondence to Dr J. Winfield, Sheffield Centre for the Investigation and Treatment of Rheumatic Diseases, Nether Edge Hospital, Sheffield Sl 9EL. plaints. Hip arthritis was particularly common and was analysed in detail. Treatment was evaluated in circumstances which appeared to minimise placebo effects. Patients and methods PATIENTS Of 75 patients being followed up at medical and/or orthopaedic clinics at the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital the first 50 who were willing and able to attend a research clinic were reviewed. All had presented with symptoms associated with radiological Paget's disease. There were 36 women and 14 men with mean ages of 67-8 years (range years) and 66X4 (range years) respectively. Their mean follow-up was 9-3 years (range 4 months to 18 years). METHODS OF ASSESSMENT Each patient and their clinical record were reviewed by one of us (J.W.) with regard to the onset and subsequent course of the disease. The patients were 769
2 770 Winfield, Stamp questioned about their bone and joint pain-its nature, severity, origin, and radiation-and about previous injury or arthritis. Conditions associated with arthritis such as psoriasis, inflammatory bowel disease, urethritis, or iritis were sought, and family histories were taken. Physical examination helped to reveal the extent of Paget's disease, and arthritis was diagnosed by pain, tenderness, and warmth or swelling of a joint, accompanied by pain and/or limitation in active or passive movement of that joint. Joint radiographs were taken, but full skeletal surveys were performed only in clinically extensive Paget's disease. Bone scans were not done routinely. Patients were finally grouped after evaluation according to the principal source of their pain. Hips with radiological OA were further grouped into four patterns described by Roper6: Type 1. Degenerative hip disease and coincidental Paget's disease with narrowing of the superior joint space, bony sclerosis, subarticular cyst formation, and osteophytes. Type 2. Early Paget's disease of the hip joint with medial joint space narrowing rather than superior narrowing. Paget's disease was probably important in the development of these changes. Type 3. Type 2 with the development of protrusio acetabuli. Type 4. Late Paget's disease of hip joint with concentric joint space loss and protrusio acetabuli. Response to treatment for Paget's disease and arthritis was evaluated symptomatically and biochemically. Results Referral pattern. Of the 50 patients, general practitioners had initially referred 22 to orthopaedic surgeons (17 being later referred for consideration of medical treatment), 13 direct to a metabolic unit, 11 to physicians in other hospitals, 3 to rheumatologists, and 1 to a geriatrician. The mean duration of symptoms for the whole group before referral for specialist opinion was 4-9 years (range 2 months to 15 years). In the majority this was the time that elapsed before specific medical or surgical treatment was considered. Presentation. Pain was the presenting symptom in 42 of the 50 patients (84%). Twenty-four patients presented with pain that was typically well localised to the site of clinical and radiological Paget's disease and was described as dull, nagging, or like 'toothache'. Pain was not relieved by immobilisation in any particular position. The finding of a deformed, thickened, tender long bone caused no diagnostic difficulty. The bones affected symptomatically, in order of frequency, were tibiae (7 patients), lumbar vertebrae (7 patients), pelvic bones (3 patients), humerus (1 patient) an.d radius (1 patient). These patients were judged to have bone pain alone. Twelve patients (24%) presented with joint pain rather than bone pain, 11 having hip arthritis and one having knee arthritis. Five (10%) presented with difficulty in walking due to progressive hip stiffness without pain; these had marked hip OA with Paget's disease in the adjacent pelvis and/or femur. Three patients presented with girdle pain and groin and/or thigh pain. In these it was impossible to determine the exact origin of symptoms, and they were designated as symptomatic of both pelvic Paget's disease and OA of hip. In the group as a whole 19 patients (38%) had hip joint symptoms as their presenting feature and a further six developed them during follow-up. Hip arthritis. Combining presentation and followup, we found 25 patients had symptomatic OA of hip, commonly with pain on movement, weight bearing, and walking. It was felt in the groin, buttock, outer gluteal region, or perineum and was frequently referred distally to the thigh or knee. Immobility stiffness without pain was noted by five patients. Other common symptoms were loss of mobility, leg weakness, difficulty in climbing stairs, or putting on footwear. Pain was usually relieved by rest, only two patients complaining of rest or night pain. Examination invariably revealed loss of mobility and stiffness, and the testing of hip movement, including standing and walking, usually reproduced their pain. Twenty-four patients had Paget's disease of the pelvis, femur, or both with OA of the hip, only one having OA (bilateral) without adjacent Paget's disease. The incidence of acetabular Paget's disease alone with OA of hip (11 patients) was almost equal to that of combined acetabular and femoral disease (12 patients), and only one patient had femoral Paget's disease alone. Eight out of 12 with combined acetabular and upper femoral disease had coxa vara together with more marked medial joint space narrowing and, in four, protrusio acetabuli, a complication seen only with severe acetabular Paget's disease (Fig. 1). Fourteen of the 25 patients had bilateral radiological arthritis, giving a total of 39 radiologically arthritic hips; only four patients with OA hips were asymptomatic, an incidental finding confined to patients with Paget's disease of the whole pelvis without femoral involvement. Five patients with OA hips had other signs of primary generalised OA with Heberden's nodes and OA of the first carpometacarpal joints; two had family histories compatible with OA. By Roper's radiological classification6 (see 'Methods of assessment') the present series showed the following distribution: Type 1, 19 hips; type 2, 16 hips; type 3, 3 hips; type
3 z6 v v ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~. 4, 1 hip. Thus approximately half of the involved hips (type 1) had radiological changes indistinguish- Bone and joint symptoms in Paget's disease _? ' a XNX w > able from idiopathic OA. Otherjoint complicationis. Irrespective of presenting symptoms clinical arthritis was discovered in the knee in four patients, in the ankle in five, and in the wrist in four. In each case a markedly deformed long bone had altered the alignment of articular surfaces (Fig. 2). Joints were stable, dry, and had a decreased range of movement. On x-ray the joint space was narrowed, but osteophytes, sclerosis and subarticular cyst formation were characteristically absent. It was difficult, however, to assess how much true cartilage loss had occurred because of frequent obliteration of normal joint outline by the distorted articular surface. Shoulder pain and stiffness (four patients) was due to supraspinatus tendinitis without adjacent Paget's disease. Two patients developed pseudogout of the knee and showed chondrocalcinosis on x-ray. Six patients had borderline or raised serum urate levels ( mmolul), but none developed gouty arthritis. Calcitonin appeared not to affect serum urate. Fig. I Severe Paget's disease with bilateral protrusio acetabuli and concentric joint space narrowing. Signs and symptoms were of OA alone and were severe only on the right, where there was nofemoral Paget's disease. As expected, the patient had had no svmptomatic response to a trial of calcitonin. Back pain and Pagets disease. Eighteen patients complained of back pain and stiffness, particularly after immobility, and on x-ray all had degenerative disc disease characterised by disc space narrowing, sclerosis of vertebral bodies, and osteophyte formation. However, only seven had spinal Paget's Fig. 2 Paget's disease in a tibia with arthritis ofankle.
4 772 Winfield, Stamp disease. Sacral Paget's disease was frequent in this group and was associated with blurring or obliteration of the sacroiliac joints. Miscellaneous presentation. Three patients presented with pain due to fracture of Pagetic bone, two with giddiness and ataxia secondary to severe skull involvement and platybasia, and one patient with painless deformity of the tibia. Response to medical treatment. Of the 24 patients adjudged to have bone pain alone the 15 most severely affected were treated with calcitonin. All had a good response within three to six weeks. Normal dosage schedules for either porcine or salmon calcitonin were used (40-80 MRC units or MRC units respectively three to six days per week). Patients with disease in a single bone responded particularly well, often with dramatic reduction in bone pain. At review nine were still receiving regular cacitonin. Six had discontinued therapy with little or no recurrence of bone pain, three on account of side effects of porcine or salmon calcitonin, of whom one was later maintained on human calcitonin (kindly donated by Ciba Laboratories). The other nine patients had milder bone pain and responded to simple analgesics, soluble aspirin, paracetamol, Distalgesic (dextropropoxylene and paracetamol), or non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)-ibuprofen, naproxen, or indomethacin. Fourteen of 17 patients presenting with arthritic pain also received a trial of calcitonin. None gained significant improvement with calcitonin, nor could we detect a placebo response retrospectively. They responded partially to analgesics and NSAIDs. Of the 25 with hip arthritis four responded well to simple analgesia and eight to NSAIDs. Patients with knee or ankle arthritis responded poorly to NSAIDs. Other supportive measures consisted of physiotherapy and weight reduction. Total hip replacement in Paget's disease. Seven of the 50 patients came to total hip replacement because of increasing pain and disability. The mean age at operation was 68 years and the mean follow-up postoperatively 4-7 years. There was an excellent result in three, and improvement of hip mobility and pain by 70% in one patient. Significant complications were seen in three: one patient developed a loose prosthesis one year after operation; the other two had marked para-articular ectopic new bone formation around the operated hips one to three years after operation. Discussion The present review, conducted exclusively among the symptomatic 5% of patients with Paget's disease,'-3 has assessed the probable origin of these symptoms, their pattern of presentation, and response to therapy. Pain was the principal presenting symptom, arising from bone in 48%, from arthritis in 24%, and occasionally from both (6%). These figures are remarkably similar to those reported by Altman and Collins,7 who studied 290 patients with Paget's disease and found 'rheumatic syndromes' were present in 83%, with bone pain in 47%. In our study the other patients presented with progressive hip stiffness (10%), fracture (6%), painless deformity (2%) and ataxia (4%). Using Roper S6 suggested classification of OA hip into four patterns (see 'Methods of assessment'), we found that approximately half the patients with OA hip had changes (type 1) indistinguishable from idiopathic disease with superior joint space loss. Some had primary generalised OA, including OA of the side of the pelvis unaffected by Paget's disease. The other half of the patients had radiological changes such as medial or concentric joint space loss, more strongly suggestive that Paget's disease was contributing to its-development. Indeed many of these had varus deformities of the Pagetic femoral neck, suggesting a more medially directed stress within the hip joint. Concentric joint space loss is usually associated with inflammatory disease of synovium and cartilage-for example in rheumatoid arthritis-but the possibility of such changes within arthritic joints associated with Paget's disease has not been investigated. The possible role of altered mechanics within the hip joint on the basis of bone disease also requires further study. Protrusio acetabuli was associated with the most severe changes in trabecular pattern, remodelling, and in some cases marked deformity of the femoral neck and head. This study has also shown the rarity of femoral Paget's disease alone with OA of the hip. Total hip replacement has been carried out in patients with Paget's disease with considerable success.8 9 The present small, unselected group with longer follow-up than other studies shows a less favourable outcome, with loosening of the prosthesis and/or para-articular ossification in three of seven patients. Taylor et al. 1( found significant ossification after total hip replacement in 8-5% of patients with ankylosing spondylitis, 4% in idiopathic OA, and none with rheumatoid arthritis. The frequency of para-articular ossification after -total hip replacement in Paget's disease has not been previously reported, but the present incidence may be significant. None of these patients received preoperative treatment for Paget's disease to reduce bone vascularity, and excessive bleeding was not a complication. At present there does not appear to be any specific contraindication to hip replacement
5 in this group of patients. Marked protrusio acetabuli, however, may make adequate fixation of the acetabular component difficult when the Pagetic bone is soft or the medial pelvic wall very thin. Pain and stiffness in other joints (knee, wrist, ankle) were associated with distorted articular surfaces on x-ray due to the adjacent bone deformity. Other signs of joint inflammation were lacking. The frequency of lumbar pain and stiffness in the present series (36%) is consistent with that found in the two American studies,71' comparing closety with the 37% reported by Altman and Collins. However, symptomatic lumbar spondylosis was very common in patients without vertebral Paget's disease, while spinal Paget's disease alone may be asymptomatic. The similarity of back symptoms among those with and without spinal Paget's disease therefore made it difficult to determine the cause of back pain, a problem encountered by others.7 No patients had past or family histories compatible with ankylosing spondylitis, nor were syndesmophytes or bone fusions found in their lumbosacral spines. Obliteration of the sacroiliac joints in Paget's disease may be more due to bony distortion than to true inflammatory sacroiliitis, in keeping with other joint changes. The finding of Franck et al. 1 studying 55 patients with Paget's disease that hyperuricaemia, gouty arthritis, and calcific periarthritis were all common was not confirmed. Multiple symptoms may plainly result from chronic polyostotic disease, and up to 60% of patients with symptomatic Paget's disease develop articular Bone and joint symptoms in Paget's disease 773 symptoms in its course. Effective therapy may depend on accurate localisation of all symptoms, and many patients have an overlap between articular and bone symptoms. Analgesics and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs remain the basis of treatment for arthritis, and there is no evidence yet that calcitonin will inhibit its development. In selected cases orthopaedic procedures may be indicated, including osteotomy for bone deformity and joint replacement for severe degenerative disease. We are grateful to the many physicians and surgeons who referred their patients. References 1 Collins D H. Paget's disease of bone-incidence and subclinical forms. Lancet 1956; ii: Pygott F. Paget's disease of bone, the radiological incidence. Lancet 1957; i: Smith R. Paget's disease of bone. Biochemical disorders of the skeleton. 1979; London: Butterworth, 1979: Smith R. Paget's disease of bone, osteogenesis imperfecta and fibrous dysplasia. Br Med J 1977; i: Hosking D J. Paget's disease of bone. Br Med J 1981; ii: Roper B. Paget's disease involving the hip joint-a classification. Clin Orthop 1971; 80: Altman R D, Collins B. Musculoskeletal manifestations of Paget's disease of bone. Arthritis Rheum 1980; 10: Milgram J W. Orthopaedic management of Paget's disease of bone. Clin Orthop 1977; 127: Stauffer R N, Sim F H. Total hip arthroplasty in Paget's disease of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg 1976; 58A: Taylor A R, Kamdar B A, Arden G P. Ectopic calcification following total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg 1976; 58B: Franck W, Bress N, Singer F, Krane S. Rheumatic manifestations of Paget's disease of bone. Am J Med 1974; 56: Ann Rheum Dis: first published as /ard on 1 December Downloaded from on 6 October 2018 by guest. Protected by
DISEASES AND DISORDERS
 DISEASES AND DISORDERS 9. 53 10. Rheumatoid arthritis 59 11. Spondyloarthropathies 69 12. Connective tissue diseases 77 13. Osteoporosis and metabolic bone disease 95 14. Crystal arthropathies 103 15.
DISEASES AND DISORDERS 9. 53 10. Rheumatoid arthritis 59 11. Spondyloarthropathies 69 12. Connective tissue diseases 77 13. Osteoporosis and metabolic bone disease 95 14. Crystal arthropathies 103 15.
4 2 Osteoarthritis 1
 Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
Original Date: December 2015 Page 1 of 8 FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines TOTAL JOINT ARTHROPLASTY -Total Hip Arthroplasty -Total Knee Arthroplasty -Replacement/Revision Hip or Knee Arthroplasty CPT4 Codes: Please refer to
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines TOTAL JOINT ARTHROPLASTY -Total Hip Arthroplasty -Total Knee Arthroplasty -Replacement/Revision Hip or Knee Arthroplasty CPT4 Codes: Please refer to
Osteoarthritis of the Hip
 Osteoarthritis of the Hip Sometimes called "wear-and-tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is a common condition that many people develop during middle age or older. Osteoarthritis of the hip causes pain and
Osteoarthritis of the Hip Sometimes called "wear-and-tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is a common condition that many people develop during middle age or older. Osteoarthritis of the hip causes pain and
Degenerative arthritis of Hip Bone Bangalore. Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal
 Degenerative arthritis of Hip Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal Hip joint Classical Synovial joint Biomechanics of hip Force coincides with trabecular pattern Hip joint Acetabulum
Degenerative arthritis of Hip Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal Hip joint Classical Synovial joint Biomechanics of hip Force coincides with trabecular pattern Hip joint Acetabulum
Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
For Commercial products, please refer to the following policy: Preauthorization via Web-Based Tool for Procedures
 Medical Coverage Policy Total Joint Arthroplasty Hip and Knee EFFECTIVE DATE: 08/01/2017 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 06/06/2017 OVERVIEW Joint replacement surgery, also known as arthroplasty, has proved to be
Medical Coverage Policy Total Joint Arthroplasty Hip and Knee EFFECTIVE DATE: 08/01/2017 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 06/06/2017 OVERVIEW Joint replacement surgery, also known as arthroplasty, has proved to be
Musculoskeletal Referral Guidelines
 Musculoskeletal Referral Guidelines Introduction These guidelines have been developed to provide an integrated musculoskeletal service. They are based on reasonable clinical practice and will initially
Musculoskeletal Referral Guidelines Introduction These guidelines have been developed to provide an integrated musculoskeletal service. They are based on reasonable clinical practice and will initially
Osteoarthritis of the Hip
 Osteoarthritis of the Hip Information on hip osteoarthritis is also available in Spanish: Osteoartritis de cadera (topic.cfm?topic=a00608). Sometimes called "wear and tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is
Osteoarthritis of the Hip Information on hip osteoarthritis is also available in Spanish: Osteoartritis de cadera (topic.cfm?topic=a00608). Sometimes called "wear and tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is
Total Hip Replacement in Diaphyseal Aclasis: A Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 6 Number 1 Total Hip Replacement in Diaphyseal Aclasis: A Case Report V Singh, S Carter Citation V Singh, S Carter.. The Internet Journal of
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 6 Number 1 Total Hip Replacement in Diaphyseal Aclasis: A Case Report V Singh, S Carter Citation V Singh, S Carter.. The Internet Journal of
ARTHRITIS. What Is Arthritis?
 There are many types of arthritic processes that can cause joint changes, pain and loss of motion and strength in the hands. Many excellent and detailed resources are available and will be listed under
There are many types of arthritic processes that can cause joint changes, pain and loss of motion and strength in the hands. Many excellent and detailed resources are available and will be listed under
Joint Injuries and Disorders
 Joint Injuries and Disorders Introduction A joint is where two or more bones come together. Your joints include the knees, hips, elbows and shoulders. There are many types of joint disorders, including
Joint Injuries and Disorders Introduction A joint is where two or more bones come together. Your joints include the knees, hips, elbows and shoulders. There are many types of joint disorders, including
Periarticular knee osteotomy
 Periarticular knee osteotomy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4803 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. Knee joint The knee consists of two joints which allow flexion (bending)
Periarticular knee osteotomy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4803 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. Knee joint The knee consists of two joints which allow flexion (bending)
Osteoarthritis What is new? Dr Peter Cheung, Rheumatologist, NUHS
 Osteoarthritis What is new? Dr Peter Cheung, Rheumatologist, NUHS Objective Outline some clinical features that are not well appreciated in OA patients Recent advances in knowledge and management of OA
Osteoarthritis What is new? Dr Peter Cheung, Rheumatologist, NUHS Objective Outline some clinical features that are not well appreciated in OA patients Recent advances in knowledge and management of OA
DYSPLASIA EPIPHYSIALIS MULTIPLEX IN THREE SISTERS
 DYSPLASA EPPHYSALS MULTPLEX N THREE SSTERS \\T WAUGH, LONDON, ENGLAND From the Orthopaedic Department, King s College Hospital, London Dysplasia epiphysialis multiplex, first described by Fairbank (1947),
DYSPLASA EPPHYSALS MULTPLEX N THREE SSTERS \\T WAUGH, LONDON, ENGLAND From the Orthopaedic Department, King s College Hospital, London Dysplasia epiphysialis multiplex, first described by Fairbank (1947),
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 7/28/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 83 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 7/28/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 83 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA)
 www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHRITIS/ENTHESITIS- RELATED ARTHRITIS (SpA-ERA)
www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHRITIS/ENTHESITIS- RELATED ARTHRITIS (SpA-ERA)
Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle
 Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. It can cause pain and stiffness in any joint in the body, and is common in the small joints of the foot and ankle.
Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. It can cause pain and stiffness in any joint in the body, and is common in the small joints of the foot and ankle.
Osteoarthritis of the Hip
 Page 1 of 8 Osteoarthritis of the Hip Information on hip osteoarthritis is also available in Spanish: Osteoartritis de cadera (topic.cfm?topic=a00608). Sometimes called "wear-and-tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis
Page 1 of 8 Osteoarthritis of the Hip Information on hip osteoarthritis is also available in Spanish: Osteoartritis de cadera (topic.cfm?topic=a00608). Sometimes called "wear-and-tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis
Medical Policy Original Effective Date: Revised Date: 07/26/17 Page 1 of 9
 Page 1 of 9 Disclaimer Description Coverage Determination/ Clinical Indications Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on
Page 1 of 9 Disclaimer Description Coverage Determination/ Clinical Indications Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on
Joint Disorders. Musculoskeletal Disorders (Part B-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10. Overview Disorders of the Muscular System Disorders of the Skeletal System
 Musculoskeletal Disorders (Part B-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Disorders of the Muscular System Disorders of the Skeletal System Susie Turner, MD 1/9/13 Joint Disorders Arthritis Inflammation of Joint
Musculoskeletal Disorders (Part B-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Disorders of the Muscular System Disorders of the Skeletal System Susie Turner, MD 1/9/13 Joint Disorders Arthritis Inflammation of Joint
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) 6565 Fannin Street Houston, TX 77030 Phone: 713-790-3333 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) 6565 Fannin Street Houston, TX 77030 Phone: 713-790-3333 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE TRAPEZIOSCAPHOID JOINT
 375 OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE TRAPEZIOSCAPHOID JOINT A. CAROLINE PATTERSON Isolated osteoarthritis (OA) of the trapezioscaphoid (TS) joint is little recognized. Nine cases that were examined clinically and
375 OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE TRAPEZIOSCAPHOID JOINT A. CAROLINE PATTERSON Isolated osteoarthritis (OA) of the trapezioscaphoid (TS) joint is little recognized. Nine cases that were examined clinically and
PARADIGM SPINE. Patient Information. Treatment of a Narrow Lumbar Spinal Canal
 PARADIGM SPINE Patient Information Treatment of a Narrow Lumbar Spinal Canal Dear Patient, This brochure is intended to inform you of a possible treatment option for narrowing of the spinal canal, often
PARADIGM SPINE Patient Information Treatment of a Narrow Lumbar Spinal Canal Dear Patient, This brochure is intended to inform you of a possible treatment option for narrowing of the spinal canal, often
Arthritis of the Shoulder
 Arthritis of the Shoulder Simply defined, arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. In a diseased shoulder, inflammation causes pain and stiffness. Although there is no cure for arthritis
Arthritis of the Shoulder Simply defined, arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. In a diseased shoulder, inflammation causes pain and stiffness. Although there is no cure for arthritis
Arthritis of the Shoulder
 Page 1 of 7 Arthritis of the Shoulder This article is also available in Spanish: Artritis del hombro (Arthritis of the Shoulder) (topic.cfm?topic=a00723). In 2011, more than 50 million people in the United
Page 1 of 7 Arthritis of the Shoulder This article is also available in Spanish: Artritis del hombro (Arthritis of the Shoulder) (topic.cfm?topic=a00723). In 2011, more than 50 million people in the United
High Impact Rheumatology
 High Impact Rheumatology Evaluation and Management of Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis: Case 1 A 65-year-old man comes to your office complaining of knee pain that began insidiously about a year ago. He has
High Impact Rheumatology Evaluation and Management of Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis: Case 1 A 65-year-old man comes to your office complaining of knee pain that began insidiously about a year ago. He has
Hip and Knee Pain What are my options?
 Hip and Knee Pain What are my options? Jonathan Surdam, MD Dr. Surdam has performed nearly 1,000 joint replacements in southern Indiana Creighton University School of Medicine Residency in orthopedic surgery
Hip and Knee Pain What are my options? Jonathan Surdam, MD Dr. Surdam has performed nearly 1,000 joint replacements in southern Indiana Creighton University School of Medicine Residency in orthopedic surgery
Arthritis of the Shoulder
 Arthritis of the Shoulder In 2011, more than 50 million people in the United States reported that they had been diagnosed with some form of arthritis, according to the National Health Interview Survey.
Arthritis of the Shoulder In 2011, more than 50 million people in the United States reported that they had been diagnosed with some form of arthritis, according to the National Health Interview Survey.
Latest Treatments for Hip Arthritis. Michael J. Repine MD Boulder Medical Center Orthopedics You re Not Alone
 Latest Treatments for Hip Arthritis Michael J. Repine MD Boulder Medical Center Orthopedics 303-502-9404 You re Not Alone More than 43 million people have some form of arthritis. It is estimated that the
Latest Treatments for Hip Arthritis Michael J. Repine MD Boulder Medical Center Orthopedics 303-502-9404 You re Not Alone More than 43 million people have some form of arthritis. It is estimated that the
MUSCULOSKELETAL RADIOLOGY
 MUSCULOSKELETAL RADOLOGY SECTON www.cambridge.org Achilles tendonopathy/rupture Characteristics Describes pathology of the combined tendon of the gastro-soleus complex, which inserts onto the calcaneum.
MUSCULOSKELETAL RADOLOGY SECTON www.cambridge.org Achilles tendonopathy/rupture Characteristics Describes pathology of the combined tendon of the gastro-soleus complex, which inserts onto the calcaneum.
Case reports CASE 1. A 67-year-old white man had back pain since the age. our clinic several years later with progressive symptoms.
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 574-578 Late-onset peripheral joint disease in ankylosing spondylitis MARC D. COHEN AND WILLIAM W. GINSBURG From the Division ofrheumatology and Internal Medicine,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 574-578 Late-onset peripheral joint disease in ankylosing spondylitis MARC D. COHEN AND WILLIAM W. GINSBURG From the Division ofrheumatology and Internal Medicine,
YOUR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT
 YOUR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Dr. M.S. Barrow Barrow Physiotherapy MBBch (Wits), FCS (SA) Orth. Waterfall City Hospital Orthopaedic Surgeon Tel: 011 304 7829 Suite 5, East Wing, Sunninghill Hospital www.barrowphysiotherapy.co.za
YOUR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Dr. M.S. Barrow Barrow Physiotherapy MBBch (Wits), FCS (SA) Orth. Waterfall City Hospital Orthopaedic Surgeon Tel: 011 304 7829 Suite 5, East Wing, Sunninghill Hospital www.barrowphysiotherapy.co.za
OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORAL HEAD AND NECK
 908 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORL HED ND NECK DONLD RESNICK Osteophytes are frequently considered the most characteristic abnormality of degenerative joint disease. In patients with osteoarthritis,
908 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORL HED ND NECK DONLD RESNICK Osteophytes are frequently considered the most characteristic abnormality of degenerative joint disease. In patients with osteoarthritis,
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
A Patient s Guide to Spondyloarthropathies
 A Patient s Guide to Spondyloarthropathies 763 Larkfield Road 2nd Floor Commack, NY 11725 Phone: (631) 462-2225 Fax: (631) 462-2240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Spondyloarthropathies 763 Larkfield Road 2nd Floor Commack, NY 11725 Phone: (631) 462-2225 Fax: (631) 462-2240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
Message of the Month for GPs June 2013
 Message of the Month for GPs June 2013 Dr Winn : Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist, Manchester Royal Infirmary Imaging of the musculoskeletal system Musculoskeletal pain is a common problem in the
Message of the Month for GPs June 2013 Dr Winn : Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist, Manchester Royal Infirmary Imaging of the musculoskeletal system Musculoskeletal pain is a common problem in the
Facet syndrome in the cervical (upper) spine
 Dr. Michael J Walls, MD 320 Thomas More Parkway. Ste 202 Crestview Hills, KY 41017 Phone: (859) 331-0956 Facet syndrome in the cervical (upper) spine Cervical facet syndrome, also known as cervical facet
Dr. Michael J Walls, MD 320 Thomas More Parkway. Ste 202 Crestview Hills, KY 41017 Phone: (859) 331-0956 Facet syndrome in the cervical (upper) spine Cervical facet syndrome, also known as cervical facet
Epidemiology of Low back pain
 Low Back Pain Definition Pain felt in your lower back may come from the spine, muscles, nerves, or other structures in that region. It may also radiate from other areas like the mid or upper back, a inguinal
Low Back Pain Definition Pain felt in your lower back may come from the spine, muscles, nerves, or other structures in that region. It may also radiate from other areas like the mid or upper back, a inguinal
Total Joint Replacement. Hip and Knee Pain Lawrence P. Johnson, MD Merrimack Valley Orthopedic Associates Lowell General Hospital
 Hip and Knee Pain Lawrence P. Johnson, MD Merrimack Valley Orthopedic Associates Lowell General Hospital This talk will touch upon the following topics: Understanding the Causes of Hip and Knee pain Treatment
Hip and Knee Pain Lawrence P. Johnson, MD Merrimack Valley Orthopedic Associates Lowell General Hospital This talk will touch upon the following topics: Understanding the Causes of Hip and Knee pain Treatment
Facet Joint Syndrome / Arthritis
 Facet Joint Syndrome / Arthritis Overview Facet joint syndrome is an arthritis-like condition of the spine that can be a significant source of back and neck pain. It is caused by degenerative changes to
Facet Joint Syndrome / Arthritis Overview Facet joint syndrome is an arthritis-like condition of the spine that can be a significant source of back and neck pain. It is caused by degenerative changes to
Rheumatoid involvement of the lumbar spine
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 524-531 Rheumatoid involvement of the lumbar spine H. SIMS-WILLIAMS,' M. I. V. JAYSON,1 AND H. BADDELEY2 From the Department of Medicine, University ofbristol,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 524-531 Rheumatoid involvement of the lumbar spine H. SIMS-WILLIAMS,' M. I. V. JAYSON,1 AND H. BADDELEY2 From the Department of Medicine, University ofbristol,
Osteoarthritis - suspected
 Care map information Resources for patients, carers and clinicians Red flags - Septic arthritis - Fracture Clinical presentation and history Examination -Pain on movement of the joint is a critical finding
Care map information Resources for patients, carers and clinicians Red flags - Septic arthritis - Fracture Clinical presentation and history Examination -Pain on movement of the joint is a critical finding
the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 109-114 A prospective study of the radiological changes in the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease J. WINFIELD, D. COOKE,' A. S. BROOK,2 AND MARY CORBETT
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 109-114 A prospective study of the radiological changes in the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease J. WINFIELD, D. COOKE,' A. S. BROOK,2 AND MARY CORBETT
Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery
 Mako TM Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery for Total Hip Replacement A Patient s Guide Causes of Your Hip Pain Your joints are involved in almost every activity you do. Movements such as walking, bending and
Mako TM Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery for Total Hip Replacement A Patient s Guide Causes of Your Hip Pain Your joints are involved in almost every activity you do. Movements such as walking, bending and
 www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Peak onset between 20 and 30 years Form of spondyloarthritis (cause inflammation around site of ligament insertion into bone) and association with HLA-B27 Prevalence as high
www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Peak onset between 20 and 30 years Form of spondyloarthritis (cause inflammation around site of ligament insertion into bone) and association with HLA-B27 Prevalence as high
Anterior knee pain following total knee replacement caused by isolated Paget's disease of patella
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 9 Number 2 Anterior knee pain following total knee replacement caused by isolated Paget's disease of patella R Gupta, S Canty, W Ryan Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 9 Number 2 Anterior knee pain following total knee replacement caused by isolated Paget's disease of patella R Gupta, S Canty, W Ryan Citation
Post test for O&P 2 Hrs CE. The Exam
 Post test for O&P 2 Hrs CE The Exam This examination is taken in "open book" format. That means you are free to answer the questions after research or discussion with your fellow workers. We feel this
Post test for O&P 2 Hrs CE The Exam This examination is taken in "open book" format. That means you are free to answer the questions after research or discussion with your fellow workers. We feel this
Total Joints and Arthritis. Marc A. Roux, M.D. Chief of Surgery, Baylor Medical Center at Waxahachie August 25, 2012
 Total Joints and Arthritis Marc A. Roux, M.D. Chief of Surgery, Baylor Medical Center at Waxahachie August 25, 2012 Joint Replacement Will focus on Knee and Hip OA amd joint replacement Over 500,000
Total Joints and Arthritis Marc A. Roux, M.D. Chief of Surgery, Baylor Medical Center at Waxahachie August 25, 2012 Joint Replacement Will focus on Knee and Hip OA amd joint replacement Over 500,000
Non-inflammatory joint pain
 Non-inflammatory joint pain Lawrence Owino Okong o, Mmed (UoN); Mphil. (UCT). Lecturer, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, University of Nairobi. Paediatrician/ Rheumatologist. INTRODUCTION Musculoskeletal
Non-inflammatory joint pain Lawrence Owino Okong o, Mmed (UoN); Mphil. (UCT). Lecturer, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, University of Nairobi. Paediatrician/ Rheumatologist. INTRODUCTION Musculoskeletal
The Painful Hip. Jennifer R Marks, MD
 The Painful Hip Jennifer R Marks, MD The Painful Hip A 64 yo F presents to clinic complaining of a sore hip What further questions do you have for this patient? What is on your differential diagnosis?
The Painful Hip Jennifer R Marks, MD The Painful Hip A 64 yo F presents to clinic complaining of a sore hip What further questions do you have for this patient? What is on your differential diagnosis?
Ankle Arthroscopy.
 Ankle Arthroscopy Key words: Ankle pain, ankle arthroscopy, ankle sprain, ankle stiffness, day case surgery, articular cartilage, chondral injury, chondral defect, anti-inflammatory medication Our understanding
Ankle Arthroscopy Key words: Ankle pain, ankle arthroscopy, ankle sprain, ankle stiffness, day case surgery, articular cartilage, chondral injury, chondral defect, anti-inflammatory medication Our understanding
DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE
 DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Preferred Clinical Services for Leading Age Florida August 26-27, 2015 MUSCULOSKELETAL FUNCTIONS
DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Preferred Clinical Services for Leading Age Florida August 26-27, 2015 MUSCULOSKELETAL FUNCTIONS
Hths 2231 Laboratory 13 Alterations in Musculoskeletal
 Watch Movie: Osteoporosis Answer the movie questions on the worksheet. Complete activities 1-4. Activity #1: Click on the website link in activity 1 to review the structure and function of bone. Activity
Watch Movie: Osteoporosis Answer the movie questions on the worksheet. Complete activities 1-4. Activity #1: Click on the website link in activity 1 to review the structure and function of bone. Activity
W37 Total prosthetic replacement of hip joint using cement. W38 Total replacement of hip joint not using cement
 Bedfordshire and Hertfordshire Priorities Forum statement Number: 32 Subject: Referral criteria for patients from primary care presenting with hip pain due to ostoarthritis, and clinical thresholds for
Bedfordshire and Hertfordshire Priorities Forum statement Number: 32 Subject: Referral criteria for patients from primary care presenting with hip pain due to ostoarthritis, and clinical thresholds for
Questions and Answers About Spinal Stenosis
 Questions and Answers About Spinal Stenosis http://www.niams.nih.gov/hi/topics/spinalstenosis/spinal_sten.htm Questions and Answers About Spinal Stenosis This fact sheet contains general information about
Questions and Answers About Spinal Stenosis http://www.niams.nih.gov/hi/topics/spinalstenosis/spinal_sten.htm Questions and Answers About Spinal Stenosis This fact sheet contains general information about
Osteoarthritis. Dr. Siddharth Kumar Das M. D. Professor and Head, Department of Rheumatology, Chhatrapati Shahu Maharaj Medical University, Lucknow
 Osteoarthritis Dr. Siddharth Kumar Das M. D. Professor and Head, Department of Rheumatology, Chhatrapati Shahu Maharaj Medical University, Lucknow Das S.K. Osteoarthritis In Wagh S. (Ed). Rheumatology
Osteoarthritis Dr. Siddharth Kumar Das M. D. Professor and Head, Department of Rheumatology, Chhatrapati Shahu Maharaj Medical University, Lucknow Das S.K. Osteoarthritis In Wagh S. (Ed). Rheumatology
Arthritis of the Knee
 Arthritis of the Knee There are three basic types of arthritis that may affect the knee joint. Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of knee arthritis. OA is usually a slowly progressive
Arthritis of the Knee There are three basic types of arthritis that may affect the knee joint. Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of knee arthritis. OA is usually a slowly progressive
Arthritis and Rheumatism
 Understanding Arthritis and Rheumatism Doctor Jennifer G. Worrall Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT This book is intended not
Understanding Arthritis and Rheumatism Doctor Jennifer G. Worrall Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT This book is intended not
Resources for patients, carers and clinicians. Referral indicators. Patient with previous THR - loosening/wear, pain
 Care map information Resources for patients, carers and clinicians. Referral indicators Red flags -infection in previous Total Hip Replacement (THR) -pathological fracture Hip arthritis Patient with previous
Care map information Resources for patients, carers and clinicians. Referral indicators Red flags -infection in previous Total Hip Replacement (THR) -pathological fracture Hip arthritis Patient with previous
Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies. Dr. M Jokar
 Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies Dr. M Jokar 1 Definition The spondyloarthropathies are a group of disorders that share certain clinical features and an association with the HLA-B27 allele 2 Spondyloarthropathies
Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies Dr. M Jokar 1 Definition The spondyloarthropathies are a group of disorders that share certain clinical features and an association with the HLA-B27 allele 2 Spondyloarthropathies
Non Surgical Management Of Hip And Knee Osteoarthritis Toolkit. Evaluation and Diagnosis of Osteoarthritis in Primary Care
 Non Surgical Management Of Hip And Knee Osteoarthritis Toolkit Evaluation and Diagnosis of Osteoarthritis in Primary Care OA-HxPE-716.indd 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS HISTORY TAKING... 3 EVALUATION OF SUSPECTED
Non Surgical Management Of Hip And Knee Osteoarthritis Toolkit Evaluation and Diagnosis of Osteoarthritis in Primary Care OA-HxPE-716.indd 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS HISTORY TAKING... 3 EVALUATION OF SUSPECTED
Mr Aslam Mohammed FRCS, FRCS (Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Specialising in Lower Limb Arthroplasty and Sports Injury
 Mr Aslam Mohammed FRCS, FRCS (Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Specialising in Lower Limb Arthroplasty and Sports Injury I qualified from the Welsh National School of Medicine in Cardiff in 1984. I
Mr Aslam Mohammed FRCS, FRCS (Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Specialising in Lower Limb Arthroplasty and Sports Injury I qualified from the Welsh National School of Medicine in Cardiff in 1984. I
Medicare Regulations for Chiropractors. Presented by Clinic Pro Software Inc. Marilyn K. Gard. CEO, MBA
 Medicare Regulations for Chiropractors Presented by Clinic Pro Software Inc. Marilyn K. Gard. CEO, MBA Use AT modifier which means active treatment. Claims submitted for Chiropractic manipulative treatment
Medicare Regulations for Chiropractors Presented by Clinic Pro Software Inc. Marilyn K. Gard. CEO, MBA Use AT modifier which means active treatment. Claims submitted for Chiropractic manipulative treatment
Ad-Hoc Rheumatology Subcommittee of PTAC meeting held 8 March. (minutes for web publishing)
 Ad-Hoc Rheumatology Subcommittee of PTAC meeting held 8 March 2011 (minutes for web publishing) Ad-Hoc Rheumatology Subcommittee minutes are published in accordance with the Terms of Reference for the
Ad-Hoc Rheumatology Subcommittee of PTAC meeting held 8 March 2011 (minutes for web publishing) Ad-Hoc Rheumatology Subcommittee minutes are published in accordance with the Terms of Reference for the
UG CURRICULUM FOR ORTHOPAEDICS UNIVERSITY OF DELHI
 UG CURRICULUM FOR ORTHOPAEDICS UNIVERSITY OF DELHI OBJECTIVES OF THE COURSE: At the end of the program, student should acquire the following: 1. Diagnose the common musculo-skeletal disease process from
UG CURRICULUM FOR ORTHOPAEDICS UNIVERSITY OF DELHI OBJECTIVES OF THE COURSE: At the end of the program, student should acquire the following: 1. Diagnose the common musculo-skeletal disease process from
Section 1. What is osteoporosis? Your bones. Bones and osteoporosis. Who is affected by osteoporosis? Consequences of osteoporosis
 4 Section 1 What is osteoporosis? Your bones Bones and osteoporosis Who is affected by osteoporosis? Consequences of osteoporosis Less common types of osteoporosis Other bone conditions 5 Osteoporosis
4 Section 1 What is osteoporosis? Your bones Bones and osteoporosis Who is affected by osteoporosis? Consequences of osteoporosis Less common types of osteoporosis Other bone conditions 5 Osteoporosis
Arthritis of the Shoulder
 Arthritis of the Shoulder This article is also available in Spanish: Artritis del hombro (Arthritis of the Shoulder) (topic.cfm?topic=a00723). In 2011, more than 50 million people in the United States
Arthritis of the Shoulder This article is also available in Spanish: Artritis del hombro (Arthritis of the Shoulder) (topic.cfm?topic=a00723). In 2011, more than 50 million people in the United States
The Relationship Between Clinical Activity And Function In Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.27, No. 3, September 2005 The Relationship Between Clinical Activity And Function In Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients Jane Kawar, MD* Hisham Al-Sayegh, MD* Objective: To assess
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.27, No. 3, September 2005 The Relationship Between Clinical Activity And Function In Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients Jane Kawar, MD* Hisham Al-Sayegh, MD* Objective: To assess
The hindfoot consists of three joints which lie around and below the ankle
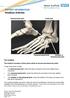 PATIENT INFORMATION Hindfoot Arthritis Talonavicular joint Ankle joint Calcaneocuboid joint Subtalar or Talocalcaneal joint The hindfoot The hindfoot consists of three joints which lie around and below
PATIENT INFORMATION Hindfoot Arthritis Talonavicular joint Ankle joint Calcaneocuboid joint Subtalar or Talocalcaneal joint The hindfoot The hindfoot consists of three joints which lie around and below
Welcome to the: Orthopaedic Opinion Online Website The website for the answer to all your Orthopaedic Questions
 Welcome to the: Orthopaedic Opinion Online Website The website for the answer to all your Orthopaedic Questions Orthopaedic Opinion Online is a website designed to provide information to patients who have
Welcome to the: Orthopaedic Opinion Online Website The website for the answer to all your Orthopaedic Questions Orthopaedic Opinion Online is a website designed to provide information to patients who have
Autosomal Dominant Type I Osteopetrosis Is Related with Iatrogenic Fractures in Arthroplasty
 Case Report Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2014;6:484-488 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.4.484 Autosomal Dominant Type I Osteopetrosis Is Related with Iatrogenic Fractures in Arthroplasty Ruud P.
Case Report Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2014;6:484-488 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.4.484 Autosomal Dominant Type I Osteopetrosis Is Related with Iatrogenic Fractures in Arthroplasty Ruud P.
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Arthritis. What is arthritis? Who is affected? What treatment options are available?
 Arthritis What is arthritis? Who is affected? What treatment options are available? What is Arthritis? arth - joint itis inflammation Arthritis inflammation of the joint(s). What is Inflammation? Inflammation
Arthritis What is arthritis? Who is affected? What treatment options are available? What is Arthritis? arth - joint itis inflammation Arthritis inflammation of the joint(s). What is Inflammation? Inflammation
Evaluation and Management of Knee Pain. Michael Cassat, MD University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences
 Evaluation and Management of Knee Pain Michael Cassat, MD University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Disclosure I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this program/presentation.
Evaluation and Management of Knee Pain Michael Cassat, MD University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Disclosure I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this program/presentation.
Degenerative spondylolisthesis at the L4 L5 in a 32-year-old female with previous fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: A case report
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2003: 11(2): 202 206 Degenerative spondylolisthesis at the L4 L5 in a 32-year-old female with previous fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: A case report RB Winter Clinical Professor,
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2003: 11(2): 202 206 Degenerative spondylolisthesis at the L4 L5 in a 32-year-old female with previous fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: A case report RB Winter Clinical Professor,
Giant granulomatous lesions of the femoral head and neck in rheumatoid arthritis
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 626 Giant granulomatous lesions of the femoral head and neck in rheumatoid arthritis C. L. COLTON AND A. J. DARBY London Local areas of subarticular bone erosion occurring
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 626 Giant granulomatous lesions of the femoral head and neck in rheumatoid arthritis C. L. COLTON AND A. J. DARBY London Local areas of subarticular bone erosion occurring
Midfoot Arthritis - Midfoot Fusion / Arthrodesis Surgery
 PATIENT INFORMATION Midfoot Arthritis - Midfoot Fusion / Arthrodesis Surgery The Midfoot The midfoot refers to the bones and joints that make up the arch and connect the forefoot to the hindfoot. Metatarsals
PATIENT INFORMATION Midfoot Arthritis - Midfoot Fusion / Arthrodesis Surgery The Midfoot The midfoot refers to the bones and joints that make up the arch and connect the forefoot to the hindfoot. Metatarsals
Types of osteoarthritis
 ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
Chondrocalcinosis after parathyroidectomy*
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 521 Chondrocalcinosis after parathyroidectomy* J. S. GLASS AND R. GRAHAME From Guy's Arthritis Research Unit, Guy's Hospital Medical School, London SE] 9RT Glass, J. S., and
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 521 Chondrocalcinosis after parathyroidectomy* J. S. GLASS AND R. GRAHAME From Guy's Arthritis Research Unit, Guy's Hospital Medical School, London SE] 9RT Glass, J. S., and
Risk Management Plan Etoricoxib film-coated tablets
 VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Osteoarthritis (OA): OA is a condition in which the cartilage of the joints is broken down. This causes stiffness, pain and leads
VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Osteoarthritis (OA): OA is a condition in which the cartilage of the joints is broken down. This causes stiffness, pain and leads
Computer aided analysis of total knee replacement
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1983, 42, 415-420 Computer aided analysis of total knee replacement in rheumatoid arthritis G. P. ARDEN From the Windsor Group of Hospitals SUMMARY A computer-aided analysis
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1983, 42, 415-420 Computer aided analysis of total knee replacement in rheumatoid arthritis G. P. ARDEN From the Windsor Group of Hospitals SUMMARY A computer-aided analysis
Evaluation and Treatment of Knee Arthritis Classification of Knee Arthritis Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis of Knee
 1 2 Evaluation and Treatment of Knee Arthritis John Zebrack, MD Reno Orthopaedic Clinic Classification of Knee Arthritis Non-inflammatory Osteoarthritis Primary Secondary Post-traumatic, dysplasia, neuropathic,
1 2 Evaluation and Treatment of Knee Arthritis John Zebrack, MD Reno Orthopaedic Clinic Classification of Knee Arthritis Non-inflammatory Osteoarthritis Primary Secondary Post-traumatic, dysplasia, neuropathic,
Surgical Care of the Lower Extremity in Rheumatoid Arthritis*
 Surgical Care of the Lower Extremity in Rheumatoid Arthritis* ROBY C. THOMPSON, JR., M. D. Professor of Orthopedic Surgery, University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville One of the most important
Surgical Care of the Lower Extremity in Rheumatoid Arthritis* ROBY C. THOMPSON, JR., M. D. Professor of Orthopedic Surgery, University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville One of the most important
New Directions in Osteoarthritis Research
 New Directions in Osteoarthritis Research Kananaskis October 22, 2015 Nick Mohtadi MD MSc FRCSC No conflicts of interest related to this presentation 1 Osteoarthritis: Disease? Fact of Life? Strong family
New Directions in Osteoarthritis Research Kananaskis October 22, 2015 Nick Mohtadi MD MSc FRCSC No conflicts of interest related to this presentation 1 Osteoarthritis: Disease? Fact of Life? Strong family
Primary care referral criteria for musculoskeletal MRI scans
 Appendix 1 Primary care referral criteria for musculoskeletal MRI scans Accepted Criteria for Direct Access MRI Body Part Symptoms Imaging indicated Lumbar Spine Low Back Pain with adverse symptoms or
Appendix 1 Primary care referral criteria for musculoskeletal MRI scans Accepted Criteria for Direct Access MRI Body Part Symptoms Imaging indicated Lumbar Spine Low Back Pain with adverse symptoms or
HIP_CASE 2_OA. Hip Forces. Function of the Hip. Property of VOMPTI, LLC. For Use of Participants Only. No Use or Reproduction Without Consent 1
 HIP_CASE 2_OA Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Eric Magrum DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT 62 yo female AM stiffness Hip pain diffuse, variable ant>lateral>post Gradual onset Tennis
HIP_CASE 2_OA Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Eric Magrum DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT 62 yo female AM stiffness Hip pain diffuse, variable ant>lateral>post Gradual onset Tennis
Osteoarthritis. RA Hughes
 Osteoarthritis RA Hughes Osteoarthritis (OA) OA is the most common form of arthritis and the most common joint disease Most of the people who have OA are older than age 45, and women are more commonly
Osteoarthritis RA Hughes Osteoarthritis (OA) OA is the most common form of arthritis and the most common joint disease Most of the people who have OA are older than age 45, and women are more commonly
Coventry Pain Clinic - Spianl Pain - Sciatica and Brachalgia
 Coventry Pain Clinic - Spianl Pain - Sciatica and Brachalgia Copyright 2002-2005 Dr. Richard S. Walker Introduction Spinal Nerve Root Pain (Radiculopathy) can arise from the problems affecting the:- C4
Coventry Pain Clinic - Spianl Pain - Sciatica and Brachalgia Copyright 2002-2005 Dr. Richard S. Walker Introduction Spinal Nerve Root Pain (Radiculopathy) can arise from the problems affecting the:- C4
Properties of Purdue. Anatomy. Positioning AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS 11/30/2018
 AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS Anatomy Complex Text book is needed Species Contrast Positioning Painful/ non cooperative Sedation General anesthesia Species Contrast 1 Slightly oblique
AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS Anatomy Complex Text book is needed Species Contrast Positioning Painful/ non cooperative Sedation General anesthesia Species Contrast 1 Slightly oblique
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery. By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4
 Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Guide to Understanding and Managing Arthritis
 Guide to Understanding and Managing Arthritis The content in this guide is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician
Guide to Understanding and Managing Arthritis The content in this guide is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician
What is Axial Spondyloarthritis?
 Physiotherapist Module 2 What is Axial Spondyloarthritis? How does it apply to physiotherapists? Claire Harris, Senior Physiotherapist, London North West Healthcare NHS Trust Susan Gurden, Advanced Physiotherapy
Physiotherapist Module 2 What is Axial Spondyloarthritis? How does it apply to physiotherapists? Claire Harris, Senior Physiotherapist, London North West Healthcare NHS Trust Susan Gurden, Advanced Physiotherapy
Adolescent Hip Dysplasia
 Adolescent Hip Dysplasia The hip is a "ball-and-socket" joint. In a normal hip, the ball at the upper end of the femur (thighbone) fits firmly into the socket, which is a curved portion of the pelvis called
Adolescent Hip Dysplasia The hip is a "ball-and-socket" joint. In a normal hip, the ball at the upper end of the femur (thighbone) fits firmly into the socket, which is a curved portion of the pelvis called
Femoral neck fracture during physical therapy following surface replacement arthroplasty: a preventable complication?
 CASE REPORT Open Access Femoral neck fracture during physical therapy following surface replacement arthroplasty: a preventable complication? A case report Timothy R Judkins, Michael R Dayton * Abstract
CASE REPORT Open Access Femoral neck fracture during physical therapy following surface replacement arthroplasty: a preventable complication? A case report Timothy R Judkins, Michael R Dayton * Abstract
WHAT DO YOU THINK? 1. How many people in the United States undergo hip replacement surgery each year? a) 80,000. b) 330,000.
 1 WHAT DO YOU THINK? 1. How many people in the United States undergo hip replacement surgery each year? a) 80,000 b) 330,000 c) 650,000 2. What disease is the leading cause of disability in the U.S.? a)
1 WHAT DO YOU THINK? 1. How many people in the United States undergo hip replacement surgery each year? a) 80,000 b) 330,000 c) 650,000 2. What disease is the leading cause of disability in the U.S.? a)
Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA)
 www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHRITIS/ENTHESITIS- RELATED ARTHRITIS (SpA-ERA)
www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHRITIS/ENTHESITIS- RELATED ARTHRITIS (SpA-ERA)
Life. Uncompromised. The KineSpring Knee Implant System Surgeon Handout
 Life Uncompromised The KineSpring Knee Implant System Surgeon Handout 2 Patient Selection Criteria Patient Selection Criteria Medial compartment degeneration must be confirmed radiographically or arthroscopically
Life Uncompromised The KineSpring Knee Implant System Surgeon Handout 2 Patient Selection Criteria Patient Selection Criteria Medial compartment degeneration must be confirmed radiographically or arthroscopically
